
USB Wireless Network
Adapter
User’ s Manual
Rev 1.1

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
2
Regulatory compliance
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
Ÿ Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Ÿ Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Ÿ Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
Ÿ Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
You are cautioned that changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void your authority to operate the equipment.
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment.
This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm
between the radiator & your body.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
3
About this manual
This User’ s Manual describes how to install and operate your USB Wireless
Network Adapter. Please read this manual before you install the product.
This manual includes the following topics:
Ø Product description and features.
Ø Hardware installation procedure.
Ø Software installation procedure.
Ø FAQ

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
4
Table of Contents
Regulatory compliance
About this manual
Chapter 1- Introduction 6
Features 6
What is Wireless LAN? 7
Wireless LAN Modes 7
Notes on Wireless LAN Configuration 8
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation 9
Package Contents 9
System Requirements for the Adapter 9
Connecting the USB Adapter 9
LEDs Indicators 10
Disconnecting the USB Adapter 11
Chapter 3 - Installation Procedures
Under Windows 98 12
What You Will Need 12
Installing the Driver Under Windows 98 12
Uninstall Procedure Under Windows 98 15
Chapter 4 - Installation Procedures
Under Windows 2000 16
What You Will Need 16
Installing the Driver Under Windows 2000 16
How to Unplug the Device Under Windows 2000 20
Uninstall Procedure Under Windows 2000 21
Chapter 5 - Installation Procedures
Under Windows ME 22
What You Will Need 22
Installing the Driver Under Windows ME 22
Uninstall Procedure Under Windows ME 24
Chapter 6 - Install and Use Configuration Utility 25
How to Install the Configuration Utility 25
Using the Configuration Utility 27
Appendix A – FAQ 33
Appendix B – Specifications 35

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
5

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
6
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the USB Wireless Network Adapter. This high-speed
USB Wireless Network Adapter provides you with an innovative wireless
networking solution. The Adapter is easy to set up and use. With this innovative
wireless technology, you can share files and printers on the network—without
inconvenient wires! Now you can carry the LAN in your pocket!
The Adapter is a network adapter with a rate of 1, 2, 5.5, and 11 Mbps operating
in the ISM band using Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) transmission
implementing the IEEE 802.11b standard. This adapter provides Device Drivers
for Windows 98, Windows 2000 and Windows ME. It also provides tools for the
configuration of the adapter. The tool, as well as the installation steps of the
plug-and-play procedure for the Microsoft Windows 98, Windows ME and
Windows 2000 operating systems, is described in this document.
Features
The USB Wireless Network Adapter offers compliance with the IEEE 802.11b
specification. This feature allows them to communicate with other wireless
devices that support the standard. Features of the adapter are:
l Uses 2.4GHz frequency band, which complies with worldwide
requirement
l Wireless interface following the IEEE 802.11b standard
l Using Universal Serial Bus (USB) interface
l Enciphering/deciphering of wireless data by the implementation of the
WEP algorithm
l Wire-free access to networked resources from anywhere beyond the
desktop
l Allows users move between Access Points without resetting their
connection reconfiguration
l Delivers data rate up to 11 Mbps
l Supports 11, 5.5, 2, and 1 Mbps rates
l Provide USB Wireless Network Adapter Configuration utility
l Antenna is built in to the Adapter with LEDs indicating Power and Link
l Supports most popular operating systems: Window 98/2000 &
Windows ME

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
7
What is Wireless LAN?
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) systems offer a great number of
advantages over traditional wired systems. WLAN is flexible and easy to setup
and manage. They are also more economical than wired LAN systems.
Using radio frequency (RF) technology, WLAN transmit and receive data
through the air. WLAN combine data connectivity with user mobility. For example,
users can roam from a conference room to their office without being
disconnected from the LAN.
Using WLAN, users can conveniently access-shared information, and network
administrators can configure and augment networks without installing or moving
network cables.
WLAN technology provides users with many convenient and cost saving
features:
• Mobility: WLAN provide LAN users with access to real-time information
anywhere in their organization, providing service opportunities that are
impossible with wired networks.
• Ease of Installation: Installing is easy for novice and expert users alike,
eliminating the need to install network cables in walls and ceilings.
• Scalability: WLAN can be configured in a variety of topologies to adapt to
specific applications and installations. Configurations are easily changed
and range from peer-to-peer networks suitable for a small number of users
to full infrastructure networks of thousands of users roaming over a broad
area.
Wireless LAN Modes
Wireless LANs can be configured in one of two ways:
Ad-hoc
Networking
Also known as a peer-to-peer network, an ad-hoc
network is one that allows all workstations and
computers in the network to act as servers to all other
users on the network. Users on the network can share
files, print to a shared printer, and access the Internet
with a shared modem. However, with ad-hoc
networking, users can only communicate with other
wireless LAN computers that are in the wireless LAN
workgroup, and are within range.
Infrastructure
Networking
Infrastructure networking differs from ad-hoc networking
in that it includes an access point. Unlike the ad-hoc
structure where users on the LAN contend the shared
bandwidth, on an infrastructure network the access
USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
8
point can manage the bandwidth to maximize
bandwidth utilization.
Additionally, the access point enables users on a
wireless LAN to access an existing wired network,
allowing wireless users to take advantage of the wired
networks resources, such as Internet, email, file
transfer, and printer sharing.
Infrastructure networking has the following advantages
over ad-hoc networking:
• Extended range: each wireless LAN computer
within the range of the access point can
communicate with other wireless LAN computers
within range of the access point.
• Roaming: the access point enables a wireless LAN
computer to move through a building and still be
connected to the LAN.
• Wired to wireless LAN connectivity: the access
point bridges the gap between wireless LANs and
their wired counterparts.
Notes on Wireless LAN Configuration
When configuring a wireless LAN (WLAN), be sure to note the following points:
• Optimize the performance of the WLAN by ensuring that the distance
between access points is not too far. In most buildings, WLAN cards
operate within a range of 100 ~ 300 feet, depending on the thickness and
structure of the walls.
• Radio waves can pass through walls and glass but not metal. If there is
interference in transmitting through a wall, it may be that the wall has
reinforcing metal in its structure. Install another access point to circumvent
this problem.
• Floors usually have metal girders and metal reinforcing struts that interfere
with WLAN transmission.
This concludes the first chapter. The next chapter deals with the hardware
installation of the Adapter.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
9
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
This chapter covers connecting your USB Wireless Network Adapter to USB
port of desktop / notebook PC.
Package Contents
Please make sure that items below are included on package.
ü One USB Wireless Network Adapter
ü One USB cables
ü One Driver / Utility CD-ROM (this use’ s manual included)
ü One Quick Installation Guide
System Requirements for the Adapter
Ø Operating System: MS Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows ME
Ø Desktop PC or notebook PC with CD-ROM drive
Ø One free USB port
Ø Pentium-Class 90MHz or higher
Connecting the USB Adapter
NOTE: These instructions apply to most desktop/notebook computers. For
detailed information on inserting USB adapters into your desktop/notebook PC,
consult the desktop/notebook PC User’ s Manual.
The Adapter’ s USB port is located on the back of the Adapter.
And your Adapter comes with a USB cable that has two different types of
connectors – type A & type B. Type A connector of the USB cable plugs into
your notebook/desktop PC’ s USB port. And type B connector of the USB cable
connects to the USB port of your USB Wireless Network Adapter.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
10
USB Type A USB Type B
LED Indicators
POWER LINK
The following table describes the meaning of LED indicators:
LED MEANING
POWER
LINK
Indicates that the Adapter is powered on when the LED
lights up.
Indicates link status. The LED lights up while the wireless
connection is linked. If the light is blinking, it means there is
data sending or receiving via wireless.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
11
Disconnecting the USB Adapter
In Win 98/ME operating systems, you do not have to power down your
notebook/desktop PC to remove the Adapter. The Adapter is hot swappable—
you can remove the Adapter when your notebook/desktop PC is powered on.
However, Microsoft recommends that you stop the Adapter before removing the
Adapter. Refer to your Win 98/ME online help for information on stopping the USB
Adapter.
WARNING: Do not remove the USB Wireless Network Adapter when a data
transmission is taking place. Exit your communications program normally, stop
the Adapter if necessary, and then remove the adapter.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
12
Chapter 3 - Installation Procedures Under
Windows 98
Use the procedures described in this chapter to install and configure the USB
Wireless Network Adapter under Windows 98.
Throughout this chapter it is assumed that you have a basic working knowledge
of Windows 98 and of how to install new network adapters on them. However, in
this paragraph, some specific features of Windows 98 are briefly explained.
What You Will Need
During the installation, you may be prompted to load operating system files from
the Windows installation disc. Please have this disc handy.
You will also need the Drivers/Utility CD provided with your package.
Installing the Driver Under Windows 98
1. Connecting the Adapter to the USB port of a notebook or desktop PC. (Refer
to Connecting the USB Adapter at Chapter 2)
2. The Add New Hardware Wizard will indicate that Windows have
recognized a new device that has not been used before.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
13
3. Click Next to continue the installation. A screen appears prompting you to
select an installation method:
4. Select Search for the best driver for your device. (Recommended) and
click Next. The following screen appears:
5. Ensure that the CD-ROM drive box is checked.
6. Insert the driver/utility disc into your CD-ROM drive and click Next. The
following screen appears:
USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
14
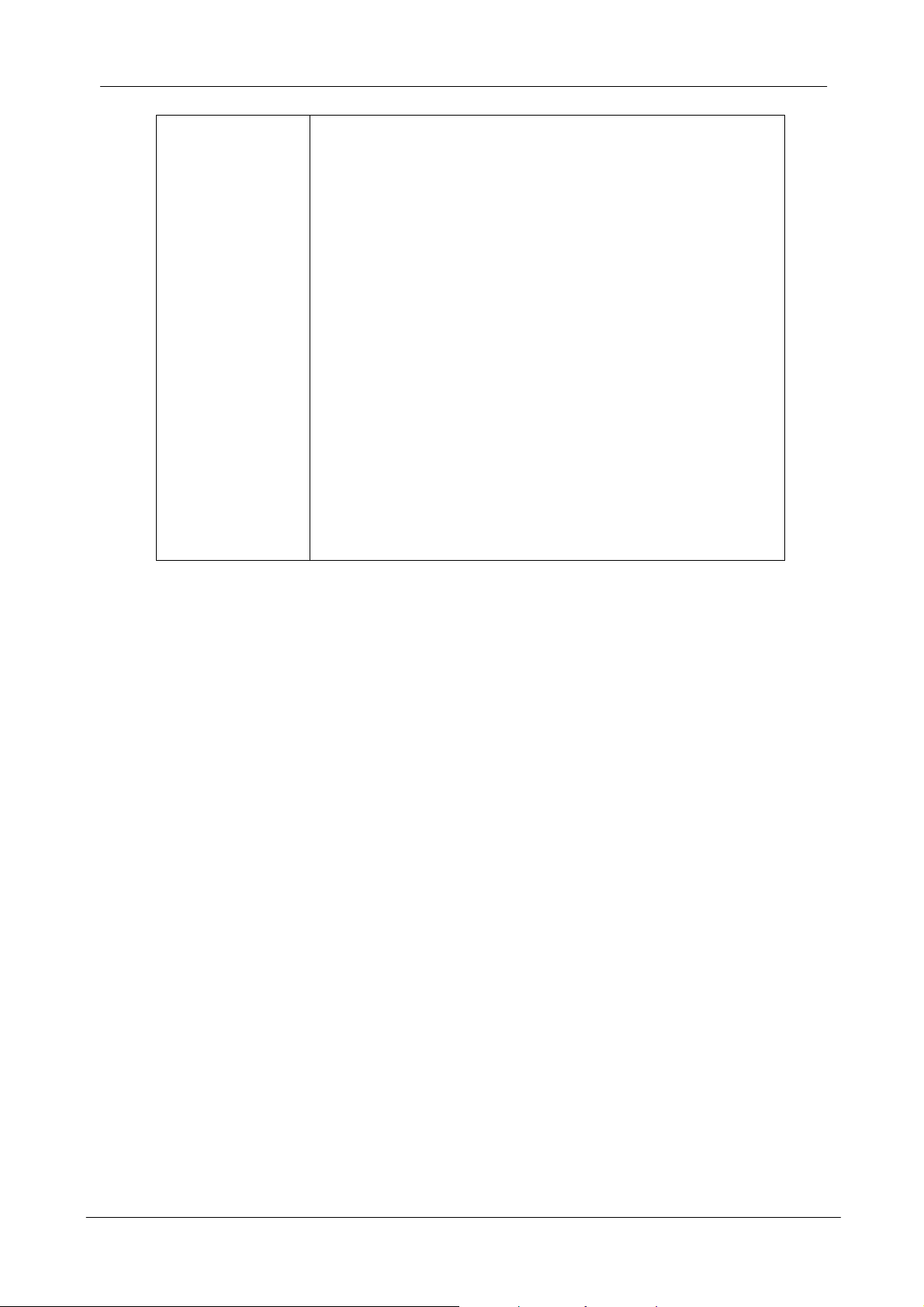
7. Click Next to continue. Windows 98 copies files to your hard disk drive, and
you see the following screen:
8. Click Finish to complete the installation.
9. Go to “Chapter 6 – Install and Use Configuration Utility” to install the
Configuration Utility.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
15
Uninstall Procedures Under Windows 98
In order to uninstall the Adapter from Windows 98, you must double click on the
“Network” icon in the “Control Panel” (Start -> Settings -> Control Panel).
Select the “USB Wireless Network Adapter” from the list and press the
“Remove” button. The system will prompt you to re-boot. Press "Yes" to re-boot.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
16
Chapter 4 - Installation Procedures Under
Windows 2000
Use the procedures described in this chapter to install and configure the USB
Wireless Network Adapter under MS Windows 2000.
Throughout this Chapter it is assumed that you have a basic working knowledge
of Windows 2000 and of how to install new network adapters on them. However,
in this paragraph, some specific features of Windows 2000 are briefly explained.
What You Will Need
During the installation, you may be prompted to load operating system files from
the Windows installation disc. Please have this disc handy.
You will also need the Drivers/Utility CD provided with your package.
Note: In order to be able to install the Adapter on to your notebook/desktop PC
running under Windows 2000, you will need to log on as “Administrator” .
Installing the Driver Under Windows 2000
1. Connecting the Adapter to the USB port of a notebook or desktop PC. (Refer
to Connecting the USB Adapter at Chapter 2)
2. The Found New Hardware Wizard will indicate that Windows have
recognized a new device that has not been used before.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
17
3. Click Next to continue the installation. A screen appears prompting you to
select an installation method:
4. Select Search for a suitable driver for my device (recommended) and
click Next. The following screen appears:

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
18
5. Ensure that the CD-ROM drives box is checked and insert the driver/utility
disc into CD-ROM drive. Click Next to continue. The following screen
appears:
6. Click Next to continue.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
19
7. Windows may display the message “Digital Signature Not Found” . Ignore
it by pressing “Yes” . Windows will start copying the files and then the
following screen appears:
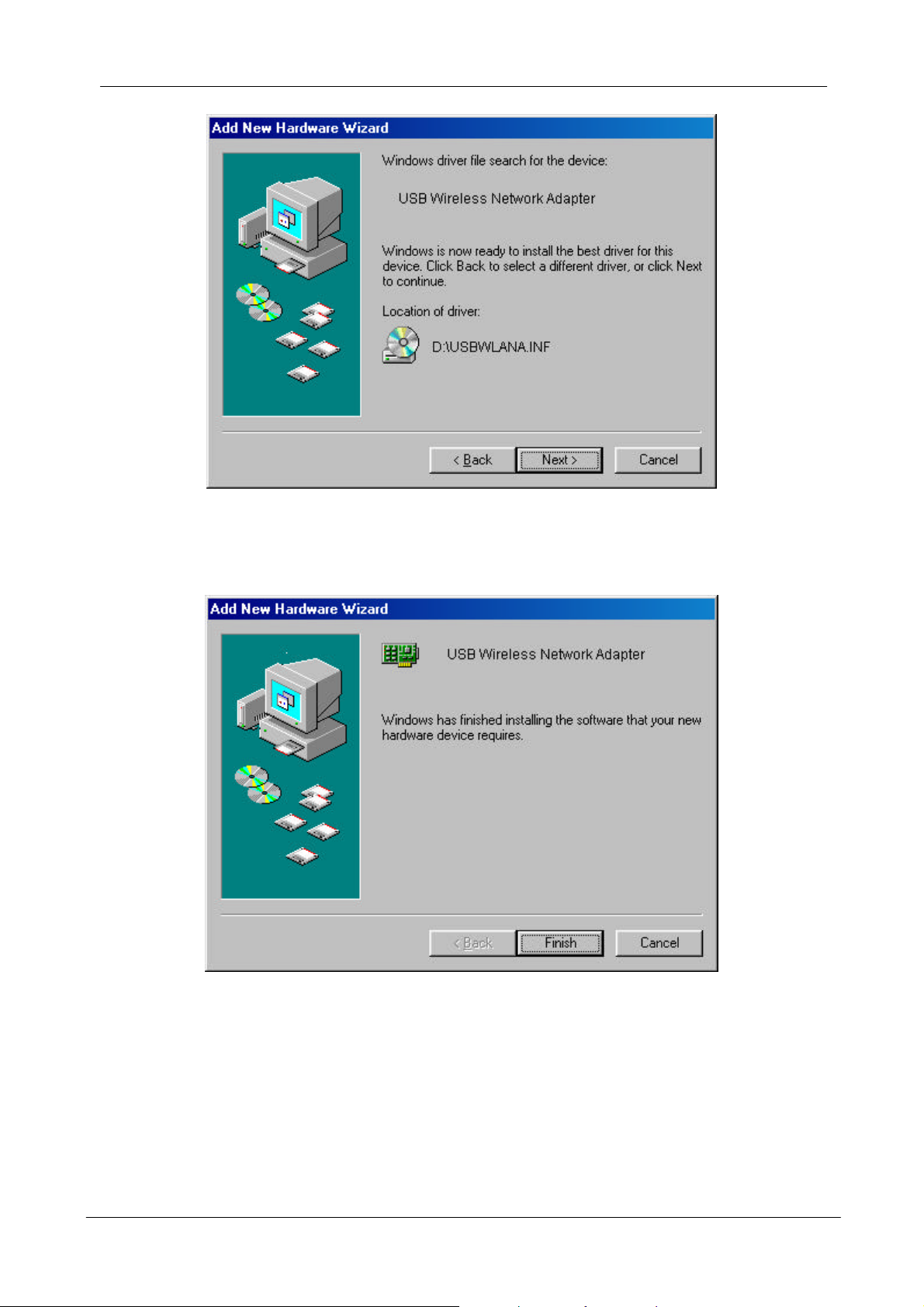
8. Click Finish to complete the installation.
9. Go to “Chapter 6 – Install and Use Configuration Utility” to install the
Configuration Utility.
USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
20
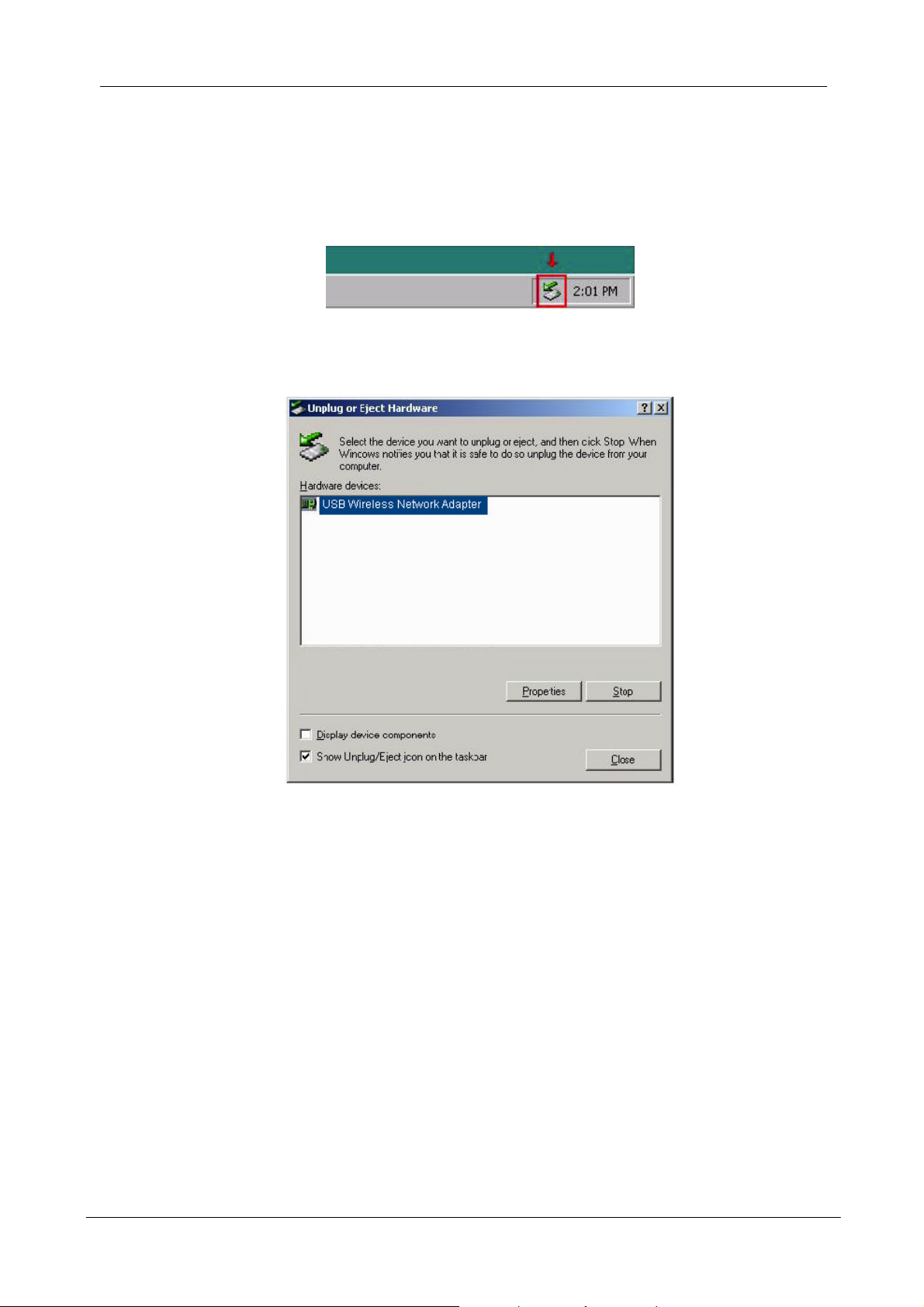
How to Unplug the Device Under Windows 2000
After the successful installation of the Adapter, you will see an icon
corresponding to the device in the Windows taskbar for as long as the device is
connected to the PC.
If you want to unplug the device, double click on this icon. The dialog of Unplug
or Eject Hardware will appear.
Select USB Wireless Network Adapter and press “Stop” . Now it is safe to
unplug the device from the PC.
In case you unplug the device without having followed the above procedure, the
dialog Unsafe Removal of Device will appear reminding you the problems this
action may have caused. Press “OK” . It is recommended not to unplug the
device unless you have followed first the above procedure to stop the Adapter.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
21
Uninstall Procedures Under Windows 2000
In order to uninstall the Adapter you must select it in the Device Manager
(Start -> Settings -> Control Panel -> System -> Hardware -> Device
Manager) of Windows 2000 and press the “Uninstall” icon . The
“Uninstall” procedure can be performed only if the Adapter is plugged-into your
computer.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
22
Chapter 5 - Installation Procedures Under
Windows ME
Use the procedures described in this chapter to install and configure the USB
Wireless Network Adapter under Windows ME
Throughout this Chapter it is assumed that you have a basic working knowledge
of Windows ME and of how to install new network adapters on them. However,
in this paragraph, some specific features of Windows ME are briefly explained.
What You Will Need
During the installation, you may be prompted to load operating system files from
the Windows installation disc. Please have this disc handy.
You will also need the Drivers/Utility CD provided with your package.
Installing the Driver Under Windows ME
1. Connecting the Adapter to the USB port of a notebook or desktop PC.
(Refer to Connecting the USB Adapter at Chapter 2)
2. The Add New Hardware Wizard will indicate that Windows have
recognized a new device that has not been used before.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
23
3. Select Automatic search for a better driver (Recommended) and insert the
driver/utility disc into CD-ROM drive. Click Next to continue.
4. The system will find the setup files and follow the instruction of the setup file
to copy drivers. After the drivers were copied, the following screen appears:
5. Click Finish to complete the installation.
6. Go to “Chapter 6 – Install and Use Configuration Utility” to install the
Configuration Utility.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
24
Uninstall Procedures Under Windows ME
In order to uninstall the Adapter from Windows ME, you must double click on the
“Network” icon in the “Control Panel” (Start -> Settings -> Control Panel).
Select the “USB Wireless Network Adapter” from the list and press the
“Remove” button. The system will prompt you to re-boot. Press "Yes" to re-boot.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
25
Chapter 6 – Install and Use Configuration
Utility
The Configuration Utility is a powerful utility that helps you to configure the
Adapter and monitor the statistics of the communication. The Adapter offers the
Configuration Utility for Windows 98, Windows 2000 and Windows ME.
How to Install the Configuration Utility
1. Run the program SETUP.EXE, which you will find in the “CONFIG UTILITY”
folder of your driver/utility CD.
2. The following screen appears:
3. Click Next to continue.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
26
4. Click Next to continue, if you want to install the Configuration Utility in the
default folder. Otherwise, click Browse and select another folder to install to
a different folder.
5. Start installing the utility. When it finish, the following screen appears:

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
27
6. Select “Yes, I want to restart my computer now” and click Finish to
restart your system.
7. After system restarted, utility will start running and will appear as an icon on
the system tray. (And you also can find the utility under Start -> Programs
-> USB Wireless Network Adapter -> USB Wireless Network Adapter
Configuration Utility.)
Using the Configuration Utility
The Configuration Utility appears as an icon on the system tray of Windows
every time the Adapter is running. You can open it by double-clicking on this
icon. While the station is in infrastructure mode and not associated to an access
point, the color of the icon is red. As soon as the station associates itself to an
access point, the icon color turns to green. In ad-hoc mode the color is always
green, except when the Adapter is resetting where it turns to red during the
reset procedure.
1. Double-clicking the icon on the system tray to open the utility, the following
screen will appears:

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
28
This screen shows you the wireless connection status. You can click "OK"
to close the utility.
2. Or, select the "Configuration" tab. The following screen will appears:
You can set the following Wireless Network USB Adapter operational

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
29
parameters:
• Profile: The profile setting allows you to save configurations in different
profiles for different working environments. The default profile will
contain the initial configuration setting when you install the adapter.
You can type a new profile name and click “Create” button to create a
new profile. When you click the “Create” button, the utility will create a
profile contains the current configuration setting. If you want to change
the setting, make sure to click “Apply changes” button to save the
change in profile. If you want to use existed profile, just select the
profile from the dropdown list and click “Activate” button to activate the
profile setting. To remove a existed profile, select the profile from the
dropdown list, then click “Remove” button to remove it.
• Wireless Mode: Infrastructure mode or Ad-Hoc mode.
Infrastructure mode allows the Adapter to communicate with a wired
network which employing an access point. Ad-Hoc mode allows PC-toPC, peer-to-peer communication.
• SSID: Key in the SSID to be used.
The SSID can be either the SSID of the access point to which the
station will be associated if in Infrastructure Mode, or the SSID of the
Ad-Hoc network in case the station will operate in Ad-Hoc mode. In the
latter case, all stations participating in the Ad-Hoc network should have
the same SSID.
• Transfer Rate: Select the rate to be used among the following options:
1 Mbps, 2 Mbps, 5.5 Mbps, 11Mbps or Auto Rate.
• Channel: Select the channel to be used. There are 11 channels
available at North America, and 13 channels available at Europe.
In Infrastructure Mode, you do not need to select the channel manually.
The channel will be set as same as the access point automatically. In
Ad-Hoc Mode, the channel being used should be set as same as the
other points in the network.
• Power Saving Mode: Disabled or Enabled
Select Enabled to allow your Adapter to go to sleep mode while the
adapter doesn’ t proceed the data transmission. Select Disabled to
make the adapter never go to sleep mode.
If any operational parameter has been changed, click "Apply
Changes" to save the settings in the current profile you open.
3. Select the "Site Survey" tab. The following screen will appears:

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
30
Available access points and their features will be listed on the screen. Click
on the desired access point. And click "Connect" to link to the access point.
Click "OK" when you are finished.
4. Select the "Encryption" tab. The following screen will appears:

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
31
Under "Encryption (WEP)" drop-box, you can select Disabled, 64 Bits or
128 Bits. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is an encryption scheme, and it
has been used to protect wireless data communication.
If any operational parameter has been changed, click "Apply Changes" to
save the settings in the current profile you open.
5. Select the “Advanced” tab. The following screen will appears.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
32
You can set the following operational parameters:
Fragmentation Threshold : The threshold defines the maximum data
frame size your adapter will transmit. For those transmitted data frames
which are larger than the threshold value will be fragmented into several
frames. The slider bar allows you to adjust the fragmentation threshold.
When the packet error rate is high, you may set the threshold value to
transmit shorter frames.
RTS/CTS Threshold: The threshold defines when will your adapter send
out RTS/CTS frames to reserve bandwidth for transmission. For those
transmitted data frames which are larger than the threshold value will cause
RTS/CTS frames be sent out to request bandwidth for the transmitted data
frames. By using the RTS/CTS function, you may request bandwidth from
AP to allow you have better chance to send out your data.
Security: It’ s only applicable while WEP is enabled.
Deny Unencrypted Data Frames: Check the box will deny to receive
unencrypted data frames to prevent from unknown intruders probe your
station.
Authentication Type: Which authentication algorithm is used. The current
supported algorithms are Open System, and Shared Key. The algorithm will
be invoked when associated to Access Point. To associate to the desired
Access Point you must set the same algorithm as the one of the desired
Access Point.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
33
Preamble Type: Preamble is for framing synchronization. The possible
setting are long and Short. The setting must be the same as the setting of
the Access Point you are going to associate.
If any operational parameter has been changed, click "Apply Changes" to
save the settings in the current profile you open.
6. Select the "About" tab. The following screen will appears:
You can find version information about the driver, the Configuration Utility
and the firmware on this screen. Click OK to complete the configuration.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
34
Appendix A – FAQ
1. What is IEEE 802.11 standard?
Ø The IEEE 802.11 is a wireless LAN industry standard, and the objective
of IEEE 802.11 is to make sure that different manufactures’ wireless
LAN devices can communicate to each other.
2. What is WEP?
Ø As described in the IEEE 802.11 standard, WEP (Wired Equivalent
Privacy) is a data privacy mechanism based on a 40 bit shared key
algorithm.
3. My notebook / desktop PC cannot recognize the USB Wireless
Network Adapter.
Ø Please make sure that the Adapter is inserted into the USB port of your
notebook / desktop PC properly.
Ø And also make sure that the USB controller is enabled in the BIOS of
your notebook / desktop PC.
4. How to check that the USB controller on my notebook / desktop PC is
working properly?
Ø Right click on My Computer and select Properties. Click on the
Device Manager tab and select the Universal Serial Bus Controllers.
Click on Properties button. In the General tab, check under “Device
status” that the USB controller is working properly.
5. The Adapter does not work properly.
Ø Check that the Adapter drivers are loaded properly. You can easily
check it through the Network Adapter (Right click on My Computer
and select Properties. Click on the Device Manager tab and select the
Network Adapter). If there is a yellow exclamation mark on USB
Wireless Network Adapter, the resource may be conflicting. Please
uninstall the Adapter and restart your notebook / desktop PC. The
repeat hardware and software installation as specified in this manual.
6. In Infrastructure mode, my notebook / desktop PC cannot
communicate with the others PCs on the network.
Ø First, make sure that the SSID is same as the others PC.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
35
Ø Check that your Adapter is configured on the same channel & WEP as
the others PCs on the network.

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’ s Manual
36
Appendix B – Specifications
Standards: IEEE 802.11b
USB 1.0, 1.1
Channels: 11 Channels (US, Canada)
13 Channels (Europe)
14 Channels (Japan)
Antenna: Dipole Antenna inside
Frequency: 2.4 to 2.4835GHz (Industrial Scientific Medical Band)
Data Rate: up to 11Mbps
Operating Ranges: Indoor:
Up to 30M @ 11Mbps
Up to 50M @ 5.5Mbps
Up to 70M @ 2Mbps
Up to 90M @ 1Mbps
Outdoor:
Up to 150M @ 11Mbps
Up to 250M @ 5.5Mbps
Up to 350M @ 2Mbps
Up to 450M @ 1 Mbps
 Loading...
Loading...