TRIMBLE EUROPE 800963, 800964 Operators Guide

Z-Max®.Net
Getting Started Guide

English
Copyright Notice
Copyright 2003-2006 Magellan Navigation. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
All product and brand names mentioned in this publication
are trademarks of their respective holders.
FCC Notice
Z-Max.Net Receiver complies with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to the Part 15 of the FCC rules
when it is used in Portable Mode. See Note below related
to Class B device.
Class B digital devices NOTE: This equipment has been
tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instructions , may cause harmful inte rference to
radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If
this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning
the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try and
correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
- Reorient or locate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician
for help.
When Z-Max.Net is used with an external power supply or
connected to an external device using the USB port, it
complies with the limits fo r a Class A digital device, p ursuant to the Part 15 of the FCC rules. See Note below related
to Class A device.
Class A digital devices NOTE: This equipment has been
tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the instruction
manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area
is likely to cause harmfu l interference in which case the
user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
Remark: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by Magellan Navigation, could void the right for
user to operate the equipment.
RF Safety Exposure To Radio Frequency Energy (SAR)
Radio transmitting devices radiate Radio Frequency (RF)
energy during its operation. RF energy can be absorbed
into the human body and potentially can cause adverse
health effects if excessive levels are absorbed. The unit of
measurement for human exposure to RF energy is "Specific
Absorption Rate" (SAR).
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC), Industrie
Canada (IC), and other agencies around the world have established limits that in corporate a substanti al safety margin designed to assure the safety of all persons using this
equipment. In order to certify this unit for sale in the US,
Canada and Europe this unit has been tested for RF exposure compliance at a qualified test laboratory and found to
comply with the regulations regarding exposure to RF Energy. SAR was measured with the unit (GSM Module) transmitting at its maximum certified RF power. Often, however,
during normal operation the unit (GSM Module) will transmit much less than maximum power. Transmit power is
controlled automatically and, in general is reduced as you
get closer to a cellular base station. This reduction in trans-
mit power will result in a lower R F energy exposure and resulting SAR value.
SAR: ANSI/IEEE C95.1 1992
FCC OET Bulletin 65 Supplement C
1999/519/CE
The SAR value for this wireless survey system when worn
on the body, as described in this user guide, is always less
than 1.45 W/kg.
Caution! FCC RF exposure requirements: SAR compliance
for body-worn operations is restricted to belt-clips,
holsters, and accessories supplied or designated for this
product. Use of other accessories may not ensure
compliance with FCC RF exposure guidelines.
FCC and CE UHF Safety Statement
The different versions of the UHF Transmitters are FCC and
CE compliant.
In order to comply with FCC and CE RF exposure safety
guidelines as body-worn, normal use of unit, the following
must be followed:
A distance of AT LEAST 10 feet (3 m) of separation between the users body and the unit (UHF Transmitter). This
distance has been defined taken into account the FCC and
CE Requirements and the worst output power configuration.
Do NOT use the device in a manner such that it is in direct
contact with the body (e.g. on the lap). Such use will likely
exceed FCC RF safety exposure limits. See www.fcc.gov/
oet/rfsafety/ for more i nformation on RF expo sure safety.
Antenna Care/Unauthorized Modifications
Use only the supplied integral antenna. Unauthorized antenna modifications or attachments could damage the unit
and may violate FCC and CE regulations. Any changes or
modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Replacing the Magellan U-Link Transmitter Power Fuse
The Magellan U-Link transmitter is protected by a 4-A fuse
inserted in the data/ power cable. This Y-s haped cable is
used to connect the U-Link transmitter to the Z-Max.Net
receiver via a 7-pin connector, and to the power battery.
Should you have to replace this fuse, please get a spare
fuse, 4 A, fast act ing, ATO type, and then do the following:
- Unplug the battery end of the data/power cable
- Open the fuse holder located along the data/power cable
- Extract the damaged fus e
- Insert the new fuse and then push the holder lid back into
place
- Connect the data/power cable back to the battery.
Where to Find Informatio n
This manual is designed to guide you through the basic
Z-Max.Net procedures. You can find additional information
in the Z-Max.Net Reference Manual, also provided on the
Z-Max.Net CD.
Warranties
Refer to the Z-Max.Net Reference Manual.

Table of Contents
Introduction............................................................. 1
System Components Overview..........................................1
Locating the Basic Components .......................................3
Z-Max.Net Front Panel ....................................................3
Bluetooth® Port........................................................ 4
Status LEDs ............................................................. 4
Front Panel Display ................................................... 5
Control Keys ............................................................. 5
Power Key ................................................................ 6
SD Card Reader and USB .......................................... 6
Z-Max.Net Rear Panel.....................................................6
GNSS Antenna Configurations .........................................7
Base ........................................................................ 7
Pole-Mounted Rover .................................................. 7
Backpack-Mounted Rover .......................................... 7
Preparing For First-Time Use..................................... 8
Charging the Power Module .............................................8
Attaching the Lateral Modules .........................................9
Attaching the GNSS Antenna Module ...............................9
Inserting a Memory Card ...............................................10
Turning On/Off the System ............................................10
Initializing the System ..................................................11
Checking that Z-Max.Net Receives Satellites...................12
RTK Surveying ....................................................... 13
RTK Surveying Method Requirements............................. 13
RTK Base Setup...........................................................14
Choosing the Installation Site................................... 14
Setting Up the RTK Base ......................................... 14
RTK Rover Setup.......................................................... 16
Establishing Bluetooth Communication with Z-Max.Net....18
Introduction ........................................................... 18
Powering up the Whole Equipment ........................... 19
Detecting Bluetooth-Enabled Devices........................ 19
Finding Bluetooth Services ...................................... 20
Assigning Virtual Ports to Bluetooth .......................... 20
Saving Bluetooth Serial Port Settings ........................ 21
Defining/Saving Bluetooth Settings for FAST Survey ... 22
Toggling Bluetooth Between Base and Rover.............. 23
Configuring the RTK Base .............................................23
Launching FAST Survey........................................... 23
Configuring the Base and the Data Link .................... 24
Entering the Base Position and ID ............................ 25
Setting the Radio .................................................... 26
Configuring the RTK Rover ............................................27
Case #1: Rover Using a UHF Radio Data Link ............ 28
Case #2: Rover Using a GSM/GPRS Data Link ........... 30
English

English
Saving Base and Rover Settings .................................... 32
Running an RTK Survey ............................................... 32
Logging RTK Points ................................................ 33
Logging RTK Points in Continuous Mode .................. 34
Staking out RTK Points ........................................... 35
Downloading RTK Results to GNSS Solutions ................. 37
Post-processing Surveying....................................... 39
Reminder on the Static Surveying Method...................... 39
Running a Static Survey ............................................... 40
Equipment Setup ................................................... 40
Getting the Z-Max.Net Unit Started in Static ............. 41
Starting Data Collection .......................................... 43
End of Data Collection ............................................ 43
Downloading Field Data to your PC ................................ 45
Post-Processing Field Data ........................................... 46
Front Panel Interface Function Diagram ................... 48

1. Introduction
Congratulations! You have just acquired your new dualfrequency Z-Max™.Net GNSS Surveying System from
Magellan!
GNSS (or Global Navigation Satellite System) has
revolutionized control surveys, topographic data collection
and construction surveying. Purchasing the right tools for a
professional job is essential in today's competitive business
environment.
Learning to put these tools to work quickly and efficiently will
be the focus of the present guide.
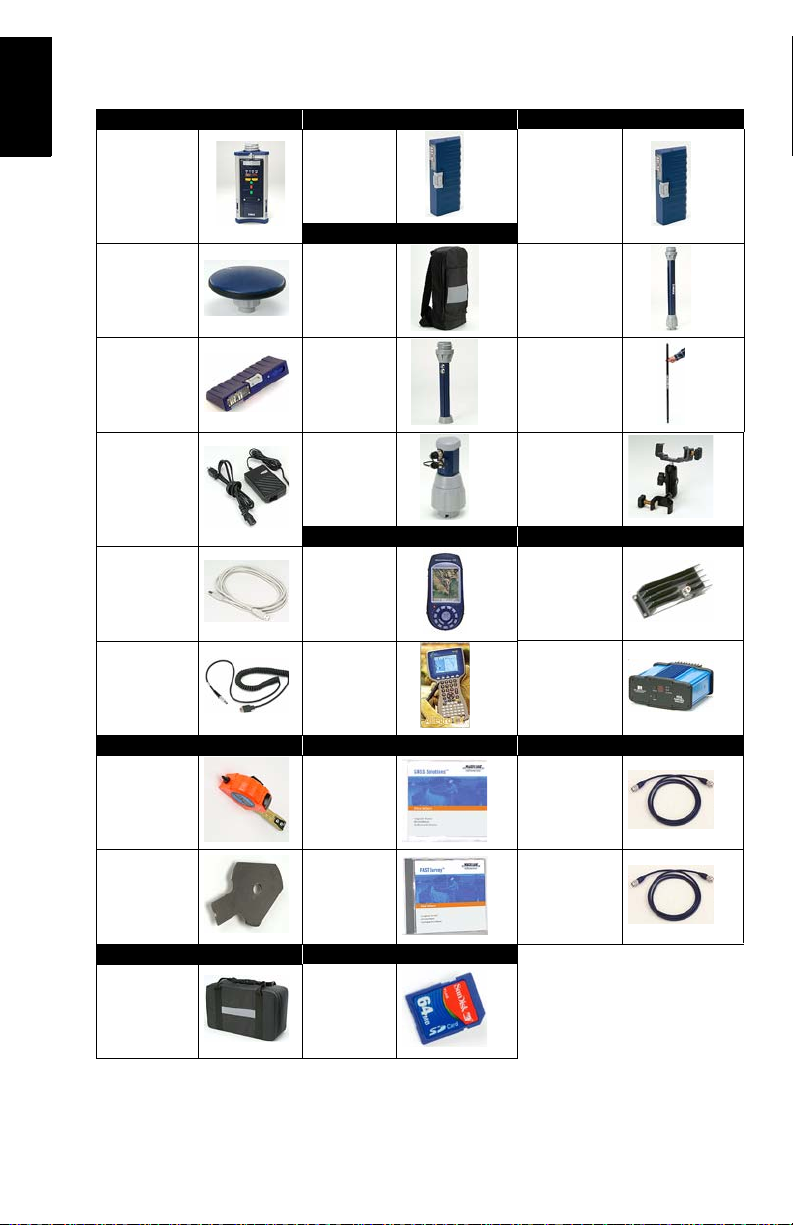
System Components Overview
The table below provides an overview of the different key
items composing the Z-Max.Net System. Depending on your
purchase, based on the type of survey you wish to perform, you
may only have part of the listed items. Please refer to the
delivered packing list for an accurate description of the
equipment that has been delivered to you.
Conversely, as this table is just an overview, it does not list all
the possible items and accessories. For example, the list of all
the possible field terminals is provided but we intentionally do
not mention the field brackets that usually come along with
them. For more information on these items, please contact
your dealer.
For ordering information, please refer to the Z-Max.Net
Reference Manual.
English
1
English
Basic Post-Processing Rover, RTK
GPS Receiver
Module
GNSS Antenna
Module
Power Module Range Pole
Charger
USB Cable
Serial Data
Cable
Static, Base Software RF Cables
V-Module (1)
(Void module)
Rover, Backpack
Backpack
RF Adapter
Max RF
Adapter
Field Terminal Radio
Magellan
MobileMapper CE
Juniper
Allegro CX
Communication
Module
UHF Antenna
Module (2)
Range Pole
Mounting
Bracket
Magellan U-Link
transmitter
Pacific-Crest
UHF Transmitter
HI measurement tool
eHI Measure-
ment Plate
Transport Case Memory Device
Soft case
GNSS Solutions CD
FAST Survey
CD
SD Card (sold
by Magellan)
2
GPS-RF cable
UHF-RF cable
(1) Also used in an RTK base using a
UHF radio as the data link.
(2) A void UHF antenna module also
exists.

Locating the Basic Components
2. GNSS Antenna Module
3. Power Module 4. Communication Module
or V-Module
1. Receiver
Module
As you are facing the front panel of the GPS receiver module,
the power module attaches to the left-hand side of the
receiver module and the communication module (or Vmodule) to the right-hand side.
Z-Max.Net Front Panel
English
Z-Max.Net Bluetooth®
Status LEDs
Front Panel User Interface
Control keys
Power key
3
English
Bluetooth® Port
This device allows you to communicate with the Z-Max.Net
through a Bluetooth wireless connection. This port is
identified as “port C” on the Z-Max.Net.
Status LEDs
From left to right, the LEDs are:
• RTK Solution. This LED is only operational when the
receiver is configured as an RTK rover.
Color Meaning
Off Not a RTK rover
Blinking green Fixed solution
Blinking orange Float solution
Blinking red No RTK solution
• Communication. This LED indicates when real-time data
is transmitted (base) or received (rover).
Color Meaning
Off No data link has been configured
Blinking green
Blinking red
Not blinking
Base: Transmits data
Rover: Base data received and used
Base: Irrelevant
Rover: Base data received but not used
Base: No data transmitted
Rover: No base data received
• Data Log. This LED shows the data logging status.
Color Meaning
Off No data logging in progress
Blinking green
Red Unable to log data (memory full)
Data logging in progress. Blinks at the frequency of the
recording interval setting (20 seconds by default).
• Satellite/Power. After power up, this LED will continue to
blink red once every 1-2 seconds to indicate that the unit
is powered on. Between each red blink, the LED will also
blink green once for each satellite that the receiver is
tracking.
4
Up key
Enter key
Down key
Front Panel Display
The front panel display is an 8-character, alphanumeric LED
display that is used to monitor receiver status, set receiver
parameters and configure the receiver to perform different
types of surveys.
The screen displays up to eight characters at one time.
Messages or parameters longer than eight characters are
scrolled from right to left.
Control Keys
The four control keys are used in conjunction with the front
panel display. They will work differently depending on whether
the screen is in Display or Edit mode.
English
Cancel key
Display Mode:
Key Operation
UP (yellow) Scrolls menu (at same level) forward
DOWN (yellow) Scrolls menu (at same level) backward
ENTER (green) Selects and moves down to next level or enters Edit mode
CANCEL (red) Returns to upper level
Edit Mode:
Key Operation
Data entry context: Scrolls forward through characters
UP (yellow)
DOWN (yellow)
ENTER (green)
CANCEL (red)
Parameter list context: Scrolls forward
Fast scrolling if held depressed for 3 seconds
Data entry context: Scrolls backward through characters
Parameter list context: Scrolls backward
Fast scrolling if held depressed for 3 seconds
Parameter list context: Selects parameter
Data entry context: Accepts character and moves to ne xt spac e
or quits Edit mode
Data entry context: Deletes last edited character, stays in Edit
mode
Parameter list context: Moves from Edit mode to Display mode
without selecting the parameter.
See Z-Max.Net Reference Manual for more information.
5

English
Power Key
This key is used to power up, power down or initialize the unit
(see page 10).
Power key
SD Card Reader and USB
Below the four control keys is a small door fastened by two
thumbscrews. Unscrew the attaching screws and open the
door to reveal the SD Card slot and the USB port.
The SD card slot holds the SD card that serves as the
receiver's data storage memory. All data recorded by the unit
is stored on the SD card. Warning! Use exclusively SD cards
sold by Magellan.
The USB port is one of the external ports available for
connecting to a computer. The USB port is a type-B
connector.
Z-Max.Net Rear Panel
Handle
External Power In (10-28 V DC)
Port A (RS232)
Port B (RS232 or RS422)
For connector pinout, see Z-Max.Net Reference Manual.
6

GNSS Antenna Configurations
(A)
(B)
In all cases of use, the GNSS antenna module must be
connected to the receiver module. But there are three
different ways of doing this, as explained below.
Base
The GNSS antenna module (A) is directly attached to the
receiver module (B).
(A)
Pole-Mounted Rover
The GNSS antenna module (A) is attached
to the receiver module (B) via a UHF
antenna module or a Void UHF antenna
module (C).
(C)
(B)
Backpack-Mounted Rover
The GNSS antenna module (A) is attached to the receiver
module (B) via a UHF antenna module or Void UHF antenna
module (C), a range pole adapter (D), a dual RF cable (E) and
a Max-RF adapter (F).
(A)
(E)
GPS
English
(D)
(C)
(F)
UHF
(B)
7

English
Use of non-Magellan
power supplies for
charging the power
module is not
recommended.
2. Preparing For First-Time Use
Charging the Power Module
To charge the power module:
• Plug in your charger and connect the power module to the
charger as shown opposite.
• Charge for a minimum of five hours or preferably overnight
(even if the charger indicates that the battery is full).
• Verify that the battery is fully charged by pressing the button on the back side of the power module. The four LEDs
should light up green.
The power module contains rechargeable lithium-ion battery
cells and “smart” charging circuitry. Recharging the power
module is done using the AC/DC power supply, included with
the system.
This power supply can also be used to provide power directly
to the Z-Max.Net through an external connector. The charger
is designed to work with a 110-240 VAC power source and
delivers 12 V DC of input voltage with at least 4-A current
capability to the power module.
For more information on the characteristics and management
of the power module, see Z-Max.Net Reference Manual.
8

Attaching the Lateral Modules
Please take all precau-
tions to keep connector
pins clean and avoid
touching them.
Whatever the type of module you are
attaching to the receiver module, i.e. a
power module on the left, or a
communication or V-module on the
right, do the following:
• Insert the small ledge of the module
into the rear of the housing first as
shown opposite (left and right). This
will correctly align the module.
• Using the ledge like a hinge, start
swinging the module. To make sure
the module is correctly positioned vertically, take care to
align the protruding edges, on either side of the connector
pins, with the grooves in the receiver module casting.
Then swing the module closed until the latch on the module clicks into place.
• Make sure the module is well seated and the latch on the
edge of the module clicks shut.
Attaching the GNSS Antenna Module
The base of the GNSS antenna module is circular except for a
flattened area. The top of the receiver module, UHF antenna
module or Void UHF antenna module is keyed so there is only
one way the GNSS antenna module can be inserted.
• Make sure the base of the GNSS antenna module is oriented so that the flattened area is lined up with the flattened area of the receptacle.
• Once aligned, insert the GNSS antenna module into the
antenna receptacle. The module should push easily into
place.
English
9

English
Use exclusively SD
cards sold by Magellan!
It is important to power
off the receiver using
the Power key on the
Front Panel before
removing the SD card.
• Once in place, twist the threaded collar on the GNSS
antenna module until the antenna is securely locked in
place.
Inserting a Memory Card
A memory card is required if you want to run a post-processing
survey or more generally, when you want to log raw data with
your Z-Max.Net.
To install the SD Memory Card into the reader:
• Orient it so that the chamfered corner of the card is oriented downwards, as shown opposite.
• Gently push the card into the reader until you feel a soft
“click”. The click indicates that the card is properly
seated. A correctly inserted SD card should not move once
you have removed your hand from the card.
Turning On/Off the System
• Power on the system by pressing the Power button on the
receiver front panel for about 2 seconds (until a beep is
emitted) and then releasing the Power button.
The SV/Power LED should begin to blink red once per second to indicate that the receiver is powered up.
• To turn off the system, just press and hold the power key
for two seconds. The receiver will generate a beep every
second, a “shutdown” message will be displayed, and the
receiver will then power down.
10

Initializing the System
Initializing the system is recommended the first time you use
your system to:
• Clear the internal memory
• Reset the user settings to their default values
• Clear ephemeris and almanac information in memory
• Re-format the SD card. Note that initialization should also
be performed every time you prepare your SD card for a
new survey project. It’s always better to delete files from
the SD Card by running an initialization sequence rather
than using any other method.
Initializing the system is also appropriate any time the
Z-Max.Net does not work as expected.
To initialize the system from the Power button, assuming the
system is off, do the following:
• Press the Power button for at least 5 seconds.
The display will show “re-init”, indicating that the receiver
is in the initialization process.
The initialization process will take several minutes
depending on the size of the SD card. The front panel will
continue to display “re-init” until the process is complete.
When complete, the receiver will be powered on and in the
normal state with the front panel displaying “SYSINFO”
and the SD card ready to use.
English
11

English
Please go outside after
initialization and make
sure your system has a
clear view of the sky in
all directions.
Checking that Z-Max.Net Receives Satellites
If the GPS antenna has a reasonably good view to the sky,
within a few minutes, the receiver should begin to track
satellites. This is indicated by the SV/Power LED:
1. It should blink red once per second to indicate that power
is on, and blink green several times between each red
blink.
2. It will blink green once for each satellite that is being
tracked. In normal conditions of reception, the system
should receive about eight satellites on average.
12

3. RTK Surveying
When the base setup is
under your responsibil-
ity, make sure the base
is sited in a clear area
giving the best possible
view of the sky!
When this is possible,
avoid trees, buildings
or any high obstacles in
the vicinity of the base.
Having a clear view of
the sky will allow the
base to collect data
from a maximum of vis-
ible satellites, which is
highly recommended to
perform a successful,
accurate and fast sur-
vey.
RTK Surveying Method Requirements
Key information is provided below.
Two units are needed: one (the base) is operated on an accu rately known
1.
position while the other (the rover) is used in the working area.
A data link must be established from the base to the rover. This data link
2.
can be implemented in three differ ent ways:
- UHF radio
- Cellular modem (GSM)
- Other external device
Depending on the chosen data link, the base will be either:
3.
- A “real” base system (with UHF radio, GSM, or other external device)
- Or a “virtual” base system that delivers its data via a cellular modem
(GPRS).
The main Z-Max.Net RTK system configurations are illustrated below:
GPRS
Internet
Data Link
Rover
UHF Radio
Base
GSM
Base
Data Link
Data Link
Rover
Rover
English
Two differe nt rover setups can be used, backpack or range pole, yet oper-
4.
ated similarly. Only the pole-mounted rover system will be described in
this Guide. For more information on the backpack mo unting, refer to the Z-
Max.Net Reference Manual.
RTK is easier to operate using a field terminal running FAST Survey. RTK
5.
can also be operated from the receiver front panel display.
Whatever the base used (“real” or “virtual”), i ts distance to the ro ver , ca lled
6.
“baseline” (up to 50 km or 30 miles), must roughly be known to make sure
RTK results will achieve the expected level of accuracy.
13
 Loading...
Loading...