Page 1
TEG-S224 Series
Stackable NWay Ethernet
Switch
User’s Guide
First Edition (Feb. 2000)
Printed In Taiwan
RECYCLABLE
Page 2

FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with this user’s guide, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in
which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may
cause radio interference in which case the user may be required to take
adequate measures.
VCCI Warning
BSMI Warning
Page 3

TABLE OF C ONTENTS
0 ABOUT THIS GUIDE.........................................................................................X
CONVENTIONS..........................................................................................................X
OVERVIEW OF THIS USER’S G UIDE.......................................................................X
1 INTRODUCTION................................................................................................1
FAST ETHERNET TECHNOLOGY ...........................................................................1
G IGABIT ETHERNET TECHNOLOGY ..................................................................... 2
SWITCHING TECHNOLOGY ....................................................................................3
FEATURES.................................................................................................................4
Ports .......................................................................................................................4
Performance features..........................................................................................5
Management .........................................................................................................6
2 UNPACKING AND SETUP................................................................................7
UNPACKING..............................................................................................................7
SETUP ........................................................................................................................ 8
DESKTOP OR SHELF INSTALLATION...................................................................8
RACK INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 9
POWER ON..............................................................................................................10
Power Failure....................................................................................................11
3 IDENTIFYING EXTERNAL COMPONENTS...............................................12
FRONT PANEL ........................................................................................................ 12
REAR PANEL...........................................................................................................13
SIDE PANELS .......................................................................................................... 14
STACK OPERATION..............................................................................................15
OPTIONAL PLUG-IN MODULES...........................................................................17
100BASE-FX (MT-RJ) Module.......................................................................18
100BASE-FX (SC) Module..............................................................................18
100BASE-TX Module........................................................................................19
1000BASE-SX Gigabit Module.......................................................................20
Page 4

1000BASE-LX Gigabit Module.......................................................................21
LED INDICATORS...................................................................................................21
4 CONNECTING THE SWITCH........................................................................24
SWITCH TO END NODE........................................................................................24
SWITCH TO HUB OR SWITCH..............................................................................25
10BASE-T Device...............................................................................................26
100BASE-TX Device..........................................................................................27
5 SWITCH MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS .......................................................28
LOCAL CONSOLE MANAGEMENT.......................................................................28
Diagnostic (Console) Port (RS-232 DCE)...................................................29
IP ADDRESSES AND SNMP COMMUNITY NAMES............................................29
TRAPS......................................................................................................................30
MIBS........................................................................................................................32
PACKET FORWARDING.........................................................................................33
Aging Time..........................................................................................................33
Filtering Database............................................................................................34
SPANNING TREE ALGORITHM............................................................................35
STA Operation Levels.......................................................................................35
On the Bridge Level...........................................................................................36
On the Port Level..............................................................................................36
User-Changeable STA Parameters.................................................................37
Illustration of STA.............................................................................................38
PORT TRUNKING....................................................................................................40
VLAN .......................................................................................................................42
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs..........................................................................................43
VLAN Segmentation..........................................................................................43
Sharing Resources Across VLANs....................................................................44
VLANs Spanning Multiple Switches................................................................45
VLANs Over 802.1Q -compliant Switches.............................................. 47
BROADCAST MANAGEMENT...............................................................................49
Broadcast Storms...............................................................................................49
Port-based Broadcast Packet Filter..............................................................50
MAC-based Broadcast Packet Filter.............................................................50
6 USING THE CONSOLE I NTERFACE............................................................51
CONNECTING TO THE SWITCH...........................................................................51
Page 5

CONSOLE USAGE CONVENTIONS.........................................................................52
FIRST TIME CONNECTING TO THE SWITCH.....................................................53
User Accounts Management............................................................................54
Save Changes.....................................................................................................56
LOGIN ON THE SWITCH CONSOLE BY REGISTERED USERS...........................57
Create/Modify User Accounts..........................................................................57
View/Delete User Accounts..............................................................................59
SETTING UP THE SWITCH...................................................................................60
System Configuration.......................................................................................60
Configure IP Address........................................................................................61
Configure Console.............................................................................................63
Configure Switch Stack......................................................................................65
Information of Individual Switch Unit......................................................66
Advance Settings........................................................................................67
Configure Port ...................................................................................................68
Configure Trunk................................................................................................71
Configure Port Mirroring...................................................................................72
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol.....................................................................73
STP Parameter Settings............................................................................74
STP Custom Settings.................................................................................78
Configure Filtering and Forwarding Table.........................................................79
Configure Static Forwarding Table Entry...............................................81
Configure MAC Address Filtering............................................................82
Configure Permanent Multicast Filtering................................................83
Configure IGMP ..........................................................................................84
Configure VLANs & MAC-based Broadcast Domains....................................88
Configure MAC-based Broadcast Domains..........................................90
Configure IEEE 802.1Q VLANs...............................................................93
Update Firmware and Configuration Files..................................................98
Special Note Concerning Firmware Updates...................................................100
System Utilities................................................................................................100
Ping Test..........................................................................................................101
Save Settings to TFTP Server..........................................................................102
Save Switch History to TFTP Server..............................................................103
Clear Address Table........................................................................................104
Community Strings and Trap Stations.......................................................104
SWITCH MONITORI NG....................................................................................... 106
Network Monitoring......................................................................................106
Page 6

Traffic Statistics ..............................................................................................107
Port Utilization...........................................................................................107
Port Traffic Statistics.................................................................................108
Port Packet Error Statistics.....................................................................110
Port Packet Analysis Statistics...............................................................112
Browse Address Table....................................................................................113
Switch History ................................................................................................114
Browse IGMP Status......................................................................................115
RESETTING THE SWITCH...................................................................................117
Restart System.................................................................................................117
Factory Reset...................................................................................................118
Logout...............................................................................................................119
7 WEB-BASED NETWORK M ANAGEMENT.............................................120
INTRODUCTION...................................................................................................120
G ETTING STARTED............................................................................................. 121
MANAGEMENT ....................................................................................................121
Configuration..................................................................................................122
IP Address.......................................................................................................123
Switch..............................................................................................................124
Advanced ................................................................................................... 126
Switch Unit.................................................................................................127
Port..................................................................................................................128
Port Trunk.......................................................................................................130
Port Mirroring.................................................................................................131
Spanning Tree Protocol...................................................................................132
STP Parameters Setting..........................................................................133
STP Custom Setting.................................................................................134
Forwarding and Filtering..................................................................................135
Static Forwarding Table..........................................................................137
MAC Address Filtering Table.................................................................139
Permanent Multicast Filtering.................................................................141
IGMP .............................................................................................................. 142
IGMP Settings............................................................................................143
802.1Q IGMP.............................................................................................144
VLANs & MAC-based Broadcast Domains...................................................145
MAC-Based Broadcast Domains...........................................................146
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs................................................................................151
Page 7

Management .................................................................................................... 154
Community Strings and Trap Stations............................................................155
User Account...................................................................................................156
Console............................................................................................................158
Monitoring.......................................................................................................159
Switch Overview .............................................................................................159
Port Utilization................................................................................................160
Port Traffic Statistics ......................................................................................161
Port Error Packet Statistics .............................................................................163
Port Packet Analysis Statistics .......................................................................165
Browse Address Table....................................................................................167
Browse IGMP Status......................................................................................168
Switch History ................................................................................................169
Maintenance....................................................................................................169
Firmware and Configuration Update...............................................................170
Save Settings To TFTP Server........................................................................171
Save Switch History To TFTP Server............................................................172
Save Changes ...................................................................................................173
Factory Reset ..................................................................................................174
Restart System................................................................................................175
8 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS................................................................176
9 RJ-45 PIN SPECIFICATION.......................................................................180
10 SAMPLE CONFIGURATION FILE.............................................................183
Commands:......................................................................................................183
Notes about the Configuration File:................................................................184
11 RUNTIME SOFTWARE DEFAULT SETTINGS........................................186
12 INDEX ...............................................................................................................188
Page 8

F IGURES AND TABLES
Figure 2-1. Switch installed on a Desktop or Shelf...........................................9
Figure 2-2A. Attaching the mounting brackets to the Switch.........................9
Figure 2-2B. Installing the Switch in an equipment rack .............................10
Figure 3-1. Front panel view of the Switches...................................................12
Figure 3-2. Rear panel view of the Switches.....................................................14
Figure 3-3. Side panel views of the Switch........................................................15
Figure 3-4. Switch stack with one master and three clients..........................16
Figure 3-5. Switch stack with example of possible connections...................17
Figure 3-6. Two-port, 100BASE-FX (MT-RJ) module.....................................18
Figure 3-7. One-port, 100BASE-FX (SC) module............................................18
Figure 3-8. Two-port, 100BASE-TX module......................................................19
Figure 3-9. One-port, 1000BASE-SX gigabit module.....................................20
Figure 3-10. One-port, 1000BASE-LX gigabit module...................................21
Figure 3-11. The Switch LED indicators...........................................................22
Figure 4-1. Switch connected to an End Node.................................................25
Figure 4-2. Switch connected to a normal (non-Uplink) port on a hub or
switch using a straight or crossover cable.........................................................26
Figure 5-1. Before Applying the STA Rules.......................................................39
Figure 5-2. After Applying the STA Rules..........................................................39
Table 5-1. User-selective STA parameters.........................................................40
Figure 5-3. Port trunking example.....................................................................41
Figure 5-4. Example of typical VLAN configuration.......................................44
Table 5-2. Example of possible VLAN assignments..........................................45
Figure 5-5. Data transmissions between 802.1Q -compliant Switches.........48
Figure 6-1. Initial Screen, first time connecting to the Switch......................53
Table 6-1. Administrator and Normal User Privileges....................................56
Figure 6-4. User Accounts Management menu.................................................58
Figure 6-5. Add/Modify User Accounts screen.................................................58
Figure 6-6. View/Delete User Accounts screen.................................................60
Figure 6-7. System Configuration menu............................................................61
Figure 6-8. IP Address Configuration screen...................................................62
Figure 6-9. Console Options screen...................................................................64
Page 9

Figure 6-10. Switch Stack Configuration screen.............................................65
Figure 6-11 Information of Individual Switch Unit screen............................66
Figure 6-12. Configure Advanced Switch Features screen............................67
Figure 6-13. Port Configuration screen............................................................68
Figure 6-14. Port Trunk screen...........................................................................71
Figure 6-15. Port Mirroring Configuration screen.........................................73
Figure 6-16. Configure Spanning Tree Protocol menu..................................74
Figure 6-17. STP Parameter Setting screen......................................................75
Figure 6-18. STP Custom Settings screen..........................................................78
Figure 6-19. Configure Filtering and Forwarding table screen..................80
Figure 6-20. Static Forwarding Table Configuration screen.......................81
Figure 6-21. Custom Filtering Table screen.....................................................83
Figure 6-22. Static Multicast Filtering Table Configuration screen...........84
Figure 6-23. IGMP Configuration screen..........................................................85
Figure 6-24. IEEE 802.1q IGMP Configuration screen..................................86
Figure 6-25. Add/Remove IGMP Entry screen..................................................87
Figure 6-26. IEEE 802.1Q IGMP Configuration screen.................................88
Figure 6-27. VLANs & MAC-based Broadcast Domains Configuration
screen ......................................................................................................................... 89
Figure 6-28. MAC-Based Broadcast Domains Configuration menu............91
Figure 6-29. Add/Remove MAC-based Broadcast Domains screen..............91
Figure 6-30. Add/Remove MAC-based Broadcast Domain Members screen
.....................................................................................................................................92
Figure 6-31. Add/Remove MAC-based Broadcast Domain Members screen
.....................................................................................................................................93
Figure 6-32. IEEE 802.1Q VLANs Configuration menu.................................94
Figure 6-33. Ingress Filtering Check screen....................................................95
Figure 6-33. Default port VLAN assignment screen........................................96
Figure 6-34. 802.1Q Static VLAN Settings screen...........................................97
Figure 6-35. Browse 802.1Q VLAN Entries screen..........................................98
Figure 6-36. Update Firmware and Configuration Files screen..................99
Figure 6-37. Utilities menu.................................................................................101
Figure 6-38. Ping Test screen............................................................................101
Figure 6-39. Save Settings to TFTP Server screen.........................................102
Figure 6-40. Save Switch History to TFTP Server screen.............................103
Figure 6-41. SNMP Manager Configuration screen.....................................105
Figure 6-42. Network Monitoring menu..........................................................106
Figure 6-43. Traffic Statistics menu..................................................................107
Page 10

Figure 6-44. Port Utilization screen.................................................................108
Figure 6-45. Port Traffic Statistics screen.......................................................109
Figure 6-46. Port Packet Error Statistics table.............................................110
Figure 6-47. Packet Analysis Statistics table.................................................112
Figure 6-48. Browse Address Table..................................................................114
Figure 6-49. Switch History screen...................................................................115
Figure 6-50. IP Multicast Information screen.................................................116
Figure 6-51. Restart System screen...................................................................118
Figure 6-52. Factory Reset NV-RAM to Default Value screen.....................119
Figure 7-1. Configure IP Address window......................................................123
Figure 7-2. Configure Switch Stack window..................................................124
Figure 7-3. Configure Switch Stack – Advanced window............................126
Figure 7-4. Information Of Individual Switch Unit window........................127
Figure 7-5. Configure Port window..................................................................128
Figure 7-6. Port Trunk window.........................................................................130
Figure 7-7. Port Mirroring window..................................................................131
Figure 7-8. STP Parameter Setting window....................................................133
Figure 7-9. Spanning Tree Custom Setting window......................................134
Figure 7-10. Configure Forwarding Table And Filtering Table window.136
Figure 7-11. Static Forwarding Table window..............................................137
Figure 7-12. Static Forwarding Table---Edit window..................................138
Figure 7-13. Static MAC Address Filtering window.....................................139
Figure 7-14. Static MAC Address Filtering---Edit window.........................140
Figure 7-15. Static Permanent Multicast Filtering window........................141
Figure 7-16. Static Permanent Multicast Filtering--Edit window.............142
Figure 7-17. Configure IGMP window.............................................................143
Figure 7-18. Add/Remove IGMP Table window.............................................144
Figure 7-19. Add/Remove IGMP Table-Edit window....................................145
Figure 7-20. Configure VLAN window.............................................................146
Figure 7-21. Add/Remove MAC-based Broadcast Domains window.........147
Figure 7-22. Add/Remove MAC-based Broadcast Domains --- Edit window
...................................................................................................................................148
Figure 7-23. Add/Remove MAC-based Broadcast Domain Member window
...................................................................................................................................149
Figure 7-24. Add/Remove MAC-based Broadcast Domain Member ---Edit
window....................................................................................................................150
Figure 7-25. Default Port VLAN ID window...................................................151
Figure 7-26. Port Ingress Filtering Check window.......................................152
Page 11

Figure 7-27. 802.1Q Static VLAN Entry window (num ber one).................153
Figure 7-28. 802.1Q Static VLAN Entry window (number two).................154
Figure 7-29. Community Strings and Trap Stations window......................155
Figure 7-30. User Accounts window.................................................................156
Figure 7-31. User Account-Edit window.........................................................157
Figure 7-32. Configure Console window........................................................158
Figure 7-33. Switch Statistics window.............................................................159
Figure 7-34. Port Utilization window..............................................................160
Figure 7-35. Port Traffic Statistics window....................................................161
Figure 7-36. Port Error Packet Statistics window........................................163
Figure 7-37. Port Packet Analysis window.....................................................165
Figure 7-38. Browse Address Table window...................................................167
Figure 7-39. Browse IGMP Status window.....................................................168
Figure 7-40. Switch History window................................................................169
Figure 7-41. Firmware and Configuration Update window........................170
Figure 7-42. Save Settings To TFTP Server window.....................................171
Figure 7-43. Save Switch History To TFTP Server window.........................172
Figure 7-44. Save Changes window.................................................................173
Figure 7-45. Factory Reset to Default Value window...................................174
Figure 7-46. Restart System window................................................................175
Figure B-1. The standard RJ-45 receptacle/connector ..................................180
Table B-1. The standard Category 3 cable, RJ-45 pin assignment..............181
Figure B-2. Straight cable for Switch (uplink MDI-II port) to switch/Hub or
other devices connection.....................................................................................181
Figure B-3. Crossover cable for Switch (MDI-X port) to switch/hub or other
network devices (MDI-X port) connection.......................................................182
Page 12
Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
0 A BOUT THIS GUIDE
This User’s Guide tells you how to install your Stackable NWay
Ethernet Switch, how to connect it to your Ethernet network, and
how to set its configuration using either the built-in console interface
or Web-based management (please note that Netscape
Communicator/Navigator, 4.x or later, or Microsoft Internet
Explorer, 4.x or later, are recommended).
Conventions
References in this manual to the TEG-S224 Series are frequently
written simply as “Switch” or “Switches” where the text applies to all
models. Model numbers are normally used only to differentiate
among specific Switches where necessary.
Unless differentiated by model number, all information applies to all
models.
Overview of this User’s Guide
? ?Chapter 1, Introduction. Describes the Switch and its features.
? ?Chapter 2, Unpacking and Setup. Helps you get started with
the basic installation of the Switch.
x About This Guide
Page 13

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?Chapter 3, Identifying External Components. Describes the
front panel, rear panel, optional plug-in modules, and LED
indicators of the Switch.
? ?Chapter 4, Connecting the Switch. Tells how you can connect
the Switch to your Ethernet network.
? ?Chapter 5, Switch Management Concepts. Talks about Local
Console Management via the RS-232 DCE console port and
other aspects about how to manage the Switch.
? ?Chapter 6, Using the Console Interface. Tells how to use the
built-in console interface to change, set, and monitor Switch
performance and security.
? ?Chapter 7, Web-Based Network Management. Tells how to
manage the Switch through an Internet browser.
? ?Appendix A, Technical Specifications. Lists the technical
specifications of the Switch.
? ?Appendix B, RJ-45 Pin Specifications. Shows the details and
pin assignments for the RJ-45 receptacle/connector.
? ?Appendix C, Sample Configuration File .
? ?Appendix D, Runtime Software Default Settings.
About This Guide xi
Page 14

Page 15

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
1
1 INTRODUCTION
This section describes the features of the Switch, as well as giving
some background information about Ethernet/Fast Ethernet, Gigabit
Ethernet, and switching technology.
Fast Ethernet Technology
The growing importance of LANs and the increasing complexity of
desktop computing applications are fueling the need for high
performance networks. A number of high-speed LAN technologies are
proposed to provide greater bandwidth and improve client/server
response times. Among them, Fast Ethernet, or 100BASE-T, provides
a non -disruptive, smooth evolution from the current 10BASE-T
technology. The dominating market position virtually guarantees
cost effective and high performance Fast Ethernet solutions in the
years to come.
100Mbps Fast Ethernet is a standard specified by the IEEE 802.3
LAN committee. It is an extension of the 10Mbps Ethernet standard
with the ability to transmit and receive data at 100Mbps, while
maintaining the Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision
Detection (CSMA/CD) Ethernet protocol.
Introduction 1
Page 16

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Gigabit Ethernet Technology
Gigabit Ethernet is an extension of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet utilizing the
same packet structure, format, and support for CSMA/CD protocol,
full duplex, flow control, and management objects, but with a tenfold
increase in theoretical throughput over 100Mbps Fast Ethernet and a
one hundred-fold increase over 10Mbps Ethernet. Since it is
compatible with all 10Mbps and 100Mbps Ethernet environments,
Gigabit Ethernet provides a straightforward upgrade without wasting
a company’s existing investment in hardware, software, and trained
personnel.
The increased speed and extra bandwidth offered by Gigabit Ether net
is essential to coping with the network bottlenecks that frequently
develop as computers and their busses get faster and more users use
applications that generate more traffic. Upgrading key components,
such as your backbone and servers to Gigabit Ethernet can greatly
improve network response times as well as significantly speed up the
traffic between your subnets.
Gigabit Ethernet enables fast optical fiber connections to support
video conferencing, complex imaging, and similar data-intensive
applications. Likewise, since data transfers occur 10 times faster
than Fast Ethernet, servers outfitted with Gigabit Ethernet NIC’s
are able to perform 10 times the number of operations in the same
amount of time.
In addition, the phenomenal bandwidth delivered by Gigabit Ethernet
is the most cost-effective method to take advantage of today and
tomorrow’s rapidly improving switching and routing internetworking
technologies. And with expected advances in the coming years in
silicon technology and digital signal processing that will enable
Gigabit Ethernet to eventually operate over unshielded twisted-pair
(UTP) cabling, outfitting your network with a powerful 1000Mbpscapable backbone/server connection creates a flexible foundation for
the next generation of network technology products.
2 Introduction
Page 17

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Switching Technology
Another key development pushing the limits of Ethernet technology
is in the field of switching technology. A switch bridges Ethernet
packets at the MAC address level of the Ethernet pr otocol
transmitting among connected Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, or Gigabit
Ethernet LAN segments.
Switching is a cost-effective way of increasing the total network
capacity available to users on a local area network. A switch
increases capacity and decreases network loading by making it
possible for a local area network to be divided into different segments
which don’t compete with each other for network transmission
capacity, giving a decreased load on each.
The switch acts as a high-speed selective bridge between the
individual segments. Traffic that needs to go from one segment to
another (from one port to another) is automatically forwarded by the
switch, without interfering with any other segments (ports). This
allows the total network capacity to be multiplied, while still
maintaining the same network cabling and adapter cards.
For Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet networks, a switch is an
effective way of eliminating problems of chaining hubs beyond the
“two-repeater limit.” A switch can be used to split parts of the
network into different collision domains, for example, making it
possible to expand your Fast Ethernet network beyond the 205 meter
network diameter limit for 100BASE-TX networks. Switches
supporting both traditional 10Mbps Ethernet and 100Mbps Fast
Ethernet are also ideal for bridging between existing 10Mbps
networks and new 100Mbps networks.
Switching LAN technology is a marked improvement over the
previous generation of network bridges, which were characterized by
higher latencies. Routers have also been used to segment local area
networks, but the cost of a router and the setup and maintenance
Introduction 3
Page 18

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
required make routers relatively impractical. Today’s switches are an
ideal solution to most kinds of local area network congestion
problems.
Features
The TEG-S224 series of Switches can include one master (either a
TEG-S224M or a TEG-S224MF) and up to three clients (TEG-S224S
or TEG-S224SF). They are designed for easy installation and high
performance in an environment where traffic on the network and the
number of users increases continuously.
Switch features include:
Ports
? ?20 high performance NWay ports all operating at 10/100 Mbps
for connection to servers and hubs (19 ports 10/100 fixed
Ethernet TP interface and one MDI-II/MDI-X jack connection
are supported) (TEG-S224M and TEG-S224MF) or 22 high
performance NWay ports all operating at 10/100 Mbps for
connection to servers and hubs (20 ports 10/100 fixed Ethernet
TP interface and two MDI-II/MDI-X jack connections are
supported) (TEG-S224S and TEG-S224SF).
? ?All ports can be auto-negotiated between 10Mbps/100Mbps,
half-duplex or full duplex connections.
? ?Gigabit uplink/MDI-II (media dependent interface) slide-in
module in the rear panel for uplink to another Switch. Oneport or two-port models are available (TEG-S224M and TEGS224MF only).
4 Introduction
Page 19

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?RS-232 DCE console port for diagnosing the Switch via a
connection to a PC and Console/Out-of-band management
(TEG-S224M or TEG-S224MF only).
? ?One slide-in module interface in the front panel for 1 or 2 ports
10/100M Ethernet connection. Three optional modules are
available: 2-port TX, 2-port FX (MT -RJ), and 1-port FX (SC).
? ?Stacking Input/Output port slide-in module in the rear panel
for stacking to another device to implement a high-port count,
manageable switch. Three-port module for master device and
one-port module for a client device.
Performance features
? ?Store and forward switching scheme capability to support rate
adaptation and protocol conversion.
? ?Full and half-duplex for 10Mbps and 100Mbps connections. The
1000BASE-SX module operates at full-duplex only. Full-duplex
allows the switch port to simultaneously transmit and receive
data, and only works with connections to full-duplex capable
end stations and switches. Connections to hubs must take
place at half-duplex.
? ?Auto polarity detection and correction of incorrect polarity on
the receive twisted pair at each port.
? ?Data forwarding rate 14,880 pps per port at 100% of wire-speed
for 10Mbps speed.
? ?Data forwarding rate 148,800 pps per port at 100% of wire-
speed for 100Mbps speed.
? ?Data forwarding rate 1,488,100 pps per port at 100% of wire-
speed for 1000Mbps speed.
Introduction 5
Page 20

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?Data filtering rate eliminates all error packets, runts, etc. at
14,880 pps per port at 100% of wire-speed for 10Mbps speed.
? ?Data filtering rate eliminates all error packets, runts, etc. at
148,800 pps per port at 100% of wire-speed for 100Mbps speed.
? ?Data filtering rate eliminates all error packets, runts, etc. at
1,488,100 pps per port at 100% of wire-speed for 1000Mbps
speed.
? ?12K active MAC address entry table per device with automatic
learning and aging (10 to 9999 seconds).
? ?12 MB packet buffer per device.
? ?Supports Broadcast Storm filtering.
? ?Supports IGMP Multicast snooping.
Management
? ?RS-232 console port for out-of-band network management via a
console terminal or PC.
? ?Spanning Tree Algorithm Protocol for creation of alternative
backup paths and prevention of indefinite network loops.
? ?Fully configurable either in-band or out-of-band control via
SNMP based software.
? ?Flash memory for software upgrade. This can be done in-band
via BOOTP/TFTP. Out-of-band console can also initiate a
download request.
? ?Built-in SNMP management: Bridge MIB (RFC 1493), RMON
MIB (RFC 1757), and MIB-II (RFC 1213).
6 Introduction
Page 21

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
2
2 U NPACKING AND
S ETUP
This chapter provides unpacking and setup information for the
Switch.
Unpacking
Open the shipping carton of the Switch and carefully unpack its
contents. The carton should contain the following items:
? ?One Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch
? ?Mounting kit: two mounting brackets and screws
? ?Four rubber feet with adhesive backing
? ?One AC power cord
? ?This user’s guide on CD-ROM with a Registration Card
If any item is found missing or damaged, please contact your local
reseller for replacement.
Unpacking and Setup 7
Page 22

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Setup
The setup of the Switch can be performed using the following steps:
? ?The surface must support at least 5 kg.
? ?The power outlet should be within 1.82 meters (6 feet) of the
device.
? ?Visually inspect the power cord and see that it is secured fully
to the AC power connector.
? ?Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation from and
adequate ventilation around the Switch. Do not place heavy
objects on the Switch.
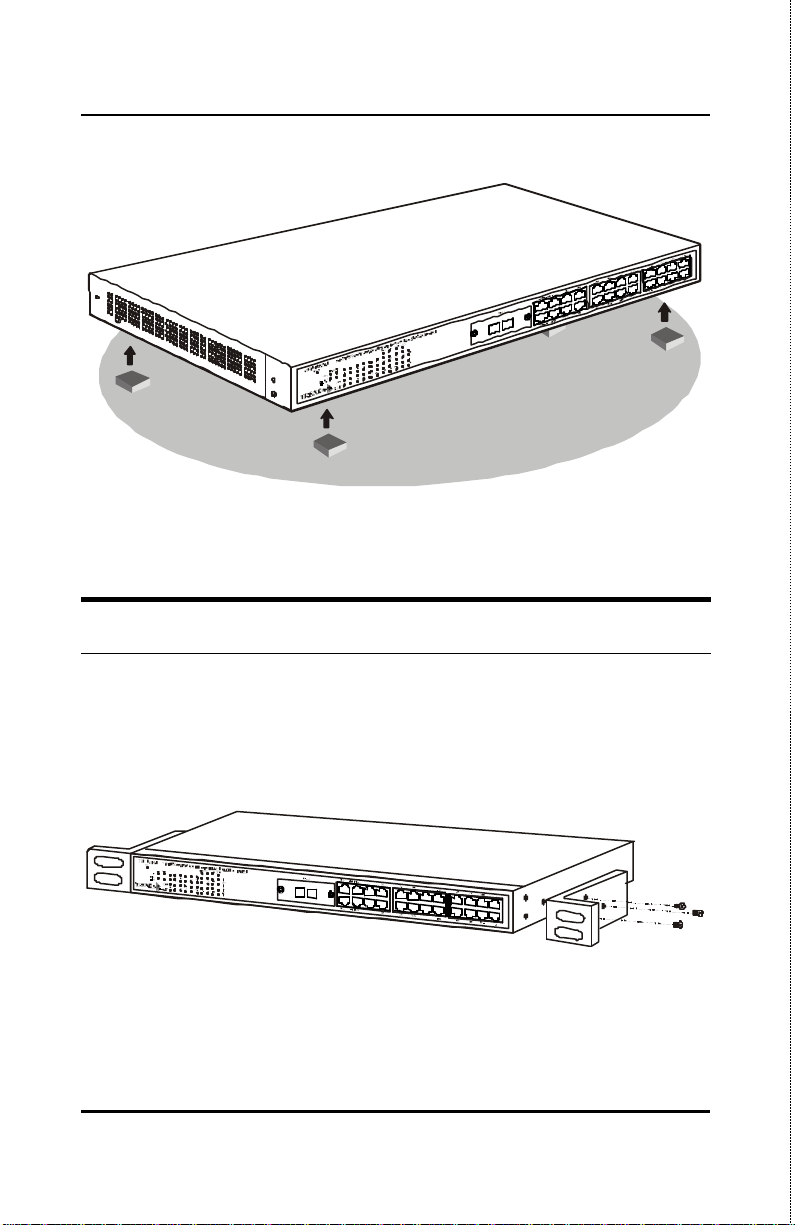
Desktop or Shelf Installation
When installing the Switch on a desktop or shelf, the rubber feet
included with the device must be first attached. Attach these
cushioning feet on the bottom at each corner of the device. Allow
enough ventilation space between the device and the objects around
it.
8 Unpacking and Setup
Page 23
Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
TEG-S224S
Figure 2-1. Switch installed on a Desktop or Shelf
Rack Installation
The Switch can be mounted in an EIA standard size, 19-inch rack,
which can be placed in a wiring closet with other equipment. To
install, attach the mounting brackets on the switch’s front panel (one
on each side) and secure them with the screws provided.
Figure 2-2A. Attaching the mounting brackets to the Switch
Unpacking and Setup 9
Page 24
Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
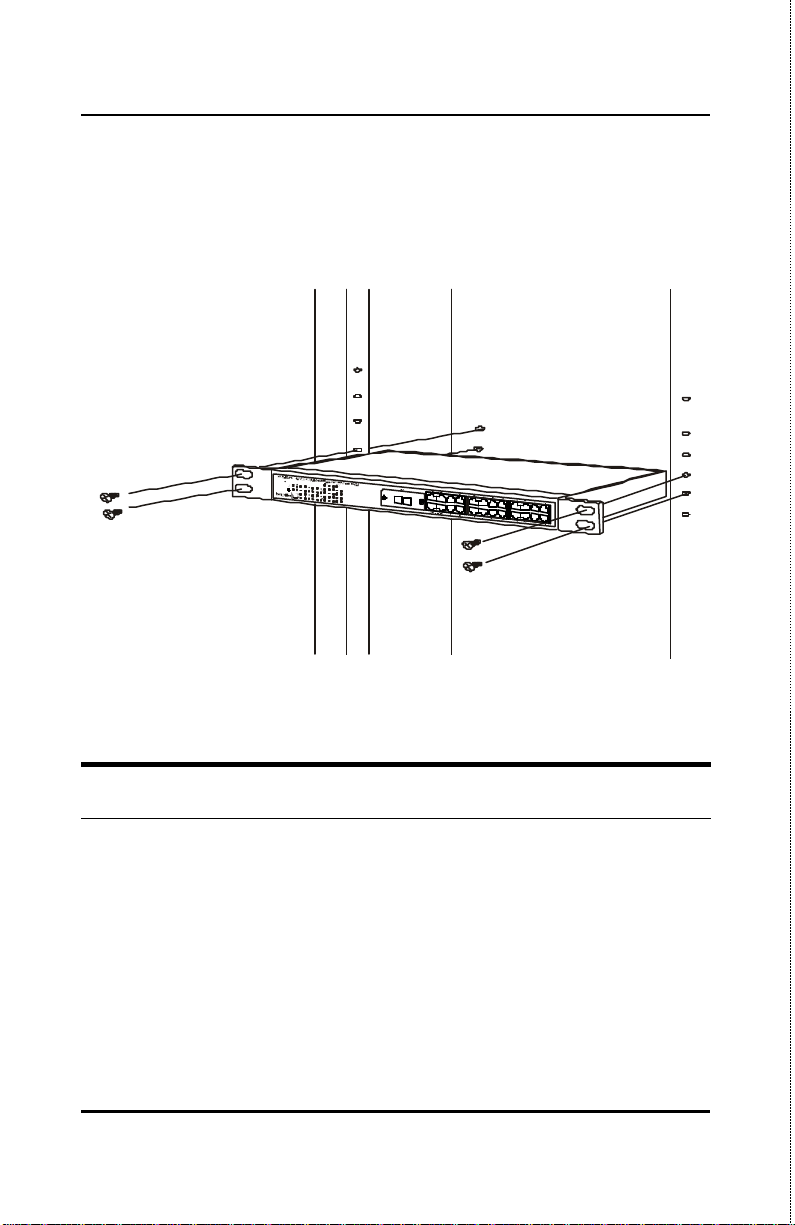
Then, use the screws provided with the equipment rack to mount the
Switch in the rack.
Figure 2-2B. Installing the Switch in an equipment rack
Power on
The Switch can be used with AC power sources 100 - 240 VAC, 50 60 Hz. The power switch is located at the rear of the unit adjacent to
the AC power connector and the system fan. The Switch’s power
supply will adjust to the local power source automatically and may be
turned on without having any or all LAN segment cables connected.
After the power switch is turned on, the LED indicators should
respond as follows:
10 Unpacking and Setup
Page 25

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?All LED indicators will momentarily blink. This blinking of
the LED indicators represents a reset of the system.
? ?The power LED indicator will blink while the Switch loads
onboard software and performs a self-test. After approximately
40 seconds, the LED will light continuously to indicate the
Switch is in a ready state.
? ?The console LED indicator will remain ON if there is a
connection at the RS-232 port, otherwise this LED indicator is
OFF.
? ?The 100M LED indicator may remain ON or OFF depending
on the transmission speed.
Power Failure
As a precaution, the Switch should be unplugged in case of power
failure. When power is resumed, plug the Switch back in.
Unpacking and Setup 11
Page 26
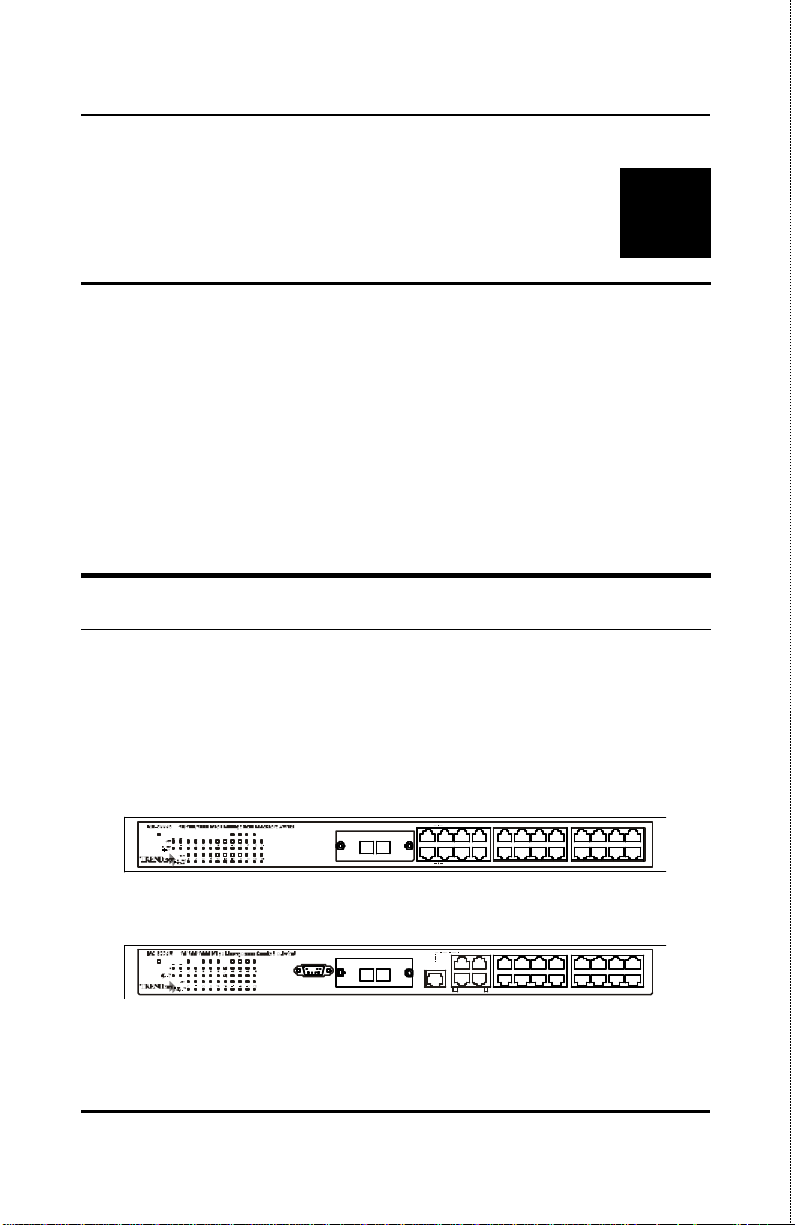
Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
TEG-S224S
15x
18x
17x
20x
19x
22x
21x7x10x9x12x
11x
14x
13x
16x
Slot1
3
3 IDENTIFYING
E XTERNAL COMPONENTS
This chapter describes the front panel, rear panel, optional plug-in
modules, and LED indicators of the Switch
Front Panel
The front panel of the Switch consists of either 19 or 20 (10/100
Mbps) Ethernet/Fast Ethernet ports, one or two uplink jacks, a slidein module slot for 10/100 Mbps Ethernet ports, an RS-232
communication port (TEG-S224M and TEG-S224MF only), and LED
indicators.
Uplink
Uplink
2x 4x 6x5x8x
Uplink
3x1x
3x1x
2x 4x 6x5x8x
10x9x12x
15x
17x
11x
19x7x
13x
18x
20x
14x
16x
Power
Slot1
TEG-S224M
Console Giga1Giga2 Slot2 Sio1 Sio2 Sio3Slot3
Power
Slot2 Sio1 Sio2 Sio3
RS-232 DCE,9600,n,8,1
Slot1
Slot1
Figure 3-1. Front panel view of the Switches
12 Identifying External Components
Page 27
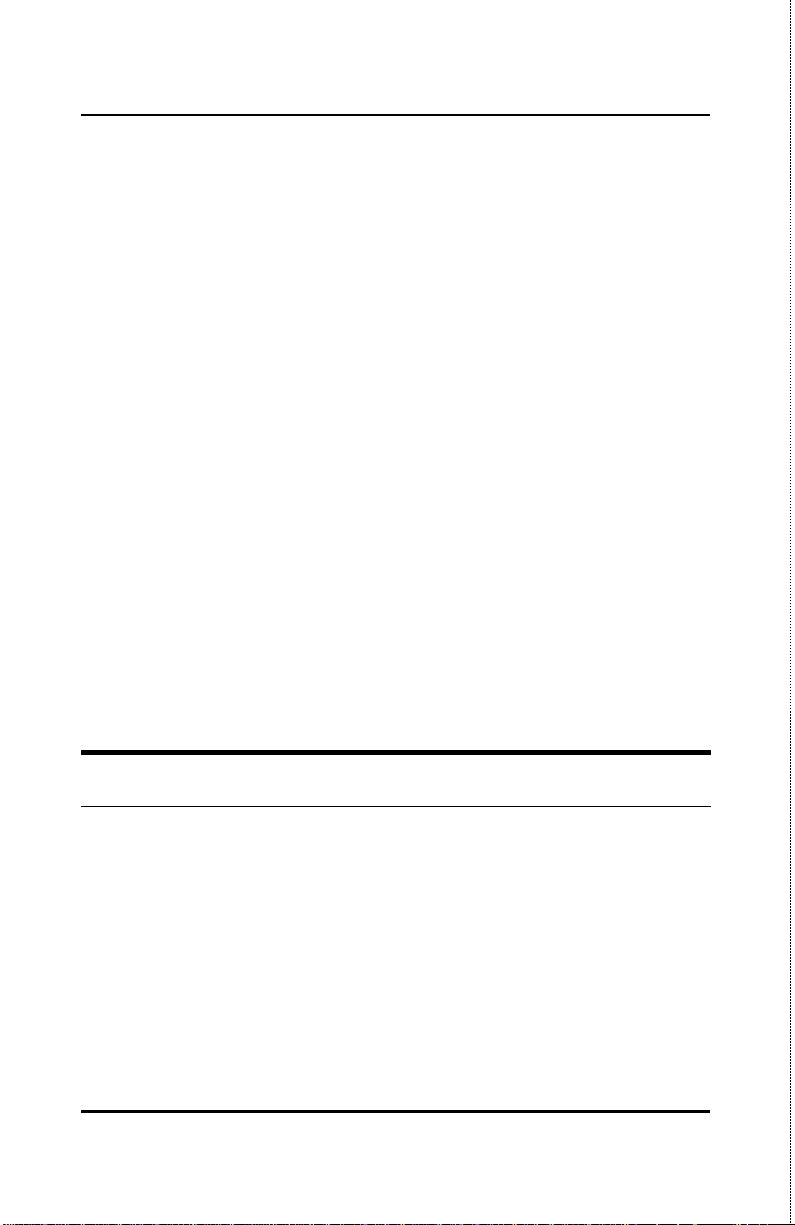
Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?Comprehensive LED indicators display the conditions of the
Switch and status of the network. A description of these LED
indicators follows (see LED Indicators).
? ?An RS-232 DCE console port is used to diagnose the Switch via
a connection to a PC and Local Console Management (TEGS224M and TEG-S224MF only).
? ?Nineteen or 20 high performance NWay ports all operate at
10/100 Mbps for connection to servers and hubs. All ports can
be auto-negotiated between 10Mbps or 100Mbps.
? ?A slide-in module slot (labeled Slot1) for 10/100 Mbps Ethernet
ports can accommodate the following modules: 2-port TX, 2port FX (MT -RJ), or 1-port FX (SC).
? ?One or two MDI-II uplink jacks are supported. Port numbers 1
and 2 on the TEG-S224S and the TEG-S224SF are equipped
with MDI-X jacks for normal end-node connections and MDI-II
jacks for uplink connections. Port number 1 on the TEGS224M and TEG-S224MF are equipped with an MDI-X jack for
normal end-node connection and an MDI-II jack for uplink
connection.
Rear Panel
The rear panel of the TEG-S224S and the TEG-S224SF consist of a
slot (labeled Slot2) for a Stacking input/output port and an AC power
connector. The rear panel of the TEG-S224M and TEG-S224MF
consist of two slots (labeled Slot2 and Slot3). Slot2 is for Stacking
input/output ports Sio1, Sio2, and Sio3. Slot3 is for an optional
Gigabit Ethernet uplink (MDI-II) port. The following shows the rear
panel of the Switches.
Identifying External Components 13
Page 28

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
TEG-S224S
TEG-S224M
Figure 3-2. Rear panel view of the Switches
? ?The optional Gigabit Ethernet slide-in module is an
uplink/MDI-II (media dependent interface) port for uplink to
another Switch (TEG-S224M and TEG-S224MF only). Two
models are available, one-port and two-port.
? ?The Stacking input/output port slide-in module in the rear
panel is for stacking to another device to implement a highport count, manageable Switch. The three-port module is for a
master device and a one-port module is for a client device.
? ?The AC power connector is a three-pronged connector that
supports the power cord. Plug in the female connector of the
provided power cord into this connector, and the male into a
power outlet. Supported input voltages range from 100 ~ 240
VAC at 50 ~ 60 Hz.
Side Panels
The right side panel of the Switch contains two system fans (see the
bottom part of the diagram below). The left side panel contains heat
vents.
14 Identifyi ng External Components
Page 29
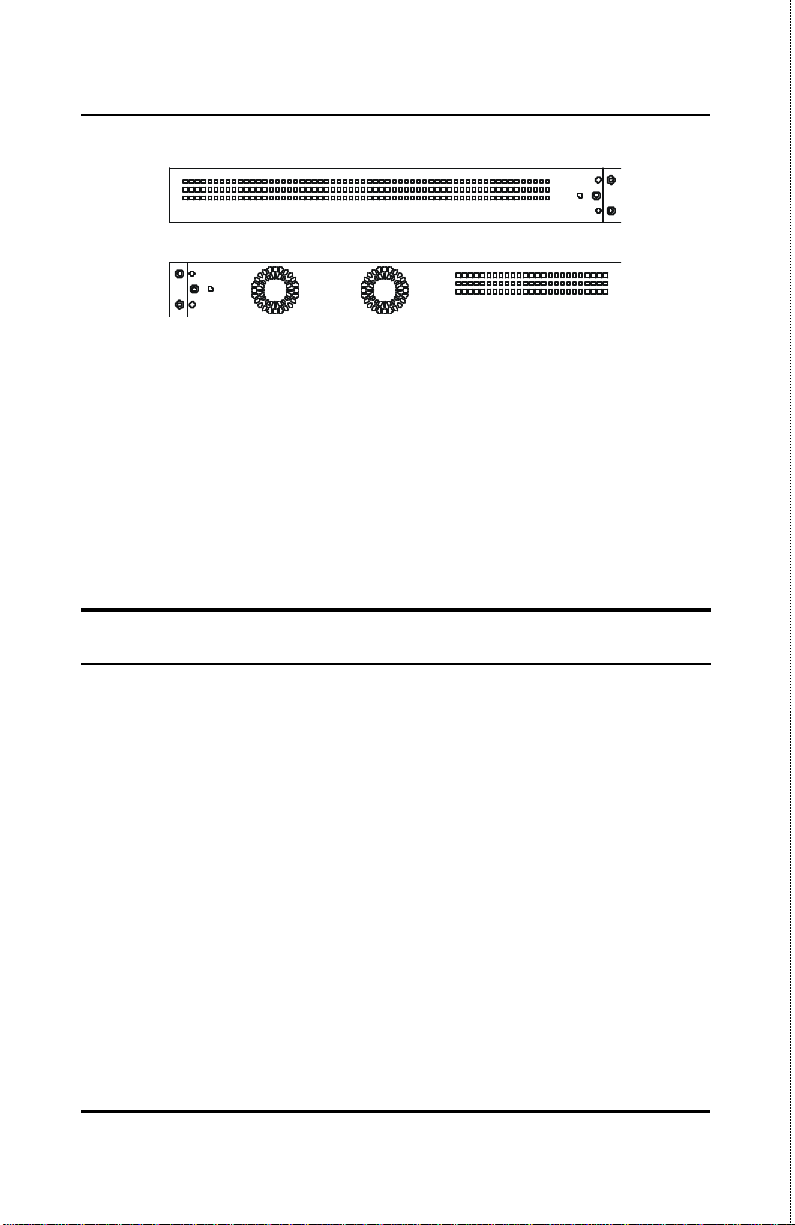
Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Figure 3-3. Side panel views of the Switch
? ?The system fans are used to dissipate heat. The sides of the
system also provide heat vents to serve the same purpose. Do
not block these openings, and leave adequate space at the rear
and sides of the Switch for proper ventilation. Be reminded
that without proper heat dissipation and air circulation,
system components might overheat, which could lead to
system failure.
Stack Operation
The TEG-S224M and the TEG-S224MF are intelligent Switches
capable of acting as a master for up to three client Switches (TEGS224S and TEG-S224SF). Each port is referred to by unit ID and
port number in your TEG-S224 Series stack.
To set up a stack, a one-port Stacking input/output module is
needed for each client Switch and a three-port Stacking
input/output module is needed for the master Switch. Once the
modules have been installed, use a cascade cable to connect each
client Switch to the master Switch.
Identifying External Components 15
Page 30
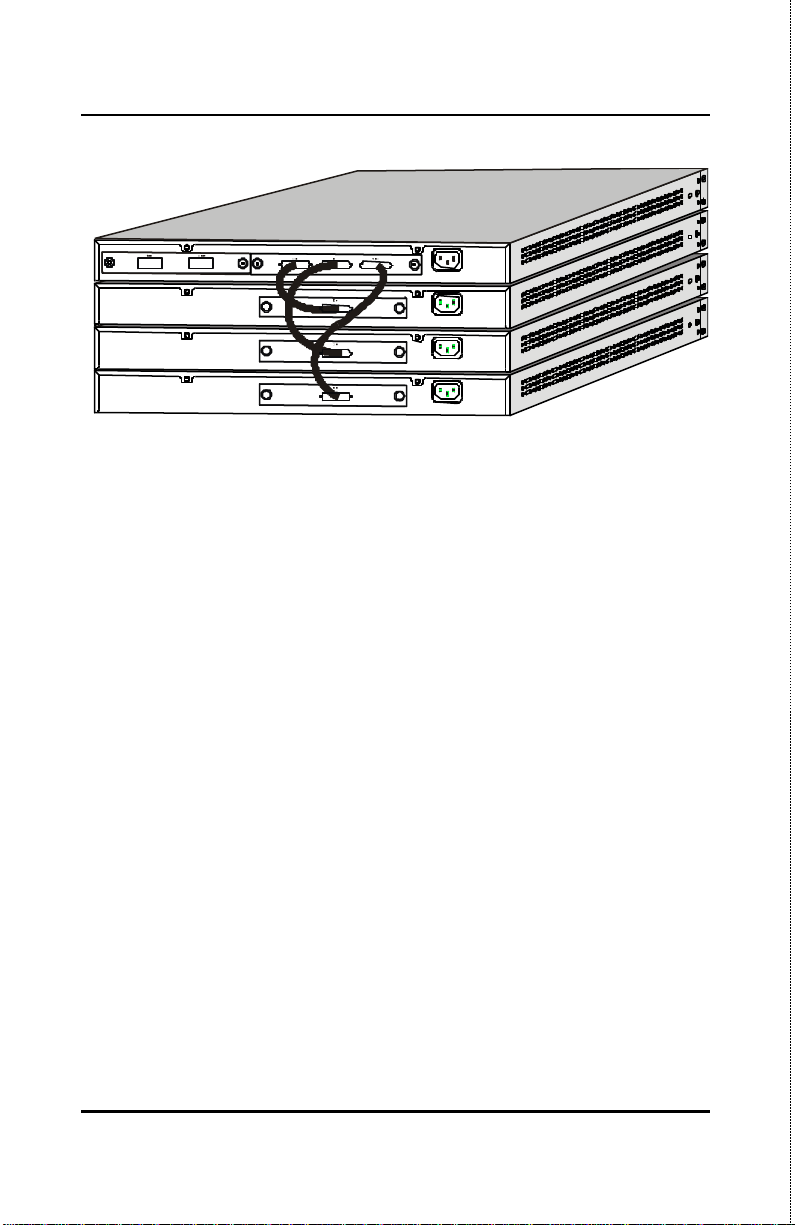
Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
TEG-S224S
TEG-S224M
Figure 3-4. Switch stack with one master and three clients
Please note that two client switches can also be connected via the
Stacking input/output ports.
The following diagram displays some possible switch stack
connections:
16 Identifying External Components
Page 31

10/100Mbps Hub
10/100Mbps Hub
10/100Mbps Hub
100Mbps server
10Mbps printer
10/100Mbps Hub
Local
10Mbps printer
Local
10Mbps printer
TEG-S224M
TEG-S224S
10/100Mbps Hub
pc
pc
Local
10Mbps printer
Local
10Mbps printer
pc
pc
Local
100Mbps server
Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Local
10Mbps printer
Local
pc
Local
10Mbps printer
Local
100Mbps
server
pc
Local
100Mbps
server
Local
pc
Figure 3-5. Switch stack with example of possible connecti ons
Optional Plug-in Modules
The TEG-S224M/TEG-S224MF Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch is
able to accommodate a range of plug-in modules in order to increase
functionality and performance.
Identifying External Components 17
Page 32

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
100BASE-FX (MT-RJ) Module
TEG-S224S
Figure 3-6. Two-port, 100BASE-FX (MT-RJ) module
? ?Two-port, front-panel module.
? ?Connects to 100BASE-FX devices at full- or half-duplex.
? ?Supports multi-mode fiber-optic cable connections of up to 412
meters in half-duplex or 2 km in full-duplex mode.
100BASE-FX (SC) Module
TEG-S224S
Figure 3-7. One -port, 100BASE-FX (SC) module
18 Identifying External Components
Page 33

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?One-port, front panel module.
? ?Connects to a 100BASE-FX device at full- or half-duplex.
? ?Supports multi-mode fiber-optic cable connections of up to 412
meters in half-duplex or 2 km in full-duplex mode.
100BASE-TX Module
TEG-S224S
Figure 3-8. Two-port, 100BASE-TX module
? ?Two-port, front-panel module.
? ?Connects to 100BASE-TX devices at full or half duplex.
? ?Supports Category 5 UTP or STP cable connections of up to 100
meters.
Identifying External Components 19
Page 34

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
1000BASE-SX Gigabit Module
Figure 3-9. One -port, 1000BASE-SX gigabit module
? ?One- or two-port, rear-panel module.
? ?Connects to 1000BASE-SX devices at full duplex.
? ?Allows connections using multi-mode fiber optic cable in the
following configurations:
62.5?m 62.5?m 50?m 50?m
Modal bandwidth
(min. overfilled launch)
Unit: MHz*km
Operating distance
Unit: meters
Channel insertion loss
Unit: dB
20 Identifying External Components
160 200 400 500
220 275 500 550
2.33 2.53 3.25 3.43
Page 35

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
1000BASE-LX Gigabit Module
Figure 3-10. One -port, 1000BASE-LX gigabit module
? ?One-port, rear-panel module.
? ?Connects to a 1000BASE-LX device at full duplex.
? ?Allows connections up to 5 km in length using single-mode fiber
optic cable.
LED Indicators
The LED indicators of the Switch include Power, Console, Slot, Giga,
Speed, and Link/Act. The following shows the LED indicators for the
Switch along with an explanation of each indicator.
Identifying External Components 21
Page 36

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
TEG-S224S
RS-2
TEG-S225M
Figure 3-11. The Switch LED indicators
? ?Power This indicator on the front panel should light green
after approximately 2 seconds to indicate the ready state of the
Switch when the device is powered on. The LED will blink
when the Power-On Self-Test (POST) is running or if the
system’s configuration has changed. This LED will light
orange when an error occurs.
? ?Console This indicator is lit green when the switch is being
managed via out-of-band/local console management through
the RS-232 console port using a straight-through serial cable.
When a secured connection is established, this LED is lit. The
indicator blinks when the console RS-232 is accessed.
? ?Slot2 This indicator is lit green when a slide-in module is
present in the rear panel of the Switch.
22 Identifying External Components
Page 37

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?Slot3 This indicator is lit green when a slide-in module is
present in the rear panel of the Switch.
? ?Giga1 This indicator is lit green when a link is established. It
blinks green when the Gigabit port is active.
? ?Giga2 This indicator is lit green when a link is established. It
blinks green when the Gigabit port is active.
? ?Sio1 This indicator is lit green when a Stacking IO port is
present in the rear panel of the Switch.
? ?Sio2 This indicator is lit green when a Stacking IO port is
present in the rear panel of the Switch.
? ?Sio3 This indicator is lit green when a Stacking IO port is
present in the rear panel of the Switch.
? ?100M These indicators are illuminated green when a 100
Mbps device is connected to any of the 22+2 or 20+2 ports or
uplink port. If a 10 Mbps device is connected to any of the 24
ports or uplink port, these LEDs remain dark. When a port is
active, these indicators will blink green.
? ?Link/Act These indicators are lit when there is a secure
connection (or link) to a device at any of the ports. The LEDs
blink whenever there is reception or transmission (i.e. Activity-
-Act) of data occurring at a port.
Identifying External Components 23
Page 38

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
4
4 C ONNECTING THE
S WITCH
This chapter describes how to connect the Switch to your Ethernet
network.
Switch to End Node
End nodes include PCs outfitted with a 10, 100 or 10/100 Mbps RJ-45
Ethernet/Fast Ethernet Network Interface Card (NIC) and most
routers. The RJ-45 UTP ports on NICs and most routers are MDI-II.
When using a normal straight-through cable, an MDI-II port must
connect to an MDI-X port.
An end node can be connected to the Switch via a two-pair Category
3, 4, 5 UTP/STP straight cable (be sure to use Category 5 UTP or
STP cabling for 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet connections). The end node
should be connected to any of the twenty-two ports (1x - 22x) of the
Switch or to either of the two 100BASE-TX ports on the front-panel
module that came preinstalled on the Switch. An end node should not
be connected to an Uplink port (unless using a crossover cable), and if
the top Uplink port is in use, Port 1x must remain vacant; if the
bottom Uplink port is in use, Port 2x cannot be used.
24 Connecting The Switch
Page 39

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
RJ-45 JACK
15x
18x
17x
20x
19x
22x
21x7x10x9x12x
11x
14x
13x
16x
TEG-S224S
Uplink
2x 4x 6x5x8x
Uplink
3x1x
Slot1
Figure 4-1. Switch connected to an End Node
The LED indicators for the port the end node is connected to are lit
according to the capabilities of the NIC. If LED indicators are not
illuminated after making a proper connection, check the PC’s LAN
card, the cable, switch conditions, and connections.
The following LED indicator states are possible for an end node to
switch connection:
1. The 100M LED indicator comes ON for a 100 Mbps and stays
OFF for 10 Mbps.
2. The Link/Act LED indicator lights up upon hooking up a PC
that is powered on.
Switch to Hub or Switch
These connections can be accomplished in a number of ways. The
most important consideration is that when using a normal, straightthrough cable, the connection should be made between a normal
crossed port (Port 1x, 2x, etc.) and an Uplink (MDI-II) port. If you are
using a crossover cable, the connection must be made from Uplink to
Uplink, or from a crossed port to another crossed port.
? ?A 10BASE-T hub or switch can be connected to the Switch via
Connecting The Switch 25
a two-pair Category 3, 4 or 5 UTP/STP straight cable.
Page 40

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
15x
18x
17x
20x
19x
22x
21x7x10x9x12x
11x
14x
13x
16x
? ?A 100BASE-TX hub or switch can be connected to the Switch
via a four-pair Category 5 UTP/STP straight cable.
If the other switch or hub contains an unused Uplink port, we
suggest connecting the other device’s Uplink (MDI-II) port to any of
the switch’s (MDI-X) ports (1x - 22x, or one of the 100BASE-TX
module ports) using a normal straight-through cable, as shown
below.
If the other device does not have an unused Uplink port, make the
connection with a normal straight-through cable from one of the
Uplink ports on the switch to any normal crossed port on the hub.
Alternatively, if you have a crossover cable you can save the Uplink
ports for other connections and make this one from a crossed port to
another crossed port.
Uplink
Uplink
2x 4x 6x5x8x
3x1x
Slot1
Figure 4-2. Switch connected to a normal (non-Uplink) port on a
hub or switch using a straight or crossover cable
10BASE-T Device
For a 10BASE-T device, the Switch’s LED indicators should display
the following:
? ?100M LED speed indicator is OFF.
? ?Link/Act indicator is ON.
26 Connecting The Switch
Page 41

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
100BASE-TX Device
For a 100BASE-TX device, the Switch’s LED indicators should
display the following:
? ? 100M LED speed indicator is ON.
? ? Link/Act is ON.
Connecting The Switch 27
Page 42

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
5
5 S WITCH MANAGEMENT
C ONCEPTS
This chapter discusses many of the features used to manage the
switch, and explains many concepts and important points regarding
these features. Configuring the Switch to implement these concepts is
discussed in detail in the next chapters.
Local Console Management
Local console management involves the administration of the Switch
via a direct connection to the RS-232 DCE console port. This is an
Out-Of-Band connection, meaning that it is on a different circuit
than normal network communications, and thus works even when
the network is down.
The local console management connection involves a terminal or PC
running terminal emulation software to operate the Switch’s built-in
console program (see Chapter 6, “Using the Console Interface”).
Using the console program, a network administrator can manage,
control and monitor the many functions of the Switch.
Hardware components in the Switch allow it to be an active part of a
manageable network. These components include a CPU, memory for
data storage, other related hardware, and SNMP agent firmware.
28 Switch Management Concepts
Page 43

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Activities on the Switch can be monitored with these components,
while the Switch can be manipu lated to carry out specific tasks.
Diagnostic (Console) Port (RS-232 DCE)
Out-of-band management requires connecting a terminal, such as a
VT-100 or a PC running terminal emulation program (such as
HyperTerminal, which is automatically installed with Microsoft
Windows) a to the RS-232 DCE console port of the Switch. Switch
management using the RS-232 DCE console port is called Local
Console Management to differentiate it from management done via
management platforms, such as D-View, HP OpenView, etc.
The console port is set for the following configuration:
? ? Baud rate: 9,600
? ? Data width: 8 bits
? ? Parity: none
? ? Stop bits: 1
? ? Flow Control none
Make sure the terminal or PC you are using to make this
connection is configured to match these settings.
If you are having problems making this connection on a PC, make
sure the emulation is set to VT -100 or ANSI. If you still don’t see
anything, try hitting <Ctrl> + r to refresh the screen.
IP Addresses and SNMP Community
Names
Each Switch has its own IP Address, which is used for
communication with an SNMP network manager or other TCP/IP
Switch Management Concepts 29
Page 44

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
application (for example BOOTP, TFTP). You can change the default
Switch IP Address to meet the specification of your networking
address scheme.
In addition, you can also set an IP Address for a gateway router. This
becomes necessary when the network management station is located
on a different IP network as the Switch, making it necessary for
management packets to go through a router to reach the network
manager, and vice-versa.
For security, you can set in the Switch a list of IP Addresses of the
network managers that you allow to manage the Switch. You can
also change the default Community Name in the Switch and set
access rights of these Community Names.
Traps
Traps are messages that alert you of events that occur on the Switch.
The events can be as serious as a reboot (someone accidentally turned
OFF the Switch), or less serious like a port status change. The
Switch generates traps and sends them to the network manager (trap
managers). The following lists the types of events that can take place
on the Switch.
? ? System resets
? ? Errors
? ? Status changes
? ? Topology changes
? ? Operation
30 Switch Management Concepts
Page 45

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
You can also specify which network managers may receive traps
from the Switch by setting a list of IP Addresses of the authorized
network managers.
Trap managers are special users of the network who are given
certain rights and access in overseeing the maintenance of the
network. Trap managers will receive traps sent from the Switch;
they must immediately take certain actions to avoid future failure or
breakdown of the network.
The following are trap types a trap manager will receive:
? ?Cold Start This trap signifies that the Switch has been
powered up and initialized such that software settings are
reconfigured and hardware systems are rebooted. A cold start
is different from a factory reset.
? ?Warm Start This trap signifies that the Switch has been
rebooted, however the Power -On Self-Test (POST) is skipped.
? ?Authentication Failure This trap signifies that someone
has tried to logon to the switch using an invalid SNMP
community name. The switch automatically stores the source
IP address of the unauthorized user.
? ?New Root This trap indicates that the Switch has become
the new root of the Spanning Tree, the trap is sent by a bridge
soon after its election as the new root. This implies that upon
expiration of the Topology Change Timer the new root trap is
sent out immediately after the Switch’s selection as a new root.
? ?Topology Change A Topology Change trap is sent by the
Switch when any of its configured ports transitions from the
Learning state to the Forwarding state, or from the
Forwarding state to the Blocking state. The trap is not sent if
a new root trap is sent for the same transition.
Switch Management Concepts 31
Page 46

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?Link Change Event This trap is sent whenever the link of a
port changes from link up to link down or from link down to
link up.
? ?Port Partition This trap is sent whenever a port is
partitioned as a result of more than sixty-two collisions on the
port (i.e., is automatically partitioned). The number of
collisions that triggers this trap is the same at either 10Mbps
or 100Mbps.
? ?Broadcast Storm This trap is sent whenever the port
reaches the broadcast storm rising or falling threshold.
MIBs
Management information and counters are stored in the Switch in
the Management Information Base (MIB). The Switch uses the
standard MIB-II Management Information Base module.
Consequently, values for MIB objects can be retrieved from any
SNMP-based network manager software. In addition to the standard
MIB-II, the Switch also supports its own proprietary enterprise MIB
as an extended Management Information Base. These MIBs may also
be retrieved by specifying the MIB’s Object-Identity (OID) at the
network manager. MIB values can be either read-only or read-write.
Read-only MIBs variables can be either constants that are
programmed into the Switch, or variables that change while the
Switch is in operation. Examples of read-only constants are the
number of ports and types of ports. Examples of read-only variables
are the statistics counters such as the number of errors that have
occurred, or how many kilobytes of data have been received and
forwarded through a port.
32 Switch Management Concepts
Page 47

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Read-write MIBs are variables usually related to user-customized
configurations. Examples of these are the Switch’s IP Address,
Spanning Tree Algorithm parameters, and port status.
If you use a third-party vendors’ SNMP software to manage the
Switch, a diskette listing the Switch’s propriety enterprise MIBs can
be obtained by request. If your software provides functions to browse
or modify MIBs, you can also get the MIB values and change them (if
the MIBs’ attributes permit the write operation). This process
however can be quite involved, since you must know the MIB OIDs
and retrieve them one by one.
Packet Forwarding
The Switch learns the network configuration and uses this
information to forward packets. This reduces the traffic congestion on
the network, because packets, instead of being transmitted to all
segments, are transmitted to the destination only. Example: if Port
1 receives a packet destined for a station on Port 2, the Switch
transmits that packet through Port 2 only, and transmits nothing
through the other ports.
Aging Time
The Aging Time is a parameter that affects the auto-learn process of
the Switch in terms of the network configuration. Dynamic Entries,
which make up the auto-learned-node address, are aged out of the
address table according to the Aging Time that you set.
The Aging Time can be from 10 seconds to 9999 seconds. A very long
Aging Time can result with the out-of-date Dynamic Entries that
may cause incorrect packet filtering/forwarding decisions.
Switch Management Concepts 33
Page 48

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
On the other hand, if the Aging Time is too short, many entries may
be aged out soon, resulting in a high percentage of received packets
whose source addresses cannot be found in the address table, in
which case the Switch will broadcast the packet to all ports, negating
many of the benefits of having a switch.
Filtering Database
A switch uses a filtering database to segment the network and
control communications between segments. It also filters packets
off the network for intrusion control (MAC Address filtering).
For port filtering, each port on the switch is a unique collision
domain and the switch filters (discards) packets whose destination
lies on the same port as where it originated. This keeps local
packets from disrupting communications on other parts of the
network.
For intrusion control, whenever a switch encounters a packet
originating from or destined to a MAC address defined by the user,
the switch will discard the packet.
Filtering includes:
1. Dynamic filtering Automatic learning and aging of MAC
addresses and their location on the network. Filtering occurs to
keep local traffic confined to its segment.
2. MAC address filtering The manual entry of specific MAC
addresses to be filtered from the network.
3. Filtering done by the Spanning Tree Protocol Can filter
packets based on topology, making sure that signal loops don’t
occur.
4. Filtering done for VLAN integrity. Packets from a
member of a VLAN (VLAN 2, for example) destined for a device
on another VLAN (VLAN 3) will be filtered.
34 Switch Management Concepts
Page 49

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Spanning Tree Algorithm
The Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) in the Switch allows you to
create alternative paths (with multiple switches or other types of
bridges) in your network. These backup paths are idle until the
Switch determines that a problem has developed in the primary
paths. When a primary path is lost, the switch providing the
alternative path will automatically go into service with no operator
intervention. This automatic network reconfiguration provides
maximum uptime to network users. The concept of the Spanning
Tree Algorithm is a complicated and complex subject and must be
fully researched and understood. Please read the following before
making any changes.
? ?Network loop detection and prevention With STA, there
will be only one path between any two LANs. If there is more
than one path, forwarded packets will loop indefinitely. STA
detects any looped path and selects the path with the lowest
path cost as the active path, while blocking the other path and
using it as the backup path.
? ?Automatic topology re-configuration When the path for
which there is a backup path fails, the backup path will be
automatically activated, and STA will automatically reconfigure the network topology.
STA Operation Levels
STA operates on two levels: the bridge level and the port level. On the
bridge level, STA calculates the Bridge Identifier for each Switch,
then sets the Root Bridge and the Designated Bridges. On the port
level, STA sets the Root Port and Designated Ports. Details are as
follows:
Switch Management Concepts 35
Page 50

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
On the Br idge Level
? ?Root Bridge The switch with the lowest Bridge Identifier is
the Root Bridge. Naturally, you will want the Root Bridge to be
the best switch among the switches in the loop to ensure the
highest network performance and reliability.
? ? Bridge Identifier This is the combination of the Bridge
Priority (a parameter that you can set) and the MAC address of
the switch. Example: 4 00 80 C8 00 01 00, where 4 is the
Bridge Priority. A lower Bridge Identifier results in a higher
priority for the switch, and thus increases it probably of being
selected as the Root Bridge.
? ?Designated Bridge From each LAN segment, the attached
Bridge that has the lowest Root Path Cost to the Root Bridge is
the Designated Bridge. It forwards data packets for that LAN
segment. In cases where all Switches have the same Root Path
Cost, the switch with the lowest Bridge Identifier becomes the
Designated Bridge.
? ?Root Path Cost The Root Path Cost of a switch is the sum of
the Path Cost of the Root Port and the Root Path Costs of all
the switches that the packet goes through. The Root Path Cost
of the Root Bridge is zero.
? ? Bridge Priority This is a parameter that users can set. The
smaller the number you set, the higher the Bridge Priority is.
The higher the Bridge Priority, the better the chance the
Switch will be selected as the Root Bridge.
On the Port Level
? ?Root Port Each switch has a Root Port. This is the port that
has the lowest Path Cost to the Root Bridge. In case there are
several such ports, then the one with the lowest Port Identifier
is the Root Port.
36 Switch Management Concepts
Page 51

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?Designated Port This is the port on each Designated Bridge
that is attached to the LAN segment for which the switch is
the Designated Bridge.
? ?Port Priority The smaller this number, the higher the Port
Priority is. With higher Port Priority, the higher the
probability that the port will be selected as the Root Port.
? ?Path Cost This is a changeable parameter and may be
modified according to STA specifications. Each 10Mbps and
100Mbps segment has an assigned Path Cost of 19.
User-Changeable STA Parameters
The factory default setting should cover the majority of installations.
However, it is advisable to keep the default settings as set at the
factory, unless it is absolutely necessary. The user changeable
parameters in the Switch are as follows:
? ?Bridge Priority A Bridge Priority can be from 0 to 65535. 0
is equal to the highest Bridge Priority.
? ?Bridge Hello Time The Hello Time can be from 1 to 10
seconds. This is the interval between two transmissions of
BPDU packets sent by the Root Bridge to tell all other
Switches that it is indeed the Root Bridge. If you set a Hello
Time for your Switch, and it is not the Root Bridge, the set
Hello Time will be used if and when your Switch becomes the
Root Bridge.
Note: The Hello Time cannot be longer than the Max. Age.
Otherwise, a configuration error will occur.
? ?Bridge Max. Age The Max. Age can be from 6 to 40 seconds.
At the end of the Max. Age, if a BPDU has still not been
received from the Root Bridge, your Switch will start sending
its own BPDU to all other Switches for permission to become
Switch Management Concepts 37
Page 52

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
the Root Bridge. If it turns out that your Switch has the lowest
Bridge Identifier, it will become the Root Bridge.
? ? Bridge Forward Delay The Forward Delay can be from 4 to
30 seconds. This is the time any port on the Switch spends in
the listening state while moving from the blocking state to the
forwarding state.
Observe the following formulas when you set the above
parameters:
1. Max. Age = 2 x (Forward Delay - 1 second)
2. Max. Age = 2 x (Hello Time + 1 second)
? ?Port Priority A Port Priority can be from 0 to 255. The
lower the number, the greater the probability the port will be
chosen as the Root Port.
Illustration of STA
A simple illustration of three Bridges (or the Switch) connected in a
loop is depicted in Figure 5-1. In this example, you can anticipate
some major network problems if the STA assistance is not applied.
For instance, if Bridge 1 broadcasts a packet to Bridge 2, Bridge 2
will broadcast it to Bridge 3, and Bridge 3 will broadcast it to Bridge
1 and so on. The broadcast packet will be passed indefinitely in a
loop, causing a serious network failure.
To alleviate network loop problems, STA can be applied as shown in
Figure 5-2. In this example, STA breaks the loop by blocking the
connection between Bridge 1 and 2. The decision to block a particular
connection is based on the STA calculation of the most current Bridge
and Port settings. Now, if Bridge 1 broadcasts a packet to Bridge 3,
then Bridge 3 will broadcast it to Bridge 2 and the broadcast will end
there.
38 Switch Management Concepts
Page 53

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
STA setup can be somewhat complex. Therefore, you are advised to
keep the default factory settings and STA will automatically assign
root bridges/ports and block loop connections. However, if you need to
customize the STA parameters, refer to Table 5-1.
Figure 5-1. Before Applying the STA Rules
Figure 5-2. After Applying the STA Rules
Switch Management Concepts 39
Page 54

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
STA parameters Settings Effects Comment
Bridge Priority lower the #,
higher the
priority
Hello Time 1 - 10 sec. No effect, if not
Max. Age Time 6 - 40 sec. Compete for Root
Forward Delay 4 - 30 sec. High # delays the
Port Level STA parameters
Enable / Disable Enable /
Disable
Port Priority lower the #,
higher the
priority
Increases chance of
becoming the Root
Bridge
Root Bridge
Bridge, if BPDU is
not received
change in state
Enable or disable
this LAN segment
Increases chance of
become Root Port
Table 5-1. User-selective STA parameters
Avoid, if the switch is
used in workgroup level
of a large network
Never set greater than
Max. Age Time
Avoid low number for
unnecessary reset of
Root Bridge
Max. Age ??2 x
(Forward Delay - 1)
Max. Age?? 2 x (Hello
Time + 1)
Disable a port for
security or problem
isolation
Port Trunking
Port trunking is used to combine a number of ports together to make
a single high-bandwidth data pipeline. The participating parts are
called members of a trunk group, with one port designated as the
anchor of the group. Since all members of the trunk group must be
configured to operate in the same manner, all settings changes made
to the anchor port are applied to all members of the trunk group.
40 Switch Management Concepts
Page 55

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
200 Mbps
200 Mbps
10/100 Mbps Hub
Workstation
Server #2
10/100 Mbps Backbone Switch
10 Mbps
100 MBps
10 Mbps
10 Mbps
100 Mbps
100 MbpsPCPCPCPCPCPC
PCPCPC
100 Mbps
Workstation
Workstation
100 Mbps
100 Mbps
Thus, when configuring the ports in a trunk group, you only need to
configure the anchor port.
The Switch supports 3 trunk groups, which may include from 2 to 8
switch ports each, except for the third trunk group which consists of
the 2 ports of the Slot 1, 100BASE-TX or 100BASE-FX front-panel
module. The anchor port for the first group is preset as port 5, the
anchor port for the second group is port 13 and the anchor port for
the third group is the first port (1x) on the 2-port modu le.
15x
17x
19x
21x7x
11x
Uplink
Slot2Sio1 Sio2Sio3
Power
Slot1
Slot1
Uplink
2x 4x 6x5x8x
13x
3x1x
18x
20x
14x
16x
22x
800 Mbps
Port-Trunking Uplink
Server #1
10x9x12x
TEG-S224M (SWITCH)
Giga1Giga2 Slot2 Sio1Sio2 Sio3
Console
Slot3
Power
Slot1
Uplink
3x1x
2x 4x 6x5x8x
Slot1
10x9x12x
15x
17x
19x7x
11x
13x
18x
20x
14x
16x
100 Mbps
10/100 Mbps Hub
10 Mbps 10 Mbps 100 Mbps
10/100 Mbps Hub
10 Mbps
Figure 5-3. Port trunking example
The switch treats all ports in a trunk group as a single port. As such,
trunk ports will not be blocked by Spanning Tree (unless a redundant
link with higher STP priority is present).
Data transmitted to a specific host (destination address) will always
be transmitted over the same port in a trunk group. This allows
Switch Management Concepts 41
Page 56

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
packets in a data stream to arrive in the same order they were sent.
A trunk connection can be made with any other switch that
maintains host-to-host data streams over a single trunk port. A
trunk connection cannot be made with switches that perform loadbalancing on a per -packet basis.
VLAN
VLANs are a collection of switch ports grouped together in a secure,
autonomous broadcast and multicast domain. VLANs allow a
network to be segmented in order to reduce the size of broadcast
domains. All Ethernet packets (unicast, broadcast, multicast,
unknown, etc.) entering a VLAN will only be forwarded to the ports
that are members of that VLAN.
Another benefit of VLANs is that you can change the network
topology without physically moving stations or changing cable
connections. Stations can be “moved” simply by changing VLAN
settings from one VLAN (the sales VLAN, for example) to another
VLAN (the marketing VLAN). This allows VLANs to accommodate
network moves, changes, and additions with the utmost flexibility.
VLANs can also provide a level of security to your network. Portbased VLANs allow you to configure ports to not send or receive
packets outside of the VLAN.
The untagging feature of IEEE 802.1Q VLANs allow VLANs to work
with legacy switches and NICs that don’t recognize VLAN tags in
packet headers. The tagging feature allows VLANs to span multiple
802.1Q-compliant switches through a single physical connection and
allows Spanning Tree to be enabled on all ports and work normally.
42 Switch Management Concepts
Page 57

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
The Switch supports up to 96 IEEE 802.1Q (port-based) VLANs. Portbased VLANs limit traffic that flows into and out of switch ports.
Thus, all devices connected to a port are members of the VLAN(s) the
port belongs to, whether there is a single computer directly connected
to a switch, or an entire department.
On port-based VLANs, NICs do not need to be able to identify 802.1Q
tags in packet headers. NICs send and receive normal Ethernet
packets. If the packet’s destination lies on the same segment,
communications take place using normal Ethernet protocols. Even
though this is always the case, when the destination for a packet lies
on another switch port, VLAN considerations come into play to decide
if the packet gets dropped by the switch or delivered.
There are two key components to understanding IEEE 802.1Q
VLANs; Port VLAN ID numbers (PVID) and VLAN ID numbers
(VID). Both variables are assigned to a switch port, but there are
important differences between them. A user can only assign one
PVID to each switch port. The PVID defines which VLAN a switch
will forward packets from the connected segment on, when packets
need to be forwarded to another switch port or somewhere else on the
network. On the other hand, a user can define a port as a member of
multiple VLANs (VIDs), allowing the segment connected to it to
receive packets from many VLANs on the network. These two
variables control a port’s ability to transmit and receive VLAN
traffic, and the difference between them provides network
segmentation, while still allowing resources to be shared across more
than one VLAN.
VLAN Segmentation
Take for example a packet that is transmitted by a machine on Port
1 that is a member of VLAN 2 and has the Port VLAN ID number 2
(PVID=2). If the destination lies on another port (found through a
normal forwarding table lookup), the switch then looks to see if the
Switch Management Concepts 43
Page 58

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Port
VIDs=1
Network Server
Workstation
VLAN1
VLAN2
VLAN3
other port (Port 10) is a member of VLAN 2 (and can therefore
receive VLAN 2 packets). If port 10 is not a member of VLAN 2, then
the packet will be dropped by the switch and will not reach it’s
destination. If Port 10 is a member of VLAN 2, the packet will go
through. This selective forwarding feature based on VLAN criteria is
how VLANs segment networks. The key point being that Port 1 will
only transmit on VLAN 2, because it’s Port VLAN ID number is 2
(PVID=2).
Sharing Resources Across VLANs
Network resources such as printers and servers however, can be
shared across VLANs. This is achieved by setting up overlapping
VLANs as shown in the diagram below.
In the above example, there are three different VLANs and each port
can transmit packets on one of them according to their Port VLAN
ID (PVID). However, a port can receive packets on all VLANs (VID)
that it belongs to. The assignments are as follows:
44 Switch Management Concepts
Port
VIDs=3
Workstations
Port
VIDs=2
Graphics
Figure 5-4. Example of typical VLAN configuration
Page 59

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Transmit on VLAN # Member of VLAN #
Port PVID VID Ports
Port 1 1 1 1,2,3,7
Port 2 1
Port 3 1
Port 7 3 3 1,2,3,7,11,1
2
Port 11 2 2 11,12,7
Port 12 2
Table 5-2. Example of possible VLAN assignments
The server attached to Port 7 is shared by VLAN 1 and VLAN 2
because Port 7 is a mem ber of both VLANs (it is listed as a member
of VID 1 and 2). Since it can receive packets from both VLANs, all
ports can successfully send packets to it to be printed. Ports 1, 2 and
3 send these packets on VLAN 1 (their PVID=1), and Ports 11 and 11
send these packets on VLAN 2 (PVID=2). The third VLAN (PVID=3)
is used by the server to transmit files that had been requested on
VLAN 1 or 2 back to the computers. All computers that use the
server will receive transmissions from it since they are all located on
ports which are members of VLAN 3 (VID=3).
VLANs Spanning Multiple Switches
VLANs can span multiple switches as well as your entire network.
Two considerations to keep in mind while building VLANs of this sort
are whether the switches are IEEE 802.1Q-compliant and whether
VLAN packets should be tagged or untagged.
Definitions of relevant terms are as follows:
? ?Tagging The act of putting 802.1Q VLAN information into the
header of a packet. Ports with tagging enabled will put the VID
Switch Management Concepts 45
Page 60

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
number, priority, and other VLAN information into all packets
that flow into and out it. If a packet has previously been tagged,
the port will not alter the packet, thus keeping the VLAN
information intact. Tagging is used to send packets from one
802.1Q-compliant device to another.
? ?Untagging The act of stripping 802.1Q VLAN information out of
the packet header. Ports with untagging enabled will take all
VLAN information out of all packets that flow into and out of a
port. If the packet doesn’t have a VLAN tag, the port will not alter
the packet, thus keeping the packet free of VLAN information.
Untagging is used to send packets from an 802.1Q-compliant
switch to a non -compliant device.
? ?Ingress port A port on a switch where packets are flowing into
the switch and VLAN decisions must be made. Basically, the
switch examines VLAN information in the packet header (if
present) and decides whether to forward the packet. If the packet
is tagged with VLAN information, the ingress port will first
determine if the ingress port itself is a member of the tagged
VLAN and can thus receive the packet (if the Ingress Filter is
enabled), and then it decides if the destination port is a member of
the VLAN. Assuming both ports are members of the tagged
VLAN, the packet will be forwarded. If the packet doesn’t have
VLAN information in its header (is untagged), the ingress port
first determines if the ingress port itself can receive the packet (if
the Ingress Filter is enabled), will tag it with its own PVID (if it
defined as a tagging port), and check to see if the destination port
is on the same VLAN as its own PVID and can thus receive the
packet. If Ingress filtering is disabled and the destination port is a
member of the VLAN used by the ingress port, the packet will be
forwarded. If the ingress port is an untagging port, it will only
check the filter condition --if the filter condition is enabled-- before
forwarding the packet.
? ?Egress port A port on a switch where packets are flowing out of
the switch, either to another switch or to an end station, and
tagging decisions must be made. If an egress port is connected to
46 Switch Management Concepts
Page 61

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
an 802.1Q-compliant switch, tagging should be enabled so the
other switch can take VLAN data into account when making
forwarding decisions. If an egress connection is to a non -compliant
switch or end-station, tags should be stripped so the (now normal
Ethernet) packet can be read by the receiving device.
VLANs Over 802.1Q-compliant Switches
When switches maintaining the same VLANs are 802.1Q-compliant,
it is possible to use tagging. Tagging puts 802.1Q VLAN information
into each packet header, enabling other 802.1Q-compliant switches
that receive the packet to know how to treat it. Upon receiving a
tagged packet, an 802.1Q-compliant switch can use the information
in the packet header to maintain the integrity of VLANs, carry out
priority forwarding, etc.
Data transmissions between 802.1Q-compliant switches take place as
shown below.
Switch Management Concepts 47
Page 62

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Server #2
1. Station in VLAN 2
transmits packet to
2. Ingress port (untagging)
forwards packet on VLAN 2
4. Ingress port (tagging) reads tag,
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
Server #1
5. Egress port (untagging)
TEG-S224M (SWITCH #2)
Console Giga1 Giga2 Slot2 Sio1Sio2Sio3Slot3
Power
Slot1
Uplink
3x1x
2x 4x 6x5x8x
10x9x12x
Slot1
11x
13x
14x
15x
17x
18x
16x
strips tag
19x7x
20x
forwards packet to server
3. Egress port (tagging)
TEG-S244M (SWITCH #1)
Console Giga1 Giga2 Slot2 Sio1 Sio2 Sio3Slot3
Power
Slot1
Slot1
PVID=1
tags packet with VID
Uplink
2x 4x 6x5x8x
11x
3x1x
10x9x12x
15x
13x
14x
16x
PVID=2
17x
19x7x
18x
20x
Server #2
VLAN 1 VLAN 2
Figure 5-5. Data transmissions between 802.1Q-compliant
Switches
In the above example, step 4 is the key element. Because the packet
has 802.1Q VLAN data encoded in its header, the ingress port can
make VLAN -based decisions about its delivery: whether server #2 is
attached to a port that is a member of VLAN 2 and, thus, should the
packet be delivered; the queuing priority to give to the packet, etc. It
can also perform these functions for VLAN 1 packets as well, and, in
fact, for any tagged packet it receives regardless of the VLAN
number.
If the ingress port in step 4 were connected to a non-802.1Qcompliant device and was thus receiving untagged packets, it would
48 Switch Management Concepts
Page 63

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
tag its own PVID onto the packet and use this information to make
forwarding decisions. As a result, the packets coming from the non compliant device would automatically be placed on the ingress ports
VLAN and could only communicate with other ports that are
members of this VLAN.
Broadcast Management
Broadcast transmissions, packets sent to every devices on the LAN,
are a vital part of any network. However, they can often cause
problems on the network and even network failure. For this reason
the Switch has a number of tools for managing broadcast packets on
your network.
Broadcast Storms
Broadcast storms are a common problem on today’s networks.
Basically, they consist of broadcast packets that flood and/or are
looped on a network causing noticeable performance degradation and
in extreme cases, network failure. Some of the causes of broadcast
storms are network loops, malfunctioning NICs, bad cable
connections, and applications or protocols that generate broadcast
traffic.
Broadcast storms can originate from any number of sources, and
once they are started, they can be self-perpetuating, and can even
multiply the number of broadcast packets on the network over time.
In the best case, network utilization will be high and bandwidth
limited until the hop counts for all broadcast packets have expired,
whereupon the packets will be discarded and the network will return
to normal. In the worst case, they will multiply, eventually using up
all the network bandwidth (although network applications will
usually crash long before this happens), and cause a network
meltdown.
Switch Management Concepts 49
Page 64

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Broadcast storms have long been a concern for network
administrators with routers traditionally being used to prevent their
occurrence, and if that failed, limit their scope. However, switches
are now able to limit broadcast domains better and cheaper than
routers. Also, many switches have broadcast sensors and filters built
into each port to further control broadcast storms—such as the
Switch you have purchased.
Port-based Broadcast Packet Filter
The Switch is equipped with sensors that count the number of
broadcast frames arriving at each port. When a certain level (rising
threshold) is reached, the sensors can initiate a broadcast filter
(rising action) which drops all broadcast packets arriving at the
affected port. This effectively partitions the broadcast packets from
the rest of the network, thereby limiting the effects of a broadcast
storm. The port-based Broadcast Storm Filter settings can be set by
the user. Please refer to the Configure Ports section of this manual
for more detailed explanations regarding port-based Broadcast Storm
filter settings.
MAC-based Broadcast Packet Filter
Broadcast domains can also be managed on the MAC level. In this
case, broadcast domains can be defined to include specific devices
(MAC addresses). To do this, simply enter the MAC addresses of the
computers and peripherals you wish to include in the broadcast
domain(s). Any unknown or broadcast packets generated within the
Mac-based broadcast domain will only be sent to the other members.
Other parts of the network are effectively shielded. Configuring MACbased broadcast domains is done in the VLANs and MAC-based
Broadcast Domains submenus of the Console or Web-based
management programs.
50 Switch Management Concepts
Page 65

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
6
6 U SING THE CONSOLE
INTERFACE
Your Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch supports a console
management interface that allows you to set up and control your
Switch, either with an ordinary terminal (or terminal emulator), or
over the network using the TCP/IP TELNET protocol. You can use
this facility to perform many basic network management functions.
In addition, the console program will allow you to set up the Switch
for management using an SNMP-based network management
system. This chapter describes how to use the console interface to
access the Switch, change its settings, and monitor its operation.
Connecting to the Switch
You can use the console interface by connecting the Switch to a
VT100-compatible terminal or a computer running an ordinary
terminal emulator program (e.g., the terminal program included with
the Windows operating system ) using an RS-232C serial cable. Your
terminal parameters will need to be set to:
? ?VT-100/ANSI compatible
? ?Arrow keys enabled
Using the Console Interface 51
Page 66

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?9,600 baud
? ?8 data bits
? ?No parity
? ?One stop bit
You can also access the same functions over a Telnet interface. Once
you have set an IP address for your Switch, you can use a Telnet
program (in a VT-100 compatible terminal mode) to access and
control the Switch. All of the screens are for the most part identical,
whether accessed from the console port or from a Telnet interface.
Console Usage Conventions
The console interface makes use of the following conventions:
1. Items in <angle brackets> can be toggled on or off using the
space bar.
2. Items in [square brackets] can be changed by typing in a new
value. You can use the backspace and delete keys to erase
characters behind and in front of the cursor.
3. The up and down arrow keys, the left and right arrow keys,
the Tab key and the Backspace key, can be used to move
between selected items. It is recommended that you use the tab
key and backspace key for moving around the console.
4. Items in UPPERCASE are commands. Moving the selection to
a command and pressing Enter will execute that command,
e.g., SAVE or EXIT.
Please note that the command APPLY only applies for the current
session. Use Save Changes from the main menu for permanent
52 Using the Console Interface
Page 67

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
changes. An asterisk “*” indicates a change has been made but won’t
take effect until the Switch has been rebooted.
First Time Connecting To The Switch
The Switch supports user-based security that can allow you to
prevent unauthorized users from accessing the Switch or changing
its settings. This section tells how to log onto the Switch.
Note: The passwords used to access the Switch are case sensitive;
therefore, “S” is not the same as “s.”
When you first connect to the Switch, you will be presented with
the first login screen (shown below). Press Ctrl+R (hold down the
Ctrl key, press the R key, and release both keys) to call up the
screen, if the initial login screen does not appear. Also Ctrl+R can
be used at any time to refresh the screen.
Figure 6-1. Initial Screen, first time connecting to the Switch
Note: There is no initial username or password. Leave the username
and password fields blank.
Using the Console Interface 53
Page 68

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Press <Enter> or <Return> in the username and password fields.
You will be given access to the main menu shown below:
Figure 6-2. Main Menu
The first user automatically gets Administrator privileges (See Table
6-1). It is recommended to create at least one Administrator -level
user for the Switch.
User Accounts Management
From the screen above, move the cursor to the User Accounts
Management menu and press Enter, then the Users Accounts
Management menu appears.
1. Choose Create/Modify User Accounts from the User
Accounts Management menu and the Add/Modify User
Accounts menu appears.
2. Enter the new user name, assign an initial password, and then
confirm the new password. Determine whether the new user
should have Administrator or Normal User privileges. (Use
the space bar to toggle between the two options).
3. Press APPLY to let the user addition take effect.
54 Using the Console Interface
Page 69

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
4. Press Esc. to return to the previous screen or Ctrl+T to go to the
root screen.
5. To see a listing of all user accounts and access levels, press Esc.
Then choose View/Delete User Accounts. The View/Delete
User Accounts screen appears.
Administrator and Normal User Privileges
There are two levels of user privileges: Administrator and Normal
User. Some menu selections available to users with Administrator
privileges may not be available to Normal Users. The main menus
shown are the menus for the two types of users:
The following table summarizes Administrator and Normal User
privileges:
Menu Administrator Normal User
Configuration Yes Yes, view only.
Privilege
Network Monitoring Yes Yes, view only.
Community Strings and Trap Stations Yes Yes, view only.
Update Firmware and Configuration
Files
User Accounts Management
Create/Modify User Accounts Yes Yes, view only.
View/ Delete User Accounts Yes Yes, view only.
System Utilities Yes Yes, (Ping Test);
Factory Reset Yes No
Restart System Yes No
Using the Console Interface 55
Yes Yes, view only.
view only for the
rest.
Page 70

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Table 6-1. Administrator and Normal User Privileges
After establishing a User Account with Administrator-level
privileges, press Esc. twice. Then choose the Save Changes menu
(see below). Pressing any key will return to the main menu. You are
now ready to operate the Switch.
Save Changes
The Switch has two levels of memory normal RAM and non -volatile
or NV-RAM. Settings need to be changed in all screens by pressing
Ctrl + S. When this is done, the settings will be immediately applied
to the switching software in RAM, and will immediately take effect.
Some settings, though, require you to restart the Switch before they
will take effect. Restarting the Switch will erase all settings in RAM
and reload them from the NV-RAM. Thus, it is necessary to save all
settings to the NV-RAM before restarting the Switch.
In order to retain any modifications made in the current session, it is
necessary to choose Save Changes from the main menu. The
following screen will appear to indicate your new settings have been
processed:
Figure 6-3. Save Changes screen
56 Using the Console Interface
Page 71

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
After the settings have been saved to NV-RAM, they will become the
default settings for the Switch, and they will be used every time it is
powered on, reset or rebooted. The only exception to this is a factory
reset, which will clear all settings and restore them to their initial
values listed in Appendix D, which were present when the Switch
was purchased.
Login On The Switch Console By
Registered Users
To log in once you have created a register ed user,
1. Type in your username and press Enter.
2. Type in your password and press Enter.
3. The main menu screen will be displayed based on your
Administrator or Normal User access level or privilege.
Create/Modify User Accounts
To add or change your user password:
1. Choose Users Accounts Management from the main menu.
The following User Accounts Management menu appears:
Using the Console Interface 57
Page 72

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Figure 6-4. User Accounts Management menu
2. Choose Create/Modify User Accounts. The following screen
appears:
Figure 6-5. Add/Modify User Accounts screen
3. Type in your Username and press Enter.
58 Using the Console Interface
Page 73

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
4. If you are an old user, type in the Old Password and press
Enter.
5. Type in the New Password you have chosen, and press
Enter. Type in the same new password in the following field to
verify that you have not mistyped it.
6. Determine whether the new user should have Normal User or
Administrator privileges.
7. Choose the APPLY command to let the password change take
effect.
This method can also be used by an Administrator-level user to
change another user’s password.
View/Delete User Accounts
Access to the console, whether using the console port or via Telnet, is
controlled using a user name and password. Up to three of these user
names can be defined. The console interface will not let you delete the
current logged-in user, however, in order to prevent accidentally
deleting all of the users with Administrator privilege.
Only users with the Administrator privilege can delete users.
To view a user account:
Choose View/Delete User Accounts from the User Accounts
Management menu. The following screen appears:
Using the Console Interface 59
Page 74

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Figure 6-6. View/Delete User Accounts screen
To delete your user password:
1. Toggle the Delete field of the user you wish to remove to Yes.
2. Press APPLY to let the user deletion take effect.
Setting Up The Switch
This section will help prepare the Switch user by describing the
System Configuration, Update Firmware and Configuration
Files, Save Changes, and System Utilities menus and their
respective sub-menus.
System Configuration
Choose System Configuration to access the first item of the
Switch’s main menu. The following menu appears:
60 Using the Console Interface
Page 75

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Figure 6-7. System Configuration menu
You will need to change some settings to allow you to be able to
manage the Switch from an SNMP-based Network Management
System such as SNMP v1 or to be able to access the Switch using the
Telnet protocol. See the next chapter for Web-based network
management information.
Configure IP Address
The Switch needs to have a TCP/IP address assigned to it so that an
in-band network management system or Telnet client can find it on
the network. The IP Address Configuration screen allows you to
change the settings for the two different interfaces used on the
Switch: the Ethernet interface used for in-band communication, and
the SLIP interface used over the console port for out-of-band
communication.
Choose Configure IP Address to access the first item on the
System Configuration menu. The following screen appears:
Using the Console Interface 61
Page 76

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Figure 6-8. IP Address Configuration screen
The fields listed under the Current Settings heading are those that
are presently being used by the Switch. Those fields listed under the
Restart Settings heading will be used after the Switch has been reset.
Fields that can be set include:
? ?BOOTP Service Determines whether the Switch should send
out a BOOTP broadcast request when it is powered up. The
BOOTP protocol allows IP addresses, network masks, and
default gateways to be assigned on a central BOOTP server ; if
this option is set the Switch will first look for a BOOTP server
to provide it with this information before using the supplied
settings.
? ?IP Address Determines the IP address used by the Switch for
receiving SNMP and Telnet communications. These fields
should be of the form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where each xxx is a
number (represented in decimal) between 0 and 255. This
address should be a unique address on a network assigned to
you by the central Internet authorities. The same IP address is
shared by both the SLIP and Ethernet network interfaces.
62 Using the Console Interface
Page 77

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?Subnet Mask Bitmask that determines the extent of the
subnet that the Switch is on. Should be of the form
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where each xxx is a number (represented in
decimal) between 0 and 255. If no subnetting is being done, the
value should be 255.0.0.0 for a Class A network, 255.255.0.0
for a Class B network, and 255.255.255.0 for a Class C
network.
? ?Default Gateway IP address that determines where frames
with a destination outside the current subnet should be sent.
This is usually the address of a router or a host acting as an IP
gateway. If your network is not part of an internetwork, or you
do not want the Switch to be accessible outside your local
network, you can leave this field blank.
Configure Console
You can use the Console Options screen to choose whether to use
the Switch’s RS-232C serial port for console management or for outof-band TCP/IP communications using SLIP, and to set the bit rate
used for SLIP communications. Note that the TEG-S224M has an
RS-232C serial port but the TEG-S224S does not.
Choose Configure Console to access the last item on the System
Configuration menu. The following screen appears:
Using the Console Interface 63
Page 78

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Figure 6-9. Console Options screen
The following fields can be set:
Settings on Restart:
? ?Console Timeout This setting for the restart of the console
is 15 mins, 30 mins, 45 mins, 60 mins, or Never.
? ?Serial Port Determines whether the serial port should be
used for out-of-band (SLIP) management or for console
management, starting from the next time the Switch is
restarted. In this field, you can toggle between SLIP or console
port type settings.
? ?Baud Rate Determines the serial port bit rate that will be
used the next time the Switch is restarted. Applies only when
the serial port is being used for out-of-band (SLIP)
management; it does not apply when the port is used for the
console port. Available speeds are 2400, 9600, 19,200 and
38,400 bits per second. The default setting in this Switch
version is 9600.
64 Using the Console Interface
Page 79

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
The top of the screen displays the current settings for Console
Timeout and Serial Port as well as the Baud Rate,
Character Size, and Stop Bit for Out of Band and Console
settings, respectively.
Configure Switch Stack
The Switch Stack Configuration screen shows various pieces of
information about your Switch, and allows you to set the System
Name, System Location, and System Contact. These settings
can be retrieved from the Switch using SNMP requests, allowing
these settings to be used for network management purposes.
Choose Configure Switch Stack to access the second item on the
System Configuration menu. The following screen appears:
Figure 6-10. Switch Stack Configuration screen
The fields you can set are:
? ?System Name Corresponds to the SNMP MIB II variable
system.sysName, and is used to give a name to the Switch
for administrative purposes. The Switch’s fully qualified
Using the Console Interface 65
Page 80

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
domain name is often used, provided a name has been
assigned.
? ?System Location Corresponds to the SNMP MIB II variable
system.sysLocation, and is used to indicate the
physical location of the Switch for administrative purposes.
? ?System Contact Corresponds to the SNMP MIB II variable
sysContact, and is used to give the name and contact
information for the person responsible for administering the
Switch.
Information of Individual Switch Unit
This screen allows you to view information for each Switch in your
stack, including the Module, Type, and Hardware Version. Press
Information of Individual Switch Unit on the Switch Stack
Configuration screen to access the Information of Individual
Switch Unit screen:
Figure 6-11. Information of Individual Switch Unit screen
Use the space bar to select the desired Switch in your stack.
66 Using the Console Interfa ce
Page 81

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Advance Settings
The Configure Advanced Switch Features screen allows you to
set an expiration time for MAC address entries and enable or disable
auto-partitioning on all ports. Press ADVANCE SETTINGS on the
Switch Stack Configuration screen to access the Configure
Advanced Switch Features screen:
Figure 6-12. Configure Advanced Switch Features screen
The fields you can set are:
? ?Port Auto-Partition Capability on All Ports When this
function is enabled, if too many consecutive collisions occur on an
individual port, the port will be blocked off until a good packet is
seen on the wire. If a port is partitioned, the Switch can only
transmit data, not receive it.
? ?Head Of Line (HOL) Blocking Prevention Enables or
disables Head-Of-Line Blocking Prevention. Head-of Line blocking
occurs when a packet originating on Port 1, for instance, needs to
be forwarded to Ports 2 and 3. If Port 2 is occupied (causing the
Using the Console Interface 67
Page 82

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
packet to be held in memory until the port is free), the packet
destined for Port 3 will also be delayed, even though the port may
be free. Cumulatively, these delays can have a noticeable effect on
overall network performance. Enabling HOL Blocking Prevention
prevents Head-of-Line blocking from occurring, meaning that the
packet destined for Port 3 gets delivered immediately.
Configure Port
The port configuration screen allows you to change the port state in
the case when you would like to partition a port due to excessive
collision, or for observation, device repair, or security reasons. Great
caution, however, must be observed when partitioning a port; you
should make sure that the partitioned port is not being used as the
port to control or monitor the condition of other devices.
Figure 6-13. Port Configuration screen
Items in the above window are defined as follows:
? ?Switch Specifies the Switch where the port is being
configured.
68 Using the Console Interface
Page 83

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?Module Specifies the module where the port is being
configured.
? ?Port Specifies the port that will be configured.
? ?Port Type Specifies the speed and cable type of the selected
port.
? ?State Enables or Disables the port. This amounts to turning
the port on or off.
? ?Speed/Duplex Selects the desired Speed and Duplex settings
for the port. Possibilities include: Auto, 100M/Full,
100M/Half, 10M/Full, or 10M/Half. If a Gigabit module is
being used, 1000M/Full will be displayed in this field.
Choosing Auto enables NWay auto-configuration on the port.
? ?Flow Ctrl Toggles flow control On or Off. It is useful during
periods of heavy network activity when the Switch’s buffers
can receive too much traffic and fill up faster than the Switch
can forward the information. In such cases, the Switch will
intervene and tell the transmitting device to pause to allow the
information in the port buffer to be sent. Confirm that Flow
Control is in force by checking the Status field.
? ?Priority Selects Normal, High or Low. The Switch has two
packet queues where incoming packets wait to be processed for
forwarding; a high priority and low priority queue. The high
priority queue should only be used for data in which latency
can have adverse affects on the function of an application, such
as video or audio data, where latency can produce distorted
sounds and images. Packets in the low priority queue will not
be processed unless the High priority queue is empty. Setting
the port priority to High will deliver all packets arriving at the
port to the high priority queue, a Low setting will send them
all to the low priority queue. The Normal setting causes the
port to examine the packet for an IEEE 802.1p/q priority tag. If
no tag exists, the packet will be sent to the low priority queue.
If the priority tag field in the packet header contains a value of
Using the Console Interface 69
Page 84

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
0-3, the packet will be placed in the low priority queue; a value
of 4-7 causes the packet to be placed in the high priority queue.
? ?Port Lock When Enabled, automatic learning for all stations
connected to this port will stop and entries in the Forwarding
Table for all devices residing on this port will age out. The only
traffic this port will allow is traffic from machines whose MAC
address is manually entered in the Static Forwarding Table.
? ?Broadcast Storm Rising Action This setting will be
activated when a Broadcast Storm Rising Threshold is met.
When triggered, the port can be configured to Do Nothing,
Blocking or Blocking-Trap. The Do Nothing setting causes the
switch to operate normally, in other words, ignore the
broadcast storm condition. The Blocking setting causes the
port to drop all broadcast frames, thus isolating the broadcast
storm. Blocking-Trap performs the same action as Blocking,
except it also sends a trap to the designated Trap Recipient
informing them of the situation. For more information on
broadcast storms, please refer to the previous chapter.
? ?Broadcast Storm Falling Action This setting will be
activated when the Broadcast Storm Rising Threshold and
then the Broadcast Storm Falling Threshold are each met.
This setting can be configured to Do Nothing, Forwarding or
Forwarding-Trap. The Do Nothing setting causes the switch
to operate normally, that is, to ignore the situation. If the port
had met the Broadcast Storm Rising Action criteria and
started Blocking broadcast packets, it will continue doing so.
The Forwarding setting causes the port to begin forwarding
broadcast frames, thus removing the Blocking state imposed
by the Broadcast Storm Rising Action. Forwarding-Trap
performs the same action as Forwarding, except it also sends a
trap to the designated Trap Recipient informing them of the
situation.
70 Using the Console Interface
Page 85

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Press CTRL+S to let the changes take effect. If you wish these
changes to be the default for the switch, return to the main menu
and choose Save Changes.
STP Port State (whether the Spanning Tree Protocol is enabled or
disabled on this port) and Status reflect the current conditions of the
port. They are read-only fields and cannot be changed.
Configure Trunk
Ports on the Switch can be grouped together in a single logical port
called a trunk. This is discussed in detail in the Port Trunking
section of the “Switch Management Concepts” chapter of this manual.
To set up a trunk group, choose Configure Trunk on the System
Configuration menu. The following screen appears:
Figure 6-14. Port Trunk screen
The fields you can set are:
? ?Anchor There are either two or three listings representing the
anchor port for each of the three trunk groups available on the
Switch (the third listing will only be displayed if an optional two-
Using the Console Interface 71
Page 86

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
port plug-in module is being used). The anchor port must fall
within the port range and be included as a member port.
? ?Name Enter the desired group name. In the example pictured
above the first trunk group designates a trunk connection between
a Switch on the 6th floor and this one on the 7th floor
? ?Members Select between 2 to 8 ports in the first two entries for
this field. The number of ports defined here start from the anchor
port. Thus, in the example pictured above containing 4 ports in
the first trunk, the ports in the trunk group will include ports
(anchor), 5, 6, 8, and 11. The third entry (used for 2-port frontpanel modules) has a permanent setting of 2 ports.
? ?State Enabled, Disabled or Clear. Be careful when clearing
trunk groups as the connections will return to normal operation
and may cause signal loops.
Port Range is a read-only field which lists the possible ports in a
selected trunk.
Press APPLY to let the changes take effect.
Configure Port Mirroring
The Switch allows you to copy frames transmitted and received on a
port and redirect the copies to another port. You can attach a
monitoring device to the mirrored port, such as a sniffer or an RMON
probe, to view details about the packets passing through the first
port. This is useful for network monitoring and troubleshooting
purposes.
Choose Configure Port Mirroring on the System Configuration
menu to access the following screen:
72 Using the Console Interface
Page 87

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Figure 6-15. Port Mirroring Configuration screen
To configure a mirror port, select the Switch, Module, and Port
from where you want to copy frames in the Source fields. Then
select the Switch, Module, and Port which receive the copies from
the source port in the Destination fields. The destination (or target)
port is where you will connect a monitoring/troubleshooting device
such as a sniffer or an RMON probe.
Note: You cannot mirror a fast port onto a slower port. For example,
if you try to mirror the traffic from a 100 Mbps port onto a 10
Mbps port, this can cause throughput problems. The port you
are copying frames from should always support an equal or
lower speed than the port to which you are sending the
copies. Also, the target port cannot be a member of a trunk
group.
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol
The Spanning Tree Algorithm Parameters can be used for creating
alternative paths in your network. The Protocol Parameters allow
you to change the behind the scene parameters of the Spanning Tree
Algorithm at the bridge level. The parameters for this section have
Using the Console Interface 73
Page 88

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
been fully explained in the previous chapter. It is recommended that
you read this, as well as the introductory section in the same chapter
entitled Spanning Tree Algorithm, before changing any of the
parameters.
STP Parameter Settings
To change the Protocol Parameters:
1. Choose Configure Spanning Tree Protocol from the
System Configuration menu. The following Configure
Spanning Tree Protocol menu will be displayed:
Figure 6-16. Configure Spanning Tree Protocol menu
2. Choose STP Parameter Setting to access the following
screen:
74 Using the Console Interface
Page 89

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Figure 6-17. STP Parameter Setting screen
3. Change the Disabled setting to Enabled in the Spanning
Tree Protocol field.
4. Enter the Bridge Max Age in the Max Age(6-40 sec) field.
5. Enter the Bridge Hello Time in the Hello Time(1-10 sec)
field.
6. Enter the Bridge Forward Delay time in the Forward
Delay(4-30 sec) field.
7. Enter the Bridge Priority in the Bridge Priority(0-65535)
field.
The information on the screen is described as follows:
? ?Spanning Tree Protocol Select Enabled to implement the
Spanning Tree Protocol.
? ?Time Since Topology Change(Sec) Read-only object
displays the last time changes were made to the network
topology. These changes usually occur when backup paths
are activated due to primary path failures.
Using the Console Interface 75
Page 90

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?Topology Change Count Read-only object displays the
number of times (since the current management session
with the device was started) changes were made to the
network topology. Changes usually occur on the network
when backup paths are activated.
? ?Designated Root Read-only object displays the MAC
(Ethernet) addr ess of the bridge/switch on the network that
has been chosen as the STP root.
? ?Root Cost Read-only object displays the cost for the path
between the switch and the root bridge. If the switch is the
root bridge, then the root cost is zero.
? ?Root port Read-only object identifies the port (on the
bridge) that offers the least path cost from the bridge to the
root bridge. In the event of a network loop, data packets will
pass through the root port.
? ?Max Age(Sec) Read-only object indicates the maximum age
of STP information learned from the network (on any port)
before it is discarded.
? ?Forward Delay(Sec) Read-only object indicates how fast
any port on the bridge can change its spanning state when
moving towards the forwarding state. The value determines
how long the port stays in each of the listening and learning
states, which precede the forwarding state.
? ?Hold Time(Sec) Read-only object displays the time interval
during which no more than two configuration BPDUs shall be
transmitted by the bridge.
? ?Root Priority Read-only object displays the priority
number of the root bridge of the Spanning Tree. The value is
used in conjunction with the bridge MAC address to set the
bridge ID, which in turn is used when determining the root
bridge of a multibridged network. The root bridge is
responsible for processing data packets when network loops
76 Using the Console Interface
Page 91

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
occur. The smaller the number set, the higher the bridge
priority is. The higher the bridge priority, the more chance
the bridge has of becoming the root bridge. A bridge priority
ranges from 0 to 65535, with 0 being the highest priority.
? ?Max Age(6-40 Sec) Maximum Age is a read-write object
that can be set from 6 to 40 seconds. At the end of the
Maximum Age, if a BPDU has still not been received from
the Root ridge, your Switch will start sending its own BPDU
to all other switches for permission to become the Root
Bridge. If it turns out that your Switch has the lowest
Bridge Identifier, it will become the Root Bridge.
? ?Hello Time(1-10 Sec) Hello Time is a read-write object
that can be set from 1 to 10 seconds. This is the interval
between two transmissions of BPDU packets sent by the
Root Bridge to tell all other switches that it is indeed the
Root Bridge. If you set a Hello Time for your Switch, and it
is not the Root Bridge, the set Hello Time will be used if and
when your Switch becomes the Root Bridge.
? ?Forward Delay(4-30 Sec) The Forward Delay is a read-
write object that can be set from 4 to 30 seconds. This is the
time any port on the Switch spends in the listening state
while moving from the blocking state to the forwarding
state.
? ?Bridge Priority(0-65535) A Bridge Priority is a read-write
object that can be set from 0 to 65535. This is the priority
number of the bridge. The value is used in conjunction with
the bridge MAC address to set the bridge ID, which in turn
is used when determining the root bridge of a multibridged
network. The root bridge is responsible for processing data
packets when network loops occur. The smaller the number
set, the higher the bridge priority is. The higher the bridge
priority, the more chance the bridge has of becoming the root
bridge. Zero is the highest priority.
Using the Console Interface 77
Page 92

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
STP Custom Settings
To change the parameters on individual ports:
1. Choose Configure Spanning Tree Protocol from the
System Configuration menu.
2. Choose STP Custom Settings from the Configure
Spanning Tree Protocol menu. The following screen
appears:
Figure 6-18. STP Custom Settings screen
Items in the above window are described as follows:
? ?STP State Sets the Spanning Tree Protocol on a particular
port to Enabled or Disabled.
? ?Cost Defines the cost for the connection.
? ?Priority Port Priority is a read-write object that can be set
from 0 to 255. This is the priority number of the port. The
higher the port priority, the more chance the bridge has of
becoming the root port. Zero is the highest priority.
78 Using the Console Interface
Page 93

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Note: If a port is a member of a trunk group but is not the
anchor, the items shown in the above table will be readonly and the values will be the same as those for the
anchor port.
Configure Filtering and Forwarding Table
When a packet hits the Switch, it looks in the filtering and
forwarding tables to decide what to do with the packet; either to filter
it off the network, or to forward it through the port on which its
destination lies.
Dynamic Filtering and Static Filtering are among the two important
features of the Custom Filtering Table. They are defined here
briefly as follows. Dynamic Filtering is defined when a dynamic entry
is created by the Learning Process as a result of observation of
network traffic in the Filtering Database. Static Filtering is defined
as static entries that may be added and removed from the Filtering
Database by the user. They are not automatically removed by any
timeout mechanism.
The Configure Filtering and Forwarding table screen allows
you to stop or start address learning, change the way the Switch
treats MAC address table entries, and select an age-out time of the
MAC address in the selected address table. This screen also permits
you to access three additional configuration screens from the menu at
the bottom of the window.
Choose Configure Filtering and Forwarding Table from the
System Configuration menu to access the following screen:
Using the Console Interface 79
Page 94

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Figure 6-19. Configure Filtering and Forwarding table screen
The following fields at the top of the screen can be set:
? ?Lock Address Table(STOPs Learning) Mostly used for
security purposes, when the forwarding table is locked the Switch
will no longer learn the MAC addresses for new hosts. If your
network configuration doesn’t change, locking the forwarding
table helps keep intruders off your network since any packet
coming from an unknown source address will be dropped by the
Switch.
? ?Address Table Lookup Mode This setting allows the user to
tailor the MAC address look up procedure. Choices are Level 0,
Level 1, Level 2, Level 3, Level 4, Level 5, Level, 6, Level 7. The
higher the level, the more MAC addresses can be learned by the
Switch. However, a side effect is that throughput will be degraded
the higher the level you select. This setting will take effect after
your system reboots.
? ?MAC Address Aging Enter the desired MAC address age-out
time in this field (10 to 9999 seconds).
80 Using the Console Interface
Page 95

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Please refer to the Packet Forwarding section of the “Switch
Management Concepts” chapter of this manual for more detailed
information.
Configure Static Forwarding Table Entry
The Static Forwarding Table displays a list of manually defined
static unicast MAC address entries.
To access the Static Forwarding Table Configuration screen,
choose Configure Filtering and Forwarding Table from the
System Configuration menu. Then select Configure Static
Forwarding Table Entry from the bottom of the Configure
Filtering and Forwarding table screen. The following screen
appears:
Figure 6-20. Static Forwarding Table Configuration screen
By mapping a MAC address to a destination port, the switch can
permanently forward traffic for a specified device through a specific
port, even after long periods of network inactivity or during times of
network congestion.
The following fields at the top of the screen can be set:
Using the Console Interface 81
Page 96

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
? ?Action Choose Add or Remove for each entry from the table.
? ?MAC Address Enter a MAC address in this field at the top of
the screen. This is the MAC address of the device that you are
creating a permanent forwarding address for. A total of ten
destination addresses per page will be seen at the bottom of the
screen. The Switch can hold up to 256 entries.
? ?Switch, Module, and Port The Switch, module, and port
number are entered in these fields at the top of the screen. The
Switch will always forward traffic to the specified device
through this port. The bottom of the screen will display each
corresponding destination address for these three items.
Status is a read-only field which lists the status of the static
forwarding table entry. It can be “in use” or “not apply.” “Not
apply” means that there is a static filter for the same MAC
address. Static filters always take precedence over static
forwarding entries. The Switch will automatically upgrade the
Status to “in use” once the static filter is removed.
Configure MAC Address Filtering
The Custom Filtering Table contains filtering information
configured into the Switch by (local or network) management
specifying destination addresses which are not allowed to be
forwarded. The Switch will check both the destination and source
MAC addresses on all packets.
To access the Custom Filtering Table, select Configure
Filtering and Forwarding Table from the System
Configuration menu. Then select Configure MAC Address
Filtering from the bottom of the Configure Filtering and
Forwarding table screen. The following screen appears:
82 Using the Console Interface
Page 97

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Figure 6-21. Custom Filtering Table screen
To make a change to the Custom Filtering Table, choose Add or
Remove in the Action field. Then enter the MAC Address and
press APPLY.
Configure Permanent Multicast Filtering
Multicast filtering allows you to block or forward traffic over each
port for one multicast group.
To access the Static Multicast Filtering Table Configuration
screen, select Configure Filtering and Forwarding Table from
the System Configuration menu. Then select Configure
Permanent Multicast Filtering from the bottom of the
Configure Filtering and Forwarding table screen. The following
screen appears:
Using the Console Interface 83
Page 98

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Figure 6-22. Static Multicast Filtering Table Configuration
screen
To make a change to the Static Multicast Filtering Table, choose
Add or Remove in the Action field. Then enter the MAC Address
and the member port numbers in the desired fields, for example
Master and Slave 1 if there are two Switches in your stack. Press
APPLY to put the changes into effect.
Configure IGMP
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) allows multicasting on
your network. When IP Multicast Filtering is enabled, the Switch
can intelligently forward (rather that broadcast) IGMP queries and
reports sent between devices connected to the Switch and an IGMP enabled device hosting IGMP on your network.
Basically, in these submenus you define whether the Switch can
intelligently forward IGMP packets, and you must also define which
802.1Q VLANs (if present) can send and receive IGMP and Multicast
packets.
84 Using the Console Interface
Page 99

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
To access the IGMP Configuration screen, select Configure
Filtering and Forwarding Table from the System
Configuration menu. Then select Configure IGMP from the
bottom of the Configure Filtering and Forwarding table screen.
The following screen appears:
Figure 6-23. IGMP Configuration screen
Items in the above window are defined as follows:
? ? IP Multicast Filtering Age-out Timer (30-9999) When this
timer expires and the switch has not observed (snooped) any
IGMP query packets asking whether any stations belong to any
Multicast groups, the switch itself will send out queries and
become the IGMP host on your network.
? ? IP Multicast Filtering (IGMP Snooping) This
enables/disables the switch to intelligently forward IGMP and
Multicast packets instead of broadcasting (flooding) them on all
ports. This setting also enables IGMP Snooping, which enables
the switch to read IGMP packets being forwarded through the
switch in order to obtain forwarding information from them
(learn which ports contain Multicast members).
Using the Console Interface 85
Page 100

Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
The bottom of this screen contains a command for VLAN settings
that leads to the IEEE 802.1q IGMP Configuration menu.
Highlight Configure 802.1Q IGMP and press Enter to access this
screen:
Figure 6-24. IEEE 802.1q IGMP Configuration screen
Choose Add/Remove IGMP Control Table from the screen above
to define up to 12 VLANs on the Switch which can send and receive
IGMP packets:
86 Using the Console Interface
 Loading...
Loading...