
Z-Max®.Net
Getting Started Guide

English
Copyright Notice
Copyright 2003-2006 Magellan Navigation. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
All product and brand names mentioned in this publication
are trademarks of their respective holders.
FCC Notice
Z-Max.Net Receiver complies with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to the Part 15 of the FCC rules
when it is used in Portable Mode. See Note below related
to Class B device.
Class B digital devices NOTE: This equipment has been
tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instructions , may cause harmful inte rference to
radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If
this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning
the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try and
correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
- Reorient or locate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician
for help.
When Z-Max.Net is used with an external power supply or
connected to an external device using the USB port, it
complies with the limits fo r a Class A digital device, p ursuant to the Part 15 of the FCC rules. See Note below related
to Class A device.
Class A digital devices NOTE: This equipment has been
tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the instruction
manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area
is likely to cause harmfu l interference in which case the
user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
Remark: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by Magellan Navigation, could void the right for
user to operate the equipment.
RF Safety Exposure To Radio Frequency Energy (SAR)
Radio transmitting devices radiate Radio Frequency (RF)
energy during its operation. RF energy can be absorbed
into the human body and potentially can cause adverse
health effects if excessive levels are absorbed. The unit of
measurement for human exposure to RF energy is "Specific
Absorption Rate" (SAR).
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC), Industrie
Canada (IC), and other agencies around the world have established limits that in corporate a substanti al safety margin designed to assure the safety of all persons using this
equipment. In order to certify this unit for sale in the US,
Canada and Europe this unit has been tested for RF exposure compliance at a qualified test laboratory and found to
comply with the regulations regarding exposure to RF Energy. SAR was measured with the unit (GSM Module) transmitting at its maximum certified RF power. Often, however,
during normal operation the unit (GSM Module) will transmit much less than maximum power. Transmit power is
controlled automatically and, in general is reduced as you
get closer to a cellular base station. This reduction in trans-
mit power will result in a lower R F energy exposure and resulting SAR value.
SAR: ANSI/IEEE C95.1 1992
FCC OET Bulletin 65 Supplement C
1999/519/CE
The SAR value for this wireless survey system when worn
on the body, as described in this user guide, is always less
than 1.45 W/kg.
Caution! FCC RF exposure requirements: SAR compliance
for body-worn operations is restricted to belt-clips,
holsters, and accessories supplied or designated for this
product. Use of other accessories may not ensure
compliance with FCC RF exposure guidelines.
FCC and CE UHF Safety Statement
The different versions of the UHF Transmitters are FCC and
CE compliant.
In order to comply with FCC and CE RF exposure safety
guidelines as body-worn, normal use of unit, the following
must be followed:
A distance of AT LEAST 10 feet (3 m) of separation between the users body and the unit (UHF Transmitter). This
distance has been defined taken into account the FCC and
CE Requirements and the worst output power configuration.
Do NOT use the device in a manner such that it is in direct
contact with the body (e.g. on the lap). Such use will likely
exceed FCC RF safety exposure limits. See www.fcc.gov/
oet/rfsafety/ for more i nformation on RF expo sure safety.
Antenna Care/Unauthorized Modifications
Use only the supplied integral antenna. Unauthorized antenna modifications or attachments could damage the unit
and may violate FCC and CE regulations. Any changes or
modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Replacing the Magellan U-Link Transmitter Power Fuse
The Magellan U-Link transmitter is protected by a 4-A fuse
inserted in the data/ power cable. This Y-s haped cable is
used to connect the U-Link transmitter to the Z-Max.Net
receiver via a 7-pin connector, and to the power battery.
Should you have to replace this fuse, please get a spare
fuse, 4 A, fast act ing, ATO type, and then do the following:
- Unplug the battery end of the data/power cable
- Open the fuse holder located along the data/power cable
- Extract the damaged fus e
- Insert the new fuse and then push the holder lid back into
place
- Connect the data/power cable back to the battery.
Where to Find Informatio n
This manual is designed to guide you through the basic
Z-Max.Net procedures. You can find additional information
in the Z-Max.Net Reference Manual, also provided on the
Z-Max.Net CD.
Warranties
Refer to the Z-Max.Net Reference Manual.

Table of Contents
Introduction............................................................. 1
System Components Overview..........................................1
Locating the Basic Components .......................................3
Z-Max.Net Front Panel ....................................................3
Bluetooth® Port........................................................ 4
Status LEDs ............................................................. 4
Front Panel Display ................................................... 5
Control Keys ............................................................. 5
Power Key ................................................................ 6
SD Card Reader and USB .......................................... 6
Z-Max.Net Rear Panel.....................................................6
GNSS Antenna Configurations .........................................7
Base ........................................................................ 7
Pole-Mounted Rover .................................................. 7
Backpack-Mounted Rover .......................................... 7
Preparing For First-Time Use..................................... 8
Charging the Power Module .............................................8
Attaching the Lateral Modules .........................................9
Attaching the GNSS Antenna Module ...............................9
Inserting a Memory Card ...............................................10
Turning On/Off the System ............................................10
Initializing the System ..................................................11
Checking that Z-Max.Net Receives Satellites...................12
RTK Surveying ....................................................... 13
RTK Surveying Method Requirements............................. 13
RTK Base Setup...........................................................14
Choosing the Installation Site................................... 14
Setting Up the RTK Base ......................................... 14
RTK Rover Setup.......................................................... 16
Establishing Bluetooth Communication with Z-Max.Net....18
Introduction ........................................................... 18
Powering up the Whole Equipment ........................... 19
Detecting Bluetooth-Enabled Devices........................ 19
Finding Bluetooth Services ...................................... 20
Assigning Virtual Ports to Bluetooth .......................... 20
Saving Bluetooth Serial Port Settings ........................ 21
Defining/Saving Bluetooth Settings for FAST Survey ... 22
Toggling Bluetooth Between Base and Rover.............. 23
Configuring the RTK Base .............................................23
Launching FAST Survey........................................... 23
Configuring the Base and the Data Link .................... 24
Entering the Base Position and ID ............................ 25
Setting the Radio .................................................... 26
Configuring the RTK Rover ............................................27
Case #1: Rover Using a UHF Radio Data Link ............ 28
Case #2: Rover Using a GSM/GPRS Data Link ........... 30
English

English
Saving Base and Rover Settings .................................... 32
Running an RTK Survey ............................................... 32
Logging RTK Points ................................................ 33
Logging RTK Points in Continuous Mode .................. 34
Staking out RTK Points ........................................... 35
Downloading RTK Results to GNSS Solutions ................. 37
Post-processing Surveying....................................... 39
Reminder on the Static Surveying Method...................... 39
Running a Static Survey ............................................... 40
Equipment Setup ................................................... 40
Getting the Z-Max.Net Unit Started in Static ............. 41
Starting Data Collection .......................................... 43
End of Data Collection ............................................ 43
Downloading Field Data to your PC ................................ 45
Post-Processing Field Data ........................................... 46
Front Panel Interface Function Diagram ................... 48

1. Introduction
Congratulations! You have just acquired your new dualfrequency Z-Max™.Net GNSS Surveying System from
Magellan!
GNSS (or Global Navigation Satellite System) has
revolutionized control surveys, topographic data collection
and construction surveying. Purchasing the right tools for a
professional job is essential in today's competitive business
environment.
Learning to put these tools to work quickly and efficiently will
be the focus of the present guide.
System Components Overview
The table below provides an overview of the different key
items composing the Z-Max.Net System. Depending on your
purchase, based on the type of survey you wish to perform, you
may only have part of the listed items. Please refer to the
delivered packing list for an accurate description of the
equipment that has been delivered to you.
Conversely, as this table is just an overview, it does not list all
the possible items and accessories. For example, the list of all
the possible field terminals is provided but we intentionally do
not mention the field brackets that usually come along with
them. For more information on these items, please contact
your dealer.
For ordering information, please refer to the Z-Max.Net
Reference Manual.
English
1
English
Basic Post-Processing Rover, RTK
GPS Receiver
Module
GNSS Antenna
Module
Power Module Range Pole
Charger
USB Cable
Serial Data
Cable
Static, Base Software RF Cables
V-Module (1)
(Void module)
Rover, Backpack
Backpack
RF Adapter
Max RF
Adapter
Field Terminal Radio
Magellan
MobileMapper CE
Juniper
Allegro CX
Communication
Module
UHF Antenna
Module (2)
Range Pole
Mounting
Bracket
Magellan U-Link
transmitter
Pacific-Crest
UHF Transmitter
HI measurement tool
eHI Measure-
ment Plate
Transport Case Memory Device
Soft case
GNSS Solutions CD
FAST Survey
CD
SD Card (sold
by Magellan)
2
GPS-RF cable
UHF-RF cable
(1) Also used in an RTK base using a
UHF radio as the data link.
(2) A void UHF antenna module also
exists.

Locating the Basic Components
2. GNSS Antenna Module
3. Power Module 4. Communication Module
or V-Module
1. Receiver
Module
As you are facing the front panel of the GPS receiver module,
the power module attaches to the left-hand side of the
receiver module and the communication module (or Vmodule) to the right-hand side.
Z-Max.Net Front Panel
English
Z-Max.Net Bluetooth®
Status LEDs
Front Panel User Interface
Control keys
Power key
3
English
Bluetooth® Port
This device allows you to communicate with the Z-Max.Net
through a Bluetooth wireless connection. This port is
identified as “port C” on the Z-Max.Net.
Status LEDs
From left to right, the LEDs are:
• RTK Solution. This LED is only operational when the
receiver is configured as an RTK rover.
Color Meaning
Off Not a RTK rover
Blinking green Fixed solution
Blinking orange Float solution
Blinking red No RTK solution
• Communication. This LED indicates when real-time data
is transmitted (base) or received (rover).
Color Meaning
Off No data link has been configured
Blinking green
Blinking red
Not blinking
Base: Transmits data
Rover: Base data received and used
Base: Irrelevant
Rover: Base data received but not used
Base: No data transmitted
Rover: No base data received
• Data Log. This LED shows the data logging status.
Color Meaning
Off No data logging in progress
Blinking green
Red Unable to log data (memory full)
Data logging in progress. Blinks at the frequency of the
recording interval setting (20 seconds by default).
• Satellite/Power. After power up, this LED will continue to
blink red once every 1-2 seconds to indicate that the unit
is powered on. Between each red blink, the LED will also
blink green once for each satellite that the receiver is
tracking.
4
Up key
Enter key
Down key
Front Panel Display
The front panel display is an 8-character, alphanumeric LED
display that is used to monitor receiver status, set receiver
parameters and configure the receiver to perform different
types of surveys.
The screen displays up to eight characters at one time.
Messages or parameters longer than eight characters are
scrolled from right to left.
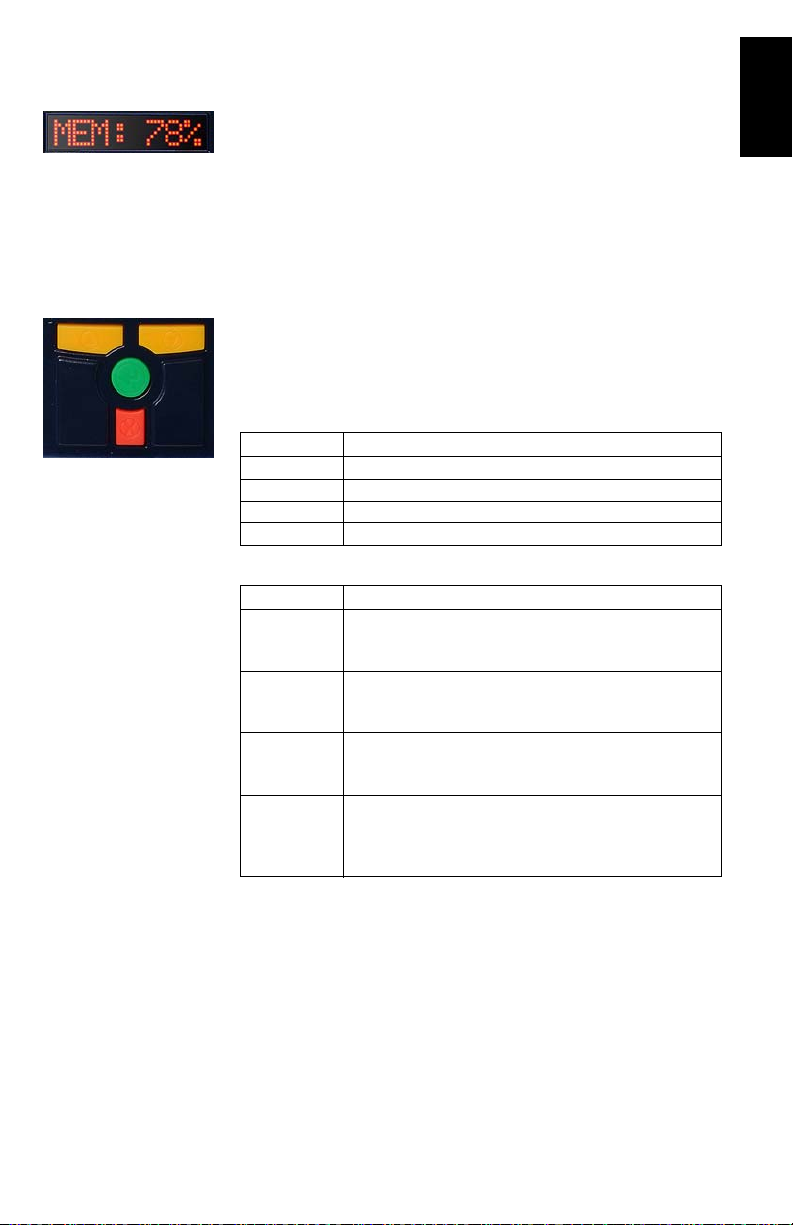
Control Keys
The four control keys are used in conjunction with the front
panel display. They will work differently depending on whether
the screen is in Display or Edit mode.
English
Cancel key
Display Mode:
Key Operation
UP (yellow) Scrolls menu (at same level) forward
DOWN (yellow) Scrolls menu (at same level) backward
ENTER (green) Selects and moves down to next level or enters Edit mode
CANCEL (red) Returns to upper level
Edit Mode:
Key Operation
Data entry context: Scrolls forward through characters
UP (yellow)
DOWN (yellow)
ENTER (green)
CANCEL (red)
Parameter list context: Scrolls forward
Fast scrolling if held depressed for 3 seconds
Data entry context: Scrolls backward through characters
Parameter list context: Scrolls backward
Fast scrolling if held depressed for 3 seconds
Parameter list context: Selects parameter
Data entry context: Accepts character and moves to ne xt spac e
or quits Edit mode
Data entry context: Deletes last edited character, stays in Edit
mode
Parameter list context: Moves from Edit mode to Display mode
without selecting the parameter.
See Z-Max.Net Reference Manual for more information.
5

English
Power Key
This key is used to power up, power down or initialize the unit
(see page 10).
Power key
SD Card Reader and USB
Below the four control keys is a small door fastened by two
thumbscrews. Unscrew the attaching screws and open the
door to reveal the SD Card slot and the USB port.
The SD card slot holds the SD card that serves as the
receiver's data storage memory. All data recorded by the unit
is stored on the SD card. Warning! Use exclusively SD cards
sold by Magellan.
The USB port is one of the external ports available for
connecting to a computer. The USB port is a type-B
connector.
Z-Max.Net Rear Panel
Handle
External Power In (10-28 V DC)
Port A (RS232)
Port B (RS232 or RS422)
For connector pinout, see Z-Max.Net Reference Manual.
6

GNSS Antenna Configurations
(A)
(B)
In all cases of use, the GNSS antenna module must be
connected to the receiver module. But there are three
different ways of doing this, as explained below.
Base
The GNSS antenna module (A) is directly attached to the
receiver module (B).
(A)
Pole-Mounted Rover
The GNSS antenna module (A) is attached
to the receiver module (B) via a UHF
antenna module or a Void UHF antenna
module (C).
(C)
(B)
Backpack-Mounted Rover
The GNSS antenna module (A) is attached to the receiver
module (B) via a UHF antenna module or Void UHF antenna
module (C), a range pole adapter (D), a dual RF cable (E) and
a Max-RF adapter (F).
(A)
(E)
GPS
English
(D)
(C)
(F)
UHF
(B)
7

English
Use of non-Magellan
power supplies for
charging the power
module is not
recommended.
2. Preparing For First-Time Use
Charging the Power Module
To charge the power module:
• Plug in your charger and connect the power module to the
charger as shown opposite.
• Charge for a minimum of five hours or preferably overnight
(even if the charger indicates that the battery is full).
• Verify that the battery is fully charged by pressing the button on the back side of the power module. The four LEDs
should light up green.
The power module contains rechargeable lithium-ion battery
cells and “smart” charging circuitry. Recharging the power
module is done using the AC/DC power supply, included with
the system.
This power supply can also be used to provide power directly
to the Z-Max.Net through an external connector. The charger
is designed to work with a 110-240 VAC power source and
delivers 12 V DC of input voltage with at least 4-A current
capability to the power module.
For more information on the characteristics and management
of the power module, see Z-Max.Net Reference Manual.
8

Attaching the Lateral Modules
Please take all precau-
tions to keep connector
pins clean and avoid
touching them.
Whatever the type of module you are
attaching to the receiver module, i.e. a
power module on the left, or a
communication or V-module on the
right, do the following:
• Insert the small ledge of the module
into the rear of the housing first as
shown opposite (left and right). This
will correctly align the module.
• Using the ledge like a hinge, start
swinging the module. To make sure
the module is correctly positioned vertically, take care to
align the protruding edges, on either side of the connector
pins, with the grooves in the receiver module casting.
Then swing the module closed until the latch on the module clicks into place.
• Make sure the module is well seated and the latch on the
edge of the module clicks shut.
Attaching the GNSS Antenna Module
The base of the GNSS antenna module is circular except for a
flattened area. The top of the receiver module, UHF antenna
module or Void UHF antenna module is keyed so there is only
one way the GNSS antenna module can be inserted.
• Make sure the base of the GNSS antenna module is oriented so that the flattened area is lined up with the flattened area of the receptacle.
• Once aligned, insert the GNSS antenna module into the
antenna receptacle. The module should push easily into
place.
English
9

English
Use exclusively SD
cards sold by Magellan!
It is important to power
off the receiver using
the Power key on the
Front Panel before
removing the SD card.
• Once in place, twist the threaded collar on the GNSS
antenna module until the antenna is securely locked in
place.
Inserting a Memory Card
A memory card is required if you want to run a post-processing
survey or more generally, when you want to log raw data with
your Z-Max.Net.
To install the SD Memory Card into the reader:
• Orient it so that the chamfered corner of the card is oriented downwards, as shown opposite.
• Gently push the card into the reader until you feel a soft
“click”. The click indicates that the card is properly
seated. A correctly inserted SD card should not move once
you have removed your hand from the card.
Turning On/Off the System
• Power on the system by pressing the Power button on the
receiver front panel for about 2 seconds (until a beep is
emitted) and then releasing the Power button.
The SV/Power LED should begin to blink red once per second to indicate that the receiver is powered up.
• To turn off the system, just press and hold the power key
for two seconds. The receiver will generate a beep every
second, a “shutdown” message will be displayed, and the
receiver will then power down.
10

Initializing the System
Initializing the system is recommended the first time you use
your system to:
• Clear the internal memory
• Reset the user settings to their default values
• Clear ephemeris and almanac information in memory
• Re-format the SD card. Note that initialization should also
be performed every time you prepare your SD card for a
new survey project. It’s always better to delete files from
the SD Card by running an initialization sequence rather
than using any other method.
Initializing the system is also appropriate any time the
Z-Max.Net does not work as expected.
To initialize the system from the Power button, assuming the
system is off, do the following:
• Press the Power button for at least 5 seconds.
The display will show “re-init”, indicating that the receiver
is in the initialization process.
The initialization process will take several minutes
depending on the size of the SD card. The front panel will
continue to display “re-init” until the process is complete.
When complete, the receiver will be powered on and in the
normal state with the front panel displaying “SYSINFO”
and the SD card ready to use.
English
11

English
Please go outside after
initialization and make
sure your system has a
clear view of the sky in
all directions.
Checking that Z-Max.Net Receives Satellites
If the GPS antenna has a reasonably good view to the sky,
within a few minutes, the receiver should begin to track
satellites. This is indicated by the SV/Power LED:
1. It should blink red once per second to indicate that power
is on, and blink green several times between each red
blink.
2. It will blink green once for each satellite that is being
tracked. In normal conditions of reception, the system
should receive about eight satellites on average.
12

3. RTK Surveying
When the base setup is
under your responsibil-
ity, make sure the base
is sited in a clear area
giving the best possible
view of the sky!
When this is possible,
avoid trees, buildings
or any high obstacles in
the vicinity of the base.
Having a clear view of
the sky will allow the
base to collect data
from a maximum of vis-
ible satellites, which is
highly recommended to
perform a successful,
accurate and fast sur-
vey.
RTK Surveying Method Requirements
Key information is provided below.
Two units are needed: one (the base) is operated on an accu rately known
1.
position while the other (the rover) is used in the working area.
A data link must be established from the base to the rover. This data link
2.
can be implemented in three differ ent ways:
- UHF radio
- Cellular modem (GSM)
- Other external device
Depending on the chosen data link, the base will be either:
3.
- A “real” base system (with UHF radio, GSM, or other external device)
- Or a “virtual” base system that delivers its data via a cellular modem
(GPRS).
The main Z-Max.Net RTK system configurations are illustrated below:
GPRS
Internet
Data Link
Rover
UHF Radio
Base
GSM
Base
Data Link
Data Link
Rover
Rover
English
Two differe nt rover setups can be used, backpack or range pole, yet oper-
4.
ated similarly. Only the pole-mounted rover system will be described in
this Guide. For more information on the backpack mo unting, refer to the Z-
Max.Net Reference Manual.
RTK is easier to operate using a field terminal running FAST Survey. RTK
5.
can also be operated from the receiver front panel display.
Whatever the base used (“real” or “virtual”), i ts distance to the ro ver , ca lled
6.
“baseline” (up to 50 km or 30 miles), must roughly be known to make sure
RTK results will achieve the expected level of accuracy.
13

English
RTK Base Setup
A typical base setup is described in this section in which:
• A conventional tripod is used
• A Magellan U-Link radio is used for the data link
• RTK corrections data are transmitted in Ashtech CPD
(DBEN) format
• An external 12-V DC battery is used for powering both the
Z-Max.Net base and the U-Link transmitter
• A Bluetooth-enabled field terminal (MobileMapper CE) is
used, running the FAST Survey software, to set up the
base.
For other base configurations, it’s easy to extrapolate from the
instructions given below, knowing that configuring a base
always implies: 1) entering its geographical location and 2)
defining the data link.
Choosing the Installation Site
The installation site should offer the best possible GPS
reception conditions. The GNSS antenna should have a clear
view of the sky in all directions. There should be no, or a
minimum of satellite obstructions in the vicinity.
Setting Up the RTK Base
14
1. Connect the system components (power module, GNSS
antenna and V-module) as explained on page 9.
Because a UHF radio transmitter is used for the data link,
a V-module, and not a communication module, can be
attached to the right side of the receiver module.
2. Center and level the tripod over the ground mark.

3. Insert the brass tribrach adapter through the hole in the
HI measurement plate and screw the adapter/plate into
the 5/8” threaded receptacle in the bottom of the
Z-Max.Net receiver module.
4. Carefully place the Z-Max.Net assembly into the tribrach
mounted on the tripod over the point.
5. Use the tape to measure from the reference point on the
ground to the measurement point of the Z-Max.Net (see
Hb opposite). Later on, you will have to enter the value
read on the tape (see point 5. on page 25).
English
“Hb” read
on tape
(C)
(D)
6. Using the power cable supplied (P/N
730477), connect the Z-Max.Net power
input (marked “PWR”) to the external 12-V
DC battery.
7. Install the tripod for the UHF radio transmitter a few meters away from the
Z-Max.Net tripod. The distance between the
two tripods is limited by the length (10 meters) of the
data/power cable connecting the Z-Max.Net receiver to the
radio (see point 10 below).
8. Screw the radio antenna (A) to the antenna connector on
the U-Link radio (B).
9. Hook the flange on the radio into the mounting bracket
(A)
(C), and attach the mounting bracket to the telescoping
survey pole (D).
(B)
10.Connect the Y-shaped data/power cable (P/N 730476)
(E)
between 7-pin connector port B on the Z-Max.Net and the
15-pin data/power port on the U-Link radio (E).
11.Connect the free end of the data/power cable to the battery
12.Raise the UHF radio and its antenna together as high as
possible to maximize transmission distance.
15

English
The diagram below summarizes the different connections
described previously.
Use exclusively a 12-V
DC battery to power
the U-Link transmitter.
Using a 24-V DC bat-
tery is only allowed for
powering the
Z-Max.Net.
Z-Max.Net
Power
A
B
P/N 430477
P/N 730476
External 12-V Battery
U-Link Transmitter
RTK Rover Setup
Two typical RTK rover setups are described:
• Rover Setup #1: RTK rover using a UHF radio data link to
communicate with an RTK base such as the one described
in the previous chapter.
• Rover Setup #2: RTK rover using a GSM/GPRS data link to
acquire corrections data from a provider using the NTRIP
protocol.
16

The rover setup procedure is the following
1. Connect the system components (power module, GNSS
and UHF antenna modules, com module) as explained on
page 9, taking into account the following:
- Rover Setup #1: Because a UHF radio is used as the
data link, a UHF communication module, and not a Vmodule, should be attached to the right side of the
receiver module. Connect the UHF antenna module
directly to the top of the receiver module and attach
the GNSS antenna module to the top of the UHF
antenna module.
- Rover Setup #2: Because a GSM/GPRS modem is
used as the data link, a GSM communication module,
and not a V-module, should be attached to the right
side of the receiver module. Because a UHF antenna is
not needed, connect a void UHF antenna module
directly to the top of the receiver module and attach
the GNSS antenna module to the top of the void UHF
antenna module.
2. Mount the Z-Max.Net assembly on the survey pole:
- Remove the brass adapter from the top of the pole and
attach it to the base of the Z-Max.Net assembly.
- Seat the Z-Max.Net onto the pole.
If no adapter is available, just thread the pole directly
on to the base of the receiver.
3. Determine the height of the range pole (see Hr opposite).
If you are using a standard pole, this height is given by the
pole manufacturer so you don’t need to measure it.
You will later have to remember this height when setting
the rover (see point 2. on page 28)
4. Mount the field terminal on its field bracket and then
secure the assembly onto the survey pole.
English
Hr
17

English
Base
Rover
Bluetooth
Manager
COM3
COM4
Field
Terminal
Establishing Bluetooth Communication with Z-Max.Net
Introduction
This section explains how to control the Z-Max.Net system
from a Bluetooth-enabled field terminal (Magellan
MobileMapper CE).
Please carefully read these preliminary notes:
• When using Bluetooth communication, you will be asked
repeatedly to enter the Z-Max.Net PIN number while setting up the base or the rover. By default, the PIN number
for all Z-Max.Net units is “12345”.
To enter the PIN number using MobileMapper CE’s virtual keyboard, follow the instructions below:
- To display the virtual keyboard, tap
then
Keyboard. Don’t forget to tap inside the Enter PIN field
before entering the PIN number.
- To hide the virtual keyboard, tap in the task bar and then
Hide Input Panel. If the task bar is hidden by the virtual key-
board, first tap and hold the keyboard’s title bar and move it
upward until the task bar becomes visible, then select
Input Panel
from the task bar.
• The “Tap and hold an item” instruction mentioned several
times in what follows means you have to:
- Tap on the item using the stylus
- And keep the stylus in contact with the screen until
dots and then a pop-up menu appears. Then you will
have to tap one of the functions in the prompted
menu.
in the task bar and
Hide
18

Powering up the Whole Equipment
It is assumed that the base and rover you have set up are next
to each other.
1. First of all, turn on each of the Z-Max.Net units you will be
using (a base and a rover, or simply a rover) by pressing
the power button for about two seconds until a beep is
emitted.
2. Press the red Power button on the MobileMapper CE until
the Power LED lights up (green).
Detecting Bluetooth-Enabled Devices
In this step, you will run Bluetooth Manager to find the
Bluetooth-enabled devices within range of the field terminal.
1. On the MobileMapper CE, tap in the task bar, then
Settings and then Control Panel.
2. Double-tap the Bluetooth Manager icon.
3. In the Bluetooth Manager window, tap on the ON button.
Wait until Bluetooth Manager has detected the Z-Max.Net
unit(s) you have just turned on. Bluetooth Manager will
also detect any Bluetooth-enabled devices present in the
vicinity such as cell phones, computers, etc. (The larger
the number of Bluetooth-enabled devices, the longer the
time to detect all of them.)
4. In the Authentication Request window that appears following
the detection of the Z-Max.Net units, tap successively the
PIN number for each unit
be different) (see Introduction on page 18 to do this).
5. Tap OK. Bluetooth Manager then updates the list of Bluetooth-enabled devices to show the serial number of the ZMax.Net units (rather than obscure Bluetooth ID numbers).
(“12345” by default, yours may
English
19

English
Finding Bluetooth Services
In this step, you will list the services available from the
detected Bluetooth-enabled devices.
For each detected Z-Max.Net unit
1. Tap and hold the now green Z-Max.Net icon in the list and
then tap Find Services from the pop-up menu. Wait until a
“+” sign appears before the icon.
2. Expand the Z-Max.Net icon by tapping on the “+” sign.
This unveils Bluetooth Serial Port that is currently red
crossed. (“Bluetooth Serial Port” is the only Bluetooth service available from the Z-Max.Net units.)
, do the following:
Assigning Virtual Ports to Bluetooth
In this step, you will ask Bluetooth Manager to assign a virtual
port in the field terminal for each Bluetooth connection you
need.
For each detected Z-Max.Net unit
1. Tap and hold Bluetooth Serial Port and then tap Configure.
This opens the Configure Serial Port window.
2. Select a free virtual port (COM3: for the base, COM4: for
the rover) and then tap OK to close the window.
3. Tap and hold Bluetooth Serial Port and then tap Connect. Reenter the PIN number if requested. Wait until the Bluetooth Serial Port line appears with a green mark meaning
that the Bluetooth connection with the Z-Max.Net is now
established.
, do the following:
20

Saving Bluetooth Serial Port Settings
You will save much time when next starting your system if you
follow the procedure below the first time you set up the
required Bluetooth connections.
For each detected Z-Max.Net unit
1. Tap and hold Bluetooth Serial Port and then tap successively
Auto Connect and then Save Settings.
With these options activated, and provided you do not turn
off Bluetooth Manager before shutting down the field terminal, Bluetooth Manager will automatically restore the
Bluetooth connections when you next turn on your field
terminal.
Obviously, Bluetooth Manager will only be able to restore
connections with the Z-Max units that are present in the
vicinity and powered up at that time.
You will then simply be asked to re-enter the PIN number
for each of these units
Before moving on to FAST Survey, do the following:.
2. Tap OK in the upper-right corner to close the Bluetooth
Manager window. This does not turn off Bluetooth Manager but simply frees the screen for other tasks.
3. For the same reason, close the Control Panel window.
Note the presence of the Bluetooth icon ( ) in the task
bar meaning that Bluetooth continues to be active.
.
, do the following:
English
21

English
Defining/Saving Bluetooth Settings for FAST Survey
FAST Survey can communicate with only one Z-Max.Net unit
at a time. This step provides the procedure to let FAST Survey
communicate with the desired Z-Max.Net unit via Bluetooth
and save these settings in a configuration file so these settings
can quickly be restored whenever necessary.
1. Run FAST Survey on the field terminal
2. In FAST Survey, tap on the Equip tab and then on the
Comm Setup function.
3. In the Port Number field, select “COM3” (for communicating with the base)
4. Check the This is a Bluetooth port option and then select
“Other” as the Bluetooth Driver
5. Tap OK to close the window. FAST Survey is now communicating with the base through COM3. At this stage, you
can communicate with the base for configuration or monitoring purposes.
6. Tap on top of the screen
7. Tap the Save button
8. Name the configuration file (for example “Z-Max Base”)
9. Tap OK and then Close
10.Repeat the above steps 2 to 9 for the Z-Max.Net rover you
are using. This time you will select “COM4” and not
“COM3” in the Comm Set up window (point 3.) and you
will enter “Z-Max Rover” as the name for the configuration
file (point 8.).
22

New Job screen
FAST Survey virtual
keyboard
Toggling Bluetooth Between Base and Rover
Now that you have saved the two ways FAST Survey can
communicate with your Z-Max.Net system, it’s easy to toggle
Bluetooth communication from the base to the rover or the
other way around:
1. Tap on top of the screen
2. Tap on the name of the configuration corresponding to the
unit you wish to communicate with and then tap Select. As
a result, FAST Survey automatically updates the settings
in the Comm Setup function to let you communicate with
the chosen unit.
Configuring the RTK Base
Launching FAST Survey
1. On the field terminal, launch the FAST Survey software by
double-tapping on the FAST Survey icon.
2. Choose Select New/Existing Job. A new screen is now displayed.
3. In the Name field, type in the name of the job you wish to
create. For example, type in “Job1.crd”.
Note that FAST Survey has its own, large, virtual keyboard
(see opposite). If you tap inside the Name field, FAST Survey will automatically display its virtual keyboard. You just
have to type in a name using this keyboard and then tap
OK.
4. Tap OK to create the job. The screen then displays the
Units tab.
5. On the Units tab, set the desired units and parameters for
the job.
English
23

English
6. Tap on the GPS tab.
7. On the GPS tab, choose the coordinate system to be used
in the job as well as the geoid model. Note that the coordinate system and the geoid model may have been uploaded
earlier to the field terminal using one of the GNSS Solutions tools (see GNSS Solutions Reference Manual for
more information). A large number of coordinate systems
are stored in FAST Survey. To select one of them, tap on
the Edit Projection List button and then Add Predefined.
8. After selecting all the desired parameters, tap OK (located
on top of the screen).
GPS tab screen
Configuring the Base and the Data Link
Reminder: In this example, you will be configuring a UHF data
link to provide the rover with RTK corrections data in CPD
(DBEN) format.
1. Tap on the Equip tab, then the Instrument function, select
“Magellan Professional and Ashtech” from the scroll-down
menu and finally tap OK.
2. Tap on top of the screen
3. Tap on the name of the configuration corresponding to the
base (e.g. “Z-Max Base”) and then tap Select. As a result,
FAST Survey automatically updates the settings in the
Comm Setup function to let you communicate with the
base.
Alternately, you can tap on the Comm Setup button on the
Equip tab and then, in the Port Number field, select the port
you assigned to communicate with the base (see point 2.
in Assigning Virtual Ports to Bluetooth on page 20). Also,
enable “This is a Bluetooth port” and select “Other” as
the Bluetooth Driver. Then tap OK
4. Tap on the Configure Base button and then choose “Z-Max”
from the Receiver Type scroll-down menu.
24

5. Enter the antenna height you measured previously (see
point 5. page 15) as well as the method you used for this
measurement. If you used the method described on
page 15, check Slant.
6. Select the type of GPS antenna used, i.e. “[Z-Max GPS]
Magellan Professional” as you are using the Z-Max.Net
antenna directly connected to the receiver.
7. Tap on the Ports tab. With Bluetooth and the Magellan
radio used, make the following choices:
• Type: “Magellan” (Magellan Radio)
• Data Port: “C” (Bluetooth connection to field terminal)
• Radio Port: “B”
• Message Type: “Ashtech CPD”.
8. Tap OK to send these parameters to the Z-Max.Net
receiver. Re-enter the PIN number. The Z-Max.Net emits a
beep. A new menu appears asking you to enter the initialization position for the base.
Entering the Base Position and ID
Up to six different options are possible to enter this position:
English
25

English
Base Station ID screen
Base coordinates
screen
9. Choose the option that suits you best. For example, to
enter the coordinates of the base:
- Tap successively on From New Position, then Enter Lat/
Lon
- Type in the latitude, longitude and altitude and then
tap OK. FAST Survey then displays the WGS84 coordinates of this position after making the transformation
to WGS84 if necessary.
- Tap Yes.
10.FAST Survey then asks you to enter the Reference Station ID
(4 characters max.).
11.Enter the ID you would like to assign to the base and then
tap OK. The message “Connecting to Receiver” is displayed
and a beep is emitted meaning that the Z-Max.Net is
being configured. After a few seconds, FAST Survey
prompts you to check the radio settings:
Setting the Radio
12.Tap Yes. In the US, a channel/frequency table will be
shown. In Europe, a single channel will be displayed along
with the corresponding frequency.
13.For example, if the frequency must be set to
444.125 MHz (it’s always a multiple of 12.5 kHz), type in
“444.125” in the Frequency to Set field and then tap Set
Radio.
14.Wait until FAST Survey displays the “Base Configuration
Successful” message and the Z-Max.Net emits a beep.
26

15.Check the LEDs on the Z-Max.Net front panel to make
sure the system is functioning correctly (refer to page 4 to
read the meaning of each LED). Typically, two LEDS
should blink green as shown opposite.
You can also monitor the Z-Max.Net rover from the
MobileMapper CE screen using FAST Survey’s Equip
tab>Monitor Skyplot function (see figure below).
Current position
Computation
uncertainties
GPS constellation
geometry
Number of
received satellites
Tap Back to return to the menu.
16.You can now let the base operate on its own and move on
to the rover configuration. Keep the field terminal on.
Also, keep FAST Survey running and leave the job open as
this is needed to configure the rover (see hereafter).
English
Configuring the RTK Rover
1. Tap on top of the screen
2. Tap on the name of the configuration corresponding to the
rover (e.g. “Z-Max Rover”) and then tap Select. As a result,
FAST Survey automatically updates the settings in the
Comm Setup function to let you communicate with the
rover.
27

English
Alternately, you can tap on the Comm Setup button on the
Equip tab and then, in the Port Number field, select the port
you assigned to communicate with the rover (see point 2.
in Assigning Virtual Ports to Bluetooth on page 20). Also,
enable “This is a Bluetooth port” and select “Other” as
the Bluetooth Driver. Then tap OK.
Case #1: Rover Using a UHF Radio Data Link
1. Tap on Configure Rover
2. In the Rod Hgt field, type in the height mentioned earlier
(Hr; see point 3. on page 17) and then check the Vertical
option.
3. Tap on the Receiver tab and check that the receiver used is
“Z-Max”. Also, as you are using a UHF antenna module although a void one- between the GNSS antenna and the
receiver module, select the “[Z-Max GPS UHF] Magellan
Professional” antenna in the Antenna Type field.
4. Tap on the Ports tab and make the following choices:
- Base Config field (at the bottom): “Manual”
- Type: “Magellan” (Magellan radio)
- Data Port: “C” (Bluetooth connection to field terminal)
- Radio Port: “D”
- Message Type: “Ashtech (CPD/DSNP LRK)”
5. Tap the OK button located on top of the screen. The message “Connecting to Receiver” is displayed and the
Z-Max.Net emits a beep meaning that it’s being configured.
28

6. After a few seconds, another message is displayed
prompting you to check the radio settings:
7. Tap Yes. In the US, a channel/frequency table will be
shown. In Europe, a single channel will be displayed along
with the corresponding frequency.
8. For example, if the frequency must be set to
444.125 MHz (it’s always a multiple of 12.5 kHz), type in
“444.125” in the Frequency to Set field and then tap Set
Radio.
9. Wait a few seconds. A beep is emitted by the Z-Max.Net
once it has been configured as a rover.
The survey can now begin.
You can first check the LEDs on the Z-Max.Net front panel
to make sure the system is functioning correctly (refer to
page 4 to know the meaning of each LED).
You can also monitor the Z-Max.Net rover from the field
terminal screen using FAST Survey’s Equip tab>Monitor
Skyplot function.
English
29

English
Case #2: Rover Using a GSM/GPRS Data Link
Reminder: You do not need to install and run your own base
as in this case you will be using RTK corrections data from a
provider using the NTRIP protocol. This means you just have
to set up and use your rover. Below is the key information you
need to know in this case of use:
• A GPRS data link is used to receive RTK corrections data
from an NTRIP caster. The GPRS provider is assumed to
have delivered the following information so you can start
your modem:
Modem SIM PIN number (if any)
Access Point Name
Log in for GPRS connection
Password for GPRS connection
• The NTRIP service provider is assumed to have delivered
the following information so you can access the NTRIP
service:
Caster IP address (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx)
IP port number
Log in for access to NTRIP caster
Password for access to NTRIP caster
Follow the instructions below to set up the rover:
1. Tap on Configure Rover
2. In the Rod Hgt field, type in the height mentioned earlier
(Hr; see point 3. on page 17) and then check the Vertical
option.
3. Tap on the Receiver tab and check that the receiver used is
the Z-Max.Net. Also, select the “[Z-Max GPS UHF] Magellan Professional” antenna in the Antenna Type field.
4. Tap on the Ports tab and make the following choices:
- Base Config field (at the bottom): “Manual”
30

- Type: “NTRIP”
- Data Port: “C”
5. Tap the Add button located at the bottom of the screen.
6. Enter the properties of the GPRS provider. The screen
opposite only gives examples of what these properties
might be.
By appropriately naming this set of information (Name
field on top), you will be able to directly select this configuration from the Base Config field on the previous screen.
7. Tap the NTRIP Settings button and enter the properties of
the NTRIP service you want to use. The screen opposite
only gives examples of what these properties might be.
8. Tap OK three times.
9. The message “Connecting to Receiver” is displayed and a
beep is then emitted indicating that the Z-Max.Net is
being configured.
A new screen appears on which you can see the current
status of the com module’s modem (READY; see screen
opposite).
10.Tap Connect. The Connecting to Caster message is displayed. Then a new screen appears from which you can
see all the stations available from your NTRIP provider
11.From the drop-down list associated with the Mount Point
field, select the base station you would like to work with.
The rest of the screen provides information on the
selected station. The Format field is automatically preset
following the selection of a station but you can still
change it if the pre-setting is incorrect (see screen opposite).
English
31

English
12.Tap OK. After a while, The GSM STATUS switches to
ONLINE (see screen opposite) and the Z-Max.Net should
start receiving corrections data. After a few seconds the
RTK Solution LED (far left) should blink green meaning
that the RTK position solution is fixed and so you can start
surveying.
13.Tap Close and proceed with the survey as such (see next
chapters).
You can monitor the Z-Max.Net rover from the field termi-
nal screen using FAST Survey’s Equip tab>Monitor Skyplot
function.
Saving Base and Rover Settings
When you configure your base or rover from FAST Survey, a
Save operation is automatically performed at the end of the
procedure and so you don’t need to save anything manually.
After a power cycle, your base or rover will therefore continue
to operate according to the last loaded configuration.
Running an RTK Survey
If you have followed all the instructions provided in this RTK
Surveying chapter, your rover is now fully configured and so
you can start your survey using your field-terminal-controlled
rover.
NOTE: To start the survey with the correct antenna height
when using FAST Survey, the rover should always have been
set up last.
The present section describes the main types of surveys you
can perform with FAST Survey and your Z-Max.Net, namely:
- RTK point logging (Stop & Go survey)
- RTK point logging in continuous mode (trajectory survey)
- RTK staking out.
32

Logging RTK Points
1. Tap on the Surv tab and then on Store Points. The screen
Logging point
with offset
Logging point
(general case)
Current status of
position solution
Enter the point name and
description in these two fields
Current position and related
quality figures
now displayed allows you to log all your points.
The figure below summarizes all the functions available
from that screen.
Logging point with
position averaging
Configures general
case of point logging
Provides access to
monitor screen
Your current position
and heading
Graphic Display area
GPS antenna height
English
Zoom settings
Viewing parameters
For example, you are on a point that you want to log. Do
the following:
2. Type in the point name and description in the corresponding two fields (see above)
3. Tap on the “A” button
4. Enter the number of readings you want before FAST Survey is allowed to compute an average position for this
point. For example, type in “5” and tap OK.
Messages follow successively indicating that the system is
taking the 5 requested readings. Then FAST Survey displays the average coordinates it has determined.
5. Tap OK if you agree. The “Point Stored” message appears
briefly. The screen then shows the location of the point
together with its name and description.
33

English
6. After logging all your points, tap MENU in the upper-right
corner of the screen to return to the menu.
Logging RTK Points in Continuous Mode
1. On the Surv tab, select the Auto by Interval function. Two
different modes are possible: Time or Distance.
2. If you choose Distance, enter the horizontal and vertical
increment value respectively in the X/Y and Z fields,
according to the chosen unit. If you choose Time, enter the
increment value, in seconds.
3. Enter a point Id. for the start point in the Starting Pt ID
field. This field will be incremented by one after each
point logging. You do not need to define a name finishing
with a figure. FAST Survey will place one anyway when
incrementing this field.
4. Press OK to switch to the graphic screen (see figure below)
and start logging the first point.
Used to log a point’s
position manually
Used to pause/resume
data logging
34
Point Id.
incremented
automatically
The S button lets you instantly log the position of a point.
The X button allows you to pause data logging in continu-
ous mode.
If data logging in continuous mode is paused, you can still
continue to log points in manual mode using the S button.

Name of point to
be staked out
Coordinates of point
to be staked out
Tap t h e X button again (changed into a right arrow during
pause) to resume data logging in continuous mode.
If you come back to the main menu by tapping on MENU,
then data logging in continuous mode is automatically
stopped.
Staking out RTK Points
1. Tap on the Surv tab and then select Stakeout Points. The
screen now displayed allows you to stake out your points.
2. On this screen, FAST Survey asks you to choose the point
you want to stake out. You can either type in its coordinates in the Northing, Easting and Elevation fields, or select
a pre-defined point from the points list (see File>List
Points). You can also, define graphically this point by tapping on the point on the graphic screen, or define that
point according to azimuth, slope and horizontal distance.
Provides access to points list.
Example of points list:
Provides access to
graphic screen
English
35

English
3. Once you have chosen a point, tapping on the OK button
Stakeout screen
Next point
Logs the point
Provides access to the detailed
stakeout screen below
Detailed stakeout screen
Point to be staked out
will display a graphic screen from which you can easily
stake out your point:
Takes you back to the point
selection screen
Configures general
case of point logging
Provides access to
monitor screen
Point to be staked out (target)
Your current position and
heading
36
Your current position
and heading
4. Tapping on the STORE button allows you to start perform-
Used to select which guidance
data to display
Used to select which data to
display for the point:
coordinates or quality data
The target radius is automatically changed as the distance
from you to the point changes.
When getting closer to the point, markers appear at the
four corners of the target (see below left) informing you
that you have arrived at the target. You can now materialize and log the position of this point.
ing measurements to determine the target position.

The number of measurements will depend on the value
entered earlier through the File tab>Configure Readings
function. Once the position has been determined, FAST
Survey displays the results of the computation so that you
can check them (see below right).
5. Tap OK if you are satisfied with the results. FAST Survey
will then save these results and will take you back to the
stakeout screen for the next point.
Downloading RTK Results to GNSS Solutions
English
Back at the office, do the following to download and view the
RTK results stored in the job you have just finished.
1. Prepare your field terminal for data downloading. With
MobileMapper CE, do the following:
- Clip the I/O module at the back of the unit.
- Connect the MobileMapper CE’s I/O module to the PC
using the USB cable provided.
2. Switch on the field terminal and then launch FAST Survey
3. Select File>6. Data Transfer>Carlson SurvCadd/Carlson Survey.
37

English
NOTE: When next
downloading RTK
results, the connection
to the field terminal
does not need to be re-
configured. This means
you can skip this step
by checking the Automatic Transfer option in
the Data Transfer dialog
box.
4. On the PC:
- Launch GNSS Solutions and then click Create a new
Project
- Name the project and click OK
- Select the spatial reference system that was used
during your RTK survey, select the appropriate time
zone and then click OK
- Click Do Not Import Anything Now. A new empty project
opens in GNSS Solutions.
- Select Tools>Preferences and make sure Show RTK
functions is enabled otherwise check it and then click
OK
- From the menu bar, select Project>Download Positions
from External Device
- In the dialog that opens, select RTK Results in the left
pane and then FAST Survey data collector in the right
pane
- Click OK. This opens the Data Transfer dialog box.
- To be able to configure the connection to the
MobileMapper CE the first time you download RTK
results, clear the Automatic transfer option and then
click OK. Two error messages may appear in the next
step. Just click OK when this happens. The SurvCom
window then appears on the screen.
- In the SurvCom window, click on the Options button
and then select the ActiveSync option in the upperright combo box (this option is last in the list)
- Click OK
- Select the “Data” folder on the MobileMapper CE and
click Exit
- In the new dialog that appears, you can now see the
list of jobs stored in the MobileMapper CE
- Click on the job you want to download. The name of
the selected job appears in the upper field.
-In the Directory field, choose the folder on your PC
where you would like to store this job
- Click OK. RTK results are now downloaded to the
project open in GNSS Solutions. At the end of the
transfer, these results can be seen on the project’s
Survey view.
38

4. Post-processing Surveying
Make sure the base is
sited in a clear area giv-
ing the best possible
view of the sky!
When this is possible,
avoid trees, buildings
or any high obstacles in
the vicinity of the base.
Having a clear view of
the sky will allow the
base to collect data
from a maximum of vis-
ible satellites, which is
highly recommended to
perform a successful,
accurate and fast sur-
vey.
This chapter only discusses the static mode of surveying. For
more information on Continuous (Trajectory) or Stop&Go
kinematic methods, please refer to the Z-Max.Net Reference
Manual.
Reminder on the Static Surveying Method
Typical Use: Surveying a New Control Point.
Equipment Involved Field Organization
Time Organization
Data collected at base:
Data collected on surveyed point:
Key Instructions:
Two units needed: one (the base) operated on an accurately known
1.
position and the other (the rover) on the point to be surveyed. There
can be several rovers logging data at the same time.
Approximate distance between the two units (baseline) must be
2.
known.
Data must be collected simultaneously by the two units. Use the
3.
same logging interval on both units.
Observation time is determined by last unit set up (start) and first unit
4.
turned off (end). We recommend that you start the base first and you
turn it off last.
Required observation time mainly depends on distance between the
5.
two units (+ reception conditions). Rover unit estimates observation
time needed.
When Estimated Base Line Len on the Z-Max.Net front panel
decreases down to “000km”, you can stop collecting data.
Base
Baseline
Known Point Survey Point
(Range)
Observation time
Rover
English
39

English
Running a Static Survey
A typical survey is described in this chapter using a
conventional tripod. No field terminal is used as controlling
system operation from the Z-Max.Net front panel is quite easy
in this case.
Equipment Setup
The equipment setup instructions are the same for both the
base and the rover. Install and run the base first.
In both cases, the installation site should offer the best
possible GPS reception conditions. The antenna should have
a clear view of the sky in all directions. There should be no, or
a minimum of satellite obstructions in the vicinity.
1. Make sure the chosen point is suitable for GNSS observations.
2. Connect the system components as explained on page 9.
For postprocessing surveys, a V-module, and not a communication module, should be attached to the right side
of the receiver module.
3. A memory card is required to log raw data. Insert this card
as explained on page 10. Formatting a memory card for
the Z-Max.Net requires that you re-initialize the Z-Max.Net
with the SD card inserted (see page 11).
4. Position the tripod over the chosen point
5. Insert the brass tribrach adapter through the hole in the
HI measurement plate and screw the adapter/plate into
the 5/8” threaded receptacle in the bottom of the
Z-Max.Net receiver module.
40

“Hb” read
on tape
Up key
Down key
Enter key
Cancel key
6. Once the tripod is accurately centered and leveled over
the point, and the tribrach adapter and HI measurement
plate are attached to the receiver module, carefully place
the assembly into the tribrach mounted on the tripod over
the point.
7. Use the tape measure to measure from the center of the
point to the measurement point of the Z-Max.Net (see Hb
opposite). Later on, you will have to enter the value read
on the tape (see point 4. on page 42).
Getting the Z-Max.Net Unit Started in Static
1. Press the Power button on the receiver module front panel
for 2 seconds until a beep is emitted.
2. Configure the system to perform a static survey: By
default, the Z-Max.Net system is configured to perform a
static survey. When turned on and once enough satellites
are received above 10 degrees of elevation, the receiver
automatically begins to collect and store data in a new
data file with a data recording interval of 10 seconds.
In the event the Z-Max.Net would not be configured to run
in static, do the following to re-configure the Z-Max.Net:
• Press the Down key until SURVCONF is displayed
• Press the Enter key
• Press the Down key and then the Enter key again
• Press the Down key until STATIC is displayed
• Press ENTER The screen now displays MODE:STATIC.
(The front panel interface is thoroughly described in the Z-
Max.Net Reference Manual. See also page 48 in this
guide.)
English
41

English
Up key
Down key
Enter key
Cancel key
3. Enter the Site ID:
• Press the Cancel key to return to SURVCONF
• Press the Down key until the screen displays
SURVEY:STATIC
• Press the Enter key. SITE ID:??? is displayed. You can
now enter the site ID:
• Press the Enter key again
• Enter the first of the four characters making up the
Site ID pressing the Up or Down arrow until the
desired character is displayed, then press Enter. Set
the second character using the same Up or Down key,
etc.
• After defining the last character, press the Enter key to
validate the site ID. The screen displays the entered
site ID (e.g. “SITE ID:0005”)
4. Enter the Hb height measured earlier with the tape (see
point 7. on page 41):
• Press the Up key. The screen displays ANT HT:..
• Press the Enter key
• Enter the first character of the antenna height measured previously using the Up or Down key, then press
Enter. Set the second character using the same Up or
Down key, etc.
• After defining the last character, press the Enter key to
validate the HI. The screen displays the entered HI
(e.g. “ANT HT:01.5703m”)
5. Set the recording interval:
• Press the Cancel key to return to SURVEY:STATIC
• Press the Up key until SURVCONF is displayed
• Press the Enter key. You can now enter the recording
interval:
42

• Press the Enter key
• Enter the first character of the recording interval using
the Up or Down key, then press Enter. Set the second
character using the same Up or Down key, etc.
• After defining the last character, press the Enter key to
validate the recording interval. The screen displays the
entered interval (e.g. “REC INT:20.0s”)
6. For the static “rover” only, enter the approximate length of
the baseline:
• Return to the SURVEY :STATIC root menu, press Enter,
press the Up key twice and then enter this length
(ESTIMATED BASELINE LEN:xxxkm). This parameter is
very important as it will be used by the Z-Max.Net to
help you determine the end of data collection.
Starting Data Collection
1. Start raw data logging as follows:
• Return to the root menu and then press the Down key
until SESSIONS is displayed
•Press Enter. START SESSION is now displayed.
• Press Enter again. Start Session? is now displayed.
• Press Enter again. DONE is displayed for a few sec-
onds. Data logging is now in progress as indicated on
the Data Log LED which should blink green once at
the frequency of the data recording interval.
English
End of Data Collection
1. Return to the SURVEY:STATIC root menu, press Enter, press
the Up key twice. The screen should now display the ESTI-
MATED BASE LINE LEN parameter.
43

English
2. Let the Z-Max.Net rover collect data until this parameter
goes down to “000 km”. A message is then displayed
informing you that you can stop data collection. But
always use your own judgement to decide the moment
when to stop data collection.
Remember the amount of data required is dependent on a
number of factors including:
- The quality of the satellite geometry (PDOP),
- The number of satellites above the elevation mask,
- Any obstructions between the satellites and the GPS
antenna
- The distance (or vector length) between the receivers
collecting data simultaneously.
3. To end data collection, just turn off the Z-Max.Net system
by pressing the Power button for 2 seconds. When the
receiver is powered down the active measurement file is
automatically closed.
When the receiver is powered back up a new measurement
file will be automatically created.
After data collection is complete, take all Z-Max.Net systems used in the survey to the office and download the
data to an office computer as described in Downloading
Field Data to your PC on page 45. The data is now ready
for post-processing using GNSS Solutions.
44

Downloading Field Data to your PC
After downloading your
field data, do not forget to
re-insert the SD card into
the Z-Max.Net before tak-
ing it back to the field!
The easiest and fastest way to download your field data is to
use the card reader attached to the office PC. This procedure
is described in the present section. It is assumed that GNSS
Solutions has already been installed on your PC.
If you don’t have a card reader, you can download your field
data directly from the Z-Max.Net via a USB or RS 232 link.
This procedure is described in the Z-Max.Net Reference
manual. Please refer to this manual for more information.
Back in your office, do the following to download your field
data.
1. On the Z-Max.Net:
- Remove the SD card from the Z-Max.Net
- Insert the SD Card in your local SD card reader.
2. On the PC:
- From the Windows task bar, select Start>Pro-
grams>GNSS Solutions>Tools>Download.
(Double-click in the right side of the window if
you want to change to the parent directory and open
another folder on your PC.)
- In the Download window, click on the drive combo box
(see below) in the left-hand pane and select the letter
corresponding to the local SD card reader (example:
SD card reader is “F:”).
English
45

English
Files resulting from the
downloading of an
observation file are
named as follows:
X<Downloadedfilename>
where prefix X = “E” for
Ephemeris Data, “B”
for Position Data, “D”
for GPS Raw Data and
“W” for SBAS Data.
The left side of the Download window then lists the
files present on the SD card.
- Select the files you want to download. If necessary,
hold down the Ctrl key to make a multiple selection.
- Press the F5 key. A Copying file dialog appears during
data transfer.
After the transfer is complete, notice in the right side
of the Download window that each downloaded file has
been split into different files named with a prefix as
explained opposite.
- Close the Download window.
3. Repeat the previous two steps for each of the Z-Max.Net
units involved in the project to download their respective
files to the same project folder on your office computer.
Post-Processing Field Data
1. On your office computer, launch GNSS Solutions
2. Click Create a New Project, enter a project name and then
click OK.
3. Click Import Raw Data from Files.
4. Browse your computer to change to the folder containing
the data files you have just downloaded.
5. Select the files you want to import and click Open.
46

The Importing GPS Data dialog lists the files you want to
import (top). Each row describes one of these files (filename, associated Site ID, etc.)
6. At the bottom of the window, define which of the sites is
the control point (base) and enter or check its known coordinates. You can also fix the control point if necessary by
selecting one of the options available in the Fixed column.
If you select <Blank>, the point won’t be fixed.
7. Click OK>To Import to import the data into the project.
Depending on the type of survey, you can go even faster by
running, in one operation, the Import, Process and Adjust
functions.
For more information on GNSS Solutions, please refer to the
GNSS Solutions Reference Manual.
English
47

English
Thin arrow - Enter or Cancel Key
5. Front Panel Interface Function Diagram
SYSINFO
RCVR
VERSION
RCVR
S/N
OPTIONS
BAT
MEM
SURVEY:
Current Mode
STATIC
SITE
ANT HT
BASELINE
STATUS
OR
KINEMATIC
SITE
ANT HT
STATUS
OR
RTK BASE
SITE
ANT HT
ANT RAD
BASE POS
STATUS
OR
RTK ROVER
SURVCONF
STATIC
REC INT
ELEV MASK
SBAS
Select SURVEY MODE
OR
KINEMATIC
EPOCH CNTR
MIN SV
REC INT
ELEV MASK
Select SURVEY MODE
OR
RTK BASE
PORT/TYPE
REC INT
ELEV MASK
Select SURVEY MODE
OR
RTK ROVER
Symbology:
Thick Arrow - Up or Down Key
See Reference Manual
SESSIONS
STOP
SESSION
START
SESSION
LIST
SESSION
NEW
SESSION
DELETE
ALL
SETTINGS
MEMORY
RESET
RESET TO
FACTORY
DEFAULTS
BAUD
RATE
LANGUAGE
BEEP
SAVE
COM
OPTN
MAGELLAN
RADIO
PDL
GSM
ROVER
GSM
BASE
48

Index
A
Access Point Name 30
Auto connect (Bluetooth)
B
Backpack 2, 13
Baseline
13, 39
Baseline length
Bluetooth
Bluetooth icon
Bluetooth port
43
18
21
4
C
Caster IP address 30
Cellular modem
Charger
Charging the power module
Collar (threaded)
Communication LED
Communication module
Control keys
Coordinate system
13
2, 8
5
D
Data collection 43
Data link
Data Log LED
DBEN
Detecting Bluetooth devices
Display mode
Downloading field data
13, 24
4
14, 24
5
E
Edit mode 5
Entering base position
Entering height
Estimated baseline length
External power
External Power In
15, 17, 25, 28, 42
15
F
FAST Survey 13
FAST Survey CD
Field bracket
Finding Bluetooth services
Flattened area
Formatting, re-formatting SD card
Front panel display
Front panel interface
2
1
9
G
Geoid model 24
GNSS antenna module
GNSS Solutions CD
21
8
10
4
2
24
19
45
25
43
6
20
5
41
2, 7
2
11
GNSS Solutions software 45
GPRS
13, 30
GPS receiver module
GPS-RF cable
2, 3
2
H
Handle 6
HI measurement plate
HI measurement tool
2, 15, 40
2
I
Initializing 11
Inserting modules
IP port number
9
30
J
Job 23
Juniper Allegro CX
2
L
Latch 9
Log in for access to NTRIP caster
Log in for GPRS connection
Logging interval
39
30
30
M
Magellan MobileMapper CE 2
Magellan U-Link transmitter
Max RF adapter
Modem SIM PIN number
Monitor skyplot
Mounting bracket
2
27, 29
2
2
30
N
NTRIP 30
O
Observation time 39
Ordering information
Other external device
1
13
P
Pacific-Crest UHF Transmitter 2
Password for access to NTRIP caster
Password for GPRS connection
PIN number
Port A
Port B
Post-processing field data
Power key
Power Module
18, 19
6
6
6
2
30
46
R
Range pole 2
Range pole RF adapter
Range-Pole
RTCM 3.0
RTK Solution LED
13
31
2
4
English
30

English
S
Satellite/Power LED 4
Saving Bluetooth connections for FAST
Survey
22
Saving Bluetooth settings
SD Card
2, 10
SD card reader
Serial data cable
Site ID
Soft case
Stake out
Static
41
Status LEDs
Stop & Go
T
Tap and hold 18
Toggling from base to rover
Trajectory
Turning On/Off
U
UHF antenna module 2
UHF radio
UHF-RF cable
U-Link
Units
23
USB cable
USB port
V
Virtual (ports) 20
V-module
6
2
42
2
35
4
39
39
10
13
2
14
2
6
2, 3
21
23


Z-Max®.Net
Getting Started Guide
Magellan
Survey Solutions Contact Information:
In USA
+1 408 615 3970 ■Fax +1 408 615 5200
Toll Free (Sales in USA/Canada) 1 800 922 2401
In South America +56 2 273 3214 ■Fax +56 2 273 3187
Email surveysales@magellangps.com
In Singapore +65 6235 3678 ■Fax +65 6235 4869
In China +86 10 6566 9866 ■Fax +86 10 6566 0246
Email surveysalesapac@magellangps.com
In France +33 2 28 09 38 00 ■Fax +33 2 28 09 39 39
In Germany +49 81 6564 7930 ■Fax +49 81 6564 7950
In Russia +7 495 956 5400 ■Fax +7 495 956 5360
In the Netherlands +31 78 61 57 988 ■Fax +31 78 61 52 027
veysalesemea@magellangps.com
Email sur
o.magellanGPS.com
.pr
www
Magellan follows a policy of continuous product improvement; specifications and descriptions are thus subject to change without notice. Please contact Magellan for the latest product information.
©2003-2006 Magellan Navigation, Inc. All rights reserved. Z-Max is a trademark of Magellan Navigation, Inc. All other product and brand names are trademarks of their respective holders.
P/N 631520-01D
 Loading...
Loading...