Page 1

Smart 216/232 IP
User Guide
1111 W. 35th Street, Chicago, IL 60609 USA
www.tripplite.com/support
Copyright ©2012 Tripp Lite. All rights reserved.
Page 2

Legal Notice
Legal Notice
This manual and the software described in it are furnished under license, and may be
used or copied only in accordance with the terms of such license. The content of this
manual is provided for informational use only, and is subject to change without
notice. It should not in and of itself be construed as a commitment by Minicom
Advanced Systems Limited, which assumes no responsibility of liability for any errors
or inaccuracies that may appear in this book.
The software that accompanies this manual is licensed for use by the Licensee only,
in strict accordance with the software license agreement, which the Licensee should
read carefully before commencing use of the software. Except as permitted by the
license, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system, or
transmitted in any form of by any means, electronic, mechanical, recording, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of Minicom Advanced Systems
Limited.
ii | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 3

About this Document
About this Document
This document provides installation and operation instructions for the Smart 216/232
IP system, produced by Minicom Advanced Systems Limited. It is intended for system
administrators and network managers.
Chapters and Their Contents
1 Introduction Provides an introduction to the document, Smart
216/232 IP product overview, features and benefits of
Smart 216/232 IP, client computer operating system
requirements, technical precautions, trademarks, and
terminology used in the document. It also describes
how to safely handle the device, provide feedback on
the user guide, and WEEE Information for Minicom
Customers and Recyclers.
2 Installation Lists Smart 216/232 IP system components, describes
the functionalities of the Smart 216/232 IP elements,
and provides instructions for rack mounting the unit
and connecting the system.
3 Configuring the
Network
Provides instructions for logging into the Web
configuration interface, configuring the device ID, IP
address, and Centralized Management settings,
adding, editing, removing, and blocking system Users,
configuring the KVM switch, Serial port, security, user
targets, system date and time, power outlets, and
power device settings. It also provides instructions for
installing an SSL certificate, upgrading firmware,
upgrading RICCs/ROCs, restoring factory settings,
backing up and restoring configuration data, and
saving changes and logging out.
Pg. 11
Pg. 13
Pg. 22
4 Conducting a Remote
Session
5 Managing the Events
Log
6 Troubleshooting –
Restoring Factory
Settings
7 Operating the Smart
216/232 IP Switching
Describes how to start a remote session, set the
session profile, full screen mode, view system
information, adjust video settings, power manage
target servers, manage keyboard sequences,
synchronize mouse pointers, switch to a different
server or device, and disconnect the remote session.
Describes how to view, reload, clear, and save the
Events Log.
Describes how to restore the device to its factory
settings using a USB drive.
Describes how to operate Smart 216/232 IP using the
OSD.
Pg. 48
Pg. 69
Pg. 71
Pg. 72
User Guide | iii
Page 4

About this Document
System Locally
8 Technical
Specifications
9 Video Resolution and
Refresh Rates
Style Conventions
Convention Used for
Verdana
Arial Bold
Arial Italics
Monospace
Regular text.
Names of menus, commands, buttons, and other elements of the user interface.
Special terms, the first time they appear.
Text entered by the user.
Notes, which offer an additional explanation or a hint on how to overcome a
common problem.
Warnings, which indicate potentially damaging user operations and explain
how to avoid them.
Lists and describes Smart 216/232 IP specifications. Pg. 78
Lists video resolutions and refresh rates. Pg. 78
iv | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 5

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
LEGAL NOTICE ........................................................................................... II
ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT ...........................................................................III
TABLE OF CONTENTS .................................................................................. V
TABLE OF FIGURES ....................................................................................IX
1 INTRODUCTION .................................................................................. 11
1.1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW ...........................................................................11
1.1.1 Features and Benefits ............................................................11
1.2 TERMINOLOGY ...................................................................................12
1.3 COMPATIBILITY ..................................................................................12
1.4 CLIENT COMPUTER OPERATING SYSTEM .....................................................12
1.5 TECHNICAL PRECAUTIONS......................................................................12
1.6 SAFETY ...........................................................................................13
1.7 TRADEMARKS ....................................................................................13
1.8 WEEE COMPLIANCE ............................................................................13
2 INSTALLATION ................................................................................... 14
2.1 OVERVIEW .......................................................................................14
2.2 SYSTEM COMPONENTS..........................................................................14
2.2.1 The Smart 216/232 IP Unit ....................................................14
2.3 PRE-INSTALLATION GUIDELINES ..............................................................16
2.4 RACK MOUNTING THE SMART 216/232 IP UNIT...........................................16
2.4.1 Rack Mounting Safety Considerations ......................................16
2.4.2 Mounting the Unit .................................................................17
2.5 CONNECTING THE SYSTEM .....................................................................18
2.6 CONNECTING TO THE SERVERS................................................................18
2.6.1 Connecting a ROC PS/2 .........................................................19
2.6.2 Connecting a ROC USB ..........................................................20
2.7 CONNECTING TO THE NETWORK...............................................................20
2.8 CONNECTING THE CAT5 CABLES .............................................................20
2.9 CONNECTING THE KVM CONSOLE ............................................................21
2.10 CONNECTING THE POWER SUPPLY ............................................................21
3 CONFIGURING THE NETWORK ............................................................ 22
3.1 BOOT-UP PROCESS .............................................................................22
3.2 LOGGING ONTO THE WEB CONFIGURATION INTERFACE....................................23
3.2.1 Web Configuration Interface Tabs ...........................................25
User Guide | v
Page 6

Table of Contents
3.2.2 Web Configuration Toolbar Buttons .........................................26
3.3 CHANGING YOUR PASSWORD ..................................................................26
3.4 CONFIGURING THE NETWORK SETTINGS.....................................................27
3.4.1 Configuring Device ID Settings ...............................................27
3.4.2 Configuring the Device IP Address...........................................27
3.4.3 Configuring Centralized Management Settings ..........................28
3.5 CONFIGURING USER SETTINGS ...............................................................29
3.5.1 Adding a User.......................................................................29
3.5.2 Deleting User(s) ...................................................................30
3.5.3 Blocking a User.....................................................................31
3.5.4 Editing User Information ........................................................31
3.6 CONFIGURING THE KVM SWITCH.............................................................32
3.7 CONFIGURING THE SERIAL PORT SETTINGS .................................................33
3.8 CONFIGURING THE SECURITY SETTINGS .....................................................34
3.9 CONFIGURING USER TARGETS ................................................................36
3.10 CONFIGURING THE SYSTEM DATE AND TIME ................................................37
3.11 CONFIGURING POWER DEVICES...............................................................38
3.11.1 Editing a Power Device ..........................................................39
3.11.2 Removing a Power Device ......................................................39
3.12 CONFIGURING POWER OUTLETS ..............................................................40
3.13 PERFORMING ADDITIONAL CONFIGURATION OPERATIONS.................................41
3.13.1 Installing an SSL Certificate ...................................................41
3.13.2 Upgrading Firmware ..............................................................42
3.13.3 Upgrading RICCs/ROCs ..........................................................43
3.13.4 Restoring Factory Settings .....................................................44
3.13.5 Backing Up and Restoring ......................................................45
3.14 RELOADING A PAGE.............................................................................46
3.15 SAVING CHANGES AND LOGGING OUT .......................................................46
4 CONDUCTING A REMOTE SESSION...................................................... 48
4.1 STARTING A REMOTE SESSION................................................................48
4.1.1 Remote Session Toolbar Buttons .............................................50
4.2 SHARING A REMOTE SESSION.................................................................51
4.2.1 Exclusive Session..................................................................51
4.3 DISPLAYING THE TOOLBAR.....................................................................52
4.4 SETTING THE SESSION PROFILE ..............................................................52
4.4.1 Full Screen Mode ..................................................................53
4.5 VERIFYING REMOTE PRESENCE SOLUTIONS INFORMATION ................................53
4.6 CHANGING THE VIDEO PERFORMANCE SETTINGS...........................................54
vi | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 7

Table of Contents
4.7 ADJUSTING THE VIDEO .........................................................................55
4.7.1 Refreshing the Video Image ...................................................55
4.7.2 Automatically Adjusting the Video Image .................................56
4.7.3 Manually Adjusting Video Settings ...........................................56
4.8 POWER MANAGING THE TARGET SERVERS...................................................58
4.9 MANAGING KEYBOARD SEQUENCES...........................................................58
4.9.1 Adding a Keyboard Sequence .................................................59
4.9.2 Recording a New Custom Key .................................................60
4.9.3 Editing a Key Sequence .........................................................61
4.9.4 Deleting Key Sequence(s) ......................................................61
4.10 SYNCHRONIZING MOUSE POINTERS ..........................................................62
4.10.1 Manually Synchronizing the Mouse ..........................................62
Selecting the Mouse Mode .............................................................................................. 64
Relative Mouse Position Mode ......................................................................................... 65
4.10.2 Aligning the Mouse Pointers....................................................67
4.10.3 Calibrating Mouse Pointers .....................................................67
4.11 SWITCHING TO A DIFFERENT SERVER/DEVICE..............................................67
4.12 DISCONNECTING THE REMOTE SESSION .....................................................68
5 MANAGING THE EVENTS LOG .............................................................. 69
5.1 VIEWING THE EVENTS LOG ....................................................................69
5.2 RELOADING THE EVENTS LOG .................................................................69
5.3 SAVING THE EVENTS LOG......................................................................70
5.4 CLEARING THE EVENT LOG.....................................................................70
6 TROUBLESHOOTING – RESTORING FACTORY SETTINGS ..................... 71
7 OPERATING THE SMART 216/232 IP SWITCHING SYSTEM LOCALLY .. 72
7.1 DISPLAYING THE OSD..........................................................................72
7.2 NAVIGATING THE OSD .........................................................................72
7.3 SELECTING A COMPUTER .......................................................................73
7.4 POWER MANAGING A SERVER .................................................................73
7.5 MOVING THE CONFIRMATION LABEL (F1) ...................................................74
7.6 TUNING (F5) ....................................................................................74
7.7 CONFIGURING THE OSD SETTINGS (F2)....................................................75
7.7.1 Changing the Network Parameters ..........................................75
Configuring the Device IP Address................................................................................... 75
Configuring AccessIT Centralized Management Settings ..................................................... 76
7.7.2 Changing the OSD Hotkey ......................................................76
7.7.3 Changing the Keyboard Language ...........................................77
7.7.4 Inputting and Updating DDC Information (F10).........................77
7.7.5 Saving Changes to Settings ....................................................77
User Guide | vii
Page 8

Table of Contents
8 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................. 78
9 VIDEO RESOLUTION AND REFRESH RATES ......................................... 80
viii | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 9

Table of Figures
Table of Figures
Figure 1 – Smart 216 IP Unit Front Panel................................................................. 14
Figure 2 – Smart 216 IP Unit Rear Panel.................................................................. 15
Figure 3 – Smart 232 IP Rear Panel ........................................................................ 15
Figure 4 – Bracket Positions ................................................................................... 17
Figure 5 – Bracket Connected for Rear Facing .......................................................... 17
Figure 6 – Smart 216/232 IP System Overview ........................................................ 18
Figure 7 – ROC PS/2 ............................................................................................. 18
Figure 8 – ROC USB .............................................................................................. 19
Figure 9 – ROC PS/2 Connections ........................................................................... 19
Figure 10 – ROC USB ............................................................................................ 20
Figure 11 – OSD Main Window ............................................................................... 23
Figure 12 – Settings Window.................................................................................. 23
Figure 13 – Web Page ........................................................................................... 24
Figure 14 – Logon Page ......................................................................................... 24
Figure 15 – Network Configuration – Device Tab ...................................................... 25
Figure 16 – Change Password Page......................................................................... 26
Figure 17 – Users Page ......................................................................................... 29
Figure 18 – Add User Page..................................................................................... 29
Figure 19 – Delete User Confirmation...................................................................... 30
Figure 20 – Edit User Page..................................................................................... 31
Figure 21 – KVM Switch Configuration Page for Smart 232 IP..................................... 32
Figure 22 – Serial Port Page................................................................................... 33
Figure 23 – Security Page ...................................................................................... 35
Figure 24 – User Targets Page ............................................................................... 37
Figure 25 – Date and Time Page ............................................................................. 38
Figure 26 – Power Devices Page ............................................................................. 38
Figure 27 – Add PDU Page ..................................................................................... 38
Figure 28 – Added Power Devices ........................................................................... 39
Figure 29 – Edit PDU Page ..................................................................................... 39
Figure 30 – Delete PDU Confirmation Page............................................................... 40
Figure 31 – Power Outlets Page .............................................................................. 40
Figure 32 – Assigning Servers to Power Outlets Page ................................................ 41
Figure 33 – SSL Certificate Page ............................................................................. 42
Figure 34 – Device Version Upgrade Page ................................................................ 43
Figure 35 – Reboot Confirmation Page..................................................................... 43
Figure 36 – RICCs/ROCs Upgrade Page ................................................................... 44
Figure 37 – Restore Factory Settings Page ............................................................... 45
Figure 38 – Backup/Restore Data Page.................................................................... 45
Figure 39 – Device Reboot Confirmation Message ..................................................... 46
Figure 40 – Save Succeeded Message ..................................................................... 47
User Guide | ix
Page 10

Table of Figures
Figure 41 – Device Rebooting Progress Box ............................................................. 47
Figure 42 – Logon Page after Rebooting .................................................................. 47
Figure 43 – Server Targets .................................................................................... 49
Figure 44 – Remote Session Page ........................................................................... 50
Figure 45 – Shared Remote Session ........................................................................ 51
Figure 46 – Session Profile Dialog Box..................................................................... 52
Figure 47 – Remote Presence Solutions Information ................................................. 54
Figure 48 – Performance Settings ........................................................................... 55
Figure 49 – Video Adjust Progress .......................................................................... 56
Figure 50 – Manual Video Adjustments Controls ....................................................... 57
Figure 51 – Power Menu ........................................................................................ 58
Figure 52 – Special Key Manager ............................................................................ 59
Figure 53 – Add a Predefined Key Dialog Box ........................................................... 60
Figure 54 – Record Macro Box ................................................................................ 61
Figure 55 – Delete Key(s) Confirmation Box............................................................. 62
Figure 56 – Relative Mouse Settings ....................................................................... 63
Figure 57 – Absolute Mouse Settings....................................................................... 64
Figure 58 – Windows 7 Mouse Properties ................................................................. 65
Figure 59 – Mouse Emulation Box ........................................................................... 66
Figure 60 – Events Log.......................................................................................... 69
Figure 61 – Clear Events Confirmation Window ........................................................ 70
Figure 62 – OSD Main Window ............................................................................... 72
Figure 63 – Power Control Dialog Box ..................................................................... 73
Figure 64 – Power Prompt ..................................................................................... 73
Figure 65 – Image Tuning Label ............................................................................. 74
Figure 66 – OSD Settings Window .......................................................................... 75
x | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 11

Introduction
Product Overview
1 Introduction
Congratulations on adding Smart 216/232 IP to your remote access tools.
This document provides installation and operation instructions for Minicom’s Smart
216/232 IP. It is intended for system administrators and network managers, and
assumes that readers have a general understanding of networks, hardware, and
software.
Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 of this guide describe how to configure and operate the
Smart 216/232 IP system remotely over IP. Chapter 7 explains how to operate the
Smart 216/232 IP switching system locally through the On Screen Display (OSD).
1.1 Product Overview
The Smart 216/232 IP system extends your KVM (keyboard, video, and mouse) from
any computer or server over TCP/IP via LAN, WAN, or Internet connection. This
enables two remote users to simultaneously control, monitor, and manage up to
16/32 remote (PS/2, USB) servers from wherever they are, inside or outside the
organization. Simultaneously, one local user can also access the servers.
Simultaneously, two more remote users can operate serial devices, such as routers or
managed network switches. Alternatively, one more user can use a PDU.
Smart 216/232 IP is a cost-effective hardware solution, for secure, remote KVM
access and control of 16/32 computers/servers from the BIOS level – independent of
the OS.
Smart 216/232 IP is based on Minicom’s innovative ROC technology, in which each
computer/server is directly connected to the switch via ROC dongles using only a
standard CAT5 cable at a distance of up to 30 m / 100 ft in a star configuration. No
external power is needed at the remote ROC.
The Smart 216 IP and Smart 232 IP are functionally the same. The Smart 216 IP has
16 Server ports; the Smart 232 IP has 32 Server ports.
1.1.1 Features and Benefits
Smart 216/232 IP has the following features and benefits:
BIOS level control to any server’s brand and model, regardless of the server
condition and network connectivity. Covers the entire spectrum of crash
scenarios.
Compatible with all major operating systems. Supports many hardware and
software configurations for the remote client and the Target server computers, as
well as the KVM switch in use.
Web-based control – Browser based control to a target server from any location,
via a secured standard IP connection.
User Guide | 11
Page 12

Introduction
Terminology
Security – Supports the highest security standards for encryption (256-bit AES
and HTTPS) and authentication for remote user and advanced OSD management,
with multi-layer security for the local user.
Centralized Management – Can be controlled by Minicom’s Centralized Management
system – AccessIT, for centralized over-IP management of distributed data center
locations.
1.2 Terminology
The following table describes terms used in this guide.
Term Definition
Target server
Client computer
Remote session
The computer/server that is accessed remotely via Smart 216/232 IP
The PC running a remote Smart 216/232 IP session
The process of accessing and controlling target servers connected to Smart 216/232 IP
from a user workstation
1.3 Compatibility
Smart 216/232 IP is compatible with:
PS/2, SUN, and USB computers/servers
VGA, SVGA, and XGA monitors
Windows, Linux, UNIX, and other major operating systems
1.4 Client Computer Operating System
The client computer operating system must be one of the following:
Windows 2000 or later, with Firefox 3 or Internet Explorer 32-bit 7.0 or later
version
Linux with Firefox 3; 128-bit encryption support is required
1.5 Technical Precautions
This equipment generates radio frequency energy, and if not installed in accordance
with the manufacturer’s instructions, may cause radio frequency interference.
This equipment complies with Part 15, Subpart J of the FCC rules for a Class A
computing device. This equipment also complies with the Class A limits for radio noise
emission from digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulation of the
Canadian Department of Communications. These above rules are designed to provide
reasonable protection against such interference when operating the equipment in a
commercial environment. If operation of this equipment in a residential area causes
12 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 13

Introduction
Safety
radio frequency interference, the user, and not Minicom Advanced Systems Limited,
will be responsible.
Changes or modifications made to this equipment not expressly approved by Minicom
Advanced Systems Limited could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
1.6 Safety
The device must only be opened by an authorized Minicom technician. Disconnect the
device from the power source and all cables from the device before service operation!
1.7 Trademarks
All trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1.8 WEEE Compliance
This section provides WEEE Information for Minicom Customers and Recyclers.
Under the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive and
implementing regulations, when customers buy new electrical and electronic
equipment from Minicom, they are entitled to:
Send old equipment for recycling on a one-for-one, like-for-like basis (this varies
depending on the country)
Send back the new equipment for recycling when it ultimately becomes waste
Instructions for both customers and recyclers / treatment facilities wishing to obtain
disassembly information are provided in our website www.minicom.com.
User Guide | 13
Page 14

Installation
Overview
2 Installation
2.1 Overview
Install the Smart 216/232 IP system as follows:
1. Remove the Smart 216/232 IP system from the package, and check that all
components are present and in good working condition.
2. Mount the Smart 216/232 IP unit in a rack.
3. Make all hardware connections between the power source, Smart 216/232 IP,
services, network, and KVM console.
4. Power on the Smart 216/232 IP unit.
2.2 System Components
Before installing the Smart 216/232 IP system, verify that you have all the
components on the following list, as well as any other items required for installation.
The Smart 216/232 IP system consists of:
One Smart 216/232 IP (p/n 1SU70036) or one Smart 232 IP (p/n 1SU70037)
One RS232 Download cable (p/n 5CB40419)
ROCS - PS/2, USB (ordered separately)
CAT5 cables (1.5 m provided)
A rack mounting kit (p/n 5AC20247)
2.2.1 The Smart 216/232 IP Unit
The Smart 216/232 IP Unit front panel is illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1 – Smart 216 IP Unit Front Panel
The following table describes the functionality of the LEDS on the front panel of the
Smart 216/232 IP.
14 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 15

LED Functionality
Installation
System Components
Power LED
Remote 1,
Remote 2 LEDs
Link
Indicates the state of the Smart 216/232 IP unit: Green indicates that the unit is powered
on; Red indicates that the unit is powered off.
Illuminate to indicate that a remote session is active.
Illuminates to indicate that the unit is connected to the network.
The Smart 216 IP unit rear panel is illustrated in Figure 2; it has 16 server ports. The
Smart 232 IP unit rear panel is illustrated in Figure 3; it has 32 server ports.
Figure 2 – Smart 216 IP Unit Rear Panel
The following connector table describes the functionality of the ports on the rear
panel of the Smart 216/232.
Port Functionality
Console KVM
Serial 1
Serial 2
Flash
For connecting a keyboard, video, and mouse to operate the Smart 216/232 IP locally;
optional.
For connecting the Smart 216/232 IP unit to any serial manageable devices, such as power
management units and routers, via the RS232 cable.
Note: Minicom’s Serial Remote PowerSwitch must be connected to Serial 1.
For connecting the Smart 216/232 IP unit to any Serial device.
For updating firmware of the analogue part of the Smart 216/232 IP system - OSD,
Switch, RICCs, and ROCs.
Figure 3 – Smart 232 IP Rear Panel
User Guide | 15
Page 16

Installation
Pre-Installation Guidelines
Port Functionality
LAN
Server ports For connecting to the servers via ROCs.
For connecting to the 10/100 Mbit Ethernet. The LED illuminates yellow when the unit is
connected to LAN; green when a remote session is in progress.
2.3 Pre-Installation Guidelines
Place cables away from fluorescent lights, air conditioners, and machines that are
likely to generate electrical noise.
Place the Smart 216/232 IP unit on a flat, clean and dry surface.
The Smart 216/232 IP unit is not intended for connection to exposed outdoor
lines.
Ensure that the maximum distance between each computer and the Smart
216/232 IP unit, does not exceed 30 m / 100 ft for ROCs.
2.4 Rack Mounting the Smart 216/232 IP Unit
2.4.1 Rack Mounting Safety Considerations
When mounting Smart 216/232 IP onto a rack, avoid the following conditions:
Elevated operating ambient temperature – The operating ambient temperature of
the rack environment may be greater than the room ambient temperature.
Therefore, take special care when installing the unit in a closed or multi-unit rack
assembly that the environment is compatible with the maximum rated ambient
temperature.
Reduced airflow – Install the equipment in a rack in such a way that the amount of
airflow required for safe operation is not compromised. Leave a gap of at least 5
cm / 2” on each side of Smart 216/232 IP.
Uneven mechanical loading – Uneven loading can cause damage to the equipment
or personal injury. Mount the equipment in the rack in such a way that a
hazardous condition does not result due to uneven mechanical loading.
Circuit overloading – When connecting the equipment to the supply circuit, make
sure that the total power of all the components does not exceed the circuit
capabilities. Overloading of circuits can affect over-current protection and supply
wiring, potentially resulting in fire and shock hazards.
Unreliable earthing – Maintain reliable earthing of rack-mounted equipment. Pay
attention to supply connections other than direct connections to the branch circuit
(for example, use of power strips).
16 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 17
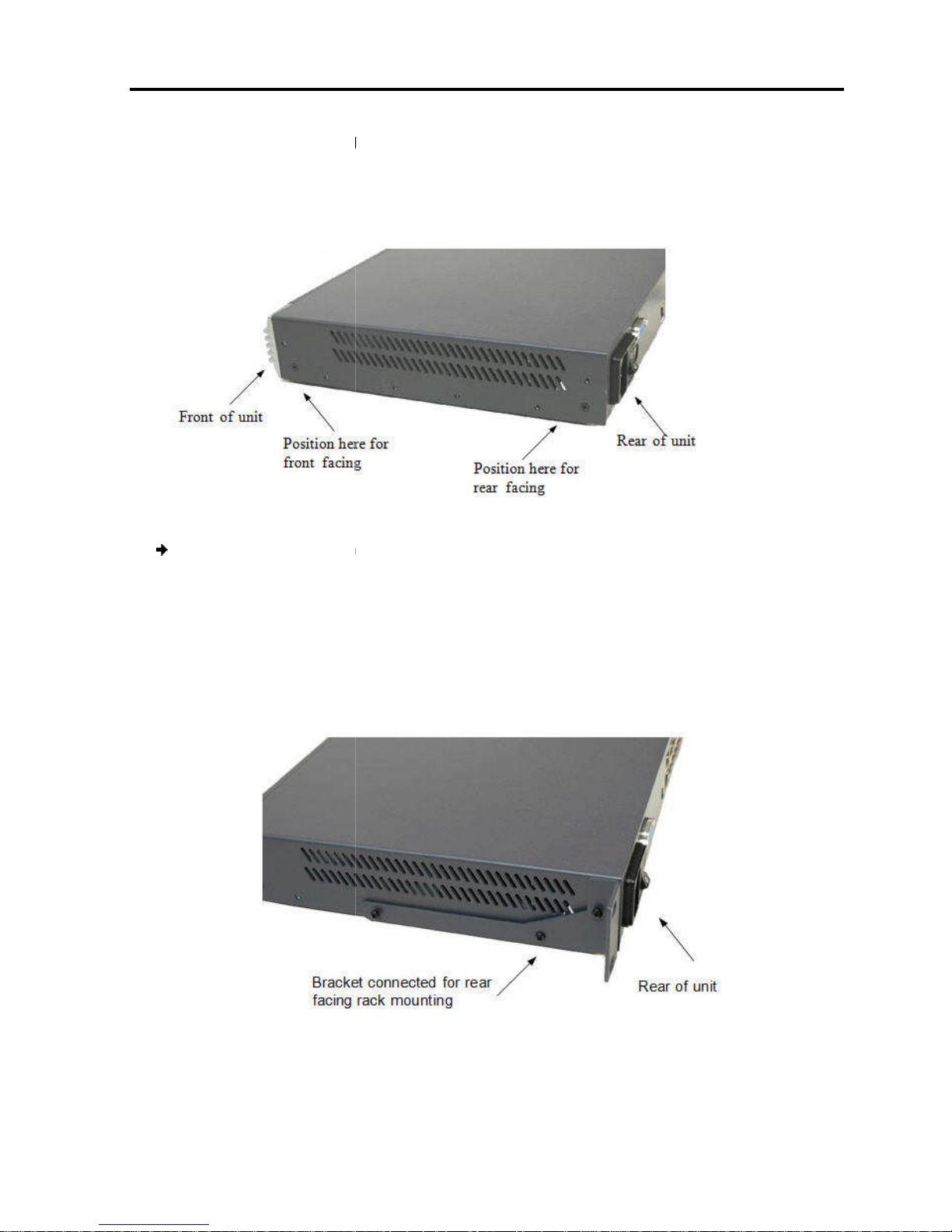
2.4.2
Mounting the Unit
Smart
The brackets can be placed in
Smart
on the unit in either of the following ways:
owards the front of the unit so that the unit can be mounted
owards the rear of the unit so that the unit can be mounted rear
illustrates the bracket connected for rear facing.
Screw the bracket to the Smart
Figure
216/232
the rack with screws, according to the
Mounting the Smart 216/232 IP Unit
, using the supplied rack
, as illustrated in
front facing
screws provided
nit into the server rack by connecting the bracket to
rack manufacturer’s instructions.
Installation
Rack
You can connect the
mounting kit.
the following figure.
To rack mount the
1. Place the brackets
T
216/232 IP unit to a server rack
two possible positions
Figure 4 – Bracket Positions
216/232 IP unit:
T
Figure 5
2.
3. Install the Smart
216/232 IP unit using the
5 – Bracket Connected for Rear Facing
IP
facing
.
User Guide | 17
Page 18

Installation
Connecting the System
2.5 Connecting the System
Figure 6 illustrates the Smart 216/232 IP system overview.
Figure 6 – Smart 216/232 IP System Overview
2.6 Connecting to the Servers
Each computer/server is directly connected to the Smart 216/232 IP via an
appropriate ROC using a CAT5 cable in star configuration. No external power is
needed at the remote ROCs. The ROCs draw their power from the computer’s
keyboard port (ROC PS/2, SUN) or from the USB port (ROC USB). Figure 7 and Figure
8 illustrate the ROC PS/2 and ROC USB.
18 | Smart 216/232 IP
Figure 7 – ROC PS/2
Page 19

2.6.1
Connecting a ROC PS/2
illustrates the
You can connect the ROC PS/2 to a powered on computer
in order
ROC PS/2
Connect the Mouse connector to the computer’s Mouse port.
Connect the Keyboard connector to the computer’s Key
Connect the Screen connector to the computer’s Video
Connecting
, by performing the steps of
Installation
to the Servers
Figure 8 – ROC USB
The following figure
ROC PS/2 connections.
Figure 9 – ROC PS/2 Connections
the following procedure
To connect the
.
to a powered on computer:
1.
2.
3.
board port.
card.
User Guide | 19
Page 20
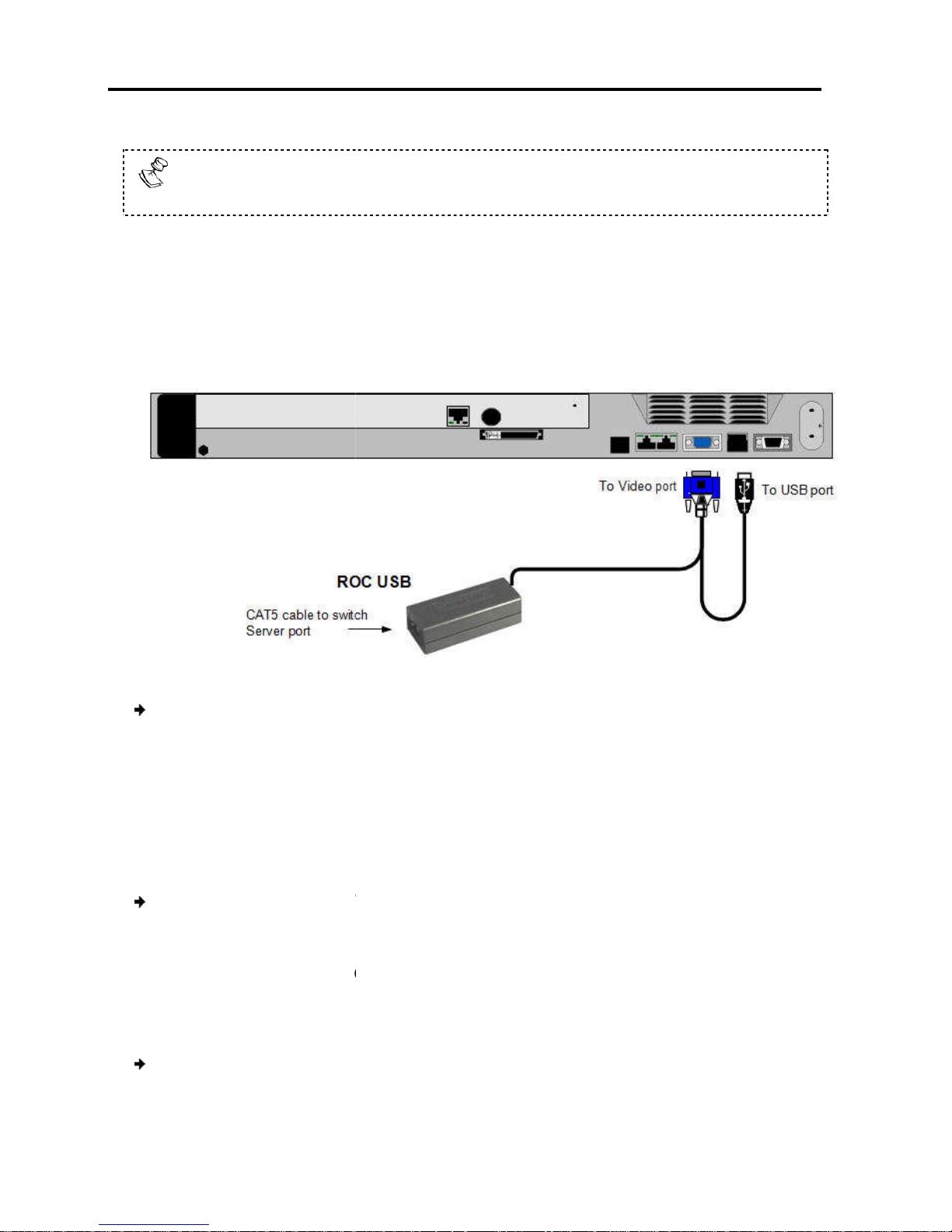
Installation
Failure to connect in the above order while the server is running may lead to
the mouse malfunctioning until the server is rebooted.
ROC
ROC USB supports Windows 98 SE and later, MAC, SUN
The following figure illustrates the R
Connect the Screen connector to the computer’s video
connector to the computer’s
Connecting to the Network
216
216/232
onnect the network cable to the LAN port of
Connecting the CAT5
the following procedure for each computer to which you want to connect
CAT5 cables
t one connector to the ROC
and SGI, and all modern
216/232
Connecting to the Network
2.6.2 Connecting a
The
Linux distributions.
To connect the ROC USB:
USB
,
OC USB and its connections.
Figure 10 – ROC USB
1.
2. Connect the USB
2.7
Before powering on Smart
network.
To connect the Smart
1. C
2.8
Perform
CAT5 cables.
To connect the
1. Connec
20 | Smart 216/232 IP
card.
USB port
/232 IP, you can connect the Smart
IP to the network:
the Smart 216/232 IP.
.
Cables
:
RJ45 port.
IP to the
Page 21

her connector to one of the Smart
Connecting the
You can connect a KVM console to Smart
a KVM console to Smart
Connect the monitor’s connector to the Smart
Connect the keyboard’s
USB
Connecting the Power Supply
the power supply
Using the power cord provided, connect
grounding connection.
Only use the power cord supplied with the unit.
216/232
Connecting
omputer ports
operate the system
IP’s Monitor port.
USB
USB
IP to a socket outlet with a
Installation
the KVM Console
2. Connect the ot
2.9
locally.
To connect
1.
2.
port.
3. Connect the mouse’s
2.10
To connect
1.
216/232 IP c
KVM Console
216/232 IP, in order to
216/232 IP:
216/232
USB connector to the Smart 216/232 IP’s
connector to the Smart 216/232 IP’s
to Smart 216/232 IP:
Smart 216/232
.
Keyboard
Mouse port.
2. Switch on Smart
IP.
User Guide | 21
Page 22

Configuring the Network
Configuring the Network
After the system has been installed and all connections have been made, you must
216/232
216/232
’s IP address
Centralized Management
Add, edit, remove, and block system Users
Configure the KVM switch settings
Configure the Serial port settings
Configure the security settings
Configure the user targets.
date
Configure power devices.
You can also perform the following additional operations, as required:
.
Back up and restore configuration data.
Up Process
IP
u
IP
You can identify the IP address from the OSD at the local position. Also, where there
set the IP address locally via the OSD
set the IP address locally via the OSD
From the local keyboard, press
app
network settings, which includes configuring:
r
The DHCP server
a valid IP address, gateway address, and subnet mask.
, as described in the
Boot-Up Process
3
configure the Smart
1. Configure Smart
Device ID settings
Smart 216/232 IP
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7. Configure the system
8.
9. Configure power outlets.
1. Install an SSL certificate
2. Upgrade firmware.
IP system as follows:
IP’s
.
.
.
.
and time.
3. Upgrade RICCs/ROCs.
4. Restore factory settings.
5.
3.1 Boot-
By default, Smart 216/232
DHCP (Dynamic Host Config
assigns the Smart 216/232
is no DHCP server, you can
following procedure.
To
1.
The OSD Main window
22 | Smart 216/232 IP
boots with an automatically assigned IP add
ration Protocol) server on the network.
:
Shift twice.
ears.
ess from a
Page 23

Figure 11 – OSD Main Window
2. Press F2.
The Settings window appears see Figure 12.
Configuring the Network
Logging Onto the Web Configuration Interface
Figure 12 – Settings Window
3. In the Settings window, navigate downwards using the Tab key. At the bottom of
the window, press Tab to go to the top of the window. Change settings by typing in
the selected area or by pressing the spacebar – whichever is relevant.
4. If DHCP is disabled, in the Settings window, type the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and
Gateway, as given by your Network Administrator.
Otherwise, if a DHCP server is active on the same network to which Smart
216/232 IP is connected, DHCP provides automatic IP assignment.
5. Once the IP address is satisfactory, proceed to log onto the Web interface to
complete the configuration.
3.2 Logging Onto the Web Configuration
Interface
You can complete the initial setup of the Smart 216/232 IP system via the Web
configuration interface.
Only one Administrator at a time can log onto the Web configuration interface. An idle
timeout of 30 minutes terminates the session.
User Guide | 23
Page 24

Configuring the Network
Onto the Web Configuration Interface
Before logging on the first time, verify that you have the latest Java installed on your
computer. If not, you can download and install Java from:
http://www.java.com/en/download/index.jsp
log into the Web interface
Open your Web browser (Internet Explorer
Enter
Java installs. After installation has completed, the log
, type the default Administrator name
The Targets page opens, displaying all your available target servers
In the menu in the left pane, click
https://IP
n page appears.
, type
(see
Logging
To
1.
2. Type the Smart 216/232
address/, and press
The Web page appears.
3. Click Log On.
:
7.0 / Firefox 3 or later).
IP system IP address http://IP address/ or
.
Figure 13 – Web Page
o
Figure 14 – Logon Page
4. In User
admin and in Password
(both lower case).
5. Click Enter.
43).
6.
24 | Smart 216/232 IP
.
access
Figure
Page 25

Configuring the Network
Logging Onto the Web Configuration Interface
The Network configuration page appears with the Device tab open.
Figure 15 – Network Configuration – Device Tab
From the Configuration menu, you can configure the network, Users, Switch
Configuration, Serial Port, Security, User Targets, Date & Time, Power Outlets,
and Power Devices settings. After making all configuration changes, you must click
the button in the toolbar for the changes to go into effect.
3.2.1 Web Configuration Interface Tabs
The following table summarizes the Web configuration interface tabs.
Tab Description
Device
Users
Switch Configuration
Serial Port
Security
User Targets
Date & Time
For configuration of the device settings, IP address, and centralized management
For adding, editing, deleting, and blocking system Users
For configuration of the KVM switch settings
For configuration of the Serial port settings
For configuration of the security settings
For configuration of the access rights of each user to target servers
For configuring the system date and time
User Guide | 25
Page 26

Configuring the Network
Description
For matching a server to each power outlet of all power devices defined in the
For configuring the details of all power devices in the system
Web Configuration Toolbar Buttons
The following table describes the functionality of the Web configuration toolbar
Functionality
aves the configuration
eloads the device settings into the configuration page parameter settings
eboots the device
pgrades the device firmware
theRestores the device with factory settings
Backs up or restores
nstalls the SSL certificate onto the device
Changing your Password
You can change your password, according to the set password policy.
In the menu in the left pane, click
The Change Password page is displayed.
Figure
Changing your Password
Tab
Power Outlets
Power Devices
3.2.2
buttons.
Button
system
S
R
R
U
Upgrades
I
3.3
To change the password:
1.
changes
RICC/ROC firmware
configuration data to/from a file
.
16 – Change Password Page
26 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 27

type a new password, according to the password naming convention
retype the new password.
The new password is saved in the system.
Configuring the
configuration page (see
Centralized Management
Consult your Network Administrator for the network settings.
Configuring Device ID Settings
n a name to
efault device name consists of the letter ‘D’ followed by the 6
printed
P server is published in the DNS server, you
using the device name, as follows:
You can select any TCP port
Centralized Management, the port number
Firewall or router security access list must enable inbound communication
through the selected TCP port for the
default
lient computer access from a secured LAN, the selected ports should be
open for outbound communication.
type a name for
type the number of the port (from 800 to 65535)
the
When a DHCP server is active on the same network to which
can provide automatic I
Configuring
Use it next time you log on.
), you can configure the following
, and select a TCP port.
digit device
on the silver label on the underside of the
connect to the
https://DeviceName
800 to 65535. When managed by
management
’s IP address. (Default
216/232
However, best practices
the Network
2. In Password,
3. In Confirm Password,
4. Click .
3.4
On the network
Device ID
Device IP address
3.4.1
You can assig
Network Settings
Figure 15
the Smart 216/232 IP device
Configuring
the Network Settings
s.
:
The d
number (D.N.), which is
216/232 IP box.
If the DHC
216/232 IP system
interface, if needed.
TCP port is 900;
For c
To configure Device ID
1. In Device Name,
2. In TCP Port,
from port #
Web interface TCP port is 443.)
settings:
can be changed from the
Smart 216/232 IP
Smart 216/232 IP.
can
Smart
Smart
.
.
3.4.2 Configuring
connected, the DHCP
Device IP Address
P assignment.
Smart
IP is
User Guide | 27
Page 28

Configuring the Network
recommend using MAC address reservations in the DHCP server to ensure that the IP
216/232
your Network Administrator regarding the use of the DHCP
access to the server
device name will appear on the DHCP server’s interface, making it easy to
the device IP address
address
enable a DHCP server that is active on the same network to which
is connected, to provide automatic IP assignment
Select manual IP address assignment
type the
, provided by your Network Administrator
Configuring Centralized Management Settings
Minicom’s Centralized Management IP
servers and network devices,
environment. The Centralized Management systems combine
access with modern IT standards and requirements. They are the most
nsive remote server maintenance solutions available in the market today.
Centralized Management settings
Enable Centralized Management
be remotely managed by a Centralized Management system
When managed by Centralized Management, only Network Configuration is
available from the Smart
as Device Upgrade, Factory Restore, and SSL Certificate are disabled and are
managed from Centralized Management.
Manager Auto Discovery
automatically detect
, type the static IP address of the Centralized Management
Although not required, it is
Centralized Management Manager
Smart
checkbox to
Smart
checkbox to disable
Default Gateway
secure control of
power and user administration in the data center
216/232
IP configuration page. All other settings, such
the Centralized Management
on the same
Manager IP Address
as the
Configuring the Network Settings
address of the Smart
Consult
If you have
locate.
To configure
Select automatic IP
IP
the DHCP, and then
LAN 1
3.4.3
IP will not be changed.
, your configured (or default)
, do one of the following:
assignment – Select the Enable DHCP
.
– Clear the Enable DHCP
IP Address, Subnet Mask, and
.
-based systems ensure
and
out-of-band
.
216/232 IP
216/232
for
KVM via IP
comprehe
To configure
1. Select the
2. Select the
system to
network segment.
OR
In Manager IP Address
Manager.
if the Smart 216/232
:
checkbox to enable Smart
.
216/232
checkbox to cause
Smart 216/232 IP, if they both reside
recommended to type the
IP resides on the same network segment
.
IP to
even
28 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 29

3.5
Configuring User Settings
add, edit, remove
There are two levels of user
has unrestricted access to all windows and settings, and can
change the name and password of all users
and
settings and power cycle
From the configuration menu, select
The Users page opens and displays the existing
The Add User page appears.
Configuring
Configuring
ervers, but cannot use advanced mouse
guration interface
the Network
User Settings
An Administrator can
Administrator –
User – can access
3.5.1 Adding a User
To add a User:
1.
, and block Users.
access:
control target s
; cannot access the Web confi
Users.
Users.
Figure 17 – Users Page
2. Click the Add button.
Figure 18 – Add User Page
User Guide | 29
Page 30

Configuring the Network
Password
cannot include the user name, even if other characters are
The “special” characters
assword
on page
, retype the password.
dropdown menu
the list of
You can delete one or multiple Users at a time from the system.
You cannot delete an Administrator who is logged onto the system.
Figure
by selecting the first User in the
The Delete confirmation page appears.
Figure
deleted from the
alphanumeric
cannot be used for either the user name
assword
parameters depend on the security level chosen
Administrator
group
button, and then
Configuring User Settings
3. Type a User Name and
characters long and
added.
or password.
The User Name and P
(see Section 3.8
4. In Confirm Password
5. In the Permission
User.
6. Click OK.
The User is added to
3.5.2 Deleting User(s)
. The password must be at least six
&, <, >, and ”
34).
, select the permission type:
Users.
or
To delete a User:
1. In the Users page (see
selecting the last User.
2. Click the Delete button.
3. Click Yes.
The User(s) are
17), select User(s) to delete. Select a
group, pressing the Shift
19 – Delete User Confirmation
system.
of Users
30 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 31

3.5.3
Blocking a User
An alternative to deleting a
and password is stored, but the
(see
Information
of the following User
information
(see
The Edit User page appears, with the User’s information in the parameters.
Permission
To change the password, c
parameter opens. In the upper textbox, type the new password; in
the lower textbox, confirm the new password.
You cannot change the password of an
User page opens with the user information changed accordingly
Configuring
Configuring
ser. This means that the
select
Access
button
currently logged on
the Network
User Settings
To block a User:
1. In the Add User page
checkbox.
3.5.4 Editing User
You can change any
Password.
To edit User
1. In the Users page
User is blocking a U
User is unable to access the system.
Figure 18), in the Access parameter,
parameters: Permission,
:
Figure 17), select a User and click the Edit
User’s name
the Block
, and
.
Figure 20 – Edit User Page
2. Change the
3.
The Password
to the system.
4. Click OK.
The
and/or Access as required.
lick .
Administrator who is
.
User Guide | 31
Page 32

Configuring the Network
Configuring the KVM Switch
When a KVM switch is connected to the
:The names of the servers connected to the KVM switch
give the servers connected to Smart
accessing the system can easily identify the servers.
The number of POCs attached to those servers that are configured with POCs
configure a KVM switch
From the configuration menu, select
The KVM Switch Configuration
KVM
system, configure the
It is recommended to
IP unique names, so that users
Configuring the KVM Switch
3.6
following switch parameters
attached to them
Smart 216/232 IP
–
216/232
1.
To
:
Switch Configuration.
page appears.
Server
name
Figure 21 –
32 | Smart 216/232 IP
Switch Configuration Page for Smart 232 IP
Page 33

e connected to the selected KVM switch,
The number of servers that appear corresponds to the
16 for Smart
The following information is displayed for each potential server:
The server number
hange the name of a connected
Configuring the Serial
When you have Serial device
of each device
If you have a Minicom Serial Remote
serial port settings
From the configuration menu, select
appears.
Configuring
Configuring
the Serial Port Settings
appear in the
number of ports in
server
you must configure the
Power Switch, it must be connected to Serial
the Network
The servers that ar
section.
the KVM switch –
The server name
2. To c
type a new name.
3.7
Serial Port settings
Port 1.
To configure the
1.
216 IP; 32 for Smart 232 IP.
server, highlight the current
Port Settings
(s) connected to the system,
.
:
Serial Port.
Servers
name, and
The Serial Port page
Figure 22 – Serial Port Page
User Guide | 33
Page 34

Configuring the Network
Configuring the Security Settings
2. For each serial device connected, type a Device Name and choose the correct device
parameters.
3.8 Configuring the Security Settings
This section describes how to configure the security features, such as Account
Blocking, Password Policy, Idle Timeout, and Serial Terminal Policy.
For local and remote users, you have the option of a standard or high security level of
password. The following table describes both these options.
Standard Security Policy High Security Policy
At least six characters At least eight characters; must include at least one digit, one
uppercase letter, and one of the following “special” characters: !, @, #,
$, %, ^, *, (), _, -, +, =, [], ’, :, ;, ?, /, or {}
Must not include the user name Must not include the user name
For a local user, access to the OSD can be password enabled or disabled (default),
with the option of a standard or high security level of password, as explained above.
User access permissions are the same regardless of whether access is done
locally or remotely.
Serial Terminal Policy
The Smart 216/232 IP device enables you to control serial devices by connecting to
them via the device’s Web interface, as follows:
Logging into the Smart 216/232 IP Web interface
Clicking a serial port
Connecting
This way, the Smart 216/232 IP internal SSH client is opened and used for the
session.
Alternatively, you can bypass the Web interface and connect directly to the serial
device itself. To do so, the Smart 216/232 IP device should be configured to “Enable
direct SSH connection”, which will redirect all serial communication messages to/from
the connected device via a dedicated TCP port.
This will enable you to use your preferred SSH client to communicate directly to the
serial device via the specified TCP port, opening and closing sessions autonomously
without the need for a Web interface.
The default TCP ports used to operate Serial connections 1 and 2 are TCP ports 4001
and 4002 respectively.
34 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 35

when “Enable direct SSH connection” is selected
to the Serial device, by
followed by the TCP port number in your SSH client.
in to the Smart 216/232 IP SSH shell with the user name and password
Smart 216/232 IP.
Restart the Smart 216/232 IP device after adding Telnet permissions to the
users in order to enable login over SSH connection.
These settings are customizable, enabling you to choose the TCP port used for that
already taken by another service on your network. You can
operate the serial connection by using any SSH client, such as PuTTY and SecureCRT.
configure the security settings
From the configuration menu, select
appears.
ing
e
username or password
Configuring
ddress of the Smart 216/232 IP,
in with a wrong
attempts within
the Network
Hence,
1. Connect
2. Log
configured in the
purpose, if that port is
To
1.
The Security page
typing the IP a
:
Security.
:
Configuring
the Security Settings
Figure 23 – Security Page
2. In the Account Block
In Block after, typ
section:
the number of allowable attempts to log
in a time period specified in
forced time lock.
, prior to a
User Guide | 35
Page 36

Configuring the Network
select
or a total block
High security password policy
password policy; clear the checkbox for the standard security policy to apply.
SD password
. By default, p
, select the timeout inactivity period after whi
system. Select
use your preferred SSH client
direct SSH Connection
Serial 1 TCP port
, respectively.
Configuring User Targets
By default, administrators are allowed access to
define the access rights of each user separately.
Perform the following procedure for each User.
From the configuration menu, select
appears.
to block the account for a specified period of
checkbox to enable the high security
checkbox, to require a password for local user
ch the user is
communicate directly to the serial device via
ports
all servers. For other users, you must
Configuring User Targets
In Block account,
time, or forever f
3. Select the
4. Select the Enable O
access to the OSD
5. In Disconnect after
disconnected from the
6. To
the specified TCP ports:
1. Select the Enable
2. Select
4001 and 4002
3.9
for period
.
assword is disabled.
No Timeout to disable timeout.
to
checkbox.
and Serial 2 TCP port values. Their default
are
To configure User targets:
1.
The User Targets page
User Targets.
36 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 37

dropdown menu, select a
Select the checkboxes of all the Target servers that the User can access (according
to the User’s access permissions).
r
Configuring the System Date and Time
This section describes how to configure the
and date are used when recording log events (see
configure the date and time
From the configuration menu, select
page
Configuring
Configuring
the System Date and Time
r
system date and time. The system time
the Network
2. From the User
3.
To select all Target se
3.10
To
1.
The Date and Time
Figure 24 – User Targets Page
User.
vers, click Select All Targets.
Chapter 5).
:
Date & Time.
appears.
User Guide | 37
Page 38

Configuring the Network
Figure
, type the current date:
, type the current time:
Configuring Power Devices
This section describes how to
These details include the PDU
device
From the configuration menu, select
Figure
The Add PDU page opens.
a meaningful name for the PDU
select the PDU type
configure the details of all power devices in the system.
name, type, and IP address.
Configuring Power Devices
25 – Date and Time Page
2. In Date
3. In Time
3.11
To configure a power
1.
The Power Devices page
2. Click the Add button.
Day, Month, and Year.
Hour, Minute, and Second.
(power device)
:
Power Devices.
appears.
26 – Power Devices Page
Figure 27 – Add PDU Page
3. In PDU Name, type
4. In Type,
38 | Smart 216/232 IP
.
.
Page 39

The number of outlets in the device is displayed in
5. In IP
, type the IP address of the PDU.
The PDU is added to the Power Devices page.
Editing a Power Device
You can modify the information of any defined power device.
modify power device details
In the Power Devices page, select a power device, and click the
appears.
pe new values for the
The Power Devices page opens with the modified details.
Removing a Power Device
You can remove a power device that no longer exists in the system.
device
In the Power Devices page, select a power device, and click the
Delete PDU confirmation page
Configuring
Configuring
Edit
address, as required.
Delete
6. Click OK.
3.11.1
the Network
Power Devices
Outlets.
Figure 28 – Added Power Devices
To
1.
The Edit PDU page
2. Select/ty
3. Click OK.
:
button.
Figure 29 – Edit PDU Page
PDU Name, Type, and/or IP
3.11.2
To delete a power
1.
The
:
appears.
button.
User Guide | 39
Page 40

Configuring the Network
Figure
The Power Devices page opens
Configuring Power Outlets
a server to each power outlet of a power device defined in the
When you want to power manage the
you need to assign multiple outlets to the same KVM port.
Perform the following procedure for each power device defined in the system.
configure the power outlets
From the configuration menu, select
appears.
Figure
, select the PDU for which you want to configure the power
and Server Name dropdown menus
.
; the deleted PDU does not appear on the page.
servers with double or more power supplies,
outlets.
s
.
Configuring Power Outlets
2. Click Yes.
3.12
You must match
system.
30 – Delete PDU Confirmation Page
To
1.
The Power Outlets page
2. In Name
The number of outlets
type of the selected PDU
:
Power Outlets.
31 – Power Outlets Page
correspond
to the
40 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 41

323.For each Outlet, select
Performing Additional Configuration Operations
You can perform the following additional operations on
Install an SSL certificate
tore factory settings
Back up and restore data.
Installing an SSL Certificate
install an SSL Certificate
install an SSL Certificate
page
Configuring
Performing
Additional Configuration Operations
of the server
, to ensure secure transactions between the Web
the Network
Figure
connected to it.
3.13
Upgrade firmware.
Upgrade RICCs/ROCs.
Res
3.13.1
You can
servers and browsers.
To
– Assigning Servers to Power Outlets Page
the Server Name from the dropdown list
Smart 216/232
.
.
:
IP:
1. In the toolbar, select
The SSL Certificate
appears.
.
User Guide | 41
Page 42

Configuring the Network
Additional Configuration Operations
Figure
, browse to locate the
locate the
ype the password required to upload the Private Key file.
Private Key file is generated with a
The SSL Certificate is installed.
Save the changes and restart the system,
Upgrading Firmware
216/232
Download the firmware from Minicom’s website at:
http://www.minicom.com/phandlh.htm.
Save the firmware file on the client computer.
Device Version Upgrade
button,
firmware to take advantage of new features.
firmware
Performing
33 – SSL Certificate Page
2. In Certificate file
3. In Private key file,
4. In Key password, t
Each
5. Click Install.
6.
the button.
3.13.2
You can upgrade the Smart
To upgrade firmware:
1.
2.
Cer file.
private key file in Microsoft pvk format.
unique password.
by clicking the
IP
and then
3. In the toolbar, select
The
version on the device.
42 | Smart 216/232 IP
page appears, displaying the current
.
Page 43

Figure
Version to upgrade with
Verify the current and uploaded version of the firmware.
completion, on the toolbar, click
A confirmation box appears
Figure
The unit reboots. After about 30 seconds, the Login page appears.
Depending on the type of firmware upgrade, the following settings ma
erased: User settings, KVM switch settings, mouse and video adjustments
The network settings remain intact.
to the firmware release notes.
Upgrading RICCs/ROCs
RICC/ROC
Download the firmware from
http://www.minicom.com/.
Save the firmware file on the client computer.
Configuring
Performing
Additional Configuration Operations
, browse to locate and upload the firmware file
For more information
firmware to take advantage of new features.
Minicom’s website at:
34 – Device Version Upgrade Page
the Network
4. In
5.
6. Click Start Upgrade.
The upgrade starts.
7. On upgrade
8. Click Yes.
.
.
.
35 – Reboot Confirmation Page
RS232 settings.
3.13.3
You can upgrade the
To upgrade firmware:
1.
2.
the Support section of
y be
, and
, refer
User Guide | 43
Page 44

Configuring the Network
Performing Additional Configuration Operations
3. In the toolbar, select .
The RICCs/ROCs Upgrade page appears.
Figure 36 – RICCs/ROCs Upgrade Page
4. Select the checkboxes of the servers connected to the RICCs/ROCs that you want
to upgrade. Click Select All to select all the servers.
5. Click Show Versions to verify the current hardware and firmware versions of the
selected servers.
6. In Upgrade File, locate and select the firmware upgrade file.
7. Click the Start Upgrade button.
3.13.4Restoring Factory Settings
You can restore the Smart 216/232 IP unit to its factory settings. This restores the
original Smart 216/232 IP parameters, resetting all the information added by the
administrators, including: Network settings*, Servers, Switches, Users, and
Passwords.
You have the option to preserve Network settings – as explained in the following
procedure.
Once reset, the data cannot be retrieved.
44 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 45

restore factory settings
Factory Settings
Figure
To preserve network settings, select the
Factory settings are restored
Backing Up and Restoring
You can backup all configuration data and restore it at a later date.
Data
Figure
click the Browse button to
store the configuration data.
The configuration data is backed up.
Configuring
Performing
Additional Configuration Operations
checkbox
locate and select the file on which to
the Network
To
1. In the toolbar, select
The Restore
2.
3. Click Restore.
3.13.5
:
.
page appears.
37 – Restore Factory Settings Page
Preserve network settings
.
.
To back up data:
1. In the toolbar, select
The Backup/Restore
2. In Backup to file,
3. Click Backup.
.
page appears.
38 – Backup/Restore Data Page
4. Click Close.
User Guide | 45
Page 46

Configuring the Network
In the Backup/Restore Data
Browse button to locate and select the file which contains the data to restore
configuration data is restored.
Reloading a Page
You can load the parameters on any configuration page with the settings from the
device. This is convenient if you have already ch
the page, and want to restore the device settings.
Configuration page
The parameters are populated with the device settings.
Saving Changes
Once you have completed configuration changes, you must save them.
hanges to the SSL Certificate
Saving the configuration changes after changing the Device page restarts the unit
Configuration page
f you made changes to the Device page, the system automatically prompts you
to reboot and restart the device, by displaying
A message box informs that Save has completed.
data from
anged settings on
pages require saving and restarting.
the following device reboot
Reloading a Page
To restore data:
1.
2. Click Restore.
The
3. Click Close.
3.14
Smart 216/232 IP
To reload a page:
1. In the
3.15
C
page (see Figure 38), in Restore
toolbar, click the button.
and Logging Out
and Security
file, click the
.
automatically.
To save changes:
1. In the
I
confirmation box:
3. Click Yes.
Figure 39
toolbar, click the button.
– Device Reboot Confirmation Message
46 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 47

Figure
4. Click OK.
Device reboots, and when it completes a Logon page appears.
Figure
Figure
name and
The Configuration page opens.
In the screen toolbar, click the
The Configuration screen is closed, and the session closes.
Configuring
Changes and Logging Out
the Network
Saving
40 – Save Succeeded Message
5. Type your User
To log off:
1.
41 – Device Rebooting Progress Box
42 – Logon Page after Rebooting
Password and click Enter.
button.
User Guide | 47
Page 48

Conducting a Remote Session
Conducting a Remote Session
remote session enables remotely accessing
. Before starting a remote session,
You can perform the following from the remote session
Display the session in full screen mode.
Verify Remote Presence Solutions information.
the target servers.
Manage keyboard sequences.
Synchronize mouse pointers.
Switch to a different server or device.
Starting a Remote Session
You can start a remote session by
ogging into the system, as explained in steps 1 to 5 of the procedure in Secti
Selecting the target that you want to connect to
Displaying the target inside a remote console window
Log into the Smart 216/232 IP system
Targets screen appears
As an
appear on the Targets page
connected to
must be
steps 1 to 5 of the procedure
Only targets that the User is permitted to use,
Administrator can access all connected targets, they all
Starting a Remote Session
4
A
Smart 216/232 IP
configured.
Display/hide the toolbar.
Set the session profile.
Adjust video settings.
Power manage
4.1
any of the target servers
Smart 216/232 IP
:
fully
L
3.2
To start a remote session:
1.
in Section 3.2.
The
appear on the page.
:
on
, by following
.
, as in the following figure.
48 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 49

Conducting a Remote Session
Starting a Remote Session
Figure 43 – Server Targets
The following table describes the Targets page parameters and buttons.
Parameter/Button Description
Server Name
Server Status The status of the server. It can be available, off, busy (meaning that
User
The server name. The server name can be changed in the
Configuration settings to give the server an identifiable name (see
Section 3.6).
another user is accessing the server), or Remote Active Session.
The current user (if any) accessing the target server.
Pressing this button reloads the page. Can also be accessed from the
Action dropdown menu.
Pressing this button starts a remote session for the selected target
server. Can also be accessed from the Action dropdown menu.
2. In the Server Name column, select the target server that you want to connect to, by
highlighting it and clicking , or by double-clicking it.
User Guide | 49
Page 50

Toolbar
Conducting a Remote Session
Starting a Remote Session
A server being used by another user cannot be accessed.
The screen of the selected target server that is connected directly to Smart
216/232 IP, appears inside a remote console window with the remote session
toolbar.
Also, the Server Status of the server becomes Remote Active Session.
4.1.1 Remote Session Toolbar Buttons
The following table describes the functionality of the Remote Session toolbar buttons.
Button Description
Toggle button for displaying/hiding toolbar.
Session button. Pressing this button opens up a dropdown menu for selecting:
Session Profile – enables configuring remote session profile session
About – displays client, firmware, Switch File, and KME version information
50 | Smart 216/232 IP
Figure 44 – Remote Session Page
Page 51

Button Description
Video button. Pressing this button opens up a dropdown menu for performing:
Refresh – for refreshing the video image
Video Adjust – for automatically adjusting the video image
Advanced – for manually setting video settings
Performance – changing video performance by changing mode and/or bandwidth
Keys button. Pressing this button opens up a dropdown menu with predefined key sequence
names and Special Keys item which enables you to: add a keyboard sequence, record a new
custom key, edit an existing key sequence, and delete a key sequence
Mouse button. Pressing this button opens up a dropdown menu for performing:
Calibrate – calibrates the speeds of the mouse pointers of the target server and client
computer in Win98, NT or 2000
Align – for aligning the local mouse pointer with the remote target server mouse pointer
Mouse Settings – for manually synchronizing the mouse pointers
Server/Serial button. Pressing this button displays the connected servers and serial devices.
You can switch to a different server/device.
Conducting a Remote Session
Sharing a Remote Session
Restore button. To toggle Full screen mode on and off.
Logoff button. Closes the current remote session and displays the logon Web page.
4.2 Sharing a Remote Session
Users who want to remotely work on a server at the same time and collaborate their
work, can share a remote session. All users in the remote session can connect to see
the video at the same time and share the Keyboard/Mouse control. Up to five users
can share the same remote session.
When connecting to a target server that other users are already connected to, the
following message appears:
Figure 45 – Shared Remote Session
4.2.1 Exclusive Session
When starting a remote session and there are no other logged in users, a user can
prevent other users from connecting to the session (see Section 4.4, step 4). This
User Guide | 51
Page 52

Conducting a Remote Session
means that the user is the only one who can see the video and control the
Keyboard/Mouse, enabling the user to work on the server without anyone seeing or
er’s work.
Displaying the Toolbar
The Toolbar appears briefly at the top of the screen (see
when the mouse is not over it. To make it reappea
toolbar
Setting the Session Profile
the remote session
Select the format of the mouse pointer, or
Display the session in full screen mode
you are working on a local computer, using full screen mode.
the desktop window disappears, and is replaced by the accessed ta
Prevent other users from logging into the same session
The Session Profile window appears.
Figure
select
mouse pointer:
). It disappears
r, glide the mouse over the top of
on the
s
In Full Screen mode,
rget server
the appearance of
Displaying the Toolbar
interfering in the us
4.3
Figure 44
the screen. To display the
4.4
You can set
Hide the toolbar.
desktop.
To set the session profile:
1. On the toolbar, select
permanently, click the tack icon
display features, as follows:
hide it.
– You can work on the target
> Session Profile.
toolbar.
erver as if
.
46 – Session Profile Dialog Box
2. In Local Mouse Pointer,
the client computer
52 | Smart 216/232 IP
one of the following options to set
Page 53

None –
to hide the mouse pointer
for the mouse pointer to appear as a dot
for the mouse pointer to appear as a regular
, select:
to hide the
display
next connection onwards.
the Restore button
, select the
session and there are no other logged in users
logging into the session
Full Screen Mode
You can work on the target server as if you are working on a local computer, using
full screen mode. In Full Screen mode, the desktop window disappears, and is
replaced by the accessed target server
To work in full screen mode:
Ensure that the client computer has the same screen resolution as the target
On the toolbar, click the Restore button
d
To exit full screen mode:
On the toolbar, click the Restore button
The desktop window appears.
Full screen mode can also be activated from the Session Profile box, see
, step 3.
Verifying Remote Presence Solutions
f
Switch file versions installed on your
system administrators in troubleshooting and support.
verify Remote Presence Solutions information
elect
Conducting
Remote Presence Solutions Information
shaped mouse cursor
from the next connection onwards
the remote session screen in full screen mode from the
To toggle full screen mode on and off,
checkbox when starting a remote
other use
f
irmware, KME (Keyboard/Mouse Emulation firmware), and
This information can assist
Dot –
a Remote Session
Verifying
Default –
3. In Auto Connect
Auto hide –
Full Screen – to
4. In Exclusivity
4.4.1
1.
server.
2.
toolbar
(see Section 4.4.1).
Exclusive Session
.
desktop.
; this prevents
.
-
you can click
rs from
The desktop window
1.
Section 4.4
4.5
Information
You can verify the client,
To
1. On the toolbar, s
isappears.
.
Smart 216/232 IP.
:
> About.
User Guide | 53
Page 54

Conducting a Remote Session
Changing the Video Performance Settings
The information screen appears.
Figure 47 – Remote Presence Solutions Information
4.6 Changing the Video Performance Settings
From the toolbar, you can alter the video performance settings, by selecting a
different mode or bandwidth.
The mode can be set to:
Fixed – Enables you to select any bandwidth option. For example, in a LAN
environment, it is best to set the bandwidth setting to High. For VPN and Internet
environments, you may want to alter the settings to increase responsiveness.
Adaptive – Automatically adapts to the best compression and colors according to
the network conditions.
You can choose to display more colors for more fidelity, or less colors to reduce the
volume of data transferred through the network. Choosing more colors requires more
bandwidth.
The bandwidth can be set to:
Maximum – For optimal performance when working on a LAN. This gives no
compression and high color (16 bit)
High – For low compression and high color (16 bit)
Medium – For medium compression and either high color or 256 colors;
Recommended when using a standard Internet connection
Low – For high compression and 16 colors
54 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 55

To alter the settings:
elect
The Performance dialog box appears.
or
Bandwidth
The chosen setting take
Adjusting the Video
There are three ways to adjust the video image:
Refreshing the video image
Automatically adjusting the video image
Manually changing advanced video settings
Refreshing the Video Image
require refreshing
r. Refreshing completely regenerates the video image.
refresh the video image
elect
Conducting
(high color or 256
effect and the screen of the last accessed
r
a Remote Session
Adjusting the Video
1. On the toolbar, s
2. In Mode, select Fixed
> Performance.
Figure 48 – Performance Settings
Adaptive.
3. For Fixed mode, in
colors), or Low.
4. Click OK.
appears.
4.7
4.7.1
The video image may
target serve
To
1. On the toolbar, s
, select Maximum, High, Medium
s
when changing the display att
:
> Refresh.
target server
ibutes of a
User Guide | 55
Page 56

Conducting a Remote Session
Automatically Adjusting the Video Image
The video view may need to be adjusted for each target server or new screen
resolution. In most cases, adjusting the video view using the default video settings
adjust the video image
progress of video adjustment is displayed
Figure
i
i
Manually Adjusting Video Settings
automatic adjustment of video generally optimizes the video view, you may
tune the results.
dvanced video adjustment options
erver video settings after auto adjustment
dapt to a noisy environment
screen DOS/CLI m
After adjusting the video settings manually, you can always revert to automatically
adjusting the video settings, as explained in Section
manually adjust the video settings
manual controls appear
a few
ab
target server
Adjusting the Video
The image is refreshed.
4.7.2
gives the optimal view.
To automatically
1. On the toolbar, select
The
The process takes a few
an indication that there
verify that no dynamic v
4.7.3
Although
want to fine-
:
> Video Adjust.
.
49 – Video Adjust Progress
seconds. If the process runs more than
s an abnormal noise level. Check the video c
deo application is running on the
times, it is
le and
’s desktop.
You can use the a
To fine-tune the target s
To a
When in full-
To
1. On the toolbar, select
The
56 | Smart 216/232 IP
> Advanced.
or a nonstandard VGA signal
ode
:
.
:
4.7.2.
Page 57

Conducting a Remote Session
Adjusting the Video
Figure 50 – Manual Video Adjustments Controls
2. In Brightness and Contrast, use the scales to adjust the brightness and contrast of
the displayed image, respectively. Move the sliders to change the displayed image.
Click in the area of the sliders for fine-tuning.
3. In the Offset, Phase and Scale section:
In H. Offset, select the starting position of each line on the displayed image.
In V. Offset, select the vertical starting position of the displayed image.
In Phase, select the point at which each pixel is sampled.
In Scale, select the scale resolution of the session image.
Adjust Phase and Scale to reduce the noise level to a minimum.
4. In Filter, select the filter of the input video from the server. A higher filter reduces
the noise level but makes the image heavier. Options are: Auto, No Filter, Low,
Medium, and High.
5. Level displays the Video "noise" level when a static screen is displayed.
User Guide | 57
Page 58

Conducting a Remote Session
Power Managing the Target Servers
a Minicom Remote Power switch or POC is connected to the Serial port of the
, you can power manage the
power manage the target servers
.
Power menu appears
one of the following options:
to send a power cycle to the currently accessed
meaning that the target server is first powered down and then powered up
to power up the currently accessed
to power down the currently accessed
Only the currently accessed
target server
Managing Keyboard Sequences
You can select any keyboard sequence
that appears in the dropdown menu of the
send it to the target server to initiate
key sequence to the
key sequences
This section describes how to
ard sequences to the list of keyboard sequences
Create customized keyboard sequences
Edit existing keyboard sequences
Delete existing keyboard sequences
s via the Power
target server,
, to power
you must access each one individually.
(a combination of keys that performs a
toolbar button
. For example, select
to initiate its
, and do not
Power Managing the Target Servers
6. Click OK.
4.8
When
Smart 216/232 IP unit
menu.
target server
To
1. On the toolbar, click
The
2. Select
Power Cycle –
Power Up –
Power Down –
manage other
:
.
Figure 51 – Power Menu
target server
target server
target server is affected. Therefore
s,
4.9
specific process)
Ctrl-Alt-Del sends this three-
Shutdown/Login process.
When clicked, these
affect the client computer.
Add predefined keybo
58 | Smart 216/232 IP
to
its associated process
target server
transmit directly to the target server
:
ing
Page 59

4.9.1 Adding a
Keyboard Sequence
dd predefined keyboard sequences to the list of keyboard
can be accessed directly from the dropdown list of the
add a keyboard sequence
The Special Key Manager box appears
Add Predefined
A list of existing sequences appears.
Conducting
Keyboard Sequences
sequences that
You can a
a Remote Session
Managing
To
1. On the toolbar, click
:
> Special Keys.
.
toolbar item
.
2. Click the
Figure 52 – Special Key Manager
button.
User Guide | 59
Page 60

Conducting a Remote Session
533.Select a key sequence and click
n4.In the Special Key Manager box,
The sequence appears in the Keyboard Key sequence list
New Custom Key
This section describes how to define a new keyboard sequence. After defining the
keyboard sequence, you can add it to t
accessed directly from the dropdown list of the
record a keyboard sequence
g
p
he list of keyboard sequences that can be
(see Section
Record New Custom Key
Managing Keyboard Sequences
Figure
The sequence appears i
4.9.2 Recording a
To
1. In the Special Key Mana
The Record Macro box a
– Add a Predefined Key Dialog Box
OK.
the Special Key Manager box.
click OK.
toolbar item
:
er box (see Figure 52), click
pears.
.
4.9.1).
.
60 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 61

, type a name for the new key
ress the keys
he names of the pressed keys
The new key sequence is now on the list of predefined key sequences.
Editing a Key Sequence
edit a predefined keyboard sequence
n
box a
Label
ress the keys
he names of the pressed
The key sequence definition is updated in the system.
Deleting Key Sequence(s)
You can delete a single or
Conducting
Keyboard Sequences
Figure 54 – Record Macro Box
), select the desired key
ame of the key sequence to
a Remote Session
Managing
2. In Label
3. Click Start Recording.
4. On your keyboard, p
T
5. Click Stop Recording.
6. Click OK.
4.9.3
To
1. In the Special Key Ma
and click Edit.
The Record Macro
edit appears in the
2. Click Start Recording.
3. On your keyboard, p
T
sequence.
to include in the key sequence.
appear in the provided area.
:
ager box (see Figure 52
ppears (see Figure 54). The n
field.
to include in the key sequence.
keys appear in the provided area.
sequence
4. Click Stop Recording.
5. Click OK.
4.9.4
multiple key sequences from the system.
User Guide | 61
Page 62

Conducting a Remote Session
To delete a keyboard sequence:
g
. Select a group of keys by selecting the first key in the group, pressing
button, and then selecting the last key.
The delete confirmation box appears.
55
Synchronizing Mouse Pointers
For best mouse performance and superior customer experience, Minicom
t you set certain mouse settings in the target operating system. This
applies to all targets running Windows, such as
When working at the client computer, two mouse pointers appear
computer and one of the target server; the former is on top of the latter. The mouse
pointers should be synchronized. The following explains what to do if they are not
Before synchronizing mouse pointers, adjust the video of the tar
); otherwise, mouse synchronization may not work.
Calibrate
Relative Mouse Position
Manually Synchronizing the Mouse
If the mouse settings on the
or SUN Solaris
manually synchronize mouse pointers
), select the desired key sequence
, Windows Server 2003, and
one of the
get server (see
menu,
changed, or when the
2008 Server, Linux,
you must synchronize the mouse pointers
Synchronizing Mouse Pointers
1. In the Special Key Mana
to delete
the Shift
2. Click Delete.
Figure
4.10
recommends tha
Windows Server 2008.
er box (see Figure 52
– Delete Key(s) Confirmation Box
XP, Windows 7
(s)
synchronized.
Section 4.7
The Align and
4.10.1
system on the target server
Novell, SCO UNIX,
manually.
To
1. On the toolbar, select
options are available from the Mouse
mode.
target server have been
is Windows XP / 2003 Server / 7 /
,
:
> Mouse Settings.
–
client
only for
operating
62 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 63

Conducting a Remote Session
Synchronizing Mouse Pointers
The Mouse Settings box appears.
For SMART 216/232 IP PS/2 devices, the default mode is Relative Mouse Position
(see Figure 56); for SMART 216/232 IP USB devices, the default mode is Absolute
Mouse Position (see Figure 57)
Figure 56 – Relative Mouse Settings
User Guide | 63
Page 64

Conducting a Remote Session
Synchronizing Mouse Pointers
Figure 57 – Absolute Mouse Settings
Selecting the Mouse Mode
On the Mouse Settings page, there are three selectable modes:
Absolute Mouse Position
Apple Macintosh Mouse
Relative Mouse Position
The mouse mode that you can select depends on the type of SMART 216/232 IP
device and on the target operating system / computer:
For SMART 216/232 IP USB devices:
If the operating system on the Target is Windows ME or later, select Absolute
Mouse Position mode (see Figure 57); this is the default mode for SMART
216/232 IP USB devices.
If the operating system on the target is Windows 98 or Linux, Novell, UNIX or
SUN, select Relative Mouse Position mode.
If the target is a MAC computer, select Apple Macintosh Mouse mode.
For SMART 216/232 IP PS/2 devices: Relative Mouse Position is the only possible
mode.
64 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 65

Relative Mouse Position Mode
Selecting
Relative Mouse Position
The USB Option
onfigure settings for the Relative Mouse Position mode
, from the dropdown menu, select the target’s operating
r2.Follow the instructions and set any relevant sliders to the same values as set
target’s Mouse Properties window.
The mouse pointers are synchronized.
The following are examples of the instructions for two different target operating
systems. After performing the instructions for the selected operating system, you
to synchronize the mouse pointers.
Go to the Mouse Properties on the Target and clear the
checkbox.
Figure
If Mouse Properties
they have been returned to their original state
Conducting
Synchronizing
mode enables you to configure mouse settings, set
Advanced Mouse
were ever changed for the target
checkbox
the USB option (see
Emulation).
a Remote Session
Mouse Pointers
), and advanced settings (see
To c
1. In Operating System
system.
Instructions and slide
3. Click OK.
Examples
should click OK
1. For Windows 7:
pointer precision
:
s appear.
in the
Enhance
58 – Windows 7 Mouse Properties
2. For Windows 2000:
– clear the Default
.
– even if
User Guide | 65
Page 66

Conducting a Remote Session
if you have USB to PS2 conversion between SMART
216/232 IP and the target server via any of
nsupported operating systems
Use this option if you are sure of the custom acceleration algorithm you are using, or
so by customer support.
Advanced Mouse Emulation
Mouse settings, you can set the type of mouse that you would like
to emulate. It is recommended not to change the advanced
settings unless there is erratic mouse behavior (for example, the mouse is making
random clicks and jumping arbitra
To set the type of mouse that you want
Mouse Settings box
The Mouse Emulation box appears.
Figure
Select the mouse connected to the Local Console port on the
h
Microsoft Mouse
Microsoft mouse or Microsoft optical mouse
the maximum mouse report rate.
u
if you have USB to PS2 conversion between SMART
SMART 216/232 IP
h
n
e
Synchronizing Mouse Pointers
The USB Option
You can use the USB option
USB-to-PS/2 adapter
U
SUN Solaris
have been informed to do
In the Advanced
SMART 216/232 IP
the following:
rily around the screen).
SMART 216/232 IP to emulate:
1. In the
2.
as follows:
Standard Mouse – if t
this case, clear the
(see Figure 57), click Advanced.
59 – Mouse Emulation Box
e local mouse is a non-Microsoft two-butto
checkbox.
,
mouse; in
Wheel Mouse –
3. In Max Rate, select
For Sun Solaris the defa
66 | Smart 216/232 IP
lt value is 20 in order to support older Sun v
rsions.
Page 67

4. Click OK.
Aligning the Mouse Pointers
When accessing the target server, the mouse pointers may appear at a distance to
each other, due to the mouse on
the host system. You can align the local mouse pointer with the remote target
To align the mouse pointers:
li
Calibrating Mouse Pointers
A target server may have a different mouse pointer speed than the
Calibrating automatically discovers the mouse speed of the target server and aligns
You can perform automatic calibration when the target server
Windows NT4, 2000, or 98.
saves this alignment so that calibration is only needed once per
To perform the calibration:
If the Video Noise Level is above zero, calibration may not wor
Video Adjustment and try to eliminate the noise by automatically adjusting the video
) and/or adjusting the
), and then performing the mouse calibration
If the mouse settings on the target server have
synchronize mouse pointers manually, as explained below.
Switching to a Different Server/Device
In the middle of a remote session, you can switch to a different server or device.
connect to a different server or device
r
server/device of the remote session.
Click the desired server or Serial device.
Conducting
to a Different Server/Device
losing sync with the mouse on
client computer.
perating system is
k. In this case, go to
bars in manual video adjust (see Section
been changed, you must
There is a checkmark near the
4.10.2
device’s mouse pointer.
a Remote Session
Switching
SMART 216/232 IP
1. On the toolbar, select
The mouse pointers a
4.10.3
the two pointers.
SMART 216/232 IP
target server.
1. On the toolbar, select
(see Section 4.7.2
4.7.3
> Align (or press Ctrl+M).
gn.
o
> Calibrate.
.
4.11
To
1. On the toolbar, click
A list of connected se
2.
.
vers/devices appears.
:
User Guide | 67
Page 68

Conducting a Remote Session
The screen of the server or Serial device terminal emulation window appears.
Disconnecting the Remote Session
disconnect the session
.
e appe
Disconnecting the Remote Session
4.12
To
1. On the toolbar, click
The Login Web pag
:
ars. You can re-login or close the browserwindow.
68 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 69

Managing the Event
how to manage the
log
log
log
Viewing the Event
all system events.
Log
In the menu in the left pane, click
The log of all system events is displayed.
Reloading the Events Log
events are constantly added to the log, you can reload the Events Log at any
reload the Events Log
In the Events Log page (see
The Events Log page is refreshed.
Managing
Viewing
the Events Log
the Events Log
5
This chapter describes
Viewing the Events
Reloading the Events
Clearing the Events
Saving the Events log
5.1
You can view a log of
To view the Events
1.
s Log
Events log, including:
s Log
:
.
Figure 60 – Events Log
5.2
As new
time.
To
1.
:
Figure 60), in the toolbar, click
.
User Guide | 69
Page 70

Managing the Events Log
ing the Event
You can download and save the Event
or compatible software.
In the Events Log page (see
As window is displayed.
, and click
Clearing the Event Log
You can clear all the events in the log
In the Events Log page (see
A confirmation window appears.
61
The Events Log is cleared.
The file can then be viewed
Saving the Events Log
5.3 Sav
using Microsoft Excel
To save the Events Log:
1.
The Save
2. Type a name for the file
5.4
To clear the Events Log:
1.
s Log
s Log to a .csv file.
Figure 60), in the toolbar, click
Save.
.
Figure 60), in the toolbar, click
.
.
2. Click Yes.
70 | Smart 216/232 IP
Figure
– Clear Events Confirmation Window
Page 71

Troubleshooting
restore factory defaults from
43
have forgotten the Username or Password
To restore factory defaults
the root of the USB drive
Place the USB drive into one of the USB ports of the Smart 216/232 IP and restart
it by power cycling it.
The Smart 216/232 IP reboot
he unit to the factory settings, erase
the unit reverts to the factory settings
Troubleshooting –
Restoring Factory
Clearing the Event Log
Restoring Factory
the Web configuration interface, as described in
(for example,
restore factory defaults
and recognize the presence of the default file
and reboot
Settings
6
Settings
You can
Section 3.13.3 on page
USB drive.
1. In
2.
then restores t
rebooting,
–
. However, if you cannot access the GUI
), you can
using a USB drive:
, create an empty file named “default”.
s
s this file,
.
you
using a
. It
s. After
User Guide | 71
Page 72

Operating the Smart 216/232
IP Switching System Locally
Operating the Smart
Switching System Locally
This chapter explains how to operate the Smart
he OSD
From the local keyboard, press the left
The OSD Main window appears.
Figure
Lines with the sun icons in the
computers/servers. A switched off computer has no sun icon. When a server is
the entire line appears in red characters.
Navigating the OSD
You can navigate the OSD, as follows:
jump from one column to the next (when relevant)
To exit the OSD or return to a previous window within the OSD
IP Switching system locally
key.
Press
Displaying the OSD
7
7.1 Displaying t
To display the OSD:
1.
216/232 IP
216/232
Shift key twice.
.
busy,
7.2
To move up and down –
To
72 | Smart 216/232 IP
62 – OSD Main Window
PM column show switched on active
Use the Up and Down arrow keys.
– Use the Tab
–
Esc.
Page 73

7.3
Selecting a Computer
to the desired computer line.
port number of the desired computer.
The selected computer is accessed. A Confirmation label appears showing which
.
Power Manag
power manage a server connected to a power management switch.
power manage a server
Navigate to the line of the computer that you want to power manage
The Power Control dialog box
Figure
If you change the OSD hotkey from Shift to Ctrl, the power management
hotkey becomes left Ctrl, F12.
o n
IP Switching System Locally
Selecting a Computer
le
To select a computer:
1. Navigate
OR
Type the two-digit
2. Press Enter.
computer is accessed
Operating the Smart 216/232
7.4
You can
To
1.
2. Use the arrow keys t
option.
ing a Server
:
appears.
63 – Power Control Dialog Box
avigate up and down, and press Enter to se
.
ct the power
A prompt appears.
Figure 64 – Power Prompt
User Guide | 73
Page 74

Operating the Smart 216/232
IP Switching System
on
s s
Confirmation
The Confirmation label appears briefly, showing which computer is currently
ou can position the Confirmation label anywhere on the screen.
ain window (see
arrow keys
The selected screen image and
Use the arrow keys to move the label to the desired position.
to save and exit.
he image of any computer screen from the
adjust the screen image
OSD Main window (see
he screen image of the selected computer appears, together with the
Figure
arrow keys to adjust the image
When the image is satisfactory, press
Picture quality is relative to distance. The further away a remote computer is
216/232
place the higher resolution computers closer to the Switch
navigate to the desired computer using
that
IP, the lower the image quality, and the more tuning
Moving the Confirmation Label (F1)
Locally
3. Select the desired opti
The power command i
7.5 Moving the
accessed. Y
To position the label:
1. In the OSD M
the Up and Down
2. Press F1.
3.
4. Press Esc
7.6 Tuning (F5)
You can tune t
and press Enter.
ent.
Label (F1)
Figure 62),
.
Confirmation label appear.
Main window.
To
1. In the
to adjust.
2. Press F5.
T
Tuning label.
3. Use the Right and Left
4.
from the Smart
required. Therefore,
:
Figure 62), navigate to the computer
65 – Image Tuning Label
.
Esc.
you want
Image
is
.
74 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 75

Configuring t
You can configure the following OSD settings:
configure the OSD settings
ndow
, you can
bottom of the window, press
settings by typing in the selected area or by pressi
Network Parameters
Configuring the Device IP Address
When a DHCP server is active on the same network to which Smart 216/232 IP is
DHCP can provide automatic IP assignment. However, best practices
recommend using MAC address reservations in the DHCP server to ensure that the IP
216/232
your Network Administrator regarding the use
Selecting Automatic IP Address Assignment
Operating the Smart 216/232
IP Switching System Locally
Configuring the OSD
key. At the
to go to the top of the window. Change
whichever is
Settings (F2)
7.7
Network parameters
OSD hotkey
Keyboard Language
To
1. Press F2.
The OSD Settings wi
he OSD Settings (F2)
:
appears.
In the Settings window
relevant.
7.7.1 Changing the
You can configure the:
Device IP address
KVM.Net address
connected, the
address of the Smart
Consult
Figure 66 – OSD Settings Window
navigate downwards using the Tab
the Tab key
ng the spacebar –
IP will not be changed.
of the DHCP.
User Guide | 75
Page 76

Operating the Smart 216/232
IP Switching System Locally
select automatic IP address assignment
ettings window
Enable
DHCP server that is active on the same network to which
connected, to provide automatic IP assignment
Assignment
select manual IP address assignment
ettings window
able
, and type
Subnet Mask
Centralized
centralized
system remotely manages the Smart 216/232 IP unit.
Centralized
ettings window
and press the Space bar until
KVM.NET ADD
Centralized Management Manager
Centralized
ettings window
and press the Space bar until
Changing the OSD Hotkey
Shift, Shift
the OSD hotkey
ettings window
Press the Space bar to toggle between
From now on, you can press this new hotkey t
line
216
line
provided by you
, and type values for them.
that Minicom’s AccessIT
KVM NET MANG
AccessIT
KVM NET MANG
line.
Configuring the OSD Settings (F2)
To
1. In the OSD S
the Space bar until
The
Selecting Manual IP Address
To
1. In the OSD S
the Space bar until Dis
2. Navigate to IP Address
Administrator.
3. Similarly, navigate to
Configuring AccessIT
You can enable AccessIT
Centralized Management
To enable AccessIT
1. In the OSD S
:
(see Figure 66), navigate to the DHCP
appears.
.
:
(see Figure 66), navigate to the DHCP
appears.
the IP address for LAN 1
and Default Gateway
Management Settings
management, so
Management:
(see Figure 66), navigate to the
Enable appears.
Smart
, and press
/232 IP is
, and press
r Network
line,
2. Navigate to
To disable AccessIT
1. In the OSD S
7.7.2
By default, pressing
You can replace
Ctrl, Ctrl
Ctrl, F11
Print Screen
To change the hotkey:
1. In the OSD S
2.
, and modify the static IP address of the
.
Management:
(see Figure 66), navigate to the
Disable appears.
displays the OSD.
Shift, Shift with any of the following:
(see Figure 66), navigate to the Hotkey
the available options.
o display the OSD.
line,
76 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 77

7.7.3
Changing the Keyboard Language
is preset to US English
rench (FR) or
This refers to the OSD keyboard language and not the computer keyboard
change the keyboard language
ettings window
Press the Space bar to toggle between
and Updating DDC Information (F10)
Display Data Channel (DDC) is a VESA standard for communication between a
monitor and a video adapter.
The ROC emulates the DDC information to the connected computer.
system
216/232
To input the DDC information:
ettings window
Please wait” flashes a few times and disappears.
pdate the DDC information in any of the following circumstances:
When replacing the monitor connected to Smart
When adding a new ROC to the system
When reconnecting an existing ROC that was temporarily used in a different
To update the DDC information, follow the steps in the procedure for input
Saving Changes to Settings
save changes to the settings
In the OSD Settings window (see
Settings are saved. The OSD Main window appears (see
IP Switching System Locally
Configuring the OSD
keyboard
Keyboard Language
rmation of the monitor
e memories of all connected ROC
DD
).
Operating the Smart 216/232
Settings (F2)
The keyboard language
language to F
language.
To
1. In the OSD S
line.
2.
7.7.4 Inputting
When first installing the
connected to the Smart
. You can change the
German (DE).
:
(see Figure 66), navigate to the
the available options.
, emulate the DDC info
IP switch into th
s.
1. From the OSD S
“
is sent to all ROCs.
You should u
system
information.
7.7.5
To
1.
(see Figure 66), press F10.
The monitor’s
216/232 IP Switch
:
Figure 66), press Esc.
C information
ting DCC
Figure 62
User Guide | 77
Page 78

Technical Specifications
8 Technical Specifications
Specification Description
Operating systems Target server – DOS, Windows, Novell, Linux, or SUN Solaris for PC
Client computer – Windows 2000 or later with Internet Explorer 7.0 /
Firefox 3.0 and later; Linux x86 with Firefox 3.0 and later
Resolution Target server – Up to 1600 x 1200 @ 85 Hz
Client computer – Recommended resolution should be higher than on
target server
Distance from Switch to ROCs
Video and mouse synchronization
Security
Connections Ethernet – RJ45 – 10/100 Mbit/sec autosensing
Weight
Dimensions (H x D x W)
Power input
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Humidity
Up to 30 m / 99 ft
Both auto and manual modes
SSL, high grade 256-bit AES encryption
Serial – RJ45 x 2
Local KVM connection – Screen HDD15; Keyboard/Mouse – 2 USB
Server – RJ45
2.343 Kg / 5.165 lbs
44 x 270 x 431 mm / 1.7 x 10.6 x 17"
100-240 VAC, 0.8 A, 50/60 Hz
0°C to 40°C / 32° to 104°F
-40°C to 70°C / -40°F to 158°F
80% non-condensing relative humidity
Specification ROC PS/2 ROC USB
Connections VGA – HDD15
KM – MiniDin6
System – RJ45
Power
Product Weight
Shipping Weight
Dimensions (H x D x W)
From Keyboard port From USB port
78 | Smart 216/232 IP
VGA – HDD15
KM – USB
System - RJ45
100 g / 0.20 lb
172 g / 0.38 lb
65 x 25 x 25 mm / 2.6 x 0.98 x 0.98 in
Page 79

Technical Specifications
User Guide | 79
Page 80

Video Resolution and Refresh Rates
9 Video Resolution and Refresh Rates
Hz →
640x480
720x400
800x600
1024x768
1152x864
1152x900
1280x720
1280x768
1280x960
1280x1024
1600x1200
56 60 65 66 70 72 73 75 76 85 86
x x x x x x
x x
x x x x x x
x x x x x x x
x
x x
x
x x
x x
x x x x x
x x x x x
80 | Smart 216/232 IP
Page 81

201204202 • 933211_EN
 Loading...
Loading...