
ULTRAFEED® VAF-4
Wirefeeder
Operating
Manual
English
Art # A-12466
Revision: AB Issue Date: June 27, 2014 Manual No.: 0-5329
Tweco.com

WE APPRECIATE YOUR BUSINESS!
Congratulations on receiving your new Tweco product. We are proud to have you as our customer and
will strive to provide you with the best service and support in the industry. This product is backed by
our extensive warranty and world-wide service network.
We know you take pride in your work and we feel privileged to provide you with this high performance
product that will help you get the job done.
For more than 75 years Tweco has provided quality products you can trust, when your reputation is on
the line.
YOU ARE IN GOOD COMPANY!
Tweco is a Global Brand of Arc Welding Products for Victor Technologies Inc. We distinguish
ourselves from our competition through market-leading innovation and truly dependable products that
will stand the test of time.
We strive to enhance your productivity, efficiency and welding performance enabling you to excel in
your craft. We design products with the welder in mind delivering- advanced features, durability, ease
of use and ergonomic comfort.
Above all, we are committed to a safer working environment within the welding industry. Your
satisfaction with this product and its safe operation is our ultimate concern. Please take the time to
read the entire manual, especially the Safety Precautions.
If you have any questions or concerns regarding your new Tweco product, please contact our friendly
and knowledgeable Customer Service Team at:
1-800-462-2782 (USA) and 1-905-827-4515 (Canada),
or visit us on the web at www.Tweco.com

!
WARNINGS
Read and understand this entire Manual and your employer’s safety practices before installing,
operating, or servicing the equipment.
While the information contained in this Manual represents the Manufacturer’s best judgement,
the Manufacturer assumes no liability for its use.
Operating Manual Number 0-5329 for:
Tweco ULTRAFEED VAF-4 Wirefeeder Part Number W3400002
Published by:
Victor Technologies International, Inc.
16052 Swingley Ridge Road,
Suite 300 St. Louis, MO 63017
USA
www.victortechnologies.com
Copyright © 2014 by
Victor Technologies International, Inc.
® All rights reserved.
Reproduction of this work, in whole or in part, without written permission of the publisher is
prohibited.
The publisher does not assume and hereby disclaims any liability to any party for any loss
or damage caused by any error or omission in this Manual, whether such error results from
negligence, accident, or any other cause.
Publication Date: June 13, 2014
Revision Date: June 27, 2014
Record the following information for Warranty purposes:
Where Purchased: ____________________________________
Purchase Date: ____________________________________
Equipment Serial #: ____________________________________

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1: SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS ............................................... 1-1
1.01 Arc Welding Hazards ....................................................................................... 1-1
1.02 General Safety Information for Victor Regulator ............................................... 1-5
1.03 Principal Safety Standards .............................................................................. 1-7
1.04 Symbol Chart .................................................................................................. 1-8
1.05 Precautions De Securite En Soudage A L’arc .................................................. 1-9
1.06 Dangers relatifs au soudage à l’arc ................................................................. 1-9
1.07 Informations Générales de Sécurité .............................................................. 1-14
1.08 Principales Normes De Securite ................................................................... 1-16
1.09 Graphique de Symbole .................................................................................. 1-17
SECTION 2: INTRODUCTION .............................................................................. 2-1
2.01 How to Use This Manual ................................................................................. 2-1
2.02 Equipment Identification ................................................................................. 2-1
2.03 Receipt of Equipment ...................................................................................... 2-1
2.04 Description ..................................................................................................... 2-2
2.05 User Responsibility ......................................................................................... 2-2
2.06 Transportation Methods .................................................................................. 2-2
2.07 Packaged Items .............................................................................................. 2-2
2.08 Specifications ................................................................................................. 2-3
2.09 Optional Accessories ...................................................................................... 2-3
SECTION 3: INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP ................................................ 3-1
3.01 Environment ................................................................................................... 3-1
3.02 Location .......................................................................................................... 3-1
3.03 Ventilation ....................................................................................................... 3-1
3.04 Mains Supply Voltage Requirements .............................................................. 3-1
3.05 Electromagnetic Compatibility ........................................................................ 3-1
3.06 Front Panel Controls, Indicators and Features ................................................ 3-3
3.07 Rear Panel Controls and Features ................................................................... 3-8
3.08 Advanced Features Mode ................................................................................ 3-9
3.09 Wirefeeder Configuration for Different Power Sources ................................. 3-14
3.10 Attaching Tweco No. 4 MIG Torch ................................................................. 3-15
3.11 Installing Handle Assembly ........................................................................... 3-16
3.12 Installing Lifting Eye Kit (Optional) ............................................................... 3-17
3.13 Installing Wire Spool Cover (optional) .......................................................... 3-18
3.14 Installing Welding Wire Spool ....................................................................... 3-21
3.15 Wire Reel Brake ............................................................................................ 3-22
3.16 Inserting Wire into Feed Mechanism ........................................................... 3-23
3.17 Feed Roll Pressure Adjustment ..................................................................... 3-23
3.18 Installing and Changing the Feed Roll / Removing Inlet Guide & Torch Adaptor ...
3-24
3.19 Shielding Gas Regulator Operating Instructions ........................................... 3-25
3.20 Wire Feeder Set Up MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gas Shielded MIG Wire ...... 3-28
3.21 Wire Feeder Set Up MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gasless MIG Wire .............. 3-30
3.22 Prewelding Procedure ................................................................................... 3-32
3.23 Arc Signal Override (SIL_1 #2) ..................................................................... 3-32
3.24 Welding- 2T Operation .................................................................................. 3-33
3.25 Spot Operation .............................................................................................. 3-33
3.26 Welding- 4T Operation .................................................................................. 3-34

TABLE OF CONTENTS
3.27 Stitch Operation ............................................................................................ 3-35
3.28 PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) Protection of Power Source Contactor
Control Output .............................................................................................. 3-36
3.29 Ground Fault Operation ................................................................................. 3-36
3.30 Electronic Motor Protection .......................................................................... 3-36
SECTION 4: SERVICE....................................................................................... 4-1
4.01 Cleaning The Unit ............................................................................................ 4-1
4.02 Cleaning The Feed Rolls .................................................................................. 4-1
4.03 System Maintenance ....................................................................................... 4-1
4.04 Troubleshooting Guide .................................................................................... 4-1
4.05 Error Codes and Remedies ............................................................................. 4-2
4.06 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Basic Welding Technique ............................................... 4-4
4.07 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Welding Troubleshooting ............................................... 4-7
4.08 TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................................... 4-10
SECTION 5: PARTS LIST ................................................................................... 5-1
5.01 Equipment Identification ................................................................................. 5-1
5.02 How To Use This Parts List ............................................................................. 5-1
5.03 Replacement Parts (without wirefeed plate) ................................................... 5-2
5.04 Replacement Parts- Wirefeed Plate ................................................................. 5-3
APPENDIX 1: CONNECTION DIAGRAM .................................................................. A-1
TWECO - LIMITED WARRANTY TERMS

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
SECTION 1: SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH. KEEP CHILDREN AWAY.
PACEMAKER WEARERS KEEP AWAY UNTIL CONSULTING YOUR DOCTOR. DO NOT LOSE THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
READ OPERATING/INSTRUCTION MANUAL BEFORE INSTALLING, OPERATING OR SERVICING THIS EQUIPMENT.
Welding products and welding processes can cause serious injury or death, or damage to other equipment or
property, if the operator does not strictly observe all safety rules and take precautionary actions.
Safe practices have developed from past experience in the use of welding and cutting. These practices must be
learned through study and training before using this equipment. Some of these practices apply to equipment
connected to power lines; other practices apply to engine driven equipment. Anyone not having extensive training
in welding and cutting practices should not attempt to weld.
Safe practices are outlined in the American National Standard Z49.1 entitled: SAFETY IN WELDING AND CUTTING.
This publication and other guides to what you should learn before operating this equipment are listed at the
end of these safety precautions. HAVE ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION, MAINTENANCE, AND REPAIR WORK
PERFORMED ONLY BY QUALIFIED PEOPLE.
1.01 Arc Welding Hazards
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
Touching live electrical parts can cause fatal
shocks or severe burns. The electrode and
work circuit is electrically live whenever the
output is on. The input power circuit and
machine internal circuits are also live when
power is on. In semi-automatic or automatic
wire welding, the wire, wire reel, drive roll
housing, and all metal parts touching the
welding wire are electrically live. Incorrectly
installed or improperly grounded equipment
is a hazard.
1. Do not touch live electrical parts.
2. Wear dry, hole-free insulating gloves and body
protection.
3. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry
insulating mats or covers.
4. Disconnect input power or stop engine before
installing or servicing this equipment. Lock input
power disconnect switch open, or remove line fuses
so power cannot be turned on accidentally.
5. Properly install and ground this equipment according
to its Owner’s Manual and national, state, and local
codes.
6. Turn off all equipment when not in use. Disconnect
power to equipment if it will be left unattended or
out of service.
7. Use fully insulated electrode holders. Never dip
holder in water to cool it or lay it down on the ground
or the work surface. Do not touch holders connected
to two welding machines at the same time or touch
other people with the holder or electrode.
8. Do not use worn, damaged, undersized, or poorly
spliced cables.
9. Do not wrap cables around your body.
10. Ground the workpiece to a good electrical (earth)
ground.
11. Do not touch electrode while in contact with the work
(ground) circuit.
12. Use only well-maintained equipment. Repair or
replace damaged parts at once.
13. In confined spaces or damp locations, do not use a
welder with AC output unless it is equipped with a
voltage reducer. Use equipment with DC output.
14. Wear a safety harness to prevent falling if working
above floor level.
15. Keep all panels and covers securely in place.
Manual 0-5329 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS 1-1

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
WARNING
ARC RAYS can burn eyes and skin; NOISE
can damage hearing. Arc rays from the
welding process produce intense heat and
strong ultraviolet rays that can burn eyes
and skin. Noise from some processes can
damage hearing.
1. Wear a welding helmet fitted with a proper shade
of filter (see ANSI Z49.1 listed in Safety Standards)
to protect your face and eyes when welding or
watching.
2. Wear approved safety glasses. Side shields
recommended.
AWS F2.2:2001 (R2010), Adapted with permission of the American Welding Society (AWS), Miami, Florida
Guide for Shade Numbers
Process
Shielded Metal Arc Welding
(SMAW)
Electrode Size in.
(mm)
Less than 3/32 (2.4)
3/32-5/32 (2.4-4.0)
5/32-1/4 (4.0-6.4)
More than 1/4 (6.4)
3. Use protective screens or barriers to protect others
from flash and glare; warn others not to watch the
arc.
4. Wear protective clothing made from durable,
flame-resistant material (wool and leather) and foot
protection.
5. Use approved ear plugs or ear muffs if noise level
is high.
WARNING
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous to
your health.
Welding produces fumes and gases.
Breathing these fumes and gases can be
hazardous to your health.
Arc Current
(Amperes)
Less than 60
60-160
160-250
250-550
Minimum
Protective
Shade
7
8
10
11
Suggested*
Shade No.
(Comfort)
10
12
14
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
and Flux Cored Arc Welding
(FCAW)
Gas Tungsten arc Welding
(GTAW)
Air Carbon Arc Cutting (CAC-A)
Plasma Arc Welding (PAW)
Plasma Arc Cutting (PAC)
* As a rule of thumb, start with a shade that is too dark to see the weld zone. Then go to a lighter
shade which gives sufficient view of the weld zone without going below the minimum. In oxyfuel gas
welding, cutting, or brazing where the torch and/or the flux produces a high yellow light, it is desirable
to use a filter lens that absorbs the yellow or sodium line of the visible light spectrum.
(Light)
(Heavy)
Less than 60
60-160
160-250
250-550
Less than 50
50-150
150-500
Less than
500
500-1000
Less than 20
20-100
100-400
400-800
Less than 20
20-40
40-60
60-80
80-300
300-400
400-800
7
10
10
10
8
8
10
10
11
6
8
10
11
4
5
6
8
8
9
10
11
12
14
10
12
14
12
14
6 to 8
10
12
14
4
5
6
8
9
12
14
1-2
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
Manual 0-5329
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
1. Keep your head out of the fumes. Do not breathe
the fumes.
2. If inside, ventilate the area and/or use exhaust at the
arc to remove welding fumes and gases.
3. If ventilation is poor, use an approved air-supplied
respirator.
4. Read the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs)
and the manufacturer’s instruction for metals,
consumables, coatings, and cleaners.
5. Work in a confined space only if it is well ventilated,
or while wearing an air-supplied respirator. Shielding
gases used for welding can displace air causing
injury or death. Be sure the breathing air is safe.
6. Do not weld in locations near degreasing, cleaning,
or spraying operations. The heat and rays of the
arc can react with vapors to form highly toxic and
irritating gases.
7. Do not weld on coated metals, such as galvanized,
lead, or cadmium plated steel, unless the coating
is removed from the weld area, the area is well
ventilated, and if necessary, while wearing an airsupplied respirator. The coatings and any metals
containing these elements can give off toxic fumes
if welded.
6. Be aware that welding on a ceiling, floor, bulkhead,
or partition can cause fire on the hidden side.
7. Do not weld on closed containers such as tanks or
drums.
8. Connect work cable to the work as close to the
welding area as practical to prevent welding current
from traveling long, possibly unknown paths and
causing electric shock and fire hazards.
9. Do not use welder to thaw frozen pipes.
10. Remove stick electrode from holder or cut off
welding wire at contact tip when not in use.
WARNING
FLYING SPARKS AND HOT METAL can cause
injury.
Chipping and grinding cause flying metal. As
welds cool, they can throw off slag.
1. Wear approved face shield or safety goggles. Side
shields recommended.
2. Wear proper body protection to protect skin.
WARNING
WARNING
WELDING can cause fire or explosion.
Sparks and spatter fly off from the welding
arc. The flying sparks and hot metal, weld
spatter, hot workpiece, and hot equipment
can cause fires and burns. Accidental contact
of electrode or welding wire to metal objects
can cause sparks, overheating, or fire.
1. Protect yourself and others from flying sparks and
hot metal.
2. Do not weld where flying sparks can strike flammable
material.
3. Remove all flammables within 35 ft (10.7 m) of the
welding arc. If this is not possible, tightly cover them
with approved covers.
4. Be alert that welding sparks and hot materials from
welding can easily go through small cracks and
openings to adjacent areas.
5. Watch for fire, and keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
CYLINDERS can explode if damaged.
Shielding gas cylinders contain gas under
high pressure. If damaged, a cylinder can
explode. Since gas cylinders are normally
part of the welding process, be sure to treat
them carefully.
1. Protect compressed gas cylinders from excessive
heat, mechanical shocks, and arcs.
2. Install and secure cylinders in an upright position by
chaining them to a stationary support or equipment
cylinder rack to prevent falling or tipping.
3. Keep cylinders away from any welding or other
electrical circuits.
4. Never allow a welding electrode to touch any
cylinder.
5. Use only correct shielding gas cylinders, regulators,
hoses, and fittings designed for the specific
application; maintain them and associated parts in
good condition.
6. Turn face away from valve outlet when opening
cylinder valve.
Manual 0-5329 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS 1-3

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
7. Keep protective cap in place over valve except when
cylinder is in use or connected for use.
8. Read and follow instructions on compressed
gas cylinders, associated equipment, and CGA
publication P-1 listed in Safety Standards.
3. Have only qualified people remove guards or
covers for maintenance and troubleshooting as
necessary.
4. To prevent accidental starting during servicing,
disconnect negative (-) battery cable from
battery.
WARNING
Engines can be dangerous.
WARNING
ENGINE EXHAUST GASES can kill.
Engines produce harmful exhaust gases.
1. Use equipment outside in open, well-ventilated
areas.
2. If used in a closed area, vent engine exhaust outside
and away from any building air intakes.
WARNING
ENGINE FUEL can cause fire or explosion.
Engine fuel is highly flammable.
1. Stop engine before checking or adding fuel.
2. Do not add fuel while smoking or if unit is near any
sparks or open flames.
5. Keep hands, hair, loose clothing, and tools away
from moving parts.
6. Reinstall panels or guards and close doors when
servicing is finished and before starting engine.
WARNING
SPARKS can cause BATTERY GASES TO
EXPLODE; BATTERY ACID can burn eyes
and skin.
Batteries contain acid and generate explosive gases.
1. Always wear a face shield when working on a battery.
2. Stop engine before disconnecting or connecting
battery cables.
3. Do not allow tools to cause sparks when working
on a battery.
4. Do not use welder to charge batteries or jump start
vehicles.
5. Observe correct polarity (+ and –) on batteries.
3. Allow engine to cool before fueling. If possible, check
and add fuel to cold engine before beginning job.
4. Do not overfill tank — allow room for fuel to expand.
5. Do not spill fuel. If fuel is spilled, clean up before
starting engine.
WARNING
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
Moving parts, such as fans, rotors, and belts can cut
fingers and hands and catch loose clothing.
1. Keep all doors, panels, covers, and guards
closed and securely in place.
2. Stop engine before installing or connecting unit.
1-4
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING
STEAM AND PRESSURIZED HOT COOLANT
can burn face, eyes, and skin.
The coolant in the radiator can be very hot
and under pressure.
1. Do not remove radiator cap when engine is hot.
Allow engine to cool.
2. Wear gloves and put a rag over cap area when
removing cap.
3. Allow pressure to escape before completely
removing cap.
Manual 0-5329
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
!
1.02 General Safety Information for
!
WARNING: This product contains chemicals, including
lead, known to the State of California to cause birth
defects and other reproductive harm.
after handling.
NOTE
Considerations About Welding And The
Effects of Low Frequency Electric and Mag
netic Fields
WARNING
Wash hands
-
A Fire Prevention
Welding and cutting operations use fire or combustion
as a basic tool. The process is very useful when properly
controlled. However, it can be extremely destructive
if not performed cor rectly in the proper environment.
Victor Regulator
1. The work area must have a fireproof floor.
2. Work benches or tables used during welding or
cutting operations must have fireproof tops.
The following is a quotation from the General Conclusions Section of the U.S. Congress, Office of Technology
Assessment, Biological Effects of Power Frequency
Electric & Magnetic Fields - Background Paper, OTABP-E-63 (Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing
Office, May 1989): “...there is now a very large volume
of scientific findings based on experiments at the cellular level and from studies with animals and people
which clearly establish that low frequency magnetic
fields interact with, and produce changes in, biological systems. While most of this work is of very high
quality, the results are complex. Current scientific
understanding does not yet allow us to interpret the
evidence in a single coherent framework. Even more
frustrating, it does not yet allow us to draw definite
conclusions about questions of possible risk or to offer
clear science-based advice on strategies to minimize or
avoid potential risks.”
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace, use the
following procedures.
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or taping
them.
3. Use heat resistant shields or other approved material to protect nearby walls or unprotected flooring
from sparks and hot metal.
4. Keep an approved fire extinguisher of the proper
size and type in the work area. Inspect it regularly to ensure that it is in proper working order.
Know how to use the fire extin guisher.
5. Move combustible materials away from the work
site. If you can not move them, protect them
with fireproof covers.
WARNING
NEVER perform welding, heating, or cutting operations on a container that has held
toxic, combustible or flammable liq uids, or
vapors. NEVER perform welding, heating,
or cutting operations in an area containing
combustible vapors, flam mable liquids, or
explosive dust.
B Housekeeping
2. Arrange cables to one side and away from the
operator.
3. Do not coil or drape cable around the body.
4. Keep welding Power Source and cables as far
away from body as practical.
ABOUT PACEMAKERS:
The above procedures are among those
also normally recommended for pacemaker
wearers. Consult your doctor for complete
information.
Manual 0-5329 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS 1-5
NEVER allow oxygen to contact grease, oil, or
other flam mable substances. Although oxygen by itself will not burn, these substances
become highly explosive. They can ignite
and burn violently in the presence of oxygen.
Keep ALL apparatus clean and free of grease, oil and
other flammable substances.
WARNING
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
!
!
C Ventilation
WARNING
Ade quately ventilate welding, heating, and
cutting work areas to prevent accumulation of explosive or toxic concen trations
of gases. Certain combinations of metals,
coatings, and gases generate toxic fumes.
Use respiratory protection equipment in
these circumstances. When welding/brazing,
read and understand the Material Safety Data
Sheet for the welding/brazing alloy.
D Personal Protection
Gas flames produce infrared radiation which may have
a harm ful effect on the skin and especially on the eyes.
Select goggles or a mask with tempered lenses, shaded
4 or darker, to protect your eyes from injury and provide
good visibility of the work.
Always wear protective gloves and flame-resistant clothing
to protect skin and clothing from sparks and slag. Keep
collars, sleeves, and pockets buttoned. DO NOT roll up
sleeves or cuff pants.
When working in a non-welding or cutting environment,
always wear suitable eye protection or face shield.
WARNING
Practice the following safety and operation
precautions EVERY TIME you use pressure
regulation equipment. Deviation from the
following safety and operation instructions
can result in fire, explosion, damage to
equipment, or injury to the operator.
E Compressed Gas Cylinders
The Department of Transportation (DOT) approves the
design and manufacture of cylinders that contain gases
used for welding or cutting operations.
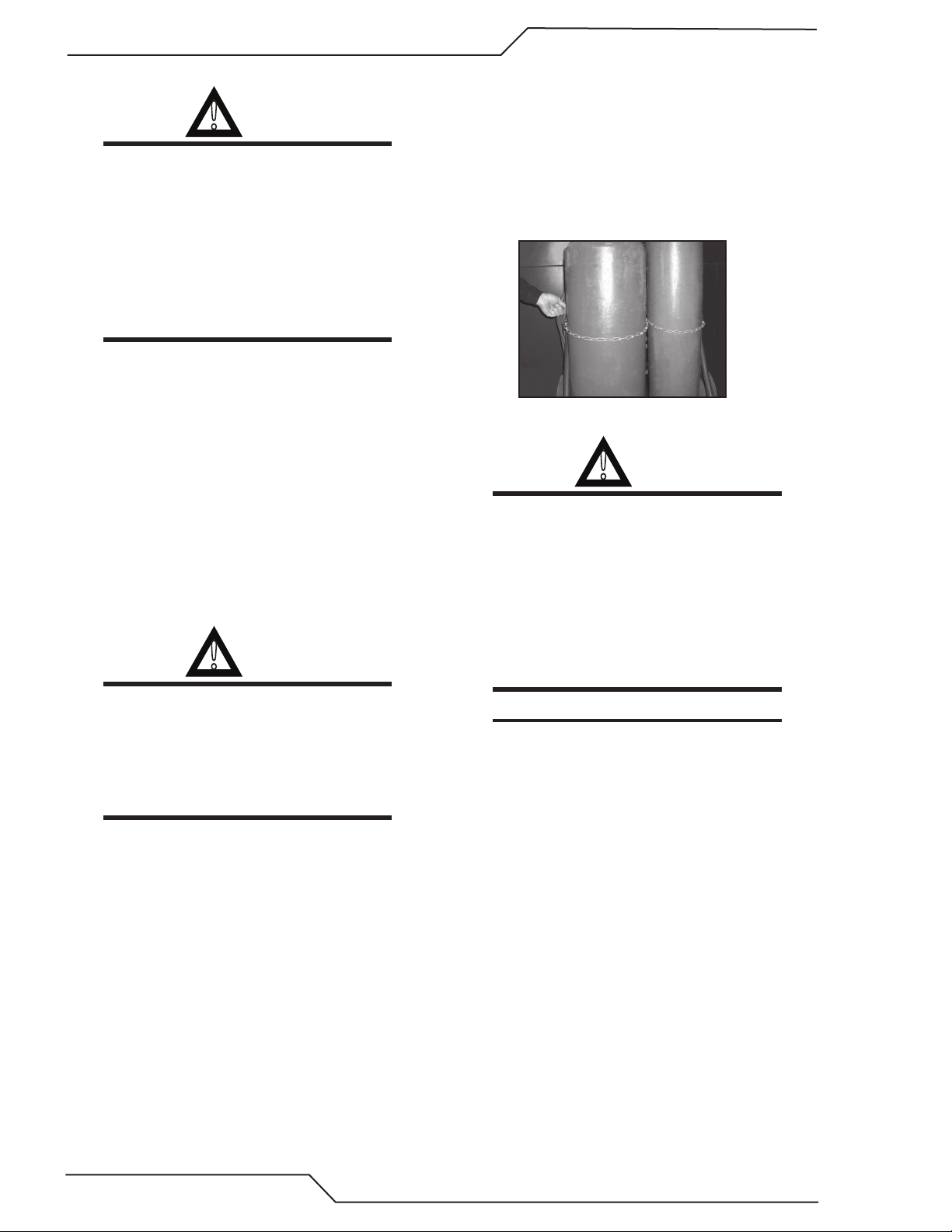
1. Place the cylinder (Figure 1-1) where you will
use it. Keep the cylinder in a vertical position.
Secure it to a cart, wall, work bench, post, etc.
Figure 1-1: Gas Cylinders
WARNING
Cylinders are highly pressurized. Handle
with care. Serious accidents can result from
improper handling or mis use of compressed
gas cylinders DO NOT drop the cylinder,
knock it over, or expose it to excessive heat,
flames or sparks. DO NOT strike it against
other cylinders. Contact your gas supplier
or refer to CGA P-1 “Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Containers” publication.
NOTE
CGA P-1 publication is available by writing
the Compressed Gas Association, 4221
Walney Road, 5th Floor, Chantilly,VA 201512923
1-6
2. Place the valve protection cap on the cylinder
whenever mov ing it, placing it in storage, or not
using it. Never drag or roll cylinders in any way.
Use a suitable hand truck to move cylin ders.
3. Store empty cylinders away from full cylinders.
Mark them “EMPTY” and close the cylinder
valve.
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
Manual 0-5329
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
4. NEVER use compressed gas cylinders without
a pressure reducing regulator attached to the
cylinder valve.
5. Inspect the cylinder valve for oil, grease, and
damaged parts.
WARNING
DO NOT use the cylinder if you find oil,
grease or damaged parts. Inform your gas
supplier of this condition immediately.
6. Momentarily open and close (called “cracking”)
the cylinder valve to dislodge any dust or dirt that
may be present in the valve.
CAUTION
Open the cylinder valve slightly. If you open
the valve too much, the cylinder could tip
over. When cracking the cylinder valve, DO
NOT stand directly in front of the cylinder
valve. Always perform cracking in a well
ventilated area. If an acetylene cylinder
sprays a mist when cracked, let it stand for
15 minutes. Then, try to crack the cylinder
valve again. If this problem persists, contact
your gas supplier.
1.03 Principal Safety Standards
Safety in Welding and Cutting, ANSI Standard Z49.1,
from American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd.,
Miami, FL 33126.
Safety and Health Standards, OSHA 29 CFR 1910,
from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government
Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402.
Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for
Welding and Cutting of Containers That Have Held
Hazardous Substances, American Welding Society
Standard AWS F4.1, from American Welding Society,
550 N.W. LeJeune Rd., Miami, FL 33126.
National Electrical Code, NFPA Standard 70, from
National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch Park,
Quincy, MA 02269.
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, CGA
Pamphlet P-1, from Compressed Gas Association,
1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Suite 501, Arlington,
VA 22202.
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting, CSA Standard
W117.2, from Canadian Standards Association,
Standards Sales, 178 Rexdale Boulevard, Rexdale,
Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3.
Safe Practices for Occupation and Educational Eye and
Face Protection, ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American
National Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York,
NY 10018.
Cutting and Welding Processes, NFPA Standard 51B,
from National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch
Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
Manual 0-5329 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS 1-7
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Gas Tungsten Arc
Welding (GTAW)
Air Carbon Arc
Cutting (CAC-A)
Constant Current
Constant Voltage
Or Constant Potential
High Temperature
Fault Indication
Arc Force
Touch Start (GTAW)
Variable Inductance
Voltage Input
Single Phase
Three Phase
Three Phase Static
Frequency ConverterTransformer-Rectifier
Dangerous Voltage
Off
On
Panel/Local
Shielded Metal
Arc Welding (SMAW)
Gas Metal Arc
Welding (GMAW)
Increase/Decrease
Circuit Breaker
AC Auxiliary Power
Remote
Duty Cycle
Percentage
Amperage
Voltage
Hertz (cycles/sec)
Frequency
Negative
Positive
Direct Current (DC)
Protective Earth
(Ground)
Line
Line Connection
Auxiliary Power
Receptacle RatingAuxiliary Power
Art # A-04130_AB
115V 15A
t
t1
t2
%
X
IPM
MPM
t
V
Fuse
Wire Feed Function
Wire Feed Towards
Workpiece With
Output Voltage Off.
Preflow Time
Postflow Time
Spot Time
Spot Weld Mode
Continuous Weld
Mode
Press to initiate wirefeed and
welding, release to stop.
Purging Of Gas
Inches Per Minute
Meters Per Minute
Welding Gun
Burnback Time
Press and hold for preflow, release
to start arc. Press to stop arc, and
hold for preflow.
4 Step Trigger
Operation
2 Step Trigger
Operation
S
See Note
See Note
S
Note: For environments with increased hazard of electrical shock, Power Supplier bearing the mark conform to EN50192
when used in conjunction with hand torches with exposed tips, if equipped with properly installed standoff guides.
Cannot be disposed with household garbage.
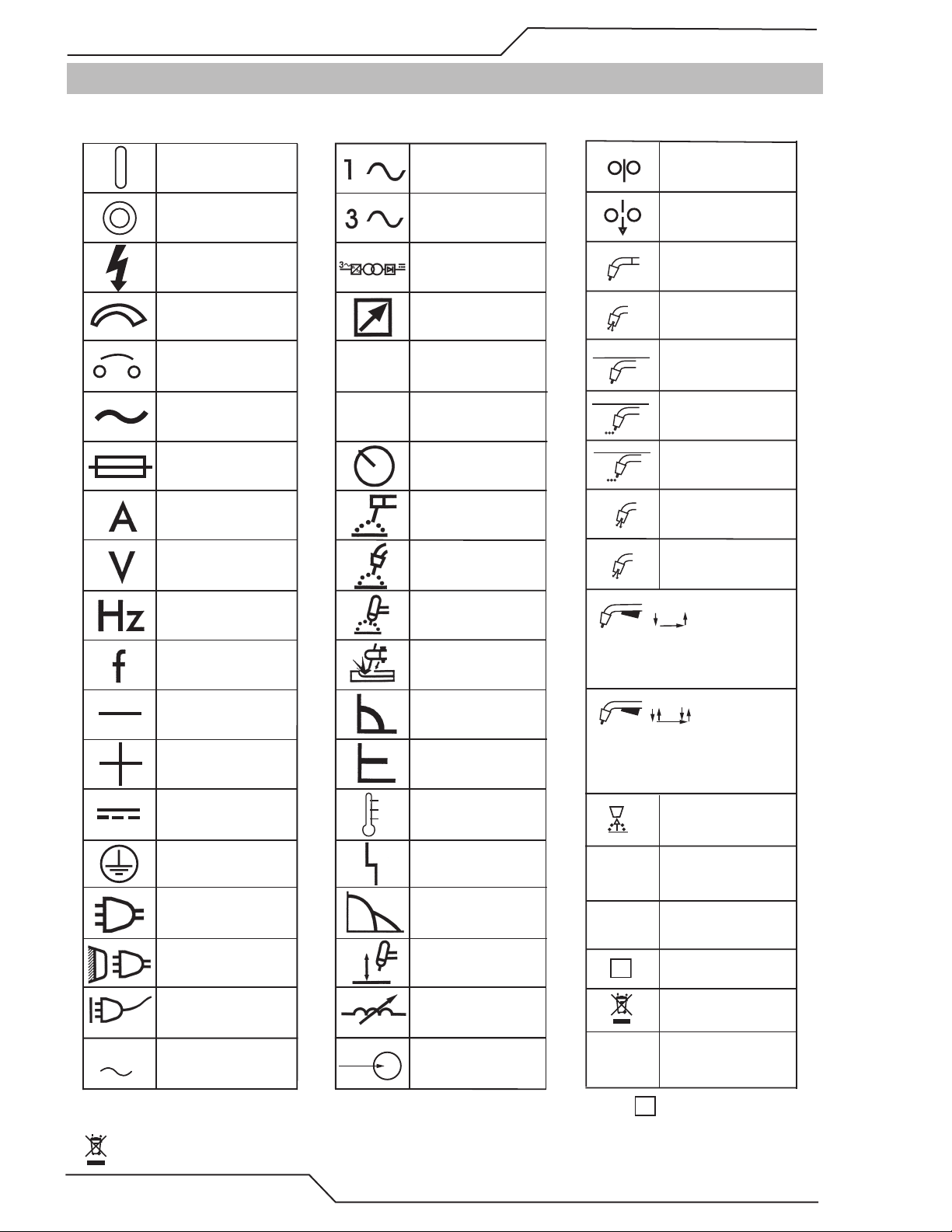
1.04 Symbol Chart
Note that only some of these symbols will appear on your model.
1-8
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
Manual 0-5329
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
1.05 Precautions De Securite En Soudage A L’arc
MISE EN GARDE
LE SOUDAGE A L’ARC EST DANGEREUX
PROTEGEZ-VOUS, AINSI QUE LES AUTRES, CONTRE LES BLESSURES GRAVES POSSIBLES OU LA MORT. NE
LAISSEZ PAS LES ENFANTS S’APPROCHER, NI LES PORTEURS DE STIMULATEUR CARDIAQUE (A MOINS QU’ILS
N’AIENT CONSULTE UN MEDECIN). CONSERVEZ CES INSTRUCTIONS. LISEZ LE MANUEL D’OPERATION OU LES
INSTRUCTIONS AVANT D’INSTALLER, UTILISER OU ENTRETENIR CET EQUIPEMENT.
Les produits et procédés de soudage peuvent sauser des blessures graves ou la mort, de même que des dommages au reste du matériel et à la propriété, si l’utilisateur n’adhère pas strictement à toutes les règles de sécurité
et ne prend pas les précautions nécessaires.
En soudage et coupage, des pratiques sécuritaires se sont développées suite à l’expérience passée. Ces pratiques
doivent être apprises par étude ou entraînement avant d’utiliser l’equipement. Toute personne n’ayant pas suivi
un entraînement intensif en soudage et coupage ne devrait pas tenter de souder. Certaines pratiques concernent
les équipements raccordés aux lignes d’alimentation alors que d’autres s’adressent aux groupes électrogènes.
La norme Z49.1 de l’American National Standard, intitulée “SAFETY IN WELDING AND CUTTING” présente les
pratiques sécuritaires à suivre. Ce document ainsi que d’autres guides que vous devriez connaître avant d’utiliser
cet équipement sont présentés à la fin de ces instructions de sécurité.
SEULES DES PERSONNES QUALIFIEES DOIVENT FAIRE DES TRAVAUX D’INSTALLATION, DE REPARATION,
D’ENTRETIEN ET D’ESSAI.
1.06 Dangers relatifs au soudage à l’arc
AVERTISSEMENT
L’ELECTROCUTION PEUT ETRE MORTELLE.
Une décharge électrique peut tuer ou
brûler gravement. L’électrode et le circuit
de soudage sont sous tension dès la mise
en circuit. Le circuit d’alimentation et les
circuits internes de l’équipement sont aussi
sous tension dès la mise en marche. En
soudage automatique ou semi-automatique
avec fil, ce dernier, le rouleau ou la bobine
de fil, le logement des galets d’entrainement
et toutes les pièces métalliques en contact
avec le fil de soudage sont sous tension.
Un équipement inadéquatement installé ou
inadéquatement mis à la terre est dangereux.
1. Ne touchez pas à des pièces sous tension.
2. Portez des gants et des vêtements isolants, secs et
non troués.
3 Isolez-vous de la pièce à souder et de la mise à la
terre au moyen de tapis isolants ou autres.
4. Déconnectez la prise d’alimentation de l’équipement
ou arrêtez le moteur avant de l’installer ou d’en faire
l’entretien. Bloquez le commutateur en circuit ouvert
ou enlevez les fusibles de l’alimentation afin d’éviter
une mise en marche accidentelle.
5. Veuillez à installer cet équipement et à le mettre à
la terre selon le manuel d’utilisation et les codes
nationaux, provinciaux et locaux applicables.
6. Arrêtez tout équipement après usage. Coupez
l’alimentation de l’équipement s’il est hors d’usage
ou inutilisé.
7. N’utilisez que des porte-électrodes bien isolés. Ne
jamais plonger les porte-électrodes dans l’eau pour
les refroidir. Ne jamais les laisser traîner par terre ou
sur les pièces à souder. Ne touchez pas aux porteélectrodes raccordés à deux sources de courant en
même temps. Ne jamais toucher quelqu’un d’autre
avec l’électrode ou le porte-électrode.
8. N’utilisez pas de câbles électriques usés, endommagés, mal épissés ou de section trop petite.
Manual 0-5329 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS 1-9
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
9. N’enroulez pas de câbles électriques autour de votre
corps.
10. N’utilisez qu’une bonne prise de masse pour la mise
à la terre de la pièce à souder.
11. Ne touchez pas à l’électrode lorsqu’en contact avec
le circuit de soudage (terre).
12. N’utilisez que des équipements en bon état. Réparez
ou remplacez aussitôt les pièces endommagées.
13. Dans des espaces confinés ou mouillés, n’utilisez
pas de source de courant alternatif, à moins qu’il
soit muni d’un réducteur de tension. Utilisez plutôt
une source de courant continu.
14. Portez un harnais de sécurité si vous travaillez en
hauteur.
15. Fermez solidement tous les panneaux et les capots.
AWS F2.2:2001 (R2010), Adapted with permission of the American Welding Society (AWS), Miami, Florida
Guide for Shade Numbers
Process
Shielded Metal Arc Welding
(SMAW)
Electrode Size in.
(mm)
Less than 3/32 (2.4)
3/32-5/32 (2.4-4.0)
5/32-1/4 (4.0-6.4)
More than 1/4 (6.4)
AVERTISSEMENT
LE RAYONNEMENT DE L’ARC PEUT BRÛLER
LES YEUX ET LA PEAU; LE BRUIT PEUT
ENDOMMAGER L’OUIE.
L’arc de soudage produit une chaleur et des
rayons ultraviolets intenses, susceptibles de
brûler les yeux et la peau. Le bruit causé par
certains procédés peut endommager l’ouïe.
1. Portez une casque de soudeur avec filtre oculaire
de nuance appropriée (consultez la norme ANSI Z49
indiquée ci-après) pour vous protéger le visage et
les yeux lorsque vous soudez ou que vous observez
l’exécution d’une soudure.
Arc Current
(Amperes)
Less than 60
60-160
160-250
250-550
Minimum
Protective
Shade
7
8
10
11
Suggested*
Shade No.
(Comfort)
10
12
14
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
and Flux Cored Arc Welding
(FCAW)
Gas Tungsten arc Welding
(GTAW)
Air Carbon Arc Cutting (CAC-A)
Plasma Arc Welding (PAW)
Plasma Arc Cutting (PAC)
* As a rule of thumb, start with a shade that is too dark to see the weld zone. Then go to a lighter
shade which gives sufficient view of the weld zone without going below the minimum. In oxyfuel gas
welding, cutting, or brazing where the torch and/or the flux produces a high yellow light, it is desirable
to use a filter lens that absorbs the yellow or sodium line of the visible light spectrum.
(Light)
(Heavy)
Less than 60
60-160
160-250
250-550
Less than 50
50-150
150-500
Less than
500
500-1000
Less than 20
20-100
100-400
400-800
Less than 20
20-40
40-60
60-80
80-300
300-400
400-800
7
10
10
10
8
8
10
10
11
6
8
10
11
4
5
6
8
8
9
10
11
12
14
10
12
14
12
14
6 to 8
10
12
14
4
5
6
8
9
12
14
1-10
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
2. Portez des lunettes de sécurité approuvées. Des
écrans latéraux sont recommandés.
3. Entourez l’aire de soudage de rideaux ou de cloisons
pour protéger les autres des coups d’arc ou de
l’éblouissement; avertissez les observateurs de ne
pas regarder l’arc.
4. Portez des vêtements en matériaux ignifuges et durables (laine et cuir) et des chaussures de sécurité.
5. Portez un casque antibruit ou des bouchons d’oreille
approuvés lorsque le niveau de bruit est élevé.
AVERTISSEMENT
LES VAPEURS ET LES FUMEES SONT
DANGEREUSES POUR LA SANTE.
Le soudage dégage des vapeurs et des
fumées dangereuses à respirer.
1. Eloignez la tête des fumées pour éviter de les respirer.
2. A l’intérieur, assurez-vous que l’aire de soudage est
bien ventilée ou que les fumées et les vapeurs sont
aspirées à l’arc.
3. Si la ventilation est inadequate, portez un respirateur
à adduction d’air approuvé.
4. Lisez les fiches signalétiques et les consignes
du fabricant relatives aux métaux, aux produits
consummables, aux revêtements et aux produits
nettoyants.
5. Ne travaillez dans un espace confiné que s’il est bien
ventilé; sinon, portez un respirateur à adduction d’air.
Les gaz protecteurs de soudage peuvent déplacer
l’oxygène de l’air et ainsi causer des malaises ou la
mort. Assurez-vous que l’air est propre à la respiration.
6. Ne soudez pas à proximité d’opérations de dégraissage, de nettoyage ou de pulvérisation. La chaleur et
les rayons de l’arc peuvent réagir avec des vapeurs
et former des gaz hautement toxiques et irritants.
7. Ne soudez des tôles galvanisées ou plaquées au
plomb ou au cadmium que si les zones à souder ont
été grattées à fond, que si l’espace est bien ventilé;
si nécessaire portez un respirateur à adduction d’air.
Car ces revêtements et tout métal qui contient ces
éléments peuvent dégager des fumées toxiques au
moment du soudage.
LE SOUDAGE PEUT CAUSER UN INCENDIE
OU UNE EXPLOSION
L’arc produit des étincellies et des projec
tions. Les particules volantes, le métal
chaud, les projections de soudure et
l’équipement surchauffé peuvent causer
un incendie et des brûlures. Le contact accidentel de l’électrode ou du fil-électrode
avec un objet métallique peut provoquer des
étincelles, un échauffement ou un incendie.
1. Protégez-vous, ainsi que les autres, contre les étincelles et du métal chaud.
2. Ne soudez pas dans un endroit où des particules
volantes ou des projections peuvent atteindre des
matériaux inflammables.
3. Enlevez toutes matières inflammables dans un rayon
de 10, 7 mètres autour de l’arc, ou couvrez-les soigneusement avec des bâches approuvées.
4. Méfiez-vous des projections brulantes de soudage
susceptibles de pénétrer dans des aires adjacentes
par de petites ouvertures ou fissures.
5. Méfiez-vous des incendies et gardez un extincteur
à portée de la main.
6. N’oubliez pas qu’une soudure réalisée sur un plafond, un plancher, une cloison ou une paroi peut
enflammer l’autre côté.
7. Ne soudez pas un récipient fermé, tel un réservoir
ou un baril.
8. Connectez le câble de soudage le plus près possible
de la zone de soudage pour empêcher le courant de
suivre un long parcours inconnu, et prévenir ainsi
les risques d’électrocution et d’incendie.
9. Ne dégelez pas les tuyaux avec un source de courant.
10. Otez l’électrode du porte-électrode ou coupez le fil
au tube-contact lorsqu’inutilisé après le soudage.
11. Portez des vêtements protecteurs non huileux, tels
des gants en cuir, une chemise épaisse, un pantalon
revers, des bottines de sécurité et un casque.
AVERTISSEMENT
-
Manual 0-5329 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS 1-11
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
AVERTISSEMENT
LES ETINCELLES ET LES PROJECTIONS
BRULANTES PEUVENT CAUSER DES BLESSURES.
8. Lisez et respectez les consignes relatives aux
bouteilles de gaz comprimé et aux équipements
connexes, ainsi que la publication P-1 de la CGA,
identifiée dans la liste de documents ci-dessous.
Le piquage et le meulage produisent des
particules métalliques volantes. En refroid
issant, la soudure peut projeter du éclats
de laitier.
1. Portez un écran facial ou des lunettes protectrices approuvées. Des écrans latéraux sont
recommandés.
2. Portez des vêtements appropriés pour protéger
la peau.
AVERTISSEMENT
LES BOUTEILLES ENDOMMAGEES PEUVENT EXPLOSER
Les bouteilles contiennent des gaz pro
tecteurs sous haute pression. Des bouteilles
endommagées peuvent exploser. Comme
les bouteilles font normalement partie du
procédé de soudage, traitez-les avec soin.
1. Protégez les bouteilles de gaz comprimé contre les
sources de chaleur intense, les chocs et les arcs de
soudage.
2. Enchainez verticalement les bouteilles à un support
ou à un cadre fixe pour les empêcher de tomber ou
d’être renversées.
3. Eloignez les bouteilles de tout circuit électrique ou
de tout soudage.
4. Empêchez tout contact entre une bouteille et une
électrode de soudage.
5. N’utilisez que des bouteilles de gaz protecteur, des
détendeurs, des boyauxs et des raccords conçus
pour chaque application spécifique; ces équipements et les pièces connexes doivent être maintenus
en bon état.
AVERTISSEMENT
LES MOTEURS PEUVENT ETRE DANGEREUX
LES GAZ D’ECHAPPEMENT DES MOTEURS
PEUVENT ETRE MORTELS.
Les moteurs produisent des gaz d’échappement nocifs.
1. Utilisez l’équipement à l’extérieur dans des aires
ouvertes et bien ventilées.
2. Si vous utilisez ces équipements dans un endroit
confiné, les fumées d’échappement doivent être
envoyées à l’extérieur, loin des prises d’air du bâtiment.
AVERTISSEMENT
LE CARBURANT PEUR CAUSER UN INCENDIE OU UNE EXPLOSION.
Le carburant est hautement inflammable.
1. Arrêtez le moteur avant de vérifier le niveau e carburant ou de faire le plein.
2. Ne faites pas le plein en fumant ou proche d’une
source d’étincelles ou d’une flamme nue.
3. Si c’est possible, laissez le moteur refroidir avant de
faire le plein de carburant ou d’en vérifier le niveau
au début du soudage.
4. Ne faites pas le plein de carburant à ras bord: prévoyez de l’espace pour son expansion.
5. Faites attention de ne pas renverser de carburant.
Nettoyez tout carburant renversé avant de faire
démarrer le moteur.
6. Ne placez pas le visage face à l’ouverture du robinet
de la bouteille lors de son ouverture.
7. Laissez en place le chapeau de bouteille sauf si en
utilisation ou lorsque raccordé pour utilisation.
1-12
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
Manual 0-5329
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
5. Utilisez la polarité correcte (+ et –) de l’accumulateur.
AVERTISSEMENT
DES PIECES EN MOUVEMENT PEUVENT
CAUSER DES BLESSURES.
Des pièces en mouvement, tels des ventila
teurs, des rotors et des courroies peuvent
couper doigts et mains, ou accrocher des
vêtements amples.
1. Assurez-vous que les portes, les panneaux, les
capots et les protecteurs soient bien fermés.
2. Avant d’installer ou de connecter un système, arrêtez
le moteur.
3. Seules des personnes qualifiées doivent démonter
des protecteurs ou des capots pour faire l’entretien
ou le dépannage nécessaire.
4. Pour empêcher un démarrage accidentel pendant
l’entretien, débranchez le câble d’accumulateur à la
borne négative.
5. N’approchez pas les mains ou les cheveux de pièces
en mouvement; elles peuvent aussi accrocher des
vêtements amples et des outils.
6. Réinstallez les capots ou les protecteurs et fermez
les portes après des travaux d’entretien et avant de
faire démarrer le moteur.
AVERTISSEMENT
LA VAPEUR ET LE LIQUIDE DE REFROIDISSEMENT BRULANT SOUS PRESSION
PEUVENT BRULER LA PEAU ET LES YEUX.
Le liquide de refroidissement d’un radiateur
peut être brûlant et sous pression.
1. N’ôtez pas le bouchon de radiateur tant que le moteur
n’est pas refroidi.
2. Mettez des gants et posez un torchon sur le bouchon
pour l’ôter.
3. Laissez la pression s’échapper avant d’ôter complètement le bouchon.
!
AVERTISSEMENT: Ce produitcontient des produits
chimiques, notamment du plomb, reconnu par l’Étatde
la Californie pour causerdes malformations congénitaleset d’autresdommages touchant le système
reproductif.
Se laver les mains après manipulation.
AVERTISSEMENT
REMARQUE
Facteurs relatifs au soudage et aux effets
des champs magnétiques et électriques de
basse fréquence
AVERTISSEMENT
DES ETINCELLES PEUVENT FAIRE EXPLOSER UN ACCUMULATEUR; L’ELECTROLYTE
D’UN ACCUMU-LATEUR PEUT BRULER LA
PEAU ET LES YEUX.
Les accumulateurs contiennent de
l’électrolyte acide et dégagent des vapeurs
explosives.
1. Portez toujours un écran facial en travaillant sur un
accumu-lateur.
2. Arrêtez le moteur avant de connecter ou de déconnecter des câbles d’accumulateur.
3. N’utilisez que des outils anti-étincelles pour travailler
sur un accumulateur.
4. N’utilisez pas une source de courant de soudage
pour charger un accumulateur ou survolter momentanément un véhicule.
Manual 0-5329 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS 1-13
Voici une citation tirée du chapitre des conclusions
générales du document de base de l’Office of Technology
Assessment (bureau des évaluations technologiques)
del’U.S. Congress, « Biological Effects of Power
Frequency Electric & Magnetic Fields », OTA-BP-E-63
(Washington, DC : U.S. Government Printing Office, mai
1989) : « ... il existe de nos jours, un nombre très élevé
de travaux scientifiques qui rapportent les résultats
d’expériences menées au niveau cellulaire et d’études
auprès d’homme et d’animaux qui établissent nettement
le rapport entre les champs magnétiques de basse
fréquence et les systèmes biologiques, soit par des
interactions ou des modifications. Quoique la plupart
de ces travaux soient de très bonne qualité, les résultats
sont complexes. Àla lumière des connaissances
scientifiques actuelles, il nous est encore impossible
d’interpréter les évidences en un seul cadre de référence
cohérent. La situation est toutefois très contrariante.
En effet, il nous est aussi impossible de tirer des
conclusions définitives quant aux risques éventuels ou
de proposer des stratégies fondées sur

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
!
!
des faits scientifiques visant à atténuer ou éviter des
risques potentiels ».
Pour atténuer les champs magnétiques sur les lieux
detravail, respectez les procédures qui suivent :
1. Maintenez les câbles l’un près de l’autre en les
entrelaçant ou les reliant ensemble au ruban.
2. Acheminez les câbles à un côté du soudeur, le
plus loin possible.
3. N’enroulez pas de câble autour du corps.
4. Maintenez le bloc d’alimentation du poste
desoudage et les câbles aussi loin que possible
du corps.
AVERTISSEMENT
N’effectuez JAMAIS d’opérations de soudage
sur un récipient qui a contenu des liquides
ou vapeurs toxiques, combustibles ou inflammables. N’effectuez JAMAIS d’opérations
de soudage dans une zone contenant des
vapeurs combustibles, des liquides inflammables ou des poussières explosives.
B Entretien des Locaux
AVERTISSEMENT
STIMULATEURS CARDIAQUES :
Les procédures décrites ci-dessus sont
habituellement celles recommandées pour
les porteurs de stimulateurs cardiaques.
Pour de plus amples renseignements,
consulter unmédecin.
1.07 Informations Générales de Sécurité
A Prévention D’incendie
Les opérations de soudage utilisent le feu ou la combustion
comme outil de base. Ce processus est très utile quand il
est cor rectement contrôlé.
1. La zone doit comporter un sol ignifugé.
2. Les établis ou tables utilisés pendant les opérations de soudage doivent avoir un revêtement
ignifuge.
3. Utilisez des écrans résistants à la chaleur ou en
matériau approuvé pour protéger les cloisons
proches ou le sol vul nérable des étincelles et du
métal chaud.
4. Gardez un extincteur approuvé du bon type et de
la bonne taille dans la zone de travail. Inspectez-le
régulièrement pour vous assurer qu’il est en état de
fonctionner. Apprenez à vous en servir.
5. Enlevez tous les matériaux combustibles de la
zone de travail. Si vous ne pouvez pas les enlever,
protégez-les avec une cou vre ignifuge.
Ne laissez jamais l’oxygène en contact avec
la graisse, l’huile ou d’autres substances in
flammables. Bien que l’oxygène elle même ne
brûle pas, ces substances peuvent devenir
extrême ment explosives. Elles peuvent pren
dre feu et brûler violem ment en présence
d’oxygène.
Gardez TOUS les appareils propres et exempts de graisse,
huile ou autres substances inflammables.
C Aération
AVERTISSEMENT
Ventilez les zones de soudage, chauffage et
découpage de façon adéquate pour éviter
l’accumulation de gaz explosifs ou toxiques.
Certaines combinaisons de métaux, revête
ments et gaz génèrent des fumées toxiques:
Utilisez un équipement de protection respiratoire dans ces circonstances. Si vous
soudez ou brasez, lisez et assimilez la fiche
technique de sécurité de matériau relative à
l’alliage de soudage/brasage.
D Protection Personnelle
Les flammes de gaz produisent une radiation infrarouge
qui peut avoir un effet néfaste sur la peau, et particulièrement sur les yeux. Choisissez des lunettes ou un
masque avec des verres trempés assombris au niveau 4
ou plus sombre, pour protéger vos yeux des dommages
et garder une bonne visibilité sur le travail.
Portez en permanence des gants de protection et des
vête ments ignifuges pour la protection de la peau et des
vêtements contre les étincelles et le laitier. Gardez col,
-
-
-
1-14
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
Manual 0-5329
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
!
!
manches et poches boutonnés. Il ne faut pas remonter
vos manches ou les pantalons à revers.
Quand vous travaillez dans un environnement non
dédié au soudage ou découpage, portez toujours une
protection des yeux appropriées ou un masque facial.
AVERTISSEMENT
Mettez en pratique les procédures de sécurité et de mode opératoire suivantes à
chaque fois que vous utilisez cet appareil
de régulation de pression. Si vous déviez de
ces procédures, cela peut entraîner incendie,
explosion, dégâts matériels et/ou blessures
corporelles pour l’opérateur.
E Bouteilles de Gaz Comprimé
Le Département des Transports américain (DOT) ap-
prouve la conception et la fabrication des bouteilles
qui contiennent les gaz utilisés pour les opérations de
soudage ou de découpage.
AVIS
Ce document CGA p. t peut être obtenu en
écrivant à “Compressed Gas Association”,
4221 Walney Roed, 5th Floor. Chantilly, VA
20151.2923, USA.
2. Placez le bouchon de protection de vanne sur
la bouteille à chaque fois que vous la déplacez
ou ne l’utilisez pas. Ne faites jamais glisser ou
rouler d’aucune manière les bouteilles. Utilisez
un diable approprié pour les déplacer.
3. Entreposez les bouteilles vides à l’écart des
bouteilles pleines. Marquez-les “VIDE” et refermez leur vanne.
4. N’utilisez
sans un régulateur de pression en série sur la
vanne de bouteille.
5. Inspectez la vanne de bouteille pour y détecter
de l’huile ou de la graisse, ou dès pièces
endommagées.
JAMAIS des bouteilles de gaz comprimé
1. Placez la bouteille (Le schéma 1) là où elle sera
utilisée. Gardez-la en position verticale. Fixez-la sur
un chariot une cloison, un établi, etc.
Le schéma 1-1: Cylindres de gaz
AVERTISSEMENT
Les bouteilles sont sous haute pression. Manipulez-les avec précautions. Des accidents sérieux
peuvent résulter d’une mauvaise manutention
ou d’un mauvais emploi des bouteilles de gaz
comprimé. NE faites PAS tomber la bouteille,
ne la cognez pas, ne l’exposez pas à une chaleur
excessive, aux flammes ou étincelles. NE la cognez
PAS contre d’autres bouteilles. Contactez votre
fournisseur de gaz ou reportez vous à la publication
CGA P-1 “Manipulation sécurisée des gaz comprimés en conteneur” pour plus d’informations sur
l’utilisation et la manutention des bouteilles.
AVERTISSEMENT
N’UTILISEZ PAS la bouteille si vous trouvez
de l’huile, de la graisse ou des pièces endommagées. Informez immédiate ment votre
fournisseur de’ gaz de cet état.
6. Ouvrez et fermez momentanément la vanne de
la bouteille, délogeant ainsi d’éventu lIes poussières ou saletés. qui pour raient être présentes
dans la vanne.
Mise en Garde
Ouvrez la vanne de bouteille légèrement.
Si vous l’ouvrez trop en grand, la bouteille
pourrait se renverser. Quand vous ouvrez/
fermez rapidement la vanne de bouteille, ne
vous tenez pas directement devant. Opérez
toujours cette opération dans une zone bien
ventilée. Si une bouteille d’acétylène crache
un brouillard, laissez reposer pendant 15
minutes. Essayez de nouveau la vanne. Si le
problème persiste, con tactez votre fournisseur de gaz.
Manual 0-5329 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS 1-15

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
1.08 Principales Normes De Securite
Safety in Welding and Cutting, norme ANSI Z49.1, American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd., Miami, FL
33128.
Safety and Health Standards, OSHA 29 CFR 1910, Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office,
Washington, D.C. 20402.
Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of Containers That Have Held Hazardous
Substances, norme AWS F4.1, American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd., Miami, FL 33128.
National Electrical Code, norme 70 NFPA, National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA
02269.
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, document P-1, Compressed Gas Association, 1235 Jefferson
Davis Highway, Suite 501, Arlington, VA 22202.
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting, norme CSA W117.2 Association canadienne de normalisation, Standards
Sales, 276 Rexdale Boulevard, Rexdale, Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3.
Safe Practices for Occupation and Educational Eye and Face Protection, norme ANSI Z87.1, American National
Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018.
Cutting and Welding Processes, norme 51B NFPA, National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy,
MA 02269.
1-16
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
Manual 0-5329
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Soudage á L’arc Avec
Electrode Non Fusible
(GTAW)
Decoupe Arc Carbone
(CAC-A)
Courant Constant
Tension Constante
Ou Potentiel Constant
Haute Température
Force d'Arc
Amorçage de L’arc au
Contact (GTAW)
Inductance Variable
Tension
Mono Phasé
Trois Phasé
Tri-Phase Statique
Fréquence Convertisseur
Transformateur-Redresseur
Tension dangereuse
Hors Tension
SousTension
Panneau/Local
Soudage Arc Electrique
Avec Electrode Enrobé
(SMAW)
Soudage á L’arc Avec
Fil Electrodes Fusible
(GMAW)
Augmentez/Diminuer
Disjoncteur
Source AC Auxiliaire
Distant
Facteur de Marche
Pourcentage
Intensité de Courant
Tension
Hertz (cycles/sec)
Fréquence
Négatif
Positif
Courant Continue (DC)
Terre de Protection
Ligne
Connexion de la Ligne
Source Auxiliaire
Classement de PriseSource Auxiliaire
Art # A-07639_AB
115V 15A
t
t1
t2
%
X
IPM
MPM
t
Fusible
Déroulement du Fil
Alimentation du Fil Vers
la Pièce de Fabrication
Hors Tension
Durée de Pré-Dèbit
Durée de Post-Dèbit
Duréc du Pulse
Soudure Par Point
Appuyez pour dèruarer
l’alimentation du fils et la soudure,
le relâcher pour arrêter.
Purge Du Gaz
Mode Continu de
Soudure
Pouces Par Minute
Mètres Par Minute
Torch de
Soudage
Probléme de Terre
Maintenez appuyez pour pré-dèbit,
relailez pour initier l'arc. Appuyez
pour arrêter l'arc, et mainteuir pour
pré-dèbit.
Détente à 4-Temps
Détente à 2-Temps
V
S
S
Voir Note
Voir Note
Note: Pour les environnements avec des risques de choc électrique, le fournisseur d'énergie portant la marque conforme
à EN50192 lorsqu'utilisé en conjonction avec des lampes de poche avec des conseils exposés, si équipés avec des guide à
l'hauteur de buse correctement installé.
Ne pas déposer avec les déchets ménagers.
1.09 Graphique de Symbole
Seulement certains de ces symboles apparaîtront sur votre modèle.
Manual 0-5329 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS 1-17

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
This Page Intentionally Blank
1-18
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
Manual 0-5329
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
SECTION 2: INTRODUCTION
2.01 How to Use This Manual
To ensure safe operation, read the entire manual, including the chapter on safety instructions and warnings.
Throughout this manual, the word WARNING, CAUTION
and NOTE may appear. Pay particular attention to the information provided under these headings. These special
annotations are easily recognized as follows:
WARNING
Gives information regarding possible personal
injury. Warnings will be enclosed in a box
such as this.
CAUTION
Refers to possible equipment damage. Cautions will be shown in bold type.
NOTE
Offers helpful information concerning certain
operating procedures. Notes will be shown
in italics
Additional copies of this manual may be purchased by
contacting Tweco at the address and phone number for
your location listed in the inside back cover of this manual.
Include the Owner’s Manual number and equipment identification numbers.
2.02 Equipment Identification
The unit’s identification number (specification or part
number), model, and serial number usually appear on
a nameplate attached to the machine. Equipment which
does not have a nameplate attached to the machine is
identified only by the specification or part number printed
on the shipping container. Record these numbers for
future reference.
2.03 Receipt of Equipment
When you receive the equipment, check it against the
invoice to make sure it is complete and inspect the equipment for possible damage due to shipping. If there is any
damage, notify the carrier immediately to file a claim.
Furnish complete information concerning damage claims
or shipping errors to the location in your area listed in the
inside back cover of this manual.
Include all equipment identification numbers as described
above along with a full description of the parts in error.
Move the equipment to the installation site before uncrating the unit. Use care to avoid damaging the equipment when using bars, hammers, etc., to un-crate the unit.
Manual 0-5329 INTRODUCTION 2-1
ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
2.04 Description
The Ultrafeed VAF-4 offers both load and line voltage
compensation helping to maintain a constant wire feed
speed, even with changes in the input voltage and/or load.
The Ultrafeed VAF-4’s sheet metal box totally encloses the
solid state control circuitry. A hinged, latched feedhead
cover allows quick and easy access to the feedhead featuring quick change feed rolls, and tool-less knobs and
clamps for changeover of guides and guns.
The Ultrafeed VAF-4 comes with an abundance of standard
features including:
• anon/offrockerswitch
• 2circuitbreakersfortotalsystemprotection
• awirefeedspeedcontrol
• apowersourcevoltagecontrol
• aninchswitch
• agaspurgeswitch
• a2T/4T/Spotselectorswitch
• PCboardadjustmentsforenhancedrunincontrol
• asolidstateelectronicbrakefordynamicbraking
this regard can be obtained by contacting an Accredited
Tweco Distributor.
This equipment or any of its parts should not be altered
from standard specification without prior written approval
of Tweco. The user of this equipment shall have the sole
responsibility for any malfunction which results from
improper use or unauthorized modification from standard
specification, faulty maintenance, damage or improper repair by anyone other than appropriately qualified persons
approved by Tweco.
2.06 Transportation Methods
!
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. DO NOT TOUCH live
electrical parts. Disconnect wire feeder from
Power Source before moving the wire feeder.
WARNING
FALLING EQUIPMENT can cause serious personal injury and equipment damage.
• twoquickchange,gear-drivenfeedrolls
• agasvalvesolenoid
• twoisolatedguntriggersforoperatorsafety
• avarietyofadd-onoptionstoconguretheunitfor
any wire-welding situation.
The Ultrafeed VAF-4 has been designed to comply with
IEC 60974-5, CSA E60974-5 and ANSI/IEC 60974-5
standards.
The instructions in the next section detail how to correctly and safely set up the machine and give guidelines
on gaining the best efficiency and quality from the Power
Source. Please read these instructions thoroughly before
using the unit.
2.05 User Responsibility
This equipment will perform as per the information contained herein when installed, operated, maintained and
repaired in accordance with the instructions provided.
This equipment must be checked periodically. Defective
equipment (including welding leads) should not be used.
Parts that are broken, missing, plainly worn, distorted or
contaminated, should be replaced immediately. Should
such repairs or replacements become necessary, it is
recommended that such repairs be carried out by appropriately qualified persons approved by Tweco. Advice in
Lift unit with integrated handle at the top of the unit.
Use handcart or similar device of adequate capacity.
If using a fork lift vehicle, place and secure unit on a proper
skid before transporting.
2.07 Packaged Items
Ultrafeed VAF-4 Wirefeeder (Part No.: W3400002)
• UltrafeedVAF-4Wirefeeder
• Controlcable,6ft,19pin
• Powercable,6ft,50mmmale-50mmfemale
• OperatingManual
• CD
• Drive Roll.035"/.045"(0.9mm/1.2mm) V-groove
fitted
• HandleAssembly
2-2 INTRODUCTION Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
2.08 Specifications
Description Ultrafeed VAF-4 Wirefeeder
Wirefeeder Part Number W3400002
Wirefeeder Dimensions H 13.6” x W 10.8” x D 24.0”
Wirefeeder Weight 41.9lb (19kg)
Input Voltage 42VAC or 115VAC, 350VA
Input Voltage Tolerance ±15%
Input Frequency 50/60 Hz
Gas Solenoid Voltage 24vdc
Maximum Gas Pressure 100 psi (7 bar)
MIG Welding Output, 40°C, 10 min
Wirefeed Speed Range 53 - 878 IPM (1.35 - 22.3 MPM)
Operating Temperature Range 0°C - 40°C
Interconnection Plug 19pin
Solid
Wire Sizes
Aluminium .035” - 1/16” (0.9 mm - 1.6 mm)
Flux Cored
450A @ 60%
350A @ 100%
.030"-1/16"(0.8mm-1.6mm)
.030"-5/64"(0.8mm-2.0mm))
Maximum Wire Spool Weight 60 lb./ 27kg
Table 2-1 Ultrafeed VAF-4 Specification
NOTE
Due to variations that can occur in manufactured products, claimed performance, voltages, ratings, all capacities, measurements,
dimensions and weights quoted are approximate only. Achievable capacities and ratings in use and operation will depend upon
correct installation, use, applications, maintenance and service.
In the interest of continuous improvement, Tweco reserves the right to change the specifications or design of any of its products
without prior notice.
2.09 Optional Accessories
Feed Rolls
Part Number Description
W4017019 Drive Roll .023” & .030” V groove
W4017020 Drive Roll .035” & .045” V groove*
W4017021 Drive Roll .045” & 1/16” V groove
W4017120 Drive Roll .030” & .035” U groove
W4017121 Drive Roll .040” & .045” U groove
W4017122 Drive Roll .045” & 1/16” U groove
W4017222 Drive Roll .030” & .035” V groove knurled
W4017223 Drive Roll .045” & 1/16” V groove knurled
W4017224 Drive Roll 1/16” & 5/64” V groove knurled
Table 2-2 Feed Rolls
Wire Type
Hard
Hard
Hard
Soft
Soft
Soft
Cored
Cored
Cored
NOTE
NOTE 1: Two feed rolls are required for each wire size.
NOTE 2: * indicates fitted as standard.
Manual 0-5329 INTRODUCTION 2-3

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Other Accessories
Accessories Part Number Description
Spool Cover Assy W4016301
Lifting Eye Kit W4016701 Electrically insulated.
Suitable for spools up to 300mm diameter.
Contains plastic spool cover and all necessary
mounting hardware.
Heavy Duty 4 Wheel Trolley W4000002
Power Cable, 70mm male to
70mm female, 6 ft
W4015850
Table 2-3 Options and Accessories
Heavy duty, large castor wheel trolley for moving the
Wirefeeder around the work area.
2-4 INTRODUCTION Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
!
SECTION 3: INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3.01 Environment
These units are designed for use in environments with
increased hazard of electric shock as outlined in IEC
60974-5.
A. Examples of environments with increased hazard of
electric shock are:
1. In locations in which freedom of movement is restricted, so that the operator is forced to perform the
work in a cramped (kneeling, sitting or lying) position
with physical contact with conductive parts.
2. In locations which are fully or partially limited by conductive elements, and in which there is a high risk of
unavoidable or accidental contact by the operator.
3. In wet or damp hot locations where humidity or perspiration considerably reduces the skin resistance
of the human body and the insulation properties of
accessories.
B. Environments with increased hazard of electric shock
do not include places where electrically conductive parts in
the near vicinity of the operator, which can cause increased
hazard, have been insulated.
3.02 Location
Be sure to locate the wirefeeder according to the following guidelines:
A. In areas, free from moisture and dust.
B. Ambient temperature between 0° C to 40° C.
C. In areas, free from oil, steam and corrosive gases.
D. In areas, not subjected to abnormal vibration or shock.
E. In areas, not exposed to direct sunlight or rain.
F. The enclosure design of this Wire Feeder meets the
requirements of IP23S as outlined in IEC 60529. This
provides adequate protection against solid objects
(greaterthan1/2",12mm),anddirectprotectionfrom
vertical drops. Under no circumstances should the unit
be operated or connected in a micro environment that
will exceed the stated conditions. For further information please refer to IEC 60529.
G. Precautions must be taken against the Wire Feeder
toppling over. The Wire Feeder must be located on
a suitable horizontal surface in the upright position
when in use.
3.03 Ventilation
WARNING
Since the inhalation of welding fumes can be
harmful, ensure that the welding area is effectively ventilated.
3.04 Mains Supply Voltage Requirements
CAUTION
This wirefeeder cannot be connected directly
to the mains supply. It must be connected
to a suitable wirefeeder control socket on a
power source.
3.05 Electromagnetic Compatibility
WARNING
Extra precautions for Electromagnetic Compatibility may be required when this Welding
Power Source is used in a domestic situation.
A. Installation and Use - Users Responsibility
The user is responsible for installing and using the welding
equipment according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
If electromagnetic disturbances are detected then it shall
be the responsibility of the user of the welding equipment
to resolve the situation with the technical assistance of
the manufacturer. In some cases this remedial action
may be as simple as earthing the welding circuit, see
NOTE below. In other cases it could involve constructing
an electromagnetic screen enclosing the Welding Power
Source and the work, complete with associated input
filters. In all cases, electromagnetic disturbances shall be
reduced to the point where they are no longer Trouble-
some.
NOTE
The welding circuit may or may not be earthed
for safety reasons. Changing the earthing arrangements should only be authorised by a
person who is competent to assess whether
the changes will increase the risk of injury,
e.g. by allowing parallel welding current return
paths which may damage the earth circuits of
other equipment. Further guidance is given in
IEC 60974-10 Arc Welding Equipment - Instal-
lation and use (under preparation).
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-1

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
B. Assessment of Area
2. Maintenance of Welding Equipment
Before installing welding equipment, the user shall make
an assessment of potential electromagnetic problems in
the surrounding area. The following shall be taken into
account.
1. Other supply cables, control cables, signalling and
telephone cables; above, below and adjacent to the
welding equipment.
2. Radio and television transmitters and receivers.
3. Computer and other control equipment.
4. Safety critical equipment, e.g. guarding of industrial
equipment.
5. The health of people around, e.g. the use of pacemakers and hearing aids.
6. Equipment used for calibration and measurement.
7. The time of day that welding or other activities are to
be carried out.
8. The immunity of other equipment in the environment:
the user shall ensure that other equipment being used
in the environment is compatible: this may require
additional protection measures.
The size of the surrounding area to be considered will
depend on the structure of the building and other activities
that are taking place. The surrounding area may extend
beyond the boundaries of the premises.
C. Methods of Reducing Electromagnetic Emissions
1. Mains Supply
Welding equipment should be connected to the
mains supply according to the manufacturer’s
recommendations. If interference occurs, it may be
necessary to take additional precautions such as
filtering of the mains supply. Consideration should
be given to shielding the supply cable of permanently
installed welding equipment in metallic conduit or
equivalent. Shielding should be electrically continuous
throughout its length. The shielding should be
connected to the Welding Power Source so that good
electrical contact is maintained between the conduit
and the Welding Power Source enclosure.
The welding equipment should be routinely maintained
according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. All
access and service doors and covers should be closed
and properly fastened when the welding equipment
is in operation. The welding equipment should not
be modified in any way except for those changes
and adjustments covered in the manufacturer’s
instructions.
3. Welding Cables
The welding cables should be kept as short as possible
and should be positioned close together but never
coiled and running at or close to the floor level.
4. Equipotential Bonding
Bonding of all metallic components in the welding
installation and adjacent to it should be considered.
However, metallic components bonded to the work
piece will increase the risk that the operator could
receive a shock by touching the metallic components
and the electrode at the same time. The operator
should be insulated from all such bonded metallic
components.
5. Earthing/grounding of the Work Piece
Where the work piece is not bonded to earth for electri-
cal safety, nor connected to earth because of its size
and position, e.g. ship’s hull or building steelwork,
a connection bonding the work piece to earth may
reduce emissions in some, but not all instances. Care
should be taken to prevent the earthing of the work
piece increasing the risk of injury to users, or damage
to other electrical equipment. Where necessary, the
connection of the work piece to earth should be made
by direct connection to the work piece, but in some
countries where direct connection is not permitted, the
bonding should be achieved by suitable capacitance,
selected according to national regulations.
6. Screening and Shielding
Selective screening and shielding of other cables
and equipment in the surrounding area may alleviate
problems of interference. Screening the entire welding
installation may be considered for special applications.
3-2
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
3.06 Front Panel Controls, Indicators and Features
Art # A-12467
Figure 3-1 Front Panel View
WARNING
DO NOT TOUCH the electrode wire while it is being fed through the system. The electrode wire will be at
welding voltage potential.
1. POWER Indicator
The red power indicator will be illuminated when the Wirefeeder is turned ON and indicates the presence of power.
2. FAULT Indicator
The yellow fault indicator will be illuminated when any faults are detected. Should a fault condition occur refer to Sections 3.29, 3.30, 4.05 or 4.08 for further information.
If the Fault indicator is flashing while welding refer to Section 3.31 as the motor overload protection is active.
3. AMPS Indicator
The red AMPS indicator will be illuminated when the Left Display displays the amperage.
4. IPM Indicator
The red IPM indicator will be illuminated when the Left Display displays WFS in Inches Per Minute (IPM).
5. MPM Indicator
The red MPM indicator will be illuminated when the Left Display displays WFS in Metres Per Minute (MPM).
6. Left Knob
The control knob adjusts Wire Feed Speed (WFS) (which in turn adjusts the output current by turning the amount of
MIG wire delivered to the welding arc). The optimum WFS required is dependent on the type of welding application.
The value may also be adjusted while a weld is in progress – if this occurs, the left display will briefly switch to show
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-3

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
the adjusted value as the knob is turned, and will automatically revert back to show the weld current measurements
when the knob is not being turned. Turn the left knob either clockwise to increase WFS or counterclockwise to decrease
WFS by increments of 3.94 IPM. To increment in steps of 39.4 IPM while holding the left knob depressed turn it either
clockwise to increase WFS or counterclockwise to decrease WFS.
The Left digital meter display option can be changed either via the Advanced Features Menu (refer to Section 3.08)
OR
By simply depressing the Left Amps control knob for 3 seconds while welding, then by releasing the knob and then
holding it depressed for a further 3 seconds will increment to the next available display option that is shown on the
left digital display. i.e. Amps
Press Left Knob (Amps) and Right Knob (Volts) for 1.2 seconds to enter or exit from the advanced programming
mode. Please refer to Section 3.08 for Advanced Features Details.
7. Right Knob
WFS ---- (blank).
The control knob adjusts the output voltage of the power source. The welding voltage is increased by turning the
knob clockwise or decreased by turning the knob counter-clockwise. The value may also be adjusted while a weld is
in progress – if this occurs, the right display will briefly switch to show the adjusted value as the knob is turned, and
will automatically revert back to show the weld voltage measurements when the knob is not being turned. Turn the
right knob either clockwise to increase voltage or counterclockwise to decrease voltage by increments of 0.1V. To
increment in steps of 1V while holding the right knob depressed turn it either clockwise to increase WFS or counterclockwise to decrease WFS.
The Right digital meter display option can be changed either via the Advanced Features Menu (refer to Section 3.08)
OR
By simply depressing the Right Amps control knob for 3 seconds while welding, then by releasing the knob and then
holding it depressed for a further 3 seconds will increment to the next available display option that is shown on the
right digital display. i.e. VARC
---- (blank).
Press Left Knob (Amps) and Right Knob (Volts) for 1.2 seconds to enter or exit from the advanced programming
mode. In advanced programming mode, turning the knob clockwise to increase and counter-clockwise to decrease
the value on right display. Please refer to Section 3.08 for Advanced Features Details.
3-4
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
8. Left Digital Display
Left display is a 4- digit display.
Inadvancedprogrammingmode,thisdisplayisusedtodisplayadvancedfeaturesdetailsorsimply"----".Pleaserefer
to Section 3.08 for Advanced Features Details.
When welding, this digital meter will display WFS in Inches Per Minute (IPM) or Metres Per Minute (MPM) and actual
weldingamperageofthepowersource;itcanalsosimplydisplay"----"whentheVAF-4isconnectedtoapowersource
without a control signal on pin U of the 19 pin interconnection. The VAF-4 uses this signal on pin U of the 19 pin
interconnection to display welding amps, if this signal is not present from the power source, set the display to show
"----".Pressleftknobandselecttheinformationonleftdisplay.Attimesofnon-welding,thedigitalmeterwilldisplay
a pre-set (preview) WFS value. This value can be adjusted by turning the Left Knob (Control No. 6).
At the completion of welding, the digital meter will hold the last recorded value for a period of approximately 10 sec-
onds. The meter will hold the value until: (1) any of the front panel controls are adjusted in which case the unit will
revert to preview mode, (2) welding is recommenced, in which case actual welding amperage will be displayed, or (3)
a period of 10 seconds elapses following the completion of welding in which case the unit will return to preview mode.
The display is also used for providing error messages to the user. Please refer to Section 4.05 for Error Codes and
Remedies.
9. Right Digital Display
Right display is a 4- digit display.
This digital meter is used to display the pre-set (preview) Voltage in MIG mode and actual welding voltage of the power
sourceorsimply"----"whentheVAF-4isconnectedtoapowersourcewithoutacontrolsignalonpinCofthe19
pin interconnection. The VAF-4 uses this signal on pin C of the 19 pin interconnection to display welding volts, if this
signalisnotpresentfromthepowersource,setthedisplaytoshow"----".Pressrightknobandselecttheinformation
on right display. At times of non-welding, the digital meter will display a pre-set (preview) value of Voltage. This value
can be adjusted by turning the Right Knob (Control No 7).
At the completion of welding, the digital meter will hold the last recorded voltage value for a period of approximately
10 seconds in all modes. The voltage meter will hold the value until: (1) any of the front panel controls are adjusted
in which case the unit will revert to preview mode, (2) welding is recommenced, in which case actual welding voltage
will be displayed, or (3) a period of 10 seconds elapses following the completion of welding in which case the unit
will return to preview mode.
The display is also used for providing error messages to the user and showing other information. Please refer to Section 4.05 for Error Codes and Remedies.
10. 2T - 4T- SPOT Trigger Mode Control Button
Press and release the button to change the selected operating mode of the trigger. The selected mode can be “2T”,
“4T”or"Spot”operation.Theredindicatornexttothebuttonwillilluminatetoidentifywhichmodeisselected.Inthe
4T mode once the weld has been started you can release the trigger and continue welding until the trigger is activated
again or the welding arc is broken to stop the welding arc. Please refer to Section 3.24 - 3.27 for more details.
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-5

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
NOTE
In Advanced Features Mode Trigger Mode and SCH1-SCH2 can't be changed. In Spot Mode Stitch Mode
is not available. Crater is only available in 4T Trigger Mode.
11. SCH 1-SCH 2 Button
This allows the user to save parameter settings in either Schedule 1 (SCH 1) or Schedule 2 (SCH 2) locations. Press
the button to select either SCH 1 or SCH 2. The red indicator will illuminate to identify which schedule is selected.
Adjust the wire speed and weld volts, along with parameters such as burnback, pre flow, post flow etc, to the desired
setting. While holding the volts knob depressed at the same time press the SCH 1-SCH 2 button for 1.8 seconds to
save the schedule. The SCH 1 or SCH 2 LED will flash 3 times to indicate the save has been successful. Note that all
adjustable parameters are saved with each schedule.
If the user wishes to load settings saved in either SCH 1 or SCH 2 locations, press and release the SCH 1-SCH 2 button
to select either SCH 1 or SCH 2, the red indicator will illuminate to identify which Schedule is selected.
12. INCH Button
After turning the power ON, press this button and hold it to start cold feeding. Left display shows actual WFS and right
display shows INCH. If the user wishes to adjust WFS, turn left knob and left display shows preset WFS. 1 second
later, it shows actual WFS. Release the button when it feeds the wire to the torch.
13. PURGE Button
This button is used to initiate gas line purge function to fill the gas line with the shielding gas from the connected gas
cylinder. Press and hold the button depressed to start gas flow, at which time a count down timer will count down
from 30 seconds while you press the button. You can stop the gas purge any time by releasing the button.
14. MIG Torch Adaptor
The MIG Torch adaptor is the connection point for the MIG welding Torch. Connect the MIG Torch by pushing the MIG
Torch connector into the brass MIG Torch adaptor firmly and screwing the plastic MIG Torch nut clockwise to secure
in position. To remove the MIG Torch simply reverse these directions.
3-6
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
15. Remote Control Socket
The 8 pin Remote Control Socket is used to connect remote control devices to the welding power source. To make
connections, align keyway, insert plug, and rotate threaded collar fully clockwise.
1
2
3
1
2
5
8
3
4
6
7
4
5
6
7
8
Remote Wirespeed in GMAW mode
Figure 3-2 Remote Control Socket
Trigger Switch
W
V
Remote Volts in
GMAW Mode
Socket Pin
1 Not connected
2 Trigger Switch Input
3 Trigger Switch Input
4 Not connected
5 5k ohm (maximum) connection to 5k ohm remote control potentiometer.
6 Zero ohm (minimum) connection to 5k ohm remote control potentiometer.
7 Wiper arm connection to 5k ohm remote control Wirespeed MIG mode potentiometer.
8 Wiper arm connection to 5k ohm remote control Volts MIG mode potentiometer.
Function
Table 3-1 Pin Function in Remote Control Socket
NOTE
The remote/ local setting in Advanced Features Menu should be set to remote for the remote wire feeder
amperage/voltage controls to be operative.
16. 4 Pin Trigger Socket
The 4 pin Trigger Socket is used to connect remote control devices to the welding power source. To make connections,
align keyway, insert plug, and rotate threaded collar fully clockwise.
1
3
2
4
1
2
3
4
Trigger Switch
Socket Pin
1 Trigger Switch Input
2 Trigger Switch Input
3 Not connected
4 Not connected
Table 3-2 Pin Function in 4 Pin Trigger Socket
Manual 0-5329
Figure 3-3 4 Pin Trigger Socket
Function
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-7

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Keyway
3.07 Rear Panel Controls and Features
Art # A-12468
Figure 3-4 Rear Panel View
17. ON/ OFF Switch
Press this switch to turn ON or turn OFF the Wirefeeder.
18. Gas Inlet
Gas inlet allows to connect the shield gas.
19. Control Cable Socket
The control cable connects to the power source at this 19pin amphenol connector. It contains the signals required
to allow the welding power source and the wire feeder to
work together as a system.
WARNING
The protective earth ground (pin G) of the
control cable is established ONLY when the
power source is properly grounded. See the
power source owner’s manual for proper
grounding methods.
20. Welding Cable Connector
This connector allows to connect welding cable with
Wirefeeder. Please make sure that it is secured firmly, or
it will heat and generate arc.
21. 4A Circuit Breaker
This circuit breaker protects the wirefeeder from electrical faults on the 115VAC circuit. In the event of a fault
occuring this circuit breaker will trip (pop out). A short
cooling period must be allowed before an attempt is made
to reset it by pressing it back in. Refer to Section 4.08 for
further details.
L
KUNB
HS RD
A
M
CPVTJ
EFG
Figure 3-5 Pin Identification
Control Cable
Pin
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
S
T
U
V
Contactor + (Shorted to B
to turn ON Power Source)
Contactor- (Shorted to A to
turn ON Power Source)
Voltage Feedback ( 1
Volt is 10 Arc Volts)
Not Used
115 VAC Hot
42VAC and 115VAC Neutral
Protective Earth Ground
Remote Control Maximum
Remote Control Signal
Not Used
Power Source Common
Arc Established (= +15 VDC)
Power Source Select Line
Not Used
Not Used
42VAC Live Wire
Not Used
Current Feedback (1 Volt
is 100 Arc Amps)
Not Used
Function
Table 3-3 Control Cable Pin Functions
22. 8A Circuit Breaker
This circuit breaker protects the wirefeeder from electrical
faults on the 42VAC circuit. In the event of a fault occuring this circuit breaker will trip (pop out). A short cooling
period must be allowed before an attempt is made to
reset it by pressing it back in. Refer to Section 4.08 for
further details.
3-8
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
3.08 Advanced Features Mode
Enter Advanced Features Mode by pressing both the left knob and right knob at the same time for more than 1.2 seconds.
NOTE
In Advanced Features Mode the Trigger Mode Control Button, SCH 1-SCH 2 button is inactive.
Exit Advanced Features Mode by pressing both the left knob and right knob at the same time for more than 1.2 seconds
to Save the Settings and exit advanced features mode. Note if there has been no user input for 30 seconds, the VAF-4
will save settings and automatically exit advanced programming mode.
Advanced Feature Left Display
Local / Remote
This is used to select local panel
control on the Wirefeeder, or remote
control from the 8 pin remote
control socket on the front of the
Default Local / Remote = Local
This is used to provide gas to the
weld zone prior to the wire striking
Default Pre Flow = 0.1 sec
(Creep wirefeed speed)
This is used to change Wirespeed to
a percentage of the value set by the
operator. It can improve arc starts
by controlling the wire speed at the
instant the wire touches the base
Default Run In = 70%
Manual 0-5329
Wirefeeder
Pre Flow
an arc.
Run In
metal.
If MIG Remote is selected but no remote control device is connected to the 8 pin
control socket then the wirefeed speed will be 50 IPM (minimum wirespeed) and
For example if you have 472 inches/min set speed and have 50% selected for Run-
in Speed, the speed of the wire will be 6m/min until the arc is established. Once
Right Display
Feature Description
the voltage will be 14V (minimum volts).
the arc is established, the speed ramps up to the set speed at the rate set (472
inches/min) with Ramp Time described below.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-9
Parameter / Selection
Local / Remote
0.0 – 5.0 seconds
30 – 150% of
Wirefeeder Speed
Setting

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Advanced Feature Left Display
Feature Description
Ramp Time
This is used to set the time to ramp
from the creep wire feed speed to
the selected wirefeed speed setting.
Default Ramp Time = 0.2 sec
This is used to adjust the post
gas flow time once the arc has
Default Post Flow = 0.1 sec
This is used to adjust the amount
of MIG wire that protrudes from the
MIG torch after the completion of
MIG welding (commonly referred to
Default Burn Back = 0.15 sec
This is used to fill in the “crater” at
the end of the weld. It only works
with 4T mode and the Crater Volts /
Crater Wirefeed Speed must be set.
Default Crater = Off
(only if Crater mode is ON)
This sets the reduced volts during
crater operation in 4T at the end of
Default Crater Volts = 70%
An example is if Preview Volts is
set to 26V and crater volts is set to
70% crater volts will be 18.2V. Note
minimum crater volts is determined
by minimum preview voltage of
Post Flow
extinguished.
Burn Back
as stick out)
Crater
Crater Volts
the weld.
wirefeeder.
Ramp Time plus Run In is used to optimize arc starting characteristic.
This control is used to dramatically reduce weld porosity at the completion of the
If the Burn Back time is set too long, the MIG wire may burn back to the tip of the
Right Display
Parameter / Selection
0.1 to 1.0 seconds
0.0 – 30 seconds
weld.
0.00 to 1.00
seconds
MIG torch.
Crater Mode ON /
OFF
0 – 100% of
Welding Volts
Setting
3-10
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Advanced Feature Left Display
Feature Description
Crater Wirefeed Speed
(only if Crater mode is ON)
This sets the reduced wire speed
during crater operation in 4T at the
end of the weld.
Default Crater Wirefeed Speed =
An example is if Preview Wirefeed
speed is set to 551 IPM and
crater wirefeed speed is set to
70% crater wirefeed speed will be
386 IPM. Note minimum crater
wirefeed speed is determined by
minimum preview wirefeed speed of
This is used to weld two thin plates
together by melting the top &
bottom plates together to form a
nugget between them. The weld time
is set by the Spot Time.
Default Spot Time = 2.0 sec
This is used to weld two or more
components by stitch or interval
weld together. The weld time is set
by the Stitch Time and the non weld
time is set by the Dwell Time (off
Default Stitch Mode = Off
(only if Stitch mode is ON)
This sets the “welding on” time in
Default Stitch Time = 2.0 sec
70%
wirefeeder.
Spot Time
Stitch Mode
time).
Stitch Time
Stitch mode.
Right Display
Parameter / Selection
0 – 100% of
Welding Wirefeed
Speed Setting
0.1 to 20.0 seconds
Stitch feature is not available in spot mode.
Stitch Mode ON /
OFF
Stitch is only available in 2T or 4T modes.
0.2 to 4.0 seconds
Dwell Time
(only if Stitch mode is ON)
This sets the “welding off” time in
Stitch mode.
Default Dwell Time = 0.5 sec
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
0.1 to 1.0 seconds
3-11

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Advanced Feature Left Display
Feature Description
Wirefeed Speed Units
This allows setting of the Wirefeed
Speed Meter to display in IPM or
Default Wirefeed Speed = IPM
Arc Hours Accumulated Run Time
A Read Only display of the total of
actual arc hours.
Left Display Type
This allows the user to select what
is shown on the LEFT Display when
With some power sources, it may
not be possible to display welding
amps on the VAF-4 display when
welding, in this case, set the display
to wirefeed speed (WFS) or Blank
Default Left Display = AMPS
Right Display Type
This allows the user to select what is
shown on the RIGHT Display when
With some power sources, it may
not be possible to display welding
volts on the VAF-4 display when
welding, in this case, set the display
to Blank (BLNK)
Default Left Display = VARC
MPM units.
welding.
(BLNK)
welding.
Right Display
Parameter / Selection
IPM (inches per
minute)
MPM (metres per
minute)
0.0 – 999.9 hours
(It will rollover to 0
once 999.9 hours
have been reached.)
Display AMPS when
welding or
Display WIREFEED
SPEED when
welding or
Display BLANK
when welding
Display ARC VOLTS
when welding or
Display BLANK
when welding
3-12
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Advanced Feature Left Display
Restore Factory Defaults 1
This resets all the user adjustable
values in this table (except Arc
Hour Accumulated Runtime) to the
Factory Default Values.
Factory Default Setting
Right Display
Feature Description
Parameter / Selection
Restore Factory
Default No / YES
CAUTION
Schedule SCH1 & SCH2 settings will be reset to factory default
settings when YES is selected with Restore Factory Defaults.
Exit Advanced Features Mode: by pressing both the left knob and right knob at the
same time for more than 1.2 seconds to Save the Settings and exit advanced features
mode. Note if there has been no user input for 30 seconds, the VAF-4 will save settings
and automatically exit advanced programming mode.
Table 3-4 Advanced Features
Advanced Feature Left Display
Feature
Right Display
(Default)
Comments
Description
MIG Control MIG/CNTR LOCL
Pre Flow PRE/FLOW 0.1
Run In RUN/IN 70
Ramp Time RAMP/TIME 0.2
Post Flow POST/FLOW 0.1
Burn Back BURN/BACK 0.15
Crater CRAT OFF Only in 4T Mode
Crater Volts CRAT/ VOLT 70
Crater Wirefeed Speed CRAT/ WFS 70
Spot Time SPOT/TIME 2.0 Only in Spot Mode
Stitch Mode STCH OFF Only in 2T & 4T Modes
Stitch Time STCH/TIME 2.0 Only when Stitch is ON
Dwell Time DWEL/TIME 0.5 Only when Stitch is ON
Wirefeed Speed Units WFS/UNIT IPM
Left Display Type LEFT/DISP AMPS
Right Display Type RGHT/DISP VARC
Only when in 4T Mode
and Crater is ON
Only when in 4T Mode
and Crater is ON
Manual 0-5329
Table 3-5 Factory Default Setting
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-13

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
3.09 Wirefeeder Configuration for Different Power Sources
WARNING
There are dangerous voltage and power levels inside this product. Turn OFF wirefeeder and disconnect
from the power source before removing cover from wirefeeder.
The factory default setting for the wirefeeder is set for the ArcMaster 401MST power source. If a different power
source is being used then the user will need to set the Display PCB DIP switch as to Table 3-5 according to the power
source being used.
Art # A-12469
DIP Switch
Display PCB
Figure 3-6 DIP Switch on Display PCB
S3S4S5 Vmin Vmax Vsetmin(J&K) Vsetmax(J&K) Welder
S3=Off(0), S4=On(1), S5=On(1) 10 36 2.3 8.17
S3=Off(0), S4=Off(0), S5=Off(0) 14 50 3.182 11.364 Powermaster 550i
S3=On(1), S4=On(1), S5=Off(0) 14 40 3.182 9.091 Powermaster 350i
S3=On(1), S4=Off(0), S5=Off(0) 10 44 2.273 10 Transmig 500i
S3=On(1), S4=On(1), S5=On(1) 8 50
ArcMaster 401MST (default)
ArcMaster 400MST
User Type Setting (The Service
Manual outlines how to set the
wirefeeder for other Power Sources.)
Table 3-6 Voltage Setting
NOTE
When S6=ON(1), calibration functions in Advanced Features Mode is enabled; when S6=OFF(0), calibration
functions are disabled.
NOTE
When S1=OFF(0),S2=ON(1), WFS Setting is applicable for Ultrafeed VAF-4 and it ranges from 50 IPM to
875 IPM.
3-14
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
3.10 Attaching Tweco No. 4 MIG Torch
1. Insert the 4 pin plug into the 4 Pin Trigger Socket, and rotate threaded collar fully clockwise to lock the
plug into position.
2. Fit the Tweco No. 4 MIG torch to the Wirefeeder by pushing the MIG Torch Connector into the Tweco No.
4 Torch Adaptor and secure it by tightening the Thumb Screw supplied.
Tweco No. 4
MIG Torch Connector
4 Pin Trigger Socket
Art # A-12470
4 Pin Plug
Tweco No. 4
MIG Torch
Thumb Screw
Figure 3-7 Attaching the Tweco No. 4 MIG Torch
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-15

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Handle Assembly
!
Handle Assembly
3.11 Installing Handle Assembly
!
WARNING
This handle is not designed to lift wirefeeder by mechanical means. Handle is to be used for Lifting by
Hand Only.
For Mechanical Lifting use Lifting Eye Kit W4016700.
The following components are included:
Description Quantity
Handle Assembly 1
Bolt, M10 × 50 (with torque 45~59 N.m.) 2
Flat Washer, M10 (with torque 45~59 N.m.) 4
Spring Washer, M10 (with torque 45~59 N.m.) 2
Nut, M10 (with torque 45~59 N.m.) 2
Table 3-7 Handle Assembly
Install the handle assembly as below:
Secure the handle assembly to the base assembly with M10 x 50 Bolts, M10 Flat Washers, M10 Spring Washers
and M10 Nuts as shown in Figure 3-8.
Bolt, M10 × 50
Flat Washer, M10
Spring Washer, M10
Nut, M10
Art # A-12471
Figure 3-8 Installing Handle Assembly
WARNING
Fully tighten all the fasteners with torque 45~59 N.m.
Refer to the figure below for the assembled handle assembly:
3-16
Art # A-12472
Figure 3-9 Assembled Handle Assembly
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Flat Washer
!
3.12 Installing Lifting Eye Kit (Optional)
The following components are included:
Description Quantity
Lifting Eye 1
Insulator Plate 1
Bolt, M8 × 40 (with torque 45~59 N.m.) 2
Flat Washer (smaller), M8 (with torque 45~59 N.m.) 2
Flat Washer (larger), M8 (with torque 45~59 N.m.) 2
Insulator Washer, M8 (with torque 45~59 N.m.) 2
Spring Washer, M8 (with torque 45~59 N.m.) 2
Nut, M8 (with torque 45~59 N.m.) 2
Table 3-8 Lifting Eye Kit
Install the lifting eye as below:
1. Loosen the M10 x 50 Bolts, M10 Flat Washers, M10 Spring Washers and M10 Nuts with 17mm wrench that
secure the handle assembly and remove the handle assembly and fixings from the base assembly. Refer to
Figure 3-8.
2. Use 14mm wrench to secure the lifting eye and insulator plate to the base assembly using the M8 x 40 Bolts,
M8 Flat Washers, M8 insulator washers, M8 Spring Washers and M8 Nuts as supplied with this kit.
Bolt, M8 × 40
(smaller), M8
Art # A-12473
Figure 3-10 Installing Lifting Eye
Fully tighten all the fasteners with torque 45~59 N.m.
Refer to the figure below for the assembled lifting eye.
Lifting Eye
Insulator Plate
Insulator Washer, M8
Flat Washer (larger), M8
Spring Washer, M8
Nut, M8
WARNING
Manual 0-5329
Lifting Eye
Art # A-12474
Figure 3-11 Assembled Lifting Eye
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-17

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
3.13 Installing Wire Spool Cover (optional)
The following components are included in this kit:
Item Description Quantity
1 Bolt, M12 x 30 2
2 Star Washer, M12 2
3 Flat Washer, M12 2
4 Screw, Countersunk, M5 x 12 2
5 Spool Cover Mounting Bracket 1
6 Spool Cover 1
7 Spool Cover Mounting Bracket 1
Table 3-9 Spool Cover Assembly
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Art # A-12475
Figure 3-12 Spool Cover Assembly
3-18
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Spring Washer
M12 x 30 Bolts;
Spool cover is assembled in the following steps:
1. Remove the spool hub assembly.
a. Remove the clip from the spool hub.
b. Unscrew the 3-lobe screw.
c. Remove the spool hub parts and the spacer in the following sequence. Note that the spacer is not
required when fitting the spool cover.
Flat Washer,large hole
Spacer
Friction Washer
Keyed Washer
Flat Washer, small hole
Shaft
Hub Wire Reel
Compression Spring
3-lobe Screw
Retaining Clip
Hexagon Nut
Art # A-12476
Figure 3-13 Removing Spool Hub Assembly
2. Assemble the Spool Cover Mounting Brackets, one inside and one outside the spool cover, with the two
countersunk screws M5 x 12.
3. Secure the spool cover assembly to the spool support arm with M12 x 30 Bolts, Star Washers, M12, and
Flat Washers, M12 as shown in the diagram below.
Spool Cover
Friction Washer
Keyed Washer
Flat Washer, small hole
Hub Wire Reel
3-lobe Screw
Retaining Clip
Manual 0-5329
Compression Spring
Countersunk Screws,
M5×12
Spool Cover Mounting Brackets
Figure 3-14 Installing Spool Cover
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-19
Star Washers, M12;
Flat Washers, M12
Art # A-12477

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
4. Install the spool hub component parts over the spool hub shaft in the following sequence.
Spool Hub
Spring
3-lobe Screw
Retaining Clip
Flat Washer
Keyed Washer
Friction Washer
Figure 3-15 Spool Hub Assembly
!
Fully tighten all fasteners.
Refer to the figures below for the assembled spool cover:
Art # A-12478
WARNING
Figure 3-16a Assembled Spool Cover (door opened)
Figure 3-16b Assembled Spool Cover
3-20
Art # A-12479
Art # A-12480
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Screw Hole for
3.14 Installing Welding Wire Spool
!
WARNING
Fully tighten all fasteners.
Thereare3holesonthespoolhubsupport.Thetopscrewholeisforinstallingacoilof16"(66lbs)diameter.Inthis
casea66lbscoilholdermustbeused.The66lbscoilholderisattachedtothespoolhubinthesamewayasfora12"
spool, then the coil is placed over the 66lbs coil holder & locked in place. The middle hole is for installing a spool of
12"diameter(asshowninFigure3-17).Thebottomholeisforinstallingaspoolof8"diameter.Asdeliveredfromthe
factory,theunithasthespoolhubttedintothemiddle(12"spool)position.
1. Remove the retaining clip from the spool hub.
2. Install the wire spool over the spool hub, locating the hole in the spool, with the alignment pin on the spoolhub.
3. Insert the retaining clip back into the spool hub.
NOTE
Install the welding wire spool so that the wire feeds from the bottom of the spool into the input wire guide.
16" Spool
Screw Hole for
12" Spool
Wire Spool (12")
Spool Hub
Alignment Pin
Retaining Clip
Retaining clip
3-lobe Screw
position for
8" spool
Screw Hole for
8" Spool
Figure 3-17 Installing Welding Wire Spool
Art # A-12481
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-21

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Wire Spool Hub
3.15 Wire Reel Brake
The wire reel hub incorporates a 3-lobe screw which is adjusted during manufacture for optimum braking.
If it is considered necessary, adjustment can be made by turning the 3-lobe Screw inside the open end of the hub
clockwise to tighten the brake. Correct adjustment will result in the wire reel circumference continuing no further
than0.39-0.79"afterreleaseofthetrigger.Theelectrodewireshouldbeslackwithoutbecomingdislodgedfromwire
spool. Please refer to Figure 3-18.
Alignment Pin
Retaining Clip
3-lobe Screw
Art # A-12482
Figure 3-18 Spool Hub Assembly (with spool hub assembly installed)
CAUTION
Overtension of brake will cause rapid wear of mechanical WIREFEED parts, overheating of electrical componentry and possibly an increased incidence of electrode wire Burnback into contact tip.
3-22
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Pressure Roll Arm
3.16 Inserting Wire into Feed Mechanism
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL! Make certain the input power is disconnected from the power source before
proceeding. Do not reattach the input power until told to do so in these instructions.
WARNING
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
1. Swing the Pressure Adjusting Knobs down and the two Pressure Roll Arms automatically spring up.
2. Make sure the end of the wire is free of any burrs and is straight. Pass the end of wire through the Input Wire
Guide and over the Feed Rolls. Make certain the proper groove is being used.
3. Pass the MIG wire over the feed roll groove and out past the MIG Torch Adaptor. Then fit the welding torch as
per Section 3.10 ensuring the MIG wire passes into the MIG Torch liner of the MIG Torch.
4. Lower the Pressure Roll Arms.
5. Swing the Pressure Adjusting Knobs back into place.
6. Use the Pressure Adjusting Knobs to create a “snug” condition. (Clockwise to tighten and Counter Clockwise
to loosen).
7. Turn ON the power supply. Set proper WFS and remove the tip from the welding torch. Depress INCH button
until the wire reaches the top of welding torch. Tighten the tip again and finish inserting wire.
Pressure Roll
Feed Roll
Pressure Adjusting Knob
Inlet Guide
Art # A-11253
Figure 3-19 Wire Feeding
3.17 Feed Roll Pressure Adjustment
The roll on the swing arm applies pressure to the grooved roll via an adjustable tension device. The pressure adjusting
knobs should be set to a minimum pressure that will provide satisfactory wire feed without slippage. If slipping occurs,
and inspection of the wire out of the MIG Gun reveals no deformation or wear, the conduit liner should be checked
for kinks or clogging from metal flakes. If this is not the cause of slipping, the Feed Roll pressure can be increased
by rotating the pressure adjusting knobs clockwise. The use of excessive pressure may cause rapid wear of the Feed
Roll, motor shaft and motor bearings.
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-23

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Pressure Roll Arm
3.18 Installing and Changing the Feed Roll / Removing Inlet Guide & Torch Adaptor
WARNING
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
Make sure wirefeeder is switched OFF Before changing feedrolls, guides or adaptors.
NOTE
Feed rolls often come with a rust prohibitive coating that needs to be cleaned off before installation.
1. Loosen the Thumb Screw as shown in the figure below and lift up the finger guard.
2. Swing the Pressure Adjusting Knob down and the Pressure Roll Arm automatically springs up.
3. Rotate the Screw counter-clockwise and remove the Screw, Washer and Feed Roll.
4. Make the two Positioning Holes on the Feed Roll align at the two Positioning Pins, and install the Feed Roll,
Washer and Screw.
5. Tighten the screw clockwise.
6. Lower the Pressure Roll Arm.
7. Swing the Pressure Adjusting Knob back into place.
8. Use the Pressure Adjusting Knobs to create a “snug” condition. (Clockwise to tighten and Counter Clockwise
to loosen). Secure the finger guard with the Set Screw and Thumb Screw.
9. To remove the inlet guide remove the thumb screw as shown in the figure below then use the 3mm allen key
to remove the set screw that fixes inlet guide.
10. To remove the Tweco No. 4 torch adaptor remove the thumb screw as shown in the figure below then use the
3mm allen key to remove the set screw that fixes the torch adaptor.
Inlet Guide
Art# A-11254
Note: for clarity of picture,
only feed roll at right side shown.
Set Screw
(for fixing inlet guide)
Positioning Hole
Pressure Adjusting Knob
Positioning Pin
Feed Roll
Washer
Set Screw
(for fixing torch adaptor)
Screw
Thumb Screw
Figure 3-20 Changing Feed Roll (Right Side as Example)
3-24
Finger Guard
Thumb Screw
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
NOTE
All grooved Feed Rolls have their wire size or range stamped on the side of the roll. On rolls with different
size grooves, the outer (visible when installed) stamped wire size indicates the groove in use.
WARNING
The welding wire is electrically Hot if it is fed by depressing MIG Gun switch. Electrode contact to work
piece will cause an arc with MIG Gun switch depressed.
3.19 Shielding Gas Regulator Operating Instructions
!
WARNING
This equipment is designed for use with welding grade (Inert) shielding gases only.
Shielding Gas Regulator Safety
This regulator is designed to reduce and control high pressure gas from a cylinder or pipeline to the working pressure
required for the equipment using it.
If the equipment is improperly used, hazardous conditions are created that may cause accidents. It is the user's responsibility to prevent such conditions. Before handing or using the equipment, understand and comply at all times
with the safe practices prescribed in this instruction.
SPECIFIC PROCEDURES for the use of regulators are listed below.
1. NEVER subject the regulator to inlet pressure greater than its rated inlet pressure.
2. NEVER pressurize a regulator that has loose or damaged parts or is in a questionable condition. NEVER loosen
a connection or attempt to remove any part of a regulator until the gas pressure has been relieved. Under
pressure, gas can dangerously propel a loose part.
3. DO NOT remove the regulator from a cylinder without first closing the cylinder valve and releasing gas in the
regulator high and low pressure chambers.
4. DO NOT use the regulator as a control valve. When downstream equipment is not in use for extended periods
of time, shut off the gas at the cylinder valve and release the gas from the equipment.
5. OPEN the cylinder valve SLOWLY. Close after use.
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-25

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
User Responsibilities
This equipment will perform safely and reliable only when installed, operated and maintained, and repaired in accordance
with the instructions provided. Equipment must be checked periodically and repaired, replaced, or reset as necessary
for continued safe and reliable performance. Defective equipment should not be used. Parts that are broken, missing,
obviously worn, distorted, or contaminated should be replaced immediately.
The user of this equipment will generally have the sole responsibility for any malfunction, which results from improper
use, faulty maintenance, or by repair by anyone other than an accredited repairer.
CAUTION
Match regulator to cylinder. NEVER CONNECT a regulator designed for a particular gas or gases to a cylinder containing any other gas.
INLET
CONNECTION
OUTLET
CONNECTION
FLOW GAUGE (DELIVERY)
PRESSURE
ADJUSTING
SCREW
HIGH PRESSURE
GAUGE (SUPPLY)
Art # A-12126
Figure 3-21
Installation
1. Remove cylinder valve plastic dust seal. Clean the cylinder valve outlet of impurities that may clog orifices and
damage seats before connecting the regulator.
Crack the valve (open then close) momentarily, pointing the outlet away from people and sources of ignition.
Wipe with a clean lint free cloth.
2. Match regulator to cylinder. Before connecting, check that the regulator label and cylinder marking agree and
that the regulator inlet and cylinder outlet match. NEVER CONNECT a regulator designed for a particular gas
or gases to a cylinder containing any other gas.
3. Connect the regulator inlet connection to cylinder or pipeline and tighten it firmly but not excessively, with a
suitable spanner.
4. Connect and tighten the outlet hose firmly and attach down-stream equipment.
5. To protect sensitive down-stream equipment a separate safety device may be necessary if the regulator is not
fitted with a pressure relief device.
3-26
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Operation
With the regulator connected to cylinder or pipeline, and the adjustment screw/knob fully disengaged, pressurize as
follows:
1. Stand to one side of regulator and slowly open the cylinder valve. If opened quickly, a sudden pressure surge
may damage internal regulator parts.
2. With valves on downstream equipment closed, adjust regulator to approximate working pressure. It is recommended that testing for leaks at the regulator connection points be carried out using a suitable leak detection
solution or soapy water.
3. Purge air or other unwanted welding grade shielding gas from equipment connected to the regulator by individually opening then closing the equipment control valves. Complete purging may take up to ten seconds or
more, depending upon the length and size of the hose being purged.
Adjusting Flow Rate
Figure 3-22 Adjust Flow Rate
With the regulator ready for operation, adjust working flow rate as follows:
1. Slowly turn adjusting screw/knob in (clockwise) direction until the outlet gauge indicates the required flow
rate.
NOTE
It may be necessary to re-check the shielding gas regulator flow rate following the first weld sequence due
to back pressure present within shielding gas hose assembly.
2. To reduce flow rate, allow the welding grade shielding gas to discharge from regulator by opening the downstream valve. Bleed welding grade shielding gas into a well ventilated area and away from any ignition source.
Turn adjusting screw counterclockwise, until the required flow rate is indicated on the gauge. Close downstream
valve.
Shutdown
Close cylinder valve whenever the regulator is not in use. To shut down for extended periods (more than 30 minutes).
1. Close cylinder or upstream valve tightly.
2. Open downstream equipment valves to drain the lines. Bleed gas into a well ventilated area and away from any
ignition source.
3. After gas is drained completely, disengage adjusting screw and close downstream equipment valves.
4. Before transporting cylinders that are not secured on a cart designed for such purposes, remove regulators.
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-27

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
GROOVE “B”GROOVE “A”
3.20 Wire Feeder Set Up MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gas Shielded MIG Wire
Power Source Connections
A. Remove all packaging materials. Do not block the air vents at the front or rear of the Power Source.
B. Connect the work lead to the negative welding terminal (-) [positive welding terminal(+) for flux cored electrode
wire]. If in doubt, consult the electrode wire manufacturer. Welding current flows from the Power Source via dinse
terminals. It is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical
connection.
CAUTION
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the male plug being fused in the
terminal.
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work piece make sure the mains power supply is switched off.
Secure the welding grade shielding gas cylinder in an upright position by chaining it to a suitable stationary
support to prevent falling or tipping.
C. Position a gas cylinder on the rear tray of the Power Source and lock securely to the Power Source cylinder bracket
with the chain provided. If this arrangement is not used or the Power Source is not fitted with a gas cylinder tray
then ensure that the gas cylinder is secured to a building pillar, wall bracket or otherwise securely fixed in an upright
position.
D. Select MIG mode with the process selection control button.
WIREFEEDER CONNECTIONS
A. Connect the welding power cable from the Wirefeeder's interconnection cables to the positive welding terminal (+)
[negative welding terminal (-) for flux cored electrode wire]. If in doubt, consult the electrode wire manufacturer.
Welding current flows from the Power Source via dinse terminals. It is essential, however, that the male plug is
inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
B. Connect the control cable from the Wirefeeder to the 19 PIN socket on the Power Source as applicable.
C. Fit the gas regulator and flowmeter to the gas cylinder then connect the gas hose from the rear of the Wirefeeder
to the flowmeter outlet.
D. Dual groove feed rollers are supplied as standard. Select the roller required with the chosen wire size marking
facing outwards.
Art # A-08739
GROOVE “B” SIZE
GROOVE “A” SIZE
E. Fit the electrode wire spool to the wire reel hub. Ensure that the wire reel hub alignment pin engages the mating
hole in the wire spool. Push the retaining clip into place to retain the wire spool securely. The electrode wire should
feed from the bottom of the spool.
F MIG Torch Connection (Please refer to Section 3.10)
G Lift up the wire feeder pressure levers and pass the electrode wire through the inlet guide, between the rollers,
through the centre guide, between the rollers, through the outlet guide and into the MIG gun.
3-28
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
!
!
WARNING
DO NOT WEAR GLOVES WHILE THREADING THE WIRE OR CHANGING THE WIRE SPOOL.
H. Lower the pressure levers and with the gun lead reasonably straight, feed the electrode wire through the gun. Fit
theappropriatecontacttip,ega.035"tipfor.035"wire.
I Press the INCH button to feed the wire through the gun.
WARNING
If the Gun Trigger is used to feed wire through the gun, the electrode wire will be at welding voltage potential
while it is being fed through the wirefeeder system.
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work piece make sure the mains power supply is switched off.
Connection to Powermaster 350i, 550i
Positive Welding
Terminal (+)
Work Lead
VAF4 Wirefeeder
Mig Torch
Figure 3-23 Setup for Wirefeeder with MIG (GMAW) Welding
Negative Welding Terminal (-)
19 Pin Control Socket
Art # A-12483
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-29

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
GROOVE “B”GROOVE “A”
!
3.21 Wire Feeder Set Up MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gasless MIG Wire
Power Source Connections
A. Remove all packaging materials. Do not block the air vents at the front or rear of the Power Source.
B. Connect the work lead to the positive welding terminal(+). If in doubt, consult the electrode wire manufacturer.
Welding current flows from the Power Source via dinse terminals. It is essential, however, that the male plug is
inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
CAUTION
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the male plug being fused in the
terminal.
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work piece make sure the mains power supply is switched off.
Secure the welding grade shielding gas cylinder in an upright position by chaining it to a suitable stationary
support to prevent falling or tipping.
C. Select MIG mode with the process selection control button.
WIREFEEDER CONNECTIONS
A. Connect the welding power cable from the Wirefeeder's interconnection cables to the negative welding terminal
(-). If in doubt, consult the electrode wire manufacturer. Welding current flows from the Power Source via dinse
terminals. It is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical
connection.
B. Connect the control cable from the Wirefeeder to the 19 PIN socket on the Power Source as applicable.
C. Dual groove feed rollers are supplied as standard. Select the roller required with the chosen wire size marking
facing outwards.
Art # A-08739
GROOVE “B” SIZE
D. Fit the electrode wire spool to the wire reel hub. Ensure that the wire reel hub alignment pin engages the mating
hole in the wire spool. Push the retaining clip into place to retain the wire spool securely. The electrode wire should
feed from the bottom of the spool.
E MIG Torch Connection (Please refer to Section 3.10)
F Lift up the wire feeder pressure levers and pass the electrode wire through the inlet guide, between the rollers,
through the centre guide, between the rollers, through the outlet guide and into the MIG gun.
GROOVE “A” SIZE
WARNING
DO NOT WEAR GLOVES WHILE THREADING THE WIRE OR CHANGING THE WIRE SPOOL.
G. Lower the pressure levers and with the gun lead reasonably straight, feed the electrode wire through the gun. Fit
theappropriatecontacttip,ega.035"tipfor.035"wire.
H Press the INCH button to feed the wire through the gun.
3-30
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
!
WARNING
If the Gun Trigger is used to feed wire through the gun, the electrode wire will be at welding voltage potential
while it is being fed through the wirefeeder system.
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work piece make sure the mains power supply is switched off.
Connection to Powermaster 350i, 550i
Positive Welding
Terminal (+)
Work Lead
Negative Welding Terminal (-)
19 Pin Control Socket
Art # A-12484
VAF4 Wirefeeder
Mig Torch
Figure 3-24 Setup for Wirefeeder with MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gasless MIG Wire
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-31

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
Art # A-11268_AB
3.22 Prewelding Procedure
Follow all installation instructions for the wire feeder, the welding power source, and the welding gun before attempting to operate the Ultrafeed VAF-4.
1. Make sure all necessary connections have been made (Refer to Section 3.01 of this manual).
2. Turn ON the power source and the wire feeder.
3. All the displays and discrete LED's start self-examination and all the lights on the panel are on for 1 second.
LeftdisplayshowsrmwareinformationofdisplayPCB"DFX.X"andrightdisplayshowshardwareinformation
ofdisplayPCB"DHX.X".1.5secondslaterleftdisplayshowsrmwareinformationofmotorcontrolPCB"PF
X.X"andhardwareinformationofmotorcontrolPCB"PHX.X".
4. Push the PURGE switch of the feeder and adjust the flow of shield gas.
5. Push the INCH switch of the feeder and adjust the WFS to the desired value by means of WFS control.
WARNING
If the gun switch is depressed, the electrode (welding wire) is electrically “hot”. Do not permit it to touch any
metal or a welding arc may be established which may be injurious to someone’s eyes (flash) or skin (burn).
6. Adjust the voltage of the power source to the desired value. The gun switch must be triggered to close power
source contactor.
WARNING
In wire welding, the welding wire, wire reel (if used), input guide, feed rolls, output guide, feedhead, and
welding gun metal parts are all ELECTRICALLY “HOT”.
3.23 Arc Signal Override (SIL_1 #2)
WARNING
There are dangerous voltage and power levels inside this product. Turn OFF wirefeeder and disconnect
from the power source before removing cover from wirefeeder.
This switch on the motor control PCB configures the wire feeder for the presence of Arc Established signals from a
power source. If the power source has an Arc Established, then this switch should be OFF. If the power source does
not have these ‘Arc Signals’, then this switch should be ON. This switch allows the 2T / 4T and timer features to work,
although they will not be timed from the true start of the arc, but instead from when the gun trigger is pulled.
ArcMaster 401MST, Powermaster 350i and 550i, and Transmig 500i have the arc established signal and current feedback
signal and SIL_1#2 should be set to OFF. Note that the DIP switch SIL1-#2 is factory default set to OFF.
SIL_1 Switch
3-32
Figure 3-25 SIL_1 Switch on Motor Control PCB
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329
Motor Control PCB

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
3.24 Welding- 2T Operation
Position the welding gun above the workpiece and depress the gun switch trigger. Depressing the gun switch trigger
enables the gas valve. When preflow ends, wire feed motor and power source are enabled; the welding process begins.
To end the weld, release the gun switch trigger which disables the gas valve, wire feed motor, and power source.
Gun Trigger
Arc Established
Gas
Contactor
Wire feed
3.25 Spot Operation
Preflow
Run In %
Ramp
Figure 3-26 Welding- 2T Operation
Art# A-11262
Burnback
Postflow
Position the welding gun above the workpiece and depress the gun switch trigger. Depressing the gun switch trigger
enables the gas valve. When preflow ends, wire feed motor and power source are enabled; the welding process begins.
When spot time is over, welding process ends and release the gun switch trigger.
Gun Trigger
Arc Established
Gas
Contactor
Wire feed
Spot Time
Art# A-11258_AB
Preflow
Run In %
Ramp
Burnback
Postflow
Figure 3-27 Spot Operation
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-33

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
3.26 Welding- 4T Operation
Welding- 4T Operation (Crater=ON)
Position the welding gun above the workpiece, depress the gun switch trigger, it enables power source and gas valve,
and the wire will begin feeding. Welding arc is established. Release the gun switch trigger and the welding process
continues. To end the weld, depress the gun switch trigger again and the welding voltage and welding current turn to
preset crater voltage and crater current. Release the gun switch trigger and the welding process ends.
NOTE
In 4T welding (Crater=ON), the user can independently control the amount of crater-filler time by adjusting
the amount of time the gun switch is depressed.
Gun Trigger
Arc Established
Gas
Contactor
Art # A-11259
Voltage
Wire feed
Preflow
Crater WFS %
Run In %
Ramp
Burnback
Postflow
Crater Volts %
Figure 3-28 Welding- 4T Operation (Crater=ON)
Welding- 4T Operation (Crater=OFF)
Position the welding gun above the workpiece, depress the gun switch trigger, it enables power source and gas valve,
and the wire will begin feeding. Welding arc is established. Release the gun switch trigger and the welding process
continues. To end the weld, depress the gun switch trigger again.
Art # A-11263_AB
Gun Trigger
Arc Established
Gas
Contactor
Wire feed
Preflow
Figure 3-29 Welding- 4T Operation (Crater=OFF)
3-34
Run In %
Ramp
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Postflow
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
3.27 Stitch Operation
After selecting stitch operation in advanced features menu, select 2T Stitch or 4T Stitch by pressing 2T/ 4T button
on front panel.
2T Stitch Operation
Position the welding gun above the workpiece and depress the gun switch trigger. Depressing the gun switch trigger
enables the gas valve. When preflow ends, wire feed motor and power source are enabled the welding process begins.
When Stitch Time is over, arc extinguishes and it will stop feeding. When Dwell Time is over, the welding gun will
starting welding again. This process repeats until releasing the gun switch trigger.
Gun Trigger
Dwell time
Arc Established
Gas
Contactor
Art # A-11272_AB
Run In %
StitchTime
Ramp
Postflow
Burnback
Burnback
Wire feed
Preflow
Figure 3-30 Welding- 2T Stitch Operation
4T Stitch Operation (Crater=ON)
Position the welding gun above the workpiece and depress the gun switch trigger. Depressing the gun switch trigger
enables the gas valve. When preflow ends, wire feed motor and power source are enabled the welding process begins.
Release the gun switch trigger and the welding process continues. To end the welding, depress the gun switch trigger
again and welding current and welding voltage will turn to preset crater voltage and crater current. Release the gun
switch trigger and the welding process ends.
Gun Trigger
Dwell time
Arc Established
Gas
Contactor
Voltage
StitchTime
Wire feed
Art # A-11273_AB
Crater Volts %
Preflow
Run In %
Ramp
Burnback
Burnback
Crater WFS %
Burnback
Postflow
Figure 3-31 Welding- 4T Stitch Operation (Crater=ON)
4T Stitch Operation (Crater=OFF)
Position the welding gun above the workpiece and depress the gun switch trigger. Depressing the gun switch trigger enables the gas valve. When preflow ends, wire feed motor and power source are enabled the welding process
begins. When Stitch Time is over, arc extinguishes and it will stop feeding. When Dwell Time is over, the welding gun
will starting welding again.
Manual 0-5329
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-35

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
3.28 PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) Protection of Power Source Contactor
Control Output
The Power Source Contactor control circuit on the Ultrafeed VAF-4 provides a relay closure to the power source through
pins A and B of the 19 pin control cable. This allows the welding wire to become electrically ‘HOT’ when the gun switch
trigger on the welding gun is pulled. If this relay closure is NOT provided for any reason, the welding wire WILL NOT
be electrically ‘HOT’. The wire will feed, but there will be NO arc when the wire touches the work.
The Ultrafeed VAF-4 has a thermal, self reset protection device in the A-B contactor circuit to protect the circuitry
against a fault or overload condition. This protection device will only allow a maximum steady state current in the
range of 180 to 450 milliamps (dependent on ambient temperature) to flow through pins A and B of the 19 pin control
cable to the A-B contactor circuit on the Ultrafeed VAF-4.
If this acceptable current range is exceeded for any reason, the self-reset protection circuit located on the motor
control PCB will be activated effectively disabling the A-B contactor circuit. Once the fault or overload condition has
been corrected and the current has returned to an acceptable level, the protection device will automatically reset and
normal operation can resume.
NOTE
The protection circuit will remain activated (there will be NO arc when the wire touches the work) as long
as the acceptable current range is exceeded.
3.29 Ground Fault Operation
The Ultrafeed VAF-4 has been equipped with a ground fault protection circuit. This protection circuit is activated whenever excessive current flow in the protective earth ground is detected. If the ground fault protection circuit is activated,
the yellow FAULT indicator on the front of the feeder will flash at a rate of approximately 0.5 second on, 0.5 second off.
When a ground fault occurs, the feeder will immediately shut down the feeder, gas valve, and power source contactor.
Once the ground fault protection circuit has been set, the wire feeder will not respond to a gun switch closure until
the power is reset by turning the feeder off and back on.
NOTE
Before resetting power to the wire feeder after a ground fault occurrence, determine what caused the ground
fault and correct the problem before attempting to weld again.
3.30 Electronic Motor Protection
The Ultrafeed VAF-4 utilizes an electronic protection circuit to protect the motor against overcurrent caused by excessive load on the motor. This protection will normally trip if the motor stays in current limit for about 10 seconds and
during this 10 second period the fault light will flash at a rate of approximately 0.3 second on, 0.3 second off. Once
this 10 second timing period completes, the protection circuit will trip which will cause the FAULT indicator LED to
light continuously, error code ERR 03 or ERR 04 (refer to Section 4.05 Error Code and Remedies) will be displayed
and the wirefeeder will shutdown. In order to reset this condition, the power to the wirefeeder must be turned OFF
then ON to reset and clear Error Code from display.
NOTE
Should this condition occur, check the wire feeding path, and make sure that there is not any restrictions
or binding on the wire, and that the feedrolls aren’t locked by some obstruction.
3-36
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
SECTION 4: SERVICE
4.01 Cleaning The Unit
Periodically, clean the inside of the wire feeder and
feedhead assembly by using a vacuum cleaner or clean,
dry compressed air of not more than 25 psi (172 kPa)
pressure. After cleaning the unit, check all electrical
components for loose or faulty connections and correct
if necessary.
4.02 Cleaning The Feed Rolls
Clean the grooves on the lower feed roll frequently. This
cleaning operation can be done by using a small wire
brush. Also, wipe off or clean the grooves on the upper
bearing roll. After cleaning the feed rolls, tighten the feed
roll retaining knobs accordingly.
4.03 System Maintenance
The user has been given a visual tool in the feed monitor
display. Use the feed monitor display in determining when
a new contact tip, liner, and/or wire guide is needed.
4.04 Troubleshooting Guide
NOTE
Refer to the Connection Diagram in the Appendix chapter of this manual for graphical assistance in disassembling and troubleshooting
the wire feeder.
Scope
The troubleshooting guide is intended to be used by
qualified service technicians. The troubleshooting guide
contains information which can be used to diagnose and
correct unsatisfactory operation or failure of the various
components of the wire feeder. Each symptom of trouble
is followed by a list of probable causes and the procedure
necessary to correct the problem.
Safety
To ensure safe operation and service, read this entire
manual before attempting to service or repair this machine. The service technician may be asked to check
voltage levels while the machine is turned ON. To assure
safety, use care and follow all instructions accordingly.
Manual 0-5329 SERVICE 4-1

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
4.05 Error Codes and Remedies
Error Code
Left
Display
ERR 01-- This protection
ERR 02-- Control cable
ERR 03-- Emergency
Right
Display
Description Cause Remedy
circuit is activated
whenever weld
current flows in
the ground fault
protective circuit.
Fault light flashes
at a rate of
approximately 0.5
second ON, 0.5
second OFF.
connecting
Wirefeeder and
Power Source not
correctly connected.
shutdown
Weld current is detected
running through the ground
fault protective circuit.
1. 19 pin plug control plug
connection is loose at either
socket on Wirefeeder or
Power Source.
2. Control cable is damaged
or has faulty connection/s.
3. Ensure that the 19 Pin
socket is selected on the
Power Source.
Motor current exceeds
10amps due to seized motor
or clogged liner or filler metal
wire too big for MIG torch
liner or spool hub tension too
tight, etc.
1. Look for metallic dust
build up between the wirefeed
plate assembly/motor and the
Wirefeeder frame and remove the
metallic dust build up. Turn OFF
Wirefeeder then ON again to clear
ERR 01.
2. If ERR 01 appears again with
the next weld or metallic dust
build up cannot be located then
contact your Accredited TWECO
Service Provider to investigate
the fault.
1. Check control cable
connections at the Wirefeeder
and Power Source are tight.
2. If the Control Cable is
damaged then repair or replace
cable.
3. Check the Power Source is set
to 19 Pin socket mode.
Turn OFF Wirefeeder then check
motor / feed mechanism can
rotate or replace liner or install
correct size liner for filler metal
or adjust spool hub tension.
Turn ON Wirefeeder and if
ERR 03 appears again with the
next weld then contact your
Accredited TWECO Service
Provider to investigate the fault.
ERR 04-- Protective shutdown Motor current exceeds
5amps for 10 seconds due to
clogged liner or filler metal
wire too big for MIG torch
liner or spool hub tension too
tight, etc.
4-2 SERVICE Manual 0-5329
Turn OFF Wirefeeder then check
motor / feed mechanism can
rotate or replace liner or install
correct size liner for filler metal
or adjust spool hub tension.
Turn ON Wirefeeder and if
ERR 04 appears again with the
next weld then contact your
Accredited TWECO Service
Provider to investigate the fault.

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Error Code
Left
Display
ERR 05-- Feedback signal of
ERR 06-- Output current of
ERR 07-- Power Source
ERR 08-- Main control PCB
ERR 20-- Display PCB settings
Right
Display
Description Cause Remedy
motor lost
Wirefeeder exceeds
allowed maximum
value limit
Arc Established
signal has not
been received
within 20 seconds
of commencing
welding
settings save or read
error
save or read error
Table 4-1 Error Codes and Remedies
Tachometer feedback wiring
between Wirefeeder motor
and motor control PCB not
connected or motor is stalled.
1. Current running through
Wirefeeder exceeds 650A for
4 minutes.
2. Welding current signal
from Power Source is too
high with respect the actual
weld current.
Power Source does not
provide an Arc Establish
signal.
Motor Control PCB Memory
IC read/write cycle limit has
been exceeded.
Display PCB Memory IC read/
write cycle limit has been
exceeded.
Disconnect Wirefeeder from
Power Source. Check wiring
between Wirefeeder motor
Tachometer and motor control
PCB is correctly connected.
Reconnect Wirefeeder to Power
Source and if ERR 05 appears
again with the next weld then
contact your Accredited TWECO
Service Provider to investigate
the fault.
1. Turn OFF Wirefeeder and
allow it to cool for 10 minutes
then reduce voltage / wirespeed
setting to reduce welding current
below 650A@40%.
2. Contact your Accredited
TWECO Service Provider to
investigate the fault.
Override the Arc Established
signal, refer to Section 3.23 or
retrigger the wirefeeder.
1. Turn Wirefeeder OFF then ON
and check to see if settings can
then be saved.
2. Contact your Accredited
TWECO Service Provider to
investigate the fault.
1. Turn Wirefeeder OFF then ON
and check to see if settings can
then be saved.
2. Contact your Accredited
TWECO Service Provider to
investigate the fault.
NOTE
Once cause of error has been corrected then the power to the Wirefeeder must be turned OFF then ON to
reset and clear Error Code from the display.
Please follow Section 4.08 for more information regarding troubleshooting.
Manual 0-5329 SERVICE 4-3

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Shielding Gas
4.06 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Basic Welding Technique
Two different welding processes are covered in this section (GMAW and FCAW), with the intention of providing the
very basic concepts in using the Mig mode of welding, where a MIG Torch is hand held, and the electrode (welding
wire) is fed into a weld puddle, and the arc is shielded by an inert welding grade shielding gas or inert welding grade
shielding gas mixture.
GAS METAL ARC WELDING (GMAW): This process, also
known as MIG welding, CO2 welding, Micro Wire Welding,
short arc welding, dip transfer welding, wire welding etc.,
is an electric arc welding process which fuses together the
parts to be welded by heating them with an arc between
a solid continuous, consumable electrode and the work.
Shielding is obtained from an externally supplied welding
grade shielding gas or welding grade shielding gas mixture. The process is normally applied semi automatically;
however the process may be operated automatically and
can be machine operated. The process can be used to
weld thin and fairly thick steels, and some non-ferrous
metals in all positions.
Shielding Gas
Molten Weld Metal
Solidified
Weld Metal
GMAW Process
Nozzle
Electrode
Arc
Base Metal
Art # A-8991_AB
Position of MIG Torch
The angle of MIG Torch to the weld has an effect on the
width of the weld.
Push
Vertical
Drag/Pull
Art # A-07185_AB
Figure 4-3 Position of MIG Torch
The MIG Torch should be held at an angle to the weld joint.
(See Secondary Adjustment Variables below)
Hold the MIG Torch so that the welding seam is viewed
at all times. Always wear the welding helmet with proper
filter lenses and use the proper safety equipment.
Figure 4-1 GMAW Process
FLUX CORED ARC WELDING (FCAW): This is an electric
arc welding process which fuses together the parts to be
welded by heating them with an arc between a continuous flux filled electrode wire and the work. Shielding is
obtained through decomposition of the flux within the
tubular wire. Additional shielding may or may not be obtained from an externally supplied gas or gas mixture. The
process is normally applied semi automatically; however
the process may be applied automatically or by machine. It
is commonly used to weld large diameter electrodes in the
flat and horizontal position and small electrode diameters
in all positions. The process is used to a lesser degree for
welding stainless steel and for overlay work.
Nozzle
(Optional)
Flux Cored
Electrode
Arc
Base Metal
Slag
(Optional)
Molten Metal
Molten
Slag
Solidified
Weld Metal
CAUTION
Do NOT pull the MIG Torch back when the
arc is established. This will create excessive
wire extension (stick-out) and make a very
poor weld.
The electrode wire is not energized until the MIG Torch
trigger switch is depressed. The wire may therefore be
placed on the seam or joint prior to lowering the helmet.
5° to 15°
Longitudinal
Angle
90°
Transverse
Angle
Direction of
Travel
Art # A-08993
Butt & Horizontal Welds
Figure 4-4 Butt & Horizontal Welds
FCAW Process
Art # A-08992_AB
Figure 4-2 FCAW Process
4-4 SERVICE Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
10° to 20° Longitudinal
Direction of Travel
Electrode Stick-Out
Preselected Variables
5° to 15°
Longitudinal Angle
Direction of
Travel
30° to 60°
Transverse Angle
Art # A-08994
Preselected variables depend upon the type of material
being welded, the thickness of the material, the welding
position, the deposition rate and the mechanical properties. These variables are:
• Typeofelectrodewire
Horizontal Fillet Weld
Figure 4-5 Horizontal Fillet Weld
10°
Longitudinal Angle
30° to 60°
Transverse
Angle
Direction of Travel
Vertical Fillet Welds
Angle
30° to 60°
Transverse
Angle
Art # A-08995
Figure 4-6 Vertical Fillet Weld
30° to 60°
Transverse Angle
5° to 15°
Longitudinal
Angle
Art # A-08996
Overhead Weld
Figure 4-7 Overhead Weld
Distance from the MIG Torch Nozzle to the Work Piece
The electrode wire stick out from the MIG Torch nozzle
shouldbebetween3/8"(10mm)and3/4"(20mm).This
distance may vary depending on the type of joint that is
being welded.
Travel Speed
The speed at which the molten pool travels influences
the width of the weld and penetration of the welding run.
• Sizeofelectrodewire
• Typeofgas((notapplicableforFCAWselfshielding
wires)
• Gasowrate(notapplicableforFCAWselfshielding
wires)
Primary Adjustable Variables
These control the process after preselected variables have
been found. They control the penetration, bead width, bead
height, arc stability, deposition rate and weld soundness.
They are:
• ArcVoltage
• Weldingcurrent(wirefeedspeed)
• Travelspeed
Secondary Adjustable Variables
These variables cause changes in primary adjustable
variables which in turn cause the desired change in the
bead formation. They are:
1. Stick-out (distance between the end of the contact tube (tip) and the end of the electrode wire).
Maintainatabout3/8"(10mm)stick-out
2. Wire Feed Speed. Increase in wire feed speed
increases weld current, Decrease in wire feed
speed decreases weld current.
Gas Nozzle
Tip to
Work Distance
Average Arc Length
Contact Tip (Tube)
Electrode Wire
Actual Stick-out
Art # A-08997_AD
Figure 4-8 Electrode Stick-out
MIG Welding (GMAW) Variables
Most of the welding done by all processes is on carbon
steel. The items below describe the welding variables in
short-arc welding of 0.024” (0.6mm) to ¼” (6.4mm) mild
sheet or plate. The applied techniques and end results
in the GMAW process are controlled by these variables.
Manual 0-5329 SERVICE 4-5
3. Nozzle Angle. This refers to the position of the MIG
Torch in relation to the joint. The transverse angle
is usually one half the included angle between
plates forming the joint. The longitudinal angle
is the angle between the centre line of the MIG
Torch and a line perpendicular to the axis of the
weld. The longitudinal angle is generally called the

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Transverse
Direction of Gun Travel
Nozzle Angle and can be either trailing (pulling)
or leading (pushing). Whether the operator is left
handed or right handed has to be considered to
realize the effects of each angle in relation to the
direction of travel.
Angle
Longitudinal
Angle
Axis of Weld
Transverse and Longitudinal
Nozzle Axes
Figure 4-9 Transverse and Longitudinal Nozzle Axes
Art # A-08998_AB
Setting of the Power Source
Power source and Wirefeeder setting requires some practice by the operator, as the welding plant has two control
settings that have to balance. These are the Wirespeed
control and the welding Voltage Control. The welding
current is determined by the Wirespeed control, the current will increase with increased Wirespeed, resulting
in a shorter arc. Less wire speed will reduce the current
and lengthen the arc. Increasing the welding voltage
hardly alters the current level, but lengthens the arc. By
decreasing the voltage, a shorter arc is obtained with a
little change in current level.
When changing to a different electrode wire diameter, different control settings are required. A thinner electrode
wire needs more Wirespeed to achieve the same current
level.
A satisfactory weld cannot be obtained if the Wirespeed
and Voltage settings are not adjusted to suit the electrode
wire diameter and the dimensions of the work piece.
Leading or “Pushing”
Angle
(Forward Pointing)
Nozzle Angle, Right Handed Operator
90°
Trailing or “Pulling”
Angle
(Backward Pointing)
Art # A-08999_AC
Figure 4-10 Nozzle Angle, Right Handed Operator
Establishing the Arc and Making Weld Beads
Before attempting to weld on a finished piece of work, it
is recommended that practice welds be made on a sample
metal of the same material as that of the finished piece.
The easiest welding procedure for the beginner to experiment with MIG welding is the flat position. The equipment
is capable of flat, vertical and overhead positions.
For practicing MIG welding, secure some pieces 0.06”
(1.5mm) or 0.08” (2.0mm) mild steel plate 6” x 6” (150
x 150mm). Use 0.030” (0.8mm) flux cored gasless wire
or a solid wire with shielding gas.
If the Wirespeed is too high for the welding voltage,
“stubbing” will occur as the wire dips into the molten pool
and does not melt. Welding in these conditions normally
produces a poor weld due to lack of fusion. If, however,
the welding voltage is too high, large drops will form on
the end of the wire, causing spatter. The correct setting
of voltage and Wirespeed can be seen in the shape of the
weld deposit and heard by a smooth regular arc sound.
Refer to the Weld Guide located on the inside of the wirefeed compartment door for setup information.
Electrode Wire Size Selection
The choice of Electrode wire size and shielding gas used
depends on the following
• Thicknessofthemetaltobewelded
• Typeofjoint
• CapacityofthewirefeedunitandPowerSource
• Theamountofpenetrationrequired
• Thedepositionraterequired
• Thebeadproledesired
• Thepositionofwelding
• Costofthewire
4-6 SERVICE Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
4.07 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Welding Troubleshooting
Solving Problems Beyond the Welding Terminals
The general approach to fix Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) problems is to start at the wire spool then work through
to the MIG Torch. There are two main areas where problems occur with GMAW; Porosity and Inconsistent wire feed.
Problem 1 - Porosity
When there is a gas problem the result is usually porosity within the weld metal. Porosity always stems from some
contaminant within the molten weld pool which is in the process of escaping during solidification of the molten metal.
Contaminants range from no gas around the welding arc to dirt on the work piece surface. Porosity can be reduced by
checking the following points.
FAULT CAUSE
Shielding gas cylinder contents and flow
1
meter.
Gas leaks. Check for gas leaks between the regulator/cylinder connection and in the gas
2
Internal gas hose in the Power Source. Ensure the hose from the solenoid valve to the MIG Torch adaptor has not
3
Welding in a windy environment. Shield the weld area from the wind or increase the gas flow.
4
Welding dirty, oily, painted, oxidized or
5
greasy plate.
Distance between the MIG Torch nozzle
6
and the work piece.
Maintain the MIG Torch in good working
7
order.
Ensure that the shielding gas cylinder is not empty and the flow meter is
correctly adjusted to 15 litres per minute.
hose to the Power Source.
fractured and that it is connected to the MIG Torch adaptor.
Clean contaminates off the work piece.
Keep the distance between the MIG Torch nozzle and the work piece to a
minimum.
Ensure that the gas holes are not blocked and gas is exiting out of the torch
A
nozzle.
Do NOT restrict gas flow by allowing spatter to build up inside the MIG Torch
B
nozzle.
Check that the MIG Torch O-rings are not damaged.
C
Table 4-2 MIG (GMAW / FCAW) Welding Troubleshooting
Manual 0-5329 SERVICE 4-7

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
!
Problem 2 - Inconsistent Wire Feed
WARNING
Disengage the feed roll when testing for gas flow by ear.
Wire feeding problems can be reduced by checking the following points.
FAULT CAUSE
Feed roller driven by motor in the cabinet
1
slipped.
Wire spool unwound and tangled. Wire spool brake is too loose.
2
Wire spool brake is too tight.
Worn or incorrect feed roller size
3
Wire rubbed against the misaligned guides and
4
reduced wire feed ability.
Liner blocked with swarf
5
Incorrect or worn contact tip
6
Poor work lead contact to work piece If the work lead has a poor electrical contact to the work piece then
7
Bent liner This will cause friction between the wire and the liner thus reducing
8
Use a feed roller matched to the size you are welding.
A
Replace feed roller if worn.
B
Misalignment of inlet/outlet guides
Increased amounts of swarf are produced by the wire passing
A
through the feed roller when excessive pressure is applied to the
pressure roller adjuster.
Swarf can also be produced by the wire passing through an
B
incorrect feed roller groove shape or size.
Swarf is fed into the conduit liner where it accumulates thus
C
reducing wire feed ability.
The contact tip transfers the weld current to the electrode wire. If
A
the hole in the contact tip is too large then arcing may occur inside
the contact tip resulting in the wire jamming in the contact tip
When using soft wire such as aluminium it may become jammed in
B
the contact tip due to expansion of the wire when heated. A contact
tip designed for soft wires should be used.
the connection point will heat up and result in a reduction of power
at the arc.
wire feed ability
Table 4-3 Wire Feeding Problems
4-8 SERVICE Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
Basic MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Welding Troubleshooting
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
1
Undercut
Welding arc voltage too high.
A
Incorrect MIG Torch angle
B
Excessive heat input
C
Decrease voltage or increase the wire feed speed.
A
Adjust angle.
B
Increase the MIG Torch travel speed and/or decrease welding
C
current by decreasing the voltage or decreasing the wire feed
speed.
Lack of penetration
2
Lack of fusion Voltage too low Increase voltage.
3
Excessive spatter
4
Irregular weld shape
5
Weld cracking
6
Welding current too low
A
Joint preparation too narrow or
B
gap too tight
Shielding gas incorrect
C
Voltage too high
A
Voltage too low
B
Incorrect voltage and current
A
settings. Convex, voltage too
low. Concave, voltage too high.
Wire is wandering.
B
Incorrect shielding gas
C
Insufficient or excessive heat
D
input
Weld beads too small
A
Weld penetration narrow and
B
deep
Excessive weld stresses
C
Increase welding current by increasing wire feed speed and
A
increasing voltage.
Increase joint angle or gap.
B
Change to a gas which gives higher penetration.
C
Decrease voltage or increase the wirespeed control.
A
Increase the voltage or decrease wirespeed.
B
Adjust voltage and current by adjusting the voltage control and
A
the wirespeed control.
Replace contact tip.
B
Check shielding gas.
C
Adjust the wirespeed control or the voltage control.
D
Decrease travel speed
A
Reduce current and voltage and increase MIG Torch travel speed
B
or select a lower penetration shielding gas.
Increase weld metal strength or revise design
C
Cold weld puddle
7
Arc does not have a crisp
8
sound that short arc
exhibits when the wirefeed
speed and voltage are
adjusted correctly.
Excessive voltage
D
Cooling rate too fast
E
Loose welding cable connection.ACheck all welding cable connections.
A
Low primary voltage
B
Fault in power source
C
The MIG Torch has been
connected to the wrong voltage
polarity on the front panel.
Decrease voltage.
D
Slow the cooling rate by preheating part to be welded or cool
E
slowly.
Contact supply authority.
B
Have an Accredited TWECO Service Provider test then replace the
C
Connect the MIG torch to the positive (+) welding terminal
for solid wires and gas shielded flux cored wires. Refer to the
electrode wire manufacturer for the correct polarity.
Table 4-4 GMAW (MIG) Welding Problems
Manual 0-5329 SERVICE 4-9

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
4.08 Troubleshooting
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
Follow all safety precautions.
Do not touch live electrical parts.
Turn OFF input power before servicing the machine unless otherwise noted.
Only qualified technicians are to service the machine.
WARNINGS
PC boards and their components are static sensitive devices.
Use static proof bags.
Use grounded wrist strap.
Only qualified personnel should test or handle these devices.
Use only genuine replacement parts.
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
1 Power On Indicator
light is not lit and
welding arc cannot be
established.
2 Error Code is
displayed and yellow
fault indicator is lit
when Wirefeeder is
turned ON.
3 Power Indicator light
is not lit but welding
arc can be established.
A
Switch on rear panel of Wirefeeder
is not turned ON.
B
Power Source is not turned ON.
19 Pin control cable is not
C
connected between the power
source and Wirefeeder.
D
Circuit Breaker/s on rear panel
is tripped (pops out). Refer to
Section 3.07 for further detail.
Faulty 19 Pin control cable
E
connecting power source and
Wirefeeder.
Error condition present. Refer to Error Codes and Remedies
Faulty Indicator light on display
PCB.
A
Turn switch on rear panel of
Wirefeeder to ON.
B
Turn power source ON and ensure it
is in the correct mode of operation.
C
Connect 19 Pin control cable
between the power source and
Wirefeeder.
D
Reset circuit breaker by pushing
it in. If it fails to reset have an
Accredited TWECO Service Provider
investigate the fault.
Repair or replace the 19 Pin control
E
cable.
Table in Section 4.05.
Have an Accredited TWECO Service
Provider investigate the fault.
4 Power ON Indicator
light is lit but when the
torch trigger switch
is depressed nothing
happens.
4-10 SERVICE Manual 0-5329
A
Torch trigger switch leads are
disconnected.
B
Faulty trigger switch/lead.
A
Re connect Torch trigger switch
leads.
B
Repair or replace torch trigger lead.

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
5 Power indicator is
ON, no wire feed but
gas flows from the
MIG Torch when the
torch trigger switch is
depressed.
A
Preflow is operating.
B
Electrode wire stuck in conduit
liner or contact tip (burn-back
jam).
C
Faulty motor control PCB.
A
Adjust preflow time setting. Refer
to Section 3.08.
B
Check for clogged / kinked MIG
Torch conduit liner or worn contract
tip. Replace faulty components.
Have an Accredited TWECO Service
C
Provider investigate the fault.
6 Wire feeds when the
torch trigger switch
is depressed but arc
cannot be established.
7 Wirefeed motor
operates but wire does
not feed.
8 Jerky wire feed A
9 No gas flow A
10 Gas flow continues
after the torch trigger
switch has been
released.
11 Wire does not feed
when torch trigger is
depressed
12 Wire continues to feed
when torch trigger
released
A
Poor or no work lead contact.
B
Wirefeeder signal is not initiating
the power source which could
be caused by a loose 19 pin plug
connection.
C
A fault or overload condition has
occurred in pins A & B of the 19
pin interconnection lead control
cable and the P.T.C. protection has
activated.
A
Pressure on feed rolls not
correctly adjusted.
B
Incorrect feed rolls used.
C
Worn feed roll.
Worn or dirty contact tip.
B
Worn feed roll.
C
Excessive back tension from wire
reel hub.
D
Worn, kinked or dirty conduit liner.
Gas hose is cut.
B
Gas passage contains impurities.
C
Gas regulator turned off.
D
Empty Cylinder
A
Postflow is operating.
B
Gas valve has jammed open due
to impurities in the gas or the gas
line.
Faulty trigger switch / lead. Repair or replace Torch / trigger
A BWirefeeder in 4T (LATCH) mode
Torch trigger leads shorted.
A
Clean work clamp area and ensure
good electrical contact.
B
Tighten 19 pin plug connection,
repair or replace the 19 Pin control
cable.
C
Refer to Section 3.28 Protection
of Power Source Contactor
Output Control. (P.T.C.) or have an
Accredited TWECO Service Provider
investigate the fault.
A
Adjust pressure on feed rolls so
that it will be set to a minimum
pressure that will provide
satisfactory wire feed without
slippage.
B
Check that feed roll being used
matches the wire size and type
being used.
C
Replace feed roll.
A
Replace contact tip.
B
Replace feed roll.
C
Reduce brake tension on spool hub.
D
Clean or replace conduit liner.
A
Replace or repair.
B
Disconnect gas hose from the
rear of Wirefeeder then raise gas
pressure and blow out impurities.
C
Turn on Regulator and adjust to
correct pressure.
D
Replace cylinder.
A
Adjust postflow time setting. Refer
to Section 3.08.
B
Have an Accredited TWECO Service
Provider repair or replace gas valve.
lead.
A BChange to 2T (NORMAL) mode.
Repair or replace Torch / trigger
lead.
Manual 0-5329 SERVICE 4-11

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
13 There is no wire
feed the yellow Fault
indicator is lit and ERR
01 is displayed
14 Circuit breaker/s has
tripped on rear panel
Refer to Section 3.07
15 Wirefeeder is only
displaying 50 IPM
(min) and/or 14V
(min) and cannot be
adjusted when trigger
is depressed.
16 Crater does not
function when 4T
Mode is selected
and Crater is turned
ON and ERR 07 is
displayed after 20
seconds.
Earth Fault Protection circuit has
operated.
A
Short circuit on the 42 or 115VAC
rear outlets or 14 / 19 pin
receptacles.
B
Internal fault in Wirefeeder.
In Advanced Features the MIG
Control function is set to Remote
but no remote device is connected
to the 8 pin remote socket on the
Wirefeeder front panel.
Power Source has not provided an
Arc Establish signal to Wirefeeder.
A BRefer to Section 4.05 Error Codes
and Remedies ERR 01.
Have an Accredited TWECO Service
Provider investigate the fault.
A
Have an Accredited TWECO Service
Provider check and repair as
necessary.
B
Have an Accredited TWECO Service
Provider check and repair as
necessary.
Set MIG Control mode to local
OR
If a remote control device is fitted
to the 8 pin remote control socket
then the remote control device is
faulty. Have an Accredited TWECO
Service Provider check and repair
as necessary.
Override Arc Establish signal, refer
to Section 3.23.
17 Spot time exceeds
user setting when Spot
Mode is selected and
ERR 07 is displayed
up to after 20 seconds.
18 Stitch does not
function when Stitch is
turned on in 2T or 4T
Modes and ERR 07 is
displayed up to after
20 seconds.
Power Source has not provided an
Arc Establish signal to Wirefeeder.
Power Source has not provided an
Arc Establish signal to Wirefeeder.
Table 4-5 Troubleshooting
Override Arc Establish signal, refer
to Section 3.23.
Override Arc Establish signal, refer
to Section 3.23.
4-12 SERVICE Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
SECTION 5: PARTS LIST
5.01 Equipment Identification
All identification numbers as described in the Introduction Chapter must be furnished when ordering parts or making
inquiries. This information is found on the nameplate attached to the equipment. Be sure to include any dash numbers
following the Specification or Assembly numbers.
PART NUMBER
W3400002
5.02 How To Use This Parts List
The Parts List is a combination of an illustration (Figure Number) and a corresponding list of parts which contains
a breakdown of the equipment into assemblies, subassemblies, and detail parts. All user-serviceable parts are listed
except for commercially available hardware, bulk items such as wire, cable, sleeving, tubing, etc. The part descriptions
may be indented to show part relationships.
To determine the part number, description, quantity, or application of an item, locate the item in question from the
illustration and refer to that item number in the corresponding Parts List.
Manual 0-5329 PARTS LIST 5-1

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
12
5.03 Replacement Parts (without wirefeed plate)
Item # Qty Description Part Number
1 1 PCB Display,WF W7005699
2 1 PCB Motor Control,WF W7005701
3 1 Valve,Solenoid,24VDC,WF W7005702
4 1 Circuit Breaker, 8A, WF W7005706
5 1 Circuit Breaker, 4A, WF W7005705
6 1 Switch,ON/OFF, WF W7005704
7 2 Rectifier,Bridge,1000V, 35A, WF W7005703
8 1 Socket, 19 Pin, Male, Panel Mtg W7005715
2
9 1 Socket Panel, Dinse, Male, 50mm
10 1 SPOOL HUB ASSY W7005609
11 1 Wire Guide, Outlet, 0.8-1.2, WF W4017700
12 1 Adaptor, Tweco No. 4 W4017800
13 1 Handle Kit W7005717
W7005716
11
13
6
10
7
8
9
5
4
3
Art # A-12485
2
1
Figure 5-1 Replacement Parts (without wirefeed plate)
5-2 PARTS LIST Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
5.04 Replacement Parts- Wirefeed Plate
Item # Qty Description Part Number
14 1 Motor, 42V, WF W7005713
15 1 Wire Drive Assy, 4R, WF W7005707
16 1 Wire Guide, Inlet, 0.8-1.6, WF W7005710
17 1 Wire Guide, Centre, 0.8-1.6, WF W7005711
18 2 Feed Roll Refer to Section 2.09
19 2 Idler Gear, 4R W7005708
20 1 Drive Gear, 4R W7005709
14
16
17
18
15
Figure 5-2 Replacement Parts- Wirefeed Plate
20
19
Art # A-11357
Manual 0-5329 PARTS LIST 5-3

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
This page intentionally blank
5-4 PARTS LIST Manual 0-5329

ULTRAFEED VAF-4
APPENDIX 1: CONNECTION DIAGRAM
Art # A-12510
8 PIN SOCKET 4 PIN SOCKET
MOTOR CONTROL PCB
DISPLAY PCB
19 PIN SOCKET
BASE & REAR PANEL
EARTH
FRONT PANEL BASE & REAR PANEL
EARTH
EARTH
EARTH
CENTRE DIVIDER PANELDOOR PANEL
EARTH
Manual 0-5329 APPENDIX A-1

TWECO - LIMITED WARRANTY TERMS
LIMITED WARRANTY: Tweco®, Inc, A Victor Technologies Company, warrants to customers of its authorized
distributors hereafter “Purchaser” that its products will be free of defects in workmanship or material. Should
any failure to conform to this warranty appear within the time period applicable to the Tweco products as stated
below, Tweco shall, upon notification thereof and substantiation that the product has been stored, installed, operated, and maintained in accordance with Tweco’s specifications, instructions, recommendations and recognized
standard industry practice, and not subject to misuse, repair, neglect, alteration, or accident, correct such defects
by suitable repair or replacement, at Tweco’s sole option, of any components or parts of the product determined
by Tweco to be defective.
TWECO MAKES NO OTHER WARRANTY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. THIS WARRANTY IS EXCLUSIVE AND IN LIEU
OF ALL OTHERS, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR
ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: TWECO SHALL NOT UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES BE LIABLE FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SUCH AS, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, LOST PROFITS AND BUSINESS INTERRUPTION. The remedies of the Purchaser set forth herein are exclusive and the liability of Tweco with respect to
any contract, or anything done in connection therewith such as the performance or breach thereof, or from the
manufacture, sale, delivery, resale, or use of any goods covered by or furnished by Tweco whether arising out
of contract, negligence, strict tort, or under any warranty, or otherwise, shall not, except as expressly provided
herein, exceed the price of the goods upon which such liability is based. No employee, agent, or representative of
Tweco is authorized to change this warranty in any way or grant any other warranty.
PURCHASER’S RIGHTS UNDER THIS WARRANTY ARE VOID IF REPLACEMENT PARTS OR ACCESSORIES ARE
USED WHICH IN TWECO’S SOLE JUDGMENT MAY IMPAIR THE SAFETY OR PERFORMANCE OF ANY TWECO
PRODUCT. PURCHASER’S RIGHTS UNDER THIS WARRANTY ARE VOID IF THE PRODUCT IS SOLD TO PURCHASER BY NON-AUTHORIZED PERSONS.
The warranty is effective for the time stated below beginning on the date that the authorized distributor delivers
the products to the Purchaser. Notwithstanding the foregoing, in no event shall the warranty period extend more
than the time stated plus one year from the date Tweco delivered the product to the authorized distributor.

Warranty SCHEDULE
5 Years Parts* / 3 Years Labor
ArcMaster, Excelarc, Fabricator, Fabstar, PowerMaster
Portafeed, Ultrafeed, Ultima 150, WC 100B
* 5 years on the Original Main Power Transformer and Inductors not mounted on PCBoards.
* 3 years on Power Supply Components
2 Years Parts and Labor Unless specified
Auto-Darkening Welding Helmet (electronic Lens), ** 1 Month Harness Assy
Victor Regulator for Fabricator 141i (No labor)
1 Years Parts and Labor Unless specified
95S, Water recirculators
All Plasma Welding consols (i.e WC-1 Controller, WT Timer,
WF-100 Capstain Feeder, etc)
180 days parts and Labor Unless specified
Plasma Welding Torch and leads packages
Gas Regulators "Supplied with power sources" (No Labor)
90 days parts / No Labor
Remote Controls
MIG and TIG Torches (Supplied with power sources)
Replacement repair parts
30 days parts / No Labor
MIG Torch for Fabricator 141i
5-2-1 years Parts / No Labor
FirePower® Welders
5 Years Parts / No Labor
Victor® Professional
Victor Technologies limited warranty shall not apply to:
Consumable Parts for MIG, TIG, Plasma welding, Plasma cutting and Oxy fuel torches, O-rings, fuses, filters or other parts that fail due
normal wear
* Warranty repairs or replacement claims under this limited warranty must be submitted by an authorized VICTOR TECHNOLOGIES® repair
facility within thirty (30) days of the repair.
* No employee, agent, or representative of VICTOR TECHNOLOGIES® is authorized to change this warranty in any way or grant any other
warranty, and VICTOR TECHNOLOGIES® shall not be bound by any such attempt. Correction of non-conformities, in the manner and time
provided herein, constitutes fulfillment of VICTOR TECHNOLOGIES®’s obligations to purchaser with respect to the product.
* This warranty is void, and seller bears no liability hereunder, if purchaser used replacement parts or accessories which, in VICTOR
TECHNOLOGIES®'s sole judgment, impaired the safety or performance of any VICTOR TECHNOLOGIES® product. Purchaser’s rights
under this warranty are void if the product is sold to purchaser by unauthorized persons.

THE AMERICAS
Denton, TX USA
U.S. Customer Care
Ph 1-800-426-1888 (tollfree)
Fax: 1-800-535-0557 (tollfree)
International Customer Care
Ph 1-940-381-1212
Fax: 1-940-483-8178
Miami, FL USA
Sales Office, Latin America
Ph 1-954-727-8371
Fax: 1-954-727-8376
Oakville, Ontario, Canada
Canada Customer Care
Ph 1-905-827-4515
Fax: 1-800-588-1714 (tollfree)
EUROPE
Chorley, United Kingdom
Customer Care
Ph +44 1257-261755
Fax: +44 1257-224800
Milan, Italy
Customer Care
Ph +39 0236546801
Fax: +39 0236546840
ASIA/PACIFIC
Cikarang, Indonesia
Customer Care
Ph 6221-8990-6095
Fax: 6221-8990-6096
Rawang, Malaysia
Customer Care
Ph +603 6092-2988
Fax: +603 6092-1085
Melbourne, Australia
Australia Customer Care
Ph 1300-654-674 (tollfree)
Ph 61-3-9474-7400
Fax: 61-3-9474-7391
International
Ph 61-3-9474-7508
Fax: 61-3-9474-7488
Shanghai, China
Sales Office
Ph +86 21-64072626
Fax: +86 21-64483032
Singapore
Sales Office
Ph +65 6832-8066
Fax: +65 6763-5812
INNOVATION TO SHAPE THE WORLD™
T ECHNOLOGIES
™
U.S. Customer Care: 800-426-1888 / FAX 800-535-0557
Canada Customer Care: 905-827-4515 / FAX 800-588-1714
International Customer Care: 940-381-1212 / FAX 940-483-8178
© 2014 Victor Technologies International, Inc. www.victortechnologies.com Printed in China
 Loading...
Loading...