Page 1
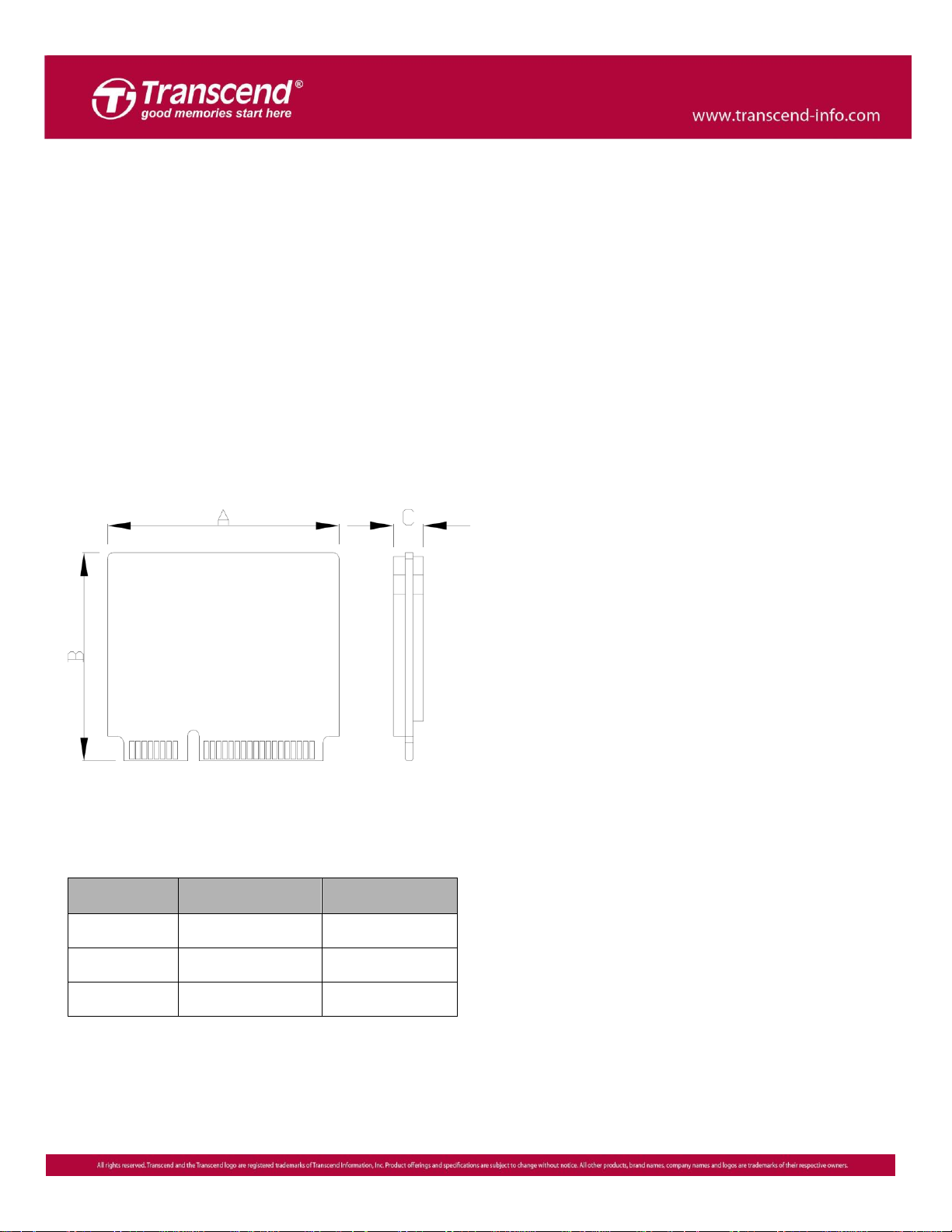
Side
Millimeters
Inches
A
29.85 +/-0.15
1.06 +/-0.006
B
26.8 +/-0.15
1.175 +/-0.006
C
3.85 (Max)
0.152 (Max)
MSM360 –
SATA III 6Gb/s mSATA mini SSD
Transcend MSM360 series are mSATA mini Solid State
Drives (SSDs) with high performance and quality Flash
Memory assembled on a printed circuit board. These
devices feature cutting-edge technology to enhance
product life and data retention. MSM360 is designed
specifically for various applications, such as Ultrabooks,
industrial PCs, vehicle PCs and road surveillance
recording.
Placement
Features
RoHS compliant
Power Supply: 3.3V±5%
Operating Temperature: -0oC to 70oC
Built-in 66 bits per 1KByte ECC (Error Correction Code)
functionality ensures highly reliable of data transfer.
Global wear-leveling algorithm eliminates excessive write
operation and extends product life.
Supports S.M.A.R.T (Self-defined)
Supports Security Command
Supports Device Sleep
Fully compatible with devices and OS that support the
SATA 6Gb/s standard
Compliant with JEDEC MO-300B
Supports Transcend SSD Scope Pro (Optional)
Dimensions
Page 2
Physical Specification
Form Factor
MO-300B
Storage Capacities
128GB
Dimensions
Length
26.8 0.15 mm
Width
29.85 0.15 mm
Height
3.85 mm (Max)
Input Voltage
3.3V 5%
Weight
3g
Connector
PCI Express Mini Card Connector
Environmental Specifications
Operating Temperature
0 ℃ to 70 ℃
Storage Temperature
- 45 ℃ to 85 ℃
Humidity
Operating
0% to 95% (Non-condensing)
Non-Operating
0% to 95% (Non-condensing)
Performance
Model P/N
Sequential
Read*
Sequential
Write*
Random
Read
(4KB QD32)*
Random
Write
(4KB QD32)*
IOPS
Random Read
(4KB QD32)**
IOPS
Random Write
(4KB QD32)**
TS128GMSM360
514.1
160.4
117.5
156.4
32743
38150
Reliability
Data Reliability
Supports BCH ECC 66 bits per 1K byte
MTBF
1,000,000 hours
Endurance (Terabytes Written)
128G
TBT
Regulations
Compliance
CE, FCC and BSMI
Specifications
Note: Maximum transfer speed recorded
* 25 °C , test on GA-Z87Z-UD3H, 4GB, Windows® 8.1 x64 with AHCI mode, benchmark utility CrystalDiskMark (version 3.0.1), copied file 1000MB
** Random read/write performance based on IOmeter2008 with 4K file size and queue depth of 32
*** The recorded performance is obtained while the SSD is not operating as an OS disk
Page 3
Actual Capacity
Model P/N
User Max. LBA
Cylinder
Head
Sector
TS128GMSM360
250,069,680
16,383
16
63
Power Requirements
Input Voltage
3.3V 5%
Mode
Max. (mA)
TS128GMSM360
Write
(peak)
523
Read
(peak)
379
Idle
(peak)
115
Devslp
(peak)
1.5
Page 4
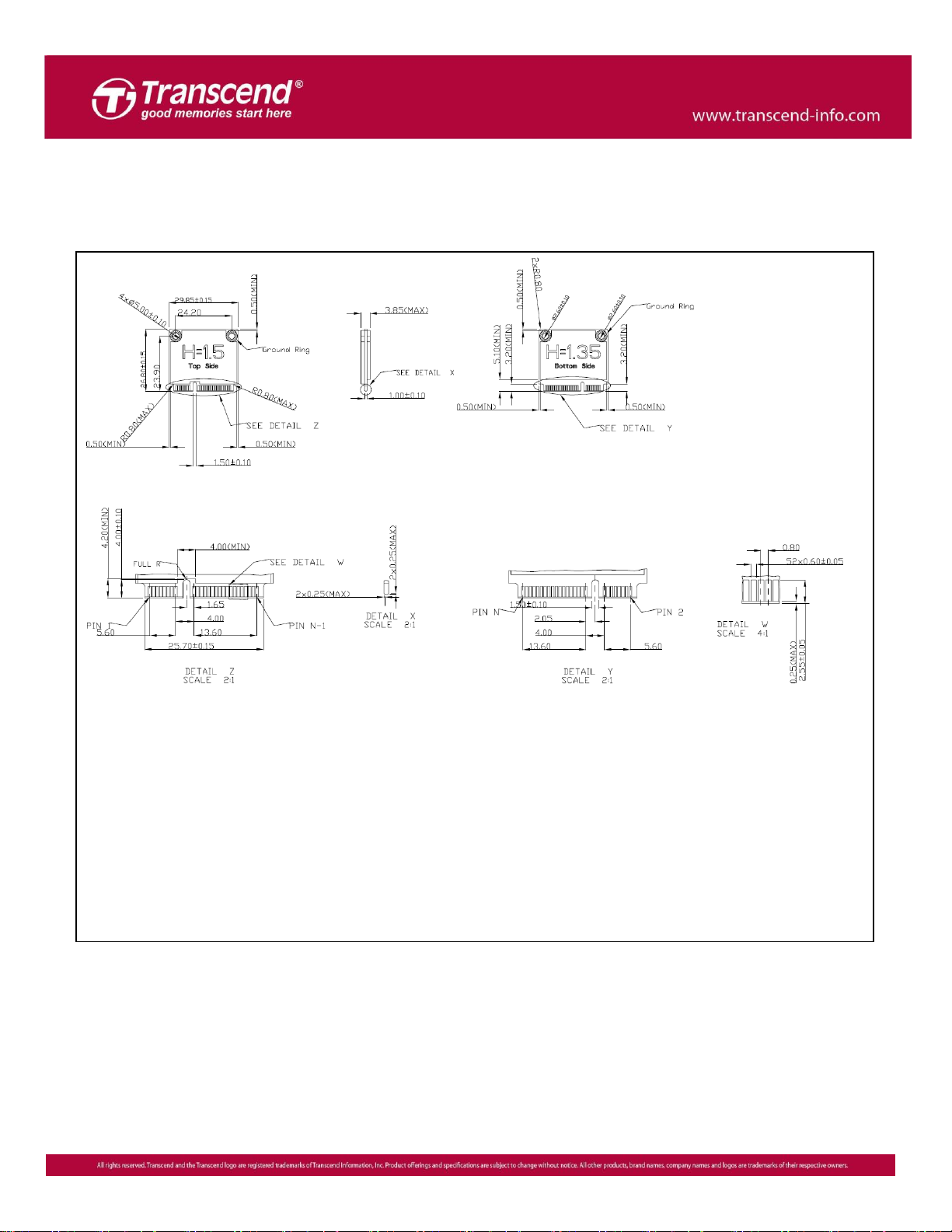
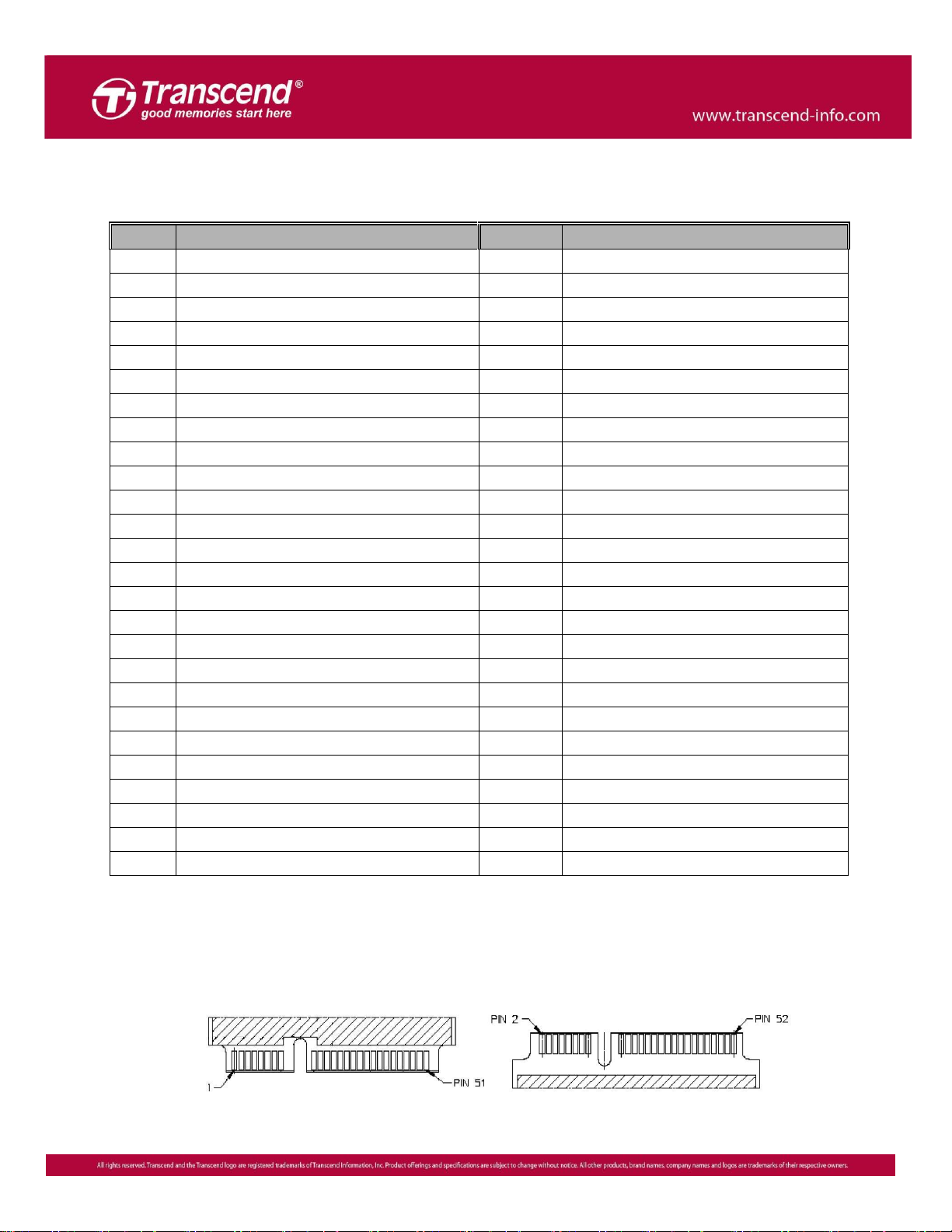
Package Dimensions
The figure below illustrates the Transcend MSM360 mSATA mini Solid State Disk. All dimensions are in mm.
*Note: Tighten mounting screws with no more than 1.0kgf-cm (0.07LB-ft) of torque.
Page 5
Pin No.
Pin Name
Pin No.
Pin Name
01
NC
02
3.3V
03
NC
04
GND
05
NC
06
NC
07
NC
08
NC
09
GND
10
NC
11
NC
12
NC
13
NC
14
NC
15
GND
16
NC
17
NC
18
GND
19
NC
20
NC
21
GND
22
NC
23
TX+
24
3.3V
25
TX-
26
GND
27
GND
28
NC
29
GND
30
NC
31
RX-
32
NC
33
RX+
34
GND
35
GND
36
NC
37
GND
38
NC
39
3.3V
40
GND
41
3.3V
42
NC
43
NC
44
NC/DEVSLP(optional)
45
Vendor
46
NC
47
Vendor
48
NC
49
DAS/DSS*
50
GND
51
Presence Detection**
52
3.3V
Pin Assignments
* Device Activity Signal / Disable Staggered Spin-up
** Connect to GND internally
Pin Layout
Page 6
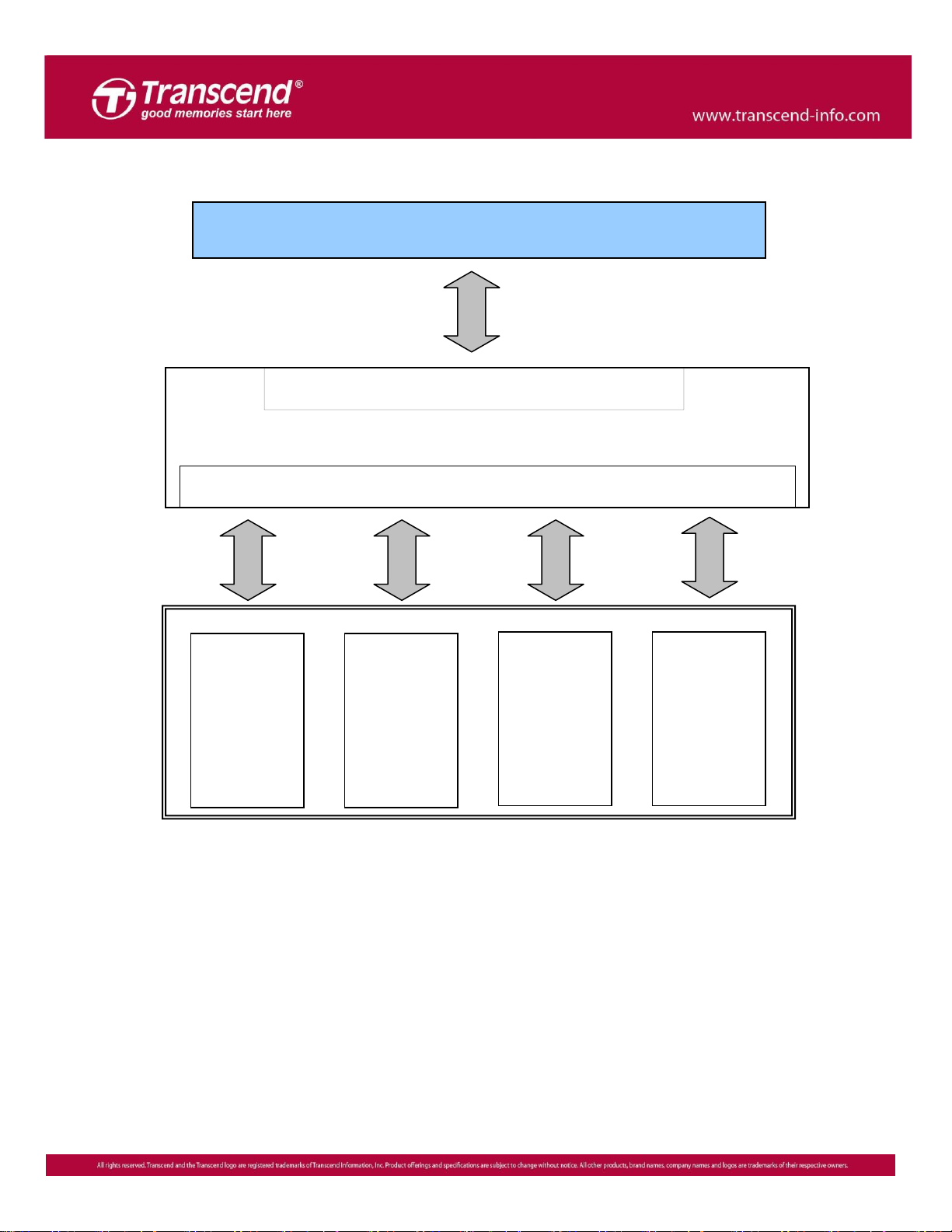
SATA Host
NAND
Flash
NAND
Flash
NAND
Flash
NAND
Flash
SSD Controller
Flash Interface
SATA Interface
Block Diagram
Page 7
Features
Wear Leveling Algorithm
The controller supports static/dynamic wear leveling. When the host writes data, the controller will find and use the block
with the lowest erase count among the free blocks. This is known as dynamic wear leveling. If the free block erase count is
higher than a threshold value plus data blocks, it will activate the static wear leveling, replacing the not so frequently used
user blocks with the high erase count free blocks.
ECC Algorithm
Using a BCH 66 bit Error Correction Code algorithm with each channel, the controller can correct up to 66 random bit
errors per 1K byte data sector for MLC NAND flash. The hardware executes parity generation and error
detection/correction features.
Bad Block Management
When the flash encounters an ECC, program or erase failure, the controller will mark the block as a bad block to
prevent use of this block and cause data loss in the future.
Page 8

Support ATA/ATAPI Command
Code
Protocol
General Feature Set
EXECUTE DIAGNOSTICS
90h
Device diagnostic
FLUSH CACHE
E7h
Non-data
IDENTIFY DEVICE
ECh
PIO data-In
INITIALIZE DRIVE PARAMETERS
91h
Non-data
READ DMA
C8h
DMA
READ LOG EXT
2Fh
PIO data-In
READ MULTIPLE
C4h
PIO data-In
READ SECTOR(S)
20h
PIO data-In
READ VERIFY SECTOR(S)
40h or 41h
Non-data
SET FEATURES
EFh
Non-data
SET MULTIPLE MODE
C6h
Non-data
WRITE DMA
CAh
DMA
WRITE MULTIPLE
C5h
PIO data-out
WRITE SECTOR(S)
30h
PIO data-out
NOP
00h
Non-data
READ BUFFER
E4h
PIO data-In
WRITE BUFFER
E8h
PIO data-out
Power Management Feature Set
CHECK POWER MODE
E5h or 98h
Non-data
IDLE
E3h or 97h
Non-data
IDLE IMMEDIATE
E1h or 95h
Non-data
SLEEP
E6h or 99h
Non-data
STANDBY
E2h or 96h
Non-data
STANDBY IMMEDIATE
E0h or 94h
Non-data
Security Mode Feature Set
SECURITY SET PASSWORD
F1h
PIO data-out
SECURITY UNLOCK
F2h
PIO data-out
SECURITY ERASE PREPARE
F3h
Non-data
SECURITY ERASE UNIT
F4h
PIO data-out
SECURITY FREEZE LOCK
F5h
Non-data
SECURITY DISABLE PASSWORD
F6h
PIO data-out
SMART Feature Set
SMART Disable Operations
B0h
Non-data
SMART Enable/Disable Autosave
B0h
Non-data
SMART Enable Operations
B0h
Non-data
SMART Execute Off-Line Immediate
B0h
Non-data
SMART Read Log
B0h
PIO data-In
SMART Read Data
B0h
PIO data-In
SMART Read Threshold
B0h
PIO data-In
SMART Return Status
B0h
Non-data
SMART Save Attribute Values
B0h
Non-data
SMART Write Log
B0h
PIO data-out
Host Protected Area Feature Set
Read Native Max Address
F8h
Non-data
ATA Command Register
This table with the following paragraphs summarizes the ATA command set.
Page 9

Set Max Address
F9h
Non-data
Set Max Set Password
F9h
PIO data-out
Set Max Lock
F9h
Non-data
Set Max Freeze Lock
F9h
Non-data
Set Max Unlock
F9h
PIO data-out
48-bit Address Feature Set
Flush Cache Ext
EAh
Non-data
Read Sector(s) EXt
24h
PIO data-In
Read DMA Ext
25h
DMA
Read Multiple Ext
29h
PIO data-In
Read Native Max Address Ext
27h
Non-data
Read Verify Sector(s) Ext
42h
Non-data
Set Max Address Ext
37h
Non-data
Write DMA Ext
35h
DMA
Write Multiple Ext
39h
PIO data-out
Write Sector(s) Ext
34h
PIO data-out
NCQ Feature Set
Read FPDMA Queued
60h
DMA Queued
Write FPDMA Queued
61h
DMA Queued
Others
Data Set Management
06h
DMA
Seek
70h
Non-data
Page 10

ATA Command Specifications
FLUSH CACHE (E7h)
This command is used by the host to request the device to flush the write cache. If there is data in the write cache, that data
shall be written to the media. The BSY bit shall remain set to one until all data has been successfully written or an error
occurs.
IDENTIFY DEVICE (ECh)
This commands read out 512Bytes of drive parameter information. Parameter Information consists of the arrangement and
value as shown in the following table. This command enables the host to receive the Identify Drive Information from the
device.
INITIALIZE DEVICE PARAMETERS (91h)
This command enables the host to set the number of logical sectors per track and the number of logical heads minus 1, per
logical cylinder for the current CHS translation mode.
READ DMA (C8h)
Read data from sectors during Ultra DMA and Multiword DMA transfer. Use the SET FEATURES command to specify the
mode value. A sector count of zero requests 256 sectors.
READ LOG EXT (2Fh)
This 48-bit command is for devices implementing the GPL feature set. It returns the specified log to the host.
READ MULTIPLE (C4h)
This command performs similarly to the Read Sectors command. Interrupts are not generated on each sector, but on the
transfer of a block which contains the number of sectors defined by a Set Multiple command.
READ SECTOR(S) (20h)
This command reads 1 to 256 sectors as specified in the Sector Count register from sectors which is set by Sector number
register. A sector counts of 0 requests 256 sectors. The transfer beings specified in the Sector Number register.
READ VERIFY SECTOR(S) (40h/41h)
This command verifies one or more sectors on the drive by transferring data from the flash media to the data buffer in the
drive and verifying that the ECC is correct. This command is identical to the Read Sectors command, except that DRQ is
never set and no data is transferred to the host.
SET FEATURES (EFh)
This command set parameter to Features register and set drive’s operation. For transfer mode, parameter is set to Sector
Count register. This command is used by the host to establish or select certain features.
SET MULTIPLE MODE (C6h)
This command enables the device to perform READ MULTIPLE and WRITE MULTIPLE operations and establishes the
block count for these commands.
WRITE DMA (CAh)
Write data to sectors during Ultra DMA and Multiword DMA transfer. Use the SET FEATURES command to specify the
mode value.
WRITE MULTIPLE (C5h)
This command is similar to the Write Sectors command. Interrupts are not presented on each sector, but on the transfer of
a block which contains the number of sectors defined by Set Multiple command.
WRITE SECTOR(S) (30h)
Write data to a specified number of sectors (1 to 256, as specified with the Sector Count register) from the specified
address. Specify “00h” to write 256 sectors.
Page 11

NOP (00h)
The device shall respond with command aborted. For devices implementing the Overlapped feature set, subcommand
code 00h in the Features register shall abort any outstanding queue. Subcommand codes 01h through FFh in the Features
register shall not affect the status of any outstanding queue.
READ BUFFER (E4h)
The READ BUFFER command enables the host to read a 512-byte block of data.
WRITE BUFFER (E8h)
This command enables the host to write the contents of one 512-byte block of data to the device’s buffer.
Power Management Feature Set
CHECK POWER MODE (E5h or 98h)
The host can use this command to determine the current power management mode.
IDLE (E3h or 97h)
This command causes the device to set BSY, enter the Idle mode, clear BSY and generate an interrupt. If sector count is
non-zero, the automatic power down mode is enabled. If the sector count is zero, the automatic power mode is disabled.
IDLE IMMEDIATE (E1h or 95h)
This command causes the device to set BSY, enter the Idle(Read) mode, clear BSY and generate an interrupt.
SLEEP (E6h or 99h)
This command causes the device to set BSY, enter the Sleep mode, clear BSY and generate an interrupt.
STANDBY (E2h or 96h)
This command causes the device to set BSY, enter the Sleep mode (which corresponds to the ATA “Standby” Mode), clear
BSY and return the interrupt immediately.
STANDBY IMMEDIATE (E0h or 94h)
This command causes the drive to set BSY, enter the Sleep mode (which corresponds to the ATA “Standby” Mode), clear
BSY and return the interrupt immediately.
Page 12

Word
Content
0
Control word
Bit 0
Bits 1-7
Bit 8
Bits 9-15
Identifier
Reserved
Master Password Capability
Reserved
0=set user password
1=set master password
0=High
1=Maximum
1-16
Password (32 bytes)
17
Master Password Identifier. This word is valid if word 0 bit 0is set to one.
18-255
Reserved
Word
Content
0
Control word
Bit 0
Bits 1-15
Identifier
Reserved
0=compare user password
1=compare master password
1-16
Password (32 bytes)
17-255
Reserved
Security Mode Feature Set
SECURITY SET PASSWORD (F1h)
This command set user password or master password. The host outputs sector data with PIO data-out protocol to indicate
the information defined in the following table.
Security set Password data content1
SECURITY UNLOCK (F2h)
This command disables LOCKED MODE of the device. This command transfers 512 bytes of data from the host with PIO
data-out protocol. The following table defines the content of this information
Security Unlock information2
Page 13

SECURITY DISABLE PASSWORD (F6h)
Disables any previously set user password and cancels the lock. The host transfers 512 bytes of data, as shown in the
following table, to the drive. The transferred data contains a user or master password, which the drive compares with the
saved password. If they match, the drive cancels the lock. The master password is still saved. It is re-enabled by issuing
the SECURITY SET PASSWORD command to re-set a user password.
SECURITY ERASE PREPARE (F3h)
This command shall be issued immediately before the Security Erase Unit command to enable erasing and unlocking. This
command prevents accidental loss of data on the drive.
SECURITY ERASE UNIT (F4h)
The host uses this command to transfer 512 bytes of data, as shown in the following table, to the drive. The transferred
data contains a user or master password, which the drive compares with the saved password. If they match, the drive
deletes user data, disables the user password, and cancels the lock. The master password is still saved. It is re-enabled by
issuing the SECURITY SET PASSWORD command to re-set a user password.
SECURITY FREEZE LOCK (F5h)
Causes the drive to enter Frozen mode. Once this command has been executed, the following commands to update a lock
result in the Aborted Command error:
• SECURITY SET PASSWORD
• SECURITY UNLOCK
• SECURITY DISABLE PASSWORD
• SECURITY ERASE PREPARE
• SECURITY ERASE UNIT
The drive exits from Frozen mode upon a power-off or hard reset. If the SECURITY FREEZE LOCK command is
issued when the drive is placed in Frozen mode, the drive executes the command, staying in Frozen mode.
Page 14

Word
Address
Default
Value
Total
Bytes
Data Field Type Information
0
0040h
2
General configuration
1
XXXXh
2
Default number of cylinders
2
0000h
2
Reserved
3
00XXh
2
Default number of heads
4
0000h
2
Obsolete
5
0240h
2
Obsolete
6
XXXXh
2
Default number of sectors per track
7-8
XXXXh
4
Number of sectors per card (Word 7 = MSW, Word 8 = LSW)
9
0000h
2
Obsolete
10-19
XXXXh
20
Serial number in ASCII (Right Justified)
20
0002h
2
Obsolete
21
0002h
2
Obsolete
22
0000h
2
Obsolete
23-26
XXXXh
8
Firmware revision in ASCII. Big Endian Byte Order in Word
27-46
XXXXh
40
Model number in ASCII (Left Justified) Big Endian Byte Order in Word
47
8001h
2
Maximum number of sectors on Read/Write Multiple command
48
0000h
2
Reserved
49
0F00h
2
Capabilities
50
4000h
2
Capabilities
51
0200h
2
PIO data transfer cycle timing mode
52
0000h
2
Obsolete
53
0007h
2
Field Validity
54
XXXXh
2
Current numbers of cylinders
55
XXXXh
2
Current numbers of heads
56
XXXXh
2
Current sectors per track
57-58
XXXXh
4
Current capacity in sectors (LBAs)(Word 57 = LSW, Word 58 = MSW)
59
0101h
2
Multiple sector setting
60-61
XXXXh
4
Total number of sectors addressable in LBA Mode
62
0000h
2
Reserved
63
0207h
2
Multiword DMA transfer. Supports MDMA Mode 0,1,and 2
64
0003h
2
Advanced PIO modes supported
65
0078h
2
Minimum Multiword DMA transfer cycle time per word. In PC Card modes this
value shall be 0h
66
0078h
2
Recommended Multiword DMA transfer cycle time. In PC Card modes this
value shall be 0h
67
0078h
2
Minimum PIO transfer cycle time without flow control
Identify Device Information Default Value
Page 15

Word
Address
Default
Value
Total
Bytes
Data Field Type Information
68
0078h
2
Minimum PIO transfer cycle time with IORDY flow control
69
4000h
2
Additional supported
70-74
0000h
10
Reserved
75
001Fh
2
Queue depth
76
070Eh
2
Serial ATA capacities
.Supports Serial ATA Gen3
.Supports Serial ATA Gen2
.Supports Serial ATA Gen1
.Supports PHY event counters log
.Supports receipt of host initiated power management requests
.Supports Native Command Queuing
77
0080h
2
Serial ATA additional capability
.DevSleep_to_ReducedPwerState
78
0148h
2
Serial ATA features supported
.Supports Device Sleep
. Supports software setting preservation
.Device supports initiating power management
79
0040h
2
Reserved
80
03F0h
2
Mijor version number (ACS-2)
81
0000h
2
Minor version number
82
742Bh
2
Command sets supported 0
83
7500h
2
Command sets supported 1
84
4023h
2
Command sets supported 2
85-87
XXXXh
6
Command set/feature enabled
88
007Fh
2
Ultra DMA Mode Supported and Selected
89
0003h
2
Time required for a Normal Erase mode Security Erase Unit command
90
0001h
2
Time required for an Enhanced Erase mode Security Erase Unit command
91
0000h
2
Current Advanced power management value
92
FFFEh
2
Master password identifier
93-99
0000h
14
Reserved
100-103
XXXXh
8
Maximum user LBA for 48-bit address feature set
104
0000h
2
Reserved
105
0100h
2
Maximum number of 512-byte blocks per Data Set Management command
106-127
0000h
44
Reserved
128
0001h
2
Security status
129-159
XXXXh
64
Vendor specific
160
0000h
2
Power requirement description
161
0000h
2
Reserved
162
0000h
2
Key management schemes supported
163
0000h
2
CF Advanced True IDE Timing Mode Capability and Setting
164-168
0000h
10
Reserved
Page 16

169
0001h
2
Data Set Management supported
170-216
XXXXh
94
Reserved
217
0001h
2
Non-rotating media (SSD)
218-221
0000h
8
Reserved
222
107Fh
2
Transport major revision (SATA Rev 3.1)
223-254
0000h
64
Reserved
255
XXXXh
2
Integrity word
Page 17

Value
Command
Value
Command
D0h
Read Data
D5h
Read Log
D1h
Read Attribute Threshold
D6h
Write Log
D2h
Enable/Disable Autosave
D8h
Enable SMART Operations
D3h
Save Attribute Values
D9h
Disable SMART Operations
D4h
Execute OFF-Line Immediate
DAh
Return Status
SMART Command Support
If the reserved size is below a threshold, status can be read from the Cylinder Register using the Return Status command
(DAh).
Page 18

BYTE
F / V
Description
0-1 X Revision code
2-361
X
Vendor specific
362
V
Off-line data collection status
363
X
Self-test execution status byte
364-365
V
Total time in seconds to complete off-line data collection activity
366
X
Vendor specific
367
F
Off-line data collection capability
368-369
F
SMART capability
370
F
Error logging capability
7-1 Reserved
0 1=Device error logging supported
371
X
Vendor specific
372
F
Short self-test routine recommended polling time (in minutes)
373
F
Extended self-test routine recommended polling time (in minutes)
374
F
Conveyance self-test routine recommended polling time (in minutes)
375-385
R
Reserved
386-395
F
Firmware Version/Date Code
396-399
F
Reserved
400-406
V
‘SMI2246XT’
407-415
X
Vendor specific
416 F Reserved
417 F Program/write the strong page only
418-419
V
Number of spare block
420-423
V
Average erase count
424-510
X
Vendor specific
511
V
Data structure checksum
F=the content of the byte is fixed and does not change.
V=the content of the byte is variable and may change depending on the state of the device or the commands
executed by the device.
X=the content of the byte is vendor specific and may be fixed or variable.
R=the content of the byte is reserved and shall be zero.
SMART DATA Structure
Page 19

Attribute ID
(hex)
Raw Attribute Value
Attribute Name
01
MSB
00
00
00
00
00
Read Error Rate
05
LSB
MSB
00
00
00
00
Reallocated sectors count
09
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Reserved
0C
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Power Cycle Count
A0
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Uncorrectable sectors count when
read/write
A1
LSB
MSB
00
00
00
00
Number of valid spare block
A2
LSB
MSB
00
00
00
00
Number of cache data block
A3
LSB
MSB
00
00
00
00
Number of initial invalid block
A4
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Total erase count
A5
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Maximum erase count
A6
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Minimum erase count
A7
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Average erase count
C0
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Power-off retract Count
C2
MSB
00
00
00
00
00
Controlled temperature
C3
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Hardware ECC recovered
C4
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Reallocation event count
C7
LSB
MSB
00
00
00
00
UltraDMA CRC Error Count
F1
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Total LBA written (each write unit =
32MB)
F2
LSB - -
MSB
00
00
Total LBA read (each read unit =
32MB)
SMART Attributes
The table below shows the vendor specific data in byte 2 to 361 of the 512-byte SMART data
Page 20

USA
Los Angeles:
E-mail: sales-us@transcend-info.com
Maryland:
E-mail: sales-us@transcend-info.com
www.transcend-info.com
CHINA
E-mail: sales@transcendchina.com
cn.transcend-info.com
TAIWAN
No.70, XingZhong Rd., NeiHu Dist., Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C
TEL +886-2-2792-8000
Fax +886-2-2793-2222
E-mail: sales-tw@transcend-info.com
tw.transcend-info.com
GERMANY
E-mail: sales-de@transcend-info.com
de.transcend-info.com
HONG KONG
E-mail: sales-hk@transcend-info.com
hk.transcend-info.com
JAPAN
E-mail: sales-jp@transcend-info.com
jp.transcend-info.com
THE NETHERLANDS
E-mail: sales-nl@transcend-info.com
nl.transcend-info.com
United Kingdom
E-mail: sales-uk@transcend-info.com
uk.transcend-info.com
KOREA
E-mail: sales-kr@transcend-info.com
kr.transcend-info.com
TS XG MSM 360
Capacity
128GB
mSATA mini SSD
Transcend Product
SATA III
Ordering Information
The above technical information is based on commercial standard data and has been tested to be reliable. However,
Transcend makes no warranty, either expressed or implied, as to its accuracy and assumes no liability in connection with the
use of this product. Transcend reserves the right to make changes to the specifications at any time without prior notice.
Page 21

Revision History
Version
Date
Modification Content
Modified Page
V1.0
2015/02/26
Formal release
 Loading...
Loading...