Page 1

Page 2

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction 1
Features................................................................................................................................... 1
Safety Instructions ..................................................................................................................2
Package Contents.................................................................................................................... 3
Description.............................................................................................................................. 3
LED Indicators 4
Diagnostic Push Button 4
Chapter 2 LAN Installation 5
Procedure ................................................................................................................................ 5
Chapter 3 Wireless Print Server Configuration 6
Overview ................................................................................................................................ 6
Using the Windows Wizard.................................................................................................... 6
Procedure 6
Wireless Configuration ........................................................................................................... 8
Chapter 4 Client PC Configuration 9
Overview ................................................................................................................................ 9
Printing Methods 9
Which printing method should I use? 10
Checking your Network Protocols (Windows 9x) 10
Windows Peer-to-peer Printing.............................................................................................12
Windows 2000/XP Setup 12
Windows 9x/ME Setup 16
PTP Printer Port Setup 17
Windows SMB Printing........................................................................................................ 20
Printing from MS-DOS Programs 21
Windows with Server-based Print Queues............................................................................ 23
Macintosh (AppleTalk)......................................................................................................... 24
Software Requirements 24
AppleTalk Setup 24
Printing 24
Advanced Setup and Management 24
Macintosh OS X ................................................................................................................... 25
LPR printing Setup 25
Page i
Page 3

Chapter 5 BiAdmin Management Utility 26
Requirements ........................................................................................................................ 26
Installation ............................................................................................................................26
Operation .............................................................................................................................. 26
Main Screen 26
Menus 29
Configuration 29
Chapter 6 Web-Based Management 39
Overview .............................................................................................................................. 39
Preparation............................................................................................................................ 39
Connecting to the Wireless Print Server............................................................................... 40
Configuration Screens...........................................................................................................40
AppleTalk 40
NetBEUI 41
TCP/IP 42
Configure Server 43
Wireless Configuration 44
Other Screens 46
Chapter 7 Special Features 47
Overview .............................................................................................................................. 47
Internet Printing Protocol (IPP) ............................................................................................ 47
IPP Server Configuration 47
IPP Client Setup - Windows 95/98/Me/NT 4.0/XP 48
IPP Client Setup - Windows 2000/XP 50
Using IPP Printers 51
Internet Mail Printing............................................................................................................ 52
System Requirements 52
Internet Mail Printing Configuration 53
User Software 54
Using the new Port 55
Checking the Printer Driver 56
Printing through the Internet................................................................................................. 56
Chapter 8 Troubleshooting 57
Overview .............................................................................................................................. 57
Hardware & LAN Problems ................................................................................................. 57
AppleTalk (Macintosh)......................................................................................................... 58
Windows Printing Problems ................................................................................................. 60
Page ii
Page 4

Appendix A Specifications 64
General Specifications ..........................................................................................................64
Parallel Port Pin Assignments 64
Protocol Support 65
Feature Support 65
Appendix B Network Server Configuration 66
Windows NT4.0 Server ........................................................................................................ 66
Adding TCP/IP Printing Support 66
Adding a TCP/IP Remote Printer 66
Windows 2000/2003 Server.................................................................................................. 67
Unix Systems........................................................................................................................ 68
Wireless Print Server IP Address Configuration 68
Other Wireless Print Server Configuration 68
LPD Configuration 69
Netware Systems ..................................................................................................................74
Page iii
Page 5

Chapter 1
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of your Wireless Print Server's features.
1
Features
Congratulations on the purchase of your new TEW-P1U1P Wireless Print Server. Your
Wireless Print Server was designed to provide a simple and efficient network printing solution.
It is packed with features, including:
Versatility. The Wireless Print Server supports up to four protocols: TCP/IP, SMB
(Service Message Block), AppleTalk (EtherTalk), and NetBEUI. It features one or two
Ethernet interface ports and operating system support includes Unix, NetWare (NDPS
LPR printing), and Microsoft Windows.
Easy Installation. The Wireless Print Server makes adding printers or plotters to your
network simple. The auto-sensing feature on the LAN interface means that there is no need
to set jumpers or perform software configuration to select the network interface used.
Easy Setup. A number of utility programs are supplied to simplify setup. For Windows
95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP users, the BiAdmin program makes it easy to configure the
Wireless Print Server for a variety of network and server configurations.
Web-based Interface. The Web-based interface provides an easy method of
configuration in TCP/IP networks to every model.
Compact Size. This allows the Wireless Print Server to be used even where space is
limited.
Remote Management Tools. A variety of software tools are provided. In most
environments, both the Wireless Print Server and attached bi-directional printers can be
configured remotely.
Internet Printing Protocol (IPP) Support. The Wireless Print Server can act as an
IPP (Internet Printing Protocol) Server, allowing clients, suppliers, colleagues and others
to print to your printer from anywhere on the Internet. Windows IPP Client software is
also supplied.
Wireless LAN Support. Wireless stations supporting the IEEE 802.11b standard can
interoperate with the Wireless Print Server. Both LAN and WLAN users can print to the
attached printer.
Page 1
Page 6

Safety Instructions
For your own safety, and to protect your Wireless Print Server, please observe the following
safety advice.
1. Unplug this device from its power source before cleaning. Use only a slightly dampened
cloth for cleaning. Do not use liquid or aerosol cleaners.
2. Avoid using this product near water. Exposure to water poses an electric-shock hazard.
3. Do not place the Wireless Print Server on an unstable surface. The device may fall causing
serious damage to the device.
4. This device should only be used with the power supply type specified on the marking
label. If you are not sure of type of your local power supply, consult your dealer or the
local power company.
5. Do not pinch, crimp or otherwise damage the power cord. If exposed to foot traffic,
ensures that the cable is properly shielded and does not pose a tripping hazard.
6. If using an extension cord, makes sure the total ampere rating of the products using the
cord does not exceed the extension cord's ampere rating.
7. Do not attempt to service this device, as opening or removing casing may expose you to
dangerous voltage points or other risks. Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel.
8. The Wireless Print Server should be serviced by qualified service personnel under the
following conditions:
• The power cord is damaged or frayed.
• Liquid has been spilled onto the product.
• The product has been exposed to rain or water.
• The product does not operate normally in accordance with the operating instructions.
• The device has been dropped or the casing has been damaged.
Page 2
Page 7
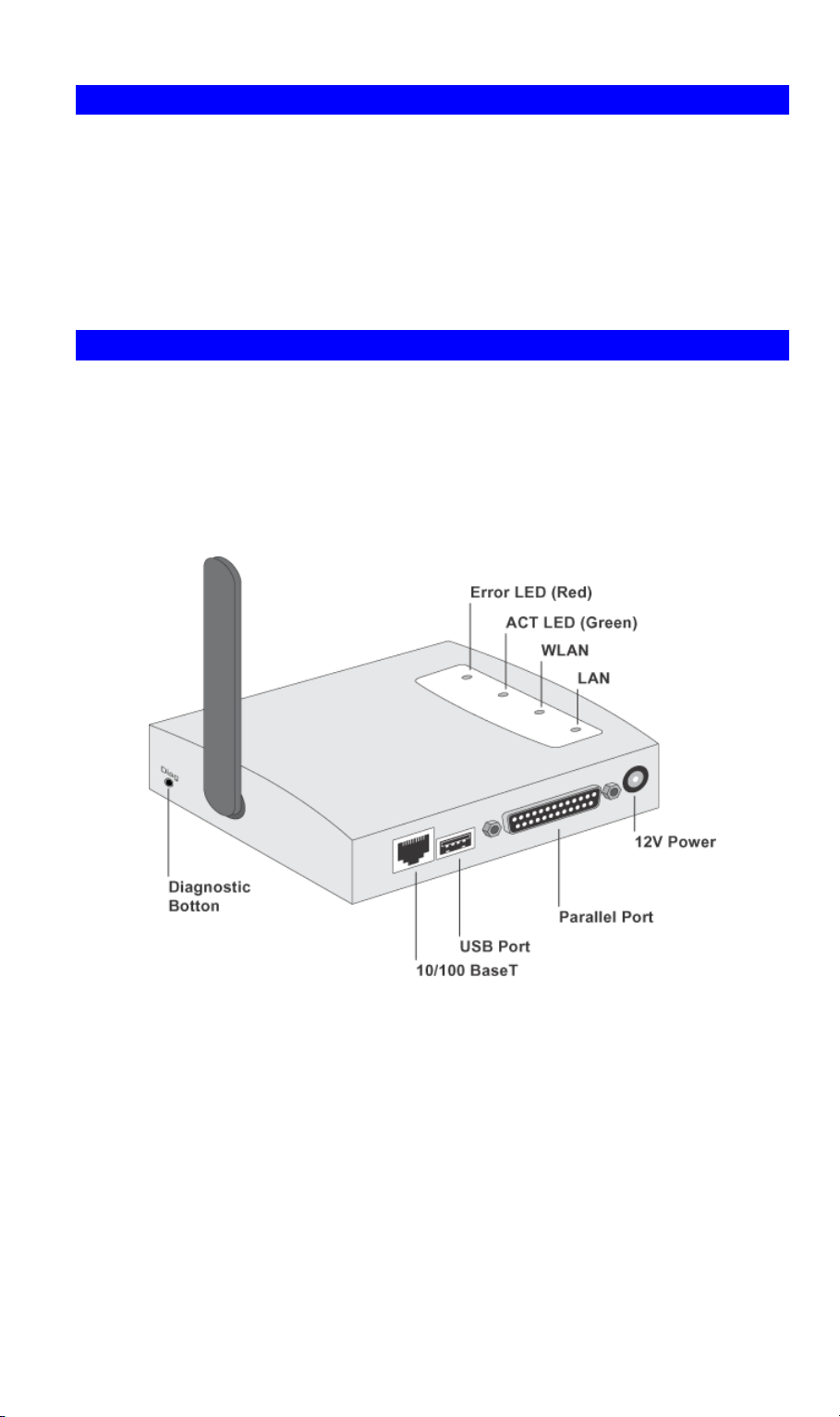
Package Contents
You should find the following items packaged with your Wireless Print Server. If any items are
missing, contact your dealer immediately.
• The Wireless Print Server
• Power Adapter
• One CD-ROM containing all support programs and this manual
• Quick Install Guide
Description
TEW-P1U1P Wireless Print Server
• 1 USB Printer Port
• 1 Parallel Printer Port
• IEEE 802.11b Wireless Station
• 10/100BaseT LAN connection
Figure 1 TEW-P1U1P Wireless Print Server
Page 3
Page 8
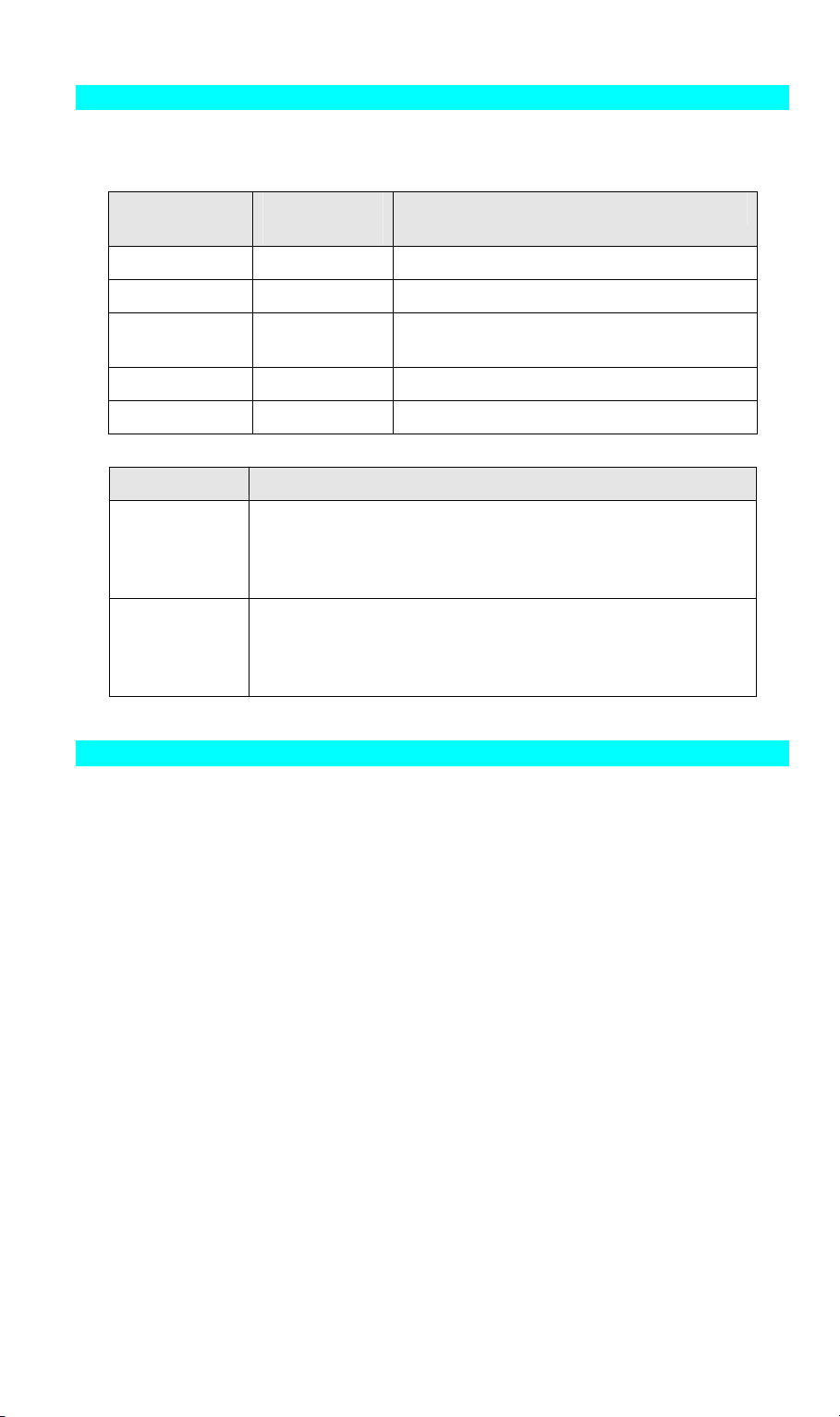
LED Indicators
The Error LED is red. The Status indicator LED is green. The LED indicator modes are
described in the following table.
ACT LED
(Green)
Off Off No power.
On Off Normal operation - Idle.
Flashing Off Normal operation - transmitting or receiving
On On Hardware error.
Flashing Flashing Firmware upgrade in progress.
LED Description
WLAN ACT
LAN ACT
ERR LED
(Red)
Off - No Wireless connection available.
On - Wireless connection available.
Flashing - Transmitting or receiving data via the Wireless LAN.
Off - No LAN connection
On - LAN connection available.
Flashing - Transmitting or receiving data via the wired LAN.
Status Description
packets from the network.
Diagnostic Push Button
The Wireless Print Server is fitted with a Diagnostic Push Button. The button is recessed; a pin
or paper clip can be used to press it. This button has 2 functions:
• Restore the factory default settings
• Print a test page containing all current settings.
To restore the factory default settings:
1. Turn the Wireless Print Server OFF.
2. Press and hold the diagnostic button. While pressing the button, switch the Wireless Print
Server ON.
3. If you continue pressing the button for 10 seconds, a diagnostic page will be printed,
showing the new (default) settings.
To generate a Diagnostic print out
1. Ensure that both the Wireless Print Server and the printer attached to port 1 (parallel port)
are ON.
2. Press the diagnostic button, and hold it in for 2 seconds.
3. The test page, containing the current settings, will be printed.
Note:
PostScript printers are unable to print this page. If you have a PostScript printer on Port 1,
the test page will not be printed.
Page 4
Page 9

Chapter 2
LAN Installation
This chapter describes how to install the Wireless Print Server in your LAN.
2
Procedure
1. Preparation
• Ensure the power is OFF.
• Find the Default Server Name for your Wireless Print Server. The Default Server Name is
shown on a sticker on the base of the device. It consists of 8 letters and/or digits. Record
this name; it may be needed during configuration.
2. Connect the Printer or Printers
Connect the printer or plotter cables to the appropriate port on the Wireless Print Server unit.
Parallel port cables should be less than 3 meters long.
3. Connect to the Network
• For Wired Networks
Use a standard RJ-45 LAN cable to connect the LAN port on the Print Server to a
10/100Base-TX hub or switch.
If the LAN port is not connected to a functioning network device, the
LAN port is disabled. To enable the LAN port, please power off the
Print Server, connect the LAN port to a working network device and
then power on the Print Server.
• For Wireless Networks
Change your PC's Wireless settings to match the Print Server's default settings:
• Mode: Ad-hoc
• SSID: ANY
• Channel: 11
• WEP: Disabled
In Infrastructure mode, you can use EITHER the Wireless OR the
LAN interface on the Print Server, but not both
4. Power Up and check the LED
Connect the supplied Power Adapter, power up both the Printer and Print Server, and check the
Error LED on the Print Server.
• It should flash, then go off.
• It will remain On if there is a hardware problem.
Use only the Power Supply unit provided with the device. Power Supply units for
different models are not interchangeable.
Page 5
Page 10

Chapter 3
Wireless Print Server
3
Configuration
This chapter provides an overview of the configuration process.
Overview
The Wireless Print Server is designed to support many different platforms, and the
configuration required would depend upon the environment in which it is installed.
• The Wireless Print Server usually requires configuration, but if there's a DHCP server on
your network, then the device is just plug-and-play. A Windows-based setup Wizard is
also provided on the CD-ROM to simplify this task.
• PCs wishing to use the printer attached to the Wireless Print Server always require
configuration. See Chapter 4- Client Configuration for details.
• If you wish to use a queue-based printing system using Windows NT Server/Windows
2000/Windows XP, the Network Server must be configured as detailed in Appendix B -
Network Server Configuration. However, it is not necessary to use a Network Server-based
queue; client PCs can print directly to the Wireless Print Server using the Peer-to-peer
Printing installed by the User setup option on the CD-ROM.
Configuration Methods
The following methods are available to perform the required Print Server configuration:
• Windows-based Wizard - see below for details.
• BiAdmin management utility program - see Chapter 8 for details.
• Web-based setup - see Chapter 6 for details.
Advanced Configuration and Management
The BiAdmin management utility is provided for advanced configuration and management.
This program is installed by default when the Administrator install option is chosen. See
Chapter 5 for details on using BiAdmin.
Using the Windows Wizard
The Windows-based Wizard is supplied on the CD-ROM, and runs on Windows 95, 98,
NT4.0, ME, Windows 2000 and Windows XP.
Using this Wizard is the recommended method to configure the Print Server.
It can be used configure the Wireless Print Server for your Network environment, even if the
Print Server does not have a valid IP address.
Procedure
1. Insert the supplied CD-ROM into your drive. If the setup program does not start
automatically, run AutoRun.exe in the root folder.
2. On the first screen, shown below, click Setup Wizard.
Page 6
Page 11
Figure 2: Wireless Print Server Screen
3. Click Next on the first screen of the Wizard, to view a list of Wireless Print Servers on
your LAN.
4. Select your new Wireless Print Server, then click Next to continue.
5. Enter the required data on the following screen.
• Name of the Print Server can be changed if you wish.
• Comment is optional.
• Select or enter the Workgroup name for this Wireless Print Server.
6. Click Next to configure the TCP/IP Screen:
• Select Obtain IP Address automatically if your LAN has a DHCP Server, otherwise
select Fixed IP Address.
• For Fixed IP Address, enter an unused address from the range used on your LAN, or
click the Suggest New Values Button.
Use the same Network Mask and Gateway as PCs on your LAN.
7. On the Wireless Screens, the settings should be set to match your other Wireless Stations.
For details about each setting, refer to the following section Wireless Configuration.
8. Click Finish to save the data to the Wireless Print Server.
Note: To install the Wizard on your PC, use the "Installation" option.
If the desired Wireless Print Server is not listed:
• Check all cables to the Wireless Print Server.
• Check the Wireless Print Server's LEDs:
• The Red LED should be OFF and the Green LED should be ON or flashing.
• Check the LAN and WLAN LEDs. Both should be On (if a LAN cable is connected).
• Check that your PC and the Wireless Print Server are on the same LAN segment. (If
you don't have a Router or Gateway on your LAN, you only have 1 segment.)
• If using the Wireless connection, ensure that your PC's Wireless settings match the
Print Server.
• Check that your PC has either the TCP/IP or NetBEUI network protocols installed. See
Checking your Network Protocols on page 10 for details.
Page 7
Page 12
Wireless Configuration
The Wireless Print Server is a Wireless station, NOT access point. Like all other Wireless
stations, they have 2 modes:
• Ad Hoc mode (Default)- no Access Point is used, Wireless stations communicate directly
with each other.
• Infrastructure - all Wireless stations connect to the Access Point. This allows connection
to both other Wireless stations and the wired LAN.
The Wireless Print Server does NOT allow both a LAN connection
and "Infrastructure" mode.
In "Infrastructure" mode, connecting a LAN cable will disable the
Wireless interface.
To use both the LAN and Wireless interfaces, "Ad-hoc" mode
must be used.
Required configuration
Ad-hoc Mode (Default) Infrastructure Mode
SSID
Default : ANY
Channel
Default : 11
WEP Settings
In Ad Hoc mode, the Wireless Print
Must match the Access Point.
Server will join any group with the
same SSID.
If there's no Ad Hoc group available in
the environment, the Wireless Print
Server will create a group using the
SSID value as configured.
In Ad Hoc mode, the Print Server will
scan all Channels to look for
compatible groups it can join. If there
is no existing Hoc group available, the
Wireless Print Server will create the
group using its own Channel number.
Access Point sets the Channel
used.
Wireless stations
automatically locate the
correct channel.
Must match the other Wireless stations. Must match the Access Point.
Page 8
Page 13
Chapter 4
Client PC Configuration
The chapter details the client configuration required on LAN clients to use the printer
or printers attached to the Wireless Print Server.
4
Overview
Before performing client configuration, the Wireless Print Server must be installed on your
LAN, and configured as described in Chapter 3. Both the Wireless Print Server and the
attached printer must be powered ON.
Printing Methods
The Wireless Print Server supports a number of printing methods:
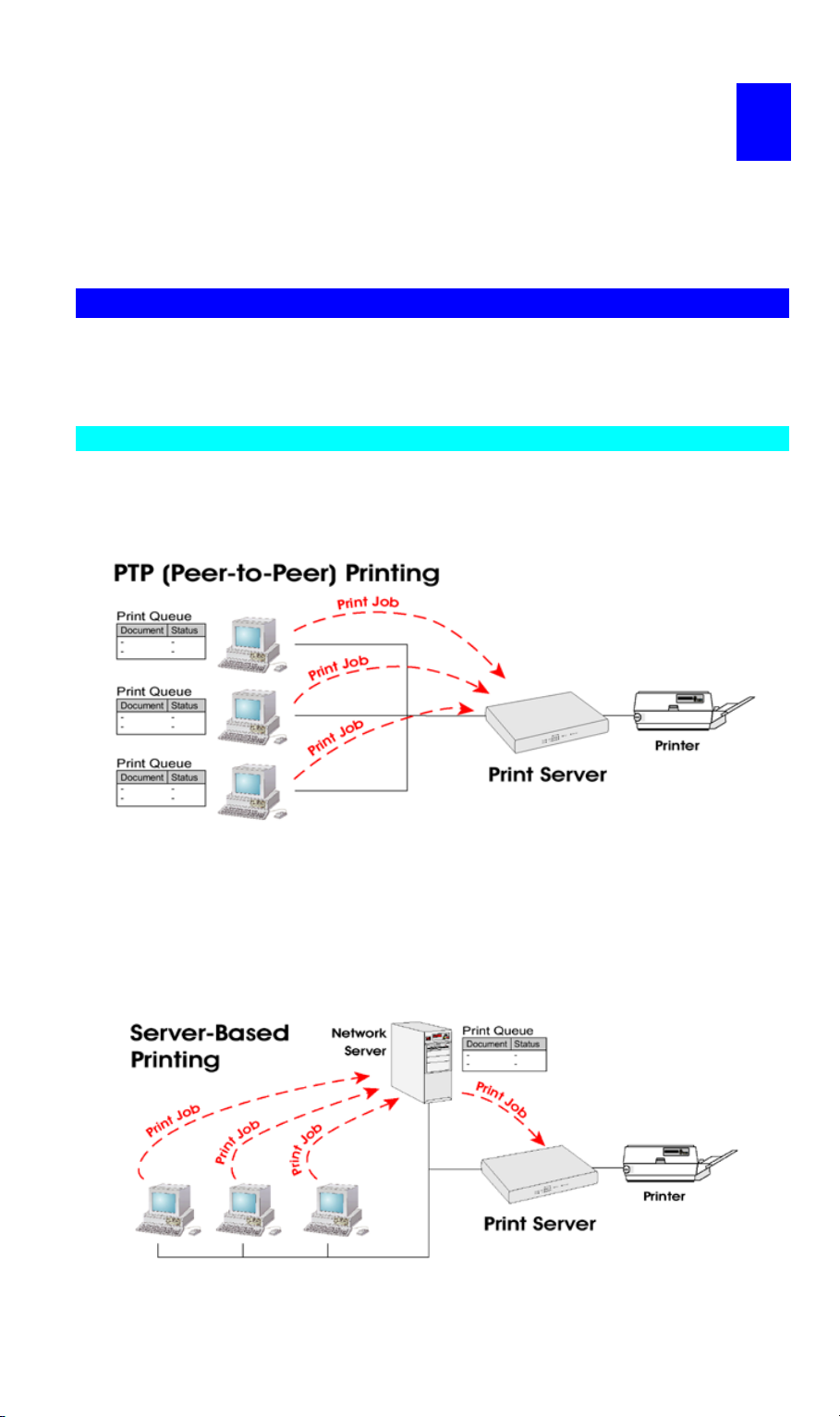
• Peer-to-peer Printing means that the print jobs are stored (queued) on your PC, and sent
directly to the Wireless Print Server when it is available.
Figure 3: Peer-to-Peer Printing
• Server-based Printing means that all print jobs are stored (queued) on the Network Server
(e.g. Windows 2000 Server) and then sent to the Wireless Print Server. This allows the
Network Administrator to modify the Print Queue. For example, an important job can be
moved to the head of the queue.
See Appendix B for details of configuring your Network Server to work with the Print
Server.
Figure 4: Server-based Print Queue
Page 9
Page 14
• Windows SMB printing is a Microsoft standard for using a "Network Printer". No
additional software needs to be installed on your Windows PC, and printing from MSDOS programs is supported. However, because the Wireless Print Server can not store
files, large print jobs may cause problems.
• AppleTalk is also supported, and normally no configuration of the Wireless Print Server is
required. See the Macintosh section of this chapter for details of client configuration.
Which printing method should I use?
• If using Windows 95, 98, NT, Me, 2000, or XP, the easiest method to use is Peer-to-peer
Printing.
• If using Windows, and you need to print from MS-DOS programs, or you don't wish to
install additional software, use SMB.
However, SMB is not suitable for large, complex documents, so if you need this as well as
MS-DOS printing, you should install BOTH Peer-to-peer Printing and SMB printing. MSDOS programs can use the SMB printer, Windows programs should use Peer-to-peer
Printing.
• If your LAN has Network Servers (e.g. Windows NT, Windows 2000 Server) use the
method advised by your Network Administrator. The Wireless Print Server can print via a
queue located on a Network server, if desired.
See Appendix B for details of configuring your Network Server to work with the Print
Server.
• Unix users - refer to Appendix B.
• Macintosh users - refer to the Macintosh section of this chapter.
Checking your Network Protocols (Windows 9x)
Your PC must have EITHER the TCP/IP or NetBEUI protocols installed. (All versions of
Windows after Windows 95 have TCP/IP installed by default.)
• If using the Peer-to-peer Printing, the installation program will check this for you.
• If using other methods, you must check manually, as follows:
1. Select the Settings - Control Panel - Network option on the Start Menu. You should see a
screen like the one following:
Figure 5: Network Configuration
• The top line in the list (NetBEUI -> PCI Fast Ethernet Adapter) indicates that the
NetBEUI protocol is installed on this PC. Your PC will show the name of the your
Network card rather than "PCI Fast Ethernet Adapter".
Page 10
Page 15

• The highlighted line (TCP/IP -> PCI Fast Ethernet Adapter) indicates that TCP/IP is
installed. Your PC will show the name of the your Network card rather than "PCI Fast
Ethernet Adapter".
2. If neither line is present:
• Install the NetBEUI protocol by selecting Add - Protocol - Microsoft - NetBEUI - OK.
You may be prompted for your Windows CD-ROM.
• If required, you can also install TCP/IP. However, depending on your LAN
environment, TCP/IP may require further configuration.
3. If either protocol is already installed, proceed with installation.
Page 11
Page 16
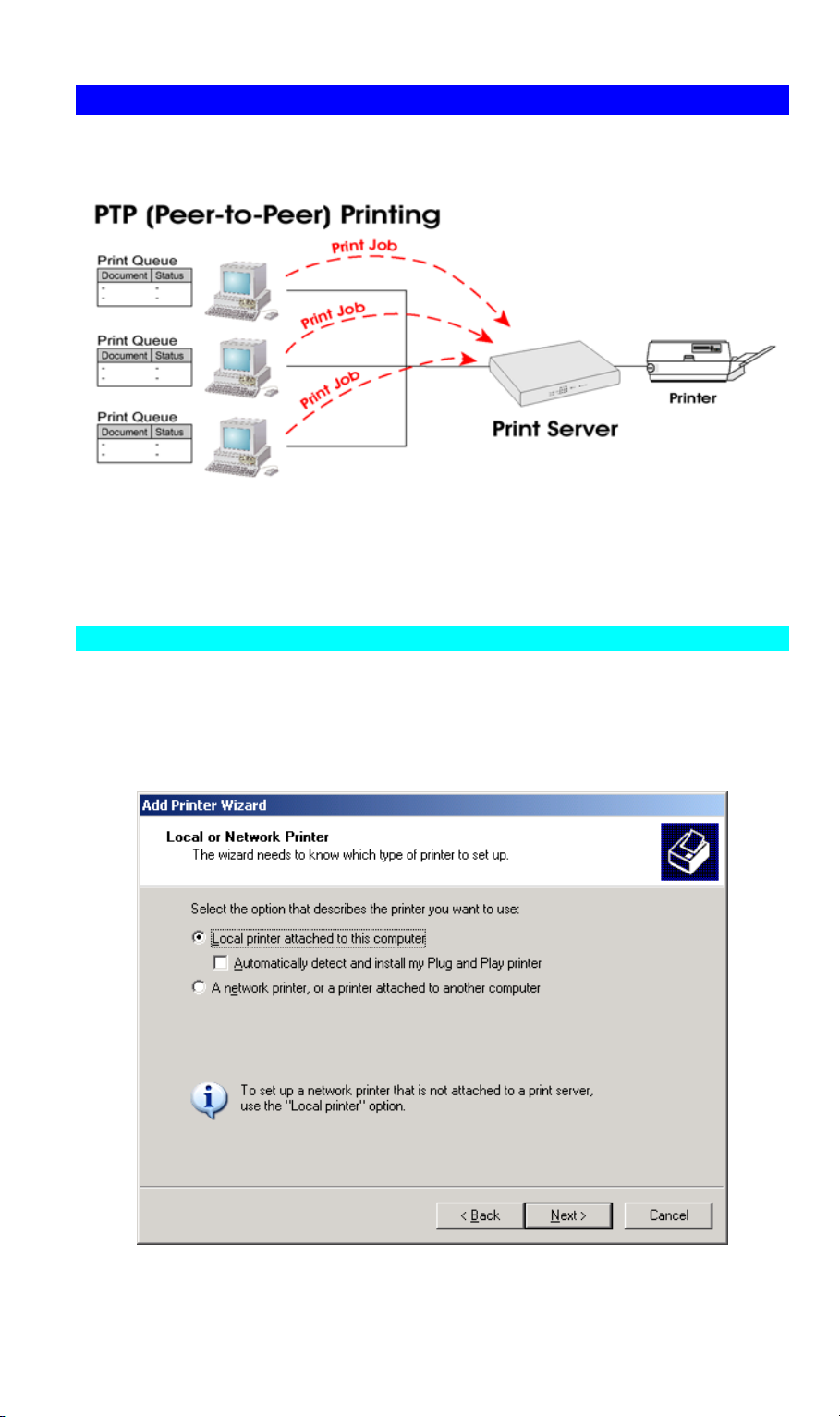
Windows Peer-to-peer Printing
With this printing method, print jobs are stored (queued) on your PC, and then sent to the
Wireless Print Server when it is available.
Figure 6: Peer-to-Peer Printing
Windows 2000 & XP require no additional software.
For other versions of Windows, the supplied PTP (Peer-to-Peer) Printer Port software must be
installed on each PC.
Windows 2000/XP Setup
The recommended printing method is to use LPR, as follows:
1. Open your Printers folder, click on Add a Printer and click Next to Start adding a printer
to your PC
2. Select Local printer option as shown in the figure 7 below and click Next to proceed
Figure 7: Local printer
Page 12
Page 17
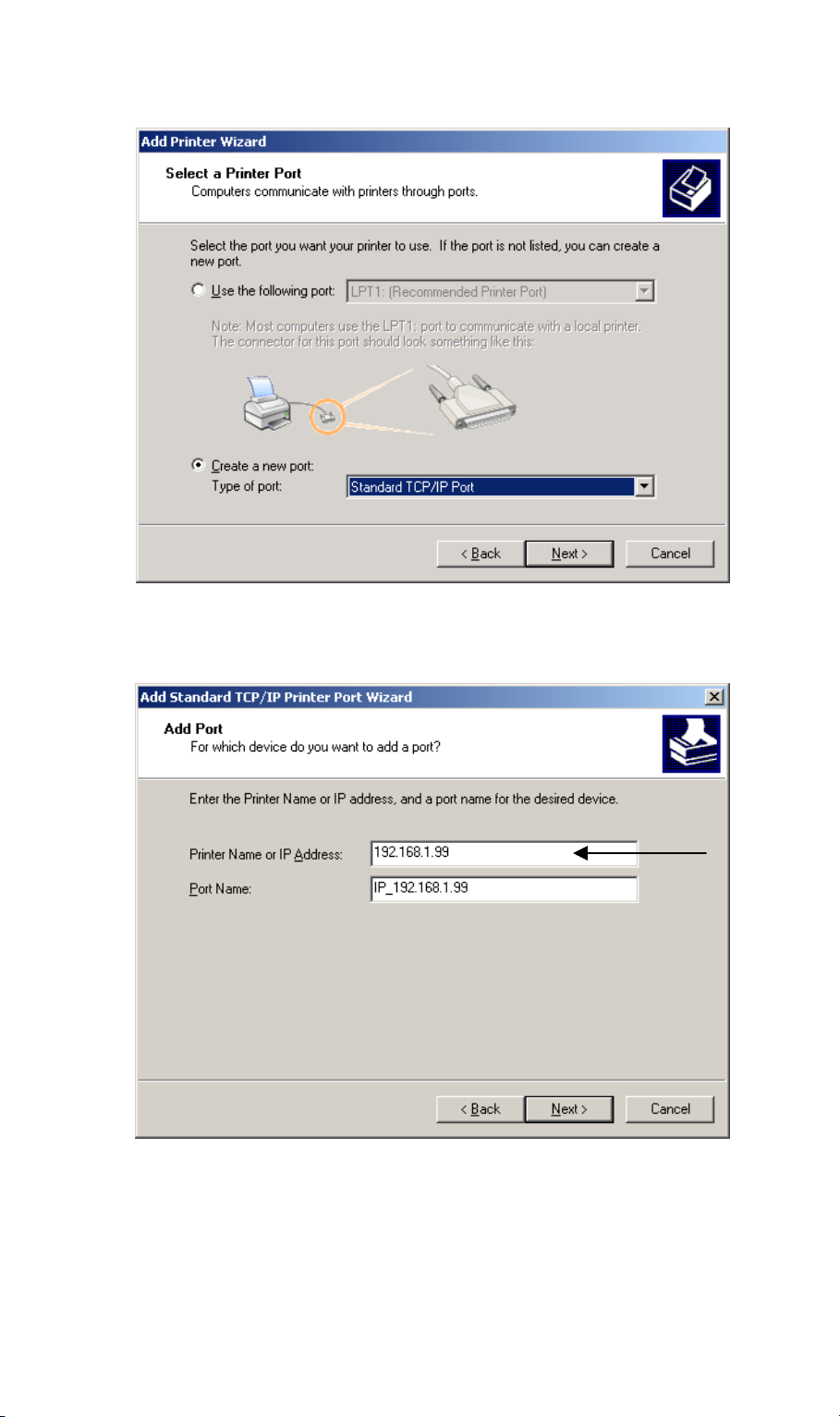
3. Choose Create a new port and select Standard TCP/IP Port, and click Next to proceed
Figure 8: Create new Port Screen
4. Enter the IP Address of the Print Server in the Printer Name or IP Address field, then click
Next.
Figure 9: Enter Print Server IP address
Page 13
Page 18
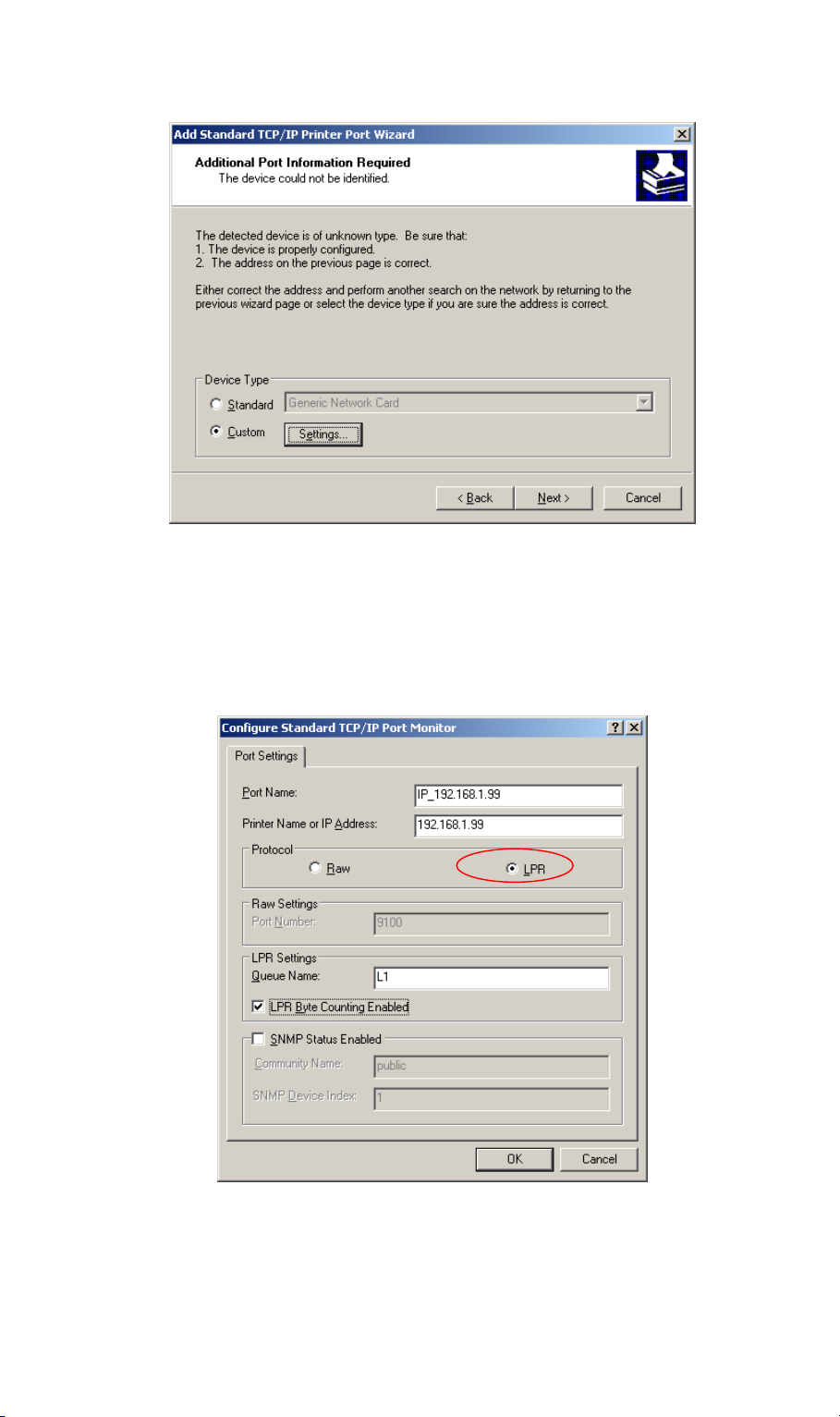
5. On this screen, select Custom, and click the Settings button.
Figure 10: Custom Screen
6. On the Port Settings screen:
• Choose LPR in the Protocol section
• Enter a Queue name (L1 for Parallel port, L2 for USB port)
• Ensure the LPR Byte Counting Enabled setting is Enabled.
• Click OK to confirm your changes, then click Next to continue.
Figure 11: Port Settings Screen
7. Follow the prompts to complete the Wizard.
8. Go back to Printer folder, click on the new created printer and right-click on the printer
icon and select Properties
Page 14
Page 19
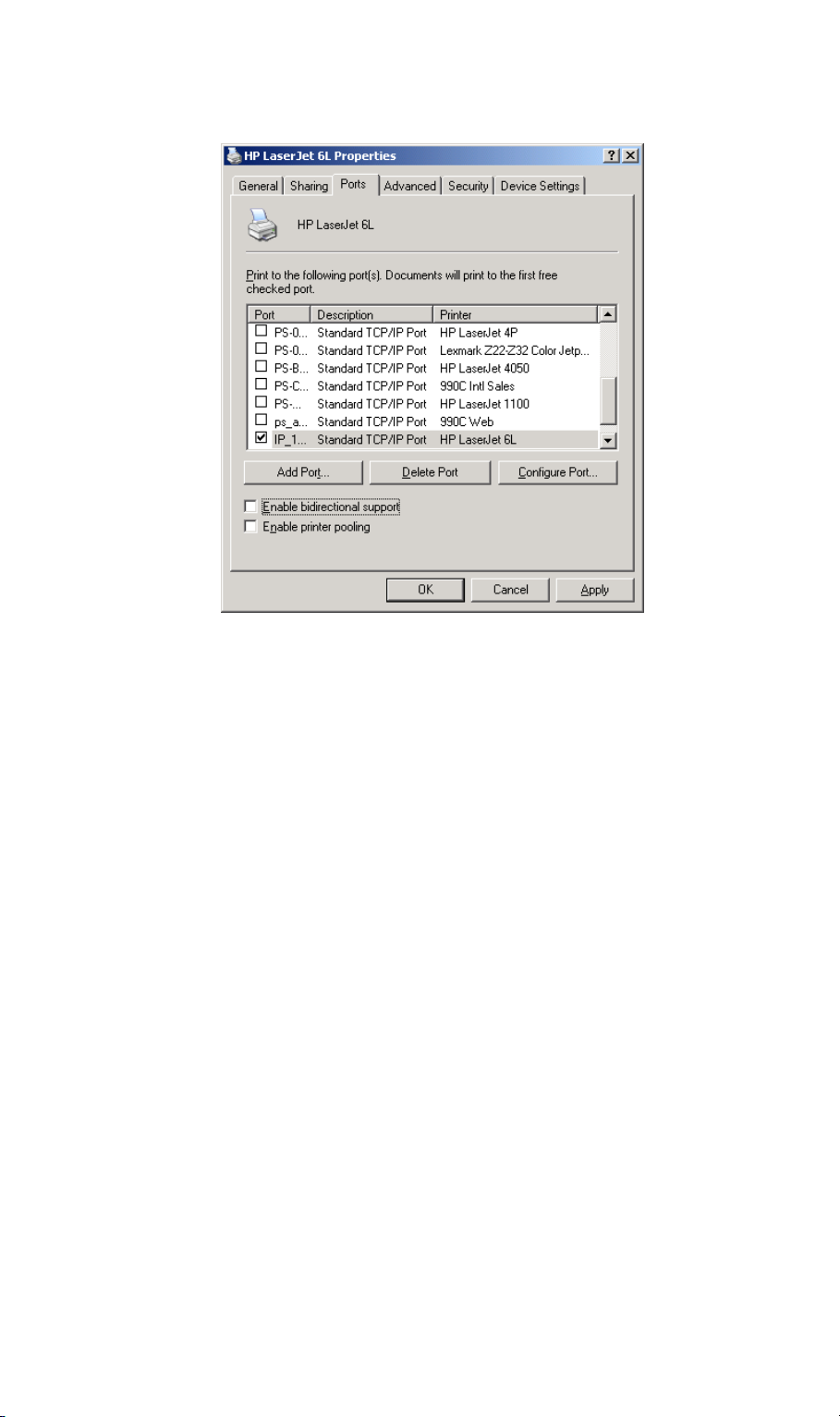
9. Go to the Ports tab, disable Bi-Directional Support and click on OK to complete the
installation
Figure 12 :Ports Tab - Bidirectional Support
Page 15
Page 20

Windows 9x/ME Setup
Before performing the following procedure, the Wireless Print Server must be installed on your
LAN, and configured as described in Chapter 3. Both the Wireless Print Server and the
attached printer should be powered ON.
1. Insert the supplied CD-ROM into your drive. If the setup program does not start, run
SETUP.exe in the root folder.
2. Click Installation button, then select the User Install.
Figure 13: Installation Screen
3. Follow the prompts to complete the installation of the Peer-to-peer Printer Port Driver.
(Refer to the Windows section of Chapter 8 - Troubleshooting if there is a problem with
the installation.)
4. The Print Driver Setup will then run.
In future, you can use Start - Programs – Print Server Utility – Printer Driver Setup to run the
program again.
Page 16
Page 21
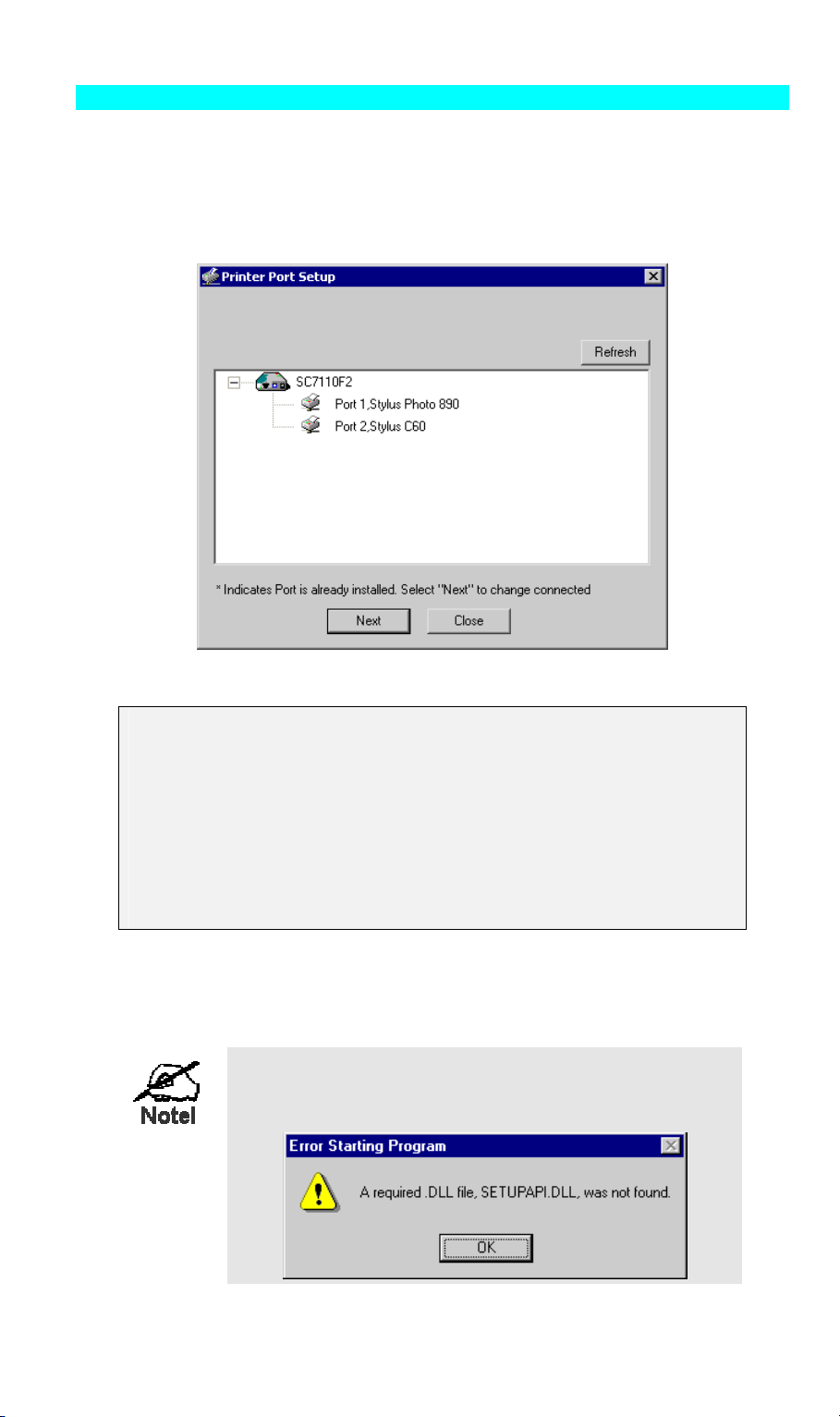
PTP Printer Port Setup
1. The program will search for Printer Servers on the network, and a screen like the following
will be displayed.
• If desired, click Refresh.
• The name of the attached printer will be displayed if possible. If "No printer" is
displayed, check that the printer is properly connected and powered on.
Figure 14: Print Port Setup (Peer-to-peer Printing)
If your Wireless Print Server is not listed:
• Click the "Refresh" button.
• Check that both the Wireless Print Server and the printer are properly
connected, and powered on.
• Check that the Wireless Print Server has been configured. (Use the Setup
Wizard on the CD-ROM.)
• If using TCP/IP, try installing the NetBEUI protocol. (See the earlier section
Checking your Network Protocols for details.). Then try again.
2. Select the desired port on a Wireless Print Server (Port 1: Parallel port, Port 2: USB port),
then click Next. A pop-up message will inform you if the port has been created
successfully.
If you see the following error message, either install Internet
Explorer 4 or later, or follow the procedure in the "Trouble
Shooting - Windows" section of Chapter 8.
Page 17
Page 22
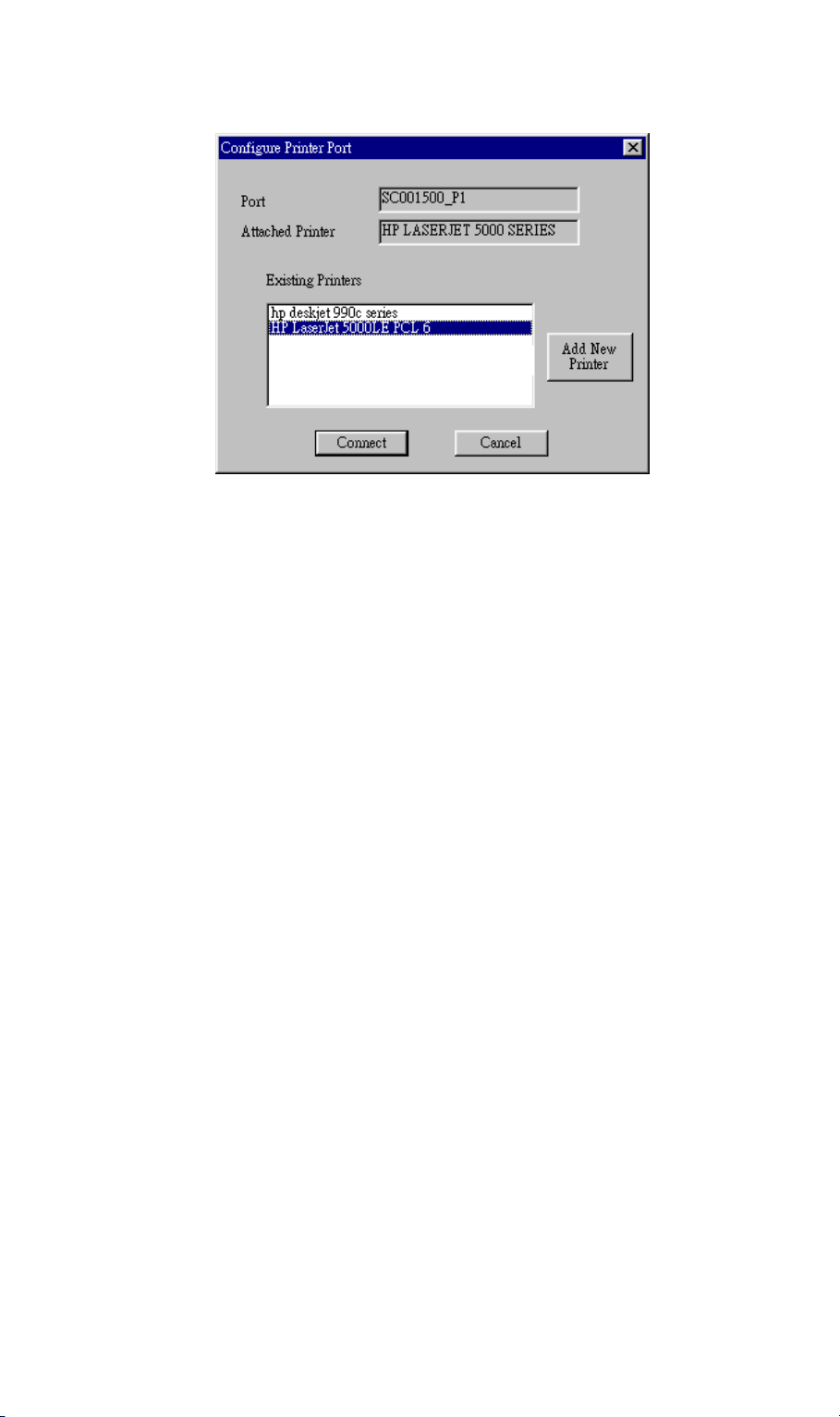
3. The printer port will be created, and a screen like the following will be displayed.
Figure 15: Configure Printer Port
4. Select the correct Windows printer in the Existing Printers list, and click the Connect
button.
If the correct printer type is not listed, click "Add New Printer" to run the Windows Add
Printer wizard. Step through the Wizard and install the required printer:
• Select the correct Printer Manufacturer and Model, or use the "Have Disk" option if
appropriate.
• We recommend changing the Printer name to indicate which device is on.
(e.g. HP2100 on SCA43600_P1)
• If prompted about Sharing the printer, do NOT enable Sharing.
• When the Printer installation is finished, it will be listed in the Configure Printer Port
screen above. Select it and click Connect.
5. Installation is now complete. You can now print using this printer.
• To install additional Printers, repeat steps 4.
• Use the Start menu to run this program in future. The default installation is Start -
Programs – Print Server Utility - Print Driver Setup.
Note:
If using the Epson Spooler Manager, this program must be disabled, as follows:
1. Run the Epson Spooler Manager.
2. Select "Queue Setup" from the menu.
3. Click "Use Print Manager for this port".
4. Click "OK" to exit.
Management
• Print jobs can be managed like any Windows printer. Open the Printers folder (Start -
Settings - Printers) and double-click any printer to see the current print jobs.
• If the printer attached to the Wireless Print Server is changed, just run this program again,
and select the correct printer.
Page 18
Page 23
• To delete a port created by this setup program, use the Windows Delete Port facility:
• Right-click any printer in the Printers folder, and select Properties.
• Locate the Delete Port button. This button is on the Details or Ports tab, depending on
your version or Windows.
• If the Wireless Print Server's IP Address is changed, and you can no longer print, delete
the port (see procedure above) and re-install it.
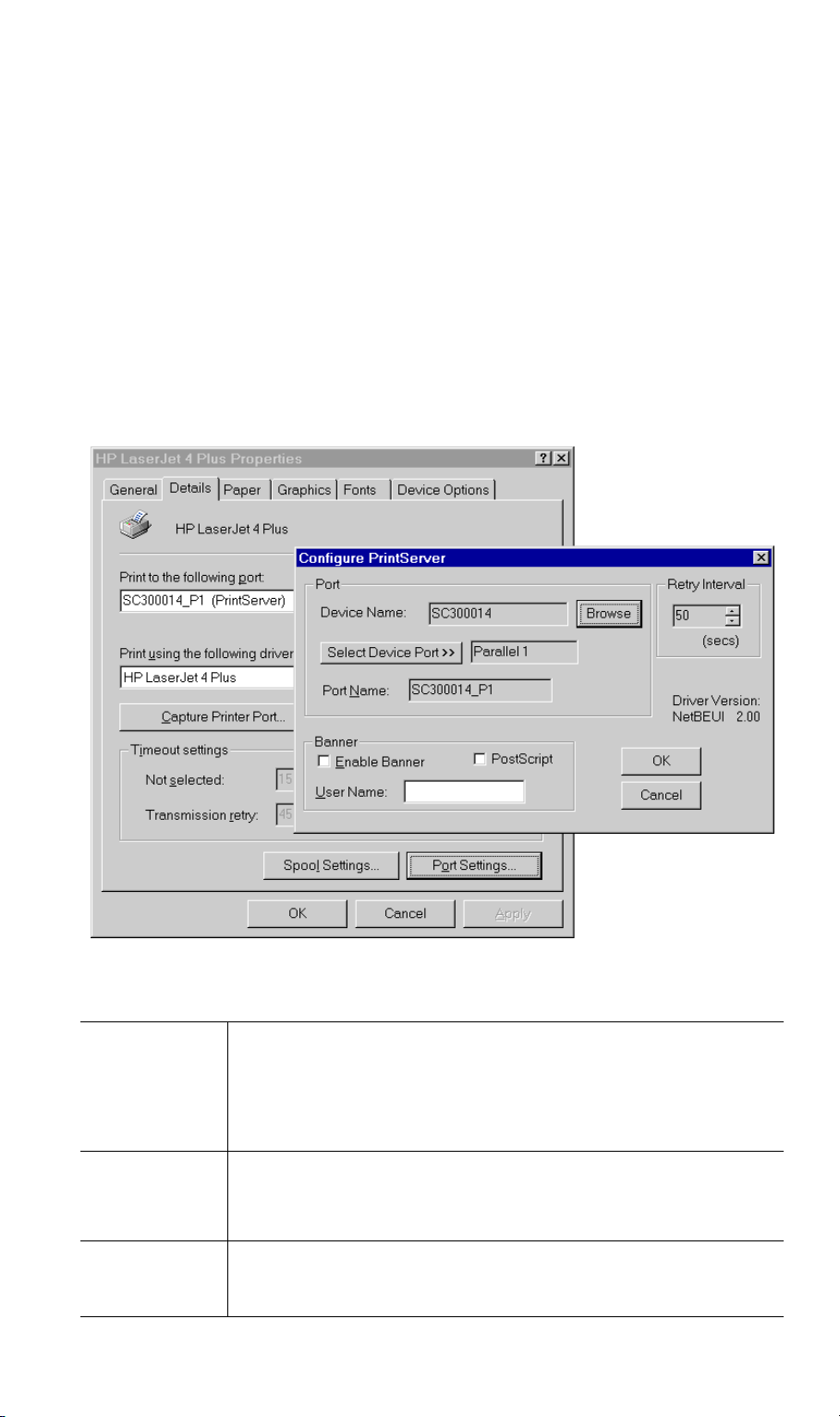
Advanced Port Options
The options for the Peer-to-peer Printing are accessed via the Port Settings button.
Use Start - Settings - Printers to open the Printers folder, then right-click the Printer, and select
Properties. The Port Settings button is on the Details or Ports tab, depending on your version
of Windows.
An example screen is shown below:
Figure 16: Port Settings (Peer-to-peer Driver)
Items shown on this screen are as follows:
Port
If desired, click Browse to select a different Wireless Print Server. If the
selected device has multiple ports, the Select Device Port button can be
used to select the port.
The Port Name can not be changed after installation. This name is
shown in the Printer's Properties.
Banner
Check this option to print a banner page before each print job.
• If using a PostScript Printer, check the PostScript box.
• The User Name will be printed on the banner page.
Retry Interval
Sets how often Windows will poll the Wireless Print Server to establish
a connection when the printer is busy. Increase this value if you get too
many warning messages.
Page 19
Page 24
Windows SMB Printing
This method requires no additional software to be installed, but the NetBEUI or TCP/IP
protocol must be installed on your PC. Use the following procedure to install the Wireless Print
Server's printer as a Windows SMB network printer:
1. Double-click the Network Neighborhood icon on the desktop.
2. On the View menu, select Details.
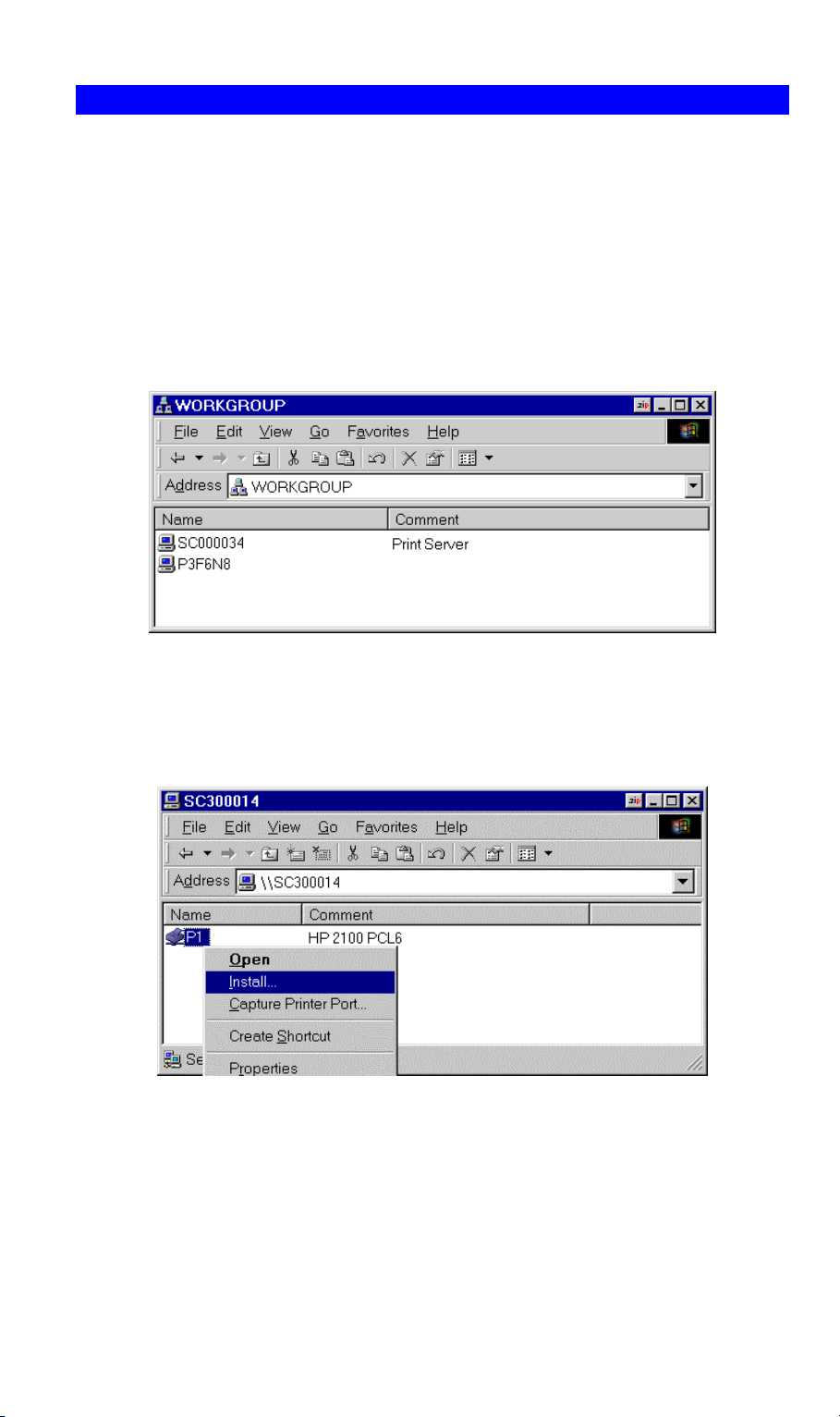
3. Locate the desired Wireless Print Server, as shown below:
• If it is the same Workgroup as your PC, it will be listed on screen.
• If it is in a different workgroup, double-click Entire Network, then double-click the
appropriate Workgroup to open it.
Figure 17: Network Neighborhood
4. Double-click the Wireless Print Server icon to view a Printer icon for each printer port.
The "Comment" field may indicate what type of printer is connected to the port.
5. To install a printer, right-click the desired printer icon, and choose "Install", as shown
below. This will start the Add Printer wizard.
Figure 18: Install SMB Printer
6. Follow the prompts to complete the installation.
• For information about the question "Do you print from MS-DOS programs?", see
Printing from MS-DOS Programs below.
• Select the Printer Manufacturer and Model to match the printer connected to this port
on the Wireless Print Server, and complete the Wizard.
7. This printer will now appear in your Printers folder (Start - Settings - Printers) and can be
used like any other printer. However, SMB printing is not suitable for large complex print
jobs - you should use the Peer-to-peer Printing instead.
Page 20
Page 25

Printing from MS-DOS Programs
Windows can redirect print data from a parallel port on your PC (e.g. LPT1) to a network
printer. This redirection is called "Capture Printer Port", and is useful for MS-DOS programs.
The MS-DOS program is configured to use LPT1 (parallel port 1 on the PC), but Windows
"captures" the print data and sends it to the network printer.
Capture Settings - Windows 98/ME
1. Select Start - Settings - Printers to open the Printers folder.
2. Right-click the desired Printer, and select Properties,
Figure 19: Capture Printer Port - Windows 98/ME
3. On the Details tab, shown above, click the Capture Printer Port button to view the
Capture Printer Port dialog, as shown below.
Figure 20: Capture Dialog - Windows 98/ME
4. On this dialog:
• Select the Device (port) on the PC to be captured. Normally, this will be LPT1
(parallel port 1).
• Enter or select the Path to the printer. This will be the same as the path shown as Print
to the following port on the Printer Properties window.
• Check the Reconnect at logon checkbox. If this is not done, the capture setting will be
lost when Windows is restarted.
Page 21
Page 26

Capture Settings - Windows 2000/XP
1. Login as Administrator.
2. Open the command prompt window.
3. Enter the following command to capture data from LPT1 (parallel port 1)
net use lpt1 \\server_name\printer_name /persistent:yes
Where
\\server_name\ printer_name is replaced with the actual path to your printer.
e.g.
net use lpt1 \\SC3000014\P1 /persistent:yes
4. Close the command prompt window.
To terminate this capture, use the following command at the command prompt:
net use lpt1 /delete
Page 22
Page 27

Windows with Server-based Print Queues
With a Server-based Print Queue, the Print Server is installed on an existing Network Server
(Windows, Unix, or NetWare), and is invisible to your PC.
If your Network Administrator chooses to use this system, the required setup procedure on
each Windows client is as follows:
1. Open your Printers folder, and start the Add Printer Wizard.
2. When prompted, select Network Printer.
3. When prompted for Network Path or Queue Name, click the Browse button, and locate the
Server and Printer (or Print Queue) which your Network Administrator advised you to use.
4. Click OK, then Next.
5. Select the correct printer Manufacturer and Model, as advised by your Network
Administrator, and click Next.
6. Follow the prompts to complete the Wizard.
The new printer will be listed with any other installed printers, any may be selected when
printing from any Windows application.
Page 23
Page 28

Macintosh (AppleTalk)
The Wireless Print Server supports AppleTalk (EtherTalk), PAP, ATP, NBP, ZIP and DDP
protocols, enabling Macintosh computers on the network to view and use the Wireless Print
Server as a regular AppleTalk printer.
Normally, no configuration is required.
Software Requirements
System 9.x OS or newer.
AppleTalk Setup
1. Click the apple icon and choose Control Panel - AppleTalk.
2. Ensure that Ethernet is selected under AppleTalk Connection.
3. Click Chooser. The Chooser panel will open.
4. Click on either the LaserWriter 8 icon (recommended) or the LaserWriter 7 icon.
LaserWriter 8 makes use of the fonts installed in the printer itself, so the printing response
time is quicker. LaserWriter 7 uses the fonts installed in the computer, which increases
network traffic and takes more printing time.
5. Choose a PostScript printer from the list.
6. Click Create and it will search PPD automatically.
7. Select a printer description from the list.
8. Click Select.
Configuration is now complete.
Printing
Printing with the Wireless Print Server installed in an AppleTalk network is identical to normal
printing. Just select File - Print and choose the desired printer.
Advanced Setup and Management
In a mixed Windows PC/Macintosh environment, you can use BiAdmin to configure the
Wireless Print Server. See Chapter 5 for details on installing and using BiAdmin.
Page 24
Page 29

Macintosh OS X
If using LPR printing, you need to ensure the Wireless Print Server has a valid IP address
before configuring your Mac as follows.
LPR printing Setup
1. Select the Printer List icon.
Figure 21: Printer List
2. Click the Add Printer button.
3. Choose LPR Printers Using IP.
Figure 22: LPR Screen
4. Enter the IP address of the Print Server in the LPR Printer's Address field, and enter the
Queue Name (L1 for the parallel port, L2 for the USB port).
5. Select the Printer Model from the drop-down list.
6. Click Add.
Configuration is now complete.
Page 25
Page 30

Chapter 5
BiAdmin Management Utility
This chapter describes the installation and operation of the BiAdmin Configuration &
Management program.
5
Requirements
This program requires:
• Windows 95, Windows 98 or ME
• Windows NT 3.51, Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000 or XP
Additional Recommendations:
• Screen resolution of 800 * 600 or greater.
Installation
Use the supplied CD-ROM. This CD-ROM will usually auto-run. If auto-run is disabled on
your PC, run the SETUP.exe program in the root folder.
• Select Installation and this will give you the options for BiAdmin installation
• BiAdmin is always installed if the Administrator option is chosen.
• If using the Custom option on the CD-ROM, select BiAdmin.
Operation
• Start the program by using the icon created by the setup program.
• When run, the program searches the network for all active Wireless Print Servers, then
lists them on screen, as shown by the example screen below.
Main Screen
Figure 23: BiAdmin Main Screen
Page 26
Page 31

Device List
The left panel displays a list of all Wireless Print Servers found on the network. When a
Wireless Print Server is selected from the list, its details are displayed in the right panel.
Note: If the IP address is "Null", please click the Refresh icon to get the value again.
If the desired Wireless Print Server is not listed, try the following:
• Check that the device is installed and ON, then Refresh the list.
• If the Wireless Print Server is on another LAN segment, use the InitDevice - Attached
Remote menu option to locate and display the Wireless Print Server.
Icons
Device Status
Menu equivalent: Main - Device Status
All of the settings for the current device are displayed in a read-only scrollable list
in the left panel.
You can use the "Save to File" and "Restore to Device" buttons on this screen to
save a copy of the selected device's CONFIG file to your PC, or restore a
previously saved file to the selected Wireless Print Server.
Printer Status
Menu equivalent: Main - Printer Status
After selecting this icon, a Detail button will be available to show more
information about the printer.
Page 27
Page 32

Select the desired port from the drop-down list to display the current status of the
printer attached to the port. Possible states are:
• Status - On-line, Off-line, or Out of Paper
• Printing Information - Idle, Printing
If the printer is Bi-directional, and is not busy, the Configuration button will be
available, allowing you to change the configuration of the attached printer. This
button will be grayed out if the printer does not support this option, or if the
printer is busy printing.
Configuration
Menu Equivalent: Main - Configure
This option allows you to configure the selected Wireless Print Server.
See the following section for details.
Wizard
This Wireless Print Server Wizard allows you to do the basic configuration for
the selected device. The screens are similar to the Wizard run from the CD-ROM,
as described in Chapter 3.
Upgrade
Menu Equivalent: Main - Upgrade
This option allows you to upgrade the firmware for the selected Wireless Print
Server. Before using this option, you need to obtain the .BIN file for the firmware
upgrade, and copy it to the same directory as BiAdmin.
Refresh
Menu Equivalent: Main - Refresh
Select this icon to update the Wireless Print Server device listing after changing
the name or IP Address.
Exit
Menu Equivalent: Main - Exit
Exit the BiAdmin program. This does not save any changes you have made; you
must Save to Device on each screen.
Page 28
Page 33

Menus
Main Menu
Device Status
Printer Status
Configure
Upgrade
Refresh
Exit
InitDevice Menu
Reset Device
Restore to Factory
Default
Attached Remote
Connected
Protocol
Same as Device Icon.
Same as Printer Status Icon.
Same as Configure Icon.
Same as Upgrade Icon.
Same as Refresh Icon.
Same as Exit Icon.
This will cause the device to reboot. This should be done after
making any configuration changes, or if the device stops responding
after some problems.
This will restore ALL device values to their factory defaults. To
restore only the current screen, use the Set to Default button on the
screen.
This is used to connect to a Wireless Print Server device on another
LAN segment. You need to know the IP address of the remote
Wireless Print Server.
If your LAN does not have a Router, you can ignore this option.
This option allows you to designate which LAN protocol will be used
for communication between the selected device and this application.
You should select ONE protocol only.
Diagnostics menu
Print Test Page
Use this option to print a test sheet from the selected Wireless Print
Server port. The test print out will include status information.
Configuration
When the Configuration icon is clicked, or the Configure option on the Main menu is selected,
a tabbed window will open. The tabs available will vary depending on the Wireless Print
Server model selected. The possible tabs are:
• System
• TCP/IP
• AppleTalk
• NetBEUI
• Internet Printing
• Port
• Wireless
Page 29
Page 34

System Tab
This screen allows you to:
• Change the name of the Wireless Print Server.
• Change the "Password" for the Wireless Print Server.
• Set the Network Protocols used the selected Wireless Print Server. (Any protocols not used
on your LAN may be disabled. This may improve performance.)
Figure 24: System Screen
Page 30
Page 35

TCP/IP Tab
Selecting this tab will allow configuration for the TCP/IP network protocol. The basic options
are:
• Dynamic IP Address (DHCP) - The IP address is obtained automatically, from a DHCP
Server on your network.
• Fixed IP Address - You must enter the IP address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address.
• IP Address - Select an unused IP address from the address range used on your LAN.
• Subnet Mask - Use the same values as PCs on your LAN (or on the same LAN
segment, if you have a Router).
• Gateway - Use the same values as PCs on your LAN (or on the same LAN segment, if
you have a Router).
The TEW-P1U1P also supports the Auto-IP function. If the TEW-P1U1P is set to Dynamic IP
Address, but there's no DHCP server found on the network, the TEW-P1U1P will get an IP
from the range of 169.254.1.1 ~ 169.254.254.254 automatically. In this case, even though the
TEW-P1U1P was initialized with an Auto-IP, it will change to DHCP whenever a DHCP
server is detected.
Figure 25: TCP/IP Screen
The TCP session parameters should only be changed if advised to do so by your Network
Administrator or Print Server Technical Support.
Page 31
Page 36

AppleTalk Tab
Generally, no Wireless Print Server configuration is required in order to use AppleTalk.
This screen allows you to:
• Set the Zone Name field to determine which Apple systems can gain access to this printer.
• The Printer Type field is used to describe the printer driver used for each port.
• Set Communication Protocol to ASCII or Binary. This must match the setting on the
Apple computer systems using the Wireless Print Server.
Figure 26: AppleTalk Screen
Page 32
Page 37

NetBEUI Tab
This screen allows you to:
• Choose the Domain name for the selected Wireless Print Server.
• Set how fast jobs are sent to the printer by using the Response Time field.
• Set the desired option for the Abort Job if Error Occured setting.
• YES causes a print job to be terminated if a printing error occurs.
• NO (default) will try to continue but may cause print errors.
Figure 27: NetBEUI Screen
Page 33
Page 38

Internet Printing Tab
The Internet Printing feature allows you to send print jobs to the Wireless Print Server using
Internet E-mail.
Please see Internet Mail Printing Configuration for details of using this feature.
Figure 28: Internet Printing Screen
Page 34
Page 39

Port Tab
This screen has 2 panels - Physical Port and Logical Port.
Physical Port
The following settings are available:
• Selected Physical Port - Select the Physical Printer Port you wish to configure.
• Handshake Signal - Select Busy Only or Busy & Ack for the Physical Port.
• Printer Type - Select High Speed or Low Speed for the Printer Type.
Logical Port
Logical Ports (printers) can be used in the Unix environment. The following settings are
available:
• Selected Logical Port - Select the Logical Printer Port you wish to configure.
• Map to Physical Port - Select the physical Printer Port which the Logical printer will use.
(By default, L1 is the parallel port, and L2 is the USB port)
• Convert LF to LF+CR - If checked, LF (line feed) characters are changed to CR+LF
(carriage return + line feed).
• Prefix of Job - The printer control string (in hex) to be sent to the printer before each print
job. This string cannot exceed 15 characters.
• Suffix of Job - The printer control string (in hex) to be sent to the printer after each print
job. This string cannot exceed 15 characters.
Figure 29: Port Screen
The Get Defaults button will reset all settings to their factory-default values.
Page 35
Page 40

Wireless Tab
This tab will be displayed if the selected device has the capability to serve as a Wireless
Stations for your LAN.
Figure 30: Wireless Screen
Change the settings to suit your environment. Generally, you must match the settings of other
'Wireless stations. The available settings are described below.
Selected Device
SSID
This shows the name of the Print Server.
• If using an ESS (Extended Service Set, with multiple access
points) this ID is called an ESSID (Extended Service Set
Identifier).
• To communicate, all Wireless stations MUST use the same
SSID/ESSID. Change this value, or change the other Wireless
stations, to ensure each Wireless station has the same value.
• The default value is "ANY", so the Wireless station can join any
Ad-hoc group.
Note! The SSID is case sensitive.
Channel No
The effect of this setting depends on the Network Type setting:
• In Infrastructure mode, this setting has no effect. The Channel is
selected automatically, to match the Channel used by the Access
Point.
• In Ad-hoc mode, Wireless stations will scan all Channels looking
for compatible groups to join. The Channel setting is used as a
default Channel.
If you experience interference (shown by lost connections and/or slow
data transfers) you may need to experiment with different channels.
Page 36
Page 41

Network Type
WEP Encryption
WEP Disable/
Enable
WEP
Authentication
64 Bits/128Bits
Key Table
Select the correct value for your Wireless LAN.
• Ad-hoc mode is used when there is no Wireless Access Point, and
each Wireless station communicates directly with other Wireless
stations.
• Infrastructure mode is used when each Wireless station connects
to the Wireless Access point. This also provides access to the
wired LAN.
If Disabled (default), data is NOT encrypted before being transmitted.
If Enabled, you must provide either the 64 Bit key table or the 128 Bit
keys. The key is used to encrypt the data before transmission.
Options are "Open System" or "Shared Key".
Select the method (Open System or Shared Key) used by other
Wireless Stations.
Shared Key is more secure than Open System.
Select "64Bits" or "128Bits" as required to match other Wireless
stations on your WLAN. Stations which do not have matching settings
will be unable to communicate.
128 bit Keys are more secure than 64 bit Keys.
Enter the key values to match other Wireless stations on your WLAN.
Default Key
This table is used when Encrypting and Decrypting data. All stations
always transmit data encrypted using their default key (see below).
The key number (1, 2, 3, 4) is also transmitted. The receiving station
will use the key number (1, 2, 3, 4) to determine which key value to
use for decryption. If the key value does not match the transmitting
station, decryption will fail.
The easiest way to ensure there are no problems is to have every
Station, including the Access Point, use the same key table (all entries
identical). Then, it does not matter which key is used as the default
key.
Select the key you wish to be the default. Transmitted data is
ALWAYS encrypted using the Default Key; the other Keys are for
decryption only.
Page 37
Page 42

Wireless Link Info Screen
After clicking the "Link Info" button on the Wireless Screen, a screen like the example below
will be shown.
State
Current Channel
Current TX Rate
Throughput (Tx )
Throughput ( Rx )
Link Quality
Signal Strength
Figure 31:Link Info Screen
This indicates which access point is currently in use.
The current channel which has been used.
The current transmitting speed.
This will show how much data has been transmitted per second.
This will show how much data has been received per second.
This indicates the quality of the Wireless connection
This indicates the strength of the Wireless signal being received.
The "Link Quality" and "Signal Strength" data is not
available if using "Ad-hoc" mode.
Page 38
Page 43

Chapter 6
Web-Based Management
This chapter explains how to use your Web Browser to configure the Wireless Print
Server.
6
Overview
The Wireless Print Server incorporates a HTTP server. This allows you to connect to the
Wireless Print Server and configure it using your Web Browser. Most browsers should work,
provided they support tables and forms.
Preparation
Because it supports dynamic IP Address allocation using DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP, the
Wireless Print Server ships with an IP Address of 0.0.0.0. This is NOT a valid IP Address.
Therefore, you must do ONE of the following:
• Check your DHCP server (if you have one), and determine the IP Address allocated to the
Wireless Print Server.
• Use the Diagnostic Button (if fitted) to print a report which includes the current IP
address. (Press the Diagnostic Button, and hold it for 2 seconds.)
• Use the Setup Wizard, BiAdmin or another Wireless Print Server utility to allocate a
valid IP Address to the Wireless Print Server.
• Add an entry to the arp table to associate the hardware address of the Wireless Print
Server with the desired IP address, as follows:
arp -s IP_Address 00:c0:02:xx:xx:xx (Unix)
arp -s IP_Address 00-c0-02-xx-xx-xx (Windows)
Where:
IP_Address is the IP Address you wish to assign to the Wireless Print Server.
00:c0:02:xx:xx:xx is the hardware address of the Wireless Print Server.
Example (Unix):
arp -s 192.168.0.21 00:c0:02:12:34:56
Example (Windows):
arp -s 192.168.0.21 00−c0−02−12−34−56
Note: The hardware address of the Wireless Print Server is shown on a sticker on the base of
the device.
Page 39
Page 44

Connecting to the Wireless Print Server
1. Start your Web Browser.
2. In the Address box, enter HTTP:// followed by the IP Address of the Wireless Print Server.
e.g.
http://192.168.0.21
3. You will then be prompted for the password. If no password has been set, just press
E
NTER.
4. Use the menu bar on the top of the screen to move about. Remember to save each screen
before changing to a different screen.
Configuration Screens
Depending on your model and Firmware version, the Web-based interface may look different
to the images shown in this User's Manual.
The functions have not changed, and the description of each setting is correct. Only the
appearances are different.
AppleTalk
AppleTalk zone
Printer Object
Type
Communication
Protocol
Figure 32: AppleTalk Screen
This determines which Apple systems can gain access to this printer.
These are text fields, used to describe the printer driver used for
each port. The Wireless Print Server is designed to work with
LaserWriter (or 100% compatible) printers.
Sets whether the port uses ASCII or Binary Communication
Protocol.. The default is Binary.
Page 40
Page 45

NetBEUI
Figure 33: NetBEUI Screen
Domain Name
Response Time
Abort Job if Error
Enter the designated work group to be serviced by the Wireless
Print Server. This field is not case sensitive, so names with different
case will be considered to be the same name.
Set how fast jobs are sent to the printer. The default value of zero
(0) delay should be increased only if your printer cannot cope with
no delays.
YES terminates a print job if a printing error occurs. NO (default)
will try to continue but may cause print errors. If print errors occur,
try setting this value to YES.
Page 41
Page 46

TCP/IP
IP Address
Figure 34: TCP/IP Screen
IP Address assigned to this device. If using dynamic IP Addresses
(DHCP, BOOTP, rarp), this should be left at 0.0.0.0.
Subnet Mask
(Network Mask)
Gateway
Address
Connection
Delay before
reconnection
attempts
Number of
reconnection
attempts
If the Router (Gateway) Address is 0.0.0.0, the Subnet Mask should
also be left at 0.0.0.0. If you have a router, enter the Subnet mask for
the segment to which the Wireless Print Server is attached.
If your network segment has a router or gateways, enter its IP
Address here. Otherwise, leave the address as 0.0.0.0.
Sets how long the Wireless Print Server should wait before retrying a
TCP/IP connection which is lost. Allowable values are from 0 to 255
seconds, with 2 as the default.
Set how many attempts at reconnection will be made. After that, the
TCP/IP session will be terminated.
Allowable values are from 0 to 255, with 254 as the default.
Page 42
Page 47

Configure Server
Print Server Name
Figure 35: Configure Server Screen
Change the default name if you wish. The new name must not
contain any spaces or blanks.
Password
Enable Protocols
Enter the device password, and again in the Verify field. Once a
password is entered, it is required in order to gain access and
change the configuration.
Non-TCP/IP may be disabled if they are not required on your LAN.
The available protocols depend on the Print Server model.
Page 43
Page 48

Wireless Configuration
The settings on this screen must match the other Wireless stations in order for communication
to occur.
Figure 36: Wireless Screen
Page 44
Page 49

Configuration
Regulatory
Domain
Station name
SSID
(ESSID)
Channel No.
Network Type
Link Info
Button
It is illegal to use this device in any location outside of the regulatory
domain.
This is the same as the Device (Host) Name on the WAN screen. On
your PC, some Wireless status screens may display this name as the
Access Point in use.
To communicate, all Wireless stations MUST use the same
SSID/ESSID.
The default value is ANY.
Note! The SSID is case sensitive.
Select the value you wish to use on your Wireless LAN. If you
experience lost connections and/or slow data transfers you may need to
experiment with different channels to see which is the best.
Select the correct value for your Wireless LAN.
• Ad-hoc mode is used when there is no Wireless Access Point, and
each Wireless station communicates directly with other Wireless
stations.
• Infrastructure mode is used when each Wireless station connects to
the Wireless Access point. This also provides access to the wired
LAN.
Click this button will open the sub screen.
WEP Data Privacy
Off
64 Bit
Encryption
If OFF (default), data is NOT encrypted before being transmitted.
If selected, data is encrypted, using the default key, before being
transmitted.
The receiving station must be set to 64 Bit Encryption, and have the
same Key value in the same position in its key table. Otherwise, it will
not be able to decrypt the data.
Default Key
Select the key you wish to be the default. Transmitted data is ALWAYS
encrypted using the Default Key; the other Keys are for decryption only.
Key Table:
This table is used when Encrypting and Decrypting data. All stations,
including this Access Point, always transmit data encrypted using their
default key. The key number (1, 2, 3, 4) is also transmitted. The
receiving station will use the key number (1, 2, 3, 4) to determine which
key value to use for decryption. If the key value does not match the
transmitting station, decryption will fail.
The easiest way to ensure there are no problems is to have every Station,
including the Access Point, use the same key table (all entries identical).
Then, it does not matter which key is used as the default key.
Page 45
Page 50

128 Bit
Encryption
WEP
Authentication
If selected, data is encrypted using the key before being transmitted. The
receiving station must be set to use 128 Bit Encryption, and have the
same Key value. Otherwise, it will not be able to decrypt the data.
Key
Enter the key value you wish to use. Other stations must have the same
key
Options are "Open System" or "Shared Key".
Some Wireless cards do not support both methods. Check your Wireless
card's documentation to determine the correct value.
Ensure that all Wireless stations use the same setting as the Access Point.
Other Screens
Server Status
This screen shows server system data and the current settings for all of the other screens. It is
read-only; no data can be input on this screen.
Printer Ports
This screen displays the current status of each port. For each port, the following data is listed:
• Connected Printer- the model name of the printer connected to the port, if the printer
name is known. (If the printer is not bi-directional, this information is unavailable.)
• Status - the current status of the printer (On-line, Off-line, Out of paper)
• Printing Information - this will show either Idle or Printing.
Logical Printers
Logical Printers (ports) can be used under Unix. For each Logical Printer, the following fields
are available:
Logical Printer
(Port)
Port
Pre-string
Post String
Convert LF to
CR+LF
Select the Logical Printer Port you wish to configure. (e.g L1)
Click the Get Data button to update the display with the current data
for the selected logical printer.
Select the Printer Port which the Logical printer will use.
The printer control string (in hex) to be sent to the printer before
each print job. This string cannot exceed 15 characters.
The printer control string (in hex) to be sent to the printer after each
print job. This string cannot exceed 15 characters.
If checked, LF (line feed) characters are changed to CR+LF (carriage
return + line feed).
Internet Printing
See Internet Mail Printing in Chapter 7 for details of this feature.
Page 46
Page 51

Chapter 7
Special Features
This chapter covers the special features of the Wireless Print Server.
7
Overview
The Wireless Print Server has two special features:
• Wireless Print Servers support IPP (Internet Printing Protocol).
• Support the proprietary Internet Mail Printing system.
Internet Printing Protocol (IPP)
IPP (Internet Printing Protocol) is a new standards-based system to allow remote printing from
a PC to any accessible printer. Normally, the printer will be attached to a computer or other
device which functions as an IPP Server.
For client PCs, it is necessary to install a compatible IPP Client program. The Client must also
know the IP Address or URL or the IPP Server.
IPP Server Configuration
The Wireless Print Server contains the necessary firmware to act as an IPP Server. No
additional configuration is necessary. However, the following requirements must be met.
• The Wireless Print Server must have a valid IP Address. For printing via the Internet, the
Wireless Print Server's IP Address must be external (allocated by your ISP), rather than an
IP Address on your local LAN.
• Any Router, Gateway or Firewall linking your LAN to the Internet must NOT block the
IPP protocol.
• You must advise clients of the correct URL or IP Address of the IPP Server. To use a URL
rather than an IP Address, you need to register the domain name for the URL.
• Unless clients are using Windows 2000, you must provide your clients with the supplied
IPP Client software. If it is not convenient to provide the CD-ROM, supply the
IPP_CLIENT.EXE file, located in the IPP folder.
Page 47
Page 52

IPP Client Setup - Windows 95/98/Me/NT 4.0/XP
The IPP Client Software can be installed on any of the following systems:
• Window 95/98/Me/2000/XP
• Windows NT 4.0
Installing from the CD-ROM
1. Insert the CD-ROM in your drive. If the program does not start automatically, run the
SETUP program in the top-level folder.
2. Follow the prompts until you reach the Select Installation screen, and select IPP Client.
3. At the next screen, select the Install IPP Client option.
4. Click Next, and step though the remaining screens to complete the installation.
Installing using IPP_CLIENT.EXE
1. Run this program to unzip the included files.
2. The IPP Setup program will then run.
3. Follow the prompts to complete the installation.
IPP Client Configuration (Windows 95/98/ME/2000/XP/NT 4.0)
1. Run the "Add IPP Port" program entry created by the installation. A screen like the
following will be displayed.
Figure 37: IPP Port
2. If Internet access from your location is via a Proxy Server, check Access IPP Server via
Proxy Server, and enter details of your Proxy Server. (This will be the same as your
Browser configuration.)
3. Enter the IP Address or URL of the IPP Server.
4. Click Select Device Port to view the available ports on the IPP Server, and select the
appropriate port. A connection to the IPP Server will be established at this time.
Page 48
Page 53

5. Click Save to create the IPP port on your system. You will see a message confirming that
the port has been created, then the following dialog:
Figure 38: Select Printer for IPP Port
6. Either select an existing printer to use the new port, and click OK.
OR
Click the Add New Printer button to create a new printer to use the IPP port. This will start
the Add Printer wizard. Follow the prompts to complete the process. Ensure that the new
printer uses the IPP port.
Installation is now complete.
• To create additional IPP Ports, repeat the entire procedure.
• The Proxy Server and other options are set individually for each IPP Port.
Changing the IPP Port Settings
After the IPP port is created, you can reach the screen shown in Figure 37: IPP Port using the
Windows Port Settings button:
1. Open the Printers folder (Start - Settings - Printers)
2. Right-click the IPP Printer, and select Properties.
3. Locate and click the Port Settings button (Details or Port tab, depending on your version
of Windows).
There are 2 settings - Retry Interval and Retry Count - which can be adjusted if you have
problems connecting to the IPP Server.
• Retry Interval sets the time interval (in seconds) between connection attempts. Increase
this number if you have a poor connection, or the remote server is very busy.
• Retry Count sets how many connection attempts will be made. Increase this number if
you have a poor connection, or the remote server is very busy.
Page 49
Page 54

IPP Client Setup - Windows 2000/XP
Windows 2000 has its own IPP Client, and there is no need to install the supplied IPP Client
Software. To use Windows 2000's IPP Client with the Wireless Print Server, follow this
procedure:
1. Start the Add Printer wizard.
2. Select Network Printer, and click "Next" to see the Locate your Printer screen, as shown
below.
Figure 39: Windows 2000 - Locate your Printer
3. Select Connect to a printer on the Internet or on your Intranet, and enter the URL of the
IPP Server as follows, where ip_address represents the IP Address of the IPP Server,
and 631 is the port number.
Port 1
Port 2 (if exists)
ip_address:631/ipp/P1
ip_address:631/ipp/P2
These entries are case sensitive. They must be
entered as shown, with "ipp" in lower case, and
P1, P2 and P3 in UPPER case.
4. If the connection can be established, and the printer on that port is on-line, the following
dialog will be displayed.
Figure 40: Windows 2000: No printer driver
Page 50
Page 55

5. Click "OK", and then select the printer manufacturer and model to match the printer
connected to the port on the IPP Server.
6. Click "Next", and complete the Wizard.
The IPP printer is now ready for use.
Using IPP Printers
The IPP Printer can be selected and used like any other Windows printer. If the IPP Server is
not on your network, your Internet connection needs to be active.
If you wish to check the availability of the remote IPP Server, you can use the Query IPP
Printer program installed with Add IPP Port.
An IPP Server may be unavailable for any of the following reasons:
• It is powered off.
• A printer problem has caused the IPP Server to cease responding, and a restart (reboot) is
required.
• The Server's IP Address has changed.
• The Internet connection for the IPP Server is down.
• Network congestion causes the connection attempt to time out.
If using the supplied IPP Client software, there are 2 settings - Retry Interval and Retry Count which can be adjusted if you have problems connecting to the IPP Server.
See the previous section Changing the IPP Port Settings for details.
Page 51
Page 56

Internet Mail Printing
The Internet Mail Printing System allows users to print data to your printer across the Internet.
Users send the Internet Wireless Print Server an E-Mail, with the print job normally sent as an
attachment to the E-Mail. The Wireless Print Server will retrieve the E-Mail and print it.
System Requirements
Mail Server
• Accessibility. The Mail Server must be accessible by the intended clients or users.
Normally, this means a permanent connection to the Internet.
• Protocols. The Mail Server must support the POP3 and SMTP protocols. The Internet
Printing System uses these protocols and the most common E-Mail formatting standards:
• MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)
• Base64 Encoding (for mail attachments)
Internet Wireless Print Server
• TCIP/IP Protocol. The LAN must use the TCP/IP protocol.
• Mail Server Access. The Wireless Print Server must be able to access the Mail Server
using a single IP address.
• Mail Account. The Wireless Print Server must have a Mail Account. Users print by
sending an E-Mail to this mail account.
User (Client) Requirements
• Internet Connection. Either through a LAN, or dial-up.
• E-Mail address. This is used to notify the user that their print job has been done, or if
there any problems.
• Printer Driver. Users must have a printer driver which matches the printer connected to
the remote Internet Wireless Print Server.
• Print Capture Software. To print more than plain text, users require InterNet Printing
Port software to capture the print job and convert it into an E-Mail attachment.
The Internet Printing Port software is available for the following operating systems:
• Microsoft Windows 95, 98, or ME
• Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000
Page 52
Page 57

Internet Mail Printing Configuration
The Wireless Print Server must be configured with the data in the following table.
The supplied BiAdmin utility program, or the Web interface can be used to set the following
entries on the TCP/IP screen.
Mail Server IP Address
Mail Account
Mail Account Password
Check Mail Interval
Redirect Mail Account
Default Printer Port
Printer Model
Print every E-Mail
Print Banner
Mail Response when
Printed
The IP Address of the E-Mail Server used by the Wireless
Print Server.
The name of the E-Mail Account used by the Wireless Print
Server.
Enter the password for the above Mail Account here.
Sets how often to check for mail.
Jobs which can not be printed will be sent to this account. If
blank, unprintable jobs will be discarded.
Printer number for all Internet print jobs. Only one port can
be selected. Users on the LAN can also use this port.
This text field identifies the printer used for Internet
printing. This value is sent to remote users upon request.
If ON, then all E-Mail received is printed. Otherwise, only
E-Mail from the InterNet Printing Port will be printed.
If YES (default), a banner page is printed to identify the
owner of the print job.
If YES, all print jobs receive an E-Mail response. If NO,
only users who set this option in their InterNet Printing Port
software receive an E-Mail.
Page 53
Page 58

User Software
The software provided for remote users (InterNet Printing Port) should be installed by
everyone intending to use Internet printing. Otherwise, remote users can print correctly only if:
• They send an E-Mail directly to the Wireless Print Server Mail Account, using their
normal E-Mail application.
• The E-Mail contains plain text only.
• The Internet Wireless Print Server is configured with Print every E-Mail ON.
Installation of the InterNet Printing Port software will create a new printer port. After attaching
the correct printer to this port, users can print to the Internet Printer using any Windows
application.
Installation - User Software
1. Run the InterNet Printing Port installation program SETUP.EXE
2. Default values for the installation are:
• Directory - C:\Program Files\Internet_Printer
• Start Menu folder - InterNet Printing Port Driver
3. You will then see the Configure Port screen, as shown in the following screenshot.
Figure 41: InterNet Printer Port
Page 54
Page 59

4. The following data must be provided.
Port Name
Remote Printer
E-mail Address
Mail Server Name
or IP Address
Your Internet
E-mail Address
Retry Interval
(Seconds)
Reply Notification
Mail
5. On completion, a new printer port will have been created.
Enter a descriptive name (e.g. "WAN") for the new
printer port.
The E-Mail address for the Internet printer. Your print
jobs will be sent to this E-Mail address.
This is the name or IP Address of your Mail Server. If
you are on a LAN, ask the LAN Administrator. If using
a dial-up connection, use the data provided by your ISP.
The normal address that people use to send you E-mail.
If unable to connect to the E-Mail server, retry after this
time period (1 to 255 seconds, 30 is usually OK).
Check to receive an E-Mail when your print job has
been processed.
Using the new Port
The Windows Control Panel is used to connect the correct printer to the InterNet Printing Port.
In Windows 95/NT, the procedure is:
1. Select the Printer which matches the remote printer, then choose Properties, as shown in
the example below.
Figure 42: InterNet Printer Properties
2. Select the new port - WAN (InterNet Printer) in the example - as the port for this printer.
• If you do not have the correct printer driver, or you wish to create another printer
using an existing driver, use the Windows Add Printer facility.
• Using the Windows Port Settings or Configure Port facility will reveal the same
Configure Port screen shown in Figure 41: InterNet Printer Port.
Page 55
Page 60

• If you wish to print to multiple Internet Printers, use the Windows Add Port facility to
add a new InterNet Printer port. Ensure that the correct data is entered in each port,
and that each port has a unique name.
Checking the Printer Driver
To make sure that the correct printer driver for the remote printer is installed on your system,
you can use the InterNet Printing Port to send an E-Mail to the Internet Printer. The procedure
is as follows:
1. Connect your default printer to the InterNet Printing Port.
2. Check that "Reply Notification Mail" in the InterNet Printing Port is ON.
3. From Notepad or another text editor, print a short message (e.g. "This is a test print") to
the Internet Printer.
You will receive a reply E-Mail containing the "Printer ID" which will identify the printer
attached to the Wireless Print Server. If this does not match the printer driver you are using,
install the correct printer driver.
Printing through the Internet
1. Create or open the document you wish to print.
2. Select the Printer connected to the InterNet Printing Port.
3. If you do not have a permanent Internet connection, establish a connection now. (Note:
The InterNet Printing Port will NOT establish a dial-up connection, but it will send the EMail the next time you are connected.)
4. Print the document.
5. The InterNet Printing Port will generate an E-Mail and send it to the remote printer. The
document will be encoded and sent as an attachment to the E-Mail. You will see a progress
screen similar to the example below:
Figure 43 InterNet Printing Progress
6. Close the Internet connection if you opened it in Step 3.
7. If the "Notify after print job" option is set, you will receive an E-Mail when your job is
printed.
Page 56
Page 61

Chapter 8
Troubleshooting
This chapter describes some problem situations, which may arise, and the solutions to
them.
8
Overview
If you encounter printing difficulties, please refer to the appropriate section.
If, after following the advice in these documents, the Wireless Print Server still does not
function properly, please contact your dealer for further advice.
Hardware & LAN Problems
Problem No. 1 All the Wireless Print Server's LEDs are off.
Solution No. 1 Check the power supply or power connection.
Problem No. 2 Wireless Print Server's status light continuously stays lit.
Solution No. 2 Reset Wireless Print Server by unplugging the power supply and
plugging it back in.
Problem No. 3 Wireless Print Server's status light and power light stay on
continuously and do not turn off.
Solution No. 3 Reset the Wireless Print Server by unplugging the power supply or by
pushing the reset push button, if fitted.
Problem No. 4 The Wireless Print Server unit can not be found on the LAN, so
configuration is not possible.
Solution No. 4
• If using the LAN connection, check the Hub or Switch. The link
LED for the port to which the Wireless Print Server is connected
should be ON. If it is Off, there is a problem in the network cable.
• If using a Wireless - only network, the Printer Server must match
the settings on other Wireless stations. Use the wired LAN
connection to check the Wireless configuration.
Remember that you can’t just plug in the LAN cable. You must
power off the Print Server, connect the LAN cable, then power on.
• Check the LEDs on the Print Server.
In Infrastructure mode, either the LAN or WLAN LED should be
On.
In Ad-hoc mode, both the LAN and WLAN LEDs should be On.
If using TCP/IP:
• Ensure that there are no routers between the Wireless Print Server
and the PC used for configuration.
• Ensure that the PC used for configuration has the TCP/IP network
protocol installed. Test its network connection by seeing if you can
locate other LAN devices from the PC. (e.g. Use Network
Neighborhood and try to browse the network.)
Page 57
Page 62

Problem No. 5 I am using DHCP, and getting an IP Address conflict involving the
Wireless Print Server.
Solution No. 5 If the Wireless Print Server is left on, but the DHCP server is turned
off, then the Wireless Print Server will retain its IP Address without the
DHCP Server being aware of it. Simply reset the Wireless Print Server
so it will obtain a new IP Address.
This problem would also arise if you assigned static IP Address, which
is within the range used by the DHCP server. If so, use another address
which is NOT within the range used by the DHCP server.
AppleTalk (Macintosh)
Problem No. 1 Why do I get an incorrect printout?
Solution No. 1 Some possible reasons are:
• You may have chosen Binary encoding to print the file. Try to use
ASCII encoding.
• Some of the fonts, which are in your print file may not be
supported by the printer. Try selecting LaserWriter 7 instead of
LaserWriter 8.
Problem No. 2 Can't find the Wireless Print Server's name in the Chooser.
Solution No. 2 Try the following:
1. Make sure that AppleTalk is on (the button next to Active is
highlighted in the Chooser).
2. Make sure the printer has been on and in the READY state for a
few minutes.
3. Make sure the printer has not been renamed since its last
appearance in the Chooser.
4. If the printer resides on a network with multiple zones, make sure
the correct zone is selected from the AppleTalk Zones box in the
Chooser.
Problem No. 3 My document didn't print to the right printer.
Solution No. 3 Check the following:
• Another Wireless Print Server with the same name may have
received your print job. Use the PSTOOL to reconfigure your
Wireless Print Server name and ensure all Wireless Print Servers
have unique names.
• Make sure your application output encode is set to ASCII. If not,
change it to ASCII.
Problem No. 4 My file doesn't print with the correct fonts.
Solution No. 4 Try changing your printer driver to LaserWriter 7.
Problem No. 5 My EPS file doesn't print with the correct fonts.
Solution No. 5 This is a problem that occurs in some application programs. Try
downloading the fonts contained in the EPS file before printing the
saved EPS file.
Page 58
Page 63

Problem No. 6 I can't select the "Remaining from:" item in the print dialog box.
Solution No. 6 If you have selected the Layout value, "2 Up", or "4 Up", you cannot
access the Remaining from item. Choose other selections.
Problem No. 7 A cover page prints either on the first or the last page of the
document.
Solution No. 7 Select one of these solutions:
• Turn the cover page feature off.
• Insert extra page breaks in your document to avoid the cover page
printing on the first or last page of your document.
• Install the Apple LaserWriter 7 driver. You are having trouble
printing with the Apple LaserWriter 8 driver.
Problem No. 8 Why do I have trouble printing with the LaserWriter 8?
Solution No. 8 Your application software may not be compatible with the LaserWriter
8 driver or your system may not meet the requirements of the
LaserWriter 8 driver. Use the Apple LaserWriter 7 driver instead.
Problem No. 9 The colors on my printed output do not match the colors on my
computer screen.
Solution No. 9 When the printer receives a color file, it tries to match the printed
output color to the screen color. Sometimes the printer cannot match up
the colors as closely as wanted. To alleviate this problem, perform the
following steps:
• Choose "Calibrated Color/Grayscale" in the Print pop-up menu in
the Print Options dialog box. The printer will make adjustments
to match the colors.
• Check your monitor to make sure all settings (for example,
brightness) are adjusted correctly.
Problem No. 10 When I send a print job, I get a PostScript Command error or no
print out.
Solution No. 10 Check the communication protocols. The computer, Wireless Print
Server and printer must all be configured to the same
communication protocol.(either Binary or ASCII).
To configure your system:
1. Choose which protocol you are going to use. You should check
your printer; it may not give you a choice.
2. Set your printer to the correct protocol.
3. Use the computer's Print submenu to configure your computer to
use the protocol you have chosen.
4. Configure the Wireless Print Server to use the same protocol as the
printer and computer.
Page 59
Page 64

Windows Printing Problems
Problem No. 1 When I tried to install the Printing software for Peer-to-Peer
printing, I received an error message and the installation was
aborted..
Solution No. 1 This may be caused by an existing installation of the printer port
software. Before attempting another installation:
• Remove the existing installation
• Restart your PC
To remove an existing printer port installation:
1. Open Start - Settings - Control Panel - Add/Remove Programs
2. Look for an entry with a name like "Shared Port", "Shared Printer
Port", " Print Server Driver" or " Print Server Port".
3. Select this item, click "Add/Remove", and confirm the deletion.
Problem No. 2 On Windows 95, I installed the Print Port Driver for Peer-to-Peer
Printing, but when I selected a port on a Wireless Print Server and
clicked "Add", the printer was not installed.
Solution No. 2 Try installing the Printer using the standard Windows tools, as follows:
1. Start the Add Printer Wizard.
2. Select Network Printer when prompted "How is the printer attached
to your Computer?", and click Next.
3. When prompted for the Network Path or Queue, enter a dummy
value such as shown below. (Do NOT select Yes for "Do you print
for MS-DOS programs?")
4. The printer wizard will display a message stating that "The Network
Printer is off-line". This is OK. Continue the Add Printer Wizard
until finished.
5. Go to the Printers folder (Control Panel-Printers). The printer icon
will be grayed out indicating the printer is not ready.
6. Right-click the Printer, and select Properties. Then select the Details
tab, as shown below.
Page 60
Page 65

7. Click the Add Port button. On the resulting screen, select Other,
then Printer Server, as the port to add, as shown below.
8. Click OK to see the Print Port Configuration screen, as shown
below.
Page 61
Page 66

9. Click the Browse Device button, select the desired Wireless Print
Server, and click OK.
10. Click OK to return to the Printers folders, and right-click on the
Printer. Ensure that the Work off-line option is NOT checked.
The Printer should no longer be grayed out, and is ready for use.
Problem No. 3 I connected and configured a WPS (Windows Printing System)
printer as described, but I can't get the print job to print.
Solution No. 3 Printer drivers for WPS printers poll the printer before sending print
data. Since the printer is networked, the printer is not found and no data
is sent. The solution is to add your printer as a network printer as
described in Solution 2 above.
Note: The screens shown in Solution 2 are from Windows 95. Other
versions of Windows may look slightly different, but the process is
identical. If using Window NT or 2000, do NOT enable Sharing for the
printer.
Problem No. 4 When printing from some software applications such as Power
Point, it takes a long time and the print out is incorrect.
Solution No. 4 The problem is due to the printer, which is being configured to Start
printing after the first page is spooled. To change this setting:
• Go to Control Panel - Printers and click on your printer.
• Then select File - Properties - Details.
• When the Details screen appears, click the Spool Settings button.
• When the Spool Settings dialogue box appears, choose Start
printing after last page is spooled and click OK.
Page 62
Page 67

Problem No. 5 A printing device connected to the Wireless Print Server port cannot
print or prints garbage.
Solution No. 5 Check the following:
• Cable connection between Wireless Print Server and printer.
• Printer driver in the application program or Windows matches the
printer.
Problem No. 6 The Configuration button on the Printer Status screen in BiAdmin is
grayed out, even though my printer is bi-directional.
Solution No. 6 The button is unavailable if the printer is busy. You must wait until the
printer is idle.
Problem No. 7 When I send a print job, cannot print or prints garbage.
Solution No. 7 The problem may be due to the printer, if the printer you used is an old
model with low speed, the following steps may solve this problem:
Try the following:
• Open the BiAdmin Utility.
• Click the Printer Status icon.
• Change the Printer Type setting to Low Speed or set the Handshake
Signal setting to Ack & Busy.
Page 63
Page 68

Appendix A
Specifications
General Specifications
TEW-P1U1P Wireless Print Server
Power Consumption 5.5w max.
External Power Adapter 12V DC
LEDs 4
USB Port (1.1) 1
Parallel Port 1
Ethernet Interface 10/100BaseT
Wireless Interface IEEE802.11b WLAN standard
FCC / CE FCC, CE. Class B
Environmental Specifications
Operating Temperature 0 ~ 40°C
Storage Temperature -10 ~ 70°C
Shipping Temperature -40 ~ 70°C
Operating Humidity 10 ~ 80%
Storage Humidity 5 ~ 90%
Shipping Humidity 5 ~ 100%
A
Parallel Port Pin Assignments
Pin Signal Name Direction
1 - Strobe To printer
2 +Data 0 To printer
3 +Data 1 To printer
4 +Data 2 To printer
5 +Data 3 To printer
6 +Data 4 To printer
7 +Data 5 To printer
8 +Data 6 To printer
9 +Data 7 To printer
10 - ACK To Server
11 + Busy To Server
12 + Paper End To Server
13 + Select To Server
14 - Auto Feed To printer
15 - Error To Server
16 - Init To printer
17 - Select In To printer
18-25 GND Ground
Page 64
Page 69

Protocol Support
Model TCP/IP NetBeui AppleTalk
TEW-P1U1P √ √ √
Feature Support
Model HTTP
TEW-P1U1P √ √ √ √
Setup
E-mail
Printing
IPP
Support
AutoIP
FTP/Telnet
Support
Page 65
Page 70

Appendix B
Network Server Configuration
B
Windows NT4.0 Server
If using Windows Windows NT 4.0, Microsoft TCP/IP Printing Support must be installed.
• If it is already installed, add a TCP/IP Remote Printer, as described below.
• Otherwise, install TCP/IP printing support, then add a TCP/IP Remote Printer.
Adding TCP/IP Printing Support
1. Go to Start-Settings-Control Panel-Network.
2. Click the Service option and ensure that Microsoft TCP/IP Printing is enabled. If it is not
enabled, select the Add option and enable it as usual.
3. If you added services in step 2, reboot the computer for the changes to take affect.
Adding a TCP/IP Remote Printer
1. Go to Start-Settings-Printer and invoke the Add Printer wizard.
2. When prompted with This printer will be managed by, select My Computer and click
Next.
3. Select Add Port…, then select LPR Port and click New Port.
4. In the Name of Address of server providing lpd: Dialog box, enter the Wireless Print
Server's IP address.
5. In the Name of printer or print queue on that server dialog box, enter the appropriate
logical printer number. (L1 for Parallel Port, L2 for USB Port).
6. Click OK. When returned to the Printer Ports window, simply select Close and then install
your printer driver as usual.
7. When prompted whether or not the printer will be shared, select the Sharing radio button.
8. In the Shared dialog box, enter the shared printer name. (The shared name is how other
users will see this printer.) Click OK to save and exit.
Client PCs can now be configured as described in Chapter 4 - Client Configuration.
Page 66
Page 71

Windows 2000/2003 Server
1. Start the Add Printer Wizard, select Network Printer, then click Next to browse for the
Wireless Print Server.
2. Locate and double-click the Wireless Print Server, select the desired port (L1 for Parallel
Port, L2 for USB Port), and click Next.
A message like the following will be displayed:
Figure 44: Windows 2000 Message
Figure 45: Windows2003 Message
3. Click "OK", and select the correct Manufacturer and Model for this printer.
4. Follow the prompts to complete the installation.
5. In the Printers folder, right-click the new printer, and select Sharing.
• Select "Shared As:" and enter an appropriate name for this printer. Users will see this
name when browsing for the printer during installation.
• If desired, click "Additional Drivers" and install printer drivers for other versions of
Windows, such as Windows 98. This will assist users during the installation process.
6. Click OK to close this Window. Configuration is now complete.
Client PCs can now be configured as described in Chapter 4 - Client Configuration.
Page 67
Page 72

Unix Systems
Your Wireless Print Server supports the LPD Unix printing method, which is supported by all
common Unix systems.
You must configure both the Wireless Print Server itself and your Unix system, as described in
the following sections.
Wireless Print Server IP Address Configuration
Because it supports dynamic IP Address allocation using DHCP or BOOTP, the Wireless Print
Server ships with an IP Address of 0.0.0.0. This is NOT a valid IP Address.
Therefore, you must do ONE of the following:
• Check your DHCP server (if you have one), and determine the IP Address allocated to the
Wireless Print Server.
• Configure your BOOTP Server (if you have one), to provide an IP address to the Wireless
Print Server, then restart the Wireless Print Server.
• Use a Windows platform and run the Setup Wizard or BiAdmin utility to allocate a valid
IP Address to the Wireless Print Server.
• Add an entry to the arp table to associate the hardware address of the Wireless Print
Server with the desired IP address, as follows:
arp -s IP_Address 00:c0:02:xx:xx:xx
Where:
IP_Address is the IP Address you wish to assign to the Wireless Print Server.
00:c0:02:xx:xx:xx is the hardware address of the Wireless Print Server.
Example
arp -s 192.168.0.21 00:c0:02:12:34:56
You should then assign this IP address to the Wireless Print Server using your Web
Browser, as described in Chapter 6 - Web-based Management.
Note:
The hardware address of the Wireless Print Server is shown on a sticker on the base of the
device.
Other Wireless Print Server Configuration
The recommended method to configure the Wireless Print Server is to use the Web-based
interface, as described in Chapter 6 - Web-based Management.
• Ensure that the TCP/IP settings are correct for your network.
• The logical printers (e.g. L1) must be configured correctly to match your system.
Page 68
Page 73

LPD Configuration
Configuration for the most common platforms is described below.
LPD on IBM AIX 4.15
Before proceeding, ensure that the Wireless Print Server has been assigned an IP Address. To
setup your AIX system for LPD printing, perform the following steps.
1. Add the Wireless Print Server to /etc/hosts.lpd, using the name you assigned to the
Wireless Print Server.
2. Start the LPD daemon if it is not running, using the following command:
start src -s qdaemon
3. Start the system administration tool smit and select Print Spooling.
4. Create the required number of queues (one for each logical printer) by selecting:
Add a Print Queue
Remote (Printer attached to Remote Host)
Standard Processing
5. Use the following information:
Field Entry
Name of queue to add
Hostname for remote server
Name of queue on remote
server
Type of print spooler on
remote server
6. Ensure that the logical printers are configured in the Wireless Print Server.
7. Print using the following command:
lp -d printer_queue file_name
Where
printer_queue is one of the entries used in Name of queue to add.
file_name is the file you wish to print.
Use a single-word queue name, which
indicates which printer is attached.
Wireless Print Server name as used in
/etc/hosts.lpd.
Logical printer number (e.g. L1) to service
this queue.
Use default value. (AIX Version xxx)
Page 69
Page 74

LPD on System V
Before beginning LPD Setup, ensure that an IP Address has been assigned to the Wireless Print
Server. Keep the following points in mind:
The remote host name is the name of the Wireless Print Server.
The remote printer name is the print queue name for the Logical Printer. Logical printers also
need to be configured on the Wireless Print Server itself.
If your UNIX asks for the LPD type, be sure to identify the service type as BSD. The Wireless
Print Server’s LPD protocol meets BSD system standards.
In the sample commands shown, printer_name is the name of the Print Queue serviced by the
Wireless Print Server, and Spooler_directory is the name of the directory, which is used to
spool the print jobs.
Procedure
Action Sample Command
Stop Print Services
Add a System Printer
Restart the Print Services
Enable printing to the new
/usr/lib/lpshut
/usr/lib/lpadmin -p printer_name -v /dev/null
/usr/lib/lpsched
enable printer_name
printer device
Start accepting jobs for the
accept printer_name
new printer device
Create a spooling directory
Make spooling daemon the
mkdir /usr/spool/Spooler_directory
chown daemon /usr/spool/Spooler_directory
owner of this directory
Create read/write permissions
Give permissions to LPD
chmod 775 /usr/spool/Spooler_directory
chgrp daemon /usr/spool/Spooler_directory
processes.
Add remote printer(s)
See following section
Adding Remote Printers
A remote printer is added by inserting the following line in the /etc/printcap file.
The entry is really one line, but can be entered as shown.
Use a TAB character where shown.
Printer_name|Remote_Printer_Alias:\
[T
AB] :lp=:\
[T
AB] :rm=PS_NAME:\
[T
AB] :rp=Logical_Printer_name:\
[T
AB] :sd=Spooler_directory:\
[T
AB] :mx#0:
Page 70
Page 75

Where:
Printer_name is the Print Queue name used to store jobs for the corresponding logical
printer.
PS_NAME is the Wireless Print Server name defined in /etc/hosts.
Logical_Printer_name is the logical printer name on the Wireless Print Server. (e.g. L1)
Spooler_directory is the directory you created in Step 6.
Example:
Marketing|RP1_PS123456:\
[T
AB] :lp=:\
[T
AB] :rm=PS_Rm203:\
[T
AB] :rp=L1:\
[T
AB] :sd=/usr/spool/Marketing:\
[T
AB] :mx#0:
Repeat this process for each Logical Printer/Print Queue combination that you wish to create.
LPD on Linux
If using the command line, the procedure is the same as for System V. (above)
On recent Linux distributions, you can use the graphical X-windows interface instead of the
command line. The procedure is described below, but may vary according to your version of
Linux.
1. Start your X-windows shell.
2. Select Control Panel, then Printer Configuration.
3. Select Add. For the printer type, select Remote Unix (lpd) Queue.
4. Use the following data to complete the resulting dialog.
Field Data
Name Enter a name for this printer
Spool Directory /var/spool/lpd/name_of_printer
File Limit 0 (no limit)
Remote Host Name or IP Address of Wireless Print Server
e.g. SC3000014
Note: host file entry is required to use the name
instead of IP Address
Remote Queue Ln
Where n is the Logical Printer number
By default, L1 is port 1, and L2 is port 2 if the Print
Server has 2 ports.
5. Save this data, and exit the Printer Configuration. Configuration is now completed, and the
printer is now available for use.
Page 71
Page 76

LPD on BSD
Before continuing, ensure that an IP Address has been assigned to the Wireless Print Server.
Remember the following:
The remote host name is the name of the Wireless Print Server.
The remote printer name is the logical printer (e.g. L1) on the Wireless Print Server.
If asked for the LPD type, enter the service type as BSD.
In the sample commands shown, printer_name is the Print Queue serviced by the logical
printer on the Wireless Print Server, and Spooler_dir is the name of the directory, which is
used to spool the print jobs.
Procedure
Action Sample Command
Create a spooling directory mkdir /usr/spool/Spooler_dir
Set spooling daemon as owner
chown daemon /usr/spool/Spooler_dir
of this directory
Create read/write permissions chmod 775 /usr/spool/Spooler_dir
Give permissions to LPD
chgrp daemon /usr/spool/Spooler_dir
processes
Add remote printer(s) See below
Start lpc print mechanism lpc start printer_name
Adding Remote Printers
A remote printer is added by inserting the following line in the /etc/printcap file.
The entry is really one line, but can be entered as shown.
Use a TAB character where shown.
Printer_name|Remote_Printer_Alias:\
[T
AB] :lp=:\
[T
AB] :rm=PS_NAME:\
[T
AB] :rp=Logical_Printer_name:\
[T
AB] :sd=Spooler_directory:\
[T
AB] :mx#0:
Where:
Printer_name is the Print Queue name used to store jobs for the corresponding logical
printer.
PS_NAME is the Wireless Print Server name defined in /etc/hosts.
Logical_Printer_name is the logical printer name on the Wireless Print Server. (e.g. L1)
Spooler_directory is the directory you created in Step 6.
Page 72
Page 77

Example:
Marketing|RP1_PS123456:\
[TAB] :lp=:\
[T
AB] :rm=PS_Rm203:\
[T
AB] :rp=L1:\
[T
AB] :sd=/usr/spool/Marketing:\
[T
AB] :mx#0:
Repeat this process for each Logical Printer/Print Queue combination that you wish to create.
Printing using LPD
For LPD printing instructions, refer to your UNIX manual. The following example is for a
BSD system:
lpr -P printer_name filename
Where:
printer_name is the name of the Print Queue defined on the Unix host.
filename is the name of the file you wish to print.
Example:
lpr -P Marketing /etc/hosts
In the above example, the /etc/hosts file is sent to the printer queue Marketing. It will then be
sent to the logical printer associated with this queue.
Page 73
Page 78

Netware Systems
Overview
• The Print Server must be configured as a valid device on your TCP/IP network.
• To use NDPS (Novell Distributed Printing Services), the Novell server must be running
Novell NetWare 5, and the PCs (clients) must be running IntranetWare Client V2.2. or
later.
The following procedure is designed to enable Public Access Printing under NDPS. Public
Access Printing allows anybody on the network to access the printer.
Creating an NDPS Manager Object
If an NDPS Manager Object already exists, skip this procedure and proceed to Creating an
NDPS Printer Agent.
1. Login to NetWare 5.0 Server as Admin and start the NetWare Administrator program
Nwadmn32.exe.
2. Select the container on NetWare Administrator where you want the NDPS Manager object
to reside. (e.g. TeSupp)
3. Select Create - Object from the menu bar to view the New Object dialog.
4. Select NDPS Manager as the object to create. The Create NDPS Manager Object window
shown below will appear.
Figure 46: Create NDPS Manager Object
5. Type a name in the NDPS Manager Name.(e.g. SerMGR in Figure 1 above)
6. Browse the Resident Server and select where you want the NDPS Manager object to be
assigned. (e.g. TECH_50.TeSupp in figure 1 above)
7. Browse the Database Volume and select where you want the NDPS Manager database to
be assigned. (e.g. TECH_50_SYS.TeSupp in figure 1 above)
8. Click Create. The new NDPS Manager will appear in the main browser window.
To start the NDPS Manager in future, enter the following command at the console:
LOAD NDPSM
then select the NDPS Manager object.
To start the NDPS Manager whenever you bring up the server, add a command like
the following to your server's AUTOEXEC.NCF file:
LOAD NDPSM SerMGR.TeSupp
The last item is the name of the NDPS Manager object you wish to load.
Page 74
Page 79

9. After creating an NDPS Manager, you can create NDPS printers by using NetWare
Administrator, as explained below.
Creating an NDPS Printer Agent
To create Public Access Printers using the NDPS Manager Object in NetWare Administrator,
follow this procedure:
1. Start the NDPS Manager object you will be using to control the Printer Agent.
2. At the Identification page, click the Printer Agent List.
3. Click New to see the Create Printer Agent window, as shown below.
Figure 47: Create Printer Agent
4. Enter the desired name for the Printer Agent (PA) Name.
5. Normally, the NDPS Manager will be the NDPS Manger object you are using.
6. Select Novell Printer Gateway in the Gateway Type. (see figure2 above)
7. Click OK and then select the available printer.
8. Select Remote (LPR on IP) in the Connection Type.
9. Click Next to see the following Configure Port Handler screen.
Figure 48 Configure Port Handler
10. In the Host address IP field, enter the IP Address previously assigned to the Print Server
device.
11. In the Printer Name field, enter the Logical Port name on the Print Server. (L1 for Parallel
Port, L2 for USB Port).
Page 75
Page 80

12. Click Finish, then select appropriate drivers for Windows 3.1, Windows 95/98 etc as
required.
13. The new Printer Agent will now appear in the Printer Agent List window.
Repeat this procedure for any other ports on the Print Server, or for any other logical printers
you wish to use.
Client PCs can now be configured as described in Chapter 4 - Client Configuration.
Page 76
 Loading...
Loading...