
Tomcat i7230A S5160 User’s Manual
Tomcat i7230A
///
S5160
Revision 1.00
Copyright © TYAN Computer Corporati on, 2005. All rights reserved. No part of this manual
may be reproduced or translated without pr ior wr it t e n c onsent from TYAN Computer Corp.
All registered and unregiste red trademarks and c ompany names con tained in this manual are
property of their respective owners including, but not limited to the following.
TYAN, Tomcat, i7230A and S5160 are trademarks of TYAN Computer Corporation.
Intel, Pentium 4, and combinations thereof are trademarks of Intel Corporation.
Phoenix, PhoenixBIOS are trademarks of Phoenix Software Incorporated.
Microsoft and Windows are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Linux is a trademark of Linus Torvalds.
IBM, PC, AT and PS/2 are trademarks of IBM Corporation.
XGI, XGI Volari is a trademark of XGI Technologies Incorporated.
SMSC is a trademark of Standard Microsystems Corporation.
Winbond is a trademark of Winbond Electronics Corporation.
Portable Document Format (PDF) is a trademark of Adobe Corporation.
Information contained in this document is furnished by TYAN Computer Corporation and has
been reviewed for accuracy and reliability prior to printing. TYAN assumes no liability
whatsoever, and disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of
TYAN products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose or
merchantability. TYAN retains the right to make changes to product descriptions and/or
specifications at any time, without notice. In no event will TYAN be held liable for any direct or
indirect, incidental or consequential damage, loss of use, loss of data or other malady resulting
from errors or inaccuracies of information contained in this document.
i
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 User’s Manual
Table of Contents
Before you begin… ................................................................................................................. iii
Chapter 1: Introduction............................................................................................................1
1.1 – Congratulations!.........................................................................................................1
1.2 – Hardware Specifications ............................................................................................2
Chapter 2: Board Installation .................................................................................................. 4
2.1 – Board Diagram...........................................................................................................5
2.2 – Board Parts................................................................................................................ 6
2.3 – Jumper Settings & Definitions....................................................................................7
2.4 – Mounting the Motherboard....................................................................................... 13
2.5 – Installing Memory..................................................................................................... 14
2.5.1 Memory Installation Procedure.........................................................................14
2.6 – Installing the Processor and Cooling Fan .............................. ..... ..... ..... .... ..... ..........15
2.7 – Installing Drive Cables .............................................................................................18
2.8 – Installing Expansion Cards ...................................................................................... 19
2.9 – Connecting External Devices................................................................................... 20
2.10 – Onboard LAN LED Color Definition .......................................................................20
2.11 – Installing the Power Supply....................................................................................21
2.12 – Finishing Up........................................................................................................... 21
Chapter 3: BIOS Setup...........................................................................................................22
3.1 About the BIOS........................................................................................................... 22
3.2 Main Menu .................................................................................................................. 24
3.2.1 IDE Primary/Master, Primary/Slave Setup....................................................... 25
3.2.2 SATA Port 1/2/3/4............................................................................................. 26
3.2.3 Memory Cache..................................................................................................27
3.2.4 Boot Features ................................................................................................... 29
3.3 Advanced....................................................................................................................30
3.3.1 Advanced Chipset Control................................................................................32
Integrated LAN Control..............................................................................................37
3.3.2 Advanced Processor Options ...........................................................................38
3.3.3 I/O Device Configuration................................................................................... 40
3.3.4 Hardware Monitor ............................................................................................. 42
3.3.5 DMI Event Logging ........................................................................................... 43
3.4 Security....................................................................................................................... 44
3.5 Power..........................................................................................................................45
3.6 Boot.............................................................................................................................46
3.7 Exit.............................................................................................................................. 47
Chapter 4: Diagnostics ..........................................................................................................48
4.1 Beep Codes ................................................................................................................ 48
4.2 Flash Utility..................................................................................................................48
Appendix I: Glossary ............. ..... .......... ......... .......... ......... .......... ......... .......... ..... ......... .......... 49
Appendix II: Post Error Code for BIOS ................................................................................ 55
Appendix III: SMDC Information ........................................................................................... 58
Technical Support............................................................................................................. 59
ii
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Before you begin…
Before you begin…
Check the box contents!
The retail motherboard package should contain the following:
1x Tomcat i7230A S5160 motherboard
1x 34-Pin floppy drive cable
1x Ultra-DMA-133/100/66/33 IDE cable
1x Tomcat i7230A S5160 User’s Manual
1x Tomcat i7230A S5160 Quick Reference Guide
1x TYAN driver CD
1x I/O shield
2 x Serial ATA power cable
If any of these items are missing, please contac t your vendor/dealer for replacement before
continuing with the installation p r oc e s s .
4 x Serial ATA data cable
iii
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 – Congratu lations!
You have purchased one of the most powerful server solutions for the Intel Pentium
processors and Pentium® Extr eme Edition processors
the Intel E7230 chipset. Th e Tomcat i7230A S5160 is an ATX form fa ctor server board and
features two onboard Gigabit Ethernet ports, four 3.0Gps Serial ATA RAID ports, two PCIExpress x16 slots, and an onboard XGI 16MB PCI VGA contro ller. This platform also offers
convenient remote Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) monitoring through
Tyan’s optional Server Mana gement Daughter Card. Add the ca pability to support up to 4GB
of Unbuffered DDR-II 533/667 memory, the Tomcat i7230A becom es a compelling choice for
any entry to mid-range single processor server application.
Remember to visit Tyan’s website at http://www.tyan.com
all of Tyan’s products with up-to-date FAQs, a list of worldwide distributors, Tyan software
utilities, the latest drivers, memor y c om pa tib il ity l isti n gs , and BIOS s ett ing e xp lanations.
. the Tomcat i7230A S51 60 based on
. There, you can find info rmation on
®
D
1
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 1: Introduction
1.2 – Hardware Specifications
Processor
Single LGA775 socket
Supports Intel
Cedar Mill” processor
®
“Prescott / Smithfield /
1066/800/533MHz FSB
Chipset
Intel “Mukilteo“ E7230 MCH + ICH7R
chipset
Support for 1066MHz (1.066GHz) FSB
SMSC SCH5017 Super I/O chip
Memory
Four 240-pin DDR2 DIMM sockets
Supports ECC/non-ECC DIMMs
Maximum of 8GB Unbuffered DDR2-
533/667
Expansion Slots
One (1) PCI Express x16 slot (w/ x8
signal) from Mukilteo MCH
One (1) PCI Express x16 slot (w/ x4
signal) from ICH7R
Four (4) PCI 32-bit, 33MHz slots
Integrated I/O
One 9-pin 16550 UART serial port
One ECP/EPP/SPP parallel port (via
header)
One 15-pin VGA port
Eight (8) USB 2.0 ports (four at rear,
three headers via cable, one internal
vertical USB connector)
PS/2 mouse and keyboard conn ec to rs
Standard/integrated SATA connectors
Two RJ-45 10/100/1000 LAN ports
System Management
CPU thermal & voltage monitor support
4-pin fan monitoring header w/ PWM
Integrated SATA 2.0 Controller
Four SATA2.0 ports from Intel ICH7R
Integrated Host RAID 0,1 support
Integrated Video Controller
Integrated LAN Controllers
Two Broadcom® BCM5721 LAN
controllers
– PCIe x1 interface
1000/100/10Mb/s speed
Intelligent Platform Management
Interface
Renesas H8S2167/2168 Baseboard
Management Controller (BMC)
Tailored for IPMI 2.0 specification
Supports remote Power on/off and
reset support (IPMI-over-LAN)
Server Management Daughter card
via built-in 2x25 header
BIOS
PhoenixBIOS® on 8Mbit Flash ROM
Support APM 1.2, ACPI 1.0b
Serial Console Redirect
PXE via Ethernet, USB device boot
PnP, DMI 2.0, WfM 2.0 Power
Management
User-configurable H/W monitoring
Watchdog timer (from Super I/O)
Multiple boot options
48-bit LBA support
Power management: S0, S1, S3,
S4, S5
Form Factor
ATX (12” x 9.6”, 305mm x 244mm)
EPS12V/SSI (24 + 8pin) power
connectors
Stacked PS/2 keyboard and mouse
connectors
USB 2.0 (four) rear connectors
Serial (one) and VGA (one)
connectors
Two RJ-45 LAN connectors with
LEDs
Regulatory
FCC Class B (DoC)
European Communit y CE ( Do C )
XGI XG20 PCI Controller
16MB DDR memory
2
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 1: Introduction
Software Specifications
OS (Operating S ystem) Support
Microsoft Windows XP
Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server
Microsoft Windows Server 2003 64bit/32bit
Microsoft Windows Enterprise Sever 2003 64bit/32bit
SuSE Server Enterprise 9.0 64bit/32bit
Other distributions of Linux pending validation
TYAN reserves the right to add support or discontinue support for any OS with or
without notice.
3
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
Chapter 2: Board Installation
Installation
You are now ready to install your motherboard. The mounting holes pattern of the Tomcat
i7230A S5160 matches the ATX specificatio n. Bef ore conti nuing with installat ion, conf irm that
your chassis supports a standard ATX motherboard.
How to install our products right…. the first time!
The first thing you should do re ad this user’s manual. It contains important infor mation that
will make configuration and setu p much easier. Here are some precautions you should take
when installing your motherboard:
(1) Ground yourself properly before removing your motherbo ard from the ant istatic bag .
Unplug the power from your computer power supply and then touch a safely
grounded object to release static charge (i.e. power supply case). For the safest
conditions, TYAN recommends wearing a static safety wrist strap.
(2) Hold the motherboard by its edges and do not touch the bottom of the board, or flex
the board in any way.
(3) Avoid touching the motherboard components, IC chips, connectors, memory
modules and leads.
(4) Place the motherboard on a grounded antistatic surface or on the antistatic ba g that
the board was shipped in.
(5) Inspect the board for damage.
The following pages include details on how to install your m otherboard into your chassis, as
well as installing the processor, memory, disk drives and cables.
Note: DO NOT APPLY POWER TO THE BOARD IF IT HAS BEEN DAMAGED
4
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
2.1 – Board Diagram
The following is a block diagram of the Tomcat i7230A S5160.
The following page includes details on the vital components of this motherboard.
5
http://www.tyan.com
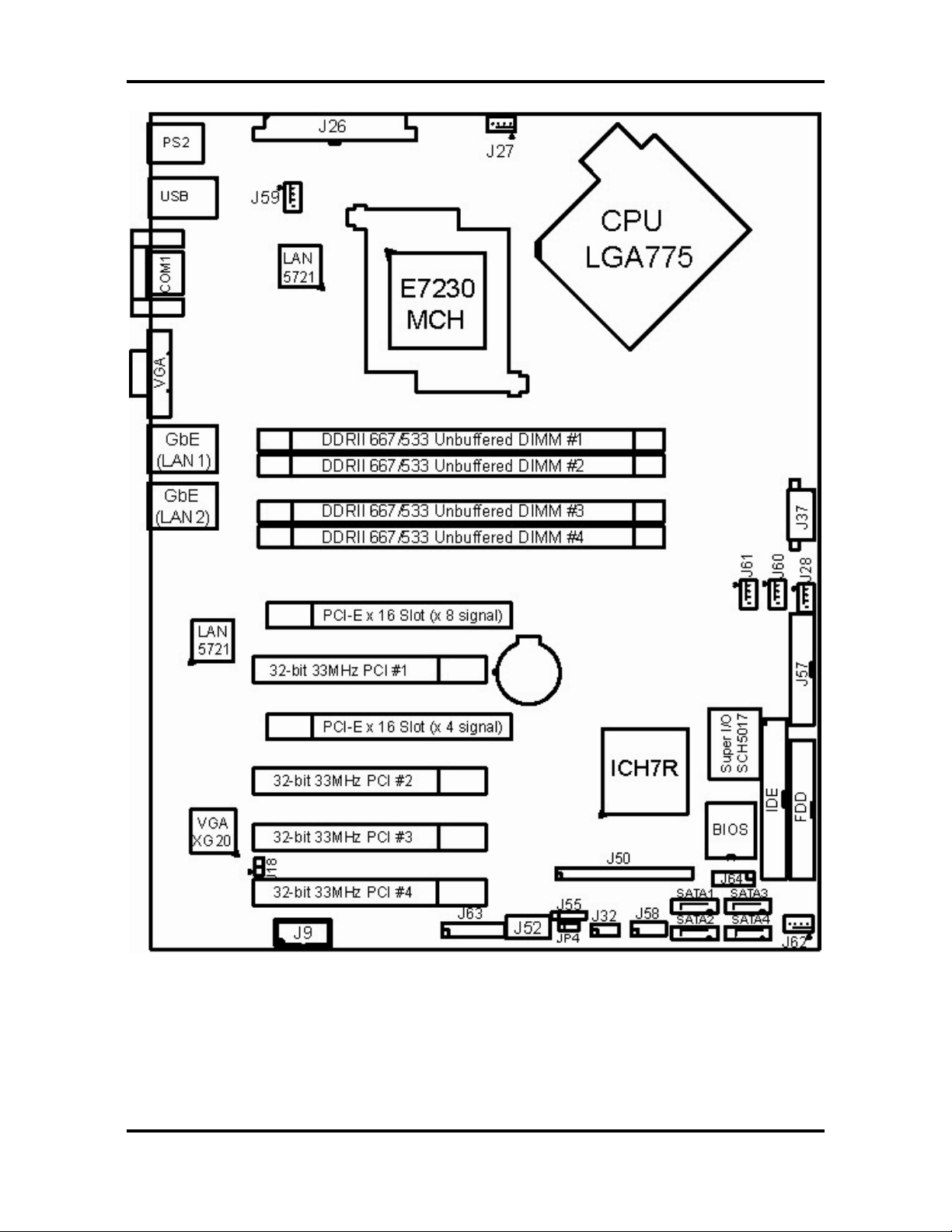
Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
2.2 – Board Parts
This jumper diagram is representative of the la test board revision available at the time
of publishing. The board you receive may or may not look exactly like the above
diagram. The board parts are not to scale.
6
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
2.3 – Jumper Settings & Definit ions
Jumper / Connector Function Ref. Page
JP4 CMOS Clear See Section 2.3.1
J32 TYAN IPMB Connector See Section 2.3.2
J27, J28, J60 Fan Connector with Smart Fan Control See Section 2.3.3
J59, J61, J62 Fan Connector w See Section 2.3.3
J9 COM2 connector See Section 2.3.4
J50 SMDC Header See Section 2.3.5
J63 TYAN Front Panel Connector See Section 2.3.6
J55 USB Header See Section 2.3.7
J58 USB Header See Section 2.3.8
J64 TYAN Front LED Connector See Section 2.3.9
J13, J15, J16, J17 Serial ATA RAID Connector See Section 2.3.10
Jumper Example
OPEN - Jumper OFF Without jumper cover
CLOSED - Jumper ON With jumper cover
To indicate the location of pin-1
To indicate the location of pin-1
7
http://www.tyan.com
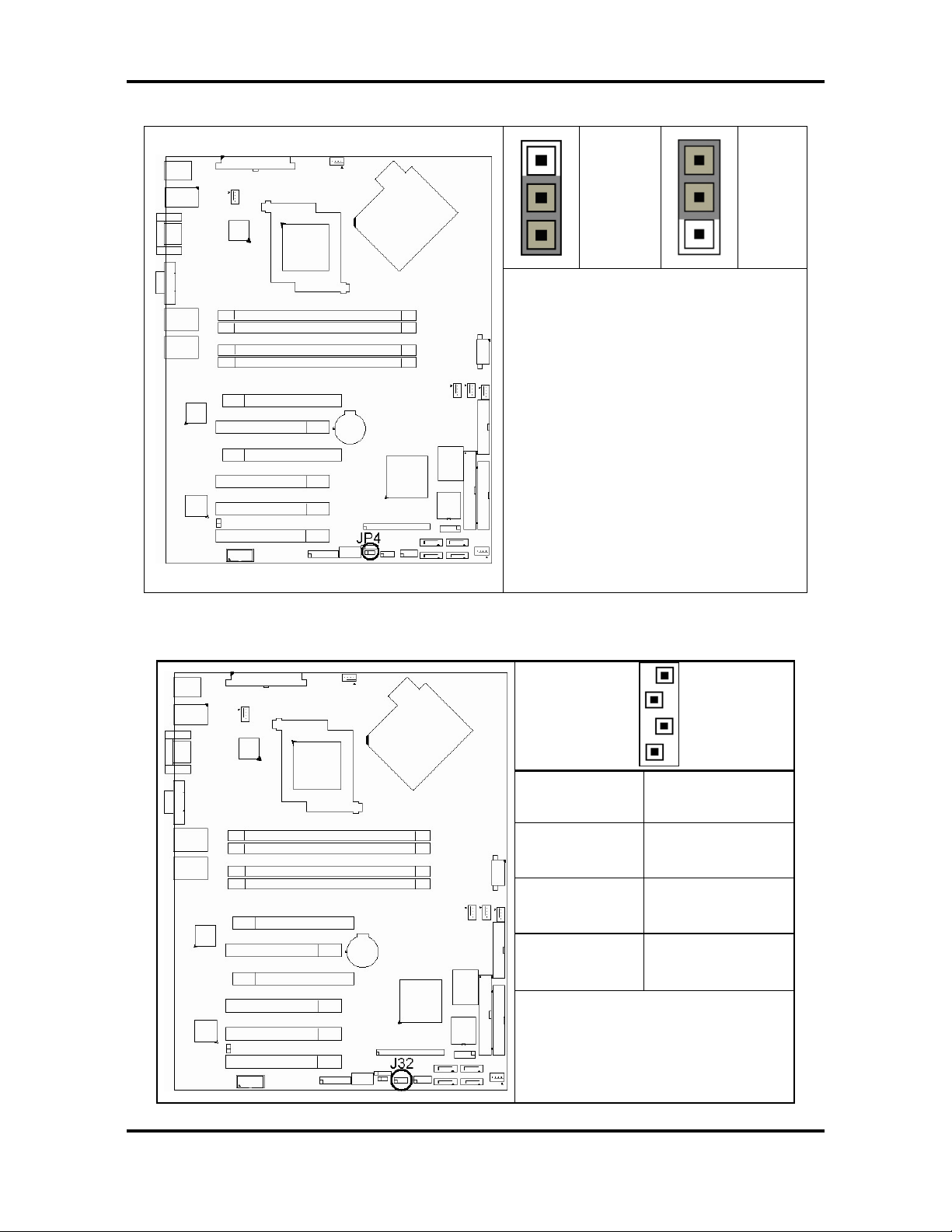
Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
2.3.1 - Clear CMOS Jumper (JP4)
Pin_3
Default
Pin_3
Clear
Pin_1
You can reset the CMOS settings by
using this jumper if you have forg otten
your system/setup password or need
to clear system BIOS setting.
Reconnect power & power on system
2.3.2 – TYAN IPMB Connector (J32: I²C Bus Connector)
Pin_1
- Power off system and
disconnect both power
connectors from the
motherboard
- Use jumper cap to close
Pin_2 and Pin_3 for
several seconds to Clear
CMOS
- Put jumper cap back to
Pin_1 and Pin_2 (default
setting)
1
4 NC
3 I2C CLK
2 GND
1 I2C DA
Use this connector to connect SM
BUS.
8
http://www.tyan.com
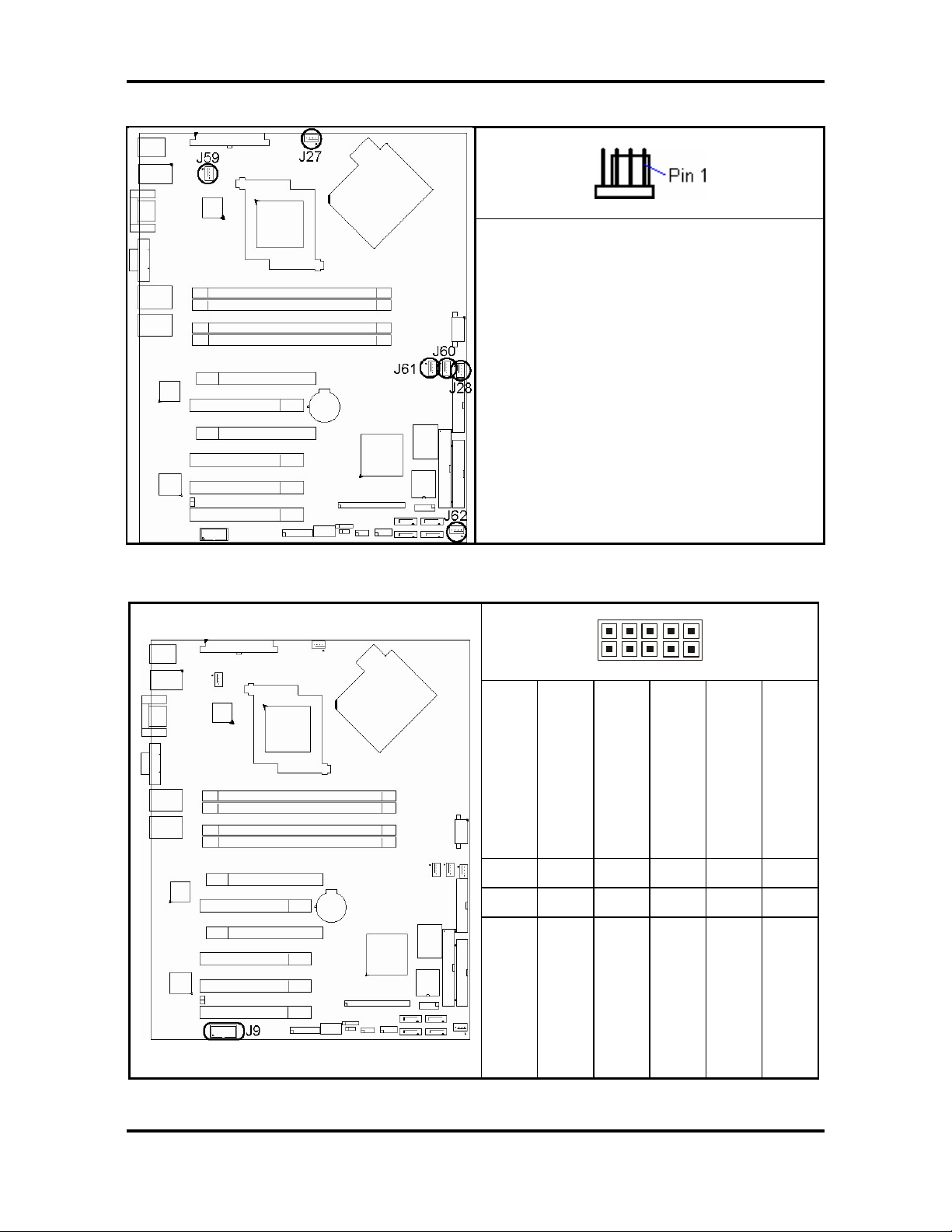
Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
(
2.3.3 - Fan Connectors (J27, J28, J59, J60, J61, J62)
2.3.4 – COM2 Connector (J9)
This 4-pin fan connector supports a new
standard fan with integrated fan speed
control on the fan itself for better fan life.
The first 3 pins of this 4-pin fan connector
are backward compatible with a traditional
3-pin fan connector without PWM fan
speed control. (Pin4 will be unconnected
for connecting a 3-pin fan).
There are six 4-pin fan connectors on
Thunder i7230A S5160 board.
Support Smart fan ctrl (J27, J28, J60)
Do not support Speed Fan ctrl
J61, J59,
J62)
9 1
10 2
DTR
Signal Description
Pin#
Pin#
GND
(Ground)
9 7 6 3
10 8 5 4
NC/Key
(Data-Terminal-Ready)
RI
(Ring-Indicator)
Signal Description
TX
(Transfer-Data)
RX
CTS
RTS
(Clear-to-Send)
(Receive-Data)
(Request-to- Send)
DCD
(Data Carrier Detect)
1
2
DSR
(Data-Set-Ready)
9
http://www.tyan.com
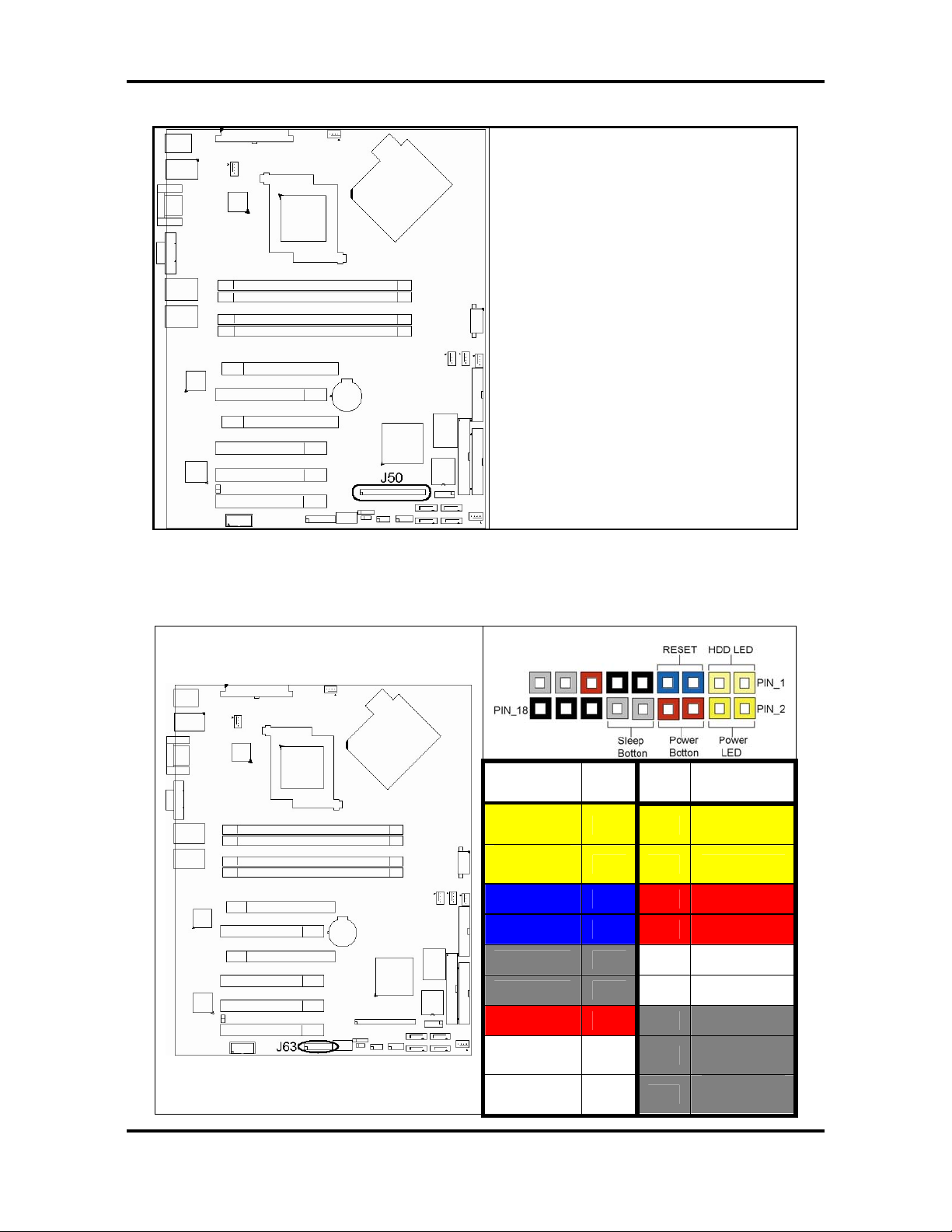
Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
2.3.5 - SMDC Header (J50)
Connect Server Management Daughter
Card (SMDC)
Compatible with Tyan M3291(SMDC)
See Appendix III for details about the
Tyan SMDC
2.3.6 – TYAN Front Panel Connector (J63)
Your chassis will usually come with connectors to install onto the motherboard, such as HDD
and Power LEDs. The TYAN Front Panel Connector (TYFP) has been implemented for such
purposes.
PIN # PIN
Function
HDD
LED+
HDD
LED-
GND 5 6 SB3V
RESET 7 8 SWT_BTN
SB3V 9 10 NC
NMI 11 12 3.3V
# Function
1 2
3 4 PWR LED-
PWR
LED+
SB5V 13 14 KEY
SMB
DATA
SMB CLK 17
10
http://www.tyan.com
15
16
18
Chassis
Intru Chassis
Intru +

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
2.3.7 - Front USB Connector (J55)
Pin # Signal Description
2.3.8 - Front USB Connector (J58)
1
2
3
4
5
Signal
Description
VCC
USB Channel_1 Data -
USB Channel_1 Data +
GND
GND
Pin # Pin # Signal
Description
VCC
USB Channel_0
Data -
USB Channel_0
Data +
GND
KEY
11
http://www.tyan.com
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
VCC
USB Channel_1
Data -
USB Channel_1
Data +
GND
GND
Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
y
g
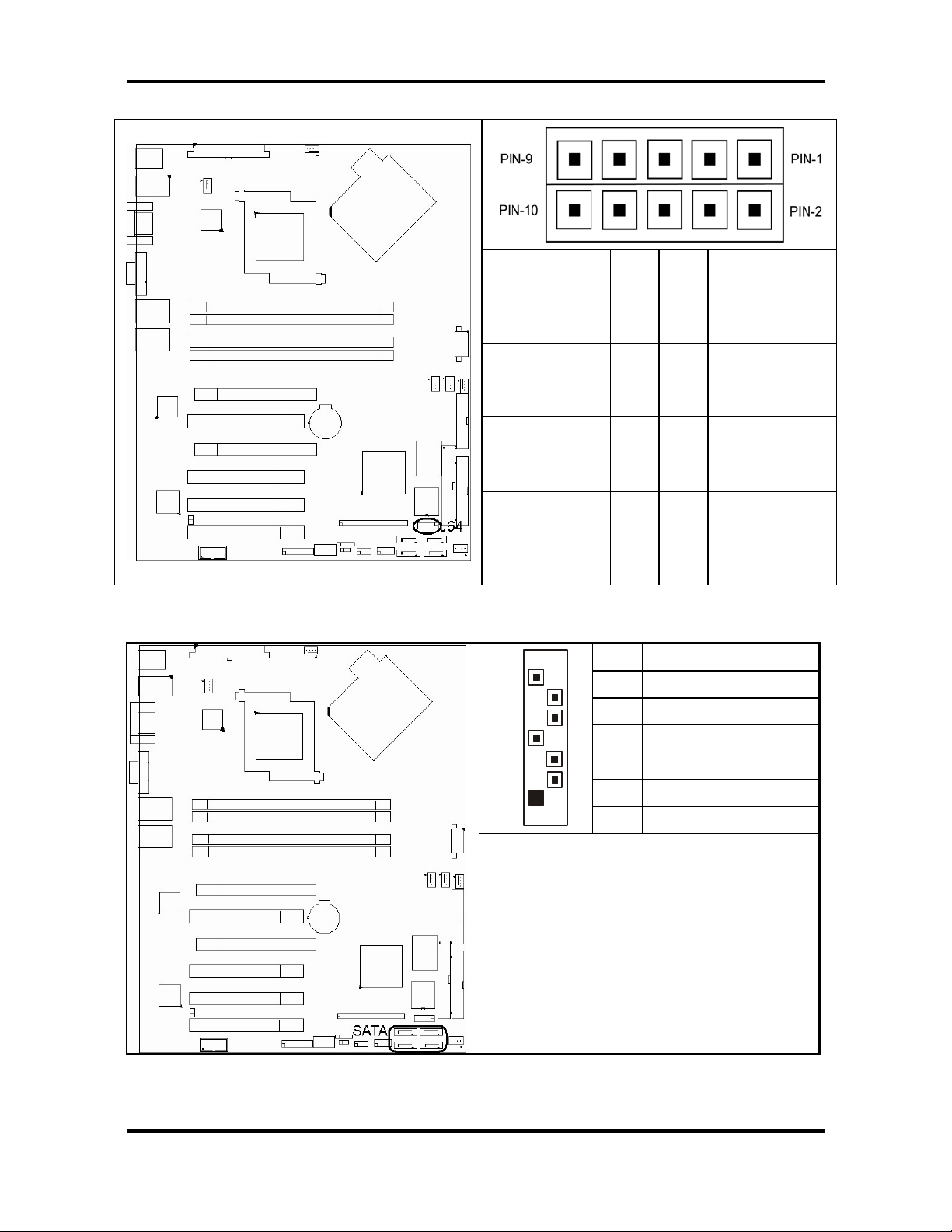
2. 3.9 - TYAN Front Panel LED Header (J64)
Signal
Description
Pin # Pin # Signal
Description
LAN0_ACTLED
_N
LAN1_ACTLED
_N
Front Panel
LED
Front Panel ID
buttom
IDLED INPUT
2.3.10 - Serial ATA RAID Connectors: J13, J15, J16, J17
7
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
7 GND
6 RXP
5 RXN
4 GND
3 TXN
1
2 TXP
1 GND
Connects to the Serial ATA ready drives
via the Serial ATA cable
You ma
use any the four Serial ATA
ports to have the support of RAID 0 and 1
through the on board ICH7R south brid
e
chip.
12
http://www.tyan.com
Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
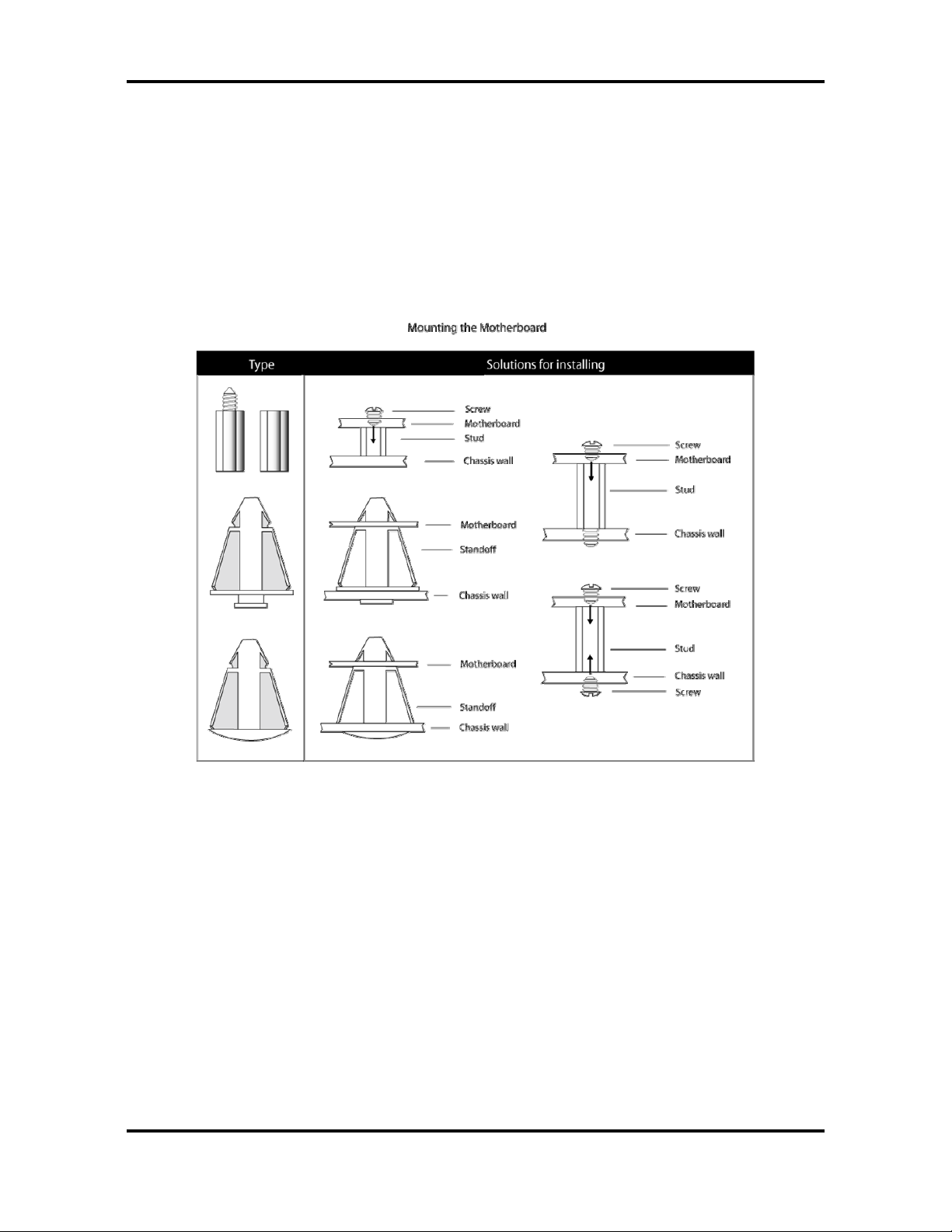
2.4 – Mounting the Motherboard
Before installing your m otherboard, ensure that your chas sis is fully compatible. The Tomc at
i7221 S5150 motherboard conforms fully to the ATX specification. Your chassis should include
preinstalled mounting posts that match exactly with the mounting holes in the motherboard.
Lay the motherboard on top of the mounting holes to ensure that all the necessary m ounting
posts exist in your chassis and that they match the mounting holes on the motherboard.
Some chassis’ include plastic studs instead of metal. Although the plastic studs are usab le,
TYAN recommends using metal studs with screws that will fasten the motherboard more
securely in place.
See the diagram below for some examples of typical motherboard fixing studs.
TIP: Use metal s tuds if possible, as they hold the motherboard into place more se curely than
plastic standoffs.
13
http://www.tyan.com
Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
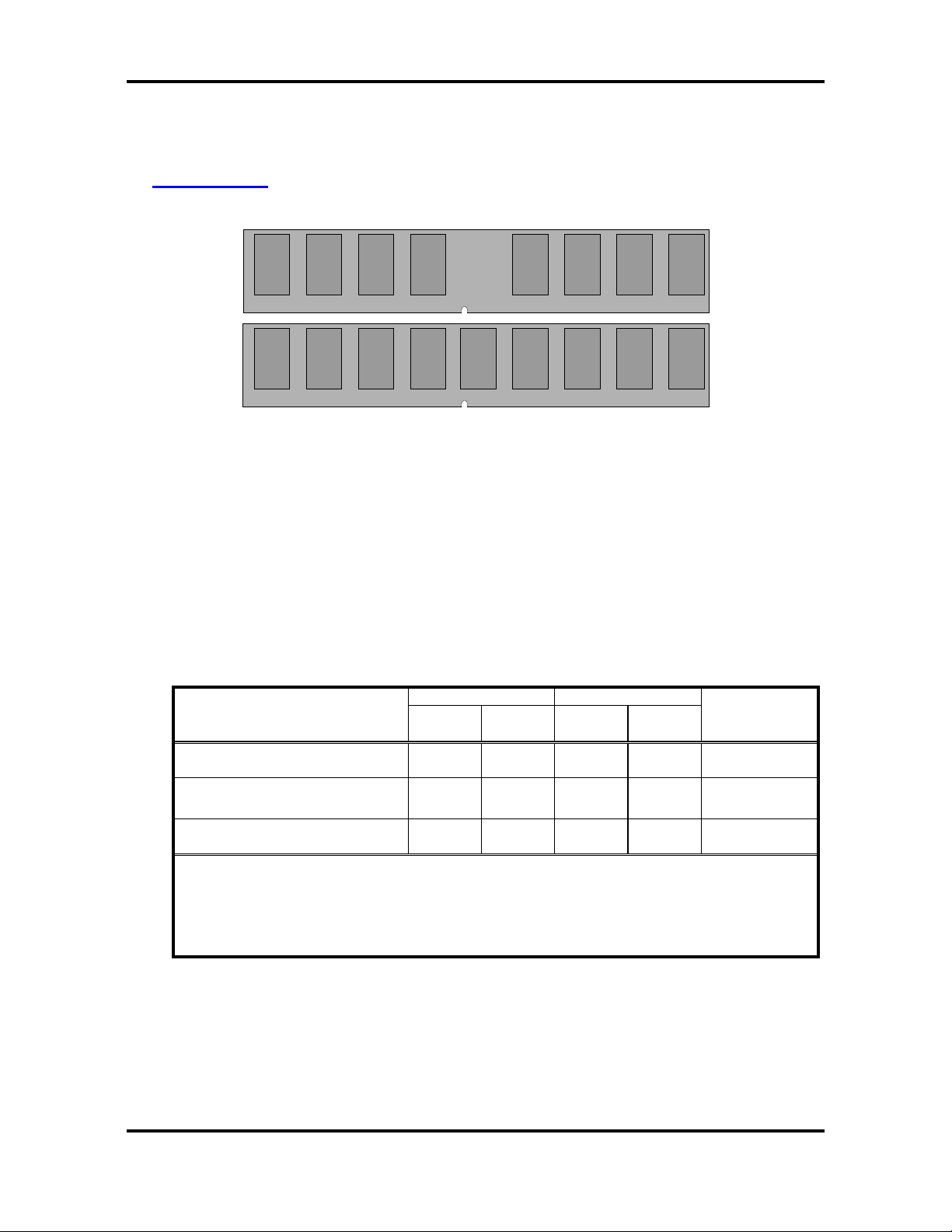
2.5 – Install ing Memory
Before installing memory, ensure that the memory you have is compatible with the
motherboard and processor. DDR -II 533/6 67 modu les are requ ire d. Check the TYAN Web site
at: www.tyan.com
The following diagram shows common types of memory modules.
for details of the type of memory recommended for your motherboard.
DDR Unbuffered
DDR Unbuffered ECC
Key points to note before installing memory:
• 128MB, 256MB, 512MB ,1GB and 2GB Non-Reg/ECC or Non-Reg/Non-ECC DDR-
II 533/667
memory modules are supported
• All installed memory will be automatically detected and no jumpers or settings need
to be set.
• The Tomcat i7230A S5160 supports up to 8GB of memory
• Registered Memory is NOT supported.
• You can install either single or double-sided modules on this motherboard. Each
DIMM can work in single-channel mode or dual-channel mode. Please note that
memory modules of the same type and density are required while using dualchannel DDR. Mismatched memory may cause system instability.
Refer to the following table for details of dual-channel DDR.
Channel A Channel B
Dual-Channel Mode
Two DIMM Symmetrical
Population
Two DIMM Symmetrical
Population
Four DIMM Symmetrical
Population
Note
1. 9= Installing 128MB ~ 2GB Memory modules
2. Symmetrical DIMMs must be identical
- Same DRAM Technology, eg 128M-bit, 256-bit, etc.
- Same DRAM bus width, eg x8 or x16
- Matched Sided DIMMs (Single Sided or Double Sided)
DIMM1 DIMM2 DIMM3 DIMM4
9 9 256MB~4GB
9 9 256MB~4GB
9 9 9 9 512MB~8GB
System
Density
2.5.1 Memory Installation Procedure
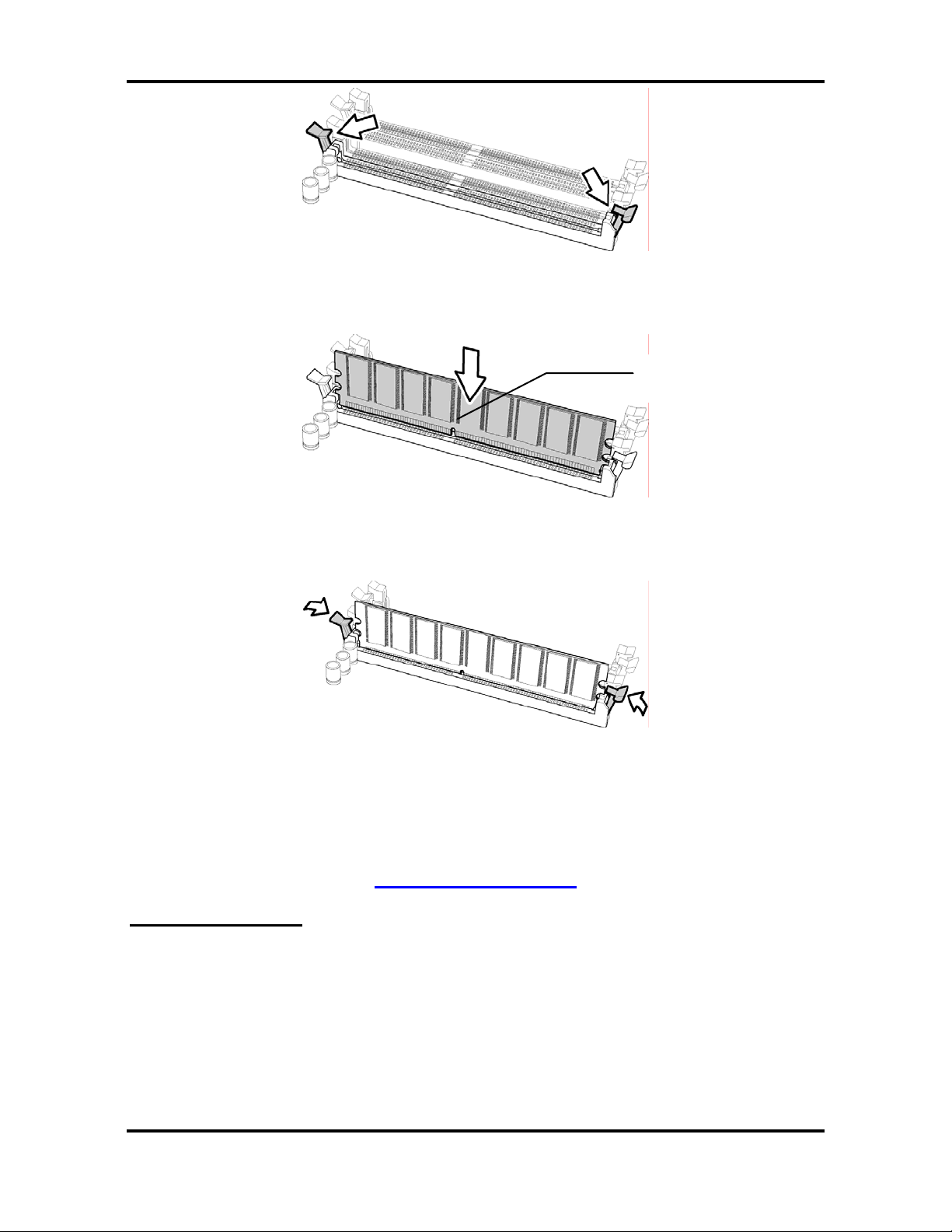
Follow these instructions to install memory modules into the Tomcat i7230A S5160.
1. Press the locking levers in the direction shown in the following illustration.
14
http://www.tyan.com
Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
2. Align the memory module with the socket. The memory module is keyed to fit only one
way in the socket.
Key slot
3. Seat the module firmly into the socket by gently pressing down until it sits flush with the
socket. The locking levers pop up into place.
2.6 – Install ing the Processor and Cooling Fan
Your Tomcat i7230A S5160 su pports the latest process or technologies from Intel. Check the
TYAN website for latest processor support:
http://www.tyan.com
Processor Installation
The processor should be insta lled c areful ly. M ake sure you ar e wearing an ant istat ic s trap and
handle the processor as little as possible.
Follow these instructions to install your processor
1. Locate the processor socket on the motherboard and lift the protective cover off as
shown.
15
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
WARNING:
This new processor socket designed by
Intel is easily damaged. The processor has
to be installed very carefully to prevent the
contact pins of the socket from breaking. It
is strongly recommended that the
processor installation job to be handled by
an experienced technician.
2. Pull the locking lever out of it’s locked position and let it spring into the open position.
3. Lift the metal cover to expose the socket interior and p lace the socket in as shown.
4. Close the cover and return the locking lever to its locked position.
Cooling Fan Installation
After you have installed the processor, the heatsink should be installed to ensure that the
processor runs efficiently and does not overheat. Use the heatsink supplied for best results.
Follow these instructions to install the heatsink shown.
16
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
1. Apply some thermal compound (also called heatsink compound or thermal grease) to
the top of the processor. Try and apply a thin, even layer over the top of the processor.
2. Align the heatsink with the four holes around the processor socket.
3. Press the heatsink down until the four white, plastic pegs are securely seated in the
holes.
4. Press down the black pegs until they click to lock the heatsink in place.
To remove the heatsink you will ne ed to twist each of the black locking pegs until they spring
up and unlock the heatsink from the motherboard.
Remember to connect the power supply for the fan to complete the installation.
Some heat sinks require a bracket to be installed beneath the motherboard before the heat
sink is placed on the top side of the motherboard. To install a heat sink like this:
1 Turn the motherboard upside down and place the rear bracket in position with the
mounting posts poking through the corresponding holes in the motherboard.
2 Turn the motherboard the right way up, holding the bracket in place.
3 Place the heat sink assembly on top of the processor.
It should match up with the mounting holes on the rear bracket.
4 Screw the heat sink assembly into place.
17
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
If there is a fan on the heat sink you will need to connect the power lead for the fan to one of
the fan power supply pin headers on the motherboard.
2.7 – Install ing Drive Cables
IDE and FDD connectors are “keyed” to only allow insertion only one way. TYAN
motherboards have two on-board IDE channels, each supporting two drives. The black
connector is the Primary IDE connector.
Insert the IDE cable as shown in the diagram.
TIP: When connecting to an IDE cable to a drive, Pin 1 on the IDE
cable (usually designated by a colored wire) should be closest to the
drive power connector.
The blue end of the cable connects directly to the motherboard and the
black end of the connector goes to the IDE device.
Serial ATA
Attaching Serial ATA cables to the Serial ATA connectors are illustrated below:
Plug in one end of the Serial ATA cable into the motherboard Serial ATA
connector, and the other end into the drive. Each standard Serial ATA cable has
two connectors, one at each end. Connectors are the same on both ends.
Floppy Drives
Floppy disk drive (FDD) cables are installed the same way as IDE cables. Usually connectors
are keyed to prevent insert ion the wro ng way. In most cases the cable sho uld be inserte d into
the drive with pin 1 closest to the power input. FDD ca bles usually hav e a single red wire that
marks pin 1. See the diagram below.
Colored cable denotes pin 1
18
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
Troubleshooting Floppy Drives
See the chart below for troubleshooting floppy disk drive installations.
Symptoms of incorrectly installed floppy drives
Drive is not automatically detected
Drive Fail message at boot up
Drive does not power on
Drive activity light is constantly on
Usually caused by faulty cables, cables put in
backwards or a faulty floppy drive. Try another
floppy drive or try replacing the cable. Check to
see if the onboard floppy c ontroller is enabled in
the BIOS setup.
The cable, floppy drive or motherboard may be
faulty. Try another drive or cable.
Check power cable and cabling. A faulty power
supply or drive cable could be the problem.
Usually signifies that the cable on the drive is
inserted backwards. Reverse the cable at the
floppy drive end and try again.
2.8 – Installing Expansion Cards
Before installing add-in cards, it’s helpful to know if they are fully compatible with your
motherboard. For this reason, we’ve provided the diagrams below, showing the most comm on
slots that may appear on your motherbo ard. Not all of the slots sh own will necessa rily appear
on your motherboard, however, there will be combinations of what you see here.
Simply find the appropriate slot for your add-in card and insert the card firmly. Do not force any
add-in cards (or anything else) into any slots if they won’t seat in place. It’s better to try
another slot or return the faulty card rat her than d amaging both the motherboa rd and the add in card.
TIP: It’s a good practice to install add-in cards in a staggered manner, rather than directly
adjacent to each other. This allows air to more eas ily circulate within th e chassis, providing
improved cooling for all installed devices.
Notes
Unplug the power connector to the motherboard before
performing system hardware changes, to avoid damaging the
board or expansion cards
19
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
2.9 – Connectin g External Devices
Connecting external devices to the motherboard is an easy task. The standard devices you
should expect to plug into the motherboard are keyboards, mouse, and printer cables. The
following diagram will detail the ATX port stack for the following board:
Tomcat i7230A S5160
Besides being used primarily to connect printers, the Printer Port is also used for devices such
as Zip drive, some external CD-RW drives and or other external devices. More on the
uncommon side these days are the Serial Ports. They were primarily used to connect external
modems, but most modems today are using USB or are installed internally.
TIP: While the ports have been creat ed to accept c onnectors in only one di rection, make s ure
to be careful when inserting connectors. At times, attaching connectors in the incorrect
orientation can damage, bend and or break the pins.
2.10 – Onboard LAN LED Color Definit ion
The two onboard Ethernet ports have green and yellow LEDs to indicate LAN status. The
chart below illustrates the different LED states.
10/100/1000 Mbps LAN Link/Activity LED Scheme
Left LED Right LED
10 Mbps
Link Green Off
Active Blinking Green Off
100 Mbps
1000 Mbps
Link Green Green
Active Blinking Green Green
Link Green Orange
Active Blinking Green Orange
No Link Off Off
20
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 2: Board Installation
2.11 – Installing the Power Supply
There are two power connectors on this motherboard. By default, this motherboard requires
that you have an ATX12V power supply that has the standard ATX-style 20-pin connector, as
well as an additional 4-pin square connector. The CPU power is provided by the onboard
switching voltage regulator, which is sourced by +12V power. This +12V CPU power source is
from the onboard 4-pin square connector. The +12V power on the 20-pin ATX power
connector is for system board and separated from CPU +12V regulator power source.
Therefore, the CPU will not be powered if you do not connect the 4-pin square ATX 12V power
connector.
J26: 24-pin EPS 12V power connector
J37: 8-pin EPS 12V power connector
Note
Unplug the power supply before plugging in the 24-pin and 8-pin
power cables to motherboard.
2.12 – Finishing U p
Congratulations on making it this far! You’re finished setting up the hardware aspec t of your
computer. Before closing up your chassis, make sure that all cables and wires are connected
properly, especially IDE cables and most importantly, jumpers. You may have difficulty
powering on your system if the motherboard jumpers are not set correctly.
In the rare circumstance that you have experienced difficulty, you can find help by asking your
vendor for assistance. If they are not available for assistance, please find setup information
and documentation online at our website or by calling your vendor’s support line.
21
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.1 About the BIOS
The BIOS is the basic input/outpu t system , the firm ware on the m othe rboard tha t ena bles you r
hardware to interface with your so ftware. This cha pt er des cribes diff erent setti ngs for the BIOS
that can be used to configure your sys tem .
The BIOS section of this manual is subject to change without notice and is provided for
reference purposes only. The settings and configurations of the BIOS are current at the time of
print, and therefore may not match exactly what is displayed on screen.
This section describes the BIOS setup program. The setup program lets you modify basic
configuration settings. The settings are then stored in a dedicated, battery-backed memory
(called NVRAM) that retains the information when the power is turned off.
This motherboard’s BIOS is a customized v ersion of the industry-standard BIOS for IBM PC
AT-compatible personal computers. The BIOS provides critical, low-level support for the
system’s central processing unit (CPU), memory, and I/O subsystems.
This BIOS has been customized by adding important features such as virus and password
protection, power management, and chipset “tuning” features that control the system. This
section will guide you through the process of configuring the BIOS for your system setup.
Starting Setup
The BIOS is immediately activated when you turn on the computer. The BIOS reads system
configuration in CMOS RAM and begins the process of checking out the system and
configuring it through the Power-On-Self-Test (POST).
When these preliminary tests are completed, the BIOS searches for an operating system on
one of the system’s data storage devices (hard drive, CD-ROM, etc). If one is found, the BIOS
will launch that operating system and hand c ontrol over to it. You can ent er the BIO S s etup b y
pressing the [Delete] key when the machine boots up and begins to show the memory count.
Setup Basics
The table below shows how to use the setup program with the keyboard.
Key Function
Tab Moves from one selection to the next
Left/Right Arrow Keys Changes from one menu to the next
Up/Down Arrow Keys Moves between selections
Enter Opens highlighted section
PgUp/PgDn Keys Changes settings.
Getting Help
Pressing [F1] displays a small help window that describes the appropriate keys to use and the
possible selections for the hig hlighted item. To exi t the Help Window, press [ ESC] or the [F1]
key again.
In Case of Problems
If you discover that you have trouble booting the computer after making and saving the
changes with the BIOS setup program, res tart the co mputer by hol ding the p ower butto n dow n
until the computer shuts off (usu ally within 4 seconds); resett ing by pressing CTRL-AL T-DEL;
or clearing the CMOS.
The best advice is to only alter settings that you thoroughly understand. In particular, do not
change settings in the Chipset section unless you are sure of the outcome. TYAN or your
22
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
system manufacturer has carefully chosen the chipset defaults for best performance and
reliability. Even a seemingly small change to the Chipset setup options may cause the system
to become unstable or unusable.
Setup Variations
Not all systems have the same BIOS setup layout or options. While the basic look and function
of the BIOS setup remains more or less the same for most systems, the appearance of your
Setup screen may differ from the charts shown in this section. Each system design and
chipset combination requ ires a custom configuration. In addit ion, the final appearance of the
Setup program depends on the system designer. Your system designer may decide that
certain items should not be available for user configuration, and remove them from the BIOS
setup program.
The BIOS contains the following menu:
Main
Use this menu for basic system configuration.
Advanced
Use this menu to set the Advanced Features available on your system.
Security
Use this menu to configure security settings for your system.
Power
Use this menu to specify your settings for power management.
Boot
Use this menu to configure boot options for your system.
Exit
This contains the various BIOS exit options.
Note
On the following pages, options written in bold type represent the
BIOS Setup default.
23
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.2 Main Menu
In this section, you can alter general features such as the date and time, as well as access to
the IDE configuration options. Note that the options listed below are for options that can
directly be changed within the Main Setup screen. Users use the arrow keys to highlight the
item and then use the <PgUp> or <PgDn> keys to select the value you want in each item.
System Time / Date setup
System Time: Adjusts the system clock.
HH Hours (24hr. format)
MM Minutes
SS Seconds
System Date: Adjusts the system date.
MM Months
DD Days
YYYY Years
Legacy Diskette A
Defines the floppy drive type
NONE / 360K, 5.25 in / 1.2 M, 5.25 in / 720 K, 3.5 in / 1.44 M, 3.5 in / 2.88
M, 3.5 in
Installed Memory
This displays the amount of system memory present on the system.
24
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.2.1 IDE Primary/Master, Primary/Slave Setup
Computer detects IDE drive type from drive C to drive F.
Press Enter on any of the Primary/Master, Primary/Slave optio ns to view advanced details of
the corresponding drive. The system displays advanced details like the number of
heads/cylinders/sectors on the detected disk and the maximum storage capacity of the disk.
Multi-Sector Transfers
This option allows you to specify the number of sectors per block for multiple sector transfers.
16 Sectors / 2 Sectors / 4 Sectors / 8 Sec tors /Disabled
LBA Mode Control
Enables or disables LBA Mode.
When LBA is turned on, the BIOS will enable geometry translation. This translation may be
done in the same way that it is done in Extended CHS or large mode, or it may be done using
a different algorithm called LBA-assist translation. The translated geometry is still what is
presented to the operating system for use in Int 13h calls. The difference between LBA and
ECHS is that when using ECHS the BIOS translates the parameters used by these calls from
the translated geometry to the drive's logical geometry. With LBA, it translates from the
translated geometry directly into a logical blo ck (sector) number.
Disabled / Enabled
32 Bit I/O
Enables or disables 32 bit data transfer mode.
Enabling this option causes the PCI hard disk interface controller to bundle together two 16-bit
chunks of data from the drive into a 32-bit group, which is then transmitted to the processor or
memory. This results in a small performance increase.
Enabled / Disabled
25
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
Transfer Mode
These modes determine the speed at which data is transferred to and from the drive. The Auto
option automatically determines t h e co rrec t transfer rates.
Auto / Standard / Fast PIO 1 / Fast PIO 2 / Fast PIO 3 / Fast PIO 4 / FPIO
3 / DMA 1 / FPIO 4 / DMA 2
Ultra DMA Mode
Enables or disables Ultra DMA Mode.
Ultra DMA (UDMA, or, more accurately, Ultra DMA/33) is a protocol for transferring data
between a hard disk drive through the computer's data paths (or bus) to the comp uter's
random access memory (RAM). The Ultra DMA/33 protocol transfers data in burs t m od e at a
rate of 33.3 MBps (megabytes per second), twice as fast as the previous Direct Memory
Access (DMA) interface.
Ultra DMA support in your computer means that it will boot (start) and open new applications
more quickly. It will also help users of graphics-intensive and other applications that require
large amounts of access to data on the hard drive. Ultra DMA uses Cyclical Redundancy
Checking (CRC), offering a new level of data protection.
Disabled / Mode 0 / Mode 1 / Mode 2
3.2.2 SATA Port 1/2/3/4
Press Enter on any of the Primary/Master, Primary/Slave optio ns to view advanced details of
the corresponding drive.
26
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.2.3 Memory Cache
This setting allows you to tweak the various cache settings for optimal performance of your
system. Press Enter to display the various cache settings.
Cache System BIOS Area
This feature is only available when the system BIOS is shadowed. It enables or disables the
caching of the system BIOS RO M at F0000h-FFFFFh via the L2 cache. This grea tly speeds
up accesses to the system BIOS. However, this does not necessarily make the system
perform better because the OS does not need to access the system BIOS often.
As such, it would be a waste of L2 cache bandwid th to cache the system BIOS instead of data
that are more critical to the system's performance. In addition, if any program writes into this
memory area, it will result in a system crash. So, it is recommended that you write protect this
area for optimal system performance.
NULL / Write Protect
Cache Video BIOS Area
This feature is only valid when the video BIO S is sh adowed. It en ables or dis ables the cac hing
of the video BIOS ROM at C0000h-C7FFFh via the L2 cache. This greatly speeds up
accesses to the video BIOS. However, this does not necessarily make the system perform
better because the OS bypasse s the BIOS and uses the graphics driver to access the video
card's hardware directly.
As such, it would be a waste of L2 cache bandwidth to cache the video BIOS instead of data
that are more critical to t he system's performance. In a ddition, if any program writes into this
memory area, it will result in a system crash. So, it is recommended that you write protect this
area for optimal system performance.
NULL / Write Protect
27
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
Cache Base 0-512K
This feature allows you to control caching of 512K base memory.
Uncached / Write Back / Write Through / Write Pr otect
Cache Base 512K-640K
This feature allows you to control caching of 512K 640K base memory.
Uncached / Write Back / Write Through / Write Protect
Cache Extended Memory Area
This feature allows you to control caching of system memory above one megabyte.
Uncached / Write Back / Write Through / Write Pr otect
Cache A000-AFFF/B000-BFFF
These features allow you to control caching of A000-AFFF/B000-BFFF memory.
USMC Caching / Disabled / Write Through / Write Protect / Write Back
Cahe C8000-CBFF/Cache CC00-CFFF/Cahe D000-D3FF/Cahe D400-D7FF/Cache D800D8FF/Cahe DC00-DFFF
These feature allows you to control caching of C8000-CBFF/CC00-CFFF/D000-D3FF/D400D7FF/D800-D8FF/DC00-DFFF memory.
Disabled / Write Through / Write Protect / Write Back
28
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.2.4 Boot Features
This option allows setting boot parameters. Press Enter to view the Boot Features screen.
Floppy Check
This feature is used to verify floppy type on boot. Selecting “Disabled” will speed the boot
process.
Disabled / Enabled
Summary Screen
Enables or disables the display of the summary screen during boot up.
When Summary Screen is Enabled (the default), a Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility summary
screen appears during system boot a fter the power-on self-te st (POST). The sum mary screen
lists many of the system setup settings. When this option is set to Disabled, the summary
screen does not appear.
Enabled / Disabled
Boot-time Diagnostic Screen
This feature is used to display the diagnostic screen during the boot process.
Enabled / Disabled
Quick Boot Mode
This BIOS feature allows you to decrease the time it takes to boot up the computer by
shortening or skipping certain standard booting procedures.
If enabled, the BIOS will shorten the booting process by skipping som e tests and shortening
others. In addition, it will also perform the following to further speed up the booting process:
29
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
• Spin up the hard disks as soon as power is supplied (or as soon as
possible)
• Initialize only critical parts of the chipset
• Read memory size from the SPD (Serial Presence Detect) chip on the
memory modules
• Eliminate logo delays
If disabled, the BIOS will run the whole gamut of boot-up tests.
It is recommended that you disa ble this featu re when you boot up a new compute r for the first
time or whenever you install a new piece of hardware. This allows the BIOS to run full
diagnostic tests to detect any problems that may slip past Quick Boot's abbreviated testing
scheme.
After a few error-free test runs, you should enable this feature for much faster booting.
Enabled / Disabled
Extended Memory Testing
Determines the tests that will be run on extended memory (memory above 1MB) during boot
up.
Normal / Just zero it / None
3.3 Advanced
This section facilitates configuring advanced BIOS options for your system.
Installed OS
Select the operating system installed on the PC.
Note: An incorrect setting can cause the operating system to behave unpredictably.
Other / Win95 / Win98 / WinMe / Win2000
30
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
Reset Configuration Data
If you install a new piece of hardware or modify your computer's hardware configuration, the
BIOS will automatically detect the changes and reconfigure the ESCD (Extended System
Configuration Data). Therefore, there is usually no need to manually force the BIOS to
reconfigure the ESCD.
However, sometimes, the BIOS may not be able to detect the hardware changes. A serious
resource conflict may oc cur and the operating syste m may not even boot as a result. This is
where the Reset Configuration Data BIOS feature comes in.
This BIOS feature allows you to manually force the BIOS to clear the previously saved ESCD
data and reconfigure the settings. All you need to do is enable this BIOS feature and then
reboot your computer. The new ESCD should resolve the conflict and allow the operating
system to load normally.
Please note that the BIOS will automatically reset it to the default setting of No after
reconfiguring the new ESCD. So, there is no ne ed fo r you to manually disable this feature after
rebooting.
Yes / No
Large Disk Access Mode
This option determines whether a hard drive with more than 1024 cylinders, more than 16
heads and or more than 64 tracks per sector is present on the system. Set this option to DOS
if such a hard drive is present. Else, set this option to Other.
Virtually, all mode rn hard disks have t hese ch aract ers so le ave th is option at DOS, unless you
know otherwise.
DOS / Other
Route Port 80h cycles to
This feature allows you to route Port 80h I/O cycles to LPC or PCI bus.
LPC / PCI
Legacy USB Support
When enabled, the BIOS takes control of the US B ports. Enab le th is only if you run an OS that
does not support USB (e.g. DOS ) or when you have USB hardware like USB mice tha t you
want to use even before the operating system loads.
Enabled / Disabled
31
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.3.1 Advanced Chipset Control
This section allows you to fine tune the chipset configuration.
ECC Condition
This feature is used to select ECC Error condition to be detected.
Multiple bit / None / Single bit / Both
ECC Error Handler
When an ECC error occurs, it generates an interrupt. This feature is used to select the type of
interrupt to report.
SMI / NMI / SCI
Parallel ATA
This feature is used to enable the PATA function.
Enabled / Disabled
Serial ATA
This feature is used to enable the SATA function.
Enabled / Disabled
Native Mode Operation
This feature is used to choose Native Mode for A TA. However, certain OS is not supported
under Native Mode.
Auto / Serial ATA
SATA Controller Mode Option
This feature is us ed to select SATA contro ller mode. In “compat ible mode”, SATA and PATA
drives are auto-detected and plac ed in Legacy mode. In “Enh anced (non-AH CI) mode”, SATA
and PATA drives are auto-detected and placed in Native IDE mode.
Compatible / Enhanced (non-AHCI)
32
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
SATA RAID Enable
This feature is used to enable SATA RAID functionality.
Disabled / Enabled
SATA AHCI Enable
This feature is used to enable SATA AHCI functionality.
Disabled / Enabled
3.3.1.1 Integrated Device Control Sub-Menu
These items are for determining whether the integrated PCI devices will be enabled in PCI
configuration space.
USB Device 29, Function 3:
Enable or Disable this USB Device by setting item to the desired value.
Enabled / Disabled
USB Device 29, Function 2 & 3:
Enable or Disable these 2 USB Functions by setting item to the desired value.
Enabled / Disabled
USB Device 29, Function 1 & 2 & 3:
Enable or Disable these 3 USB Functions by setting item to the desired value.
Enabled / Disabled
USB Device 29, Function 0 & 1 & 2 & 3:
Enable or Disable these 4 USB Functions by setting item to the desired value.
Enabled / Disabled
USB Device 29, Function 7:
Control USB 2.0 functionality through this Setup Item.
Enabled / Disabled
33
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.3.1.2 PCI Express Sub-Menu
These items are for debugging the PCI Express Ports.
34
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.3.1.2.1 Slot 1 (x8 Port) Sub-Menu
These items are for PCI Express MCH Dev1 port control options.
PCI Express MCH Dev 1
This feature is used to enable PCI Express MCH Dev1 port control.
Enabled / Disabled
35
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.3.1.2.2 Slot 2 (x4 Port) Sub-Menu
These items are for PCI Express Root Port #1 control options.
PCI Express Port #1
This feature is used to enable PCI Express Port #1 control.
Auto / Enabled / Disabled
36
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.3.1.2.3 Integrated LAN1/LAN2 (BCM5721) Sub-Menu
These items are for Integrated LAN1/LAN2 control option.
Integrated LAN Control
This feature is used to enable Integrated LAN control.
Auto / Enabled / Disabled
Option ROM Scan
This feature is used to enable the functionality of option ROM scanl.
Disabled / Enabled
37
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.3.2 Advanced Processor Options
This section allows you to fine-tune the processor options.
Hyperthreading
Enable this only if you have an Intel Hyper Threading processor.
Hyper-Threading Technology en ables multi-thre aded software app lications to exec ute threads
in parallel. Hyper-Threading Technology provides thread-level-parallelism (TLP) on each
processor resulting in increased utilization of processor execution resources. As a result,
resource utilization yields higher processing throughput. Hyper-Threading Technology is a
form of simultaneous multi-threading technology (SMT) where multiple threads of software
applications can be ru n simultaneously on one pro cessor. This is ac hieved by duplicating the
architectural state on each processor, while sharing one set of processor execution resources.
Hyper-Threading Technology also delivers faster response times for multi-tasking workload
environments. By allowing the processor to use on-die resources that would otherwise have
been idle, Hyper-Th reading Techn ology provides a performance b oost on multi- threading and
multi-tasking operations for the Intel NetBurst® microarchitecture.
Enabled / Disabled
Single Logical Proc. Mode
This feature is used to enable the Single Logical Processor mode.
Disabled/ Enabled
L3 Cache
This feature is used to enable the L3 cache funtionality.
Enabled / Disabled
38
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
Thermal Management 2
Thermal Management throttles the processor back as it reaches its maximum operating
temperature. Throttling reduces the number of processing cycles, thereby diminishing the heat
dissipation of the CPU. This cools the unit. Once the CPU has reached a safe operating
temperature, thermal throttling is automatically disabled, and normal full speed processing
begins again.
The BIOS supports two types of thermal management.
• Thermal Monitor 1: Thermal Monitor 1 uses a highly accurate on-die
temperature sensing circuit in the CPU that has the ability to act quickly
upon any thermal issues (~50ns). This circuitry keeps an eye on the most
taxed areas of the CPU-die at all times and will quickly act upon
temperatures going over the safety limits. The thermal monitor’s control
circuit, when active, lowers the CPU tem p erature by throttling the int er nal
CPU clock speed. This is done with a 50% duty-cycle, which means that a
2GHz CPU will then effectively run at a 1GHz clock speed. Due to the fast
response time of the thermal monitor circuit (~50ns) the CPU will only be
‘throttled’ for a very brief period. Once the CPU-die temperature is within
safe operating limits again it’ll set back to the 2GHz clock speed it
originally operated at.
• Thermal Monitor 2: Thermal Monitor 2 decreases or increases the CPU
clock and core voltage according to the CPU load. This information is read
from the five VID pins of the CPU. Accordingly, the CPU temperature is
also automatically decreased, when the core voltage is decreased. This
improves the CPU lifespan. Th e states switch is so fast that the
performance decrease is insignificant.
Disabled / Enabled
Set Max Ext CPUID=3
Sets Max CPUID extended function value to 3.
Disabled / Enabled
C1 Enhanced Mode
This feature is used to enable the C1 Enhanced mode.
Disabled / Enabled
VT Feature
This feature is used to enable the VT feature.
Disabled / Enabled
No Execute Mode Mem Protection
This feature is used to enable the function of No Execute Mode Mem Protection.
Enabled / Disabled
Frequency Ratio
This feature is used to set the Frequency Ratio
X 8 / 19 /14 /15 / 16 / 17 / 18
Processor Power Management
This feature is used to set the Processor Power Management.
GV1/ GV3 Only / Disabled / C States Only / Enabled
39
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.3.3 I/O Device Configuration
This setting allows you to configure I/O devices.
Serial Port A:
This defines how the first serial port is detected and configured.
Disabled / Enabled
Base I/O Address:
Set the base I/O address for serial port A.
3F8 / 2F8 / 3E8 / 2E8
Interrupt:
Set the interrupt for serial port A.
IRQ3 / IRQ4
Parallel Port
This defines how the parallel port is detected and configured.
Disabled / Enabled
Mode
This field allows the user to s elect the parallel port mode. The def ault value is Standard that
automatically selects the correct mode to use. The other modes are explained as follows:
SPP works with all parallel port devices. However, it is the slowest transfer mode and should
only be used when faster transfer modes cannot be used.
There are two faster bidirect ional modes av ailable - the ECP (Exten ded Capabilit ies Port) and
EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port) modes.
40
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
ECP uses the DMA protocol to achieve data transfer rates of up to 2.5 Mb/s and provides
symmetric bidirectional communication. On the other hand, EPP uses existing parallel port
signals to provide asymmetric bidirectional communication.
Generally, because of its FIFOs and the DMA channel it uses, ECP is good for large data
transfers (useful for scanners and printers). On the other hand, EPP is better with links that
switch directions frequently (like parallel port drives).
SPP / EPP / ECP
Base I/O Address / Interrupt
This determines the base address and interrupt of the parallel port.
378 / IRQ7 / Disabled / 278 / IRQ5 / 3BC / IRQ7
DMA Channel
This BIOS feature determines which DMA channel the parallel port should use when it is in
ECP mode.
The ECP mode uses the DMA protocol to achieve data transfer rates of up to 2.5 Mbits/s and
provides symmetric bidirectional communications. For all this, it requires the use of a DMA
channel.
By default, the parallel port uses DMA Channel 3 when it is in ECP mode. This works fine in
most situations.
This feature is provided just in case one of your add-on cards requires the use of DMA
Channel 3. In such a case, you can use this BIO S feature to force the paralle l port to use the
alternate DMA Channel 1.
Please note that there is no perf ormance advantage in choosing DMA Channel 3 over DMA
Channel 1 or vice versa. As long a s e ither Cha nnel 3 or Channel 1 is av ailabl e for your parallel
port to use, the parallel port will be able to function properly in ECP mode.
DMA 1 / DMA 3
Floppy Disk Controller
This defines how the floppy disk controller is detected and configured.
Enabled / Disabled
41
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.3.4 Hardware Monitor
Auto Fan Control
This feature is used to set function of Auto Mode Fan Control.
Disabled / Enabled
42
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.3.4.1 Voltage Monitoring
3.3.5 DMI Event Logging
These items are used to view and modify DMI event logs.
43
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
Event Logging
Select Enabled to allow logging of DMI events
Disabled / Enabled
ECC Event Logging
Select Enabled to allow logging of ECC events
Disabled / Enabled
Clear all DMI event logs
Setting this to ‘Yes’ will clear the DMI event log after rebooting.
No / Yes
3.4 Security
These settings allow you to configure the security options for your system.
The system displays the current supervisor and user passwords.
Set Supervisor Password
This option allows the superv isor t o set th e supe rvis or pass word to rest rict acc ess to th e BIOS
settings.
Set User Password
This option allows the user to set the user password.
Diskette access
This option allows the user to control access to diskette drives.
Supervisor / Disabled
44
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
Fixed disk boot sector
This option allows the user to write protect boot sector on hard disk to protect against viruses.
Normal / Write Protect
Virus check reminder
This feature is used to display reminder message at the boot process.
Disabled / Enabled
System backup reminder
This feature is used to display reminder message at the boot process.
Disabled / Enabled
Password on boot
When enabled, the system will ask for a password at every boot. The system will continue
booting only if the co rrect password is entere d. If the wrong pass word is entered three t imes,
the system will automatically shut down.
Disabled / Enabled
FirstWare Authentication Level
This feature is used to select FirstWare Authentication Level.
High / Medium / Low
3.5 Power
These settings allow you to configure the power options for your system.
45
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
Resume On Time
When enabled, this allows the system to be worked up at a specified time. This time is
specified by the Resume Time parameter.
Off / On
Resume Time
This option allows the user to specify the time when the system is to wake up.
Power Button Behavior
This specifies the behavior of the system after the power button is pressed.
• On/Off - This powers on / powers off the system after the power button is
pressed.
• Wake/Sleep - This wakes the system from/puts the system to sleep.
Suspend Mode
This feature is used to select the mode of suspend mode.
Suspend / On
After Power Failure
Specifies the mode of operation after the system recovers from a p ower loss.
• Enabled: This restores the system to the last state it was in before the
power loss occurred.
• Disabled: This keeps the power switched off till the power button is
pressed.
3.6 Boot
Use this screen to select options for the Boot Settings Configuration.
46
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 3: BIOS Setup
3.7 Exit
These settings set the exit options on your system.
Exit Saving Changes
This exits BIOS setup after saving the changes made.
Exit Discarding Changes
This exits BIOS setup after discarding the changes made.
Load Setup Defaults
Loads the factory default values.
Discard Changes
Discards all changes made without exiting BIOS setup.
Save Changes
Saves all changes made without exit BIOS.
47
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Chapter 4: Diagnostics
Chapter 4: Diagnostics
Note: if you experience problems with setting up your system, always check the following
things in the following order:
Memory, Video, CPU
By checking these items, you will mos t likely find o ut what the prob lem might ha ve been whe n
setting up your system. For more information on tr oubleshooting , check the TYAN website at:
http://www.tyan.com
4.1 Beep Codes
Fatal errors, which halt the boot process, are communicated through a series of audible
beeps. For example, if the BIOS POST can initialize the video but an error occurs, an error
message will be displayed. If it cannot dis play the mess age, it will rep ort the error a s a series
of beeps.
The most common type of error is a memory error.
Before contacting your vendor or TYAN Technical Support, be sure that you note as much as
you can about the beep code length and order that you experience. Also, be ready with
information regarding add-in cards, drives and O/S to speed the support process and come to
a quicker solution.
.
4.2 Flash Utility
Every BIOS file is unique for the motherboard it was designed for. For Flash Uti lities, BIOS
downloads, and information on how to properly use the Flash Utility with you r motherboard,
please check the TYAN web site: http://www.tyan.com/
Note: Please be aware that by flas hing your B IOS, you agree that i n the eve nt of a BIOS flas h
failure, you must contact your dealer or third party vendor for a replacement BIOS. There are
no exceptions. TYAN doe s not have a p olicy for replacin g BIOS chips dire ctly with end users .
In no event will TYAN be held responsible for damages done by the end user.
48
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Appendix I: Glossary
Appendix I: Glossary
ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface): a power manageme nt specification
that allows the operating s ystem to control the amount of p ower distributed to the compute r’s
devices. Devices not in use can be turned off, reducing unnecessary power expenditure.
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port): a PCI-based interface which was designed specifically for
demands of 3D graphics applications. The 32-bit AGP channel directly links the graphics
controller to the main memory. While the channel runs at only 66 MHz, it supports data
transmission during both the rising and falling ends of the clock cycle, yielding an effective
speed of 133 MHz.
ATAPI (AT Attachment Packet Interface): also known as IDE or ATA; a drive
implementation that inc ludes the disk controller on the dev ice itself. It allows CD-ROMs and
tape drives to be configured as master or slave devices, just like HDDs.
ATX: the form factor designed to replace the AT form factor. It improves on the AT design by
rotating the board 90 degrees, so that the IDE connectors are closer to the drive bays, and the
CPU is closer to the power supply and cooling fan. The keyboard, mouse, USB, serial, and
parallel ports are built-in.
Bandwidth: refers to carrying capacity. The greater the bandwidth, the more data the bus,
phone line, or other electrical path, can c arry. Greater bandwidth, then, also resu lts in greater
speed.
BBS (BIOS Boot Specification): is a feature within the BIOS that creates, prioritizes, and
maintains a list of all In itial Program Load (IPL) de vices, and then stores that list in NVRAM.
IPL devices have the abilit y to load and execute an OS, as well as provide the abi lity to retur n
to the BIOS if the OS load process fa ils for some reason. At that point, the next IPL device is
called upon to attempt loading of the OS.
BIOS (Basic Input/O utput System): the progra m that resides in th e ROM chip, and provides
the basic instructions for contr olling you r compu ter’s h ardware. Bot h the operat ing sy stem and
application software use BIOS routines to ensure compatibility.
Buffer: a portion of RAM which is used to temporarily store data, usually from an application,
though it is also used when printing, and in most keyboard drivers. The CPU can manipulate
data in a buffer before copying it, all at once, to a disk drive. While this improves system
performance --- reading to or writing from a d isk drive a single time is much faster than doi ng
so repeatedly --- there is also the possibility of losing your data should the system crash.
Information stored in a buffer is temporarily stored, not permanently saved.
Bus: a data pathway. The term is used especially to refer to the connection between the
processor and system memory, and between the processor and PCI or ISA local buses.
Bus mastering: allows peripheral devices and IDEs to access the system memory without
going through the CPU (similar to DMA channels).
Cache: a temporary storage area fo r data that will be needed ofte n by an applica tion. Using a
cache lowers data acces s times, since the need ed information is s tored in the SRAM instead
of in the slow DRAM. Note that the c ache is also much smaller than your regular mem ory: a
typical cache size is 512KB, while you may have as much as 4GB of regular memory.
49
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Appendix I: Glossary
Cache size: refers to the physical size of the cache onboard. This should not be confused with
the cacheable area, which is th e t otal amount of memory which ca n be sc anned by t he sys tem
in search of data to put into the cache. A typical setup would be a cache size of 512KB, and a
cacheable area of 512MB. In this case, up to 512KB of the main memory onboard is capable
of being cached. However, only 512KB of this memory will be in the cache at any given
moment. Any main memory above 512MB could never be cached.
Closed and open jumpers: jumpers and jumper pins are active when they are “on” or
“closed”, and inactive when they are “off” or “open”.
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductors): chips that hold the basic startup
information for the BIOS.
COM port: another name for the serial port, which is called as such because it transmits the
eight bits of a byte of dat a along one wire, and receiv es data on another single wire (that is,
the data is transmitted in serial form, one bit aft er another). Para llel ports transmit the bits of a
byte on eight different wires at th e same time (that is, in parallel form, eight bits at the same
time).
DDR (Double Data Rate): is a technology designed to doub le the cloc k s peed of the memor y.
It activates output on both the rising and falling edge of the syst em clock rather than on just
the rising edge, potentially doubling output.
DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module): faster and more capacious form of RAM than SIMMs,
and do not need to be installed in pairs.
DIMM bank: sometimes called DIMM sockets, because the physical slot and the logical unit
are the same. That is, one DIMM modu le fits in to one DIM M soc ket, wh ich is c apable of acting
as a memory bank.
DMA (Direct Memory Access): channels that are similar to IRQs. DMA channels allow
hardware devices (like soundcards or keyboards) to access the main memory without
involving the CPU. This frees up CPU resources for other tasks. As with IRQs, it is vital that
you do not double up devices on a single line. Plug-n-Play devices will take care of this for
you.
Doze mode: in this mode, only the CPU’s speed is slowed.
DRAM (Dynamic RAM): widely available, very affordable form of RAM which has the
unfortunate tendency to los e data if it is not rec harged regul arly (every few mi lliseconds). Th is
refresh requirement makes DRAM three to ten time s slower than non-recha rged R AM suc h as
SRAM.
ECC (Error Correction Code or Error Checking and Correcting): allows data to be
checked for errors during run-time. Errors can subsequently be corrected at the same time
that they’re found.
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM): also called Flash BIOS, is a ROM
chip which can, unlike normal ROM, be updated . This allows you to ke ep up with changes in
the BIOS programs without having to buy a n ew chip. TYAN’s BIOS updates can be found at
http://www.tyan.com
50
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Appendix I: Glossary
EMRL: Embedded RAID Logic. An Adaptec specific RAID technology.
ESCD (Extended System Configuration D ata): a format for storing informatio n about Plug-
n-Play devices in the sys tem BIO S. This inform ation helps p roperly c onfigure the s ystem ea ch
time it boots.
Fault-tolerance: a term describing a system where one component can quickly be replaced
without causing a loss of service, such as in a RAID system.
Firmware: low-level software that controls the system hardware.
Form factor: an industry term for the size, s hape, power supp ly type, and ext ernal connec tor
type of the Personal Compute r Board (PCB) or motherboard. The standard form factors are
the AT and ATX, although TYAN also makes some Baby-AT and ATX Footprint boards.
Global timer: onboard hardware timer, such as the Real-Time Clock (RTC).
Handshaking: a process where two devices initiate communications. One device, typically the
server, sends a message to another device, typically a client, in order to request establishment
of a communications chan ne l. The two devices will then exc h an ge messages back and forth in
order to settle on a communications protocol.
HDD: stands for Hard Disk Drive, a type of fixed drive.
H-SYNC: controls the horizontal synchronization/properties of the monitor.
IC (Integrated Circuit): the formal name for the computer chip.
IDE (Integrated Device/Drive Electronics): a simple, self-contained HDD interface. It can
handle drives up to 8.4 GB in size. Almost all IDEs sold now are in fact Enhanced IDEs
(EIDEs), with maximum capacity determined by the hardware controller.
IDE INT (IDE Interrupt): a hardware interrupt signal that goes to the IDE.
I/O (Input/Output): the connection between your computer and another piece of hardware
(mouse, keyboard, etc.)
Initial Program Load (IPL): a feature built into BBS-compliant devices, describing those
devices as capable of loading and executing an OS, as well as being able to provide control
back to the BIOS if the loading attempt fails.
IPL: see Initial Program Load.
IRQ (Interru pt Request ): an electronic request th at runs from a hardware dev ice to the CPU.
The interrupt controller as s igns priorities to incoming requests and delivers them to the CPU. It
is important that there is onl y one device hook ed up to each IRQ lin e; doubling up devices on
IRQ lines can lock up your system. Plug-n-Play operating systems can take care of these
details for you.
ISA (Industry Standard Architecture): a slower 8- or 16-bit bus (data pathway).
51
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Appendix I: Glossary
Latency: the amount of time that one part of a system spe nds waiti ng for an other part to catch
up. This is most common when the system sends data out to a peripheral device, and it
waiting for the periphera l to sen d s ome data back (per ipherals ten d to be slower th an onboa rd
system components).
Mirroring: see RAID.
NVRAM: ROM and EEPROM are both examples of Non-Vo latile RAM, memory that holds its
data without power. DRAM, in contrast, is volatile.
OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers): Compaq or IBM package other companies’
motherboards and hardware inside their case and sell them.
Parallel port: transmits the bits of a byte on eight different wires at the same time (that is, in
parallel form, eight bits at the same time).
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect): a 32 or 64-bit local bus (data pathw ay) which is
faster than the ISA bus. Local buses are those which operate within a single system (as
opposed to a network bus, which connects multiple systems).
PCI PIO (PCI Programmable Input/Output) modes: the data transfer modes used by IDE
drives. These modes us e the CPU for data transfer (in cont rast, DMA channels do not). PCI
refers to the type of bus used by these modes to communicate with the CPU.
PCI-to-PCI bridge: allows you to connect multiple PCI devices onto one PCI slot.
Pipeline burst SRAM: a type of RAM that can maintain it’s data as long as power is provided
to the memory chips. In th is configuration, SRAM requests are pipelined, which means that
larger packets of data are sent to the memory at one time, and acted upon qu ickly. This type
of SRAM operates at bus speeds higher than 66MHz.
Pipelining: improves system performance by allowing the CPU to begin executing a second
instruction before the first is co mpleted. A pipeline can be likene d to an assembly line, with a
given part of the pipeline repeatedly executing a set part of an operation on a series of
instructions.
PM timers (Power Management timers): software timers that count down the number of
seconds or minutes until the system times out and enters sleep, suspend, or doze mode.
PnP (Plug-n-Play): a design standard that has become ascendant in the industry. Plug-n-Play
devices require little set -up to use. Novice end users can simply plug them in to a computer
that is running on a Plug-n-Play aware operating system (such as Windows 98), and go to
work. Devices and operating systems that are not Plug-n-Play require you to reconfigure your
system each time you add or change any part of your hardware.
PXE (Preboot Execution Environme nt): one of four components that toget her make up the
Wired for Management 2.0 baseline specification. PXE was designed to define a standard set
of preboot protocol services within a client, towards the goal of allowing networked-based
booting to boot using industry standard protocols.
52
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Appendix I: Glossary
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): a way for the same data to be stored in
different places on many hard drives. By using this method, the data is stored redundantly,
also the multiple hard drives will appear as a single drive to the operating system. RAID level 0
is known as striping, where data is striped (or overlapped) across multiple hard drives, but
offers no fault-tolerance. RAID level 1 is known as mirroring, which stores the data within at
least two hard drives, but does not stripe. RAID l evel 1 also allows for faster acc ess time and
fault-tolerance, since eithe r hard drive can be read at the sam e time. RAID level 0+1 is both
striping and mirroring, providing fault-tolerance, striping, and faster access all at the same
time.
RAIDIOS: stands for RAID I/O Steering, a type of RAID technology from Inte l. RAIDIOS is a
specification used to enable an embedded I/O controller, embedded on the motherboard, to be
used as just an I/O controller or to be the I/O co mponent of a hard ware RAID subs ystem. The
RAIDIOS circuit allows an I/O Processor (either embedded on the motherboard or on an addin card) to configure the I/O controller and service the I/O controller’s interrupts. The I/O
controller and the I/O P rocessor together are two of the prim ary components of a hardware
RAID subsystem.
RAM (Random Access Memor y): technically refers to a t ype of memory wh ere any byte can
be accessed without touc hing the adjacent data, is often used to refe r to the system’s main
memory. This memory is available to any program running on the computer.
ROM (Read-Only Memory): a storage chip which contains the BIOS; the basic instru ctions
required to boot the computer and start up the operating system.
SATA (Serial ATA): is an evolutionary replacement for the Parallel ATA physical storage
interface. Serial ATA is a drop-in solution in that it is compatible with today’s software and
operating systems. It will provide for systems wh ich are easier to design, with cables that a re
simpler to route and install, smaller cable connectors, and lower voltage requirements.
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM): called as such because it can keep two sets of
memory addresses open simultaneously. By transferring data alternately from one set of
addresses and then the other, SDRAM cuts down on the delays associated with nonsynchronous RAM, which must close one address bank before opening the next.
Serial port: called as such because it transmits the eight bits of a byte of data along one wire,
and receives data on another single wire (that is, the data is transmitted in serial form, one bit
after another).
SCSI Interrupt Steering Logic (SISL): Architecture that allows a RAID controller, such as
AcceleRAID 150, 200 or 250, to im plemen t RA ID on a syste m boa rd-e mbe dde d SCS I bus or a
set of SCSI busses. SISL: SCSI Interrupt Steering Logic ( LSI ) (only on LSI SCSI boards)
SIMM (Single In-line Memory Module): formally the most common form of RAM for
motherboards. They must be inst alled in pairs, and do not have the carrying c apacity or the
speed of DIMM modules.
Sleep/Suspend mode: in this mode, all devices except the CPU shut down.
SRAM (Static RAM): unlike DRAM, this type of R AM does not need to be refreshed in o rder
to prevent data loss. Thus, it is faster and mo re expensive.
53
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Appendix I: Glossary
SSI (Server System Infrastructure): an industry initiative intended to provide ready-to-use
design specifications for common server hardware elements (chassis, power supplies, and
racks) to promote and support server industry growth.
Standby mode: in this mode, the video an d hard drives s hut down; all other dev ices cont inue
to operate normally.
Striping: see RAID
UltraDMA-33/66/100: a fast version of the old DMA channel. UltraDMA is also called
UltraATA. Without proper UltraDMA c ontroller, your system cannot take advantage of higher
data transfer rates of the new UltraDMA/UltraATA hard drives.
USB (Universal Serial Bus): a versatile port. This one port type can function as a serial,
parallel, mouse, keyboard or joystick port. It is fast enough to support video transfer, and is
capable of supporting up to 127 daisy-chained peripheral devices.
VGA (Video Graphics Array): the PC video display standard
V-SYNC: controls the vertical scanning properties of the monitor.
ZCR: Zero Channel RAID. PCI card that allows a RAID card to use the onboard SCSI chip,
thus lowering cost of RAID solution
ZIF Socket (Zero Insertion Force socket): these sockets make it possible to insert CPUs
without damaging the sensitive CPU pins. The CPU is lightly placed in an open ZIF socket,
and a lever is pulled down. This shift th e proces sor ove r and d own, guiding into the boa rd and
locking it into place.
54
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Appendix II: Post Error Code for BIOS
Appendix II: Post Error Code for BIOS
Code Beeps / Description Code Beeps / De scr iption
02h Verify Real Mode 32h Test CPU bus-clock frequency
03h Disable Non-Ma skable Interrup t
(NMI)
04h Get CPU type 36h Warm start shut d own
06h Initialize system hardware 38h Shadow system BIOS ROM
08h Initialize chipset with initial
POST values
09h Set IN POST flag 3Ch Advanced configuration of
0Ah Initialize CPU registers 3Dh Load alternate registers with
0Bh Enable CPU cache 42h Initialize interrupt vectors
0Ch Initialize caches to initial PO ST
values
0Eh Initialize I/O component 46h 2-1-2-3. Check ROM copyright
0Fh Initialize the local bus IDE 48h Check video configuration
10h Initialize Power Management 49h Initialize PCI bus and devices
11h Load alternate registers with
initial POST values
12h Restore CPU control word
during warm boot
13h Initialize PCI Bus Mastering
devices
14h Initialize keyboard controller 4Eh Display BIOS copyright notice
16h 1-2-2-3. BIOS ROM checksum 5 0h Display CPU type and speed
17h Initialize cache before memory
autosize
18h 8254 timer initialization 52h Test keyboard
1Ah 8237 DMA controller
initialization
1Ch Reset Programmable Interrupt
Controller
20h 1-3-1-1. Test DRAM refresh 59h Initialize POST display service
22h 1-3-1-3. Test 8742 KBD
Controller
24h Set ES segment register to 4
GB
26h Enable A20 line 5Ch Test RAM between 512 and
28h Autosize DRAM 60h Test extended memory
29h Initialize POST Memory
Manager
2Ah Clear 512 KB base RAM 64h Jump to UserPatch1
2Ch 1-3-4-1. RAM failure on
address
2Eh 1-3-4-3. RAM failure on data
bits of low byte of memory bus
2Fh Enable cache before system
BIOS shadow
30h 1-4-1-1. RAM failure on data
bits of high byte of memory bus
33h Initialize Phoenix Dispatch
Manager
3Ah Autosize cache
chipset registers
CMOS values
45h POST device initialization
notice
against CMOS
4Ah Initialize all video adapters in
system
4Bh QuietBoot start (optional)
4Ch Shadow video BIOS ROM
51h Initialize EISA board
54h Set key click if enabled
58h 2-2-3-1. Test for unexpected
interrupts
5Ah Display prompt "Press F2 to
enter SETUP"
5Bh Disable CPU cache
640 KB
62h Tes t extended m emory addres s
lines
66h Configure advanced cache
registers
67h Initialize Multi Processor APIC
68h Enable external and CPU
caches
69h Setup System Management
Mode (SMM) area
55
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Appendix II: Post Error Code for BIOS
Code Beeps / Des cri p tion Code Beeps / Description
6Ah Display external L2 cache size A2h Check key lock
6Bh Load custom defaults (optional) A4h Initialize Typematic rate
6Ch Display shadow-area message A8h Erase F2 prompt
6Eh Display possible high address
AAh Scan for F2 key stroke
for UMB recovery
70h Display error messages ACh Enter SETUP
72h Check for configuration errors AEh Clear Boot flag
76h Check for keyboard errors B0h Check for errors
7Ch Set up hardware interrupt
vectors
B2h POST done - prepare to boot
operating system
7Eh Initialize coprocessor if present B4h One short beep before boot
80h Disable onboard Super I/O
B5h Terminate QuietBoot (optional)
ports and IRQs
81h Late POST device initialization B6h Check password (optional)
82h Detect and install external
B9h Prepare Boot
RS232 ports
83h Configure non-MCD IDE
BAh Initialize DMI parameters
controllers
84h Detect and install external
BBh Initialize PnP Option ROMs
parallel ports
85h Initialize PC-compatible PnP
BCh Clear parity checkers
ISA devices
86h. Re-initialize onboard I/O ports. BDh Display Mult iBoot menu
87h Configure Motherboard Devices BEh Clear screen (optional)
88h Initialize BIOS Data Area BFh Check virus and backup
reminders
89h Enable Non-Maskable
C0h Try to boot with INT 19
Interrupts (NMIs)
8Ah Initialize Extended BIOS Data
Area
C1h Initialize POST Error Manager
(PEM)
8Bh Test and initialize PS/2 mouse C2h Initialize error logging
8Ch Initialize floppy controller C3h Initialize error display function
8Fh Determine number of ATA
C4h Initialize system error handler
drives (optional)
90h Initialize hard-disk controllers C5h PnPnd dual CMOS (optional)
91h Initialize local-bus hard-disk
controllers
C6h Initialize notebook docking
(optional)
92h Jump to UserPatch2 C7h Initialize notebook docking late
93h Build MPTABLE for multi-
C8h Force check (optional)
processor boards
95h Install CD ROM for boot C9h Extended checksum (optional)
96h Clear huge ES segment
D2h BIOS Boot Block
register
97h Fixup Multi Processor table E0h BIOS Boot Block
98h 1-2. Search for option ROMs. E1h BIOS Boot Block
99h Check for SMART Drive
E2h Initialize the CPU
(optional)
9Ah Shadow option ROMs E3h Initialize system timer
9Ch Set up Power Management E4h Initialize system I/O
9Dh Initialize security engine
E5h Check force recovery boot
(optional)
9Eh Enable hardware interrupts E6h Checksum BIOS ROM
9Fh Determine number of ATA and
E7h Go to BIOS
SCSI drives
A0h Set time of day E8h Set Huge Segment
56
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Appendix II: Post Error Code for BIOS
Code Beeps / Des cri p tion Code Beeps / Description
E9h Initialize Multi Processor F1h Initialize Run Time Clock
EAh Init ialize OEM special code F2h Initialize video
EBh Initialize PIC and DMA F3h Initialize System Management
Mode
ECh Initialize Memory type F4h Output one beep before boot
EDh Initialize Memory size F5h Boot to Mini DOS
EEh Shadow Boot Block F6h Clear Huge Segment
EFh System memory test F7h Boot to Full DOS
F0h Initialize interrupt vectors
57
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7230A S5160 Appendix III: SMDC Information
Appendix III: SMDC Information
Tyan Server Management Daug hter Card (SMDC) is a powerful yet cost-eff icient solution for
high-end server management hardware packages. Tyan’s goal is to provide remote system
monitoring and control even when the operating system is absence or simply fails. This
empowers Tyan’s server board with advanced industrial-standard features.
Tyan SMDC is a snap-in card that provides essential server management solution. It enables
any IT Manager by providing multi-interfaces to access the hardware remotely and perform
monitor, control and diagnose activities effectively.
Tyan SMDC is powered by an int elligent cont roller known as Baseboard Manageme nt Control
(BMC). BMC is a standalone mini-CPU and runs on its own Real Time Operating System
(RTOS) to complete all different kinds of tasks. Backed by Qlogic’s ARM7 technology, IT
manager can rest assure his server machines are always taken care.
Tyan SMDC is not a peripheral card. Unlike regular peripheral card such as AGP card,
Network card or SCSI card, SMDC does not requ i re an y ha rdwa re spe cific dr iv er. As long as a
standby power comes into the system, SMDC will begin looking after the system.
Tyan SMDC provides dive rsified methods to com municate w ith th e hardwa re. IT m anager ha s
the flexibility to choose among Keyboard Controller Style (KCS), Block Transfer (BT) style,
Intelligent Chassis Management Bus (ICMB), Intelligent Platform Management Bus (IPMB),
Emergency Management Port (EM P) and standard IPMI -Over-LAN comm unication as defined
in latest IPMI 1.5 specification.
Tyan SMDC is compatible with all IPMI-compliance software as well as Tyan System
Operator
By adding SMDC, Tyan’s server board becomes a highly manageable and IPMI compatible
system with all the advanced features suggesting in IPMI Spec.
More detailed information on Tyan’s SMDC card can be found on our website:
http://www.tyan.com
TM
(TSO) software package.
58
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7221 S5150 Technical Support
Technical Support
If a problem arises with your system, you should first turn to your dealer for direct support.
Your system has most likely been configured or designed by them and they should have the
best idea of what hardware and s oftware your system contains. Hence , they should be of the
most assitance for you. Furthermore, if you purchased your system from a dealer near you,
take the system to them directly to have it serviced instead of attempting to do so yourself
(which can have expensive consequences).
If these options are not available for you then Tyan Computer Corporation can hel p. Besides
designing innovative and quality products for over a decade, Tyan has continuously offered
customers service beyond their expectations. Tyan's website (www.tyan.com
easy-to-access resourc es such as in-depth Linux Online S upport sections with downloadable
Linux drivers and co mprehensive compatibility reports for chassis, memory and much more.
With all these convenient resources just a few keystrokes away, users can easily find the
latest softare and operating system components to keep their systems running as powerful
and productive as possible. Tyan also ranks high for its commitment to fast and friendly
customer support through email. By offering plenty of options for users, Tyan serves multiple
market segments with the industry's most competitive services to support them.
"Tyan's tech suppor t is some of the most impr essive we've seen, with grea t response
time and exceptional organization in general" - Anandtech.com
Please feel free to contact us directly for this service at techsupport@tyan.com
Help Resources:
1. See the beep codes section of this manual.
2. See the TYAN website for FAQ’s, bulletins, driver updates, and
other information: http://www.tyan.com
3. Contact your dealer for help BEFORE calling TYAN.
4. Check the TYAN user group: alt.comp.periphs.mainboard.TYAN
) provides
Returning Merchandise for Service
During the warranty period, contact your distributor or system vendor FIRST for any product
problems. This warranty only covers normal customer use and does not cover damages
incurred during shipping or failure due to the alteration, misuse, abuse, or improper
maintenance of products.
NOTE: A receipt or copy of your invoice marked with th e date of purchase is required bef ore
any warranty service can be rendered. You may obtain service by calling the manufacturer for
a Return Merchandise Au thorizat ion (RMA) n umbe r. The RMA n um ber should be pro minentl y
displayed on the outside o f the shipping carton and the package should be mailed prepaid.
TYAN will pay to have the board shipped back to you
59
http://www.tyan.com

Tomcat i7221 S5150 Technical Support
Notice for the USA
Compliance Information Statement (Declaration of Conformity
Procedure) DoC
FCC Part 15: This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules
Operation is subject to the following conditions:
1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2) This device must accept any interference received including interference that may
cause undesired operation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Plug the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that of the
receiver.
• Consult the dealer on an experienced radio/television technician for help.
Notice for Canada
This apparatus complies with the Class B limits for radio interference as specified in the
Canadian Department of Communications Radio Interference Regulations. (Cet appareil est
conforme aux norms de Classe B d’interference radio tel que specifie par le Ministere
Canadien des Communications dans les reglements d’ineteference radio.)
Notice for Europe (CE Mark)
This product is in conformity with the Council Directive 89/336/EEC,
CAUTION: Lithium battery included with this board. Do not puncture, mutilate, or dispose of
battery in fire. Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the
same or equivalent type r ecomme nded by m anufa cturer. D ispose of used b attery ac cording t o
manufacturer instructions and in accordance with your local regulations.
92/31/EEC (EMC).
Document #: D1685 - 100
60
http://www.tyan.com
 Loading...
Loading...