Page 1

Wireless LAN
IEEE802.11g PCI Card
User Manual
Page 2

Table of Contents
FCC Information ………………………………………………………….…….. I
Chapter 1 About Wireless LAN PCI Card…………………………………… 1
1-1 Features and Benefits ………………………………………………………… 1
1-2 Applications
…..……………………………………………….……….. 1
1-3 Product Kit
………………………………..…………………………………… 2
Chapter 2 Getting Started……………………………………………………… 3
2-1 Before Installation……………………………………………………………… 3
2-2 Insert the 802.11g Wireless LAN PCI Card
…………………………………… 3
Chapter 3 Install Driver for Windows ……………………………………… 4
3-1 Setup IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for Windows XP………………… 4
3-2 Setup IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for Windows 2000
……………… 7
3-3 Setup IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for Windows ME
……………… 11
3-4 Setup IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for Windows 98SE
…………… 13
Limited Warranty ……………………………………………………………… 16
Glossary………………………………………………………………… 17
Page 3

FCC Information
This device, IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card, complies with Part 15 of
the FCC rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not
cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received; including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Statement
This Equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Warning: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user authority to operate the
equipment.
Tested to comply with FCC standard. FOR HOME OR OFFICE USE.
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement:
1. This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth
for an uncontrolled environment, under 47 CFR 2.1093 paragraph (d)(2).
2. This Transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with
any other antenna or transmitter.
i
Page 4

The IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card has been tested to the FCC
exposure requirements (Specific Absorbtion Rate).
The antenna(s) used for this transmitter must be installed to provide a
separation distance of at least 20 cm from all persons.
ii
Page 5

Chapter 1 About Wireless LAN PCI Card
The IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card is a standard PCI Card that fits into
any standard PCI slot in a desktop. The IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card
is an enhanced high-performance, that supports high-speed wireless
networking at home, or at office. The IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card is
able to communicate with any 802.11b and 802.11g compliant products.
1-1 Features and Benefits
1. Supports 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps and up to 54Mbps data rate.
2. Working range up to 800 ft. in an open environment.
3. Seamless connectivity to wired Ethernet and PC network LAN’s augments
existing networks quickly and easily.
4. Greater flexibility to locate or move networked PCs.
5. Wireless connection without the cost of cabling.
6. Easy to install and user friendly, just Plug and Play.
7. Low power consumption.
8. Supports a variety of operating systems (Win98SE/ME/2000/XP)
9. 64-bit and 128-bits WEP encryption capable.
10. Provides Window-based Diagnostic Tools, most notably, Site Survey, Link
Quality Test and Access Point Browser.
1-2 Applications
IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card offers a fast, reliable, cost-effective
solution for wireless client access to the network in applications like these:
1. Remote access to corporate network information
E-mail, file transfer and terminal emulation.
2. Difficult-to-wire environments
Historical or old buildings, asbestos installations, and open area where
wiring is difficult to deploy.
3. Frequently changing environments
Retailers, manufacturers and those who frequently rearrange the
workplace and change
4. Temporary LANs for special projects or peak time
• Trade shows, exhibitions and construction sites where a temporary
network will be practical.
• Retailers, airline and shipping companies need additional
- 1 -
Page 6

workstations during peak period.
• Auditors requiring workgroups at customer sites.
5. Access to database for mobile workers
Doctors, nurses, retailers, accessing their database while being mobile in
the hospital, retail store or office campus.
6. SOHO (Small Office and Home Office) users
SOHO users need easy and quick installation of a small computer
network.
7. High security connection
The secure wireless network can be installed quickly and provide
flexibility.
1-3 Product Kit
IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card comes with the following items. Please
go through each item below. If any of listed items appears to be damaged or
missing, please contact your local dealer.
IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card x1
802.11g PC Card Software and Documentation CD x1
- 2 -
Page 7

Chapter 2 Getting Started
This chapter describes the instructions that guide you through the proper
installation of your IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for the Windows
XP/2000/ME/98SE operating systems. The complete installation of the IEEE
802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card consists of the following steps:
Step 1: Insert your IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card into your PC.
Step 2: Install the corresponding driver and utility.
Step 3: Set basic settings.
Step 4: Finish Installation.
2-1 Before Installation
In addition to the items shipped with the client Card, you will also need the
following in order to install the Card:
1. A computer equipped with a PCI 2.2 slot.
2. Windows XP/2000/98SE/ME (with a Windows installation CD-ROM,
diskettes for use during installation).
3. Minimum 5 Mbytes free disk space for installing driver and utility
program.
2-2 Insert the 802.11g Wireless LAN PCI Card
To install the IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card, please do the following:
1. Find an available PCI slot on your computer.
2. Insert the PCI Card into the PCI slot.
- 3 -
Page 8
Chapter 3 Install Driver for Windows
This section describes the installation of the IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN
Card driver for the Windows 98SE/ME/2000 and Windows XP operating
systems. The installation procedures for Windows XP refer to 3-1 Set up
IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for Windows XP; for Windows 2000
please see 3-2 Set up IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for Windows 2000;
for Windows ME refer to 3-3 Set up IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for
Windows ME; for Windows 98SE refer to 3-3 Set up IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless
LAN Card for Windows 98SE.
Note: Before you start the installation, you are advised to keep the Windows CD-ROM in
case you might need certain system files.
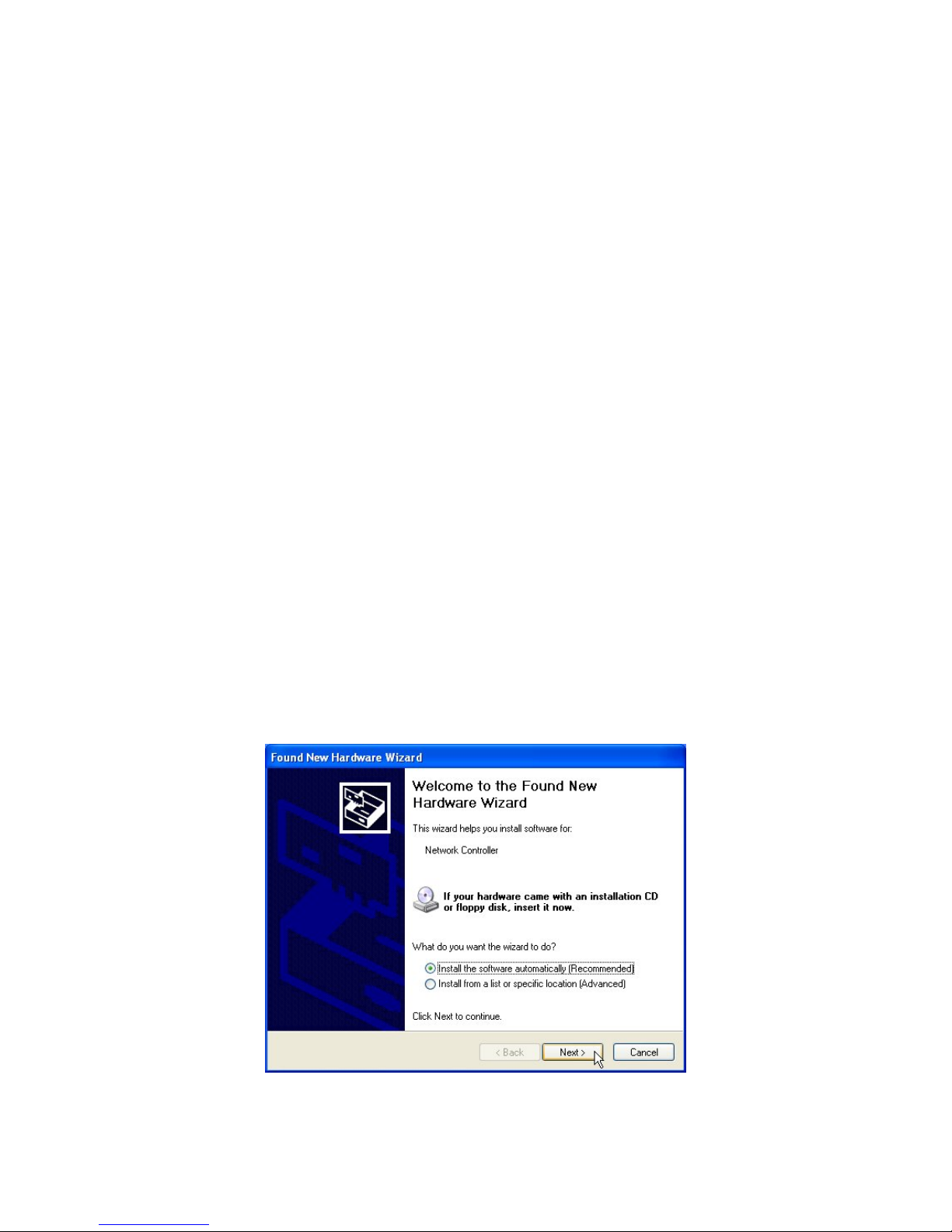
3-1 Set up IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for Windows XP
Step 1: After inserting the IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card into the PCI
slot on your PC and turn PC on, the Windows will auto-detect the PCI
Wireless LAN Card and a “Found New Hardware Wizard” window
will show up.
Insert the Product CD-ROM into the appropriate drive and select
“Install the software automatically (Recommended)”.
Then press Next button to install the driver.
- 4 -
Page 9

Step 2: The windows will appear the message about the IEEE802.11g PCI
Wireless LAN Card has not passed Windows Logo testing to verify its
compatibility with Windows XP.
Click on Continue Anyway button to continue installing.
The windows will find “IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card” and
starting copy corresponding files into the system. Click on Next to
continue.
Step 3: Click Finish to complete the installation.
- 5 -
Page 10

Step 4: Right click “My Computer” from Start, select Properties, go to the
Hardware tab and click the Device Manager button to see if any
exclamation mark appears next to the Network Adapters/IEEE
802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card. If no, your IEEE 802.11g PCI
Wireless LAN Card is working well.
- 6 -
Page 11
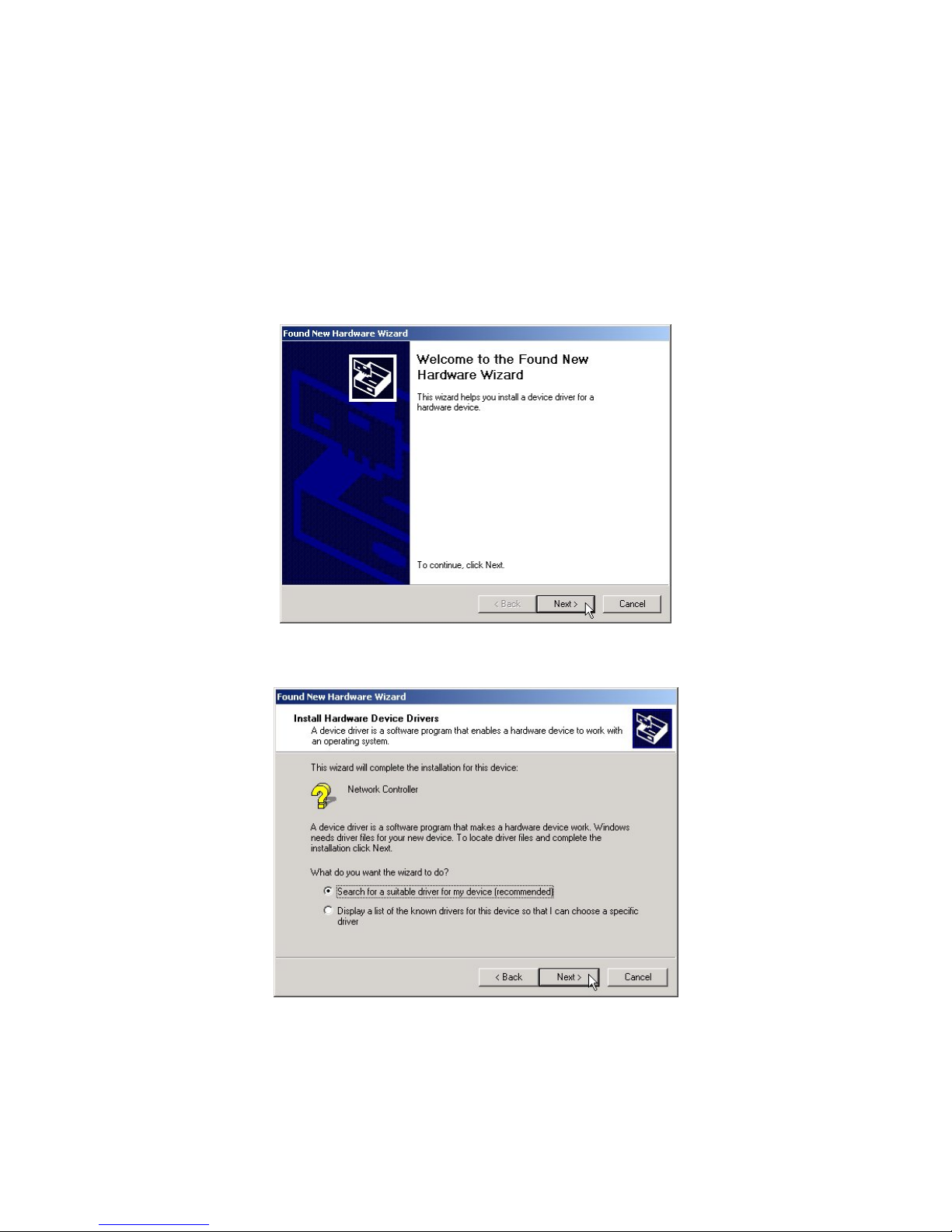
3-2 Set up IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for Windows 2000
Step 1: After inserting the IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card into the PCI
slot on your PC, Windows will auto-detect the IEEE 802.11g PCI
Wireless LAN Card.
A “Found New Hardware Wizard” window shows up. Click on Next
to proceed.
Step 2: Select “Search for a suitable driver for my device (recommended)”.
- 7 -
Page 12

Step 3: Insert the Product CD-ROM into the appropriate drive. Click on Next
to install the driver.
Step 4: The windows will find “IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card”. Click
on Next to continue.
- 8 -
Page 13

Step 5: The windows will appear the message about the Microsoft digital
signature affirms that software has not been tested with Windows and
that the software has not been altered since it was tested. Click on Yes
button to continue installing.
Step 6: Click Finish to complete the installation.
- 9 -
Page 14

Step 7: Open Control Panel/System/Device Manager, and check Network
Adapters to see if any exclamation mark appears. If no, your IEEE
802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card is working well.
- 10 -
Page 15
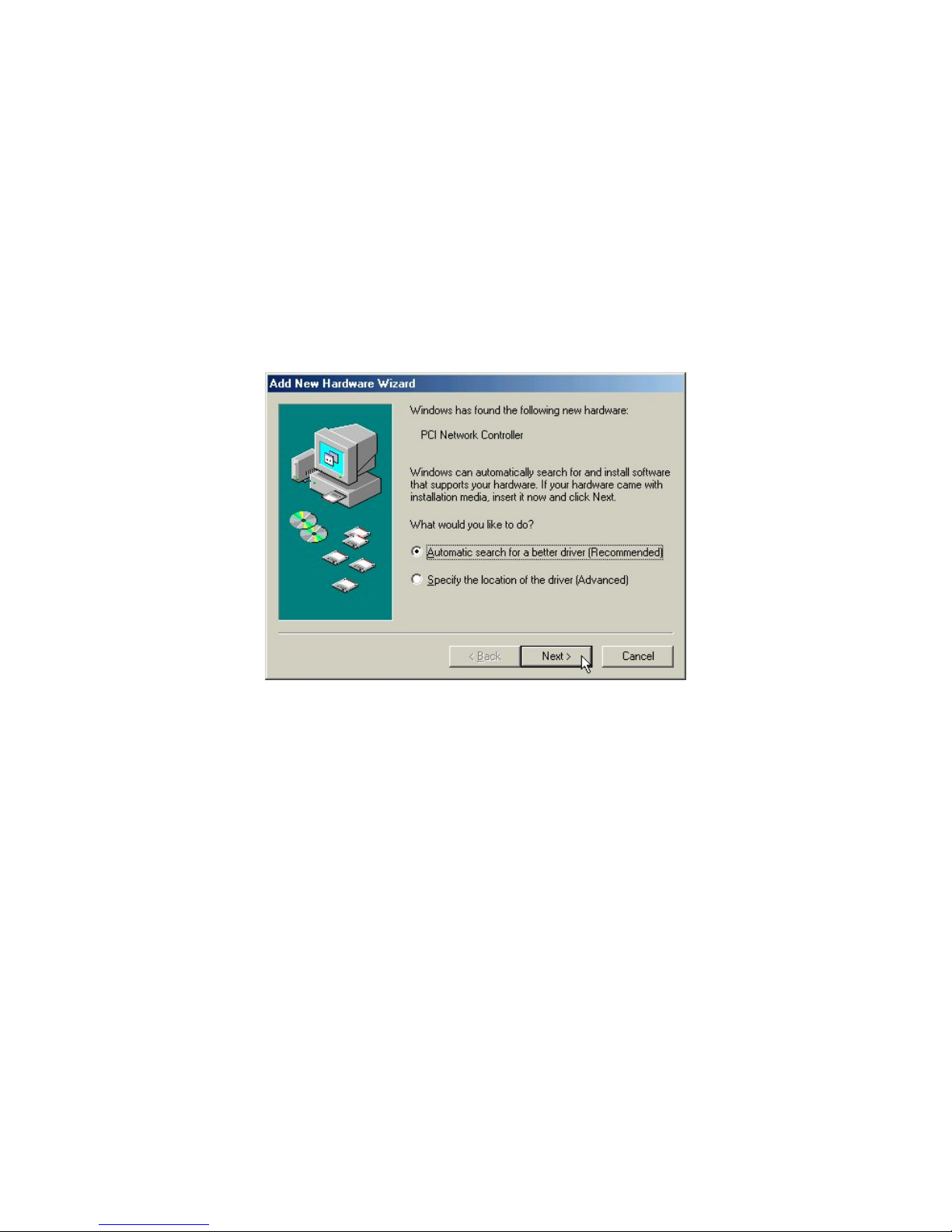
3-3 Set up IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for Windows ME
Step 1: After inserting the IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card into the PCI
slot on your PC, Windows will auto-detect new hardware and will
display an “Add New Hardware Wizard” window.
Insert the Product CD-ROM into the appropriate drive.
Select “Automatic search for a better driver (Recommended)” and
click on Next to continue.
Step 2: Once the [Please insert the disk labeled ‘Windows ME CD-ROM”, and
then click OK] window appears, insert and enter the path corresponding to
the appropriate drives and click OK. Usually these files can be found at
C:\Windows or C:\Windows\system.
Step 3: Click Finish to complete the software installation.
- 11 -
Page 16
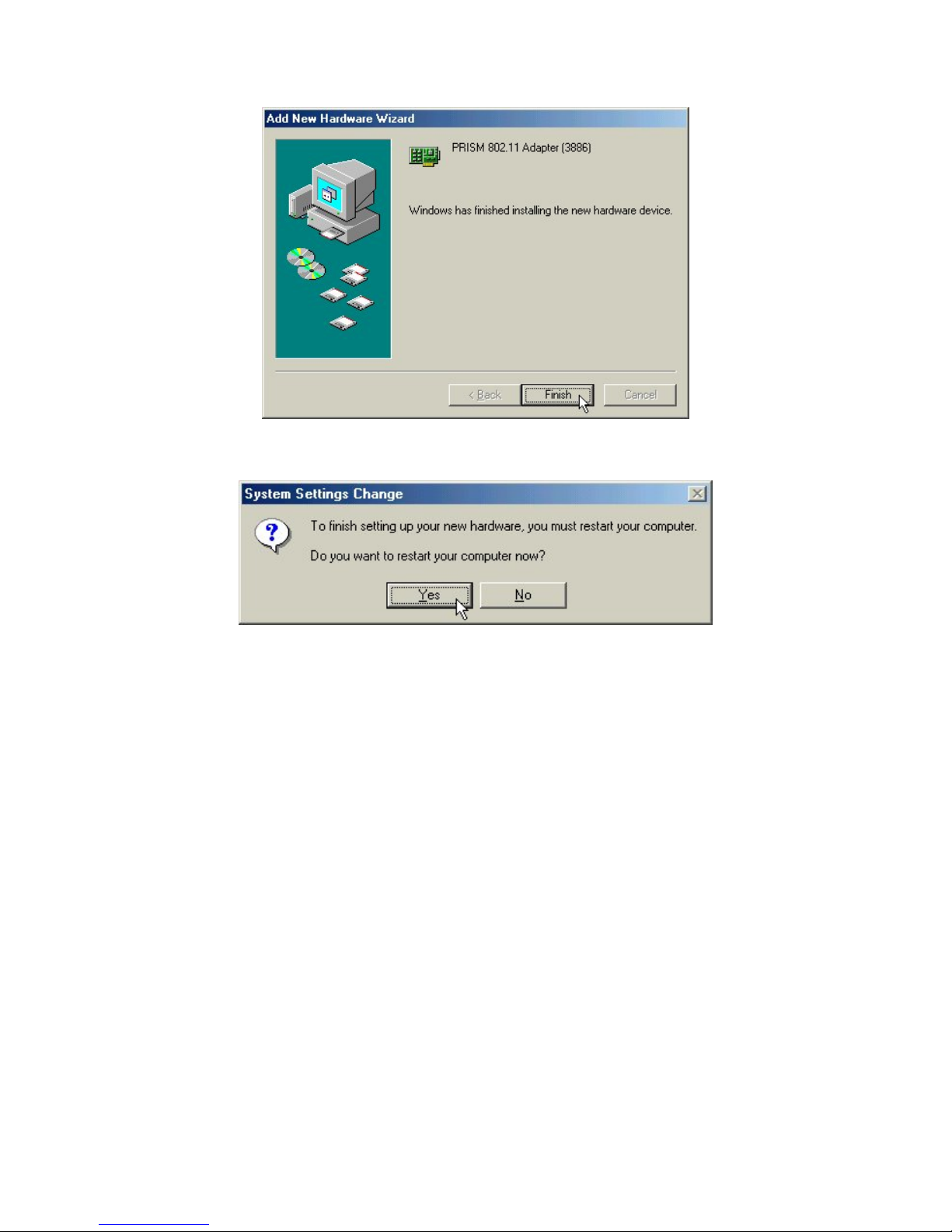
Step 4: Click Yes button to restart the computer.
Step 5: Open Control Panel/System/Device Manager, and check Network
Adapters to see if any exclamation mark appears next to the IEEE 802.11g PCI
Wireless LAN Card. If no, your IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card is
working well.
- 12 -
Page 17
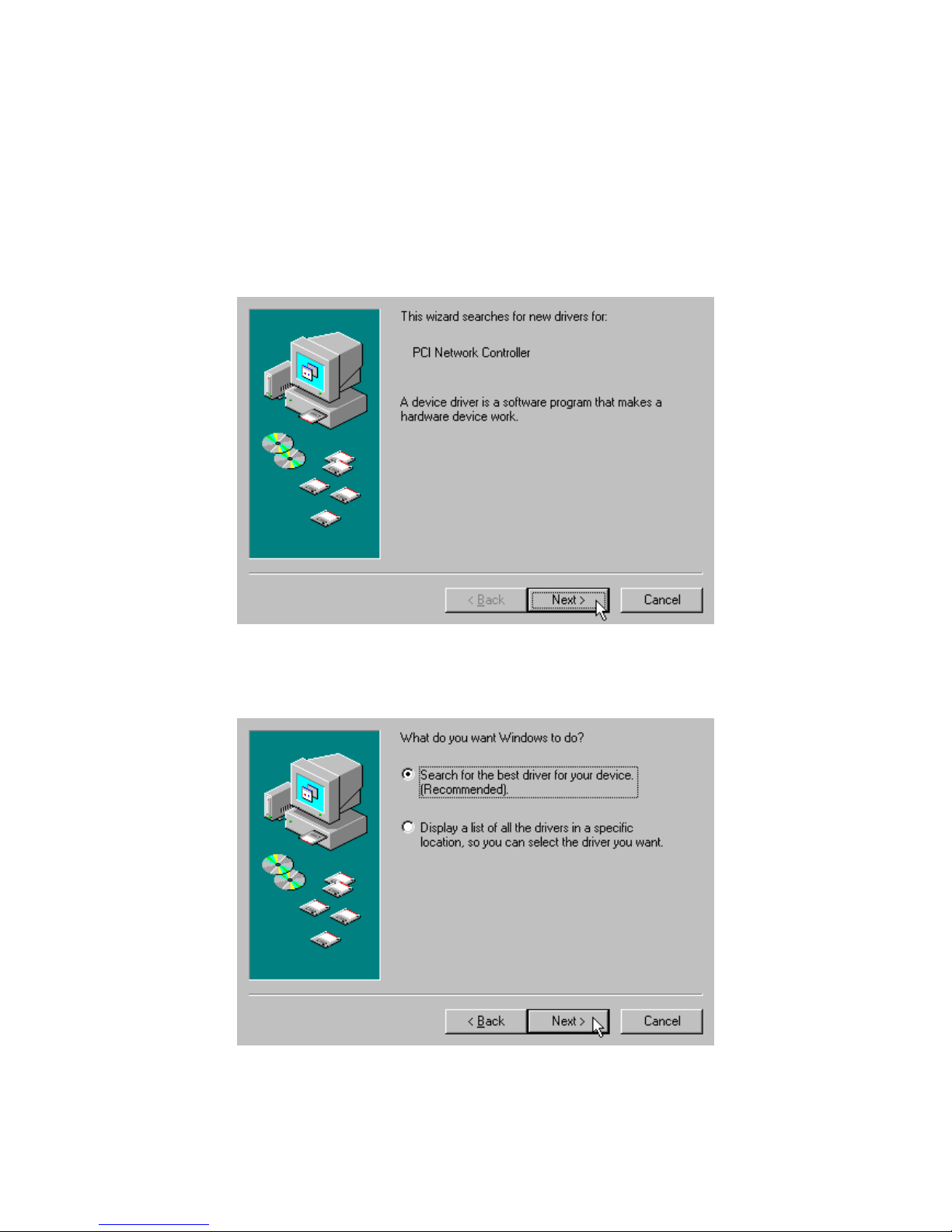
3-4 Set up IEEE802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card for Windows 98SE
Step 1: After inserting the IEEE 802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card into the PCI
slot on your PC, Windows will auto-detect new hardware and will
display an “Add New Hardware Wizard” window. Click on Next to
continue.
Step 2: Select “Search for the best driver for your device (Recommended)”
and click on Next.
- 13 -
Page 18
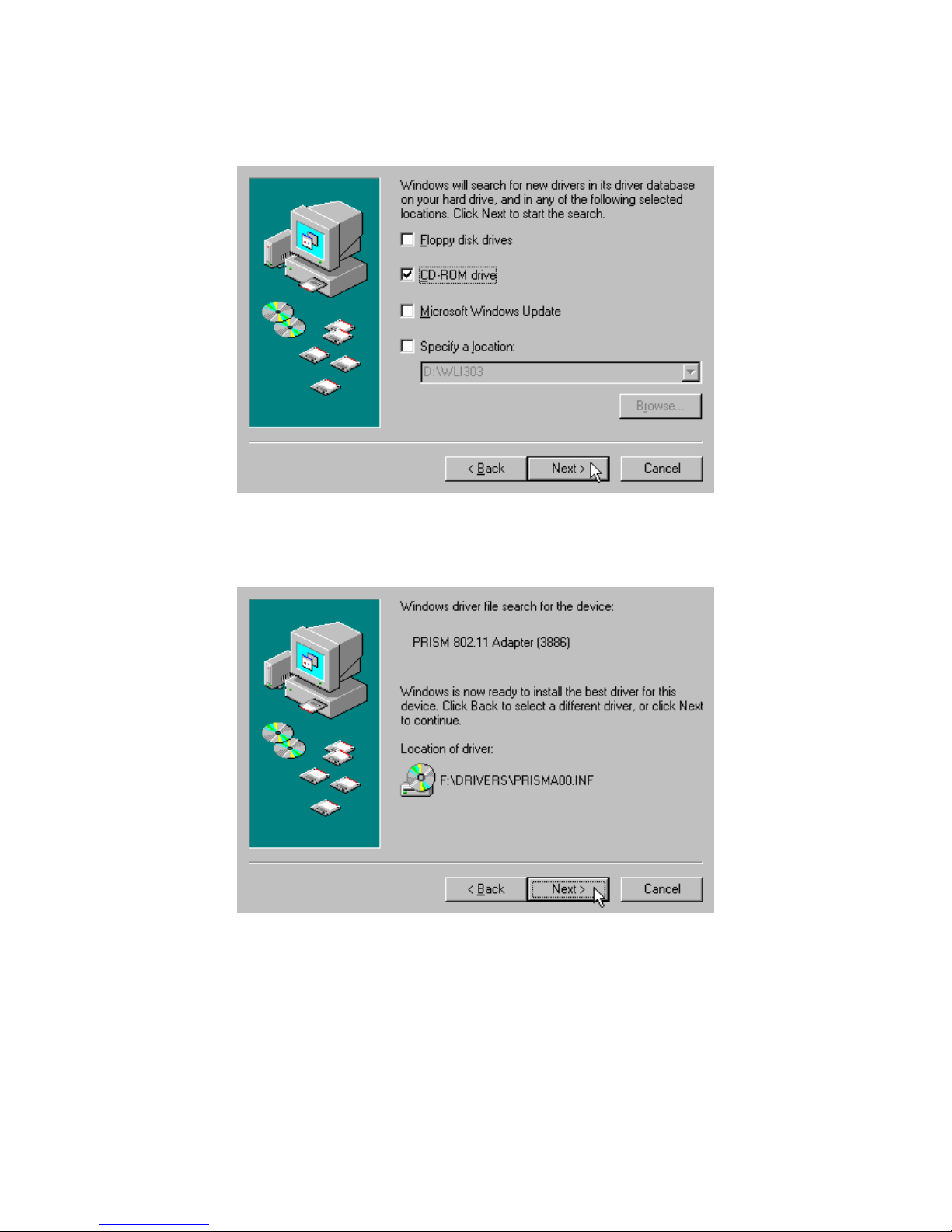
Step 3: Insert the Product CD-ROM into the appropriate drive. Select
CD-ROM drive, and click on Next to install the driver.
Step 4: The Windows will find “PRISM 802.11 Adaptor (3886)”.
Click on Next to continue.
- 14 -
Page 19

Step 5: Once the [Please insert the disk labeled ‘Windows 98 Second Edition
CD-ROM”, and then click OK] window appears, insert and enter the
path corresponding to the appropriate drives and click OK. Usually
these files can be found at C:\Windows or C:\Windows\system.
Step 6: Click Finish to complete the software installation.
Step 7: Click on Yes to restart the computer.
Step 8: Open Control Panel/System/Device Manager, and check Network
Adapters to see if any exclamation mark appears next to the IEEE
802.11g PCI Wireless LAN Card. If no, your IEEE 802.11g PCI
Wireless LAN Card is working well.
- 15 -
Page 20

Limited Warranty
This Warranty constitutes the sole and exclusive remedy of any buyer or
reseller’s equipment and the sole and exclusive liability of the supplier in
connection with the products and is in lieu of all other warranties, express,
implied or statutory, including, but not limited to, any implied warranty of
merchantability of fitness for a particular use and all other obligations or
liabilities of the supplier.
In no even will the supplier or any other party or person be liable to your or
anyone else for any damages, including lost profits, lost savings or other
incidental or consequential damages, or inability to use the software provided
on the software media even if the supplier or the other party person has been
advised of the possibility of such damages.
The following are special terms applicable to your hardware warranty as well
as services you may use during part of the warranty period. Your formal
Warranty Statement, including the warranty applicable to our Wireless LAN
products, appears in the Quick Installation Guide that accompanies your
products.
Duration of Hardware Warranty: One Year
Replacement, Repair or Refund Procedure for Hardware:
If your unit needs a repair or replacement, return it to your dealer/distributor
in its original packaging. When returning a defective product for Warranty,
always include the following documents:
The Warranty Repair Card
A copy of the invoice/proof of purchase, and the RMA Report Form (To
receive a Return Materials Authorization form (RMA), please contact the
party from whom you purchased the product).
- 16 -
Page 21

Glossary
IEEE 802.11 Standard
The IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN standards subcommittee, which is formulating
a standard for the industry.
Access Point
An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless
networks together.
Ad Hoc
An Ad Hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with a WLAN
adapter, connected as an independent wireless LAN. Ad Hoc wireless LAN is
applicable at a departmental scale for a branch or SOHO operation.
BSSID
A specific Ad Hoc LAN is called a Basic Service Set (BSS). Computers in a BSS
must be configured with the same BSSID.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - a method in which IP addresses are
assigned by server dynamically to clients on the network. DHCP is used for
Dynamic IP Addressing and requires a dedicated DHCP server on the
network.
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
This is the method the wireless adapters use to transmit data over the
frequency spectrum. The other method is frequency hopping. Direct sequence
spreads the data over one frequency range (channel) while frequency hopping
jumps from one narrow frequency band to another many times per second.
ESSID
An Infrastructure configuration could also support roaming capability for
mobile workers. More than one BSS can be configured as an Extended Service
Set (ESS). Users within an ESS could roam freely between BSSs while served
as a continuous connection to the network wireless stations and Access Points
- 17 -
Page 22

within an ESS must be configured with the same ESSID and the same radio
channel.
Ethernet
Ethernet is a 10/100Mbps network that runs over dedicated home/office
wiring. Users must be wired to the network at all times to gain access.
Gateway
A gateway is a hardware and software device that connects two dissimilar
systems, such as a LAN and a mainframe. In Internet terminology, a gateway
is another name for a router. Generally a gateway is used as a funnel for all
traffic to the Internet.
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Infrastructure
An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an Infrastructure
configuration. Infrastructure is applicable to enterprise scale for wireless
access to central database, or wireless application for mobile workers.
ISM Band
The FCC and their counterparts outside of the U.S. have set aside bandwidth
for unlicensed use in the so-called ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical)
band. Spectrum in the vicinity of 2.4 GHz, in particular, is being made
available worldwide. This presents a truly revolutionary opportunity to place
convenient high-speed wireless capabilities in the hands of users around the
globe.
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN is a group of computers, each equipped with the appropriate network
adapter card connected by cable/air that share applications, data, and
peripherals. All connections are made via cable or wireless media, but a LAN
does not use telephone services. It typically spans a single building or
campus.
Network
A network is a system of computers that is connected. Data, files, and
- 18 -
Page 23

messages can be transmitted over this network. Networks may be local or
wide area networks.
Protocol
A protocol is a standardized set of rules that specify how a conversation is to
take place, including the format, timing, sequencing and/ or error checking.
SSID
A Network ID unique to a network. Only clients and Access Points that share
the same SSID are able to communicate with each other. This string is
case-sensitive.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Simple Network Management Protocol is the network management protocol
of TCP/IP. In SNMP, agents-which can be hardware as well as
software-monitor the activity in the various devices on the network and
report to the network console workstation. Control information about each
device is maintained in a structure known as a management information
block.
Static IP Addressing
A method of assigned IP addresses to clients on the network. In networks
with Static IP address, the network administrator manually assigns an IP
address to each computer. Once a Static IP address is assigned, a computer
uses the same IP address every time it reboots and logs on to the network,
unless it is manually changed.
Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
TCP/IP is the protocol suite developed by the Advanced Research Projects
Agency (ARPA). It is widely used in corporate Internet works, because of its
superior design for WANs. TCP governs how packet is sequenced for
transmission the network. The term “TCP/IP” is often used generically to
refer to the entire suite of related protocols.
Transmit / Receive
The wireless throughput in Bytes per second averaged over two seconds.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
- 19 -
Page 24

A WAN consists of multiple LANs that are tied together via telephone
services and / or fiber optic cabling. WANs may span a city, a state, a country,
or even the world.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
Now widely recognized as flawed, WEP was a data encryption method used
to protect the transmission between 802.11 wireless clients and APs. However,
it used the same key among all communicating devices. WEP's problems are
well-known, including an insufficient key length and no automated method
for distributing the keys. WEP can be easily cracked in a couple of hours with
off-the-shelf tools.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
The Wi-Fi Alliance put together WPA as a data encryption method for 802.11
wireless LANs. WPA is an industry-supported, pre-standard version of
802.11i utilizing the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), which fixes the
problems of WEP, including using dynamic keys.
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
The Temporal Key Integrity Protocol, pronounced tee-kip, is part of the IEEE
802.11i encryption standard for wireless LANs. TKIP is the next generation of
WEP, the Wired Equivalency Protocol, which is used to secure 802.11 wireless
LANs. TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a
re-keying mechanism, thus fixing the flaws of WEP.
Wi-Fi Alliance
The Wi-Fi Alliance is a nonprofit international association formed in 1999 to
certify interoperability of wireless Local Area Network products based on
IEEE 802.11 specification. The goal of the Wi-Fi Alliance's members is to
enhance the user experience through product interoperability. The
organization is formerly known as WECA.
- 20 -
 Loading...
Loading...