Page 1

TS-AWE3
TS-AWH3
USER’S MANUAL
Intel
®
Socket 370 Celeron
TM
Pentium® III FC-PGA Series
Transcend
Your Supplier, Your Partner,
/
Your Friend.
Page 2

TS-A WH3 / TS-AWE3 Motherboard
Supporting Intel ® Pentium® III / Celeron™ Series Processor
66/100/133MHz Front Side Bus
Intel® 810-DC100 / 810E Chipset
Welcome !!
Congratulations on your purchase of this great value motherboard, with its range of special
features and innovative onboard functions, built around the advanced architecture of the new
Intel® 810-DC100 / 810E Chipset. More details to follow later in this manual.
Our Website
Please come and visit us at our website on http://www.transcendusa.com/ Y ou’ll find plenty of
interesting information about this and many other quality Transcend products.
Your User’s Manual
This User’s Manual is designed to help end users and system manufacturers to set up and
install the motherboard. All of the information within has been carefully checked for accuracy .
However, Transcend Information, Inc. (hereafter referred to as “Transcend”) carries no
responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies which this manual may contain. This
includes references to products and software. In addition, the information and specifications
are subject to change without prior notice.
Disclaimer
Transcend provides this manual “as is” without any warranty of any kind, either expressed or
implied, including – but not limited to – the implied warranties, conditions of merchantability or
fitness for a particular purpose. Transcend, its management, employees, distributors and agents
are in no way liable for any indirect special, incidental or consequential damages, including loss
of profits, loss of business and the like. This is even if Transcend has been advised of the
possibility of such damages arising from any defect or error in this manual or product.
Trademarks
All brands, product names and trademarks mentioned in this document are the property of their
respective owners or companies and are used solely for identification or explanation. It is
Transcend policy to respect all product rights.
Copyright
This manual may not, in whole or in part, be photocopied, reproduced, transcribed, translated
or transmitted, in whatever form or language, without the written consent of the manufacturer,
except for copies retained by the purchaser for personal archiving purposes.
Manual Version: 1.00
Release Date: April 2000
Copyright © 2000 Transcend Information, Inc.
Page 3

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1
1.1 Essential Handling Precautions.......................................................................1
1.2 Package Contents..........................................................................................2
1.3 Specifications and Features.............................................................................2
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION 5
2.1 Transcend’s TS-AWH3/TS-AWE3 Motherboard...........................................5
2.2 Layout of Transcend’s TS-AWH3/TS-AWE3 Motherboard..............................6
2.3 66/100/133MHz System configuration...........................................................7
2.4 Memory Configuration..................................................................................8
2.5 Keyboard Wake Up......................................................................................9
2.6 Primary / Secondary IDE Connectors............................................................10
2.7 Floppy Disk Drive Connector........................................................................11
2.8 Fan Power Connectors................................................................................12
2.9 Wake-on-LAN Connector..............................................................................13
2.10 IrDA-Compliant Infrared Module Connector....................................................14
2.11 Panel Connectors.........................................................................................15
2.12 Power Connector.........................................................................................17
2.13 External Back Panel I/O Ports........................................................................18
2.14 Using Jumper JPS to clear CMOS.....................................................................19
2.15 FWH Lock Jumper........................................................................................20
2.16 Onboard Audio Setting..................................................................................21
2.17 Internal Audio Connector............................................................................22
2.18 Internal Serial Port Connector COMB ..........................................................23
Page 4

CHAPTER 3 BIOS SETUP 24
3.1 BIOS Setup ............................................................................................... 24
3.2 The Main Menu ......................................................................................... 24
3.3 Standard CMOS Features........................................................................... 26
3.4 Advanced BIOS Features............................................................................ 29
3.5 Advanced Chipset Features ........................................................................ 32
3.6 Integrated Peripherals .................................................................................34
3.7 Power Management Setup...........................................................................38
3.8 PnP/PCI Configuration Setup....................................................................... 41
3.9 PC Health Status ........................................................................................43
3.10 Frequency/Voltage Control..........................................................................44
3.11 Load Fail-Safe Default.................................................................................45
3.12 Load Optimized Defaults.............................................................................45
3.13 Supervisor Password..................................................................................46
3.14 User Password...........................................................................................47
3.15 Save & Exit Setup.......................................................................................47
3.16 Exit Without Saving ................................................................................... 48
CHAPTER 4 SOFTW ARE SETUP 49
4.1 INF Update for 810 Chipset ....................................................................... 49
4.2 VGA Driver Setup.......................................................................................50
4.3 Intel Security Controller Driver.....................................................................51
4.4 Audio Driver Setup.......................................................................................52
CHAPTER 5 BIOS UPGRADE 57
5.1 How to Check Your BIOS File Name and Version ........................................ 57
5.2 How to Download Correct BIOS File from Web............................................... 57
5.3 How to Update Your Motherboard BIOS ..................................................... 58
Page 5

INTRODUCTION 1
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Essential Handling Precautions
IMPORTANT. Read this page before unpacking your motherboard!
• Power Supply
Be careful! Always ensure that the computer is disconnected from the power supply when
working on the motherboard and its components.
• Static Electricity
Static electricity may cause damage to the delicate integrated circuit chips on your
motherboard. Before handling the motherboard outside of its protective packaging, ensure
that there is no static electric charge in your body. T o avoid this risk, please observe these
simple precautions while handling the motherboard and other computer components:
1. If possible, wear an anti-static wrist strap. This fits around your wrist and is connected to
a natural earth ground.
2. T ouch a grounded or anti-static surface, or a metal fixture such as a pipe or the chassis of
your system, before touching the motherboard.
3. When you have removed the motherboard from its anti-static packaging, try to hold it only
by the edges, without touching any components.
4. Avoid contacting the components on add-on cards, motherboards, and modules with the
golden fingers (gold-colored connectors) which plug into the expansion slots.
5. It is safest to handle system components only by their mounting brackets.
6. Keep components which are not connected to the system in the anti-static packaging
whenever possible.
These precautions help to reduce the risk of static build-up and ensure any static discharge is
harmless to your equipment.
••
• Battery Replacement
••
The battery which holds the system settings memory on your motherboard should not require
replacement for at least five years, and probably much longer. In picture 2.2, it is located near
the bottom right hand corner.
Page 6

2 INTRODUCTION
Please replace your battery only with the same type, or a similar type recommended by the
manufacturer . If the battery is replaced incorrectly, there is a risk of a short circuit or explosion.
Used batteries should disposed of according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
••
• Electric Screwdrivers
••
To reduce the risk of damage to the motherboard due to excessive torque, avoid setting
electric screwdrivers above 7.5 kg/cm.
1.2 Package Contents
This motherboard package should contain the following items. Please check them as soon as
you unpack. If you find any damaged or missing items, please contact your retailer.
- TS-AWH3/TS-A WE3 motherboard
- 1 X CD-ROM
- 1 X FDD cable
- User’s Manual
- COM port cable x 1
- Ultra DMA / 66 cable x 1
1.3 Specifications and Features
• •
• CPU
• •
- Supports Intel® Petium III / CeleronTM Series
• •
• Chipset
• •
- TS-AWH3 : Intel® 810-DC100 Chipset (GMCH, ICH); FSB:66/100 MHz
- TS-AWE3 : Intel® 810E Chipset (GMCHE, ICH); FSB: 66/100/133 MHz
• •
• Display Cache Memory
• •
- 4MB Display Cache SDRAM
• •
• DRAM Memory
• •
- Supports Synchronous DRAM
- 3 X 168-pin DIMM module sockets on board
- 8~512MB memory size
- 8/16/32/64/128/256MB SDRAM DIMM
- 64 data bits structure only
Page 7

INTRODUCTION 3
• •
• I/O Bus Slot
• •
- 5 X Master / Slave PCI Bus slots (PCI 2.2 compliant)
- 1 X AMR (Audio/MODEM Riser) slot
•
Award BIOS
- Supports PC99, Plug-and-Play
- Supports ACPI,APM,DMI, Green Feature
• •
• I/O Functions
• •
- Support PIO Mode 3,4 A T API devices and Ultra DMA/33/66
- Supports 2 high speed UART 16550 COM ports
- Supports SPP/EPP/ECP LPT port
- Supports 3 mode/1.44/2.88MB floppy drive
- Supports PS/2 Mouse and PS/2 Keyboard
- Supports IrDA port
- Supports 2 USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports
- Supports VGA port
- Supports Line-out, Line-in and MIC-in jack
- Supports Game/MIDI port
•
Switching Voltage Regulator
- Intel VRM 8.4 compliant
•
Other Features
- Year 2000 compliant
- Power failure resume
- FWH (Firmware Hub) supports security manageability
- BIOS Virus protection (warning)
- PS/2 Mouse and Keyboard Wake Up
- Support Wake-on-LAN function
- Remote Ring Wake Up
- Time W ake Up
- Board voltage monitors for CPU core, +3.3V, +/-5.0V, +/-12.0V, VTT and VBAT
- CPU overheat alarm
- CPU fan auto-off in sleep mode
Page 8

4 INTRODUCTION
•
PCB Dimensions
- ATX form factor , 4-layer PCB, 20.4cm x 30.5cm (8 inch x 12 inch)
Page 9

HARDWARE INSTALLATION 5
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.1 Transcend’s TS-AWE3/TS-AWH3 Motherboard
Back panel I/O ports CP U Main Memory
Back panel I/O ports CP U Main Memory
Game/ MIDI port & Audio Jack
Game/ MIDI port & Audio Jack
·
·
(Line-in, Line-out,MIC-in)
VGA port & Serial port &
·
·
Parallel printer port
2 x USB ports
2 x USB ports
·
·
PS/2 KB & PS/2 Mouse ports
PS/2 KB & PS/2 Mouse ports
·
·
Intel® Socket 370 Celero
·
·
Penutium III CPU
TM
3x168-pin SDRAM DIMM
·
·
Up to 512MB
·
·
Intel 810 chipset
Intel 810 chipset
TS-AWH3: Intel 810DC-100
·
·
Chipset (GMCH, ICH)
Chipset (GMCH, ICH)
TS-AWE3: Intel 810E
·
·
Chipset (GMCHe,ICH)
Display Cache
Display Cache
AC97 CODEC
CO M Connector
CO M Connector
Serial COM port 2
·
·
Connector
WOL Header
Wake on LAN
·
·
·
4MB Display cache
memory.
memory.
PCI IDE Connector
PCI IDE Connector
Bus Master
Bus Master
·
·
PIO Mode 3/4
PIO Mode 3/4
·
·
DMA Mode 2
DMA Mode 2
·
·
Ultra DMA/66
Ultra DMA/66
·
·
FDD Connector
FDD Connector
Floppy Disk Drive Connector
·
·
Expansion SlotsExpansion Slots
5 x PCI Slots
5
·
·
1 x AMR connector
·
·
(Audio/Modem Riser)
(Audio/Modem Riser)
System BIOS
System BIOS
4 M Bits FWH Flash Memory
4 M Bits FWH Flash Memory
·
·
(Intel 82802AB)
(Intel 82802AB)
LPC Super I/O
Winbond 83627 HF-AW
·
·
IrDA Header
IrDA Header
SIR, CIR, ASKIR
SIR, CIR, ASKIR
·
·
Page 10
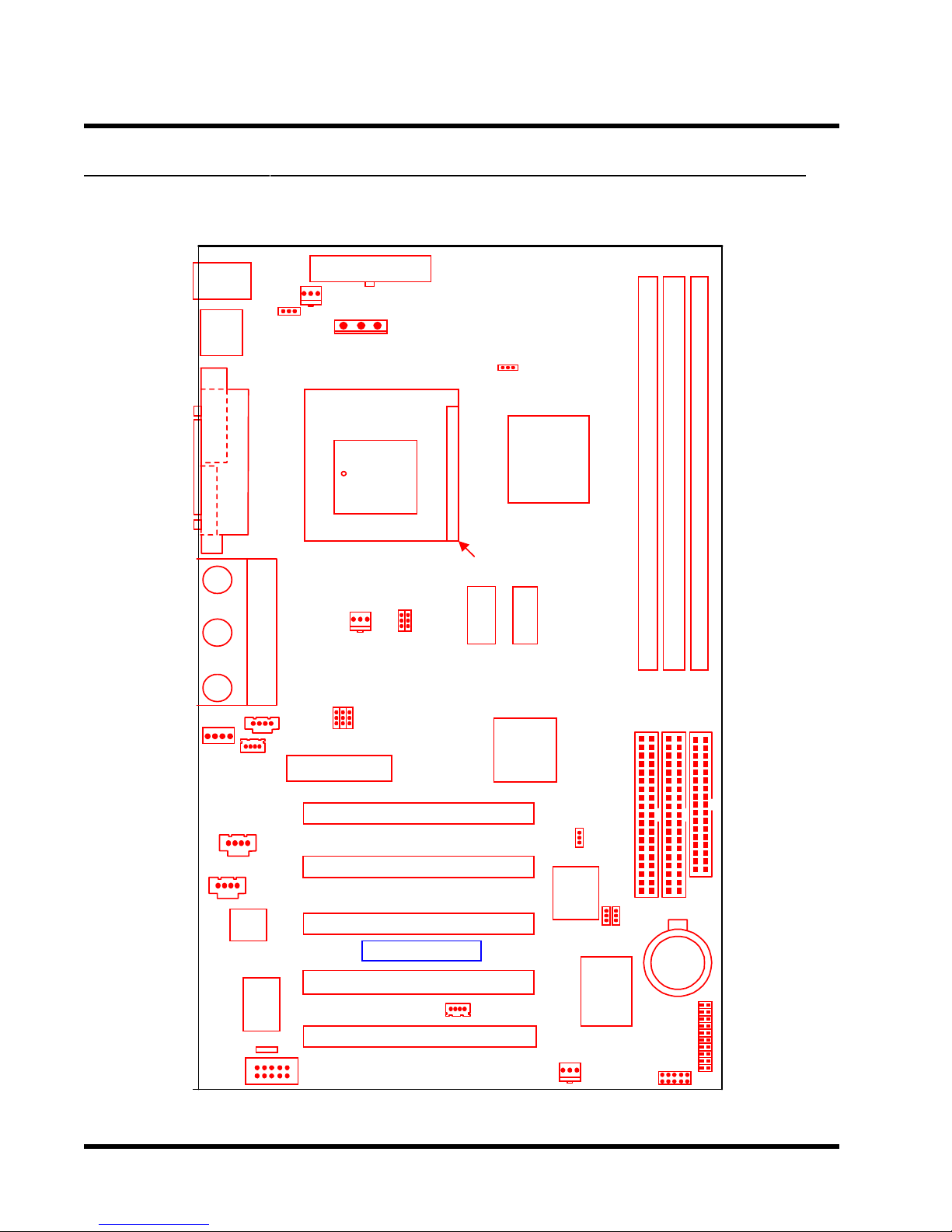
6 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
)
)
)
)
)
2.2 Layout of Transcend’s TS-AWE3/TS-AWH3 Motherboard
KB MOUSE
PS/2
T:Mouse
B:Keyboard
USB
USB
T:Port 1
B:Port 2
COMA
PRINTER
VGA
FAN1
JP1
Parallel Port
Game Port
POWER-FAN
FAN2
370
PGA
JP2
PWR-CONN
JP15
Intel
810DC-100
SDRAM
GMCH
810E/
SDRAM
DIMM3 (64bit 168pin SDRAM Module)
DIMM2 (64bit 168pin SDRAM Module)
DIMM1 (64bit 168pin SDRAM Module)
MODEM
CD1
CD2
AMR
COMB
JP3
PCI Slot1 (PCI1
PCI Slot2 (PCI2
PCI Slot3 (PCI3
Transcend
PCI Slot4 (PCI4
PCI Slot5 (PCI5
WOL
Intel
ICH
FWH
FAN3
JP5
JP6
JP7
83627
Winbond
FDCIDE2IDE1
Li Battery
Panel
IrDA
Connector
Page 11
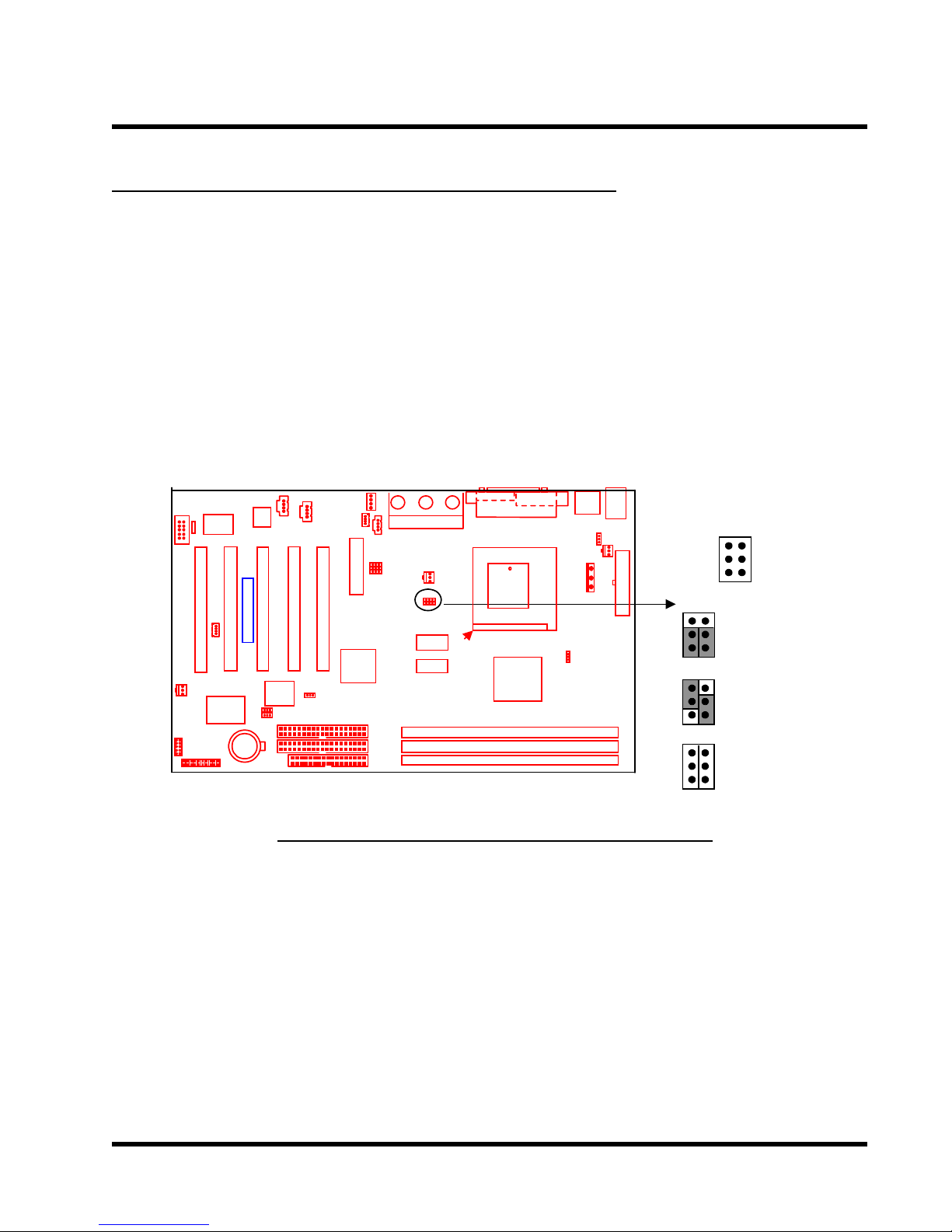
HARDWARE INSTALLATION 7
2.3 66/100/133 MHz System Configuration
The JP2 Jumper allows you to set the FSB (Front Side Bus) to either 66/100/133MHz
configuration. When you set the FSB to 66MHz, you can select a system bus frequency from
66MHz to 75MHz through “CPU Host/PCI Clock” of “Frequency/V oltage Control” in the BIOS
Setup menu (please refer to page 44). When you set the FSB to 100MHz, you can select a
system bus frequency from 100MHz to 124MHz through “CPU Host/PCI Clock” of “Frequency/
V oltage Control” in the BIOS Setup menu (please refer to page 44). When you set the FSB to
133MHz, you can select a system bus frequency from 133MHz to 150MHz through “CPU HOST
/ PCI Clock” of “Frequency / Voltage Control” in the BIOS Setup menu (please refer to page
44).
JP2
Transcend
66/100/133MHz FSB Configuration Jumper
1
5
66MHz
100MHz
133MHz
2
6
Page 12

8 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.4 Memory Configuration
This motherboard must be installed with PC100 / PC133 SDRAM DIMM. If you install one
DIMM, place it in the DIMM1 slot. If you install two DIMMs, place them in slots DIMM1 and
DIMM2. If you install three DIMMs, you can only install single sided DIMMs onto the DIMM2
and DIMM3 slots, not double-sided DIMMs. Install memory in any combination as follows:
forebmuN
seludomyromeM
1
2
3
NOTE: This motherboard supports memory module with 8/16/32/64/128/256MB. If you
have more than one RAM module, you should install them from DIMM1 to DIMM3 in
order.
1MMID2MMID3MMID
dediS-elbuoD
dediS-elgniS/
dediS-elbuoD
dediS-elgniS/
dediS-elbuoD
dediS-elgniS/
llatsnitonoD
MMIDyna
dediS-elbuoD
dediS-elgniS/
dediS-elgniSdediS-elgniS
llatsnitonoD
MMIDyna
llatsnitonoD
MMIDyna
Transcend
3.3V Position
Unbuffered Position
168-pin Unbuffered SDRAM Module (DIMM1)
168-pin Unbuffered SDRAM Module (DIMM2)
168-pin Unbuffered SDRAM Module (DIMM3)
168Pin Memory DIMM Sockets
Page 13
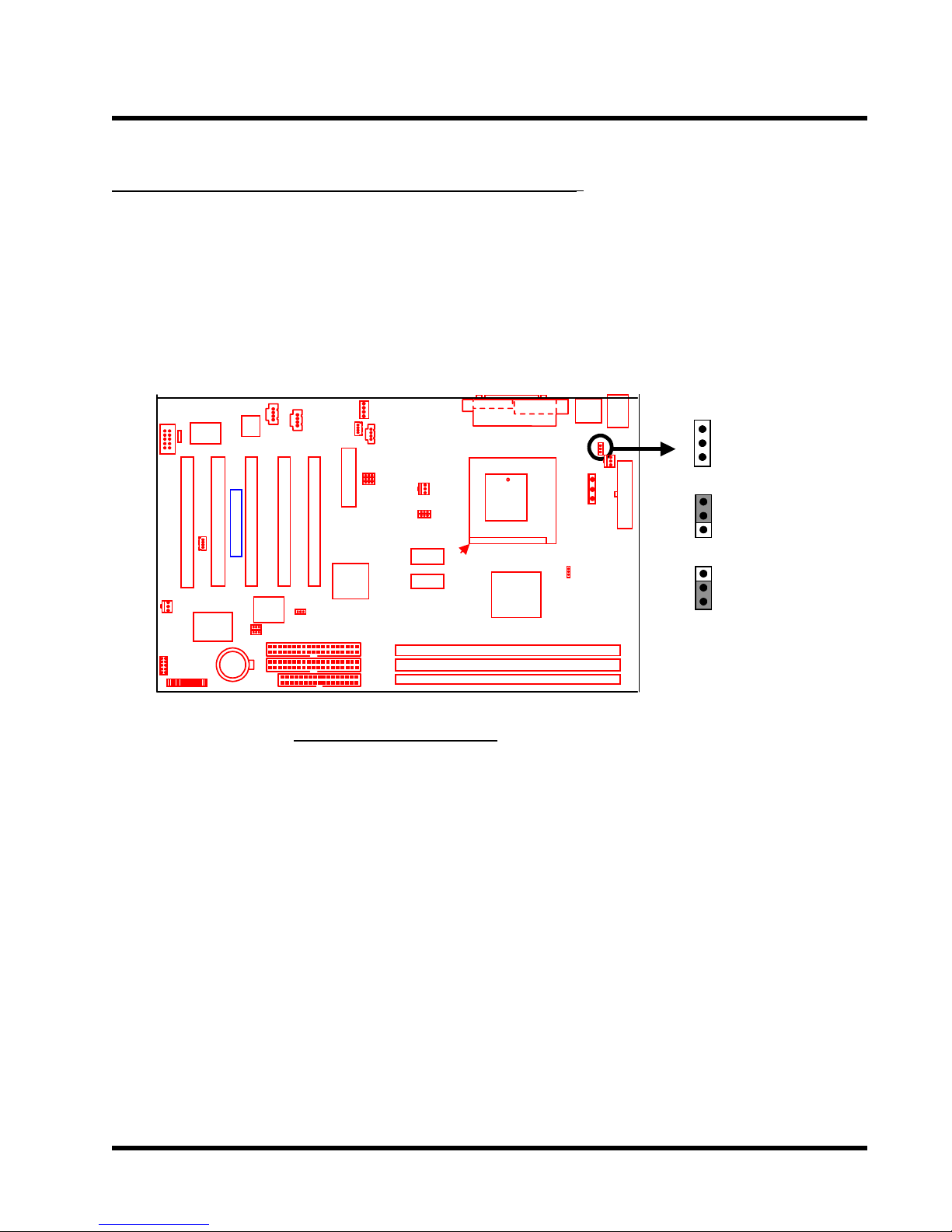
HARDWARE INSTALLATION 9
2.5 Keyboard Wake Up (3-pin KB-AWK)
This function makes the Keyboard Power Up the system. Set this jumper to “Enable” if you’d
like your Keyboard to Power Up your computer. Then, go to the”Power On Function” in the
“Integrated Peripherals” (please refer to page 35~36), and choose the setting you prefer.
JP1
1
KB-AWK
Transcend
1
Disable
Keyboard Wake Up
1
Enable
Page 14
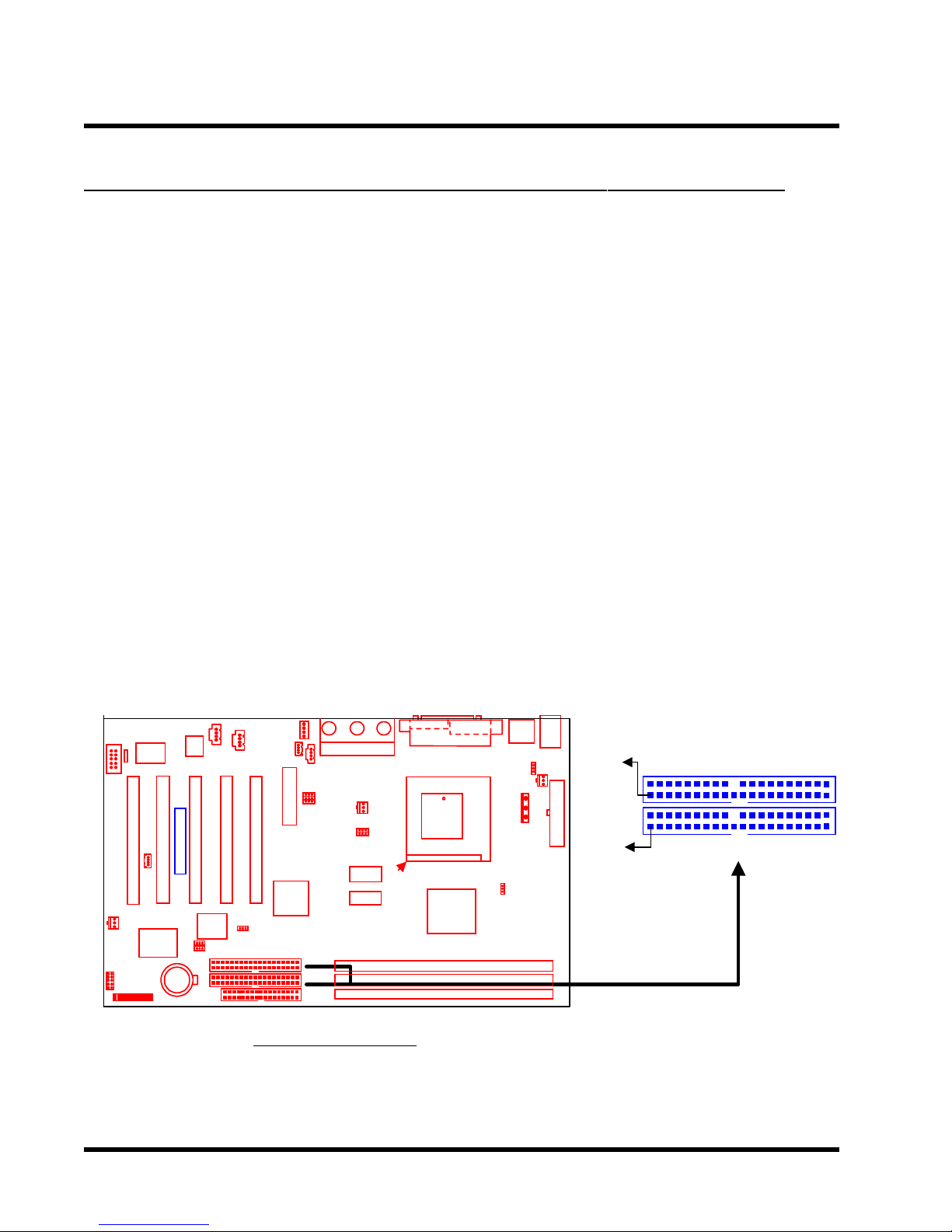
10 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.6 Primary / Secondary IDE Connectors (Two 40-pin IDE)
This motherboard supports two 40-pin IDE connectors marked as IDE1 (primary channel) and
IDE2 (secondary channel). Each channel supports two IDE devices, making a total of four
devices.
Connect your Hard Disk (the main one if you are using more than one) to the “Master” connector
(at the end of the cable) and connect it to IDE1 (see important note below). If your HDD
supports Ultra DMA/66, you must use an 80-wire cable, otherwise the HDD won’t be able to
reach this speed.
If you intend to operate two IDE devices from the same channel, one device must be set to
“Master” mode, the other to “Slave” mode. A Hard Disk, CD ROM or other IDE device can have
either setting, depending on device’s jumper. Please refer to the device’s manual for more
information.
NOTE: The Connectors must be attached to the IDE channels the right way round. Make
sure that the red stripe on one edge of the ribbon cable (this may be faint and could also
be a dotted line) is the nearest to PIN 1 (on the left as the motherboard is shown in the
picture below).
IDE
PIN1
IDE1
Transcend
IDE2
PIN1
Primary IDE Connector
Secondary IDE Connector
IDE Connectors
Page 15
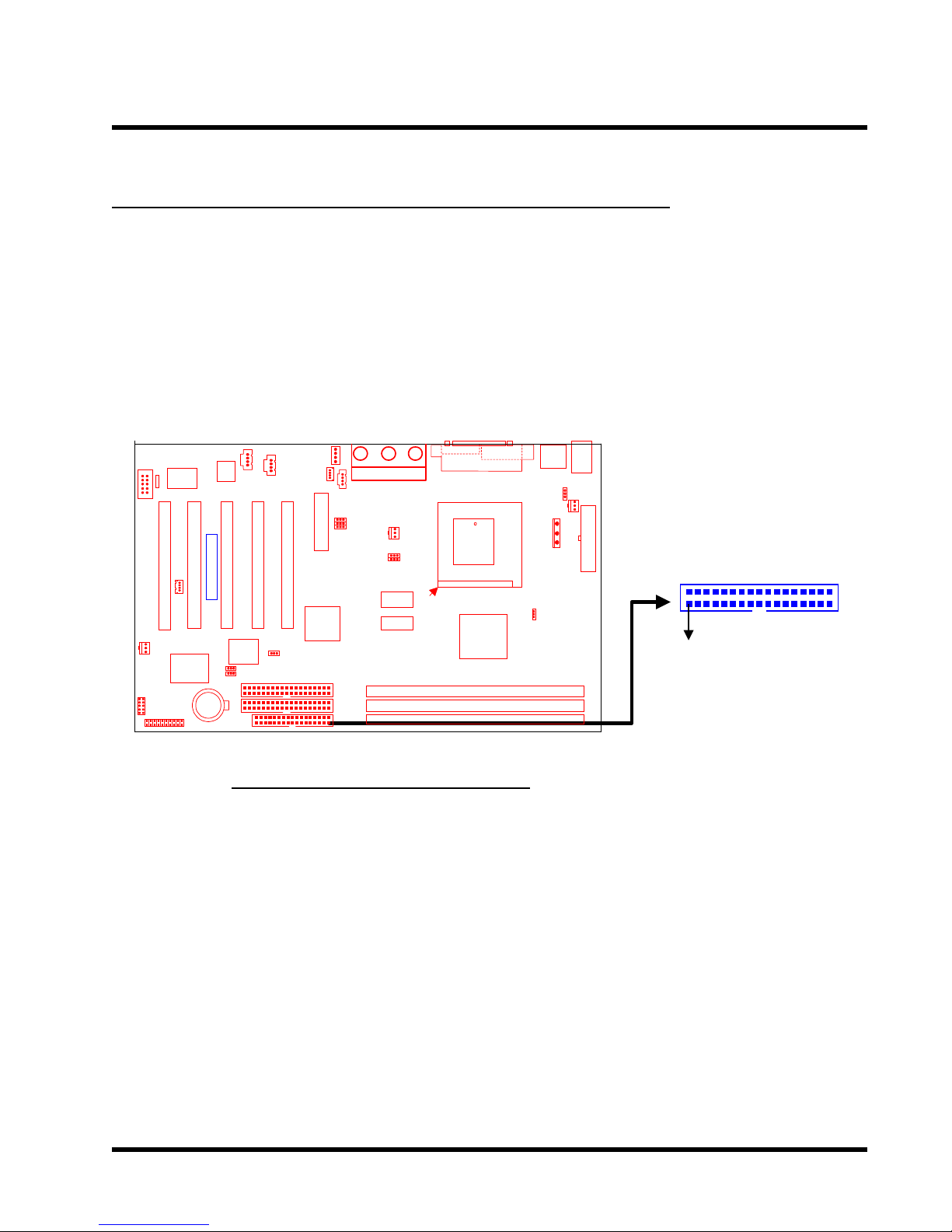
HARDWARE INSTALLATION 11
2.7 Floppy Disk Drive Connector (34-pin FDC)
This connector supports the floppy disk drive ribbon cable which is one of the items in your
motherboard package. After connecting the single end to the board, connect the two plugs at the
other end to the floppy drives. Remember, as in the last section, the red stripe on the edge of the
ribbon cable must be the nearest to PIN 1, otherwise your connection won’t work. This means it
must be on the left as the motherboard is shown below.
Transcend
Floppy Disk Drive Connector
Floppy Connector
FDC
PIN1
Page 16
12 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
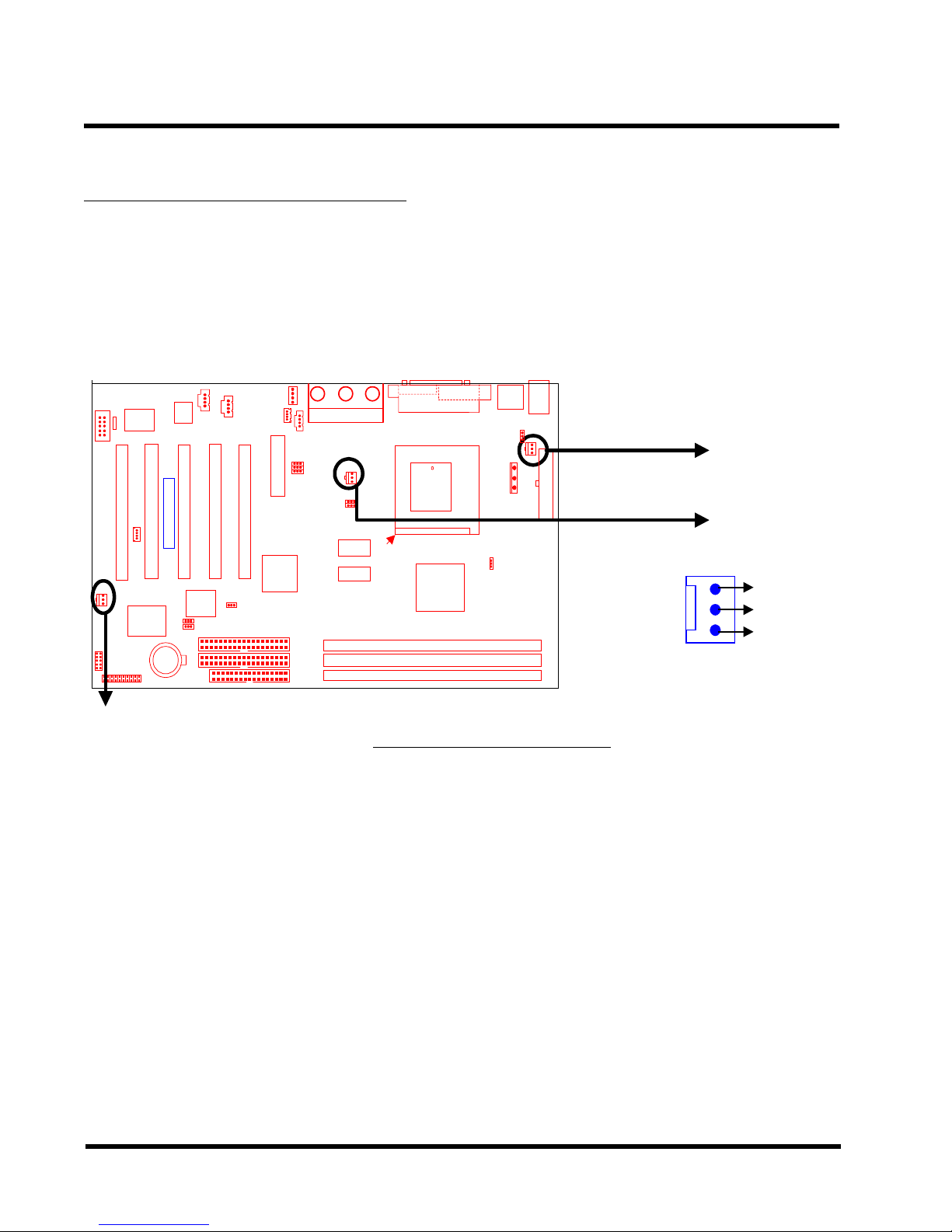
2.8 Fan Power Connectors
There are three fan power connectors on the motherboard: CPU-FAN, POWER-F AN, and CASEFAN. Each connector provides +12V power . The cables can only be attached a certain way: If
you try to put them in the wrong way , they won’t fit. These connectors support cooling fans of 500
mA (6W) or less.
CPU-FAN
Transcend
POWER-FAN
FAN
CASE-FAN
GND
+12V
Rotation
Fan Power Connectors
Page 17
HARDWARE INSTALLATION 13
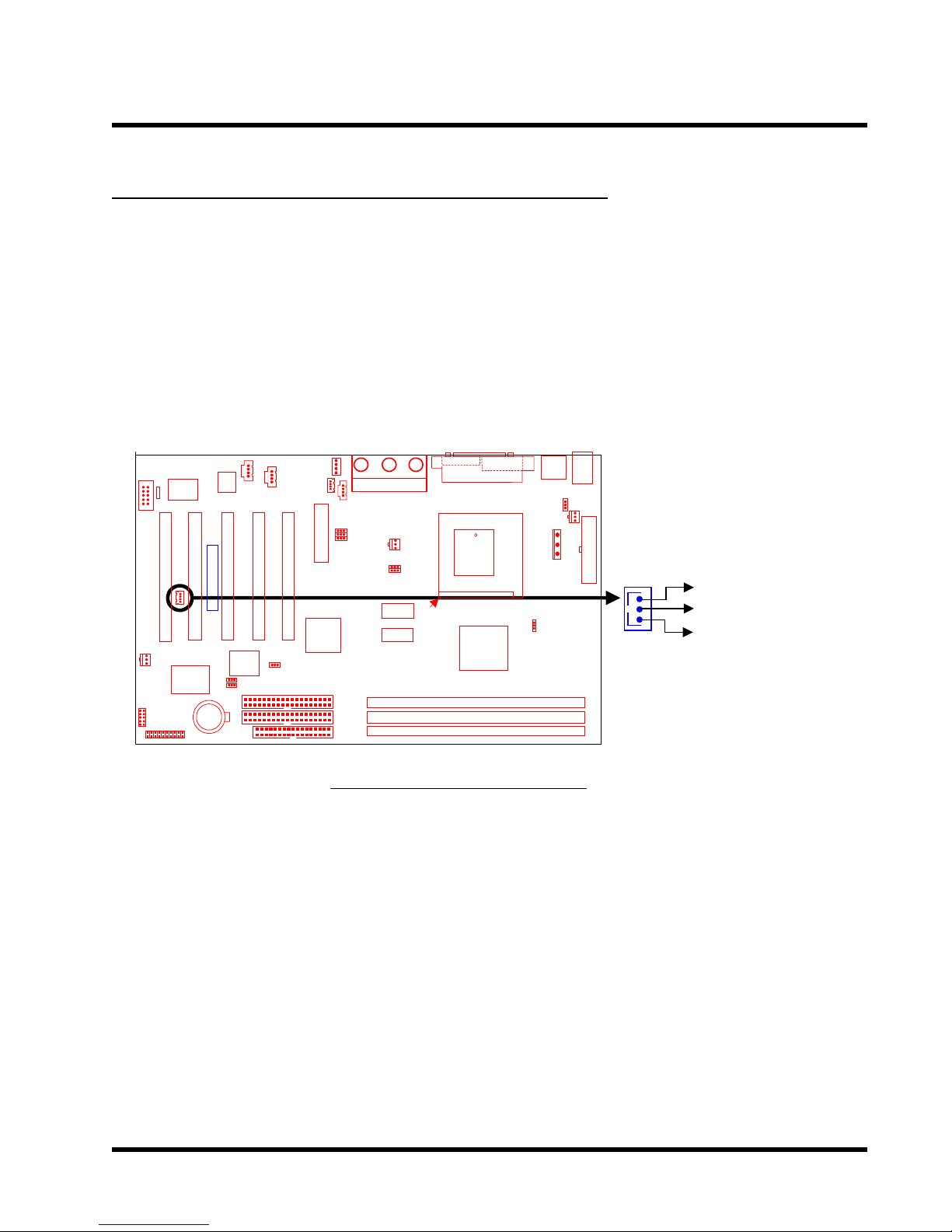
2.9 Wake-on-LAN Connector (3-pin WOL)
This connector connects to LAN cards with a Wake-on-LAN output. The system can be Powered
Up when a wakeup packet or signal is received from the LAN card.
NOTE:This function requires that the “Wake-Up by PCI & WOL” function in the “Power
Management Setup” is set to “Enabled” and that your system has an A TX power supply
with at least 720mA +5V standby power.
Transcend
WOL
+5V Standby
GND
PME
Wake-on-LAN Connector
Page 18
14 HARDW ARE INSTALLATION
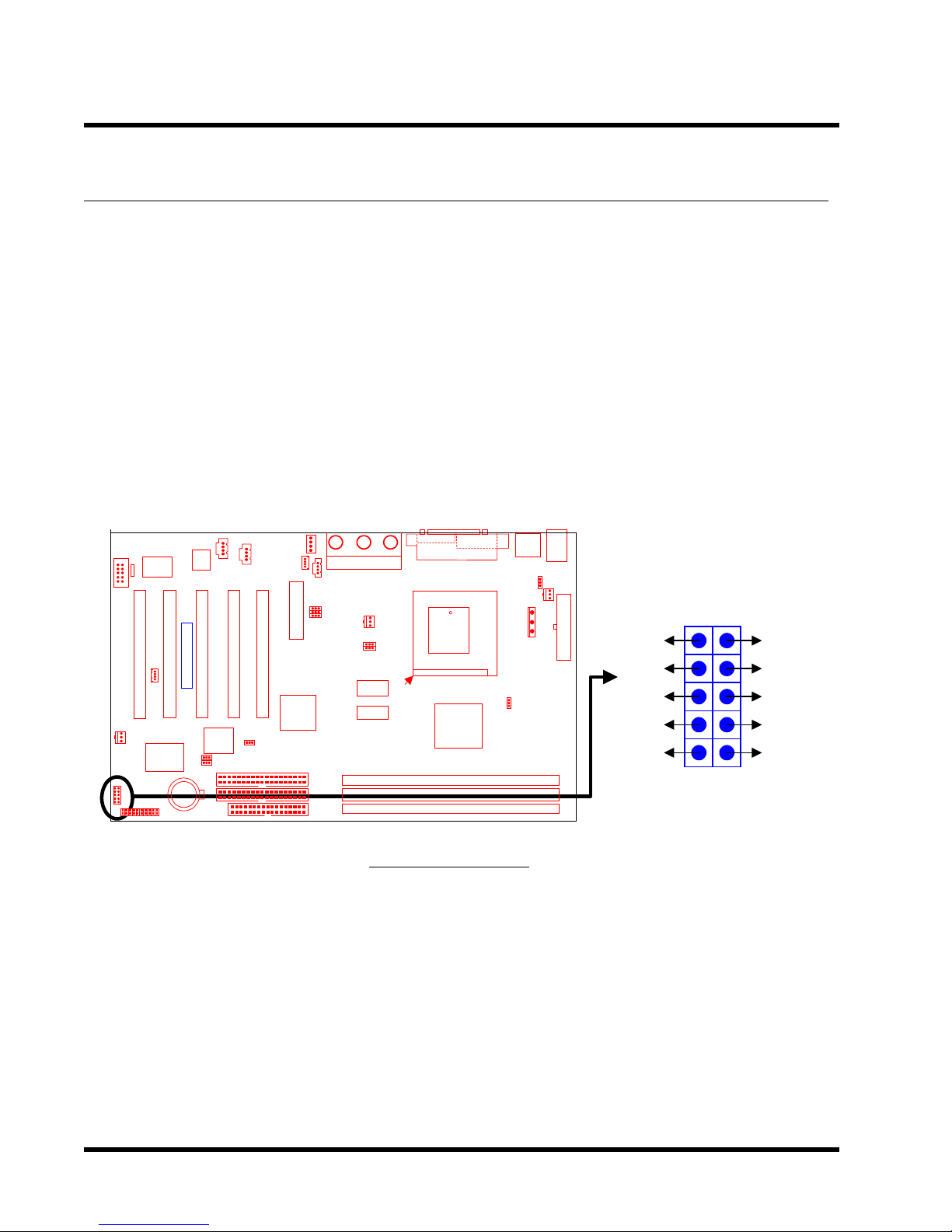
2.10 IrDA-Compliant Infrared Module Connector (10-pin IrDA)
The IrDA connector can be configured to support a wireless infrared module. With this module
and application software such as Laplink or Win95 Direct Cable Connection, users can transfer
files to or from laptops (notebooks), PDAs and printers. You must also configure the setting
through “UART Mode Select” in the “Integrated Peripherals” (please refer to page 34) to select
“IrDA”. Connect the Standard IR (SIR) device to the onboard SIR connector according to the pin
definitions. An optional Consumer Infrared (CIR) set connects to the CIR and SIR connectors
simultaneously for both wireless transmitting and remote control functions through one external
infrared module.
Transcend
IrDA Connector
+5V
NC
IRRX
GND
IRTX
IrDA
CIRSIR
12
NC
CIRRX
5VSB
NC
NC
910
Page 19
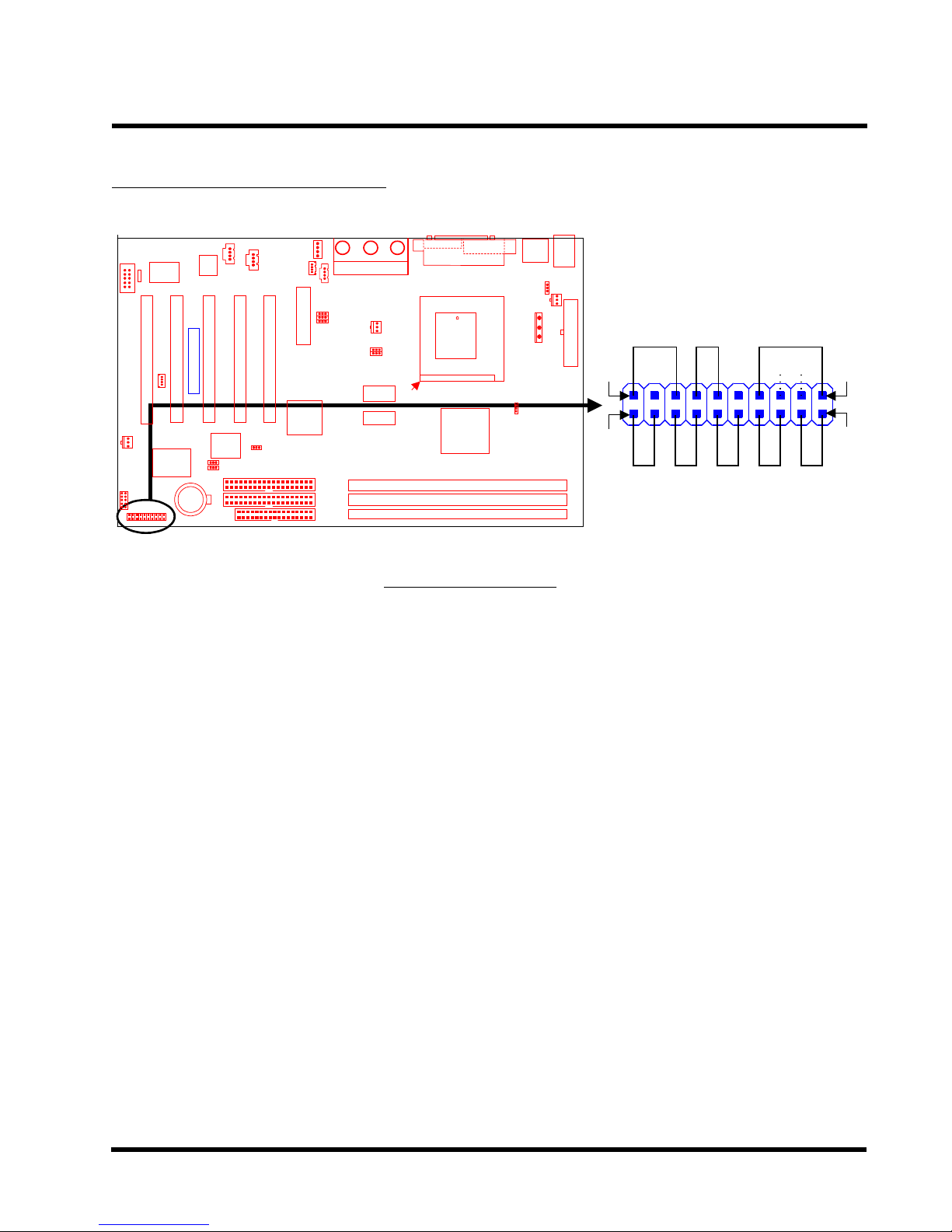
HARDWARE INSTALLATION 15
2.11 Panel Connectors
Transcend
Panel Connector
Power LED Lead (3-pin POWER LED)
This 3-pin connector attaches to the power LED.
Pin1 : +5V
Pin3 : NC
POWER LED
1 19
++
+++
S_LED HDD_LED NC RESET SOFT_OFF
KEY LOCK
SPEAKER
202
Pin5 : GND
Keylock Lead (2-pin KEYLOCK)
Use the keylock to enable or disable the Keyboard.
Pin7 : KEYLOCK
Pin9 : GND
Speaker Lead (4-pin SPEAKER)
This 4-pin connector connects to the case-mounted speaker.
Pin13 : +5V
Pin15 : GND
Pin17 : NC
Pin19 : SPK
Page 20

16 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
Suspend Mode LED Lead (2-pin S_LED)
The S_LED will light when the suspend mode works.
Pin2 : +5V
Pin4 : GND
Hard disk LED Lead (2-pin HDD_LED)
This 2-pin connector connects to the LED of the hard disk. The LED lights up when a HDD is
active.
Pin6 : +5V
Pin8 : GND
Reset Switch Lead (2-pin RESET)
This 2-pin connector connects to the case-mounted reset switch for rebooting your computer
without turning on your power switch.
Pin14 & Pin16
Software Power-Off Lead (2-pin SOFT_OFF)
Attach the SOFT_OFF switch of the panel to this connector . Use the switch to Power On/Off
your system.
Pin18 & Pin20
Page 21

HARDWARE INSTALLATION 17
y
2.12 Power Connector (20-pin PWR-CONN)
Make sure you plug the A TX power supply connector in the right direction. The pin definition is
shown below. Make sure that your ATX power supply can support at least 720mA +5V
standby power for the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) functions.
PWR-CONN
Transcend
Power Connector
+3.3V
-12.0V
GND
PSON#
GND
GND
GND
-5.0V
+5.0V
+5.0V
PSON# : Power Supply on
+3.3V
+3.3V
GND
+5.0V
GND
+5.0V
GND
Power Good
+5.0V Standb
+12.0V
Page 22

18 HARDWARE INSTALLA TION
2.13 External Back Panel I/O Ports
There are 10 kinds of external connectors on the back panel of the motherboard.
The view angle of drawing shown here is from the back panel of the housing.
1. PS/2 Mouse Port (Green 6-pin MOUSE)
The onboard PS/2 Mouse port is a 6-pin Mini-Din connector marked “MOUSE”.
2. PS/2 Keyboard Port (Purple 6-pin KB)
The onboard PS/2 Keyboard port is a 6-pin Mini-Din connector marked “KB”.
3. USB (Universal Serial Bus) Ports 1 & 2 (Black two 4-pin USBs)
Y ou can plug any USB device into the USB ports. The motherboard contains two USB
ports, which are marked “USB”.
4. Parallel Port (Burgundy 25-pin PRN)
The onboard printer port is a 25-pin D-type connector marked “PRN”.
5. Serial Port COMA (Turquoise 9-pin COMA)
The first onboard serial port is a 9-pin D-type connector marked “COMA”. (The second
onboard serial port COMB is a 10-pin header connector. Please refer to page 26 for the
location and details).
6. Display VGA Port (Blue 15-pin VGA)
The onboard VGA port is a 15-pin D-type connector marked “VGA”.
7. Game Port / MIDI Port (Gold 15-pin GAME)
The onboard Game port / MIDI Port is a 15-pin D-type connector marked “GAME”.
8. Line_out (Lime Green 1/8” LINE_OUT)
The onboard Line_out connector is a 1/8” stereo audio jack marked “LINE_OUT”.
9. Line_in (Light blue 1/8” LINE_IN)
The onboard Line_in connector is a 1/8” stereo audio jack marked “LINE_IN”.
10. MIC_in (Pink 1/8” MIC)
The onboard MIC_in connector is a 1/8” stereo audio jack connector marked “MIC”.
Page 23

HARDWARE INSTALLATION 19
4. Parallet Port
1. PS/2 Mouse
3. USB1
(Printer)
7. Game/MIDI Port
3. USB2
2. PS/2 Keyboard
5. COMA 6. VGA Port
8. Line_out
9. Line_in
10. MIC in
Back Panel I/O Ports
2.14 Using Jumper JPS to clear CMOS
To clear the CMOS data, you should turn off your computer’s power and short pin1 and pin2
in JP5.
Transcend
JP5
CMOS_CLR
1
1
CLEAR
1
NORMAL
Clear CMOS Jumper
Page 24

20 HARDW ARE INSTALLATION
2.15 FWH Lock Jumper (JP6)
This jumper controls the Firmware Hub (FWH) lock-function. When set to “LOCK”, it prevents
programming or block erase to the top block of FWH. There are 8 blocks of addressable space
controlled by the FWH. The top block (block 7, also called “Boot Block”) stores some critical
codes. T o guard against accidents (such as a virus, program bug etc.), we recommend that you
lock this block. Even if other blocks were erased, you could still recover your system easily by
following the 2 steps below:
1. Reboot with a DOS (95/98) system boot floppy disk.
2. Reflash BIOS according to section 5.3, Step 5 (Page 58).
Transcend
FWH Lock Jumper
FWH_Lock
1
1
1
JP6
UNLOCK
LOCKED
Page 25

HARDWARE INSTALLATION 21
2.16 Onboard Audio Setting (JP3 ON-BOARD AUDIO)
For the external AMR card, the onboard audio CODEC can be enabled or disabled via this
jumper. Please disable the onboard audio CODEC, If you want to use a PCI Sound Card or an
AMR Card.
JP3 Setting
Enable
onboard audio
JP3 Setting
Disable
onboard audio
Transcend
1
4
7
1
4
7
JP3
1
4
7
ON-BOARD
AUDIO
AMR Slot
Audio Selection Jumper
Page 26

22 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
g
g
g
g
2.17 Internal Audio Connector
These connectors allow you to receive stereo audio input from sound sources such as a CDROM, TV tuner, or MPEG card. The MODEM connector allows the onboard audio to interface
a voice modem card with a matched connector. It also allows the sharing of mono_in (such as
a phone) and mono_out (such as a speaker) between the onboard audio and the voice modem
card.
CD2
GND
Left Audio Channel
ht Audio Channel
Ri
Transcend
Internal Audio Connecotrs
VIDEO
Left Audio Channel
GND
Ri
CD1
Ri
GND
Left Audio Channel
MODEM
Modem-Out
(Voice from Modem)
GND
Modem-In
(Voice to Modem)
AUX
Ri
GND
Left Audio Channel
ht Audio Channel
ht Audio Channel
ht Audio Channel
Page 27

HARDWARE INSTALLATION 23
2.18 Internal Serial Port Connector COMB
You can use the provided serial port bracket to add a serial port for additional serial devices.
Regarding the onboard COMA, please refer to Section 2.14 “External Back Panel I/O Ports”
(page 20).
COMB
Transcend
DCD
SIN
SOUT
DTR
GND
12
DSR
RTS
CTS
RI
NC
910
Internal Serial Port Connector COMB
Congratulations, you have now completed Hardware Setup! This means that you can
move on to Chapter 3, the BIOS Setup section and turn on your PC.
Page 28

24 BIOS SETUP
CHAPTER 3 BIOS SETUP
3.1 BIOS Setup
Award BIOS has a built-in Setup program that allows users to modify the basic system
configuration. This information is stored in CMOS RAM, so it can retain the Setup information
when the power is turned off. When the battery of CMOS fails, it will cause the data to be lost.
If that happens, please set up your configuration parameters again after replacing the battery .
Please refer to Section 1.1, Essential Handling Precautions (Page 1).
3.2 The Main Menu
As you turn on or reboot the system, the BIOS is immediately activated. It will read the system
configuration information, and check the system through Power On Self Test (POST). During
the POST process, press the [Del] key, and you can enter the Award BIOS configuration
system. The following screen will appear.
In the Award BIOS system, you can use the arrows (
the [Enter] key to enter the sub-menu. The following keys help you navigate in Setup.
[Esc] Main Menu: Quit and not save changes into CMOS RAM
Other pages: Exit current page and return to Main Menu
[PgUp] Increase the numeric value or make changes
[PgDn] Decrease the numeric value or make changes
) to highlight an item, and press
Page 29

BIOS SETUP 25
[+] Increase the numeric value or make changes
[- ] Decrease the numeric value or make changes
[F1] General help on setup navigation keys
[F5] Load previous values from CMOS
[F6] Load the Fail-Safe Defaults from BIOS default table
[F7] Load the Optimized Defaults
[F10] Save all the CMOS changes, and exit
The Following is a brief summary of each setup category.
• Standard CMOS Features
Options in the original PC A T-compatible BIOS
• Advanced BIOS Features
Award enhanced BIOS options
• Advanced Chipset Features
Available options specific to your system Chipset
• Integrated Peripherals
I/O subsystems that depend on the integrated peripheral controllers in your system
• Power Management Setup
Advanced Power Management (APM) and Advanced Configuration Power Interface (ACPI)
options
• PnP/PCI Configurations
Plug and Play standard and PCI Local Bus configuration options
• PC Health Status
To display the fan status, CPU temperature, system temperature, etc.., and provide the
temperature monitoring option
• Frequency / Voltage Control
T o control the frequency and voltage of the CPU
• Load Fail-Safe Defaults
T o load the most basic BIOS default values required for your system to operate
• Load Optimized Defaults
T o load the BIOS default values that are factory settings for optimal system performance
Page 30

26 BIOS SETUP
• Set Supervisor / User Password
T o change, set, or disable a password
• Save & Exit Setup
T o save settings in nonvolatile CMOS RAM and exit Setup
• Exit Without Saving
T o abandon all changes and exit Setup
3.3 Standard CMOS Features
• Date (mm:dd:yy) / Time (hh:mm:ss)
Highlight the items and use [PageUp] / [PageDown] to change the value of Date/Time.
• IDE Primary / Secondary Master / Slave
Press [Enter] to enter the sub menu.
Page 31

BIOS SETUP 27
• IDE HDD Auto-Detection : Detect the HDD on this channel. If the detection is
successful, it fills the remaining fields on this menu.
• IDE Primary / Secondary Master / Slave : We recommand that you select type “AUTO”
for all drives. The BIOS can automatically detect the specifications during POST (Power
On Self Test) while the system boots. You can also choose “Manual” to set the
specifications by yourself. As to “None”, it means there is no device installed on this IDE
channel.
• Access Mode : “Normal”, “LBA”, “Large”, or “Auto”.
- Normal : Maximum number of cylinders, heads, and sectors supported are 1024, 16,
and 63 respectively .
- LBA (Logical Block Addressing) : During drive access, the IDE controller transforms
the data address described by sector, head, and cylinder number into a physical
block address. This will significantly improve data transfer rates for drives with
more than 1024 cylinders.
- Large : For drives that do not support LBA and have more than 1024 cylinders.
- Auto : The BIOS automatically determines the optimal access mode.
• Capacity : Disk drive capacity. Note that this size is slighty greater than the size of
formatted disk given by a disk-checking program.
• Cylinder : Number of cylinders
• Head : Number of heads
Page 32

28 BIOS SETUP
• Precomp : Write precompensation cylinder
• Landing Zone : Landing zone
• Sector : Number of sectors
•
Drive A / Drive B
Select the correct types of diskette drive(s) installed in the computer .
- None : No diskette drive installed
- 360K, 5.25 in. : 5-1/4 inch standard drive; 360 kilobyte capacity
- 1.2M, 5.25 in. : 5-1/4 inch high-density drive; 1.2 megabyte capacity
- 720K, 3.5 in. : 3-1/2 inch double-sided drive; 720 kilobyte capacity
- 1.44M, 3.5 in. : 3-1/2 inch double-sided drive; 1.44 megabyte capacity
- 2.88M, 3.5 in. : 3-1/2 inch double-sided drive; 2.88 megabyte capacity
•
Floppy Mode 3 Support
Supports some particular Japanese floppy drives (3-1/2 inch drive with 1.2 megabyte capacity).
•
Video
Select the type of primary video subsystem in your computer . The BIOS will detect the correct
video type automatically . The BIOS supports a secondary video subsystem, but do not select
it in this Setup.
- EGA/VGA : Enhanced Graphics Adapter/Video Graphics Array . For EGA, VGA, SEGA,
SVGA or PGA monitor adapters.
- CGA 40 : Color Graphics Adapter , powers up in 40-column mode.
- CGA 80 : Color Graphics Adapter , powers up in 80-column mode.
- MONO : Monochrome adapter , including high resolution.
•
Halt On
During the Power On Self T est (POST), the computer stops if the BIOS detects a hardware
error. You can set the BIOS to ignore certain errors during POST and continue the boot-up
process. The followings are the selections.
- All Errors : If the BIOS detects any non-fatal errors, POST stops and prompts you to take
corrective action.
- No Errors : POST does not stop for any error.
- All, But Keyboard : If the BIOS detects any non-fatal errors except keyboard, POST
stops and prompts you to take corrective action.
Page 33

BIOS SETUP 29
- All, But Diskette : If the BIOS detects any non-fatal error except floppy disk drive,
POST stops and prompts you to take corrective action.
- All, But Disk / Key : If the BIOS detects any non-fatal error except floppy disk drive or
keyboard, POST stops and prompts you to take corrective action.
3.4 Advanced BIOS Features
This “Advanced BIOS Features” option allows you to improve your system performance and set
up system features according to your preference.
•
Virus Warning
When this function is enabled, you will receive a warning message if a program (specifically ,
a virus) attempts to write to the boot sector or the partition table of the hard disk drive. Y ou
should then execute an anti-virus program. Keep in mind that this feature protects the boot
sector only , not the entire hard drive.
NOTE: Many disk diagnostic programs that access the boot sector table can trigger
the virus warning message. If you plan to run such a program, we recommend that
you first disable the virus warning.
Page 34

30 BIOS SETUP
• CPU Internal Cache / External Cache
Cache memory is additional memory that is much faster than conventional DRAM (system
memory). CPUs from 486-type and higher contain internal cache memory . Most, but not all,
modern PCs have additional (external) cache memory . When the CPU requests data, the
system transfers the requested data from the main DRAM into cache memory for even
faster access by the CPU. The “External Cache” field may not appear if your system does
not have external cache memory .
• CPU L2 Cache ECC Checking
Select “Enabled” to make sure the data is accurate.
• Processor Number Feature
Make the CPU Serial number function active. (Only in PIII CPU)
• Quick Power On Self Test
Select “Enabled” to reduce the amount of time required to run the Power On Self Test
(POST). The Quick POST skips certain steps. We recommend that you normally disable
Quick POST. It’s better to find a problem during POST than to lose data during your work.
• First / Second / Third / Other Boot Device
The original IBM PCs load the DOS operating system from drive A (floppy disk). So, IBM
PC-compatible systems are designed to search for an operating system first on drive A, and
then on drive C (hard disk). However , the BIOS attempts to load the operating system from
the devices in the sequence selected in these fields. In addition to the traditional drives A
(“Floppy”) and C (“HDD-0”), options include “HDD-1”, “HDD-2”, “HDD-3”, and “CD-ROM”;
plus a “SCSI” hard drive, a “LS/ZIP” drive and a “LAN” drive. If your boot device is not
included in the list, you can set the “Boot Other Device” field to “Enabled”, and let the system
detect the drive automatically .
• Swap Floppy Drive
This field is effective only in systems with two floppy drives. Selecting “Enabled” assigns
physical drive B to logical drive A, and physical drive A to logical drive B.
• Boot Up Floppy Seek
When you select “Enabled”, the BIOS tests (seeks) floppy drives to determine whether they
have 40 or 80 tracks. Only 360-KB floppy drives have 40 tracks; drives with 720KB, 1.2MB,
and 1.44MB capacity all have 80 tracks. Because very few modern PCs have 40-track
floppy drives, we recommend that you set this field to “Disabled” to save time.
Page 35

BIOS SETUP 31
• Boot Up NumLock Status
Toggle between “On” and “Off” to control the state of the NumLock key when the system
boots. When toggled “On”, the numeric keypad generates numbers instead of controlling
cursor operations.
• Gate A20 Option
Choose “Fast” (default) or “Normal”. “Fast” allows RAM access above 1MB to use the fast
Gate A20 line.
•
Typematic Rate Setting
When this function is disabled, the following two items (Typematic Rate and Typematic
Delay) are irrelevant. Keystrokes repeat at a rate determined by the keyboard controller in
your system. When this function is enabled, you can select a typematic rate and typematic
delay.
•
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
When the Typematic Rate setting is enabled, you can select a typematic rate (the rate at
which character repeats) when you hold down a key of “6”, “8”, “10”, “12”, “15”, “20”, “24”
or “30” characters per second.
•
Typematic Delay (Msec)
When the Typematic Delay setting is enabled, you can select a typematic delay (the delay
before key strokes begin to repeat) of “250”, “500”, “750” or “1000” milliseconds.
•
Security Option
If you have set a password, you can select whether the password is required while the
system boots, or only when you enter “Setup”.
•
OS Select for DRAM > 64MB
Select “OS2” only if you are running OS/2 operating system with more than 64 MB of RAM
on your system.
•
Report No FDD For WIN 95
Select “Yes” to release IRQ6 when there is no floppy disk drive, for compatibility with WIN
95 logo certification.
•
Delay For HDD (Secs)
Generally , you can set this field as “0”, but for some old Hard Disk Drives, you may need to
increase the delay time for BIOS to detect what type it is.
Page 36

32 BIOS SETUP
3.5 Advanced Chipset Features
This option will change the values of the chipset registers and the system setting will alter . Do
not change any values if you are unfamiliar with the chipset.
•
SDRAM CAS Latency Time
This controls the SDRAM performance: default is 3 clocks. If your SDRAM DIMM specification
is 2 CAS latency , change “3” to “2” for better performance.
•
SDRAM Cycle Time Tras / Trc
Select the number of SDRAM clocks used per access cycle.
•
SDRAM RAS-to-CAS Delay
This controls the latency between SDRAM active command and the read/write command.
Leave it on the default setting.
•
SDRAM RAS Precharge Time
This controls the idle clocks after issuing a precharge command to SDRAM. Leave it on the
default setting.
•
System BIOS Cacheable
Selecting “Enabled” allows caching of the system BIOS. This action can increase system
performance.
Page 37

BIOS SETUP 33
•
Video BIOS Cacheable
Selecting “Enabled” allows caching of the video BIOS. This action can increase system
performance.
•
Memory Hole At 15M-16M
Enabling this feature reserves memory address space (between 15 and 16MB) to ISA
expansion cards that specifically require this setting. This makes between 15 and 16MB of
memory unavailable to the system. Expansion cards can only access memory up to 16MB.
The default setting is “Disabled”.
•
Delayed Transaction
PCI access speed is faster than ISA. So PCI will release the master bus to the ISA interface
for accessing data. Then the master bus control will go back to PCI again.
•
On-Chip Video Window Size
You can select the size of mapped memory for the VGA / AGP driver to use. The choices:
“64MB”, “32MB”, and “Disabled”.
Local Memory Frequency
Onboard Display Cache Setting (Only 810E Chipset)
This field is displayed only if there is onboard display cache on the system.
•
Initial Display Cache
Select “Enabled” if you want to use the on-board display cache. The suggested selecfion
is “Enable”
• CAS# Latency
Set the CAS Latency of the onboard display cache memory .
• Paging Mode Control
Open or close the paging mode control of the onboard display cache memory .
• RAS-to-CAS Override
The default value, “by CAS# LT”, will let this field have the same configuration as
the value of the field “CAS# Latency”. Another option, “Override(2)”, will set the valu
of this field to 2.
• RAS# Timing
Set the RAS timing of the onboard display cache memory .
• RAS# Precharge Timing
Set the RAS precharge timing of the onboard display cache memory .
Page 38

34 BIOS SETUP
3.6 Integrated Peripherals
This option will load the default BIOS values. Choose the option and the following message
appears.
• •
• On-Chip Primary / Secondary PCI IDE
• •
The chipset contains a PCI IDE interface which supports two IDE channels. Select “Enabled”
to activate the first and/or second IDE interface. Select “Disabled” to deactivate this interface,
when you install a primary and/or secondary add-in IDE interface.
• •
• IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO
• •
The four IDE PIO (Programmed Input/Output) fields let you set a PIO mode (0-4) for each
of the four IDE devices that the onboard IDE interface supports. Mode 0 through 4 provide
successively increased performance. In “Auto” mode, the system automatically determines
the best one for each device.
Page 39

BIOS SETUP 35
• •
• IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UDMA
• •
Ultra DMA/33(66) implementation is possible only if your IDE hard drive can support it, and
if the operating environment includes a DMA driver (Windows 95 OSR2 or a third-party IDE
bus master driver). If both your hard disk drive and your system software can support Ultra
DMA/33(66), select “Auto” to enable BIOS support.
• •
• USB Controller
• •
Select “Enabled” if your system contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) controller and USB
peripheral(s).
• •
• USB Keyboard Support
• •
Select “Enabled” if you use a USB Keyboard.
• Init Display First
This item allows you to decide whether to activate either the PCI Slot or the AGP first.
• AC97 Audio / MODEM
If you select “Enabled”, BIOS will detect whether you are using any Audio / MODEM
devices. When an Audio / MODEM device is detected, the onboard Audio / MODEM controller
will be enabled. If you want to use your own Audio / MODEM card, set these fields to
“Disabled”. If not, set these fields “Enabled”.
• •
• IDE HDD Block Mode
• •
Block Mode is also called Block Transfer, Multiple Commands, or Multiple Sector Read/
Write. If your IDE hard drive supports Block Mode (most new drives do), select “Enabled”
for automatic detection of the optimal number of Block Read / Write per sector the drive can
support.
• •
• Power On Function
• •
- Password : Power On only if you key in correct password.
- Hot Key : Y ou can use the hot key to Power On the system.
- Mouse Left : Power On with the Mouse Left Button.
- Mouse Right : Power On with the Mouse Right Button.
Page 40

36 BIOS SETUP
- Any Key : Press any key to Power On the system.
- Button only : Power On only by pushing the button on the case (Default).
- Keyboard 98 : Y ou can Power On system by pushing the [Power-On] key of Keyboard 98.
• •
• KB Power On Password
• •
Enter the Power On Passward here. Activated only when “Password” item is selected
in the Power On Function Menu.
NOTE: If you want to use this function, please make sure that the “KB-AWK” jumper
is set to “Enabled”.
• •
• Hot Key Power On
• •
Choose [CTRL] +[ F1] ~ [F12] as a hot key to Power On the system. Activated only when
“Hot Key” is selected on the Power On Function Menu.
• •
• Onboard FDC Controller
• •
Y ou can use this function to enable or disable the onboard FDC controller .
• •
• Onboard Serial Port 1 / Port 2
• •
Select an address and the corresponding interrupt for each of the first and second serial
ports. The Choices: “Disabled”, “3F8/IRQ4”, “2F8/IRQ3”, “3E8/IRQ4”, “2F8/IRQ3”, and “Auto”.
The second serial port shares the resources (address and IRQ) with IrDA.
• •
• UART Mode Select
• •
Choose the right type of infrared device:
- Normal : Normal operation
- IrDA : IrDA compliant serial infrared port
- ASKIR : Amplitude Shift Keyed Infrared Port
• •
• RxD, TxD Active
• •
Consult your IR peripheral documentation to select the combination of RxD and TxD.
• •
• IR Transmission Delay
• •
Consult your IR peripheral documentation to select “Enabled” or “Disabled” of the IR
Transmission Delay .
• •
• Onboard Parallel Port
• •
Select a logical LPT port name and matching address for the physical parallel (printer) port.
The choices: “378/IRQ7”, “278/IRQ5”, “3BC/IRQ7” and “Disabled”.
Page 41

BIOS SETUP 37
• •
• Parallel Port Mode
• •
This field allows you to set the operation mode of the parallel port.
- SPP : Allows normal-speed operation, but in one direction only .
- EPP : Allows bi-directional parallel port operation at maximum speed.
- ECP : Allows DMA and bi-directional operation. It is faster than EPP mode.
- ECP + EPP : Allows normal speed operation in two-way mode.
• •
• EPP Mode Select
• •
Select EPP port type “1.7” or “1.9”.
• •
• ECP Mode Use DMA
• •
Assign DMA channel “1” or “3” to the port for ECP mode operation.
• •
• PWR-ON After PWR-Fail
• •
Choose if you want the system to automatically Power On after the power has failed.
- Off : Disable this function
- On : Enable this function
- Former-Sts : Not only to Power On the system, but also to return it to its former status.
• •
• Game Port Address
• •
Set Joystick Game Port Address. The choices : “Disabled”, “201” and “209”.
• •
• Midi Port Address
• •
Set Midi Port Address. The choices : “Disabled”, “330” , “300”and”290
• •
• Midi Port IRQ
• •
Assign IRQ 5 or 10 to the Midi Port.
Page 42

38 BIOS SETUP
3.7 Power Management Setup
The Power Management Setup allows you to configure your system to minimize energy
consumption, according to your own style of computer use.
•
ACPI Function
This item allows you to enable/disable the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
(ACPI).
• •
• ACPI Suspend Type
• •
Select the ACPI Suspend T ype : “S1 (POS)” or “S3 (STR)”.
If your expansion cards do not support the STR function, you must leave this field on “S1
(POS)” setting. The STR (Suspend-to-RAM) is an energy-saving feature. It takes only a
few seconds to wake up the system and return to the previous situation.
NOTE: This feature (STR) requires an ATX power supply with at least 720mA + 5V
standby power for the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) functions.
Otherwise, the system will fail to return from suspend mode.
•
Power Management
This category allows you to select the type (or degree) of power saving and is directly related
to the following modes.
Page 43

BIOS SETUP 39
1. Suspend Mode
2. HDD Power Down
There are three selections for Power Management. Two of them have fixed mode settings.
1. Min. Power Saving :
Minimum power management mode. Inactivity period is defined below:
Suspend Mode = 1 hr . HDD Power Down = 15 min.
2. Max. Power Saving :
Maximum power management mode. Inactivity period is defined below:
Suspend Mode = 1 min. HDD Power Down = 1 min.
3. User Define :
Allows you to set each mode individually. Select the time-out period for each mode
shown above.
•
Video Off Method
Defines the Video Off features.
-Blank Screen :
Only blanks the screen. Use this for monitors without power management and “green”
features.
-V/H SYNC+BLANK :
Blanks the screen and turns off vertical and horizontal scanning.
-DPMS :
The DPMS (Display Power Management System) feature allows the BIOS to control the
video display card if it supports the DPMS feature.
•
VIDEO Off In Suspend
This determines the manner in which the monitor is blanked. Select “Yes” to blank the
monitor when the system enters suspend mode.
•
Suspend Type
Select Suspend Type : “Stop Grant” or “PWR ON Suspend”.
•
MODEM Use IRQ
You can select one of the following interrupt resources for modem use: “N/A”, “3”, “4”,
“5”, “7”, “9”, ”10”, and “11”.
Page 44

40 BIOS SETUP
• Suspend Mode
After the selected period of system inactivity (1 minute to 1 hour), all devices except the
CPU will be shut down.
• HDD Power Down
After the selected period of system inactivity (1 to 15 minutes), the hard disk drive powers
down while all other devices remain active. This feature doesn’t effect SCSI hard drives.
• Soft-Off by PWR-BTTN
When set to “Instant-off”, the A TX switch can be used as a normal system Power Off button.
When set to “Delay 4 seconds”, you need to press the Power-Off button down for more than
4 seconds if you want to Power Off the system.
• Wake-Up by PCI & Card
Select “Enabled” if you want to Power On your system when a PCI or LAN event occurs.
• Power On by Ring
Select “Enabled” to Power On your system when the external MODEM receives a call.
NOTE:This function requires an external MODEM which supports the Ring Wake-Up
function.
• CPU Thermal-Throttling
Select the CPU Thermal-Throttling rate. If BIOS detects that the CPU temperature is too
high, it will slow down the CPU’s speed according to this field. The choices: “87.5%”,
“75.0%”, “62.5%”, “50.0%”, “37.5%”, “25.0%” and “12.5%”.
• Resume by Alarm
Select “Enabled” if you want to power up your system at a certain time on the same day every
month or at a certain time every day .
• Date / Time
Set the Date and Time to Power On the system. Activated only when the “Resume by
Alarm” field is enabled.
• Reload Global Timer Events
When “Enabled”, an event occurring on any device listed below restarts the global timer from
Standby Mode, and Powers On the system.
Page 45

BIOS SETUP 41
Primary IDE 0
Primary IDE 1
Secondary IDE 0
Secondary IDE 1
FDD, COM, LPT Port
PCI PIRQ[A-D]#
The settings in these fields enable or disable the detection of
IDE, floppy , serial and parallel port activities for powering down
state transition. Actually it detects the read/write to/from I/O ports.
3.8 PnP/PCI Configuration Setup
• Reset Configuration Data
Normally, you leave this field “Disabled”. Select “Enabled” to reset Extended System
Configuration Data (ESCD), if you have just installed a new add-on card and the system
reconfiguration has caused such a serious conflict that the operating system cannot boot.
The setting will automatically be set back to “Disabled” when next time the system reboots.
• Resources Controlled by
The Award Plug and Play BIOS can automatically configure all the boot and Plug and Play(PnP)
compatible devices. If you select “Auto”, all of the Interrupt Requests (IRQs) and DMA
assignment fields will be deactived as the BIOS automatically assigns them. The choices:
“Auto” and “Manual”.
Page 46

42 BIOS SETUP
• IRQ Resources
• IRQ-n Assigned to
When the resources are controlled manually , assign each System Interrupt to one of the
following, depending on which type of device is using the interrupt.
- Legacy ISA Devices requiring a specific interrupt (such as IRQ4 for serial port1),
compliant with the original PC A T bus specification.
- PCI/ISA PnP devices, whether designed for PCI or ISA bus architecture, compliant
with the Plug and Play standard.
• PCI / VGA Palette Snoop
Some VGA cards, such as graphics accelerators or MPEG video cards, might not show
colors properly . Select “Enabled” to correct this problem. If you don’t have such problems,
leave this field at “Disabled”.
Page 47

BIOS SETUP 43
3.9 PC Health Status
This menu provides two thermo-protect functions (CPU warning temperature and shutdown
temperature) and a hardware monitor center. These features let you know the health status of
your PC.
• CPU Warning Temperature
This field allows you to set the CPU warning temperature. You can choose from “50°C/
122°F” to “70°C/158°F” or even “Disabled” if you like.
• Current CPU / System Temperature
These two fields display the CPU and the on-board system temperature.
• Current CPU / Power / Case Fan Speed
These fields display the fan speeds of the CPU, Power and Case.
• Vcore
This field displays the CPU working voltage.
• VTT
This field displays the GTL bus voltage.
• 3.3VSB
This field displays the 3.3V standby power supplied to the CMOS battery .
• Shutdown Temperature
This field allows you to set the CPU shutdown temperature.
The choices: “60°C/140°F”, “65°C/149°F”, “70°C/158°F” and “75°C/167°F”.
Page 48

44 BIOS SETUP
3.10 Frequency / V oltage Control
• CPU Host / PCI Clock
This function allows you to set the FSB frequency of the CPU and the speed of PCI
bus. When JP3 is set to 66MHz, you can select the system bus frequency from 66MHz
to 68 MHz. When JP3 is set to 100MHz, you can select the system bus frequency from
100MHz to 124MHz. When JP3 is set to 133MHz, you can select the system bus frequency
from 133MHz to 150MHz.
• CPU Ratio
This function allows you to set the CPU internal frequency ratio. It determines the CPU
internal frequency according to the following formula:
CPU internal frequency = frequency ratio x system bus frequency.*
* System bus frequency is set in the previous field (“CPU Host / PCI Clock”).
The choices: “3”, “3.5”, “4”, “4.5”, “5”, “5.5”, “6”, “6.5”, “7”, “7.5”, and “8”.
NOTE: Because Intel has locked the frequency ratio for new CPU settings, this field
to adjust the frequency ratio is usually useless. However, it is effective for old version
CPUs.
Page 49

BIOS SETUP 45
3.11 Load Fail-Safe Defaults
This option allows you to load the troubleshooting default values permanently stored in the BIOS
ROM. NOTE: These default settings are non-optimal and disable all high performance
features.
3.12 Load Optimized Defaults
This option allows you to load the default values to the system configuration fields. These
default values are the optimized configuration settings for the system.
Page 50

46 BIOS SETUP
3.13 Supervisor Password
This option allows you to set a password to prevent others from changing the BIOS setting of your
system.
The password prevents any unauthorized use of your computer . If you set a password, the system
prompts for the correct password before you boot or access “Setup”.
To set a password:
1. At the prompt, type your password. Y our password can be up to 8 alpha-numeric characters.
When you type the characters, they appear as asterisks (*) on the password screen box.
2. After typing the password, press [Enter] key .
3. At the next prompt, re-type your password and press [Enter] key again to confirm the new
password. After the password entry , the screen automatically reverts to the main screen.
T o disable the password, press [Enter] key when prompted to enter the password. The screen
displays a message confirming that the password has been disabled.
Forget the password?
If you forget the password, you can clear it by erasing the CMOS Real Time Clock (RTC) RAM
with the jumper 5 (JP5: CMOS_CLR. Please refer to page 21). T o erase the R TC RAM:
1. Unplug your computer.
2. Short the JP5 for about 10 second, and restore the JP5 setting.
3. Turn On your computer .
4. Hold down [Delete] key during the POST process and enter BIOS setup to re-config BIOS.
Page 51

BIOS SETUP 47
3.14 User Password
This option allows you to set a password to prevent others from changing the BIOS setting of
your system. This operation is the same as Supervisor Password.
3.15 Save & Exit Setup
Save the setting and exit the BIOS utility .
Page 52

48 BIOS SETUP
3.16 Exit Without Saving
Abort current changes and exit the BIOS utility .
Page 53

SOFTWARE SETUP 49
CHAPTER 4 SOFTWARE SETUP
Insert the CD-ROM enclosed with your motherboard into the CD-ROM drive. After the autorun
program has executed, please check the model name showed on the screen. If the model
name doesn’t fit your motherboard, please re-select the correct one.
4.1 INF Update for 810 Chipset
This section introduces INF files in Windows 95/98 for the following items:System and Graphics,
LPS Interface, SM Bus, PCI Bridge, Bus master IDE, USB Host, Controllers. Click INF Update
Utility for Intel 810 chipset, and follow the figures as below.
Click here
1
Click here
3
Click here
2
Click here
4
Page 54

50 SOFTWARE SETUP
Click here
6
Click here
5
4.2 VGA Driver Setup
This section introduces Intel 810 DC-100 (or 810E) system and graphics controller Driver. Click
VGA Driver Setup, and the follow the figures as below:
Click here
1
Click here
2
Page 55

SOFTWARE SETUP 51
Click here
Click here
3
4.3 Intel Security Controller Driver
4
This section helps you to install a security controller for Windows 95/98. Click Security Driver
Setup, and then followthe figures as below:
Click here
1
Click here
2
Page 56

52 SOFTWARE SETUP
Click here
3
Click here
5
4.4 Audio Driver Setup
Click here
4
This section helps you to setup the onboard audio device. Click Audio Driver Setup, and choose
the opration system you use.
A. Audio Driver for Windows 95/98/2000
The figures follow are captured from Windows 98SE, and you can setup the Audio Codec in
almost the same way in Windows 95 and Windows 2000.
Page 57

SOFTWARE SETUP 53
Click h ere2
Click her e1
Click her e3
Click here5
Click here4
Click here6
Page 58

54 SOFTWARE SETUP
Click her e7
Click here9
Click here8
Click her e
11
Click here
12
Click here
10
Page 59

SOFTWARE SETUP 55
B. Audio Driver for WindowsNT
2
Click here
1
Click here
3
Click here
4
Click here
Page 60

56 SOFTW ARE SETUP
5
Click here
7
Click here
6
Click here
Click here
8
Page 61

BIOS UPGRADE 57
CHAPTER 5 BIOS UPGRADE
Caution!
Only users familiar with the upgrade procedure are recommended to update the BIOS
of the motherboard and only when there is a need to do so. Please note that you have
to download and install the right file on your motherboard. Otherwise, you might cause
some serious system malfunctions.
5.1 How to Check Y our BIOS File Name and V ersion
Please turn on PC first, the screen will display as follows (For example):
TRANSCEND MODULAR BIOS : AWE3-Ver.1.01.
Y ou can see the BIOS description on the third line.
AWE3 - Ver.1.01.
BIOS Version 1.01
( You can upgrade to a newer version if your BIOS version is older
than this version.)
BIOS File Name
(Make sure the first 5 charactors are exactly the same as your own
version, otherwise you shouldn't try to upgrade your BIOS.)
5.2 How to Download the Correct BIOS File from the Web
Please enter the Transcend website on: http://www.transcendusa.com/
On the front page, click on the”Motherboard” icon, which is the second one down: on the
Motherboard page, click on the “BIOS” icon near the top. The BIOS page contains important
information: please take time to read it carefully . Then go to the bottom of the BIOS page, click on
“Slot 1” and choose your motherboard model.
Y our BIOS file name must absolutely match the one shown on our web site. Then download the
suitable version to your disk.
Page 62

58 BIOS UPGRADE
y
Warning:
Your system could be damaged if the wrong BIOS version is
accidentl
choose, please contact us at: techsupport@transcend.com.tw
used. If you are not sure what version you should
5.3 How to Upgrade Y our Motherboard BIOS
Please follow these 5 steps listed below to upgrade your BIOS.
Step 1: Make a record of your original or existing BIOS Setup parameters.
- Press [Del] during the Power On Self T est to enter BIOS Setup Program when you
start your system.
- Write down the value of each parameter in order to re-configure your system after
BIOS updating.
Step 2: Make a System Disk
- Put a clean 3.5" disk in Drive A
MS-DOS : Key in
Windows O/S : Select the My Computer icon.
Format A:/S and press [Enter].
Click [3.5" Floppy (A:)]
Select [File/Format] from Command Bar
Under Format 3.5 Floppy (A:) Menu select
Format type = Full item, and
Other Options = Copy system files
Click [Start] button
Step 3: Download the updated Bios.exe file from the web site to a floppy disk.
(Ref 4.1 and 4.2)
Step 4: Type Bios.exe to decompress it.
Step 5: Please read the file of Readme.txt carefully , and follow the instructions step by
step.
Then you can finish the BIOS upgrade.
 Loading...
Loading...