Page 1
Insulator Drip Shield Installation Instructions
Owner's Manual Addendum
NEW!
WARNING! The Insulator Drip Shield is required for installation on your Tripp Lite DC-to-AC
Inverter/Charger when it is used in marine applications (e.g. aboard watercraft). Failure to install
it as described below may lead to personal injury and/or damage to the Inverter/Charger and
connected systems.
Installation
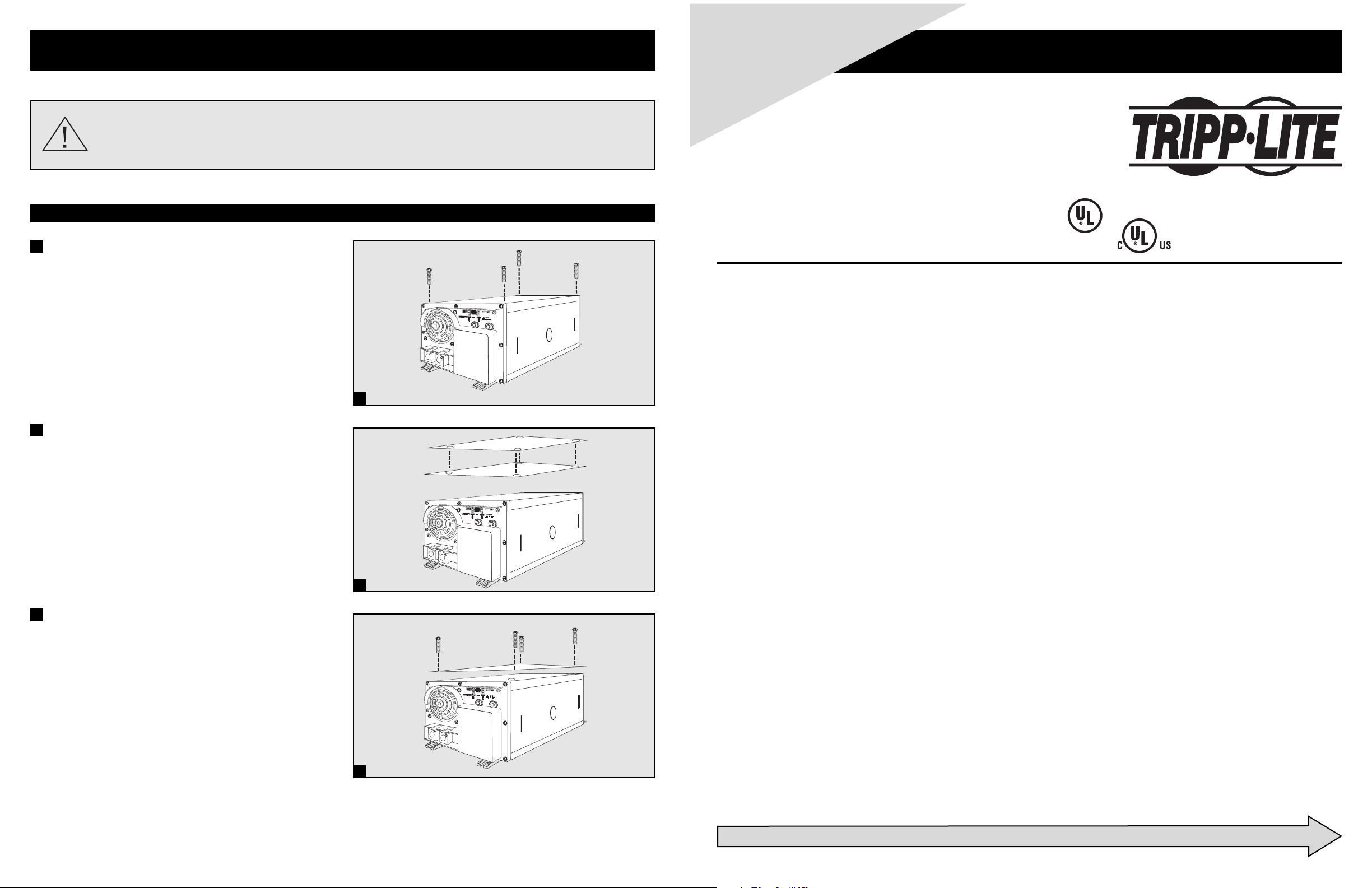
Locate and remove the four hex screws on the top panel of your
1
Inverter/Charger as shown.
Place the Insulator Drip Shield on the top panel of the Inverter/
2
Charger. Line up the holes in the shield with the exposed screw
holes on the top panel.
The Best Mobile Power Solutions
for Both RV & Marine Applications!
PowerVerter
®
RV1012UL & RV2012UL
RV & Marine DC-to-AC
Marine
Inverter/Chargers
Listed
Power Inverter
The new RV1012UL and RV2012UL are the most rugged, reliable Inverter/Chargers available—
ideal for both RV and marine applications. RVs and boats often experience severe shocks, while
driving over potholes and rough road surfaces or while navigating in choppy seas. RVs and boats
also experience constant vibration, from surface friction, drive engines and on-board generators.
The RV1012UL and RV2012UL are engineered specifically to meet the challenges of demanding
1
RV and marine environments—and are UL-tested to perform reliably under the most extreme shock
and vibration conditions.
The new RV1012UL and RV2012UL include all the features and functions of previous
versions of the RV1012UL and RV2012UL listed in the enclosed owner's manual, with the
1111 W. 35th Street, Chicago, IL 60609 USA
Customer Support: (773) 869-1234
www.tripplite.com
3
Using the hex screws, secure the Insulator Drip Shield to the top
panel of the Inverter/Charger.
following exceptions:
• Ten-Point Mounting Flanges—provide up to 10 connecting points for tight adhesion to the
mounting surface
• Splash/Condensation Drip Shield—Added protection for control panel against potentially
2
disruptive moisture in marine environments (required for marine applications)
• Battery Recharge Rate LED Meter—indicates approximate recharge rate of connected RV or
marine batteries
• UL 458 (Shock/Vibration) Tested*—performs reliably in the most demanding RV and marine
environments under the most extreme shock and vibration conditions (caused by potholes, rough
roads, high seas, surface friction or engine/generator vibration)
* Tested for conformity to UL458 and UL458 Marine Supplement—for both RV and marine applications.
3
200412030 93-2431
ATTENTION: For Marine Applications, See Inside.
Page 2
For Marine Applications Only:
Additional Important Safety Instructions! Save These Instructions!
These safety instructions augment the instructions listed in the enclosed manual, which focuses upon RV and other
land-based applications. Please use this section in addition to page 3R of the owner's manual if you operate the
RV1012UL or RV2012UL in a marine installation. In marine applications, a drip shield must be installed; see drip shield
instructions listed on the back page for installation information.
Important Safety Instructions
A) ALL MARINE CONVERTERS
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
1) SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS – This manual contains important safety and operating instructions for marine converter Models
RV1012UL and RV2012UL.
2) CAUTION – To reduce risk of injury, charge only wet cell lead acid or sealed lead acid type rechargeable batteries. Other types of batteries
may burst causing personal injury and damage.
3) Do not expose charger to rain or snow.
4) Use of an attachment not recommended or sold by the marine converter manufacturer may result in a risk of fire, electric shock, or injury to
persons.
5) Do not disassemble marine converter or inverter; take it to a qualified serviceman when service or repair is required. Incorrect reassembly
may result in a risk of electric shock or fire.
6) To reduce risk of electric shock, unplug marine converter or inverter from outlet before attempting any maintenance or cleaning. Turning off
controls will not reduce this risk.
B) MARINE POWER CONVERTERS WITH BATTERY CHARGING FEATURE
1) WARNING – RISK OF EXPLOSIVE GASES.
i) WORKING IN VICINITY OF A LEAD-ACID BATTERY IS DANGEROUS. BATTERIES GENERATE EXPLOSIVE GASES DURING
NORMAL BATTERY OPERATION. FOR THIS REASON, IT IS OF UTMOST IMPORTANCE THAT EACH TIME BEFORE SERVICING
EQUIPMENT IN THE VICINITY OF THE BATTERY, YOU READ THIS MANUAL AND FOLLOW THE INSTRUCTIONS EXACTLY.
ii) To reduce risk of battery explosion, follow these instructions and those published by battery manufacturer and manufacturer of any
equipment you intend to use in vicinity of battery. Review cautionary marking on these products and on engine.
2) PERSONAL PRECAUTIONS
i) Someone should be within range of your voice or close enough to come to your aid when you work near a lead-acid battery.
ii) Have plenty of fresh water and soap nearby in case battery acid contacts skin, clothing, or eyes.
iii) Wear complete eye protection and clothing protection. Avoid touching eyes while working near battery.
iv) If battery acid contacts skin or clothing, wash immediately with soap and water. If acid enters eye, immediately flood eye with running
cold water for at least 10 minutes and get medical attention immediately.
v) NEVER smoke or allow a spark or flame in vicinity of battery or engine.
vi) Be extra cautious to reduce risk of dropping a metal tool onto battery. It might spark or short-circuit battery or other electrical part that
may cause explosion.
vii) Remove personal metal items such as rings, bracelets, necklaces, and watches when working with a lead-acid battery. A lead-acid
battery can produce a short-circuit current high enough to weld a ring or the like to metal, causing a severe burn.
viii) NEVER charge a frozen battery.
ix) If necessary to remove battery from vessel, always remove grounded terminal from battery first. Make sure all accessories in the vessels
are off, so as not to cause an arc.
x) Be sure area around battery is well ventilated.
xi) Clean battery terminals. Be careful to keep corrosion from coming in contact with eyes.
xii) Study all battery manufacturer’s specific precautions such as removing or not removing cell caps while charging and recommended rates
of charge.
xiii) Add distilled water in each cell until battery acid reaches level specified by battery manufacturer. This helps purge excessive gas from
cells. Do not overfill. For a battery without cell caps, carefully follow manufacturer’s recharging instructions.
3) MARINE CONVERTER OR INVERTER LOCATION
i) Locate marine converter or inverter away from battery in a separate, well ventilated compartment.
ii) Never place marine converter or inverter directly above battery; gases from battery will corrode and damage marine converter.
iii) Never allow battery acid to drip on marine converter or inverter when reading gravity or filling battery.
iv) Do not operate marine converter or inverter in a closed-in area or restrict ventilation in any way.
4) DC CONNECTION PRECAUTIONS
i) Connect and disconnect DC output connections only after setting any marine converter or inverter switches to off position and removing
AC cord from electric outlet or opening AC disconnect.
5) EXTERNAL CONNECTIONS TO CHARGER SHALL COMPLY WITH THE UNITED STATES COAST GUARD ELECTRICAL
REGULATIONS (33CFR183, SUB PART I).
a) For all grounded cord-connected marine converters or inverters:
GROUNDING AND AC POWER CORD CONNECTION INSTRUCTIONS – Converters/inverters should be grounded to reduce risk of
electric shock. Converter/inverter is equipped with an electric cord having an equipment-grounding conductor and a grounding plug. The plug
must be plugged into an outlet that is properly installed and grounded in accordance with all local codes and ordinances.
DANGER – Never alter AC cord or plug provided – if it will not fit outlet, have proper outlet installed by a qualified electrician. Improper
connection can result in a risk of an electric shock.
b) For a grounded, cord-connected marine converter, with an input rating less than 15 amperes and intended for use on a nominal 120 volt
circuit:
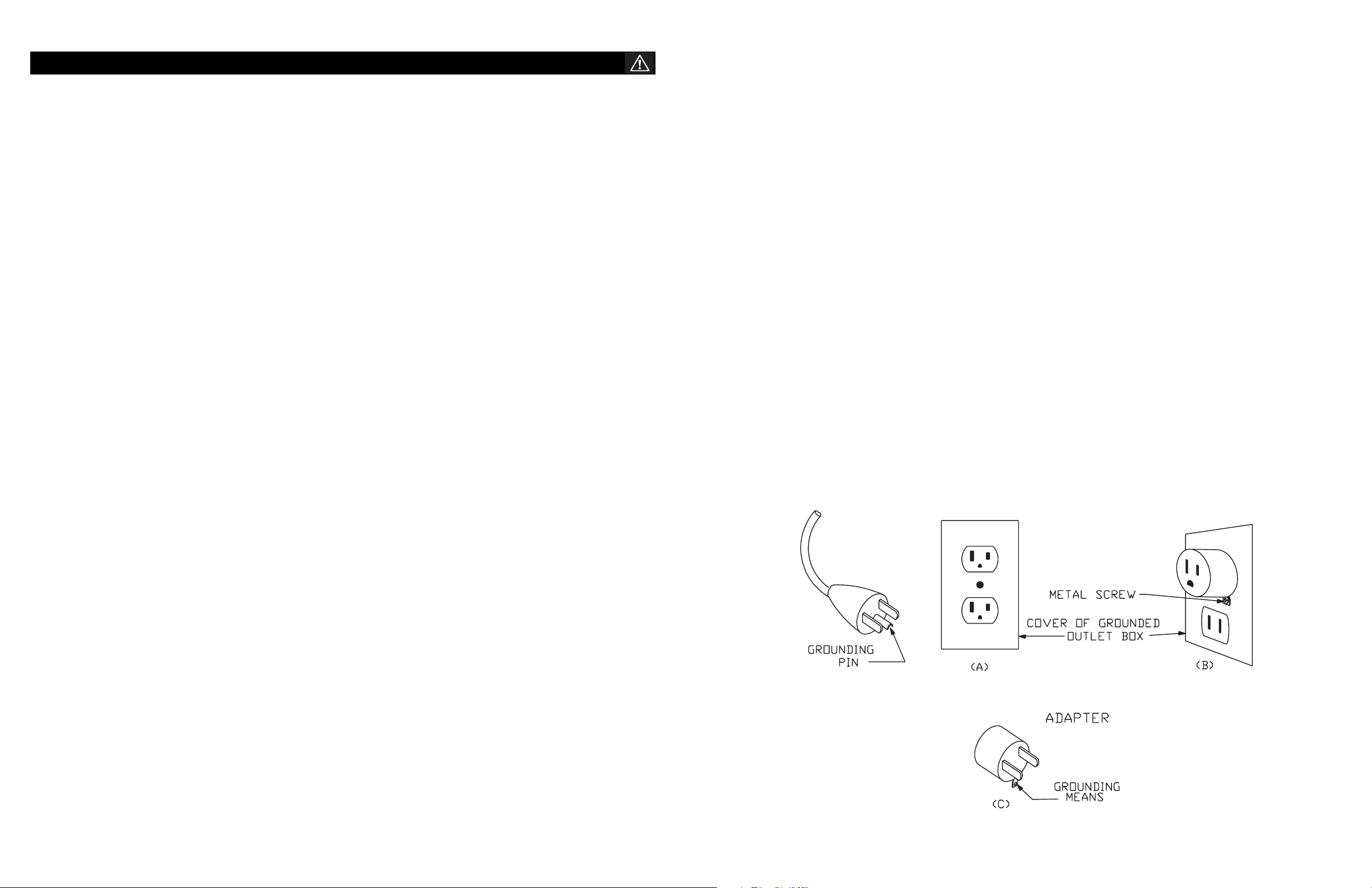
This marine converter/inverter is for use on a nominal 120 volt circuit, and has a grounding plug that looks like the plug illustrated in sketch
A in Figure 1. A temporary adapter, which looks like the adapter illustrated in sketches B and C, may be used to connect this plug to
a two-pole receptacle as shown in sketch B if a properly grounded outlet is not available. The temporary adapter should be used only until a
properly grounded outlet can be installed by a qualified electrician.
DANGER – Before using adapter as illustrated, be certain that center screw of outlet plate is grounded. The green-colored rigid ear or lug
extending from adapter must be connected to a properly grounded outlet – make certain it is grounded. If necessary, replace original outlet
cover plate screw with a longer screw that will secure adapter ear or lug to outlet cover plate and make ground connection to grounded
outlet.
c) For all other grounded, cord-connected battery chargers:
This marine converter/inverter is for use on a circuit having a nominal rating more than 120 volts (or, “This appliance is rated more than 15
amperes and is for use on a circuit having a nominal rating of 120 volts”) and is factory-equipped with a specific electric cord and plug to
permit connection to an acceptable electric circuit. Make sure that the converter or inverter is connected to an outlet having the same
configuration as the plug. No adapter should be used with this converter or inverter.
d) For a permanently connected marine converter or inverter:
GROUNDING INSTRUCTIONS – This marine converter or inverter should be connected to a grounded, metal, permanent wiring system;
or an equipment-grounding conductor should be run with circuit conductors and connected to equipment-grounding terminal or lead on
converter. Connections to converter should comply with all local codes and ordinances.
Figure 1
Grounding method
 Loading...
Loading...