Trinamic QSH6018-45-28-110, QSH6018-56-28-165, QSH6018-65-28-210, QSH6018-86-28-310 User guide
Page 1

QMOT Motor QSH6018
Manual
60mm QMOT motor family
Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
D – 20357 Hamburg, Germany
http://www.trinamic.com
Sternstraße 67
Page 2

QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 2
Table of Contents
1 Features...........................................................................................................................................................................3
2 Life support policy .......................................................................................................................................................4
3 Mechanical Dimensions ..............................................................................................................................................5
3.1 Leadwire Configuration ..................................................................................................................................... 5
3.2 Dimensions ........................................................................................................................................................... 5
4 Torque figures ............................................................................................................................................................... 6
4.1 Motor QSH6018-45-28-110 ................................................................................................................................. 6
4.2 Motor QSH6018-56-28-165 ................................................................................................................................. 6
4.3 Motor QSH6018-65-28-210 ................................................................................................................................. 7
4.4 Motor QSH6018-86-28-310 ................................................................................................................................. 7
5 Considerations for Operation....................................................................................................................................8
5.1 Choosing the best fitting Motor for an Application .................................................................................8
5.2 Motor Current Setting ........................................................................................................................................9
5.3 Motor Driver Supply Voltage..........................................................................................................................10
5.4 Back EMF (BEMF) ................................................................................................................................................11
5.5 Choosing the Commutation Scheme...........................................................................................................11
5.5.1 Fullstepping..............................................................................................................................................12
5.6 Optimum motor settings ................................................................................................................................12
5.6.1 Settings for Trinamic TMCL modules ................................................................................................12
6 Revision History ..........................................................................................................................................................13
6.1 Documentation Revision .................................................................................................................................13
List of Figures
Figure 3.1: Leadwire configuration ..................................................................................................................................5
Figure 3.2: Dimensions (all values in mm)....................................................................................................................5
Figure 4.1: QSH6018-45-28-110 Speed vs. Torque Characteristics............................................................................6
Figure 4.2: QSH6018-56-28-165 Speed vs. Torque Characteristics............................................................................6
Figure 4.3: QSH6018-65-28-210 Speed vs. Torque Characteristics............................................................................7
Figure 4.4: QSH6018-86-28-310 Speed vs. Torque Characteristics............................................................................7
List of Tables
Table 1.1: Motor technical data.........................................................................................................................................3
Table 3.1: Leadwire configuration .................................................................................................................................... 5
Table 5.1: Motor current settings...................................................................................................................................... 9
Table 5.2: Driver supply voltage considerations ........................................................................................................10
Table 5.3: Comparing microstepping and fullstepping............................................................................................11
Table 5.4: Optimum motor settings...............................................................................................................................12
Table 5.5: Optimum motor settings for TMCL modules (tested with TMCM-109).............................................12
Table 6.1: Documentation Revisions..............................................................................................................................13
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Page 3

QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 3
1 Features
These four phase hybrid stepper motors are optimized for microstepping and give a good fit to the
TRINAMIC family of motor controllers and drivers.
Main characteristics:
• NEMA 23 mounting configuration
• flange max. 60.5mm * 60.5mm
• 8.0mm axis diameter, 25mm axis length with 20mm D-cut of 0.5mm depth
• step angle: 1.8˚
• optimized for microstep operation
• optimum fit for TMC239 / TMC249 based driver circuits
• up to 75V operating voltage
• CE approved
Parameter Units
Rated Voltage V
Rated Phase Current (nominal) I
Rated Phase Current (max.
continuous)
Phase Resistance at 20°C R
V 2.1 2.52 3.36 4.17
RATED
RMS_RATED_NOM
I
RMS_RATED_MAX
Ω 0.75 0.9 1.2 1.5
COIL
-45-28-110 -56-28-165 -65-28-210 -86-28-310
A 2.8 2.8 2.8 2.8
A 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0
Phase Inductance (typ.) mH 2 3.6 4.6 6.8
Holding Torque (typ.)
Nm 1.1 1.65 2.1 3.1
oz in 156 233 297 439
Detent Torque Ncm
Rotor Inertia gcm2 275 400 570 840
Weight (Mass) Kg 0.6 0.77 1.2 1.4
Insulation Class B B B B
Insulation Resistance Ω 100M 100M 100M 100M
Dialectic Strength (for one
minute)
VAC 500 500 500 500
Connection Wires N° 4 4 4 4
Max applicable Voltage V 75 75 75 75
Step Angle ° 1.8 1.8 1.8 1.8
Step angle Accuracy % 5 5 5 5
Flange Size (max.) mm 60.5 60.5 60.5 60.5
Motor Length (max.) L
mm 45.0 56.0 65.0 86.0
MAX
Axis Diameter mm 8.0 8.0 8.0 8.0
Axis Length (visible part, typ.) mm 24.0 24.0 24.0 24.0
Axis D-cut (0.5mm depth) mm 20.0 20.0 20.0 20.0
Shaft Radial Play (450g load) mm 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Shaft Axial Play (450g load) mm 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.08
Maximum Radial Force
(20 mm from front flange)
N 75 75 75 75
Maximum Axial Force N 15 15 15 15
Ambient Temperature °C -20..+50 -20..+50 -20..+50 -20..+50
Temp Rise
(rated current, 2 phase on)
°C max. 80 max. 80 max. 80 max. 80
QSH6018 Specifications
Table 1.1: Motor technical data
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Page 4

QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 4
2 Life support policy
TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG does not
authorize or warrant any of its products for use in life
support systems, without the specific written consent
of TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG.
Life support systems are equipment intended to
support or sustain life, and whose failure to perform,
when properly used in accordance with instructions
provided, can be reasonably expected to result in
personal injury or death.
© TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG 2007
Information given in this data sheet is believed to be
accurate and reliable. However no responsibility is
assumed for the consequences of its use nor for any
infringement of patents or other rights of third
parties, which may result form its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Page 5

QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 5
3 Mechanical Dimensions
3.1 Leadwire Configuration
Cable type Gauge Coil Function
Black UL1007 AWG22 A Motor coil A pin 1
Green UL1007 AWG22 A- Motor coil A pin 2
Red UL1007 AWG22 B Motor coil B pin 1
Blue UL1007 AWG22 B- Motor coil B pin 2
Table 3.1: Leadwire configuration
black
green
A
M
B
Figure 3.1: Leadwire configuration
red
3.2 Dimensions
blue
Figure 3.2: Dimensions (all values in mm)
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Page 6

QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 6
4 Torque figures
The torque figures detail motor torque characteristics for full step operation in order to allow simple
comparison. For half step operation there are always a number of resonance points (with less torque)
which are not depicted. These will be minimized by microstep operation in most applications.
4.1 Motor QSH6018-45-28-110
Testing conditions: 30V supply voltage; 3.0A RMS phase current
Figure 4.1: QSH6018-45-28-110 Speed vs. Torque Characteristics
4.2 Motor QSH6018-56-28-165
Testing conditions: 30V supply voltage; 3.0A RMS phase current
Figure 4.2: QSH6018-56-28-165 Speed vs. Torque Characteristics
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Page 7

QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 7
4.3 Motor QSH6018-65-28-210
Testing conditions: 30V supply voltage; 3.0A RMS phase current
Figure 4.3: QSH6018-65-28-210 Speed vs. Torque Characteristics
4.4 Motor QSH6018-86-28-310
Testing conditions: 30V supply voltage; 3.0A RMS phase current
Figure 4.4: QSH6018-86-28-310 Speed vs. Torque Characteristics
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Page 8

QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 8
5 Considerations for Operation
The following chapters try to help you to correctly set the key operation parameters in order to get a
stable system.
5.1 Choosing the best fitting Motor for an Application
For an optimum solution it is important to fit the motor to the application and to choose the best
mode of operation. The key parameters are desired motor torque and velocity. While the motor
holding torque describes the torque at stand-still, and gives a good indication for comparing different
motors, it is not the key parameter for the best fitting motor. The required torque is a result of static
load on the motor, dynamic loads which occur during acceleration / deceleration and loads due to
friction. In most applications the load at maximum desired motor velocity is most critical, because of
the reduction of motor torque at higher velocity. While the required velocity generally is well known,
the required torque often is only roughly known. Generally, a longer motor and a motor with a larger
diameter delivers a higher torque. But, using the same driver voltage for the motor, the larger motor
earlier looses torque when increasing motor velocity. This means, that for a high torque at a high
motor velocity, the smaller motor might be the better fitting solution.
Please refer to the torque vs. velocity diagram to determine the best fitting motor, which delivers
enough torque at all desired velocities.
Hints:
Q: How to determine the maximum torque required by your application?
A: Just try a motor which should roughly fit. Take into consideration worst case conditions, i.e.
minimum driver supply voltage and minimum driver current, maximum or minimum environment
temperature (whichever is worse) and maximum friction of mechanics. Now, consider that you want
to be on the safe side, and add some 10 percent safety margin to take into account for unknown
degradation of mechanics and motor.
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Page 9

QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 9
5.2 Motor Current Setting
Basically, the motor torque is proportional to the motor current, as long as the current stays at a
reasonable level. At the same time, the power consumption of the motor (and driver) is proportional
to the square of the motor current. Optimally, the motor should be chosen to bring the required
performance at the rated motor current. For a short time, the motor current may be raised above this
level in order to get increased torque, but care has to be taken in order not to exceed the maximum
coil temperature of 130°C respectively a continuous motor operation temperature of 90°C.
Percentage of
rated current
Percentage of
motor torque
Percentage of static
motor power dissipation
150% ≤150% 225%
125% 125% 156%
100% 100%
= 2 * I
100%
RMS_RATED
* R
COIL
85% 85% 72%
75% 75% 56%
50% 50% 25%
38% 38% 14%
25% 25% 6%
0%
see detent
torque
0%
Comment
Limit operation to a few seconds
Operation possible for a limited time
Normal operation
Normal operation
Normal operation
Reduced microstep exactness due to
torque reducing in the magnitude of
detent torque
-“-
-“Motor might loose position if the
application’s friction is too low
Table 5.1: Motor current settings
Hints:
Q: How to choose the optimum current setting?
A1: Generally, you choose the motor in order to give the desired performance at nominal current.
For short time operation, you might want to increase the motor current to get a higher torque than
specified for the motor. In a hot environment, you might want to work with a reduced motor
current in order to reduce motor self heating.
The Trinamic drivers allow setting the motor current for up to three conditions:
- Stand still (choose a low current)
- Nominal operation (nominal current)
- High acceleration (if increased torque is required: You may choose a current above the nominal
setting, but be aware, that the mean power dissipation shall not exceed the motors nominal
rating)
A2: If you reach the velocity limit, it might be a good idea to reduce the motor current, in order to
avoid resonances occurring. Please see the hints on choosing the driver voltage.
Q: What about energy saving – how to choose standby current?
A1: Most applications do not need much torque during motor stand-still. You should always reduce
motor current during stand still. This reduces power dissipation and heat generation. Depending on
your application, you typically at least can half power dissipation. There are several aspects why
this is possible: In stand still, motor torque is higher than at any other velocity. Thus, you do not
need the full current even with a static load! Your application might need no torque at all, but you
might need to keep the exact microstep position: Try how low you can go in your application. If
the microstep position exactness does not matter for the time of stand still, you might even reduce
the motor current to zero, provided that there is no static load on the motor and enough friction in
order to avoid complete position loss.
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Page 10

QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 10
5.3 Motor Driver Supply Voltage
The driver supply voltage in many applications can not be chosen freely, because other components
have a fixed supply voltage of e.g. 24V DC. If you have to possibility to choose the driver supply
voltage, please refer to the driver data sheet, and consider that a higher voltage means a higher
torque at higher velocity. The motor torque diagrams are measured for a given supply voltage. You
typically can scale the velocity axis (steps / sec) proportionally to the supply voltage to adapt the
curve, e.g. if the curve is measured for 48V and you consider operation at 24V, half all values on the
x-Axis to get an idea of the motor performance.
For a chopper driver, consider the following corner values for the driver supply voltage (motor
voltage). The table is based on the nominal motor voltage, which normally just has a theoretical
background in order to determine the resistive loss in the motor.
Comment on the nominal motor voltage: U
COIL_NOM
(Please refer to motor technical data table.)
Parameter Value Comment
Minimum driver
supply voltage
Optimum driver
supply voltage
Maximum rated
driver supply
voltage
2 * U
COIL_NOM
≥ 4 * U
and
≤ 22 * U
25 * U
Very limited motor velocity. Only slow movement without
torque reduction. Chopper noise might become audible.
COIL_NOM
Choose the best fitting voltage in this range using the motor
torque curve and the driver data. You can scale the torque
COIL_NOM
COIL_NOM
curve proportionally to the actual driver supply voltage.
When exceeding this value, the magnetic switching losses in
the motor reach a relevant magnitude and the motor might
get too hot at nominal current. Thus there is no benefit in
further raising the voltage.
= I
RMS_RATED
* R
COIL
Table 5.2: Driver supply voltage considerations
Hints:
Q: How to determine if the given driver voltage is sufficient?
A1: Just listen to the motor at different velocities. Does the “sound” of the motor get raucous or
harsh when exceeding some velocity? Then the motor gets into a resonance area. The reason is,
that the motor back-EMF voltage reaches the supply voltage. Thus, the driver can not bring the full
current into the motor any more. This is typically a sign, that the motor velocity should not be
further increased, because resonances and reduced current affect motor torque.
A2: Measure the motor coil current at maximum desired velocity.
For microstepping: If the waveform is still basically sinusoidal, the motor driver supply voltage is
sufficient.
For Fullstepping: If the motor current still reaches a constant plateau, the driver voltage is sufficient.
If you determine, that the voltage is not sufficient, you could either increase the voltage or reduce
the current (and thus torque).
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Page 11

QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 11
5.4 Back EMF (BEMF)
Within SI units, the numeric value of the BEMF constant has the same numeric value as the numeric
value of the torque constant. For example, a motor with a torque constant of 1 Nm/A would have a
BEMF constant of 1V/rad/s. Turning such a motor with 1 rps (1 rps = 1 revolution per second =
6.28 rad/s) generates a BEMF voltage of 6.28V.
Thus, the Back EMF constant can be calculated as:
[]
AI2
[]
NmngTorqueMotorHoldi
is multiplied by 2 in this
NOM
U
BEMF
The voltage is valid as RMS voltage per coil, thus the nominal current I
formula, since the nominal current assumes a full step position, with two coils switched on. The
torque is in unit [Nm] where 1Nm = 100cNm = 1000mNm.
One can easily measure the BEMF constant of a two phase stepper motor with a (digital) scope. One
just has to measure the voltage of one coil (one phase) when turning the axis of the motor manually.
With this, one gets a voltage (amplitude) and a frequency of a periodic voltage signal (sine wave).
The full step frequency is 4 times the frequency the measured sine wave.
=
s/rad
⋅
NOM
V
5.5 Choosing the Commutation Scheme
While the motor performance curves are depicted for fullstepping, most modern drivers provide a
microstepping scheme. Microstepping uses a discrete sine and a cosine wave to drive both coils of
the motor, and gives a very smooth motor behaviour as well as an increased position resolution. The
amplitude of the waves is 1.41 times the nominal motor current, while the RMS values equals the
nominal motor current. The stepper motor does not make loud steps any more – it turns smoothly!
Therefore, 16 microsteps or more are recommended for a smooth operation and the avoidance of
resonances. To operate the motor at fullstepping, some considerations should be taken into account.
Driver Scheme Resolution Velocity range Torque Comments
Fullstepping 200 steps per
rotation
Microstepping 200 * (number
of microsteps)
per rotation
Mixed: Microstepping and
fullstepping for
high velocities
200 * (number
of microsteps)
per rotation
Table 5.3: Comparing microstepping and fullstepping
Low to very high.
Skip resonance areas
in low to medium
velocity range.
Low to high. Reduced torque at very
Low to very high. Full torque At high velocities,
Full torque if dampener
used, otherwise reduced
torque in resonance area
high velocity
Audible noise
especially at low
velocities
Low noise,
smooth motor
behaviour
there is no
audible difference
for fullstepping
Microstepping gives the best performance for most applications and can be considered as state-of-the
art. However, fullstepping allows some ten percent higher motor velocities, when compared to
microstepping. A combination of microstepping at low and medium velocities and fullstepping at
high velocities gives best performance at all velocities and is most universal. Most Trinamic driver
modules support all three modes.
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Page 12
QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 12
5.5.1 Fullstepping
When operating the motor in fullstep, resonances may occur. The resonance frequencies depend on
the motor load. When the motor gets into a resonance area, it even might not turn any more! Thus
you should avoid resonance frequencies.
Hints:
Q: How to avoid motor resonance in fullstep operation?
A1: Do not operate the motor at resonance velocities for extended periods of time. Use a reasonably
high acceleration in order to accelerate to a resonance-free velocity. This avoids the build-up of
resonances. When resonances occur at very high velocities, try reducing the current setting.
A2: A resonance dampener might be required, if the resonance frequencies can not be skipped.
5.6 Optimum motor settings
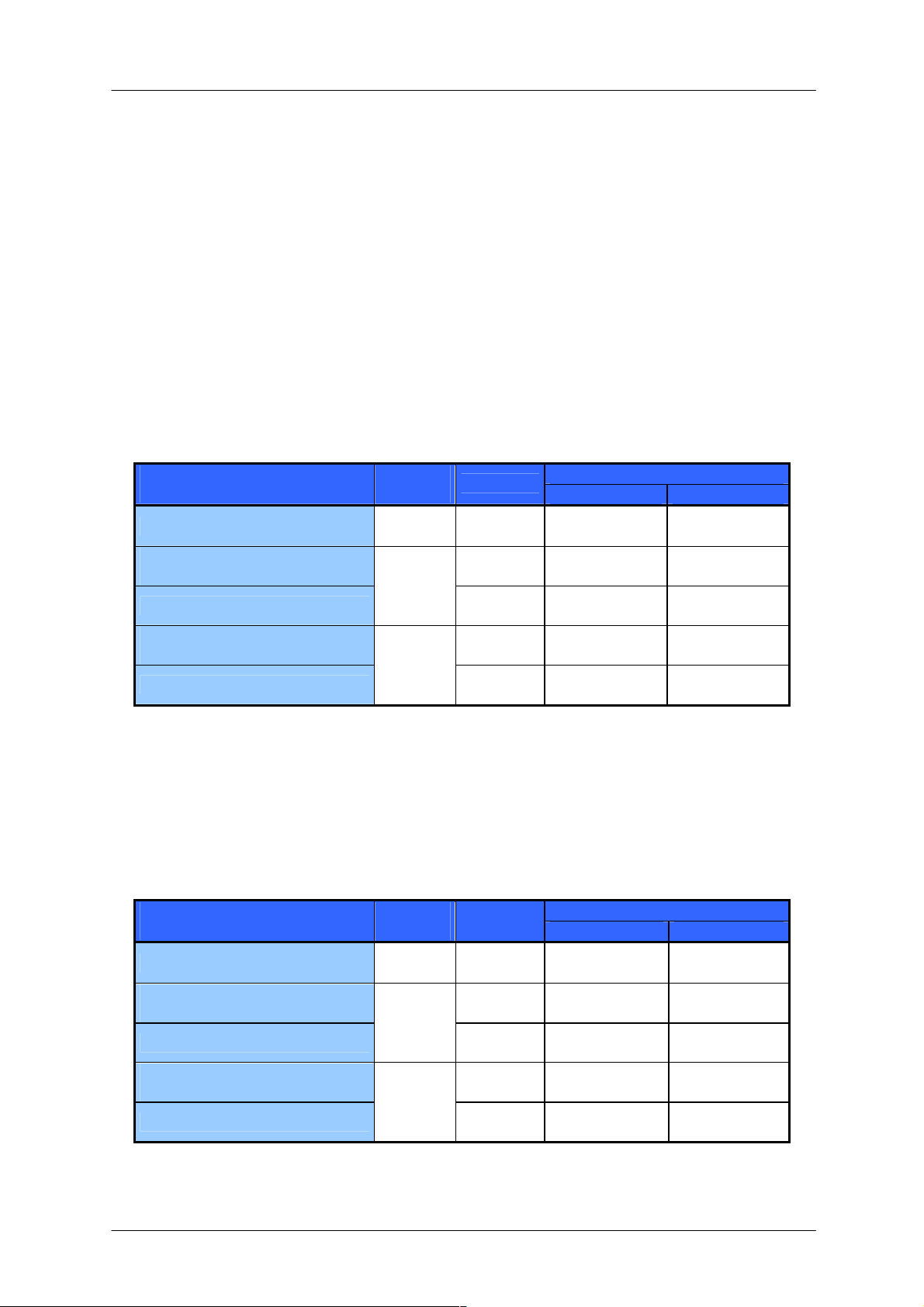
Following table shows settings for highest reachable fullstep velocities.
Motor
voltage
Unit
-65-28-210 -86-28-310
QSH6018 Optimum Motor Settings
Motor current (RMS) A 2.8 2.8
Maximum microstep velocity =
Fullstep threshold
Maximum fullstep velocity
Maximum microstep velocity =
Fullstep threshold
Maximum fullstep velocity
Table 5.4: Optimum motor settings
24
48
RPS 1.907 1.144
RPS 3.815 2.575
RPS 2.861 2.003
RPS 7.629 5.245
5.6.1 Settings for Trinamic TMCL modules
Following TMCL settings apply best for highest motor velocities and smooth motor behavior at low
velocities. They are intended for use with Trinamics controller modules.
Mixed decay should be switched on constantly. Microstep resolution is 4 (TMCL), this is 16 times
microstepping. The pulse devisor is set to 3. With a 64 microstep setting the same values are valid
with the pulse divisor set to 1.
Motor
Motor current (RMS) TMCL value 204 204
voltage
Unit
-65-28-210 -86-28-310
QSH6018 Optimum Motor Settings
Maximum microstep velocity =
Fullstep threshold
Maximum fullstep velocity
Maximum microstep velocity =
Fullstep threshold
Maximum fullstep velocity
Table 5.5: Optimum motor settings for TMCL modules (tested with TMCM-109)
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
24
48
TMCL value 200 120
TMCL value 400 270
TMCL value 300 210
TMCL value 800 550
Page 13
QSH6018 Manual (V1.03 / 06-February-2008) 13
6 Revision History
6.1 Documentation Revision
Version Comment Author Description
1.00 Initial Release HC
1.01 20-Jun-07 HC Chapter 5.6 Optimum motor settings added
1.02 13-Nov-07 HC Chapter 5.4 Back EMF (BEMF) added
1.03 06-Feb-08 GE New motors added
Table 6.1: Documentation Revisions
Copyright © 2008, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
 Loading...
Loading...