Page 1

Product Catalog
Direct-Fired Make-Up
Air Units
DFIA
DFOA
November 2009
MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 2

Introduction
Why use Trane Makeup Air Units…
Trane’s innovative Direct Fired gas heating systems add warm, fresh and clean air to your work
environment for about 20 precent less than the operation and maintenance costs of indirect gas
heat.
• Heats Without Complications: The Direct Fired gas heating system heats efficiently and cost-
• Replaces Indoor Air: The Direct Fired gas heating system replaces indoor air that can become
• Provides Ventilation: Fresh air is available simply by turning off the heating section.
• Cleans and Tempers Incoming Air: The optional filter bank removes airborne particles, and
• Trane offers two styles of Direct Fired gas heating systems:
What Is Make-Up Air?
Make-up air is an outside air supply that is brought in to relieve “air starvation.” Without make-up
air, a building is under a “negative” condition and the following will occur:
• Backdrafts in natural flues, ventilators and stacks.
• Reduced air volume handled by the exhaust fans and subsequently inadequate removal of
• Dispersal of contaminants throughout the work area by high velocity cross-currents from
• Uncomfortable and unhealthy working conditions.
• Pilot outages.
effectively using no heat exchanger.
chemical laden in an industrial process or commercial cooling application.
cleaned air is heated to create a more refreshing and comfortable indoor environment.
– Indoor units (DFIA)
– Large outdoor units (DFOA)
contaminants.
uncontrolled outside air sources.
When Is It Required?
Make-up air is required whenever exhaust fans are used. This need for a building “air change”
arises when there are:
• Processes which generate contaminants in the form of noxious fumes or dust.
• Activities which create excessive heat or undesirable odors.
• Hazardous material storage areas.
• Ventilation requirements for a building’s inhabitants.
• State and local code requirements.
Why Use Make-Up Air Units?
Outside air should not be allowed to drift in through windows, door cracks and other openings,
creating a strain on the heating system. Outside air should be controlled, tempered and
coordinated with the exhaust by a make-up air unit. The latter is reliable, efficient and does not
disrupt building activities.
Why Use Direct Gas-Firing?
Maximum economy is realized with direct gas-firing because the incoming air is heated directly in
the burner chamber. This provides 100 percent efficiency (92 percent sensible, 8 percent latent)
while eliminating a heat exchanger or combustion chamber that could burn out or corrode.
Trane direct-fired units are factory tested, include the necessary controls for operating the system
and generally cost less than alternate systems.
© 2009 Trane All rights reserved MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 3

Introduction
Installation is simple since the unit, (when shipping permits), is shipped as a complete package.
The burner is fully modulating, with a minimum firing rate of four percent of full input. This
characteristic results in just the right amount of heat under all operating conditions.
Industry Approval
ETL Labeling Requirements
A DFOA/DFIA unit can bear the ETL label if:
• The unit airflow is within the SCFM range shown in Tabl e 3 , p . 18 (DFIA) and Table 12, p. 33
(DFOA).
• The fuel is natural gas with a temperature rise not greater than 130°F or the fuel is LP and the
temperature rise not greater than 100°F.
• The motor is a single speed motor, or if the motor is a two speed motor, the burner will operate
in only one of the two speeds (high or low speed).
• Unit components are standard (there are exceptions to this).
• If the unit has return air, the unit must have a mixing box with the AdaptAire airflow station.
Maximum Emission Levels:
• If the unit has an ETL label, the maximum levels of the products of combustion meet
ANSI Z83.18 which are:
• Carbon Dioxide 4000 ppm
• Carbon Monoxide 5 ppm
• Aliphatic Aldehydes 1 ppm
• Nitrogen Dioxide 0.50 ppm
CETL Labeling Requirements (Canada)
A DFOA/DFIA unit will have a CETL label if the unit meets the first five items of “ETL Labeling
Requirements” (above), AND the unit does not have return air.
Trademarks
Trane and the Trane logo are trademarks of Trane in the United States and other countries. All
trademarks referenced in this document are the trademarks of their respective owners.
MUA-PRC007-EN 3
Page 4

Table of Contents
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Application Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
The Need for Make-Up Air Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Selection Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Unit Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Horizontal Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Vertical Configurations (DFOA only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Vertical Configurations (DFIA only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
DFIA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Model Number Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Features and Benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Performance Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Weights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Outdoor Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
What Fuel to Use? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Burner Selection Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Reliable Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Equipment Approval Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Special Construction Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
DFOA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Model Number Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Features and Benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Basic Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Gas-Fired Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Performance Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Gas Piping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Electrical Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Motorized 75/25 Damper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Mixing Box—Temperature Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Mixing Box—Manual Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Mixing Box—Building Pressure Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Motorized Inlet Damper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Exhaust Interlock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
4 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 5

UV Flame Sensor (UV Mini-Peeper) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Optional Gas Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Factory Installed Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Additional Options* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Additional Factory Installed Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Field Installed Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Mechanical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
MUA-PRC007-EN 5
Page 6
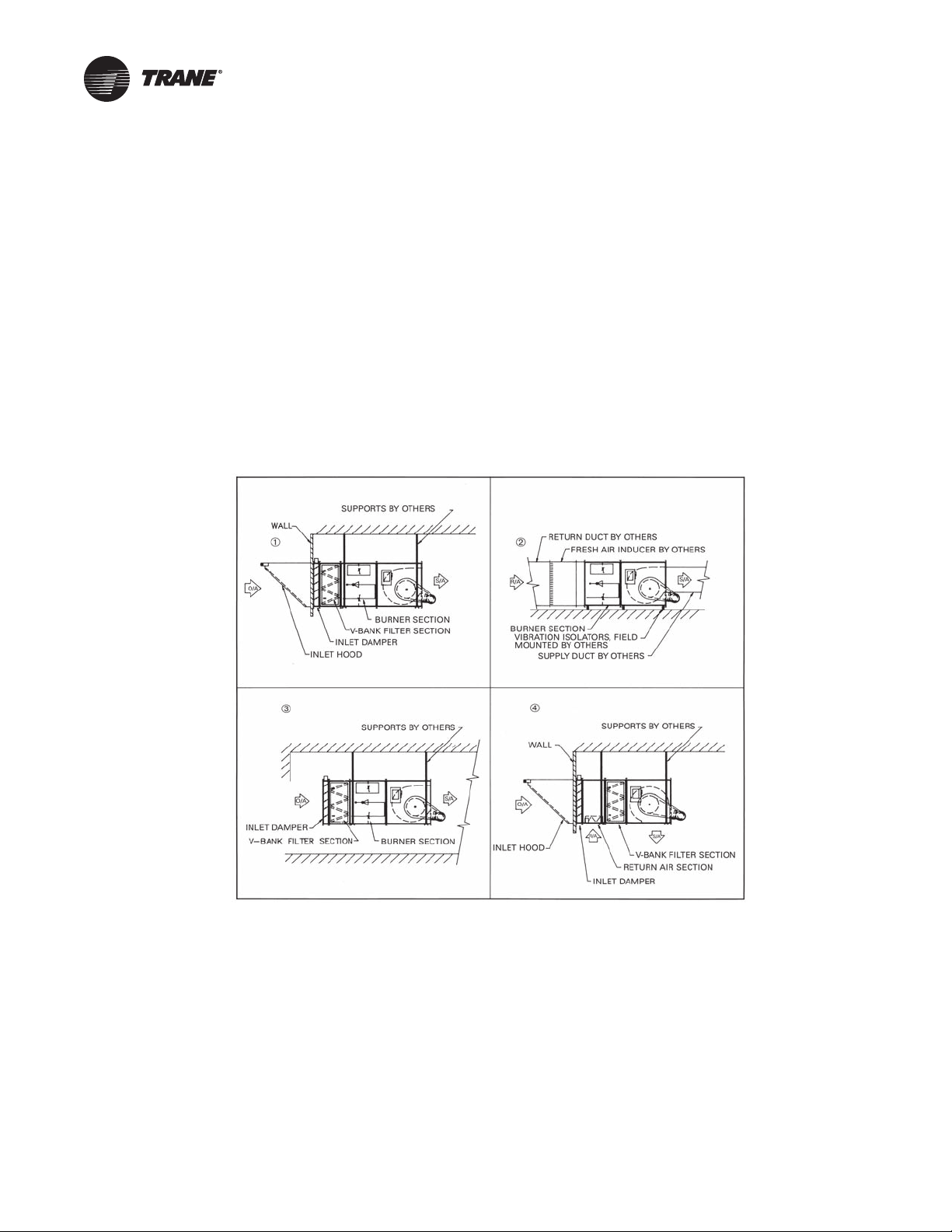
Application Considerations
The Need for Make-Up Air Units
When more air is exhausted from a building than is supplied by the mechanical systems, the
building is under a “negative” condition. Air will leak into the building through cracks, windows,
and doors.
• Make-up air units are typically used to compensate for air being exhausted from a building or
other structure.
• Application for closed systems such as ovens or paint booths (consult home office).
• For use as a door heater where outside air is heated and not prevented from infiltrating.
• The DFOA/DFIA can be used as an air handler, no burner section. Can also be used with DX,
electric, CW, HW and steam coils. Contact your Trane representative.
Figure 1. Application and various modular arrangements (DFIA only)
Outdoor Units
Outdoor make-up air units are the most common approach to relieving negative pressure inside
commercial and industrial facilities. All units offer the advantage of a full support system that is
watertight, provides a plenum for return air, and has easily accessible piping and electrical
connections.
When a negative condition exists:
• Flues and stacks may experience a backdraft and cause dangerous contaminants to remain in
the occupied space. In the case of flues, the products of combustion may condense and corrode
the equipment.
• Under negative conditions, the exhaust system sees a greater static pressure. The capacity of
each fan is reduced and this results in an inadequate removal of contaminants.
6 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 7

• Drafts and cross-currents will increase in a negative condition, causing an uncomfortable or
What Fuel to Use?
The most common fuel for heating make-up air is natural gas. This is because 100 percent of the
energy goes into the air stream (92 percent sensible, 8 percent latent). Direct firing eliminates the
need for heat exchangers or combustion chambers that can corrode or leak. Natural gas is often
the least expensive fuel and is usually readily available.
Note: Selected horizontal and vertical units are available with special coil options (DX, chilled
Application Considerations
unhealthy work environment.
water, steam or electric).
MUA-PRC007-EN 7
Page 8

Selection Procedure
Calculating Total External Static Pressure to Determine Fan Motor Horsepower. To
determine the fan motor horsepower, use the following steps:
1. Select Unit
– Determine cabinet size and cfm
2. Determine Static Pressure of Optional Accessories
– Add the static pressures of the optional accessories.
3. Determine External Static Pressure
– Calculate external static pressure of system due to ductwork, grilles, etc. This is the static
pressure external to the DFIA/DFOA unit and is up to the system designer to determine.
4. Calculate Total External Static Pressure
– Add the static pressures of the optional accessories to the external static pressure to
determine total external static pressure.
5. Use the Tabl e 1 , p . 1 6 (DFIA) and Table 10, p. 31 (DFOA) to determine the fan motor horsepower.
Example:
1. Specification calls for a 40,000 cfm unit. Select a size 225.
2. Unit will require an inlet hood, inlet damper and a v-bank filter. Therefore,the static pressure
of the optional accessories is 0.51 in. wc.
Fresh air inlet hood and birdscreen 0.13 in. wc
Motor operated inlet damper 0.13 in. wc
V-bank filter section 0.25 in. wc
Static pressure of optional accessories 0.51 in. wc
3. Engineer has determined that the external static pressure due to the ductwork is 0.75 in. wc.
4. Static Pressure of optional accessories 0.51 in. wc
External static pressure 0.75 in. wc
Total External Static Pressure 1.26 in. wc
5. For a size 225 unit at 40,000 cfm and 1.26 in. total external static pressure, a 30 hp fan motor will
be required.
8 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 9

Burner Selection Procedure
For DFIA selections, use Tab l e 3 , p . 18, and select next size larger available burner. For DFOA
selections, use Table 12, p. 33.
Note: Table is based on an entering air temperature of -40°F.
Example: an 80°F temperature rise is desired for 18000 scfm.
The table shows a MBh input of 1788 MBh.
Select the 1925 MBh input burner (Digit 14, 15 = AH)
OR
Use the following formula:
MBh input = (0.6210 x scfm x TR)
(0.6210 X ) / (460 + TR + EAT)
where:
TR = Temperature Rise (Desired leaving air temperture – entering air temperature)
EAT = Temperature Rise (Desired leaving air temperture – entering air temperature)
Selection Procedure
(460 + 80 + 10)
Example: A desired leaving air temperature of 90°F is required for 18000 scfm.
The entering air temperature is 10°F.
Temperature rise (TR) = 90 – 10 = 80°F
MBh input = (0.6210 x 18000 x 80)
(460 + 80 + 10)
Select the 1650 MBh input burner (Digit 14, 15 = AG)
= 1626 MBh input
MUA-PRC007-EN 9
Page 10
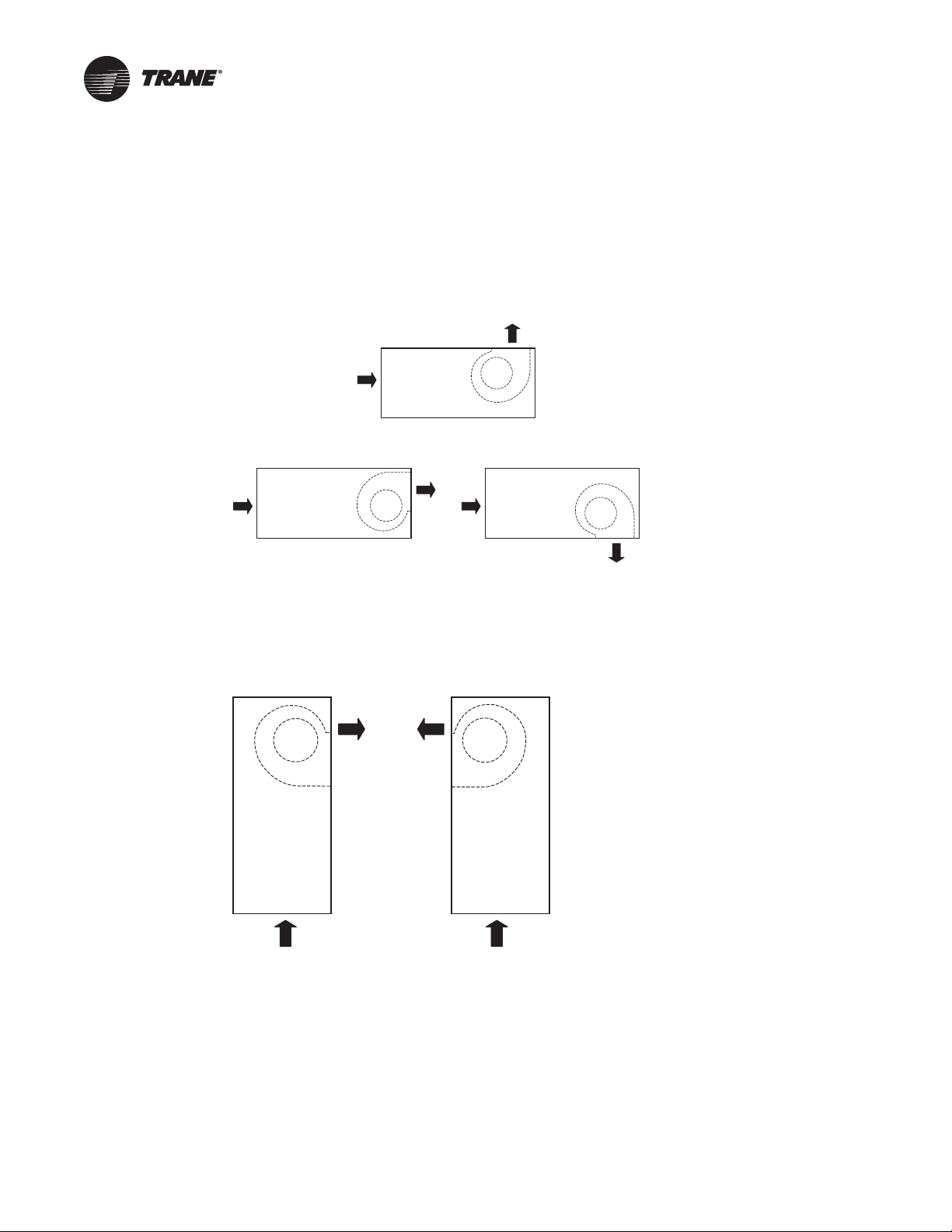
Unit Configuration
Fan Arrangement #4
Side Discharge
Fan Arrangement #6
Side Discharge
Horizontal Configurations
For all arrangements shown, controls, gas piping and fan motor are on the near side. Selected
horizontal units are available with special options — cooling coils (DX, chilled water), steam and
electric coils, no burner section. Contact your Trane representative for availability and pricing.
Figure 2. Horizontal configurations
Fan Arrangement #1
Top Discharge (For outdoor only)
Fan Arrangement #2
Side Discharge
Vertical Configurations (DFOA only)
For all arrangements shown, the gas piping and controls are on the near side. Selected vertical units
are available with special options — steam and electric coils, no burner section.
Figure 3. Vertical configuration (DFOA only)
Fan Arrangement #3
Bottom Discharge
10 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 11
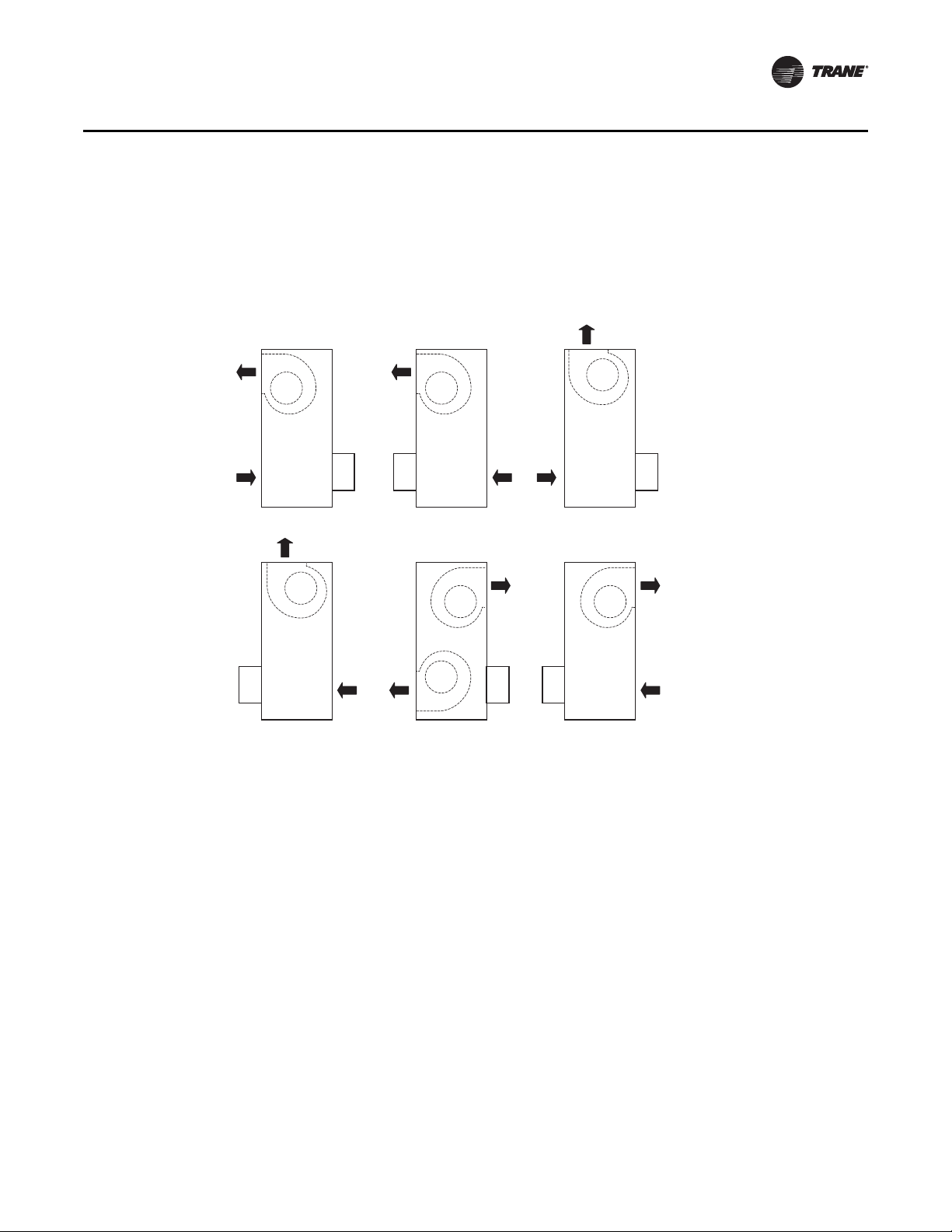
Vertical Configurations (DFIA only)
Fan Arrangement #9
Side Discharge
Fan Arrangement #6
Top Discharge
EC
EC
Fan Arrangement #8
Side Discharge
Fan Arrangement #5
Side Discharge
EC
EC
Fan Arrangement #7
Top Discharge
Fan Arrangement #4
Side Discharge
EC
EC
For all arrangements shown, the gas piping is on the near side. The electric control cabinet (EC) and
disconnect are on the side opposite the air entering side. Selected vertical units are available with
special options – steam and electric coils, no burner section. Contact your Trane representative for
availability.
Figure 4. Vertical configurations (DFIA only)
Unit Configuration
MUA-PRC007-EN 11
Page 12

DFIA
Model Number Descriptions
Digit 1, 2, 3 — Unit Description
DFI = Direct fired indoor unit
Digit 4 — Development
Sequence
A = First Generation
Digit 5 — Unit Size
109 120 215 225
112 122 218 230
115 125 220
118 130 222
Digit 8 —Burner Section
0 = No Burner Section
1 = Burner Section
Digit 9 —Main Power Supply
A = 115/60/1 D = 208/60/3
B = 230/60/1 E = 230/60/3
C = 208/60/1 F = 460/60/3
Digit 10 — Design Sequence
H = Eighth Design
Digit 11 — Fuel
N= Natural Gas
P=LP (Propane) Gas
Digit 12 — Gas Control Option
E = Modulating Discharge Temp
Control (MDT)
F = Modulating Room Temp Control
(MRT)
G = Modulating Room Temp Control
& Pro Room Sensor (MRT Pro)
H = Modulating Room Temp Control
& BACview
Digit 13 — Gas Train Approvals
0 = No Selection
1=Standard Gas Train
3 = IRI Gas Train Approval (ETL)
4 = FM Gas Train Approval (ETL)
5 = IRI Gas Train Approval (No ETL)
6 = FM Gas Train Approval (No ETL)
®
(MRT Expert)
Digit 14, 15 — Burner Input
Rating (Natural Gas/Propane)
00 = No Burner Input Selection
AA = 275/225 MBh
AB = 550/450 MBh
AC = 825/885 MBh
AE = 1100/1125 MBh
AF = 1375/1350 MBh
AG = 1650/1575 MBh
AH = 1925/1800 MBh
AJ = 220 0/2025 MBh
AK = 2475/2475 MBh
AL = 2750/2700 MBh
AN = 3025/2925 MBh
AP = 3300/3150 MBh
AQ = 3575/3375 MBh
AR = 3850/3825 MBh
AT = 4125/4050 MBh
AV = 4400/4275 MBh
AW = 4675/4500 MBh
AX = 4950/4950 MBh
AY = 5225/5175 MBh
AZ = 5500/5400 MBh
A1 = 5775/5624 MBh
A2 = 6050/5850 MBh
A3 = 6325/6075 MBh
A4 = 660 0/6525 MBh
A5 = 6875/6750 MBh
A6 = 7150/6975 MBh
A7 = 7425/7425 MBh
A8 = 770 0/7650 MBh
A9 = 7975 MBh
BA = 8250 MBh
BB = 8525 MBh
BC = 8800 MBh
BD = 9075 MBh
Digit 16 — Blower Motor
Horsepower
0 = No Selection J = 10 hp
B = 3/4 hp K = 15 hp
C=1 hp L=20 hp
D = 1-1/2 hp M = 25 hp
E=2 hp P=30 hp
F=3 hp Q=40 hp
G= 5 hp R= 50 hp
H = 7-1/2 hp T = 60 hp
Digit 17 — Motor Speed and
Starter
0 = No Selection
1 = Single Speed odp 1800 rpm
2 = Single Speed tefc 1800 rpm
3 = Single Speed Ener. Effic odp
4 = Single Speed Ener. Effic tefc
5 = 2s1w odp 1800/900 rpm
6 = 2s2w odp 1800/1200 rpm
Digit 18 — Fan Arrangement
1 = Horizontal Arrangement 1 Top
2 = Horizontal Arrangement 2 Side
3 = Horizontal Arrangement 3 Bottom
4 = Vertical Arrangement 4 Side
5 = Vertical Arrangement 5 Side
6 = Vertical Arrangement 6 Top
7 = Vertical Arrangement 7 Top
8 = Vertical Arrangement 8 Side
9 = Vertical Arrangement 9 Side
Digit 20 — V-Bank Filter Section
0 = No V-Bank Filter Section
A = V-Bank Section with Permanent
Filters
B = V-Bank Section without
Permanent Filters
C = V-Bank Section with TA Filters
D = V-Bank Section with Pleated
Filters
Digit 21 — Dampers/Mixing Box
0 = No Damper/Mixing Box Selected
(No ETL)
A = Motorized Return Air Damper
(No ETL)
B = Motorized Damper 75/25 (No ETL)
C = Mixing Box - Temperature Control
(No ETL)
D = Mixing Box - Building Press
Control (No ETL)
E = Mixing Box - Manual Control
(No ETL)
F = Mixing Box with Airflow
Station - Manual Control (ETL)
G = Mixing Box with Airflow
Station - Temp Control (ETL)
H = Mixing Box with Airflow
Station - Bldg. Press Control (ETL)
Digit 22, 23 — Controls Opposite
from Standard
** = Standard Controls
AA = Controls Opposite from Standard
Digit 24, 25 — Motorized Inlet
Damper
** = No Motorized Inlet Damper
AB = Motorized Inlet Damper
Digit 26, 27 —Insulation
AC = Insulation on Entire Unit
(Include Filter)
Digit 28, 29 —115V Duplex
Service Receptable with Trans.
AJ = 115V Duplex Service Receptacle
with Trans.
Digit 30, 31 — Painted Cabinet
AZ = Painted Cabinet
DIGIT 32, 33 — UV Flame Sensor
AL = Ultraviolet (UV) Flame Sensor
12 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 13

Digit 34, 35 —Clogged Filter
Indicator
AN = Clogged Filter Indicator
Digit 36, 37— Exhaust Interlock
AP = Exhaust Interlock
Digit 38, 39 — Interlocking Relay
AQ = Interlocking Relay
Digit 40, 41 — Omit Disconnect
Switch
DS = Disconect Switch
AT = Omit Disconnect Switch
Digit 42, 43 — High Gas Pressure
Regulator
CA = High Gas Press Reg 0.5–1 psi
AV = High Gas Press Reg –5 psi
AW = High Gas Press Reg 5–10 psi
BH = High Gas Press Reg Over 10 psi
Digit 44, 45 — Adjustable Drive
AX = Adjustable Drive
Digit 46, 47 — Low Gas Pressure
Burner
BJ = Low Gas Pressure Burner
Digit 48, 49 — Vibration Options
A5 = Vibration Feet
A6 = Vibration Hangers
Digit 50, 51 — Control Options
BD = 7-Day Time Clock
BG = On/off Night Setback Thermostat
BF = BACview
®
Remote Panel
Digit 52, 53 — Discharge Louver
AY = Discharge Louver
0=None
DFIA
MUA-PRC007-EN 13
Page 14

DFIA
Discharge fan section
Gas burner section
V-bank Filter with hinged access door
Gas manifold and control cabinet
Features and Benefits
Figure 5. DFIA features and benefits
14 MUA-PRC007-EN
Feature: Basic unit is factory assembled and wired.
Benefit: Reduces field installation cost.
Feature: Factory tested.
Benefit: Eliminates majority of field start-up problem caused by defective controls.
Feature: Adjustable motor mount.
Benefit: Belt tension can be field adjusted for maximum belt life.
Feature: All fuses factory furnished.
Benefit: Delay at start-up eliminated.
Feature: Return air cycle capability.
Benefit: Return air cycle results in fuel economy for pressurized heating systems and eliminates
need for two-speed fan operation. Minimizes heating cost.
Feature: No flues or stacks are used.
Benefit: Eliminates backdraft and dangerous contaminants from entering the space.
Page 15

Reliable Operation
The standard unit includes all of the controls needed for trouble-free operation.
If the designer does not utilize a master panel for consolidating mechanical equipment, an optional
remote control station should be ordered.
This device includes switches and signal lights for operating the make-up air unit and monitoring
its performance from any convenient location.
While rare, malfunctions can occur because a belt breaks, local power is interrupted or a
component fails. If this should happen, the unit’s control system is designed to take over. Its
overlapping fail-safe protective devices will turn on an alarm light and prevent burner operation
until the problem has been corrected.
Because of this attention to detail, combustion will be clean and odorless under the most adverse
conditions. The incoming “make-up air” will be at least five times purer than the requirements set
down by the U.S. Bureau of Standards.
Equipment Approval Options
Owners and specifiers have three very important reasons for wanting equipment approvals. One
reason is to establish a manufacturer’s reliability.
A second looks for conformance with equipment standards if any have been established for the
particular product. And finally, there may be requirements set down by an industrial user’s
insurance carrier.
Trane has gone to great lengths to satisfy these needs. In the first case, reliability is established for
our standard unit through conservative design and the use of U.L. listed components.
For industrial applications, the unit can also be furnished with special gas controls to comply with
FM or IRI. The latter is available for applications where the exact insurance approval agency has
not been established.
DFIA
Special Construction Features
• External bearings for easy service and lubrication.
• External motor for ease of service and belt maintenance.
• Hollow fan shaft on double blower models eliminate the need for a center bearing which is
difficult to service.
• Enlarged filter sections increasing filter life and reducing service time.
• Hinged filter access door.
• Service platform available as an option for easy maintenance on suspended units.
MUA-PRC007-EN 15
Page 16

DFIA
Performance Data
Table 1. Direct-Fired Indoor Air (DFIA) unit—General data
Unit Size 109 112 115 118 120 122 125 130 215 218 220 222 225 230
Airflow
Min. Airflow (cfm) 1600 3250 4 500 6500 9000 11000 14000 22000 9000 12500 18000 25000 30000 44000
Max. Airflow (cfm) 3000 4250 6 000 8500 11000 15000 20000 30000 12000 17000 26000 31000 46000 64000
Fan
Quantity - Wheel Size 1 - 9 1 - 12 1 - 15 1 - 18 1 - 20 1 - 22 1 - 25 1 - 30 2 - 15 2 - 18 2 - 20 2 - 22 2 - 25 2 - 30
Motor (hp) 1–5 1.5–5 2–7.5 3–10 5–10 5–15 7.5–20 10–30 5–15 7.5–20 7.5–25 15–30 15–50 20–60
Filters, 2-in
Quantity 4 4 9 9 10 10 24 24 18 18 35 35 42 42
Size (in) 20x20 20x20 20x16 20x16 20x25 20x25 20x16 20x16 20x15 20x15 20x16 20x16 20x20 20x20
Table 2. Direct-Fired Indoor Air (DFIA) unit—Performance data
Models
DFI
109 1–9
112 1–12
115 1–15
118 1–18
120 1–20
Note: Use the following static pressures for the optional accesso ries:
1. Motor Operated Inlet Damper: 0.13 in. wc
2. V-Bank Filter Section: 0.25 in. wc
3. Mixing Box: 0.40 in. wc
4. Discharge Louver: 0.13 in. wc
Blower
Size (in.)
Std Air
at 70
1600 1914 1111————
1900 2273 1 1 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/2 2 —
2200 2632 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/2 2 2 2 3
2600 3110 22223333
3000 3589 33333335
3250 2257 1-1/2 2222333
3500 2431 22223335
3750 2604 22333335
4000 2778 33333355
4250 2951 33333555
4500 2239 2233335—
5000 2488 33333555
5500 2736 33335555
6000 2985 35555557-1/2
6500 2265 35555557-1/2
7000 2439 5555557-1/27-1/2
7500 2613 555557-1/27-1/27-1/2
8000 2787 55557-1/27-1/27-1/27-1/2
8500 2962 5 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10
9000 2143 55557-1/27-1/27-1/2—
9500 2262 5 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 —
10000 2381 5 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10
10500 2500 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10
11000 2619 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 10
CFM
FPM
Outlet
Velocity
1/4 3/8 1/2 3/4 1 1-1/4 1-1/2 2
Total External Static Pressure (in. wc)
Horsepower
16 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 17

Table 2. Direct-Fired Indoor Air (DFIA) unit—Performance data (continued)
DFIA
Models
DFI
122 1–22
125 1–25
130 1–30
215 2–15
218 2–18
220 2–20
Note: Use the following static pressures for the optional accesso ries:
1. Motor Operated Inlet Damper: 0.13 in. wc
2. V-Bank Filter Section: 0.25 in. wc
3. Mixing Box: 0.40 in. wc
4. Discharge Louver: 0.13 in. wc
Blower
Size (in.)
Std Air
at 70
11000 2157 5 5 7 -1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 —
12000 2353 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 15
13000 2549 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 10 10 15
14000 2745 7-1/2 10 10 10 10 15 15 15
15000 2941 — 10 10 10 15 15 15 15
14000 2086 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 — — —
15000 2235 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 10 15 —
16000 2385 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 15 15 —
18000 2683 10 10 10 10 15 15 15 15
20000 2981 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 20
22000 2486 10 10 10 15 15 15 15 —
24000 2581 10 15 15 15 15 15 20 20
26000 2796 15 15 15 15 20 20 20 25
28000 3011 15 15 15 20 20 20 20 25
30000 3226 20 20 20 20 20 25 25 30
9000 2239 55555———
9500 2363 55557-1/27-1/2——
10000 2488 5 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 —
10500 2612 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 —
11000 2736 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10
11500 2861 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 10
12000 2985 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 10 15
12500 2178 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 — — —
13000 2265 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 — —
14000 2439 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 10 15 —
15000 2613 7-1/2 10 10 10 10 15 15 15
16000 2787 10 10 10 10 15 15 15 15
17000 2962 10 10 10 15 15 15 15 20
18000 2143 7-1/2 10 10 10 15 15 15 —
19000 2262 10 10 10 10 15 15 15 —
20000 2381 10 10 10 15 15 15 15 20
21000 2500 10 15 15 15 15 15 20 20
22000 2619 15 15 15 15 15 15 20 20
23000 2738 15 15 15 15 15 20 20 20
24000 2857 15 15 15 15 20 20 20 25
25000 2976 15 15 15 20 20 20 20 25
26000 3095 15 20 20 20 20 20 25 25
CFM
FPM
Outlet
Velocity
1/4 3/8 1/2 3/4 1 1-1/4 1-1/2 2
Total External Static Pressure (in. wc)
Horsepower
MUA-PRC007-EN 17
Page 18

DFIA
Table 2. Direct-Fired Indoor Air (DFIA) unit—Performance data (continued)
Models
DFI
222 2-22
225 2-25
230 2-30
Note: Use the following static pressures for the optional accesso ries:
1. Motor Operated Inlet Damper: 0.13 in. wc
2. V-Bank Filter Section: 0.25 in. wc
3. Mixing Box: 0.40 in. wc
4. Discharge Louver: 0.13 in. wc
Blower
Size (in.)
Std Air
at 70
25000 2451 15 15 15 15 20 20 20 25
26000 2549 15 15 15 20 20 20 20 25
27000 2647 15 15 15 20 20 20 25 25
28000 2745 15 20 20 20 20 25 25 30
29000 2843 20 20 20 20 25 25 25 30
30000 2941 20 20 20 20 25 25 25 30
31000 3039 20 20 20 25 25 25 30 30
30000 2235 15 15 15 15 20 20 — —
32000 2385 15 15 15 20 20 25 25 —
34000 2534 15 20 20 20 20 25 25 30
36000 2683 20 20 20 20 25 25 30 30
38000 2832 20 20 20 25 25 30 30 40
40000 2981 20 25 25 25 30 30 30 40
42000 3130 25 25 25 30 30 30 40 40
44000 3279 25 30 30 30 40 40 40 40
46000 3428 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 50
44000 2366 20 20 20 25 25 30 — —
48000 2581 20 25 25 25 30 30 40 —
52000 2796 25 25 30 30 40 40 40 50
56000 3011 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 50
60000 3226 30 40 40 40 40 50 50 50
64000 3441 40 40 40 50 50 50 50 60
CFM
FPM
Outlet
Velocity
1/4 3/8 1/2 3/4 1 1-1/4 1-1/2 2
Total External Static Pressure (in. wc)
Horsepower
Table 3. Direct-Fired Indoor Air (DFIA) unit—Burner selection table (MBh)
DFIA Model
109
112
18 MUA-PRC007-EN
CFM Std. Air
70° 70° Rise 80° Rise 90° Rise 100° Rise 110° Rise 120° Rise 130° Rise
1600 142 159 175 191 206 221 235
1900 169 189 208 227 245 262 279
2200 195 219 241 263 284 304 323
2600 231 258 285 311 335 359 382
3000 266 298 329 358 387 414 440
3250 288 323 356 388 419 449 477
3500 311 348 384 418 451 483 514
3750 333 373 411 448 483 518 550
4000 355 397 438 478 516 552 587
4250 377 422 466 508 548 587 624
Page 19

Table 3. Direct-Fired Indoor Air (DFIA) unit—Burner selection table (MBh) (continued)
DFIA Model
115
118
120
122
125
130
215
218
CFM Std. Air
70° 70° Rise 80° Rise 90° Rise 100° Rise 110° Rise 120° Rise 130° Rise
4500 399 447 493 537 580 621 661
5000 444 497 548 597 644 690 734
5500 488 546 603 657 709 759 807
6000 532 596 658 717 773 828 881
6500 577 646 712 776 838 897 954
7000 621 696 767 836 902 966 1027
7500 616 704 792 880 968 1057 1101
8000 710 795 877 955 1031 1104 1174
8500 754 845 932 1015 1096 111733 1248
9000 798 894 986 1057 1160 1242 1321
9500 798 894 986 1057 1160 1242 1321
10000 887 994 1096 1194 1289 1380 1468
10500 863 986 1109 1233 1356 1479 1541
11000 976 1039 1205 1314 1418 1518 1615
11000 976 1039 1205 1314 1418 1518 1615
12000 1065 1192 1315 1433 1547 1656 1761
13000 1153 1292 1425 1553 1676 1794 1908
14000 1242 1391 1534 1672 1804 1932 2055
15000 1331 1409 1644 1791 1933 2070 2202
14000 1242 1391 1534 1672 1804 1932 2055
15000 1331 1409 1644 1791 1933 2070 2202
16000 1419 1590 1753 1911 2062 2208 2349
17000 1508 1689 1863 2030 2191 2346 2495
18000 1597 1788 1973 2150 2320 2484 2642
20000 1774 1987 2192 2388 2578 2760 2936
22000 1952 2186 2411 2627 2836 3036 3229
24000 2129 2385 2630 2866 3093 3312 3523
26000 3207 2583 2849 3105 3351 3588 3816
28000 2484 2782 3069 3344 3609 3864 4110
30000 2661 2981 3288 3583 3867 4140 4404
9000 798 894 986 1057 1160 1242 1321
9500 798 894 986 1057 1160 1242 1321
10000 887 994 1096 1194 1289 1380 1468
10500 863 986 1109 1233 1356 1479 1541
11000 976 1039 1205 1314 1418 1518 1615
11500 1020 1143 1260 1373 1482 1587 1688
12000 1065 1192 1315 1433 1547 1656 1761
13000 1153 1292 1452 1553 1676 1794 1908
14000 1242 1319 1534 1672 1804 1932 2055
15000 1331 1490 1644 1791 1933 2070 2202
16000 1419 1590 1753 1911 2062 2208 2349
17000 1508 1689 1863 2030 2191 2346 2495
DFIA
MUA-PRC007-EN 19
Page 20

DFIA
Table 3. Direct-Fired Indoor Air (DFIA) unit—Burner selection table (MBh) (continued)
DFIA Model
220
222
225
230
CFM Std. Air
70° 70° Rise 80° Rise 90° Rise 100° Rise 110° Rise 120° Rise 130° Rise
18000 1597 1788 1973 2105 2320 2484 2642
19000 1686 1888 2082 2269 2449 2622 2789
20000 1774 1987 2192 2388 2578 2760 2936
21000 1726 1972 2219 2465 2712 2958 3082
22000 1952 2186 2411 2627 2836 3036 3229
23000 2040 2285 2521 2747 2964 3174 3376
24000 2129 2385 2630 2866 3093 3312 3523
25000 2218 2484 2740 2986 3222 3450 3670
26000 2307 2583 2849 3105 3351 3588 3816
25000 2218 2484 2740 2986 3222 3450 3670
26000 2307 2583 2849 3105 3351 3588 3816
27000 2395 2683 2959 3224 3480 3726 3963
28000 2484 2782 2069 3344 3609 3864 4110
29000 2573 2881 3064 3404 3745 4085 4257
30000 2465 2817 3178 3463 3738 4002 4257
31000 2750 3080 3397 3702 3996 4278 4550
30000 2661 2981 3288 3583 3867 4140 4404
32000 2839 3180 3507 3822 4124 4416 4697
34000 3016 3378 3726 4060 4382 4692 4991
36000 3194 3577 3945 4299 4640 4968 5284
38000 3371 3776 4164 4538 4898 5544 5578
40000 3549 3974 4384 4777 5156 5520 5871
42000 3451 3944 4437 4930 5423 5917 6165
44000 3903 4372 4822 5255 5671 6072 6458
46000 4081 4571 5041 5494 5929 6348 6752
44000 3903 4372 4822 5255 5671 6072 6458
48000 4258 4769 5260 5732 6187 6624 7046
52000 4613 5167 5699 6210 6702 7176 7633
56000 4968 5564 6317 6688 7218 7728 8220
60000 5323 5962 6575 7165 7733 8280 8807
64000 5678 6359 7014 7643 8249 8832 9394
20 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 21
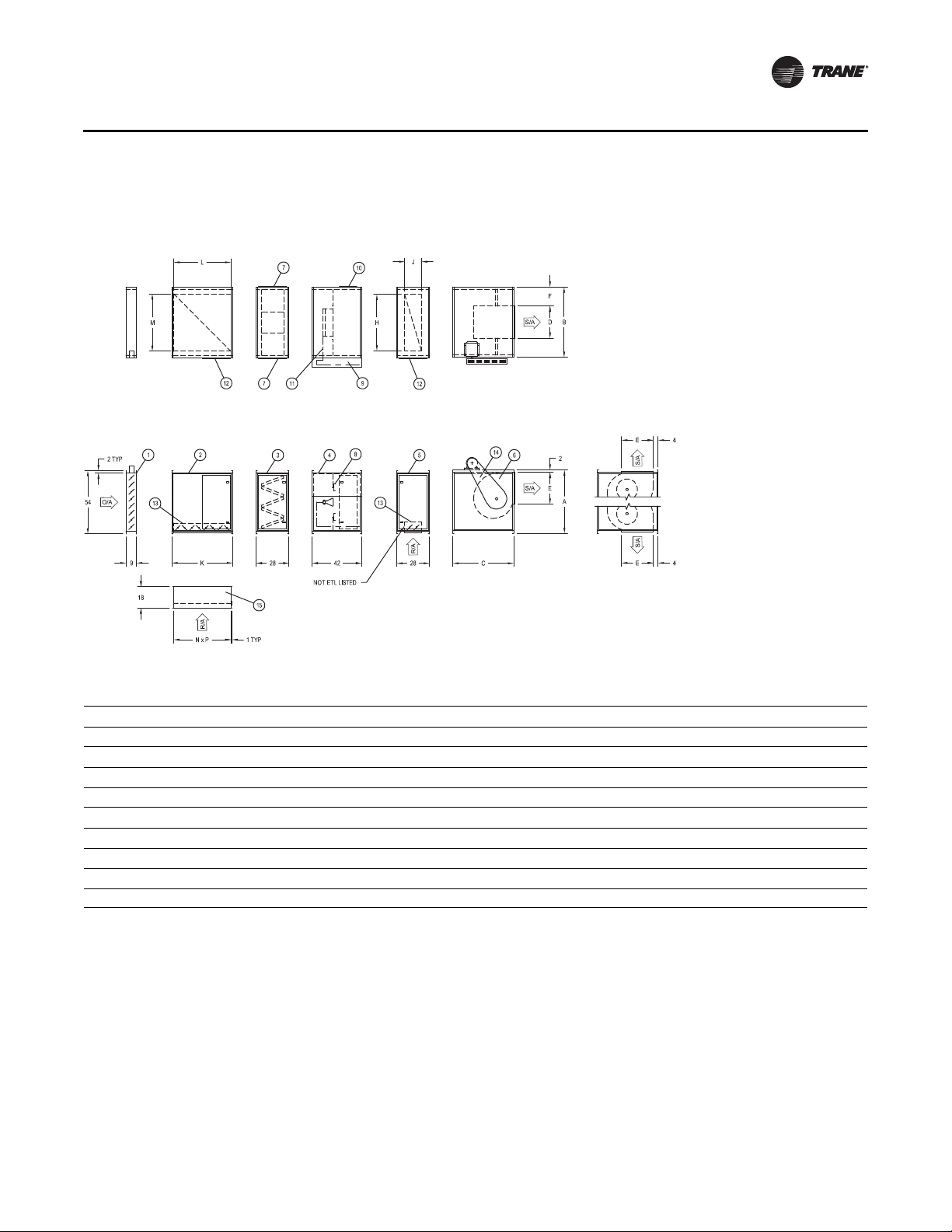
Dimensions
Plain View
Front View
Figure 6. Horizontal arrangement single blower
DFIA
Unit Components
1. Inl e t d am per
2. R/A section (before
Burner)
3. V-bank
4. Burner section
5. R/A section (after
burner)
6. Blower section
7. Filter access
8. Adjustable profile
9. Control cabinet
10. Access door (piping
compartment)
11. Gas piping manifold
12. R/A acces
13. Return air damper
14. Belt guard
Table 4. Dimensions for horizontal arrangement—Single blower DFIA
Model A B C D E F H J K L M N P
109 29 45 33 12 10-1/2 16-1/2 30 8-1/4 28 23-3/4 34 25-1/8 34-1/2
112 29 45 33 15-3/4 13-3/8 14-5/8 30 8-1/4 28 23-3/4 34 25-1/8 34-1/2
115 37-1/4 51 43 18-3/4 16 16-1/8 30 14-1/4 43 39-3/4 40 40-1/4 40-1/2
118 37-1/4 51 43 22 19 14-1/2 30 14-1/4 43 39-3/4 40 40-1/4 40-1/2
120 54 60 52 24-7/8 24-7/8 17-9/16 48 14-1/4 52 48-3/4 49 49-1/8 49-1/2
122 54 60 52 27-3/8 27-3/8 16-5/16 48 14-1/4 52 48-3/4 49 49-1/8 49-1/2
125 66 72 60 31-3/8 31-3/8 20-5/16 60 20-1/4 52 48-3/4 61 49-1/8 61-1/2
130 66 72 60 36-7/8 36-7/8 17-9/16 60 20-1/4 52 48-3/4 61 49-1/8 61-1/2
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
MUA-PRC007-EN 21
Page 22
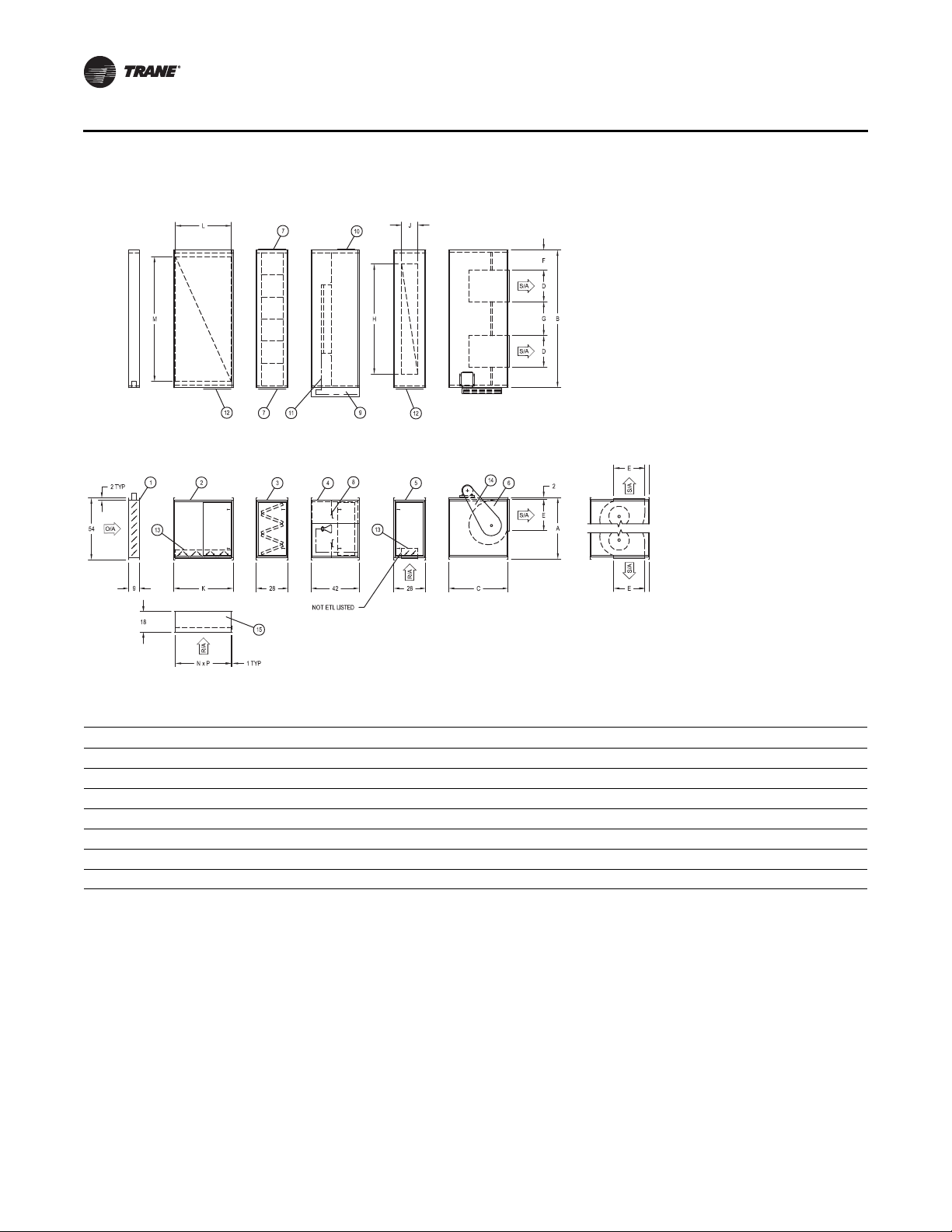
DFIA
Plan View
Front View
Figure 7. Horizontal arrangement twin blowers
Unit Components
1. Inlet damper
2. R/A section (before
Burner)
3. V-bank
4. Burner section
5. R/A section (after burner)
6. Blower section
7. Filter access
8. Adjustable profile
9. Control cabinet
10. Access door (piping
compartment)
11. Gas piping manifold
12. R/A acces
13. Return air damper
14. Belt guard
Table 5. Dimensions for horizontal arrangement—Single blower DFIA
Model A B C D E F G H J K L M N P
215 37-1/4 93 43 18-3/4 16 16-1/8 22-1/2 79 10 43 39-3/4 82 40-1/4 82-1/2
218 37-1/4 93 43 22 19 13-1/4 22-1/2 79 10 43 39-3/4 82 40-1/4 82-1/2
220 54 120 52 24-7/8 24-7/8 20-1/4 29-5/8 96 14-1/4 52 48-3/4 109 49-1/8 109-1/2
222 54 120 52 27-3/8 27-3/8 14-1/2 29-5/8 96 14-1/4 52 48-3/4 109 49-1/8 109-1/2
225 66 144 60 31-3/8 31-3/8 21-3/4 37-5/8 120 20-1/4 52 48-3/4 133 49-1/8 133-3/8
230 66 144 60 36-7/8 36-7/8 18-5/8 33 120 20-1/4 52 48-3/4 133 49-1/8 133-3/8
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
22 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 23

Figure 8. Single blower vertical units
VST Discharge
Plan View
Side View
Front View
DFIA
Unit Components
1. Inlet damper
2. R/A section (before burner)
3. V-bank
4. Burner section
5. R/A section (after burner)
6. Blower section
7. Filter access
8. Adjustable profile
9. Control cabinet
10. Access door (piping compartment)
11. Gas piping manifold
12. R/A acces
13. Return air damper
14. Belt guard
15. Screen
Table 6. Dimensions for single blower vertical units—DFIA
Model A B C D E F H J K L M N PN Q R S
109 29 45 33 12 10-1/2 16-1/8 30 8-1/4 28 23-3/4 34 25-1/8 34-1/2 36 32 17-1/4
112 29 45 33 15-3/4 13-3/8 14-5/8 30 8-1/4 28 23-3/4 34 25-1/8 34-1/2 36 32 17-1/4
115 37-1/4 51 43 18-3/4 16 16-1/8 29-5/8 14-1/4 43 39-3/4 40 40/4 40-1/2 36 32 17-1/4
118 37-1/4 51 43 22 19 14-1/2 30 14-1/4 43 39-3/4 40 40-1/4 40-1/2 36 32 20
120 54 60 52 24-7/8 24-7/8 17-9/16 48 14-1/4 52 48-3/4 49 49-1/8 49-1/2 48 44 20
122 54 60 52 27-3/8 27-3/4 16-5/16 48 14-1/4 52 48-3/4 49 49-1/8 49-1/2 48 44 20
125 66 72 60 31-3/4 31-3/8 20-5/16 60 20-1/4 52 48-3/4 61 49-1/8 61-1/2 48 44 21
130 66 72 60 36-7/8 36-7/8 17-9/16 60 20-1/4 52 48-3/4 61 49-1/8 61-1/2 48 44 21
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
MUA-PRC007-EN 23
Page 24

DFIA
VST Discharge
Plan View
Side View
Front View
Figure 9. Twin blower models vertical units
Unit Components
1. Inlet damper
2. R/A section (before
burner)
3. V-bank
4. Burner section
5. R/A section (after
burner)
6. Blower section
7. Filter access
8. Adjustable profile
9. Control cabinet
10. Access door
11. Gas piping manifold
12. R/A acces
13. Return air damper
14. Belt guard
15. Screen
Table 7. Dimensions for twin blower vertical units—DFIA
Model A B C D E F G H J K L M N P Q R S
215 37-1/4 93 43 18-3/4 16 16-1/8 22-1/2 79 10 43 39-3/4 82 40-1/4 82-1/2 36 32 18-1/2
218 37-1/4 93 43 22 19 13-1/4 22-1/2 79 10 43 39-3/4 82 40-1/4 82-1/2 36 32 22
220 54 120 52 24-7/8 24-7/8 20-1/4 29-5/8 96 14-1/4 52 48-3/4 109 49-1/8 109-1/2 48 44 22
222 54 120 52 27-3/8 27-3/8 17-3/4 29-5/8 96 14-1/4 52 48-3/4 109 49-1/8 109-1/2 48 44 23-1/2
225 66 144 60 31-3/8 31-3/8 21-3/4 37-5/8 120 20-1/4 52 48-3/4 133 49-1/8 133-1/2 48 44 32-3/4
230 66 144 60 36-7/8 36-7/8 18-5/8 33 120 20-1/4 52 48-3/4 133 49-1/8 133-1/2 48 44 32-3/4
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
24 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 25

Figure 10. DFIA Accessories dimensional data
Return air Probe Box
DFIA
Table 8. DFIA Accesories dimensional data
Model A B C D E
109–112 2 ft 5 in 3 ft 9 in 1 ft 5-3/8 in 1 ft 2-3/8 in 2 ft 4 in
115–118 3 ft 1-1/4 in 4 ft 3 in 1 ft 11 in 1 ft 8-3/8 in 3 ft 7 in
120–122 4 ft 6 in 5 ft 0 in 2 ft 4-1/2 in 3 ft 3-1/4 in 4 ft 4 in
125–130 5 ft 6 in 6 ft 0 in 3 ft 4-1/8 in 3 ft 3-1/4 in 4 ft 4 in
215–218 3 ft 1-1/4 in 7 ft 9 in 5 ft 7-3/4 in 1 ft 8-3/8 in 3 ft 7 in
220–222 4 ft 6 in 10 ft 0 in 7 ft 1-3/4 in 3 ft 3-1/4 in 4 ft 4 in
225–230 5 ft 6 in 12 ft 0 in 9 ft 1/8 in 3 ft 3-3/4 in 4 ft 4 in
MUA-PRC007-EN 25
Page 26

DFIA
RETURN AIR
Weights
Figure 11. DFIA approximate weights
Table 9. DFIA Approximate weights
Unit Size
109 350 180 55 165 104 260 104 70 67 149 67 67
112 350 180 55 165 104 260 104 70 67 149 67 67
115 535 210 70 185 178 375 116 80 94 253 94 94
118 535 210 70 185 178 375 116 80 94 253 94 94
120 916 420 120 275 2809 550 151 110 159 439 159 159
122 916 420 120 275 280 550 151 110 159 439 159 159
125 1262 570 155 310 386 700 208 125 224 590 224 224
130 1262 570 155 310 386 700 208 125 224 590 224 224
215 912 500 125 275 217 510 141 150 158 438 158 158
218 912 500 125 275 217 510 141 150 158 438 158 158
220 1501 625 233 410 420 725 226 215 268 697 268 268
222 1501 625 233 410 420 725 226 215 268 697 268 268
225 2117 845 340 500 560 1010 302 230 388 953 388 388
230 2117 845 340 500 560 1010 302 230 388 953 388 388
(a)When a mixing box option is ordered, these three accessory weights need to be totaled: Inlet Damper, V-Bank Filter, and Return Air (After Burner).
Section
Blower
Support
Stand
Vertical
(a)
Inlet
Damper
V-Bank
)
Filter
(a
Air
(Before
Burner)
Burner
Section
Return
Return
(a)
Air
(After
Burner)
Discharg
e Louver A B C D
26 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 27

DFOA
Model Number Descriptions
Digit 1, 2, 3 — Unit Type
DFO= Direct-Fired Outdoor Unit
Digit 4 — Development
Sequence
A = First Generation
Digit 5, 6, 7 — Unit Size
109 118 220 230
112 215 222
115 218 225
Digit 8 — Main Power Supply
A = 115/60/1 D = 208/60/3
B = 230/60/1 E = 230/60/3
C = 208/60/1 F = 460/60/3
Digit 9 — Fuel
N= Natural Gas
P=LP (Propane) Gas
Digit 10 — Design Sequence
H = Eighth Design
Digit 11 — Gas Control Option
E = Modulating Discharge Temp
Control
F = Modulating Room Temp Control
G = Modulating Room Temp Control
& Pro Room Sensor
H = Modulating Room Temp Control
& BACview
Digit 12 — Gas Train Approvals
0 = No Selection
1=Standard Gas Train
3 = IRI Gas Train Approval (ETL)
4 = FM Gas Train Approval (ETL)
5 = IRI Gas Train Approval (No ETL)
6 = FM Gas Train Approval (No ETL)
®
Digit 13 — Burner Input Rating
(Natural/Propane)
AA = 275/225 MBh
AB = 550/450 MBh
AC = 825/675 MBh
AE = 1100/1125 MBh
AF = 1375/1350 MBh
AG = 1650/1575 MBh
AH = 1925/1800 MBh
AJ = 220 0/2025 MBh
AK = 2475/2475 MBh
AL = 2750/2700 MBh
AN = 3025/2925 MBh
AP = 3300/3150 MBh
AQ = 3575/3375 MBh
AR = 3850/3825 MBh
AT = 4125/4050 MBh
AV = 4400/4275 MBh
AW = 4675/4500 MBh
AX = 4950/4950 MBh
AY = 5225/5175 MBh
AZ = 5500/5400 MBh
A1 = 5775/5624 MBh
A2 = 6050/5850 MBh
A3 = 6325/6075 MBh
A4 = 660 0/6525 MBh
A5 = 6875/6750 MBh
A6 = 7150/6975 MBh
A7 = 7425/7425 MBh
A8 = 770 0/7650 MBh
A9 = 7975 MBh
Digit 15 — Blower Motor
Horsepower
0 = No Selection J = 10 hp
B = 3/4 hp K = 15 hp
C=1 hp L=20 hp
D = 1-1/2 hp M = 25 hp
E=2 hp P=30 hp
F=3 hp Q=40 hp
G= 5 hp R= 50 hp
H = 7-1/2 hp T = 60 hp
Digit 16 — Motor Speed and
Starter
0 = No Selection
1 = Single Speed odp 1800 rpm
2 = Single Speed tefc 1800 rpm
3 = Single Speed Ener. Effic odp
4 = Single Speed Ener. Effic tefc
5 = 2s1w odp 1800/900 rpm
6 = 2s2w odp 1800/1200 rpm
Digit 17 — Fan Arrangement
2 = Horizontal Arrangement 2, Front
3 = Horizontal Arrangement 3,
Bottom
4 = Vertical Arrangement 4, Side
6 = Vertical Arrangement 6, Side
Digit 18— Inlet Hood and
Birdscreen
O = No Inlet Hood and Birdscreen
A = Inlet Hood/Birdscreen with
Permanent Filters
B = Inlet Hood/Birdscreen without
Permanent Filters
Digit 19 — V-Bank Filter Section
0 = No V-Bank Filter Section
A = V-Bank Section with Permanent
Filters
B = V-Bank Section without
Permanent Filters
C = V-Bank Section with TA Filters
D = V-Bank Section with Pleated
Filters
Digit 20 — Damper/Mixing Box
0 = No Damper/Mixing Box Selected
(No ETL)
A = Motorized 75/25 Damper
(Manual Control)
B = Motorized Damper 75/25
(Bldg Press Control)
C = Mixing Box - Temperature Control
(No ETL)
D = Mixing Box - Building Press
Control (No ETL)
E = Mixing Box - Manual Control
(No ETL)
F = Mixing Box with Airflow
Station - Manual Control (ETL)
G = Mixing Box with AIrflow
Station - Temp Control (ETL)
H = Mixing Box with Airflow
Station - Bldg Press Control (ETL)
Digit 21 — Controls Opposite
from Standard
0 = Standard Controls
A = Controls Opposite from Standard
Digit 22 — Motorized Inlet
Damper
0 = No Motorized Inlet Damper
B = Motorized Inlet Damper
Digit 23 — Motorized Outlet
Damper
0 = No Motorized Outlet Damper
C = Motorized Outlet Damper
Digit 24 — Insulation
D = Insulation on Entire Unit
Digit 25 — Internal Blower/Motor
Isolation
F = Internal Blower/Motor Isolation
Digit 26 — Extended Grease
Lines
G = Extended Grease Lines
Digit 27 — 115V Duplex Service
Receptable
K=115 Volt Duplex Service Receptacle
MUA-PRC007-EN 27
Page 28

DFOA
Digit 28 — Painted Basic Unit
and Accessories
M = Painted Basic Unit and
Accessories
Digit 29 — UV Flame Sensor
N = UV Flame Sensor
Digit 30 — Clogged Filter
Indicator
P = Clogged Filter Indicator
Digit 31 — Exhaust Interlock
Q = Exhaust Interlock
Digit 32 — Interlocking Relay
R = Interlocking Relay
Digit 33 — Omit Disconnect
Switch
DS = Disconect Switch
V = Omit Disconnect Switch
Digit 34 — High Gas Pressure
Regulator
7 = High Gas Press Reg 0.5–1 psi
W = High Gas Press Reg 1–5 psi
X = High Gas Press Reg 5–10 psi
6 = High Gas Press Reg Over 10 psi
Digit 35 — Adjustable Drive
Y = Adjustable Drive
Digit 36 — Low Gas Pressure
Burner
8 = Low Gas Pressure Burner
Digit 37 — Vibration Options
Z Vibration Feet—Full Unit
Digit 38 — Control Options
2 = 7-Day Time Clock
5 = On/Off Night Setback Thermostat
7 = BACview
Digit 39 — Discharge Louver
M = Discharge Louver
Digit 40 — Separator for Unit
Model Number
# = Separator for AOS Model
Number
Digit 41 — Roofcurbs
A = Curb for Basic Frame, No
Return Air
B = Curb for Basic Frame Return
Air Downstream
C = Curb for Basic Frame with
Mixing Box
®
Remote Panel
28 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 29

Features and Benefits
DFOA
MUA-PRC007-EN 29
Page 30

DFOA
Basic Unit
Feature: Casing with galvanized finish.
Benefit: Rust problem is greatly reduced.
Feature: Watertight construction.
Benefit: Designed for indoor or outdoor mounting.
Feature: Access doors are hinge mounted with industrial type hardware.
Benefit: Provides simple access to service compartments without removing sheet metal screws
and panels.
Feature: Adjustable motor mount
Benefit: Belt tension can be field adjusted for maximum belt life and for motor speed adjustment
Feature: Basic unit is factory assembled and wired.
Benefit: Reduces field installation cost.
Feature: All fuses factory furnished.
Benefit: Delay at start-up eliminated.
Feature: Factory tested before being shipped.
Gas-Fired Unit
Benefit: Eliminates majority of field start-up problems caused by defective controls.
Feature: Many units bear the ETL label.
Benefit: Meets certain specification requirements.
Feature: Optional temperature control systems available.
Benefit: Select system to satisfy application.
Feature: Optional dual fuel gas manifold.
Benefit: Standby flexibility in case natural gas supply is interrupted.
Feature: Optional construction provides returnair cycle.
Benefit: Maximum 80 percent return air cycle results in fuel economy for pressurized heating
systems and eliminates need for two-speed fan operation. Minimizes heating costs.
30 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 31

Performance Data
Table 10. Direct-Fired Outdoor Air (DFOA) unit—General data
Unit Size 109 112 115 118 215 218 220 222 225 230
Airflow
Min. Airflow (cfm) 1600 3250 4500 6500 9000 12500 18000 25000 30000 44000
Max. Airflow (cfm) 3000 4250 6000 8500 12000 17000 26000 31000 46000 64000
Fan
Quantity - Wheel Size 1 - 9 1 - 12 1 - 15 1 - 18 2 - 15 2 - 18 2 - 20 2 - 22 2 - 25 2 - 30
Motor (hp) 1–5 1.5–5 2–7.5 3–10 5–15 7.5–20 7.5–25 15–30 15–50 20–60
Filters, 2-in V-Bank Filter
Quantity 9999181825253636
Size (in) 20x15 20x15 20x15 20x15 20x15 20x15 20x20 20x20 20x25 20x25
Inlet Hood and Birdscreen
Quantity 4488161618186666
Size 20x16 20x16 20x16 20x16 20x16 20x16 20x25 20x25 20x15 20x15
Table 11. Direct-Fired Outdoor Air (DFOA) unit—Performance data
DFOA
Models
DFO
109 1–9
112 1–12
115 1–15
Note: External Pressure Drop in inches of water. Add pressure drop of the optional accessories, if used, to the pressure drop of the duct work:
1. Fresh Air Inlet Hood and Birdscreen: 13 in. wc
2. Fresh Air Inlet Hood with Filters: 25 in. wc
3. Motor Operated Inlet Damper: 13 in. wc
4. Motor Operated Discharge Damper: 50 in. wc
5. V-Bank Filter Section: 25 in. wc
6. Mixing Box: 40 in. wc
7. Discharge Louver: 13 in. wc
Blower
Size (in.)
Std Air
at 70
1600 1915 1 1 1 1 — — — —
1800 2155 1 1 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/2 — —
2000 2390 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/2 2 2 —
2250 2690 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/2 2 2 2 2 3
2500 2990 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3
2750 3290 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3
3000 3585 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 5
3250 2180 1-1/2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3
3500 2360 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 5
3750 2540 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 5
4000 2720 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 5
4250 2900 3 3 3 3 3 5 5 5
4500 2190 2 2 3 3 3 3 5 —
5000 2430 3 3 3 3 3 5 5 5
5500 2670 3 3 3 5 5 5 5 5
6000 2910 3 5 5 5 5 5 5 7-1/2
CFM
FPM
Outlet
Velocity
1/4 3/8 1/2 3/4 1 1-1/4 1-1/2 2
Total External Static Pressure (in. wc)
Horsepower
MUA-PRC007-EN 31
Page 32

DFOA
Table 11. Direct-Fired Outdoor Air (DFOA) unit—Performance data (continued)
Models
DFO
118 1–18
215 2–15
218 2–18
220 2–20
222 2–22
Note: External Pressure Drop in inches of water. Add pressure drop of the optional accessories, if used, to the pressure drop of the duct work:
1. Fresh Air Inlet Hood and Birdscreen: 13 in. wc
2. Fresh Air Inlet Hood with Filters: 25 in. wc
3. Motor Operated Inlet Damper: 13 in. wc
4. Motor Operated Discharge Damper: 50 in. wc
5. V-Bank Filter Section: 25 in. wc
6. Mixing Box: 40 in. wc
7. Discharge Louver: 13 in. wc
Blower
Size (in.)
Std Air
at 70
6500 2215 3 5 5 5 5 5 5 7-1/2
7000 2390 5 5 5 5 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2
7500 2565 5 5 5 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2
8000 2740 5 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2
8500 2915 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10
9000 2190 5 5 5 5 5 — — —
9500 2310 5 5 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 — —
10000 2430 5 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 —
10500 2550 5 5 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 —
11000 2670 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10
11500 2790 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 10
12000 2910 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7 -1/2 10 10 10 15
12500 2125 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 — — —
13000 2215 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 — —
14000 2390 7-1/2 7-1/2 7-1/2 10 10 10 15 —
15000 2565 7-1/2 10 10 10 10 15 15 15
16000 2740 10 10 10 10 15 15 15 15
17000 2915 10 10 10 15 15 15 15 20
18000 2140 7-1/2 10 10 10 15 15 15 —
19000 2260 10 10 10 10 15 15 15 —
20000 2380 10 10 10 15 15 15 15 20
21000 2500 10 15 15 15 15 20 20 20
22000 2620 15 15 15 15 15 15 20 20
23000 2740 15 15 15 15 15 20 20 20
24000 2860 15 15 15 15 20 20 20 25
25000 2980 15 15 15 20 20 20 20 25
26000 3100 15 20 20 20 20 20 25 25
25000 2450 15 15 15 15 20 20 20 25
26000 2550 15 15 15 20 20 20 20 25
27000 2650 15 15 15 20 20 20 25 25
28000 2750 15 20 20 20 20 25 25 30
29000 2850 20 20 20 20 25 25 25 30
30000 2950 20 20 20 20 25 25 25 30
31000 3050 20 20 20 25 25 25 30 30
CFM
FPM
Outlet
Velocity
1/4 3/8 1/2 3/4 1 1-1/4 1-1/2 2
Horsepower
Total External Static Pressure (in. wc)
32 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 33

Table 11. Direct-Fired Outdoor Air (DFOA) unit—Performance data (continued)
DFOA
Models
DFO
225 2–25
230 2–30
Note: External Pressure Drop in inches of water. Add pressure drop of the optional accessories, if used, to the pressure drop of the duct work:
1. Fresh Air Inlet Hood and Birdscreen: 13 in. wc
2. Fresh Air Inlet Hood with Filters: 25 in. wc
3. Motor Operated Inlet Damper: 13 in. wc
4. Motor Operated Discharge Damper: 50 in. wc
5. V-Bank Filter Section: 25 in. wc
6. Mixing Box: 40 in. wc
7. Discharge Louver: 13 in. wc
Blower
Size (in.)
Std Air
at 70
30000 2235 15 15 15 15 20 20 — —
32000 2385 15 15 15 20 20 20 25 —
34000 2535 15 20 20 20 20 25 25 30
36000 2685 20 20 20 20 25 25 30 30
38000 2835 20 20 20 25 25 30 30 40
40000 2985 20 25 25 25 30 30 30 40
42000 3135 25 25 25 30 30 40 40 40
44000 3285 25 30 30 30 40 40 40 40
46000 3430 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 50
44000 2365 20 20 20 25 25 30 — —
48000 2580 20 25 25 25 30 30 40 —
52000 2800 25 25 30 30 40 40 40 50
56000 3020 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 50
60000 3240 40 40 40 40 40 50 50 50
64000 3440 40 40 40 50 50 50 50 60
CFM
FPM
Outlet
Velocity
1/4 3/8 1/2 3/4 1 1-1/4 1-1/2 2
Horsepower
Table 12. Direct-Fired Outdoor Air (DFOA) unit—Burner selection table (MBh)
Total External Static Pressure (in. wc)
DFOA Model
109
112
115
70° 70° Rise 80° Rise 90° Rise 100° Rise 110° Rise 120° Rise 130° Rise
1600 142 159 175 191 206 221 235
1800 160 179 179 215 232 248 264
2000 177 199 219 239 258 276 294
2250 200 224 247 269 290 311 330
2500 222 248 274 299 322 345 367
2750 244 273 201 328 354 380 404
3000 266 298 329 358 387 414 440
3250 288 323 356 388 419 449 477
3500 311 348 384 418 451 483 514
3750 333 373 411 448 483 518 550
4000 355 397 438 478 516 552 587
4250 377 422 466 508 548 587 624
4500 399 447 493 537 580 621 661
5000 444 497 548 597 644 690 734
5500 488 546 603 657 709 759 807
6000 533 596 658 717 773 828 881
MUA-PRC007-EN 33
CFM Std. Air
Page 34

DFOA
Table 12. Direct-Fired Outdoor Air (DFOA) unit—Burner selection table (MBh) (continued)
DFOA Model
118
215
218
220
222
225
CFM Std. Air
70° 70° Rise 80° Rise 90° Rise 100° Rise 110° Rise 120° Rise 130° Rise
6500 577 646 712 776 838 897 954
7000 621 697 767 836 902 966 1027
7500 665 745 822 896 967 1035 1101
8000 710 795 877 955 1031 1104 1174
8500 754 845 932 1015 1096 1173 1248
9000 798 894 986 1057 1160 1242 1321
9500 843 944 1041 1135 1224 1311 1394
10000 887 994 1096 1194 1289 1380 1468
10500 932 1043 1151 1254 1353 1449 1541
11000 976 1039 1205 1314 1418 1518 1615
11500 1020 1143 1260 1373 1482 1587 1688
12000 1065 1192 1315 1433 1547 1656 1761
12500 1109 1242 1370 1493 1611 1725 1835
13000 1153 1292 1452 1553 1676 1794 1908
14000 1242 1391 1534 1672 1804 1932 2055
15000 1331 1490 1644 1791 1933 2070 2202
16000 1419 1590 1753 1911 2062 2208 2349
17000 1508 1689 1863 2030 2191 2346 2495
18000 1597 1788 1973 2105 2320 2484 2642
19000 1686 1888 2082 2269 2449 2622 2789
20000 1774 1987 2192 2388 2578 2760 2936
21000 1863 2087 2301 2508 2707 2898 3082
22000 1952 2186 2411 2627 2836 3036 3229
23000 2040 2285 2521 2747 2964 3174 3376
24000 2129 2385 2630 2866 3093 3312 3523
25000 2218 2484 2740 2986 3222 3450 3670
26000 2307 2583 2849 3105 3351 3588 3816
25000 2218 2484 2740 2986 3222 3450 3670
26000 2307 2583 2849 3105 3351 3588 3816
27000 2395 2683 2959 3224 3480 3726 3963
28000 2484 2782 3069 3344 3609 3864 4110
29000 2573 2881 3178 3463 3738 4002 4257
30000 2661 2981 3288 3583 3867 4140 4404
31000 2750 3080 3397 3702 3996 4278 4550
30000 2661 2981 3288 3583 3867 4140 4404
32000 2839 3180 3507 3822 4124 4416 4697
34000 3016 3378 3726 4060 4382 4692 4991
36000 3194 3577 3945 4299 4640 4968 5284
38000 3371 3776 4164 4538 4898 5544 5578
40000 3549 3974 4384 4777 5156 5520 5871
42000 3762 4173 4603 5016 5413 5796 6165
44000 3903 4372 4822 5255 5671 6072 6458
46000 3780 4320q 4860 5400 5940 6480 7046
34 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 35

Table 12. Direct-Fired Outdoor Air (DFOA) unit—Burner selection table (MBh) (continued)
DFOA
DFOA Model
230
CFM Std. Air
70° 70° Rise 80° Rise 90° Rise 100° Rise 110° Rise 120° Rise 130° Rise
44000 3903 4372 4822 5255 5671 6072 6458
48000 4258 4769 5260 5732 6187 6624 7046
52000 4273 4883 5494 6104 6715 7325 8807
56000 4968 5564 6317 6688 7218 7728 8220
60000 5323 5962 6575 7165 7733 8280 8807
64000 5678 6359 7014 7643 8249 8832 9394
MUA-PRC007-EN 35
Page 36

DFOA
Front View
side discharge
Right Hand Shown
Left is opposite
Front View
bottom discharge
Dimensions
Figure 12. Single blower sizes 109–130
Unit Components
1. Centrifugal supply fan
2. Fan motor
3. Line burner
4. Control cabinet
5. Hinged control
cabinet access door
6. Observation port
7. Access door
8. Access door (piping
compartment)
9. Lifting lug
10. Unit base
11. Manifold
compartment
Table 13. Dimensions for DFOA single blower sizes 109–130
Model A B C D E F G H J
109 36 52 77 17-13/16 10-3/8 15-1/8 14-7/16 11-9/16 19
112 36 52 77 17-13/16 13-9/16 13-9/16 14-7/16 11-9/16 19
115 36 52 77 23-15/16 16 12-3/8 19-7/8 8-5/8 19
118 36 52 77 23-15/16 19 12-3/8 19-7/8 6-15/16 19
120 48 78 96 29-1/2 24-7/8 13-3/16 28-1/4 10-5/32 19
122 48 78 96 29-1/2 27-3/8 13-3/16 28-1/4 11-13/32 19
125 60 91 96 38-7/8 31-3/8 17-9/16 37-3/4 11-13/16 12-5/16
130 60 91 96 38-7/8 36-7/8 17-9/16 37-3/4 14-7/16 12-5/16
Model K L M P R S T U V
109 14-1/4 14-1/2 11-15/16 27-3/4 32 54 20-1/4 42 22
112 14-1/4 12-1/2 15-15/16 27-3/4 32 54 20-1/4 42 22
115 14-1/4 11-1/8 18-15/16 27-3/4 32 54 20-1/4 42 22
118 14-1/4 7-7/8 22-1/16 27-3/4 32 54 20-1/4 42 22
120 14-1/4 12-1/8 25-1/16 48 38-1/2 60 20-1/4 68 22
122 14-1/4 12-3/8 27-9/16 48 38-1/2 60 20-1/4 68 22
125 20-1/4 15-1/8 31-1/2 49 53 65 26-1/2 81 28
130 20-1/4 15-3/8 37 49 53 65 26-1/2 81 28
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
36 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 37

Figure 13. Twin blower sizes 215–230
Plan View
Front View
(side discharge)
Right Hand Shown
left is opposite
Front View
(bottom discharge)
DFOA
Unit Components
1. Centrifugal supply
fan
2. Fan motor
3. Line burner
4. Control cabinet
5. Hinged control
cabinet access door
6. Observation port
7. Access door
8. Access door (piping
compartment)
9. Lifting lug
10. Unit base
11. Manifold
compartment
12. Airflow station
(required ETL listed
Return Air Unit)
Table 14. Dimensions for DFOA twin blower sizes 215–230
Model A B C D E F G H I J
215 36 94 77 23-15/16 16 12-3/8 19-7/8 6-15/16 22-1/4 19
218 36 94 77 23-15/16 19 12-3/8 19-7/8 6-15/16 16 19
220 48 130 96 29-7/16 24-7/8 13-3/16 28-1/4 11-7/16 29-5/8 19
222 48 130 96 29-7/16 27-3/8 13-3/16 28-1/4 11-7/16 24-5/8 19
225 60 154 96 38-7/8 31-3/8 17-9/16 37-3/4 14-7/16 37-5/8 12-5/16
230 60 154 96 38-7/8 36-7/8 17-9/16 37-3/4 14-7/16 26-5/8 12-5/16
Model K L M N P R S T U V
215 14-1/4 7-7/8 18-15/16 14 65-3/4 32 54 20-1/4 84 22
218 14-1/4 7-7/8 22-1/16 14 65-3/4 32 54 20-1/4 84 22
220 14-1/4 12-3/8 25-1/16 22-5/8 87-3/8 44-1/2 60 20-1/4 120 22
222 14-1/4 12-3/8 27-9/16 22-5/8 87-3/8 44-1/2 60 20-1/4 120 22
225 20-1/4 15-3/8 31-1/2 24-5/8 111-3/8 56-1/2 65 26-1/2 144 28
230 20-1/4 15-3/8 37 24-5/8 111-3/8 56-1/2 65 26-1/2 144 28
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
MUA-PRC007-EN 37
Page 38

DFOA
Front View
(side discharge)
Right Hand Side
left is opposite
Front View
(bottom discharge)
Figure 14. Twin blower sizes 233 and 240
.
Unit Components
1. Centrifugal supply
fan
2. Fan motor
3. Line burner
4. Control cabinet
5. Hinged control
cabinet access door
6. Observation port
7. Access door
8. Access door (piping
compartment)
9. Lifting lug
10. Unit bas e
11. M a n i f o l d
compartment
12. Airflow station
(required ETL listed
Return Air Unit)
Table 15. Dimensions for DFOA twin blower sizes 233 and 240
Model A B C D E F G H I J K
233 68 175 117 43-3/4 43-1/16 19-7/16 44 16-1/16 36 20 20-1/4
240 79-1/4 210 131 55-3/4 41 33 42 19-1/16 39-7/8 20 20-1/4
Model
233 17 39-7/8 34-1/8 45 130 56-1/2 70 31-1/4 163 28 72
240 20 53-7/8 38 45 166 51-1/2 70 31-1/4 198 28 86
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
38 MUA-PRC007-EN
LMNOPSRSTUVW
Page 39

Figure 15. Vertical models sizes 109–130
Front View
Side view
Right Hand Shown
Left is opposite
DFOA
Unit Components
1. Centrifugal supply fan
2. Fan motor
3. Line burner
4. Control cabinet
5. Hinged control
cabinet access door
6. Observation port
7. Access door
8. Access door (piping
compartment)
9. Lifting lug
10. Unit support stand
11. Manifold
compartment
Table 16. Dimensions vertical models sizes 109–130
Model A B C D E F G H J K L M
109 42 52 77 135 10-3/8 15-1/8 22 36 14-1/2 11-15/16 20-1/4 42
112 42 52 77 135 13-9/16 13-9/16 22 36 12-1/2 15-15/16 20-1/4 42
115 42 52 77 135 16 12-3/8 22 36 11-1/8 18-15/16 20-1/4 42
118 42 52 77 135 19 12-3/8 22 36 7-7/8 22-1/16 20-1/4 42
120 56 78 96 166 24-7/8 13-3/16 22 48 12-3/8 25-1/16 20-1/4 68
122 56 78 96 166 27-3/8 13-3/16 22 48 12-3/8 27-9/16 20-1/4 68
125 68 91 96 172 31-3/8 17-9/16 28 48 15-3/8 31-1/2 26-1/2 81
130 68 91 96 172 36-7/8 17-9/16 28 48 15-3/8 37 26-1/2 81
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
MUA-PRC007-EN 39
Page 40

DFOA
Front View
Side Discharge
Side View
Right Hand Shown
Left is opposite
Figure 16. Vertical models sizes 109–130 with mixing box
Unit Components
1. Centrifugal supply fan
2. Fan motor
3. Line burner
4. Control cabinet
5. Hinged control
cabinet access door
6. Observation port
7. Access door
8. Access door (piping
compartment)
9. Lifting lug
10. Unit support stand
11. Manifold
compartment
12. Airflow station
(required ETL listed
return air unit)
Table 17. Dimensions for vertical models sizes 109–130 with mixing box
Model A B C D E F G H L M T U
109 42 52 77 167 10 3/8 15 1/8 54 36 14 1/2 11 15/16 20 1/4 42
112 42 52 77 167 13 9/16 13 9/16 54 36 12 1/2 15 15/16 20 1/4 42
115 42 52 77 167 16 12 3/8 54 36 11 1/8 18 15/16 20 1/4 42
118 42 52 77 167 19 12 3/8 54 36 7 7/8 22 1/16 20 1/4 42
120 56 78 96 204 24 7/8 13 3/16 60 48 12 3/8 25 1/16 20 1/4 68
122 56 78 96 204 27 3/8 13 3/16 60 48 12 3/8 27 9/16 20 1/4 68
125 68 91 96 209 31 3/8 17 9/16 65 48 15 3/8 31 1/2 26 1/2 81
130 68 91 96 209 36 7/8 17 9/16 65 48 15 3/8 37 26 1/2 81
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
40 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 41

Figure 17. Vertical models sizes 215–230
Front View
(side discharge)
Right Hand Shown
left is opposite
Side View
DFOA
Unit Components
1. Centrifugal supply fan
2. Fan motor
3. Line burner
4. Control cabinet
5. Hinged control
cabinet access door
6. Observation port
7. Access door
8. Access door (piping
compartment)
9. Lifting lug
10. Unit support stand
11. Manifold
compartment
12. Airflow station
(required ETL listed
return air unit)
Table 18. Dimensions for vertical models sizes 215-230
Model A B C D E F G H I J K L M P
215 42 94 77 135 16 12-3/8 22 36 22-1/4 19 14-1/4 7-7/8 18-15/16 65-3/4
218 42 94 77 135 19 12-3/8 22 36 16 19 14-1/4 7-7/8 22-1/16 65-3/4
220 56 130 96 166 24-7/8 13-3/16 22 48 29-5/8 19 14-1/4 12-3/8 25-1/16 87-3/8
222 56 130 96 166 27-3/8 13-3/16 22 48 24-5/8 19 14-1/4 12-3/8 27-9/16 87-3/8
225 68 154 96 172 31-3/8 17-9/16 28 48 37-5/8 12-5/16 20-1/4 15-3/8 31-1/2 111-3/8
230 68 154 96 172 36-7/8 17-9/16 28 48 26-5/8 12-5/16 20-1/4 15-3/8 37 111-3/8
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
MUA-PRC007-EN 41
Page 42

DFOA
Front View
(side discharge)
Side View
Right Hand Shown
Left is opposite
SEPERATE HERE
FOR SHIPPING
Figure 18. Vertical models sizes 215–230 with mixing box
Unit Components
1. Centrifugal supply fan
2. Fan motor
3. Line burner
4. Control cabinet
5. Hinged control cabinet
access door
6. Observation port
7. Access door
8. Access door (piping
compartment)
9. Lifting lug
10. Unit support stand
11. Manifold compartment
12. Airflow station (required ETL
listed return air unit)
Table 19. Dimensions for vertical models sizes 215–230 with mixing box
Model A B C D E F G H I L M T U
215 42 94 77 167 16 12-3/8 54 36 22-1/4 7-7/8 18-15/16 20-1/4 84
218 42 94 77 167 19 12-3/8 54 36 16 7-7/8 22-1/16 20-1/4 84
220 56 130 96 204 24-7/8 13-3/16 60 48 29-5/8 12-3/8 25-1/16 20-1/4 120
222 56 130 96 204 27-3/8 13-3/16 60 48 24-5/8 12-3/8 27-9/16 20-1/4 120
225 68 154 96 209 31-3/8 17-9/16 65 48 37-5/8 15-3/8 31-1/2 26-1/2 144
230 68 154 96 209 36-7/8 17-9/16 65 48 26-5/8 15-3/8 37 26-1/2 144
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
42 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 43

Front View
(side discharge)
Right Hand Shown
Left is opposite
Side View
Figure 19. Vertical models sizes 233 and 240
DFOA
Unit Components
1. Centrifugal supply fan
2. Fan motor
3. Line burner
4. Control cabinet
5. Hinged control
cabinet access door
6. Observation port
7. Access door
8. Access door (piping
compartment)
9. Lifting lug
10. Unit support stand
11. Manifold
compartment
Table 20. Dimensions vertical models sizes 233 and 240
Model A B C D E F I J K L M O P W
233 76 175 117 205 43-1/16 19-7/16 36 20 20-1/4 17 39-7/8 45 130 72
240 87-1/4 210 131 219 41 33 39-7/8 20 20-1/4 20 53-7/8 45 166 86
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
MUA-PRC007-EN 43
Page 44

DFOA
Front View
(side discharge)
Right Hand Shown
Left is opposite
Side View
Figure 20. Vertical models 233 and 240 with mixing box
Unit Components
1. Centrifugal supply fan
2. Fan motor
3. Line burner
4. Control cabinet
5. Hinged control
cabinet access door
6. Observation port
7. Access door
8. Access door (piping
compartment)
9. Lifting lug
10. Unit support stand
11. Manifold
compartment
Table 21. Dimensions for vertical models 233 and 240 with mixing box
Model A B C D E F I L M T U W
233 76 175 117 247 43-1/16 19-7/16 36 17 39-7/8 31-1/4 163 72
240 87-1/4 210 131 261 41 33 39-7/8 20 58-7/8 31-1/4 198 86
Note: All dimensions in inches subject to manufacturing tolerances.
44 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 45

Figure 21. DFOA Accessories dimensional data
DFOA
Table 22. DFOA Accessories dimensional data
Model A B C D E F G H J K L M
109–112 3’ 0” 3’ 11-1/4” 1’ 5-7/16” 1’ 8-13/16” 1’ 10” 5’ 1-3/4” 2’ 8-1/4” 3’ 7-1/8” 1’ 9” 1’ 11” 4’ 4” 4’ 6”
914 1200 443 529 559 1568 819 1095 533 584 1321 1372
115–118 3’ 0” 3’ 11-1/4” 1’ 10-7/8” 2’ 2-15/16” 1’ 10” 5’ 1-3/4” 2’ 8-1/4” 3’ 7-1/8” 2’ 0” 1’ 11” 4’ 4” 4’ 6”
914 1200 581 684 559 1568 819 1095 610 660 1321 1372
215–218 3’ 0” 7’ 7-1/2” 1’ 10-7/8” 5’ 4-7/8” 1’ 10” 5’ 1-3/4” 2’ 8-1/4” 7’ 3-3/8” 2’ 0” 1’ 11” 7’ 10” 4’ 6”
914 2324 581 1648 559 1568 819 2219 610 660 2388 1372
220–222 4’ 0” 8’ 5-5/8” 2’ 7-1/4” 7’ 0-1/2” 1’ 10” 5’ 5-3/4” 3’ 8-1/4” 8’ 1-1/2” 3’ 9” 2’ 7” 10’ 10” 5’ 0”
1219 2581 794 2146 559 1670 1124 2477 1143 787 3302 1524
225–230 5’ 0” 10’ 1-3/8” 3’ 4-3/4” 8’ 9-3/8” 2’ 4” 7’ 2-1/8” 4’ 8-1/4” 9’ 9-1/4” 3’ 9” 3’ 4-3/4” 12’ 10” 5’ 5”
1524 3083 1035 2677 711 2188 1429 2978 1143 1035 3912 1651
Model R / A / ID
109–118 3’ 6” x 1’ 8-1/4” (1067 x 514)
215–218 7’ x 1’ 8-1/4” (2134 x 514)
220–222 0’ x 1’ 8-1/4” (3048 x 514)
225–230 12’ x 2’ 2-1/2” (3658 x 673)
MUA-PRC007-EN 45
Page 46

DFOA
Roof curbs for 100% make-up air units
Figure 22. Single blower roof curb dimensions
Table 23. Dimensions for single blower roof curb model sizes 109–118
Model A B C D E
109 10-3/8” 1’ 0-3/8” 11-15/16” 11-3/4” 1’ 10-13/16”
264 314 303 298 579
112 1’ 1-9/16” 10-13/16” 1’ 3-15/16” 9-3/4” 1’ 8-13/16”
344 275 405 248 529
115 1’ 4” 9-5/8” 1’ 6-15/16” 8-3/8” 1’ 7-3/16”
406 244 481 213 487
118 1’ 7” 9-5/8” 1’ 10-1/16” 5-1/8” 1’ 7-5/16”
483 244 560 130 491
46 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 47

Roof curbs for 100% make-up air units
Figure 23. Double blower roof curb dimensions
DFOA
Table 24. Double blower roof curb dimensions for model sizes 215–230
Model A B C D E F G H J K
215 1’ 4” 9-5/8” 1’ 6-15/16” 5-1/8” 1’ 10-1/4” 1’ 11-1/4” 6’ 3” 5’ 11-1/2” 7’ 8” 7’ 4-1/2”
406 244 481 130 565 591 1905 1816 2337 2248
218 1’ 7” 9-5/8” 1’ 10-1/16” 5-1/8” 1’ 4” 1’ 11-1/4” 6’ 3” 5’ 11-1/2” 7’ 8” 7’ 4-1/2”
483 244 560 130 406 591 1905 1816 2337 2248
220 2’ 0-7/8” 10-7/16” 2’ 1-1/16” 9-5/8” 2’ 5-5/8” 2’ 11-1/8” 7’ 10” 7’ 6-1/2” 10’ 8” 10’ 4-1/2”
632 265 637 244 752 892 2388 2299 3251 3162
222 2’ 3-3/8” 10-7/16” 2’ 3-9/16” 9-5/8” 2’ 0-5/8” 2’ 11-1/8” 7’ 10” 7’ 6-1/2” 10’ 8” 10’ 4-1/2”
695 265 700 244 625 892 2388 2299 3251 3162
225 2’ 7-3/8” 1’ 2-13/16” 2’ 7-1/2” 1’ 0-5/8” 3’ 1-5/8” 2’ 11-1/4” 7’ 10” 7’ 6-1/2” 12’ 8” 12’ 4-1/2”
797 376 800 321 956 895 2388 2299 3861 3772
230 3’ 0-7/8” 1’ 2-13/16” 3’ 1” 1’ 0-5/8” 2’ 2-5/8” 2’ 11-1/4” 7’ 10” 7’ 6-1/2” 12’ 8” 12’ 4-1/2”
937 376 940 321 676 895 2388 2299 3861 3772
Notes:
1. Curb to be shipped loose and assembled in the field.
2. Curb must be square and level
3. Curb requires intermediate structural support and is not to be corner post mounted.
4. Gaskets to be shipped with unit.
5. Bolting accessories shipped with curb.
6. Curb drawings shown are for units which have controls on the “standard” side.
7. Available on horizontal units only.
MUA-PRC007-EN 47
Page 48

DFOA
Roof curbs for units with return air opening downsteam of burner
Figure 24. Roof curb dimensions for single blower models sizes 109–118
Table 25. Dimensions for roof curb single blower models sizes 109–118
Model A B C D E
109 10-3/8” 1’ 0-3/8” 11-15/16” 11-3/4” 1’ 10-13/16”
264 314 303 298 579
112 1’ 1-9/16” 10-13/16” 1’ 3-15/16” 9-3/4” 1’ 8-13/16”
344 275 405 248 529
115 1’ 4” 9-5/8” 1’ 6-15/16” 8-3/8” 1’ 7-3/16”
406 244 481 213 487
118 1’ 7” 9-5/8” 1’ 10-1/16” 5-1/8” 1’ 7-5/16”
483 244 560 130 491
48 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 49

Roof curbs for units with return air opening downstream of burner
Figure 25. Roof curb dimensions for double blower models sizes 215–230
DFOA
Table 26. Roof curb dimensions for double blower models sizes 215–230
Model A B C D E F G
215 1’ 4” 9-5/8” 1’ 6-15/16” 5-1/8” 1’ 10-1/4” 1’ 11-1/4” 6’ 3”
406 244 481 130 565 591 1905
218 1’ 7” 9-5/8” 1’ 10-1/16” 5-1/8” 1’ 4” 1’ 11-1/4” 6’ 3”
483 244 560 130 406 591 1905
220 2’ 0-7/8” 10-7/16” 2’ 1-1/16” 9-5/8” 2’ 5-5/8” 2’ 11-1/8” 7’ 10”
632 265 637 244 752 892 2388
222 2’ 3-3/8” 10-7/16” 2’ 3-9/16” 9-5/8” 2’ 0-5/8” 2’ 11-1/8” 7’ 10”
695 265 700 244 625 892 2388
225 2’ 7-3/8” 1’ 2-13/16” 2’ 7-1/2” 1’ 0-5/8” 3’ 1-5/8” 2’ 11-1/4” 7’ 10”
797 376 800 321 956 895 2388
230 3’ 0-7/8” 1’ 2-13/16” 3’ 1” 1’ 0-5/8” 2’ 2-5/8” 2’ 11-1/4” 7’ 10”
937 376 940 321 676 895 2388
Model H J K L M W
215 5’ 11-1/2” 7’ 8” 7’ 4-1/2” 5’ 5-3/4” 1’ 4-1/4” 1’ 2-1/4”
1816 2337 2248 1670 413 362
218 5’ 11-1/2” 7’ 8” 7’ 4-1/2” 5’ 5-3/4” 1’ 4-1/4” 1’ 2-1/4”
1816 2337 2248 1670 413 362
220 7’ 6-1/2” 10’ 8” 10’ 4-1/2” 7’ 3-3/8” 1’ 4-1/4” 1’ 2-1/4”
2299 3251 3162 2219 413 362
222 7’ 6-1/2” 10’ 8” 10’ 4-1/2” 7’ 3-3/8” 1’ 4-1/4” 1’ 2-1/4”
2299 3251 3162 2219 413 362
225 7’ 6-1/2” 12’ 8” 12’ 4-1/2” 9’ 3-3/8” 9-9/16” 1’ 8-1/4”
2299 3861 3772 2829 243 514
230 7’ 6-1/2” 12’ 8” 12’ 4-1/2” 9’ 3-3/8” 9-9/16” 1’ 8-1/4”
2299 3861 3772 2829 243 514
MUA-PRC007-EN 49
Page 50

DFOA
Roof curbs for units with mixing box
Figure 26. Roof curb dimensions for single blower units with mixing box
Table 27. Roof curb dimensions for single blower units with mixing box models sizes 109–118
Model A B C D E
109 10-3/8” 1’ 0-3/8” 11-15/16” 11-3/4” 1’ 10-13/16”
264 314 303 298 579
112 1’ 1-9/16” 10-13/16” 1’ 3-15/16” 9-3/4” 1’ 8-13/16”
344 275 405 248 529
115 1’ 4” 9-5/8” 1’ 6-15/16” 8-3/8” 1’ 7-3/16”
406 244 481 213 487
118 1’ 7” 9-5/8” 1’ 10-1/16” 5-1/8” 1’ 7-5/16”
483 244 560 130 491
50 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 51

Roof curbs for units with mixing boxes
Figure 27. Roof curb dimensions for double blower units with mixing box
DFOA
Table 28. Roof curb dimensions for double blower units with mixing box models sizes 215–230
Model A B C D E F G H J K L M
215 1’ 4” 9-5/8” 1’ 6-15/16” 5-1/8” 1’ 10-1/4” 1’ 11-1/4” 10’ 9” 10’ 5-1/2” 7’ 8” 7’ 4-1/2” 1’ 8-1/4” 7’ 0”
406 244 481 130 565 591 3277 3188 2337 2248 514 2134
218 1’ 7” 9-5/8” 1’ 10-1/16” 5-1/8” 1’ 4” 1’ 11-1/4” 10’ 9” 10’ 5-1/2” 7’ 8” 7’ 4-1/2” 1’ 8-1/4” 7’ 0”
483 244 560 130 406 591 3277 3188 2337 2248 514 2134
220 2’ 0-7/8” 10-7/16” 2’ 1-1/16” 9-5/8” 2’ 5-5/8” 2’ 11-1/8” 12’ 10” 12’ 6-1/2” 10’ 8” 10’ 4-1/2” 1’ 8-1/4” 10’ 0”
632 265 637 244 752 892 3912 3823 3251 3162 514 3048
222 2’ 3-3/8” 10-7/16” 2’ 3-9/16” 9-5/8” 2’ 0-5/8” 2’ 11-1/8” 12’ 10” 12’ 6-1/2” 10’ 8” 10’ 4-1/2” 1’ 8-1/4” 10’ 0”
695 265 700 244 625 892 3912 3823 3251 3162 514 3048
225 2’ 7-3/8” 1’ 2-13/16” 2’ 7-1/2” 1’ 0-5/8” 3’ 1-5/8” 2’ 11-1/4” 13’ 3” 12’ 11-1/2” 12’ 8” 12’ 4-1/2” 2’ 2-1/2” 12’ 0”
797 376 800 321 956 895 4039 3950 3861 3772 673 3658
230 3’ 0-7/8” 1’ 2-13/16” 3’ 1” 1’ 0-5/8” 2’ 2-5/8” 2’ 11-1/4” 13’ 3” 12’ 11-1/2” 12’ 8” 12’ 4-1/2” 2’ 2-1/2” 12’ 0”
937 376 940 321 676 895 4039 3950 3861 3772 673 3658
Notes:
1. Curb to be shipped loose and assembled in the field.
2. Curb must be square and level.
3. Curb requires intermediate structural support and is not to be corner post mounted.
4. Gaskets to be shipped with unit.
5. Bolting accessories shipped with curb.
6. Curb drawings shown are for units which have controls on the “standard” side.
7. Available on horizontal units only.
MUA-PRC007-EN 51
Page 52

DFOA
Approximate weights
Table 29. Unit weights in pounds (approximate)
Unit
Basic
Horizontal
Size
109 760 984 170 75 105 480 47 30 70 215 215 185 145
112 760 984 170 75 105 480 47 30 70 215 215 185 145
115 760 984 170 75 105 480 47 30 70 215 215 185 145
118 810 1034 170 75 105 480 47 30 70 225 225 200 160
215 1180 1607 275 135 175 700 80 100 150 342 342 274 222
218 1300 1727 275 135 175 700 80 100 150 378 378 311 233
220 2280 3179 320 200 230 980 111 145 215 625 625 555 475
222 2370 3269 320 200 230 980 111 145 215 675 675 545 475
225 2990 4135 500 275 340 1270 135 210 230 824 824 732 610
230 3130 4275 720 275 340 1270 135 210 230 863 863 731 673
Unit
Basic
Vertical
Unit
Inlet
Hood
Inlet
Damper
V-bank
Filter
Mixing
Box
Air Flow
Station
Discharge
Damper
Discharge
Louver A B C D
Table 30. Roof curb weights in pounds
Unit Sizes
Description
Roof Curb for Basic Frame—No Return Air 150 150 150 150 200 200 270 270 300 300
Roof Curb for Basic Frame—With Return Air Downstream of Burner 150 150 150 150 200 200 270 270 300 300
Roof Curb for Basic Frame—With Mixing Box Option 215 215 215 215 270 270 340 340 375 375
109 112 115 118 215 218 220 222 225 230
52 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 53

Figure 28. Inlet hood support (by others)
Inlet Hood Support (By Others)
• The purpose of hood support is to support the weight of the unit accessories which are attached
to the inlet of the basic unit.
• The hood support can be made from two, 2” x 2” x 1/4” angle iron.
• One angle iron support should be located in, or close to, the outer corners of the hood. The
supports can be bolted to the hood.
• The bottom of the angle iron support should be fitted with a base. The base can sit on the roof
and does not have to be fixed to the roof. An isolation pad may be put between the base and
the roof.
Model A B C
109–112 3’ 0” 3’ 11-1/4” 1’ 5-7/16”
115–118 3’ 0” 3’ 11-1/4” 1’ 10-7/8”
215–218 3’ 0” 7’ 7-1/2” 1’ 10-7/8”
220–222 4’ 0” 8’ 5-5/8” 2’ 7-1/4”
225–230 5’ 0” 10’ 1-3/8” 3’ 4-3/4”
DFOA
914 1200 443
914 1200 581
914 2324 581
1219 2581 794
1524 3083 1035
MUA-PRC007-EN 53
Page 54

Gas Piping
Figure 29. Gas piping
Table 31. Gas piping component identification
GP-01 High Gas Pressure Regulator VG-03 Auxiliary Gas Valve
GP-02 Main Gas Shut-off Valve VG-04 N/O Vent Valve
GP-09 Pilot Gas Pressure Regulator VG-07 Modulating Valve
GP-11 Main Test Firing Shut-off Valve PS-04 Low Gas Pressure Switch
GP-13 Pilot Gas Shut-off Valve PS-07 High Gas Pressure Switch
GP-27 Orificed Needle Valve PS-10 High Velocity Pressure Switch
VG-01 Pilot Gas Valve PS-11 Low Velocity Pressure Switch
VG-02 Main Gas Valve
Notes:
1. V ent limiting devices provided wherever possible, when venting is required; the venting to outside is by others on indoor
units and furnished by factroy on outdoor units.
2. Units with 900 MBh and less use a pressure regulator (not shown) for high fire setting.
3. 3,300 MBh and above will require a minimum inlet pressure of 1 psig. For inlet pressures under 1 psig, please consult
factory.
4. Units that are listed to the Z83.4 standard (100% Make-Up Air) carry both ETL and CETL approvals.
5. Standard manifold meets FM requirements for inputs under 2,500 MBh for ETL listed units
6. Standard manifold meets IRI requirements for ETL listed units.
7. High gas pressure regulator required if inlet pressure exceeds 1/2 psig for inputs up to and including 900 MBh or inlet
pressures over 5 psig for inputs greater than 900 MBh.
54 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 55

Table 32. Gas pressure regulator selection
If Burner Size (BS) Is: And Gas Pressure (GP) Is: Then:
BS < 2200 GP < 7 in. wc Call factory to verify availability and pricing
7 in. wc < GP < 10 in. wc Use low gas pressure burner
10 in. wc < GP < 14 in. wc No high gas pressure regulator required
14 in. wc < GP <1 psi Use high gas pressure regualtor 14 in. wc – 1 psi (shipped loose)
1 psi < GP < 5 psi Use high gas pressure regulator 1–5 psi (shipped loose)
5 psi < GP < 10 psi Use high gas pressure regulator 5–10 psi (shipped loose)
10 psi < GP < 50 psi Use high gas pressure regulator over 10 psi (shipped loos e)
50 psi < GP Call factory to verify availability and pricing
2475 < BS < 3025 GP < 10 in. wc Call factory to verify availability and pricing
10 in. wc < GP < 14 in. wc No high gas pressure regulator required
14 in. wc < GP < 1 psi Use high gas pressure regualtor 14 in. wc – 1 psi (shipped loose)
1 psi < GP < 5 PSI Use high gas pressure r egulator 1–5 psi (shipped loose)
5 psi < GP < 10 psi Use high gas pressure regulator 5–10 psi (shipped loose)
10 psi < GP < 50 psi Use high gas pressure regulator over 10 psi (shipped loos e)
50 psi < GP Call factory to verify availability and pricing
3300 < BS < 9075 GP < 1 psi Call factory to verify availability and pricing
1 psi < GP < 5 psi No high gas pressure regulator required
5 psi < GP < 10 psi Use high gas pressure regulator 5–10 psi (shipped loose)
10 psi < GP < 50 psi Use high gas pressure regulator over 10 psi (shipped loos e)
50 psi < GP Call factory to verify availability and pricing
Gas Piping
Examples of how to read the above:
• GP < 7 in. wc: Gas pressure less than 7 in. wc
• 7 in. wc <
•10in.wc <
GP < 10 in. wc: Gas pressure greater than or equal to 7 in. wc, and less than 10 in. wc
GP < 14 in. wc: Gas pressure greater than or equal to 10 in. wc, and less than or equal
to 14 in. wc
• 50 psi < GP: Gas pressure greater than 50 psi
MUA-PRC007-EN 55
Page 56

Gas Piping
Table 33. Gas piping connection size, standard gas train
Inlet gas pressure (inches of water column)
MBh
275 1 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4
550 1-1/4 1 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4
825 2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
1,100 2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
1,375 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
1,650 — 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
1,925 — 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
2,200 — 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
2,475 — 2 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
2,750 — 2 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
3,025——22222222
3,300——22222222
3,575———— 222222
3,850———— 222222
4,125———— 222222
4,400———— 222222
4,675———— 222222
4,950———— 222222
5,225———— 222222
5,500———— 222222
5,775———— 222222
6,050———— 222222
6,325————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
6,600————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
6,875————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
7,150————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
7,700————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
8,250————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
8,800————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
9,350———— 333333
7 8–11 12–14 15–20 21–27 1 psi 2 psi 3 psi 4 psi 5 psi
56 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 57

Gas Piping
Table 34. Gas pipe connection size, FM gas train
Inlet gas pressure (inches of water column)
MBh
275 1 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4
550 1-1/4 1 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4
8251-1/41-1/41 13/4—————
1,100 1 ½ 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
1,375 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
1,650 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
1,925 2 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
2,200 — 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
2,475 — 2 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
2,750 — 2-1/2 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
3,025—32———————
3,300 — 3 2-1/2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
3,575—————2 2 2 2 2
3,850—————2 2 2 2 2
4,125—————2 2 2 2 2
4,400—————2 2 2 2 2
4,675—————2 2 2 2 2
4,950—————2 ————
5,225—————2 ————
5,500—————2 ————
5,775—————2 ————
6,050—————2 ————
6,325—————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
6,600—————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
6,875—————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
7,150—————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
7,700—————2-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/22-1/2
8,250—————2-1/2————
8,800—————2-1/2————
9,350—————3 3 3 3 3
7 8–11 12–14 15–20 21–27 1 psi 2 psi 3 psi 4 psi 5 psi
MUA-PRC007-EN 57
Page 58

Gas Piping
Table 35. Gas pipe connection size, IRI gas train
Inlet gas pressure (inches of water column)
MBh
275 1 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4
550 1-1/4 1 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4 3/4
825 1-1/4 1-1/4 3/4 3/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
1,100 2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
1,375 2-1/2 2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
1,650 2-1/2 2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
1,925 2-1/2 2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
2,200 2-1/2 2 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
2,475 — 2 1-1/2 1-1/2 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
2,750 — 2-1/2 2 1-1/2 — 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/4
3,025—2-1/22———————
3,300—2-1/222222222
3,575 — — — — — 2 2 2 2 2
3,850 — — — — — 2 2 2 2 2
4,125 — — — — — 2 2 2 2 2
4,400 — — — — — 2 2 2 2 2
4,675 — — — — — 2 2 2 2 2
4,950 — — — — — 2 2 2 2 2
5,225 — — — — — 2 2 2 2 2
5,500 — — — — — 2 2 2 2 2
5,775—————2 ————
6,050 — — — — — 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2
6,325 — — — — — 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2
6,600 — — — — — 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2
6,875 — — — — — 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2
7,150 — — — — — 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2
7,700 — — — — — 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2
8,250 — — — — — 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2 2-1/2
8,800—————2-1/2————
9,350 — — — — — 3 3 3 3 3
7 8–11 12–14 15–20 21–27 1 psi 2 psi 3 psi 4 psi 5 psi
58 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 59

Electrical Power
Table 36. Motor electrical data
hp
1/3 7.2 4 3.6 1.4 1.6 0.7
1/2 9.8 5.4 4.9 2.4 2.2 1.1
3/4 13.8 7.6 6.9 3.5 3.2 1.6
1 16 8.8 8 4.6 4.2 2.1
1-1/2 20 11 10 6.6 6 3
2 24 13.2 12 7.5 6.8 3.4
3 34 18.7 17 10.6 9.6 4.8
5 56 30.8 28 16.7 15.2 7.6
7-1/2 — — — 24.2 22 11
10 — 55 — 30.8 28 14
15 — — — 46.2 42 21
20 — — — 59.4 54 27
25 — — — 74.8 68 34
30 — — — 88 80 40
40 — — — 114 104 52
50 — — — 143 130 65
60 — — — 169 154 77
Notes:
1. Amps taken from table 430-148 (singl e phase) an d 430-150(three p hase) of the 2002 ed ition of NEC. Actual motor amps
are dependent on motor type and will be on name plate.
2. For units without a service receptacle: MCA = (Motor FLA*1.25) + (500VA transformer amps)
3. For units with a service receptable: MCA = (Motor FLA*1.25) + (500V A tr ansformer amps) + (1000V A transformer amps)
Table 37. Primary voltage
Single Phase Three Phase
115 208 230 208 230 460
115 208 230 460
500 VA 4.3 2.4 2.2 460
1000 VA 8.6 4.8 4.3 2.2
MUA-PRC007-EN 59
Page 60

Options
Motorized 75/25 Damper
Purpose
To provide a way for recirculating return air and letting building pressure control the amount of air
which is recirculated.
Operation
If building pressure is less than desired, the RA damper modulates to a more closed position and
the interlocked burner profile damper modulates to a more open position. More OA is brought into
building.
If building pressure is greater than desired, the RA damper modulates to a more open position and
the interlocked burner profile damper modulates to a more closed position. Less OA is brought into
building.
At no time will the unit provide less than 25 percent OA to the building. In general terms, the
minimum OA is 25 percent; however, there are cases where it can be as high as 40–50 percent,
depending upon unit size, burner size, gas train type and gas pressure.
Code requires that outside ventilation air be provided to the space in the amount of 4 cfm per 1 MBh
of burner rated input.
All units are provided with a means that will allow the customer to interlock OA fans when the
amount of OA provided by the unit is not sufficient to meet the 4 cfm per 1 MBh requirement.
Notes:
•
• This option can be used with either the Motorized Inlet Damper option or the Motorized Outlet
Damper option.
Option Includes:
• Return air section with damper
• Burner profile damper
•Linkage
• Modulating damper motor(s)
• Photohelic differential pressure gauge
Figure 30. Motorized 75/25 damper
60 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 61

Mixing Box—Temperature Control
Purpose
To provide a way for recirculating return air and letting mixed air temperature determine the
amount of OA/RA.
Operation
A temperature sensor located after the V-bank filter modulates the OA and RA dampers to maintain
a set temperature.
If temperature at sensor is cooler than setting, OA damper modulates to a more closed position,
and RA damper modulates to a more open position.
If temperature at sensor is warmer than setting, OA damper modulates to a more open position,
and RA damper modulates to a more closed position.The minimum OA damper position is factory
set at 25 percent supply air.
The desired temperature at the temperature sensor is set at the control cabinet at the unit.
Option Includes:
• Inlet damper
• Return air section with damper
• Modulating damper motor(s)
• V-bank filter with throwaway filters (DFIA)/Permanent (DFOA)
• Temperature sensor
Options
Figure 31. Mixing box—Temperature control
Mixing Box—Manual Control
Purpose
To provide a way for recirculating return air and using manual control to determine the amount of
OA/RA .
Operation
A manual potentiometer located at the remote control station determines the OA/RA setting. The
minimum OA damper position is factory set with a potentiometer. The minimum OA damper
opening is set at 4 cfm per 1 MBh of burner rated input, or 25 percent supply air, whichever is larger.
Options Include:
• Mixing box with V-bank filter and permanent filters (DFOA)/TA (DFIA)
MUA-PRC007-EN 61
Page 62

Options
•Dampers
• Modulating damper motor(s)
• Manual potentiometerRemote control station not included.
Figure 32. Mixing box—Manual control
Purpose
To provide a way for recirculating return air and using manual control to determine the amount of
OA/RA .
Operation
A manual potentiometer located at the remote control station determines the OA/RA setting. The
minimum OA damper position is factory set with a potentiometer. The minimum OA damper
opening is set at 4 cfm per 1 MBh of burner rated input, or 25 percent supply air, whichever is larger.
Options Include:
• Mixing box with V-bank filter and permanent filters (DFOA)/TA (DFIA)
•Dampers
• Modulating damper motor(s)
• Manual potentiometer
Note: Remote control station not included.
62 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 63

Mixing Box—Building Pressure Control
Purpose
To provide a way for recirculating return air and letting building pressure control the amount of air
which is recirculated.
Operation
If building pressure is less than desired, the RA damper modulates to a more closed position and
the OA damper modulates to a more open position. More OA is brought into building.
If building pressure is greater than desired, the RA damper modulates to a more open position and
the OA damper modulates to a more closed position. Less OA is brought into building.
The minimum OA damper position is factory set with a potentiometer. The minimum OA damper
position is set at 4 cfm per 1 MBh of burner rated input, or 25 percent supply air, whichever is larger.
The desired pressure differential is set at the photohelic.
Options Include:
• Mixing box with V-bank filter and permanent filters (DFOA)/TA (DFIA)
•Dampers
• Modulating damper motor(s)
• Photohelic differential pressure gauge
Options
Figure 33. Mixing box—Building pressure control
Motorized Inlet Damper
Purpose
To provide a shut-off damper.
Operation
When the fan switch is on, the inlet damper begins to open. As the inlet damper approaches the
full open position, a built-in end switch located inside the damper motor closes. The closed end
switch starts the fan motor. When the fan switch is turned to the “off” position, or if there is a power
failure, the inlet damper closes.
MUA-PRC007-EN 63
Page 64

Options
Option Includes:
•Damper
• Two position damper motor(s) with built-in end switch and spring return
•Linkage
Figure 34. Motorized inlet damper
Exhaust Interlock
The exhaust interlock is a pair of contacts on the unit that will close when the unit is “on.” The
customer can wire the exhaust fan to the contacts so that when the heating unit is “on,” the exhaust
fan will also be “on.” Note the heating unit turns on the exhaust fan.
The auxiliary contacts on the fan motor starter are the contacts which are used as the exhaust
interlock. The auxiliary contacts are wired to the numbered terminal strip. The customer can wire
the indicated terminals into the control circuit of the exhaust fan.
Note: If the customer wants the exhaust fan to turn the heating unit “on,” he/she has to provide
a pair of contacts that will close when the exhaust fan is “on.”
Interlocking Relay
The interlocking relay is two pair of contacts, one normally open and the other normally closed.
The contacts switch positions when the unit is “on.” The contacts are wired to the numbered
terminal strip. The customer can wire a wide range of devices to the interlocking relay by wiring
to the indicated terminals.
Seven-Day Timeclock/Night Setback Thermostat
The seven-day timeclock is used primarily for either one of the following:
1. Start and stop the unit at preset times.
Example: A building is occupied at 8:00 AM. At 4:30 PM, people leave the building. The
timeclock could be set to turn the unit on at 7:30 AM and off at 5:00 PM.
2. The timeclock can be used with an on-off night setback thermostat (NSB thermostat. The
timeclock and NSB thermostat would be wired so that during the night, the NSB thermostat
would turn the unit on and off.
Example: Same as example above, only at 5:00 PM the NSB thermostat would turn the unit on
and off. If the temperature in the space fell below the setting of the NSB thermostat, the unit
would come “on.” If the temperature rose above the setting, the unit would go “off.”
Inlet On-Off Duct Stat
Automatically turns burner off when inlet air temperature equals setting of control. Works as a
lockout for the burner.
64 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 65

Example: If we want the burner to be “off” if the entering air temperature is 65 degrees, the inlet
on-off duct stat would be set at 65 degrees.
Without the inlet on-off duct stat, if the fan switch and heat switch are both “on,” no matter how
warm the incoming air, the burner will go as low as low fire, but will not go “off.”
UV Flame Sensor (UV Mini-Peeper)
Flame sensor checks to make sure the pilot flame has ignited before gas is sent to the main burner.
Operates by sensing the light of the pilot flame.
If the flame sensor does not sense the pilot flame, the unit shuts down (fan and burner go off) and
the flame failure light on the optional remote panel goes on.
The unit has to be reset by pushing the reset button on the burner relay.
Differences between UV Flame Sensor and Flame Rod:
Both are used for the same purpose — to check if the pilot flame is on. The flame rod is “standard.”
The UV sensor needs to be ordered as an option.
If condensation forms on the flame rod while the unit is off, it may give a false signal and prevent
the unit from coming on. The wet flame rod does not sense the pilot flame and shuts the unit down.
This nuisance tripping can be avoided with the UV flame sensor.
Optional Gas Controls
Options
Constant Discharge Temperature
The constant discharge temperature, gas modulating control system consists of electronic gas
modulating system (40°F to 90°F range), which includes a discharge air sensor located in the blower
discharge, a modulator/regulator valve mounted in the gas piping manifold, an amplifier installed
in the electrical control panel, a 115 to 24 volt transformer, and a remote temperature selector.
Series 44 — Space Temperature Control
The space temperature control, gas modulating control system consists of the Maxitrol electronic
gas modulating system, which includes a Series 44 discharge air sensor (55°F to 90°F range)
mounted in the blower discharge, a modulator regulator valve mounted in the gas piping manifold,
an amplifier installed in the electric control panel, a 115 volt to 24 volt transformer, and a
Selectrastat mounted in the area where the temperature is to be sensed.
Factory Installed Options
Motors—General
All motors are provided as standard, with a starter for external overload protection, a control
transformer, and an on-fused disconnect switch.
Open Drip-Proof Motor, 60 Hz/1800 Rpm
Single Phase
Optional 115V motors are available in 3/4 hp to 3 hp models. Optional 208V motors are available
in 3/4 hp to 7-1/2 hp models. Optional 230V motors are available in 3/4 hp to 10 hp models. All
motors have rigid base construction and ball bearings. Class A insulation is on all motors up to and
including 3 hp models. Class B insulation is on 5 hp and above models.
Three-Phase
Optional 208V, 230V, 460V available in 1 hp to 60 hp models. All models have rigid base
construction and ball bearings. Class B insulation is on all three-phase motors.
MUA-PRC007-EN 65
Page 66

Options
Energy Efficient ODP 60 Hz/1800 Rp Three-Phase Only
Optional 208V motors are available in 1 hp to 30 hp models. 230V and 460V motors are available
in 1 hp to 60 hp models. All motors have rigid base construction and ball bearings. Class B
insulation is on all motors.
Totally Enclosed Motor, 60 Hz/1800 Rpm
Three-Phase Only
Optional 208V motors are available in 3/4 hp to 20 hp models. Optional 230V and 460V motors are
available in 3/4 hp to 60 hp models. All motors have rigid base construction and ball bearings.
Energy Efficient TEFC, 60 Hz/1800 Rpm
Three-Phase Only
Optional 208V motors are available in 1 hp to 30 hp models. 230V and 460V motors are available
in 1 hp to 60 hp models. All motors have rigid base construction and ball bearings. Class B
insulation is on all motors.
wo-Speed/One Winding Motors, 60 Hz/1800/900 Rpm
Three-Phase Only
Optional 208V and 230V motors available on 1 hp to 20 hp models. Optional 460V motors are
available on 1 hp to 50 hp models. All motors have rigid base construction and ball bearings.
Class B insulation is on all motors.
Two-Speed/Two Winding Motors, 60 Hz/1800/1200 Rpm
Three-Phase Only
Optional 208V and 230V motors available on 1 hp to 20 hp models. Optional 460V motors are
available on 1 hp to 50 hp models. All motors have rigid base construction and ball bearings.
Class B insulation is on all motors.
Additional Options*
Inlet Hood and Birdscreen (DFOA only)
Hood constructed of 18-gauge galvanized steel. Birdscreen is 18-gauge galvanized steel with
one-inch square openings.
V-Bank Filter Section
Not required when a mixing box is specified. Constructed of 18-gauge galvanized steel.
Dampers and Mixing Box
Motorized Return Air Damper
This option provides a way to recirculate air, with the return air opening downstream of the burner.
This option includes return air damper, a two-position damper motor, linkage and damper switch.
It is not available with two-speed motors.
Motorized 75/25 Damper
This option provides a way for recirculating return air and allows building pressure to control the
amount of air that is recirculated. This option includes a return air damper, burner profile plate
damper, damper linkage, and modulating pressure controller. It is not available with two-speed
motors.
66 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 67

Options
Mixing Box—Temperature Control
This option provides a way for recirculating return air and allows mixed air temperature to
determine the amount of OA/RA. This option includes mixing box with filter section, dampers,
damper actuator(s), and damper controls.
Mixing Box—Building Pressure Control
This option provides a way for recirculating return air and allows building pressure to control the
amount of air which is recirculated. This option includes a mixing box with filter section, dampers,
damper actuator(s), and damper controls (including a photohelic differential pressure gauge).
Mixing Box—Manual Control
This option provides a way for recirculating return air and using manual control to determine the
amount of OA/RA. This option includes a mixing box with filter section, dampers, damper
actuator(s), and a manual potentiometer.
Motorized Inlet Damper Option
This option provides a shutoff damper. On DFIA models, this option includes an outside air damper,
damper motor with built-in end switch, and linkage. It is not available with a mixing box.
On DFOA models, this option includes an outside air damper, two-position damper motor with a
built-in end switch, and linkage. It is not available with a mixing box.
Motorized Outlet Damper (DFOA)
This option provides a shut off damper and includes a discharge damper, two-position damper
motor with built-in end switch, and linkage.
Note: Based on unit design, some options can ship factory-installed or field-installed. Contact the
factory for verification.
Additional Factory Installed Options
Insulation
One-inch, 1-1/2 lb fiberglass insulation pin spotted to casing.
Internal Blower/Motor Isolation (DFOA only)
This option includes a steel frame for blower(s) and fan motor with spring type vibration isolators.
It is not available on vertical units.
Extended Grease Lines (DFOA only)
This option allows lubrication of fan bearings from the control side of the unit.
Controls Opposite from Standard
Applicable only to horizontal configurations. Locates controls, gas piping and fan motor on
opposite side of the unit.
115V Duplex Receptacle
This option includes a transformer and disconnect switch for the receptacle. Components are
mounted in the gas piping manifold, on DFOA units, and on the controls side of unit on DFIA
models.
UV Flame Sensor
The flame sensor checks to make sure the pilot flame has ignited before gas is sent to the main
burner. It operates by sensing the light of the pilot flame.
MUA-PRC007-EN 67
Page 68

Options
Clogged Filter Switch
This option includes a pressure sensing switch which senses the pressure drop across the filters.
When the pressure drop reaches the setpoint, the switch trips and lights the clogged filter light. It
is not required when City of Chicago controls are ordered.
Exhaust Fan Interlock
This option includes a pilot duty rated normally open contact on the main supply fan motor starter
that will close simultaneously with the starter (10 amp contacts).
Interlocking Relay
This option is energized by an auxiliary contact on the supply fan motor starter that can be used
for additional equipment that may need to run when the supply fan is running (12 amp contacts).
Painted Blower Section
Painted Burner Section
Painted Return Air Section
Painted Filter Section
Field Installed Accessories
Vibration Feet
Rubber-in-shear vibration isolators cannot be ordered with a roof curb – they ship unmounted.
DFIA models:
Vibration Feet—Filter Section
Vibration Feet—Blower Section
Vibration Feet—Burner Section
Vibration Feet—Return Air Section
DFOA models:
Vibration Feet—Basic Frame
Vibration Feet—Filter Section
Vibration Feet—Mixing Box
Vibration Hangers (DFIA models only)
Option includes rubber-in-shear vibration isolators, shipped unmounted.
Vibration Hangers—Blower Section
Vibration Hangers—Burner Section
Vibration Hangers—Return Air Section
Vibration Hangers—Filter Section
Seven-Day Time Clock
100 DBL Alarm Horn and Silencing Switch
To silence the alarm, the push button silencing switch is pushed.
68 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 69

Options
Remote Control Station
On-Off Night Setback Thermostat
This option will shut unit off when space temperature is above setpoint. This is a 115V thermostat
with a temperature range of 50°F to 80°F. Option is normally used together with the seven-day
timeclock option.
High Gas Pressure Regulator
Specify inlet pressure at the unit. This is required for selection of the regulator.
Roof Curbs (DFOA models only)
Roof curbs are fabricated of 12-gauge galvanized steel. Curb gasket is provided. The 12-inch high
roof curbs ship disassembled.
Roof Curb For Basic Frame —. No return air
Roof Curb For Basic Frame —. With return air downstream of the burner
Roof Curb For Basic Frame —. With mixing box option
Discharge Louver—Horizontal Vanes Adjustable Side Inlet
Discharge Louver—Horzontal Vanes, Adjustable, Top Inlet (DFOA models only)
MUA-PRC007-EN 69
Page 70

Mechanical Specifications
DFIA Unit Casing
DFIA cabinets are designated for indoor use. Unit casing and accessories shall be fabricated from
heavy-gauge bright spangled galvanized steel suitably reinforced to insure rigidity. All casings
shall be air tight. Complete access shall be provided to all components. This includes the blower,
burner, and electrical components.
DFOA Unit Casing
Unit casing and accessories shall be fabricated from heavy-gauge galvanized steel suitably
reinforced to insure rigidity. The base of the unit shall be adaptable for curb mounting. All casings
shall be airtight and weatherproof. Roof panels shall be convex to prevent ponding, and designed
with roof eaves to prevent water from getting into wall panels. Complete access shall be provided
to all components through gasketed, hinged access doors. This includes the motor, blower, burner,
elctrical components and manifold sections.
Fans
Supply fans are double width, double inlet centrifugal type with FC fan wheels. Fans are tested in
accordance with AMCA 210.
The fan or fans are mounted on a steel shaft designed for a maximum operating speed not to
exceed 75 percent of its first critical speed.
Bearings are external heavy duty industrial prelubricated type. Bearing life is 100,000 hours.
Blowers are driven by a V-belt package sized with a capacity of 25 percent greater than the motor
horsepower.
Multiple belt applications will be matched sets.
Drives are adjustable pitched diameter type up through 7-1/2 hp, fixed on motors over 7-1/2 hp.
DFIA motors are externally mounted on an adjustable slide base. Belt guard shall be provided for
DFIA units.
Burner Section
The burner section contains a burner constructed of rust resistant cast iron bodies (which serve
as the gas manifold) drilled to discharge the fuel between diverging stainless steel mixing plates.
The entire burner assembly is mounted directly in the air stream being heated. The fresh air stream
passes through the mixing plates and mixes with the fuel as combustion air: thus all available heat
from the gaseous fuel is released directly into the air stream. Air velocities across the burner
assemblies are established by the use of profile plates.
The manifold is located outside of air stream and in DFOA models is also shielded from
atmospheric conditions by means of a protective compartment with hinged access. An observation
port shall be located to provide view of pilot and main flame.
Units are supplied with a wide range burner with a modulating turndown ratio of 25 to 1.
Adjustable profile plates are provided and sized to maintain the required velocity across the line
burner. The operation of the burner is programmed through the flame safeguard with timed
prepurge and flame sensing.
The burner assembly and gas manifold are completely prepiped and factory tested prior to
shipment.
Control Enclosure
Units are provided with a control compartment. All controls mounted within this compartment are
to be wired to a numbered terminal strip. All wiring is to be color coded and in accordance with
NEC. A circuit diagram of the approved electrical drawing is laminated to the inside of the control
cabinet door. All electrical components bear the UL label.
70 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 71

Mechanical Specifications
FM for ETL Listed Units
For installations with ETL labeled units requiring Factory Mutual (FM) insurance. The standard
manifold meets FM requirements for ETL labeled units with 2475 MBh input or less. Units over
2475 MBh input will have motorized shut-off valves with visual indicator and high/low gas pressure
switch.
IRI for ETL Listed Units
For installations with ETL labeled units requiring Industrial Risk Insurers (IRI) insurance. The
standard manifold meets IRI requirements for all ETL labeled units
Block and Bleed Manifold
The block and bleed manifold consists of a manual main gas shutoff valve, a two motorized electric
main gas shut-off valves with visual indicator and proof of closure with electrical interlock, a
normally open vent valve, the Maxitrol modulating gas valve, a manual pilot gas shutoff valve, a
manual pilot gas pressure regulator, a pilot gas valve, an orifice needle valve, and a high/low gas
pressure switch. Can be used for installations with unlisted units requiring Industrial Risk Insurers
(IRI) insurance.
Modulating Room Temperature (MRT) Control System
The Modulating Room Temperature (MRT) control system controls the space temperature and
consists of setpoints for room temperature and both minimum and maximum discharge air
temperature and the unit DDC Controller with full BACnet
modulator/regulator gas valve, an inlet air sensor, a discharge air sensor, and a remote control
panel. The remote control panel consists of a remote mounted 3 gang box cover with a manual
potentiometer to enable unit and adjust leaving air temperature setpoint, Fan On light, Burner On
light, and Cool On light. The features of the DDC Controller will also include timed freeze protection,
and inlet on-off ductstat.
®
compatibility, a signal conditioner, a
Modulating Discharge Temperature (MDT) Control System
The Modulating Discharge Temperature (MDT) control system consists of the unit DDC Controller
with full BACnet® compatibility, a signal conditioner, a modulator/regulator gas valve, an inlet air
sensor, a discharge air sensor, and a remote control panel. The remote control panel consists of
a remote mounted 3 gang box cover with a manual potentiometer to enable unit and adjust leaving
air temperature setpoint, Fan On light, Burner On light, and Cool On light. The features of the DDC
Controller will also include timed freeze protection, and inlet on-off ductstat.
Modulating Room Temperature Pro (MRT Pro) Control System
The Modulating Room Temperature Pro (MRT Pro) control system controls the space temperature
and a unit DDC Controller with full BACnet
regulator gas valve, an inlet air sensor, a discharge air sensor, and a space temperature thermostat
where room temperature can be sensed and set. In addition to allowing the user to control the room
setpoint temperature the room sensor also allows over ride timing and display of current heating
and cooling setpoints, fan status, and outside air temperature. The features of the DDC Controller
will also include timed freeze protection and an inlet on-off ductstat.
®
compatibility, a signal conditioner, a modulator/
Modulating Room Temperature Expert (MRT Expert) Control System
The Modulating Room Temperature Expert (MRT Expert) control system controls the space
temperature and consists of setpoints for room temperature and both minimum and maximum
discharge air temperature and the unit DDC Controller with full BACnet
conditioner, a modulator/regulator gas valve, an inlet air sensor, a discharge air sensor, and a space
temperature sensor and a BACview
DDC Controller will also include timed freeze protection, inlet on-off ductstat, electronic time clock
with normal, holiday, and override schedules, and on-off night setback thermostat.
®
controller for remote keyboard display. The features of the
®
compatibility, a signal
MUA-PRC007-EN 71
Page 72

Mechanical Specifications
The display functions of the BACview keypad display with a minimum of four lines, sixteen
characters will include the following:
Table 38. Display functions of the BAVview keypad
Display Functions: Critical Alarm Conditions: BACview® Control Settings:
Return air temperature Airflow switch failure Heating setpoint
Outside air temperature Unit on, fan off Cooling setpoint
Discharge air temperature Unit off, fan on Economizer setpoint
Mixed air temperature Low discharge temperature Setback setpoint
Maximum allowable temperature rise Safety circuit open Freeze protection setpoint
Actual temperature rise Burner jumped Maximum discharge air temperature setpoint
Current percent of outside air Minimum ventilation opt ion and setpoint
Current building pressure Time of day schedule selection and setpoints
Current damper input voltage
Current burner input voltage
Fan operating hours since last reset
Fan start cycle count since last reset
Burner operating hours since last reset
Burner start cycle count since last reset
Cooling interlock operating hours since last reset
Cooling interlock cycle count since last reset
Gas Train Approvals
The standard gas train consists of a main manual gas shutoff valve, a motorized electric main gas
valve, modulating gas valve, a manual pilot gas shutoff valve, a manual pilot gas pressure
regulator, a pilot gas valve, an orificed needle valve and auxiliary gas valve.
The Factory Mutual (FM) gas train consists of a manual main gas shutoff valve, a motorized electric
main gas valve, modulating gas valve, a manual pilot gas shut-off valve, a manual pilot gas
pressure regulator, a pilot gas valve, an orificed needle valve, a high/low gas pressure switch, a
manual auxiliary gas shutoff valve, and an auxiliary gas valve. (Optional)
Note: The standard gas train meets FM requirements for inputs under 2500MBh for ETLlisted
units.
The Industrial Risk Insurers (IRI) gas train consists of a manual main gas shutoff valve, a motorized
electric main gas valve, modulating gas valve, a manual pilot gas shutoff valve, a manual pilot gas
pressure regulator, a pilot gas valve, an orificed needle valve, a high/low gas pressure switch, a
manual auxiliary gas shutoff valve, a normally open vent valve, and an auxiliary gas valve.
(Optional)
Note: The standard gas train meets IRI requirements for ETL listed units.
72 MUA-PRC007-EN
Page 73

www.trane.com
For more information, contact your local Trane
office or e-mail us at comfort@trane.com
Literature Order Number MUA-PRC007-EN
Date November 2009
Supersedes MUA-PRC007-EN (March 2007)
Trane has a policy of continuous product and product data improvement and reserves the right to
change design and specifications without notice. Only qualified technicians should perform the
installation and servicing of equipment referred to in this literature.
 Loading...
Loading...