Page 1

1111 W. 35th Street
Chicago, IL 60609 USA
Customer Support: (773) 869-1234
www.tripplite.com
Owner's Manual
APS INT 512
(230V, 50/60 Hz)
Automatic Power System
• Voltage and Frequency-Controlled
• Peak Power, High Efficiency
ESPAÑOL: p. 13-23
FRANÇAÍS: p. 24-34
RUSSKII: p. 35-45
Introduction: ..................................... p. 2-3
APS Installation: .............................. p. 4-5
Battery Connection: ......................... p. 6-7
Equipment Connection: ...................... p. 8
Switches, Indicator Lights
& Other Features: .......................... p. 9-10
Copyright © 2000 Tripp Lite. All rights reserved.
Troubleshooting:............................... p. 11
Warranty: .......................................... p. 12
Specifications: .................................. p. 12
Maintenance & Service: ................... p. 12
1
Page 2

Introduction
Congratulations! You’ve purchased the most advanced, feature-rich integrated inverter/battery
charger on the market. Your APS provides your equipment with utility-supplied AC power, when
present. During a blackout, overvoltage or brownout, your APS automatically switches over to an
external battery source to power connected equipment with voltage and frequency-controlled
AC power.
Multi-Function Indicator Lights
Two sets of indicator lights keep you constantly informed of battery charge levels, fault conditions and
APS operation. One set of multi-function lights displays battery charge conditions and fault warnings.
The second set of multi-function lights displays APS operation conditions.
Multi-Operation Switches
Two control points give you convenient options when operating your APS. Set a variety of voltage
levels at which your APS’s inverter will turn on to maximize equipment protection and minimize battery
drain. Other options include a remote-control setting for greater convenience and a battery type
setting for greater charging efficiency.
Frequency-Controlled Output (Invert Mode)
Your APS controls line frequency so frequency-sensitive equipment can operate properly.
Automatic Overload Protection
If you overload your APS, it will automatically protect itself and your valuable batteries from damage.
2
Page 3
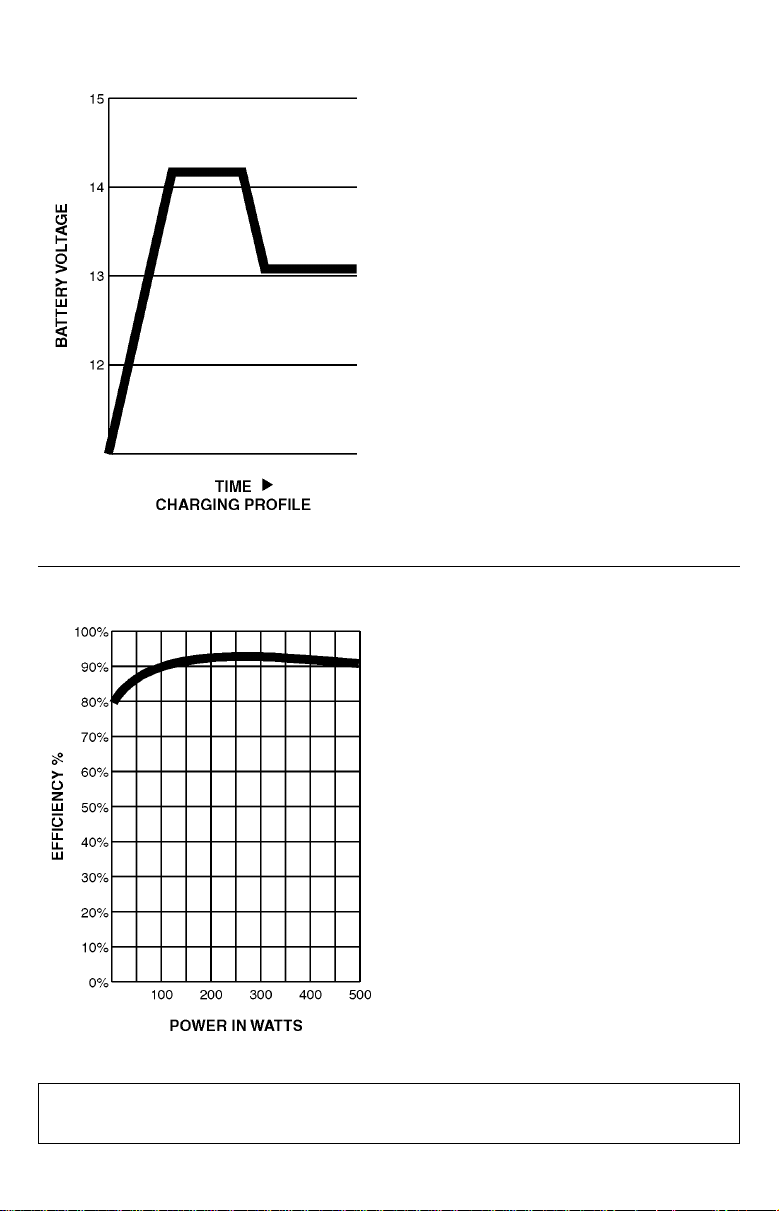
Bulk
Stage 1
Stage 2
Absorption
Stage 3
Float
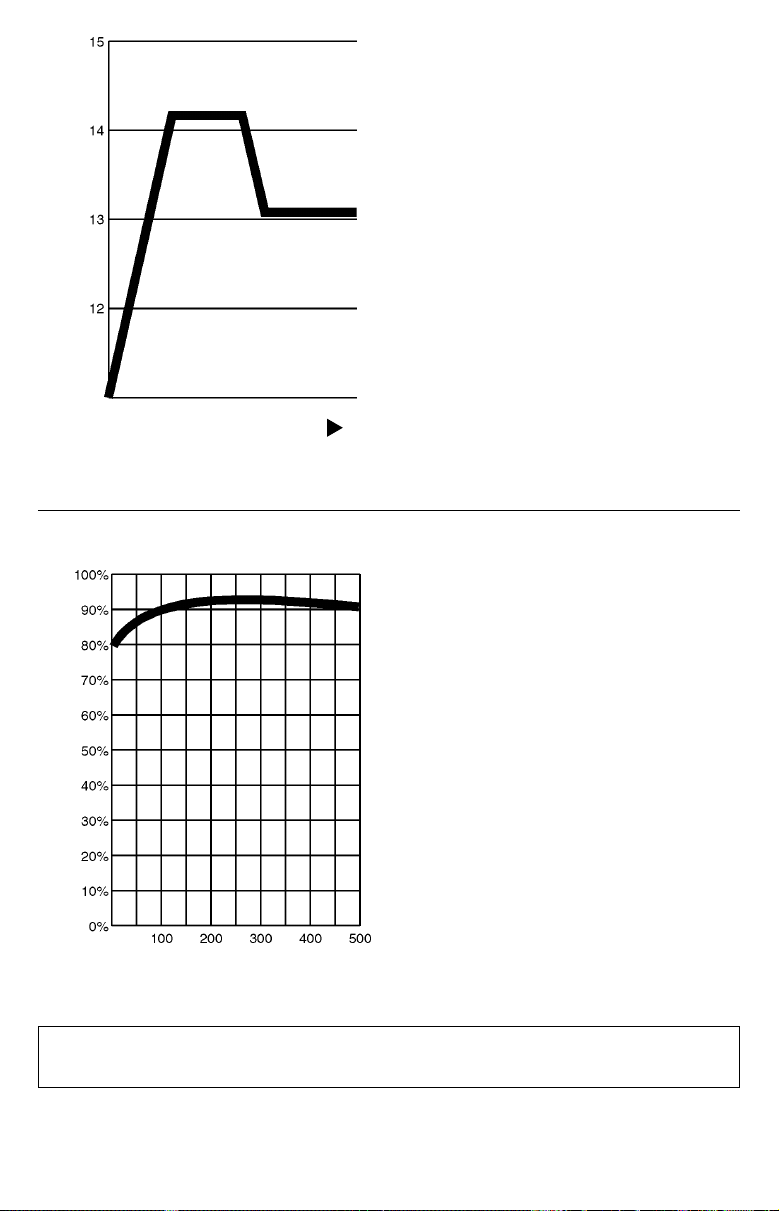
Advanced, 3-Stage
Battery Charger
Your APS recharges your battery faster
than conventional chargers because
its three-stage charger profiles (Bulk,
Absorption and Float) are optimized,
regardless of the type of battery you
use (Wet or Gel).* In addition, the
advanced charging system protects
against over-charge and overdischarge to ensure a longer service
life from your battery.
* The Absorption and Float levels vary according to battery
type which is field settable either "Wet" or "Gel" Cell.
High Efficiency Output
Your APS’s advanced circuitry produces
a more efficient DC-to-AC conversion,
minimizing energy loss. This allows you
to run connected equipment longer
between battery charges. The APS will
maintain this highly-efficient output even
as the battery charge decreases.
This manual contains important instructions and warnings that should be followed during the
handling, installation, operation and storage of Tripp Lite APS Automatic Power Systems.
3
Page 4
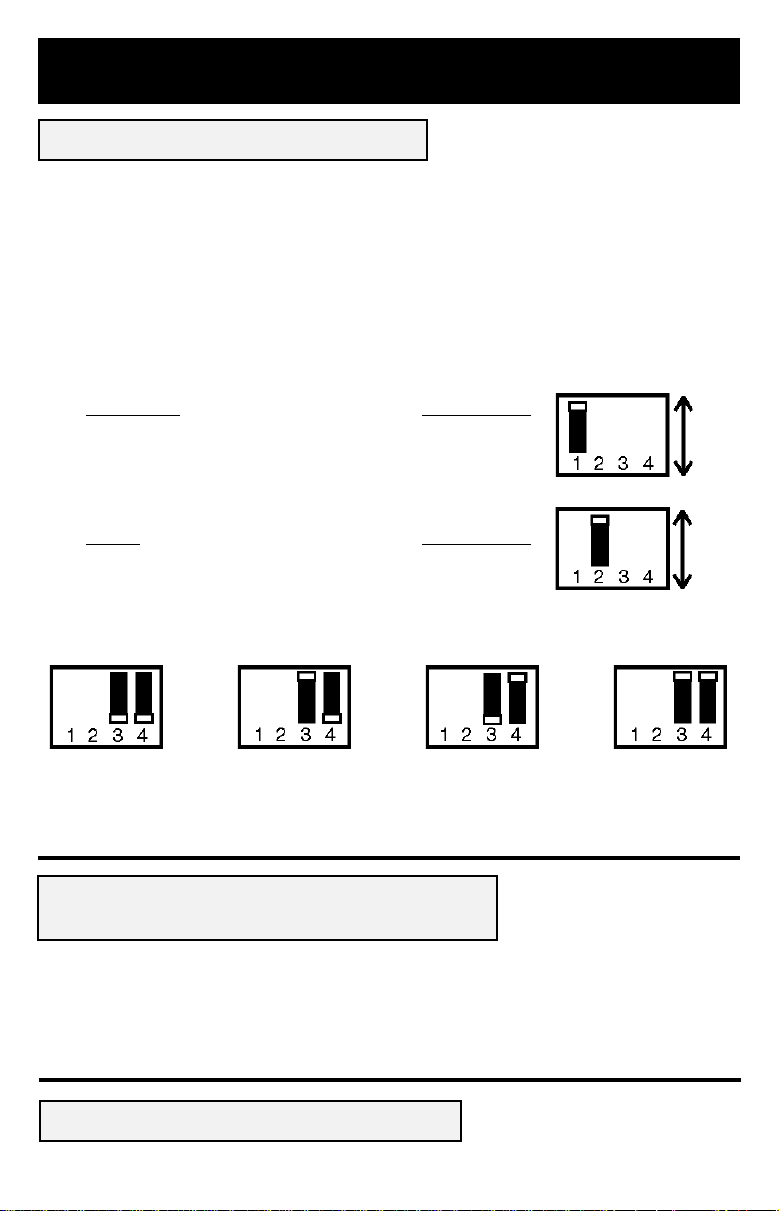
APS Installation
Configuration DIP Switch Settings*
(See Diagram 1, p. 46. Note: 1.1 is a closeup of the Configuration Dip Switches. 1.2 is “front”,
1.3 is “rear”).
Using a small tool, set the 4 Configuration DIP Switches (located on the bottom of your APS) to select
battery type and set the voltage range outside of which your APS will switch to battery power.
* Select before permanently mounting your APS.
• Select Battery Type
(DIP Switch #1)
CAUTION: The Battery Type DIP Switch setting must match the type of batteries you connect or your batteries may be degraded or
damaged over an extended period of time. See “Battery Selection,” page 6 for more information.
Battery Type Switch Position
Gel Cell (Sealed) Battery ................................. Front
Wet Cell (Vented) Battery ................................ Rear**
• Select High AC Voltage Point Switch To Battery
(DIP Switch #2)
Voltage Switch Position
276V .................................................................. Front
257V .................................................................. Rear**
• Select Low AC Voltage Point Switch To Battery
(DIP Switches #3 & #4)
Rear
Rear
Rear
Rear
Front
Rear
Front
Wet
Cell
Gel
Cell
257V
276V
Rear
Front
200V
#4 Front & #3 Front
Front
181V
#4 Front & #3 Rear
Front
162V
#4 Rear & #3 Front
Front
144V
#4 Rear
& #3 Rear**
** Factory default settings.
APS INT 512 Conversion from 50 to 60 Hz.
For Qualified Service Personnel Only*
(See Diagram 2, p. 46. Note: 2.1 is the “adjustment resistor” located in the upper right-hand
corner of the component side of the circuit board).
To permanently convert the APS INT 512 to 60 Hz., qualified service personnel should open the APS
case, locate the resistor on the circuit board and remove it.
* Turn your APS OFF and disconnect from the wall outlet before 60 Hz conversion.
Electrical Connection
Plug APS INT 512 models into outlets providing 230V AC, 50 or 60 Hz. power.
4
Page 5
APS Installation (Optional)
Permanent Mounting*
(See Diagram 3, p. 46).
• Install four 5 mm (#8) fasteners** into a rigid
diagram. (Leave head of fasteners slightly above surface in order to engage keyhole slots molded
into the bottom of the APS's feet.)
• Place the APS's four keyhole slots over the four fasteners and slide APS forward or back to secure.
Install “L”-shaped bracket* to permanently hold APS in position.
* Recommended for vehicular installation or other application requiring permanent, secure mounting.
** All fasteners and brackets are user-supplied. Turn your APS OFF and disconnect from the wall outlet before
mounting.
Splash Guard Installation*
(See Diagram 4, p. 46).
Thread four 4 mm (#8) sheet metal screws through four holes in a rigid
measuring 175 mm x 225 mm, through four 25 mm long hollow spacers and into the four blind holes
in the top panel of your APS.
* Recommended for use in wet locations. All sheet metal screws, splash guard and hollow spacers are user-supplied. Turn your APS OFF
and disconnect from wall outlet before installation.
APS INSTALLATION
SAFETY WARNINGS
• Install your APS indoors, away from excess moisture or heat, dust or direct sunlight.
• Leave adequate space around all sides of the APS for proper ventilation. The heavier
the load of your connected equipment, the more heat will be generated.
• Do not remove or modify the ground pin of the APS's plug. Do not use two-prong
adapters with the APS's plug.
• Connect your APS to a three-wire, grounded AC power outlet. Do not plug your APS
into itself; this will damage the APS and void your warranty.
horizontal
surface using the measurements in the
horizontal
splash guard
5
Page 6
Battery Selection
Selecting Battery Type
Select a battery or system of batteries that will provide your APS with 12V DC and your equipment
with an adequate amp hour capacity.*
* Even though APS models are high-efficiency converters of electricity, their rated output capacities are limited by the amp-hour size
of the external batteries.
Select ‘Deep-Cycle’ batteries to enjoy optimum performance from your APS. Select batteries of
either Wet-Cell (vented) or Gel-Cell/Absorbed Glass Mat (sealed) construction. 6 Volt “golf-cart,”
Marine Deep-Cycle or 8D Deep-Cycle batteries are also acceptable.**
** You must set Configuration DIP Switch #1 (Battery Type) to match the type of batteries you connect or your batteries
may be degraded or damaged over an extended period of time. See “APS Installation,” for more information.
Selecting Battery Amp Hour Capacity
Step 1:
Add the Wattage Ratings of your connected equipment to determine the Total Wattage Required.*
* The wattage rating is usually stated in the equipment's manuals or on their nameplates. If your equipment is rated in
amperes, convert to watts by multiplying the ampere rating by your nominal AC line voltage (230).
Step 2:
Divide the Total Wattage Required (from Step 1) by 12 to determine the DC Amperes Required.
Step 3:
Multiply the DC Amperes Required (from Step 2) by the Number of Hours Between Battery
Charging to determine the Battery Amp-Hour Rough Estimate.
Step 4:
Battery Amp-Hour ratings are usually given for a 20 hour discharge rate. Actual Amp-Hour capacity
is less when discharged at a faster rate. To compensate for this discrepency, multiply the Battery
Amp-Hour Rough Estimate (from Step 3) by 1.2 to determine the optimum battery amp-hour size
you should connect to your APS.**
** Your charging amps multiplied by the charging hours must exceed the discharge amp-hours taken from the batteries
between charges or you will eventually rundown your battery bank.
Battery Connection
SAFETY WARNINGS
• You must connect batteries in order for APS models to operate.
• Multiple battery systems must be made up of batteries of the same voltage, age, amp hour
capacity and type.
• Keep battery location well-ventilated. Explosive hydrogen gas can accumulate near the
battery if it is not kept well ventilated. Sparks may result during final battery connection.
• Do not allow objects to contact the two DC input terminals. Do not short or bridge them
together. Serious injury to person and/or property could result.
6
Page 7

Battery Connection (Standard)
Single 12V Battery Connection
(See Diagram 5, p. 46. Note: 5.1 is the fuse.)
Multiple 12V Battery System Connection (in Parallel)
(See Diagram 6, p. 47. Note: 6.1 is the fuse.)
Multiple 6V Battery System Connection (in Series)
(See Diagram 7, p. 47. Note: 7.1 is the fuse. Also, the connection will combine to provide
12V DC).
• Connect your APS's positive DC Terminal directly to a fuse near
your battery.
UL recommends that you install a recognized UL component fuse block and fuse within 18 inches of
the battery. The fuse should be rated a minimum of 100 amps. (See Figures 5, 6 and 7 for
recommended connection).
• Use the SHORTEST and HEAVIEST GAUGE battery cabling.
Use #4 cabling for DC cable lengths up to 10 feet. Use #2 cabling for lengths up to 16 feet. Shorter
and heavier gauge cabling limits DC voltage drop and allows for maximum transfer of current.*
* APS models are capable of delivering a much higher wattage output for brief periods of time. Therefore the wiring should
be configured to handle this brief high-current potential draw. Even though APS models are high-efficiency converters of
electricity, their rated output capacities are limited by the length and gauge of the wires running from the battery to the APS.
Battery Connection (Vehicular)
Choose the Basic Connection if you are running light hand tools or other small appliances for a brief
period of time (see Diagram 8, p. 47. Note: 8.1 is the alternator; 8.2 is the vehicle battery ground;
8.3 is a 12V vehicle battery; and 8.4 is the fuse). Choose the Advanced Connection if you are using
your APS to power heavy loads for extended periods of time (see Diagram 9, p. 47. Note: 9.1 is the
alternator; 9.2 is a battery isolator; 9.3 is the vehicle battery ground; 9.4 is a 12V vehicle battery;
and 9.5 is the fuse). This connection incorporates a battery isolator and separate battery system to
provide battery power to your APS while preventing it from draining your vehicle's battery. Note:
Depending on your application, you may require more than one 12V Deep Cycle Battery.
Caution: Never operate your APS from an alternator without a battery connected as show in Diagrams 8 and 9, p.47
7
Page 8
Equipment Connection
Match the power requirements of your equipment with the power
output of your APS to avoid overload.
When figuring the power requirements of your equipment, do not confuse “Continuous” power
ratings with “Peak” power ratings. Electric motors require more power to turn ON (“peak power”)
than they require to run continuously. “Peak” power ratings are usually 2 to 5 times “Continuous”
ratings. Most electric motors require “peak power” only once when they initially start. However, the
electric motors found in equipment such as refrigerators and sump pumps constantly cycle ON and
OFF in relation to demand. These motors require “peak power” at multiple, unpredictable times
during their operation.*
* After the APS has started an electric motor, it will have reserve power while the motor is running to dedicate to other
devices. Increase the APS load at your discretion. Note: If your batteries are low or the motor is very inefficient, worn or
old, the battery fuses may blow.
Connect your equipment to the APS's receptacles.*
• computers • kitchen appliances • CD players
• microwaves • refrigerators • VCRs
• sump pumps • electric motors (up to 1/6 hp) • lights
• power tools • tape recorders • turntables
• and more!
* All APS models feature Frequency Controlled Inverter Output which allows devices dependent on AC line frequency to operate
properly. Devices that are dependent on line frequency include computers, VCRs, CD players, tape recorders, clocks and turntables.
Set “Operating Mode” Switch
• Switch to “AUTO” when you are using connected equipment. ADVANTAGE: Provides battery
backup power during blackouts or brownouts.
• Switch to “CHARGE ONLY/REMOTE” when you are not using connected equipment.
(WARNING! UPS will not provide battery backup!) ADVANTAGES: A) Continues to charge battery
when power is present, and B) Turns OFF the APS’s inverter, preventing battery drain during
blackouts or brownouts.
Note: When the switch is in the “CHARGE ONLY/REMOTE” position, you can operate a
user-supplied 2-position switch to transfer between the “CHARGE ONLY” and “AUTO”
modes. (See Remote Connector description on page 10.)
• Switch to “OFF” to completely turn off the APS and connected equipment or to reset the APS after
it has shut down due to overload or overheating.
Equipment Connection
SAFETY WARNINGS
• Tripp Lite does not recommend the use of any of its APS series auto-switching emergency
power sources in any life support application when a malfunction or failure of a Tripp Lite
APS unit could cause failure or significantly alter the performance of the life support device.
Contact Tripp Lite for further information on this subject.
• Do not plug a surge suppressor, line conditioner or UPS into the AC output receptacles
of the unit.
• Do not plug your APS into itself; this will damage the APS and void your warranty.
8
Page 9
Switches, Indicator Lights
& Other Features
(See Diagram 10, p. 48 to locate the following switches, indicator lights and other features. 10.1
shows the UniPlug Universal Plug Adaptor [included with APS INT 512 models] which accepts
most worldwide plug configurations; 10.2 shows the plug and cordset. Note: 10.21=ground,
10.22=neutral, 10.23=line 1, 10.24=detachable line cord. 10.3 shows the “Configuration Dip
Switches” located on the bottom of the unit.)
Switches
1. “Operating Mode” Switch
This switch selects the APS operating mode (either “CHARGE ONLY/REMOTE”, “AUTO”, or
“OFF”. See “Equipment Connection” for the optimum switch setting.
2. “CONFIGURATION” DIP Switches
These four switches must be set for the type of battery your APS will be connected to and the voltage
range outside of which your APS will switch to battery power. The Battery Type DIP Switch #1 setting
must match the type of batteries you connect or your batteries may be degraded or damaged over
an extended period of time. Most loads will perform adequately when your APS’s High AC Voltage
Point DIP Switch #2 is set to 257V and its Low AC Voltage Point DIP Switches #3 and #4 are set to
181V. Set your APS above or below these points, however, to minimize frequent battery operation
caused by momentary high/low line voltage swings which have little effect on equipment operation.
(See “APS Installation” and Diagram 1 on page 46.)
Indicator Lights
3. “LINE”
This green light will turn continuously ON whenever connected equipment is receiving utility-supplied
AC power. It will flash intermittently when utility power is present and your APS's Operating Mode
Switch is set to “Charge Only/Remote” to warn you that the APS's inverter is OFF and that the APS
WILL NOT provide battery backup during blackouts, brownouts or overvoltages.
4. “INV”
This red light will turn continuously ON whenever connected equipment is receiving battery-supplied
AC power (during a blackout, brownout or overvoltage while connected to utility power or when
connected to batteries during vehicular operation).
5. “LOAD”
This red light will turn continuously ON when the APS’s load is between 80% and 110% of capacity.
The light will flash intermittently when the APS's inverter shuts down due to a severe overload or
overheating. If this happens, turn Operating Mode Switch OFF. Remove overload. Let the unit cool.
You may then turn the APS ON again.
9
Page 10

6. “BATTERY HI/MED/LO”
These three lights will turn ON in several sequences to show the approximate charge level and
voltage of your connected battery bank and alert you to several fault conditions:
BATTERY CHARGE INDICATION (Approximate)
Indicator Capacity Volts
Green 91% - Full 12.0 - 16.0
Green & Yellow 81% - 90% 11.8 - 12.0
Yellow 61% - 80% 11.6 - 11.8
Yellow & Red 41% - 60% 11.3 - 11.6
Red 21% - 40% 11.0 - 11.3
— 1% - 20% 10.0 - 11.0
Flashing Red 0% (Inverter shutdown) <10.0
All lights “Slow” Flash* Excessive discharge <8.0
All lights “Rapid” Flash** Overcharge >16.0
* Approximately 1/2 second on, 1/2 second off. See Troubleshooting section.
** Approximately 1/4 second on, 1/4 second off. May also indicate a battery charger fault exists. See Troubleshooting section.
Other Features
7. DC Input Terminals
The terminals' wing nuts secure the wires leading from your external battery. Connect a battery or
system of batteries that will ultimately combine to provide your APS with 12V DC and your equipment
with an adequate amp hour capacity. For best connection, use soldered lugs on your battery cable.
See Battery Selection section for more information.
8. AC Receptacles (NEMA 5-15R)
These receptacles allow connection of equipment designed to run on 230 VAC 50/60 Hz. power.
APS INT 512 models may require receptacle adapters (Universal Adapter included see Diagram
10.1, p. 48) to connect equipment to the APS.
9. AC Line Cord (NEMA 5-15P fixed or detachable)
Plug the cord into a 230V, 50/60 Hz. outlet. DO NOT plug the cord into the APS’s AC receptacles.
The APS INT 512 features an IEC-320 male plug and a detachable IEC-320 female to NEMA 5-15P
male cord set. Note the polarity of the plug in Diagram 10.2, p. 48.
10. Resettable Circuit Breaker
The circuit breaker protects your APS against damage due to output overload. Remove overload.
Wait 1 minute. Reset circuit breaker.
11. Remote “ON/OFF” Connector
This allows for remote APS control using user-supplied wire and 2-position switch. The connector
accepts a 3.5 mm 2-wire miniature phone plug. Note: The user-supplied remote switch can only
control APS operation when the APS “OPERATING MODE” switch is in the “CHARGE-ONLY”
position. The remote switch can only transfer between the “CHARGE-ONLY” and “AUTO” modes.
After completing a remote connection, determine which position is the “CHARGE-ONLY” mode and
which position is the “AUTO” mode for your particular switch. The position on your remote switch
that causes the green “LINE” indicator light to flash intermittently is the “CHARGE-ONLY” mode
position.
10
Page 11
Troubleshooting
Before sending your APS in for service, always check the following first. Call Tripp Lite Customer Service before
sending in your APS
SYMPTOM PROBLEMS CORRECTIONS
APS receptacles do not provide APS not properly connected to Connect APS to wall receptacle.
AC output (AC input present) wall receptacle.
Circuit breaker is tripped. Reset circuit breaker.
APS shutdown due to excessive Turn APS OFF. Wait 1 minute and
battery voltage (> 16V DC), indicat- switch to “AUTO”.
ing possible charger failure. Line
disconnected to prevent permanent
battery damage.
APS is set to “OFF” Set APS to “AUTO” or “CHARGE-
APS receptacles do not provide Circuit breaker is tripped. Reset circuit breaker.
AC output (AC input absent)
Operating Mode Switch is set Set Operating Mode Switch to “AUTO.”
to “Charge Only.”
Load or High temperature fault. Turn APS OFF. Wait 1 minute.
Excessive battery discharge. Check battery condition.
APS will not charge the Connected batteries are dead. Check and replace old batteries.
battery (AC input present)
Battery fuse* is blown. Check and replace fuse.
Battery cabling* is loose or degraded. Check and tighten or replace cabling.
APS charger failure. Turn APS OFF. Wait 1 minute and
All APS Indicator Lights are This is normal if the APS is set —
OFF (AC input absent) to “CHARGE-ONLY”
All APS Indicator Lights are Excessive battery discharge. Use an auxiliary charger to raise
OFF (AC input is present or battery voltage to at least 9V DC.
absent) Check external Battery connections
All APS Battery Indicator Excessive battery discharge. Use an auxiliary charger to raise
Lights are slowly flashing. battery voltage to at least 9V DC.
APS “LO” Battery Light Inverter shutdown because battery Reset by cycling control switch to
flashing voltage less than 10V DC for more OFF position then ON.
than 5 seconds. Protects battery
from permanent damage.
All APS Battery Lights are High battery voltage shutdown Check all charging sources.
rapidly flashing during Charge mode. Reset by cycling control switch to
APS “LOAD” Indicator Light Inverter overload caused by Reset by reducing load and cycling conis rapidly flashing excessive load or short circuit. trol switch to OFF position then ON.
If sustained for more then 5
seconds the Inverter is shutdown.
*User supplied
ONLY”.
Remove overload. Switch to “AUTO.”
switch to “AUTO”. If automatic shutdown occurs, call Tripp Lite
Customer Service.
and fuse. Automatically resets when
condition is cleared.
Automatically resets when condition
is cleared.
OFF position then ON.
11
Page 12

Limited Warranty
Tripp Lite warrants its products to be free from defects in materials and workmanship for a period of one year (domestic) or 120 days
(export) from the date of initial purchase. Tripp Lite’s obligation under this warranty is limited to repairing or replacing (at its sole option)
any such defective products. To obtain service under this warranty you must obtain a Returned Material Authorization (RMA) number
from Tripp Lite or an authorized Tripp Lite service center. Products must be returned to Tripp Lite or an authorized Tripp Lite service
center with transportation charges prepaid and must be accompanied by a brief description of the problem encountered and proof of
date and place of purchase. This warranty does not apply to equipment which has been damaged by accident, negligence or
misapplication or has been altered or modified in any way. This warranty applies only to the original purchaser who must have properly
registered the product within 10 days of purchase.
EXCEPT AS PROVIDED HEREIN, TRIPP LITE MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Some states do not permit limitation or exclusion of implied
warranties; therefore, the aforesaid limitation(s) or exclusion(s) may not apply to the purchaser.
EXCEPT AS PROVIDED ABOVE, IN NO EVENT WILL TRIPP LITE BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OF THIS PRODUCT, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
OF SUCH DAMAGE. Specifically, Tripp Lite is not liable for any costs, such as lost profits or revenue, loss of equipment, loss of use
of equipment, loss of software, loss of data, costs of substitutes, claims by third parties, or otherwise.
Specifications
INVERTER APS INT 512
Continuous power 20° C: 500 Watts
Surge power (5 seconds): 1200 Watts
Efficiency (Full Load): 90%
DC Input Current @ 12V DC -Full Load: 52 Amps
-No Load: 1 Amp
Nominal Input Volts: 12 VDC
DC Input Voltage Range: 10 to 15.5 V DC
Nominal Output Volts: 230 VAC +/- 5%
Nominal Output Frequency: 50/60Hz +/- .3%
Waveform: Modified Sine
BATTERY CHARGER
Charging Capacity DC: 18 Amps
Acceptance Volts VDC: Selectable ’14.4/14.2 Wet/Gel
Float Volts VDC: Selectable ’13.3/13.6 Wet/Gel
Input Voltage AC: 230 VAC
Input Current AC: 5 Amps
LINE VAC OPERATION
Minimum Input AC Volts: Selectable 144, 162, 181 or 200 VAC
Maximum Input AC Volts: Selectable 257 or 276 VAC
Maximum Input Current: 11 Amps
Input Frequency: 50/60Hz +/-10%
Maximum Output AC: 5 Amps
Automatic Transfer Time: 6 milliseconds nominal
Dimensions (H x W x D): 17.4 x 17.4 x 25.4 cm
Weight: 8.2 kg.
Maintenance & Service
Maintenance
The APS series requires no maintenance but should be kept dry at all times. Periodically check all
cable connections both at the unit and at the battery. Clean and tighten as necessary.
Service
If returning your APS to Tripp Lite, please carefully pack the APS using the ORIGINAL PACKING
MATERIAL that came with the unit. Enclose a letter describing the symptoms of the problem. If the
UPS is within the warranty period, enclose a copy of your sales receipt.
12
Page 13

Introducción
¡Enhorabuena! Acaba de adquirir el ondulador/cargador de baterías más avanzado y con el mayor
número de funciones del mercado. Su nuevo APS suministra CA a los equipamientos cuando la
energía eléctrica está presente. Que haya un corte de electricidad, una subida de tensión o una
reducción de intensidad, su APS se conecta automáticamente a un banco externo de baterías para
suministrar a los equipos conectados CA con una tensión y una frecuencia controladas.
Indicadores visuales para Funciones Múltiples
Dos barras de indicadores visuales le informan constantemente de los niveles de carga de la batería,
de las condiciones de fallo y del funcionamiento del APS. Una barra de indicadores visuales para
funciones múltiples le informa de las condiciones de carga de la batería y enciende las luces de
advertencia en caso de fallo. La otra barra de indicadores visuales para funciones múltiples le informa
de las condiciones de funcionamiento del APS.
Interruptores para Operaciones Múltiples
Las opciones de funcionamiento del sistema APS están agrupados en dos puntos de mando.
Permiten ajustar un amplio abanico de tensiones con las que desea que su APS funcione de manera
a optimizar la protección de su equipo y evitar que la batería se vacíe. Existen otras opciones que
incluyen el ajuste con un mando a distancia, mucho más cómodo, y el ajuste del tipo de baterías para
que cargar sea más eficaz .
Potencia de salida con Regulador de Frecuencia (Modo Ondulador)
Puesto que su APS controla la frecuencia de la línea, los aparatos sensibles a las frecuencias pueden
funcionar correctamente.
Protección Automática en caso de Sobrecarga
Si hay sobrecarga en el APS, el aparato se protegerá automáticamente y protegerá también las
baterías.
13
Page 14
Etapa 2
Absorción
Etapa 1
A granel
TENSIÓN DE LA BATERÍA
CURVA DE CARGA EN
FUNCIÓN DEL TIEMPO
Etapa 3
Estabilización
Cargador de Batería Avanzado
en 3 Etapas
Su APS permite volver a cargar las baterías
mucho más rápido que los cargadores
convencionales puesto que se han llegado a
optimizar las tres fases de carga (A granel,
Absorción y Estabilización) cualquiera que sea
el tipo de batería que usted utiliza (Batería
líquida o Batería Gel)*. Además, gracias al
sistema de carga avanzado, las baterías están
protegidas contra el exceso de carga o de
descarga, y tienen una duración de vida mucho
más larga.
* Los niveles de Absorción y de Estabilización pueden variar
según el tipo de batería, que el usuario puede ajustar, bien en la
posición Wet (Batería líquida) bien en la posición Gel (Batería
de gel).
Potencia de salida de Alto
Rendimiento
Los circuitos avanzados de su APS producen
una conversión de CC en CA mucho más
eficaz, por lo que se reducen las pérdidas de
energía y se puede hacer funcionar cualquier
equipo conectado durante más tiempo entre
carga y carga. El APS mantendrá una potencia
de salida de alto rendimiento incluso si la carga
de las baterías disminuye.
RENDIMIENTO (en %)
POTENCIA EN VOLTIOS
Este manual contiene instrucciones y advertencias importantes que deben seguirse durante la
instalación, operación y almacenaje de los Sistemas Automáticos de Energía APS de Tripp Lite
14
Page 15
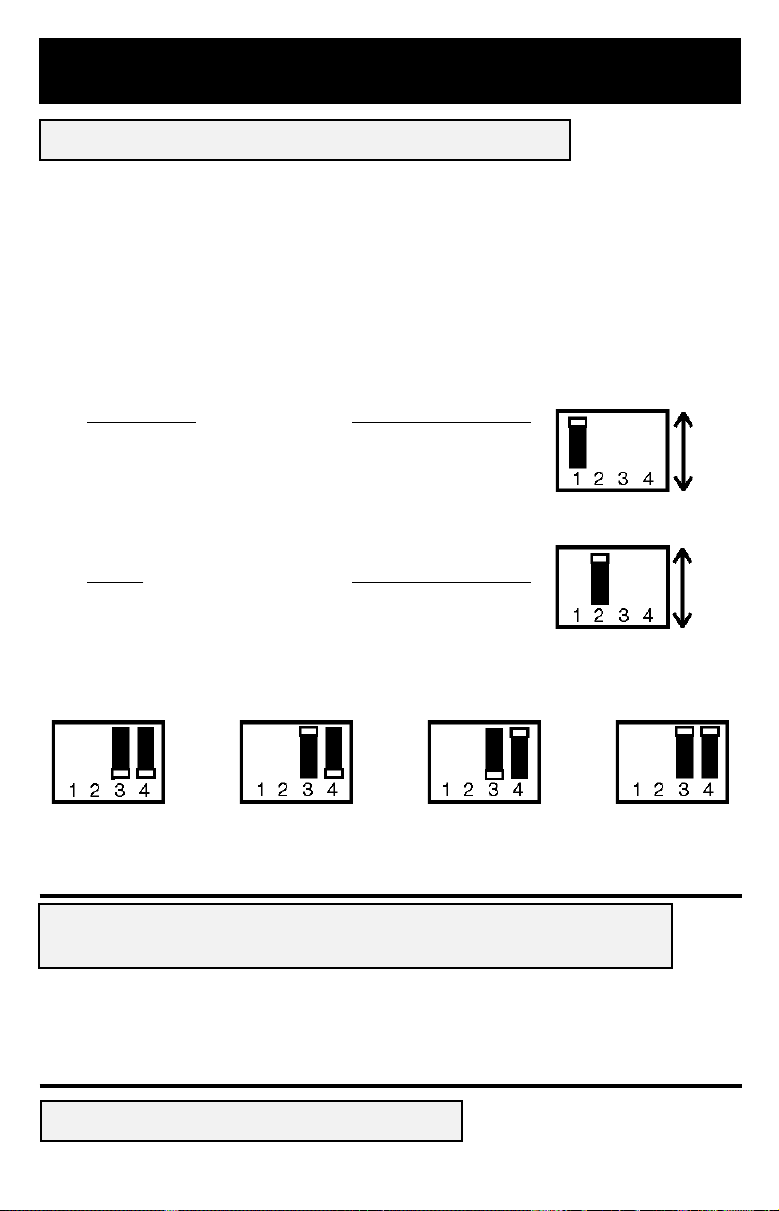
Instalación del APS
Ajustar los Conmutadores DIP de Configuración*
(Véase el esquema 1, p. 46, Nota: 1.1 muestra una vista detallada de los Conmutadores DIP de
Configuración, 1.2 corresponde a la posición parte delantera, 1.3 a la posición parte trasera).
Con la ayuda de una pequeña herramienta, ajuste los 4 Conmutadores DIP de Configuración (situados
en el panel de abajo de su APS) y seleccione el tipo de batería. Ajuste luego el nivel de tensión puesto
que en la salida el APS se conectará automáticamente a la batería que suministra la energía.
* Selecciónelos antes de montar definitivamente el APS.
• Seleccionar el Tipo de Batería
(Conmutador DIP n° 1)
CUIDADO: Cuando ajusta el Conmutador DIP para elegir el Tipo de Batería tiene que tener en cuenta el tipo de baterías que conecta
o sino dañará o degradará las baterías a largo plazo. Véase “Elegir la Batería” en la página 17 para más información.
Tipo de Batería Posición del Conmutador
Batería Gel (Hermética) ................................... Parte Delantera
Batería Líquida (Abierta) .................................. Parte Trasera**
• Seleccionar Conmutador de conversión en la
Batería cuando la CA está en Alta Tensión
(Conmutador DIP n° 2)
Tensión Posición del Conmutador
276V ................................................................. Parte Delantera
257V ................................................................. Parte Trasera**
• Seleccionar Conmutador de conversión en la Batería cuando la
CA está en Baja Tensión (Conmutadores DIP n° 3 & n° 4)
Parte Trasera
Parte Trasera
Parte Trasera
Parte Trasera
Parte Delantera
Parte Trasera
Parte Delantera
Parte Trasera
Batería
Líquida
Batería
Gel
257V
276V
Parte Delantera
200V
n°4 Parte Delantera &
n°3 Parte Delantera
** Ajustes por defecto realizados en fábrica
Parte Delantera
181V
n°4 Parte Delantera &
n°3 Parte Trasera
Parte Delantera
162V
n°4 Parte Trasera &
n°3 Parte Delantera
Parte Delantera
144V
n°4 Parte Trasera &
n°3 Parte Trasera**
Conversión de la del APS INT 512 de 50 a 60 Hz.
Sólo para personal cualificado autorizado*
(Véase esquema 2, p. 46. Nota: 2.1 corresponde a la Resistencia de ajuste situada en el
ángulo superior derecho de la parte de los componentes del circuito impreso).
Si se desea convertir la frecuencia del APS INT 512 a 60 Hz de manera permanente, se recomienda
que sólo el personal cualificado abra la unidad APS, localice la resistencia en el circuito impreso y la quite.
* Desconecte y desenchufe el APS antes de realizar la conversión.
Conexión Eléctrica
Conecte los modelos APS INT 512 a tomas que suministren 230V y de 50 ó 60 Hz.
15
Page 16

Instalación del APS (Opcional)
Para montarlo definitivamente*
(Véase esquema 3, p. 46).
• Instale cuatro junturas* de 5 mm (n°8) sobre una superficie rígida y
que aparecen en el esquema. (Deje que la cabeza de las junturas salgan ligeramente por encima de
la superficie de manera que puedan entrar dentro de los agujeros previstos a tal efecto en la parte
inferior de las patas del APS.)
• Coloque los cuatro agujeros de las patas del APS encima de las cuatro junturas y luego estabilice
el APS moviéndolo hacia adelante o hacia atrás. Para bloquear el APS en su sitio, instale la
abrazadera en forma de “L”.
* Se recomienda para utilización en vehículos o en un lugar que necesite que la unidad esté fijada con junturas permanentes y seguras.
Todas las junturas y abrazaderas las tiene que comprar el usuario. Desconecte y desenchufe el APS antes de montarlo.
Para Instalar la Protección contra las Salpicaduras*
(Véase esquema 4, p. 46).
Coloque cuatro tornillos metálicos de 4 mm (n° 8) en los cuatro agujeros de una plancha rígida y
horizontal que mida 175 mm x 225 mm que servirá para proteger el APS contra las salpicaduras.
Antes, coloque tacos huecos de 25 mm de largo en los cuatro agujeros del panel superior de su APS.
* Se recomienda para utilización en lugares húmedos. Todos los tornillos metálicos, la protección contra las salpicaduras y los tacos
huecos los tiene que comprar el usuario. Desconecte y desenchufe el APS antes de instalarlo.
INSTALACION DEL SISTEMA APS
ADVERTENCIAS DE SEGURIDAD
• Instale este sistema APS bajo techo, en un lugar libre de humedad o calor excesivo,
sin polvo o luz solar directa.
• Mantenga suficiente espacio en todos los lados del sistema APS para permitir la
ventilación apropiada. Cuanto más alta sea la demanda eléctrica de los equipos
conectados al sistema APS, más calor generará esta unidad.
• No remueva o modifique el alambre de conexión a tierra del enchufe del sistema APS.
No conecte adaptadores sin conexión a tierra al enchufe del sistema APS.
• Conecte este sistema APS a un enchufe de energía de CA de tres alambres con
conexión a tierra. No conecte el sistema APS a sí mismo; esto dañará el sistema
APS y anulará su garantía.
horizontal
y utilice las medidas
16
Page 17

Elegir las Baterías
Elegir el Tipo de Batería
Elija la batería o conjunto de baterías que suministren a su APS CC de 12V, y a su equipo con una
capacidad adecuada de amperios hora.*
* Incluso si los modelos de APS permiten convertir la corriente de manera eficaz, la capacidad amperios por hora de las baterías externas
limita las capacidades de la potencia de salida.
Elija baterías “Deep Cycle” para que su APS le brinde los mejores resultados. Elija baterías de
construcción Batería Líquida (abiertas) o bien Batería Gel/ Tampón de Vidrio Absorbido (hermética).
También acepta baterías de 6 Voltios “carritos de golf”, Marine Deep Cycle o las 8D Deep Cycle.**
** CUIDADO: Cuando ajusta el Conmutador DIP n°1 para elegir el Tipo de Batería tiene que tener en cuenta el tipo de baterías que
conecta o sino dañará o degradará las baterías a largo plazo. Véase “Instalación del APS” para más información.
Elegir la Capacidad Amperios Hora de la Batería
1er Paso:
Para determinar la capacidad total necesaria, suma las potencias nominales del equipo conectado.*
* Normalmente, la capacidad nominal está indivada en los manuales del equipo o en las placas de identificación. Si su
equipo está en amperios, conviértalos en vatios multiplicando la capacidad de amperios hora por la tensión nominal de
la línea de CA (230).
2° Paso:
Para determinar la intensidad de CC necesaria, divida por 12 la potencia total necesaria (calculada
en el 1er Paso)
er
3
Paso:
Para estimar la capacidad de una batería en Amperio Hora, multiplique la intensidad de CC necesaria
(calculada en el 2° Paso) por el número de horas que han pasado entre carga y carga de la batería.
4° Paso:
La capacidad nominal en amperio horas de una batería se dan normalmente para una duración de
20 horas hasta que se descarga. Cuando se descarga más rápido, la capacidad real de amperio
horas es inferior. Para compensar esta diferencia, multiplique por 1,2 la estimación aproximada de
la capacidad en amperio horas de la batería (calculada en el 3er Paso); se va a obtener la capacidad
óptima en amperio horas de la batería que hay que conectar a su APS.**
** El resultado de los amperios de carga multiplicados por el número de horas de carga debe ser superior a la cantidad
de amperios hora de descarga que se obtienen entre carga y carga de las baterías. Sino se descargarán completamente los
bancos de baterías.
Conexión de Baterías
ADVERTENCIAS DE SEGURIDAD
• Usted debe conectar baterías para operar el sistema APS.
• Los sistemas múltiples de baterías deben estar compuestos de baterías del mismo voltaje,
edad, capacidad en amperios/hora y tipo.
• Mantenga el lugar donde están las baterías con ventilación adecuada. Gases hidrógenos
explosivos pueden acumularse cerca de las baterías si no existe buena ventilación.
Pueden producirse chispas durante la conexión final de las baterías.
• No permita que cuerpos extraños entren en contacto con los dos bornes de entrada de
CD. No los una o permita que éstos entren en contacto. Esto puede resultar en lesiones o
daños severos.
17
Page 18

Conexión a la Batería (Estándor)
Conexión a una sola Batería 12V
(Véase esquema 5, p. 46. Nota: 5.1 indica el fusible).
Conexión a un banco de varias Baterías de 12V (en Paralelo)
(Véase esquema 6, p. 47. Nota: 6.1 indica el fusible).
Conexión a un banco de varias Baterías de 6V (en Serie)
(Véase esquema 7, p. 47. Nota: 7.1 indica el fusible. Además, la conexión permite suministrar CC de 12V).
• Conecte la Terminal de CC positiva del APS directamente a un
fusible situado cerca de su batería.
UL le aconseja que instale una caja de fusibles y un fusible reconocidos por UL a 18 pulgadas (unos
46 cms.) de la batería. El fusible deberá soportar un mínimo de 100 amperios. (Véase esquemas 5,
6 y 7 para conectarlos correctamente).
• Utilice el cableado de la batería ESTÁNDAR MÁS CORTO y DE
MÁS CALIBRE.
Utilice cableado n°4 para cables de CC que no midan más de 10 pies (3 metros y medio) de largo.
Utilice cables n°2 que no midan más de 16 pies (5 metros y medio) de largo. Los cables estándares
cuanto más cortos y de más calibre mejor puesto que permiten disminuir bajadas de tensiones de
CC y optimizar la transmisión de corriente.*
* Los modelos APS pueden suministrar una potencia en voltios de salida mucho más elevada durante periodos breves de
tiempo, por lo que se deben configurar los cables de manera que puedan soportar estos breves periodos de fuerte
corriente. Aunque los modelos APS convierten la electricidad muy eficazmente, las capacidades nominales están limitadas
por la largura y el calibre de los conductores entre la batería y el APS.
Conexión a la Batería (para Vehículos)
Si hace funcionar herramientas de mano ligeras o cualquier otro aparato pequeño durante un breve
periodo de tiempo, elija una conexión de base (véase esquema 8, p. 47. Nota: 8.1 indica el
alternador; 8.2 indica la masa de la batería del vehículo; 8.3 una batería de 12V del vehículo;
y 8.4 el fusible). Si utiliza su APS para alimentar fuertes cargas durante largos periodos de tiempo,
elija la conexión avanzada (véase esquema 9, p. 47. Nota: 9.1 indica el alternador; 9.2 un aislante
para batería; 9.3 la masa de la batería del vehículo; 9.4 una batería de 12V del vehículo; y 9.5
el fusible). Esta conexión incorpora un aislador para batería y un sistema de batería por separado
para suministrar corriente eléctrica al APS, mientras se evita que la batería del vehículo se vacíe.
Nota: Según para qué desea utilizarla, necesitará más de una batería Deep Cycle de 12V.
Cuidado: Nunca haga funcionar su APS en un alternador sin que haya una batería conectada como se muestra en los
esquemas 8 y 9, p. 47.
18
Page 19

Conexión de los Equipamientos
Si desea evitar las sobrecargas, haga que los requisitos en
cuanto a energía eléctrica de sus equipamientos correspondan
con la capacidad de alimentación de su APS.
Para calcular los requisitos en cuanto a energía eléctrica de sus equipamientos, no confunda la
potencia nominal “Continua” con la potencia nominal “Máxima”. Los motores eléctricos consumen más
energía cuando se encienden (“energía máxima”) que cuando funcionan de manera continuada. La
potencia nominal máxima es entre 2 y 5 veces más elevada que la potencia “Continua”. La mayoría
de los motores eléctricos necesitan “potencia máxima” sólo en el momento de ponerlos en marcha. Sin
embargo, los motores eléctricos que se encuentran en equipamientos tales como neveras y bombas
de los cárteres alternan constantemente entre Marcha y Paro según la demanda. Estos motores
necesitan “potencia máxima” en cualquier momento y muy a menudo mientras están en servicio.*
* Una vez que el APS ha puesto en marcha un motor eléctrico, tendrá todavía energía en reserva mientras el motor está
funcionando para poder dedicarse a otros aparatos. Se podrá aumente la carga de su APS como se desee. Nota: Si las
baterías están casi descargadas o si el motor es poco eficaz, viejo o muy gastado, los fusibles de la batería pueden saltar.
Conecte su equipo a los receptáculos del APS.*
• ordenadores • aparatos del hogar • motores eléctricos (hasta 1/6 hp)
• micro-ondas • neveras • herramientas para energía eléctrica
• lectores de CD • tocadiscos • ¡Y más aún!
• luces • aparatos de vídeo
• magnetófonos • bombas de los cárteres
* Todos los modelos de APS están dotados de un ondulador de regulación de la potencia para que los aparatos que dependen de
una línea de CA pueden funcionar correctamente. Los aparatos que dependen de las frecuencias de la línea son los ordenadores,
los aparatos de vídeo, lo s le ctores de CD, y los tocadiscos.
Ajustar el Conmutador “Modo Funcionamiento”
• Pase en modo “AUTO” cuando esté utilizando equipamientos conectados. VENTAJA: Suministra
energía de reserva a la batería durante apagones o reducciones de intensidad.
• Pase en modo “CARGAR SÓLO/REMOTO” cuando no esté utilizando equipamientos conectados.
(CUIDADO: ¡UPS no suministra energía de reserva!). VENTAJAS: A) La batería sigue cargándose
mientras haya energía eléctrica, y B) el ondulador del APS se apaga por lo que se evita que la batería
se vacíe durante los apagones o las reducciones de intensidad.
Nota: Cuando el conmutador está en posición “CARGAR SÓLO/REMOTO”, puede utilizar un
conmutador de 2 (suministrado por el usuario) para pasar del modo “CARGAR SÓLO ” al modo
“ AUTO”. (Véase la descripción del Conector Remoto en la página 21).
• Pase en modo “Paro” para apagar del todo el APS y los equipamientos conectados a él o para
reiniciar el APS después de que se haya apagado debido a una sobrecarga o a un calentamiento
excesivo.
Conexión de Equipos
ADVERTENCIAS DE SEGURIDAD
• Tripp Lite no recomienda el uso de sus fuentes automáticas de energía de emergencia de la serie APS en aplicaciones de
mantenimiento de vida donde un defecto o falla del sistema APS pudiera causar la falla o significativamente alterar el
rendimiento de dispositivos vitales. Comuníquese con Tripp Lite para obtener más información al respecto.
• No conecte un supresor de sobretensiones transitorias, regulador de voltaje, acondicionador de línea o sistema UPS / no-break a
los receptáculos de salida de esta unidad.
• No conecte el sistema APS a sí mismo; esto dañará la unidad y anulará su garantía.
19
Page 20

Interruptores, Indicadores visuales
& Otras Funciones
(Véase esquema 10, p. 48 para localizar los siguientes interruptores, indicadores visuales y demás
funciones. 10.1 muestra el Adaptador Universal UniPlug [incluido en los modelos APS INT 512]
que acepta la mayoría de las tomas de todo el mundo; 10.2 muestra el enchufe y el cordón. Nota:
10.21 = masa, 10.22 = neutro, 10.23 = línea, 10.24 = cordón de línea desmontable. 10.3 muestra los
“Conmutadores DIP de Configuración” situados en la parte inferior de la unidad.)
Conmutadores
1.Conmutador “Modo Funcionamiento”
Este conmutador elige el modo de funcionamiento del APS (bien “CARGAR SÓLO/REMOTO”,
“AUTO” o “OFF”). Véase “Conexión Equipamientos” para ajustar el conmutador lo mejor posible.
2.Conmutadores DIP “CONFIGURACIÓN”
Se deben ajustar estos cuatro conmutadores según el tipo de batería que se conectará a su APS y
según el nivel de tensión de salida con el que su APS pasará automáticamente a energía proveniente
de la batería. Cuando se ajusta el Conmutador n° 1 DIP para elegir el Tipo de Batería se tiene que
tener en cuenta el tipo de baterías que se conectan o sino se dañarán o se degradarán las baterías
durante un largo periodo de tiempo. La mayoría de las cargas se realizan correctamente si se ajusta
el Conmutador n°2 DIP de Alta Tensión de CA de su APS a 257V y los Conmutadores n°3 y n°4 DIP
de Baja Tensión de CA a 181V. Ajuste su APS por encima o por debajo de estos puntos para reducir
al máximo la frecuencia de utilización de la batería provocada por cambios momentáneos de alta/
baja tensión de la línea que no tienen una incidencia muy importante en el funcionamiento de los
equipos. (Véase “Instalación del APS” y el esquema 1 de la página 46.)
Indicadores Visuales
3.“LINE” (LÍNEA)
La luz verde se enciende cada vez que un equipo conectado recibe energía de línea de CA
proveniente de la red pública. Se volverá intermitente cada vez que hay energía de la red pública y
que el Conmutador Modo Funcionamiento de su APS está en posición de “Cargar sólo/Remoto” para
avisarle que el ondulador de su APS está apagado y que el APS NO suministrará batería de reserva
durante apagones, reducciones de intensidad o sobretensiones.
4.“INV”
La luz roja se enciende cada vez que un equipo conectado recibe energía de línea de CA proveniente
de la batería (durante apagones, reducciones de intensidad o sobretensiones mientras está
conectado a una red pública de energía o cuando está conectado a baterías si está funcionando en
un vehículo).
5.“LOAD” (CARGAR)
La luz roja se enciende cuando la carga del APS se sitúa entre un 80% y un 110% e su capacidad.
La luz se volverá intermitente cuando el ondulador del APS se apaga debido a una sobrecarga
importante o a un calentamiento excesivo. Si esto ocurre, ponga el Conmutador de Modo
Funcionamiento en OFF. Quite la sobrecarga. Deja que la unidad se enfríe. Luego podrá volver a
encender el APS.
20
Page 21

6.Conmutadores de carga alta (HI), media (ED) y floja (LO) de las baterías
Las tres luces se encienden según varias secuencias para mostrar el nivel de carga y de tensión
aproximados de su banco de baterías conectadas y le avisa de diferentes situaciones de fallo:
INDICACIÓN DE CARGA DE LA BATERÍA (Aproximadamente)
Indicador Capacidad Voltios
Verde 91% - Total 12.0 - 16.0
Verde & Amarillo 81% - 90% 11.8 - 12.0
Amarillo 61% - 80% 11.6 - 11.8
Amarillo & Rojo 41% - 60% 11.3 - 11.6
Rojo 21% - 40% 11.0 - 11.3
— 1% - 20% 10.0 - 11.0
Rojo intermitente 0% (ondulador apagado) <10.0
Todas las luces se encienden Excessive discharge <8.0
y se apagan Lentamente *
Todas las luces se encienden Overcharge >16.0
y se apagan Rápidamente **
* Aproximadamente medio segundo encendidas, medio segundo apagadas. Véase sección Buscar Fallos.
** Aproximadamente ¼ de segundo encendidas, ¼ de segundo apagadas. También pueden indicar un fallo en la carga de la batería.
Véase sección Buscar Fallos.
Otras Funciones
7.Terminales de entrada de CC
Las tuercas mariposa de las Terminales fijan los conductores provenientes de su batería externa.
Conecte una batería o un sistema de baterías que puedan suministrar 12V de CC a su APS y una
capacidad adecuada de amperios horas. Para mejorar la conexión, utilice patas soldadas en los
cables de su batería. Véase la sección Seleccionar la Batería para más información.
8.Receptáculos de CA (NEMA 5-15R)
Estos receptáculos permiten conectar equipos diseñados para funcionar con CA de 230V a 50/60
Hz. Algunos modelos APS INT 512 necesitan adaptadores para receptáculos (se incluye un
Adaptador Universal véase esquema 10.1, p. 48) para poder conectar el equipo al APS.
9.Cordón Línea CA (NEMA 5-15P fijo o desmontable)
Conecte el cordón a una toma de corriente de 230V y 50/60Hz. NO conecte el cordón a los
receptáculos de CA del APS. En su cordón macho NEMA 5-15P, el APS INT 512 lleva un enchufe
macho IEC-320 y uno hembra IEC-320 desmontable. Cuidado con la polaridad del enchufe como lo
muestra el esquema 10.2, p. 48.
10. Disyuntor Ajustable
El disyuntor protege su APS contra los daños causados por una sobrecarga. Quite la causa de la
sobrecarga. Espere 1 minuto y vuelva a poner en marcha el disyuntor.
11. Conector “ON/OFF” Remoto
Permite controlar el APS con ayuda de un cable suministrado por el usuario y de un conmutador de
2 posiciones. El conector acepta enchufes de teléfono miniatura de 2 conductores de 3,5 mm. Nota:
el conmutador remoto sólo controla el funcionamiento del APS cuando el conmutador “MODO
FUNCIONAMIENTO” del APS está en la posición “CARGAR SÓLO”. El conmutador remoto
suministrado por el usuario, sólo puede pasar del modo “CARGAR SÓLO” al modo “AUTO”. Tras
finalizar la conexión remota, se determina qué posición corresponde al modo “CARGAR SÓLO” y qué
posición corresponde al modo “AUTO” para ese conmutador en especial. La posición de su
conmutador remoto en el modo “CARGAR SÓLO” hace que el indicador visual verde “LÍNEA” esté
intermitente.
21
Page 22

Buscar Fallos
Verifique lo siguiente antes de enviar su sistema APS al centro de servicio. Llame al Departamento de Servicios
a Clientes antes de enviar el sistema APS.
SÍNTOMAS PROBLEMAS CORRECCIONES
Los receptáculos del APS no
suministran potencia de salida
(y hay CA de entrada)
Los receptáculos del APS no
suministran potencia de salida
(ni tampoco hay CA de
entrada)
El APS no carga la batería (y
hay CA de entrada)
Ningún indicador visual
funciona (ni tampoco hay CA
de entrada).
Ningún indicador visual
funciona (que haya o no CA de
entrada).
Todos los indicadores visuales
de la Batería del APS se
encienden y se apagan
lentamente.
La luz de la Batería “LO” del
APS está intermitente.
Todos los indicadores visuales
de la Batería del APS se
encienden y se apagan
rápidamente.
El indicador visual “CARGA” de
la Batería del APS se enciende
y se apaga rápidamente.
*Suministradas por el usuario.
22
No se ha conectado correctamente el
APS al receptáculo mural.
El disyuntor no funciona.
El APS no funciona debido a un exceso
de tensión de la batería (>CC de 16V),
por lo que el cargador puede que no
funcione. Desconecte la línea para evitar
provocar daños irreversibles a la batería.
El APS está apagado.
El disyuntor no funciona.
El conmutador Modo Funcionamiento
está en posición “CARGAR SÓLO”.
Fallo a nivel de la carga o debido a
temperaturas demasiado elevadas.
La batería se ha descargado demasiado.
Las baterías conectadas están muertas.
El fusible* de la batería se ha quemado.
Los cables* de la batería están
sueltos o se han degradado.
El cargador del APS no funciona.
Esto es normal si el APS está en
posición “CARGAR SÓLO”.
La batería se ha descargado
demasiado.
La batería se ha descargado
demasiado.
El ondulador no funciona porque la
tensión de la batería ha estado más de
5 segundos por debajo de los 10V de
CC. Esto permite proteger la batería de
daños irreversibles.
Apagón debido al Alta Tensión de la
batería durante el modo Carga.
Sobrecarga en el ondulador debido a
una carga excesiva o a un
cortocircuito. Si dura durante más de 5
segundos el ondulador quedará fuera
de servicio.
Conecte el APS a un receptáculo mural.
Vuelva a poner en marcha el disyuntor.
Apague el APS. Espere 1 minuto y
póngalo en modo “AUTO”.
Ajuste el APS en modo “AUTO” o
“CARGAR SÓLO”.
Vuelva a poner en marcha el disyuntor.
Ajuste el conmutador Modo
Funcionamiento en posición “AUTO”.
Apague el APS. Espere 1 minuto, quite la
sobrecarga y póngalo en modo “AUTO”.
Compruebe las condiciones de la
batería.
Compruébalo y cambie las viejas baterías.
Compruébalo y cambie el fusible.
Compruébalo y conecte o cambie los cables.
Apague el APS. Espere 1 minuto y
póngalo en modo “AUTO”. Si se apaga
automáticamente, llame al Servicio de
Atención al Cliente de Tripp Lite.
–
Utilice un cargador auxiliar que haga
aumentar la tensión de la batería hasta
un mínimo de 9V de CC.Compruebe las
conexiones externas de la Batería y el
fusible. Se pone en marcha
automáticamente cuando las
condiciones son buenas.
Utilice un cargador auxiliar que haga
aumentar la tensión de la batería hasta
un mínimo de 9V de CC.
Se pone en marcha automáticamente
cuando las condiciones son buenas.
Vuelva a poner en marcha la batería
colocando el conmutador de control en
OFF y luego en ON.
compruebe todas las fuentes de carga.
Vuelva a poner en marcha la batería
colocando el conmutador de control en
OFF y luego en ON.
Vuelva a poner en marcha la batería
reduciendo la carga y coloque el
conmutador de control en OFF y luego
en ON.
Page 23

Límites de la Garantía
Tripp Lite garantiza sus productos de cualquier defecto de material y la mano de obra durante un periodo de un año (a nivel nacional) o de 120
días (a nivel internacional) a partir de la fecha inicial de la compra. Las obligaciones de Tripp Lite resultantes de esta garantía se limitan a
reparar o cambiar cualquier producto defectuoso. Para que la garantía se aplique a su producto, tiene que recibir por parte de Tripp Lite o de
un servicio oficial Tripp Lite un número de Autorización de Material Devuelto (RMA). Hay que devolver los productos a Tripp Lite o a un servicio
oficial de Tripp Lite con los todos portes pagados y deben ir acompañados de una breve descripción del problema encontrado así como de
la prueba de compra con la fecha y el lugar donde se ha comprado el producto. Esta garantía no cubre los equipos dañados por accidente o
por negligencia en la utilización o que hayan sido alterados o modificados de cualquier manera. Esta garantía sólo cubre el verdadero
comprador que ha registrado su producto dentro del plazo de 10 días a partir de la fecha de compra.
SALVO LA QUE SE INCLUYE AQUÍ, TRIPP LITE NO HACE GARANTÍAS, NI EXPRESAS NI IMPLÍCITAS, QUE SE TRATE DE GARANTÍAS
PARA LA COMERCIALIZACÓN O PARA LA APTITUD A UN USO PERSONAL. Algunos estados no permiten las garantías limitadas o con
exclusiones, por lo que en esta caso las limitaciones y las exclusiones de nuestra garantía no se aplicarán a los compradores.
SALVO LO QUE SE INCLUYE AQUÍ, TRIPP LITE NO ES RESPONSABLE EN NINGÚN CASO DE LOS DAÑOS DIRECTOS,
INDIRECTOS, ESPECIALES, ACCIDENTALES O LOS QUE RESULTAN DE LA UTILIZACIÓN DE ESTE PRODUCTO, INCLUSO
SI SE LE AVISA DE LA POSIBILIDAD DE QUE TALES DAÑOS PUEDAN SUCEDER. En concreto, Tripp Lite no aceptará ninguna
demanda de reembolso de gastos, de pérdidas de beneficios o de recetas, de pérdida de material, pérdida de utilización de material,
pérdida de programas, pérdida de datos, gastos de devolución, reclamaciones de terceras personas, etc.
Características
INVERTER APS INT 512
Ondulador potencia continua a 20°C: 500 voltios
Punta de potencia (en 5 segundos): 1200 voltios
Rendimiento (a plena carga): 90%
Intensidad de la corriente continua a 12V – Plena carga: 52 amperios
– Sin carga: 1 amperio
Tensión nominal de entrada: 12 V CC
Franja de tensión nominal de salida: 10 to 15.5V
Nominal de salida: 230 VAC +/- 5%
Frecuencia nominal de salida: 50/60Hz +/- .3%
Forma de la onda: Sinusoide
CARGADOR DE LA BATERÍA
Capacidad de carga de CC: 18 amperios
Tensión aceptable: por e legir 14,4 /14,2 Bate ría líquida o Gel
Tensión de estabilización: por elegir 14,4/14,2 Batería líquida o Gel
Tensión de entrada: 230 V
Intensidad de la CA de entrada: 5 amperios
LINE VAC OPERATION
Tensión mínima de entrada: por elegir 144, 162, 181 ó 200 V
Tensión máxima de entrada: por elegir 257 ó 276 V
Intensidad máxima de entrada: 11 amperios
Frecuencia de entrada: 50/60Hz +/-10%
Corriente máxima de salida: 5 amperios
Duración de la transferencia automática: 6 milisegundos, duración nominal
Dimensiones (Alto x Ancho x Prof.): 17.4 x 17.4 x 25.4 cm
Peso: 8.2 kg .
Mantenimiento & Reparaciones
Mantenimiento
Los aparatos de la serie APS no necesitan ningún mantenimiento especial pero deben mantenerse en
un lugar seco cualquiera que sea el tiempo. Se tendrá que comprobar a intervalos regulares la conexión
de los cables, tanto a nivel del aparato como a nivel de la batería. Limpier i volver a apretar si necesario.
Reparaciones
Para enviar el APS a la sociedad Tripp Lite, empaquete con cuidado la unidad en su CARTÓN DE
EMBALAJE ORIGINAL. Adjunte una carta explicando con detalle los síntomas del problema
encontrado. Si la unidad de suministro eléctrico está cubierta por la garantía en ese momento,
adjunte una copia de la prueba de compra (ticket de caja).
23
Page 24

Introduction
Toutes nos félicitations ! Cet onduleur/chargeur de batteries intégré est le plus avancé et possède
le plus grand nombre de fonctions du marché. Il fournit le courant du secteur au matériel qui lui est
relié, tant que ce courant est disponible. En cas de panne, de surtension ou de réduction d’intensité,
à travers une commutation automatique sur une source de courant par batteries externes il assure
aux appareils reliés un courant alternatif à tension et fréquence régulées.
Témoins multifonctions
Deux jeux de témoins signalent en permanence le niveau de charge de la batterie, les états de panne
et de fonctionnement de l’appareil. L’un de ces jeux affiche l’état de charge des batteries et les
avertissements de panne ; l’autre affiche l’état de fonctionnement de l’appareil.
Sélecteurs à plusieurs fonctionnements
Les options de fonctionnement du système APS sont regroupées en deux points de commande. Elles
permettent de régler un grand choix de tensions pour lesquelles l’onduleur se mettra automatiquement
en marche, de façon à maximaliser la protection du matériel et à minimiser la ponction sur les
batteries. Autres options : réglage par commande à distance, ce qui augmente la commodité ;
réglage du type de batterie, pour maximaliser l’efficacité de chargement.
Sortie à régulation de fréquence (mode onduleur)
La régulation de fréquence de l’alimentation assure un fonctionnement correct des appareils
sensibles à la fréquence.
Protection automatique contre les surtensions
En cas de surtension, l’appareil se protège automatiquement et protège aussi les batteries.
24
Page 25

ème
2
étape
Absorption
étape Essentiel
de la charge
ère
1
TENSION DE LA BATTERIE
COURBE DE CHARGE EN
FONCTION DU TEMPS
RENDEMENT (en %)
ème
3
étape
Stabilisation
Chargeur de batterie avancé à
trois étapes de chargement
L’appareil APS recharge plus
rapidement les batteries que les
chargeurs classiques. En effet, sa
courbe de charge à trois étapes
(essentiel de la charge, absorption et
stabilisation) est optimalisée quel que
soit le type de batterie utilisé (batterie
hydroélectrique ou batterie à gel)*. De
plus, avec le système de charge avancé,
les batteries sont protégées contre les
excès de charge et de décharge, et ont
une plus longue durée de vie.
*Les niveaux d’absorption et de stabilisation diffèrent suivant le
type de batterie, qui peut être réglé par l’utilisateur, soit sur la
position Wet (Batterie hydroélectrique), soit sur la position Gel
(Batterie à gel).
Production à haut rendement
Les circuits avancés de l’appareil
produisent une ondulation plus efficace
du courant, ce qui minimise la perte
d’énergie et permet un plus long
fonctionnement entre les recharges.
Même lorsque la charge des batteries
diminue, l’appareil APS maintient une
sortie hautement efficace.
PUISSANCE EN WATTS
Ce manuel contient des instructions et avertissements à respecter scrupuleusement pour la
manutention, l’installation, l’utilisation et l’entreposage de nos appareils APS.
25
Page 26

Installation de l’APS
Réglage des sélecteurs de configuration*
(Voir schéma 1, page 46. Nota : 1.1 présente la configuration des sélecteurs, 1.2 correspond
à la position avant, 1.3 à la position arrière).
A l’aide d’un petit outil, régler les 4 sélecteurs (à la partie inférieure de l’appareil APS) : sélectionner
le type de batterie, régler le domaine de tension hors duquel l’appareil passe automatiquement en
alimentation sur batterie.
* Effectuer cette sélection avant le montage définitif de l’appareil.
• Comment sélectionner le type de batterie
(Sélecteur n°1)
ATTENTION : Le réglage du sélecteur de batterie doit correspondre au type de batterie installé, sinon les batteries pourraient être endommagées
ou de se détériorer à la longue. Pour plus de renseignements, on se reportera au paragraphe Sélection du type de batterie, page 28.
Type de batterie Position du sélecteur
Batterie À gel (hermétique) .......................... Avant
Batterie hydroélectrique (ouverte) ............... Arrière**
• Sélectionner le point de passage en alimentation
Arrière
Avant
sur batterie quand la tension alternative est élevée
(Sélecteur n°2)
Tension Position du sélecteur
276 V ............................................................ Avant
257 V ............................................................ Arrière**
Arrière
Avant
• Sélectionner le point de passage en alimentation sur batterie
quand la tension alternative est faible
(Sélecteurs n° 3 et 4)
Arrière
Arrière
Arrière
Arrière
Batterie
hydroélectrique
Batterie
à gel
257V
276V
Avant
200V
n°4 Avant
n°3 Avant
** Réglages effectués en usine.
Avant
181V
n°4 Avant
n°3 Arrière
Avant
162V
n°4 Arrière
n°3 Avant
Avant
144V
n°4 Arrière
n°3 Arrière
Passage de la fréquence de 50 Hz à la fréquence de 60 Hz
Ce réglage est réservé au personnel qualifié*
(Voir schéma 2 page 46. Nota : 2.1. correspond à la Résistance de réglage qui se trouve dans
l’angle supérieur droit du circuit imprimé, côté composant).
Pour régler de façon permanente l’appareil APS INT 512 sur la fréquence de 60 Hz, le personnel
qualifié devra ouvrir le boîtier*, repérer la résistance sur le circuit imprimé et retirer celle-ci.
* Avant la conversion à la fréquence de 60 Hz, arrêter et débrancher l’appareil.
Raccordement au secteur
Ne brancher l’appareil que sur des prises secteur en 230 V et 50 ou 60 Hz.
26
Page 27

Installation de l’appareil (optionnelle)
Installation définitive*
(voir schéma 3, p 46).
• Installer quatre attaches de 5 mm (n°8) sur une surface rigide
indiquées sur le schéma. (Laisser dépasser légèrement la tête des attaches pour qu’elle puisse entrer
dans les trous prévus à la partie inférieure des pattes de l’APS).
• Positionner les quatre trous des pattes de l’appareil sur les quatre attaches et stabiliser l’appareil
en le faisant glisser soit vers l’avant soit vers l’arrière. Bloquer en position à l’aide du support en L.
* Recommandé pour l’installation dans un véhicule ou dans un emplacement exigeant des attaches permanentes et sûres.
Attaches et supports à fournir par l’utilisateur. Avant tout montage l’appareil doit être mis à l’arrêt et débranché.
Installation de la protection contre les éclaboussures*
(voir schéma 4, p 46).
Installer quatre vis métalliques de 4 mm (n°8) dans les quatre trous pratiqués dans une plaque rigide
horizontale
préalable quatre entretoises creuses de 25 mm de long dans les quatre trous du panneau supérieur
de l’appareil.
* Recommandé en cas d’utilisation dans des lieux humides. Vis métalliques, protection contre les éclaboussures et entretoises creuses
à fournir par l’utilisateur. Avant tout montage l’appareil doit être mis à l’arrêt et débranché.
de 175 mm x 225 mm qui servira de protection contre les éclaboussures. Installer au
INSTALLATION DE L’APS
AVERTISSEMENTS DE SECURITE
• Installer l’appareil à l’intérieur, à l’abri de l’humidité, de la chaleur, de la poussière ou
de l’ensoleillement direct.
• Prévoir suffisamment d’espace sur tous les côtés pour une ventilation adéquate. Plus
la charge du matériel connecté sera forte, plus le dégagement de chaleur sera
important.
• Ne pas retirer ou modifier la broche de terre de la prise de l’appareil. Ne pas utiliser
d’adaptateur à deux broches.
• Brancher sur une prise secteur à trois fiches avec prise de terre. Ne pas brancher
l’appareil sur lui-même : l’appareil serait endommagé et la garantie automatiquement
annulée.
horizontale,
en utilisant les mesures
27
Page 28

Sélection des batteries
Sélection du type de batterie
Sélectionner une batterie ou un groupe de batteries susceptibles de fournir à l’appareil une alimentation
en courant continu de 12 V, et au matériel relié une capacité adéquate en quantité d’électricité.*
* Bien que nos modèles APS soient des onduleurs hautement efficaces, leur capacité théorique est limité par la capacité en ampèresheures des batteries externe.
Pour une performance optimum de l’appareil, on sélectionnera des batteries “Deep-cycle”, de types
hydroélectrique (ouvertes) ou de type à gel/tampon de verre absorbé (batteries hermétiques). Les batteries
de 6 V de type “chariot de golf”, Marine Deep-cycle ou 8D Deep–Cycle sont également acceptables.**
** Le sélecteur n°1 (type de batterie) doit être réglé de façon à correspondre au type de batterie raccordé, sinon les batteries risquent
d’être endommagées ou de se détériorer à la longue. Pour plus de renseignements on se reportera au paragraphe Installation de l’APS.
Sélection de la capacité en ampères-heures des batteries
Etape 1 :
Pour déterminer la capacité totale requise on calculera la somme des puissances nominales du
matériel raccordé.*
* La capacité nominale est habituellement indiquée sur la notice de l’appareil ou sur sa plaque d’identification. Pour
convertir en watts une indication en ampères-heures, on doit multiplier la capacité en ampères-heures par la tension
nominale du secteur (230V).
Etape 2 :
Pour déterminer l’intensité de courant continu requise, on divisera par 12 la puissance totale requise
(calculée à l’étape 1).
Etape 3 :
Pour évaluer la capacité d’une batterie en ampères-heures, on multipliera l’intensité de courant
continue requise (calculée à l’étape 2) par le nombre d’heures écoulées entre deux recharges de la
batterie.
Etape 4 :
La capacité nominale en ampères-heures d’une batterie est habituellement donnée pour une durée
de 20 heures jusqu’à la décharge. Lorsque la décharge est plus rapide, la capacité réelle est
inférieure. Pour compenser cette différence, on multipliera par 1,2 l’évaluation approximative de la
capacité en ampères-heures (calculée à l’étape 3) ; on obtiendra ainsi la capacité optimale en
ampères-heures à raccorder à l’APS.**
** Le produit des ampères de charge par le nombre d’heures de charge doit être supérieur à la quantité d’ampères-heures
de décharge tirées sur la batterie entre deux charges. Sinon il y aura décharge à plat du groupe de batteries.
Raccordement des batteries
AVERTISSEMENT DE SECURITE
• Pour pouvoir fonctionner, les modèles APS doivent être reliés aux batteries.
• Si l’on utilise plusieurs groupes de batteries, celles-ci doivent avoir la même tension, le
même âge, la même capacité en ampères-heures et le même type.
• L’emplacement des batteries doit être bien ventilé. Sinon de l’hydrogène gazeux explosif
risque de s’accumuler au voisinage des batteries. Il peut alors y avoir production d’étincelles
lors du raccordement final des batteries.
• Ne pas laisser des corps étrangers entrer en contact avec les deux bornes d’entrée de
courant continu. Ne pas les mettre en court-circuit ni de réaliser un pont électrique entre
elles. Il y a risque d’électrocution avec blessures graves ou dommages matériels graves.
28
Page 29

Raccordement à la batterie (normal)
Raccordement à une seule batterie de 12 V
(Voir schéma 5, p 46, Nota : 5.1 indique le fusible)
Raccordement à un groupe de plusieurs
batteries de 12 V (en parallèle)
(Voir schéma 6, p 47, Nota : 6.1 indique le fusible)
Raccordement à un groupe de plusieurs batteries de 6 V (en série)
(Voir schéma 7, p 47, Nota : 7.1 indique le fusible. Ce système de raccordement combiné
fournit un courant continu de 12 V).
• Raccorder directement la borne positive de l’APS à un fusible
placé au voisinage de la batterie.
UL recommande que l’on installe, à moins de 50 cm de la batterie, un fusible et bloc fusible composant
reconnu par UL. Ce fusible devra avoir une capacité d’au moins 100 ampères (voir schémas de
raccordement des figures 5, 6 et 7).
• Utiliser le câblage de batterie LE PLUS COURT ET DE PLUS
GROS CALIBRE.
Pour les câbles courant continu de moins de 3 m on utilisera du câble n°4. Pour les câbles 3 à 5 mètres
on utilisera du câble n°2. Lorsque le câble est court et de gros calibre, la chute de tension est limitée,
ce qui permet un transfert maximum du courant.*
*Les modèles APS sont capables de fournir une puissance beaucoup plus élevées pendant de brefs laps de temps. Le câblage devra donc
avoir une configuration permettant de traiter ces ponctions de courant de courte durée. Même si nos modèles APS sont des onduleurs
hautement efficaces, leur capacité nominale est limitée par la longueur et le calibre des conducteurs entre la batterie et l’APS.
Raccordement à une batterie (de véhicule)
Pour faire fonctionner des outils manuels légers ou autres petits appareils pendant un bref laps de
temps, on utilisera le raccordement de base (schéma 8, page 47. Nota : 8.1 désigne l’alternateur ;
8.2 la masse de la batterie du véhicule ; 8.3 une batterie de véhicule de 12 V ; 8.4 désigne
le fusible). Pour alimenter de fortes charges pendant des laps de temps prolongés, on choisira
le raccordement avancé (schéma 9, page 47. Nota : 9.1 désigne l’alternateur ; 9.2 un isolateur
de batterie ; 9.3 la masse de la batterie du véhicule ; 9.4 une batterie de véhicule de 12 V ;
9.5 désigne le fusible). Ce raccordement prévoit un isolateur de batterie et une batterie distincte
pour apporter du courant au système APS, tout en l’empêchant de tirer sur la batterie du véhicule.
Nota : Suivant l’application, il pourra être nécessaire d’utiliser plus d’une batterie Deep Cycle de 12
volts.
Attention : ne jamais faire fonctionner l’APS sur un alternateur sans le raccorder à une batterie (schémas 8 et 9, page 47).
29
Page 30

Raccordement des appareils
Pour éviter les surcharges, les besoins en puissance du matériel
doivent correspondre à la capacité d’alimentation de l’APS.
Pour calculer les besoins en puissance d’un appareil, on ne confondra pas puissance nominale
“continue” et puissance nominale “maximum”. Les moteurs électriques consomment plus de
puissance au démarrage que pendant leur fonctionnement continu. Leur puissance nominale
“maximum” est ainsi de 2 à 5 fois plus élevée que la puissance nominale “continue”. La plupart des
moteurs électriques ont seulement besoin de la puissance maximum au démarrage. Toutefois, les
moteurs électriques des réfrigérateurs et des pompes de puisard se mettent en marche ou s’arrêtent
en fonction de la demande. Ils ont besoin de la puissance maximale à des moments imprévisibles.*
*Lorsque l’APS a lancé un moteur électrique, il dispose, pendant que le moteur tourne, d’une réserve de puissance qui peut être consacrée
à d’autres appareils. On pourra augmenter à discrétion la charge de l’APS. Nota : si les batteries sont presque déchargées, ou si le moteur
a un mauvais rendement ou est usé ou trop âgé, les fusibles de batterie peuvent sauter.
Raccorder le matériel aux prises de l’APS.*
• ordinateurs • appareils ménagers • lecteurs de CD
• fours à micro-ondes • réfrigérateurs • magnétoscopes
• lampes • outils électriques • magnétophones
• pompes de puisard • moteurs électriques • etc.
• tourne-disques (moins de 0,16 CV)
* Tous les modèles APS sont dotés d’une sortie onduleur à régulation de fréquence qui permet un fonctionnement correct
des appareils sensibles à la fréquence du secteur : ordinateurs, magnétoscopes, lecteurs de CD, magnétophones, horloges
et tourne-disques.
Régler le sélecteur de Mode de fonctionnement
• Pour utiliser le matériel raccordé, mettre ce sélecteur sur la position Auto. AVANTAGE : l’APS
apporte une alimentation de secours en cas de pannes ou de réduction d’intensité.
• Lorsque le matériel raccordé n’est pas utilisé, on mettra ce sélecteur sur la position CHARGE
ONLY/REMOTE (Charge seule/commande à distance). (ATTENTION : les alimentations de
courant non interruptibles ne fournissent pas d’alimentation de secours). AVANTAGES : A) la
charge des batteries se poursuit tant qu’il y a du courant. B) l’onduleur de l’APS est coupé, ce qui
évite de tirer sur la batterie en cas de panne ou réduction d’intensité.
Nota : lorsque le contacteur est sur la position CHARGE ONLY/REMOTE, un interrupteur
à deux positions (fourni par l’utilisateur) permettra de passer du mode CHARGE SEULE
au mode AUTO. (Voir page 32 la description de l’interrupteur de commande à distance).
• Pour arrêter l’APS et les appareils reliés, ou pour réarmer l’APS lorsqu’il s’est arrêté à cause d’une
surcharge ou d’une surchauffe, on mettra le contacteur sur la position d’arrêt (OFF).
Raccordement des appareils
AVERTISSEMENTS DE SECURITE
• Nous ne recommandons pas d’utiliser une de nos sources de courant de secours à
commutation automatique de la série APS pour des applications de réanimation dans lesquelles
un mauvais fonctionnement ou une panne de l’unité pourrait provoquer une panne du dispositif
de réanimation ou modifier de façon sensible son comportement. Pour plus de renseignements
à cet égard, on nous contactera.
• Ne pas brancher de suppresseur de surtensions, de conditionneur de ligne ou d’unité
d’alimentation non interruptible sur les prises de sortie de courant alternatif de l’APS.
• Ne pas raccorder l’APS à lui-même ; il serait endommagé et la garantie serait automatiquement
invalidée.
30
Page 31

Contacteurs, témoins,
autres fonctions
(Voir schéma 10, p. 48, pour l’emplacement des contacteurs, témoins et autres fonctions. 10.1
correspond à l’adaptateur universel UniPlug [inclus sur les modèles APS INT 512] qui accepte
la plupart des prises ; 10.2 correspond à la prise et au cordon. Nota : 10.21 = masse ; 10.22 =
neutre ; 10.23 = phase ; 10.24 = cordon amovible ; 10.3 correspond aux sélecteurs de
configuration situés à la partie inférieure de l’unité.)
Sélecteurs
1. Sélecteur de mode de fonctionnement
Ce sélecteur sélectionne le mode de fonctionnement de l’APS (CHARGE SEULE/COMMANDE A
DISTANCE ou AUTO ou ARRET). Pour le réglage optimum de ce sélecteur, on se reportera au
paragraphe Raccordement des appareils
2. Sélecteurs de CONFIGURATION
Ces sélecteurs doivent être réglés en fonction du type de batterie auquel sera raccordé l’APS et en
fonction du domaine de tension hors duquel l’APS passera automatiquement à l’alimentation sur
batterie. Le réglage du sélecteur n°1, Type de Batterie, doit correspondre au type de batterie relié
à l ’appareil, sinon les batteries pourraient être endommagées ou se détériorer à la longue. La plupart
des appareils fonctionnent correctement si le sélecteur n°2 du point de tension haute est réglé sur
257 V et si les sélecteurs n° 3 et 4 de point de tension basse sont réglés sur 181 V. Pour réduire un
fonctionnement trop fréquent sur les batteries, provoqué par des pointes de tension hautes ou
basses, qui ont peu d’effet sur le fonctionnement des appareils raccordés, l’APS devra être réglé audessus et au-dessous de ces deux points, respectivement (voir le paragraphe Installation de l’APS
et le schéma de la page 46).
Témoins
3. Témoin “Secteur” (LINE)
Ce témoin vert reste allumé lorsque le matériel relié est alimenté sur le secteur. Il clignote lorsque
l’alimentation du secteur est présente – alors que le sélecteur de mode de fonctionnement est réglé
sur “Charge seule/commande à distance” - pour signaler que l’onduleur de l’APS est à l’arrêt et que
l’APS ne fournira pas d’alimentation de secours lors des pannes de secteur, réductions d’intensité
ou surtensions.
4. Témoin de fonctionnement en onduleur (INV)
Ce témoin rouge reste allumé lorsque les appareils reliés sont alimentés à partir des batteries (au
cours d’une panne de secteur, d’une réduction d’intensité ou d’une surtension survenant alors que
l’appareil est raccordé au secteur, ou lorsque l’appareil est relié aux batteries lors d’un fonctionnement
sur véhicule).
5. Témoin de charge (LOAD)
Ce témoin rouge reste allumé lorsque la charge de l’APS est comprise entre 80 % et 110 % de la
capacité. Il clignote lorsque l’onduleur de l’APS s’arrête par suite d’une surcharge ou d’une
surchauffe importante. Dans ce cas-là, on doit mettre le contacteur de mode de fonctionnement sur
la position d’arrêt (OFF). Supprimer la surcharge. Laisser refroidir l’appareil avant de le remettre en
marche.
31
Page 32

6. Témoins de charge élevée (HI), moyenne (MED) et faible (LO) des batteries
Ces trois témoins s’allument suivant certaines séquences pour afficher le niveau de charge et la
tension approximatifs des batteries connectées, et alerter l’utilisateur à différentes situations de
défaillance :
INDICATION (approximative) DE CHARGE DES BATTERIES
Témoin Capacité Tension
Vert entre 91 et maximale 12 à 16 V
Vert et jaune entre 81 et 90 % 11,8 à 12 V
Jaune entre 61 et 80 % 11,6 à 11,8 V
Jaune et rouge entre 41 et 60 % 11,3 à 11,6 V
Rouge entre 21 et 40 % 11 à 11,3 V
_ entre 1 et 20 % 10 à 11 V
Rouge clignotant 0 % (coupure de l’onduleur) <10 V
Clignotement lent * Décharge excessive < 8 V
de tous les témoins
Clignotement rapide ** Surcharge > 16 V
de tous les témoins
* période de clignotement : environ 1 s. Voir Recherche des pannes
** Période de clignotement : environ ½ s. Ce clignotement peut aussi indiquer qu’il existe un défaut de charge des batteries. Voir
Recherche des pannes
Autres fonctions
7. Bornes d’entrée courant continu
Les écrous à oreilles de bornes fixent les conducteurs provenant de la batterie extérieure.
Raccorder une batterie ou un groupe de batteries fournissant à l’APS un courant continu de 12 V
et aux appareils reliés une capacité adéquate en ampères-heures. Pour un raccordement optimum,
on utilisera des pattes soudées sur le câble de batterie. Pour plus de renseignements, voir Sélection
des batteries.
8. Prises de courant alternatif (NEMA 5-15R)
Ces prises permettent de raccorder des appareils prévus pour fonctionner sur du courant alternatif
de 230 V à 50/60 Hz. Certains modèles APS INT 512 exigent des adaptateurs (un adaptateur
universel est inclus. Voir Schéma 10.1, p. 48) pour le raccordement des appareils.
9. Cordon secteur (NEMA 5-15P fixe ou amovible)
Brancher le cordon sur une prise secteur de 230 V 50/60 Hz. NE PAS brancher le cordon sur les
prises de l’APS. Sur son cordon mâle NEMA 15-5P, l’APS est doté d ’une prise mâle IEC-320 et d’une
prise femelle IEC-320 amovible. Noter la polarité de la prise sur le schéma 10.2, p. 48.
10. Coupe-circuit à réarmement
Le coupe-circuit protège l’APS contre tout dégât par suite d’une surcharge. Supprimer la cause de
surcharge. Attendre une minute. Réarmer le coupe-circuit.
11. Commande de marche/arrêt à distance
Ce dispositif permet de commander l’APS à l ’aide d’un câble fourni par l’utilisateur et d’un interrupteur
à deux positions. Le connecteur accepte une prise téléphone miniature à deux conducteurs de 3,5
mm. Nota : l’interrupteur à distance fourni par l’utilisateur permettra seulement de commander le
fonctionnement de l’APS lorsque le sélecteur de fonctionnement est sur la position CHARGE SEULE
ou sur la position AUTO. Après raccordement du dispositif de commande à distance, on déterminera
quelle position de l’interrupteur correspond au mode CHARGE SEULE et quelle position correspond
au mode AUTO. La position qui déclenche le clignotement du témoin secteur (LINE) vert correspond
au mode CHARGE SEULE.
32
Page 33

Recherche des pannes
Avant d’envoyer l’appareil en réparation, ont devra effectuer les contrôles ci-dessous. Avant d’expédier l’appareil,
on appellera notre service clients.
SYMPTOME PROBLEME REMEDES
Aucun courant alternatif sur les L’APS n’est pas correctement Raccorder l’APS à la prise murale.
prises de l’APS (mais il y a du raccordé à la prise murale.
courant au niveau du secteur)
Aucun courant alternatif sur les Le coupe-circuit a fonctionné.Réarmer le coupe-circuit.
prises de l’APS (il n’y a pas de
courant au niveau du secteur)
L’APS ne charge pas la batterie Les batteries reliées sont mortes. Vérifier l’état des batteries et remplacer.
(mais il y a du courant au niveau
du secteur)
Les témoins de l’APS sont Etat normal si le sélecteur est sur la —
éteints (il n’y a pas d’arrivée de position CHARGE SEULE.
courant secteur).
Les témoins de l’APS sont Excès de décharge de la batterie. Utiliser un chargeur auxiliaire pour
éteints (il y ou il n’y a pas porter le potentiel de la batterie à au
d’arrivée de courant secteur). moins 9 V. Vérifier les raccordements
Tous les témoins de l’APS Excès de décharge de la batterie. Utiliser un chargeur auxiliaire pour
clignotent lentement. porter le potentiel de la batterie à au
Le témoin de charge faible (LO) Arrêt de l’onduleur parce que le Réarmer en faisant passer potentiel de
de la batterie clignote. la batterie a été inférieur à 10 V l’interrupteur de commande de charge
Tous les témoins de l’APS Arrêt de la batterie en cours de Vérifier toutes les sources de charge.
clignotent rapidement. charge pour surtension. Réarmer en faisant passer
Le témoin CHARGE (LOAD) de Surcharge de l’onduleur par suite de Réarmer en réduisant la charge et en
la batterie clignote rapidement. charge excessive ou de court-circuit. faisant passer l’interrupteur de
* Fourni par l’utilisateur
Le coupe-circuit a fonctionné.Réarmer le coupe-circuit.
Coupure de l’APS par suite de Arrêter l’APS. Attendre une minute et
surtension de la batterie (> 16 V). mettre sur la position AUTO.
Il y a peut-être défaillance du
chargeur. Le secteur a été
déconnecté pour interdire des
dégâts irréparables de la batterie.
L’APS est sur la position d’arrêt (OFF) Mettre sur la position AUTO ou
CHARGE SEULE
Le sélecteur de mode de Mettre le sélecteur sur la position AUTO.
fonctionnement est sur la position
Charge Seule.
Défaillance par excès de charge ou Arrêter l’APS. Attendre une minute.
de température. Supprimer la surcharge. Mettre sur la
Excès de décharge de la batterie. Vérifier l’état de la batterie.
Le fusible* de batterie est mort. Vérifier l’état du fusible et remplacer.
Les câbles* de batterie sont mal Vérifier l’état des câbles. Le cas
connectés ou détériorés. échéant, resserrer les raccordements
Défaillance du chargeur de batterie. Arrêter l’APS. Attendre une minute et
pendant plus de 5 secondes. de la position d’arrêt à la position de
Protection de la batterie contre des marche.
dégâts irréparables.
Si cet état dure plus de 5 secondes commande de charge sur la position
l’onduleur est coupé. de marche.
position AUTO.
ou remplacer le câblage.
mettre sur la position AUTO. S’il y a
arrêt automatique, entrer en contact
avec notre service clients.
externes de la batterie et le fusible.
Réarmement automatique lorsque
l’état fautif a disparu.
moins 9 V. Réarmement automatique
lorsque l’état fautif a disparu.
l’interrupteur de commande de charge
de la position d‘arrêt à la position de
marche.
33
Page 34

Garantie limitée
La société Tripp Lite garantit pendant un an (pour les Etats-Unis) et pendant 120 jours (à l’exportation) que ses produits seront dépourvus
de défauts de matériaux et d’exécution. Les obligations assumées par la présente garantie se limitent à la réparation ou au remplacement
des produits défectueux (au choix exclusif de la société Tripp Lite). Pour obtenir des réparations couvertes par la présente garantie, on
devra nous demander un numéro d’autorisation de retour de matériel (RMA) ou l’adresse d’un centre de réparation autorisé. Les produits
devront être renvoyés en port payé, soit à la société Tripp Lite soit au centre autorisé, et devront être accompagnés d’une brève description
du problème rencontré, ainsi qu’une preuve de la date et du lieu d’achat. Cette garantie ne s’applique pas au matériel qui a été
endommagé par accident, négligence ou utilisation erronée ou qui aura été altéré ou modifié d’une façon quelconque. Elle s’applique
seulement à l’acheteur d’origine qui devra avoir enregistré officiellement son produit moins de dix jours après la date d’achat.
SAUF STIPULATION DES PRESENTES, LA SOCIETE TRIPP LITE N’OFFRE AUCUNE GARANTIE EXPRESSE OU IMPLICITE,
Y COMPRIS LES GARANTIES DE VENDABILITE ET D’APTITUDE A UN BUT PARTICULIER. Certains états n’autorisant pas la
limitation ou l’exclusion des garanties limitées, les limitations ou exclusions ci-dessus ne s’appliqueront pas dans ces états.
SAUF DISPOSITION DES PRESENTES, EN AUCUN CAS LA SOCIETE TRIPP LITE NE SERA RESPONSABLE DES DOMMAGES
DIRECTS OU INDIRECTS, SPECIAUX OU FORTUITS DECOULANT DE L’UTILISATION DE CE PRODUIT, MEME SI ELLE A ETE
AVERTIE DE L’EVENTUALITE DE TELLES DEMANDES DE DOMMAGES. Plus spécifiquement, la société Tripp Lite n’acceptera
pas les demandes de remboursement de coûts, de pertes de profits ou de recettes, de perte de matériel, perte d’utilisation de matériel,
perte de logiciel, perte de données, coûts de remplacement, les réclamations par des tiers, etc.
Caractéristiques
ONDULEUR APS INT 512
Puissance continue à 20 °C: 500 watts
Pointe de puissance (en 5 secondes): 1 200 watts
Rendement (à pleine charge): 90 %
Intensité de courant continu à 12 V – pleine charge : 52 ampères
– sans charge : 1 ampère
Tension nominale à l ’entrée : 12 V courant continu
Plage de tension à l ’entrée : 10 à 15,5 V
Tension nominale à la sortie : 230 V +/- 5 %
Fréquence nominale à la sortie : 50/60 Hz +/- 5 %
Forme d’onde : sinusoïde
CHARGEUR DE BATTERIE
Capacité de charge en courant continu : 18 ampères
Tension d’acceptation : sélectionnable 14,4/14,2 batterie hydroélectrique ou à gel
Tension de stabilisation : sélectionnable 13,3/13,6 batterie hydroélectrique ou à gel
Tension à l ’entrée : 230 V
Intensité de courant alternatif à l’entrée : 5 ampères
FONCTIONNEMENT SUR SECTEUR
Tension minimum à l ’entrée : sélectionnable : 144, 162, 181 ou 200 V
Tension maximum à l ’entréesélectionnable : 257 ou 276 V
Intensité maximum à l ’entrée : 11 ampères
Fréquence à l ’entrée : 50/60 HZ +/- 10 %
Courant maximum de sortie : 5 ampères
Durée de transfert automatique : 6 millisecondes, durée nominale
Dimensions (H x L x P): 17,4 x 17,4 x 25,4 cm
Poids : 8,2 kg
Entretien et réparations
Entretien
Les appareils de la série APS n’ont pas besoin d’entretien mais doivent être maintenus au sec en tout
temps. On devra vérifier à intervalles réguliers les raccordements de câbles, tant au niveau de
l’appareil qu’à celui de la batterie. Nettoyer et resserrer si nécessaire.
Réparations
Pour renvoyer l’APS à la société Tripp Lite, emballer soigneusement l’unité dans son EMBALLAGE
D’ORIGINE. Joindre une lettre décrivant les symptômes du problème rencontré. Si l’unité d ’alimentation
non interruptible est couverte par la période de garantie, joindre une copie du bon d’achat.
34
Page 35

!"#$#%&#
!"#$%&'()*+,-&./,-0,1%2"3%*(2,1*%*$"'*4524,2#,2+*6728.),9&,%09:*;,.&+04,3"<&=04
'"#+">9".=)+2,#&%)$904,'01%)+2=*(?,.,'.=%"*990+,29'*%="%"+@,-&5,ABC,"3*.1*D2=,-&52
E(*:=%"1%23"%0,1*%*+*990+,=":"+,"37*<",1"(?#"'&92),',1*%2"$0,*<",9"%+&(?9"4,1"$&D2@,1*%2"$0,'.*"37*<";,D&.=2D9"<",9&%F5*92),E(*:=%".9&3>*92),2(2,1*%*9&1%)>*92),-&5,ABC
3F$*=,&'="+&=2D*.:2,1*%*:(6D&=?.),9&,12=&92*,"=,'9*59*<",&::F+F()="%&,2,"3*.1*D2=,-&52
E(*:=%"1%23"%0,E(*:=%"E9*%<2*4,1*%*+*99"<",=":&,:"9=%"(2%F*+"<",9&1%)>*92),2,D&.="=0@
'%()(*+%,-&(%./0%1#23"#4("1#2&%$&,.4(51
G'&,9&3"%&,.'*="'08,29$2:&="%"',$*%>&=,-&.,1".=")99",',:F%.*,"3,F%"'9*,#&%)$:2
&::F+F()="%&;,F.("'2)8,&9"+&(24,2,%&3"=*,ABC@,H$29,9&3"%,+9"<"IF9:J2"9&(?908,.'*="'08
29$2:&="%"',29I"%+2%F*=,",.".=")922,#&%)$:2,&::F+F()="%&,2,"1"'*7&*=,"3,&9"+&(2)8@,-="%"4
9&3"%,+9"<"IF9:J2"9&(?908,.'*="'08,29$2:&="%"',29I"%+2%F*=,",%&3"=*,ABC@
'%()((6#5.4&"%1#26#5#,/78.4#/&
G'&,1F9:=&,F1%&'(*92),1%*$".=&'()6=,-&+,"1=2+&(?90*,'"#+">9".=2,,E:.1(F&=&J22,.'"*<",ABC@
-0,.+">*=*,#&$&=?,$2&1&#"9,9&1%)>*92);,',:"="%"+,3F$*=,%&3"=&=?,29'*%="%,-&5*<",ABC;,2;
=&:2+,"3%&#"+;,F'*(2D2=?,#&72=F,"3"%F$"'&92),2,.'*.=2,:,+292+F+F,K=)>:FL,2#,&::F+F()="%&@
M%"+*,="<";,-0,.+">*=*,$(),3"(?5*<",F$"3.='&,2.1"(?#"'&=?,$2.=&9J2"99"*,F1%&'(*92*;,&,$()
3"(?5*4,"1=2+2#&J22,#&%)$&,N,#&$&=?,=21,&::F+F()="%&@
!1"($232,(%45(/&5+#9(:28.34(4(:2;"2&%"#54(5%(925#<&9#=
-&5,ABC,F1%&'()*=,D&.="="4,9&,(2922;,=&:2+,"3%&#"+,-&52,E(*:=%"1%23"%0,+"<F=,%&3"=&=?
3*.1*%*3"49"@
>"4(9.4&8#3,.?2@.A&4.2(426#5#%.65?<#%&?
O.(2,-0,1*%*<%F#2=*,.'"4,ABC;,"9,&'="+&=2D*.:2,#&72=2=,.*3);,&,=&:>*,-&52,$%&<"J*990*
&::F+F()="%0,"=,1"'%*>$*92)@
35
Page 36

JE:2F4.6
B()/(A#%&#
HE:2F4.6
I.)5+@,.
%.65?<#%.,,+9+/?4(5.
65(*&/02@.)5+@,&
KLLMNOP!QRSOTC2U
"5#9?
DE:2F4.6
B($@.5?$
B5()5#33&"%1:C2DEF4.6%1:
@.5?$%1:265&G(5
-&5,ABC,#&%)>&*=,&::F+F()="%,30.=%**;
D*+,"30D9"*,#&%)$9"*,F.=%"4.='";
3(&<"$&%),="+F;,D=",*<",=%*8E=&1904
1%"I2(?,#&<%F#:2,QH.9"'9&),R&<%F#:&;
!"<("7*92*,2,!"$#&%)$S,1%2.1"."3(*9
:,9&2(FD5*4,"=$&D*;,9*#&'2.2+","=,=21&
2.1"(?#F*+"<",&::F+F()="%&,Q+":%"<"
2(2,<*(2*'"<"ST@,M%"+*,="<";
."'%*+*99",%&#%&3"=&99&),.2.=*+&
#&%)$:2,#&727&*=,"=,1*%*<%F#:2,2
D*%*#+*%9"4,%&#<%F#:2,-&5
&::F+F()="%;,D=",1%"$(*'&*=,*+F,>2#9?
2,.%":,.(F>30@
!"#$%&'()"*%+,%-'(./"."0$%&'()"*%123$/14."&3$).$056"&
23&.7.8%76."%6"&.13"344080,/6%$39":%7,'1(.;"2313'67/
*%,)2%&36','8<",.=%">?%4$@;A"BCDEFG",.=%">H',.'&@;A
BIDJF"K,'8'(69
!13(,.?265(&@"($&4#/0%(340
!*%*$"'"*,=*892D*.:"*,%*5*92*,.8*+0
-&5*<",ABC,"3*.1*D2'&*=,3"(**
EII*:=2'9F6,:"9'*%.26,!%)+"<",P":&
',!*%*+*9904,P":;,1%2,:"="%"+,1"=*%2
E9*%<22,.'"$)=.),:,+292+F+F@,P&:2+
"3%&#"+,-0,+">*=*,%&3"=&=?,.
1"$:(6D*990+2,E(*:=%"1%23"%&+2
$"(?5*,',1*%2"$&8,"=,"$9"4,#&<%F#:2
&::F+F()="%&,:,.(*$F67*4@,P&:&)
'0.":&),EII*:=2'9".=?,"=$&D2,-&5*<"
ABC,3F$*=,."8%&9)=?.),$&>*,="<$&;
:"<$&,#&%)$,&::F+F()="%&,3F$*=
F+*9?5&=?.)@
'RVQRSOT2!2!4
G&99&),29.=%F:J2),."$*%>2=,'&>90*,.'*$*92);,F:&#&92),2,1%*$F1%*>$*92);
:"="%08,.(*$F*=, 1%2$*%>2'&=?.), 1%2, 1*%*9".:*;, +"9=&>*;,%&3"=*, 2, 8%&9*922@
36
Page 37

'(%4.<2WXY
Q.345(:,.2,(%*&)+5.-&(%%1Z29&,5(6#5#,/78.4#/#:2"
,(56+3#232JE5?$%1925.36(/(<#%\"1"($("[
;S9\2SZ#9+2HC2S45\2]^\2Q.2SZ#9#2H\H265#$34."/#%2,5+6%1:26/.%2,(%*&)+5.-&(%%1Z
9&,5(6#5#,/78.4#/#:\2Q.2SZ#9#2H\J2E2!&$236#5#$&C2%.2SZ#9#2H\D2E2!&$23@.$&\=
_,1"+"7?6,+&("<&3&%2=9"<",29.=%F+*9=&,'0.=&'?=*,`,:"9I2<F%&J2"9908,+2:%"1*%*:(6D&=*(),'
:"%1F.*,.,ZN%)$90+,%&.1"(">*92*+,'0'"$"',Q"92,9&8"$2=.),',92>9*4,D&.=2,-&5*<",ABCS@,-0
$"(>90,#&$&=?,'2$,&::F+F()="%&;,$2&1&#"9,9&1%)>*92);,#&,1%*$*(&+2,:"="%"<",-&5,ABC,3F$*=
1*%*:(6D&=?.),9&,&::F+F()="%9F6,E9*%<26@
!"(376$%;6'".L"*$'1&3$.6',)(%"8%(63M0"7&%'+%"NOP9
_2Q./.$,.2"&$.2.,,+9+/?4(5.
Qa2:%"1*%*:(6D&=*(?,Vb,YS
Q(.83(.'R"Q@"1%,M(@"&@763&.6)"8.4$%*'$'4,5S36',)G"%6(%7/-.;7/"4"344080,/6%$38"(3"6%"2(3S'(.'G"4%6%$%'"7%%6&'676&0'6
Q3T'80"344080,/6%$0G"6%80G"4%6%$@;"Q@"*%14,5S.6'"4"NOP9"U(3S'"7%"&$'8'('8"Q3T"344080,/6%$"=01'6"*%&$'M1'(".,.
&@;1'6".2"76$%/9"V3"=%,''"1'63,)(%;".(W%$83X.';"%=$3-3;6'7)"&"+,3&0">Q@=%$"344080,/6%$3A
-2$,&::F+F()="%& !"#2J2)+2:%"1*%*:(6D&=*()
c::F+F()="%,.,^*(2*'0+,E(*+*9="+,Q<*%+*=2D904S @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ -2$,.1*%*$2
c::F+F()="%,.,a":%0+,E(*+*9="+,Q9*<*%+*=2D904S @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ -2$,.#&$2TT
_2!134."/#%"13`#:24(8,&26#5#9#%%()(2%.65?<#%&?2.,,+9+/?4(5.
Qa2:%"1*%*:(6D&=*(?,ZS
9&1%)>*92* !"#2J2),+2:%"1*%*:(6D&=*()
Zd],- @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ -2$,.1*%*$2
ZXd,- @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ -2$, .#&$2TT
_2!134."/#%%&@`#:24(8,&26#5#9#%%()(2%.65?<#%&?2.,,+9+/?4(5.
Qa2:%"1*%*:(6D&=*(2,[,2,`S
!&$23@.$&
!&$23@.$&
!&$23@.$&
!&$23@.$&
!&$236#5#$&
!&$23@.$&
!&$236#5#$&
a":%04
E(*+*9=
^*(2*'04
E(*+*9=
257B
276B
!&$23@.$&
!&$236#5#$&
Jff2!
`,-2$,.1*%*$2,2
[,-2$,.1*%*$2
!!"Y3,31%S(@'"*3$38'6$@"%64323
!&$236#5#$&
HjH2!
`,-2$,.1*%*$2,2
[,-2$,.#&$2
!&$236#5#$&
H^J2!
`,-2$,.#&$2,2
[,-2$,.1*%*$2
!&$236#5#$&
H]]2!
`,-2$,.#&$2,2
[,-2$,.#&$2TT
WXY2abc2dHJe2B#5#Z($232df2%.2^f2g-
O(/0,(2 $/?2 ,"./&*&-&5(".%%()(2 6#53(%./.[
;S9\2SZ#9+2JC2345\2 ]^\2 B5&9#8.%&#e2 J\H2?"/?#43?2h5#@&34(5(926($345(:,&i2 &2 %.Z($&43?2 "
"#5Z%#9265."(92+)/+2%.2/&-#"(:234(5(%#23Z#9%(:26/.41\=
G(),="<";,D="30,1*%*'*.=2,ABC,UVW,XYZ,9&,1".=")99F6,%&3"=F,',]\,^J;,:'&(2I2J2%"'&9904
1*%."9&(,$"(>*9,"=:%0=?,:"%1F.,ABC;,9&4=2,%*#2.="%,9&,.8*+9"4,1(&=*,2,.9)=?,*<"@
!":$'M1'"S'8"%70-'76&,/6)"*'$'&%1"(3"Z["HXG"%64,5S.6'"\&%;"NOP"."&@()6'"'+%"T6'*7',)".2"(376'((%;"$%2'64.9
B($,/78#%,2&34(8%&,+2F/#,45(F%#5)&&
-'*$2=*,5=*1.*(?9F6,'2(:F,+"$*(2,ABC,UVW,XYZ,','08"$0,.,1*%*+*990+,9&1%)>*92*+,Z[\,-,2
+"79".=?6,X\,2(2,]\,^J@
37
Page 38

'(%4.<2WXY2;$(6(/%&4#/0%1#2"(@9(<%(34&=
S4.-&(%.5%1:2'(%4.<[
;S9\2SZ#9+2DC2345\2]^=
_ e.=&9"'2=*, D*=0%*,XN++, QVb, fS,:%*1*>90*, $*=&(2, ', >*.=:F6, !"#$%"&'()*&+,, 1"'*%89".=?, '
.""='*=.='22,.,%&#+*%&+2;,F:&#&990+2,9&,.8*+*@,^"("':2,:%*1*>908,$*=&(*4,$"(>90,.(*<:&
'0.=F1&=?,9&$,1"'*%89".=?6;,D="30,"92,1%"D9",'"5(2,',<9*#$&;,2+*672*.), 9&,1"$"5'&8, 9">*:,ABC@
_ g&.1"(">2=*,<9*#$&,',9">:&8,ABC,9&$,<"("':&+2,:%*1*>908,$*=&(*4,2,1"$'2<&4=*,ABC
'1*%*$N9&#&$;,D="30,F$".="'*%2=?.),',1%"D9".=2, 9&.&$:2@, R&:%*12=*, F<"(:"'0*, .:"30;, :"="%0*
3F$F=,1"$$*%>2'&=?,ABC,',#&$&99"4,1"#2J22,1".=")99"@
!"]'4%8'(10'67/"1,/"(3L%M1'(./"&"3&6%8%=.,'".,."1,/"*$%S.L"&.1%&".7*%,)2%&3(./G"6$'=05-.L"*%76%/((%+%"='2%*37(%+%
*%,%M'(./9"Q7'"4$'*'M(@'"1'63,.G"74%=@"*$.,3+3567/"&"4%8*,'46'9":'$'1"%70-'76&,'(.'8"%64,5S.6'"\&%;"NOP"."&@()6'"'+%
T6'*7',)".2"(376'((%;"$%2'64.9
k34.%(",.2G51@)("&,.[
;S9\2SZ#9+2]C2345\2]^=
-'29=2=*,D*=0%*,`N++,'29=&,2#,(2.="'"<",+*=&((&,D*%*#,D*=0%*,"='*%.=2),',>*.=:"+
!"#$%"&'()*&"-.3%0#<"'2:*,%&#+*%"+,YdX,++,8,ZZX,++;,D*%*#,D*=0%*,1"(08,%&.1"%:2,$(29"4
ZX,++,',D*=0%*,<(F82*,"='*%.=2);,:"="%0*,2+*6=.),','*%89*4,1&9*(2,-&5*<",ABC@
!"^+%"*$.8'('(.'"$'4%8'(10'67/"&%"&,3M(%;"8'76(%76.9"Q7'"&.(6@".2",.76%&%+%"8'63,,3G"=$@2+%&.4"."$37*%$4."*$.,3+3567/"&
4%8*,'46'9":'$'1"%70-'76&,'(.'8"%64,5S.6'"\&%;"NOP"."&@()6'"'+%"T6'*7',)".2"(376'((%;"$%2'64.9
'Mlm2nMIRB>SQRSOP
BlP2'RQO>oM2P2kSO>QR!NM2WXY
_ e.=&9"'2=*,.'"4,ABC,',1"+*7*922;,',+*.=&8;,F$&(*9908,"=,.0%".=2;,'0.":"4,=*+1*%&=F%0;
10(2,2,1%)+08,."(9*D908,(FD*4@
_ H.=&'?=*,$".=&="D9",1%".=%&9.='&,'":%F<,ABC,.",'.*8,.="%"9;,$(),'*9=2()J22@,h*+,3"(?5*
9&<%F#:&,1"$:(6D*99"<",:,9*+F,"3"%F$"'&92);,=*+,3"(?5*,3F$*=,9&<%*'@
_ i*,.92+&4=*;,9*,+*9)4=*,5=0%?,#&#*+(*92),9&,5=*1.*(*,ABC@,i*,9&.&>2'&4=*,$'F5=0%908
&$&1=*%"',9&,5=*1.*(?,ABC@
_ !"$:(6D&4=*,.'"4,ABC,:,=%*8:&3*(?90+,#&#*+(*990+,%"#*=:&+,1*%*+*99"<",=":&@,i*
1"$:(6D&4=*,.'"4,ABC,:,9*+F,>*;,=&:,:&:,E=",'0'*$*=,ABC,2#,.=%"),2,&99F(2%F*=,<&%&9=26@
38
Page 39

!1G(52.,,+9+/?4(5.
!1G(52.,,+9+/?4(5.
c::F+F()="%,2(2,9&3"%,&::F+F()="%"';,:"="%04,3F$*=,.(F>2=?, 2.="D92:"+,E9*%<"12=&92), YZN'"(?=90+
!%)+0+,P":"+,$(),-&5*<",ABC,2,9&1%)>*92), $".=&="D9"4,*+:".=?6, $(),-&528,E(*:=%"1%23"%"'T@
!"Y'78%6$/"(3"6%G"S6%"0763(%&4."NOP"/&,/567/"&@7%4%KWW'46.&(@8."4%(&'$6'$38."K,'46$.S'74%+%"6%43G".L"&@7%4.'
&%28%M(%76."(3"&@L%1'"%+$3(.S.&3567/"38*'$_S37%&%;"'84%76)5"&('T(.L"344080,/6%$%&9
jFD5*,'03%&=?,&::F+F()="%,.,K^(F3":2+,k2:("+L;,:"="%04,1"#'"(2=,-&5*+F,ABC,%&3"=&=?,.
"1=2+&(?9"4,"=$&D*4@,c::F+F()="%,+">*=,30=?,(23",.,+":%0+,E(*+*9="+,Q9*<*%+*=2D90+S;
(23",<*%+*=2D9"4,:"9.=%F:J22;,.,<*(2*'0+,E(*+*9="+@,]N'"(?=90*,E(*:=%":&%"'0*;,.F$"'0*
<(F3":"J2:("'0*,2,fl,N,<(F3":"J2:("'0*,&::F+F()="%0,=&:>*,1%2*+(*+0TT@
!!"Q@"1%,M(@"71',36)"(3,3140"*3$38'6$%&G"%6(%7/-.L7/"4"*%17%'1.(/'8@8"344080,/6%$0`$38G"7"*%89"4%(W.+0$3X.%((@L
8.4$%*'$'4,5S36',';"Babc"_"Q.1"344080,/6%$3F9"Q"*$%6.&(%8"7,0S3'"Q3T."344080,/6%$@"8%+06"*%&$'1.6)7/".,."&@;6.".2
76$%/"S'$'2"('4%6%$%'"&$'8/9"V3"=%,''"1'63,)(%;".(W%$83X.';"%="K6%8"789"+,3&0">?%(63M"NOPA9
l.38#42%#(GZ($&9(:2.96#58.3("(:2#9,(34&2.,,+9+/?4(5.
q.)2He
!"(FD2=*,.F++F, 9"+29&(?908, +"79".=*4, ', -=, '.*8, 1"$:(6D&*+08, E(*:=%"1%23"%"'@, H9&
.""='*=.='F*=,'.*4,9*"38"$2+"4,+"79".=2T@
!"Q@"(3;1'6'"7&'1'(./"%"(%8.(3,)(%;"8%-(%76."*$.=%$3"&"'+%".(76$04X..".,."(3"*37*%$6(%;"63=,.S4'9"^7,."8%-(%76)
04323(3"&"dG"*'$'&'1.6'"K6."13((@'"&"Q6"*06'8"08(%M'(./"(%8.(3,)(@L"38*'$%&"(3"(%8.(3,)(%'"(3*$/M'(.'"&3T';",.(..
:'$'8'((%+%"e%43"Bfg[F9
q.)2Je
g&#$*(2=*,.F++F;,1"(FD*99F6,',5&<*,Y,9&,YZ@,-0,1"(FD*=*,D2.(";,.""='*=.='F67**
9*"38"$2+"+F,:"(2D*.='F,&+1*%"',!%)+"<",P":&@
q.)2De
e+9">?=*,9*"38"$2+"*,:"(2D*.='",&+1*%"',1%)+"<",=":&,QE=",D2.(",1"(FD*9",',5&<*,ZS,9&
:"(2D*.='",D&."',"=,#&%)$:2,:,#&%)$:*,&::F+F()="%&@,P&:,-0,"1%*$*(2=*,1%23(2#2=*(?9"*
:"(2D*.='", &+1*%ND&."'@
q.)2]e
H30D9",9"+29&(?9&), &+1*%ND&."'&), *+:".=?, &::F+F()="%&, F:�'&*=.), 9&, Z\ND&."'"4, %&#%)$@
g*&(?9&),&+1*%ND&."'&),*+:".=?,30'&*=,+*9?5*;,:"<$&,%&#%)$:&,2$*=,30.=%**@,h="30,FD*.=?,E=F
1"<%*59".=?;,F+9">?=*,1%23(2#2=*(?9"*,:"(2D*.='",&+1*%ND&."',Q1"(FD*99"*,',5&<*,[S
&::F+F()="%&,9&,Y;Z@,P&:,-0,"1%*$*(2=*,"1=2+&(?9F6,$(),-&.,&+1*%ND&."'F6,*+:".=?
&::F+F()="%&;,:"="%04, -&+,.(*$F*=,2.1"(?#"'&=?,.", .'"2+, F.=%"4.='"+,ABC@TT
!!" V3$/1(@'" 38*'$@G" 08(%M'((@'" (3" 23$/1(@'" S37@G" 1%,M(@" *$'&@T36)" 38*'$_S37@" $32$/14." 344080,/6%$3" 8'M10
1&08/" 23$/1438.9" Q" *$%6.&(%8" 7,0S3'" Q@" .76%-.6'" $'2'$&" 7&%'+%" 344080,/6%$39
'Mlm2BlMpRSORlRoQRSOP
65&26($,/78#%&&2.,,+9+/?4(5.
_ h="30,ABC,+"<,9"%+&(?9",%&3"=&=?;,1"$:(6D&*+0*,&::F+F()="%0,$"(>90,30=?,2.1%&'90+2@
_ c::F+F()="%90*,.2.=*+0N:"+1(*:=0,$"(>90,.".=")=?,2#,&::F+F()="%"',.,"$29&:"'0+
9&1%)>*92*+;,'"#%&.="+;,&+1*%ND&."'"4,*+:".=?6,2,30=?,"$9"=2190+2@
_ -,1"+*7*922;,<$*,3F$F=,9&8"$2=?.),&::F+F()="%0;,$"(>9&,30=?,"3*.1*D*9&,8"%"5&)
'*9=2()J2)@,-,.(FD&*,9*$".=&=:&,'*9=2()J22,'":%F<,&::F+F()="%&,+">*=,.:&1(2'&=?.)
'#%0'""1&.904,'"$"%"$904,<&#@,!%2,1"$:(6D*922,&::F+F()="%&,+"<F=,"3%&#"'0'&=?.),2.:%0@
_ i2:&:2*,1%*$+*=0,9*,$"(>90,."1%2:&.&=?.),.,$'F+),'8"$90+2,:(*++&+2,!%)+"<",P":&@,i*
."*$29)4=*,28,+*>$F,."3"4@,m=",+">*=,1%2'*.=2,:,.*%?*#90+,=*(*.90+,1"'%*>$*92)+,(2J
2n2(2,:,+&=*%2&(?9"+F,F7*%3F@
39
Page 40

B($3(#$&%#%.,,+9+/?4(5.2;S4.-&(%.5%(#=
B($3(#$&%#%($%()(2HJE"(/04%()(2.,,+9+/?4(5.
;S9\2SZ#9+2d2%.2345\2]^\2B5&9#8.%&#e2d\H2E265#$(Z5.%&4#/0\=
B($3(#$&%#%%#3,(/0,&Z2HJE"(/04%1Z2.,,+9+/?4(5("2;"26.5.//#/&=
;S9\2SZ#9+2^2%.2345\2]r\2B5&9#8.%&#e2^\H2E265#$(Z5.%&4#/0\=
B($3(#$&%#%%#3,(/0,&Z2^E"(/04%1Z2.,,+9+/?4(5("2;6(3/#$(".4#/0%(=
;S9\2SZ#9+2r2%.2345\2]r\2B5&9#8.%&#e2r\H2E265#$(Z5.%&4#/0\2!9#34#26($3(#$&%&91#
.,,+9+/?4(512(G#36#8.42HJE"(/04%1:2B5?9(:2O(,\=
_2B($3(#$&%&4#26(/(8&4#/0%+72,/#99+2B5?9()(2O(,.
%#6(35#$34"#%%(2%.265#$(Z5.%&4#/025?$(9232.,,+9+/?4(5(9\
pq,%*:"+*9$F*=,F.=&9&'(2'&=?,1"(FD2'52*,*<",(2J*9#26,1%*$"8%&92=*(2,2,1%*$"8%&92=*(?90*
3(":2,9&,%&..=")922,Yf,$64+"',Q[\`;dr,++S,"=,&::F+F()="%&@,!%*$"8%&92=*(?,$"(>*9,"3(&$&=?
9*,+*9**,Y\\,c@,Qi&,.8*+&8,X;,],2,d,2#"3%&>*9,%*:"+*9$F*+04,1"%)$":,1"$."*$29*92)@S
_2P36(/0@+:4#2,.G#/02$/?2.,,+9+/?4(5.2,.,29(<%(2G(/##2,(5(4,()(
&24?<#/()(2,./&G5.\
s.1"(?#F4=*,59F%0,`,$(),:&3*(),!%)+"<",P":&,$(29"4,$",Y\,IF="',Q1%23(2#2=*(?9",[,+S@,G()
:&3*(),$(29"4,$",Y],IF="',Q1%23(2#2=*(?9",X,+S,2.1"(?#F4=*,59F%0,Z@,H<%&92D*92*,',+&..*,2
$(299*,:&3*(),"<%&92D2'&*=,'"#+">9".=?,1&$*92),9&1%)>*92),!%)+"<",P":&;,&,=&:>*
"1=2+2#2%F*=,1*%*$&DF,=":&T@
!"#763(%&4."NOP"7*%7%=(@"%='7*'S.6)"+%$321%"=%,)T05"8%-(%76)"(3"&@L%1'"&"6'S'(.'"4%$%64.L"%6$'24%&"&$'8'(.9
h,'1%&36',)(%G"('%=L%1.8%"7*'X.3,)(%"*%1%=$36)"43=',."1,/"*%6'(X.3,)(%;"634%;"&@7%4%8%-(%;"*$%104X.."K('$+..9"i3M'
=010S."&@7%4%KWW'46.&(@8."*$'%=$32%&36',/8."K,'46$%K('$+..G"&@L%1(%;"*%6'(X.3,"0763(%&%4"NOP"%+$3(.S.&3'67/"1,.(%;
."43,.=$%8"43=',';G"7&/2@&35-.L"NOP"."344080,/6%$9
B($3(#$&%#%.,,+9+/?4(5.2;."4(9(G&/0%(#=
H.F7*.='2=*,!%".=*45**,1"$."*$29*92*;,*.(2,-0,%&3"=&*=*,.,(*<:2+2,1*%*9".90+2
E(*:=%"1%23"%&+2,2(2, &11&%&=F%"4,',=*D*92*,:"%"=:"<", "=%*#:&,'%*+*92@,;S9\2SZ#9+2 jC2 345\
]r\2B5&9#8#.%&#e2 %.2 SZ#9#2 j\H2 65#$34."/#%2 )#%#5.4(5C2 %.2SZ\2j\J2E2@.@#9/#%&#
."4(9(G&/0%()(2 .,,+9+/?4(5.C2 %.2 3Z\2 j\D2 E2 HJE"(/04%1:2 ."4(9(G&/0%1:2 .,,+9+/?4(5C2 %.
3Z\2j\]2 E265#$(Z5.%&4#/0=@,H.F7*.='2=*, !"(9"*, 1"$."*$29*92*;, *.(2,ABC,.(F>2=,-&+,$()
1"$'*$*92), E(*:=%"E9*%<22, :, :%F19"<&3&%2=9"+F, E(*:=%""3"%F$"'&926, ', =*D*92*, $(2=*(?908
1*%2"$"'@,;S9\2SZ#9+2sC2345\2]r\2 B5&9#8#.%&#e2%.2SZ#9#2s\H2 65#$34."/#%2)#%#5.4(5C2%.2SZ\
s\J2E2 .9(54&@.4(5C2 %.2 3Z\2 s\D2E2@.@#9/#%."4(9(G&/0%()(2.,,+9+/?4(5.C22%.23Z\2s\]2 E2 HJE
"(/04%1:2 ."4(9(G&/0%1:2 .,,+9+/?4(5C2 %.2 3Z\2 s\d2 E2 65#$(Z5.%&4#/0=@, !%2, =&:"+
1"$."*$29*922,1%"2.8"$2=,&+"%=2#&J2), &::F+F()="%&, 2, %&#$*(*92*, &::F+F()="%908,.2.=*+@
P&:2+,"3%&#"+, 1"$&*=.),&::F+F()="%9&),E9*%<2),9&,-&5, ABC;, 1%2D*+,E9*%<2),2#
&'="+"32(?9"<",&::F+F()="%&,9*,%&.8"$F*=.)@,!%2+*D&92*o,-,#&'2.2+".=2,"=,'2$&
2.1"(?#"'&92);,-&+,+">*=,1"9&$"32=?.), 3"(**, +"7904;, D*+, YZN-, &::F+F()="%,.,K<(F3":2+
J2:("+L@
!"#$%"#&'( )#*+,-%( "&( .+-*/01%23&( 45+2( 678( "&.+49&-435&""+( *( ,&"&9%3+9:;( <&=( %**:$:/>3+9%;( *%*
#=+<9%?&"+( "%( 4@&$%@( A( #( B;( 439C( DEC
40
Page 41

B($3(#$&%#%F/#,45(65&G(5("
!(2&@G#<.%#5#%.65?<#%&?245#G(".%&?2"2F%#5)&&2!.`&Z
F/#,45(65&G(5("2$(/<%12G14023("9#34&91232"1Z($%(:
9(A%(34072!.`#)(2WXY\
!%2,%&.D*=*,1"=%*39".=*4,',E9*%<22,.'"*<",E(*:=%""3"%F$"'&92), 9*, 1*%*1F=&4=*, 1"9)=2),K%&3"D*4L
9"+29&(?9"4,+"79".=2,2,K12:"'"4L,9"+29&(?9"4,+"79".=2@, m(*:=%"$'2<&=*()+, =%*3F*=.),3"(?5*
E9*%<22,',+"+*9=,#&1F.:&,QE=",N,K12:"'&)L,+"79".=?S;,D*+,1%2, %&3"=*@,K!2:"'&)L, +"79".=?,"30D9"
',Z,N,X,%&#,1%*'05&*=,K%&3"DF6L,+"79".=?@, ~"(?529.='",E(*:=%"$'2<&=*(*4, 1%23*<&6=,:, K12:"'"4L
+"79".=2,*$29">$0;,="(?:",',+"+*9=,#&1F.:&@,-,=",>*,'%*+),.F7*.='F6=,E(*:=%"$'2<&=*(2;
%&3"=&672*,',%*>2+*,1".=")99"<",':(6D*92)N"=:(6D*92);,',#&'2.2+".=2,"=,F.("'24@,M,92+
"=9".)=.),=*;,D=",F.=&9&'(2'&6=.),9&,8"("$2(?92:&8;,'"$""=(2'908,9&.".&8@,H92, 2.1"(?#F6=
K12:"'F6L,+"79".=?,+9"<"%&#"'",2,9*1%*$.:&#F*+",',1%"J*..*,%&3"=0@T
!":%7,'"23*0743"K,'46$%1&.+36',/G"*%43"*%7,'1(.;"$3=%63'6G"NOP"=01'6"%=,3136)"$'2'$&(%;"K('$+.';G"4%6%$05"%("%61376
1$0+.8"*$.=%$38"."076$%;76&389"Q@"8%M'6'"0&',.S.6)"(3+$0240"(3"NOP"*%"M',3(.5G"(%"('"='7*$'1',)(%9":$.8'S3(.'<"'7,.
344080,/6%$"7',G".,."M'"1&.+36',)"%S'()"*,%LG"763$".,.".2(%T'(G"344080,/6%$(@'"*$'1%L$3(.6',."8%+06"*'$'+%$36)9
B($3(#$&%?:4#2F/#,45(65&G(512,23"(#9+2WXY[\
t,,(96074#51 t,G14("+724#Z%&,+ t,65(&)51".4#/&2,(96.,4E$&3,("
t,9&,5("(/%("1#26#8& t,Z(/($&/0%&,& t,"&$#(9.)%&4(*(%1
t,"($((4/&"%1#2%.3(31 t,F/#,45($"&).4#/&2;$(2Hz^2{|=
t,/.961 t,&%345+9#%4123265&"($(9 t,9.)%&4(*(%1
t,65(&)51".4#/& t,&24.,2$./##}
!"Q7'"8%1',."NOP"%=,31356"(3"&@L%1'".(&'$6%$%8"4%(6$%,/"S376%6@9"j("*%2&%,/'6"&7'8"K,'46$%*$.=%$38G"%=,3135-.8
%7%=%;"S0&76&.6',)(%76)5"4"S376%6'"(3",.(.."*'$'8'((%+%"6%43G"(%$83,)(%"W0(4X.%(.$%&36)9"k"634.8"K,'46$%*$.=%$38
%6(%7/67/"4%8*)56'$@G"&.1'%83+(.6%W%(@G"*$%.+$@&36',."4%8*346_1.74%&G"83+(.6%W%(@G"K,'46$.S'74.'"S37@".
*$%.+$@&36',.9
B(@&-&&26#5#,/78.4#/?25.G(8#)(25#<&9.2;htXuvWcabw2xtyui=
t !%2,%&3"=*,.,1"$:(6D*990+,"3"%F$"'&92*+,1".=&'?=*,9&,Kc'="+&=L,QKApWuLS@,!gOsaevO_P-Ho
!%2,'.*"3728;,D&.=2D908,9&%F5*92)8,E(*:=%".9&3>*92),1"$&*=,E9*%<26,2#,&::F+F()="%&@
t M"<$&,9*,1"(?#F*=*.?,1"$:(6D*990+,"3"%F$"'&92*+;,1".=&'?=*,',1"#2J26,KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L
QKwxAyz{,uVq|ny{}uW{LS@,Q-isacisO/,1"$&D2,E9*%<22,2#,&::F+F()="%&,9*,1%"2#"4$*=/S
!gOsaevO_P-co,cS,c::F+F()="%,1%"$"(>&=,#&%)>&=?.);,*.(2,1"$&D&,=":&,9*,1%*:%&7*9&,2,~S
s9'*%="%,ABC,"=:(6D&*=.);,3(&<"$&%),D*+F,%*#*%',&::F+F()="%&,9*,%&.8"$F*=.),'",'%*+)
'.*"37*<",2(2,D&.=2D9"<",9&%F5*92),E(*:=%".9&3>*92)@
t !%2+*D&92*o,M"<$&,1*%*:(6D&=*(?,9&8"$2=.),',1"#2J22,KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L,QKwxAyz{,uVq|ny{}uW{LS;
-0,+">*=*,1"(?#"'&=?.),$'F81"#2J2"990+,1*%*:(6D&=*(*+,Q"9,1%2(&<&6=.),',:"+1(*:=*S;,:"="%04
"3*.1*D2'&*=,'#&2+9"*,1*%*:(6D*92*,+*>$F,%*>2+&+2,KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L,KwxAyz{,uVq|L,2
Kc'="+&=L,QKcpWuLS@,Q_+@,H12.&92*,1"$:(6D*92),G2.=&9J2"99"<",F1%&'(*92),9&,.=%@,`[S@
t !*%*:(6D&4=*,',1"#2J26,Ku••L,$(),1"(9"<","=:(6D*92),ABC,2,1%2(*<&67*<","3"%F$"'&92);,&
=&:>*,$(),'"#'%&7*92),',9"(?,ABC,1".(*,*<","=:&#&, '.(*$.='2*,1*%*9&1%)>*92),2(2,1*%*<%*'&@
'Mlm2BlMpRSORlRoQRSOP
65&26($,/78#%&&&2F/#,45(65&G(5("
t P%211,j&4=,9*,%*:"+*9$F*=,2.1"(?#"'&=?,92:&:2*,2#,1%"2#'"$2+08,:"+1&92*4,F.=%"4.=',ABC,€
&'="+&=2D*.:2+,&'&%2490+,1"$:(6D*92*+,:,2.="D92:&+,E9*%<22,',1%2+*9*922,:, +*$2:"N
:"+1*9.&="%9"4,&11&%&=F%*;,=&:,:&:,'9*#&1904,'08"$,2#,.=%"),2(2,9*.%&3&=0'&92*,+"<F=, .*%?*#9"
1"'%*$2=?,2,$&>*,":"9D&=*(?9",'0'*.=2,2#,.=%"),=&:F6,,+*$2:"N:"+1*9.&="%9F6, &11&%&=F%F@,R&
3"(**,$*=&(?9"4,29I"%+&J2*4,1",E="+F,'"1%".F,"3%&7&4=*.?,',:"+1&926,P%211,j&4=@
t i*,1"$:(6D&4=*,&'&%24908,%&#%)$92:"';,(29*4908,:"9$2J2"9*%"',2,1%"D28,.2.=*+
3*.1*%*3"49"<",E(*:=%"12=&92),:,'08"$90+,:(*++&+,!*%*+*99"<",P":&,F.=&9"':2,ABC@
t i*,1"$:(6D&4=*,.'"4,ABC,:,9*+F,.&+"+F@,P&:2*,'08"$:2,&99F(2%F6=,-&5F,<&%&9=26@
41
Page 42

BMlMN~•€>OM~PC2S!MOR!mM
PQpPN>ORlm2P2O\B\
;l.36(/(<#%F4&Z26#5#,/78.4#/#:C23"#4("1Z2&%$&,.4(5("2&265\2+,.@.%(2%.2SZ#9#2HfC
345\2]j\2Q.23Z#9#2Hf\H265#$34."/#%2k%&B/.)2E2k%&"#53./0%1:2`4#63#/0E6#5#Z($%&,2;(%
65&/.).#43?2,29($#/?92WXY2abc2dHJ=C2,(4(51:26($Z($&42,2G(/0`&%34"+2`4#63#/#:25.@%1Z
345.%C265.,4&8#3,&2/7G(:2,(%*&)+5.-&&\2Q.2SZ#9#2Hf\J2&@(G.5<#%2`4#63#/0232%.G(5(9
F/#,45(65("($,&\2B5&9#8.%&#e2Hf\JH2E2@.@#9/&4#/0%1:C2Hf\JJ2E2%#:45./0%1:C2Hf\JD2E2/&%&?
HC2Hf\J]2E2(43(#$&%&91:2`%+5\2Q.2SZ#9#2Hf\D265#$34."/#%.2hN(%*&)+5.-&?
9&,5(6#5#,/78.4#/#:2"2,(56+3#232JE5?$%1925.36(/(<#%\"1"($("iC2,(4(5.?2%.Z($&43?
%.26($#2+345(:34".\
B#5#,/78.4#/&
H\2 B#5#,/78.4#/02 hl.G(8&:2 5#<&9i
m="=,1*%*:(6D&=*(?,1"#'"()*=,'03%&=?,%*>2+,%&3"=0,Q2(2,',1"#2J22,KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L,N
KwxAyz{,uVq|ny{}uW{L;,2(2,1"#2J26,Kc'="+&=L,N,KApWuL,2(2,"=:(6D*92*,N,Ku••LS@,G()
"1=2+&(?9"4,9&.=%"4:2,1*%*:(6D&=*(*4,.+@,<(&'F,K!"$."*$29*92*,1%23"%"'L@
J\2hN(%*&)+5.4&"%1#29&,5(6#5#,/78.4#/&2"2,(56+3#232JE5?$%1925.36(/(<#%\"1"($("i
m=2,D*=0%*,1*%*:(6D&=*(),$"(>90,30=?,"=%*<F(2%"'&90,',.""='*=.='22,.,'2$"+,&::F+F()="%&;,:
:"="%"+F,3F$*=,1"$'*$*9,-&5,ABC;,2,$&990+2,",.2(*,9&1%)>*92),Q'"(?=&>S;,"=,:"="%"<",-&5
ABC,3F$*=,1*%*:(6D&=?.),9&,&::F+F()="%9F6,E(*:=%"E9*%<26@,a2:%"1*%*:(6D&=*(*+,Vb,Y
#&$&4=*,-2$,3&=&%*4;,:"="%0*,-0,2.1"(?#F*=*;,',1%"=2'9"+,.(FD&*,.",'%*+*9*+,-&52,3&=&%*2
2.1"%=)=.),2(2,>*,3F$F=,+*9**,EII*:=2'90@,i&1%)>*92*,1"D=2,(63"4,.2(0,3F$*=,$*4.='*99";
*.(2,+2:%"1*%*:(6D&=*(?,Vb,Z;,"=9".)724.),:,'0.":"'"(?=9"+F,9&1%)>*926,1*%*+*99"<"
=":&;,3F$*=,9&.=%"*9,9&,ZXd,•;,&,+2:%"1*%*:(6D&=*(2,Vb,[,2,`;,"=9".)72*.),:,92#:"'"(?=9"+F
9&1%)>*926,1*%*+*99"<",=":&;,3F$F=,9&.=%"*90,9&,YfY,•@,P*+,9*,+*9**;,9&.=%"4=*,.'"4,ABC
1"92>*,2(2,1"'05*,E="4,"=+*=:2;,D="30,1"7&$2=?,&::F+F()="%,',+"+*9=,D&.=08
:%&=:"'%*+*9908,1*%*1&$"',9&,(2922,2#,'0.":"<",',92#:"*,9&1%)>*92*@,m=2,1*%*1&$0,',.'"6
"D*%*$?,9*,"=%&>&6=.),9&,%&3"=*,1"$:(6D*99"<","3"%F$"'&92)@,Q_+@,<(&'F,Ka"9=&>,ABCL,2
_8*+F,Vb,Y,9&,.=%@,`]S@
S"#4("1#2P%$&,.4(51
D\2h•abui2E2h~&%&?i
m=&,#*(*9&),(&+1"D:&,3F$*=,~O_!gOg‚-iH,^HgOPƒ,="<$&;,:"<$&,1"$:(6D*99"*,"3"%F$"'&92*
3F$*=,1"(FD&=?,1*%*+*9904,=":,2#,.*=2,"37*<",1"(?#"'&92)@,H9&,3F$*=,+2<&=?;,:"<$&,=":,2#,.*=2
"37*<",1"(?#"'&92),2+**=.);,&,1*%*:(6D&=*(?,',%&3"D24,%*>2+,-&5*<",ABC,1".=&'(*9,'
1"#2J26,KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L,QKwxAyz{,uVq|ny{}uW{LS;,2,=&:2+,"3%&#"+,1%*$F1%*>$&=?,-&.,"
="+;,D=",29'*%="%,ABC,"=:(6D*9;,2,D=",ABC,,iO,!HGc_P,%*#*%'9F6,&::F+F%2%"'&99F6,E9*%<26
',.(FD&*,'.*"37*<";,D&.=2D9"<",9&%F5*92),E(*:=%".9&3>*92);,2(2,>*,1*%*9&1%)>*92)@
]\2hab‚i
m=&,:%&.9&),(&+1"D:&,3F$*=,~O_!gOg‚-iH,^HgOPƒ,="<$&;,:"<$&,1"$:(6D*99"*,"3"%F$"'&92*
3F$*=,1"(FD&=?,1*%*+*9904,=":,2#,&::F+F()="%&,Q'",'%*+),'.*"37*<";,D&.=2D9"<",9&%F5*92)
E(*:=%".9&3>*92),2(2,1*%*9&1%)>*92);,',=",>*,'%*+),3F$FD2,1"$:(6D*990+,:,.*=2,"37*<"
1"(?#"'&92),2(2,>*,:,&'="+"32(?9"+F,&::F+F()="%FS@
d\2h•tWyi
m=&,:%&.9&),(&+1"D:&,3F$*=,~O_!gOg‚-iH,^HgOPƒ,="<$&;,:"<$&,9&<%F#:&,ABC,9&8"$2=.),'
1%"+*>F=:*,"=,f\„,$", YY\„,1"(9"4,+"79".=2@, m=&,(&+1"D:&,3F$*=,+2<&=?,',.(FD&*
"=:(6D*92),29'*%="%&, ABC, '.(*$.='2*, D*%*#+*%9"4, 1*%*<%F#:2, 2(2, 1*%*<%*'&@,O.(2,=&:&)
.2=F&J2),'"#92:9*=;, 1".=&'?=*, 1*%*:(6D&=*(?,%&3"D*<", %*>2+&, ',1"(">*92*, Ku••L@, _92+2=*
9&<%F#:F@,G&4=*, F.=&9"':*, '%*+), ".=0=?@, !".(*, E="<", -0, +">*=*, .9"'&, ':(6D2=?, .'"4, ABC@
42
Page 43

^\2„…Wccuv†2‡azxuyz•tˆ
m=2,=%2,(&+1"D:2,3F$F=,':(6D&=?.),',%&#(2D908,:"+329&J2)8,2,F:�'&=?,1%23(2#2=*(?904
F%"'*9?,9&<%F#:2,2,9&1%)>*92),%*#*%'9"4,E9*%<22,9&,1"$:(6D*99"+,&::F+F()="%*;,&,=&:>*
1%*$F1%*>$&=?,-&.,",9*:"="%08,'2$&8,&9"+&(24;,:&:,="o
!HMcRcisˆ,H,ic^geRMO,cMMeaejˆPHgc,Q!%23(2>*99"S
~.96(8,. '(A%(340 !(/041
R*(*9&) H=,rY,„,$",1"(9"4 YZ@\,N,Y]@\
R*(*9&),2,‰*(=&) H=,fY,„,$",r\„ YY@f,N,YZ@\
‰*(=&) H=,]Y,„,$",f\,„ YY@],N,YY@f
‰*(=&),2,M%&.9&) H=,`Y,„,$",]\,„ YY@[, N,YY@]
M%&.9&) H=,ZY,„,$",`\,„ YY@\,N,YY@[
N H=,Y,„,$",Z\,„ Y\@\,N,YY@\
M%&.9&),+2<&67&) \,„,Q"=:&#,29'*%="%&S Š,Y\@\
-.*,(&+1"D:2,+2<&6=,+*$(*99",T h%*#+*%9&), %&#<%F#:& Š, f@\
-.*,(&+1"D:2,+2<&6=,30.=%",TT !*%*9&1%)>*92* ‹,Y]@\
!":$.=,.2.6',)(@;"X.4,"8.+3(./"_"*%,_7'40(1@"(3"+%$'(.'"."*%,_7'40(1@"(3"*%60L3(.'9"h89"+,3&0"j"('.7*$3&(%76/L".
7*%7%=3L".L"076$3('(./9
!!":$.=,.2.6',)(@;"X.4,"8.+3(./"_"*%"c`l"7'40(1@"(3"+%$'(.'"."(3"*%60L3(.'9"?%M'6"634M'"0432@&36)"(3"(3,.S.'
('.7*$3&(%76."(3"0$%&('"23$/1(%+%"&@*$/8.6',/"344080,/6%$39"h89"+,3&0">j"('.7*$3&(%76/L"."7*%7%=3L".L"076$3('(./A9
BlR€PM2K~M'MQOm
r\2!Z($%1#2 ,/#9912 B5?9()(2 O(,.
M%0(?D&=0*,<&4:2,:(*++,#&727&6=, 1%"'"$&;, 2.8"$)72*, 2#,-&5*<",'9*59*<", &::F+F()="%&@
!"$."*$292=*,c::F+F()="%,2(2,&::F+F()="%0;,:"="%0*,."'+*.=9",3F$F=,"3*.1*D2'&=?,-&5,ABC
YZN'"(?=90+,1%)+0+,=":"+;,&,-&5*,"3"%F$"'&92*,N,.""='*=.='F67*4,&+1*%ND&."'"4,*+:".=?6@
h="30,F(FD52=?,."*$29*92*;,2.1"(?#F4=*,.1&*990*,(*1*.=:2,9&,:&3*(*,c::F+F()="%&@,R&,3"(**
1"(9"4,29I"%+&J2*4,"3%&7&4=*.?,:,<(&'*,K-03"%,&::F+F()="%&L@
j\2l(@#4,&2B#5#9#%%()(2O(,.2;buxW2dEHdv=
m=2,%"#*=:2,1%*$9 &D*90,$(),1"$."*$29*92),"3"%F$"'&92);,%&3"=&67*<",9&,+"79".=2,Z[\,!*%*+*99"<",P":&,X\n]\,^J@,G(),1"$:(6D*92),:,"3"%F$"'&926,+"$*(2,ABC,UVW,XYZ,+"<F=
9F>$&=?.), ', 1*%*8"$92:&8, $(), E=28, %"#*=":, ;k%&"#53./0%1:2 >$.64#52 65&/.).#43?\2 S9\
SZ#9+2Hf\HC2345\2]j=@
s\2~&%#:%1:2 `%+52 B#5#9#%%()(2O(,.2 ;buxW2 dEHdX23ƒ#9%1:=
!"$."*$292=*,59F%, ',%"#*=:F,Z[\,-;,X\N]\, ^J@, iO,!HGMj…hc†PO,E="=,59F%,', %"#*=:2
!*%*+*99"<",P":&,ABC@,ABC,UVW,XYZ,2+**=,''"$2+04,5=*1.*(?,=21&,U{wN[Z\,2,.‡*+904
"8'&=0'&6724,U{wN[Z\,:,''"$2+"+F,59F%F,V{}A,XNYXB@,!"()%9".=?,5=*1.*(),F:&#&9&,i&,_8*+*
Y\@Z;,.=%@,`f@
Hf\2!(334.%."/&".#91:2"2&3Z\26(/(<#%+G&/0%&,
gF32(?92:,#&727&*=,-&5,ABC,"=,1"'%*>$*924;,'0#0'&*+08,1*%*<%F#:"4,9&,'08"$*@,_92+2=*
2#30="D9"*,9&1%)>*92*@,!"$">$2=*,Y,+29F=F@,!".=&'?=*,%F32(?92:,',2.8"$9"*,1"(">*92*@
HH\2p"+Z6(@&-&(%%1:23(#$&%&4#/02h!,/78#%&#ER4,/78#%&#i232$&34.%-&(%%192+65."/#%
H9,$*4.='F*=,1%2,F.=&9"':&8,ABC,.,$2.=&9J2"990+,F1%&'(*92*+;,., 2.1"(?#"'&92*+, 59F%&;, Q"9
1%2(&<&*=.),',:"+1(*:=*S;,2,$'F81"#2J2"99"<",1*%*:(6D&=*()@,m="=,."*$292=*(?, $"1F.:&*=
2.1"(?#"'&92*,$'F8N1%"'"$9"<",[;XN+2((2+*=%"'"<",=*(*I"99"<",5=*1.*()@,!%2+*D&92*o
1*%*:(6D&=*(?,.,$2.=&9J2"990+,F1%&'(*92*+;,"9,1%2(&<&6=.),',:"+1(*:=*;, +">*=, :"9=%"(2%"'&=?
%&3"=F,ABC,="(?:",="<$&;,:"<$&,1*%*:(6D&=*(?,%&3"D*<",%*>2+&,QKuB{yAWUVz,}ul{LS,9&8"$2=.)
',1"#2J22,KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L,QKwxAyz{,uVq|LS@, G2.=&9J2"9904, 1*%*:(6D&=*(?,+">*=,1*%*:(6D&=?
2#,1"#2J22,KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L,QKwxAyz{,uVq|LS,', 1"#2J26, Kc'="+&=L,QKApWuLS@,H.F7*.='2'
$2.=&9J2"99"*,1"$:(6D*92*;,"1%*$*(2=*.?;,',:&:"4,1"#2J22,-&5,(2D904,1*%*:(6D&=*(?,"#9&D&*=
KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L,QKwxAyz{,uVq|LS;,&,',:&:"4,N, %*>2+,Kc'="+&=L,QKApWuLS@,P&,1"#2J2),9&,-&5*+
(2D9"+,1*%*:(6D&=*(*;,1%2,:"="%"4,#*(*904,.'*="'"4,29$2:&="%,Kj292)L,QKqUV{LS,+2<&*=;,)'()*=.)
1"#2J2*4,%*>2+&,KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L,QKwxAyz{,uVq|LS@
43
Page 44

!m‰!~MQPM2P2kSOl>QMQPM2QMPSBl>!QRSOMŠ
!%*>$*,D*+,"=".(&=?,.'"4,ABC,9&,%*+"9=;,'.*<$&,1%"'*%?=*,.(*$F67**@,!*%*$,"=1%&'(*92*+,.'"*<",ABC,9&,1"D29:F,1"#'"92=*,'
H=$*(,"3.(F>2'&92),1"=%*32=*(*4,:"+1&922,P%21,j&4=@
-2$,9*2.1%&'9".=2 !%2D29& _1"."3,F.=%&9*92)
g"#*=:2,ABC,9*,$&6=,!*%*+*99"<"
P":&,9&,'08"$&8,Q',=",'%*+),:&:,9&
'8"$&8,!*%*+*9904,P":,2+**=.)S
g"#*=:2,ABC,9*,$&6=,!*%*+*99"<"
P":&,9&,'08"$&8,Q9&,'8"$&8
!*%*+*9904,P":,"=.F=.='F*=S
ABC,9*,+">*=,#&%)$2=?,&::F+F()="%
Q9&,'8"$&8,!*%*+*9904,P":
2+**=.)S
i2,"$29,.'*="'"4,29$2:&="%,9*
<"%2=,Q9&,'8"$&8,!*%*+*9904,P":
"=.F=.='F*=S
i2,"$29,.'*="'"4,29$2:&="%,9*
<"%2=,Q9&,'8"$&8,!*%*+*9904,P":
2+**=.),2(2,"=.F=.='F*=S
-.*,.'*="'0*,29$2:&="%0
&::F+F()="%&,F.=%"4.='&,ABC
+*$(*99",+2<&6=
a2<&*=,(&+1"D:&,KquL,&::F+F()="%&
ABC
-.*,.'*="'0*,29$2:&="%0
&::F+F()="%&,F.=%"4.='&,ABC
30.=%",+2<&6=
_'*="'"4,29$2:&="%,KquAlL
F.=&9"':2,ABC,30.=%",+2<&*=
!"Q"4%8*,'46'"('"*$.,3+3'67/
44
ABC,1("8",1"$."*$29*9,:,.=*99"4,%"#*=:*@
gF32(?92:,"=:(6D*9
ABC,"=:(6D&*=.),'.(*$.='2*
D*%*#+*%9"<",9&1%)>*92),&::F+F()="%&;
ABC,9&8"$2=.),',1"#2J22,K'0:(6D*9L
QKu••LS
gF32(?92:,"=:(6D*9
!*%*:(6D&=*(?,%&3"D*<",%*>2+&
QKuB{yAWUVz,}ul{LS,9&8"$2=.),',1"#2J22
KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L,QKwxAyz{,uVq|LS
i*2.1%&'9".=?,.')#&9&,.
1*%*9&1%)>*92*+,2(2,'0.":"4
=*+1*%&=F%"4
c::F+F()="%,.(25:"+,%&#%)$2(.)
c::F+F()="%0,K'0$"8(2.?L
!%*$"8%&92(?,&::F+F()="%&,1*%*<"%*(T
!%"'"$:&,&::F+F()="%&,".(&3(*9&,2(2
2#9".2(&.?T
i*1"(&$:&,9&,#&%)$9"+,F.=%"4.='*,ABC
m=",9*,&9"+&(2);,*.(2,ABC,9&.=%"*9,9&
%*>2+,KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L,QKwxAyz{
uVq|LS
c::F+F()="%,.(25:"+,%&#%)$2(.)
c::F+F()="%,.(25:"+,%&#%)$2(.)
s9'*%="%,"=:(6D&*=.);,=@:@,9&1%)>*92*
".=&*=.),1"$,"=+*=:"4,Y\,-,!%)+"<",=":&
3"(**,],.*:@,!%*$"8%&9)*=,&::F+F()="%,"=
'08"$&,2#,.=%")
-0.":"*,9&1%)>*92*,',&::F+F()="%*
1&$&*=,'",'%*+),#&%)$:2
!*%*<%F#:&,29'*%="%&,"3F.("'(*9&
D%*#+*%90+,9&1%)>*92*+,2(2,:"%"=:2+
#&+0:&92*+@,!%2,3"(**,D*+,XN.*:F9$9"4
1*%*<%F#:*,29'*%="%,"=:(6D&*=.)
!"$."*$292=*,ABC,:,%"#*=:*,',.=*9*@
!".=&'?=*,%F32(?92:,',2.8"$9F6,1"#2J26
H=:(6D2=*,ABC@,!"$">$2=*,Y,+29F=F,2
1*%*:(6D2=*,9&,&'="+&=,QKApWuLS
-0.=&'?=*,1"#2J26,Kc'="+&=L,QKApWuLS,2(2
KP"(?:",#&%)$:&L,QKwxAyz{,uVq|LS
!".=&'?=*,%F32(?92:,',2.8"$9F6,1"#2J26
!".=&'?=*,1*%*:(6D&=*(?,%&3"D*<",%*>2+&
QKuB{yAWUVz,}ul{LS,',1"#2J26,Kc'="+&=L
QKApWuLS
-0:(6D2=*,ABC@,!"$">$2=*,Y,+29F=F@
_92+2=*,9&1%)>*92*@,!*%*:(6D2=*,9&
&'="+&=,QKApWuLS
!%"'*%?=*,.".=")92*,&::F+F()="%&
!%"'*%?=*,2,#&+*92=*,&::F+F()="%0
!%"'*%?=*,2,#&+*92=*,1%*$"8%&92=*(?
!%"'*%?=*,2,F1%"D92=*,2(2,#&+*92=*
1%"'"$:F
-0:(6D2=*,ABC@,!"$">$2=*,Y,+29F=F@,!*%*:(6D2=*
9&,&'="+&=,QKApWuLS@,-,.(FD&*,&'="+&=2D*.:"<"
"=:(6D*92),"3%&7&4=*.?,',H=$*(,"3.(F>2'&92)
1"=%*32=*(*4,:"+1&922,P%21,j&4=
N
s.1"(?#F4=*,'.1"+"<&=*(?9"*,#&%)$9"*
F.=%"4.='";,D"30,1"$9)=?,9&1%)>*92*
&::F+F()="%&,8"=),30,$",r,-,!%)+"<",P":&@
!%"'*%?=*,."*$29292),'9*59*<"
&::F+F()="%&,2,1%*$"8%&92=*()@,_3%".
1%"2.8"$2=,&'="+&=2D*.:2;,1".(*,%*5*92)
1%"3(*+0
s.1"(?#F4=*,'.1"+"<&=*(?9"*,#&%)$9"*
F.=%"4.='";,D"30,1"$9)=?,9&1%)>*92*
&::F+F()="%&,8"=),30,$",r,-,!%)+"<",P":&@
_3%".,1%"2.8"$2=,&'="+&=2D*.:2;,1".(*
%*5*92),1%"3(*+0
_$*(&4=*,.3%".,1F=*+,9&.=%"4:2
1*%*:(6D&=*(),F1%&'(*92),9&,1"#2J26
K'0:(6D*9"L,Qu••S;,&,#&=*+,K':(6D*9"L,QuVS
!%"'*%?=*,'.*,2.="D92:2,#&%)$:2@,_$*(&4=*
.3%".,1F=*+,9&.=%"4:2,1*%*:(6D&=*()
F1%&'(*92),9&,1"#2J26,K'0:(6D*9"L,Qu••S;,&
#&=*+,K':(6D*9"L,QuVS
H.F7*.='2=*,.3%".,1F=*+,F+*9?5*92)
9&1%)>*92),2,9&.=%"4:"4,1*%*:(6D&=*()
F1%&'(*92),9&,1"#2J26,K'0:(6D*9"L,Qu••S;,&
#&=*+,K':(6D*9"L,QuVS@
Page 45

Rgl>QP€MQQ>‰2g>l>QOP‰
P%211,j&4=,1":%0'&*=,<&%&9=2*4,:"+1(*:=F672*,2,=*8@, "3.(F>2'&92*, .'"*4,1%"$F:J22, 1%"$"(>2=*(?9".=?6, "$29, <"$,', 1%*$*(&8, .=%&90;,YZ\, $9*4
1%2,E:.1"%=*;,.D2=&),.",$9),1":F1:2,"3"%F$"'&92)@, !", E="4,<&%&9=22, P%211, j&4=,1%292+&*=, "3)#&=*(?.='&, 1",%*+"9=F, 2(2, #&+*9*,$*I*:=9"<"
="'&%&@,G(),1"(FD*92),F.(F<,1",E="4,<&%&9=22,-0, $"(>90, .9&D&(&,1"(FD2=?, i"+*%9"*, g&#%*5*92*,9&, '"#'%&7*92*,1%"$F:J22, Qy}AS, F,P%211, j&4=
2(2,F,.=&9J22,=*8@"3.(F>2'&92),N,$2(*%&, 9&5*4, :"+1&922@, !%"$F:J26,.(*$F*=, "=.0(&=?, :"+1&922, P%211, j&4=,2(2, .=&9J22, =*8@"3.(F>2'&92), N, $2(*%&
9&5*4,:"+1&922@,g&.8"$0,9&,1*%*.0(:F,9*.*=,1"=%*32=*(?@, -"#'%&7&*+04,="'&%, $"(>*9, ."1%"'">$&=?.),:%&=:2+, "12.&92*+,9*1"(&$:2, 2
$":F+*9="+,",$&=*,2,+*.=*,1":F1:2,="'&%&@,m=&,<&%&9=2),9*,1":%0'&*=,"3"%F$"'&92*;, '05*$5**,2#,.=%"), 2(2,1"'%*>$*99"*, '.(*$.='2*
9*3%*>9"<","3%&7*92);,2.1"(?#"'&92),9*,1",9 &D*926;,&, =&:>*,+"$2I2J2%"'&99"*, ,"3"%F$"'&92*;, :"="%"*, 10=&(2.?,1*%*$*(&=?@, m=&, <&%&9=2)
1%2+*9)*=.),2.:(6D2=*(?9",:,1*%'"9&D&(?9"+F,1":F1&=*(6;,:"="%04,$"(>*9, $"(>90+,"3%&#"+, "I"%+2=?;, #&%*<2.=%2%"'&=?,1":F1:F, ',=*D*92*, Y\N
$9*'9"<",.%":&,1".(*,**,."'*%5*92)@
Rc,!gOGOjcas,sRjH‰OiiH^H,RGO_ƒ;,Pgs!!,jc†P,iO,GOjcOP,is,_!Okscjƒi‚Œ;,is,!HGgcReaO-cOa‚Œ,^cgciPs†;
-Mj…hc…vsŒ,^cgciPss,ic,g‚iHhi‚†,_!gH_;,McM,s,^cgciPs†,!H,s_!HjƒRH-cis…,!H,H_H~Hae,icRichOis…@,-,9*:"="%08
.=%&9&8,"<%&92D*92*,<&%&9=24;,2.:(6D*92*,'"#+">9".=2,1"$%&#F+*'&*+08,<&%&9=24;,1"E="+F,F:&#&99"*,"<%&92D*92*,QF:&#&990*
"<%&92D*92)S,2,2.:(6D*92*,Q2.:(6D*92)S,+"<F=,9*,%&.1%".=%&9)=?.),9&,1":F1&=*()@
Rc,s_Mj…hOisOa,-‚•O_McRciiH^H;,is,-, MHOa, _jehcO,Pgs!!, jc†P, iO,~eGOP, _hsPcPƒ_ˆ, -siH-i‚a,-, !gˆa‚Œ;, H!H_gOGH-cii‚Œ;
icgHhi‚Œ;,_jehc†i‚Œ,sjs,-PHgshi‚Œ, !H-gO‰GOisˆŒ, s, evOg~O;, iciO_Oii‚Œ, -_jOG_P-sO, s_!HjƒRH-cisˆ, mPH†,!gHGeMkss;
Gc‰O,O_js,!HMe!cPOjˆ,s,!gOGe!gOGsjs, H,!HPOikscjƒiH†, -HRaH‰iH_Ps,PcMH^H, evOg~c@, P%211,j&4=, 9*, "='*D&*=,92, #&, :&:2*
+&=*%2&(?90*,1"=*%2;,:&:,=",o,F1F7*992*,$"8"$"', 2(2,1%230(2;, 1"=*%),"3"%F$"'&92), 2(2,'"#+">9".=2, 2.1"(?#"'&92),"3"%F$"'&92);, 1"=*%)
1%"<%&++908,.%*$.=';,1"=*%),$&9908;,%&.8"$0,9&,#&+*99F6, 1%"$F:J26;,%*:(&+&J22,"=, =%*=?28,(2J, 2,1%"D&)@
SBM‹PLPN>‹PP
PQ!MlORl WXY2abc2dHJ
g&3"D&),+"79".=?,Z\bw X\\,-=
c'&%249&),+"79".=?,QX,.*:S YZ\\,-=
M!G,Q!%2,1"(9"4,9&<F%#:*S r\,„
!%)+"4,P":,9&,'8"$*,1%2,YZ,-,N !"(9"4,9&<F%#:* XZ,c
i"+29&(?9"*,9&1%)>*92*,9&,'8"$* YZ,-,!%)+"<",P":&
G2&1&#"9,9&1%)>*92),!%)+"<",P":&,9&,'8"$* "=,Y\,$",YX;X,i"+29&(?9"*,9&1%)>*92*,9&,'08"$* Z[\,-,!*%*+*99"<",P":&,•nN,X,„
i"+29&(?9&),D&.="=&,9&,'8"$* X\n]\,^J,•nN,[,„
-"(9& s#+*9*9&
I>Bl>!R€QmŠ2!mBl‰'POM~T
R&1%&'"D9&),*+:".=?;,!%)+"<",P":& Yf,c
G"1F.:,9&1%)>*92);,-,!%P R&$&'&*+@,Y`@`,n,Y`@Z,_F8,n,^*(2*'@
!(&'&6724,1"=*9J2&(;,-,!%P R&$&'&*+@,Y[@[,n,Y[@],_F8,n,^*(2*'@
i&1%)>*92*,9&,'8"$*;,!*%*+*99"<",P":& Z[\,-,!*%*+*99"<",P":&
P":,9&,'8"$*;,!*%*+*99"<",P":& X,c
~PQP‰2Q>Bl‰oMQP‰2BMlM'MQQRgR2ORN>2!2l>nR€M'2lMoP'M
a29@,9&1%)>*92*,9&,'8"$*,!*%*+*99"<",P":& R&$&'&*+@,Y``;,Y]Z;,YfY,2(2,Z\\,-,!*%*+*99"<",P":&
a&:.@,9&1%)>*92*,9&,'8"$*,!*%*+*99"<",P":& R&$&'&*+@,ZXd,2(2,Zd],-,!*%*+*99"<",P":&
a&:.@,=":,9&,'8"$* YY,c
h&.="=&,9&,'8"$* X\,n,]\,^J,•nNY\,„
a&:.@,!*%*+*9904,P":,9&,'08"$* X,c
-%*+),&'="+&=2D*.:"<",1*%*'"$& 9"+29&(?9",N,],+2((2.*:F9$
^&3&%2=0,Qx,•,q,•,BS Yd;`,8,Yd;`,8,ZX;`,.+
a&..& f;Z,:<
~*#,9&<F%#:2 Y,c
lMNR'MQp>‹PP2BR2kŒRpk2P2OMŒQP€MSNRM2RnS~koP!>QPM
l#,(9#%$.-&&26(2+Z($+
_*%2490*,+"$*(2,ABC,9*,=%*3F6=,92:&:"<","."3"<",F8"$&;,9",28, .(*$F*=,."$*%>&=?, ',9*1%*+*99"
.F8"+,.".=")922@,-%*+),"=,'%*+*92,$*(&4=*,".+"=%,'.*8,."*$29*924,1%"'"$"',2, 59F%"',:&:, 9&
F.=&9"':*;,=&:,2,9&,&::F+F()="%*@,!%"D27&4=*,2,F:%*1()4=*,1",+*%*,9*"38"$2+".=2@
O#Z%&8#3,(#2RG3/+<&".%&#
!%2,"=.0(:*,.'"*<",ABC,',P%211,j&4=;,1">&(F4.=&;,=7&=*(?9",F1&:F4=*,ABC,',*<",Žc~gashie…
e!cMH-Me;,=F;,',:"="%"4,"9,1%"$&'&(.)@,!%2(">2=*,"12.&92*,'9*5928,1%")'(*924,Q.2+1="+"'S
9*1"(&$:2@,O.(2,*<",<&%&9=24904,.%":,9*,'05*(;,1%2(">2=*,:"126,I&:=F%0N.D*=&,",1":F1:*@
45
Page 46

Diagrams / Esquemas / Schémas /
•Z#91
1
1.3
^
^
1.2
1.1
3 4
2
2.1
46
5.1
5
Page 47

6
7
6.1
7.1
8
8.1
9
9.1
9.2
8.4
8.3
8.2
9.5
9.4
9.3
9.4
9.3
47
Page 48

10
11
6
1
3
4
5
8
10
9
48
10.1
10.3
2
7
10.2
10.24
10.21
10.23
10.22
93-1323 (200002089) 6/00
 Loading...
Loading...