Page 1

User’s Guide
802.11b Print Server
Part Number 40148-100
Revision 1.0
Page 2

ii
Copyright Notice
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored, in a
retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission
of TROY Group, Inc. The information contained herein is designed only for use
with this TROY product. TROY is not responsible for any use of this information
as applied to other products.
Neither TROY nor its affiliates shall be liable to the purchaser of this product or
third parties for damages, losses, costs, or expenses incurred by purchaser or third
parties as a result of accident, misuse or abuse of this product or unauthorized
modifications, repairs, or alterations to this product, or (excluding the U.S.) failure
to strictly comply with TROY’S operating and maintenance instructions.
Warranty Notice
TROY GROUP, INC. SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS OF THIS PRODUCT
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. TROY shall not be liable for any errors contained in this manual or for any damages resulting from loss of use, data profits, or
any incidental or consequential damages arising from the use of TROY products
or services.
Trademark Notice
EtherWind and EtherSync are trademarks of TROY Group, Inc.
General Notice: Other product names used herein are for identifications purposes
only and may be trademarks of their respective owners. TROY disclaims any and
all rights in those marks.
Copyright © 2001 by TROY Group, Inc.
Page 3

Contents
Introduction
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Network Operting Systems Supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Network Protocols Supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
1 Installing the EtherWind Print Server Hardware
Before You Begin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-1
Unpacking the Print Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-1
EtherWind Connectors, Switches, and LED’S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
Connecting the Serial EtherWind to an RS-232 Serial Device . . . . . . . .1-3
Connecting to a Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Verifying Successful Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Verifying the Connection to the Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
2 Configuring the EtherWind 802.11b and IP Settings . . . . .2-1
3 Management Methods
WP-Admin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
XAdmin32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
WebXAdmin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
EtherWind Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-2
4 Microsoft Windows Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-1
5 AppleTalk Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-1
6 Novell NetWare Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-1
7 UNIX Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-1
8 DEC LAT Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-1
9 Banyan VINES Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-1
10 PrintraNet Internet Remote Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-1
iii
Page 4

iv
11 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Frequently Asked Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-1
Loading the Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-3
Uninstalling the EtherWind Wireless Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-4
12 Where to Get Help
Worldwide Web Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-1
Contacting TROY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-1
Returning Products . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-1
Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-2
13 Notices
FCC Compliance Statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-1
Declaration of Conformity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-2
Page 5

Introduction
The EtherWind 802.11b Wireless Print Server lets you communicate with printers
from anywhere on an 802.11b wireless network. You can use the print server in
ad-hoc (peer-to-peer) or infrastructure (access point) wireless mode, as shown
below.
The print server operates at speeds of up to 11 Mbps on any IEEE 802.11b wireless compatible network. Your printer can be simultaneously connected to your
PC or Macintosh via the USB port.
Follow the instructions in this manual to install the print server for your printer.
For more information and software downloads, check the TROY web site
(www.troygroup.com).
1
Ad-Hoc Mode
(Peer-to-Peer)
Infrastructure Mode
(With Access Point)
Laptop computer with
802.11b capabilities
Laptop computer with
802.11b capabilities
EtherWind
EtherWind
802.11b
Access Point
Local Area Network
(or Cable/DSL connection)
Printer
Printer
Page 6

System Requirements
To use the EtherWind for printing from a wireless network, you need an 802.11b
wireless network. The wireless network will consist of either of the following:
◗ An 802.11b wireless enabled PC or Macintosh printing straight to the printer
(Ad-Hoc or Peer-to-Peer Mode).
◗ An 802.11b wireless Access point allowing wireless and wired Ethernet enabled
computers to print to the EtherWind.
To configure and print to the EtherWind, you need the following:
◗ The MAC address from the label of the EtherWind (for example:
004017023F96).
◗ The following information from your wireless network administrator:
• Wireless Mode (Infrastructure or Ad-Hoc)
• The SSID (service set identifier) for your wireless network.
• The Radio Frequency Channel of the wireless network.
• If you are using TCP/IP (recommended for Windows Networks) and are
not connected to a DHCP server (for obtaining an IP Address automatically), you will need a unique IP Address for the EtherWind wireless print
server (for example: 192.168.1.14). If the EtherWind is not on the same
IP subnet as the computers you are printing from, you will also need a
subnet mask and a router (default gateway) address.
Operating Systems Supported
◗ Windows 95, 98, ME, NT 4, 2000, XP
◗ MacOS 7.xx, 8.xx, 9.xx, MacOS X
Network Protocols Supported
◗ TCP/IP
• LPD/LPR
• Raw TCP/IP (port 9100)
• NetBIOS over IP (with SMB)
• Multiple configurable TCP port numbers
◗ TELNET
◗ WINS
◗ DHCP
2
Page 7

◗ AppleTalk
• Apple Printer Utility compatibility
• Binary AppleTalk support
• AppleTalk spoofing
◗ IPX/SPX
• NetWare RPrinter Bindery mode
• NetWare PServer Bindery mode
• NetWare NPrinter NDS mode with NDPS support
• NetWare PServer NDS mode
• Ethernet II, 802.3, 802.2, 802.2 SNAP Frame types
• Compatible with PCONSOLE, NWADMIN, PRINTCON, and other
Novell utilities
◗ NetBEUI
◗ DEC LAT (-N models only)
◗ Banyan VINES (-N models only)
◗ PrintraNet Internet Printing
3
Page 8

4
Page 9

Installing the
EtherWind Print
Server Hardware
Before You Begin
Before you install the EtherWind wireless print server, make sure that your printer
or other device and your computer already function properly via a parallel, serial
or USB printer cable. Refer to your printer’s documentation for instructions on
using and maintaining your printer.
In addition, make sure that you have properly installed the 802.11b wireless
equipment and software you are using to communicate to the EtherWind as
described in the documentation that came with that equipment.
Unpacking the Print Server
Your package should contain the following items:
◗ EtherWind Wireless Print Server
◗ EtherWind Wireless Print Server desktop mounting base
◗ EtherWind Wireless Print Server User’s Guide (This Book)
◗ IEEE 1284 Parallel Cable – 25 Pin Male to 36 Pin Male
◗ Power Supply (some international models also include a separate power cable)
◗ Installation CD-ROM
If anything is missing from the box, please contact TROY.
1-1
1
Page 10

EtherWind Connectors, Switches, and LEDs
Test Switch. Press down this switch for less than 5 seconds to print a test page on
the printer. The test page will show the current wireless and network settings of
the EtherWind wireless print server. Press it down for more than 5 seconds to
reset the EtherWind to its factory default parameters. If you hold the test switch
down upon powering up, the print server will power up in Ad-Hoc mode on RF
Channel 11 with the SSID of printer.
Power Connector. Plug the power supply into this connector.
LED status indicators. The green light comes on when the unit is powered on,
then goes out. The yellow light will come on solid when a wireless network link is
established. The green light blinks during wireless network activity.
Parallel Port (DB25). This port is used for connecting to a parallel printer.
Serial Port (DB9). This port is used for connecting a serial printer or other serial
device. Can also be used to access the command line console of the EtherWind for
configuration and diagnostics.
1-2
Test Switch
Serial Port (DB9)
Parallel Port (DB25)
Power Connector
LED Status
Indicators
Page 11

Connecting to a Printer
Follow these steps to connect the EtherWind wireless print server to your printer:
1. Attach the EtherWind to the desktop mounting base.
2. Make sure the printer is off.
3. Connect the parallel cable to the print server and the printer.
4. Plug the power cord from the power supply into a wall outlet or power strip.
5. Connect the the power supply to the EtherWind.
6. Turn the printer on.
Verifying Successful Installation
When the print server is powered on, the EtherWind will go through the following startup sequence:
◗ It runs through a set of power-up diagnostics for a few seconds. If the
EtherWind is operating properly, the yellow and green LEDs will blink
momentarily and then go out. If the green light blinks continuously in a regular patter, there is a problem. Try unplugging the power and then plugging it
in again. If the problem persists, contact TROY.
◗ When a successful connection is made to the EtherWind from another
802.11b wireless device like an access point or PC, the yellow light will stay lit.
The green light will blink whenever there is wireless networking activity.
Verifying the Connection to the Printer
Before attempting to print, it is very important to verify the connection between
the EtherWind and the printer. If this connection is not good, you will not be
able to print!
To verify this connection, make sure that both the EtherWind and the printer are
powered on and ready. Make sure that the cable is connected securely from the
EtherWind to the printer. Then print a test page by pushing the test switch and
letting go immediately.
If the test page does not print, first make sure all the connections are secure, and
make sure the printer is operating correctly and is not out of ink, toner, paper, etc.
Then power the EtherWind off and then on again, and try printing the self-test
page again.
If you cannot print a test page, refer to the Troubleshooting section of this manual.
1-3
Page 12

Connecting the EtherWind to an RS-232 Serial Device
Note: Skip this section if you are not using the EtherWind serial port.
The EtherWind has one standard PC-compatible 9-pin female D-connectors. The
serial port uses PC-compatible 9-pin male D-connectors. Note that the standard
off-the-shelf 9-pin female to 25-pin male PC cables will require a null modem in
order to connect to most printers or terminals. The pin-outs are as follows:
DB9 DTE DCE
pin Signal Signal pin pin
1 Not used Not used - 2 Receive Data Transmit Data 2 3
3 Transmit Data Receive Data 3 2
4 DTR out DSR in 6 20
5 Signal Ground Signal Ground 7 7
6 DSR in DTR out 20 6
7RTS out CTS in 5 4
8 CTS in RTS out 4 5
9 Not used Not used - -
Basically, the cable must connect input signals (e.g., Receive Data) on the TROY
EtherWind to the equivalent output signals (e.g., Transmit Data) on the device
and vice-versa.
The serial port can be set to operate in console mode to allow you to configure
and diagnose the EtherWind via a serial terminal (or PC with a terminal emulation program). To enable the console mode manually, unplug the power supply
from the serial server, hold down the Test switch and simultaneously plug in the
power supply.
The port will remain in console mode until the unit is power off.
You may also nable console mode by connecting remotely to the EtherWind via
WebXAdmin, TELNET, NCP, or XConfig (refer to Chapter 3 for information on
how to use these utilities). With WebXAdmin, select Configure Port from the
main menu, click on serial port S1, select Console Mode, and click Submit.
With TELNET or XCONFIG, use the following command:
1-4
Page 13

SET PORT S1 CONSOLE ENABLED
You can remotely restore the port to normal serial operation by unselecting
Console Mode from WebXAdmin or by using the console command SET PORT
serialport CONSOLE DISABLED.
The serial ports are factory set at 115200bps, 8-bit data, CTS/RTS (Hardware)
flow control, and no parity. If your printer or serial device requires different settings, you must use WebXAdmin or a console terminal connected to port S1 as
described in the previous paragraph. With WebXAdmin, select Configure Port
from the main menu, click on S1, choose the desired settings, and click Submit.
With the console terminal, use one or more of the following commands:
SET PORT S1 SPEED
baudrate
SET PORT S1 PARITY
parity_type
SET PORT S1 FLOW
flowctrl
SET PORT S1 CHARACTER
charsize
Note that the serial port always operates at 115200bps when in console mode.
Don't forget to set the serial port settings on your printer or other device to match
the settings of the EtherWind.
1-5
Page 14

1-6
Page 15

Configuring the
EtherWind 802.11b
and IP Settings
Configuring the EtherWind
There are three basic steps required to configure the EtherWind:
1. Configuring the EtherWind 802.11b settings. To operate on an 802.11b net-
work, you must set the wireless (ad-hoc or infrastructure), SSID, channel, data
rate and WEP encryption. All nodes of a wireless network need to have the
same settings in order to communicate with each other.
2. Configuring the IP address settings. You will need to set the IP address, subnet
mask, and router address if you are using TCP/IP, NetBIOS IP, or PrintraNet,
or if you want to use the WebXAdmin web-based management utility.
3. Configuring the EtherWind for operation with the network operating systems. The
final step is to configure the EtherWind so that you can print to it using one
or more network operating systems (for example, Windows NT/2000,
NetWare, AppleTalk, etc.).
Before You Begin
◗ Make sure that you have properly configured your computer for communica-
tion on a wireless network. If you are connecting to the printer through an
access point, make sure your computer is in infrastructure mode and it is associated with the access point. If you are printing directly to the printer without
an access point, you should be in ad-hoc mode. See the documentation for
your wireless adapter for instructions.
Note:
If your wireless adapter includes an option for 802.11 Ad-hoc, you must
select it if you want to use the printer in ad-hoc mode. If it doesn’t include
2-1
2
Page 16

this option, select Ad-hoc Computer-to-Computer, or whatever mode your
adapter uses to communicate on a wireless network without an access
point.
◗ If you are using WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption on your wireless network,
you will need to temporarily disable WEP on your PC in order to configure the print
server. If you are using an access point with WEP enabled and it does not allow nonwep clients to communicate with other non-wep clients, then you will also need to
temporarily change the wireless mode of your computer to Ad-hoc (802.11) mode.
Note:
If no computers on your network can be set to Ad-hoc mode, you will need
to temporarily disable WEP on your access point. When you are done configuring the print server, you can re-enable WEP on your computer and
change the wireless mode back if necessary.
◗ If you are using TCP/IP, note your computer’s IP address. The print server will need to
be on the same IP segment as the other nodes on your network in order to communicate.
◗ If you are using infrastructure mode, make sure you have a good signal between your
computer and the access point. Most wireless adapters have a utility that shows the
wireless signal strength. See your wireless adapter’s documentation for details.
◗ If you are using a Macintosh with an Airport
®
base station or non-Apple access point:
• If your Macintosh has an Airport wireless card installed, make sure that AirPort is
enabled in the AppleTalk and TCP/IP Control Panels. If both your Macintosh and
the AirPort base station or access point are connected to an existing Ethernet network, select Ethernet in the AppleTalk and TCP/IP Control Panel.
• To use the printer in infrastructure mode, use the Airport application to select the
Airport Network name that corresponds to the base station or access point from
the AirPort Networks list.
• To use the printer in computer-to-computer (Ad-hoc) mode, use the Airport application to create or join a computer-to-computer network. See your AirPort documentation for details.
• If you are using password protection, you will need to temporarily create a computer-to-computer network with no password protection to configure the print server,
then re-join the network with the password protection.
• In order to make the Apple Airport password protection compatible with the 64-bit
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) on the EtherWind, you will need to use 0x followed by the 10 digit WEP key.
◗ If you are using a home gateway or router, you will want to configure the EtherWind
from a PC on the same network segment that you want the EtherWind to be on.
2-2
Page 17

Installing the Software
Follow these steps to install the WP-Admin software and configure the print server.
1. Insert the EtherWind Wireless Configuration CD-ROM into your PC or
Macintosh.
Note:
There is also a Linux version of the WP-Admin utility available on the TROY
website (www.troygroup.com).
2. If you are using a Windows computer, click on Install TROY EtherWind
Utilities, then click on Install EtherWind Configuration Utilities and
Printing Software. If you are using a Macintosh computer, open the Mac
folder (for Mac OS 8.x or 9.x) or the Mac OS X folder.
Note:
If you are using Windows and don’t have the Java Runtime installed on your
system, you will be prompted to install it, click Continue.
3. Follow the on-screen instructions for installing the utility. When WP-Admin
starts, you will see the WP-Admin Wireless Server Search screen, which
will look like this:
4. Click START to begin searching for print servers. WP-Admin will get the
information from the print server(s) and list the Server Name and Ethernet
Address (which should correspond with the label on the back of the print server). It might take a minute or two for the print server to show up, especially if
you have a large wireless network. Note that by default the name of the
EtherWind print server is XCD_xxxxxx, where xxxxxx is the last six digits of
the Ethernet (MAC) address (for example, XCD_08B2C7).
2-3
Page 18

Note:
If you don’t see the print server in the list, hold down the button for more
than 5 seconds to reset it to factory defaults and try the search again. If you
still don’t see it, check the troubleshooting section (chapter 11).
5. When you see the print server you want to configure in the list, highlight it
and click Configure. If you are using DHCP, wait until the print server gets
an IP Address from the DHCP server and is updated on the search screen
before configuring (the IP address will change from the default 192.0.0.192 to
a new value).
Note:
If the wireless signal is less than 50% on the search screen, printing perfor-
mance could be affected. To improve the signal strength, try moving the print
server closer to the computer or access point and away from other radio
devices such as BluetoothTMwireless devices, microwave ovens, or cordless
phones.
6. You will be prompted for the configuration password (the default password is
access), type in the password and click OK to continue. The Wireless
Server Configuration screen will come up which will look like this:
Note: If you are having trouble configuring a print server, click Cancel to get
back to the Search screen, click Clear to clear the list of print servers, and start
again from step 4 above.
7. The settings of the EtherWind you selected in the Wireless Server Search
screen will be displayed. Many of the fields will be configured automatically to
match the network being used, so you will probably NOT need to change the
Wireless Mode, RF Channel, SSID, and Data Rate settings unless you want to
want to change the EtherWind to a different wireless network.
2-4
Page 19

• If your network uses WEP encryption, you will need to enable WEP and
enter the appropriate WEP key(s). Contact your system manager to determine what information .
• If you are using TCP/IP (recommended for Windows printing) and you
do not have a DHCP server (see note below), you will need to manually
assign a valid IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway and then set the
Boot Method to Static.
• If you are using a Macintosh, no further configuration should be necessary.
When you are done configuring, click OK.
For a Glossary of Terms used for all the settings in WP-Admin, see chapter 11.
Note:
If you are using DHCP on your network, the EtherWind may have acquired
valid IP settings at this point and no further configuration is necessary. This
might work well if your DHCP server allows the print server to keep this
address permanently, but in most cases, you will want to use a static
address outside the range reserved for DHCP (See your DHCP server documentation for details). This is because when you configure your printer port,
it will go to a static IP address.
Your Print Server should be configured correctly at this point. Configuring the
EtherWind to print under various operating systems is covered in chapters 4
through 9.
2-5
Page 20

2-6
Page 21

3-1
Management
Methods
TROY offers a variety of ways to configure and monitor the EtherWind. These
methods are:
WP-Admin Utility
◗ This utility runs on Windows and Macintosh computers, and is used for initial
configuration of the print server and allows you to set the wireless settings as
well as the basic network settings including TCP/IP.
◗ See the previous section (Configuring the EtherWind 802.11b and IP Settings)
for detailed use instructions
◗ Can be downloaded from our web site (www.troygroup.com)
◗ After initial installation, this utility can be run from the START menu under
START>Programs>TROY Group>EtherWind>WP-Admin
◗ Default password is ACCESS
XAdmin32
◗ This utility runs on Windows computers and is used for advanced configura-
tion of the print server; it allows you to configure for Netware, TCP/IP,
AppleTalk settings and more.
◗ A 32-bit graphical utility
◗ Compatible with Windows PC’s running TCP/IP or IPX/SPX Protocols
◗ Included on CD-ROM
◗ Can be downloaded from our web site (http://www.troygroup.com)
◗ After initial installation, this utility can be run from the START menu under
START>Programs>TROY Group>EtherWind>XAdmin32
◗ Default password is ACCESS
WebXAdmin
◗ Allows the user to configure the EtherWind with a standard web browser like
Netscape Navigator or Microsoft Internet Explorer.
3
Page 22

◗ No additional software is needed on the system.
◗ Can be used on any system that supports web browser capabilities.
◗ Simply type the IP address into your web browser address bar to connect
◗ Default password is ACCESS
*Both the EtherWind and the PC must be configured with an IP address and your
browser must be configured to work across a LAN in order to use WebXAdmin.
EtherWind Console
◗ A command-line oriented console
◗ Contains features not available through WP-Admin, Xadmin32 or
WebXAdmin
◗ Default password is ACCESS.
◗ Can be accessed via:
• TELNET
• DEC NCP
• DEC NCL
• ULTRIX ccr
• TROY XCD XConfig NetWare Utility
• Serial port
• WebXAdmin
Note:
In all cases, when you are connected, hit RETURN or ENTER to get the "#"
prompt, enter password ACCESS (it will not echo) and type anything in
response to the "Enter Username>" prompt. When you get the "Local>" prompt,
you are ready to enter commands.
HP JetAdmin
◗ HP Windows-based utility (TROY EtherWinds work transparently with
JetAdmin).
◗ Can be downloaded from the HP web site (http://www.hp.com)
Note: The TROY EtherWind will not appear in the list of configured servers
unless TCP/IP or IPX is running on the computer.
HP Web JetAdmin
◗ An HP utility for Windows NT Advanced Server and Windows 2000
◗ Can be downloaded from the HP web site (http://www.hp.com).
Once it is installed, a web browser on any computer that has access to the
Windows NT/2000 server may be used to access the TROY EtherWind.
3-2
Page 23

Microsoft Windows
Network Configuration
The EtherWind includes the easy-to-use ExtendNet Connect IP Monitor software
for printing from Windows computers over an 802.11b wireless link. This software creates a network port on the Windows system, which acts like a normal parallel port. As a result, it works transparently with any standard Windows printer
driver and application program. Because this software uses the industry-standard
TCP/IP protocol, it can be used with IP routers and other IP-based equipment.
Installing the Software
1. Install the ExtendNet Connect IP Port Monitor by inserting the EtherWind
CD, selecting Install EtherWind Utilities, then Install ExtendNet Connect
Port Monitor. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete this installation.
2. Install the printer driver software according to the documentation for the printer.
3. Click the Windows Start button, select Settings, and then Printers.
4. Right-Click on the printer you wish to associate with the network port, and
select Properties.
4
4-1
Page 24
5. If you are using Windows NT/2000/XP, go to the Ports tab. If you are using
Windows 95/98/ME, go to the Details tab.
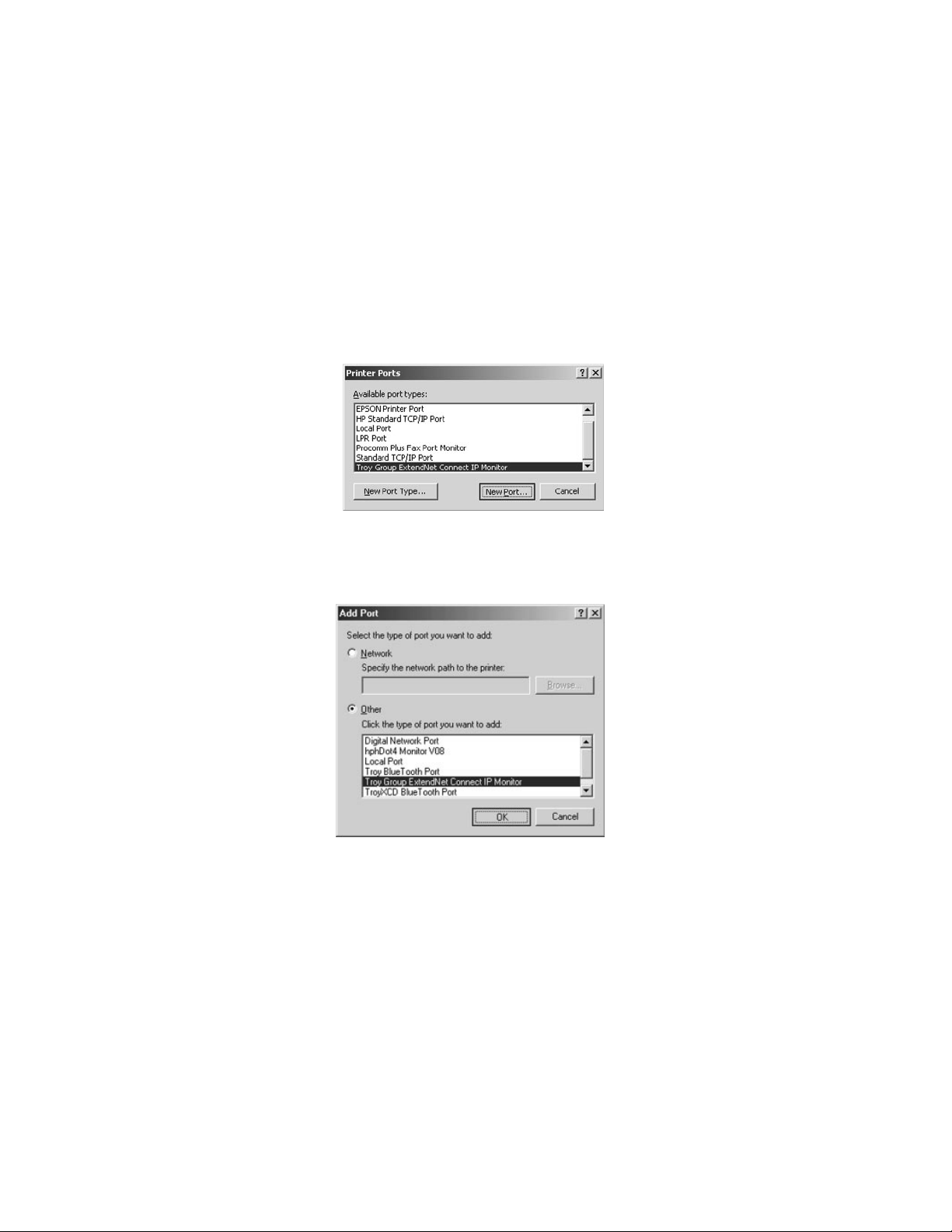
6. Click on Add Port.
7. If you are using Windows NT/2000/XP system, highlight Troy Group
ExtendNet Connect IP Monitor, and click New Port.
If you are running Windows 95/98/ME, select Other, highlight Troy Group
ExtendNet Connect IP Monitor, and click OK.
4-2
Page 25
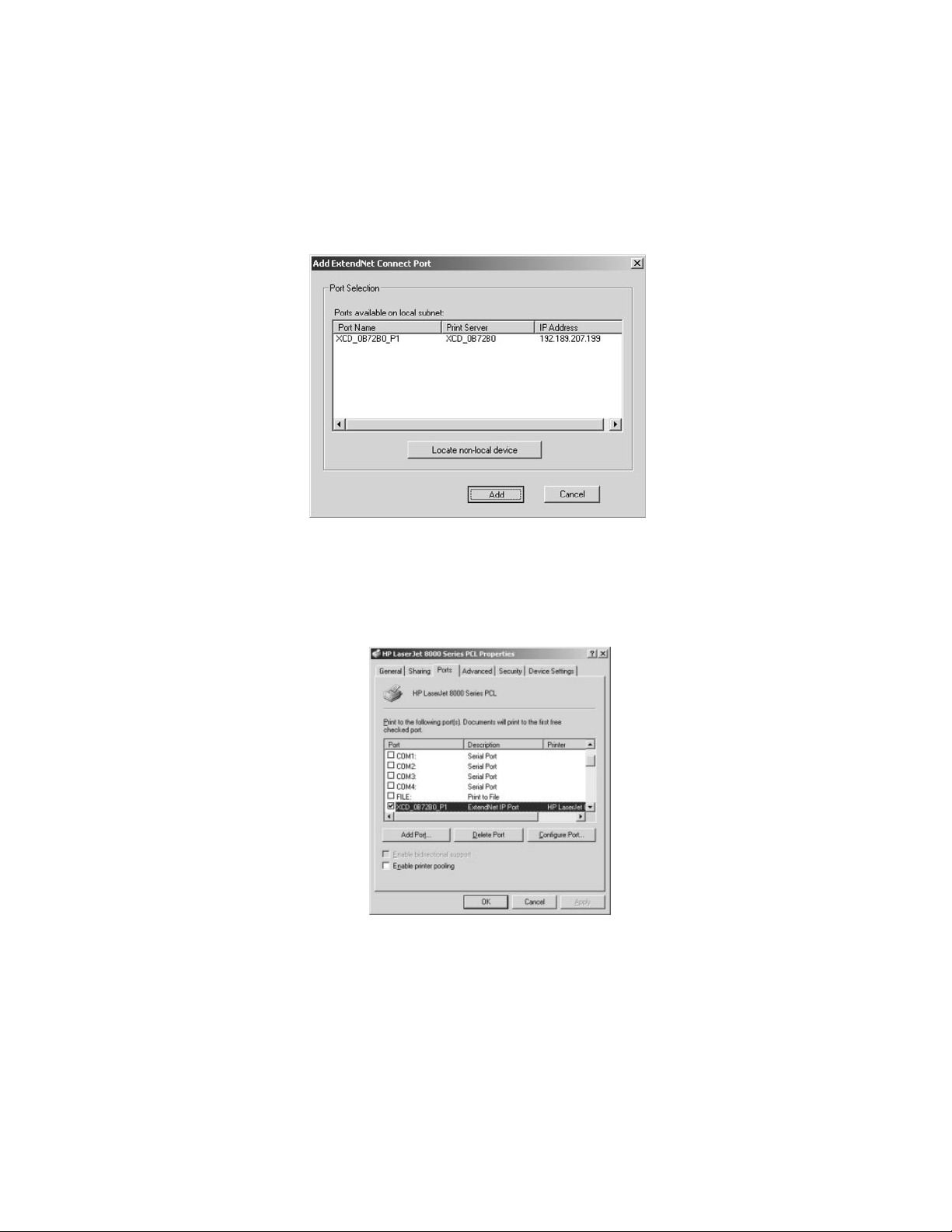
4-3
8. The search will begin for available print servers, highlight the print server you
would like to create the port for, and click ADD.
9. Make sure the port you created is chosen and click Apply.
If you are using Windows NT/2000/XP, the Ports tab should look something
like this:
Page 26

If you are running Windows 95/98/ME, the Details tab should look something like this:
You are now ready to print.
Additional Windows Configuration Methods
EtherWind print servers are also compatible with other methods of printing from
Windows. These include the Standard TCP/IP Port option in Windows 2000/XP,
and the LPR Port option in Windows NT that are built into the operating system.
In addition, you can download the NetBEUI/NetBIOS Port monitor from the
TROY Wireless web site (www.troygroup.com), or use TROY’s PrintraNet Port
monitor for printing across the Internet (see chapter 10).
4-4
Page 27

AppleTalk Network
Configuration
The EtherWind runs over wireless Ethernet (also known as Ethertalk). This capability allows Macintosh computers to print jobs to a printer simultaneously with
jobs from Windows, NetWare, and other computers.
The print server will appear as a shareable printer node on an Appletalk Phase 2
network. The print server broadcasts information to Macintoshes on the network
and automatically appears in the Chooser on each Macintosh. Application programs can print without any modification or special software on the Macintosh.
Configuring the Macintosh
1. Identify the printer to which the print server is connected, and install the
printer driver.
2. Verify that Airport is enabled from the Network Control Panel or AppleTalk
Control Panel if you are using an Airport enabled Macintosh. If you are using
a Macintosh connected to an Airport base station (or other Wireless Access
Point) via the wired Ethernet, you will want to be sure Ethernet is selected.
Setting Up Printing (MacOS 8.x and 9.x)
1. At a Macintosh workstation, from the Apple menu, open the Chooser.
2. If the Chooser window displays an AppleTalk zone list, select the necessary zone.
3. Click on the icon for the printer driver you are going to use. If you have a
Postscript printer, you can use the LaserWriter driver.
4. Select the print server name (the default is XCD_xxxxxx_P1_AT, where
"xxxxxx" are the last six digits of the Ethernet address.).
5-1
5
Page 28

5. Close the Chooser. You can now print to the printer using any standard
Macintosh application program.
Setting Up Printing (MacOS X)
1. If you haven't done so already, set the name of your computer by going to the
Applications folder*, selecting System Preferences, and then Sharing.
Type in the computer name in the Network Identity section (you can also set
the IP address here if you want).
2. Turn on the Airport and AppleTalk by clicking on the Applications folder
and then clicking on Network. Next to Configure: select either Airport or
Built-in Ethernet, depending on which network port you are using (you can
leave the Location: setting as Automatic).
3. If you are using the Airport card, select the SSID of the wireless network as the
Preferred Network. If there is a network password enabled, enter it here.
4. Then click on the AppleTalk tab, make sure that the box next to Make
AppleTalk Active is checked. If necessary select the appropriate AppleTalk
Zone. You can leave the Configure: setting as Automatically.
5. Now go to the Applications folder, open the Utilities folder, and select Print
Center. The Printer List will appear (it will be empty if you have no printers
configured). Click on Add Printer... and then select AppleTalk instead of
Directory Services.
6. All of the available AppleTalk printers on the network should appear. Click on
the one you wish to add, and then click Add. The printer will now appear in
the Printer List.
7. To print from an application program, go to File and then Print, select the
desired printer, and then click on Print.
*Note that the Applications folder can generally be reached by double clicking on the Macintosh HD icon on
the desktop.
5-2
Page 29

NetWare Network
Configuration
Configuring the Print Server and Print Queue with XAdmin32 (Queue Server Mode)
This section covers installation using the Novell client.
Note:
TROY recommends you use the Novell 32-bit client on your Windows workstation instead of the Microsoft NetWare client, because it allows direct configuration of print queues without the need for a Novell utility like NWAdmin or PCONSOLE.
The EtherWind automatically makes itself known on a NetWare network. The
default NetWare Print Server name is XCD_xxxxxx_P1, where "xxxxxx" is the last
six digits of the Ethernet address (the Ethernet address is on a label that is affixed
to the EtherWind). Note that the NetWare Print Server name is used for either
NDS or bindery mode configuration.
If you are configuring the first port with XAdmin32, the NDS Printer Name for
this port is automatically assigned as "XCD_xxxxxx_P1 Printer". If you are using
an alternate configuration method like NWAdmin, you may assign any unique
name for the printer.
The Print Server and Printer names are used extensively during the configuration
process, so be sure to remember them. Note that these names are actually the
names of the print server's NetWare services. If desired, you can change the default
names using XAdmin32 or WebAdmin.
Follow these steps to configure the queue server:
1. Make sure you are logged in as ADMIN or equivalent (NetWare 4.xx and
above) or SUPERVISOR (NetWare 2.xx and 3.xx).
6-1
6
Page 30

2. Click Start, select Programs, select the XAdmin32 folder, and then select
XAdmin32.
3. Click on the IPX/SPX icon under Filters to set the operating mode to
IPX/SPX (TCP/IP mode will not allow you to configure NetWare print
queues directly). The EtherWind should appear in the list of available printers.
If it does not, try selecting Devices from the menu bar and then Search
Active Devices.
4. Double click the printer you want to configure, enter the configuration password (ACCESS is the default), and click OK.
5. A series of index card tabs will be displayed. Click on the NetWare P1 tab.
6. If it is not already selected, select Queue Server as the operating mode.
7. Click on the inverted triangle button and select the NDS tree.
8. Click the Change... button to select the NDS context where the queue will
reside. (If you are using the Microsoft client, you must type in the name of the
context.)
The box labeled "Print Server" contains the name of the NetWare Print Server. If
you are configuring any other port, this box contains the name of the NDS
Printer. If desired, you can change these names.
You may now create a print queue. Follow these steps:
1. Click on the Change NDS Queues... button to configure an NDS print
queue or click the Change Bindery Queues... to configure a bindery mode
queue.
2. Two windows will appear: Available Print Queues and Serviced Print
Queues. Go to the Available Print Queues window.
3. If you are configuring an NDS queue, click on the context where the print
queue will reside.
4. If you are configuring a bindery queue, click on the volume where the queue
will reside (a volume name will have a file server icon next to it).
6-2
Page 31

6-3
5. Click on New Queue. Enter any unique name for the Queue name.
◗ If you are configuring a bindery queue, click OK and proceed to step 8.
◗ If you are configuring an NDS queue, click Browse, select the file server
volume where you want the queue to reside (a volume name will have a file
server icon next to it), and click OK.
6. The queue name will now appear in the Available Print Queues under the
selected volume (for bindery mode) or in the selected context (for NDS
mode). Click on the desired queue and click Add.
The name will now appear in the Serviced Print Queues window.
7. Click Close and then OK. You can now use the print queue from your
NetWare workstation.
If you want to configure additional queues and ports, you must use the Novell
NWAdmin utility (this program is usually found in the Public directory on the
NetWare file server). Follow these steps:
1. Start the NWAdmin utility and make sure you are in the right context. (If not,
select NDS Browser from the Tools menu and then browse for the desired
context.)
2. Select the container where you want the print queue to reside.
3. Select Print Services Quick Setup from the Tools menu.
4. Browse for the NetWare Print Server by clicking on the button next to the
Print Server Name window.
5. Enter the name of the NDS Printer for the desired port in the Name box (for
example, XCD_04ECBA_P1).
6. The Type box should be left at the default Parallel setting.
7. Select the desired banner type.
8. Enter any desired name for the print queue.
9. If necessary, browse for the volume.
10. Click Create to create the print queue. You are now ready to use the queue
from a NetWare workstation.
Page 32

6-4
Page 33

UNIX Network
Configuration
The EtherWind print server appears to the network as a UNIX host computer with a
unique IP address running the line printer daemon (lpd) protocol. As a result, any
host computer that supports the Berkeley remote-LPR command can spool jobs to
the print server without the need for any special software on the host computer.
Important Note:
Before configuring a UNIX print queue, the EtherWind must have a valid IP
address.
Berkeley UNIX Host Configuration
Berkeley UNIX host computers include Linux, Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital UNIX, OSF/1, and ULTRIX; Compaq Tru64 UNIX; SunOS (not
Solaris), SCO UNIX; and many others. Sun Solaris, HP/UX, IBM AIX users
should skip to the appropriate sections later in this manual.
Important Note:
Do not use the Linux X-Windows graphical user interface printer configuration
utility, because it does not work with TROY print servers. Instead, Linux users
should follow the configuration steps listed in this section.
Important Note:
SCO UNIX users should use the rlpconf command to create a printer and automatically configure the /etc/printcap file (you will still need to edit the /etc/hosts
file). Enter the print server's service name (XCD_xxxxxx_P1) as the name of the
printer (refer to the print server self-test for the exact name of this service), and
enter the name of the print server that you assigned in the /etc/hosts file as the
remote host name; note that because this name must be unique for each printer, we recommend using the XCD_xxxxxx_P1 service instead of the normal
BINARY_P1 service.
1. Edit the /etc/hosts file: (or equivalent local host table). For example:
192.189.207.33 xcdprinter
7-1
7
Page 34

1. Edit the printcap file: An example of a typical entry in the printcap file is:
LaserPrinter:\
:lp=:\
:rm=XCD:\
:rp=BINARY_P1:\
:sd=/usr/spool/lpd/LaserPrinter:
"LaserPrinter" is the queuename.
"XCD" matches the name in the hosts file.
"BINARY_P1" is the print server's service name. (NOTE: Use
TEXT_P1 instead of BINARY_P1 for text files.)
"sd" is the spool directory.
2. Create the spool directory: The lpd spool directory is usually located in the
/usr/spool directory. To create a new spool directory, use the mkdir command; for example:
mkdir /usr/spool/lpd/LaserPrinter
3. Print using the standard lpr command:
lpr –PLaserJet filename
4. For AT&T based UNIX systems, such as SCO, use the standard lp command:
lp –dLaserJet filename
Sun Solaris Configuration
To use a TROY print server with Sun Solaris, first use the Host Manager in the
Admintool utility to add the print server IP address and name to the /etc/hosts
file.
1. Click on None - Use /etc files on host
2. Click on Apply
3. Click on Edit and then Add Host
4. Enter the print server name as the Host Name (this name is anything you
want, but should not have an "_" character in it).
5. Enter the IP address and Ethernet address of the print server (the Ethernet
address has the format aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff)
6. Click Add and then close the Host Manager windows
7-2
Page 35

Then use the Printer Manager in the Admintool utility under Open Windows
as follows:
◗ Select Edit
◗ Select Add
◗ Select Add Access to Remote Printer
◗ At the PrinterName prompt, type any desired name for the print queue
◗ At the Printer Server prompt, type:
name\!servicename
(for example, LaserJet\!BINARY_P1), where:
- name matches the print server name as entered in the hosts table.
- servicename is the print service name. For binary graphics files use the ser-
vice BINARY_P1; for text files use the service TEXT_P1.
◗ Make sure that the Print Server OS is set to BSD (this is the default setting).
◗ Select Add
◗ To print, use the standard lp command; for example:
lp –dLaserJet filename
Notes:
◗ We recommend using the /etc/hosts file for the printer name rather than NIS
or other name services.
◗ Due to a bug in the Sun lpd implementation on Solaris 2.4 and earlier
releases, may cause problems printing very long print jobs. The workaround
is to configure the EtherWind as an HP JetDirect card using the HP
JetAdmin for UNIX software.
◗ Solaris print queues can also be configured from the UNIX shell using the
lpadmin command.
HP/UX Configuration
To configure a print server using HP/UX 10.x, use the sam program and execute
the following steps:
1. When you get a list of options, select Printers and Plotters.
2. Select LP Spooler.
3. Select Printers and Plotters.
4. Select Actions and then Add Remote Printer/Plotter.
5. Enter any name as the Printer Name (this will be the name of the print queue).
6. Enter the IP address of the print server as the Remote System Name.
7. Enter the desired print server service name (BINARY_P1 for binary files or
TEXT_P1 for text files) as the Remote Printer Name.
8. Check the box next to Remote Printer is on BSD System.
7-3
Page 36

9. You may accept the default values for the remaining items.
10. Click OK to configure the printer.
11. You should now be able to print using the lp -dcommand with the printer name.
Notes:
◗ The configuration for HP Distributed Print Services and for earlier versions of
HP/UX is slightly different.
◗ The print server can also be configured as a JetDirect card using HP/UX. To
do this, you will need the HP UNIX Host Printing Software (part of HP's
JetAdmin for UNIX).
IBM AIX Configuration
To configure a print server on IBM AIX 4.x, use the SMIT program as follows:
1. Enter smit and select Devices
2. Select Printer/plotter
3. Select Manage remote printer subsystem
4. Select Client services
5. Select Remote printer queues
6. Select Add a remote queue
7. Enter the following remote queue settings:
• Name of queue to add (user selectable)
• Activate the queue (Yes)
• Destination host (EtherWind IP address; or if you have configured the
/etc/hosts file, use the name of the print server that you specified in that file)
• Name of queue on remote printer (BINARY_P1 for binary files or
TEXT_P1 for text files)
• Name of device to add (user selectable; for example lp0)
8. You should now be able to print using the normal lp -d command.
Notes:
◗ The configuration for earlier versions of AIX is slightly different. Refer to the
Administrator's Manual on the CD-ROM for details.
◗ The print server can also be configured as a JetDirect card using AIX. To do
this, refer to your AIX documentation.
Configuration on Other Systems
The EtherWind can be used with any computer system that supports either the
lpr/lpd protocol or the HP JetDirect card (the EtherWind parallel port is port
9100 while the serial port is port 9101). Refer to your system’s documentation for
information on configuring lpr/lpd or JetDirect print queues.
7-4
Page 37

DEC LAT Network
Configuration
Note:
Only TROY EtherWind-N models include DEC LAT support.
The EtherWind wireless print server acts as a node on an Ethernet network that
offers printing services to other devices. The print server comes preconfigured to
run on a LAT network and does not require any additional setup.
Each print server has a default node name of XCD_xxxxxx (where "xxxxxx" are the
last six digits of the Ethernet address of the unit). The port name is P1 for the
EIO, MIO, or first parallel port; S1 for the first serial port, P2 for the second parallel port, and S2 for the second serial port.
VMS LAT Host Configuration
Use the VMS editor to create a text file with the necessary configuration commands
to create a LAT application port and then a VMS print queue. For example:
$MCR LATCP
CREATE PORT LTAxx:/APPLICATION
SET PORT LTAxx:/NODE=
nodename
/PORT=
port
SHOW PORT LTAxx:
EXIT
$SET TERM LTAxx:/PASSTHRU/PASSALL/TAB/NOBROADCAST/PERM
$SET DEVICE/SPOOL LTAxx:
$INIT/QUEUE/START/ON=LTAxx:/PROC=LATSYM
queuename
Note:
LTA
xx
is the available LAT port to be used
nodename
is the node name of the print server
port
is the port, e.g. P1, S1, P2, S2 & LN
queuename
is any unique name for the print queue.
8-1
8
Page 38

Execute the command file. At the VMS "$" prompt type:
@filename
where filename is the name of the text file created in step 1.
Note: The @filename command can be included in the system startup file so that
the procedure is executed automatically when the system is booted.
Use the VMS PRINT command with the name of the queue and the file you wish
to print as shown below:
PRINT/QUEUE=
queuename filename
Note:
queuename
is the name of the print queue created in step1.
filename
is the name of the file to be printed.
For graphics or PostScript jobs, the form MUST be defined for NOTRUNCATE
and NOWRAP to prevent printer errors.
DEFINE/FORM DEFAULT/NOTRUNCATE/NOWRAP
8-2
Page 39

Banyan VINES
Network Configuration
Note:
Only TROY EtherWind-N models include Banyan VINES support.
EtherWind wireless print servers support the Banyan VINES IP protocol to allow
printers to be shared on a Banyan VINES network. Users on client PC’s send
their jobs to any VINES file server running the Banyan PCPrint software, which
in turn spools jobs to the print server. Printing is transparent to user applications,
and the print server can be managed using standard VINES utilities such as
MANAGE, MUSER, MSERVICE and Operator Console.
File Server User Configuration
1. From any VINES workstation log in as supervisor and run the MANAGE program.
2. Select Users, and press ENTER.
3. At the Manage Users screen, select Add a User.
4. Type in a StreetTalk name for the print server, (entering a password is optional). Press F10 when finished.
5. From the Add User Profile screen select a blank user profile.
6. Enter NO in response to the message "Do you want to force the user to change
passwords on the next login?". Press ENTER
7. Press ESCAPE twice to return to the main menu.
File Server Queue Configuration
1. Run the MANAGE utility, and from the main menu select 1-Services.
2. From the Manage Services menu, select Add a server-based service and
press ENTER.
3. From the Add a Service screen type the desired StreetTalk name for the print
queue and press ENTER, followed by a description and press ENTER.
9-1
9
Page 40

4. Select the desired File server and press ENTER.
5. Select the disk where the print service will reside.
6. Press F10 in response to the message "The service is running but not yet available to users."
7. Type in the maximum number of jobs and maximum size of job for the queue
at the Configure Queue screen. Or press F10 for unlimited number and
size.
8. If desired choose a default paper format at the Configure Paper Formats
screen, otherwise press F10 to select the default settings.
9. If desired enter the authorized user names at the Access Lists screen, or press
F10 for the defaults.
10.At the Add a Destination screen, select PCPrint and press ENTER.
11.At the Destination Attributes screen, enter the StreetTalk name of the print
server. Press F10.
12.At the Output Strings screen, press F10 to accept the output string values.
13.At the Enable Strings screen, press F10 to select the defaults.
14.Select NO in response to the message "Would you like to add another destination at this time?"
15.At the Print Queue Status screen, change both values to Yes to enable the
print queue to accept and print jobs. Press F10.
16.Press ESCAPE multiple times to exit the Manage utility.
Print Server Configuration
1. Install the XAdmin software from the CD-ROM provided with the print server.
Note: Use XAdmin, not XAdmin32, when configuring a VINES-only network.
You can use XAdmin32 on a VINES network only if the PC is running TCP/IP
and both the PC and print server have valid IP addresses.
2. Double-click on the XAdmin icon to start the program under Windows.
3. The print server will show up as "XCD_xxxxxx_P1" where "xxxxxxx" is the
last six digits of the Ethernet address.
4. Click on the Configure button.
5. Click on the Banyan tab.
6. If necessary change the hop count (default hop count is 2).
7. Enter the StreetTalk name of the print server, this must exactly match the
StreetTalk name of the user that was created using the Manage Users utility.
8. Click on the Services tab.
9. Select the desired service to be configured, (default is BINARY_P1).
10. Enter the StreetTalk name of the queue created using the Manage Services utility.
11.Click on OK, and then OK again to save the configuration.
12.Click OK and OK again to exit XAdmin
9-2
Page 41

PrintraNet Internet
Printing Configuration
TROY's PrintraNet product is a software driver for Windows that allows a PC
user at one location to send a print job to a printer connected to an EtherWind
wireless print server at a remote location across the Internet in a simple and transparent manner.
For example, a user on a PC in New York could print a document directly from
his Microsoft Excel application program to a printer in Chicago. The PC may be
attached to a Local Area Network, or it may be connected via a dial-up PPP link
to an Internet Service Provider. Because of the low cost of accessing the Internet,
the PrintraNet software can save the user a significant amount of money in toll
charges, particularly when international communications is involved.
A new PrintraNet feature allows a user at a remote site to send a text E-mail message directly to a printer connected to a TROY print server at a remote site. The
E-mail will be automatically printed on the printer without the need to run an Email program at the remote site.
There are two parts to the PrintraNet configuration, the configuration of the local
Windows PC and the configuration of the remote EtherWind print server.
Installing the Software on a Windows PC at the Local Site
You may configure the local Windows PC to communicate over a LAN using the
MAPI or WINSOCK protocol, or to communicate over a dial-up PPP connection
to an Internet Service Provider.
To install the PrintraNet software on a Windows PC, execute the following steps:
1. Make sure that the PC is running an E-mail program (for example, Microsoft
Outlook) that is capable of sending E-mail messages using either MAPI or
WINSOCK. MAPI (Messaging Applications Program Interface) is used by
most popular Windows E-mail packages, while WINSOCK is used by
10
10-1
Page 42

TCP/IP-based mail packages and dial-up Internet Service Providers. If you
do not know which method you are using, consult your system manager.
2. Make sure that your E-mail server is capable of sending messages across the
Internet. Alternatively, if you are communicating directly from the PC via a
modem to an Internet Service Provider, make sure that you have an Internet
mail account on the ISP, and that the PC is configured to send E-mail using
this account.
3. Start the PrintraNet installation program from the CD ROM and follow the
step-by-step instructions. You will need to know the following:
- The mail transport protocol: MAPI or WINSOCK
- The port name you wish to assign to the PrintraNet port (this port is used
to access the remote TROY print server): The name must start with
"PNET" and end with a number (for example, PNET3"). Note that each
remote EtherWind print server must have a unique port name associated
with it.
- E-Mail Address: Enter any unique legal Internet E-mail address for the
remote EtherWind print server (for example, emailprinter@xyz.com). Note:
Internet E-mail addresses cannot have spaces in them.
- Service Name: Enter the service name on the remote EtherWind print server that you wish to use for printing. This is normally XCD_xxxxxx_P1 for
the first parallel port, XCD_xxxxxx_S1 for the first serial port,
XCD_xxxxxx_P2 for the second parallel port, or XCD_xxxxxx_S2 for the
second serial port., where "xxxxxx" is the last six digits of the Ethernet
address (the exact service names can be found by running the print server
self-test). If you do not know the service name, you may leave this field
blank and the default binary service will be used.
- Your E-Mail Address (WINSOCK users only): enter your E-mail address
(for example, shari@abc.com).
- SMTP E-Mail Server (SMTP users only): Enter the IP address of your
SMTP E-mail server (consult your network administrator if you do not
know this address).
- Desired Notification: You may optionally have the remote EtherWind print
server notify you when the job is complete or when the job fails or both
when the job is complete and if it fails. Select the desired option and then
enter the E-mail address where you want the notification sent (generally you
would want the notification sent to your own E-mail address).
4. You must now create a printer on your Windows system using the standard
Windows printer setup procedure. To do this, go the Start button, select
Settings and then Printers. Select Add Printer to begin the printer installation and follow the instructions on the screen.
10-2
Page 43

5. Select Local Printer or My Computer (not Network Printer) when you are
asked how the printer is connected to your computer.
6. You will also need to know the following
- The manufacturer and model of the printer at the remote site (for example,
Hewlett-Packard LaserJet 5). In some cases, you will need to provide a disk
with the appropriate printer driver.
- The name of the PrintraNet port that you defined for the remote
EtherWind print server in step 3 (PNET1 by default).
7. With PrintraNet 2.0, you can also:
- Click on the Address Book button to configure other remote destinations.
This capability lets you send print jobs to more than one destination without having to create a separate printer for each destination.
- Select the partial E-mail printing option to break up the print job into several small E-mail messages. This allows PrintraNet to work with mail
servers that restrict the size of incoming E-mail messages.
8. Select No when asked if you want to print a test page, unless you have already
configured the remote EtherWind print server to receive PrintraNet print jobs.
You have now finished installing the PrintraNet software. If you have only one Email printer, go to Step 2, Configuring the Remote EtherWInd Print Server.
Adding a Second PrintraNet Destination
You should not re-run the install program to add a new E-Mail printer port.
Instead, press the Start button, select Settings, and open the Printers window.
Click on the icon of a PrintraNet printer, select File from the menu bar, and then
choose Properties. Click on the Details tab (or Ports tab) and push the Add
Port button.
In the Add Port dialog, select the Other radio button and then "PrintraNet
Port". Click on OK and it will give you the Port Name dialog (like in the install
program). Any unique name can be given here as long as it starts with "PNET"
and another port does not already exist with the same name. Then enter the port
settings as described in step 3 of the Installing the Software on a Windows PC at the
Local Site section.
10-3
Page 44

Configuring the Remote TROY Print Server
The next step is to configure the EtherWind print server at the remote site. The
remote print server can be configured with TROY's XAdmin32 Windows configuration utility, or with the EtherWind WebXAdmin browser-based facility.
Before configuring the print server to receive PrintraNet print jobs, check the following:
1. Make sure that the E-mail server at the remote site (the receiving end) is configured to handle the TCP/IP POP3, and SMTP protocols (SMTP is only
required if the notification feature is enabled).
2. Configure the POP3 server on the E-mail server at the remote site with a mail
account and password for the remote printer (generally, the mail account name
will be the first part of the name that you assigned in step 3 of the previous
section; for example, if you assigned the name emailprinter@xyz.com, the
account name would be emailprinter). The procedure for configuring a POP3
server varies depending on the operating system of the E-mail server, so consult your operating system documentation for details.
3. Make sure that the EtherWind print server is installed and running with
TCP/IP enabled and has a valid IP address assigned to it.
Because access to the E-mail server on most networks is usually restricted, you
may need to have your network administrator check the configuration and add the
mail account.
WebXAdmin allows the print server to be managed by any standard web browser
using the TCP/IP protocol. In order to use WebXAdmin, IP address must be
assigned to the print server and to the PC used for configuration.
The steps required to configure the print server to receive print jobs from a
Windows PC running the PrintraNet software are as follows:
1. Select the name of the desired EtherWind print server from the list by double
clicking on it (XAdmin32) or entering its IP address (WebXAdmin).
2. Click on the Internet tab or button.
3. Enter the IP address of the POP3 server (consult your network administrator if
you do not know this address).
10-4
Page 45

4. Enter the mailbox name for the remote EtherWind print server. Usually this
will be the first part of the E-mail address that you entered in step 3 of the
Installing the Software on the Windows PC at the Local Site section (for example,
if the E-mail address of the remote print server is emailprinter@xyz, then the
mailbox name would be emailprinter.
5. Enter the password for the mailbox, if any.
6. The print server is configured by default to poll the POP3 server every 30 seconds. You may change this value, if desired.
7. If you have enabled notification, enter the IP address of your SMTP server
(consult your network administrator if you do not know this address).
8. Press the OK button., and exit XAdmin32. You have now configured the print
server to receive print jobs.
Printing to the Remote TROY Print Server
To print to the remote EtherWind print server from the local Windows PC, you
simply select the printer that you created in Step 1 and print to it the normal
manner. For example, to print the remote printer named Email Printer, you
would select Print from the menu bar, choose the printer named Email Printer,
and then click OK.
At this point, the Port Settings dialog box will appear (you may disable this by
unchecking the Show this dialog for each Print Job box). You may then use
the Address Book capability or change other parameters. Click OK when you are
ready to print, and the job will then be sent over the Internet to the remote
EtherWind print server.
Troubleshooting
The first step in troubleshooting is to make sure that you have a valid E-mail connection on both the sending PC and the receiving print server. Try sending an Email message from the PC to a user at the remote site who can receive mail via the
POP3 server. If this does not work, there may be an E-mail configuration problem on the PC, on the local E-mail server, or on the remote POP3 server. Double
check to make sure that the E-mail parameters that you configured on the PC and
on the remote print server match those that are configured on the E-mail servers.
10-5
Page 46

If you get an SMTP error when using a WINSOCK connection, you may need to
configure the hosts file on your Windows system. To do this create a file named
HOSTS in the \WINDOWS\SYSTEM directory (or edit this file if it already
exists) and add an entry for your mail server similar to the following using the
DOS editor (substitute the actual IP address and name of your SMTP mail server):
192.189.207.222 mail.troy.com
If you can print small files OK but are having trouble printing large files, the
problem may be in the E-mail system. Some E-Mail systems have difficulties
printing files that are larger than about 400KB in length. To verify this, try sending the large file as an attachment to an E-mail message. If the file does not reach
its destination intact, then the problem is with the E-Mail system. The problem
can be fixed by using the PrintraNet Partial E-mail Printing option.
10-6
Page 47

Troubleshooting
and Maintenance
Troubleshooting Printing Problems
◗ First, check the printer to be sure it is online, and has paper and ink or toner.
◗ If the printer is working fine, test the connection between the printer and the
print server by pushing the test button on the back of the printer for less than
5 seconds.
Note:
The test page will work on most printers, but not on some inkjet printers. The
test page will work on PCL, Postscript and some others like Epson and HP
inkjets. Remember, just because you can’t print a test page doesn’t mean
it’s not going to print. Set up the printer as you normally would and try printing from an application.
◗ If the test page does not print, try resetting the print server to factory defaults
by holding the test button for more than 5 seconds.
Troubleshooting Wireless Configuration Problems
◗ Make sure your computer’s wireless adapter and/or access point is configured
properly and note the settings paying special attention to the wireless mode,
SSID or network name, WEP or security, and IP Address settings so you can
configure your print server to the same wireless settings.
◗ Make sure you have a good wireless signal from your PC and from the print
server, that the print server is within range (90 meters or 300 feet), and it is
away from metal objects and other devices with radio signals (like Bluetooth,
Cordless Phones, and Microwave ovens).
◗ Make sure your computer is set to infrastructure mode if you are connecting
through an access point, or ad-hoc (802.11) if you are connecting to the print
11-1
11
Page 48

server without an access point. See the documentation for your wireless
adapter for details.
◗ If you are using WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption or security on
your wireless network, you will need to temporarily disable WEP on your PC
in order to configure the print server. If you are using an access point with
WEP enabled and it does not allow non-wep clients to communicate with
other non-wep clients, then you will also need to temporarily change the wireless mode of your computer to Ad-hoc (802.11) mode. Note: If no computers
on your network can be set to Ad-hoc mode, you will need to temporarily disable WEP on your access point. When you are done configuring the print
server, you can re-enable WEP on your computer and change the wireless
mode back if necessary.
◗ If you want to use WEP encryption or password protect your wireless network,
and your wireless adapter or access point normally uses a password or
passphrase instead of WEP, it should allow you to enter 0x followed by a ten
digit (for 40-bit or 64-bit WEP) or twenty-six digit (for 128-bit WEP) key in
hexadecimal format (0-9 or A-F).
◗ If you are experiencing slow performance or are having intermittent problems
connecting, try changing the RF channel of your wireless network. This can be
done in the WP-Admin Wireless Server Configuration screen for the print
server. See your wireless adapter and/or access point documentation for more.
You will want to change it to at least 3 channels lower or higher than any
other wireless networks within range.
Troubleshooting Network Configuration
◗ If you are using TCP/IP, make sure that your computer and the print server are
on the same IP segment or can reach each other with a PING command from
the host. The IP Address you assign to the print server must be on the same
logical network as your host computers (e.g., if your computer has an IP
address of 192.189.207.3, the EtherWind™ print server should have an IP of
192.189.207.x, where x is an integer between 1 and 254), or you must properly configure your router address to work with the print server.
◗ If your print server is set to Auto or DHCP for obtaining an IP Address, it’s
possible the print server’s IP Address can change. Either configure your DHCP
Server to give the print server a permanent lease, or configure the print server
to be on a STATIC address outside the scope of DHCP addresses.
11-2
Page 49

Wireless Server Configuration Screen Fields
Listed below is a description of each of the fields displayed on the Wireless
Server Configuration screen and reasonable values for that field. Once these are
all set, click OK to close the Configuration Screen and write the changes to the
Server. If you decide NOT to CHANGE the values, select CANCEL to close the
Configuration Screen and revert to the prior values.
Server Name
This is the name of the wireless print server. The default is XCD_xxxxxx (where
xxxxxx are the last six digits of the MAC/Ethernet address). You can choose any
name for this setting. Many companies have suggested naming practices; check
with your System Administrator or Network Manager for policies and practices.
Serial Number
This is the fixed number which identifies the EtherWind Server. It is set during
manufacture and does not change after that.
Password
This is the EtherWind Wireless Print Server configuration password. For security,
the password is never shown. (The field displays asterisks (*) if you type characters
into it.) You must know the password before WP-Admin will show you the
Configuration Screen. Users should only put text into this field if they want to
change the password. Ask your System Administrator or Network Manager for the
correct password; be sure the Administrator/Manager is informed and concurs
BEFORE the password is changed.
Firmware Revision
This is a static string displaying the correct version of the software embedded in
the Server. It can not be modified.
IP Address
The IP Address is a set of four bytes, separated by periods. Each byte can have any
value between zero (0) and 255 includive. Most company networks have ranges
for their IP Addresses. Many have automatic IP set-up, so the IP address may not
require configuration. Consult with your network administrator if you are not sure
what to put in this field.
WorkGroup/Domain
This is the Microsoft Network WorkGroup or Domain in which you want the
print server. If you are using NetBIOS or NetBEUI to print, this value should
match the PC from which you are printing.
11-3
Page 50

Subnet Mask
Companies often have ranges of IP Addresses that can be described by one or
more Masks. For example, a mask of 255.255.255.0 allows variation in the last
position only. (The first three positions are fixed. The last position can be any
value between 1 and 255.) Larger organizations may have masks of 255.255.0.0 -the first two positions are static and the last two positions are variable. If the IP
Address is set automatically, this mask may also be defined automatically.
Boot Method
This is the method the wireless print server uses to obtain an IP address. This can
be set to Auto, DHCP, BOOTP, RARP, or Static. Auto will try DHCP, BOOTP
and RARP, and then set to Static if the IP Address isn't set automatically by the
other methods. If your network uses Static configuration, it will be necessary to set
the Boot Method to Static and the IP to a particular address.
Gateway (or Router)
The Gateway or Router allows connections between different subnets. For example, if a corporation has separate subnets for the Hardware Department, the
Software Department, and the Testing Department, they will need a Gateway
between subnets to allow the separate groups to communicate.
RF Channel
The RF Channel is the wireless channel the print server uses to communicate. The
EtherWind will be able to automatically configure itself in most cases, but you
might need to manually set it to the same RF channel as the 802.11b wireless network. This value must match for all nodes on a network to communicate with
each other.
MAC Address
This series of six numbers, separated by periods, defines the Ethernet address of
the Server. For the EtherWind Servers, the MAC Address is set during manufacturing and will not change. (This should avoid problems caused by mutlitple
devices on an Ethernet network with the same address.)
Data Rate
This is the throughput speed in Mbps of the wireless Ethernet connection (1, 2,
5.5, or 11). In most cases with an 802.11b wireless network, it should be set to 11
Mbps. The Data Rate usually does not need setting as it will automatically negotiate to the highest possible rate.
SSID
This is the Service Set Identifier (Sometimes referred as Network Name or
ESSID). This value must match for all nodes on a subnetwork to communicate
with each other.
11-4
Page 51

Wireless Mode
◗ Ad-Hoc (sometimes referred to as Peer-to-Peer, Computer-to-Computer,
802.11 Ad-Hoc, or IBSS compliant Ad-Hoc) modes are used when your wireless enabled PC is printing straight to the printer.
◗ Infrastructure mode is used when you have an Access point or base station as
the hub of your wireless network.
◗ Pseudo Ad-Hoc is only used for testing and some older 802.11b implementa-
tions of Ad-Hoc. Auto mode attempts connection with each of the other
methods in turn.
Note: If the options on your 802.11b enabled computer are Ad-Hoc, 802.11b AdHoc, and Infrastructure, use the following to determine the settings of the print
server:
Computer Print Server
Ad-Hoc Pseudo Ad-Hoc
802.11 Ad-Hoc Ad-Hoc (802.11)
Infrastructure Infrastructure
WEP Key
Disabled. The other Options are 64Bit WEP Key Size and 128Bit WEP Key Size.
Be careful -- if one part of the wireless network has WEP enabled, they all must
have it enabled with the same key or they cannot communicate.
WEP Key Index
This is which WEP key you want to use out of the 4 entered in the 128 / 64
WEP Key field.
128 Bit / 64 Bit WEP Key
This is the 64 or 128 bit WEP key that must match other nodes’ encryption keys
in order to communicate: 10 characters for 64 bit, or 26 characters for 128 bit.
The EtherWind uses a Hexadecimal value for WEP. All 802.11b devices have a
way of translating their WEP or Security values to 10 (for 40-bit or 64-bit WEP)
or 26 (for 128-bit WEP) digit HEX values. Ask the manufacturer of your wireless
product how this is done for your PC and/or Access Point.
Loading the Firmware
1. Run the XAdmin32 utility from the Start menu, it should be found under
START>Programs>TROY Group>EtherWind>XAdmin32
11-5
Page 52
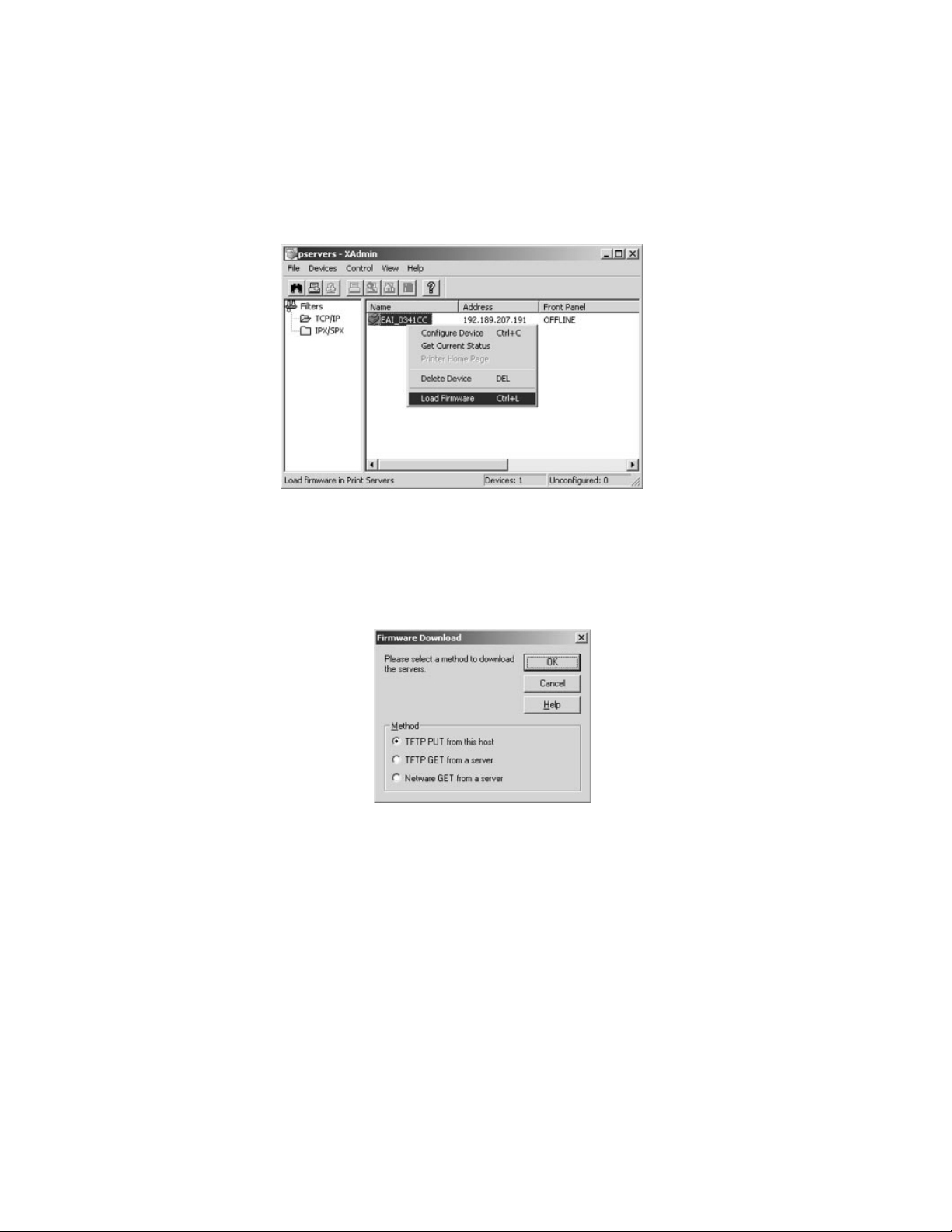
2. Right-Click on the print server to be upgraded in the list, and select Load
Firmware.
3. If you are using TCP/IP to upgrade, select TFTP PUT from this host. If you
are upgrading using IPX/SPX on a NetWare network to upgrade, select
Netware GET from a server (If you are using Netware to upgrade, you
need to put the .bin firmware file in the LOGIN directory of the Netware
server). Click OK.
4. If you selected TFTP PUT from this host in step 3, enter the configuration
password (default is ACCESS) and click Browse to find the .bin firmware
11-6
Page 53

file you downloaded. Click Load. The firmware on your EtherWind will be
upgraded to the new version.
If you selected Netware GET from a server in step 3, enter the configura-
tion password (default is ACCESS). Enter the name of the Netware server
where you saved the .bin file as the Host Name. Enter the name of the
firmware file for File. Click OK. The firmware on your EtherWind will be
upgraded to the new version.
11-7
Page 54

Uninstalling the EtherWind Wireless Software
On Macintosh Systems, simply delete the directory that you installed the software on.
Follow the instructions to uninstall the EtherWind utilities on Windows systems:
1. Click the Start Menu, go to Settings, and select Control Panel.
2. Double-Click Add/Remove Programs.
3. Select EtherWind 802.11b Wireless Print Server from the list and click
Change/Remove.
4. Select Remove and follow the on-screen instructions.
The software should now be removed from the system.
11-8
Page 55

Where to Get Help
TROY offers several customer support options to assist you in the event you experience difficulties with your EtherWind, including telephone support, repair services, extended warranty, and advance replacement.
Worldwide Web Support
The TROY worldwide web site provides a quick and easy way to answer many
common technical questions. It includes a wide variety of technical support tips,
as well as copies of product manuals, product literature, and firmware load images.
The web site is located at http://www.troygroup.com.
Contacting TROY
Your first point of contact for technical support is the Distributor or Dealer from
whom you bought your EtherWind. They are familiar with your needs, and will
generally be able to provide you with the fastest and most comprehensive support.
If your Distributor or Dealer is unable to answer your questions or is for some reason not available, then contact TROY directly at:
United States: (208) 955-1000 (E-mail: support@troyxcd.com)
Germany: 0800-3002210 (E-mail: support@troygroup.de)
Other Europe/Africa: +49 (0) 7032-9454-21 (E-mail: support@troygroup.de)
All Other Countries: +1 (208) 955-1000 (E-mail: support@troyxcd.com)
Before contacting technical support, please check the Troubleshooting chapter of
this manual or the TROY site to isolate any problems and be sure to write down
any error messages. Also, make sure that you have the serial number of the product (located on the product label on the card).
12-1
12
Page 56

Returning Products
If you need to return a TROY product for any reason (failures, incorrect shipments, etc.), first contact TROY at +1 (208) 955-1000 (Americas, Asia, and
Australia) or +49 (0) 7032-9454-21 (Europe and Africa) and request a Return
Authorization Number from the TROY Technical Support Group. Make sure that
you put this number on the outside of the shipping container you use to return
the product and (if out-of-warranty) on your purchase order. You will also be
asked for the serial number of the defective product. Ship the unit freight prepaid
back to TROY at the address provided by the Technical Support Group (adequate
insurance is recommended).
If the unit is not in warranty, you will be billed for the standard repair charges. If
you do not have a valid TROY account number, you may be asked for payment in
advance (Mastercard, Visa, American Express, check, or money order).
Warranty
TROY EtherWind products are warranted to be free of defects in materials and
workmanship for a period of five years. This period begins upon the date of shipment if the Hardware is installed by the Purchaser, or upon installation if the
Hardware is installed by TROY. During the warranty period, TROY will repair or
replace the unit at no charge provided it is returned to TROY freight prepaid as
described in the "Returning Products" section of this chapter. To ensure prompt
service, please fill out the enclosed warranty card.
The warranty on repaired products or replacement products is 30 days or the last
day of the warranty of the original defective product, whichever is longer.
This warranty does not apply if the Product has been damaged by accident, misuse, natural catastrophe, modification, improper service, or conditions resulting
from causes external to the Product. The warranty shall be void if the TROY serial numbers have been removed.
DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES. THE ABOVE WARRANTIES ARE THE
EXCLUSIVE WARRANTIES, AND NO OTHER WARRANTY, EXPRESSED
OR IMPLIED, SHALL APPLY. TROY SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
PURCHASER'S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDY FOR ANY BREACH OF
THIS WARRANTY, REGARDLESS OF THE FORM OF ACTION,
WHETHER CONTRACT, TORT, OR OTHERWISE, SHALL BE TROY'S
OBLIGATION TO REPAIR OR REPLACE AS SET FORTH ABOVE.
12-2
Page 57

Notices
FCC Compliance Statement
For United States Users
This equipment has been tested and found to comply within the limits for a Class
B digital device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed
to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause interference to radio and television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
◗ Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
◗ Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver,
◗ Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
◗ Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The radiated output power of EtherWind is far below the FCC radio frequency
exposure limits. Nevertheless, the EtherWind shall be used in such a manner
that the potential for human contact during normal operation is minimized.
WARNING
The connection of a non-shielded equipment interface cable to this equipment will
invalidate the FCC Certification of this device and may cause interference levels
which exceed the limits established by the FCC for this equipment. It is the responsi-
13-1
13
Page 58

bility of the user to obtain and use a shielded equipment interface cable with this
device. If this equipment has more than one interface connector, do not leave cables
connected to unused interfaces. Changes or modifications not expressly approved by
the manufacturer could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
For European Users
This product is in conformity with the protection requirements of EU Council
Directive 89/336/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the Member States
relating to electromagnetic compatibility. TROY Group cannot be responsible for
any failure to satisfy the protection requirements resulting from a nonrecommended modification of the product.
This product has been tested and found to comply with the limits for Class B
Information Technology Equipment according to CISPR 22/European Standard
EN55022. The limits for Class B equipment were derived for typical residential
environments to provide reasonable protection against interference with licensed
communications devices.
For Canadian Users
This Class B apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la class B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
DECLARATION of CONFORMITY
According to 47CFR, Part 2 and 15 for Class B Personal
Computers and Peripherals; and/or CPU Boards and Power
Supplies used with Class B Personal Computers:
We: TROY GROUP, INC.
Located at: 1692 Browning
Irvine, CA 92606 USA
Declare under sole responsibility that the product identified herein, complies with
47CFR Part 2 and 15 of the FCC rules as a Class B digital device. Each product
marketed, is identical to the representative unit tested and found to be compliant
with the standards. Records maintained continue to reflect the equipment being
produced can be expected to be within the variation accepted, due to quantity
production and testing on a statistical basis as required by 47CFR §2.909.
13-2
Page 59

Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not
cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Trade Name: TROY
Type of Product: 802.11b Print Server
Model EtherWind
REGULATORY INFORMATION
European Union (EU)
TROY hereby declares that the 802.11b wireless technology built into the
EtherWind print server is in compliance with the essential requirements and other
relevant provisions of European Directive 1999/5/EC. The internal function is a
radio device using the 2.4 GHz frequency band (2.400GHz – 2.4835GHz). It is
intended for wireless communication with other 802.11b enabled devices.The
internal 802.11b technology complies with all applicable regulations FOR
INDOOR USE in the following countries: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland,
Greece, Germany, Iceland, Ireland, Luxembourg, Norway, Portugal, Sweden,
The use of 802.11b wireless technology in other countries than those listed above
may be restricted: before using 802.11b products, please confirm with the frequency management authority in the country where you plan to use it. OUTDOOR USE REQUIRES A LICENSE IN MANY COUNTRIES AND IS FORBIDDEN IN ITALY. In some situations or environments, the use of 802.11b
wireless technology might be restricted by the proprietor of the building or
responsible representatives of the organization, for example onboard airplanes, in
hospitals or in any other environment where the risk of interference with other
devices or services is perceived or identified as harmful.
If you are uncertain of the policy that applies to the use in a specific organization
or environment, you are encouraged to ask for authorization to use 802.11b wireless technology prior to switching it on. Consult your physician or the manufacturer of personal medical devices (pacemakers, hearing aids, etc.) regarding any
restrictions on the use of 802.11b wireless technology.
United States of America and Canada
Tested to Comply With FCC Standards FOR HOME OR OFFICE USE. See
FCC 47CFR, Part 15.19(b)(2).
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules and with RSS-210 / RSS-139
of the Industry Canada.
13-3
Page 60

Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not
cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Note that any changes or modifications to this equipment not expressly approved
by the manufacturer may void the FCC authorization to operate this equipment.
Canada (IC notice)
To prevent radio interference to the licensed service, this device is intended to be
operated indoors and away from windows to provide maximum shielding.
Equipment that is installed outdoors is subject to licensing.
Pour empêcher un brouillage radioèlectrique au service fasant l'object d'une
licence, cet appareil doit être utilisé à l'interieur et loin des fenêtres afin de founir
un écran de blindage maximal. Au cas aù un installation en plain air, le materiel
doit faire l'objet d'une licence.
13-4
 Loading...
Loading...