Page 1

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
quad-band GSM/GPRS
Data and Voice Modules
System Integration Manual
29.5 x 18.9 x 3.0 mm
www.u-blox.com
locate, communicate, accelerate
Abstract
This document describes the features and integration of the
LEON-G100/G200 quad-band GSM/GPRS data and voice modules.
The LEON-G100/G200 are complete and cost efficient solutions,
bringing full feature quad-band GSM/GPRS data and voice
transmission technology in a compact form factor.
Page 2
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3
Page 2 of 125
Document Information
Title
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
Subtitle
quad-band GSM/GPRS
Data and Voice Modules
Document type
System Integration Manual
Document number
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3
Document status
Preliminary
Document status information
Objective
Specification
This document contains target values. Revised and supplementary data will be published
later.
Advance
Information
This document contains data based on early testing. Revised and supplementary data will
be published later.
Preliminary
This document contains data from product verification. Revised and supplementary data
may be published later.
Released
This document contains the final product specification.
This document applies to the following products:
Name
Type number
Firmware version
PCN / IN
LEON-G100
LEON-G100-04S-00
LEON-G100-05S-00
LEON-G100-06S-00
LEON-G100-06S-01
LEON-G100-07S-00
LEON-G100-08S-00
LEON-G100-06A-00
LEON-G100-07A-00
07.40.00
07.50.00
07.60.00
07.60.02
07.70
07.83
07.60.00
07.70
GSM.G1-SW-10007
GSM.G1-SW-10008
GSM.G1-SW-10012
GSM.G1-SW-10013
GSM.G1-SW-12002
UBX-TN-13001
GSM.G1-SW-10012
GSM.G1-SW-12002
LEON-G100 ECALL
LEON-G100-71S-00
TBD
TBD
LEON-G200
LEON-G200-04S-00
LEON-G200-05S-00
LEON-G200-06S-00
LEON-G200-06S-01
07.40.00
07.50.00
07.60.00
07.60.02
GSM.G1-SW-10007
GSM.G1-SW-10008
GSM.G1-SW-10012
GSM.G1-SW-10013
This document and the use of any information contained therein, is subject to the acceptance of the u-blox terms and conditions. They
can be downloaded from www.u-blox.com.
u-blox makes no warranties based on the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this document and reserves the right to make
changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time without notice.
u-blox reserves all rights to this document and the information contained herein. Reproduction, use or disclosure to third parties without
express permission is strictly prohibited. Copyright © 2013, u-blox AG.
u-blox® is a registered trademark of u-blox Holding AG in the EU and other countries.
Trademark Notice
Microsoft and Windows are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other
countries. All other registered trademarks or trademarks mentioned in this document are property of their respective owners.
Page 3
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Preface
Page 3 of 125
Preface
u-blox Technical Documentation
As part of our commitment to customer support, u-blox maintains an extensive volume of technical
documentation for our products. In addition to our product-specific technical data sheets, the following manuals
are available to assist u-blox customers in product design and development.
AT Commands Manual: This document provides the description of the supported AT commands by the LEON
GSM/GPRS Voice and Data Modules to verify all implemented functionalities.
System Integration Manual: This Manual provides hardware design instructions and information on how to
set up production and final product tests.
Application Note: document provides general design instructions and information that applies to all u -blox
Wireless modules. See Section Related documents for a list of Application Notes related to your Wireless
Module.
How to use this Manual
The LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 System Integration Manual provides the necessary information to successfully
design in and configure these u-blox wireless modules.
This manual has a modular structure. It is not necessary to read it from the beginning to the end.
The following symbols are used to highlight important information within the manual:
An index finger points out key information pertaining to module integration and performance.
A warning symbol indicates actions that could negatively impact or damage the module.
Questions
If you have any questions about u-blox Wireless Integration, please:
Read this manual carefully.
Contact our information service on the homepage http://www.u-blox.com
Read the questions and answers on our FAQ database on the homepage http://www.u-blox.com
Technical Support
Worldwide Web
Our website (www.u-blox.com) is a rich pool of information. Product information, technical documents and
helpful FAQ can be accessed 24h a day.
By E-mail
Contact the nearest of the Technical Support offices by email. Use our service pool email addresses rather than
any personal email address of our staff. This makes sure that your request is processed as soon as possible. You
will find the contact details at the end of the document.
Helpful Information when Contacting Technical Support
When contacting Technical Support please have the following information ready:
Module type (e.g. LEON-G100) and firmware version
Module configuration
Clear description of your question or the problem
A short description of the application
Your complete contact details
Page 4
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Contents
Page 4 of 125
Contents
Preface ................................................................................................................................ 3
Contents .............................................................................................................................. 4
1 System description ....................................................................................................... 7
1.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................................. 7
1.2 Architecture .......................................................................................................................................... 8
1.2.1 Functional blocks ........................................................................................................................... 9
1.2.2 Hardware differences between LEON-G100 and LEON-G200 ...................................................... 10
1.3 Pin-out ............................................................................................................................................... 10
1.4 Operating modes ................................................................................................................................ 13
1.5 Power management ........................................................................................................................... 15
1.5.1 Power supply circuit overview ...................................................................................................... 15
1.5.2 Module supply (VCC) .................................................................................................................. 16
1.5.3 Current consumption profiles ...................................................................................................... 23
1.5.4 Battery charger (LEON-G200 only) ............................................................................................... 26
1.5.5 RTC Supply (V_BCKP) .................................................................................................................. 31
1.6 System functions ................................................................................................................................ 32
1.6.1 Module power on ....................................................................................................................... 32
1.6.2 Module power off ....................................................................................................................... 36
1.6.3 Module reset ............................................................................................................................... 37
1.6.4 Note: Tri-stated external signal .................................................................................................... 40
1.7 RF connection ..................................................................................................................................... 40
1.8 SIM interface ...................................................................................................................................... 41
1.8.1 SIM functionality ......................................................................................................................... 42
1.9 Serial Communication......................................................................................................................... 43
1.9.1 Asynchronous serial interface (UART)........................................................................................... 43
1.9.2 DDC (I2C) interface ...................................................................................................................... 55
1.10 Audio .............................................................................................................................................. 60
1.10.1 Analog Audio interface ............................................................................................................... 60
1.10.2 Digital Audio interface ................................................................................................................. 66
1.10.3 Voice-band processing system ..................................................................................................... 69
1.11 ADC input (LEON-G100 only) .......................................................................................................... 70
1.11.1 ADC Calibration .......................................................................................................................... 71
1.12 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) ............................................................................................. 73
1.12.1 LEON-G100-06x / LEON-G200-06S and subsequent versions ....................................................... 73
1.12.2 LEON-Gx00-04S and LEON-Gx00-05S versions ............................................................................ 75
1.13 Schematic for module integration ................................................................................................... 79
1.14 Approvals ........................................................................................................................................ 80
1.14.1 Compliance with FCC and IC Rules and Regulations .................................................................... 80
2 Design-In ..................................................................................................................... 83
Page 5
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Contents
Page 5 of 125
2.1 Design-in checklist .............................................................................................................................. 83
2.1.1 Schematic checklist ..................................................................................................................... 83
2.1.2 Layout checklist ........................................................................................................................... 83
2.1.3 Antenna checklist ........................................................................................................................ 84
2.2 Design Guidelines for Layout .............................................................................................................. 84
2.2.1 Layout guidelines per pin function ............................................................................................... 84
2.2.2 Footprint and paste mask ............................................................................................................ 90
2.2.3 Placement ................................................................................................................................... 92
2.3 Module thermal resistance .................................................................................................................. 92
2.4 Antenna guidelines ............................................................................................................................. 93
2.4.1 Antenna termination ................................................................................................................... 94
2.4.2 Antenna radiation ....................................................................................................................... 95
2.4.3 Antenna detection functionality .................................................................................................. 97
2.5 ESD Immunity Test Precautions ........................................................................................................... 99
2.5.1 General precautions .................................................................................................................. 100
2.5.2 Antenna interface precautions ................................................................................................... 102
2.5.3 Module interfaces precautions ................................................................................................... 103
3 Feature description .................................................................................................. 104
3.1 Firmware (upgrade) Over The Air (FOTA) (LEON-G200 only) .............................................................. 104
3.2 Firmware (upgrade) Over AT (FOAT) ................................................................................................. 104
3.2.1 Overview ................................................................................................................................... 104
3.2.2 FOAT procedure ........................................................................................................................ 104
3.3 Firewall ............................................................................................................................................. 104
3.4 TCP/IP ............................................................................................................................................... 104
3.4.1 Multiple IP addresses and sockets .............................................................................................. 104
3.5 FTP ................................................................................................................................................... 105
3.6 HTTP ................................................................................................................................................. 105
3.7 SMTP ................................................................................................................................................ 105
3.8 GPS .................................................................................................................................................. 105
3.9 Jamming detection ........................................................................................................................... 105
3.10 Smart Temperature Management ................................................................................................. 106
3.10.1 Smart Temperature Supervisor (STS) .......................................................................................... 106
3.10.2 Threshold Definitions ................................................................................................................. 108
3.11 Hybrid positioning and CellLocateTM .............................................................................................. 108
3.11.1 Positioning through cellular information: CellLocateTM ............................................................... 108
3.11.2 Hybrid positioning ..................................................................................................................... 110
4 Handling and soldering ........................................................................................... 111
4.1 Packaging, shipping, storage and moisture preconditioning ............................................................. 111
4.2 Soldering .......................................................................................................................................... 111
4.2.1 Soldering paste.......................................................................................................................... 111
4.2.2 Reflow soldering ....................................................................................................................... 111
4.2.3 Optical inspection ...................................................................................................................... 113
4.2.4 Cleaning .................................................................................................................................... 113
Page 6
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Contents
Page 6 of 125
4.2.5 Repeated reflow soldering ......................................................................................................... 113
4.2.6 Wave soldering.......................................................................................................................... 113
4.2.7 Hand soldering .......................................................................................................................... 113
4.2.8 Rework ...................................................................................................................................... 113
4.2.9 Conformal coating .................................................................................................................... 113
4.2.10 Casting ...................................................................................................................................... 114
4.2.11 Grounding metal covers ............................................................................................................ 114
4.2.12 Use of ultrasonic processes ........................................................................................................ 114
5 Product Testing......................................................................................................... 115
5.1 u-blox in-series production test ......................................................................................................... 115
5.2 Test parameters for OEM manufacturer ............................................................................................ 115
5.2.1 ‘Go/No go’ tests for integrated devices ...................................................................................... 116
5.2.2 Functional tests providing RF operation ..................................................................................... 116
A Glossary .................................................................................................................... 119
Related documents......................................................................................................... 121
Revision history .............................................................................................................. 122
Contact ............................................................................................................................ 125
Page 7
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 7 of 125
1 System description
1.1 Overview
LEON-G100/LEON-G200 GSM/GPRS modules integrate a full-featured Release 99 GSM-GPRS protocol stack,
with the following main characteristics.
Quad-band support: GSM 850 MHz, EGSM 900 MHz, DCS 1800 MHz and PCS 1900 MHz
Power class 4 (33 dBm nominal maximum output power) for GSM/EGSM bands
Power class 1 (30 dBm nominal maximum output power) for DCS/PCS bands
GPRS multi-slot class 10
All GPRS coding schemes from CS1 to CS4 are supported
GPRS bit rate: 85.6 kb/s (max.), 53.6 kb/s (typ.) in down-link; 42.8 kb/s (max.), 26.8 kb/s (typ.) in up-link
CS (Circuit Switched) Data calls are supported in transparent/non transparent mode up to 9.6 kb/s
Encryption algorithms A5/1 for GSM and GPRS support
Bearer service fax Group 3 Class 2.0 support
Class B Mobile Stations (i.e. the data module can be attached to both GPRS and GSM services, using one
service at a time)
Network operation modes I to III are supported
GPRS multi-slot class determines the maximum number of timeslots available for upload and download and thus
the speed at which data can be transmitted and received: higher classes typically allow faster data transfer rates.
GPRS multi-slot class 10 uses a maximum of 4 slots in download (reception) and 2 slots in upload (transmission),
with 5 slots in total.
The network automatically configures the number of timeslots used for reception or transmission (voice calls
take precedence over GPRS traffic). The network also automatically configures channel encoding (CS1 to CS4).
The maximum GPRS bit rate of the mobile station depends on the coding scheme and number of time slots.
Page 8
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 8 of 125
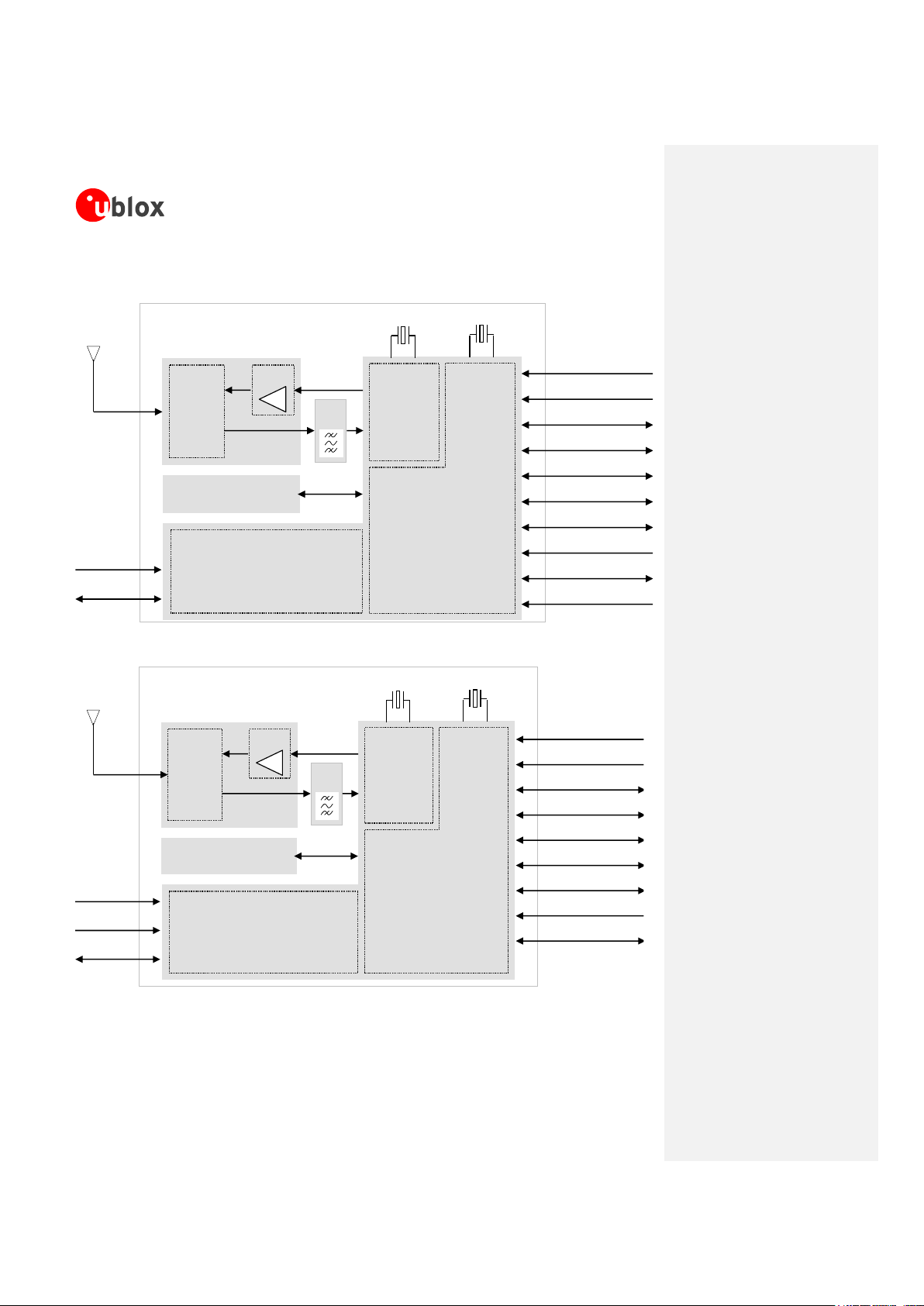
1.2 Architecture
Memory
UART
2 Analog Audio
DDC (for GPS)
GPIO
ADC
SIM Card
Vcc
V_BCKP
Power-On
Reset
26 MHz
32.768 kHz
Headset Detection
RF
Transceiver
Power
Management
Baseband
ANT
SAW
Filter
Switch
PA
Digital Audio
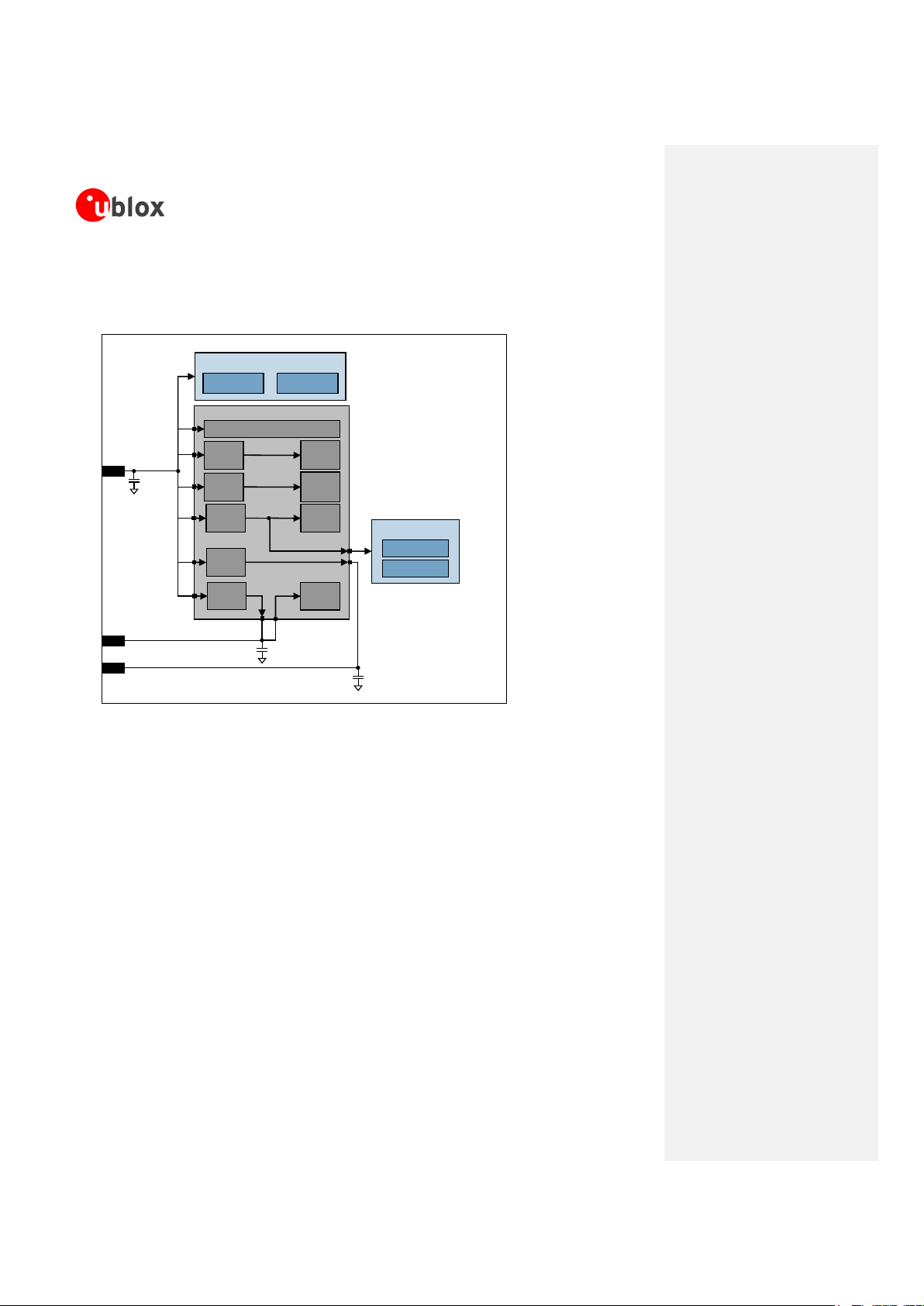
Figure 1: LEON-G100 block diagram
Memory
Vcc
V_BCKP
26 MHz
32.768 kHz
Charger
RF
Transceiver
Power
Management
Baseband
ANT
SAW
Filter
Switch
PA
UART
2 Analog Audio
DDC (for GPS)
GPIO
SIM Card
Power-On
Reset
Headset Detection
Digital Audio
Figure 2: LEON-G200 block diagram
Page 9
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 9 of 125
1.2.1 Functional blocks
LEON-G100/LEON-G200 modules consist of the following functional blocks:
RF
Baseband
Power Management
1.2.1.1 RF
The RF block is composed of the following main elements:
RF transceiver (integrated in the GSM/GPRS single chip) performing modulation, up-conversion of the
baseband I/Q signals, down-conversion and demodulation of the RF received signals. The RF transceiver
includes:
Constant gain direct conversion receiver with integrated LNAs;
Highly linear RF quadrature demodulator;
Digital Sigma-Delta transmitter modulator;
Fractional-N Sigma-Delta RF synthesizer;
3.8 GHz VCO;
Digital controlled crystal oscillator.
Transmit module, which amplifies the signals modulated by the RF transceiver and connects the single
antenna input/output pin of the module to the suitable RX/TX path, via its integrated parts:
Power amplifier;
Antenna switch;
RX diplexer SAW (band pass) filters
26 MHz crystal, connected to the digital controlled crystal oscillator to perform the clock reference in active
or connected mode
1.2.1.2 Baseband
The Baseband block is composed of the following main elements:
Baseband integrated in the GSM/GPRS single chip, including:
Microprocessor;
DSP (for GSM/GPRS Layer 1 and audio processing);
Peripheral blocks (for parallel control of the digital interfaces);
Audio analog front-end;
Memory system in a multi-chip package integrating two devices:
NOR flash non-volatile memory;
PSRAM volatile memory;
32.768 kHz crystal, connected to the oscillator of the RTC to perform the clock reference in idle or power-
off mode
1.2.1.3 Power Management
The Power Management block is composed of the following main elements:
Voltage regulators integrated in the GSM/GPRS single chip for direct connection to battery
Charging control circuitry
Page 10
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 10 of 125
1.2.2 Hardware differences between LEON-G100 and LEON-G200
Hardware differences between the LEON-G100 and the LEON-G200 modules:
Charging control circuitry is available on the LEON-G200 module only
ADC input is provided on the LEON-G100 module only
1.3 Pin-out
Table 1 describes the pin-out of LEON-G100/LEON-G200 modules, with pins grouped by function.
Function
Pin
No
I/O
Description
Remarks
Power
VCC
50 I Module Supply
Clean and stable supply is required: low ripple and
low voltage drop must be guaranteed.
Voltage provided has to be always above the
minimum limit of the operating range.
Consider that there are large current spike in
connected mode, when a GSM call is enabled.
See section 1.5.2
GND
1, 3, 6,
7, 8, 17,
25, 36,
45, 46,
48, 49
N/A
Ground
GND pins are internally connected but good (low
impedance) external ground can improve RF
performances: all GND pins must be externally
connected to ground
V_BCKP
2
I/O
Real Time Clock supply
V_BCKP = 2.0 V (typical) generated by the module
to supply Real Time Clock when VCC supply
voltage is within valid operating range.
See section 1.5.5
VSIM
35 O SIM supply
SIM supply automatically generated by the
module.
See section 1.8
V_CHARGE
(LEON-G200-xx)
4 I Charger voltage supply
input
V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE must be
externally connected.
The external supply used as charging source must
be voltage and current limited.
See section 1.5.4
CHARGE_SENSE
(LEON-G200-xx)
5 I Charger voltage
measurement input
V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE must be
externally connected.
The external supply used as charging source must
be voltage and current limited.
See section 1.5.4
RF
ANT
47
I/O
RF antenna
50 nominal impedance.
See section 1.7, 2.2.1.1 and 2.4
Audio
HS_DET
(LEON-Gx00-05S
or previous)
18 I Headset detection input
Internal active pull-up to 2.85 V enabled.
See section 1.10.1.3
HS_DET
(LEON-G100-06x
LEON-G200-06S
or subsequent)
18
I/O
GPIO
Internal active pull-up to 2.85 V enabled when the
“headset detection” function is enabled (default).
See section 1.12 and section 1.10.1.3
I2S_WA
26 O I2S word alignment
Check device specifications to ensure compatibility
of supported modes to LEON-G100/LEON-G200
module.
Add a test point to provide access to the pin for
debugging.
See section 1.10.2.
Page 11
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 11 of 125
Function
Pin
No
I/O
Description
Remarks
I2S_TXD
27 O I2S transmit data
Check device specifications to ensure compatibility
of supported modes to LEON-G100/LEON-G200
module.
Add a test point to provide access to the pin for
debugging.
See section 1.10.2.
I2S_CLK
28 O I2S clock
Check device specifications to ensure compatibility
of supported modes to LEON-G100/LEON-G200
module.
Add a test point to provide access to the pin for
debugging.
See section 1.10.2.
I2S_RXD
29 I I2S receive data
Internal active pull-up to 2.85 V enabled. Check
device specifications to ensure compatibility of
supported modes to LEON-G100/LEON-G200
module.
Add a test point to provide access to the pin for
debugging.
See section 1.10.2.
HS_P
37 O First speaker output
with low power singleended analog audio
This audio output is used when audio downlink
path is “Normal earpiece“ or “Mono headset“.
See section 1.10.1
SPK_P
38 O Second speaker output
with high power
differential analog audio
This audio output is used when audio downlink
path is “Loudspeaker“.
See section 1.10.1
SPK_N
39 O Second speaker output
with power differential
analog audio output
This audio output is used when audio downlink
path is “Loudspeaker“.
See section 1.10.1
MIC_BIAS2
41 I Second microphone
analog signal input and
bias output
This audio input is used when audio uplink path is
set as “Headset Microphone“.
See section 1.10.1
MIC_GND2
42 I Second microphone
analog reference
Local ground of second microphone.
See section 1.10.1
MIC_GND1
43 I First microphone analog
reference
Local ground of the first microphone.
See section 1.10.1
MIC_BIAS1
44 I First microphone analog
signal input and bias
output
This audio input is used when audio uplink path is
set as “Handset Microphone“.
See section 1.10.1
SIM
SIM_CLK
32 O SIM clock
Must meet SIM specifications
See section 1.8.
SIM_IO
33
I/O
SIM data
Internal 4.7k pull-up to VSIM.
Must meet SIM specifications
See section 1.8.
SIM_RST
34 O SIM reset
Must meet SIM specifications
See section 1.8.
UART
DSR
9 O UART data set ready
Circuit 107 (DSR) in V.24.
See section 1.9.1.
RI
10 O UART ring indicator
Circuit 125 (RI) in V.24.
See section 1.9.1.
DCD
11 O UART data carrier detect
Circuit 109 (DCD) in V.24.
See section 1.9.1.
DTR
12 I UART data terminal
ready
Internal active pull-up to 2.85 V enabled.
Circuit 108/2 (DTR) in V.24.
See section 1.9.1.
RTS
13 I UART ready to send
Internal active pull-up to 2.85 V enabled.
Circuit 105 (RTS) in V.24.
See section 1.9.1.
CTS
14 O UART clear to send
Circuit 106 (CTS) in V.24.
See section 1.9.1.
Page 12
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 12 of 125
Function
Pin
No
I/O
Description
Remarks
TxD
15 I UART transmitted data
Internal active pull-up to 2.85 V enabled.
Circuit 103 (TxD) in V.24.
See section 1.9.1.
RxD
16 O UART received data
Circuit 104 (RxD) in V.24. See section 1.9.1.
DDC
SCL
30 O I2C bus clock line
Fixed open drain. External pull-up required.
See section 1.9.2
SDA
31
I/O
I2C bus data line
Fixed open drain. External pull-up required.
See section 1.9.2
ADC
ADC1
(LEON-G100-xx)
5 I ADC input
Resolution: 12 bits.
Consider that the impedance of this input changes
depending on the operative mode
See section 1.11
GPIO
GPIO1
20
I/O
GPIO
Add a test point to provide access to the pin for
debugging.
See section 1.12
GPIO2
21
I/O
GPIO
See section 1.12 and section 1.9.2
GPIO3
(LEON-G100-06x
LEON-G200-06S
or subsequent)
23
I/O
GPIO
See section 1.12 and section 1.9.2
GPIO4
(LEON-G100-06x
LEON-G200-06S
or subsequent)
24
I/O
GPIO
See section 1.12 and section 1.9.2
System
PWR_ON
19 I Power-on input
PWR_ON pin has high input impedance.
Do not keep floating in noisy environment:
external pull-up required.
See section 1.6.1
RESET_N
22
I/O
Reset signal
See section 1.6.3
Reserved
Reserved
(LEON-Gx00-05S
or previous)
23
Do not connect
Reserved
(LEON-Gx00-05S
or previous)
24
Do not connect
Reserved
40
Do not connect
Reserved
(LEON-G100-xx)
4
Do not connect
Table 1: LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 pin-out
Page 13
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 13 of 125
1.4 Operating modes
LEON-G100/LEON-G200 modules include several operating modes, each have different features and interfaces.
Table 2 summarizes the various operating modes and provides general guidelines for operation.
Operating Mode
Description
Features / Remarks
Transition condition
General Status: Power-down
Not-Powered
Mode
VCC supply not present or
below normal operating
range.
Microprocessor switched off
(not operating).
RTC only operates if supplied
through V_BCKP pin.
Module is switched off.
Application interfaces are not accessible.
Internal RTC timer operates only if a valid
voltage is applied to V_BCKP pin.
Any external signal connected to the
UART I/F, I2S I/F, HS_DET, GPIOs must be
tristated to avoid an increase of module
power-off consumption.
Module cannot be switched on by a
falling edge provided on the PWR_ON
input, neither by a preset RTC alarm, nor
by charger detection on the V_CHARGE
and CHARGE_SENSE pins.
Power-Off Mode
VCC supply within normal
operating range.
Microprocessor not
operating.
Only RTC runs.
Module is switched off: normal
shutdown after sending the
AT+CPWROFF command (refer to u-blox
AT Commands Manual [2]).
Application interfaces are not accessible.
Only internal RTC timer in operation.
Any external signal connected to the
UART I/F, I2S I/F, HS_DET, GPIOs must be
tristated to avoid an increase of the
module power-off consumption.
Module can be switched on by a falling
edge provided on the PWR_ON input, by
a preset RTC alarm, or by charger
detection on the V_CHARGE and
CHARGE_SENSE pins.
General Status: Normal Operation
Idle-Mode
Microprocessor runs with
32 kHz as reference oscillator.
Module does not accept data
signals from an external
device.
If power saving is enabled, the module
automatically enters idle mode whenever
possible.
If hardware flow control is enabled, the
CTS line indicates that the module is in
active-mode and the UART interface is
enabled: the line is driven in the OFF
state when the module is not prepared
to accept data by the UART interface.
If hardware flow control is disabled, the
CTS line is fixed to ON state.
Module by default is not set to
automatically enter idle mode whenever
possible, unless power saving
configuration is enabled by appropriate
AT command (refer to u-blox AT
Commands Manual [2], AT+UPSV).
If the module is registered with the
network and power saving is enabled, it
automatically enters idle mode and
periodically wakes up to active mode to
monitor the paging channel for the
paging block reception according to
network indication.
If module is not registered with the
network and power saving is enabled, it
automatically enters idle mode and
periodically wakes up to monitor external
activity.
Module wakes up from idle-mode to
active-mode for an incoming voice or
data call.
Module wakes up from idle mode to
active mode if an RTC alarm occurs.
Module wakes up from idle mode to
active mode when data is received on
UART interface (refer to 1.9.1 section).
Module wakes up from idle mode to
active mode when the RTS input line is
set to the ON state by the DTE if the
AT+UPSV=2 command is sent to the
module (refer to 1.9.1 section).
Active-Mode
Microprocessor runs with
26 MHz as reference
oscillator.
The module is ready to accept
data signals from an external
device.
Module is switched on and is fully active:
power saving is not enabled.
The application interfaces are enabled.
If power saving is enabled, the module
automatically enters idle mode whenever
possible.
Page 14
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 14 of 125
Operating Mode
Description
Features / Remarks
Transition condition
Connected-Mode
Voice or data call enabled.
Microprocessor runs with
26 MHz as reference
oscillator.
The module is ready to accept
data signals from an external
device.
The module is switched on and a voice
call or a data call (GSM/GPRS) is in
progress.
Module is fully active.
Application interfaces are enabled.
When call terminates, module returns to
the last operating state (Idle or Active).
General Status: Charging (LEON-G200 only)
Pre-charge mode
Battery connected to VCC.
Battery voltage level is below
the VCC normal operating
range.
Charger connected to
V_CHARGE and
CHARGE_SENSE inputs with
proper voltage and current
characteristics.
Charging of the deeply
discharged battery is enabled
while the module is switched
off.
Microprocessor switched off
(not operating).
Module is switched off and cannot be
switched on (not powered mode).
The Pre-Charge phase of the charging
process is enabled: charging of the
deeply discharged battery is forced by
HW at low current while the module is
switched off
When battery voltage level reaches the
VCC normal operating range with a
charger connected to V_CHARGE and
CHARGE_SENSE inputs, the module
enters charge mode.
Charge-mode
Battery connected to VCC.
Battery voltage level is within
the VCC normal operating
range.
Charger connected to
V_CHARGE and
CHARGE_SENSE inputs with
proper voltage and current
characteristics.
Charging process enabled
while the module is switched
on and normal operations are
enabled.
Microprocessor runs with
32 kHz or 26 MHz as
reference oscillator.
Module is switched on and normal
operations are enabled (Idle mode,
Active mode or Connected mode).
The charging process is enabled:
charging of battery is controlled by the
microprocessor while the module is
switched on
When the charger is removed from
V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE
inputs, the module returns to normal
operations (Idle-mode, Active-mode or
Connected-mode).
Table 2: Module operating modes summary
Page 15
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 15 of 125
1.5 Power management
1.5.1 Power supply circuit overview
V_BCKP
GSM/GPRS Chipset
PSRAM
NOR Flash
MCP Memory
4-Bands GSM FEM
Antenna
Switch
PA
LDOs BB
LDOs RF
RTC
LDO
LDO EBU
Charging Control
1 µF
1 µF
LDO
VSIM
VCC
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
2 x 22 µF
2
35
50
Figure 3: Power supply concept
Power supply is via VCC pin. This is the only main power supply pin.
VCC pin connects the RF Power Amplifier and the integrated power management unit within the module: all
supply voltages needed by the module are generated from the VCC supply by integrated voltage regulators.
V_BCKP is the Real Time Clock (RTC) supply. When the VCC voltage is within the specified extended operating
range, the module supplies the RTC: 2.0 V typical are generated by the module on the V_BCKP pin. If the VCC
voltage is under the minimum specified extended limit, the RTC can be externally supplied via V_BCKP pin.
When a 1.8 V or a 3 V SIM card type is connected, LEON-G100/LEON-G200 automatically supply the SIM card
via VSIM pin. Activation and deactivation of the SIM interface with automatic voltage switch from 1.8 to 3 V is
implemented, in accordance to the ISO-IEC 78-16-e specifications.
The integrated power management unit also provides the control state machine for system start up, including
start up with discharged batteries, pre-charging and system reset control.
LEON-G100/LEON-G200 feature a power management concept optimized for most efficient use of battery
power. This is achieved by hardware design utilizing power efficient circuit topology, and by power management
software controlling the power saving configuration of the module. Battery management runs in the context of
the operation and maintenance process:
Battery charging control, in order to maintain the full capacity of the battery
Collecting and processing of measurements of battery voltage
Page 16
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 16 of 125
1.5.2 Module supply (VCC)
LEON-G100/LEON-G200 modules must be supplied through VCC pin by a DC power supply. Voltages must be
stable, due to the surging consumption profile of the GSM system (described in the section 1.5.3).
Name
Description
Remarks
VCC
Module Supply
Clean and stable supply is required: low ripple and low
voltage drop must be guaranteed.
Voltage provided has to be always above the minimum limit
of the operating range.
Consider that there are large current spike in connected
mode, when a GSM call is enabled.
GND
Ground
GND pins are internally connected but good (low impedance)
external ground can improve RF performances: all GND pins
must be externally connected to ground.
Table 3: Module supply pins
VCC pin ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F). A higher protection level could be required
if the line is externally accessible on the application board. A higher protection level can be achieved
mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) on the line connected to this
pin if it is externally accessible on the application board.
The voltage provided to VCC pin must be within the normal operating range limits specified in the LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1]. Complete functionality of the module is only guaranteed within the specified
operational normal voltage range.
The module cannot be switched on if the VCC voltage value is below the specified normal operating
range minimum limit: ensure that the input voltage at VCC pin is above the minimum limit of the
normal operating range for more than 1 second after the start of the switch-on of the module.
When LEON-G100/LEON-G200 modules are in operation, the voltage provided to VCC pin can exceed the
normal operating range limits but must be within the extended operating range limits specified in
LEON-G100/LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1]. Module reliability is only guaranteed within the specified operational
extended voltage range.
The module switches off when VCC voltage value drops below the specified extended operating range
minimum limit: ensure that the input voltage at VCC pin never drops below the minimum limit of the
extended operating range when the module is switched on, not even during a GSM transmit burst,
where the current consumption can rise up to maximum peaks of 2.5 A in case of a mismatched
antenna load.
Operation above the extended operating range maximum limit is not recommended and
extended exposure beyond it may affect device reliability.
Stress beyond the VCC absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the
module: if necessary, voltage spikes beyond VCC absolute maximum ratings must be limited to
values within the specified boundaries by using appropriate protection.
Page 17
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 17 of 125
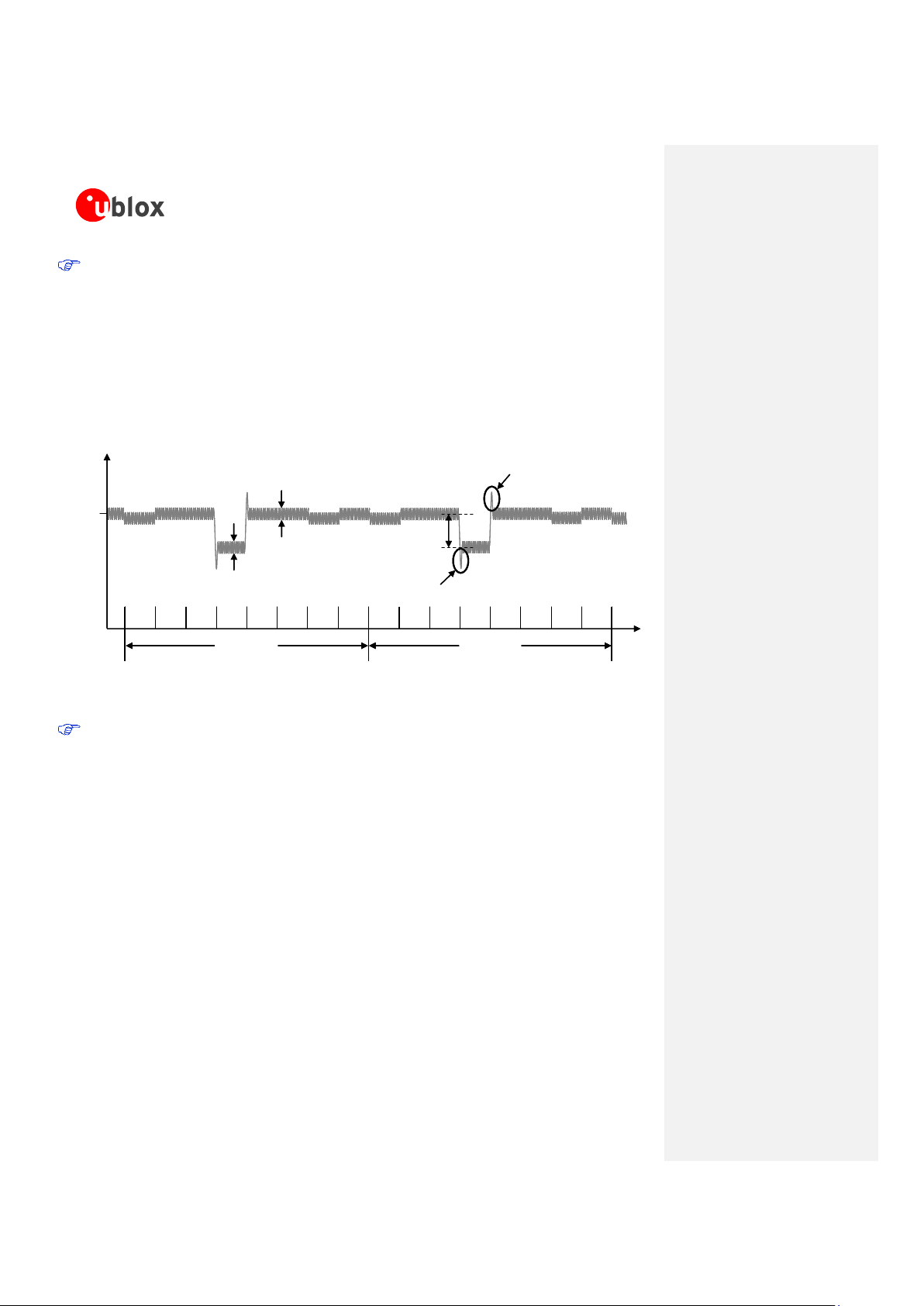
When designing the power supply for the application, pay specific attention to power losses and
transients. The DC power supply has to be able to provide a voltage profile to the VCC pin with the
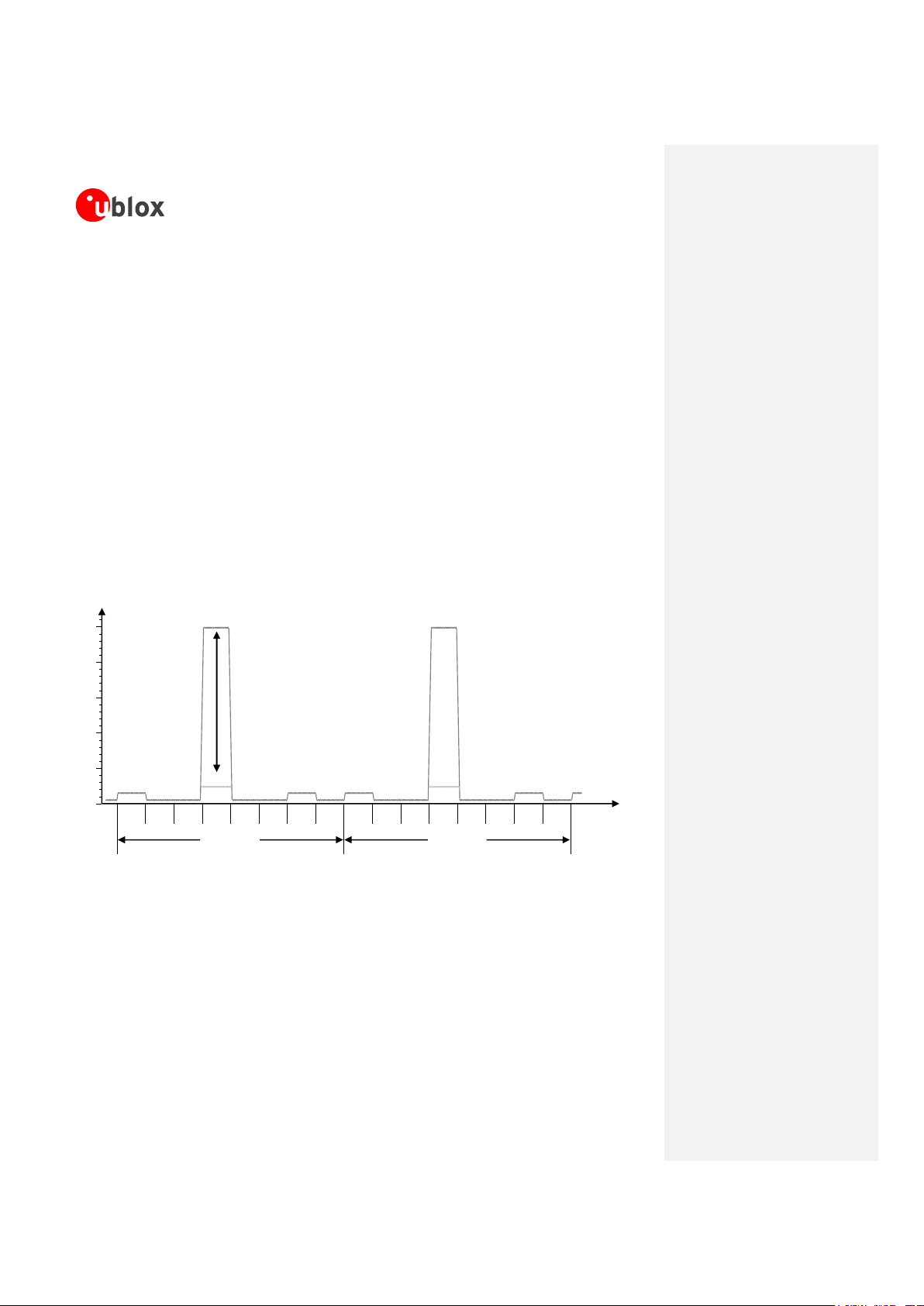
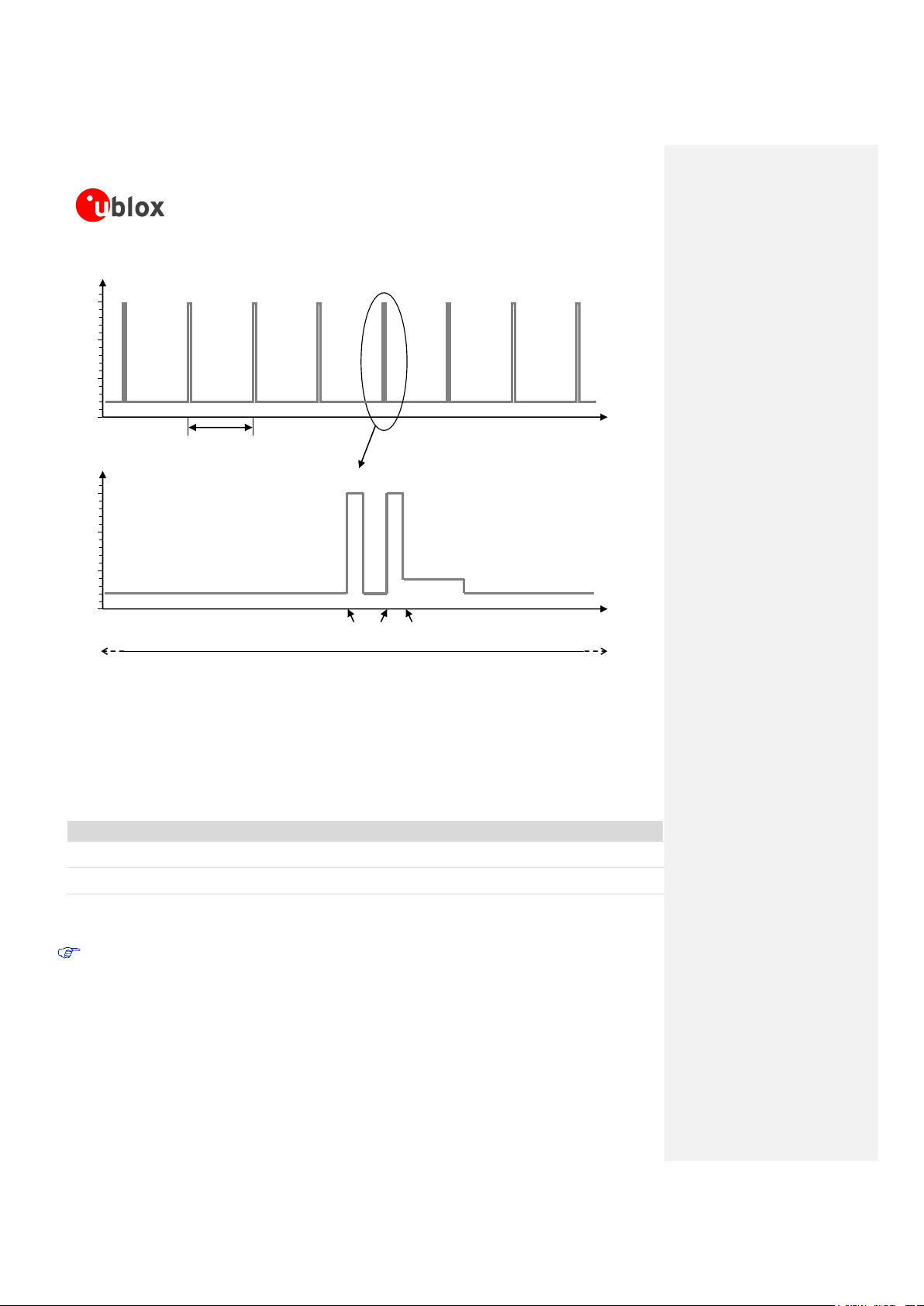
following characteristics:
o Voltage drop during transmit slots has to be lower than 400 mV
o Undershoot and overshoot at the start and at the end of transmit slots have to be not present
o Voltage ripple during transmit slots has to be:
lower than 100 mVpp if f
ripple
≤ 200 kHz
lower than 10 mVpp if 200 kHz < f
ripple
≤ 400 kHz
lower than 2 mVpp if f
ripple
> 400 kHz
Figure 4: Description of the VCC voltage profile versus time during a GSM call
Any degradation in power supply performance (due to losses, noise or transients) will directly affect the
RF performance of the module since the single external DC power source indirectly supplies all the
digital and analog interfaces, and also directly supplies the RF power amplifier (PA).
1.5.2.1 VCC application circuits
The LEON module must be supplied through the VCC pin by one (and only one) proper DC power supply from
the following:
Switching regulator
Low Drop-Out (LDO) linear regulator
Rechargeable Li-Ion battery
Primary (disposable) battery
Time
undershoot
overshoot
ripple
ripple
drop
Voltage
3.8 V
(typ)
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
Time
undershoot
overshoot
ripple
ripple
drop
Voltage
3.8 V
(typ)
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
Page 18
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 18 of 125
Main Supply
Available?
Battery
Li-Ion 3.7 V
Linear LDO
Regulator
Main Supply
Voltage >5 V?
Switching
Step-Down
Regulator
No, portable device
No, less than 5 V
Yes, greater than 5 V
Yes, always available
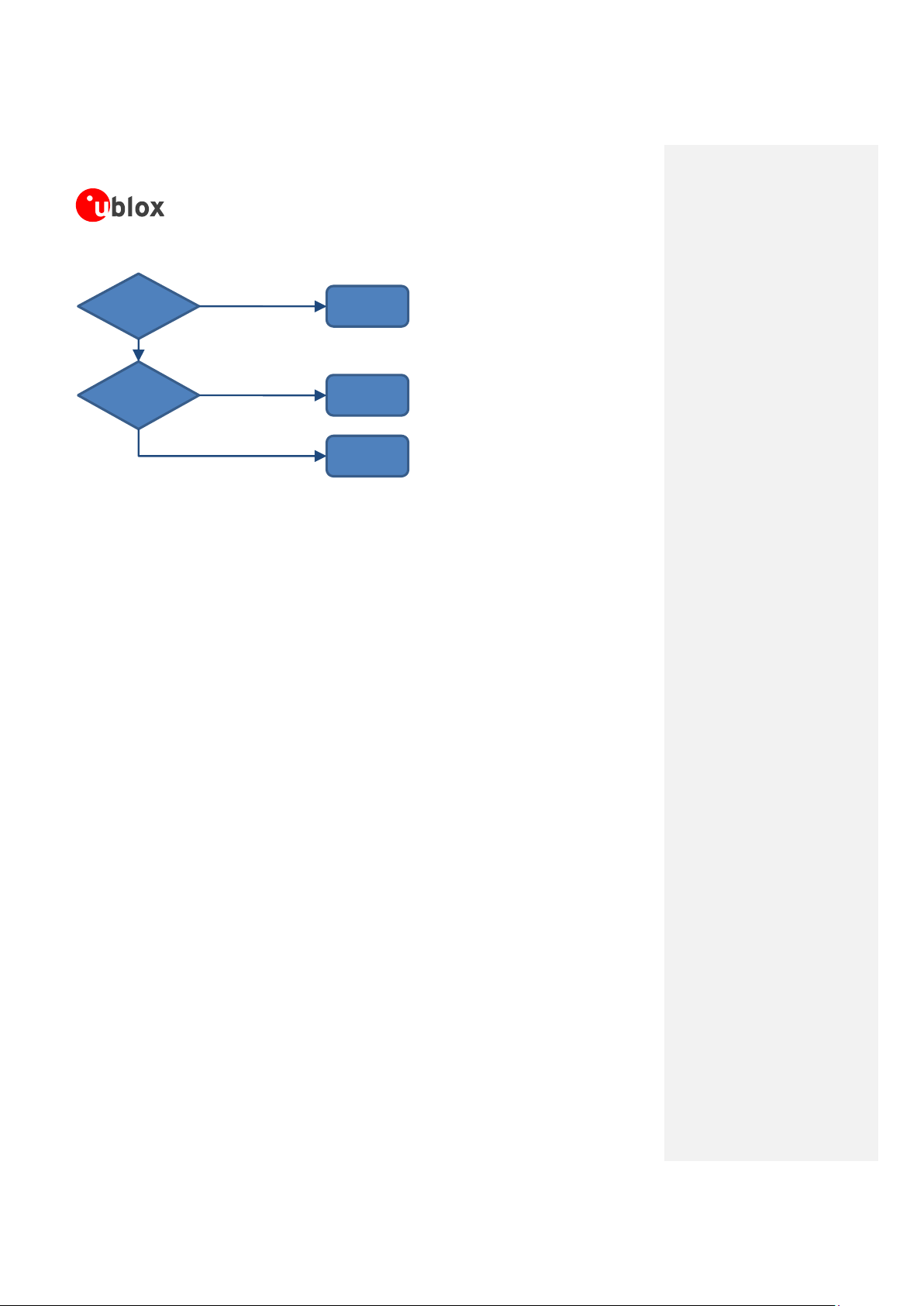
Figure 5: VCC supply concept selection
The switching step-down regulator is the typical choice when the available primary supply source has a nominal
voltage much higher (e.g. greater than 5 V) than the LEON-G100/LEON-G200 operating supply voltage. The use
of switching step-down provides the best power efficiency for the overall application and minimizes current
drawn from main supply source.
The use of an LDO linear regulator becomes convenient for primary supplies with relatively low voltage (e.g. less
than 5 V). In this case a switching regulator with a typical efficiency of 90% reduces the benefit of voltage
step-down for input current savings. Linear regulators are not recommended for high voltage step-down as they
will dissipate a considerable amount of power in thermal energy.
If the LEON-G100/LEON-G200 is deployed in a mobile unit with no permanent primary supply source available,
then a battery is required to provide VCC. A standard 3-cell Lithium-Ion battery pack directly connected to VCC
is the typical choice for battery-powered devices. Batteries with Ni-MH chemistry should be avoided, since they
typically reach a maximum voltage during charging that is above the maximum rating for VCC.
The use of primary (disposable) batteries is uncommon, since the typical cells available are seldom capable of
delivering the burst peak current for a GSM call due to high internal resistance.
The following sections highlight some design aspects for each of these supplies.
Switching regulator
The characteristics of the switching regulator connected to the VCC pin should meet the following requirements:
Power capabilities: the switching regulator with its output circuit must be capable of providing a proper
voltage value to the VCC pin and delivering 2.5 A current pulses with a 1/8 duty cycle to the VCC pin
Low output ripple: the switching regulator and output circuit must be capable of providing a clean (low
noise) VCC voltage profile
High switching frequency: for best performance and for smaller applications select a switching frequency
≥ 600 kHz (since an L-C output filter is typically smaller for high switching frequency). Using a switching
regulator with a variable switching frequency or with a switching frequency lower than 600 kHz must be
carefully evaluated since this can produce noise in the VCC voltage profile and therefore impact and worsen
GSM modulation spectrum performance. An additional L-C low-pass filter between the switching regulator
output and the VCC supply pin can mitigate the ripple on VCC, but adds extra voltage drop due to resistive
losses in series inductors
PWM mode operation: select preferably regulators with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) mode. Pulse
Frequency Modulation (PFM) mode and PFM/PWM mode transitions while in active mode must be avoided
to reduce the noise on the VCC voltage profile. Switching regulators able to switch between low ripple
Page 19
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 19 of 125
PWM mode and high efficiency burst or PFM mode can be used, provided the mode transition occurs when
the GSM module changes status from idle mode (current consumption approximately 1 mA) to active mode
(current consumption approximately 100 mA): it is permissible to use a regulator that switches from the
PWM mode to the burst or PFM mode at an appropriate current threshold (e.g. 60 mA)
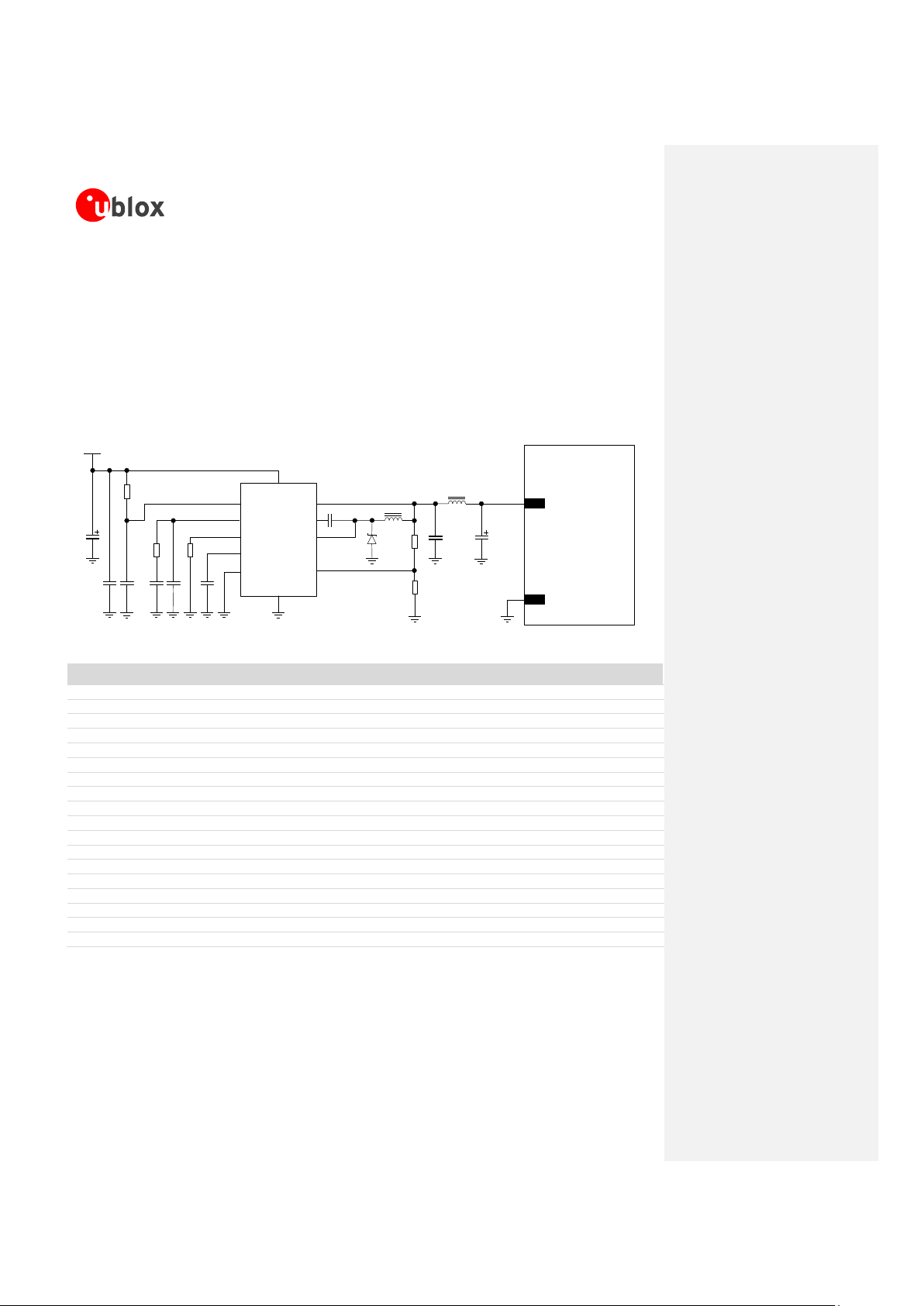
Figure 6 and the components listed in Table 4 show an example of a high reliability power supply circuit, where
the VCC module supply is provided by a step-down switching regulator capable to deliver 2.5 A current pulses,
with low output ripple, with 1 MHz fixed switching frequency in PWM mode operation. The use of a switching
regulator is suggested when the difference from the available supply rail and the VCC value is high: switching
regulators provide good efficiency transforming a 12 V supply to the 3.8 V typical value of the VCC supply. The
following power supply circuit example is implemented on the LEON Evaluation Board.
LEON-G100
LEON-G200
12V
C6
R3
C5
R2
C3C2
C1
R1
VIN
RUN
VC
RT
PG
SYNC
BD
BOOST
SW
FB
GND
6
7
10
9
5
C712
3
8
11
4
C8 C9
L2
D1
R4
R5
L1
C4
U1
50
VCC
GND
Figure 6: Suggested schematic design for the VCC voltage supply application circuit using a step-down regulator
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
47 µF Capacitor Aluminum 0810 50 V
MAL215371479E3 - Vishay
C2
10 µF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 5750 15% 50 V
C5750X7R1H106MB - TDK
C3
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C4
680 pF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71H681KA01 - Murata
C5
22 pF Capacitor Ceramic COG 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1H220JZ01 - Murata
C6
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C7
470 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0603 10% 25 V
GRM188R71E474KA12 - Murata
C8
22 µF Capacitor Ceramic X5R 1210 10% 25 V
GRM32ER61E226KE15 - Murata
C9
330 µF Capacitor Tantalum D_SIZE 6.3 V 45 mΩ
T520D337M006ATE045 - KEMET
D1
Schottky Diode 40 V 3 A
MBRA340T3G - ON Semiconductor
L1
10 µH Inductor 744066100 30% 3.6 A
744066100 - Wurth Electronics
L2
1 µH Inductor 7445601 20% 8.6 A
7445601 - Wurth Electronics
R1
470 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
2322-705-87474-L - Yageo
R2
15 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
2322-705-87153-L - Yageo
R3
33 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
2322-705-87333-L - Yageo
R4
390 kΩ Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RC0402FR-07390KL - Yageo
R5
100 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
2322-705-70104-L - Yageo
U1
Step Down Regulator MSOP10 3.5 A 2.4 MHz
LT3972IMSE#PBF - Linear Technology
Table 4: Suggested components for VCC voltage supply application circuit using a high reliability step-down regulator
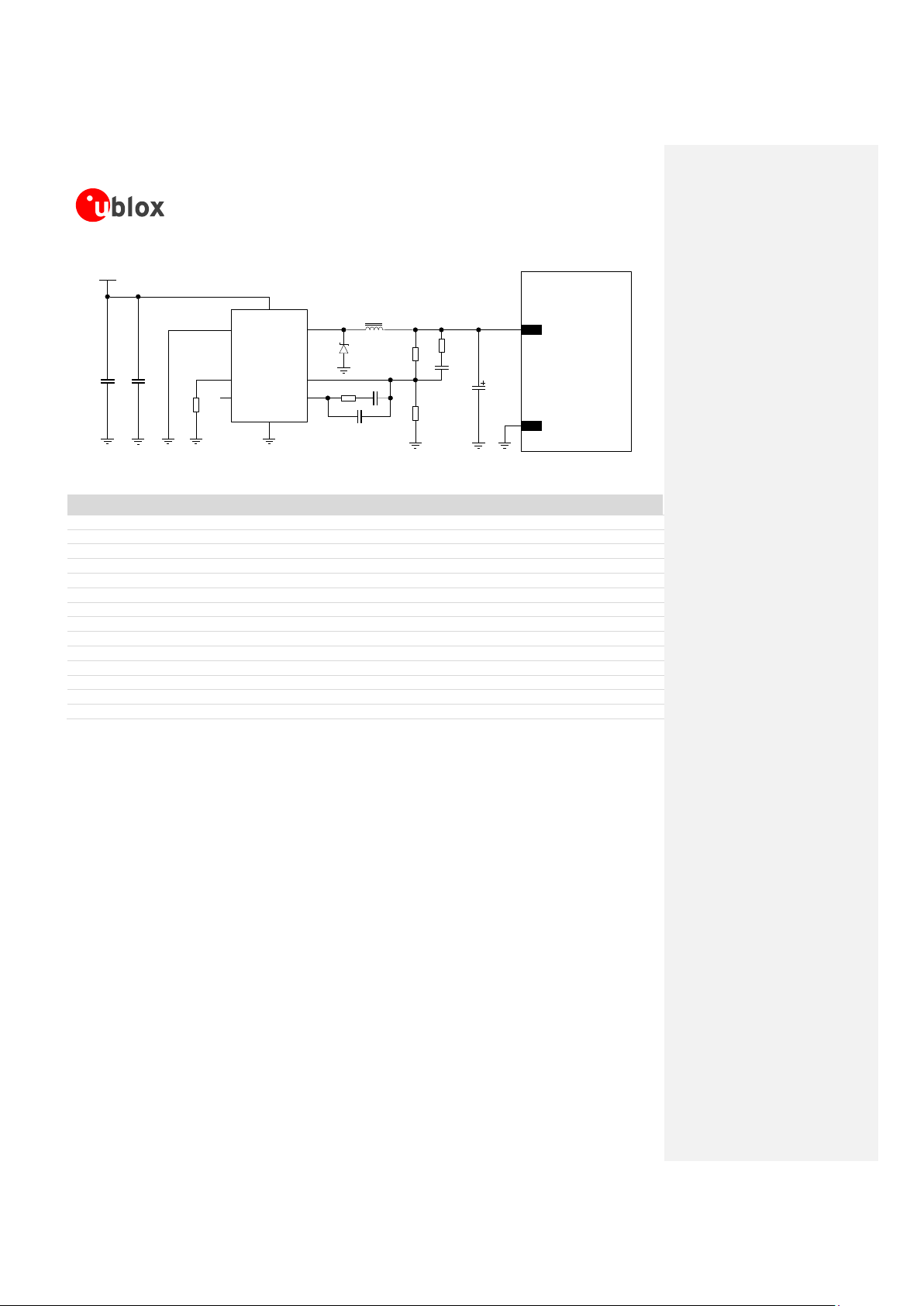
Figure 7 and the components listed in Table 5 show an example of a low cost power supply circuit, where the
VCC module supply is provided by a step-down switching regulator capable of delivering 2.5 A current pulses,
transforming a 12 V supply input.
Page 20
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 20 of 125
LEON-G100
LEON-G200
12V
R5
C6C1
VCC
INH
FSW
SYNC
OUT
GND
2
6
3
1
7
8
C3
C2
D1
R1
R2
L1
U1
50
VCC
GND
FB
COMP
5
4
R3
C4
R4
C5
Figure 7: Suggested schematic design for the VCC voltage supply application circuit using a low cost step-down regulator
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
22 µF Capacitor Ceramic X5R 1210 10% 25 V
GRM32ER61E226KE15 – Murata
C2
100 µF Capacitor Tantalum B_SIZE 20% 6.3V 15mΩ
T520B107M006ATE015 – Kemet
C3
5.6 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 50 V
GRM155R71H562KA88 – Murata
C4
6.8 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 50 V
GRM155R71H682KA88 – Murata
C5
56 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H560JA01 – Murata
C6
220 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0603 10% 25 V
GRM188R71E224KA88 – Murata
D1
Schottky Diode 25V 2 A
STPS2L25 – STMicroelectronics
L1
5.2 µH Inductor 30% 5.28A 22 mΩ
MSS1038-522NL – Coilcraft
R1
4.7 kΩ Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RC0402FR-074K7L – Yageo
R2
910 Ω Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RC0402FR-07910RL – Yageo
R3
82 Ω Resistor 0402 5% 0.063 W
RC0402JR-0782RL – Yageo
R4
8.2 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.063 W
RC0402JR-078K2L – Yageo
R5
39 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.063 W
RC0402JR-0739KL – Yageo
U1
Step Down Regulator 8-VFQFPN 3 A 1 MHz
L5987TR – ST Microelectronics
Table 5: Suggested components for VCC voltage supply application circuit using a low cost step-down regulator
Low Drop-Out (LDO) linear regulator
The characteristics of the LDO linear regulator connected to VCC pin should meet the following requirements:
Power capabilities: the LDO linear regulator with its output circuit has to be capable to provide a proper
voltage value to VCC pin and has to be capable to deliver 2.5 A current pulses with 1/8 duty cycle to VCC
pin
Power dissipation: the power handling capability of the LDO linear regulator has to be checked to limit its
junction temperature to the maximum rated operating range (i.e. check the voltage drop from the max input
voltage to the min output voltage to evaluate the power dissipation of the regulator)
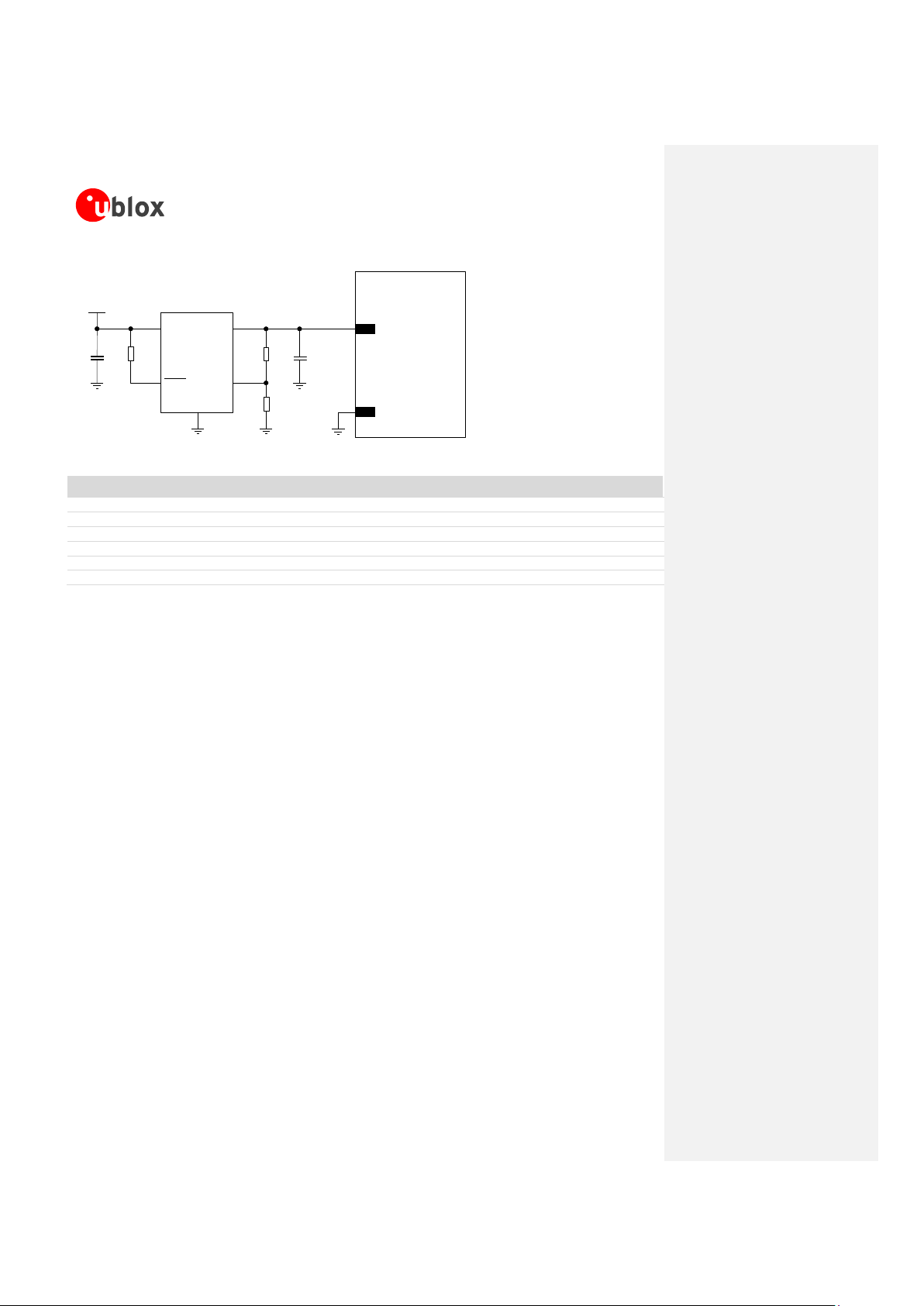
Figure 8 and the components listed in Table 6 show an example of a power supply circuit, where the VCC
module supply is provided by an LDO linear regulator capable to deliver 2.5 A current pulses, with proper power
handling capability. The use of a linear regulator is suggested when the difference from the available supply rail
and the VCC value is low: linear regulators provide good efficiency transforming a 5 V supply to the 3.8 V typical
value of the VCC supply.
Page 21
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 21 of 125
5 V
C1 R1
IN OUT
ADJ
GND
1
2
4
5
3
C2R2
R3
U1
SHDN
LEON-G100
LEON-G200
50
VCC
GND
Figure 8: Suggested schematic design for the VCC voltage supply application circuit using an LDO linear regulator
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
10 µF Capacitor Ceramic X5R 0603 20% 6.3 V
GRM188R60J106ME47 - Murata
C2
10 µF Capacitor Ceramic X5R 0603 20% 6.3 V
GRM188R60J106ME47 - Murata
R1
47 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-0747KL - Yageo Phycomp
R2
4.7 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-074K7L - Yageo Phycomp
R3
2.2 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-072K2L - Yageo Phycomp
U1
LDO Linear Regulator ADJ 3.0 A
LT1764AEQ#PBF - Linear Technology
Table 6: Suggested components for VCC voltage supply application circuit using an LDO linear regulator
Rechargeable Li-Ion battery
The characteristics of the rechargeable Li-Ion battery connected to VCC pin should meet the following
requirements:
Maximum pulse and DC discharge current: the rechargeable Li-Ion battery with its output circuit has to
be capable to deliver 2.5 A current pulses with 1/8 duty cycle to VCC pin and has to be capable to deliver a
DC current greater than the module maximum average current consumption to VCC pin. The maximum
pulse discharge current and the maximum DC discharge current are not always reported in batteries data
sheet, but the maximum DC discharge current is typically almost equal to the battery capacity in Amperehours divided by 1 hour
DC series resistance: the rechargeable Li-Ion battery with its output circuit has to be capable to avoid a
VCC voltage drop greater than 400 mV during transmit bursts
Maximum charging voltage (overcharge detection voltage): if the charging process is managed by the
GSM module, the overcharge detection voltage of the used battery pack, which enables battery protection,
must be greater or equal than 4.3 V, to be charged by the GSM module
Charging operating temperature range: if the charging process is managed by the GSM module, the
charging operating temperature range of the used battery pack must include the 0°C -40°C range, to be
charged by the GSM module
Maximum DC charging current: the rechargeable Li-Ion battery has to be capable to be charged by the
charging current provided by the selected external charger. The maximum DC charging current is not always
reported in batteries data sheet, but the maximum DC charging current is typically almost equal to the
battery capacity in Ampere-hours divided by 1 hour
Primary (disposable) battery
The characteristics of the primary (non-rechargeable) battery connected to VCC pin should meet the following
requirements:
Page 22
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 22 of 125
Maximum pulse and DC discharge current: the no-rechargeable battery with its output circuit has to be
capable to deliver 2.5 A current pulses with 1/8 duty cycle to VCC pin and has to be capable to deliver a DC
current greater than the module maximum average current consumption to VCC pin. The maximum pulse
and the maximum DC discharge current is not always reported in batteries data sheet, but the maximum DC
discharge current is typically almost equal to the battery capacity in Ampere-hours divided by 1 hour
DC series resistance: the no-rechargeable battery with its output circuit has to be capable to avoid a VCC
voltage drop greater than 400 mV during transmit bursts
Additional hints for the VCC supply application circuits
To reduce voltage drops, use a low impedance power source. The resistance of the power supply lines
(connected to VCC and GND pins of the module) on the application board and battery pack should also be
considered and minimized: cabling and routing must be as short as possible in order to minimize power losses.
To avoid undershoot and overshoot on voltage drops at the start and at the end of a transmit burst during a
GSM call (when current consumption on the VCC supply can rise up to 2.5 A in the worst case), place a 330 µF
low ESR capacitor (e.g. KEMET T520D337M006ATE045) located near VCC pin of LEON-G100/LEON-G200.
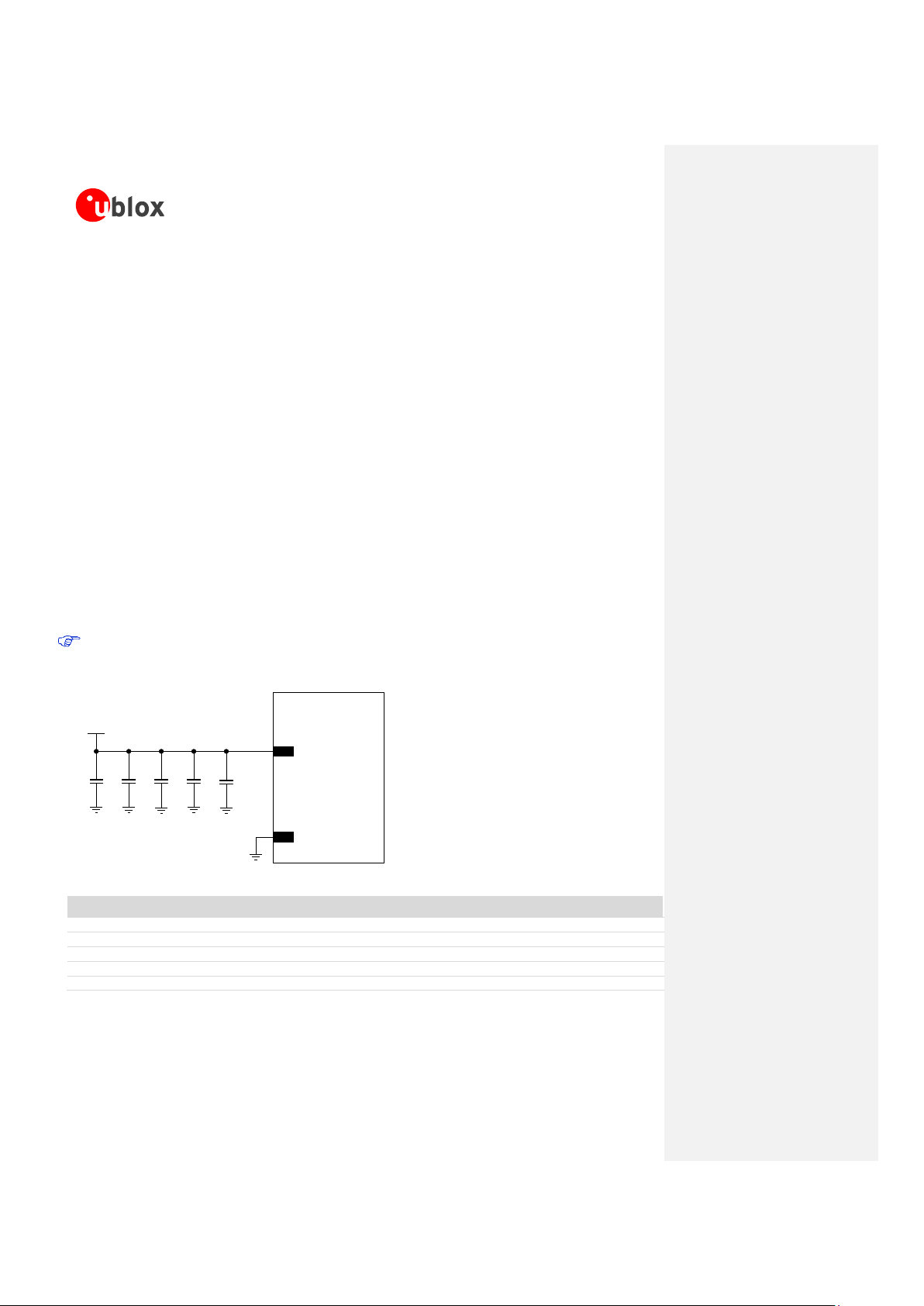
To reduce voltage ripple and noise, place near VCC pin of the LEON-G100/LEON-G200 the following
components:
100 nF capacitor (e.g Murata GRM155R61A104K) to filter digital logic noises from clocks and data sources
10 nF capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM155R71C103K) to filter digital logic noises from clocks and data sources
10 pF capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1E100J) to filter transmission EMI in the DCS/PCS bands
39 pF capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1E390J) to filter transmission EMI in the GSM/EGSM bands
Figure 9 shows the complete configuration but the mounting of the each single component depends on
application design.
VBAT
C1 C4
LEON-G100
LEON-G200
50
VCC
GND
C3C2
C5
+
Figure 9: Suggested schematics design to reduce voltage ripple, noise and avoid undershoot and overshoot on voltage drops
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
330 µF Capacitor Tantalum D_SIZE 6.3 V 45 mΩ
T520D337M006ATE045 - KEMET
C2
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R61A104KA01 - Murata
C3
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C4
39 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1E390JA01 - Murata
C5
10 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1E100JA01 - Murata
Table 7: Suggested components to reduce voltage ripple and noise and avoid undershoot and overshoot on voltage drops
Page 23
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 23 of 125
1.5.3 Current consumption profiles
During operation, the current consumed by LEON-G100/LEON-G200 through VCC pin can vary by several orders
of magnitude. This is applied to ranges from the high peak of current consumption during the GSM transmitting
bursts at maximum power level in connected mode, to the low current consumption in idle mode when power
saving configuration is enabled.
1.5.3.1 Current consumption profiles – Connected mode
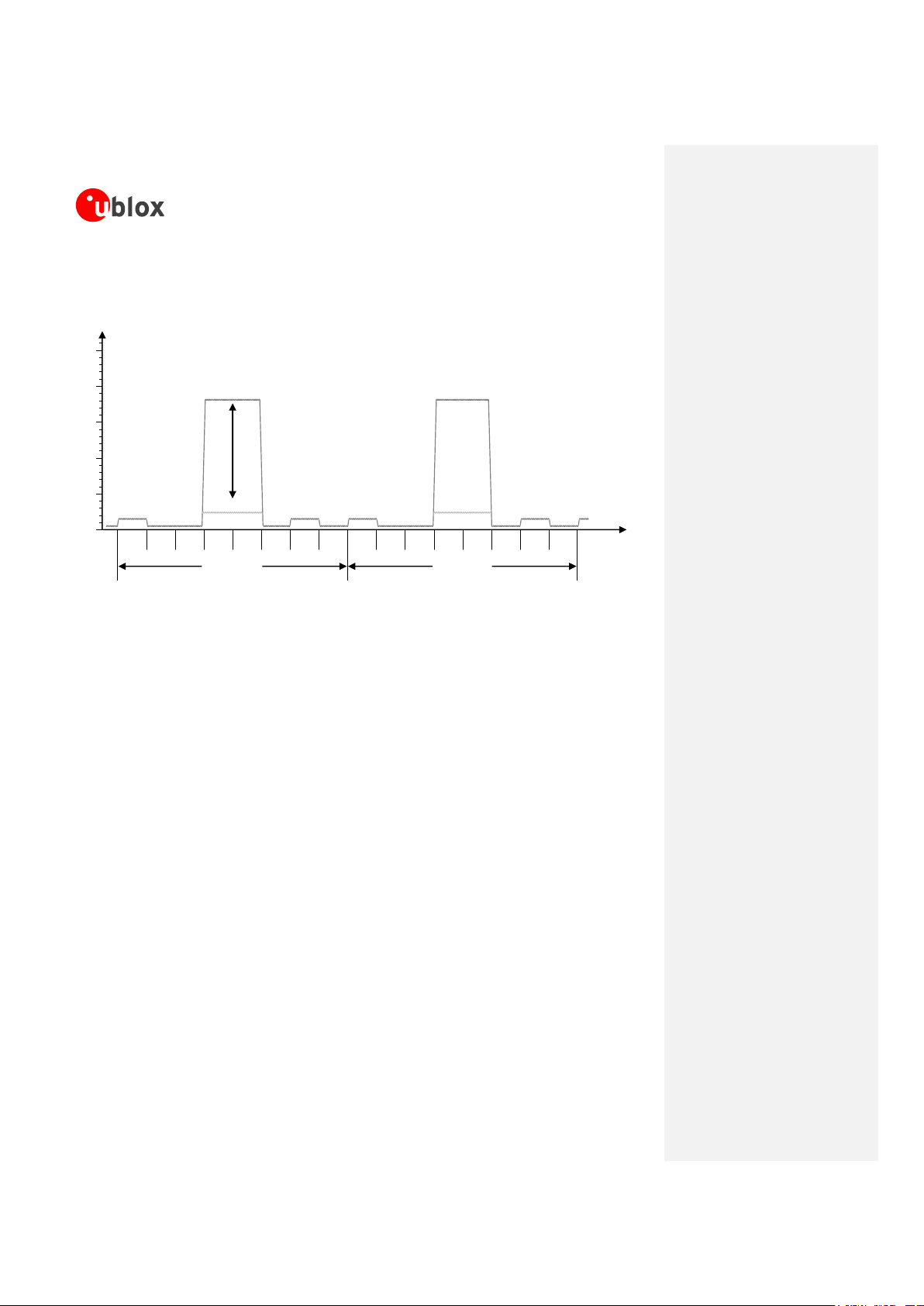
When a GSM call is established, the VCC consumption is determined by the current consumption profile typical
of the GSM transmitting and receiving bursts.
The current consumption peak during a transmission slot is strictly dependent on the transmitted power, which
is regulated by the network. If the module transmits in GSM talk mode in the GSM 850 or in the EGSM 900
band at the maximum power control level (32.2 dBm typical transmitted power in the transmit slot/burst), the
current consumption can reach up to 2500 mA (with highly unmatched antenna) for 576.9 µs (width of the
transmit slot/burst) with a periodicity of 4.615 ms (width of 1 frame = 8 slots/bursts), so with a 1/8 duty cycle,
according to GSM TDMA.
During a GSM call, current consumption is in the order of 100-200 mA in receiving or in monitor bursts and is
about 30-50 mA in the inactive unused bursts (low current period). The more relevant contribution to determine
the average current consumption is set by the transmitted power in the transmit slot.
Figure 10 shows an example of current consumption profile of the data module in GSM talk mode.
Time [ms]
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
Current [A]
200 mA
~170 mA
2500 mA
Peak current
depends on
TX power
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
2.5
2.0
~170 mA
~40 mA
Figure 10: Description of the VCC current consumption profile versus time during a GSM call (1 TX slot)
When a GPRS connection is established there is a different VCC current consumption profile also determined by
the transmitting and receiving bursts. In contrast to a GSM call, during a GPRS connection more than one slot
can be used to transmit and/or more than one slot can be used to receive. The transmitted power depends on
network conditions and sets the peak of current consumption, but following the GPRS specifications the
maximum transmitted power can be reduced if more than one slot is used to transmit, so the maximum peak of
current consumption is not as high as can be the case in a GSM call.
If the module transmits in GPRS class 10 connected mode in the GSM 850 or in the EGSM 900 band at the
maximum power control level (30.5 dBm typical transmitted power in the transmit slot/burst), the current
consumption can reach up to 1800 mA (with highly unmatched antenna) for 1.154 ms (width of the 2 transmit
Page 24
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 24 of 125
slots/bursts) with a periodicity of 4.615 ms (width of 1 frame = 8 slots/bursts), so with a 1/4 duty cycle, according
to GSM TDMA.
In the following figure is reported the current consumption profiles with 2 slots used to transmit.
Time [ms]
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
Current [A]
200mA
~170 mA
1800 mA
Peak current
depends on
TX power
~170 mA
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
2.5
2.0
~40 mA
Figure 11: Description of the VCC current consumption profile versus time during a GPRS connection (2 TX slots)
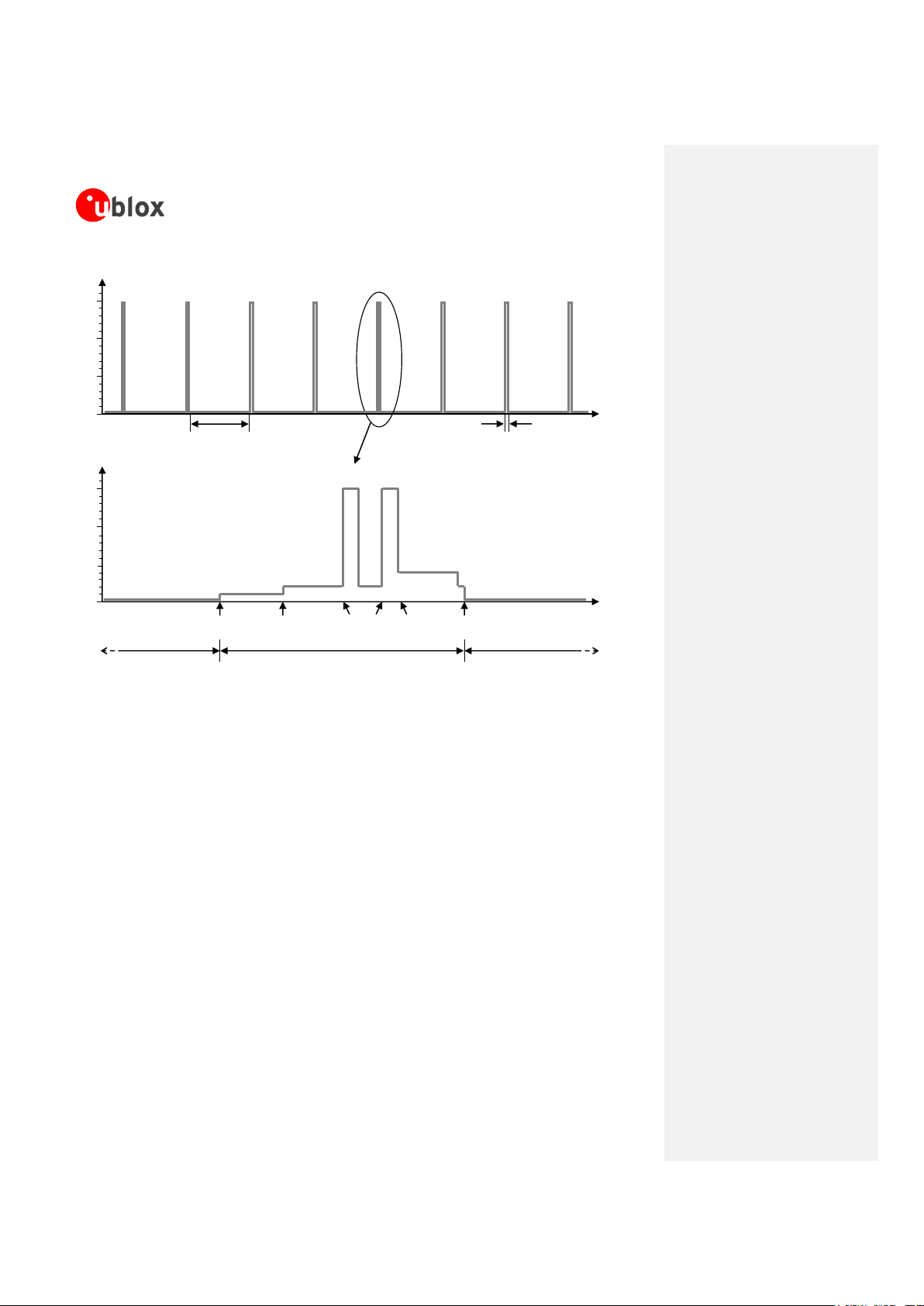
1.5.3.2 Current consumption profiles – Cyclic idle/active mode (power saving enabled)
The power saving configuration is by default disabled, but it can be enabled using the appropriate AT command
(refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2], AT+UPSV command). When the power saving is enabled, the module
automatically enters idle-mode whenever possible.
When power saving is enabled, the module is registered or attached to a network and a voice or data call is not
enabled, the module automatically enters idle-mode whenever possible, but it must periodically monitor the
paging channel of the current base station (paging block reception), in accordance to GSM system requirements.
When the module monitors the paging channel, it wakes up to active mode, to enable the reception of paging
block. In between, the module switches to idle-mode. This is known as GSM discontinuous reception (DRX).
The module processor core is activated during the paging block reception, and automatically switches its
reference clock frequency from the 32 kHz used in idle-mode to the 26 MHz used in active-mode.
The time period between two paging block receptions is defined by the network. It can vary from 470.76 ms
(width of 2 GSM multiframes = 2 x 51 GSM frames = 2 x 51 x 4.615 ms) up to 2118.42 ms (width of 9 GSM
multiframes = 9 x 51 frames = 9 x 51 x 4.615 ms): this is the paging period parameter, fixed by the base station
through broadcast channel sent to all users on the same serving cell.
An example of the current consumption profile of the data module when power saving is enabled is shown in
Figure 12: the module is registered with the network, automatically goes into idle mode and periodically wakes
up to active mode to monitor the paging channel for paging block reception (cyclic idle/active mode).
Page 25
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 25 of 125
~30 ms
IDLE MODE ACTIVE MODE IDLE MODE
500-700 µA
8-10 mA
20-22 mA
~150 mA
Active Mode
Enabled
Idle Mode
Enabled
PLL
Enabled
RX
Enabled
500-700 µA
~150 mA
0.44-2.09 s
IDLE MODE
~30 ms
ACTIVE MODE
Time [s]
Current [mA]
150
100
50
0
Time [ms]
Current [mA]
150
100
50
0
38-40 mA
DSP
Enabled
Figure 12: Description of the VCC current consumption profile versus time when power saving is enabled: the module is in idle
mode and periodically wakes up to active mode to monitor the paging channel for paging block reception
1.5.3.3 Current consumption profiles – Fixed active mode (power saving disabled)
Power saving configuration is by default disabled, or it can be disabled using the appropriate AT command (refer
to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2], AT+UPSV command). When power saving is disabled, the module doesn’t
automatically enter idle-mode whenever possible: the module remains in active mode.
The module processor core is activated during active-mode, and the 26 MHz reference clock frequency is used.
An example of the current consumption profile of the data module when power saving is disabled is shown in
Figure 13: the module is registered with the network, active-mode is maintained, and the receiver and the DSP
are periodically activated to monitor the paging channel for paging block reception.
Page 26
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 26 of 125
ACTIVE MODE
20-22 mA 20-22 mA
20-22 mA
~150 mA
0.47-2.12 s
Paging period
Time [s]
Current [mA]
150
100
50
0
Time [ms]
Current [mA]
150
100
50
0
RX
Enabled
DSP
Enabled
~150 mA
38-40 mA
Figure 13: Description of the VCC current consumption profile versus time when power saving is disabled: active-mode is
always held, and the receiver and the DSP are periodically activated to monitor the paging channel for paging block reception
1.5.4 Battery charger (LEON-G200 only)
For battery charging functionalities the module is provided with integrated circuitry and software. Two pins are
available to connect the positive pole of the external DC supply used as charger.
Name
Description
Remarks
V_CHARGE
Charger Voltage Supply Input
V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE pins must be externally
connected together.
CHARGE_SENSE
Charger Voltage Measurement Input
V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE pins must be externally
connected together.
Table 8: Battery charger pins
V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE pins ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F). A higher
protection level could be required if the lines are externally accessible on the application board. A higher
protection level can be achieved mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor
array) on the lines connected to these pins if they are externally accessible on the application board.
Page 27
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 27 of 125
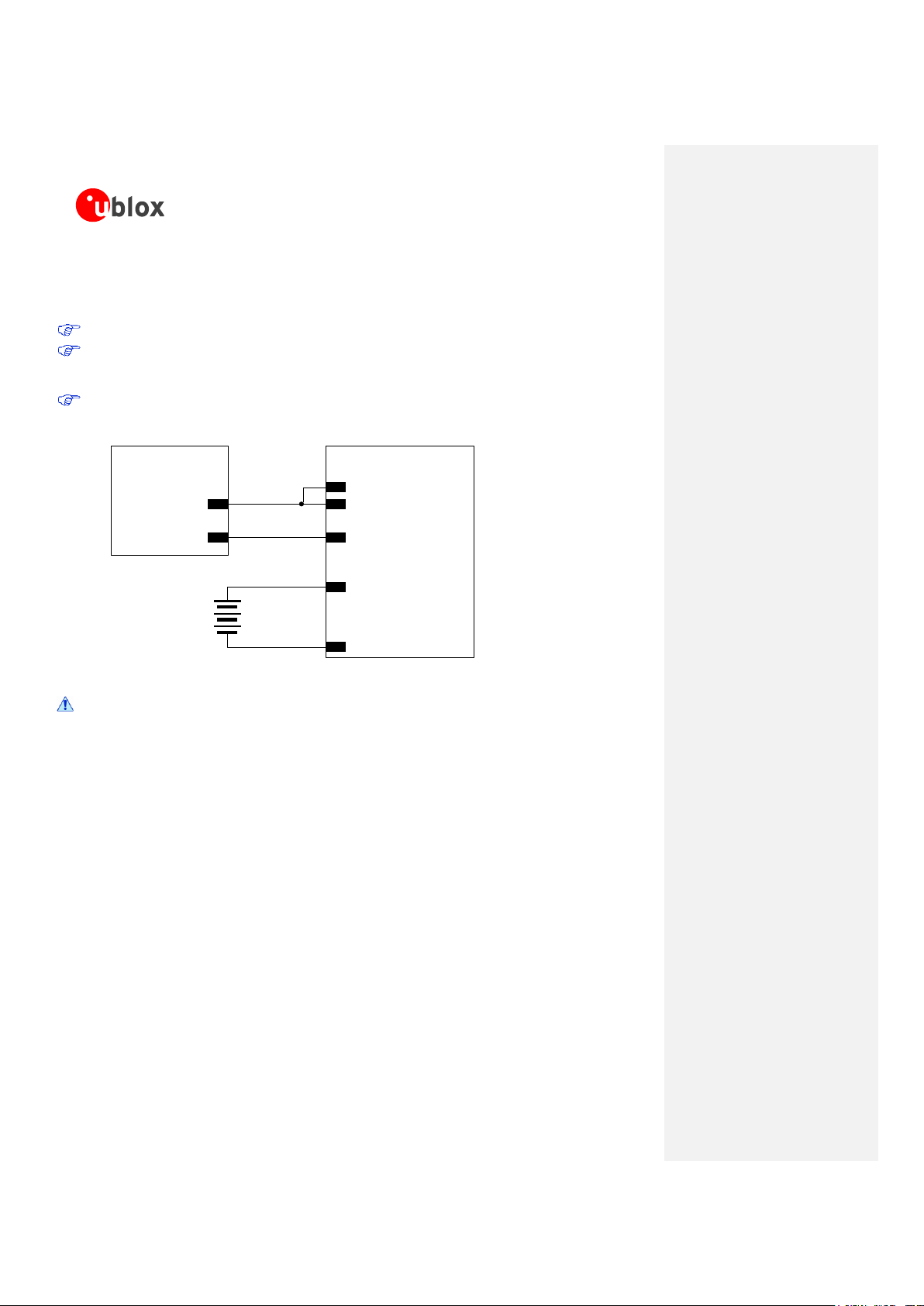
The V_CHARGE pin is the charger supply input: it sinks the charge current that is typically in the order of several
hundred of mA. The CHARGE_SENSE pin is connected to an internal ADC converter to measure the charging
voltage: it senses the charger voltage and sinks a few µA.
V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE pins must be externally connected together as shown in Figure 14.
There may not be any capacitor on the charge path: a straight connection must be provided between
the output of the external supply used as charging source and V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE pins
of the module.
If the battery charging process is not managed by the GSM module, V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE
pins can be left floating on the application board.
LEON-G200
+
Charger
Voltage and
current limited
Li-Ion
Battery
5
CHARGE_SENSE
4
V_CHARGE
GND
50
VCC
GND
-
+
-
Figure 14: Connection of an external DC supply used as charger and a Li-Ion battery to the LEON-G200 module
To prevent damage to the module and the battery, use only chargers that comply with the
characteristics given in section 1.5.4.2.
1.5.4.1 Charging process description
A valid charger is recognized if the voltage provided to V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE pins are within the
operating range limits (5.6 V minimum, 15 V maximum). If the module is switched off, the charger circuitry
generates the power on in charging mode after charger detection.
The algorithm that controls battery charging, implements a classic Li-Ion battery charging process, divided into 4
phases:
1. Pre-Charge, at low current, for deeply discharged batteries (VCC voltage within 0 V and 3.1 V typical)
2. Fast Charge, at the maximum current provided by the external DC supply used as charger that must be
current limited, for discharged batteries (VCC voltage within 3.1 V typical and 4.2 V typical)
3. Top Charge, to complete the over-charging of the batteries, after the maximum voltage is reached (VCC
voltage equal to 4.2 V typical)
4. Trickle Charge, to maintain the battery at higher level of charge, if the external DC supply used as charger
remains connected
If the batteries are deeply discharged (VCC voltage within 0 V and 3.1 V typical with 7% tolerance due to
change in temperature and life time), and the device is in not-powered mode, the charger circuit starts
pre-charging when a valid voltage is provided to V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE pins of the module. In the
pre-charging phase, the charge transistor switch mounted inside the module is pulsed with a 100 Hz clock and
an on-time of 12.5% of a period. This means the average charge current is reduced to avoid overheating of
Page 28
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 28 of 125
charger parts and to gently charge the deeply discharged batteries: the average pre-charge current is ~1/8 (i.e.
12.5%) of the current provided by the external charger, so it is ~1/8 of the external charger current limit.
Pre-charging phase is hardware controlled and continues as long as the VCC voltage reaches the 3.1 V typical
limit, so the module is able to start the following fast charging phase.
During fast charging phase (following the pre-charging phase) the charge transistor switch mounted inside the
module is pulsed with a 100 Hz and an on-time of 99% of a period: the average charge current is almost equal
(i.e. 99%) to the current provided by the external charger, so it is almost equal to the external charger current
limit. The remaining off time (i.e. 1% of a period) is used to check if the external charger is still connected since
detection is critical when charging switch is closed.
The integrated charging circuit doesn’t have any voltage or current limitation, therefore the charger must be
chosen very carefully: during the fast charging phase, the battery is charged with the maximum DC current
provided by the external DC supply used as charger, which must be current limited as described in the charger
specification section.
When the battery voltage reaches the nominal maximum voltage (4.2 V typical with 2% tolerance due to change
in temperature and life time), charging enters the constant voltage phase (top charge algorithm): in this phase
the average charging current decreases until the battery is completely charged.
After the constant voltage phase, the battery is maintained at a higher level of charge with the trickle charge
algorithm until an external charger is connected to the module.
The charging process is enabled only within the temperature range from 0°C to 40°C, with a 5°C hysteresis to
prevent rapid switching on and off as the temperature drifts around the set point: charging is disabled when the
temperature falls below 0°C and then enabled when it rises above 5°C; charging is disabled when the measured
temperature rises above 40°C and then enabled when falls below 35°C.
Battery over-voltage detection is implemented to switch-off charging if the battery is removed during charging.
The VCC over-voltage threshold level is set to the nominal value of 4.47 V (evaluated with 2% of tolerance due
to change in temperature and life time).
The charging process is disabled when an external charger is removed from V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE
pins.
1.5.4.2 External charger specification
It is suggested to use a charger with the following electrical characteristics:
6 V DC voltage
500 mA current limit (if it is less than the maximum DC charging current specified by the used battery)
To avoid damage to the module, the external supply used as charging source must be voltage
and current limited, with a voltage limit ≤ 15 V and a current limit ≤ 1.0 A.
DC supplies with fold-back current protection cannot be used as charger for the module.
The V-I output characteristics of the external supply used as charger must be within the valid area delineated by:
the maximum acceptable charging voltage (equal to 15 V in any case)
the minimum open circuit voltage valid for charger detection (equal to 5.6 V in any case)
the maximum acceptable charging current (equal to 1.0 A or to the maximum DC charging current specified
by the used battery if it is less than 1.0 A)
the minimum charging current (specified by the application, e.g. 400 mA)
Page 29
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 29 of 125
Maximum voltage
The voltage limit of the external charger must be ≤ 15 V. Since the module is not provided with an internal
overvoltage protection circuit on V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE pins, the charging voltage must be lower or
equal to the maximum acceptable charging voltage value of 15 V at any time: voltage spikes that may occur
during connection or disconnection of the charger must be limited within this value, so the external supply used
as charging source must be voltage limited with a voltage limit ≤ 15 V.
Minimum voltage
The charger must be able to provide a minimum open circuit output voltage ≥ 5.6 V for the valid charger
detection.
Maximum current
The current limit of the external charger must be ≤ 1.0 A (that is the module absolute maximum rating as
charging current) and must be lower than the maximum DC charging current specified by the used battery.
Since the module is not provided with an internal over-current protection circuit on V_CHARGE and
CHARGE_SENSE pins, the charging current must be lower or equal to the maximum acceptable charging
current value at any time: current spikes that may occur during charger connection or disconnection must be
limited within this value, so the external supply used as charging source must be current limited with a proper
current limit.
Minimum current
A minimum acceptable value for the charging current is not specified, but the charging current value should be
large enough to perform the whole battery charging process within the time interval defined by the application
and the charging current value should be greater than the highest possible average current consumption of the
system that is supplied by the battery (i.e. the module plus any additional device on the application board) to let
the increase of the battery level while the system reaches its highest current consumption. For example, if the
battery supplies only the module and the charging current value is equal to 400 mA, the battery level can be
increased also when the module reaches its highest current consumption (during a GPRS connection). If some
other devices are supplied by the battery beside the module, when the battery is deeply discharged (VCC below
3.1 V typical), the module is switched off and the pre-charging current (~1/8 of the external charger current
limit) is enabled: this current should be greater than the highest possible average current consumption of the
system to let the increase of the battery level while the system reaches its highest current consumption.
For example, Figure 15 shows the valid area for the charger V-I output characteristics using a battery with a
maximum DC charging current equal to 600 mA: the maximum acceptable charging current is defined by the
battery requirement (600 mA).
Page 30
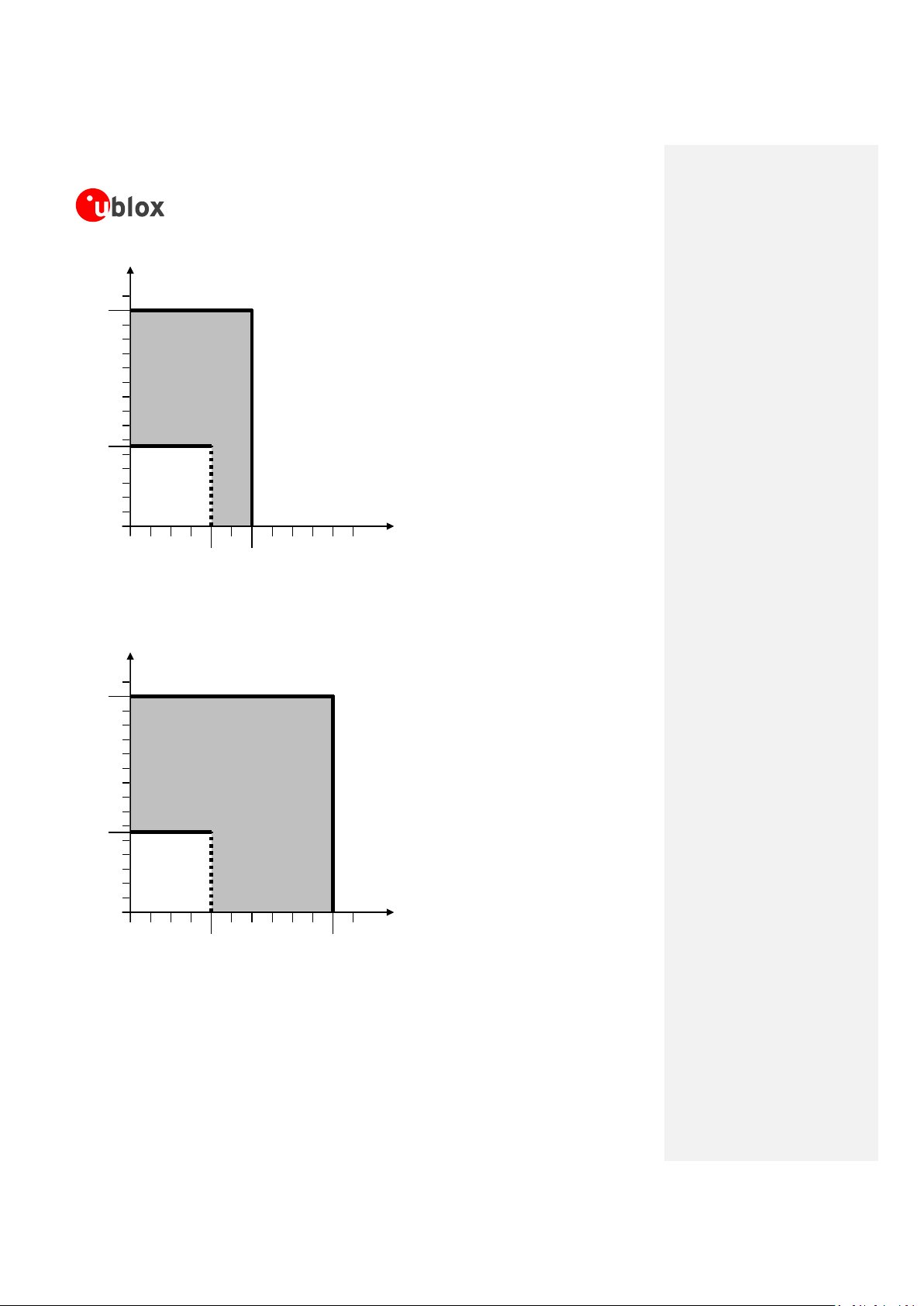
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 30 of 125
16
15.0
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
800700500
400
3002001000 900 1000 1100
mA
V
5.6
600
Figure 15: Valid area for the charger V-I output characteristics using a battery with a max DC charging current equal to 600 mA
For example, Figure 16 shows the valid area for the charger V-I output characteristics using a battery with a
maximum DC charging current greater than 1000 mA: the maximum acceptable charging current is defined by
the module requirement (1000 mA).
16
15.0
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
800700500
400
3002001000 900600 1100
mA
V
5.6
1000
Figure 16: Valid area for the charger V-I output characteristics using a battery with a max DC charging current greater than 1 A
Page 31

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 31 of 125
1.5.5 RTC Supply (V_BCKP)
V_BCKP connects the Real Time Clock (RTC) supply, generated internally by a linear regulator integrated in the
module chipset. The output of this linear regulator is enabled when the main voltage supply providing the
module through VCC is within the valid operating range, or if the module is switched-off.
Name
Description
Remarks
V_BCKP
Real Time Clock supply
V_BCKP = 2.0 V (typical) generated by the module to supply
Real Time Clock when VCC supply voltage is within valid
operating range.
Table 9: Real Time Clock supply pin
V_BCKP pin ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F). A higher protection level could be
required if the line is externally accessible on the application board. A higher protection level can be
achieved by mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) on the line
connected to this pin if it is externally accessible on the application board.
The RTC provides the time reference (date and time) of the module, also in power -off mode, since the RTC runs
when the V_BCKP voltage is within its valid range (specified in LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1]). The
RTC block is able to provide programmable alarm functions by means of the internal 32.768 kHz clock.
The RTC block has very low, but highly temperature dependent power consumption. For example at 25°C and a
V_BCKP voltage of 2.0 V the power consumption is approximately 2 µA, whereas at 85°C and an equal voltage
it increases to 5 µA.
The RTC can be supplied from an external back-up battery through V_BCKP, when the main voltage supply is
not provided to the module through VCC. This enables the time reference (date and time) to run even when the
main supply is not provided to the module. The module cannot switch on if a valid voltage is not present on
VCC, even when RTC is supplied through V_BCKP (meaning that VCC is mandatory to switch-on the module).
If V_BCKP is left unconnected and the main voltage supply of the module is removed from VCC, the RTC is
supplied from the 1 µF buffer capacitor mounted inside the module. However, this capacito r is not able to
provide a long buffering time: within 0.5 seconds the voltage on V_BCKP will fall below the valid range (1 V
min).
If RTC is not required when VCC supply is removed, V_BCKP can be left floating on the application
board.
If RTC has to run for a time interval of T [seconds] at 25°C and VCC supply is removed, place a capacitor of
nominal capacitance of C [µF] at the V_BCKP pin. Choose the capacitor using the following formula:
C [µF] = (Current_Consumption [µA] x T [seconds]) / Voltage_Drop [V] = 2 x T [seconds]
The current consumption of the RTC is around 2 µA at 25°C, and the voltage drop is equal to 1 V (from the
V_BCKP typical value of 2.0 V to the valid range minimum limit of 1.0 V).
For example, a 100 µF capacitor (such as the Murata GRM43SR60J107M) can be placed at V_BCKP to provide a
long buffering time. This capacitor will hold V_BCKP voltage within its valid range for around 50 seconds at
25°C, after the VCC supply is removed. If a very long buffering time is required, a 70 mF super-capacitor (e.g.
Seiko Instruments XH414H-IV01E) can be placed at V_BCKP, with a 4.7 k series resistor to hold the V_BCKP
voltage within its valid range for around 10 hours at 25°C, after the VCC supply is removed. The purpose of the
series resistor is to limit the capacitor charging current due to the big capacitor specifications, and also to let a
fast rise time of the voltage value at the V_BCKP pin after VCC supply has been provided. These capacitors will
allow the time reference to run during a disconnection of the VCC supply.
Page 32

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 32 of 125
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
C1
(a)
2
V_BCKP
R2
C2
(superCap)
(b)
2
V_BCKP
2V
(c)
2
V_BCKP
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
Figure 17: Real time clock supply (V_BCKP) application circuits: (a) using a 100 µF capacitor to let the RTC run for 50 seconds at
25°C; (b) using a 70 mF capacitor to let the RTC run for ~10 hours at 25°C when the VCC supply is removed; (c) using a not
rechargeable battery
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
100 µF Tantalum Capacitor
GRM43SR60J107M - Murata
R2
4.7 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-074K7L - Yageo Phycomp
C2
70 mF Capacitor
XH414H-IV01E - Seiko Instruments
Table 10: Example of components for V_BCKP buffering
If longer buffering time is required to allow the time reference to run during a disconnection of the VCC supply,
a rechargeable battery, which has to be able to provide a 2.0 V nominal voltage and must not exceed the
maximum operating voltage value of 2.25 V, can be connected to the V_BCKP pin with a proper series resistor.
Otherwise a not rechargeable battery, which has to be able to provide a 2.0 V nominal voltage and must not
exceed the maximum operating voltage value of 2.25 V, can be connected to the V_BCKP pin with a proper
series resistor and a proper series diode. The purpose of the series resistor is to limit the battery charging current
due to the battery specifications, and also to let a fast rise time of the voltage value at the V_BCKP pin after
VCC supply has been provided. The purpose of the series diode is to avoid a current flow from the V_BCKP pin
of the module to the not rechargeable battery.
1.6 System functions
1.6.1 Module power on
The power-on sequence of the module is initiated in one of 4 ways:
Rising edge on the VCC pin to a valid voltage as module supply
Low level on the PWR_ON signal
RTC alarm
Charger detection on the V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE pins (LEON-G200 only)
Name
Description
Remarks
PWR_ON
Power-on input
PWR_ON pin has high input impedance.
Do not keep floating in noisy environment: external pull-up
required.
Table 11: Power-on pin
PWR_ON pin ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F). A higher protection level could be
required if the line is externally accessible on the application board. A higher protection level can be
achieved mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) on the line
connected to this pin if it is externally accessible on the application board.
Page 33

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 33 of 125
1.6.1.1 Rising edge on VCC
When a supply is connected to VCC pin, the module supply supervision circuit controls the subsequent activation
of the power up state machines: the module is switched-on when the voltage rises up to the VCC normal
operating range minimum limit (3.35 V) starting from a voltage value lower than 2.25 V.
1.6.1.2 Low level on the PWR_ON
Power-on sequence of the module starts when a low level is forced on the PWR_ON signal for at least 5 ms.
The electrical characteristics of the PWR_ON input pin are different from the other digital I/O interfaces: the high
and the low logic levels have different operating ranges and the pin is tolerant against voltages up to the battery
voltage. The detailed electrical characteristics are described in LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1].
PWR_ON pin has high input impedance and is weakly pulled to the high level on the module. Avoid
keep it floating in noisy environment. To hold the high logic level stable, the PWR_ON pin must be
connected to a pull-up resistor (e.g. 100 kΩ) biased by the V_BCKP supply pin of the module.
If PWR_ON input is connected to a push button that shorts the PWR_ON pin to ground, the V_BCKP supply pin
of the module can be used to bias the pull-up resistor.
If PWR_ON input is connected to an external device (e.g. application processor), it is suggested to use an open
drain output of the external device with an external pull-up. Connect the pull-up the V_BCKP supply pin of the
module.
If PWR_ON pin is connected to a push-pull output pin of an application processor, the pull-up can be provided
to pull high the PWR_ON level when the application processor is switched off. If the high-level voltage of the
push-pull output pin of the application processor is greater than 2.0 V, the V_BCKP supply cannot be used to
bias the pull-up resistor: the supply rail of the application processor, or the VCC supply could be used but this
will increase the V_BCKP (RTC supply) current consumption when the module is in not-powered mode (i.e. VCC
supply not present). Using a push-pull output of the external device, take care to fix the proper level in all the
possible scenarios to avoid an inappropriate switch-on of the module.
The module can be switched-on by forcing a low level for at least 5 ms on the PWR_ON pin: the
module is not switched-on by a falling edge provided on the PWR_ON pin. The suggested PWR_ON
pull-up resistor value is 100 kΩ: lower resistance value will increase the module power-off consumption.
The suggested supply to bias the pull-up resistor is the V_BCKP supply pin of the module.
Page 34

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 34 of 125
Power-on
push button
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
19
PWR_ON
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
19
PWR_ON
Application Processor
100 k
2
V_BCKP
ESD
100 k
2
V_BCKP
Figure 18: Power on (PWR_ON) application circuits using a push button or using an application processor
1.6.1.3 RTC alarm
The module can be switched-on by the RTC alarm if a valid voltage is applied to VCC pin, when Real Time Clock
system reaches a pre-defined scheduled time. The RTC system will then initiate the boot sequence by indicating
to the power management unit to turn on power. Also included in this setup is an interrupt signal from the RTC
block to indicate to the baseband processor, that a RTC event has occurred.
1.6.1.4 Charger detection on V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE pins (LEON-G200 only)
The module can be switched-on by a charger: when a voltage value within the valid range for charger detection
is applied to the module V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE pins (See LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1]),
the module is switched on in charge mode.
1.6.1.5 Additional considerations
The module is switched on when the voltage rises up to the VCC normal operating range: the first time that the
module is used, it is switched on in this way. Then, the proper way to switch-off the module is by means of the
AT+CPWROFF command. When the module is in power-off mode, i.e. the AT+CPWROFF command has been
sent and a voltage value within the normal operating range limits is still provided to the VCC pin, the digital
input-output pads of the baseband chipset (i.e. all the digital pins of the module) are locked in tri-state (i.e.
floating). The power down tri-state function isolates the pins of the module from its environment, when no
proper operation of the outputs can be guaranteed. To avoid an increase of the module current consumption in
power down mode, any external signal of the digital interfaces connected to the module must be set low or tristated when the module is in not-powered mode or in the power-off mode.
The module can be switched on from power-off mode by forcing a proper start-up event (i.e. a low level on the
PWR_ON pin, or an RTC alarm, or a charger detection). After the detection of a start-up event, all the digital
pins of the module are held in tri-state until all the internal LDO voltage regulators are turned on in a defined
power-on sequence. Then, as described in Figure 19, the baseband core continues to be held in reset state for a
time interval: the module still pulls the RESET_N pin low and any signal from the module digital interfaces is
held in reset state. The reset state of all the digital pins is reported in the pin description table of the LEON-G100
/ LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1]. When the module releases the RESET_N pin, the level at this pin will be pulled high
Page 35

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 35 of 125
by the action of the internal pull-up and the configuration of the module interfaces will start: during this phase
any digital pin is set in a proper sequence from reset state to the default operational configuration. The module
is fully ready to operate when all the interfaces are configured.
VCC
V_BCKP
PWR_ON
LDOs
RESET_N
System State
BB Pads State
Rese t → Opera tiona l Operational
Tristate / Floating
Rese t
OFF
ON
*
Start-up
event
0 ms
~22 ms
~23 ms
~45 ms
PWR_ON
can be set high
Start of interfaces'
configuration
All interfaces
are configured
Figure 19: Power on sequence description (* - the PWR_ON signal state is not relevant during this phase)
Page 36

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 36 of 125
1.6.2 Module power off
The correct way to switch off LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules is by means of the AT command AT+CPWROFF
(more details in u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]): in this way the current parameter settings are saved in the
module’s non-volatile memory and a proper network detach is performed.
An under-voltage shutdown will be done if VCC falls below the extended operating range minimum limit (see
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1]), but in this case the current parameter settings are not saved in the
module’s non-volatile memory and a proper network detach cannot be performed.
When the AT+CPWROFF command is sent, the module starts the switch-off routine replying OK on the AT
interface: during this phase, the current parameter settings are saved in the module’s non-volatile memory, a
network detach is performed and all module interfaces are disabled (i.e. the digital pins are locked in tri-state by
the module). Since the time to perform a network detach depends on the network settings, the duration of this
phase can differ from the typical value reported in Figure 20. At the end of the switch-off routine, the module
pulls the RESET_N pin low to indicate that it is in power-off mode: all the digital pins are locked in tri-state by
the module and all the internal LDO voltage regulators except the RTC supply (V_BCKP) are turned off in a
defined power-off sequence. The module remains in power-off mode as long as a switch-on event doesn’t occur
(i.e. a low level on the PWR_ON pin, or an RTC alarm, or a charger detection), and enters not-powered mode if
the supply is removed from the VCC pin.
To avoid an increase of module current consumption in power-down mode, any external signal
connected to the module digital pins (UART interface, Digital audio interface, HS_DET, GPIOs) must be
tri-stated when the module is in the not-powered or power-off modes. If the external signals connected
to the module digital pins cannot be set low or tri-stated, insert a switch (e.g. Texas Instruments
SN74CB3Q16244, or Texas Instruments TS5A3159, or Texas Instruments TS5A63157) between the twocircuit connections. Set the switch to high impedance when the module is in power-down mode (to
avoid an increase of the module power consumption).
Figure 20 describes the power-off sequence.
VCC
V_BCKP
PWR_ON *
LDOs
RESET_N
System State
BB Pads State Operational
OFF
Tristate / Floating
ON
Operational → Tristate / Floating
AT+CPWROFF
sent to the module
OK
replied by the module
Figure 20: Power off sequence description (* - the PWR_ON signal state is not relevant during this phase)
Page 37

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 37 of 125
1.6.3 Module reset
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules can be reset using the RESET_N pin: when the RESET_N pin is forced low
for at least 50 ms, an “external” or “hardware” reset is performed, that causes an asynchronous reset of the
entire module, except for the RTC. Forcing an “external” or “hardware” reset, the current parameter settings
are not saved in the module’s non-volatile memory and a proper network detach is not performed.
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules can also be reset by means of the AT command AT+CFUN (more details in
u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]): in this case an “internal” or “software” reset is performed, that causes, like
the “external” or “hardware” reset, an asynchronous reset of the entire module except for the RTC. Forcing an
“internal” or “software” reset, the current parameter settings are saved in the module’s non-volatile memory
and a proper network detach is performed.
The RESET_N pin is pulled low by the module when the module is in power-off mode or an internal reset
occurs. In these cases an internal open drain FET pulls the line low.
Name
Description
Remarks
RESET_N
Reset signal
A series Schottky diode is integrated in the module as protection.
An internal 12.6 kΩ pull-up resistor pulls the line to 1.88 V when
the module is not in the reset state. An internal open drain FET
pulls the line low when an internal reset occurs and when the
module is in power down mode.
Table 12: Reset pin
RESET_N pin ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F). A higher protection level could be
required if the line is externally accessible on the application board. A higher protection level can be
achieved mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) on the line
connected to this pin if it is externally accessible on the application board.
For more details about the general precautions for ESD immunity about RESET_N pin, refer to chapter
2.5.1.
The reset state of each digital pin is reported in the pin description table in the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data
Sheet [1].
The electrical characteristics of RESET_N are different from the other digital I/O interfaces. The high and low
logic levels have different operating ranges and absolute maximum ratings. The detailed electrical characteristics
are described in the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1].
As described in the Figure 21, a series Schottky diode is mounted inside the module on the RESET_N pin to
increase the maximum allowed input voltage up to 4.5 V as operating range. Nevertheless the module senses a
low level when the RESET_N pin is forced low from the external.
As described in Figure 21, the module has an internal pull-up resistor (12.6 kΩ typical) which pulls the level on
the RESET_N pin to 1.88 V (typical) when the module is not in reset state. Therefore an external pull-up is not
required on the application board.
Forcing RESET_N low for at least 50 ms will cause an external reset of the module. When RESET_N is released
from the low level, the module automatically starts its power-on reset sequence.
If RESET_N is connected to an external device (e.g. an application processor on an application board) an open
drain output can be directly connected without any external pull-up. Otherwise, use a push-pull output. Make
sure to fix the proper level on RESET_N in all possible scenarios, to avoid unwanted reset of the module.
As an ESD immunity test precaution, a 47 pF bypass capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H470JA01) and a series
ferrite bead (e.g. Murata BLM15HD182SN1) must be added on the RESET_N line pin to avoid a module reset
caused by an electrostatic discharge applied to the application board (for more details, refer to chapter 2.5.1).
Page 38

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 38 of 125
Reset
push button
OUT
IN
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
12.6 k
1.88 V
22
RESET_N
OUT
IN
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
12.6 k
1.88 V
22
RESET_N
Application Processor
ESD
Ferrite Bead
Ferrite Bead
47 pF
47 pF
Figure 21: Application circuits to reset the module using a push button or using an application processor
When the module is in power-off mode or an internal reset occurs, RESET_N is pulled low by the module itself:
RESET_N acts as an output pin in these cases since an internal open drain FET (illustrated in Figure 21 and in
Figure 22) pulls the line low.
The RESET_N pin can indicate to an external application that the module is switched on and is not in the reset
state: RESET_N is high in these cases and is low otherwise. To sense the RESET_N level (i.e. both the high level
and the low level), the external circuit has to be able to cause a small current through the series Schottky diode
integrated in the module as protection (illustrated in Figure 21 and Figure 22) by means of a very weak pulldown. One of the following application circuits can be implemented to determine the RESET_N status:
RESET_N connected to an LED that emits light when the module is powered up and not in reset state and
doesn’t emit light otherwise, through a biased inverting NPN transistor, with a series base resistor with a
resistance value greater or equal to 330 kΩ
RESET_N connected to an input pin of an application processor that senses a low logic level (0 V) when the
module is powered up and is not in reset state and senses a high logic level (i.e. 3.0 V) otherwise, through
an inverting and level shifting NPN transistor, with a series base resistor with a resistance value greater or
equal to 330 kΩ
RESET_N connected to an input pin of the application processor that senses a high logic level (1.8 V) when
the module is powered up and is not in reset state and senses a low logic level (0 V) otherwise, through a
weak pull-down resistor, with a resistance value greater or equal to 680 kΩ.
Figure 22 shows examples of application circuits to sense the RESET_N level.
Page 39

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 39 of 125
OUT
IN
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
12.6 k
1.88 V
22
RESET_N
Application Processor
680 k
OUT
IN
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
12.6 k
1.88 V
22
RESET_N
Application Processor
INPUT
INPUT
22 k
330 k
OUT
IN
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
12.6 k
1.88 V
22
RESET_N
330 k
220
Ferrite Bead
47 pF
Ferrite Bead
47 pF
Ferrite Bead
47 pF
Figure 22: Application circuits to sense if the module is in the reset state
The RESET_N is set low by the module for 160 µs to indicate that an internal reset occurs.
The exact low level time interval depends on the implemented circuit, since the fall time of the RESET_N low
pulse depends on the pull-down value, which must be greater or equal to 680 kΩ.
For example, if LEON RESET_N pin is connected through a 680 kΩ pull-down resistor to an input pin of an
application processor in the 1.8 V domain (i.e. Vih = 0.7 x 1.8 V = 1.26 V, Vil = 0.3 x 1.8 V = 0.54 V), the low
level time interval will be ~145 µs, since the 680 kΩ pull-down forces a ~35 µs 100%-0% fall time, as illustrated
in the Figure 23.
Page 40

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 40 of 125
Depends on the
pull-down strength
(~35 µs with 680 k)
time [µs]
1600
LOW = 0 V
HIGH = 1.88 V
Reset state start Reset state end
RESET_N
Figure 23: RESET_N behavior due to an internal reset
1.6.4 Note: Tri-stated external signal
Any external signal connected to the UART interface, I2S interfaces and GPIOs must be tri-stated when the
module is in power-down mode, when the external reset is forced low, and during the module power-on
sequence (at least for 3 s after the start-up event), to avoid latch-up of circuits and allow a proper boot of the
module. If the external signals connected to the wireless module cannot be tri-stated, insert a multi channel
digital switch (e.g. Texas Instruments SN74CB3Q16244, TS5A3159, or TS5A63157) between the two-circuit
connections and set to high impedance during module power down mode, when external reset is forced low
and during power-on sequence.
1.7 RF connection
The ANT pin has 50 Ω nominal impedance and must be connected to the antenna through a 50 Ω transmission
line to allow transmission and reception of radio frequency (RF) signals in the GSM operating bands.
Name
Description
Remarks
ANT
RF antenna
50 nominal impedance.
Table 13: Antenna pin
ANT port ESD immunity rating is 4 kV (according to IEC 61000-4-2). A higher protection level could be
required if the line is externally accessible on the application board. A higher protection level can be
achieved with an external high pass filter, consists of a 15 pF capacitor (e.g. the Murata
GRM1555C1H150JA01) and a 39 nH coil (e.g. Murata LQG15HN39NJ02) connected to the ANT port.
The antenna detection functionality will be not provided implementing this high pass filter for ESD
protection on the ANT port.
Choose an antenna with optimal radiating characteristics for the best electrical performance and overall module
functionality. An internal antenna, integrated on the application board, or an external antenna, connected to the
application board through a proper 50 Ω connector, can be used. See section 2.4 and 2.2.1.1 for further details
regarding antenna guidelines.
Page 41

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 41 of 125
The recommendations of the antenna producer for correct installation and deployment (PCB
layout and matching circuitry) must be followed.
If an external antenna is used, the PCB-to-RF-cable transition must be implemented using either a suitable 50 Ω
connector, or an RF-signal solder pad (including GND) that is optimized for 50 Ω characteristic impedance.
If antenna supervisor functionality is required, the antenna should have built in DC diagnostic resistor to ground
to get proper antenna detection functionality (See section 2.4.3 Antenna detection functionality).
1.8 SIM interface
An SIM card interface is provided on the board-to-board pins of the module. High-speed SIM/ME interface is
implemented as well as automatic detection of the required SIM supporting voltage.
Both 1.8 V and 3 V SIM types are supported: activation and deactivation with automatic voltage switch from 1.8
to 3 V is implemented, according to ISO-IEC 78-16-e specifications. The SIM driver supports the PPS (Protocol
and Parameter Selection) procedure for baud-rate selection, according to the values determined by the SIM
Card.
Table 14 describes the pins related to the SIM interface:
Name
Description
Remarks
VSIM
SIM supply
1.80 V typical or 2.85 V typical automatically generated by the
module
SIM_CLK
SIM clock
3.25 MHz clock frequency
SIM_IO
SIM data
Internal 4.7 kΩ pull-up to VSIM
SIM_RST
SIM reset
Table 14: SIM Interface pins
A low capacitance (i.e. less than 10 pF) ESD protection device (e.g. Infineon ESD8V0L2B -03L or AVX
USB0002RP or AVX USB0002DP) must be placed near the SIM card holder on each line (VSIM, SIM_IO,
SIM_CLK, SIM_RST). SIM interface pins ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F): higher
protection level is required if the lines are connected to a SIM card holder/connector, so they are
externally accessible on the application board.
For more details about the general precautions for ESD immunity about SIM pins, refer to chapter 2.5.1.
Figure 24 shows the minimal circuit connecting the LEON and the SIM card. This shows the VSIM supply
connected to the VPP pin (contact C6) of the SIM card as well as VCC (contact C1). Providing VPP was a
requirement for 5 V cards, but under 3GPP TS 51.011 specification [16], 3 V and 1.8 V SIM cards do not require
VPP and the mobile equipment (ME) need not provide contact C6. If the ME provides contact C6, then it can
either provide the same voltage as on VCC or it can leave the signal open, but it cannot connect VPP to GND.
Page 42

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 42 of 125
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
C1
SIM CARD
HOLDER
CCVCC (C1)
CCVPP (C6)
CCIO (C7)
CCCLK (C3)
CCRST (C2)
GND (C5)
C2 C3 C5
D1 D2
C5C6C
7
C1C2C
3
SIM Card
Bottom View
(contacts side)
J1
35
VSIM
33
SIM_IO
32
SIM_CLK
34
SIM_RST
C4
Figure 24: SIM interface application circuit
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3, C4
47 pF Capacitor Ceramic COG 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1H470JZ01 - Murata
C5
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
D1, D2
Low capacitance ESD protection
USB0002RP or USB0002DP - AVX
J1
SIM Card Holder
Various Manufacturers,
C707-10M006-136-2 - Amphenol Corporation
Table 15: Example of components for SIM card connection
When connecting the module to a SIM card holder, perform the following steps on the application board:
Bypass digital noise via a 100 nF capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM155R71C104KA01) on the SIM supply (VSIM)
To prevent RF coupling, connect a 47 pF bypass capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H470JZ01) at each SIM
signal (VSIM, SIM_CLK, SIM_IO, SIM_RST) to ground near the SIM connector
Mount very low capacitance (i.e. less than 10 pF) ESD protection devices (e.g. Infineon ESD8V0L2B-03L or
AVX USB0002RP) near the SIM card connector
Limit capacitance and series resistance on each SIM signal to match the requirements for the SIM interface
(27.7 ns is the maximum allowed rise time on the SIM_CLK line, 1.0 µs is the maximum allowed rise time on
the SIM_IO and SIM_RST lines): always route the connections to keep them as short as possible
1.8.1 SIM functionality
The following SIM services are supported:
Abbreviated Dialing Numbers (ADN)
Fixed Dialing Numbers (FDN)
Last Dialed Numbers (LDN)
Service Dialing Numbers (SDN)
SIM Toolkit R99 is supported.
Page 43

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 43 of 125
1.9 Serial Communication
1.9.1 Asynchronous serial interface (UART)
The UART interface is a 9-wire unbalanced asynchronous serial interface that provides an AT commands
interface, GPRS data and CSD data, software upgrades.
The UART interface provides RS-232 functionality conforming with ITU-T V.24 Recommendation [4], with CMOS
compatible signal levels: 0 V for low data bit or ON state, and 2.85 V for high data bit or OFF state. An external
voltage translator (Maxim MAX3237) is required to provide RS-232 compatible signal levels. For the detailed
electrical characteristics refer to the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1].
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules are designed to operate as a GSM/GPRS modem, which represents the data
circuit-terminating equipment (DCE) as described by the ITU-T V.24 Recommendation [4]. A customer application
processor connected to the module through the UART interface represents the data terminal equipment (DTE).
The signal names of the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 UART interface conform to ITU-T V.24
Recommendation [4].
The UART interface includes the following lines:
Name
Description
Remarks
DSR
Data set ready
Module output, functionality of ITU-T V.24 Circuit 107 (Data
set ready)
RI
Ring Indicator
Module output, functionality of ITU-T V.24 Circuit 125
(Calling indicator)
DCD
Data carrier detect
Module output, functionality of ITU-T V.24 Circuit 109 (Data
channel received line signal detector)
DTR
Data terminal ready
Module input, functionality of ITU-T V.24 Circuit 108/2 (Data
terminal ready)
Internal active pull-up to 2.85 V enabled.
RTS
Ready to send
Module hardware flow control input, functionality of ITU-T
V.24 Circuit 105 (Request to send)
Internal active pull-up to 2.85 V enabled.
CTS
Clear to send
Module hardware flow control output, functionality of ITU-T
V.24 Circuit 106 (Ready for sending)
TxD
Transmitted data
Module data input, functionality of ITU-T V.24 Circuit 103
(Transmitted data)
Internal active pull-up to 2.85 V enabled.
RxD
Received data
Module data output, functionality of ITU-T V.24 Circuit 104
(Received data)
Table 16: UART pins
UART interface pins ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F). A higher protection level could
be required if the lines are externally accessible on the application board. A higher protection level can
be achieved mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) on the lines
connected to these pins if they are externally accessible on the application board.
1.9.1.1 UART features
UART interface is controlled and operated with:
AT commands according to 3GPP TS 27.007 [5]
AT commands according to 3GPP TS 27.005 [6]
AT commands according to 3GPP TS 27.010 [7]
u-blox AT commands
Page 44

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 44 of 125
All flow control handshakes are supported by the UART interface and can be set by appropriate AT commands
(see u-blox AT Commands Manual [2], AT&K command): hardware flow control (RTS/CTS), software flow control
(XON/XOFF), or no flow control.
Autobauding is supported. It can be enabled or disabled by an AT command (see u-blox AT Commands Manual
[2], AT+IPR command). Autobauding is enabled by default.
Hardware flow control is enabled by default.
For the complete list of supported AT commands and their syntax refer to the u-blox AT Commands
Manual [2].
Autobauding result can be unpredictable with spurious data if idle-mode (power-saving) is entered and
the hardware flow control is disabled.
The following baud rates can be configured using AT commands:
2400 b/s
4800 b/s
9600 b/s
19200 b/s
38400 b/s
57600 b/s
115200 b/s (default value when autobauding is disabled)
The following baud-rates are available with autobauding only:
1200 b/s
230400 b/s
Automatic frame recognition is supported: this feature is enabled in conjunction with autobauding only, which is
enabled by default. The frame format can be:
8N2 (8 data bits, No parity, 2 stop bits)
8E1 (8 data bits, even parity, 1 stop bit)
8O1 (8 data bits, odd parity, 1 stop bit)
8N1 (8 data bits, No parity, 1 stop bit)
7E1 (7 data bits, even parity, 1 stop bit)
7O1 (7 data bits, odd parity, 1 stop bit)
The default frame configuration with fixed baud rate is 8N1, described in the Figure 25.
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7
Start of 1-Byte
transfer
Start Bit
(Always 0)
Possible Start of
next transfer
Stop Bit
(Always 1)
t
bit
= 1/(Baudrate)
Normal Transfer, 8N1
Figure 25: UART default frame format (8N1) description
Page 45

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 45 of 125
1.9.1.2 UART signal behavior (AT commands interface case)
Refer to Table 2 for a description of operating modes and states referred to in this section.
At the module switch-on, before the initialization of the UART interface (each pin is first tristated and then set to
its relative reset state reported in the pin description table in LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1] (see the
power on sequence description in Figure 19). At the end of the boot sequence, the UART interface is initialized,
the module is by default in active mode and the UART interface is enabled. The configuration and the behavior
of the UART signals after the boot sequence are described below.
For a complete description of data and command mode, refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2].
RxD signal behavior
The module data output line (RxD) is set by default to OFF state (high level) at UART initialization. The module
holds RxD in OFF state until no data is transmitted by the module.
TxD signal behavior
The module data input line (TxD) is set by default to OFF state (high level) at UART initialization. The TxD line is
then held by the module in the OFF state if the line is not activated by the DTE: an active pull -up is enabled
inside the module on the TxD input.
CTS signal behavior
The module hardware flow control output (CTS line) is set to the ON state (low level) at UART initialization.
If the hardware flow control is enabled (for more details refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2], AT&K, AT\Q,
AT+IFC commands) the CTS line indicates when the module is in active mode and the UART interface is enabled:
the module drives the CTS line to the ON state or to the OFF state when it is either able or not able to accept
data from the DTE (refer to chapter 1.9.1.3 for the complete description).
If the hardware flow control is not enabled, the CTS line is always held in the ON state after UART initialization.
When the power saving configuration is enabled and the hardware flow-control is not implemented in
the DTE/DCE connection, data sent by the DTE can be lost: the first character sent when the module is
in idle-mode won’t be a valid communication character (refer to chapter 1.9.1.3 for the complete
description).
During the MUX mode, the CTS line state is mapped to FCon / FCoff MUX command for flow control
issues outside the power saving configuration while the physical CTS line is still used as a power state
indicator. For more details refer to Mux Implementation Application Note [14].
RTS signal behavior
The hardware flow control input (RTS line) is set by default to the OFF state (high level) at UART initialization.
The RTS line is then held by the module in the OFF state if the line is not activated by the DTE: an active pull-up
is enabled inside the module on the RTS input.
If the HW flow control is enabled (for more details refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2] AT&K, AT\Q,
AT+IFC commands) the RTS line is monitored by the module to detect permission from the DTE to send data to
the DTE itself. If the RTS line is set to OFF state, any on-going data transmission from the module is interrupted
or any subsequent transmission forbidden until the RTS line changes to ON state.
The DTE must be able to still accept a certain number of characters after the RTS line has been set to
OFF state: the module guarantees the transmission interruption within 2 characters from RTS state
change.
Page 46

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 46 of 125
If AT+UPSV=2 is set and HW flow control is disabled, the RTS line is monitored by the module to manage the
power saving configuration:
When an OFF-to-ON transition occurs on the RTS input line, the module switches from idle-mode to
active-mode after 20 ms and the module doesn’t enter idle-mode until the RTS input line is held in the ON
state
If RTS is set to OFF state by the DTE, the module automatically enters idle-mode whenever possible as in the
AT+UPSV=1 configuration (cyclic idle/active mode)
For more details refer to chapter 1.9.1.3 and u-blox AT Commands Manual [2], AT+UPSV command.
DSR signal behavior
If AT&S0 is set, the DSR module output line is set by default to ON state (low level) at UART initialization and is
then always held in the ON state.
If AT&S1 is set, the DSR module output line is set by default to OFF state (high level) at UART initialization. The
DSR line is then set to the OFF state when the module is in command mode and is set to the ON state when the
module is in data mode.
DTR signal behavior
The DTR module input line is set by default to OFF state (high level) at UART initialization. The DTR line is then
held by the module in the OFF state if the line is not activated by the DTE: an active pull -up is enabled inside the
module on the DTR input. Module behavior according to DTR status depends on the AT command
configuration (see u-blox AT Commands Manual [2], AT&D command).
DCD signal behavior
If AT&C0 is set, the DCD module output line is set by default to ON state (low level) at UART initialization and is
then always held in the ON state.
If AT&C1 is set, the DCD module output line is set by default to OFF state (high level) at UART initialization. The
DCD line is then set by the module in accordance with the carrier detect status: ON if the carrier is detected, OFF
otherwise. In case of voice call DCD is set to ON state when the call is established. For a data call there are the
following scenarios:
GPRS data communication: Before activating the PPP protocol (data mode) a dial-up application must
provide the ATD*99***<context_number># to the module: with this command the module switches from
command mode to data mode and can accept PPP packets. The module sets the DCD line to the ON state,
then answers with a CONNECT to confirm the ATD*99 command. The DCD ON is not related to the context
activation but with the data mode
CSD data call: To establish a data call the DTE can send the ATD<number> command to the module which
sets an outgoing data call to a remote modem (or another data module). Data can be transparent (non
reliable) or non transparent (with the reliable RLP protocol). When the remote DCE accepts the data call, the
module DCD line is set to ON and the CONNECT <communication baudrate> string is returned by the
module. At this stage the DTE can send characters through the serial line to the data module which sends
them through the network to the remote DCE attached to a remote DTE
RI signal behavior
The RI module output line is set by default to the OFF state (high level) at UART initialization. Then, during an
incoming call, the RI line is switched from OFF state to ON state with a 4:1 duty cycle and a 5 s period (ON for
1 s, OFF for 4 s, see Figure 26), until the DTE attached to the module sends the ATA string and the module
accepts the incoming data call. The RING string sent by the module (DCE) to the serial port at constant time
intervals is not correlated with the switch of the RI line to the ON state.
Page 47

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 47 of 125
Figure 26: RI behavior during an incoming call
The RI line can notify an SMS arrival. When the SMS arrives, the RI line switches from OFF to ON for 1 s (see
Figure 27), if the feature is enabled by the proper AT command (refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2],
AT+CNMI command).
Figure 27: RI behavior at SMS arrival
This behavior allows the DTE to remain in power saving mode until the DCE related event requests service.
If more than one SMS arrives coincidently or in quick succession the RI line will be independently triggered,
although the line will not be deactivated between each event. As a result, the RI line may remain in the ON state
for more than 1 second.
If an incoming call is answered within less than 1 second (with ATA or if auto-answering is set to ATS0=1) then
the RI line will be set to OFF earlier.
As a result:
RI line monitoring can’t be used by the DTE to determine the number of received SMSes
In case of multiple events (incoming call plus SMS received), the RI line can’t be used to discriminate
between the two events, but the DTE must rely on the subsequent URCs and interrogate the DCE
with the proper commands
1.9.1.3 UART and power-saving
The power saving configuration is controlled by the AT+UPSV command (for the complete description refer to ublox AT Commands Manual [2], AT+UPSV command). When power saving is enabled, the module automatically
enters idle-mode whenever possible, otherwise the active-mode is maintained by the module. The AT+UPSV
command sets the module power saving configuration, but also configures the UART behavior in relation to the
power saving configuration. The conditions for the module entering idle-mode also depend on the UART power
saving configuration.
The different power saving configurations that can be set by the AT+UPSV command are described in the
following subchapters and are summarized in Table 17. For more details on the command description, refer to
u-blox AT commands Manual [2].
SMS arrives
time [s]
0
RI ON
RI OFF
1s
SMS
time [s]
0
RI ON
RI OFF
1s
1s
time [s]
151050
RI ON
RI OFF
Call incomes
1s
time [s]
151050
RI ON
RI OFF
Call incomes
Page 48

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 48 of 125
AT+UPSV
HW flow control
RTS line
Communication during idle mode and wake up
0
Enabled (AT&K3)
ON
Data sent by the DTE will be correctly received by the module.
0
Enabled (AT&K3)
OFF
Data sent by the module will be buffered by the module and will be correctly received by
the DTE when it will be ready to receive data (i.e. RTS line will be ON).
0
Disabled (AT&K0)
ON
Data sent by the DTE will be correctly received by the module.
0
Disabled (AT&K0)
OFF
Data sent by the module will be correctly received by the DTE if it is ready to receive data,
otherwise data will be lost.
1
Enabled (AT&K3)
ON
Data sent by the DTE will be buffered by the DTE and will be correctly received by the
module when active-mode is entered.
1
Enabled (AT&K3)
OFF
Data sent by the module will be buffered by the module and will be correctly received by
the DTE when it is ready to receive data (i.e. RTS line will be ON).
1
Disabled (AT&K0)
ON
When a low-to-high transition occurs on the TxD input line, the module switches from
idle-mode to active-mode after 20 ms: this is the “wake up time” of the module. As a
consequence, the first character sent when the module is in idle-mode (i.e. the wake up
character) won’t be a valid communication character because it can’t be recognized, and
the recognition of the subsequent characters is guaranteed only after the complete wake-up
(i.e. after 20 ms).
1
Disabled (AT&K0)
OFF
Data sent by the module will be correctly received by the DTE if it is ready to receive data,
otherwise data will be lost.
2
Enabled (AT&K3)
ON
Not Applicable: HW flow control cannot be enabled with AT+UPSV=2.
2
Enabled (AT&K3)
OFF
Not Applicable: HW flow control cannot be enabled with AT+UPSV=2.
2
Disabled (AT&K0)
ON
The module is forced in active-mode and it doesn’t enter idle-mode until RTS line is set to
OFF state. When a high-to-low (i.e. OFF-to-ON) transition occurs on the RTS input line, the
module switches from idle-mode to active-mode after 20 ms: this is the “wake up time” of
the module.
2
Disabled (AT&K0)
OFF
When a low-to-high transition occurs on the TxD input line, the module switches from
idle-mode to active-mode after 20 ms: this is the “wake up time” of the module. As a
consequence, the first character sent when the module is in idle-mode (i.e. the wake up
character) won’t be a valid communication character because it can’t be recognized, and
the recognition of the subsequent characters is guaranteed only after the complete wake-up
(i.e. after 20 ms).
Table 17: UART and power-saving summary
AT+UPSV=0: power saving disabled, fixed active-mode
The module doesn’t enter idle-mode and the CTS line is always held in the ON state after UART initialization. The
UART interface is enabled and data can be received. This is the default configuration.
AT+UPSV=1: power saving enabled, cyclic idle/active mode
The module automatically enters idle-mode whenever possible, and periodically wakes up from idle-mode to
active-mode to monitor the paging channel of the current base station (paging block reception), in accordance
to GSM system requirements.
Idle-mode time is fixed by network parameters and can be up to ~2.1 s. When the module is in idle-mode, a
data transmitted by the DTE will be lost if hardware flow control is disabled, otherwise if hardware flow control
is enabled, data will be buffered by the DTE and will be correctly received by the module when active-mode is
entered.
When the module wakes up to active-mode, the UART interface is enabled and data can be received. When a
character is received, it forces the module to stay in the active-mode for a longer time.
The active-mode duration depends by:
Network parameters, related to the time interval for the paging block reception (minimum of ~11 ms)
Time period from the last data received at the serial port during the active-mode: the module doesn’t enter
idle-mode until a timeout expires. This timeout is configurable by AT+UPSV command, from 40 GSM frames
(~184 ms) up to 65000 GSM frames (300 s). Default value is 2000 GSM frames (~9.2 s)
Page 49

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 49 of 125
Every subsequent character received during the active-mode, resets and restarts the timer; hence the active-
mode duration can be extended indefinitely.
The behavior of hardware flow-control output (CTS line) during normal module operations with power-saving
and HW flow control enabled (cyclic idle-mode and active-mode) is illustrated in Figure 28.
Figure 28: CTS behavior with power saving enabled: the CTS line indicates when the module is able (CTS = ON = low level) or
not able (CTS = OFF = high level) to accept data from the DTE and communicate through the UART interface
AT+UPSV=2: power saving enabled and controlled by the RTS line
The module behavior is the same as for AT+UPSV=1 case if the RTS line is set to OFF by the DTE.
When an OFF-to-ON transition occurs on the RTS input line, the module switches from idle-mode to
active-mode after 20 ms and then the module doesn’t enter the idle-mode until the RTS input line is held in the
ON state. This configuration can only be enabled with the module HW flow control disabled.
Even if HW flow control is disabled, if the RTS line is set to OFF by the DTE, the CTS line is set by the
module accordingly to its power saving configuration (like for AT+UPSV=1 with HW flow control
enabled).
When the RTS line is set to OFF by the DTE, the timeout to enter idle-mode from the last data received
at the serial port during the active-mode is the one previously set with the AT+UPSV=1 configuration or
it is the default value.
time [s]
CTS ON
CTS OFF
max ~2.1 s
UART disabled
min ~11 ms
UART enabled
~9.2 s (default)
UART enabled
Data input
time [s]
CTS ON
CTS OFF
max ~2.1 s
UART disabled
min ~11 ms
UART enabled
~9.2 s (default)
UART enabled
Page 50

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 50 of 125
Wake up from idle-mode to active-mode via data reception
If a data is transmitted by the DTE during the module idle-mode, it will be lost (not correctly received by the
module) in the following cases:
AT+UPSV=1 with hardware flow control disabled
AT+UPSV=2 with hardware flow control disabled and RTS line set to OFF
When the module is in idle-mode, the TxD input line of the module is always configured to wake up the module
from idle-mode to active-mode via data reception: when a low-to-high transition occurs on the TxD input line, it
causes the wake-up of the system. The module switches from idle-mode to active-mode after 20 ms from the
first data reception: this is the “wake up time” of the module. As a consequence, the first character sent when
the module is in idle-mode (i.e. the wake up character) won’t be a valid communica tion character because it
can’t be recognized, and the recognition of the subsequent characters is guaranteed only after the complete
wake-up (i.e. after 20 ms).
Figure 29 and Figure 30 show an example of common scenarios and timing constraints:
HW flow control set in the DCE, and no HW flow control set in the DTE, needed to see the CTS line
changing on DCE
Power saving configuration is active and the timeout from last data received to idle-mode start is set to 2000
frames (AT+UPSV=1,2000)
Figure 29 shows the case where DCE is in idle mode and a wake-up is forced. In this scenario the only character
sent by the DTE is the wake-up character; as a consequence, the DCE will return to idle-mode when the timeout
from last data received expires. (2000 frames without data reception).
CTS OFF
CTS ON
Active mode is held for 2000 GSM frames (~9.2 s)
time
Wake up time: up to 15.6 ms
time
TxD
module
input
Wake up character
Not recognized by DCE
Figure 29: Wake-up via data reception without further communication
Page 51

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 51 of 125
Figure 30 shows the case where in addition to the wake-up character further (valid) characters are sent. The
wake up character wakes-up the DCE. The other characters must be sent after the “wake up time” of 20 ms. If
this condition is met, the characters are recognized by the DCE. The DCE is allowed to re-enter idle-mode after
2000 GSM frames from the latest data reception.
CTS OFF
CTS ON
Active mode is held for 2000 GSM frames (~9.2s)
after the last data received
time
Wake up time: up to 15.6 ms
time
TxD
module
input
Wake up character
Not recognized by DCE
Valid characters
Recognized by DCE
Figure 30: Wake-up via data reception with further communication
The “wake-up via data reception” feature can’t be disabled.
The “wake-up via data reception” feature can be used in both AT+UPSV=1 and AT+UPSV=2 case
(when RTS line is set to OFF).
In command mode, if autobauding is enabled and HW flow control is not implemented by the DTE, the
DTE must always send a character to the module before the “AT” prefix set at the beginning of each
command line: the first character will be ignored if the module is in active-mode, or it will represent the
wake up character if the module is in idle-mode.
In command mode, if autobauding is disabled, the DTE must always send a dummy “AT” to the module
before each command line: the first character will not be ignored if the module is in active-mode (i.e.
the module will reply “OK”), or it will represent the wake up character if the module is in idle-mode (i.e.
the module won’t reply).
No wake-up character or dummy “AT” is required from the DTE during connected-mode since the
module continues to be in active-mode and doesn’t need to be woken-up. Furthermore in data mode a
wake-up character or a dummy “AT” would affect the data communication.
1.9.1.4 UART application circuits
Providing the full RS-232 functionality (using the complete V.24 link)
For complete RS-232 functionality conforming to ITU-T Recommendation [4] in DTE/DCE serial communication,
the complete UART interface of the module (DCE) must be connected to the DTE as described in Figure 31.
Page 52

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 52 of 125
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
(DCE)
TxD
Application Processor
(DTE)
RxD
RTS
CTS
DTR
DSR
RI
DCD
GND
15
TXD
12
DTR
16
RXD
13
RTS
14
CTS
9
DSR
10
RI
11
DCD
GND
0 Ω
0 Ω
TP
TP
Figure 31: UART interface application circuit with complete V.24 link in the DTE/DCE serial communication
Providing the TxD, RxD, RTS and CTS lines only (not using the complete V.24 link)
If the functionality of the DSR, DCD, RI and DTR lines is not required in the application, or the lines are not
available, the application circuit described in Figure 32 must be implemented:
Connect the module DTR input line to GND, since the module requires DTR active (low electrical level)
Leave DSR, DCD and RI lines of the module unconnected and floating
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
(DCE)
TxD
Application Processor
(DTE)
RxD
RTS
CTS
DTR
DSR
RI
DCD
GND
15
TXD
12
DTR
16
RXD
13
RTS
14
CTS
9
DSR
10
RI
11
DCD
GND
0 Ω
0 Ω
TP
TP
Figure 32: UART interface application circuit with partial V.24 link (5-wire) in the DTE/DCE serial communication
If only TxD, RxD, RTS and CTS lines are provided as described in Figure 32 the procedure to enable the power
saving depends on the HW flow-control status. If HW flow-control is enabled (AT&K3, that is the default setting)
the power saving will be activated by AT+UPSV=1. Through this configuration, when the module is in idle-mode,
a data transmitted by the DTE will be buffered by the DTE and will be correctly received by the module when
active-mode is entered.
If the HW flow-control is disabled (AT&K0), the power saving can be enabled by AT+UPSV=2. The module is in
idle-mode until a high-to-low (i.e. OFF-to-ON) transition on the RTS input line will switch the module from
idle-mode to active-mode after 20 ms. The module will be forced in active-mode if the RTS input line is held in
the ON state.
Page 53

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 53 of 125
Providing the TxD and RxD lines only (not using the complete V24 link)
If the functionality of the CTS, RTS, DSR, DCD, RI and DTR lines is not required in the application, or the lines
are not available, the application circuit described in Figure 33 must be implemented:
Connect the module DTR input line to GND, since the module requires DTR active (low electrical level)
Connect the module RTS input line to GND, since the module requires RTS active (low electrical level)
Leave CTS, DSR, DCD and RI lines of the module unconnected and floating
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
(DCE)
TxD
Application Processor
(DTE)
RxD
RTS
CTS
DTR
DSR
RI
DCD
GND
15
TXD
12
DTR
16
RXD
13
RTS
14
CTS
9
DSR
10
RI
11
DCD
GND
0 Ω
0 ΩTPTP
Figure 33: UART interface application circuit with partial V.24 link (3-wire) in the DTE/DCE serial communication
If only TxD and RxD lines are provided as described in Figure 33 and HW flow-control is disabled (AT&K0), the
power saving will be enabled by AT+UPSV=1. The module enters active-mode 20 ms after a low-to-high
transition on the TxD input line; the recognition of the subsequent characters is guaranteed until the module is
in active-mode.
A data delivered by the DTE can be lost using this configuration and the following settings:
o HW flow-control enabled in the module (AT&K3, that is the default setting)
o Module power saving enabled by AT+UPSV=1
o HW flow-control disabled in the DTE
In this case the first character sent when the module is in idle-mode will be a wake-up character and
won’t be a valid communication character (refer to chapter 1.9.1.3 for the complete description).
If power saving is enabled the application circuit with the TxD and RxD lines only is not recommended.
During command mode the DTE must send to the module a wake-up character or a dummy “AT”
before each command line (refer to chapter 1.9.1.3 for the complete description), but during data mode
the wake-up character or the dummy “AT” would affect the data communication.
Additional considerations
To avoid an increase in module power consumption, any external signal connected to the UART must be
set low or tri-stated when the module is in power-down mode. If the external signals in the application
circuit connected to the UART cannot be set low or tri-stated, a multi channel digital switch (e.g. Texas
Instruments SN74CB3Q16244) or a single channel analog switch (e.g. Texas Instruments TS5A3159 or
Texas Instruments TS5A63157) must be inserted between the two-circuit connections and set to high
impedance when the module is in power-down mode.
Page 54

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 54 of 125
It is highly recommended to provide on an application board a direct access to RxD and TxD lines of the
module (in addition to access to these lines from an application processor). This enables a direct
connection of PC (or similar) to the module for execution of Firmware upgrade over the UART. The
module FW upgrade over UART (using the RxD and TxD pins) starts at the module switch-on or when
the module is released from the reset state: it is suggested to provide access to the PWR_ON pin, or to
provide access to the RESET_N pin, or to provide access to the enabling of the DC supply connected to
the VCC pin, to start the module firmware upgrade over the UART.
1.9.1.5 MUX Protocol (3GPP 27.010)
The module has a software layer with MUX functionality complaint with 3GPP 27.010 [7].
This is a data link protocol (layer 2 of OSI model) using HDLC-like framing and operates between the module
(DCE) and the application processor (DTE). The protocol allows simultaneous sessions over the UART. Each
session consists of a stream of bytes transferring various kinds of data like SMS, CBS, GPRS, AT commands in
general. This permits, for example, SMS to be transferred to the DTE when a data connection is in progress.
The following channels are defined:
Channel 0: control channel
Channel 1 – 5: AT commands /data connection
Channel 6: GPS tunneling
For more details refer to GSM Mux implementation Application Note [14].
Page 55

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 55 of 125
1.9.2 DDC (I
2
C) interface
1.9.2.1 Overview
An I2C compatible Display Data Channel (DDC) interface for communication with u-blox GPS receivers is available
on LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules. This interface is intended exclusively to access u-blox GPS receivers.
Name
Description
Remarks
SCL
I2C bus clock line
Fixed open drain. External pull-up required.
SDA
I2C bus data line
Fixed open drain. External pull-up required.
Table 18: DDC (I2C) pins
DDC (I
2
C) interface pins ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F). A higher protection level
could be required if the lines are externally accessible on the application board. A higher protection level
can be achieved mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) on the lines
connected to these pins if they are externally accessible on the application board.
u-blox has implemented special features in LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules to ease the design effort required
to integrate a u-blox wireless module with a u blox GPS receiver.
Combining a LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 wireless module with a u-blox GPS receiver allows designers full access
to the GPS receiver directly via the wireless module: it relays control messages to the GPS receiver via a dedicated
DDC (I2C) interface. A 2nd interface connected to the GPS receiver isn’t necessary: AT commands via the UART
serial interface of the wireless module allow full control of the GPS receiver from any host processor.
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules feature embedded u-blox GPS aiding functionalities for enhanced GPS
performance. These provide decreased Time To First Fix (TTFF) and allow faster position calculation with higher
accuracy.
For more details regarding the handling of the DDC (I
2
C) interface and the GPS aiding features refer to
u-blox AT Commands Manual [2] (AT+UGPS, AT+UGPRF, AT+UGPIOC commands) and GPS
Implementation Application Note [3].
Page 56

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 56 of 125
1.9.2.2 DDC application circuit
General considerations
The DDC (I2C) interface of the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules is used only to connect the wireless module to
a u-blox GPS receiver: the DDC (I2C) interface is enabled by the AT+UGPS command only (for more de tails refer
to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]). The SDA and SCL lines must be connected to the DDC (I2C) interface pins
of the u-blox GPS receiver (i.e. the SDA2 and SCL2 pins of the u-blox GPS receiver) on the application board.
To be complaint with the I2C bus specifications, the module pads of the bus interface are open drain output and
pull-up resistors must be used. Since the pull-up resistors are not mounted on the module, they must be
mounted externally. Resistor values must conform to the I2C bus specifications [8]. If LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
modules are connected through the DDC bus to a u-blox GPS receiver (only one device can be connected on the
DDC bus), use a pull-up resistor of 4.7 k. Pull-up resistors must be connected to a supply voltage of 2.85 V
(typical), since this is the voltage domain of the DDC pins (for detailed electrical characteristics see the LEON-
G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1]).
DDC Slave-mode operation is not supported, the module can act as master only.
Two lines, serial data (SDA) and serial clock (SCL), carry information on the bus. SCL is used to synchronize data
transfers, and SDA is the data line. Since both lines are open drain outputs, the DDC devices can only drive them
low or leave them open. The pull-up resistor pulls the line up to the supply rail if no DDC device is pulling it
down to GND. If the pull-ups are missing, SCL and SDA lines are undefined and the DDC bus will not work.
The signal shape is defined by the values of the pull-up resistors and the bus capacitance. Long wires on the bus
will increase the capacitance. If the bus capacitance is increased, use pull -up resistors with nominal resistance
value lower than 4.7 k, to match the I2C bus specifications [8] regarding rise and fall times of the signals.
Capacitance and series resistance must be limited on the bus to match the I
2
C specifications [8] (1.0 µs is
the maximum allowed rise time on the SCL and SDA lines): route connections as short as possible.
If the pins are not used as DDC bus interface, they can be left floating on the application board.
LEON-G100-06x / LEON-G200-06S and subsequent versions
LEON-G100-06x / LEON-G200-06S and subsequent versions support these GPS aiding types:
Local aiding
AssistNow Online
AssistNow Offline
AssistNow Autonomous
The embedded GPS aiding features can be used only if the DDC (I2C) interface of the wireless module is
connected to the u-blox GPS receivers.
The GPIO pins can handle:
The power on/off of the GPS receiver (“GPS supply enable” function provided by GPIO2)
The wake up from idle-mode when the GPS receiver is ready to send data (“GPS data ready” function
provided by GPIO3)
The RTC synchronization signal to the GPS receiver (“GPS RTC sharing” function provided by GPIO4)
GPIO2 is by default configured to provide the “GPS supply enable” function (parameter <gpio_mode> of
AT+UGPIOC command set to 3 by default), to enable or disable the supply of the u-blox GPS receiver connected
to the wireless module by the AT+UGPS command. The pin is set as
Output / High, to switch on the u-blox GPS receiver, if the parameter <mode> of AT+UGPS command is set
to 1
Output / Low, to switch off the u-blox GPS receiver, if the parameter <mode> of AT+UGPS command is set
to 0 (default setting)
Page 57

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 57 of 125
The pin must be connected to the active-high enable pin (or the active-low shutdown pin) of the voltage
regulator that supplies the u-blox GPS receiver on the application board.
The “GPS supply enable” function improves the current consumption of the GPS receiver. When GPS
functionality is not required, the wireless module controlled by the application processor can completely switch
off the GPS receiver using AT commands.
GPIO3 is by default configured to provide the “GPS data ready” function (parameter <gpio_mode> of
AT+UGPIOC command set to 4 by default), to detect when the u-blox GPS receiver connected to the wireless
module is ready to send data by the DDC (I2C) interface. The pin is set as
Input, to detect the line status, waking up the wireless module from idle mode when the u-blox GPS receiver
is ready to send data by the DDC (I2C) interface; this is possible if the parameter <mode> of +UGPS AT
command is set to 1 and the parameter <GPS_IO_configuration> of +UGPRF AT command is set to 16
Tri-state with an internal active pull-down enabled, otherwise (default setting)
The pin must be connected to the data ready output of the u-blox GPS receiver (i.e. the pin TxD1 of the u-blox
GPS receiver) on the application board.
The “GPS data ready” function provides an improvement in the power consumption of the wireless module.
When power saving is enabled in the wireless module by the AT+UPSV command, the module automatically
enters idle-mode whenever possible and when the GPS receiver doesn’t send data by the DDC (I2C) interface.
The GPIO3 pin can be used by the GPS receiver to indicate to the wireless module that it is ready to send data by
the DDC (I2C) interface: it is used by the GPS receiver to wake up the wireless module if it is in idle -mode, so that
data sent by the GPS receiver will not lost by the wireless module even if power saving is enabled.
GPIO4 is by default configured to provide the “GPS RTC sharing” function (parameter <gpio_mode> of
AT+UGPIOC command set to 5 by default), to provide a synchronization timing signal at the power up of the
u-blox GPS receiver connected to the wireless module. The pin is set as
Output, to provide a synchronization timing signal to the u-blox GPS receiver for RTC sharing if the
parameter <mode> of AT+UGPS command is set to 1 and the parameter <GPS_IO_configuration> of
+UGPRF AT command is set to 32
Output / Low, otherwise (default setting)
The pin must be connected to the synchronization timing input of the u-blox GPS receiver (i.e. the pin EXTINT0
of the u-blox GPS receiver) on the application board.
The “GPS RTC sharing” function provides an improvement in the GPS receiver performance, decreasing the Time
To First Fix (TTFF), thus allowing to calculate the position in a shorter time with higher accuracy. When the GPS
local aiding is enabled, the wireless module automatically uploads data such as position, time, ephemeris,
almanac, health and ionospheric parameter from the GPS receiver into its local memory, and restores back the
GPS receiver at next power up of the GPS receiver.
The application circuit for the connection of a LEON-G100-06x / LEON-G200-06S wireless modules (and
subsequent versions) to a u-blox 3.0 V GPS receiver is illustrated in Figure 34 and the suggested components are
listed in Table 19. A pull-down resistor is mounted on the GPIO2 line to avoid a switch on of the GPS receiver
when the wireless module is switched-off and its digital pins are tri-stated.
The V_BCKP supply output of the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 series wireless module is connected to the V_BCKP
backup supply input pin of the GPS receiver to provide the supply for the GPS real time clock and backup RAM
when the VCC supply of the wireless module is within its operating range and the VCC supply of the GPS
receiver is disabled. This enables the u-blox GPS receiver to recover from a power outage with either a hot start
or a warm start (depending on the duration of the GPS VCC outage) and to maintain the configuration settings
saved in the backup RAM.
Page 58

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 58 of 125
LEON-Gx00-06x or
subsequent
R1
INOUT
GND
GPS LDO
Regulator
SHDN
u-blox
3.0 V GPS receiver
SDA2
SCL2
R2
3V0 3V0
VMAIN3V0
U1
21
GPIO2
SDA
SCL
C1
TxD1
EXTINT0
GPIO3
GPIO4
31
30
23
24
VCC
R3
2
V_BCKPV_BCKP
Figure 34: Application circuit for LEON-G100-06x / LEON-G200-06S wireless modules (and subsequent versions) and u-blox 3.0 V
GPS receivers
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
R1, R2
4.7 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-074K7L - Yageo Phycomp
R3
47 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-0747KL - Yageo Phycomp
U1
Voltage Regulator for GPS Receiver
See GPS Receiver Hardware Integration Manual
Table 19: Components for application circuit for LEON-G100-06x / LEON-G200-06S and subsequent versions and u-blox 3.0 V GPS
receivers
LEON-Gx00-04S and LEON-Gx00-05S versions
LEON-Gx00-04S and LEON-Gx00-05S versions support 3 different types of GPS aiding:
Local aiding
AssistNow Online
AssistNow Offline
The embedded GPS aiding features can be used only if the DDC (I2C) interface of the wireless module is
connected to a u-blox GPS receiver.
GPIO pins can handle the power on/off of the GPS receiver (“GPS supply enable” function provided by GPIO2).
“GPS data ready” and “GPS RTC sharing” functions are not available on LEON -Gx00-05S and previous
versions.
LEON-Gx00-05S and previous versions don’t enter idle-mode when the DDC (I
2
C) interface is enabled by
the AT+UGPS command, even if power saving is enabled by the AT+UPSV command.
GPIO2 is by default configured to provide the “GPS supply enable” function (parameter <gpio_mode> of
AT+UGPIOC command set to 3 by default), to enable or disable the supply of the u-blox GPS receiver connected
to the wireless module by the AT+UGPS command. The pin is set as
Output / High, to switch on the u-blox GPS receiver, if the parameter <mode> of AT+UGPS command is set
to 1
Output / Low, to switch off the u-blox GPS receiver, if the parameter <mode> of AT+UGPS command is set
to 0 (default setting)
Page 59

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 59 of 125
The pin must be connected to the active-high enable pin (or the active-low shutdown pin) of the voltage
regulator that supplies the u-blox GPS receiver on the application board.
The “GPS supply enable” function improves the power consumption of the GPS receiver. When GPS
functionality is not required, the wireless module controlled by the application processor can completely switch
off the GPS receiver using AT commands.
The application circuit for connecting LEON-Gx00-04S and LEON-Gx00-05S versions to a u-blox 3.0 V GPS
receiver is illustrated in Figure 35, and the suggested components are listed in Table 20. A pull-down resistor is
mounted on the GPIO2 line to avoid a switch-on of the GPS receiver when the wireless module is switched-off
and its digital pins are tri-stated.
The V_BCKP supply output of the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 series wireless module is connected to the V_BCKP
backup supply input pin of the GPS receiver to provide the supply for the GPS real time clock and backup RAM
when the VCC supply of the wireless module is within its operating range and the VCC supply of the GPS
receiver is disabled. This enables the u-blox GPS receiver to recover from a power outage with either a hot start
or a warm start (depending on the duration of the GPS VCC outage) and to maintain the configuration settings
saved in the backup RAM.
LEON-Gx00-04S
LEON-Gx00-05S
R1
INOUT
GND
GPS LDO
Regulator
SHDN
u-blox
3.0 V GPS receiver
SDA2
SCL2
R2
3V0 3V0
VMAIN3V0
U1
21
GPIO2
SDA
SCL
C1
31
30
VCC
R3
2
V_BCKPV_BCKP
Figure 35: Application circuit for LEON-Gx00-04S and LEON-Gx00-05S versions and u-blox 3.0 V GPS receivers
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
R1, R2
4.7 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-074K7L - Yageo Phycomp
R3
47 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-0747KL - Yageo Phycomp
U1
Voltage Regulator for GPS Receiver
See GPS Receiver Hardware Integration Manual
Table 20: Component for application circuit for LEON-Gx00-04S and LEON-Gx00-05S versions and u-blox 3.0 V GPS receivers
Comment [tgri1]: This paragraph is
repeated in the previous description
(LEON-Gx00-06 and subsequent
versions). Would it be possible to
restructure or add a cross reference to
prevent the repetition?
Page 60

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 60 of 125
1.10 Audio
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules provide four analog and one digital audio interfaces:
Two microphone inputs:
First microphone input can be used for direct connection of the electret condenser microphone of a
handset. This input is used when the main uplink audio path is “Handset Microphone” (refer to u-blox
AT Commands Manual [2]; AT+USPM command: <main_uplink> parameter)
Second microphone input can be used for direct connection of the electret condenser microphone of a
headset. This input is used when the main uplink audio path is “Headset Microphone” (refer to u-blox
AT Commands Manual [2]; AT+USPM command: <main_uplink> parameter)
Two speaker outputs:
First speaker output is a single ended low power audio output that can be used to directly connect the
receiver (earpiece) of a handset or a headset. This output is used when the main downlink audio path is
“Normal earpiece” or “Mono headset” (refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]; AT+USPM
command: <main_downlink> parameter). These two downlink path profiles use the same physical
output but have different sets of audio parameters (Refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]:
AT+USGC, AT+UDBF, AT+USTN commands)
Second speaker output is a differential high power audio output that can be used to directly connect a
speaker or a loud speaker used for ring-tones or for speech in hands-free mode. This output is used
when audio downlink path is “Loudspeaker” (refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]; AT+USPM
command, <main_downlink> and <alert_sound> parameters)
Headset detection input:
If enabled, causes the automatic switch of uplink audio path to “Headset Microphone” and downlink
audio path to “Mono headset”. Enabling/disabling the detection can be controlled by parameter
<headset_indication> in AT+USPM command (refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2])
I
2
S digital audio interface:
This path is selected when parameters <main_uplink> and <main_downlink> in AT+USPM command
(refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]) are respectively “I2S input line” and “I2S output line”
Not all combinations of Input-Output audio paths are allowed. Check audio command AT+USPM in
u-blox AT Commands Manual [2] for allowed combinations of audio path and for their switching during
different use cases (speech/alert tones).
The default values for audio parameters tuning commands (Refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2];
AT+UMGC, AT+UUBF, AT+UHFP, AT+USGC, AT+UDBF, AT+USTN commands) are tuned for audio
device connected as suggested above (i.e. Handset microphone connected on first microphone input,
headset microphone on second microphone input). For a different connection, (i.e. connection of a
Hands Free microphone) these parameters should be changed on the audio path corresponding to the
connection chosen.
1.10.1 Analog Audio interface
1.10.1.1 Uplink path (microphone inputs)
The TX (uplink) path of the analog audio front-end on the module consists of two identical microphone circuits.
Two electret condenser microphones can be directly connected to the two available microphone inputs.
The main required electrical specifications for the electret condenser microphone are 2.2 k as maximum output
impedance at 1 kHz and 2 V maximum standard operating voltage.
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 pins related to the uplink path (microphones inputs) are:
First microphone input:
Page 61

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 61 of 125
MIC_BIAS1: single ended supply to the first microphone and represents the microphone signal input
MIC_GND1: local ground for the first microphone
Second microphone input:
MIC_BIAS2: single ended supply to the second microphone and represents the microphone signal input
MIC_GND2: local ground for the second microphone
For a description of the internal function blocks see Figure 41.
1.10.1.2 Downlink path (speaker outputs)
The RX (downlink) path of the analog audio front-end of the module consists of two speaker outputs available
on the following pins:
First speaker output:
HS_P: low power single ended audio output. This pin is internally connected to the output of the single
ended audio amplifier of the chipset
Second speaker output:
SPK_N/SPK_P: high power differential audio output. These two pins are internally connected to the
output of the high power differential audio amplifier of the chipset
See Figure 41 for a description of the internal function blocks.
Warning: excessive sound pressure from headphones can cause hearing loss.
Detailed electrical characteristics of the low power single-ended audio receive path and the high power
differential audio receive path can be found in LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1].
Table 21 lists the signals related to analog audio functions.
Name
Description
Remarks
HS_DET
Headset detection input
Internal active pull-up to 2.85 V enabled.
HS_P
First speaker output with low power single-ended
analog audio
This audio output is used when audio downlink path is
“Normal earpiece“ or “Mono headset“
SPK_P
Second speaker output with high power differential
analog audio
This audio output is used when audio downlink path is
“Loudspeaker“.
SPK_N
Second speaker output with power differential
analog audio output
This audio output is used when audio downlink path is
“Loudspeaker“.
MIC_BIAS2
Second microphone analog signal input and bias
output
This audio input is used when audio uplink path is set as
“Headset Microphone“. Single ended supply output and
signal input for the second microphone.
MIC_GND2
Second microphone analog reference
Local ground of second microphone. Used for “Headset
microphone” path.
MIC_GND1
First microphone analog reference
Local ground of the first microphone. Used for “Handset
microphone” path
MIC_BIAS1
First microphone analog signal input and bias output
This audio input is used when audio uplink path is set as
“Handset Microphone“. Single ended supply output and
signal input for first microphone.
Table 21: Analog Audio Signal Pins
All audio lines on an Application Board must be routed in pairs, be embedded in GND (have the ground
lines as close as possible to the audio lines), and maintain distance from noisy lines such as VCC and
from components such as switching regulators.
Audio pins ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F). A higher protection level could be
required if the lines are externally accessible on the application board. A higher protection level can be
achieved mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) on the lines
connected to these pins if they are externally accessible on the application board.
If the audio pins are not used, they can be left floating on the application board.
Page 62

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 62 of 125
1.10.1.3 Handset mode
Handset mode is the default audio operating mode of LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules. In this mode the main
uplink audio path is “Handset microphone”, the main downlink audio path is “Normal earpiece” (refer to u-blox
AT Commands Manual [2]; AT+USPM command: <main_uplink>, <main_downlink> parameters).
Handset microphone must be connected to inputs MIC_BIAS1/MIC_GND1
Handset receiver must be connected to output HS_P
Figure 36 shows an example of an application circuit connecting a handset (with a 2.2 kΩ electret microphone
and a 32 Ω receiver) to the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules. The following actions should be done on the
application circuit:
Mount a series capacitor on the HS_P line to decouple the bias
Mount a 10 µF ceramic capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM188R60J106M) if connecting a 32 Ω receiver, or a load
with greater impedance (such as a single ended analog input of a codec). Otherwise if a 16 Ω receiver is
connected to the line, a ceramic capacitor with greater nominal capacitance must be used: a 22 µF series
capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM21BR60J226M) is required
Mount a 82 nH series inductor (e.g. Murata LQG15HS82NJ02) on each microphone line and a 27 pF bypass
capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H270J) on all audio lines to minimize RF coupling and TDMA noise
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
C1
AUDIO
HANDSET
CONNECTOR
C2 C3
J1
4
3
2
1
L1
L2
37
HS_P
43
MIC_GND1
44
MIC_BIAS1
C4
D1
Figure 36: Handset connector application circuit
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3
27 pF Capacitor Ceramic COG 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1H270JZ01 - Murata
C4
10 µF Capacitor Ceramic X5R 0603 20% 6.3V
GRM188R60J106M - Murata
L1, L2
82 nH Multilayer inductor 0402
(self resonance frequency ~1 GHz)
LQG15HS82NJ02 - Murata
J1
Audio Handset Jack Connector, 4Ckt (4P4C)
52018-4416 - Molex
D1
Varistor Array for ESD protection
CA05P4S14THSG - EPCOS
Table 22: Example of components for handset connection
1.10.1.4 Headset mode
The audio path is automatically switched from handset mode to headset mode when a rising edge is detected by
the module on HS_DET pin. The audio path returns to the handset mode when the line returns to low level.
In headset mode the main uplink audio path is “Headset microphone”, the main downlink audio path is “Mono
headset” (refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]; AT+USPM command: <main_uplink>, <main_downlink>
parameters).
The audio path used in headset mode:
Headset microphone must be connected to MIC_BIAS2/MIC_GND2
Headset receiver must be connected to HS_P
Page 63

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 63 of 125
Figure 37 shows an application circuit connecting a headset (with a 2.2 kΩ electret microphone and a 32 Ω
receiver) to the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules. Pin 2 & 5 are shorted in the headset connector, causing
HS_DET to be pulled low. When the headset plug is inserted HS_DET is pulled up internally by the module,
causing a rising edge for detection.
Perform the following steps on the application board (as shown in Figure 37; the list of components to be
mounted is shown in Table 23):
Mount a series capacitor on the HS_P line to decouple the bias. 10 µF ceramic capacitor (e.g. Murata
GRM188R60J106M) is required if a 32 Ω receiver or a load with greater impedance (as a single ended
analog input of a codec) is connected to the line. 22 µF series capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM21BR60J226M) is
required if a 16 Ω receiver is connected to the line
Mount a 82 nH series inductor (e.g. Murata LQG15HS82NJ02) on each microphone line, and a 27 pF bypass
capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H270J) on all audio lines to minimize RF coupling and the TDMA noise
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
C4
AUDIO HEADSET
CONNECTOR
C1 C2 C3
J1
2
5
3
4
6
1
L1
L2
18
HS_DET
37
HS_P
42
MIC_GND2
41
MIC_BIAS2
D1
Figure 37: Headset mode application circuit
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3
27 pF Capacitor Ceramic COG 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1H270JZ01 - Murata
C4
10 µF Capacitor Ceramic X5R 0603 20% 6.3V
GRM188R60J106M - Murata
L1, L2
82nH Multilayer inductor 0402
(self resonance frequency ~1 GHz)
LQG15HS82NJ02 - Murata
J1
Audio Headset 2.5 mm Jack Connector
SJ1-42535TS-SMT - CUI, Inc.
D1
Varistor Array for ESD protection
CA05P4S14THSG - EPCOS
Table 23: Example of components for headset jack connection
1.10.1.5 Hands-free mode
Hands-free mode can be implemented using a loudspeaker and a dedicated microphone.
Hands-free functionality is implemented using appropriate DSP algorithms for voice-band handling (echo
canceller and automatic gain control), managed via software (Refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2];
AT+UHFP command).
In this mode the main downlink audio path must be “Loudspeaker”, the main uplink audio path can be
“Handset microphone” or “Headset microphone” (refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]; AT+USPM
command: <main_uplink>, <main_downlink> parameters). Use of an uplink audio path for hands-free makes it
unavailable for another device (handset/headset). Therefore:
Microphone can be connected to the input pins MIC_BIAS1/MIC_GND1 or MIC_BIAS2/MIC_GND2
High power loudspeaker must be connected to the output pins SPK_P/SPK_N
Page 64

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 64 of 125
The default parameters for audio uplink profiles “Handset microphone” and “Headset microphone”
(refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]; AT+UMGC, AT+UUBF, AT+UHFP) are for a handset and a
headset microphone. To implement hands-free mode, these parameters should be changed on the
audio path corresponding to the connection chosen. Procedure to tune parameters for hands-free mode
(gains, echo canceller) can be found in LEON Audio Application Note [12].
When hands-free mode is enabled, the audio output signal on HS_P is disabled.
The physical width of the high-power audio outputs lines on the application board must be wide
enough to minimize series resistance.
Figure 38 shows an application circuit for hands-free mode. In this example the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
modules are connected to an 8 Ω speaker and a 2.2 kΩ electret microphone. Insert an 82 nH series inductor
(e.g. Murata LQG15HS82NJ02) on each microphone line, and a 27 pF bypass capacitor (e.g. Murata
GRM1555C1H270J) on all audio lines to minimize RF coupling and the TDMA noise.
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
SPK
C1 C2
L2
L1
MIC
C3 C4
39
SPK_N
38
SPK_P
43
MIC_GND1
44
MIC_BIAS1
Figure 38: Hands free mode application circuit
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3, C4
27 pF Capacitor Ceramic COG 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1H270JZ01 - Murata
L1, L2
82nH Multilayer inductor 0402
(self resonance frequency ~1 GHz)
LQG15HS82NJ02 - Murata
SPK
Loudspeaker
MIC
Active Elected Microphone
Table 24: Example of components for hands-free connection
1.10.1.6 Connection to an external analog audio device
MIC_BIAS1 / MIC_GND single ended analog audio inputs and the HS_P single ended analog audio output of
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 can be used to connect the module to an external analog audio device.
If the external analog audio device is provided with a single ended analog audio input, the HS_P single ended
output of the module must be connected to the single ended input of the external audio device by a DC -block
10 µF series capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM188R60J106M) to decouple the bias present at the module output (see
HS_P common mode output voltage in LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1]). Use a suitable power-on
sequence to avoid audio bump due to charging of the capacitor: the final audio stage should always be the last
one enabled.
If the external analog audio device is provided with a differential analog audio input, a proper single ended to
differential circuit must be inserted from the HS_P single ended output of the module to the differential input of
the external audio device. A simple application circuit is described in Figure 39: a DC-block 10 µF series capacitor
Page 65

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 65 of 125
(e.g. Murata GRM188R60J106M) is provided to decouple the bias present at the module output. A voltage
divider is provided to correctly adapt the signal level from the module output to the external audio device input.
The DC-block series capacitor acts as high-pass filter for audio signals, with cut-off frequency depending on both
the values of capacitor and on the input impedance of the audio device. For example: in case of a single ended
connection to 600 external device, the 10 µF capacitor will set the -3 dB cut-off frequency to 103 Hz. The
high-pass filter has a low enough cut-off to not impact the audio signal frequency response.
If the external analog audio device is provided with a single ended analog audio output, the MIC_BIAS1 single
ended input of the module must be connected to the single ended output of the external audio device by a
DC-block 10 µF series capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM188R60J106M) to decouple the bias present at the module
input (see MIC_BIAS1 microphone supply characteristics in LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1]).
If the external analog audio device is provided with a differential analog audio output, a proper differential to
single ended circuit must be inserted from the differential output of the external audio device to the MIC_BIAS1
single ended input of the module. Figure 39 describes a simple application circuit: a DC-block 10 µF series
capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM188R60J106M) is provided to decouple the bias present at the module input, and a
voltage divider is provided to correctly adapt the signal level from the external audio device output to the
module input.
Use a suitable power-on sequence to avoid audio bump due to capacitor charging: the final audio stage should
always be the last one enabled.
Additional circuitry should be inserted depending on the external audio device characteristics.
To enable the audio path corresponding to these input/output, refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2],
AT+USPM command.
To tune audio levels for the external device refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2], AT+USGC, AT+UMGC
commands.
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
C1
37
HS_P
43
MIC_GND1
44
MIC_BIAS1
GND
Analog IN
Analog OUT
Audio Device
Reference
Reference
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
37
HS_P
43
MIC_GND1
44
MIC_BIAS1
GND
Positive Analog IN
Audio Device
Negative Analog OUT
Negative Analog IN
Positive Analog OUT
C3
R2
R1
R4
R3
C2
C4
Figure 39: Application circuits to connect the module to audio devices with proper single-ended or differential input/output
Page 66

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 66 of 125
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3, C4
10 µF Capacitor X5R 0603 5% 6.3 V
GRM188R60J106M - Murata
R1, R3
0 Ω Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-070RL - Yageo Phycomp
R2, R4
Not populated
Table 25: Example of components for the connection to an analog audio device
1.10.2 Digital Audio interface
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules support a bidirectional 4-wire I2S digital audio interface. The module acts as
master only. Table 26 lists the I2S pins:
Name
Description
Remarks
I2S_WA
I2S word alignment
Module output (master).1
I2S_TXD
I2S transmit data
Module output 1
I2S_CLK
I2S clock
Module output (master) 1
I2S_RXD
I2S receive data
Module input 1
Internal active pull-up to 2.85 V enabled.
Table 26: I2S interface pins
I
2
S interface pins ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F). A higher protection level could be
required if the lines are externally accessible on the application board. A higher protection level can be
achieved mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) on the lines
connected to these pins if they are externally accessible on the application board.
The I2S interface can be can be used in two modes:
PCM mode: I2Sx
Normal I
2
S mode: I2Sy
Beyond the supported transmission modality, the main difference between the PCM mode and the normal I2S
mode is represented by the logical connection to the digital audio processing system integrated in the chipset
firmware (see Figure 41):
PCM mode provides complete audio processing functionality
Normal I
2
S mode: digital filters, digital gains, side tone, some audio resources as tone generator, info tones
(e.g. free tone, connection tone, low battery alarm), and ringer are not available
The I2S interface is activated and configured using AT commands, see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]
(AT+UI2S command).
If the I2S interface is used in PCM mode, digital path parameters can be configured and saved as the normal
analog paths, using appropriate path index as described in the u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]. Analog gain
parameters of microphone and speakers are unused when digital path is selected.
Refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2], AT+UI2S command for possible combinations of connections
and settings.
Figure 40 shows an application circuit for digital audio interface.
1
Check device specifications to ensure compatibility of supported modes to LEON-G100/G200 module. Add a test point to provide access to
the pin for debugging.
Page 67

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 67 of 125
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
3.0V Digital
Audio Device
I2S_TXD (Output)
I2S_CLK (Input)
I2S_RXD (Input)
I2S_WA (Input)
I2S_RXD
I2S_CLK
I2S_TXD
I2S_WA
29
28
27
26
0 Ω
0 Ω
TP
TP
0 Ω
0 Ω
TP
TP
GNDGND
Figure 40: Digital audio interface application circuit
Any external signal connected to the digital audio interface must be tri-stated when the module is in
power-down mode and must be tri-stated during the module power-on sequence (at least for 1500 ms
after the start-up event). If the external signals connected to the digital audio interface cannot be
tri-stated, insert a multi channel digital switch (e.g. Texas Instruments SN74CB3Q16244, TS5A3159, or
TS5A63157) between the two-circuit connections and set to high impedance when the module is in
power down mode and during the module power-on sequence.
If I
2
S pins are not used, they can be left floating on the application board.
For debug purposes, include a test point at each I2S pin also if the digital audio interface is not used.
1.10.2.1 PCM mode
In PCM mode I2S_TX and I2S_RX are respectively parallel to the analog front end I2S_RX and I2S_TX as
internal connections to the voice processing system (see Figure 41), so resources available for analog path can be
shared:
Digital filters and digital gains are available in both uplink and downlink direction. They can be configured
using AT commands; refer to the u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]
Ringer tone and service tone are mixed on the TX path when active (downlink)
The HF algorithm acts on I
2
S path
Main features of the I2S interface in PCM mode:
I
2
S runs in PCM - short alignment mode (configurable with AT commands)
Module functions as I
2
S master (I2S_CLK and I2S_WA signals generated by the module)
I2S_WA signal always runs at 8 kHz
I2S_WA toggles high for 1 or 2 CLK cycles of synchronism (configurable), then toggles low for 16 CLK
cycles of sample width. Frame length can be 1 + 16 = 17 bits or 2 + 16 = 18 bits
I2S_CLK frequency depends on frame length. Can be 17 x 8 kHz = 136 kHz or 18 x 8 kHz = 144 kHz
I2S_TX, I2S_RX data are 16 bit words with 8 kHz sampling rate, mono. Data are in 2’s complement
notation. MSB is transmitted first
When I2S_WA toggles high, first synchronization bit is always low. Second synchronism bit (present only in
case of 2 bit long I2S_WA configuration) is MSB of the transmitted word (MSB is transmitted twice in this
case)
I2S_TX changes on I2S_CLK rising edge, I2S_RX changes on I2S_CLK falling edge
Page 68

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 68 of 125
1.10.2.2 Normal I
2
S mode
Normal I2S mode supports:
16 bits word
Mono interface
8 kHz frequency
Main features of I2S interface in Normal I2S mode:
I2S_WA signal always runs at 8 kHz and the channel can be either high or low
I2S_TX data 16 bit words with 32 bit frame and 2, dual mono (the word can be written on 2 channels).
Data are in 2’s complement notation. MSB is transmitted first. The MSB is first transmitted; the bits change
on I2S_CLK rising or falling edge (configurable)
I2S_RX data are read on the I2S_CLK edge opposite to I2S_TX writing edge
I2S_CLK frequency depends by the number of bits and number of channels so is 16 x 2 x 8 kHz = 256 kHz
The modes are configurable through a specific AT command (refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]) and the
following parameters can be set:
I2S_TX word can be written while I2S_WA is high, low or both
MSB can be 1 bit delayed or non-delayed on I2S_WA edge
I2S_TX data can change on rising or falling edge of I2S_CLK signal
I2S_RX data read on the opposite front of I2S_CLK signal
Page 69

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 69 of 125
1.10.3 Voice-band processing system
The digital voice-band processing on the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 is implemented in the DSP core inside the
baseband chipset. The analog audio front-end of the chipset is connected to the digital system through 16 bit
ADC converters in the uplink path, and through 16 bit DAC converters in the downlink path. The digitized TX
and RX voice-band signals are both processed by digital gain stages and decimation filter in TX, interpolation
filters in RX path. The processed digital signals of TX and RX are connected to the DSP for various tasks (i.e.
speech codec, digital mixing and sidetone, audio filtering) implemented in the firmware modules.
External digital audio devices can be interfaced to the DSP voice-band processing system via the I2S interface.
The voice-band processing system can be split up into three different blocks:
Sample-based Voice-band Processing (single sample processed at 8 kHz, every 125 µs)
Frame-based Voice-band Processing (frames of 160 samples are processed every 20 ms)
MIDI synthesizer running at 47.6 kHz
These three blocks are connected by buffers and sample rate converters (for 8 to 47.6 kHz conversion).
Multiplexer
Switch
DAC
Switch
ADC
I2S_RXD I2Sy RX
Switch
MIC 1
MIC 2
Uplink
Analog Gain
Uplink
filter 2
Uplink
filter 1
Hands-
free
To Radio
TX
Scal_Mic
Digital Gain
Sidetone
Downlink
filter 1
Downlink
filter 2
MIDI
player
SPK_P/N
HS_P
HS
Analog_gain
Switch
Switch
I2Sx TX
I2S_TXD
Scal_Rec
Digital Gain
Mix_AFE
Digital Gain
SPK
Analog_gain
Gain_out
Digital Gain
Tone
Generator
Switch
I2Sy TX
From
Radio RX
Speech
level
I2Sx RX
Sample Based Processing Frame Based
Processing
AMR
Player
Circular buffer
Voiceband Sample Buffer
Figure 41: LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 voice-band processing system block diagram
The sample-based voice-band processing main task is to transfer the voice-band samples from either analog
audio front-end TX path or I2Sx RX path to the Voice-band Sample Buffer and from the Voice-band Sample
Buffer to the analog audio front-end RX path and/or I2Sx TX path.
While doing this the samples are scaled by digital gains and processed by digital filters both in the uplink and
downlink direction. The sidetone is generated mixing scaled uplink samples to the downlink samples. The framebased voice-band processing implements the Hands Free algorithm. This consists of the Echo Canceller, the
Automatic Gain Control and the Noise Suppressor. Hands Free algorithm acts on the uplink signal only. The
frame-based voice-band processing also implements an AMR player (according to RFC3267 standard). AMR
player supported data rates are: 12.2 – 10.2 – 7.95 – 7.40 – 6.70 – 5.90 – 5.15 – 4.75 kbps. The speech uplink
path final block before radio transmission is the speech encoder. Symmetrically, on downlink path, the starting
block is the speech decoder which extracts speech signal from the radio receiver.
Page 70

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 70 of 125
The circular buffer is a 3000 word buffer to store and mix the voice-band samples from Midi synthesizer. The
buffer has a circular structure, so that when the write pointer reaches the end of the buffer, it is wrapped t o the
begin address of the buffer.
Two different sample-based sample rate converters are used: an interpolator, required to convert the samplebased voice-band processing sampling rate of 8 kHz to the analog audio front-end output rate of 47.6 kHz; a
decimator, required to convert the circular buffer sampling rate of 47.6 kHz to the I2Sx TX or the uplink path
sample rate of 8 kHz.
1.10.3.1 Audio codecs
The following speech codecs are supported by firmware on the DSP:
GSM Half Rate (TCH/HS)
GSM Full Rate (TCH/FS)
GSM Enhanced Full Rate (TCH/EFR)
3GPP Adaptive Multi Rate (AMR) (TCH/AFS+TCH/AHS)
1.10.3.2 Echo cancelation and noise reduction
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 support algorithms for echo cancellation, noise suppression and automatic gain
control. Algorithms are configurable with AT commands (refer to the u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]).
1.10.3.3 Digital filters and gains
Audio parameters such as digital filters, digital gain, Side -tone gain (feedback from uplink to downlink path) and
analog gain are available for uplink and downlink audio paths. These parameters can be modified by dedicated
AT commands and be saved in 2 customer profiles in the non-volatile memory of the module (refer to the u-blox
AT Commands Manual [2]).
1.10.3.4 Ringer mode
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules support polyphonic ring tones. The ringer tones are generated by a built-in
generator on the chipset and then amplified by the internal amplifier.
The synthesizer output is only mono and cannot be mixed with TCH voice path (the two are mutually exclusive).
To perform in-band alerting during TCH with voice path open, only Tone Generator can be used.
The analog audio path used in ringer mode can be the high power differential audio output (refer to u-blox AT
Commands Manual [2]; AT+USPM command, <main_downlink> and <alert_sound> parameters for alert sounds
routing). In this case the external high power loudspeaker must be connected to the SPK_P/SPK_N output pins
of the module as shown in the application circuit (Figure 38) described in section 1.10.1.5.
1.11 ADC input (LEON-G100 only)
One Analog to Digital Converter input is available (ADC1) and is configurable using u-blox AT command (see
u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]). The resolution of this converter is 12-bit with a single ended input range.
Name
Description
Remarks
ADC1
ADC input
Resolution: 12 bits.
Table 27: ADC pin
ADC1 pin ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F). A higher protection level could be
required if the line is externally accessible on the application board. A higher protection level can be
achieved mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) on the line
connected to this pin if it is externally accessible on the application board.
Page 71

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 71 of 125
If the ADC1 pin is not used, it can be left floating on the application board.
The electrical behavior of the measurement circuit in voltage mode can be modeled by a circuit equivalent to
that shown in Figure 42. This includes a resistor (Req), voltage source (Ueq), analog preamplifier (with typical gain
G=0.5), and a digital amplifier (with typical gain g
ADC
=2048 LSB/V).
LEON-G100
ADC1
Ueq
Req
Usig
Rsig
Uadc
G
5
gADC
Figure 42: Equivalent network for ADC single-ended measurement
The ADC software driver takes care of the parameters shown in Figure 42 (Req, Ueq, G, g
ADC
): the voltage
measured by ADC1 is U
adc
and its value expressed in mV is given by the AT+UADC=0 response (for more details
on the AT command refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2]).
The detailed electrical specifications of the Analog to Digital Converter input (Input voltage span, Input resistance
in measurement mode Req, Internal voltage Ueq): are reported in the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 Data Sheet [1].
As described in the ADC equivalent network shown in Figure 42, one part of the whole ADC circuit is outside
the module: the (U
sig
) and the (R
sig
) are characteristics of the application board because they represent the
Thévenin's equivalent of the electrical network developed on the application board.
If an external voltage divider is implemented to increase the voltage range, check the input resistance in
measurement mode (Req) of ADC1 input and all the electrical characteristics.
If the Thévenin's equivalent of the voltage source (U
sig
) has a significant internal resistance (R
sig
) compared to the
input resistance in measurement mode (Req) of the ADC, this should be taken into account and corrected to
properly associate the AT+UADC=0 response to the voltage source value, implementing the ADC calibration
procedure suggested in the section 1.11.1 below.
If the customer implements the calibration procedure on the developed application board, the influence of the
internal series resistance (R
sig
) of the voltage source (U
sig
) is taken into account in the measurement: the
AT+UADC=0 response can be correctly associated to the value of the voltage source applied on the application
board.
1.11.1 ADC Calibration
To improve the absolute accuracy of the 12-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC), it is suggested to follow the
calibration procedure here described.
The calibration aim is to evaluate the relationship between the value, expressed in mV, of the voltage source
(V_S, which Thévenin's equivalent is represented by U
sig
and R
sig
shown in Figure 42) that has to be measured and
the AT+UADC=0 response (ADC_VALUE, that is the U
adc
value expressed in mV) when V_S is applied, calculating
the calibration GAIN and OFFSET parameters value.
Page 72

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 72 of 125
Calibration is performed providing two known reference values (V_1 and V_2) instead of the voltage source
(V_S) that has to be measured by the ADC.
V_1 and V_2 values should be as different as possible: taking into account of the ADC applicable range, the
maximum limit and the minimum limit for the voltage source has to be applied to obtain the best accuracy in
calibration.
The following values are involved in the calibration procedure:
V_1: the first (e.g. maximum) reference known voltage in mV applied in the calibration procedure
V_2: the second (e.g. minimum) applied reference known voltage in mV applied in the calibration procedure
ADC_1: the AT+UADC=0 response when V_1 is applied
ADC_2: the AT+UADC=0 response when V_2 is applied
This is the procedure to calibrate the ADC:
1. Apply V_1
2. Read ADC_1
3. Apply V_2
4. Read ADC_2
5. Evaluate GAIN value with the following formula:
)2_ADC1_ADC(
)2_V1_V(
*16384=GAIN
-
-
6. Evaluate OFFSET value with the following formula:
GAIN
8192
+
)2_V1_V(
)ADC_2 * V_1 ADC_1 * V_2(
=OFFSET
-
-
Now the voltage source (V_S) value expressed in mV can be exactly evaluated from the AT+UADC=0 response
(ADC_VALUE) when V_S is applied, with the following formula:
16384
8192 - GAIN * )+_A(
=_
OFFSETVALUEDC
SV
where the parameters are defined as following:
V_S is the voltage source value expressed in mV
ADC_VALUE is the AT+UADC=0 response when V_S is applied
GAIN is calculated in the calibration procedure (see point 5)
OFFSET is calculated in the calibration procedure (see point 6)
Page 73

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 73 of 125
1.12 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules provide some pins which can be configured as general purpose input or
output, or to provide special functions via u-blox AT commands (for further details refer to u-blox AT Commands
Manual [2], AT+UGPIOC, AT+UGPIOR, AT+UGPIOW, AT+UGPS, AT+UGPRF, AT+USPM).
The number of available general purpose input/output pins and the special functions availability can vary
depending on the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 ordering code.
For each pin the GPIO configuration is saved in the non volatile memory. For more details refer to u-blox
AT commands manual [2].
1.12.1 LEON-G100-06x / LEON-G200-06S and subsequent versions
LEON-G100-06x / LEON-G200-06S and subsequent versions provide 5 general purpose input/output pins:
GPIO1, GPIO2, GPIO3, GPIO4, HS_DET. The available functions are described below:
GPS supply enable:
GPIO2 is by default configured by AT+UGPIOC command to enable or disable the supply of the u-blox GPS
receiver connected to the wireless module.
The GPIO1, GPIO3, GPIO4 or HS_DET pins can be configured to provide the “GPS supply enable” function,
alternatively to the default GPIO2 pin, setting the parameter <gpio_mode> of AT+UGPIOC command to 3.
The pin configured to provide the “GPS supply enable” function is set as
o Output / High, to switch on the u-blox GPS receiver, if the parameter <mode> of AT+UGPS
command is set to 1
o Output / Low, to switch off the u-blox GPS receiver, if the parameter <mode> of AT+UGPS
command is set to 0 (default setting)
The pin configured to provide the “GPS supply enable” function must be connected to the active-high
enable pin (or the active-low shutdown pin) of the voltage regulator that supplies the u-blox GPS receiver on
the application board.
GPS data ready:
GPIO3 is by default configured by AT+UGPIOC command to sense when the u-blox GPS receiver connected
to the wireless module is ready to send data by the DDC (I2C) interface.
Only the GPIO3 pin can be configured to provide the “GPS data ready” function, setting the parameter
<gpio_mode> of AT+UGPIOC command to 4 (default setting).
The pin configured to provide the “GPS data ready” function is set as
o Input, to sense the line status, waking up the wireless module from idle-mode when the u-blox GPS
receiver is ready to send data by the DDC (I2C) interface, if the parameter <mode> of AT+UGPS
command is set to 1 and the parameter <GPS_IO_configuration> of AT+UGPRF command is set to
16
o Tri-state with an internal active pull-down enabled, otherwise (default setting)
The pin must be connected to the data ready output of the u-blox GPS receiver (i.e. the pin TxD1 of the
u-blox GPS receiver) on the application board.
GPS RTC sharing:
GPIO4 is by default configured by AT+UGPIOC command to provide a synchronization timing signal to the
u-blox GPS receiver connected to the wireless module.
Only the GPIO4 pin can be configured to provide the “GPS RTC sharing” function, setting the parameter
<gpio_mode> of AT+UGPIOC command to 5 (default setting).
The pin configured to provide the “GPS RTC sharing” function is set as
Page 74

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 74 of 125
o Output, to provide a synchronization time signal to the u-blox GPS receiver for RTC sharing if the
parameter <mode> of AT+UGPS command is set to 1 and the parameter <GPS_IO_configuration>
of AT+UGPRF command is set to 32
o Output / Low, otherwise (default setting)
The pin must be connected to the synchronization timing input of the u-blox GPS receiver (i.e. the pin
EXTINT0 of the u-blox GPS receiver) on the application board.
Headset detection:
The HS_DET pin is by default configured by AT+UGPIOC command to detect headset presence.
Only the HS_DET pin can be configured to provide the “Headset detection” function, setting the parameter
<gpio_mode> of AT+UGPIOC command to 8 (default setting).
The pin configured to provide the “Headset detection” function is set as
o Input with an internal active pull-up enabled, to detect headset presence
The pin must be connected on the application board to the mechanical switch pin of the headset connector,
which must be connected to GND by means of the mechanical switch integrated in the headset connector
when the headset plug is not inserted, causing HS_DET to be pulled low. Refer to Figure 43 and to chapter
1.10.1.4 for the detailed application circuit. When the headset plug is inserted HS_DET is pulled up
internally by the module, causing a rising edge for detection of the headset presence.
Network status indication:
Each GPIO (GPIO1, GPIO2, GPIO3, GPIO4 or HS_DET) can be configured to indicate network status (i.e. no
service, registered home network, registered roaming, voice or data call enabled), setting the parameter
<gpio_mode> of AT+UGPIOC command to 2.
No GPIO pin is by default configured to provide the “Network status indication” function.
The pin configured to provide the “Network status indication” function is set as
o Continuous Output / Low, if no service (no network coverage or not registered)
o Cyclic Output / High for 100 ms, Output / Low for 2 s, if registered home network
o Cyclic Output / High for 100 ms, Output / Low for 100 ms, Output / High for 100 ms, Output / Low
for 2 s, if registered visitor network (roaming)
o Continuous Output / High, if voice or data call enabled
The pin configured to provide the “Network status indication” function can be connected on the application
board to an input pin of an application processor or can drive a LED by a transistor with integrated resistors
to indicate network status.
General purpose input:
All the GPIOs (GPIO1, GPIO2, GPIO3, GPIO4 and HS_DET) can be configured as input to sense high or low
digital level through AT+UGPIOR command, setting the parameter <gpio_mode> of AT+UGPIOC command
to 1.
No GPIO pin is by default configured as “General purpose input”.
The pin configured to provide the “General purpose input” function is set as
o Input, to sense high or low digital level through AT+UGPIOR command
The pin can be connected on the application board to an output pin of an application processor to sense the
digital signal level.
General purpose output:
All the GPIOs (GPIO1, GPIO2, GPIO3, GPIO4 and HS_DET) can be configured as output to set the high or
the low digital level through AT+UGPIOW command, setting the parameter <gpio_mode> of +UGPIOC AT
command to 0.
No GPIO pin is by default configured as “General purpose output”.
The pin configured to provide the “General purpose output” function is set as
o Output / Low, if the parameter <gpio_out_val> of + UGPIOW AT command is set to 0
o Output / High, if the parameter <gpio_out_val> of + UGPIOW AT command is set to 1
The pin can be connected on the application board to an input pin of an application processor to provide a
digital signal.
Page 75

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 75 of 125
Pad disabled:
All the GPIOs (GPIO1, GPIO2, GPIO3, GPIO4 and HS_DET) can be configured in tri-state with an internal
active pull-down enabled, as a not used pin, setting the parameter <gpio_mode> of +UGPIOC AT command
to 255.
The pin configured to provide the “Pad disabled” function is set as
o Tri-state with an internal active pull-down enabled
1.12.2 LEON-Gx00-04S and LEON-Gx00-05S versions
LEON-Gx00-04S and LEON-Gx00-05S versions provide 2 general purpose input/output pins: GPIO1 and GPIO2.
The available functions are described below:
GPS supply enable:
GPIO2 is by default configured by AT+UGPIOC to enable or disable the supply of the u-blox GPS receiver
connected to the wireless module.
The GPIO1 pin can be configured to provide the “GPS supply enable” function, alternatively to the default
GPIO2, setting the parameter <gpio_mode> of AT+UGPIOC command to 3.
The pin configured to provide the “GPS supply enable” function is set as
o Output / High, to switch on the u-blox GPS receiver, if the parameter <mode> of AT+UGPS
command is set to 1
o Output / Low, to switch off the u-blox GPS receiver, if the parameter <mode> of AT+UGPS
command is set to 0 (default setting)
The pin must be connected to the active-high enable pin (or the active-low shutdown pin) of the voltage
regulator that supplies the u-blox GPS receiver on the application board.
Network status indication:
Each GPIO (GPIO1 or GPIO2) can be configured to indicate network status (i.e. no service, registered home
network, registered roaming, voice or data call enabled), setting the parameter <gpio_mode> of
AT+UGPIOC AT command to 2.
No GPIO pin is by default configured to provide the “Network status indication” function.
The pin configured to provide the “Network status indication” function is set as
o Continuous Output / Low, if no service (no network coverage or not registered)
o Cyclic Output / High for 100 ms, Output / Low for 2 s, if registered home network
o Cyclic Output / High for 100 ms, Output / Low for 100 ms, Output / High for 100 ms, Output / Low
for 2 s, if registered visitor network (roaming)
o Continuous Output / High, if voice or data call enabled
The pin can be connected on the application board to an input pin of an application processor or can drive a
LED by a transistor with integrated resistors to indicate network status.
General purpose input:
All the GPIOs (GPIO1, GPIO2) can be configured as input to sense high or low digital level by AT+UGPIOR,
setting the parameter <gpio_mode> of +UGPIOC AT command to 1.
No GPIO pin is by default configured as “General purpose input”.
The pin configured to provide the “General purpose input” function is set as
o Input, to sense high or low digital level by AT+UGPIOR
The pin can be connected on the application board to an output pin of an application processor to sense the
digital signal level.
General purpose output:
All the GPIOs (GPIO1, GPIO2) can be configured as output to set the high or the low digital level by
AT+UGPIOW, setting the parameter <gpio_mode> of +UGPIOC AT command to 0.
GPIO1 is by default configured by AT+UGPIOC as output to set high/low digital level by AT+UGPIOW.
Page 76

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 76 of 125
The GPIO2 pin can be configured as general purpose output, setting the parameter <gpio_mode> of
AT+UGPIOC command to 0.
The pin configured to provide the “General purpose output” function is set as
o Output / Low, if the parameter <gpio_out_val> of AT+ UGPIOW command is set to 0 (default)
o Output / High, if the parameter <gpio_out_val> of AT+ UGPIOW command is set to 1
The pin can be connected on the application board to an input pin of an application processor to provide a
digital signal.
The “GPS data ready”, “GPS RTC sharing”, “Pad disabled” functions are not available with
LEON-Gx00-05S and previous versions.
The GPIO3, GPIO4 pins are not available with LEON-Gx00-05S and previous versions.
The HS_DET pin only provides the headset detection function and cannot be configured by AT+UGPIOC
with LEON-Gx00-05S and previous versions.
If LEON-Gx00-05S or previous versions are re-programmed with FW 07.60 (default firmware for
LEON-G100-06x / LEON-G200-06S versions), the GPIO1, GPIO2, HS_DET and Reserved pins of the
module will be configured as with the FW 07.50 (default firmware for LEON-Gx00-05S).
No
Module
Name
Description
Remarks
20
LEON-Gx00-04S
LEON-Gx00-05S
GPIO1
GPIO
By default, the pin is configured as Output / Low.
Can be alternatively configured by the AT+UGPIOC command as
Input function
Network Status Indication function
GPS Supply Enable function
LEON-G100-06x
LEON-G200-06S
or subsequent
GPIO1
GPIO
By default, the pin is configured as Pad disabled.
Can be alternatively configured by the AT+UGPIOC command as
Output function
Input function
Network Status Indication function
GPS Supply Enable function
21
LEON-Gx00-04S
LEON-Gx00-05S
GPIO2
GPIO
By default, the pin is configured to provide the GPS Supply Enable function.
Can be alternatively configured by the AT+UGPIOC command as
Output function
Input function
Network Status Indication function
LEON-G100-06x
LEON-G200-06S
or subsequent
GPIO2
GPIO
By default, the pin is configured to provide the GPS Supply Enable function.
Can be alternatively configured by the AT+UGPIOC command as
Output function
Input function
Network Status Indication function
Pad disabled function
23
LEON-Gx00-04S
LEON-Gx00-05S
Reserved
Reserved
Pad disabled
LEON-G100-06x
LEON-G200-06S
or subsequent
GPIO3
GPIO
By default, the pin is configured to provide the GPS Data Ready function.
Can be alternatively configured by the AT+UGPIOC command as
Output function
Input function
Network Status Indication function
GPS Supply Enable function
Pad disabled function
Page 77

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 77 of 125
No
Module
Name
Description
Remarks
24
LEON-Gx00-04S
LEON-Gx00-05S
Reserved
Reserved
Pad disabled
LEON-G100-06x
LEON-G200-06S
or subsequent
GPIO4
GPIO
By default, the pin is configured to provide the GPS RTC sharing function.
Can be alternatively configured by the AT+UGPIOC command as
Output function
Input function
Network Status Indication function
GPS Supply Enable function
Pad disabled function
18
LEON-Gx00-04S
LEON-Gx00-05S
HS_DET
Headset
detection
The pin is configured to provide the Headset detection function.
LEON-G100-06x
LEON-G200-06S
or subsequent
HS_DET
GPIO
By default, the pin is configured to provide the Headset detection function.
Can be alternatively configured by the AT+UGPIOC command as
Output function
Input function
Network Status Indication function
GPS Supply Enable function
Pad disabled function
Table 28: GPIO pins
The GPIO pins ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (HBM JESD22-A114F). A higher protection level could be
required if the lines are externally accessible on the application board. A higher protection level can be
achieved mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) on the lines
connected to these pins.
Figure 43 describes an application circuit for a typical GPIO usage (GPS supply enable, GPS RTC sharing, GPS
data ready, Headset detection, Network indication).
Use transistors with at least an integrated resistor in the base pin or otherwise put a 10 k Ω resistor on
the board in series to the GPIO.
Page 78

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 78 of 125
OUTIN
GND
LDO Regulator
SHDN
3V8 3V0
GPIO3
GPIO4
TxD1
EXTINT0
23
24
R1
VCC
GPIO2 21
LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200
u-blox
3.0V GPS receiver
U1
C1
R2
R4
3V8
Network Indicator
R3
GPS Supply Enable
GPS Data Ready
GPS RTC sharing
Headset Detection
20
GPIO1
DL1
T1
D1
TestPoint
Headset Connector
J1
2
5
18
HS_DET
Figure 43: GPIO application circuit
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
R1
47 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
Various manufacturers
U1
Voltage Regulator for GPS Receiver
See GPS Module Hardware Integration Manual
D1
ESD Transient Voltage Suppressor
USB0002RP or USB0002DP - AVX
J1
Audio Headset 2.5 mm Jack Connector
SJ1-42535TS-SMT - CUI, Inc.
R2
10 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
Various manufacturers
R3
47 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
Various manufacturers
R4
820 Ω Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
Various manufacturers
DL1
LED Red SMT 0603
LTST-C190KRKT - Lite-on Technology Corporation
T1
NPN BJT Transistor
BC847 - Infineon
Table 29: Components for GPIO application circuit
To avoid an increase of module power consumption any external signal connected to a GPIO must be
set low or tri-stated when the module is in power-down mode. If the external signals in the application
circuit connected to a GPIO cannot be set low or tri-stated, mount a multi channel digital switch (e.g.
Texas Instruments SN74CB3Q16244) or a single channel analog switch (e.g. Texas Instruments
TS5A3159 or TS5A63157) between the two-circuit connections and set to high impedance.
If GPIO pins are not used, they can be left unconnected on the application board.
For debug purposes, add a test point on the GPIO1 pin even if this GPIO is not used.
Page 79

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 79 of 125
1.13 Schematic for module integration
Figure 44 is an example of a schematic diagram where the LEON-G200-06S module is integrated into an
application board, using all the interfaces of the module.
47pF
SIM Card Holder
CCVCC (C1)
CCVPP (C6)
CCIO (C7)
CCCLK (C3)
CCRST (C2)
GND (C5)
47pF 47pF 100nF
35VSIM
33SIM_I O
32SIM_CLK
34SIM_RST
47pF
ESDESD ESD ESD
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
DTR
DSR
RI
DCD
GND
15 TXD
12
DTR
16 RXD
13 RTS
14 CTS
9
DSR
10
RI
11
DCD
GND
330µF
39pF
GND
10nF100nF 10pF
LEON-G200-06S
50 VCC
+
100µF
2 V_BCKP
GND
RTC
back-up
u-blox
3.0V GPS Receiver
4.7k
OUTIN
GND
LDO Regulator
SHDN
SDA
SCL
4.7k
3V8 3V0_GPS
SDA2
SCL2
GPIO3
GPIO4
TxD1
EXTINT0
31
30
23
24
47k
VCC
GPIO2
21
ANT
47
Antenna
3.0V Digital
Audio Device
I2S_RXD
I2S_CLK
I2S_TXD
I2S_CLK
I2S_TXD
I2S_WA
I2S_RXD
I2S_WA
29
28
27
26
20 GPIO1
3V8
Network
Indicator
22 RESET_N
Ferrite Bead
47pF
3.0V
Applicati on
Processor
Open
Drain
Output
19
PWR_ON
100kΩ
Open
Drain
Output
0Ω
0Ω
TP
TP
10uF
Headset Connector
27pF27pF 27pF
2
5
3
4
6
1
82nH
82nH
18HS_DET
37HS_P
42
MIC_GND2
41
MIC_BIAS2
SPK
27pF 27pF
82nH
82nH
MIC
27pF 27pF
39SPK_N
38SPK_P
43
MIC_GND1
44
MIC_BIAS1
Connector
Connector
ESD ESD ESD ESD
ESD ESD ESD ESD
0Ω
0Ω
TP
TP
0Ω
0Ω
TP
TP
TP
22k
330k
3V0_AP
Input
40
Reserved
ESD
Li-Ion
battery
3V8
4
ESD
Charger
GND
V_CHARGE
5 CHARGE_SENSE
Figure 44: Example of schematic diagram to integrate LEON-G200-06Smodule in an application board, using all the interfaces
Page 80

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 80 of 125
1.14 Approvals
1.14.1 Compliance with FCC and IC Rules and Regulations
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules are approved by the following regulatory bodies:
European Conformance CE mark: EC identification number 0682
R&TTED (Radio and Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive)
PTCRB (PCS Type Certification Review Board)
GCF (Global Certification Forum), partial compliance
AT&T network compatibility
CMIIT (China Ministry of Information Industry); SRRC (State Radio Regulation Center); Approval Code:
o LEON-G100: CMIIT ID: 2010CJ0053
o LEON-G200: CMIIT ID: 2010CJ0054
FCC (Federal Communications Commission) Identifier:
o LEON-G100: XPYLEONG100
o LEON-G200: XPYLEONG200
GOST-R, Hygienic, DoC
a-tick Australia
Radiofrequency radiation exposure Information: this equipment complies with FCC radiation
exposure limits prescribed for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be
installed and operated with a minimum distance of 20 cm between the radiator and your
body. This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
IC (Industry Canada) Certification Number:
o LEON-G100: 8595A-LEONG100
o LEON-G200: 8595A-LEONG200
Manufacturers of mobile or fixed devices incorporating LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules are
authorized to use the FCC Grants and Industry Canada Certificates of the LEON-G100 / LEONG200 modules for their own final products according to the conditions referenced in the
certificates.
The FCC Label shall in the above case be visible from the outside, or the host device shall bear
a second label stating:
LEON-G100: "Contains FCC ID: XPYLEONG100" resp.
LEON-G200: "Contains FCC ID: XPYLEONG200" resp.
The IC Label shall in the above case be visible from the outside, or the host device shall bear a
second label stating:
LEON-G100: "Contains IC ID: 8595A-LEONG100" resp.
LEON-G200: "Contains IC ID: 8595A-LEONG200" resp.
Canada, Industry Canada (IC) Notices
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003 and RSS-210.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
o this device may not cause interference
Page 81

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 81 of 125
o this device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired
operation of the device
Radio Frequency (RF) Exposure Information
The radiated output power of the u-blox Wireless Module is below the Industry Canada (IC)
radio frequency exposure limits. The u-blox Wireless Module should be used in such a manner
such that the potential for human contact during normal operation is minimized.
This device has been evaluated and shown compliant with the IC RF Exposure limits under
mobile exposure conditions (antennas are greater than 20cm from a person's body).
This device has been certified for use in Canada. Status of the listing in the Industry Canada’s
REL (Radio Equipment List) can be found at the following web address:
http://www.ic.gc.ca/app/sitt/reltel/srch/nwRdSrch.do?lang=eng
Additional Canadian information on RF exposure also can be found at the following web
address: http://www.ic.gc.ca/eic/site/smt-gst.nsf/eng/sf08792.html
IMPORTANT: Manufacturers of portable applications incorporating LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
modules are required to have their final product certified and apply for their own FCC Grant
and Industry Canada Certificate related to the specific portable device. This is mandatory to
meet the SAR requirements for portable devices.
Canada, avis d'Industrie Canada (IC)
Cet appareil numérique de classe B est conforme aux normes canadiennes ICES-003 et RSS-210.
Son fonctionnement est soumis aux deux conditions suivantes:
o cet appareil ne doit pas causer d'interférence
o cet appareil doit accepter toute interférence, notamment les interférences qui peuvent
affecter son fonctionnement
Informations concernant l'exposition aux fréquences radio (RF)
La puissance de sortie émise par l’appareil de sans fil u-blox Wireless Module est inférieure à
la limite d'exposition aux fréquences radio d'Industrie Canada (IC). Utilisez l’appareil de sans
fil u-blox Wireless Module de façon à minimiser les contacts humains lors du fonctionnement
normal.
Ce périphérique a été évalué et démontré conforme aux limites d'exposition aux fréquences
radio (RF) d'IC lorsqu'il est installé dans des produits hôtes particuliers qui fonctionnent dans
des conditions d'exposition à des appareils mobiles (les antennes se situent à plus de 20
centimètres du corps d'une personne).
Ce périphérique est homologué pour l'utilisation au Canada. Pour consulter l'entrée
correspondant à l’appareil dans la liste d'équipement radio (REL - Radio Equipment List)
d'Industrie Canada rendez-vous sur:
http://www.ic.gc.ca/app/sitt/reltel/srch/nwRdSrch.do?lang=fra
Pour des informations supplémentaires concernant l'exposition aux RF au Canada rendez-vous
sur: http://www.ic.gc.ca/eic/site/smt-gst.nsf/fra/sf08792.html
IMPORTANT: les fabricants d'applications portables contenant les modules LEON-G100 / LEON-
G200 doivent faire certifier leur produit final et déposer directement leur candidature pour
une certification FCC ainsi que pour un certificat Industrie Canada délivré par l'organisme
chargé de ce type d'appareil portable. Ceci est obligatoire afin d'être en accord avec les
exigences SAR pour les appareils portables.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Page 82

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary System description
Page 82 of 125
ICASA (Independent Communications Authority of South Africa)
ANATEL (Brazilian Agency of Telecommunications, in Portuguese, Agência Nacional de Telecomunicações)
Page 83

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 83 of 125
2 Design-In
2.1 Design-in checklist
This section provides a design-in checklist.
2.1.1 Schematic checklist
The following are the most important points for a simple schematic check:
DC supply must provide a nominal voltage at VCC pin above the minimum normal operating range limit.
DC supply must be capable to provide 2.5 A current bursts with maximum 400 mV voltage drop at VCC
pin.
VCC supply should be clean, with very low ripple/noise: suggested passive filtering parts can be inserted.
Connect only one DC supply to VCC: different DC supply systems are mutually exclusive.
V_CHARGE and CHARGE_SENSE must be externally shorted (LEON-G200 only).
The DC supply used as charger must be voltage and current limited as specified (LEON-G200 only).
Do no leave PWR_ON floating: add a pull-up resistor to a proper supply (i.e. V_BCKP).
Check that voltage level of any connected pin does not exceed the relative operating range.
Capacitance and series resistance must be limited on each SIM signal to match the SIM specifications.
Insert the suggested low capacitance ESD protection and passive filtering parts on each SIM signal.
Check UART signals direction, since the signal names follow the ITU-T V.24 Recommendation [4].
Add a proper pull-up resistor to a proper supply on each DDC (I
2
C) interface line, if the interface is used.
Capacitance and series resistance must be limited on each line of the DDC (I
2
C) interface.
Insert the suggested passive filtering parts on each used analog audio line.
Check the digital audio interface specifications to connect a proper device.
For debug purposes, add a test point on each I
2
S pin and on GPIO1 also if they are not used.
Use transistors with at least an integrated resistor in the base pin or otherwise put a 10 k Ω resistor on
the board in series to the GPIO when those are used to drive LEDs.
To avoid an increase of module current consumption in power down mode, any external signals
connected to the module digital pins (UART interface, HS_DET, GPIOs) must be set low or tri-stated
when the module is in power down mode.
Any external signal connected to the UART interface, I
2
S interfaces and GPIOs must be tri-stated when
the module is in power-down mode, when the external reset is forced low and during the module
power-on sequence (at least for 3 s after the start-up event), to avoid latch-up of circuits and let a
proper boot of the module.
Provide proper precautions for ESD immunity as required on the application board.
All the not used pins can be left floating on the application board.
2.1.2 Layout checklist
The following are the most important points for a simple layout check:
Check 50 Ω impedance of ANT line.
Follow the recommendations of the antenna producer for correct antenna installation and deployment
(PCB layout and matching circuitry).
Ensure no coupling occurs with other noisy or sensitive signals (primarily MIC signals, audio output
signals, SIM signals).
VCC line should be wide and short.
Page 84

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 84 of 125
Route VCC supply line away from sensitive analog signals.
Avoid coupling of any noisy signals to microphone inputs lines.
Ensure proper grounding.
Consider “No-routing” areas for the Data Module footprint.
Optimize placement for minimum length of RF line and closer path from DC source for VCC.
2.1.3 Antenna checklist
Antenna should have 50 Ω impedance, V.S.W.R less then 3:1, recommended 2:1 on operating bands in
deployment geographical area.
Follow the recommendations of the antenna producer for correct antenna installation and deployment
(PCB layout and matching circuitry).
Antenna should have built in DC resistor to ground to get proper Antenna detection functionality.
2.2 Design Guidelines for Layout
The following design guidelines must be met for optimal integration of LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules on
the final application board.
2.2.1 Layout guidelines per pin function
This section groups the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 pins by signal function and provides a ranking of importance
in layout design.
Pinout_Layout_R1.1(ppt)
GND
GND
ANT
GND
GND
MIC_BIAS1
MIC_GND1
MIC_GND2
MIC_BIAS2
Reserved
SPK_N
VCC
SPK_P
HS_P
GND
VSIM
SIM_RST
SIM_IO
SIM_CLK
SDA
SCL
I2S_RXD
I2S_CLK
I2S_TXD
I2S_WA
V_BCKP
GND
V_CHARGE
CHARGE_SENSE/ADC1
GND
GND
GND
DSR
RI
DCD
DTR
GND
RTS
CTS
TXD
RXD
GND
HS_DET
PWR_ON
GPIO1
GPIO2
RESET_N
Reserved
Reserved
GND
Very Important
Careful Layout
Common Practice
Legend:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
Figure 45: Module pin-out with highlighted functions
Page 85

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 85 of 125
Rank
Function
Pin(s)
Layout
Remarks
1st
RF Antenna In/out
Very
Important
Design for 50 characteristic impedance.
See section 2.2.1.1
2nd
DC Supply
Very
Important
VCC line should be wide and short. Route away
from sensitive analog signals. See section 2.2.1.2
3rd
Analog Audio
Careful Layout
Avoid coupling with noisy signals.
See section 2.2.1.3
Audio Inputs
MIC_BIAS1, MIC_GND1,
MIC_BIAS2, MIC_GND2
Audio Outputs
SPK_P, SPK_N, HS_P
4th
Ground
GND
Careful Layout
Provide proper grounding.
See section 2.2.1.4
5th
Charger
V_CHARGE,
CHARGE_SENSE
Careful Layout
Check Charger line width.
See section 2.2.1.5
6th
Sensitive Pin:
Careful Layout
Avoid coupling with noisy signals.
See section 2.2.1.6
Backup Voltage
V_BCKP
A to D Converter
(If implemented)
ADC1
Power On
PWR_ON
7th
Digital pins:
Common
Practice
Follow common practice rules for digital pin
routing
See section 2.2.1.7
SIM Card Interface
VSIM, SIM_CLK, SIM_IO,
SIM_RST
Digital Audio
I2S_CLK, I2S_RXD,
I2S_TXD, I2S_WA
DDC
SCL, SDA
UART
TXD, RXD, CTS, RTS, DSR,
RI, DCD, DTR
External Reset
RESET_N
General Purpose I/O
GPIO1, GPIO2
Table 30: Pin list in order of decreasing importance for layout design
2.2.1.1 RF Antenna connection
The RF antenna connection pin ANT is very critical in layout design. The PCB line must be designed to provide
50 Ω characteristic impedance and minimum loss up to radiating element.
Provide proper transition between the ANT pad to application board PCB
Increase GND keep-out (i.e. clearance) for ANT pin to at least 250 µm up to adjacent pads metal definition
and up to 500 µm on the area below the Data Module, as described in Figure 46
Add GND keep-out (i.e. clearance) on buried metal layers below ANT pad and below any other pad of
component present on the RF line, if top-layer to buried layer dielectric thickness is below 200 µm, to reduce
parasitic capacitance to ground (see Figure 46 for the description keep-out area below ANT pad)
The transmission line up to antenna connector or pad may be a micro strip or a stripline. In any case must be
designed to achieve 50 Ω characteristic impedance
Microstrip lines are usually easier to implement and the reduced number of layer transitions up to antenna
connector simplifies the design and diminishes reflection losses. However, the electromagnetic field extends
to the free air interface above the stripline and may interact with other circuitry
Buried stripline exhibits better shielding to incoming and generated interferences. Therefore are preferred for
sensitive application. In case a stripline is implemented, carefully check that the via pad-stack does not
couple with other signals on the crossed and adjacent layers
Minimize the transmission line length; the insertion loss should be minimized as much as possible, in the
order of a few tenths of a dB
The transmission line should not have abrupt change to thickness and spacing to GND, but must be uniform
and routed as smoothly as possible
ANT
VCC
Page 86

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 86 of 125
The transmission line must be routed in a section of the PCB where minimal interference from noise sources
can be expected
Route ANT line far from other sensitive circuits as it is a source of electromagnetic interference
Avoid coupling with VCC routing and analog audio lines
Ensure solid metal connection of the adjacent metal layer on the PCB stack-up to main ground layer
Add GND vias around transmission line
Ensure no other signals are routed parallel to transmission line, or that other signals cross on adjacent metal
layer
If the distance between the transmission line and the adjacent GND area (on the same layer) does not
exceed 5 times the track width of the micro strip, use the “Coplanar Waveguide” model for 50 Ω
characteristic impedance calculation
Don’t route microstrip line below discrete component or other mechanics placed on top layer
When terminating transmission line on antenna connector (or antenna pad) it is very important to strictly
follow the connector manufacturer’s recommended layout
GND layer under RF connectors and close to buried vias should be cut out in order to remove stray
capacitance and thus keep the RF line 50 Ω. In most cases the large active pad of the integrated antenna or
antenna connector needs to have a GND keep-out (i.e. clearance) at least on first inner layer to reduce
parasitic capacitance to ground. The layout recommendation is not always available from connector
manufacturer: e.g. the classical SMA Pin-Through-Hole needs to have GND cleared on all the layers around
the central pin up to annular pads of the four GND posts. Check 50 Ω impedance of ANT line
Min. 500 µm
Min.
250 um
Top layer Buried metal layer
GND
plane
Microstrip
50 Ω
Figure 46: GND keep-out area on the top layer around the ANT pad and on the buried metal layer below the ANT pad
Any RF transmission line on PCB should be designed for 50 Ω characteristic impedance.
Ensure no coupling occurs with other noisy or sensitive signals.
2.2.1.2 Main DC supply connection
The DC supply of LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules is very important for the overall performance and
functionality of the integrated product. For detailed description check the design guidelines in section 1.5.2.
Some main characteristics are:
VCC connection may carry a maximum burst current in the order of 2.5 A. Therefore, it is typically
implemented as a wide PCB line with short routing from DC supply (DC-DC regulator, battery pack, etc)
Page 87

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 87 of 125
The module automatically initiates an emergency shutdown if supply voltage drops below hardware
threshold. In addition, reduced supply voltage can set a worst case operation point for RF circuitry that may
behave incorrectly. It follows that each voltage drop in the DC supply track will restrict the operating margin
at the main DC source output. Therefore, the PCB connection has to exhibit a minimum or zero voltage
drop. Avoid any series component with Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) greater than a few mΩ
Given the large burst current, VCC line is a source of disturbance for other signals. Therefore route VCC
through a PCB area separated from sensitive analog signals. Typically it is good practice to interpose at least
one layer of PCB ground between VCC track and other signal routing
The VCC supply current supply flows back to main DC source through GND as ground current: provide
adequate return path with suitable uninterrupted ground plane to main DC source
A tank capacitor with low ESR is often used to smooth current spikes. This is most effective when placed as
close as possible to VCC. From main DC source, first connect the capacitor and then VCC. If the main DC
source is a switching DC-DC converter, place the large capacitor close to the DC-DC output and minimize
the VCC track length. Otherwise consider using separate capacitors for DC-DC converter and
LEON-G100/LEON-G200 tank capacitor. The capacitor voltage rating may be adequate to withstand the
charger over-voltage if battery-pack is used
VCC is directly connected to the RF power amplifier. Add capacitor in the pF range from VCC to GND along
the supply path
Since VCC is directly connected to RF Power Amplifier, voltage ripple at high frequency may result in
unwanted spurious modulation of transmitter RF signal. This is especially seen with switching DC-DC
converters, in which case it is better to select the highest operating frequency for the switcher and add a
large L-C filter before connecting to LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 in the worst case
The large current generates a magnetic field that is not well isolated by PCB ground layers and which may
interact with other analog modules (e.g. VCO) even if placed on opposite side of PCB. In this case route VCC
away from other sensitive functional units
The typical GSM burst has a periodic nature of approx. 217 Hz, which lies in the audible audio range. Avoid
coupling between VCC and audio lines (especially microphone inputs)
If VCC is protected by transient voltage suppressor / reverse polarity protection diode to ensure that the
voltage maximum ratings are not exceeded, place the protecting device along the path from the DC source
toward LEON-G100 / LEON-G200, preferably closer to the DC source (otherwise functionality may be
compromised)
VCC pad is longer than other pads, and requires a “No-Routing” area for any other signals on the top layer
of the application board PCB, below the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200
VCC line should be wide and short.
Route away from sensitive analog signals.
2.2.1.3 Analog Audio
Accurate analog audio design is very important to obtain clear and high quality audio. The GSM signal burst has
a repetition rate of 271 Hz that lies in the audible range. A careful layout is required to reduce the risk of noise
pickup from audio lines due to both VCC burst noise coupling and RF detection.
Analog audio is separated in the two paths:
1. Audio Input (uplink path): MIC_BIASx, MIC_GNDx
2. Audio Outputs (downlink path): SPK_P / SPK_N, HS_P
The most sensitive is the uplink path, since the analog input signals are in the µV range. The two microphone
inputs have the same electrical characteristics, and it is recommended to implement their layout with the same
routing rules.
Page 88

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 88 of 125
Avoid coupling of any noisy signals to microphone inputs lines
It is strongly recommended to route MIC signals away from battery and RF antenna lines. Try to skip fast
switching digital lines as well
Keep ground separation from other noisy signals. Use an intermediate GND layer or vias wall for coplanar
signals
MIC_BIAS and MIC_GND carry also the bias for external electret active microphone. Verify that microphone
is connected with right polarity, i.e. MIC_BIAS to the pin marked “+” and MIC_GND (zero Volt) to the
chassis of the device
Despite different DC level, MIC_BIAS and MIC_GND are sensed differentially within the module. Therefore
they should be routed as a differential pair of MIC_BIAS up to the active microphone
Route MIC_GND with dedicated line together with MIC_BIAS up to active microphone. MIC_GND is
grounded internally within module and does not need external connection to GND
Cross other signals lines on adjacent layers with 90° crossing
Place bypass capacitor for RF very close to active microphone. The preferred microphone should be designed
for GSM applications which typically have internal built-in bypass capacitor for RF very close to active device.
If the integrated FET detects the RF burst, the resulting DC level will be in the pass-band of the audio
circuitry and cannot be filtered by any other device
If DC decoupling is required, consider that the input impedance of microphone lines is in the k Ω range.
Therefore, series capacitors with sufficiently large value to reduce the high-pass cut-off frequency of the
equivalent high-pass RC filter
Output audio lines have two separated configurations.
SPK_P / SPK_N are high level balanced output. They are DC coupled and must be used with a speaker
connected in bridge configuration
Route SPK_P / SPK_N as differential pair, to reduce differential noise pick-up. The balanced configuration
will help reject the common mode noise
If audio output is directly connected to speaker transducer, given the low load impedance of its load, then
consider enlarging PCB lines to reduce series resistive losses
HS_P is single ended analog audio referenced to GND. Reduce coupling with noisy lines as this Audio
output line does not benefit from common mode noise rejection of SPK_P / SPK_N
Use twisted pair cable for balanced audio usage, shielded cable for unbalanced connection to speaker
If DC decoupling is required, a large capacitor needs to be used, typically in the µF range, depending on the
load impedance, in order not to increase the lower cut-off frequency due to its High-Pass RC filter response
2.2.1.4 Module grounding
Good connection of the module with application board solid ground layer is required for correct RF
performance. It significantly reduces EMC issues and provides a thermal heat sink for the module.
Connect each GND pin with application board solid GND layer. It is strongly recommended that each GND
pad surrounding VCC and ANT pins have one or more dedicated via down to application board solid ground
layer. The same applies to GND pins on the opposite side close to charger pins
If the application board is a multilayer PCB, then it is required to tight together each GND area with
complete via stack down to main board ground layer
It is recommended to implement one layer of the application board as ground plane
Good grounding of GND pads will also ensure thermal heat sink. This is critical during call connection, when
the real network commands the module to transmit at maximum power: proper grounding helps prevent
module overheating
Page 89

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 89 of 125
2.2.1.5 Charger Layout (for LEON-G200 only)
If battery charger is implemented, V_CHARGE must withstand the charge current (typically in the order of
several hundred mA) continuous current sink. Voltage drop is not as critical as for VCC, but dimension the line
width adequately to support the charge current without excessive loss that may lead to increase in PCB
temperature.
CHARGE_SENSE senses the charger voltage: it sinks a few µA. Therefore its line width is not critical. Since it is
an analog input, it must be connected to V_CHARGE away from noisy sources.
2.2.1.6 Other Sensitive pins
A few other pins on the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 require careful layout.
Backup battery (V_BCKP): avoid injecting noise on this voltage domain as it may affect the stability of
sleep oscillator
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC1): it is a high impedance analog input; the conversion accuracy will be
degraded if noise injected. Low-pass filter may be used to improve noise rejection; typically L-C tuned for RF
rejection gives better results
Power On (PWR_ON): is the digital input for power-on of the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200. It is implemented
as high impedance input. Ensure that the voltage level is well defined during operation and no transient
noise is coupled on this line, otherwise the module may detect a spurious power-on request
2.2.1.7 Digital pins
External Reset (RESET_N): input for external reset, a logic low voltage will reset the module
SIM Card Interface (VSIM, SIM_CLK, SIM_IO, SIM_RST): the SIM layout may be critical if the SIM card is
placed far away from LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 or in close vicinity of RF antenna. In the first case the long
connection may radiate higher harmonic of digital data. In the second case the same harmonics may be
picked up and create self-interference that can reduce the sensitivity of GSM Receiver channels whose carrier
frequency is coincident with harmonic frequencies. In the later case using RF bypass capacitors on the digital
line will mitigate the problem. In addition, since the SIM card typically accesses by the end use, it may be
subjected to ESD discharges: add adequate ESD protection to improve the robustness of the digital pins
within the module. Remember to add such ESD protection along the path between SIM holder toward the
module
Digital Audio (I2S_CLK, I2S_RX, I2S_TX, I2S_WA): the I
2
S interface requires the same consideration
regarding electro-magnetic interference as the SIM card. Keep the traces short and avoid coupling with RF
line or sensitive analog inputs
DDC (SCL, SDA): the DDC interface requires the same consideration regarding electro-magnetic
interference as for SIM card. Keep the traces short and avoid coupling with RF line or sensitive analog inputs
UART (TXD, RXD, CTS, RTS, DSR, RI, DCD, DTR): the serial interface require the same consideration
regarding electro-magnetic interference as for SIM card. Keep the traces short and avoid coupling with RF
line or sensitive analog inputs
Page 90

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 90 of 125
2.2.2 Footprint and paste mask
Figure 47 and Figure 48 describe the footprint and provide recommendations for the paste mask for LEON
modules. These are recommendations only and not specifications. The copper and solder masks have the same
size and position.
29.5 mm [1161.4 mil]
18.9 mm [744.1 mil]
0.8 mm [31.5 mil]
1.1 mm [43.3 mil]
1.55 mm [61.0 mil]
1.0 mm [39.3 mil]
0.8 mm [31.5 mil]
Figure 47: LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 footprint
21.3 mm [838.6 mil]
18.9 mm [744.1 mil]
Stencil: 120 µm
17.1 mm [673.2 mil]
0.6 mm
[23.6 mil]
0.8 mm [31.5 mil]
Figure 48: LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 paste mask
To improve the wetting of the half vias, reduce the amount of solder paste under the module and increase the
volume outside of the module by defining the dimensions of the paste mask to form a T-shape (or equivalent)
extending beyond the Copper mask. The solder paste should have a total thickness of 120 µm.
The paste mask outline needs to be considered when defining the minimal distance to the next
component.
The exact geometry, distances, stencil thicknesses and solder paste volumes must be adapted to the
specific production processes (e.g. soldering etc.) of the customer.
The bottom layer of LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 shows some unprotected copper areas for GND and VCC signals,
plus GND keep-out for internal RF signals routing.
Consider “No-routing” areas for the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 footprint as follows:
1. Ground copper and signals keep-out below LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 on Application Motherboard due to
VCC area, RF ANT pin and exposed GND pad on module bottom layer (see Figure 49).
2. Signals Keep-Out below module on Application Motherboard due to GND opening on LEON-G100 /
LEON-G200 bottom layer for internal RF signals (see Figure 50).
Page 91

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 91 of 125
Figure 49: Ground copper and signal keep-out below data module on application motherboard due to due to VCC area, RF ANT
pin and exposed GND pad on data module bottom layer
Page 92

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 92 of 125
Figure 50: Signals keep-out below data module on application motherboard due to GND opening on data module bottom layer
for internal RF signals
Routing below LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 on application motherboard is generally possible but not
recommended: in addition to the required keep-out defined before, consider that the insulation offered by the
solder mask painting may be weakened corresponding to micro-vias on LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 bottom layer,
thus increasing the risk of short to GND if the application motherboard has unprotected signal routing on same
coordinates.
2.2.3 Placement
Optimize placement for minimum length of RF line and closer path from DC source for VCC.
2.3 Module thermal resistance
The Case-to-Ambient thermal resistance (R
C-A
) of the module, with the LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 mounted on a
130 x 110 x 1.6 mm FR4 PCB with a high coverage of copper (e.g. the EVK-G25H evaluation kit) in still air
conditions is equal to 14°C/W.
With this Case-to-Ambient thermal resistance, the increase of the module temperature is:
Around 12°C when the module transmits at the maximum pow er level during a GSM call in the GSM/EGSM
bands
Around 17°C when the module transmits at the maximum power level during a GPRS data transfer (2 Tx +
3 Rx slots) in the GSM/EGSM bands
Page 93

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 93 of 125
Case-to-Ambient thermal resistance value will be different than the one provided if the module is
mounted on a PCB with different size and characteristics.
2.4 Antenna guidelines
Antenna characteristics are essential for good functionality of the module. The radiating performance of
antennas has direct impact on the reliability of connection over the Air Interface. Bad termination of ANT can
result in poor performance of the module.
The following parameters should be checked:
Item
Recommendations
Impedance
50 Ω nominal characteristic impedance
Frequency Range
Depends on the Mobile Network used.
GSM900: 880..960 MHz
GSM1800: 1710..1880 MHz
GSM850: 824..894 MHz
GSM1900: 1850..1990 MHz
Input Power
>2 W peak
V.S.W.R
<2:1 recommended, <3:1 acceptable
Return Loss
S11<-10 dB recommended, S11<-6 dB acceptable
Gain
<3 dBi
Table 31: General recommendation for GSM antenna
GSM antennas are typically available as:
Linear monopole: typical for fixed application. The antenna extends mostly as a linear element with a
dimension comparable to lambda/4 of the lowest frequency of the operating band. Magnetic base may be
available. Cable or direct RF connectors are common options. The integration normally requires the
fulfillment of some minimum guidelines suggested by antenna manufacturer
Patch-like antenna: better suited for integration in compact designs (e.g. mobile phone). They are mostly
custom designs where the exact definition of the PCB and product mechanical design is fundamental for
tuning of antenna characteristics
For integration observe these recommendations:
Ensure 50 Ω antenna termination, minimize the V.S.W.R. or return loss, as this will optimize the electrical
performance of the module. See section 2.4.1
Select antenna with best radiating performance. See section 2.4.2
If a cable is used to connect the antenna radiating element to application board, select a short cable with
minimum insertion loss. The higher the additional insertion loss due to low quality or long cable, the lower
the connectivity
Follow the recommendations of the antenna manufacturer for correct installation and deployment
Do not include antenna within closed metal case
Do not place antenna in close vicinity to end user since the emitted radiation in human tissue is limited by
S.A.R. regulatory requirements
Do not use directivity antenna since the electromagnetic field radiation intensity is limited in some countries
Take care of interaction between co-located RF systems since the GSM transmitted power may interact or
disturb the performance of companion systems
Place antenna far from sensitive analog systems or employ countermeasures to reduce electromagnetic
compatibility issues that may arise
Page 94

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 94 of 125
2.4.1 Antenna termination
LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules are designed to work on a 50 Ω load. However, real antennas have no
perfect 50 Ω load on all the supported frequency bands. To reduce as much as possible performance
degradation due to antenna mismatch, the following requirements should be met:
Measure the antenna termination with a network analyzer: connect the antenna through a coax ial cable to
the measurement device, the |S11| indicates which portion of the power is delivered to antenna and which
portion is reflected by the antenna back to the modem output
A good antenna should have a |S
11
| below -10 dB over the entire frequency band. Due to miniaturization,
mechanical constraints and other design issues, this value will not be achieved. A value of |S11| of about
-6 dB - (in the worst case) - is acceptable
Figure 51 shows an example of this measurement:
Figure 51: |S11| sample measurement of a penta-band antenna that covers in a small form factor the 4 GSM bands (850 MHz, 900
MHz, 1800 MHz and 1900 MHz) and the UMTS Band I
Figure 52 shows comparable measurements performed on a wideband antenna. The termination is better, but
the size of the antenna is considerably larger.
Figure 52: |S11| sample measurement of a wideband antenna
Page 95

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 95 of 125
2.4.2 Antenna radiation
An indication of the radiated power by the antenna can be approximated by measuring the |S2\| from a target
antenna to the measurement antenna, measured with a network analyzer using a wideband antenna .
Measurements should be done at a fixed distance and orientation. Compare the results to measurements
performed on a known good antenna. Figure 53 through Figure 54 show measurement results. A wideband log
periodic-like antenna was used, and the comparison was done with a half lambda dipole tune on 900 MHz
frequency. The measurements show both the |S11| and |S21| for penta-band internal antenna and for the
wideband antenna.
Figure 53: |S11| and |S21| comparison of a 900 MHz tuned half wavelength dipole and a penta-band internal antenna
The half lambda dipole tuned to 900 MHz is known to have good radiation performance (both for gain and
directivity). By comparing the |S21| measurement with the antenna under investigation for the frequency for
which the half dipole is tuned (e.g. marker 3 in Figure 53) it is possible to rate the antenna being tested. If the
performance of the two antennas is similar then the target antenna is good.
Figure 54: |S11| and |S21| comparison between a 900 MHz tuned half wavelength dipole and a wideband commercial antenna
If |S21| values for the tuned dipole are much better than for the antenna under evaluation (e.g. as seen by
markers 1 and 2 of the S21 comparison in Figure 54, where the dipole performance is 5 dB better), then it can
be concluded that the radiation of the antenna under evaluation is considerably less.
The same procedure should be repeated for other bands with the half wavelength dipole re -tuned to the band
under investigation.
Page 96

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 96 of 125
For good antenna radiation performance, antenna dimensions should be comparable to a quarter of the
wavelength. Different antenna types can be used for the module, many of them (e.g. patch antennas,
monopole) are based on a resonating element that works in combination with a ground plane. The
ground plane, ideally infinite, can be reduced down to a minimum size that must be similar to one
quarter of the wavelength of the minimum frequency that has to be radiated (transmitted/received).
Numerical sample: frequency = 1 GHz wavelength = 30 cm minimum ground plane (or antenna
size) = 7.5 cm. Below this size, the antenna efficiency is reduced.
Page 97

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 97 of 125
2.4.3 Antenna detection functionality
The internal antenna detect circuit is based on ADC measurement at ANT pin: the RF port is DC coupled to the
ADC unit in the baseband chip which injects a DC current (30 µA for 250 µs) on ANT and measures the resulting
DC voltage to evaluate the resistance from ANT pad to GND.
The antenna detection is performed by the measurement of the resistance from ANT pad to GND (DC element
of the GSM antenna), that is forced by the AT+UANTR command: refer to u-blox AT Commands Manual [2] for
more details on how to access to this feature.
To achieve good antenna detection functionality, use an RF antenna with built-in resistor from ANT signal to
GND, or implement an equivalent solution with a circuit between the antenna cable connection and the
radiating element as shown in Figure 55.
Antenna Assembly
Diagnostic Circuit
Application Board
LEON-G100/G200
ANT
ADC
Current
Source
RF
Choke
DC
Blocking
Front-End
RF Module
RF
Choke
DC
Blocking
Radiating
Element
Zo=50 Ohm
Resistor for
Diagnostic
Coaxial Antenna Cable
Internal
Resistor
Figure 55: Module Antenna Detection circuit and antenna with diagnostic resistor
Examples of components for the antenna detection diagnostic circuit are reported in the following table:
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
DC Blocking Capacitor
Murata GRM1555C1H220JA01 or equivalent
RF Choke Inductor
Murata LQG15HS68NJ02, LQG15HH68NJ02 or equivalent
Resistor for Diagnostic
15kΩ 5%, various Manufacturers
Table 32: Example of components for the antenna detection diagnostic circuit
The DC impedance at RF port for some antennas may be a DC open (e.g. linear monopole) or a DC short to
reference GND (e.g. PIFA antenna). For those antennas, without the diagnostic circuit Figure 55, the measured
DC resistance will be always on the extreme of measurement range (respectively open or short), and there will
be no mean to distinguish from defect on antenna path with similar characteristic (respectively: removal of linear
antenna or RF cable shorted to GND for PIFA antenna).
Furthermore, any other DC signal injected to the RF connection from ANT connector to radiating element will
alter the measurement and produce invalid results for antenna detection.
Page 98

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 98 of 125
It is recommended to use an antenna with a built-in diagnostic resistor in the range from 5 kΩ to 30 kΩ to
assure good antenna detection functionality and to avoid a reduction of module RF performances.
For example: consider GSM antennas with built-in DC load resistor of 15 kΩ.
Using the +UANTR AT command, the module reports the resistance value evaluated from ANT pad to GND:
Reported values close to the used diagnostic resistor nominal value (i.e. values from 10 kΩ to 20 kΩ if a
15 kΩ diagnostic resistor is used) indicate that the antenna is connected
Values above the maximum measurement range limit (about 53 k Ω) indicate that the antenna is not
connected
Reported values below the minimum measurement range limit (about 1 kΩ) indicate that the antenna is
shorted to GND
Measurement inside the valid measurement range and outside the expected range may indicate an improper
connection, damaged antenna or wrong value of antenna load resistor for diagnostic
Reported value could differ from the real resistance value of the diagnostic resistor mounted inside the
antenna assembly due to antenna cable length, antenna cable capacity and the used measurement method
Page 99

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 99 of 125
2.5 ESD Immunity Test Precautions
The immunity of the device (i.e. the application board where LEON module is mounted) to the EMS
phenomenon Electrostatic Discharge must be certified in compliance to the testing requirements standard [9]
and the requirements for radio and digital cellular radio telecommunications system equipment standards [10]
[11].
The ESD test is performed at the enclosure port [10] referred to as the physical boundary through which the EM
field radiates. If the device implements an integral antenna [10] the enclosure port is seen as all insulating and
conductive surfaces housing the device. If the device implements a removable antenna [10], the antenna port
[10] can be separated from the enclosure port. The antenna port comprises the antenna element and its
interconnecting cable surfaces.
The applicability of the ESD test depends to the device classification [10], as well the test on other ports [10] or
on interconnecting cables to auxiliary equipments depends to the device accessible interfaces and manufacturer
requirements.
Contact discharges [9] are performed at conductive surfaces whereas air discharges [9] are performed at
insulating surfaces. Indirect contact discharges are performed to the measurement setup horizontal and vertical
coupling planes [9].
Implement the following precautions to satisfy ESD immunity test requirements [9] [10] [11] performed at the
device enclosure in compliance to the category level [10] and shown in Table 33.
Application
Category
Immunity Level
All exposed surfaces of the radio equipment and ancillary equipment in
a representative configuration
Contact Discharge
4 kV
Air Discharge
8 kV
Table 33: Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) ESD immunity requirement, standards “EN 61000-4-2, EN 301 489-1 V1.8.1, EN
301 489-7 V1.3.1”
Although EMC certification (including ESD immunity testing) must be performed in the final application of the
radio equipment EUT, results are provided for LEON modules performing the test with a representative
configuration to show that requirements can be met.
The reference application design consists of a LEON soldered onto a motherboard which provides an interface to
power supply, SIM card, headset, and communication port. GSM external antenna in connected to SMA
connector provided on the motherboard.
Since an external antenna is used, the antenna port can be separated from the enclosure port. The reference
application is not enclosed in a box so the enclosure port is not identified with physical surfaces. Therefore, some
test cases cannot be applied. Only the antenna port is identified as accessible for direct ESD exposure.
The reference application implements all precautions described in the sections below. ESD immunity test results
and applicability are reported in Table 34 according to test requirements [9] [10] [11].
Page 100

LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 - System Integration Manual
GSM.G1-HW-09002-G3 Preliminary Design-In
Page 100 of 125
Category
Application
Immunity Level
Contact Discharge to coupling planes (indirect contact discharge)
Enclosure
+2 kV / -2 kV
+4 kV / -4 kV
Contact Discharges to conducted surfaces (direct contact discharge)
Enclosure port
Not Applicable2
Contact Discharges to conducted surfaces (direct contact discharge)
Antenna port
+2 kV / -2 kV
+4 kV / -4 kV
Air Discharge at insulating surfaces
Enclosure port
Not Applicable3
Air Discharge at insulating surfaces
Antenna port
+2 kV / -2 kV
+4 kV / -4 kV
+8 kV / -8 kV
Table 34: Enclosure ESD immunity level result, standards “EN 61000-4-2, EN 301 489-1 V1.8.1, EN 301 489-7 V1.3.1” for LEON
application reference design
2.5.1 General precautions
The following module interfaces can have a critical influence in ESD immunity testing, depending on the
application board handling. Some suggested precautions are provided:
RESET_N pin
A series Schottky diode is integrated in LEON-G100 / LEON-G200 modules as protection on the RESET_N pin.
The external circuit must be able to cause a current flow through the series diode to determine the RE SET_N
state.
Sensitive interface is the reset line (RESET_N pin):
A 47 pF bypass capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H470JA01) have to be mounted on the line termination
connected to the RESET_N pin to avoid a module reset caused by an electrostatic discharge applied to the
application board enclosure
A series ferrite bead (e.g. Murata BLM15HD182SN1) must be added on the line connected to the RESET_N
pin to avoid a module reset caused by an electrostatic discharge applied to the application board enclosure
It is recommended to keep the connection line to RESET_N as short as possible
2
LEON mounted on application design:
Inapplicability -> EUT with insulating enclosure surface, EUT without enclosure surface
Applicability -> EUT with conductive enclosure surface
3
LEON mounted on application design:
Applicability -> EUT with insulating enclosure surface
Inapplicability -> EUT with conductive enclosure surface, EUT without enclosure surface
 Loading...
Loading...