
i

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................. 1
Wireless ADSL Modem Router Features ........................................................................ 1
Package Contents .............................................................................................................. 5
Physical Details .................................................................................................................. 6
CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................... 8
Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 8
Procedure ........................................................................................................................... 8
CHAPTER 3 SETUP .............................................................................................................. 10
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 10
Configuration Program .................................................................................................. 12
Setup Wizard ................................................................................................................... 13
Configuring VCs .............................................................................................................. 20
Main Screen ..................................................................................................................... 23
LAN Screen ...................................................................................................................... 24
Wireless Screen ................................................................................................................ 26
Wireless Security ............................................................................................................. 29
Trusted Wireless Stations ............................................................................................... 33
Password Screen .............................................................................................................. 35
Mode Screen ..................................................................................................................... 37
Status ................................................................................................................................ 38
Connection Status - PPPoE & PPPoA ........................................................................... 41
Connection Details - Dynamic IP Address .................................................................... 42
Connection Details - Fixed IP Address .......................................................................... 43
Binding Function ............................................................................................................. 44
CHAPTER 4 COMPUTER CONFIGURATION ................................................................ 45
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 45
Windows Clients .............................................................................................................. 45
Macintosh Clients ............................................................................................................ 57
Linux Clients .................................................................................................................... 57
Other Unix Systems ......................................................................................................... 57
Wireless Station Configuration ...................................................................................... 58
Wireless Configuration on Windows XP ....................................................................... 58
CHAPTER 5 ADVANCED FEATURES .............................................................................. 69
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 69
Internet ............................................................................................................................. 69
Dynamic DNS (Domain Name Server) .......................................................................... 73
Options ............................................................................................................................. 75
Schedule............................................................................................................................ 76
Port Trigger ..................................................................................................................... 77
Port Forward ................................................................................................................... 79
Port Range Forward ....................................................................................................... 80
QoS ................................................................................................................................... 81
CHAPTER 6 ADVANCED ADMINISTRATION ............................................................... 83
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 83
PC Database ..................................................................................................................... 84
Config File ........................................................................................................................ 85
Logs ................................................................................................................................... 86
ii

E-mail ............................................................................................................................... 88
Diagnostics ....................................................................................................................... 90
Remote Administration ................................................................................................... 91
Routing ............................................................................................................................. 93
Upgrade Firmware .......................................................................................................... 97
CHAPTER 7 MODEM MODE .............................................................................................. 98
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 98
Management Connections .............................................................................................. 98
Modem Mode Main Screen ............................................................................................ 99
Operation ....................................................................................................................... 103
APPENDIX A TROUBLESHOOTING .............................................................................. 104
Overview ........................................................................................................................ 104
General Problems .......................................................................................................... 104
Internet Access ............................................................................................................... 104
Wireless Access .............................................................................................................. 105
APPENDIX B ABOUT WIRELESS LANS ........................................................................ 107
Modes ............................................................................................................................. 107
BSS/ESS.......................................................................................................................... 107
Channels ......................................................................................................................... 108
WEP ................................................................................................................................ 108
WPA-PSK ...................................................................................................................... 108
WPA2-PSK .................................................................................................................... 109
WPA-802.1x ................................................................................................................... 109
Wireless LAN Configuration ........................................................................................ 109
APPENDIX C SPECIFICATIONS ..................................................................................... 110
Multi-Function Wireless ADSL Modem Router ........................................................ 110
Wireless Interface .......................................................................................................... 110
Regulatory Approvals ................................................................................................... 113
iii

Chapter 1
Introduction
1
This Chapter provides an overview of the Wireless ADSL Modem Router's
features and capabilities.
Congratulations on the purchase of your new Wireless ADSL Modem Router. The Wireless
ADSL Modem Router is a multi-function device providing the following services:
ADSL Modem.
•
Shared Broadband Internet Access for all LAN users.
•
Wireless Access Point for 802.11n, 802.11b and 802.11g Wireless Stations.
•
4-Port Switching Hub for 10BaseT or 100BaseT connections.
•
Wireless ADSL Modem Router Features
The Wireless ADSL Modem Router incorporates many advanced features, carefully designed
to provide sophisticated functions while being easy to use.
Internet Access Features
• Shared Internet Access. All users on the LAN or WLAN can access the Internet
through the Wireless ADSL Modem Router, using only a single external IP Address. The
local (invalid) IP Addresses are hidden from external sources. This process is called NAT
(Network Address Translation).
Built-in ADSL Modem. The Wireless ADSL Modem Router has a built-in ADSL
•
modem, supporting all common ADSL connections.
1

IPoA, PPPoE, PPPoA, Direct Connection Support. The Wireless ADSL Modem
•
Router supports all common connection methods.
•
Auto-detection of Internet Connection Method. In most situations, the Wireless
ADSL Modem Router can test your ADSL and Internet connection to determine the connection method used by your ISP.
Static or Dynamic IP Address. On the Internet (ADSL port) connection, the Wireless
•
ADSL Modem Router supports both Dynamic IP Address (IP Address is allocated on
connection) and Static (Fixed) IP Address.
Advanced Internet Functions
• Application Level Gateways (ALGs). Applications which use non-standard connec-
tions or port numbers are normally blocked by the Firewall. The ability to define and
allow such applications is provided, to enable such applications to be used normally.
Port Triggering. This feature, also called Special Applications, allows you to use
•
Internet applications which normally do not function when used behind a firewall.
•
Port Forwarding. This feature allows Internet users to access Internet servers on your
LAN. The required setup is quick and easy.
•
Dynamic DNS Support. DDNS, when used with the Virtual Servers feature, allows
users to connect to Servers on your LAN using a Domain Name, even if you have a dynamic IP address which changes every time you connect.
URL Filter. Use the URL Filter to block access to undesirable Web sites by LAN users.
•
Scheduling. Both the URL Filter and Firewall rules can be scheduled to operate only at
•
certain times. This provides great flexibility in controlling Internet -bound traffic.
•
Logs. Define what data is recorded in the Logs, and optionally send log data to a Syslog
Server. Log data can also be E-mailed to you.
•
VPN Pass through Support. PCs with VPN (Virtual Private Networking) software
using PPTP, L2TP and IPSec are transparently supported - no configuration is required.
•
Multi-PVC Support. A permanent virtual circuit (PVC) can provide a continuous
connection between two or more points when needed without having to reserve a specific
physical path in advance. In this way, many companies can share a common pool of circuits. (Please note: auto-detect connection setup in Setup Wizard does not support MultiPCV. If you would like to enable the Multi-PVC feature, please use manual connection
method instead.)
Wireless Features
• Standards Compliant. The Wireless ADSL Modem Router complies with the
IEEE802.11g (DSSS) specifications for Wireless LANs.
•
Supports Pre-N Wireless Stations. The 802.11n Draft standard provides for backward
compatibility with the 802.11b standard, so 802.11n, 802.11b and 802.11g Wireless stations can be used simultaneously.
•
WEP support. Support for WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is included. Key sizes of
64 Bit and 128 Bit are supported. WEP encrypts any data before transmission, providing
protection against snoopers.
2

WPA-PSK support. Like WEP, WPA-PSK encrypts any data before transmission,
•
providing protection against snoopers. The WPA-PSK is a later standard than WEP, and
provides both easier configuration and greater security than WEP.
WPA2-PSK support. Support for WPA2 is also included. WPA2 uses the extremely
•
secure AES encryption method.
•
802.1x Support. Support for 802.1x mode is included, providing for the industrial-
strength wireless security of 802.1x authentication and authorization.
•
Wireless MAC Access Control. The Wireless Access Control feature can check the
MAC address (hardware address) of Wireless stations to ensure that only trusted Wireless
Stations can access your LAN.
Simple Configuration. If the default settings are unsuitable, they can be changed
•
quickly and easily.
•
WPS Support. WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) can simplify the process of connecting any
device to the wireless network by using the Push Button Configuration (PBC) on the
Wireless Access Point, or entering a PIN code if there's no button.
• WDS Support. Support for WDS (Wireless Distribution System) allows the Wireless
Access Point to act as a Wireless Bridge. Both Point-to-Point and Multi-Poin t Bridge
modes are supported.
LAN Features
• 4-Port Switching Hub. The Wireless ADSL Modem Router incorporates a 4-port
10/100BaseT switching hub, making it easy to create or extend your LAN.
•
DHCP Server Support. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol provides a dynamic IP
address to PCs and other devices upon request. The Wireless ADSL Modem Router can
act as a DHCP Server for your local LAN and WLAN devices.
Configuration & Management
• Easy Setup. Use your WEB browser from anywhere on the LAN or WLAN for configu-
ration.
•
Configuration File Upload/Download. Save (download) the configuration data from
the Wireless ADSL Modem Router to your computer, and restore (upload) a previouslysaved configuration file to the Wireless ADSL Modem Router.
Remote Management. The Wireless ADSL Modem Router can be managed from any
•
PC on your LAN or Wireless LAN. And, if the Internet connection exists, it can also (optionally) be configured via the Internet.
Network Diagnostics. You can use the Wireless ADSL Modem Router to perform a
•
Ping or DNS lookup.
Security Features
• Password - protected Configuration. Password protection is provided to prevent
unauthorized users from modifying the configuration data and settings.
•
Wireless LAN Security. WPA-802.1x, WPA2-802.1x and WEP and Wireless access
control by MAC address are all supported. The MAC-level access control feature can be
used to prevent unknown wireless stations from accessing your LAN.
3

NAT Protection. An intrinsic side effect of NAT (Network Address Translation) tech-
•
nology is that by allowing all LAN users to share a single IP address, the location and
even the existence of each computer is hidden. From the external viewpoint, there is no
network, only a single device - the Wireless ADSL Modem Router.
Firewall. All incoming data packets are monitored and all incoming server requests are
•
filtered, thus protecting your network from malicious attacks from external sources.
•
Protection against DoS attacks. DoS (Denial of Service) attacks can flood your
Internet connection with invalid packets and connection requests, using so much bandwidth and so many resources that Internet access becomes unavailable. The Wireless
ADSL Modem Router incorporates protection against DoS attacks.
4

Package Contents
The following items should be included. If any of these items are damaged or missing, please
contact your dealer immediately.
• TEW-635BRM
• Multi-Language Quick Installation Guide
• CD-ROM (User’s Guide)
• 1 x RJ-45 Ethernet Cable
• 1 x RJ-11 Telephone Cable
• 1 x External Power Adapter (12VDC, 1A)
5

Physical Details
Front-mounted LEDs
Power LED On (Green) - Power on.
Off - No power.
Flashing (Green) - Device is rebooting.
Status On (Orange) - Device error.
LAN
Wireless On - Wireless enabled.
ADSL On - ADSL connection established.
Internet On (Green) - Internet connection is available.
WPS On - WPS wireless security is enabled.
For each port, there are 2 LEDs. One is 100BaseT, another is 10BaseT.
• On (Green) - Corresponding LAN (hub) port is using 100BaseT.
• On (Orange) - Corresponding LAN (hub) port is using 10BaseT.
• Off - No active connection on the corresponding LAN (hub) port.
• Flashing - Data is being transmitted or received via the corresponding
LAN (hub) port.
Off - No Wireless connections currently exist.
Flashing - Data is being transmitted or received via the Wireless connec-
tion. This includes "network traffic" as well as user’s data.
Off - No ADSL connection existing.
Flashing - ADSL is synchronizing.
Off - No Internet connection available.
On (Orange) - Authentication error.
Off - WPS is disable
Flashing - The device is in the 2-minute interval to synchronize security.
6

Rear Panel
ADSL port
LAN 1~4
Power ON/OFF
Power port
WPS Button
Wireless ON/OFF
Connects ADSL line here
10/100Mbps LAN port.
Press this button to power on/off the device
Power adapter port
Push the WPS button to enable the WPS function. On your other
wireless device, push the WPS (if available) or type the pin code to
establish the secured wireless encryption connection automatically.
Press this button to switch wireless function on or off.
To restore the factory default settings
Press the Wireless and WPS buttons simultaneously for 8 seconds and release them. Wait the
Wireless ADSL Modem Router to restart. The ADSL router should restore the factory default
value.
7

Chapter 2
Installation
2
This Chapter covers the physical installation of the Wireless ADSL Modem
Router.
Requirements
• Network cables. Use standard 10/100BaseT network (UTP) cables with RJ-45 connectors.
• TCP/IP protocol must be installed on all PCs.
• For Internet Access, an Internet Access account with an ISP, and a DSL connection.
• To use the Wireless Access Point, all Wireless devices must be compliant with the IEEE
802.11g, IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11n Draft specifications.
Procedure
ADSL Line LAN Ports Power Connector
1. Choose an Installation Site
Select a suitable place on the network to install the Wireless ADSL Modem Router.
For best Wireless reception and performance, the Wireless
ADSL Modem Router should be positioned in a central
location with minimum obstructions between the Wireless
ADSL Modem Router and the computers.
Also, if using multiple Access Points, adjacent Access
Points should use different Channels.
8

Installation
2. Connect LAN Cables
Use standard LAN cables to connect computers to the Switching Hub ports on the Wireless ADSL Modem Router. Both 10BaseT and 100BaseT connections can be used
simultaneously.
3. Connect RJ-11 Telephone Cable
Connect the provided telephone cable from the ADSL port to the ADSL phone jack which
provided by your ADSL phone company.
4. Power Up
Connect the provided power adapter to the power port. Only use the provided power adapter. Using a different one may cause hardware damage.
5. Check the LEDs
• The Power LED should be ON.
• One of the LAN port should be on if there is a computer connected.
• The Wireless LED should be ON
• The ADSL LED should be ON if ADSL line is established.
• The Internet (Green) LED may be OFF. After configuration, it should be ON.
For more information, refer to Front-mounted LEDs in Chapter 1.
9
Chapter 3
Setup
3
This Chapter provides Setup details of the Wireless ADSL Modem Router.
Overview
This chapter describes the setup procedure for:
• Internet Access
• LAN configuration
• Wireless setup
• Assigning a Password to protect the configuration data.
PCs on your local LAN may also require configuration. For details, see Chapter 4 - Computer
Configuration.
Other configuration may also be required, depending on which features and functions of the
Wireless ADSL Modem Router you wish to use. Use the table below to locate detailed instructions for the required functions.
To Do this: Refer to:
Configure PCs on your LAN. Chapter 4:
Computer Configuration
Use any of the following Advanced features:
• Internet (DMZ, URL Filter)
• Access Control
• Dynamic DNS
• Options
• Schedule
• Port Trigger
• Port Forward
• Port Range Forward
• QoS
Chapter 5:
Advanced Features
10
Use any of the following Administration Configuration
settings or features:
• PC Database
• Config File
• Logs
• E-mail
• Diagnostics
• Remote A dmin
• Routing
• Upgrade Firmware
Chapter 6
Advanced Administration
11

Configuration Program
The Wireless ADSL Modem Router contains an HTTP server. This enables you to connect to
it, and configure it, using your Web Browser. Your Browser must support JavaScript.
The configuration program has been tested on the following browsers:
• Netscape 7.1 or later.
• Mozilla 1.6 or later
• Internet Explorer V5.5 or later
Preparation
Before attempting to configure the Wireless ADSL Modem Router, please ensure that:
• Your computer can establish a physical connection to the Wireless ADSL Modem Router.
The computer and the Wireless ADSL Modem Router must be directly connected (using
the Hub ports on the Wireless ADSL Modem Router) or on the same LAN segment.
• The Wireless ADSL Modem Router must be installed and powered ON.
• Wireless ADSL Modem Router's default IP Address (192.168.10.1). Make sure there is no
other device using the same IP address within the same network.
Using your Web Browser
To establish a connection from your computer to the Wireless ADSL Modem Router:
1. After installing the Wireless ADSL Modem Router in your LAN, start your computer. If
your computer is already running, restart it.
2. Start your WEB browser.
3. In the Address box, enter "HTTP://" and the IP Address of the Wireless ADSL Modem
Router, as in this example, which uses the Wireless ADSL Modem Router's default IP
Address:
HTTP://192.168.10.1
4. When prompted for the User name and Password, enter values as follows:
• User name admin
• Password password
12
If you can't connect
If the Wireless ADSL Modem Router does not respond, check the following:
• The Wireless ADSL Modem Router is properly installed, LAN connection is
OK, and it is powered ON. You can test the connection by using the "Ping"
command:
• Open the MS-DOS window or command prompt window.
• Enter the command:
ping 192.168.10.1
If no response is received, either the connection is not working, or your computer 's IP address is not compatible with the Wireless ADSL Modem Router's
IP Address. (See next item.)
• If your computer is using a fixed IP Address, its IP Address must be within the
range 192.168.10.2 to 192.168.10.254 to be compatible with the Wireless
ADSL Modem Router's default IP Address of 192.168.10.1. Also, the Network
Mask must be set to 255.255.255.0. See Chapter 4 - Computer Configuration
for details on checking your computer's TCP/IP settings.
• Ensure that your computer and the Wireless ADSL Modem Router are on the
same network segment. (If you don't have a router, this must be the case.)
• Ensure you are using the wired LAN interface. The Wireless interface can only
be used if its configuration matches your PC's wireless settings.
Setup Wizard
The common connection types are explained in the following table.
Connection Type Details ISP Data required
Dynamic
IP Address
Static (Fixed)
IP Address
PPPoE, PPPoA You connect to the ISP only
Your IP Address is allocated
automatically, when you connect to you ISP.
Your ISP allocates a permanent
IP Address to you.
Usually, the connection is
"Always on".
when required. The IP address
is usually allocated automatically.
Often, none.
Some ISP's may require you to
use a particular Hostname or
Domain name, or MAC (physical)
address.
IP Address allocated to you, and
related information, such as
Network Mask, Gateway IP
address, and DNS address.
a) User name and password are
always required.
b) If using a Static (Fixed) IP
address, you need the IP address
and related information (Network
Mask, Gateway IP address, and
DNS address)
13
IPoA
(IP over ATM)
Normally, the connection is
"Always on".
IP Address allocated to you, and
related information, such as
Network Mask, Gateway IP
address, and DNS address.
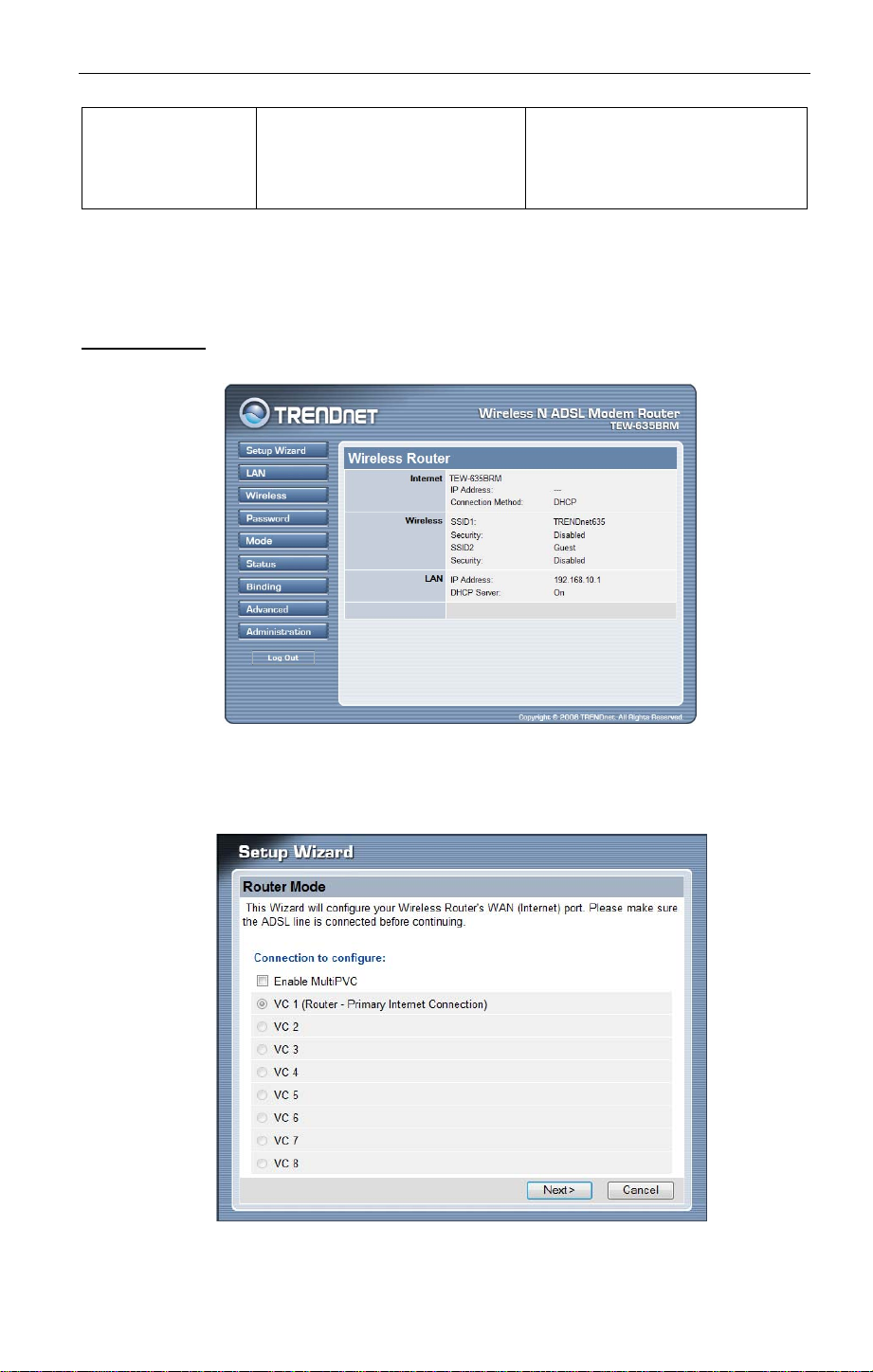
The first time you connect to the Wireless ADSL Modem Router, you should run the Setup
Wizard to configure the ADSL and Internet Connection. There are two options. One is “AutoDetect” and another is “Manual Selection”.
Auto-Detection
1. Click the Setup Wizard link on the main menu
2. On the first screen, select VC 1 (Router - Primary Internet Connection), then click "Next".
Note: Auto-detection does not support “MultiPVC”. If you would like to enable the
multi PVC feature, you must use Manual Selection to setup your ADSL line.
14
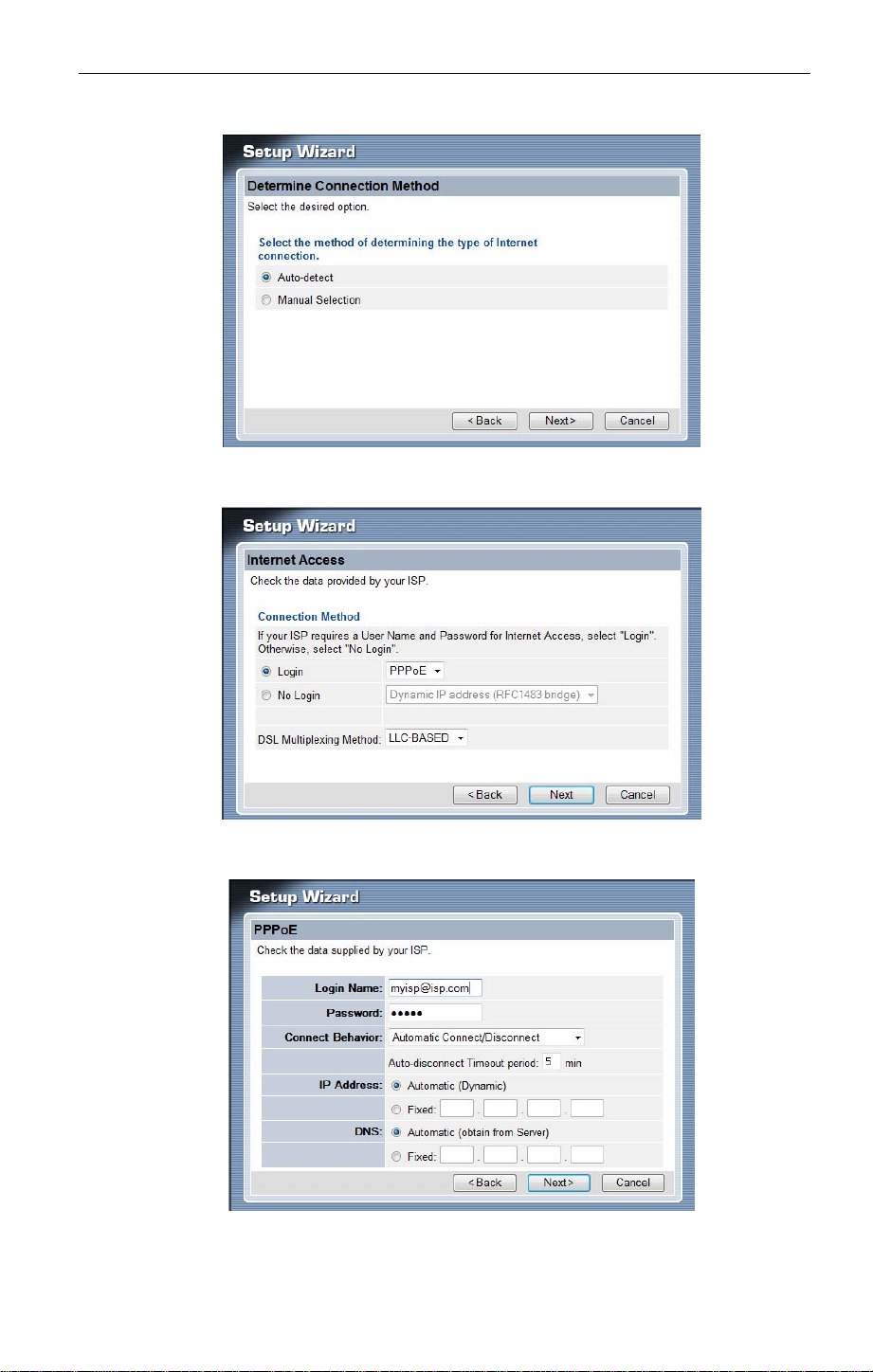
3. Select the “Auto-detect” connection method.
4. Configure the setting based on the information your IPS provided.
5. Type in the username & password if applicable
6. Waiting for the Modem Router reboot.
15
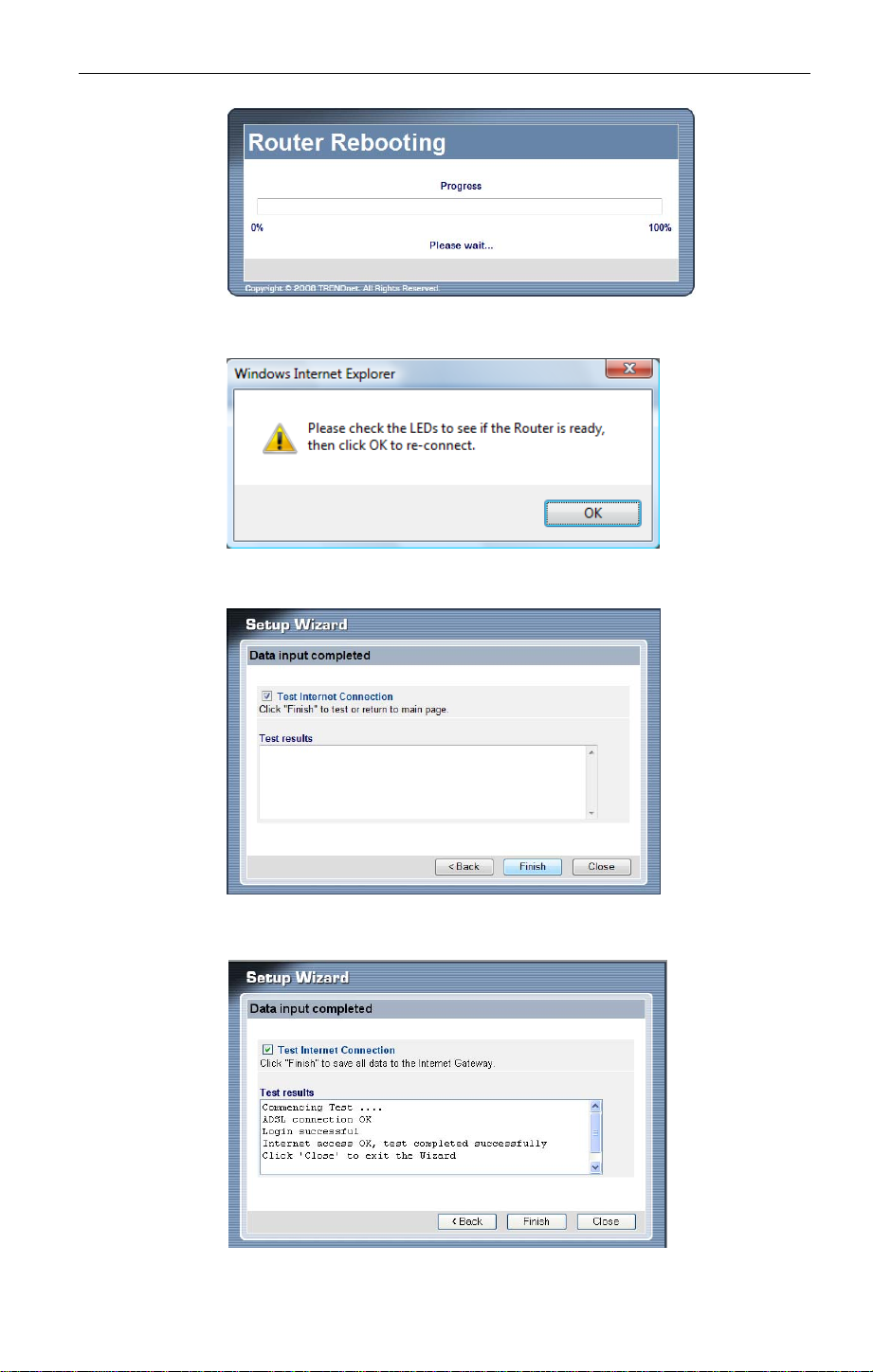
7. Click OK.
8. Click Finish to diagnostic the setting result
9. Click Close to exit the Setup Wizard
10. If the connection test fails:
16
• Check all connections, and the front panel LEDs.
• Check that you have entered all data correctly
Manual-Selection
1. Click the Setup Wizard link on the main menu
2. On the first screen, select VC 1 (Router - Primary Internet Connection), then click "Next".
If you would like to enable the “Enable MultiPVC”, please select it now.
3. Select Manual Selection
17
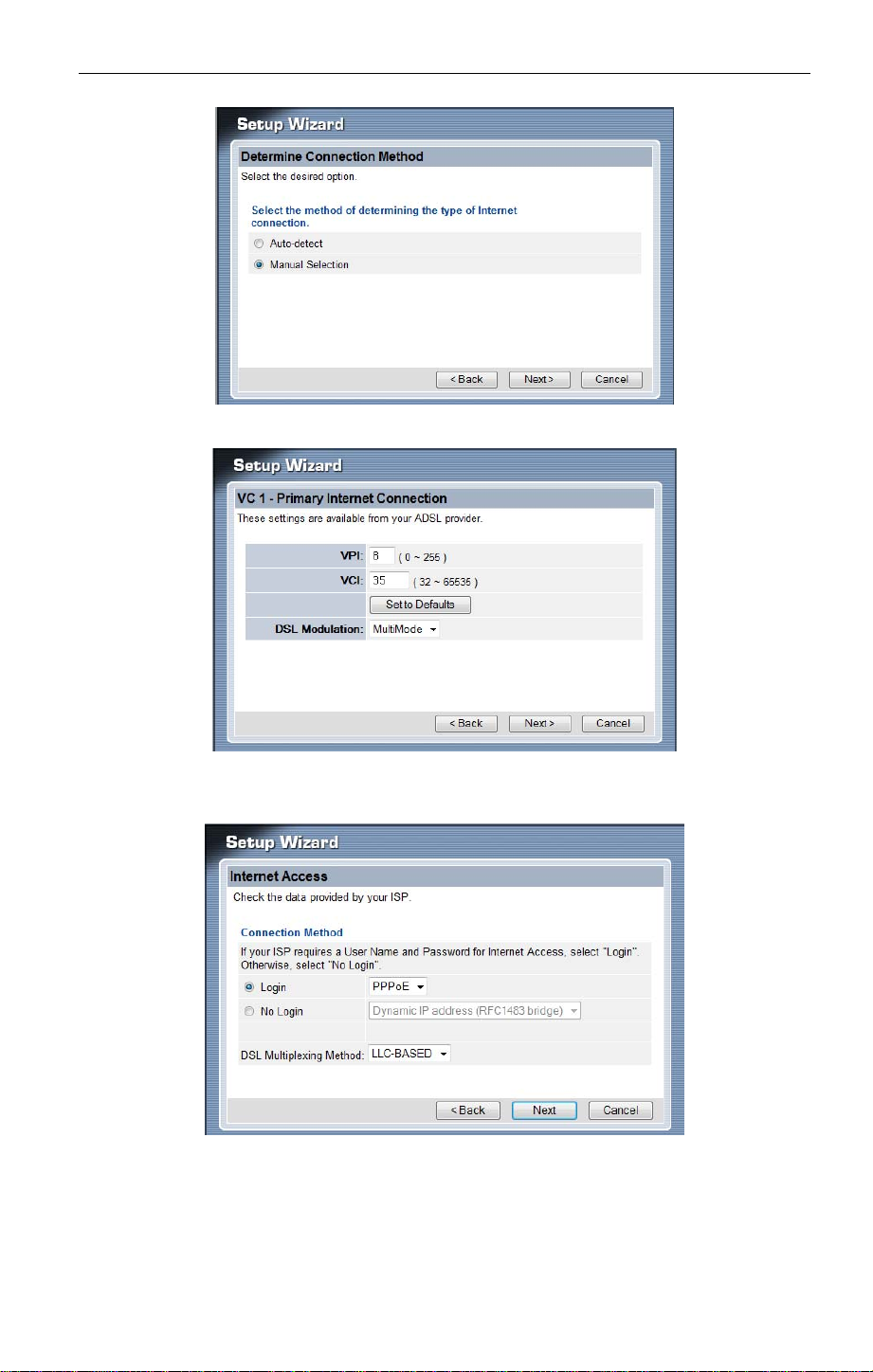
4. Type in the VPI and VCI value that provided by your ISP provider, then click "Next".
5. Configure the setting based on the information your IPS provided.
6. Type in the username & password if there is any
18

7. Waiting for the Modem Router reboot.
8. Click OK.
9. Click Finish to diagnostic the setting result
19
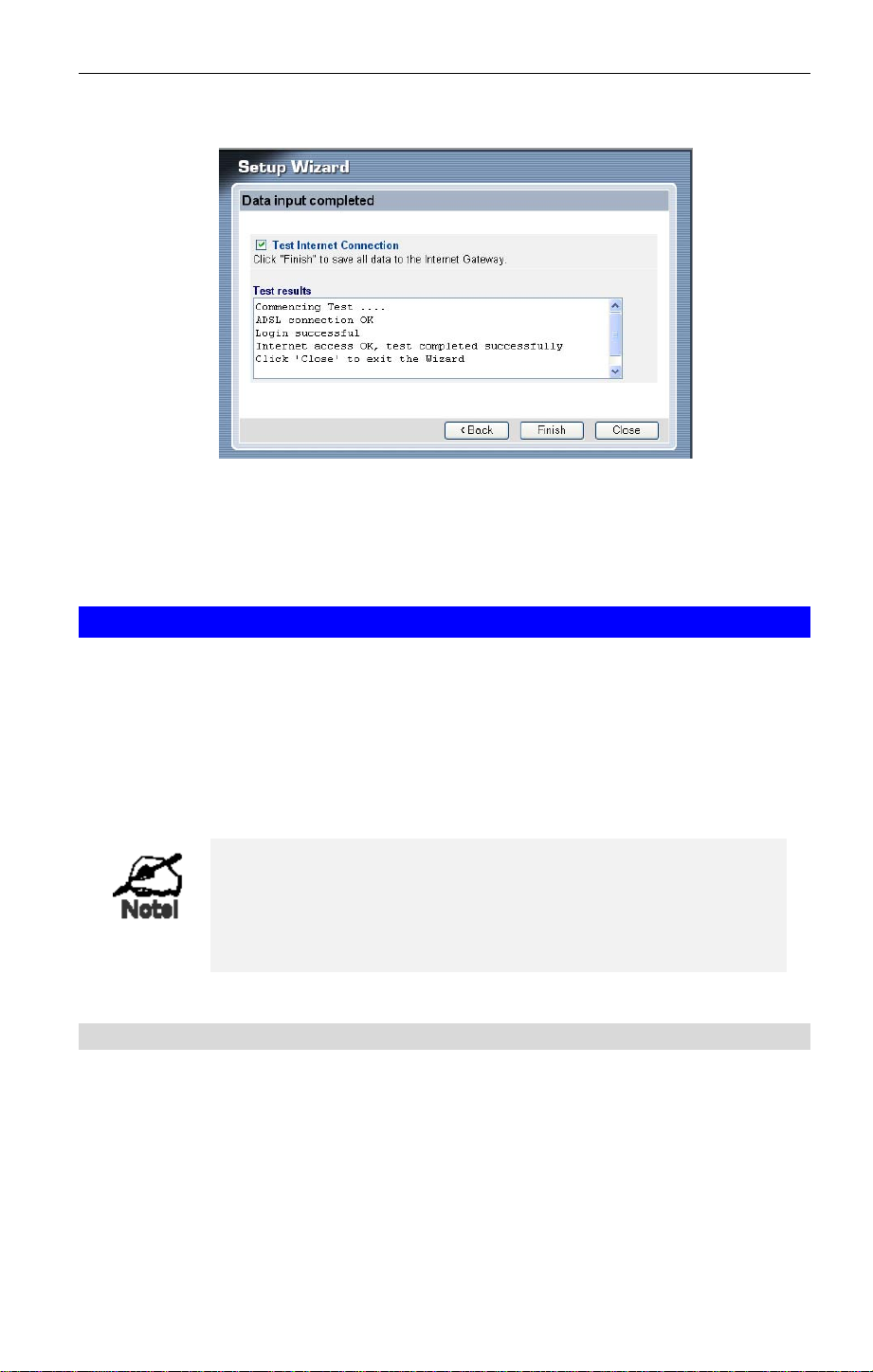
10. Click Close to exit the Setup Wizard
11. If the connection test fails:
• Check all connections, and the front panel LEDs.
• Check that you have entered all data correctly
Configuring VCs
The Wireless ADSL Modem Router supports multiple VCs (Virtual Circuits) on the ADSL
connection.
VC1 must be used for general-purpose Internet access. The other VCs are available for special
purposes, such as Video-on-Demand.
You can only use these VCs if supported by your ISP and ADSL service provider. In that case,
they will provide the necessary configuration data.
Some ISP's allow multiple PPPoE connections. This allows
multiple PCs to connect to the Internet using PPPoE client
software. When using the Wireless ADSL Modem Router,
multiple PPPoE connections are neither necessary nor supported.
To Configure additional VCs
1. Start the Setup Wizard again.
20
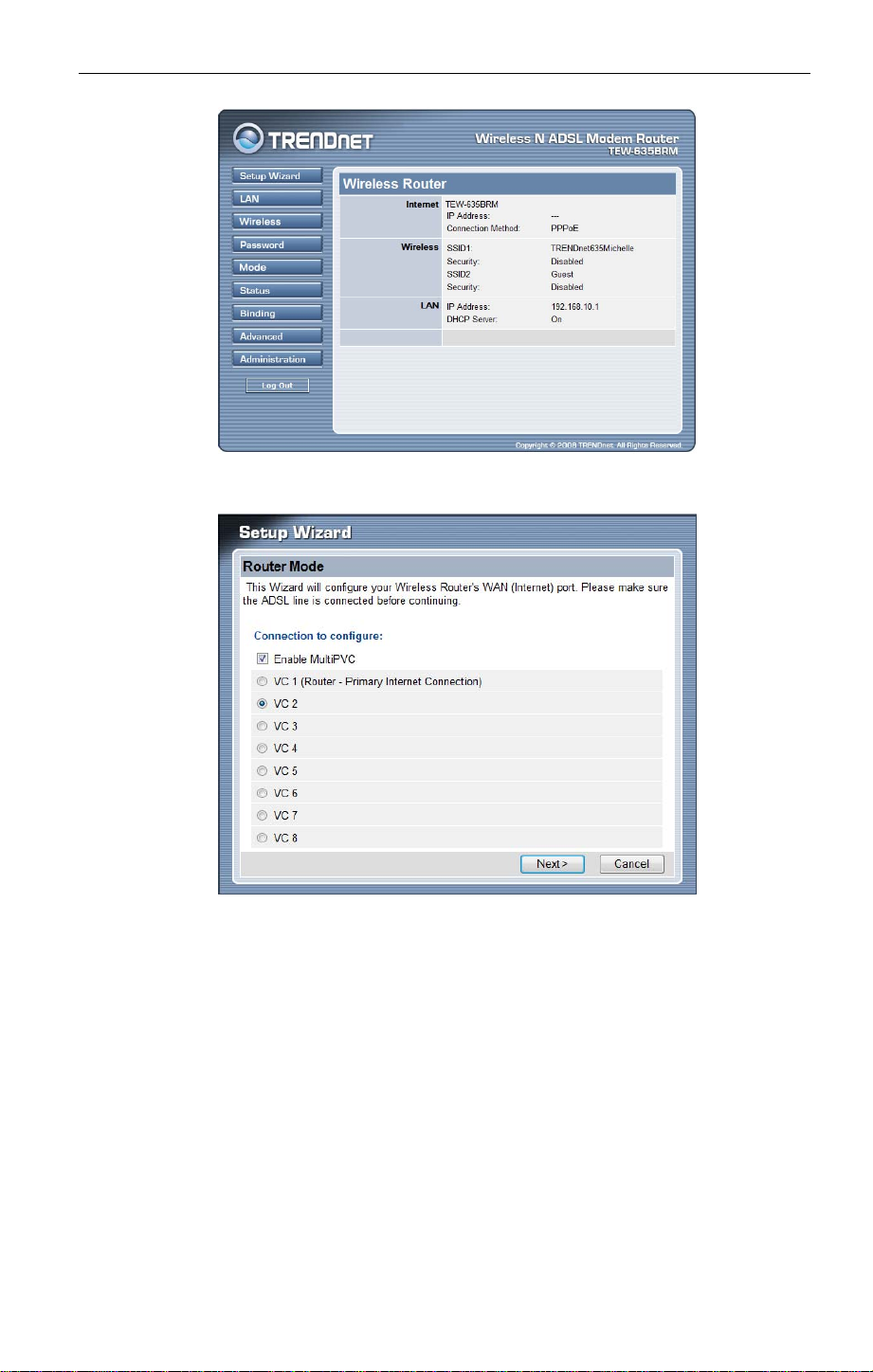
2. Select “Enable MultiPVC”, then select VC2 and click "Next"
3. Configure the VC setup screen following by the screen and information by your ISP pro-
vider to finish the VC setup.
21
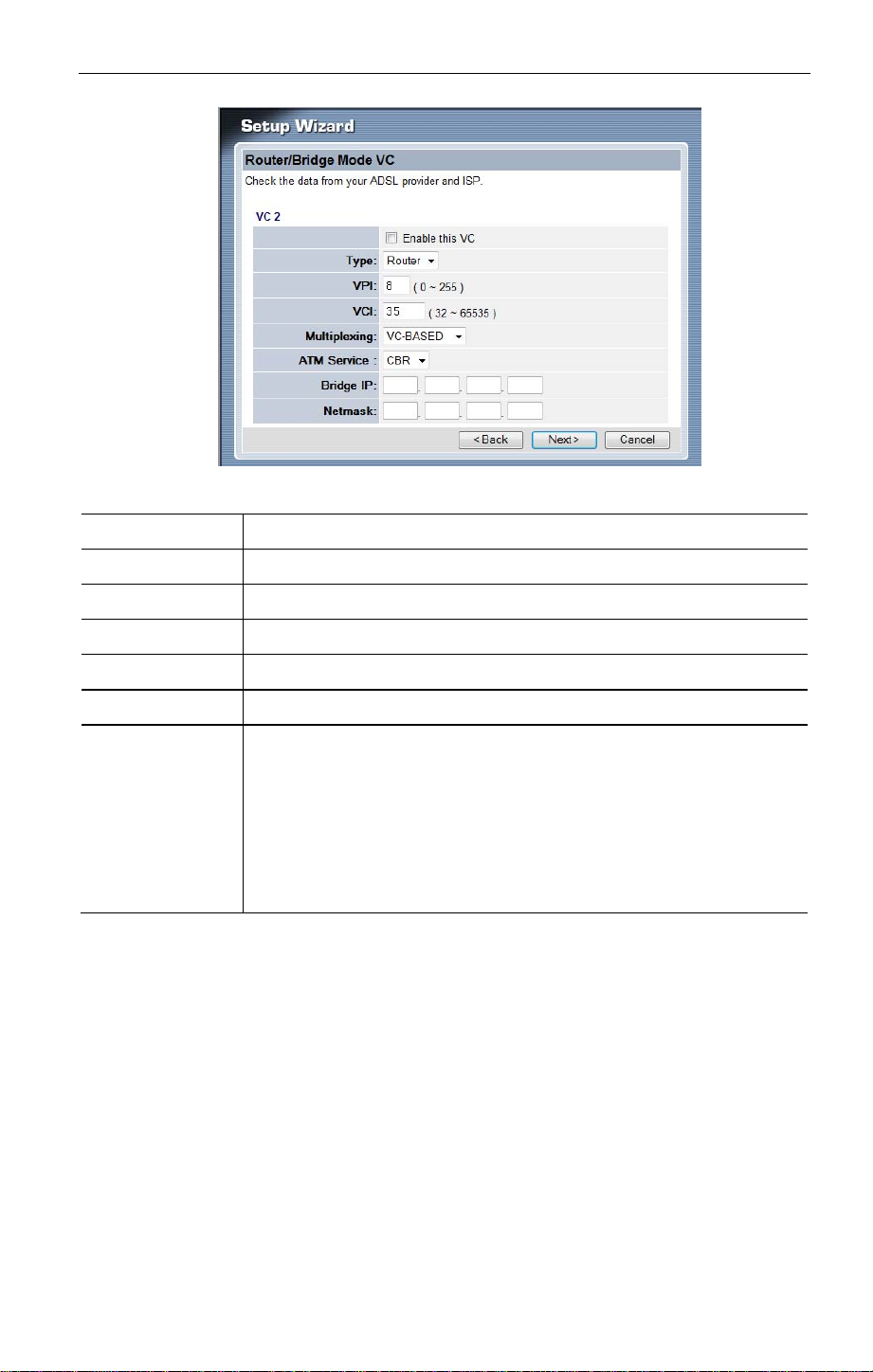
Setup Wizard VC Screen
VC
Enable
VPI
VCI
Multiplexing
ATM Service
LAN IP Address
The VC number is displayed
To use this VC, you must enable it by checking this checkbox.
Enter the VPI value provided by your ISP.
Enter the VPI value provided by your ISP.
Select the multiplexing value provided by your ISP.
Select the multiplexing value provided by your ISP.
Enter the IP address of the device on your LAN which will receive the
data on this VC.
• For Video-on-Demand, this would be the IP address of your
SetTop Box.
• For VoIP, this would be the IP address of your VoIP TA.
• Note that this IP address does not have to be in the same IP ad-
dress range as other devices on your local LAN.
22

Main Screen
After finishing the Setup Wizard, the browse will back to main screen.
Main Menu
The main menu, on the left, contains links to the most-commonly used screen. To see the links
to the other available screens, click "Advanced" or "Administration".
The main menu also contains one (1) button:
• Log Out - When finished, you should click this button to logout.
Navigation & Data Input
• Use the menu bar on the left of the screen, and the "Back" button on your Browser, for
navigation.
• Changing to another screen without clicking "Save" does NOT save any changes you may
have made. You must "Save" before changing screens or your data will be ignored.
On each screen, clicking the "Help" button will
display help for that screen.
23
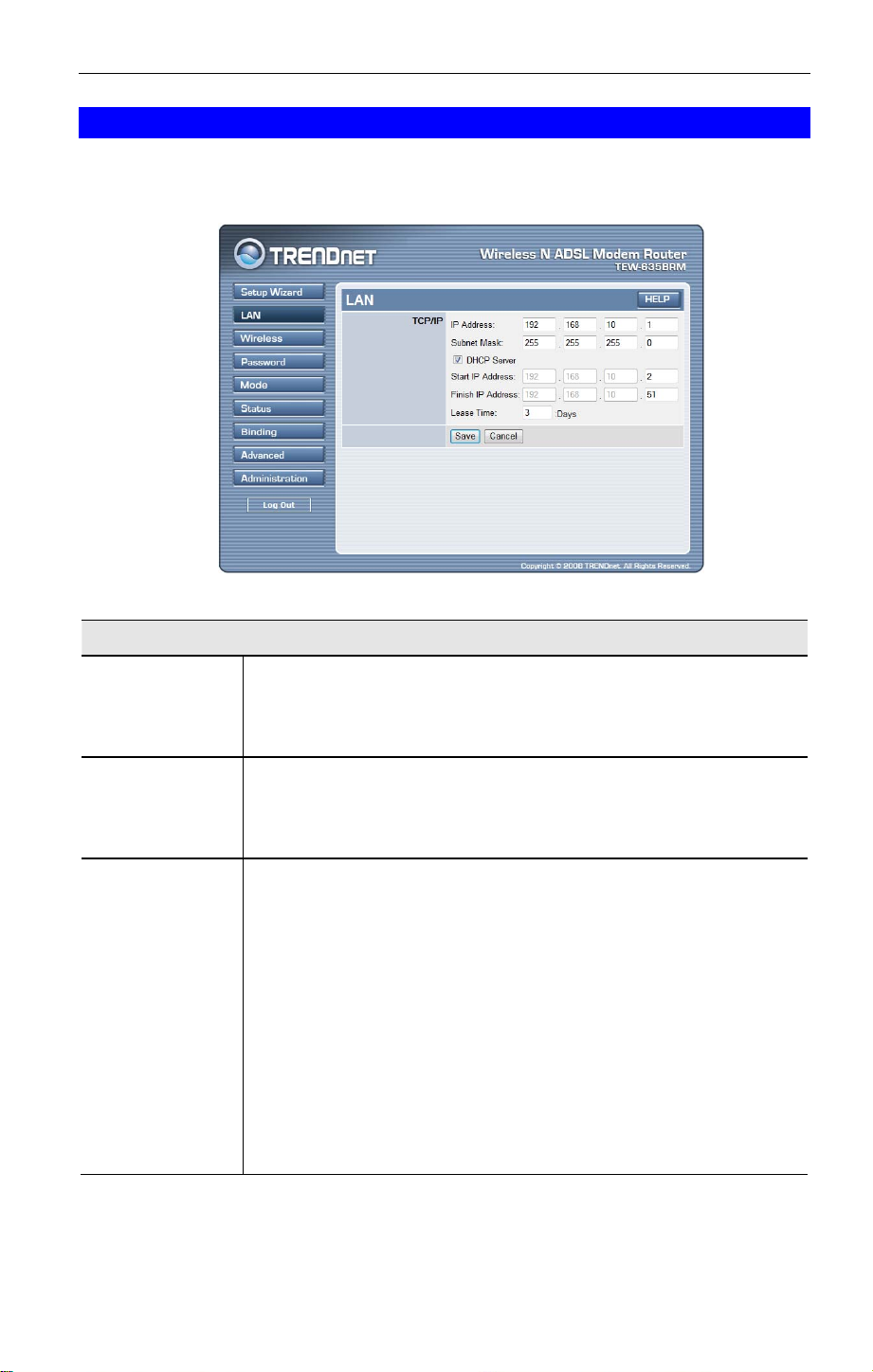
LAN Screen
Use the LAN link on the main menu to reach the LAN screen. An example screen is shown
below.
LAN Screen
TCP/IP
IP Address
Subnet Mask
DHCP Server
IP address for the Wireless ADSL Modem Router, as seen from the
local LAN. Use the default value unless the address is already in use or
your LAN is using a different IP address range. In the latter case, enter
an unused IP Address from within the range used by your LAN.
The default value 255.255.255.0 is standard for small (class "C")
networks. For other networks, use the Subnet Mask for the LAN
segment to which the Wireless ADSL Modem Router is attached (the
same value as the PCs on that LAN segment).
• If Enabled, the Wireless ADSL Modem Router will allocate IP
Addresses to PCs (DHCP clients) on your LAN when they start
up. The default (and recommended) value is Enabled.
• If you are already using a DHCP Server, this setting must be
Disabled, and the existing DHCP server must be re-configured to
treat the Wireless ADSL Modem Router as the default Gateway.
See the following section for further details.
• The Start IP Address and Finish IP Address fields set the values
used by the DHCP server when allocating IP Addresses to DHCP
clients. This range also determines the number of DHCP clients
supported. Enter the desired value for the Lease Time, which
should be between 1 and 7.
See the following section for further details on using DHCP.
24

DHCP
What DHCP Does
A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server allocates a valid IP address to a
DHCP Client (PC or device) upon request.
• The client request is made when the client device starts up (boots).
• The DHCP Server provides the Gateway and DNS addresses to the client, as well as
allocating an IP Address.
• The Wireless ADSL Modem Router can act as a DHCP server.
• Windows other non-Server versions of Windows will act as a DHCP client. This is the
default Windows setting for the TCP/IP network protocol. However, Windows uses the
term Obtain an IP Address automatically instead of "DHCP Client".
• You must NOT have two (2) or more DHCP Servers on the same LAN segment. (If your
LAN does not have other Routers, this means there must only be one (1) DHCP Server on
your LAN.)
Using the Wireless ADSL Modem Router's DHCP Server
This is the default setting. The DHCP Server settings are on the LAN screen. On this screen,
you can:
• Enable or Disable the Wireless ADSL Modem Router's DHCP Server function.
• Set the range of IP Addresses allocated to PCs by the DHCP Server function.
You can assign Fixed IP Addresses to some devices
while using DHCP, provided that the Fixed IP Addresses
are NOT within the range used by the DHCP Server.
Using another DHCP Server
You can only use one (1) DHCP Server per LAN segment. If you wish to use another DHCP
Server, rather than the Wireless ADSL Modem Router's, the following procedure is required.
• Disable the DHCP Server feature in the Wireless ADSL Modem Router. This setting is on
the LAN screen.
• Configure the DHCP Server to provide the Wireless ADSL Modem Router's IP Address
as the Default Gateway.
To Configure your PCs to use DHCP
This is the default setting for TCP/IP for all non-Server versions of Windows.
See Chapter 4 - Client Configuration for the procedure to check these settings.
25
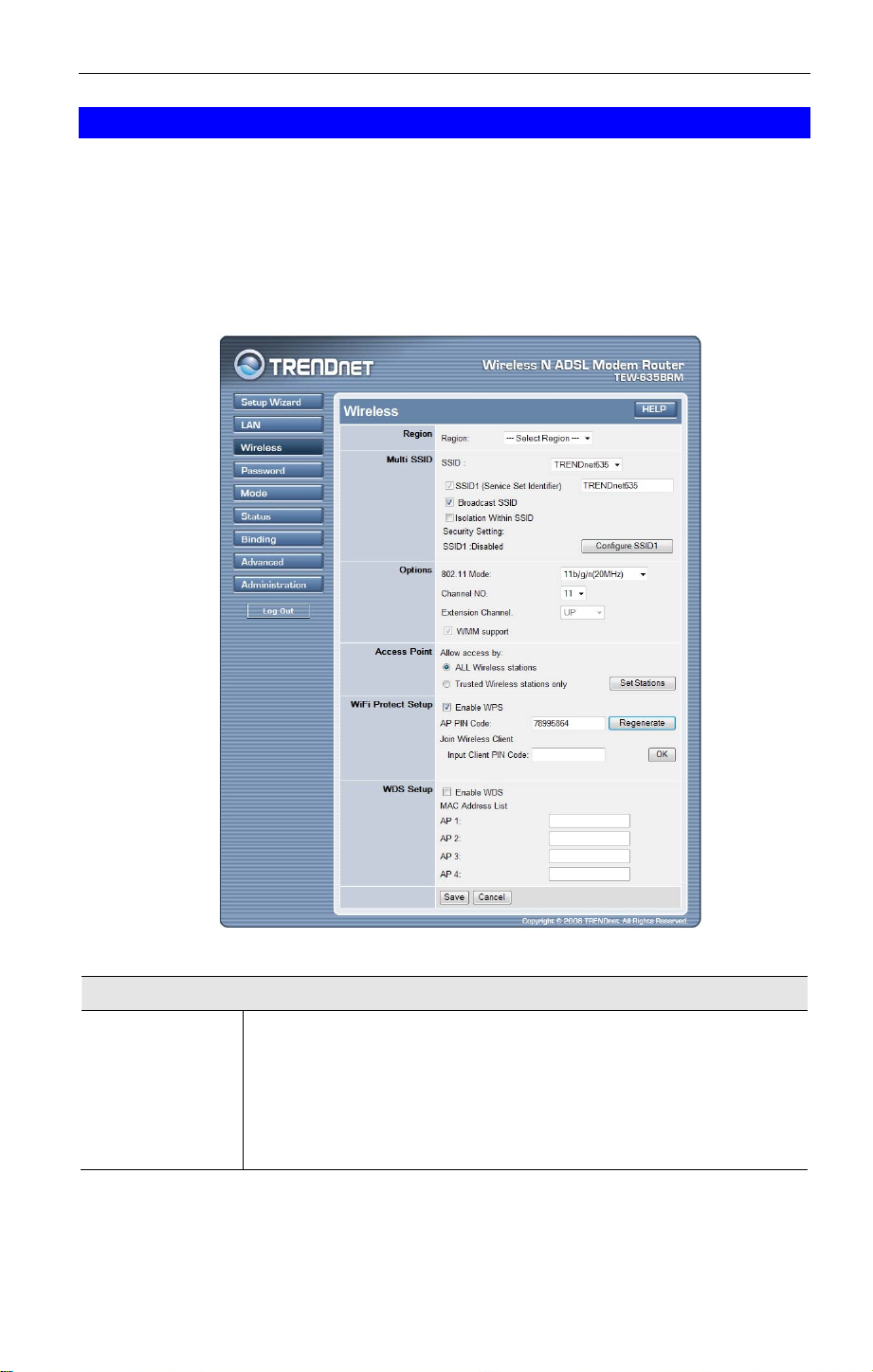
Wireless Screen
The Wireless ADSL Modem Router's settings must match the other Wireless stations.
Note that the Wireless ADSL Modem Router will automatically accept both 802.11b and
802.11g connections, and no configuration is required for this feature.
To change the Wireless ADSL Modem Router's default settings for the Wireless Access Point
feature, use the Wireless link on the main menu to reach the Wireless screen. An example
screen is shown below.
Wireless Screen
Region
Region
Select the correct domain for your location. It is your responsibility to
ensure:
• That the Wireless ADSL Modem Router is only used in domains
for which is licensed.
• That you select the correct domain, so that only the legal channels
for that domain can be selected.
26
Multi SSID
SSID
SSID 1/SSID 2
Broadcast SSID
Isolation within
SSID
Security Setting
With Multiple SSIDs, you can have 2 SSIDs on one AP. For example,
a Guest SSID without encryption for visitors to have Internet access
only, and a Admin SSID with encryption for private use to secure your
company resources.
Select the desired SSID from the list to configure.
This is also called the "Network Name".
• If using an ESS (Extended Service Set, with multiple access
points) this ID is called an ESSID (Extended Service Set Identifier).
• To communicate, all Wireless stations should use the same
SSID/ESSID.
If enabled, the Wireless ADSL Modem Router will broadcast its SSID.
This allows PCs and other wireless stations to detect this Access Point
and use the correct SSID.
If disabled, PC users will have to manually enter the SSID and other
details of the wireless interface before they can connect to this Access
Point.
If Enabled, devices that have the same SSID will not be able to see
each other.
The current Wireless security is displayed. The default value is Disabled.
Configure SSID
1/SSID2 Button
Options
802.11 Mode
Channel No.
Extension
Channel
WMM Support
Click this button to access the Wireless security sub-screen, and view
or change the settings. See the following section for details.
Select the desired mode:
• 11b + 11g - Both 802.11b and 802.11g Wireless stations will be
able to use the Wireless Broadband Router.
• 11b/g/N (20MHz) - 802.11.g, 802.11b and 802.11n (20MHz)
Wireless stations can use the Wireless Broadband Router.
• 11b/g/N (20/40MHz) - 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n (20MHz or
40MHz) Wireless stations can use the Wireless Broadband Router.
• Disable: Wireless function is off
Select the Channel you wish to use on your Wireless LAN.
• If you experience interference (shown by lost connections and/or
slow data transfers) you may need to experiment with different
channels to see which is the best.
• If using multiple Access Points, adjacent Access Points should use
different Channels to reduce interference.
Select either UP or DOWN from the list.
Enable or disable this feature as required.
27
 Loading...
Loading...