Page 1

TROY XCD External
Print Servers
for Ethernet Networks
Administrator's Guide
Part No. MAN-EXT2000 Revision 99-2
August 21, 1999 Printed in U.S.A.
TROY XCD
A TROY Group, Inc. Company
TROY XCD, Inc.
1692 Browning
Irvine, CA 92606-4809
TEL: (949) 399-0820
FAX: (949) 399-0825
support@troyxcd.com
Page 2

Notice
TROY XCD, INC. SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS OF THIS
PRODUCT FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. TROY XCD shall not be
liable for any errors contained in this manual or for any damages resulting from
loss of use, data profits, or any incidental or consequential damages arising
from the use of TROY XCD products or services.
Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
A digital device pursuant to Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed
to provide reasonable protection against such interference when operating in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in accordance with this
guide, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference
in which case the user, at his or her own expense, will be required to take
whatever measures will be required to correct the interference.
Trademarks
HP, HP/UX, LaserJet, DesignJet, DeskJet, PaintJet, JetDirect, and JetAdmin
are trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Company. DEC, DECserver, VMS, LAT,
and ULTRIX are trademarks of Digital Equipment Corporation. UNIX is a
trademark of UNIX Systems Laboratories. Ethernet is a trademark of Xerox
Corporation. PostScript is a trademark of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
NetWare is a trademark of Novell, Inc. Apple, Macintosh, LaserWriter, and
AppleTalk are trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc. IBM, LAN Server, and
AIX are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation. LAN
Manager, Windows, and MS-DOS are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
VINES is a trademark of Banyan Systems Inc. PrintKit is a trademark of
Northlake Software. QADD is a trademark of Network Compatibility Group.
LAN Attached and UNIX Printing for VINES is a trademark of Incognito
Software Inc. XJet, XMark, XConnect, and XAdmin are trademarks of TROY
XCD, Inc.
© Copyright 1992-1999 TROY XCD, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Contents
1. Introduction
Overview .................................................................................. 1-1
2. Installing the Hardware
Overview .................................................................................. 2-1
Before You Start....................................................................... 2-1
Unpacking and Handling.......................................................... 2-2
Step 1-a Setting the Switches (XConnect II/II Lite) ............... 2-3
Step 1-b Setting the Switches (XConnect 100 and Pony) ....... 2-5
Step 2 Connecting to the Printer.............................................. 2-6
Step 3 Connecting to the Ethernet ......................................... 2-12
Step 4 Connecting to a LocalTalk Network (XConnect II)... 2-15
Step 5 Verifying Successful Hardware Installation .............. 2-16
Step 6 Changing the Printer Reset......................................... 2-20
Changing the Print Server Configuration ............................... 2-22
3. TROY XCD Print Server Management Methods
Overview .................................................................................. 3-1
TROY XCD XAdmin32 and XAdmin ..................................... 3-1
TROY XCD WebXAdmin ....................................................... 3-4
TROY XCD Print Server Console ........................................... 3-5
HP JetAdmin ............................................................................ 3-7
HP Web JetAdmin.................................................................... 3-8
4. TCP/IP Network Configuration
Overview .................................................................................. 4-1
TCP/IP Concepts ...................................................................... 4-1
TCP/IP UNIX Host Configuration ........................................... 4-2
IP Security .............................................................................. 4-23
Raw TCP Ports ....................................................................... 4-23
Changing the Configuration (Optional) ................................. 4-26
5. Novell Network Configuration
Overview .................................................................................. 5-1
NetWare Concepts.................................................................... 5-1
Page 4

General Information ................................................................. 5-3
Before You Begin..................................................................... 5-4
Default Print Server Names...................................................... 5-4
Configuring the Print Server and Adding the Print Queue
in Queue Server Mode.............................................................. 5-6
Configuring the Print Queue and Adding the Print Queue
in Remote Printer Mode ......................................................... 5-18
Configuring the Worksation ................................................... 5-26
Changing the Print Server Configuration ............................... 5-30
6. AppleTalk Network Configuration
Overview .................................................................................. 6-1
AppleTalk Concepts ................................................................. 6-1
Step 1 Macintosh Configuration............................................... 6-2
Step 2 Printing .......................................................................... 6-2
Printing Binary Graphics.......................................................... 6-3
Changing the Configuration ..................................................... 6-4
7. Windows NT Network and LAN Server Configuration
Overview .................................................................................. 7-1
Windows NT IP Configuration ................................................ 7-2
Windows NT 4.xx Configuration ............................................. 7-4
Windows NT 3.5x Configuration ............................................. 7-6
IBM LAN Server Installation................................................... 7-7
8. Windows 95/98 Peer-to-Peer Configuration
Overview .................................................................................. 8-1
Configuring the Windows 95/98 PC ........................................ 8-1
9. Microsoft Network Configuration (NetBEUI/NetBIOS)
Overview .................................................................................. 9-1
Print Server Configuration ....................................................... 9-1
Windows 95/98 and Windows NT Port Monitor Installation .. 9-3
LAN Server/Warp Server Configuration ................................. 9-5
10. DLC/LLC Configuration
Overview ................................................................................ 10-1
Configuring DLC/LLC on Windows NT ............................... 10-1
Configuring DLC/LLC on Other Systems ............................. 10-4
Page 5

11. LAT Network Configuration
Overview ................................................................................ 11-1
LAT Concepts ........................................................................ 11-1
VMS LAT Host Configuration............................................... 11-2
Eliminating Blank Pages (Optional)....................................... 11-5
PATHWORKS for DOS Configuration ................................. 11-6
PATHWORKS for Macintosh Configuration ........................ 11-9
DECprint Supervisor Configuration Notes ............................ 11-9
Installation on Other Host Computers.................................. 11-10
Changing the Configuration (Optional) ............................... 11-11
12. Banyan VINES Configuration (Optional)
Overview ................................................................................ 12-1
File Server User Configuration .............................................. 12-2
File Server Queue Configuration ........................................... 12-3
Print Server Configuration Using XAdmin............................ 12-6
Print Server Configuration Using the Console....................... 12-8
Testing the Print Queue ........................................................ 12-10
13. PrintraNet Remote Internet Printing
Overview ................................................................................ 13-1
PrintraNet Concepts ............................................................... 13-1
Installing the Software on a Windows 95/98 PC ................... 13-3
Configuring the Remote TROY XCD Print Server................ 13-8
Printing to the Remote TROY XCD Print Server ................ 13-12
Troubleshooting.................................................................... 13-13
Print Server Console Command Summary .......................... 13-13
14. Troubleshooting
Overview ................................................................................ 14-1
Installation Problems (Printer Not Ready) ............................. 14-1
Installation Problems (Printer Ready) .................................... 14-2
Intermittent Problems ............................................................. 14-7
TCP/IP Troubleshooting......................................................... 14-7
AppleTalk and PATHWORKS for Mac Troubleshooting ... 14-13
NetWare Troubleshooting .................................................... 14-13
Windows NT and LAN Server Troubleshooting ................. 14-16
Windows 95/98 Peer-to-Peer Troubleshooting .................... 14-17
Page 6

LAT Troubleshooting........................................................... 14-18
Banyan VINES Troubleshooting.......................................... 14-22
15. Warranty and Service Information
Customer Support................................................................... 15-1
Whom to Call ......................................................................... 15-1
Returning Products ................................................................. 15-2
Advance Replacement and Extended Services ...................... 15-3
Warranty ................................................................................. 15-3
A. Command Summary ............................................................. A-1
B. Using Services (lpd-Plus) .......................................................B-1
C. Reloading the Firmware ........................................................C-1
D. Glossary/Index ....................................................................... D-1
Page 7
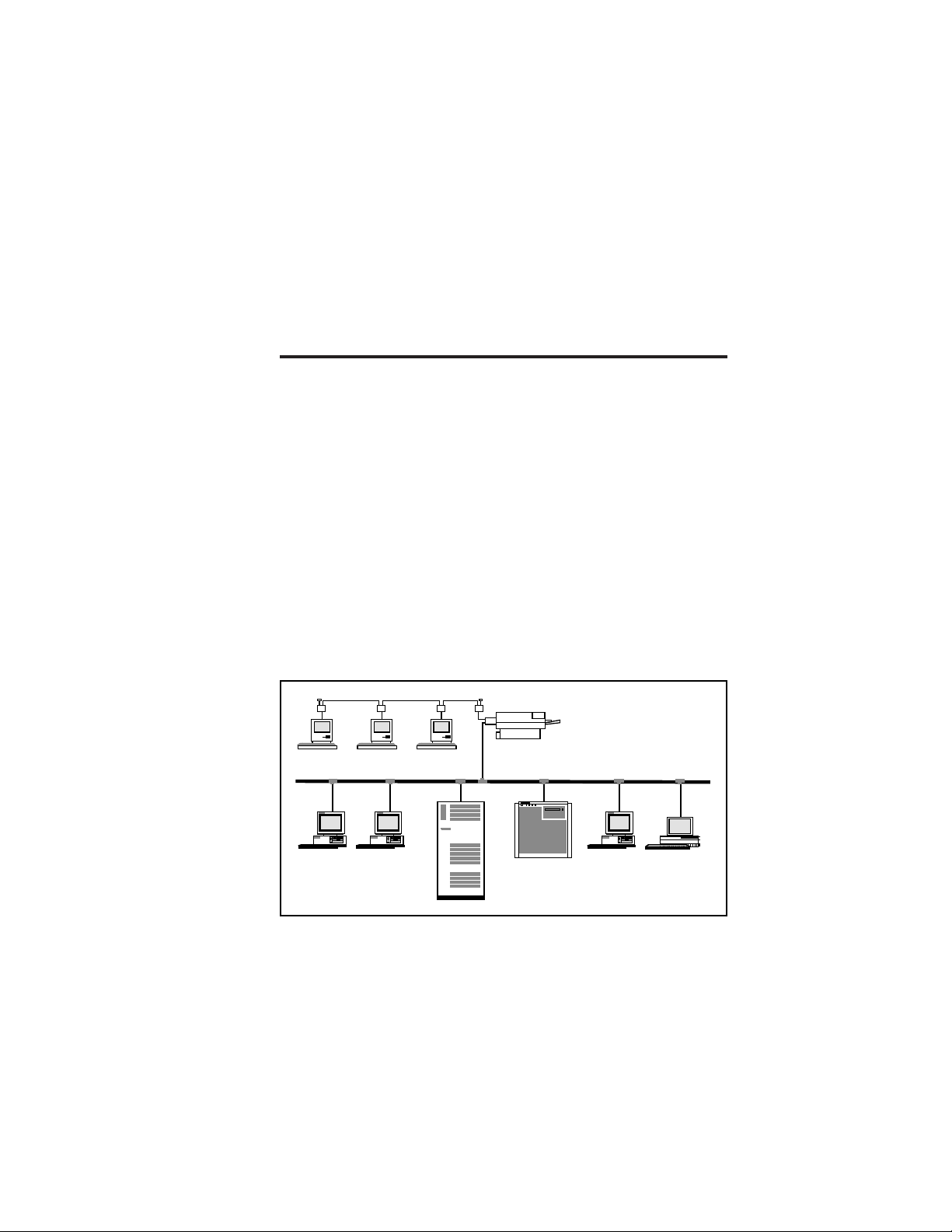
1
Introduction
Overview
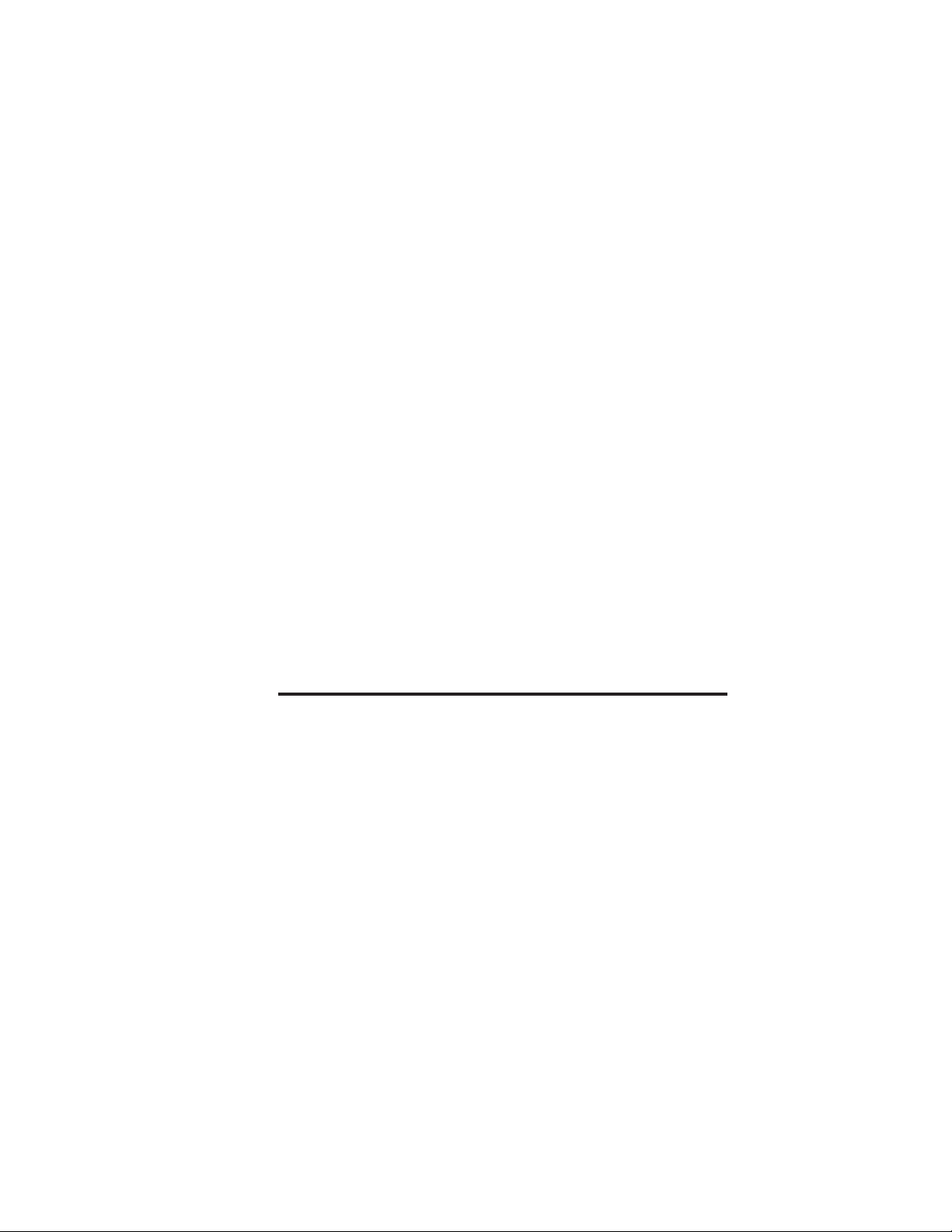
TROY XCD external print servers allow multiple host computers
to share virtually any type of printer or plotter on high-speed
local area network. The Pony Print Server Plus is an
ultracompact low-cost Ethernet print server for a single printer,
while the Pony 100, XConnect II and XConnect II Lite connect
up to two printers to an Ethernet network. The XConnect 100
handles up to four printers and works on both Ethernet (10baseT)
and Fast Ethernet (100baseT) networks.
Any user can print jobs on a printer or plotter connected to a
TROY XCD external print server as if it were directly attached
to his computer. No special software is required on the host
computers, and application programs run without any
LocalTalk
Printer with aTROY
XCD print server
Apple Macintosh Computers
NetWarePCLAN Manager
PC
UNIX Host
DEC Host
Figure 1-1
XCD External Print Server Concept
Banyan VINESPCApple
Introduction 1-1
Macintosh
Page 8

modification. Because the TROY XCD external print servers
provide multiprotocol capabilities, users on DEC, UNIX, Novell,
AppleTalk, LAN Server, Windows NT, Windows 95, LAN
Manager, and Banyan VINES computers can simultaneously
access the same printer. With the optional XConnect II
LocalTalk feature, non-Ethernet Macintosh computers can also
access the same printer. Figure 1-1 shows how TROY XCD
external print servers are used in a typical network.
Features
TROY XCD external print servers offer the widest range of
features in the industry, including:
• TCP/IP, NetWare, AppleTalk, DLC/LLC, NetBEUI, LAT,
and VINES IP protocols (protocols supported depend on
model)
• Network Operating System compatibility:
- Digital Equipment Corporation networks, including
PATHWORKS and DECprint Supervisor ((not available
on XConnect II Lite)
- UNIX systems that support either the Berkeley lpr/lpd
printing protocol, the HP JetDirect card, or printing to a
raw TCP port
- Novell NetWare V2.15 or above, V3.xx, or V4.xx,
including support for bindery mode and Novell Directory
Services (NDS)*
- AppleTalk Phase 2 (XConnect II and XConnect 100 only)
- Windows NT and NTAS V3.5 or above
- IBM OS/2, LAN Server, Warp Server
- Windows 95 (Peer-to-Peer or client mode; not supported
on XConnect II Lite)
- Windows for Workgroups (Peer-to-Peer or client mode;
Peer-to-Peer requires DLC/LLC support on print server)
Introduction 1-2
Page 9

*The NDS support on the XJet III (all models), XJet IV-2, XJet IV-T,
plus certain models of the XJet IV-Plus is limited to NPrinter mode
only.
• Very high performance DMA operation (XConnect 100 and
XConnect II only)
• High-speed Centronics parallel port compatible with IEEE
P1284 Bitronics bidirectional parallel interface standard
• Serial port for console terminal or second printer
• Optional LocalTalk support (XConnect II only)
• Superior network and printer management
- Compatible with Hewlett-Packard JetAdmin and Web
JetAdmin printer management software
- XAdmin Windows-based management utility (NetWare,
TCP/IP, or VINES)
- Web XAdmin browser-based management
- SNMP MIB I and MIB II over IP or IPX (XConnect II
and XConnect 100 only)
- Remote console management via DEC NCP, TELNET,
NetWare, or serial port
• PrintraNet software for transparently sending documents to
remote locations over the Internet
• lpd-Plus feature for providing multiple services with custom
setup and reset strings, text-to-PostScript conversion, and
character substitution
• Flash memory for easy updating of firmware via NetWare,
BOOTP, tftp (master or slave mode), DEC MOP, Banyan
VINES, or serial port
Introduction 1-3
Page 10

• AppleTalk spoofing capabilities for support of nonbidirectional parallel printers
• AppleTalk binary support on printers that support the HP
Tagged Binary Communications Protocol
• IP address configuration via DHCP, BOOTP, rarp, arp,
serial port, XAdmin, or remote console.
- IP security to restrict printing based on IP address
• Optional DEC LN03 emulation (XConnect II and XConnect
100 only)
TROY XCD External Print Server Models
The TROY XCD External Print Server family includes the
following models:
• Pony Print Server The Pony Print Server is the industry's
smallest full-featured external print server. It plugs directly
into the parallel port of the printer, and supports a 10baseT
Ethernet interface. The Pony Print Server is available in the
following models:
PPS-8S IPX/SPX, TCP/IP, AppleTalk, DLC/LLC,
PPS-8 IPX/SPX*, TCP/IP, AppleTalk, Direct
PPS-8N IPX/SPX, TCP/IP, AppleTalk, DLC/LLC,
*PPS-8 NDS support is limited to NPRINTER remote printer mode only
NetBEUI, Direct Mode IPX/IP, http
Mode IPX/IP, LAT, http
NetBEUI, Direct Mode IPX/IP, LAT,
VINES IP, http
• XConnect II. The XConnect II is an external print server
that supports the LAT, TCP/IP, NetWare, and AppleTalk
Introduction 1-4
Page 11

protocols. It features a high-speed parallel port, a serial port,
and both a thin Ethernet and UTP Ethernet connector. The
XConnect II is available in the following models:
XConnect II-8S IPX/SPX, TCP/IP, AppleTalk, DLC/LLC,
XConnect II-8 IPX/SPX*, TCP/IP, AppleTalk, Direct
XConnect II-8N IPX/SPX*, TCP/IP, AppleTalk, DLC/LLC,
XConnect II-8-LN03 XConnect II-8 with LN03 emulation option
*XConnect II-8 and XConnect II-8-LN03 NDS support is limited to
NPRINTER remote printer mode only
NetBEUI, Direct Mode IPX/IP, http
Mode IPX/IP, LAT, http
NetBEUI, Direct Mode IPX/IP, LAT,
VINES IP, http
• Pony 100 Print Server The Pony 100 Print Server is an
ultracompact print server that features both 100baseTX and
10baseT operation. It includes one parallel port and one
serial port and is available in the following models:
PPS100-8S IPX/SPX, TCP/IP, AppleTalk, DLC/LLC,
PPS100-8N IPX/SPX, TCP/IP, AppleTalk, DLC/LLC,
NetBEUI, Direct Mode IPX/IP, http
NetBEUI, Direct Mode IPX/IP, LAT,
VINES IP, http
• XConnect 100. The XConnect 100 features 100baseTX
capability for operation on 100 megabit/sec Fast Ethernet
networks. It can also work on 10baseT networks, so it is
ideal for users who plan to upgrade to 100baseTX in the
future. The XConnect 100 supports the same protocols as
the XConnect II, but has two high-speed parallel ports
instead of one. It is available in four models:
XConnect 100-8S IPX/SPX, TCP/IP, AppleTalk, DLC/LLC,
XConnect 100-8 IPX/SPX*, TCP/IP, AppleTalk, Direct
NetBEUI, Direct Mode IPX/IP, http
Mode IPX/IP, LAT, http
Introduction 1-5
Page 12

XConnect 100-8N IPX/SPX, TCP/IP, AppleTalk, DLC/LLC,
XConnect 100-8-LN03 XConnect II-8 with LN03 emulation option
*XConnect 100-8 and XConnect 100-8-LN03 NDS support is limited to
NPRINTER remote printer mode only
• XConnect II Lite The XConnect II Lite is a low-cost single
NetBEUI, Direct Mode IPX/IP, LAT,
VINES IP, http
parallel port print server that offers the same features as the
standard XConnect II, but has a single Ethernet connector
and supports only the TCP/IP and NetWare protocols
(XConnect II Lite Banyan models support VINES and TCP/
IP only). Models include:
XConnect IIL-T 10baseT; TCP/IP and IPX/SPX*
XConnect IIL-2 10base2; TCP/IP and IPX/SPX*
XConnect IIL-T-B 10baseT; TCP/IP and VINES IP
XConnect IIL-2-B 10base2; TCP/IP and VINES IP
*XConnect II Lite NDS support is limited to NPRINTER remote printer mode
only
TROY XCD External Print Server Advantages
Compared to competing products, TROY XCD print servers
offer the advantages:
• Support for the most protocols and network operating systems
in the industry. This allows TROY XCD print servers to be
used on virtually any network.
• Network management. TROY XCD offers more ways to
manage the print server, including proprietary Windows and
DOS-based utilities, Web browser management, HP
JetAdmin compatibility, and a powerful remote console.
• High performance. The TROY XCD print server family has
the highest overall throughput capabilities in the industry.
Introduction 1-6
Page 13
• More features. Capabilities like multiple services per port,
programmable setup/reset strings, IP security, and character
substitution allow TROY XCD print servers to handle
virtually any network printing situation.
Terminology
The term "TROY XCD external print server" in this manual
covers the Pony Print Server Plus, XConnect II, XConnect 100,
and XConnect II Lite. The term "XConnect II" is used to
represent either the XConnect II, II-LT, or II-LN03; the term
XConnect 100 means either an XConnect 100 or 100-LN03;
while the term "XConnect II Lite" designates either an
XConnect II Lite-T or XConnect II Lite-2 .
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This
device may not cause harmful interference and (2) this device
must accept any interference received, including interference
that may cause undesired operation.
The following information applies to the Pony Print Server Plus
(PPS-8S, PPS-8, and PPS-8N) only:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance to the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the
Introduction 1-7
Page 14
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiver.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Introduction 1-8
Page 15
2
Installing the Hardware
Overview
This chapter describes:
• How to connect a TROY XCD print server to your printer
• How to connect a TROY XCD print server to the Ethernet
cable
Before You Start
Before attempting to install a TROY XCD print server, first
make sure that you have completed installing your printer or
plotter as described in the appropriate documentation for the
device.
Unpacking and Handling
The TROY XCD print server shipping box contains the
following items:
• Pony Print Server Plus, XConnect II, Pony 100,
XConnect 100, or XConnect II Lite print server
• AC Adapter
• TROY XCD External Print Servers Administrator's Guide
Installation 2-1
Page 16
Although TROY XCD external print servers are designed to
withstand normal handling procedures, you should exercise
reasonable precautions when installing them, particularly
with regard to static discharge.
• Make sure that you are adequately grounded by touching a
bare metal part of the printer before starting the installation.
• Avoid moving around the work area in order to eliminate
static charge buildup.
• If possible, do not work on a carpeted area.
Step 1-a Setting the Switches
(XConnect II and XConnect II Lite)
Important Note: If you have an XConnect 100, Pony 100,
or Pony Print Server Plus, skip to Step 1-b below).
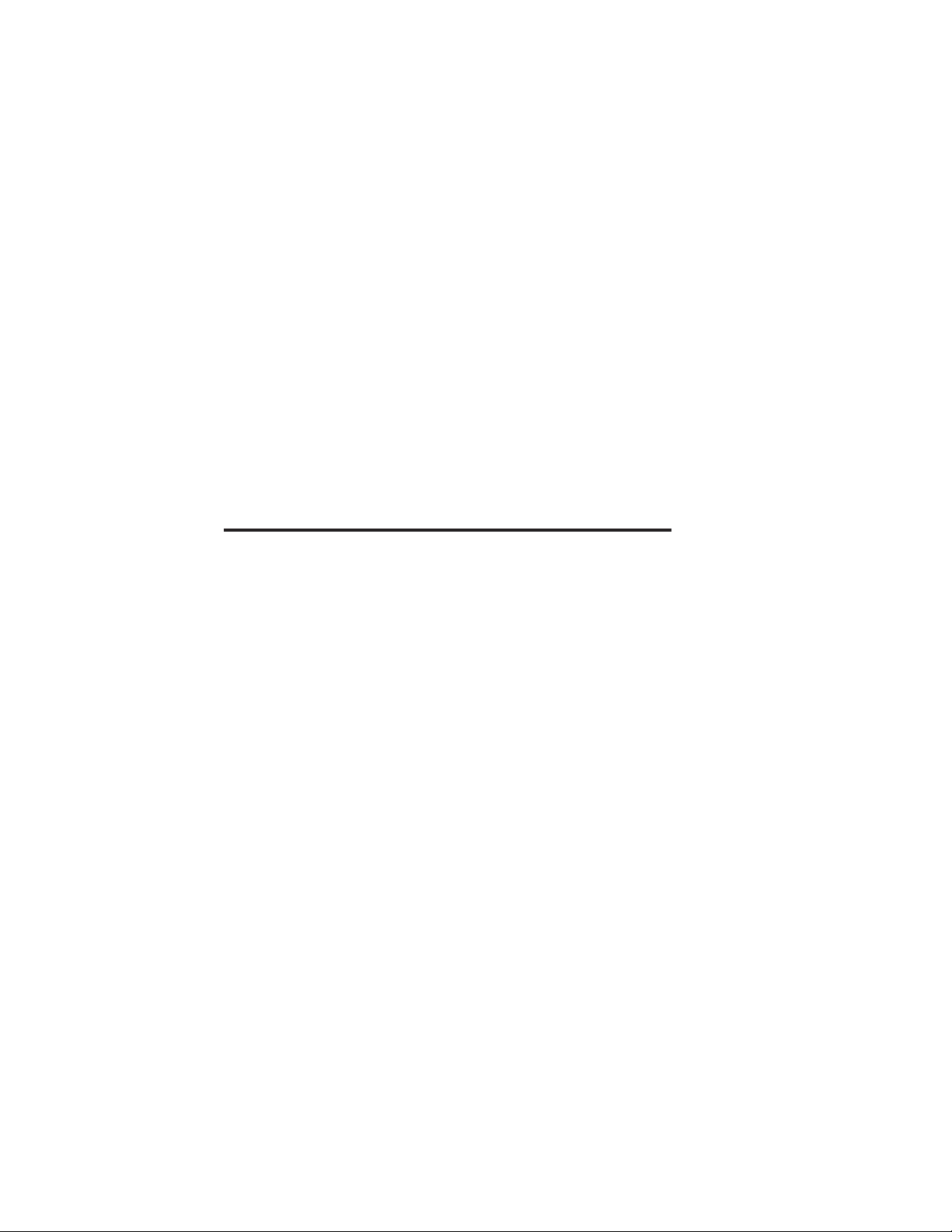
There are 4 DIP switches on one side of an XConnect II or
XConnect II Lite print server (see figure 2-1) that are used
for power-up options. As shipped, the two outside switches
are in the OFF (up) position and the two middle switches are
in the ON (down) position (OFF=0, ON=1) for operation on
either a 10baseT or 10base2 network with a printer attached
to the parallel port. If you want to configure the print server
in a different manner, use a small screwdriver or pen to
gently flip the switch as described in the following
paragraphs.
Switch 1 (Normal/Factory Default/Test)
Setting this switch ON allows you to restore the print server
parameter settings to their original factory settings. The next
2-2 Installation
Page 17
OFF
Sw2Sw1
Sw4Sw3
ON
XConnect II Rear View
Figure 2-1
XConnect II Switches
time the print server is powered on, the print server
parameters (for example, node name, serial port speed, etc.)
will be returned to the factory defaults. If you use this
switch, don't forget to put it back to the OFF position after
the factory default settings have been restored.
After the print server is powered on and running, this switch
can be used to print out a self-test page. This is done by
moving the switch to the ON position and then quickly
putting it back to the OFF position.
Switches 2 and 3 (10baseT/10base2)
These switches do not need to be changed from the default
ON position with newer versions of the XConnect II or
XConnect II Lite print server firmware. However, if you are
using 10baseT Ethernet, putting the switches in the OFF
Installation 2-3
Page 18
position will conserve energy by drawing less power from the
printer.
Note: With V3.22 or earlier firmware (included with
XConnect II and XConnect II Lite print servers shipped from
TROY XCD prior to September, 1995), switches 2 and 3
must both be in the OFF position for 10baseT operation or in
the ON position for 10base2 operation.
Switch 4 (Console/Serial Printer)
This switch defines whether the serial port will be used for a
console terminal or a serial printer. Leave switch 4 in the
default OFF position if you want to use the serial port for a
console terminal.
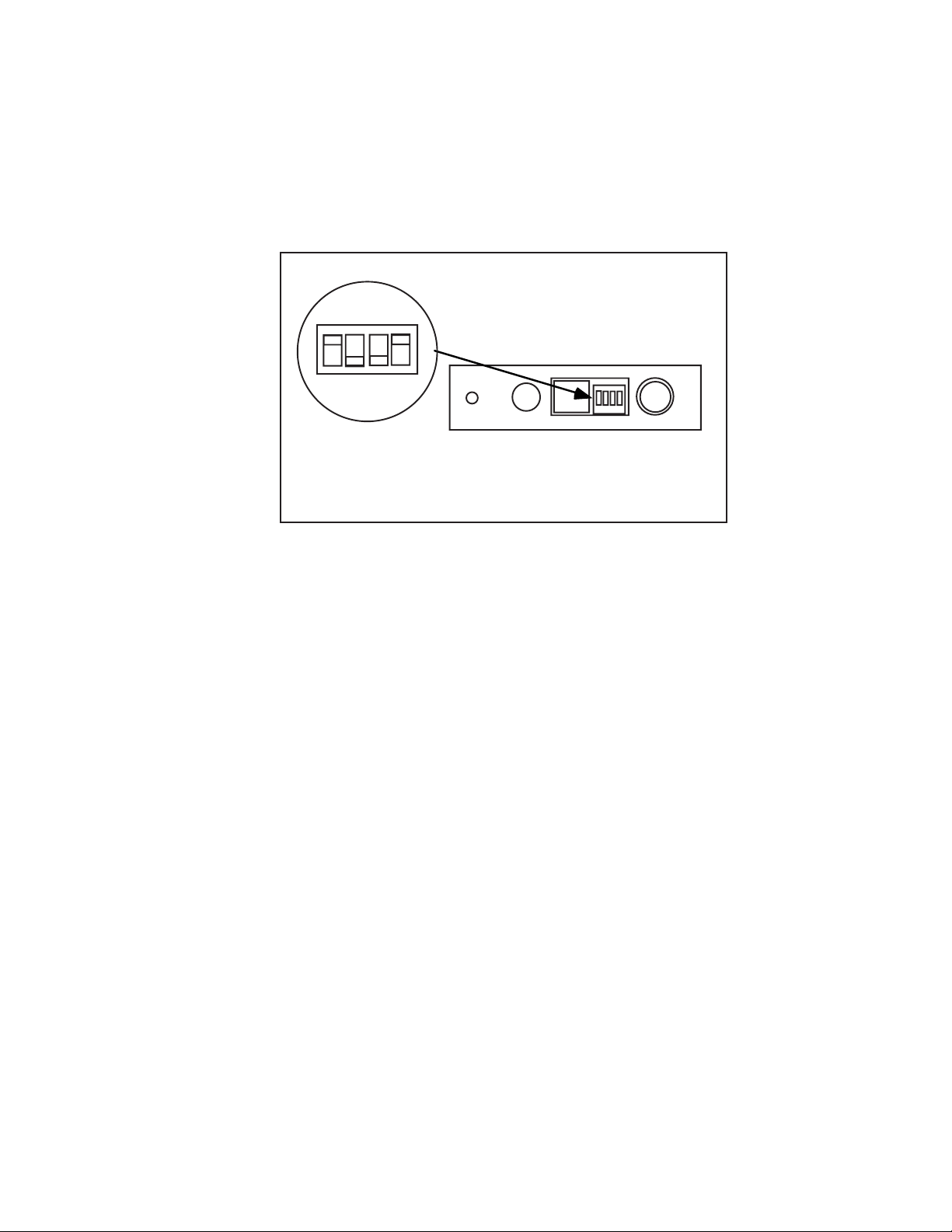
XConnect 100 Front View
Test LED
Test Switch
100baseTX/
10baseT
Connector
XConnect 100 Switch and LEDs
2-4 Installation
Link OK LED
XConnect 100 Rear View
Console/
Serial Port 1
Serial ports are 9-pin male D-connectors
Serial Port 2
Parallel Port 1
Figure 2-2
100baseTX LED
Parallel Port 2
Power Connector
Page 19
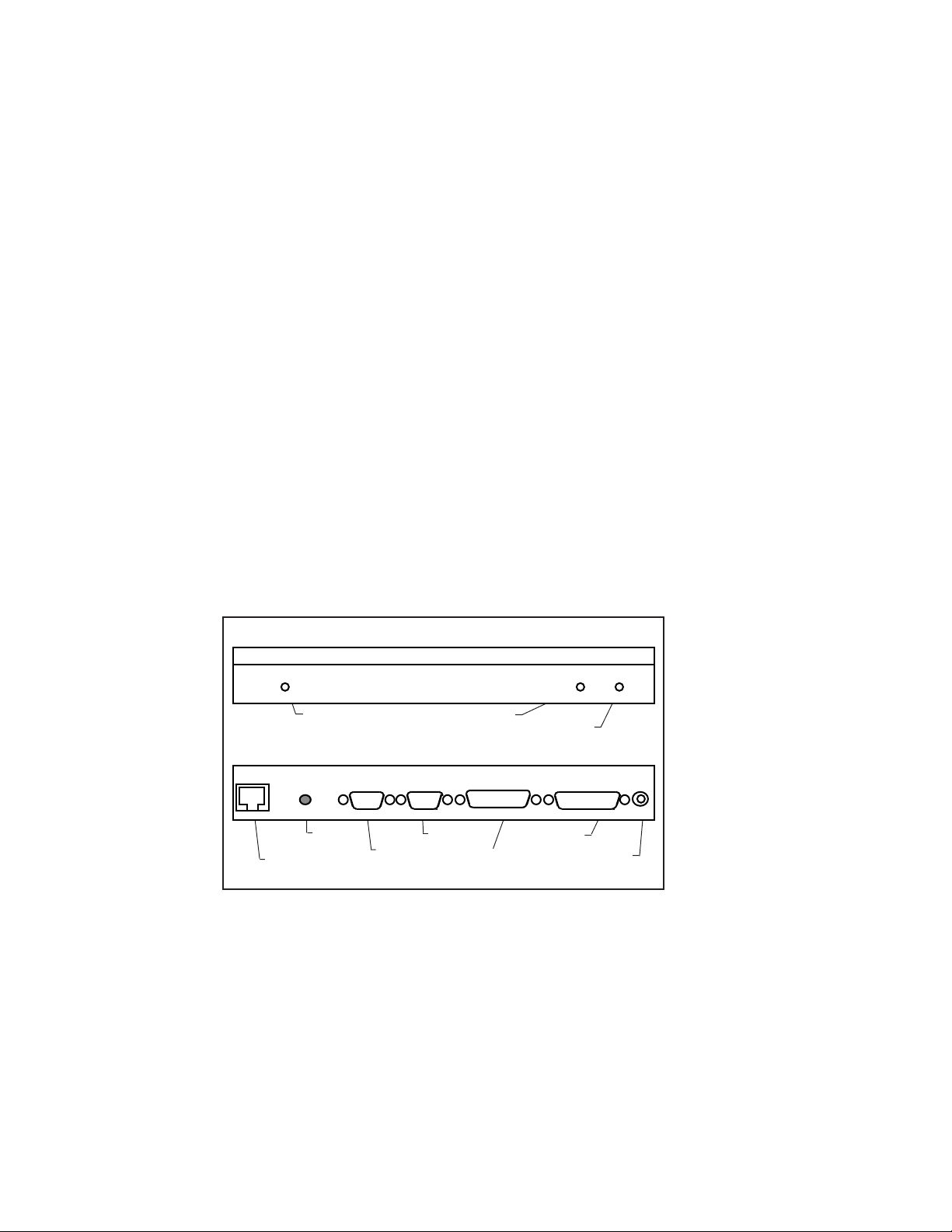
Power connector
100baseTX/10baseT
connector
Test/Factory
switch
Pony Print Server
Plus
Test LED (Top)
Test/Factory
switch
Serial port
Power connector
TEST LED Link LED
Pony 100
Figure 2-3
Pony Print Server Plus and Pony 100 Switches and LEDs
Step 1-b XConnect 100, Pony 100, and
Pony Print Server Plus Switches
Important Note: Skip this step if you have an XConnect II
or XConnect II lite.
The XConnect 100, Pony 100, and Pony Print Server Plus
have a single pushbutton switch test switch (see figures 2-2
and 2-3). This switch does not need to be used during the
configuration process. It has the following functions:
• To print a self-test page, press the switch in for at least
one-eighth second but less than five seconds.
• To reset the unit back to factory default settings, press the
switch and hold it in for at least 5 seconds
Installation 2-5
Page 20
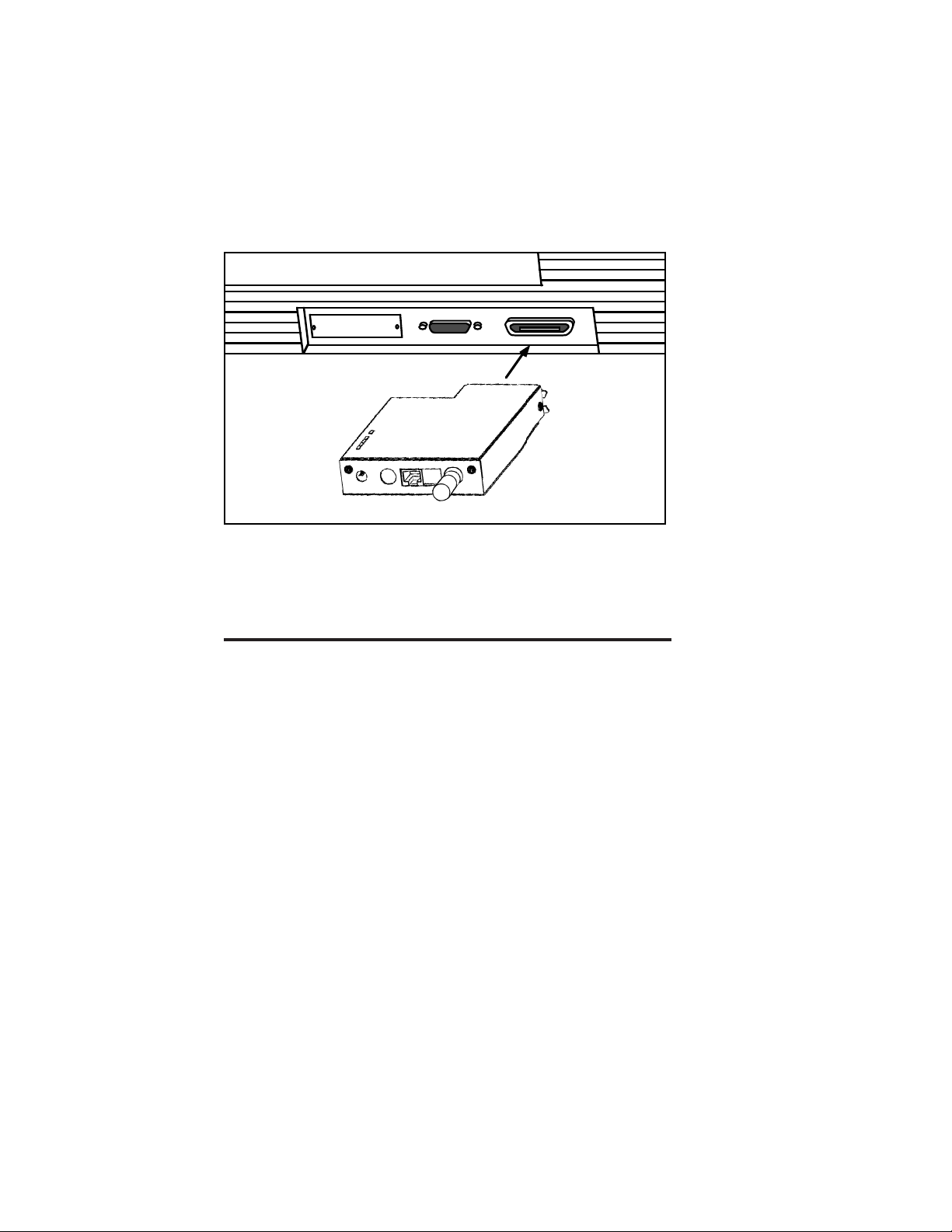
Figure 2-4
Connecting the XConnect II or XConnect II Lite to the
parallel port (Pony Print Server Plus and Pony 100
procedure is similar)
Step 2 Connecting to the Printer
TROY XCD print servers can connect to any of the
following types of printers:
• Printers with Centronics-compatible parallel interfaces
(this interface is by far the most popular type of parallel
interface)
• Printers with the new IEEE P1284 bidirectional parallel
interface
• Printers with RS-232 compatible serial interfaces (except
Pony Print Server Plus)
2-6 Installation
Page 21

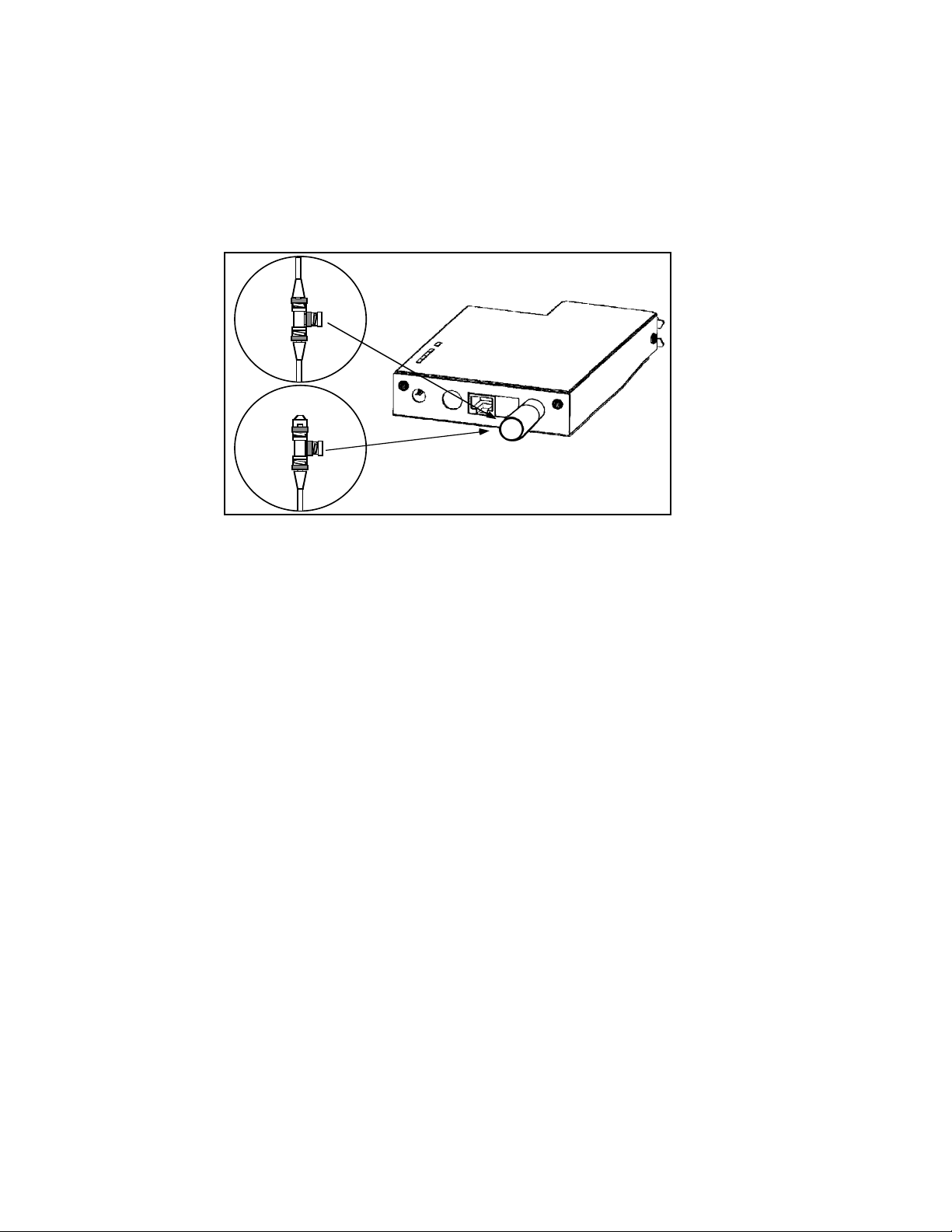
Connecting the Print Server to a Centronicscompatible printer
The XConnect II, XConnect II Lite, and Pony Print Server
Plus have a 36-pin male connector that is compatible with the
36-pin female connectors found on most printers. Simply
plug the print server directly into the connector on the printer
as shown in figure 2-4. If necessary, set your printer for
parallel port operation. No cable is generally required, but
the optional CABLE-CEN2 Centronics male-to-female cable
is available as an option in the event you cannot connect the
print server directly to the printer's Centronics connector.
The XConnect 100 has two 25-pin female connectors that are
compatible with the IBM PC standard 25-to-36 pin
Centronics cable. This cable is available at any computer
store and most office supply stores, or it can be ordered from
TROY XCD (part number CABLE-CEN).
IMPORTANT NOTE: The XConnect II, XConnect II Lite,
and XConnect 100 support a maximum parallel cable length
of 1.75 meters (six feet). Exceeding this maximum may result
in printing problems.
NOTE: Some new printers, such as the HP LaserJet 8000,
have the IEEE 1284C miniature Centronics connector instead
of the normal 36-pin Centronics connector. TROY XCD
offers the CABLE-C/B adapter cable for the XConnect II,
XConnect II Lite, and Pony Print Server Plus, and the
CABLE-C/A for the XConnect 100 to accommodate such
printers.
Maximizing Performance (Recommended)
Some printers, such as most HP LaserJets, support a highspeed handshake mode on the parallel port. TROY XCD
Installation 2-7
Page 22

print servers support this mode, which can result in up to 50
per cent higher performance. To enable this mode using
WebXAdmin, select Configure Port from the main menu,
select port P1 (or P2 for the second parallel port on the
XConnect 100), choose High Speed as the Output Method,
and click Submit. If you are using the print server console,
enter the command SET PORT P1 FSTB ENABLED.
WebXAdmin and the print server console are discussed in
Chapter 3 and Appendix B of this manual.
Connecting a TROY XCD Print Server to a
Serial Printer
The Pony 100, XConnect II and XConnect II Lite have an
RJ45 connector for connecting RS-232-compatible serial
printers, while the XConnect 100 has two standard PCcompatible 9-pin D-connectors (there is no serial port on the
Pony Print Server Plus). The XConnect II and XConnect II
Lite RJ45 connector is marked "Serial"; do not confuse it
with the 10baseT unshielded twisted pair connector, which
is also an RJ45.
Most printers use a DB25 connector for the serial
connection. Unfortunately, there are a number of variations
as to how this connector is implemented on different
printers. For example, some printers have male connectors
configured as a DTE (Receive Data on pin 3), while others
have DCE female connectors (Receive Data on pin 2).
Hewlett-Packard, Lexmark, and Apple printers generally
have female DTE connectors. You must consult the manual
for your printer in order to determine what type of adapter
cable you need. TROY XCD sells a variety of adapters for
connecting serial devices to the RJ45 connector. In the case
of the XConnect 100 9-pin connector, a null modem( a
2-8 Installation
Page 23
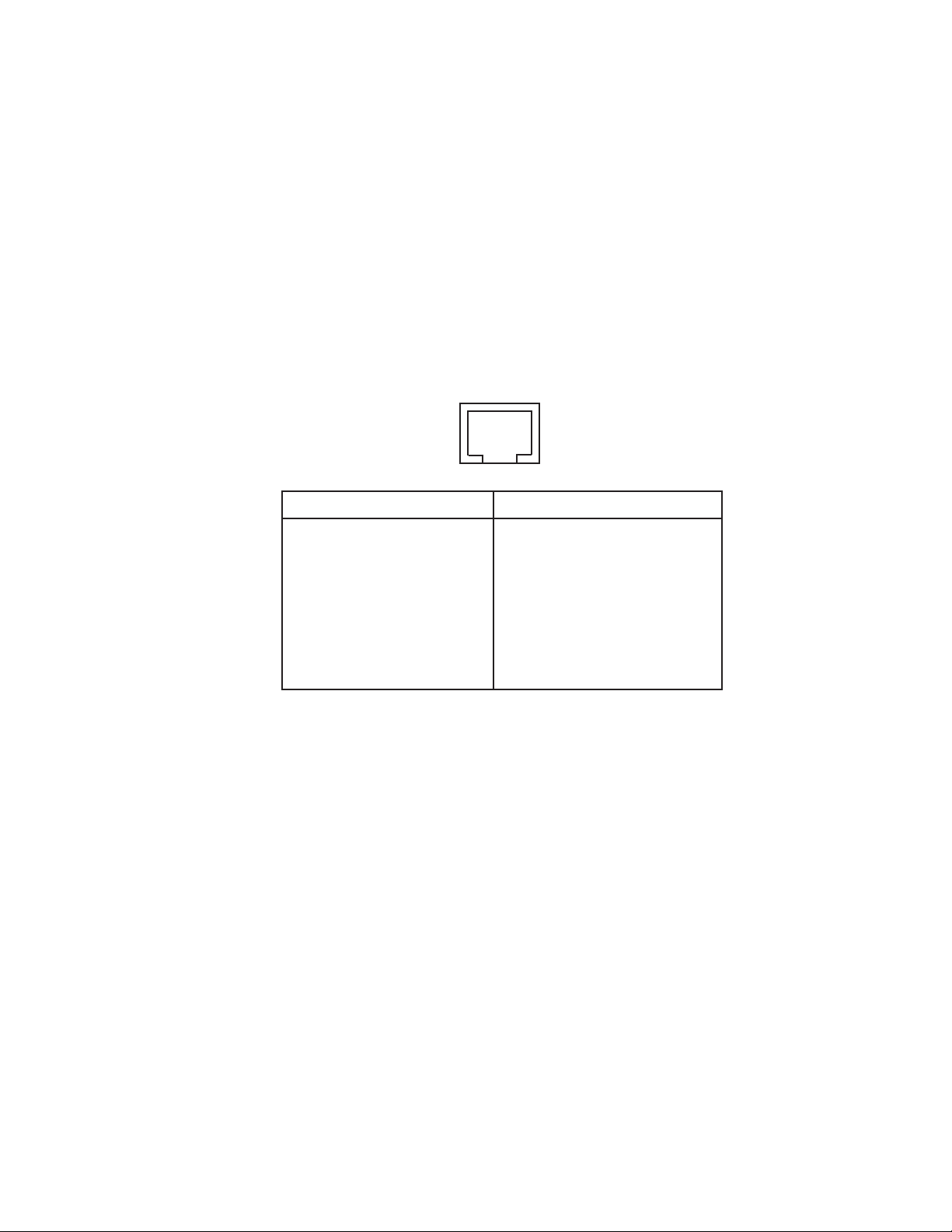
device or cable that connects the input signals on one device
to the output signals on another device) is often required since
both the printer and the print server are usually DTE devices.
The pinouts for the Pony 100, XConnect, and XConnect II
Lite RJ45 connector are shown below:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Print Server (RJ45)
RJ45 DTE DCE
pin Signal Signal pin pin
1 RTS out* CTS in 5 4
2 DTR out* DSR in 6 20
3 Transmit Data Receive Data 3 2
4 Transmit return Signal Ground 7 7
5 Receive Return Signal Ground 7 7
6 Receive Data Transmit Data 2 3
7 DSR in* DTR out 20 6
8 CTS in* RTS out 4 5
*XConnect II models with serial numbers less than 40500 have RTS on pin
8, DTR on pin 7, DSR on pin 2, and CTS on pin 1.
Printer (DB25)
The XConnect 100 serial ports use PC-compatible 9-pin male
D-connectors. Note that the standard off-the-shelf 9-pin
female to 25-pin male PC cables will require a null modem in
order to connect to most printers or terminals. The pinouts
are as follows:
Installation 2-9
Page 24
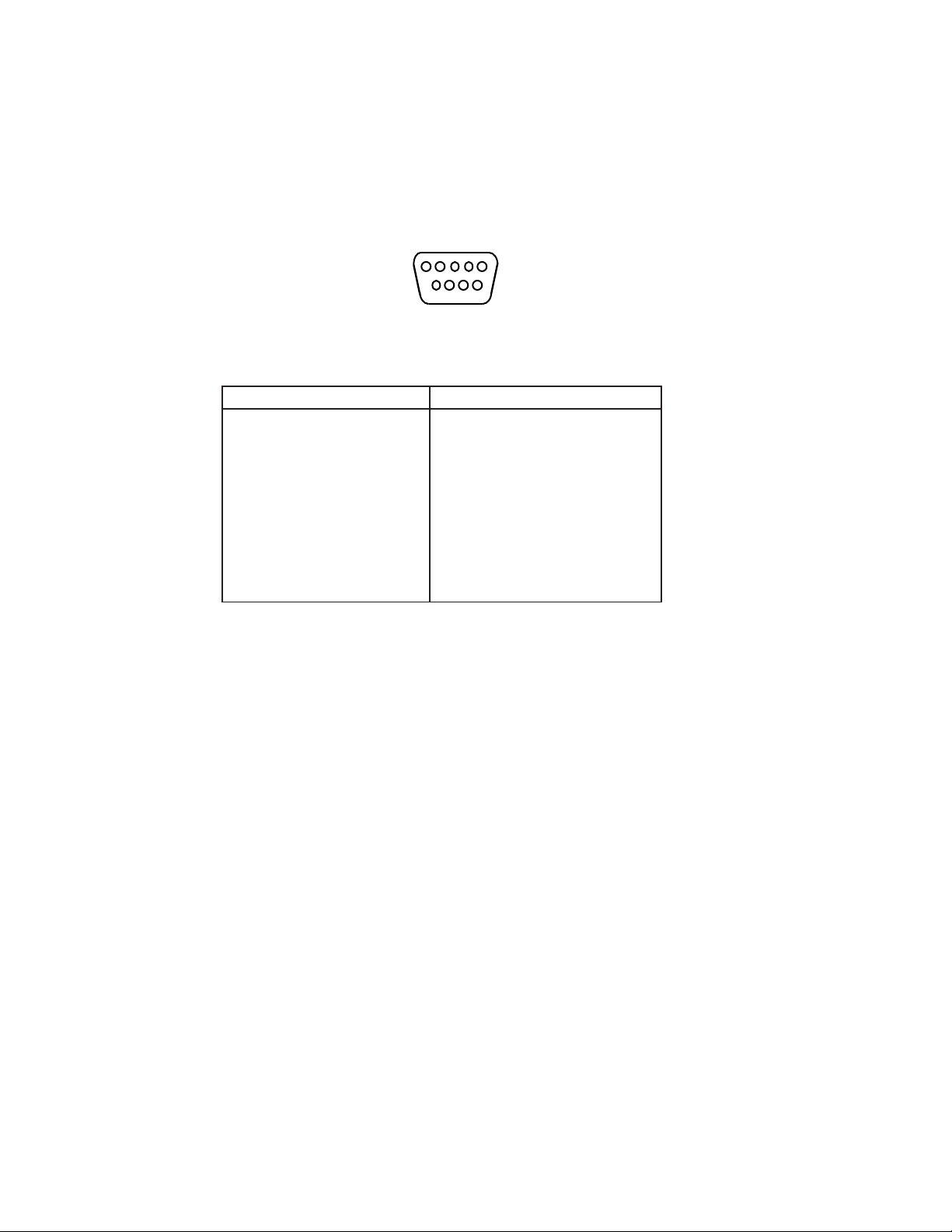
6 7 8 9
DE9 Male
(female pinouts are in
reverse order)
XConnect 100 (DE9) Printer (DB25)
DE9 DTE DCE
pin Signal Signal pin pin
1 Not used Not used - 2 Receive Data Transmit Data 2 3
3 Transmit Data Receive Data 3 2
4 DTR out DSR in 6 20
5 Signal Ground Signal Ground 7 7
6 DSR in DTR out 20 6
7 RTS out CTS in 5 4
8 CTS in RTS out 4 5
9 Not used Not used - -
Basically, the cable must connect input signals (e.g., Receive
Data) on the TROY XCD print server to the equivalent
output signals (e.g., Transmit Data) on the device and viceversa.
If you are connecting a printer to the second serial port (S2)
on the XConnect 100, you must first disable console mode on
that port. This is done by using the console command SET
PORT S2 CONSOLE DISABLED
EXIT to exit the console (refer to Chapter 3 and Appendix A
for information on using the console). To re-enable the
console function, you must either enter the command SET
PORT S2 CONSOLE ENABLED
the TROY XCD XCONFIG NetWare utility, or reset the unit
back to factory defaults.
and then typing the command
using TELNET, DEC MOP or
2-10 Installation
Page 25

The serial ports are factory set at 9600bps, 8-bit data, XON/
XOFF flow control, and no parity. If your printer requires
different settings, you must use WebXAdmin or the console
terminal (refer to Chapter 2 and Appendix A for information
on how to use these utilities) to change the settings. With
WebXAdmin, select Configure Port from the main menu,
click on the serial port (S1 for first serial port or S2 for the
XConnect 100 second serial port), choose the desired
settings, and click Submit. With the console terminal, use
one or more of the following commands (use S2 instead of S1
if you are using the second serial port on the XConnect 100):
SET PORT S1 SPEED
SET PORT S1 PARITY
SET PORT S1 FLOW
SET PORT S1 CHARACTER
baudrate
parity_type
flowctrl
charsize
Note that the serial port always operates at 9600bps when in
console mode. Also, if you are using 115200bps on one port
of the XConnect 100, you cannot set the other port to 230400
bps (57600bps and 7200bps are not supported on either port).
Important: The serial ports do not support Direct Memory
Access (DMA). Therefore, sustained transfers at high baud
rates (115200 or greater) can lock out activity on other
ports.
Don't forget to set your serial port settings on your printer to
match the settings of the print server. Also, make sure that
the XConnect II or XConnect II Lite switch 4 (console/serial
printer) is in the proper position (OFF if you are using the
serial port for a console terminal or ON if you are using it to
connect a printer.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Early versions of the XConnect 100 do
not support the second serial port (the one marked "Console/
Installation 2-11
Page 26
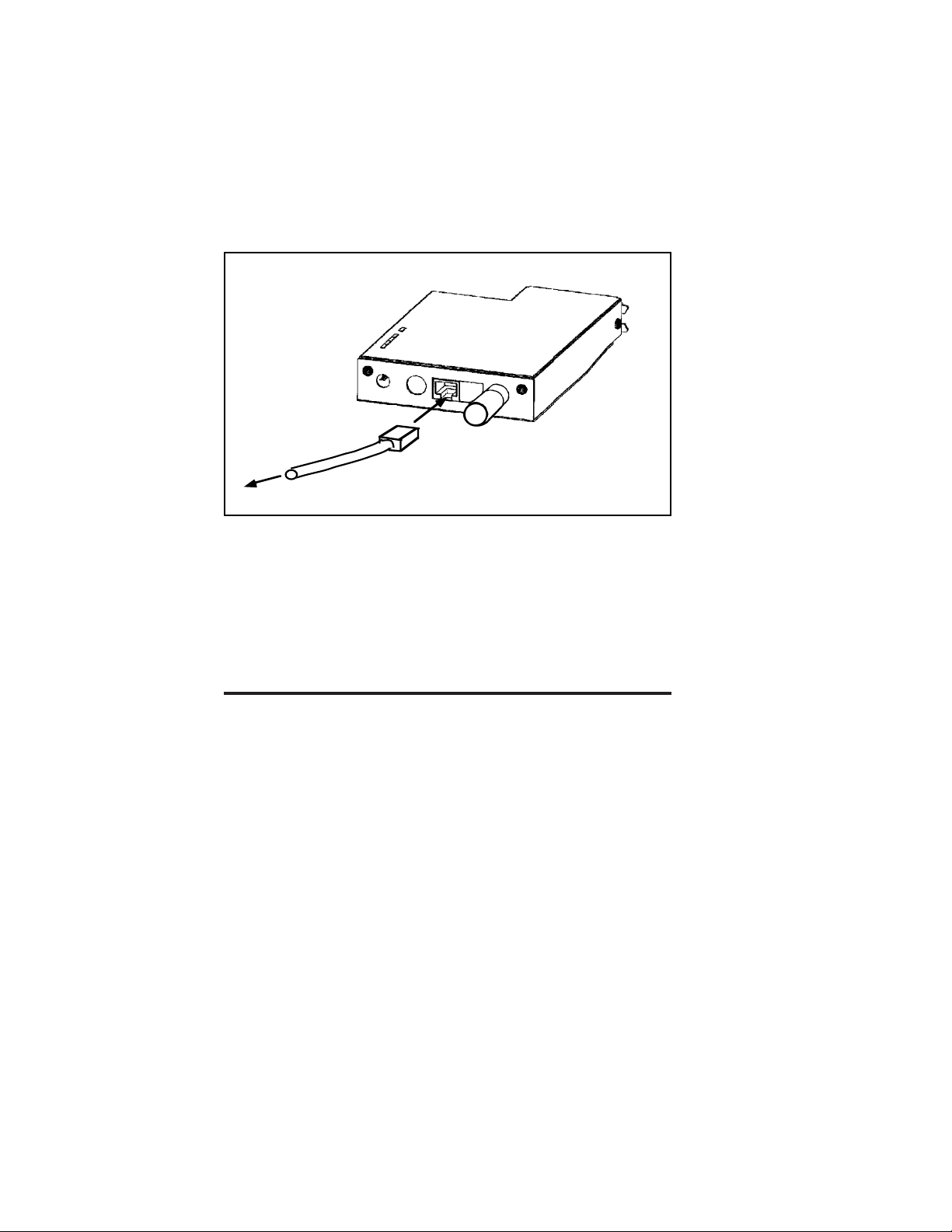
unshielded
To hub
Connecting the Print Server to a 10baseT UTP network
twisted pair cable
Figure 2-4
Serial 2) for use with serial printers. This limitation can be
fixed by upgrading to a newer version of the firmware.
Step 3 Ethernet Installation
The XConnect II can connect directly to either a 10baseT
unshielded twisted pair Ethernet or a 10base2 thin Ethernet.
The XConnect II Lite-2 can connect to a 10base2 thin
Ethernet, while the XConnect II Lite-T and the Pony Print
Server Plus can connect to a 10baseT Ethernet.
The Pony 100 and XConnect 100 connect to either a
100baseTX Fast Ethernet network or a 10baseT Ethernet
network. It automatically senses the type of network, so no
configuration is required.
2-12 Installation
Page 27

Connecting the XConnect II, XConnect 100,
XConnect II Lite-T, Pony 100, or Pony Print
Server Plus to an Unshielded Twisted Pair
Network
To connect an XConnect II, Pony 100, XConnect 100, or
XConnect II Lite-T to a 10baseT unshielded twisted pair
(UTP) Ethernet network, you will need an unshielded twisted
pair Ethernet hub with at least one unused port installed on
your network, plus an appropriate length of RJ45 modular
cable.
To connect a Pony 100 or XConnect 100 to a 100baseTX
Fast Ethernet network, you will need a 100baseTX Fast
Ethernet hub with at least one unused port, plus an
appropriate length of Category 5 RJ45 modular jack cable.
1. Connect one end of the RJ45 cable to the print server
connector labelled "10baseT" on the XConnect II or
XConnect II Lite (not the one labelled "Serial"), or
"100baseTX/10baseT" on the XConnect 100 or Pony 100
and the other end to a port on the twisted pair Ethernet
hub as shown in figure 2-4. Note that the XConnect 100
automatically determines whether it is connected to a
10baseT or 100baseTX network.
Note: If you have an older XConnect II or XConnect II
Lite with V3.22 or earlier firmware, make sure that
switches 2 and 3 are in the OFF position (not required
for newer print servers).
You have now completed the unshielded twisted pair
Ethernet installation. Proceed to the Verifying Successful
Hardware Installation section below to confirm that you
have properly installed the print server.
Installation 2-13
Page 28
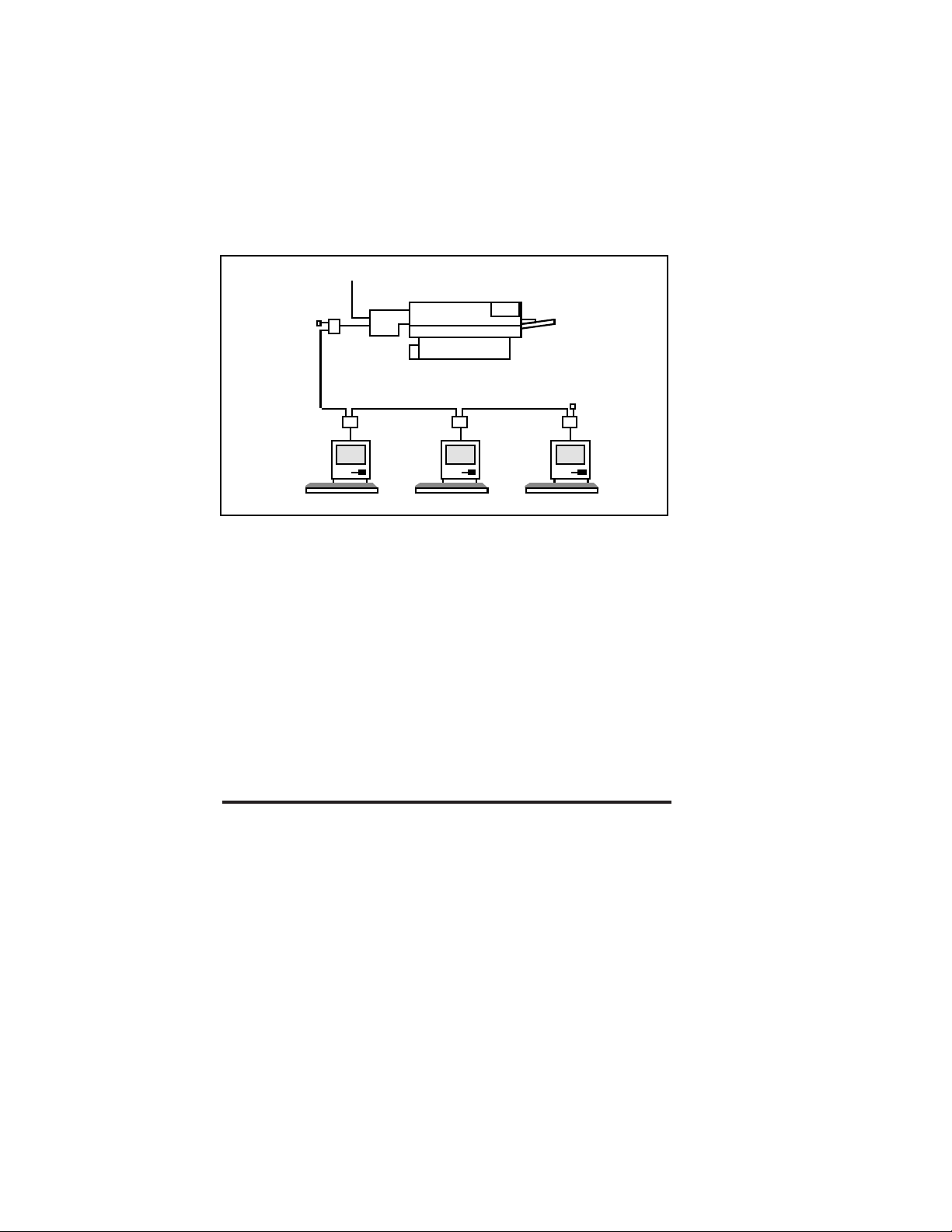
Thin
Ethernet
Cable
Thin
Ethernet
Cable
A
"T"
50 ohm
Terminator
Thin
Ethernet
Cable
"T"
B
H1000
Figure 2-5
Connecting the Print Server to a 10base2 thin Ethernet network
Connecting the XConnect II or XConnect II Lite-2
to a Thin Ethernet Network
To connect an XConnect II or XConnect II Lite-2 to a thin
Ethernet network, first check to see that switches 2 and 3
(10baseT/10base2) are in the ON position.
If you are installing the print server onto an existing network,
the "T" connector may already be installed on the cable. If
this is the case, simply connect the "T" connector to the BNC
connector on the print server's BNC connector as shown in
figure 2-5A (if the connection is in the middle of the thin
Ethernet segment) or 2-5B (if the connection is at the end of
the thin Ethernet segment). This operation can be performed
without impacting the operation of the network.
If the "T" connector is not already installed, proceed as
follows (caution: if you are connecting to a live network,
2-14 Installation
Page 29
perform the following steps as quickly as possible to
minimize disruption of the network):
1. Connect one section of the thin Ethernet cable to one end
of the "T" connector as shown in figure 2-5.
2. If you are connecting the print server in the middle of a
thin Ethernet segment, attach the second section of thin
Ethernet cable to the other end of the "T" connector as
shown in figure 2-5A. If you are connecting the print
server at the end of a thin Ethernet segment, attach a 50
ohm terminator to the other end of the "T" connector as
shown in 2-5B.
3. Connect the "T" connector to the BNC connector on the
transceiver.
You have now completed the thin Ethernet installation. Skip to
the Verifying Successful Hardware Installation section below to
confirm that you have correctly installed the print server.
Step 4 Connecting to the Optional
LocalTalk Port (XConnect II only)
If you have the LocalTalk option, you can connect the
XConnect II to an Apple LocalTalk network to allow
Macintosh computers on the LocalTalk network to print jobs
on a printer attached to the XConnect II. Both the LocalTalk
and Ethernet ports can be used simultaneously. To use the
LocalTalk feature, plug a LocalTalk-compatible connector
(such as the Apple LocalTalk connector or the Farallon
PhoneNet connector) into the XConnect II LocalTalk port as
shown in figure 2-6. Note this port can only be used for
Installation 2-15
Page 30
LocalTalk
Connector
(must be
terminated
if end node)
Ethernet
XConnect II
LocalTalk
Connector
LocalTalk
Connector
LocalTalk
Connector
Figure 2-6
Connecting the XConnect II to a LocalTalk network
printing from computers on the LocalTalk to printers
attached to the parallel or serial port of the XConnect II; it
cannot be used to allow computers on the Ethernet to print to
printers connected to the LocalTalk network.
The LocalTalk port is enabled by default. If you are not
using this port, you should enter the command SET
LOCALTALK DISABLED for maximum performance.
Step 5 Verifying Successful Installation
You are now ready to apply power to the TROY XCD print
server. Plug the AC power adapter into a wall outlet and
insert the adapter cable into the print server connector
labelled "Power". If possible, connect a terminal to the serial
port (make sure that Switch 4 is OFF when using the console
terminal with the XConnect II or XConnect II Lite).
2-16 Installation
Page 31

The TROY XCD print server will go through the following
startup sequence:
1. It will run through a set of power-up diagnostics for a
few seconds. If the print server is operating properly, the
TEST LED will blink momentarily and then go out. If
the TEST LED blinks continuously in a regular pattern,
there is a problem. If this is the case, first verify that you
have a good Ethernet connection and then try powering the
unit off and then on again. If the problem persists, refer to
the Troubleshooting chapter in this manual.
2. When the test LED goes out, the other LEDs on the print
server will come on as follows:
• On the XConnect II and XConnect II Lite, the LINK
LED will blink to show activity on the network. The
XMIT and RCV LEDs will come on solid if there is a
valid 10baseT connection (they are not used with
10base2).
• On the XConnect 100, the Link OK LED will blink if
the print server detects activity on the network. The
100baseTX LED will come on if a valid 100baseTX
connection is detected (this LED will not come on if
10baseT is used).
• On the Pony 100, the Link LED will come on solid if
there is a valid 10baseT or 100baseTX connection.
• On the Pony Print Server Plus, the LED will blink
randomly.
If the LEDs do not come on as described, there may be a
cabling problem or a bad hub port; if this is the case, try a
different cable and/or hub port.
Installation 2-17
Page 32

Verifying the Connection to the Printer
Before attempting to print, it is very important to verify the
connection between the print server and the printer. If this
connection is not good you will not be able to print!
To verify this connection, make sure that both the print
server and the printer are powered on and ready.
• If you have an XConnect II or XConnect II Lite, push
switch 1 (Normal/Factory/Test) on the print server to the
ON position and then back to the OFF position.
• If you have an XConnect 100, Pony 100, or Pony Print
Server Plus, push the Test button in briefly (more than
on-eighth second but less than five seconds).
If the connection is good, a test page will be printed on the
printer. If nothing prints out, make sure that the cable is
good and that it is securely fastened. If possible, try a
different cable. If you have an XConnect II, XConnect II
Lite, or XConnect 100, make sure that you are not exceeding
the 1.75 meter (6 foot) cable length restriction. If the cable
is OK but you still can't print the self-test page, you may
need to adjust the parallel port settings as described in the
next section.
Important Note: The test page only works with printers
that can directly print PCL, PostScript, or text. It will not
work with some low-end "Windows" printers like the HP
DeskJet 820 (which does the image rasterization in the PC),
nor will it work with HP-GL/2 or RTL plotters (unless the
PostScript option is installed). For such devices, you must
print a job from an appropriate application program in order
to test the print server-to-printer connection.
2-18 Installation
Page 33

If you are using the serial port and the test page does not
print, verify that the baud rate, parity, and character size
match on the print server and the printer. If you have an
XConnect II, make sure that switch 4 is in the ON position.
If you have an XConnect 100 and you are using the second
serial port, make sure that you have disabled console
operation via the SET PORT S2 CONSOLE DISABLED
command.
If none of the above suggestions work, contact TROY XCD
Technical Support (949-399-0820; http://www.troyxcd.com; email: support@troyxcd.com) for additional assistance.
Adjusting the Parallel Port Settings for Specific
Printers (Recommended)
The parallel port on all new TROY XCD print server models
is set by default to automatically configure itself to work
with the printer's parallel port However, it may sometimes
be necessary to adjust the print server's port settings to work
with specific printers by using the print server console or
WebXAdmin. This is particularly true with older printers.
The particular settings include:
1. pACK handshake. Older non-1284 printers require this
hardware handshake and may not operate with the newer
1284 handshake. Use the console command SET PORT
P1 ACKH ENABLED
to enable the pACK handshake.
2. DMA (Direct Memory Access). The XConnect II and
XConnect 100 use DMA for maximum performance.
However, some printers cannot handle the high data
rates. For such printers, use the console command SET
PORT P1 DMA DISABLED. Alternatively, you may
disable DMA using the Configure Port option in the
WebXAdmin menu,
Installation 2-19
Page 34

3. Bidirectional. Some printers will not operate properly if
bidirectional communications is enabled on the print
server. To disable bidirectional, use the console
command SET PORT P1 BID DISABLED, or disable it
from the WebXAdmin
4. Some printers, like most Okidata laser printers, cannot
operate fast enough even in 1284 mode to keep up with a
TROY XCD print server. On the Pony Print Server Plus
you can enable a software handshake to handle such
printers via the SET PORT P1 SWIO ENABLE console
command.
The print server console and WebXAdmin are discussed in
Chapter 3, with additional information on console commands
in Appendix B. If you are using WebXAdmin, click on
Configure Port in the main menu, select the desired port, and
then select the desired function. After you have made your
selections, click on Submit to enable them in the print server.
Step 6 Changing the Print Server Reset
(Recommended)
The printer reset is a sequence of characters that is sent to the
printer after the job is completed. It ensures that the last
page of the job is ejected from the printer and that the printer
is reset to its default state so that the next job will properly
print.
The default printer reset for TROY XCD external print
servers is a null, except on the TCP/IP text service, which
has <Formfeed> as the default (see chapter 4 and Appendix
B for information on the TCP/IP text service). A null reset
means that some print jobs may not be ejected upon
2-20 Installation
Page 35

completion. Some operating systems, such as NetWare,
provide the ability to insert a reset sequence at the end of
each job, in which case the TROY XCD print server null
reset is adequate. Also, Microsoft Windows printer drivers
typically provide a printer reset at the end of each job. But
for those operating systems that do not provide this reset
capability, TROY XCD print servers provide the ability to
customize the printer reset to meet the requirements of
virtually any type of printer.
The following predefined reset strings are available.
No. Definition Printer
1 Null (use if no reset is desired)
2 <ESC>E PCL printer
3 CTRL-D PostScript printer
4 <ESC>%-12345X PJL (use with newer HP and
11 <Formfeed> General
Lexmark/IBM printers)
Refer to your printer documentation if you do not know the
proper reset string. Use the null string if you are planning to
reset the printer from the host software (for example, from a
Windows driver). If you want to define a new reset string,
refer to Appendix B, Using Services.
Note that you can put a printer reset either before or after
each job, although generally the reset goes at the end the job.
TROY XCD print servers allow you to define multiple
services for a given port. This is useful, for example, if you
want to use different reset strings with the same printer. For
example, you might want to define a service for UNIX jobs
that contains a <ESC-E> reset, and a different service for
NetWare that has no reset.
Print jobs are normally sent to service 1 (XCD_xxxxxx_P1,
where "xxxxxx" is the last six digits of Ethernet address, for
Installation 2-21
Page 36

all protocols except LAT, TCP/IP, and AppleTalk) or service
2 (BINARY_P1, for LAT and TCP/IP). Refer to Appendix B
and the individual protocol chapters for additional
information on services.
To change the printer reset on a TROY XCD print server
with XAdmin, double click on the print server name, click on
the Services tab, double click on the desired service, and
then select the appropriate Printer Control String. With
WebXAdmin, click on Configure Service, and select the
desired service, choose the appropriate reset string, and then
click Submit.
Alternatively, you may use the print server console by typing
in the following command:
SET SERVICE
servicename
EOT
stringno
where "servicename" is the name of the service (do a
SHOW SERVICE command for a list of services) and
stringno is the number of the string. For example to use
string 3 (the PostScript CTRL-D reset) on the default
parallel port service, you would enter:
SET SERVICE BINARY_P1 EOT 3
Changing the Print Server Configuration
(Optional)
In addition to changing the printer reset string, you can
modify the TROY XCD print server configuration in a
number of other ways. The procedure and commands for
changing the configuration are described in Appendix A.
2-22 Installation
Page 37

3
TROY XCD Print Server Management Methods
Overview
TROY XCD offers a wide variety of ways to configure and
monitor the print server. These methods include:
• TROY XCD XAdmin Windows-based utility
• TROY XCD WebXAdmin Web-browser utility
• TROY XCD print server console
• HP JetAdmin Windows-based utility
• HP Web JetAdmin Web-browser utility
This chapter discusses the installation and the basic usage of
these utilities. Refer to the various chapters of this manual
for specific details on configuring the print server.
TROY XCD XAdmin
TROY XCD offers two graphical utilities for configuration
and management of TROY XCD print servers:
• XAdmin32. This 32-bit version works on either Windows
NT 4.xx or Windows 95/98 using the TCP/IP or IPX/SPX
protocols. To take full advantage of the capabilities of
XAdmin32, you should use the Novell 32-bit client
software on the PC workstation that is used for
configuring the print queues.
• XAdmin. This 16-bit version works on Windows 3.1 and
Windows 95 for NetWare and Banyan VINES.
Management Methods 3-1
Page 38

To install XAdmin32 or XAdmin, insert the appropriate
diskette or CD-ROM in the computer, select Run from the
Windows menu, select Browse, choose the appropriate drive
(these programs are in the Utilities folder if you are using a
CD-ROM), and double click on Setup.exe and then click
OK.
Note: XAdmin32 and other TROY XCD utilities are
available on the TROY XCD web site (http://
www.troyxcd.com
) if you did not receive them on disk.
1. Follow the instructions on the screen to complete the
installation.
2. Double click on the XAdmin icon or use the Windows
95/NT 4.x Start button to select XAdmin in the XCD
folder in the list of Programs.
3. A list of configured print servers will appear. If you
are running XAdmin or if you are running NetWare
with XAdmin32, skip to step 4. If you are running
TCP/IP, then you must enter an IP address into the print
server as follows (refer to Chapters 4 or 7 for alternate
methods for configuring the IP address):
- Make sure that your computer is configured for
TCP/IP with a valid IP address configured for LAN
operation (not PPP dial-up; refer to your system
documentation for additional information).
Important Note: Consult your system manager
before assigning IP addresses to your computer or to
the print server in order to avoid duplications. If
your network does not have an officially assigned
3-2 Management Methods
Page 39

block of IP addresses, you may use any unique
address between 192.168.254.1 and
192.168.254.254 (this is a reserved range of Class C
addresses for private networks that are not
connected to the Internet per RFC 1918; note that
you must also assign the print server an IP address
in this range). You may also use a subnet mask of
255.255.255.0 with no gateway address. If you
have more than one LAN adapter card, select the
one you want to use for TCP/IP.
- Click on the TCP/IP folder icon under "Filter" on
the left side of the XAdmin screen.
- Click on the Search button (the leftmost button) or
select Devices and then Search Active Devices
from the menu bar.
- If you have a DHCP, BOOTP, or rarp server (or if
the print server already has an IP address from some
other source), the print server should appear in the
list of configured print servers. If this is the case,
skip to step 4.
- If the print server does not have an IP address, then
click on the Setup Unconfigured Devices button
(the third from the left) or select Devices and then
Setup Unconfigured Devices from the menu bar.
This will display the unconfigured print servers
listed by their Ethernet address (MAC Address).
Double click on the desired print server to configure
it.
- Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway and
click OK.
Management Methods 3-3
Page 40

- The list of unconfigured print servers will again be
displayed. Click on Close to return to the main
screen.
- The print server should show up on the main
XAdmin32 screen (the default name will be
XCD_xxxxxx, where "xxxxxx" is the last six digits of
the Ethernet address). If the print server does not
appear on the main screen, click on the Search
button to find new print servers.
4. To configure a print server, double click on its name
and enter the password (ACCESS is the default
password). A series of "index cards" will be
displayed. Each of these "cards" represents a protocol
or other configurable item. Click on the appropriate
tab to configure the item.
TROY XCD WebXAdmin
WebXAdmin allows the user to configure the print server
with a standard web browser like Netscape Navigator or
Microsoft Internet Explorer. It can therefore be used on any
operating system that supports web browser capabilities. To
use WebXAdmin, you must first make sure that you have a
web browser installed on your computer and that you have
configured an IP address in both the computer and the print
server (refer to the previous XAdmin section if you do not
know how to put an IP address in the print server). Also
make sure that you have configured your TCP/IP stack to
communicate over the local area network (rather than via a
PPP dial-up connection).
To use WebXAdmin, start your web browser and enter the IP
address of the print server as the destination web site. Once
3-4 Management Methods
Page 41

you are connected, enter the password (ACCESS is the
default password) and select the protocol or other item that
you wish to configure. You will then be connected to the
appropriate web page for configuration of that item. You
may use the normal browser buttons to move forward and
back through the web pages.
TROY XCD Print Server Console
All TROY XCD print servers support a sophisticated
command-line oriented console for configuration and
management. This console contains features that are not
available through XAdmin or WebXAdmin, including
sophisticated diagnostic capabilities. The TROY XCD print
server console can be accessed via TELNET, DEC NCP/
NCL/ccr, the print server serial port (if present), and the
TROY XCD XCONFIG NetWare utility. It also available
through one of the web pages using the WebXAdmin facility.
The general configuration procedure is the same regardless
of which method is used.
DEC NCP, NCL, ccr. To connect to the print server
console with the VMS NCP utility, use the following
commands:
MCR NCP
CONNECT VIA
circuit
PHY ADD
ethernetaddress
where circuit is the circuit-ID of the VAX or Alpha (for
example, SVA-0 for most DEC workstations, MNA-0 for
XMI systems, BNA-0 for BI systems, and QNA-0 for Q-BUS
systems) and ethernetaddress is the hardware address of the
print server (for example, 00-40-17-00-61-35).
Management Methods 3-5
Page 42

Newer OpenVMS systems use NCL instead of NCP. The
NCL command to connect to the print server console is:
SET HOST/MOP/CIRCUIT=
circuit
/ADD=
ethernetaddress
ULTRIX systems use the addnode and ccr commands as
follows:
addnode
ccr
xciiname
xcdname
-c
circuit
-h
ethernetaddress
where xcdname is an arbitrary name for the print server
(each print server on the network needs a unique name).
In all cases, you will get a message like Console Connected
or Remote Console Reserved when you are connected.
When you are connected, push RETURN or ENTER to get
the "#" prompt, enter the password ACCESS (it will not print),
and type anything in response to the Enter Username>
prompt. When you get the Local> prompt, you are ready to
enter commands.
Note: The commands available are generally a subset of the
ones used on the DECserver terminal server. Note that
unlike the DECserver, there is no distinction between the SET
and DEFINE commands or between the CLEAR and PURGE
commands. Instead, when you type CTRL-D to exit the
remote console, any of these commands take effect
immediately and the results are stored permanently (for
example, it is not necessary to enter both a SET and a
DEFINE to execute a command and save the results).
TELNET. To connect to the print server using TELNET on
UNIX, Windows NT, or most other TCP/IP systems, type:
TELNET
ipaddress
3-6 Management Methods
Page 43

at the UNIX system prompt, where ipaddress is the IP
address of the print server. When you are connected, push
RETURN or ENTER to get the "#" prompt, enter the
password ACCESS (it will not print), and type anything in
response to the Enter Username> prompt. When you get
the Local> prompt, you are ready to enter commands.
XCONFIG. To connect to the print server using the TROY
XCD XCONFIG NetWare utility, insert the TROY XCD
Print Server Software diskette in Drive A and type:
A:XCONFIG
at the DOS system prompt (or choose the appropriate path if
you are running XCONFIG from your CD-ROM or hard
drive). If you have only one print server, you will be
immediately connected. If you have more than one print
server, you will be given a list of available print servers.
Type the number of the print server to which you want to
connect. When you are connected, enter the password
ACCESS (it will not print) at the "#" prompt, and type
anything in response to the Enter Username> prompt.
When you get the Local> prompt, you are ready to enter
commands.
Serial Port. To connect to the print server using the serial
port, refer to Chapter 2 for details on how to use this port.
Once you have established a connection, press RETURN or
ENTER to get the Local> prompt (no password is required).
You are now ready to enter commands.
HP JetAdmin
TROY XCD print servers work transparently with the HP
JetAdmin utility. You can download JetAdmin from the HP
web site (http://www.hp.com). Use the Windows Run
Management Methods 3-7
Page 44

command to expand the downloaded file. Then use the Run
command again to execute the SETUP.EXE file in the
destination directory that you selected (this file is generally
in the DISK1 subdirectory) and begin the installation.
Follow the instructions on the screen to complete the
installation.
Important: Windows 98 requires either JetAdmin V2.54
(this version can be installed from the Microsoft Windows
98 CD by running the SETUP.EXE file in the
DRIVERS/PRINTERS/JETADMIN/DISK1/ directory)
or V3.30 or later (available on the HP web site).
The TROY XCD print server will appear in the list of
configured print servers unless IPX is not running on the
computer and the print server is not configured with a valid
IP address. If this is the case, then select Device from the
menu bar and click on New. Select the desired print server
from the list of unconfigured devices and then press
Configure. Enter the requested information, including the IP
address, subnet mask, and gateway. Then click Close to
return to the list of configured print servers.
You may now select the print server from the list and click
on the Modify button (or select Device and then Modify
from the menu bar) to change the print server configuration.
HP Web JetAdmin
TROY XCD print servers work transparently with the HP
Web JetAdmin utility for Windows NT Advanced Server.
You can download this program at no charge from the HP
web site (http://www.hp.com). Use the Windows NT
Run command to expand the downloaded file. The files will
3-8 Management Methods
Page 45

be expanded and the installation program will be
automatically run. Follow the instructions on the screen to
complete the installation.
After you have completed the installation, you may use a
web browser on any computer that has access to the
Windows NT server to access the TROY XCD print server.
Start the browser and connect to the file server. Once you
are connected and are at Web JetAdmin home page, click on
the Find Device tab. Then click on Find All Devices to get
a list of all Web JetAdmin-compatible print servers (or you
may limit your search by using the Advanced Search
method). Click on the desired TROY XCD print server
name, and the Properties page will be displayed for that
print server. Then click on the Config tab to configure the
print server.
Management Methods 3-9
Page 46

3-10 Management Methods
Page 47

4
TCP/IP Network Configuration
Overview
TROY XCD print servers include the Transmission Control
Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) protocol suite. Since
virtually all UNIX host computers support TCP/IP, this
capability allows a printer to be shared on a UNIX Ethernet
network. TCP/IP communications can proceed concurrently
with other protocols, which means that UNIX, DEC, NetWare,
Apple, and other computers can share the same printer over an
Ethernet network using the TROY XCD print server.
TROY XCD TCP/IP Concepts
A TROY XCD print server with TCP/IP appears to the
network as a UNIX host computer with a unique IP address
running the lpd line printer daemon protocol. As a result,
any host computer that supports the Berkeley remote-LPR
command can spool jobs to the TROY XCD print server
without the need for any special software on the host
computer. Application programs run transparently and users
do not need to learn new procedures in order to use the
printer. TROY XCD print servers also support gateways for
communications with hosts on remote networks. In addition,
raw TCP ports are available for special applications and
compatibility with the HP JetDirect print server.
TROY XCD print servers come preconfigured to run on a
TCP/IP network with a minimum of setup. The only
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-1
Page 48

mandatory configuration in the print server is the entering of
an IP address (TROY XCD print servers come with a default
IP address of 192.0.0.192 (192.189.207.254 on some models)
but this should be changed to meet the addressing
requirements of your network).
TCP/IP UNIX Host Configuration
The configuration process for most UNIX systems is
described in the following steps. Unfortunately, this process
is not very standardized, so refer to your system documentation (or man pages) for additional information.
1. Configure the /etc/hosts file (or equivalent local
host table) on each UNIX host that needs to communicate
with the TROY XCD print server, or provide similar
information to a name server on the network. Use your
favorite editor to add an entry to the /etc/hosts
file containing the IP address and node name of the
TROY XCD print server. For example:
192.189.207.3 XCD_00C351
The actual format of the entry may vary depending on
your system, so check your system documentation and
also note the format of other entries in the etc/hosts
file.
Note: The node name in this file does not necessarily
need to be the same as the one that is actually
configured into the TROY XCD print server (the name
that appears on the printer self-test), but it is good
practice to make the names the same (however, some
operating systems, such as HP/UX, do not accept the
"_" character in the default name, so for these systems
4-2 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 49

you must use a different name). In any case, the
node name in the /etc/hosts file must match the
node name in the /etc/printcap file.
Note: Some systems, such as HP/UX and AIX allow
you to enter the IP address as the host name when
setting up the print queue. If this is the case, you do
not need to configure the hosts file.
2. Choose which TROY XCD print server service you
want to use. There are two types of services available
on the TROY XCD print server. Binary services pass
data through unmodified and are therefore required for
PCL or PostScript rasterized graphics printouts. Text
services add a carriage return at the end of each line for
proper formatting of UNIX text files (which end in
linefeed and do not have carriage returns). The text
service can also be used for non-rasterized graphics,
such as ASCII PostScript graphics or many types of
PCL graphics.
If you are using the first parallel port on the print
server, choose one of the available services (this
service name will be used in step 3):
BINARY_P1 Binary (parallel port)
TEXT_P1 Text (parallel port)
The XConnect II and Pony 100 also support the
following services:
BINARY_S1 Binary (serial port)
TEXT_S1 Text (serial port)
The XConnect 100 supports the following additional
services:
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-3
Page 50

BINARY_S1 Binary (serial port)
TEXT_S1 Text (serial port)
BINARY_P2 Binary (second parallelport)
TEXT_P2 Text (second parallel port)
BINARY_S2 Binary (second serial port)
TEXT_S2 Text (second serial port)
You may set up multiple print queues on your UNIX host
computer for the same TROY XCD print server, each
with a different service name (for example, one queue for
binary graphics jobs and one for text jobs). Refer to
Appendix B for additional information on using services.
3. Note: This step applies to the majority of UNIX
systems, including Sun OS (but not Solaris 2.xx),
Silicon Graphics (lpr/lpd option required), DEC
ULTRIX, DEC OSF/1, and Digital UNIX. SCO UNIX
users should follow these steps, but should also refer to
the SCO UNIX Configuration section in section 3-A.
Users of RS/6000 AIX, HP/UX, Sun Solaris 2.xx, and
other systems that do not use the printcap file should
skip to section 3-A.
Configure the /etc/printcap file on each host
computer to specify the local print queue, the TROY
XCD print server name (also called remote machine or
rm), and the TROY XCD print server service name
(also called remote printer, remote queue, or rp), and
the spool directory.
An example of a typical printcap file is as follows:
laser1|Printer on Floor 1:\
:lp=:\
:rm=XCD_003C51:\
:rp=TEXT_P1:\
:sd=/usr/spool/lpd/laser1:
4-4 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 51

This will create a queue named laser1 on the host
computer that communicates to a TROY XCD print
server with a node name (rm) of XCD_003C51 and a
service name (rp) of TEXT_P1 for printing text files to
the printer through the spool directory /usr/spool/
lpd/laser1.
If you are printing binary graphics files,
you would use the service BINARY_P1 instead of
TEXT_P1.
Note: The rm and rp options are not available on all
UNIX systems, so if necessary check your
documentation (or man pages) to determine the
equivalent options.
Users of Berkeley-compatible UNIX systems can use
the lpc command to obtain the printer status:
%lpc status
laser1:
queuing is enabled
printing is enabled
no entries
no daemon present
Users of AT&T-compatible UNIX systems can
generally use the lpstat or rlpstat commands to
obtain similar status information. Because this
procedure varies from system to system, refer to your
system documentation for the exact usage.
3-a Note: Skip this section if you have completed Step 3,
unless you have an SCO UNIX system.
If you have an HP/UX system, IBM RS/6000 AIX
computer, or Sun Solaris 2.xx, there is no printcap file.
This is also true for some other AT&T-based UNIX
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-5
Page 52

systems, as well as many VMS-based TCP/IP software
packages (for example, UCX, TGV Multinet, etc.).
Such systems generally use a printer setup program to
define the service name (remote printer), the TROY
XCD print server name (remote machine) or IP address,
and the local queue name (spool directory).
HP/UX Configuration
In the case of HP/UX 10.xx, the sam program is used to
set up the remote printer. The steps are as follows:
- Execute the sam program. When you get a list of
options, select Printers and Plotters.
- Select LP Spooler.
- Select Printers and Plotters.
- Select Actions and then Add Remote Printer/Plotter.
- Enter any name as the Printer Name (this will
be the name of the print queue)
- Enter the IP address of the print server as the
Remote System Name
- Enter the desired print server service name as the
Remote Printer Name.
- Check the box next to Remote Printer is on
BSD System.
- You may accept the default values for the
remaining items.
- Click OK to configure the printer.
- You should now be able to print using the lp -d
command with the printer name.
If you are using the HP Distributed Print Service, the
configuration procedure is slightly different because
you are sending the print jobs to a file server, which in
turn spools the jobs to the print server. You must
4-6 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 53

therefore know the name of the file server (spooler
host) in addition to the above information. You will
add a physical printer and a remote printer, and then
assign a logical printer name to the remote printer (a
unique name that does not match any other name). To
print, use the lp -d command with the logical
printer name.
Earlier versions of HP/UX use similar procedures to
10.xx:
- Enter sam and select "Peripheral Devices" and then
"Add Remote Printer" (not "networked printer")
- Enter the following remote printer settings (the
other settings do not matter):
- Line printer name (user-selectable)
- Remote system name (the TROY XCD print
server name; must match what is in hosts file or
use TROY XCD print server IP address)
- Remote printer queue (TROY XCD print server
binary or text service name)
- Remote Printer is on a BSD System (Yes)
IBM RS/6000 AIX Configuration
The RS/6000 AIX operating system uses the smit
program to set up the remote printer. The procedure is
as follows for AIX 4.0 and later:
1. Enter SMIT and select “devices”
2. Select “Printer/Plotter”
3. Select “Print Spooling”
4. Select “Add a Print Queue”
5. Select “Remote”
6. Enter the following Remote Printer Settings:
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-7
Page 54

- Name of queue (user selectable)
- Host Name of Remote Printer (TROY XCD
Print server name; must match name /etc/hosts
file or use TROY XCD print server IP address)
- Name of queue on remote server (TROY XCD
print server binary or text service name)
- Type of print spooler: BSD (press the list
button and choose BSD).
The procedure for pre-V4.0 systems is as follows:
1. Enter smit and select "Devices"
2. Select "Printer/plotter"
3. Select "Manage remote printer subsystem"
4. Select "Client services"
5. Select "Remote printer queues"
6. Select "Add a remote queue"
7. Enter the following remote queue settings:
- Name of queue to add (user selectable)
- Activate the queue (Yes)
- Destination host (TROY XCD print server
name; must match name in /etc/hosts file or use
the print server IP address)
- Name of queue on remote printer
(TROY XCD print server binary or text service
name)
- Name of device to add (user selectable; for
example lp0)
Sun Solaris 2.x Configuration
Sun Solaris 2.x uses the lpsystem and lpadmin
programs for remote printer configuration:
4-8 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 55

lpsystem -t bsd
lpadmin -p
accept
enable
queue
queue
queue
xcdname
-s
xcdname!\xcdservice
where
xcdname
queue
is the name of the local print queue,
is the TROY XCD print server name (must
match the entry in the /etc/hosts file) or IP address and
xcdservice
is the TROY XCD print server binary or
text service. If this is the first printer configured, you
must also use the lpsched command immediately prior
to the accept command.
As an alternative, you may use Printer Manager in the
admintool utility under OpenWindows. Select Edit,
Add, and Add Access to Remote Printer. Then enter
the TROY XCD print server name in the format
xcdname!\xcdservice
as described above. Make sure
that the Printer Server OS is set to BSD (the default
setting), and then click Add.
Note that we recommend that use the /etc/hosts file
for the printer name rather than NIS or other name
services. Also note that due to a bug in the Sun lpd
implementation on Solaris 2.4 and earlier releases, you
may experience problems printing very long print jobs.
If this is the case, a workaround is to use the raw TCP
port with the HP JetDirect software as described later in
this chapter.
SCO UNIX Configuration
SCO UNIX requires TCP/IP V1.2 or later to work with
TROY XCD print servers. You must first configure the
/etc/hosts and /etc/printcap files as described in
step 2. Then run the sysadmsh program as follows:
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-9
Page 56

- Select Printers.
- Select Configure.
- Select Add.
- Enter the name of the print queue you entered in
the /etc/printcap file as the Printer name,
- Enter anything as the Comment, and Class name.
- For the Use printer interface select "Existing".
- Press the F3 key to get a list of available interfaces,
and select the desired one as the Name of interface
using the arrow keys and Enter key ("Dumb” is a
good choice).
- Select "Direct" as the Connection.
- Enter the desired Device name (/dev/lp generally
works).
- Select "Hardwired" as the Device.
- Select "No" for the Require banner field.
Other Non-Standard Configurations
With DEC TCP/IP Services for VMS (UCX), you
first need to put a name for the TROY XCD print
server in the HOSTS file using the command SET
HOST
UCX> prompt, where name is the desired name for the
print server and ipaddress is the IP address for the print
server. Then use the sys$system:ucx$lprsetup
command to add a printer (print queue). Enter the
desired printer name, and then use the TROY XCD
print server name as the remote system name. Specify
one of the TROY XCD print server services (see
beginning of this section for options) as the remote
system printer name (accept the defaults for other
questions).
name
/ADDRESS=
ipaddress
at the
4-10 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 57

Process Software's TCPware simply uses the VMS
INIT/QUEU command with their special symbiont in
the following format:
INIT/QUEUE/PROC=TCPWARE_TSSSYM/ON="host,port" queue
where host is the IP address or name of the TROY
XCD print server, port is the TROY XCD print server
raw TCP port number (9100 for the parallel port, 9101
for the serial port, 9102 for the XConnect 100 second
parallel port, or 9103 for the XConnect 100 second
serial port), and queue is the VMS queue name.
TGV's Multinet requires you to run the MULTINET
CONFIGURE /PRINTERS
command, then use the ADD
command to add a printer, specifying the TROY XCD
print server IP address, a protocol type of LPD, and
one of the service options described at the beginning of
this section as the remote print queue.
With Wollongong's PATHWAY, first make sure that
you have the Access option with lpd enabled. Then
enter the print server name and IP address in the
TWG$TCP:[NETDIST.ETC]HOSTS. file, run the LPGEN
program, and execute the command add
rmachine=
xcdname
/rprinter=
service,
queue
/
where queue
is the name of the queue, xcdname is the TROY XCD
print server name from the hosts file, and service is the
TROY XCD print server service name.
To use a TROY XCD print server with an IBM AS/400
running IBM’s TCP/IP Gateway Services for OS/400
(the OS/400 system must be v3.1 or later):
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-11
Page 58

- Assign a TCP/IP address to the AS/400 and the
TROY XCD print server.
- Use the CFGTCP command at your OS/400 prompt
to add the print server’s TCP/IP address to the AS/
400 host table.
- Use the following one-line OS/400 command to
create the LPD queue:
CRTOUTQ OUTQ(<queuename> RMSTSYS
(*INTNETADR) RMTPRTO(<service>)
AUTOSTRWTR(1) CNNTYPE(*IP) DESTTYPE
(*OTHER) MFRTYPMDL (<driver>)
INTNETADR(‘<ipaddress>’) TEXT
(‘<description>’)
where <queuename> is the new AS/400 print queue
name, <service> is the TROY XCD print server
service name, <driver> is the OS/400 printer driver
name (*HP4 is recommended if in doubt), and
<ipaddress> is the IP address of the print server.
Note that the IP address and description must be
enclosed in single quotes.
Other systems use similar procedures to set up the
TROY XCD print server. These programs will
generally ask for the following information:
Requested information: You should use:
remote printer or remote TROY XCD print server
binary or text service
name
remote host computer name Any name (must match
name in printcap file, if
any) or in some cases,
you may enter the TROY
4-12 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 59

print server IP address
here
remote host IP address TROY XCD print server IP
address
Tech support specialists for these companies can usually
answer configuration questions if you provide them
with the equivalent UNIX configuration information
(tell them that the TROY XCD print server looks like a
remote UNIX host computer running the lpd line printer
daemon).
4. If you have not created a spool directory for the TROY
XCD print server on your UNIX host computer, you
will need to do so now (the printer setup utilities in HP/
UX, AIX, Solaris 2.xx, and other systems will
automatically create the spool directory). The lpd spool
directory is usually located in the /usr/spool directory
(check with your system manager to see if the location
is different for your system). To create a new spool
directory, use the mkdir command. For example, to
create a spool directory for the queue laser1, you would
enter:
mkdir /usr/spool/lpd/laser1
On some systems it is also necessary to start the
daemon. This is done on Berkeley-compatible UNIX
systems with the lpc start command as shown in the
following example:
lpc start laser1
5. The final step before printing is to add the IP address to
the TROY XCD print server. Consult with your system
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-13
Page 60

administrator before assigning an IP address to avoid
conflicts with other devices. If your network does not
have an officially assigned block of IP addresses, you
may use any unique address between 192.168.254.1 and
192.168.254.254 (this is a reserved range of Class C
addresses for private networks that are not connected to
the Internet per RFC 1918; note that you must also
assign your host computer an IP address in this range).
The IP address can be set in his can be done in any of
the following ways:
1. XAdmin32
2. HP JetAdmin
3. DHCP
4. The UNIX arp and ping commands
5 Reverse Arp (rarp)
6. BOOTP
7. DEC NCP, NCL, or ccr utilities
8. TROY XCD XCONFIG NetWare utility
9. XConnect II or XConnect 100 serial port
The easiest way to configure the IP address is using
either XAdmin32 or JetAdmin as described in Chapter
3. The remaining configuration methods are described
in the following paragraphs.
Important Note: The IP address you assign to the
print server must be on the same logical network as
your host computers (e.g., if your host has an IP address
of 192.189.207.3, the TROY XCD print server should
have an IP of 192.189.207.x, where x is an integer
between 1 and 254), or you must properly configure
your router to work with the TROY XCD print server.
4-14 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 61

Using DHCP to Configure the Print Server
IP Address
TROY XCD print servers support the DHCP protocol
for automatically loading the IP address from a host
computer that supports DHCP. By default, the print
server will automatically try DHCP, BOOTP, and rarp
before using the IP address configured in the server.
Note: This procedure may take about a minute, so the
print server cannot be accessed via TCP/IP during that
time. If a faster IP address load is required, select the
desired IP configuration method (AUTO, DHCP,
BOOTP, RARP, STATIC) via XAdmin, WebXAdmin,
or the print server console SET IP METHOD
command (STATIC is used when the IP address is
manually entered).
Using arp and ping to Configure the Print
Server IP Address
The arp and ping method is one of the simplest ways of
configuring the print server IP address (this method
requires V3.27 or later firmware). To use arp and
ping, enter the following commands at the operating
system prompt::
arp -s
ping
ipaddress ethernetaddress
ipaddress
[temp]
where ethernetaddress is the Ethernet address of the
print server and ipaddress is the IP address of the print
server. The temp parameter should be used with UNIX
systems, but is not supported by Microsoft operating
systems. For example, a typical UNIX entry would be:
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-15
Page 62

arp -s 192.189.207.2 00:40:17:00:c3:e4 temp
ping 192.189.207.2
while a typical Microsoft entry would be:
arp -s 192.189.207.2 00-40-17-00-c3-e4
ping 192.189.207.2
If everything is OK, you will get a message back on the
screen indicating that the print server is alive. If you do
not get such a message, first check the note bellow, and
then try entering the commands again.
Note: This procedure will not work through a router
(gateway) and only works if the print server IP address
has never been configured before. If you have
previously configured an IP address, then use TELNET
as described in Appendix A to change the IP address.
Note: This procedure will not work with Windows 95
unless there are already entries in the Windows 95 arp
table. If there are no entries, you can add one by
pinging a known device on the network (you cannot
ping yourself).
Using rarp to Configure the TROY XCD
Print Server IP Address
The TROY XCD print server IP address can be
configured using the Reverse ARP (rarp) facility on
your host computer. This is done by editing the /etc/
ethers
file (if this file does not exist, you can create it)
with an entry similar to the following:
00:40:17:00:01:07 XCD_000107
4-16 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 63

where the first entry is the Ethernet address of the
TROY XCD print server and the second entry is the
name of the TROY XCD print server (the name must be
the same as the one you put in the /etc/hosts file).
If the rarp daemon is not already running, start it
(depending on the system the command can be rarpd,
rarpd -a,
rarpd
in.rarpd -a or something else; type man
or refer to your system documentation for
additional information). To verify that the rarp daemon
is running on a Berkeley UNIX-based system, type the
following command:
ps -ax | grep -v grep | grep rarpd
For AT&T UNIX-based systems, type:
ps -ef | grep -v grep | grep rarpd
The TROY XCD print server will get the IP address
from the rarp daemon when it is powered on.
Using BOOTP to Configure the TROY XCD
print server IP Address
BOOTP is an alternative to rarp that has the advantage
of allowing configuration of the subnet mask and
gateway. In order to use BOOTP to configure the IP
address into the TROY XCD print server, first make
sure that BOOTP is installed and running on your host
computer (it should appear in the /etc/services file
on your host as a real service; type man bootpd or refer
to your system documentation for information).
BOOTP is usually started up via the /etc/inetd.conf file,
so you may need to enable it by removing the "#" in
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-17
Page 64

front of the bootp entry in that file. For example, a
typical bootp entry in the /etc/inetd.conf file would
be:
#bootp dgram udp wait /usr/etc/bootpd bootpd i
Depending on the system, this entry might be called
"bootps" instead of "bootp". In order to enable
BOOTP, simply use an editor to delete the "#" (if there
is no "#", then BOOTP is already enabled). Then edit
the BOOTP configuration file (usually /etc/
bootptab
) to enter the name, network type (1 for
Ethernet), Ethernet address (which can be found on the
label on the TROY XCD print server), and the IP
address, subnet mask and gateway of the TROY XCD
print server. Unfortunately, the exact format for doing
this is not standardized, so you will need to refer to
your system documentation to determine how to enter
this information (many UNIX systems also have
template examples in the bootptab file that you can use
for reference). Some examples of typical /etc/
bootptab
entries include:
xcd_000107 1 00:40:17:00:01:07
192.189.207.3
and:
xcd_000107:ht=ethernet:ha=004017000107:\
ip=192.189.207.3:
Certain BOOTP host software implementations will not
respond to BOOTP requests if you have not included a
download filename in the configuration file; if this is
the case, simply create a null file on the host and
4-18 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 65

specify the name of this file and its path in the
configuration file.
As with rarp, the TROY XCD print server will load its
IP address from the BOOTP server when the printer is
powered on.
Configuring the TROY XCD Print Server IP
Address with NCP, XCONFIG, or the Serial
Port
Users of DEC and Novell computers have additional
alternatives for configuring the TROY XCD print
server IP address by using the remote console facility,
while XConnect II, Pony 100, and XConnect 100 users
can also utilize the serial port. On VMS systems, you
will need to have DECNET running in order to use the
remote console. The procedure is as follows:
a. Connect to the remote console or serial port (see
chapter 2 for information on the serial port). If
you are using the remote console with VMS or
ULTRIX, you will need to know the circuit ID
(EWA-0 for Alpha PCI systems, QNA-0 for Q-BUS
systems, SVA-0 for DEC workstations, UNA-0 for
UNIBUS systems, BNA-0 for BI systems, and
MNA-0 for XMI systems; you can get the circuit
ID by executing the VMS NCP command SHOW
KNOWN CIRCUITS
TROY XCD print server (which you can get either
from the label on the TROY XCD print server or
via the printer self-test). On VMS systems, the
connection is made as shown in the following
example:
) and the Ethernet address of the
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-19
Page 66

$ MCR NCP
NCP>CONNECT VIA QNA-0 PHY ADD 00-40-17-00-01-07
On ULTRIX systems, you would execute
commands similar to the following example:
# addnode XCD -c qna-0 -h 00-40-17-00-01-07
# ccr XCD
On a NetWare system, you would use the
XCONFIG utility included with every TROY XCD
print server. Simply type XCONFIG at the DOS
prompt and select the desired TROY XCD print
server.
b. If you are using the remote console, you will get
the message Console connected (VMS) or
Connection established XCONFIG) or
Remote console reserved (ULTRIX). Press
RETURN and enter the password ACCESS in
response to the "#" prompt (it will not echo).
Note: You will not be asked for a password if you
are using the XConnect II or XConnect 100 serial
port.
c. You will be prompted for a user name. Enter
anything in response to this prompt (older versions
do not ask for the user name).
d. You will then get the Local> prompt. Type SET
IP ADDRESS
ipaddress
, where
ipaddress
desired IP address you wish to assign to the TROY
XCD print server (check with your network
manager for the IP address to use). For example:
Local> SET IP ADDRESS 192.189.207.3
4-20 TCP/IP Network Configuration
is the
Page 67

e. You will now need to set the subnet mask by typing
SET IP SUBNET
subnetmask
, where
subnetmask
is the desired subnet mask you wish to assign to the
TROY XCD print server (check with your network
manager for the subnet mask to use). For example:
Local> SET IP SUBNET 255.255.255.0
If you do not have any subnets, use one of the
following default subnet masks:
255.255.255.0 for class C networks
255.255.0.0 for class B networks
255.0.0.0 for class A networks
f. The type of network you have can be identified by
the leftmost group of digits in your IP address. The
value of this group ranges from 192 through 255
for Class C networks (e.g., 192.189.207.3), 128
through 191 for Class B networks (e.g.,
128.10.1.30), and 1 through 127 for Class A
networks (e.g., 13.27.7.1).
g. If you have a gateway (router), enter its address
with the command SET IP ROUTER
routeraddress
, where
routeraddress
is the
desired IP address of the gateway you wish to
assign to the TROY XCD print server. For
example:
Local> SET IP ROUTER 192.189.207.1
h. To verify that you have entered the IP information
correctly, type SHOW IP.
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-21
Page 68

i. Type EXIT or CTRL-D (i.e., hold down the control
key and type "D") to end the remote console
session.
j. With older versions of the firmware (V3.26 or
earlier), you must wait about ten second and then
power the printer off and then on again to make the
IP address take effect (not necessary with newer
versions).
6. Before attempting to print, it is very important to
verify the connection between the host and the TROY
XCD print server by using the UNIX ping command
with the IP address of the TROY XCD print server.
For example:
ping 192.189.207.3
You should get a message that the TROY XCD print
server is alive. If you get an error message or no
response, then there is no connection. You will not be
able to print if you cannot ping the TROY XCD print
server. If this is the case, verify that you have set up
the host and TROY XCD print server correctly and that
the physical connections (e.g., the transceivers and
cabling) are good. Refer to the Troubleshooting
chapter for additional information.
7. To print to the TROY XCD print server from UNIX,
use the standard lpr command with the -P option to
specify the queue name. For example, to print the file
TEST on the queue laser1, you would type:
lpr -Plaser1 TEST
4-22 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 69

Some AT&T-based UNIX systems, such as SCO and
HP/UX, use the standard lp command instead of lpr. In
these cases, use the -d option instead of -P to specify
the queue name as shown in the following example:
lp -dlaser1 TEST
Note that TROY XCD print servers implement only a
subset of the lpr options. If you want to utilize printing
options such as landscape mode, language switching,
etc., refer to Appendix B for information on using
services.
For non-UNIX systems such as VMS, the TCP/IP
printing process is normally transparent, so you use the
same commands or procedures as you would for a local
printer.
IP Security
TROY XCD print servers provide a means of allowing only
host computers with authorized IP addresses to access the print
server. This is very useful for applications like check printing,
where general access to the printer is not allowed. The console
command SET IP ACCESS ENABLED
computer IP address into the access table of the print server
(where ipaddress is the IP address of the host computer; refer to
Appendix A for information on using the print server console).
To remove an IP address, use the command SET IP ACCESS
DISABLED
command
ipaddress
SET IP ACCESS ALL.
. To reenable general access, use the
ipaddress
enters a host
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-23
Page 70

Raw TCP Ports
TROY XCD print servers provide a raw TCP port capability
that can be used by any application that can open and send
data to a TCP port. The port number is 9100 (238C hex) for
the parallel port, or 9101 for the XConnect II and XConnect
100 first serial port, and 9102 for XConnect 100 second
parallel port. The ports pass data through unmodified, so
there is no TELNET interpretation provided. When using the
raw TCP ports, make sure that TELNET interpretation is
disabled in your software or else you may get distorted
printouts.
The raw TCP port is compatible with many popular software
packages, including HP's JetDirect software for UNIX, TGV
Multinet (streams mode), IBM AIX for the RS/6000 (V3.25
or later), and any TCP/IP-based software that supports HP's
JetDirect Ethernet network interface card.
The HP JetDirect software for UNIX is available for Sun
Solaris, SunOS, and HP/UX. HP printer users can download
these utilities from HP's web site (http://www.hp.com or
FTP site (ftp.hp.com).
To use an TROY XCD print server with the HP host printing
utilities on an HP/UX or Sun system:
1. Download the software from the HP web site or FTP
site.
2. If the download file is in tar format, use the tar xvf
filename command to extract the software, where
filename is the name of the software that you
downloaded (you must be logged in as root). If the file
is in pkgadd format, use the pkgadd -d filename all
4-24 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 71

command to extract the software. Accept the default
directory to store the files. Follow the instructions in
the README files to install the software.
3. Run JetAdmin by typing jetadmin at the UNIX
prompt (on SunOS 4.xx systems, you use the hpnpcfg
program instead of JetAdmin, but the configuration
steps are similar).
4. Select item 1 (Configuration) and then select item 3
(Add printer to local spooler).
5. Enter the desired name for the TROY XCD print server
or IP address at the Enter the network
printer name/IP Name prompt.
Note: With versions of firmware earlier than 3.46, you
must enter the name (do not enter the IP address)
before configuring the print server name in the /
etc/hosts file, or in NIS or DNS. You will get a
message Unknown printer. Do you wish
to continue?". Enter "Y" to continue.
6. Select the printer type (for example, “HP LaserJet IIISi
Printers”).
7. If desired, change any of the configurable parameters
(note that the default queue name is the name of the
printer plus an “_” and a number (e.g., laser_1)). Then
enter 0 to configure the queue.
8. Answer “Y” at the “OK to Continue?” prompt. Exit the
JetAdmin utility by pressing RETURN and then “q”
twice.
TCP/IP Network Configuration 4-25
Page 72

9. Print a job using the lp command. For example,
lp -dlaser_1 /etc/hosts
If you need a different TCP port number or if you want
additional TCP ports, you may define a TCP port number on
any TROY XCD print server service by using the
SET SERVICE
servicename
TCP
nn
where servicename is the name of the service, and nn is the
desired port number (must be greater than 1023). Refer to
Appendix A for information on using the console.
Changing the Configuration (Optional)
You may use TELNET, the DEC NCP utility, the XCONFIG
NetWare utility, or the XConnect II/Pony 100/XConnect 100
serial port to connect to the TROY XCD print server remote
console and change the configuration or view the status. The
procedure and configuration commands are described in
Appendix A.
4-26 TCP/IP Network Configuration
Page 73

5
Novell Network Configuration
Overview
TROY XCD print servers allow NetWare client PCs to print
jobs on the same printer as DEC, UNIX, AppleTalk, LAN
Manager, and Banyan users. All NetWare jobs are spooled
through the Novell server, so NetWare utilities and
application programs can use the printer transparently.
NetWare Concepts
Novell NetWare is a sophisticated network operating system
that allows PC clients (and other nodes) to access network
resources such as disk drives and printers as if they were
directly connected. NetWare networks require at least one
file server, and users must log into this server to take
advantage of the NetWare capabilities.
To handle printing over the network, the file server provides
print spooling for the clients. It holds print jobs locally until
contacted by a print server on the network, which in turn
sends the job to appropriate printer. In the past, a NetWare
print server was typically either a PC dedicated to handling
printers or a Network Loadable Module (NLM) or Value
Added Process (VAP) running on the file server. Today,
NetWare print servers are often special-purpose networking
hardware like a TROY XCD print server.
Novell Network Configuration 5-1
Page 74

TROY XCD print servers can operate in two different modes
to service NetWare print queues:
• Remote Printer mode (also known as NPRINTER mode on
NetWare 4.xx or RPRINTER mode on NetWare 2.xx or
3.xx networks)
• Queue Server mode (also called print server or PSERVER
mode)
In remote printer mode (see figure 5-1), the client PC sends
the print job to the file server, which in turn spools it to a
PC Client
Workstation
File
Server
Print
Server
Printer with
XConnect II
PC
Figure 5-1
TROY XCD Print Server Operating as a NetWare Remote Printer
File
PC Client
Workstation
Server
Printer with
XConnect II
PC
Figure 5-2
TROY XCD Print Server Operating as a NetWare Queue Server
5-2 Novell Network Configuration
Page 75

print server (the print server may be a physical device like a
PC or a software NLM or VAP on the file server), which in
turn sends it to the printer. This approach provides good
performance, and has the advantage of not consuming a user
slot on the file server.
A TROY XCD print server can also act as a NetWare print
server (queue server) with an attached printer, which
therefore eliminates the need for a dedicated PC print server
or for an NLM or VAP on the file server. As shown in figure
5-2, this means that jobs from the client PC are spooled to the
file server, which in turn spools the job directly to the TROY
XCD print server. The advantage of this approach is higher
performance, but it has the drawback of requiring a user slot
on the file server.
Generally speaking, TROY XCD recommends that you use
queue server mode instead of remote printer mode because
the performance will be much higher. The exception to this
recommendation is if you have a limited number of available
user slots (for example, if you have a 5-user NetWare license
and you have five active users).
TROY XCD print servers will work with NetWare Directory
Services (NDS) or bindery emulation mode on NetWare 4.xx
and later networks (not all TROY XCD print servers support
NDS queue server mode; refer to chapter 2 for specific
protocol support information).
General Information
In order to use a TROY XCD print server on a NetWare
network, one or more file servers must be configured with a
Novell Network Configuration 5-3
Page 76

print queue that the TROY XCD print server can service.
Users send their print requests to the file server’s print
queue, and the jobs are then spooled (either directly, or in the
case or remote printer mode, via an intermediate print server)
to the TROY XCD print server.
TROY XCD print servers can be configured under Windows
using Hewlett-Packard's JetAdmin utility or TROY XCD's
XAdmin32 and XAdmin utilities. Alternatively, they can be
configured using the NetWare PCONSOLE utility in
conjunction with TROY XCD's DOS XCONFIG utility.
Important Note: Not all TROY XCD print server models
support queue server mode with Novell Directory Services
(refer to chapter 2 for protocol support information). You
must enable bindery emulation in order to use queue server
mode with these products.
Before You Begin
Before you can configure a NetWare print queue, you must
have sufficient privileges. With NetWare 3.xx and earlier,
you MUST be logged in as SUPERVISOR (not someone with
Supervisor privileges). With NetWare 4.xx and later, make
sure that you have sufficient administrator privileges to
create a print queue in the desired context.
Default Print Server Names (Service
Names)
TROY XCD print servers automatically make themselves
known on a NetWare network. Each print server port has an
associated default NetWare name; these names are used
5-4 Novell Network Configuration
Page 77

extensively during the configuration process, so be sure to
remember them. The names are as follows:
XConnect II
XCD_xxxxxx_P1 (parallel port)
XCD_xxxxxx_S1 (serial port, if enabled)
XCD_xxxxxx_LN (parallel port if LN03 option
is installed)
XConnect II
XCD_xxxxxx_P1 (parallel port)
XCD_xxxxxx_S1 (serial port, if enabled)
XCD_xxxxxx_LN (parallel port if LN03 option
is installed)
XConnect II Lite
XCD_xxxxxx_P1 (parallel port)
XCD_xxxxxx_S1 (serial port, if enabled)
Pony Print Server Plus
XCD_xxxxxx_P1 (parallel port)
The default NetWare print server names are actually the
names of the print server's NetWare services (refer to
Appendix B for more information on services). The "xxxxxx"
in all of the above cases is the last six digits of the Ethernet
address (for example, XCD_034578_P1). Refer to the label
on the print server or to the print server self-test for the
Ethernet address. If desired, you may change the default
names to something more meaningful by using XAdmin32,
XAdmin, WebXAdmin, JetAdmin, or the print server
console.
Novell Network Configuration 5-5
Page 78

Configuring the Print Server and Adding
the Print Queue in Queue Server Mode
TROY XCD print servers can be configured in Queue Server
mode for either bindery or NDS mode operation. The
simplest way to do this is with TROY XCD's XAdmin32 or
HP's JetAdmin utilities. XAdmin32 is a Windows 95/98 and
Windows NT 4.xx-based utility that allows you to configure
the print server and create NetWare print queues without
using NetWare utilities like PCONSOLE or NWAdmin (if
you have Windows 3.xx, you must use XAdmin as described
later in this chapter). JetAdmin is a Hewlett-Packard utility
that provides similar capabilities. Other methods include
TROY XCD's XAdmin or XCONFIG utilities in conjunction
with Novell's NWAdmin or PCONSOLE.
Configuring the Print Server and Print Queue with
XAdmin32 (Queue Server Mode)
NOTE: TROY XCD recommends you use the Novell 32-bit
client on your Windows 95/98/NT workstation instead of the
Microsoft NetWare client, because it allows direct
configuration of print queues without the need for a Novell
utility like NWAdmin or PCONSOLE.
NOTE: If you have a Windows 3.xx system, you must use
XAdmin as described later in this chapter.
NOTE: NDS Queue Server mode is only supported by "S"
and "N" Series models (for example, PPS-8S and XConnect
II-8N; refer to Chapter 2 for specific mode information).
1. Make sure that you are logged in as ADMIN or
equivalent (NetWare 4.xx and above) or SUPERVISOR
(NetWare 2.xx and 3.xx). Install the XAdmin32
5-6 Novell Network Configuration
Page 79

software from the TROY XCD Print Server Software
CD-ROM by clicking on the Start button and selecting
Run. Click on Browse and select the CD-ROM drive.
Open the Utilities folder, open the XAdmin32 folder,
and click on SETUP.EXE, Click OK twice and follow
the instructions on the screen.
2. Click on Start, select Programs, select the XAdmin32
folder, and then select XAdmin32.
3. Click on the IPX/SPX icon under Filters to set the
operating mode to IPX/SPX (TCP/IP mode will not
allow you to configure NetWare print queues directly).
The TROY XCD external print server should appear in
the list of available printers (the name will one of the
ones listed in the Default Print Server Names section at
the beginning of this chapter). If it does not, try going
to the menu bar and selecting Devices and then Search
Active Devices.
Important Note: V3.59 and earlier firmware do not
support more than one service and one port (the
firmware version is listed on the self-test page). If you
have an XConnect II or XConnect 100 and need to use
the serial port for printing, you must upgrade to a
newer revision of the firmware.
4. Double click on the printer that you wish to configure,
enter the configuration password (ACCESS is the
default), and press OK.
5. A series of index card tabs will be displayed. Click on
the NetWare P1 tab to configure the first parallel port,
the NetWare S1 tab to configure the serial port, the
Novell Network Configuration 5-7
Page 80

NetWare P2 tab to configure the XConnect 100 second
parallel port, or the NetWare S2 tab to configure the
XConnect 100 second serial port.
• If it is not already selected, select Queue Server as
the operating mode.
• Click on the ▼ button and select the NDS tree (if
you are using the Microsoft NetWare client, you
must type in the name of the tree)..
• Click Change... button to select the NDS context
where the queue will reside (if you are using the
Microsoft client, you must type in the name of the
context).
• If desired, you may change the print server name (do
this with caution, because it changes the print server
service name and will therefore affect any other
protocols that use this service).
If you are using the Microsoft Client for NetWare, STOP
HERE. Go to the Adding NetWare Print Queues Using
NWAdmin section to complete the configuration.
6. Click on the Change NDS Queues... button to
configure an NDS print queue or click the Change
Bindery Queues... to configure a bindery mode queue.
7. Two windows will appear, Available Print Queues and
Serviced Print Queues. First go to the Available
Print Queues window:
• If you are configuring an NDS queue, click on the
context where the print queue will reside.
5-8 Novell Network Configuration
Page 81

• If you are configuring a bindery queue, click on the
volume where the queue will reside (a volume name
will have a file server icon next to it).
8. Click on New Queue.
• Enter any unique name for the Queue name. If you
are configuring a bindery queue, click OK and
proceed to step 8.
• If you are configuring an NDS queue, click
Browse, select the file server volume where you
want the queue to reside (a volume name will have
a file server icon next to it), and click OK.
9. The queue name will now appear in the Available
Print Queues under the selected volume (for bindery
mode) or in the selected context (for NDS mode).
• Click on the desired queue.
• Click on Add>>
The name will now appear in the Serviced Print
Queues window.
10. Click Close and then OK. You can now use the print
queue from your NetWare workstation.
Configuring the Print Server and Print Queue with
HP JetAdmin 3.XX (Queue Server Mode)
NOTE: JetAdmin 1.xx and 2.xx do not allow direct
configuration of NetWare print queues. If you are using
these versions, you may configure the print server with
Novell Network Configuration 5-9
Page 82

JetAdmin and then use NWAdmin or PCONSOLE to add the
print queue. If possible, TROY XCD recommends that you
upgrade to JetAdmin 3.xx (available on the HP web site at
http://www.hp.com).
1. Make sure that JetAdmin 3.xx is running on your
system and that you have sufficient privileges to use it
to create print queues. If you are using the Microsoft
NetWare client on your workstation, make sure that you
have installed Services for NetWare Directory
Services in the Network control panel.
2. Click on Start, select Programs, select the HP
JetAdmin Utilities 3.0 folder, and then select HP
JetAdmin.
3. One or more TROY XCD print server NetWare services
will show up in the list of printers (the default service
names are listed in the Default Print Server Names
section at the beginning of this chapter). Single click
on the one that you wish to configure and then go the
menu bar, select File and then Modify.
Important Note: V3.59 and earlier firmware do not
support more than one service and one port (the
firmware version is listed on the self-test page). If you
have an XConnect II or XConnect 100 and need to use
more than one port for printing, you must upgrade to a
newer revision of the firmware.
4. If desired, change the print server name and description.
Click Next. Do this with caution because this will
change the print server service name, and will therefore
affect any other protocols that use this service.
5-10 Novell Network Configuration
Page 83

5. Make sure that NetWare Directory Services is selected
in the window on the left side of the display.
• Click on the ▼ button and select the NDS tree.
• Click Change... button to select the NDS context.
6. Click on the Operating Mode button and select Queue
Server Mode.
7. Click on the Queues button and then click on the
Change... button. Two windows will appear, Available
Print Queues and Serviced Print Queues. Go to the
Available Print Queues window:
• If you are configuring an NDS queue, click on the
context where the print queue will reside.
• If you are configuring a bindery queue, click on the
volume where the queue will reside.
8. Click on Create and enter any unique name for the
Queue name.
• If you are configuring an NDS queue, the default file
server on which the print queue will reside will be
listed.. You may optionally change this by clicking on
the ▼ button and selecting a different server. You
may also optionally change the context that you
selected in the previous step by clicking on the
Browse... button. Click OK and proceed to step 9.
• If you are configuring a bindery queue, you may
optionally click on the ▼ button to change the file
Novell Network Configuration 5-11
Page 84

server volume that you selected in the previous step.
Click OK to continue and go to step 9.
9. Click Yes when asked if you want to add the queue to
the list of serviced queues. The queue name will now
appear in the Available Print Queues in the selected
context (for NDS mode) or under the selected volume
(for bindery mode).
10. Click OK and then Next. If applicable, enter the IP
address and click Next.
11. If desired you can enable users that will be notified in
the event of printer problems. Click Finish. You can
now use the print queue from your NetWare
workstation.
Configuring the Print Server using XAdmin Version
2.0 or WebXAdmin (Queue Server Mode):
Important Note: Although XAdmin runs on Windows 95/
98, TROY XCD recommends that you use XAdmin32 on these
operating systems.
1. If you are using XAdmin 2.0, install the XAdmin
software. On Windows 3.xx systems, go the menu bar
in the Program Manager, select File, and then Run.
Click Browse to locate the Setup file (either on
floppy disk or in the \Utilities\XAdmin folder
on CD-ROM. On Windows 95, go the Start button,
select Run, and then Browse for the Setup file.
Click OK to start the installation.
5-12 Novell Network Configuration
Page 85

2. If you are using XAdmin, start it up by double clicking
on the icon.
If you are using WebXAdmin, start up your web
browser (you must have a valid IP address configured in
the PC and in the print server).
3. If you are using XAdmin, one or more TROY XCD
print server NetWare services will show up in the list of
printers (the default services names are listed in the
Default Print Server Names section at the beginning of
this chapter). Double click on the one that you wish to
configure.
If you are using WebXAdmin, enter the IP address of
the print server as the destination address in your
browser and press ENTER or RETURN.
4. Enter the configuration password (ACCESS is the
default) and press OK (XAdmin) or Submit
(WebXAdmin).
5. If you have XAdmin, click on the NetWare tab.
If you are using WebXAdmin, click on Configure
NetWare. You will see one or more enabled services
(the default service names are listed in the Default Print
Server Names section at the beginning of this manual).
Click on the desired service.
6. If you are using NDS, type in the tree and context (the
context may be entered in either the form
printers.mytree or OU=printers.O=mytree. If you
are using XAdmin, click OK, Yes, and OK to save the
Novell Network Configuration 5-13
Page 86

configuration changes. If you are using WebXAdmin,
click Submit and exit the browser. Proceed to the next
section, Adding NetWare Print Queues using NWAdmin.
If you are using bindery mode with XAdmin (not
available with WebXAdmin), you may click on the Add
Queue button to directly add a NetWare bindery queue:
• Click Create. Use the ▼ button to change the file
server volume and then enter any unique name for the
print and click OK.
• Click Yes when asked if you want to add the queue to
the service list, click OK and Close. The queue will
appear in the Bindery Print Queues window. Click
OK and then Yes. You can now use the print queue
from a NetWare workstation. Skip to the
Configuring the Windows Printer section.
If you are using bindery mode with WebXAdmin, click
Configure NetWare from the main menu, type in the
name of the file server where the print queue will
reside, and click Add. Proceed to the next section,
Configuring NetWare Print Queues using NWAdmin.
Adding NetWare Print Queues Using NWAdmin
(Queue Server Mode)
If you are using XAdmin32 with the Microsoft NetWare
client, or you are using XAdmin, WebXAdmin, or JetAdmin
1.xx or 2.xx, you need to use NWAdmin to configure the
actual NetWare print queue. This is because these utilities
only allow you to define the print server context and tree (or
file server, if you are using bindery mode). The following
steps are required:
5-14 Novell Network Configuration
Page 87

1. Start the Novell NWAdmin program by double clicking
on the icon.
2. Create a printer object:
- Click on the container where the object will reside.-
Select Object from the menu bar and then Create.
- When you get the New Object menu, select Printer
and then OK.
- Enter any desired name for the printer and select
Create.
3. Create a print queue object:
- Click on the container where the object will reside.
Select Object from the menu bar and then Create.
- When you get the New Object menu, select Print
Queue and then OK.
- Enter any desired name for the print queue
- Click on the Print Queue Volume button and select
the volume on which the print queue will reside.
- Press OK and then Create.
4. Create a print server object:
- Click on the container where the object will reside.
- Select Object from the menu bar and then Create.
- When you get the New Object menu, select Print
Server and then OK.
- Enter the name of the TROY XCD print server and
select Create. Use the default print server name (the
default names are listed in the Default Print Server
Names section at the beginning of this chapter) unless
you specifically changed it with XAdmin32, Admin,
JetAdmin, or the print server console.
Novell Network Configuration 5-15
Page 88

5. Associate the printer with the print queue:
- Change context if required and then double click on
the name of the printer you created in step 3.
- Click on Assignments and then Add...
- Change context if necessary and select the print
queue you created in step 4. Click OK and then OK
again
6. Associate the print server with the printer:
- Change context if required and then double click on
the name of the print server you created in step 5.
- Click on Assignments and then Add...
- Change context if necessary and select the printer
you created in step 3. Click OK and then OK again.
7. Exit NWAdmin. You are now ready to use the print
queue from a NetWare workstation.
Configuring the Print Server and Print Queue Using
PCONSOLE and XCONFIG (Queue Server Mode)
As an alternative to JetAdmin and XAdmin, you can use the
standard Novell PCONSOLE utility in conjunction with
TROY XCD's XCONFIG program to set up your print
queues (note that if desired, you may use TELNET, the DEC
NCP utility, or the serial port instead of XCONFIG). The
procedure is basically as follows:
1. Use XCONFIG to connect to the print server. Enter the
password (ACCESS is the default) and type anything in
response to the Enter Username> prompt.
5-16 Novell Network Configuration
Page 89

2. If you are configuring an NDS queue, enter the
commands:
SET SERVICE
SET SERVICE
servicename
servicename
TREE
treename
CONTEXT
contextname
where servicename is the service that you want to
configure (the default service names are listed in the
Default Print Server Names section at the beginning of
this chapter), treename is the name of your NDS tree,
and contextname is the NDS context where the print
server will reside. Now skip to step 3.
If you are configuring a bindery queue, enter the
command:
SET NETW QSERVER
fileserver
ON
servicename
where fileserver is the name of the file server where the
queue will reside (note that this is not necessarily the
same as the volume name), and servicename is the
name of the print server service (the default service
names are listed in the Default Print Server Names
section at the beginning of this chapter).
Note: The SET NETWARE SERVER command,
which enables file servers on a global basis, is
available for compatibility with older firmware
releases, but is not recommended for new applications.
3. Start PCONSOLE
- If necessary, change to the desired context if you
are using NDS.
Novell Network Configuration 5-17
Page 90

- Go to Print Queues, press Insert to create a new
print queue, and enter the name of the print queue.
If you are configuring an NDS queue, you will also
need to enter a volume name (press Insert to
browse for available volumes).
- Select Print Servers (NetWare 4.xx and later) or
Queue Servers (NetWare 2.xx and 3.xx), press
Insert and enter the name of the TROY XCD print
server (the default print server names are discussed
in the Default Print Server Names section at the
beginning of this manual).
- Go to Print Queues, select the desired print
queue, then select Print Servers and press Insert to
select the name of the TROY XCD print server.
- Exit PCONSOLE.
4. Go back to XCONFIG and enter the command:
SET NETWARE RESCAN
After a few seconds, do a SHOW NETWARE
command; you should see the queue you created being
serviced by the file server. You are now ready to use
the queue.
Configuring the Print Server and Adding
the Print Queue in Remote Printer Mode
To configure a TROY XCD print server for remote printer
mode, there are two basic steps required. First, you must use
5-18 Novell Network Configuration
Page 91

Novell's NWAdmin or PCONSOLE to add the print queue to
the NetWare server. Then you must configure the print
server for remote printer operation using XAdmin32,
XAdmin, JetAdmin, WebXAdmin, or the print server
console.
Important Note: You cannot configure both Queue Server
and Remote Printer mode on the same print server port. It is
possible, however, to configure a multiport print server (such
as the XConnect 100) with one port running in Queue Server
mode and the other in Remote Printer mode.
Configuring the Print Server and Print Queue using
NWADMIN and XAdmin32, XAdmin, WebXAdmin, or
JetAdmin (NDS Remote Printer Mode):
To configure an TROY XCD print server for remote printer
mode with NWADMIN (NetWare Administrator utility) and
XAdmin32, XAdmin, WebXAdmin, or JetAdmin, first make
sure that you have V3.28 or later firmware (refer to the selftest page or do a SHOW VERSION command from the
console). Then perform the following steps:
1. Make sure that the PSERVER NLM (NetWare
Loadable Module) is loaded on your file server and that
you are logged in as ADMIN in NDS mode on the
NetWare 4.xx file server.
2. Start NWADMIN by double clicking on the icon.
Select the desired Container Object (Organizational
Unit) that will contain the new printer.
3. Select
When you get the New Object menu, select Printer
and then OK.
Object from the menu bar and then Create.
Novell Network Configuration 5-19
Page 92

4. Enter the name of the printer and select Create.
5. Double click on the name of your PSERVER NLM.
Click on Assignments and then Add...
6. If necessary, change the directory context. Select the
printer you created and click OK. Note the number of
the printer, as you will use this later, then click OK.
7. Select the desired Container Object (Organizational
Unit) that will contain the default print queue, and then
click on Object and Create to get New Object menu.
8. Select Print Queue and then OK. Make sure that
Directory Service Queue is selected, and then type in
a name for the default print queue.
9. Click on the button to select the print queue volume.
Change the directory context if necessary, then select
the desired volume (Objects) and click OK. Click
Create to create the print queue.
10. Change context if required and then double click the
name of the printer you created previously.
11. Click Assignments and then Add..
12. Change context if necessary and select the print queue
you created. Click OK and then OK again, and then
exit NWADMIN.
13. Select the print server and service that you wish to
configure:
5-20 Novell Network Configuration
Page 93

• If you have XAdmin32, double click on the print
server name and then click on the appropriate
NetWare tab (NetWare P1 for the first parallel port,
NetWare S1 for the first serial port, NetWare P2
for the XConnect 100 second parallel port or
NetWare S2 for the XConnect 100 second serial
port).
• If you are using XAdmin, one or more TROY XCD
print server NetWare services will show up in the
list of printers (the default service names are listed
in the Default Print Server Names section at the
beginning of this chapter). Double click on the one
that you wish to configure and then click on the
NetWare tab.
• If you are using WebXAdmin, start your web
browser, enter the IP address of the print server as
the destination address, and then push ENTER or
RETURN. Click on Configure NetWare, and then
click on the Enabled Service that you wish to
configure (the default service names are listed in the
Default Print Server Names section at the beginning
of this chapter).
• If you are using JetAdmin, one or more TROY XCD
print server NetWare services will show up in the
list of printers (the default service names are listed
in the Default Print Server Names section at the
beginning of this chapter; note that JetAdmin
supports a maximum of three ports per print server).
Single click on the one you want to configure, go to
the menu bar and select Device and then Modify.
Then click Next and select Operating Mode.
Novell Network Configuration 5-21
Page 94

NOTE: If you want to enable remote printer
capabilities on services other than the default NetWare
services, you must define new services that are enabled
for NetWare and for the desired port (only one service
per port can be defined for NetWare). Refer to Appendix
B in this manual for information on how to do this.
14. Select the Remote Printer as the Operating Mode,
enter the name of your PSERVER NLM as the Print
Server Name, and select the number of the printer
from step 6 as the Printer Number (XAdmin32 and
JetAdmin allow you to choose from a list of available
print server NLMs rather than typing in the name).
15. If you have XAdmin 32 or XAdmin, click OK. If you
have JetAdmin, click Next two times, and then click
Finish. If you have WebXAdmin, click Submit.
16. Exit the configuration utility. You must now unload
the PSERVER NLM from your NetWare file server
console and then reload it in order for the changes to take
effect.
Configuring the Print Server and Print Queue using
PCONSOLE and XCONFIG (Remote Printer Mode)
To configure an TROY XCD print server for remote printer
mode operation using PCONSOLE and XCONFIG, first
make sure that you have V3.27 or later firmware (refer to
the self-test page or do a SHOW VERSION command from
the console). Then perform the following steps:
1. Make sure that the PSERVER NLM (NetWare
Loadable Module) is loaded on your file server.
5-22 Novell Network Configuration
Page 95

2. Log into the file server from your PC workstation as
ADMIN if you are using NetWare 4.xx (if you want
NDS support, do not login under bindery mode). If you
are using NetWare 2.XX or 3.xx, login as
SUPERVISOR.
3. Run the PCONSOLE utility from your PC workstation.
4. If you are creating a new print queue, select Print
Queue Information (NetWare 3.xx) or Print Queues
(NetWare 4.xx) from the Available Options menu.
Press INSERT, type in the desired print queue name
(with NetWare 4.xx, you will also be asked for a
volume name; press INSERT and select the
appropriate volume), and press ESCAPE to return to
the main menu.
The following steps apply to configuring a remote printer
with NDS support on NetWare 4.xx systems:
a. Select Print Servers from the PCONSOLE menu
and then select the name of the PSERVER NLM on
your host computer.
b. Select Printers.
c. Press INSERT to get Object, Class menu.
d. Press INSERT and enter the Printer Name (any
unique name is OK).
e. Highlight the printer name and press ENTER twice
to get Printer Configuration Menu.
Novell Network Configuration 5-23
Page 96

f. PCONSOLE will assign a Printer Number.
Remember this number, since it will be used later.
g. Highlight Print Queues Assigned and press
ENTER and then INSERT to get a list of available
queues.
h. Highlight the name of the print queue you wish to
assign to the remote printer and press ENTER.
i. The other settings in the menu are not required.
Push ESCAPE several times to exit PCONSOLE.
j. Skip to step 5 below.
The following steps apply to configuring a remote printer
on NetWare 3.xx systems:
a. Select Print Server Information from the
PCONSOLE main menu and choose the name of
the PSERVER NLM.
b. Select Print Server Configuration and then
Printer Configuration. Select any "Not Installed"
printer and press Enter. Remember the number of
this printer, since it will be used later in the
configuration process.
c. If desired, type in a new name for the printer.
d. Go to Type, press ENTER, highlight Remote
Other/Unknown and press ENTER again. The
other settings in this menu are not required.
5-24 Novell Network Configuration
Page 97

e. Push ESCAPE and save the changes.
f. Push ESCAPE and select Queues Serviced by
Printer.
g. Highlight the printer name that you just configured
and press ENTER.
h. Press INSERT, choose the desired print queue, and
press ENTER (you can accept the default priority).
i. Press ESCAPE several times to exit PCONSOLE.
5. Insert the TROY XCD Print Server Software diskette or
CD-ROM into your PC and run the XCONFIG utility
(in the \utilities directory on the CD-ROM)
Select the TROY XCD print server from the list of
print servers. When you get the message that the print
server is connected, press the ENTER key and type the
password ACCESS in response to the "#" prompt (the
password will not echo), and then press the ENTER key
again in response to the Enter Username>
prompt. When you get the Local> prompt, type:
SET NET NPRINTER
SET NET RESCAN
EXIT
nlm number
ON
service
where nlm is the name of the PSERVER NLM on your
file server, number is the printer number (must match
the printer number you selected during the PCONSOLE
configuration in the previous steps) and service is the
name of the service (the default service names are listed
in the Default Print Server Names section of this chapter).
Novell Network Configuration 5-25
Page 98

For example, to set up remote printer 3 for an HP printer
with the TROY XCD print server XCD_00C3E4 using
the PSERVER NLM called XCD1PS, you would type:
SET NET NPRINTER XCD1PS 3 ON XCD_00C3E4_P1
SET NET RESCAN
EXIT
NOTE: The same service cannot be used for both
queue server mode and remote printer mode.
NOTE: If you want to enable remote printer
capabilities on services other than the default NetWare
services, you must define new services that are enabled
for NetWare and for the desired port. Refer to
Appendix B in this manual for information on how to
do this.
6. You must now unload the PSERVER NLM from your
NetWare file server console and then reload it in order
for the changes to take effect.
Configuring the Workstation
The final step is to configure the workstation(s) to print to
the TROY XCD print server. The TROY XCD print server
can be used with any workstation that supports either the
Novell or Microsoft client software.
Configuring the Workstation (Windows 95/98)
To use a NetWare print queue from a Windows 95
workstation, first make sure that the appropriate NetWare
drivers are installed. Then go to the Start button, choose
Settings, and then select Printers. Double click on the Add
5-26 Novell Network Configuration
Page 99

Printer icon and then execute the following steps when you
get to the Add Printer Wizard.
1. Click on Next, Select Network Printer and click on
Next again.
2. Select Browse, double click on the appropriate file
server name, select the print queue, and click OK. If
you used JetAdmin to configure the queue, you should
double click on the HP_Network_Printers icon
instead of the file server icon, and then select the
TROY XCD print server name. Click on Next.
3. Select the desired printer manufacturer and model
(click Have Disk if your printer is not listed), and click
on Next.
4. If the driver already exists, select Keep Existing
Driver (if it does not, this step will be skipped), and
then click on Next.
5. If desired, change the name of the printer and/or make
it the default, and then click on Next.
6. Select Yes when you are asked "Would you like to
print a test page?" Click on Finish.
Configuring the Workstation (Windows NT 4.xx)
To add a queue from a Windows NT 4.xx workstation,
execute the following steps: NetWare Windows VLM
drivers and utilities installed. Then go to the Start button,
choose
the Add Printer icon and then execute the following steps
when you get to the Add Printer Wizard:
Settings, and then select Printers. Double click on
Novell Network Configuration 5-27
Page 100

1. Select Network Printer Server and click on Next.
2. Select the desired print queue and click OK. Answer
OK when asked if you want to install the printer driver.
3. Select the desired printer manufacturer and model, and
click on Next.
4. If desired, make the printer the default, and then click
on Next.
5. Click on Finish.
Configuring the Workstation (Windows 3.xx)
To use a NetWare print queue from a Windows 3.xx
workstation, first make sure that you have the appropriate
NetWare Windows VLM drivers and utilities installed. Then
execute the following steps:
1. Open the Main window of the Windows Program
Manager and start the Print Manager.
2. Select
then Network Connections.
3. Select the desired port (for example, LPT1:) under
Ports: and the desired print queue under Resources. If
you have configured the TROY XCD print server for
NDS mode, you may alternatively select the printer
name instead of the print queue name.
4. Click Capture and Permanent.
5. Close the window and select Options and then Printer
Setup.
Options (or Printer) from the menu bar and
5-28 Novell Network Configuration
 Loading...
Loading...