Page 1

Configuration Guide
Wireless Controller
AC50/AC500
1910012437 REV1.0.2
June 2018
Page 2

Content
About This Guide .................................................................................................................. 1
1 Quick Start ....................................................................................................................... 2
1.1 Determine the Network Topology ............................................................................................................ 2
1.1.1 Manage CAPs in the LAN ................................................................................................................................ 2
1.1.2 Manage CAPs in Different Network Segment ..................................................................................... 3
1.2 Log In to the AC ............................................................................................................................................... 3
1.2.1 Preparations ........................................................................................................................................................... 3
1.2.2 Log In .......................................................................................................................................................................... 4
2 Status ................................................................................................................................ 7
2.1 System Status .................................................................................................................................................. 7
2.2 Client Status ...................................................................................................................................................... 8
2.3 AP Status ............................................................................................................................................................ 9
2.4 Authentication Status ................................................................................................................................. 10
2.4.1 Authentication Status ....................................................................................................................................10
2.4.2 Non-sense Authenticated User ...............................................................................................................11
3 Network ..........................................................................................................................12
3.1 Interface........................................................................................................................................................... 12
3.2 DHCP Server .................................................................................................................................................. 13
3.2.1 DHCP Server ....................................................................................................................................................... 13
3.2.2 DHCP Client List ................................................................................................................................................ 15
3.2.3 Address Reservation ...................................................................................................................................... 15
3.3 VLAN ................................................................................................................................................................. 16
3.3.1 VLAN ........................................................................................................................................................................ 16
3.3.2 Ports .........................................................................................................................................................................18
3.3.3 Relations ................................................................................................................................................................ 19
3.4 Switch ............................................................................................................................................................... 20
3.4.1 Statistics ................................................................................................................................................................ 20
3.4.2 Mirror .......................................................................................................................................................................21
3.4.3 Rate Control .........................................................................................................................................................21
Page 3

3.4.4 Port Config ...........................................................................................................................................................22
3.4.5 Port Status ............................................................................................................................................................23
4 AP Control ......................................................................................................................24
4.1 AP Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 24
4.2 AP Firmware Upgrade ................................................................................................................................. 27
4.3 AP Database ................................................................................................................................................... 28
4.4 Load Balancing .............................................................................................................................................. 29
5 Radio ................................................................................................................................ 31
5.1 Radio Settings ............................................................................................................................................... 31
5.2 Rate Settings ................................................................................................................................................. 34
5.3 Band Steering ................................................................................................................................................ 36
5.4 Wi-Fi Roaming ............................................................................................................................................... 37
6 Wireless .......................................................................................................................... 39
6.1 Wireless Service ........................................................................................................................................... 39
7 Authentication ..............................................................................................................43
7.1 MAC Authentication .................................................................................................................................... 43
7.1.1 MAC Address ......................................................................................................................................................44
7.1.2 MAC Authentication ........................................................................................................................................ 45
7.2 Portal Authentication .................................................................................................................................. 46
7.2.1 Splash Page ......................................................................................................................................................... 47
7.2.2 Web Authentication ........................................................................................................................................49
7.2.3 Onekey Online .................................................................................................................................................... 53
7.2.4 Voucher..................................................................................................................................................................54
7.2.5 SMS .......................................................................................................................................................................... 56
7.2.6 Facebook ..............................................................................................................................................................58
7.2.7 Remote Portal ..................................................................................................................................................... 60
7.3 Local User Management ........................................................................................................................... 64
7.4 Voucher Management ................................................................................................................................ 68
7.4.1 Create Voucher .................................................................................................................................................68
7.4.2 Manage Voucher ..............................................................................................................................................69
7.5 Authentication Server ................................................................................................................................ 69
Page 4

7.5.1 Radius Server ...................................................................................................................................................... 70
7.5.2 Authentication Server Group ..................................................................................................................... 71
7.6 Authentication Config ................................................................................................................................ 72
7.6.1 Free Authentication Policy .......................................................................................................................... 72
7.6.2 Authentication Parameters ......................................................................................................................... 75
7.7 Applications ................................................................................................................................................... 75
7.7.1 Application for Web Authentication ....................................................................................................... 75
7.7.2 Application for Onekey Online ..................................................................................................................80
7.7.3 Application for Voucher ................................................................................................................................ 81
7.7.4 Application for SMS ........................................................................................................................................85
7.7.5 Application for Facebook ............................................................................................................................. 88
7.7.6 Application for Remote Portal ................................................................................................................... 91
8 Link Backup ................................................................................................................... 94
8.1 Dual-link Backup ........................................................................................................................................... 94
8.2 Application ...................................................................................................................................................... 95
9 System Tools ................................................................................................................ 98
9.1 Account ............................................................................................................................................................ 98
9.1.1 Administrator Account .................................................................................................................................. 98
9.1.2 Operator Account ............................................................................................................................................ 99
9.1.3 System Settings ................................................................................................................................................ 99
9.2 Administration .............................................................................................................................................100
9.2.1 Factory Default Restore ............................................................................................................................. 100
9.2.2 Backup & Restore .......................................................................................................................................... 100
9.2.3 Reboot ................................................................................................................................................................. 101
9.2.4 Firmware Upgrade ......................................................................................................................................... 102
9.3 Traffic Statistics ..........................................................................................................................................102
9.4 Diagnostics ...................................................................................................................................................103
9.5 Time Settings ...............................................................................................................................................104
9.6 System Log...................................................................................................................................................107
Page 5

About This Guide
This Configuration Guide provides information for managing AC500/AC50 Series Wireless
Controller. Please read this guide carefully before operation.
Intended Readers
This Guide is intended for network managers familiar with IT concepts and network
terminologies.
Conventions
When using this guide, please notice that features of the device may vary slightly
depending on the model and software version you have. All screenshots, images,
parameters and descriptions documented in this guide are used for demonstration only.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has
been made in the preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but
all statements, information, and recommendations in this document do not constitute
the warranty of any kind, express or implied. Users must take full responsibility for their
application of any products.
In this Guide, the following conventions are used:
Notes contains suggestions or references that helps you make better use of your device.
For GUI, Menu Name > Submenu Name > Tab page indicates the menu structure. Network >
DHCP Server > DHCP Client List means the DHCP Client List page under the DHCP Server
menu option that is located under the Network menu.
Bold font indicates a button, a toolbar icon, menu or menu item.
More Information
The latest software and documentations can be found at Download Center at https://
www.tp-link.com/support.
The Installation Guide (IG) can be found where you find this guide or inside the package
of the wireless controller.
Specifications can be found on the product page at https://www.tp-link.com.
A Technical Support Forum is provided for you to discuss our products at https://forum.
tp-link.com.
Our Technical Support contact information can be found at the Contact Technical
Support page at https://www.tp-link.com/support.
1
Page 6
1
Wireless Controller
IP: 192.168.0.200/24
Quick Start
The wireless controller (AC) is a device used for centralized management of access points
(APs). At present, the supported APs are TP-Link’s CAPs. The AC can configure CAPs
in batches using a web browser and conduct a real-time monitoring of each CAP in the
network. This AC supports AP automatic discovery, AP status monitoring, AP centralized
control, MAC filtering, radio management, load balance, dual-link backup and various
authentication types.
This wireless controller makes it easier to configure and manage dozens or hundreds of
CAPs in a large public environment, such as markets, hotels, companies and campuses,etc.
AC500 wireless controller supports to manage 500 CAPs at the same time and AC50
wireless controller supports 50 CAPs.
1.1 Determine the Network Topology
You can use the AC to centrally manage the CAPs in the same or different network
segment.
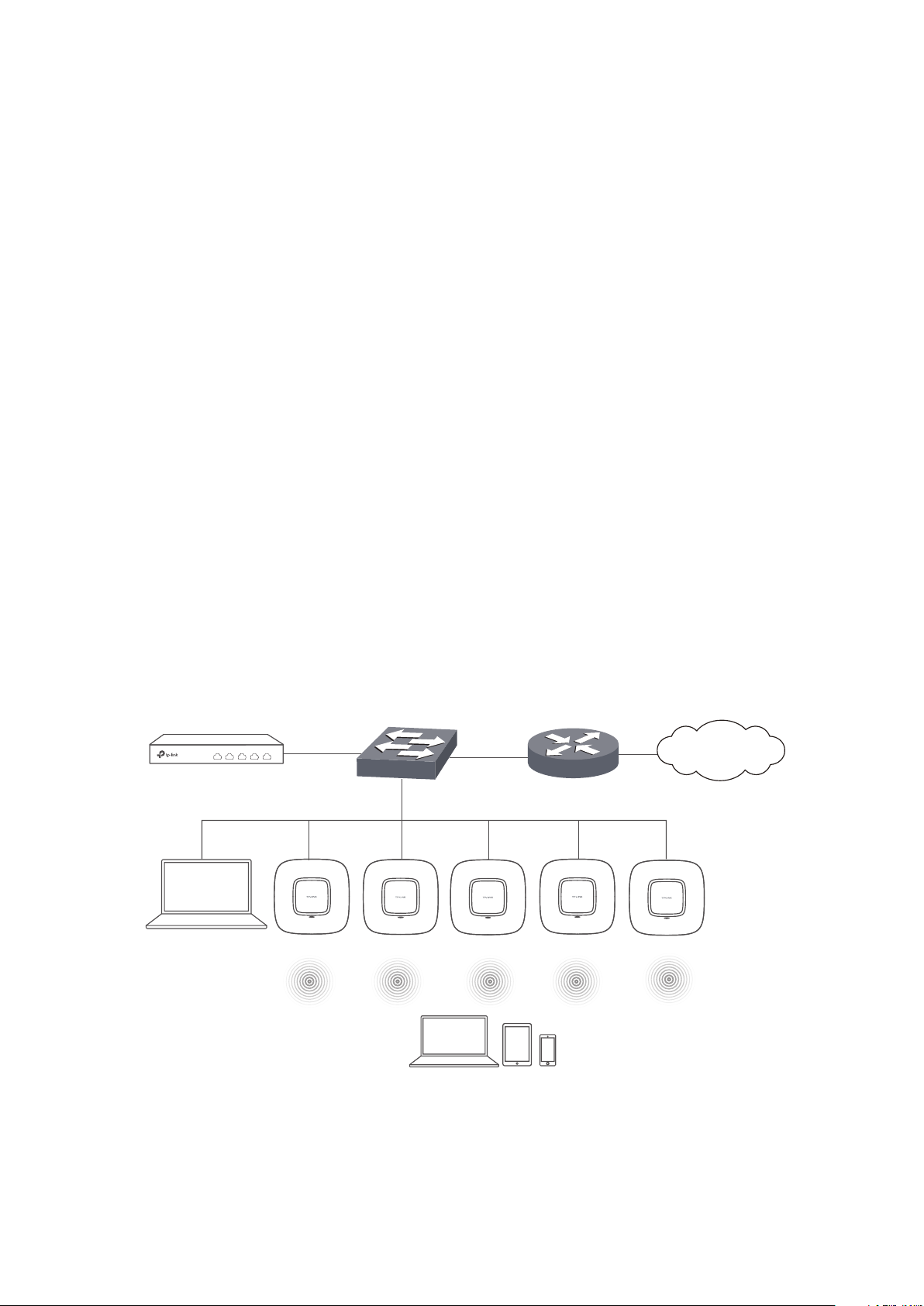
1.1.1 Manage CAPs in the LAN
If you want to manage the CAPs in the LAN, refer to the following network topology.
Router (DHCP Server)
LAN IP:192.168.0.1/24
Internet
CAPs
IP: 192.168.0.253/24
Host A
Switch
Clients
2
Page 7
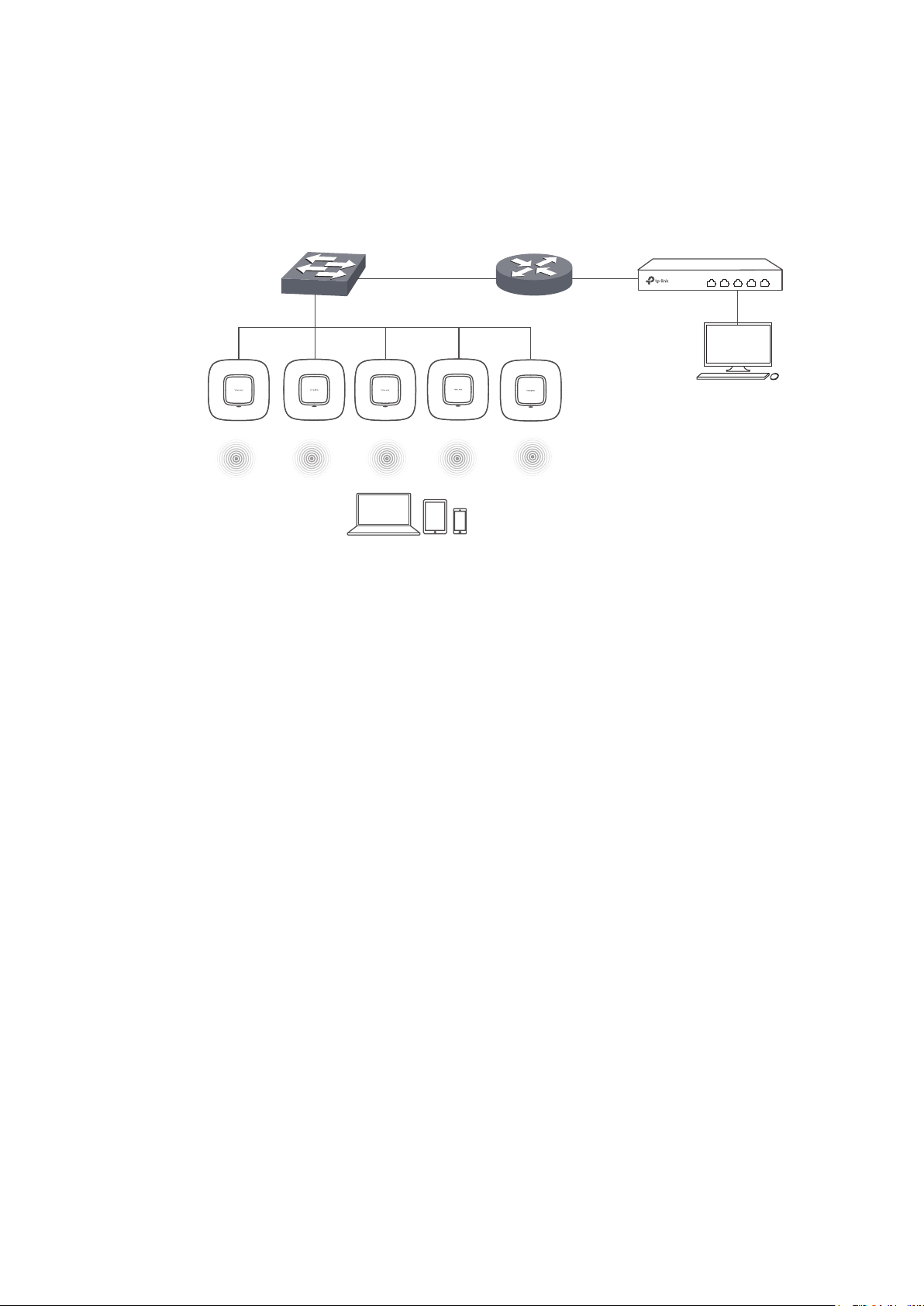
1.1.2 Manage CAPs in Different Network Segment
If the AC needs to manage CAPs in a different network segment, refer to the following
topology.
Switch
Router
1.1.1.2/24192.168.1.1/24
CAPs
Clients
Wireless Controller
IP: 1.1.1.100/24
Host A
IP: 1.1.1.101/24
Note:
In this situation, the router acting as the CAPs' DHCP server should support option 60 and option138 in DHCP
settings.
1.2 Log In to the AC
1.2.1 Preparations
Before login, you should verify the following items:
The AC is powered on and correctly connected. The management host is accessible to
the AC.
Specify the management host with a static IP address on the 192.168.0.x subnet (for
example, IP address 192.168.0.100 and subnet mask 255.255.255.0).
Operating System: Microsoft Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10.
Web Browser: Mozilla Firefox 32 (or above), Google Chrome 37 (or above), Opera 24 (or
above), or Microsoft Internet Explorer 8 (or above).
3
Page 8
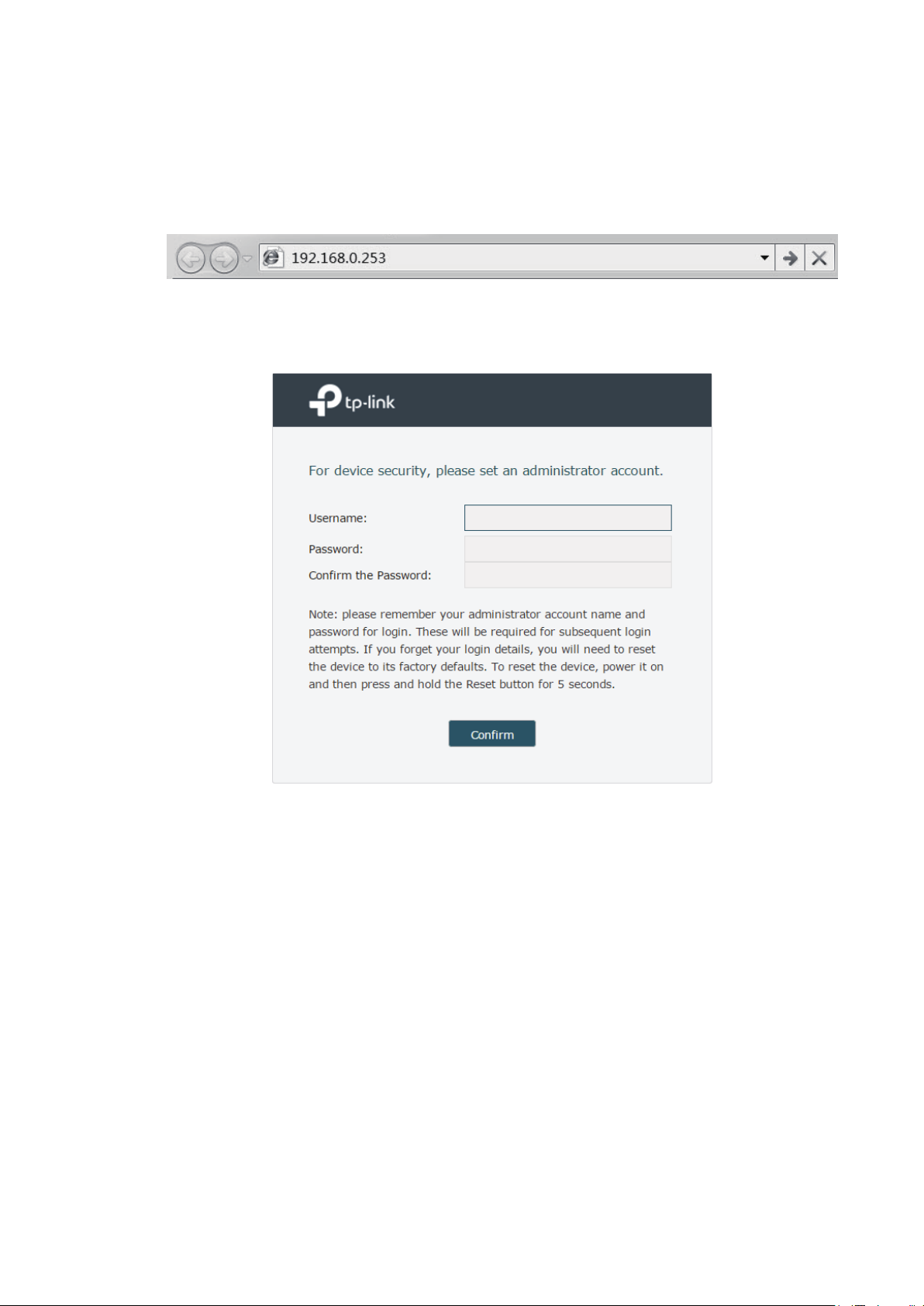
1.2.2 Log In
1 Open a web browser and enter 192.168.0.253 in the address field, then press Enter key.
Figure 1-1 Enter the IP Address
2 Create a username and a password for subsequent login attempts.
Figure 1-2 Create an account
4
Page 9
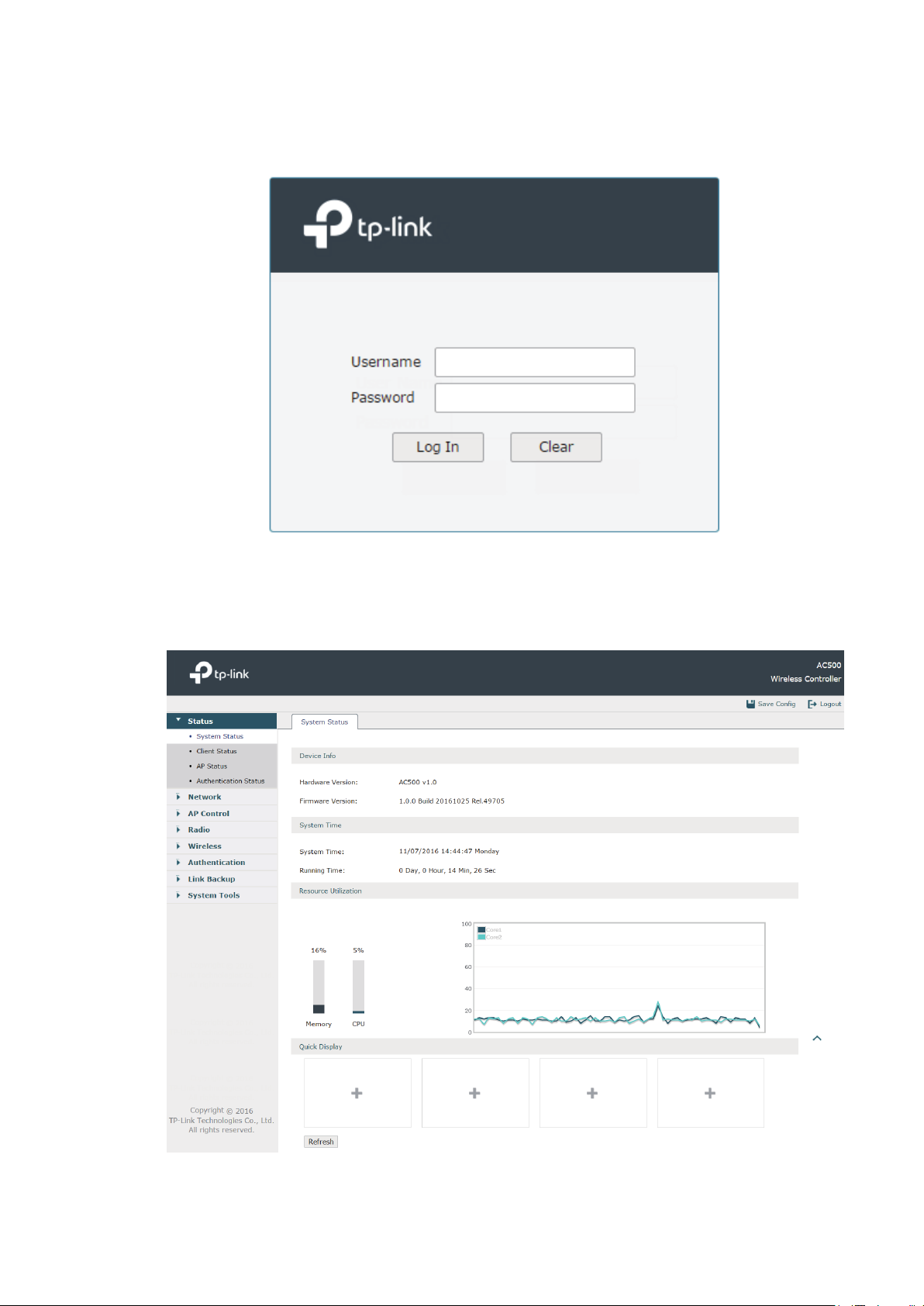
3 Use the username and password set above to log in to the webpage.
Figure 1-3 Log in to the webpage
4 After a successful login, the main page will appear as in the figure below, and you can
configure the function by clicking the setup menu on the left side of the screen.
Figure 1-4 Main Page
5
Page 10

The wireless controller’s configuration files fall into two types: the running configuration file
and the start-up configuration file. After you perform configurations on the sub-interfaces
and click Save, the modifications will be saved in the running configuration file. However,
the configurations will be lost when the device reboots.
If you need to keep the configurations even if the device reboots, please use the function
to save the configurations in the start-up configuration file. Click Save Config on the topright of the interface, especially before you power off or reboot the device.
6
Page 11
2
Status
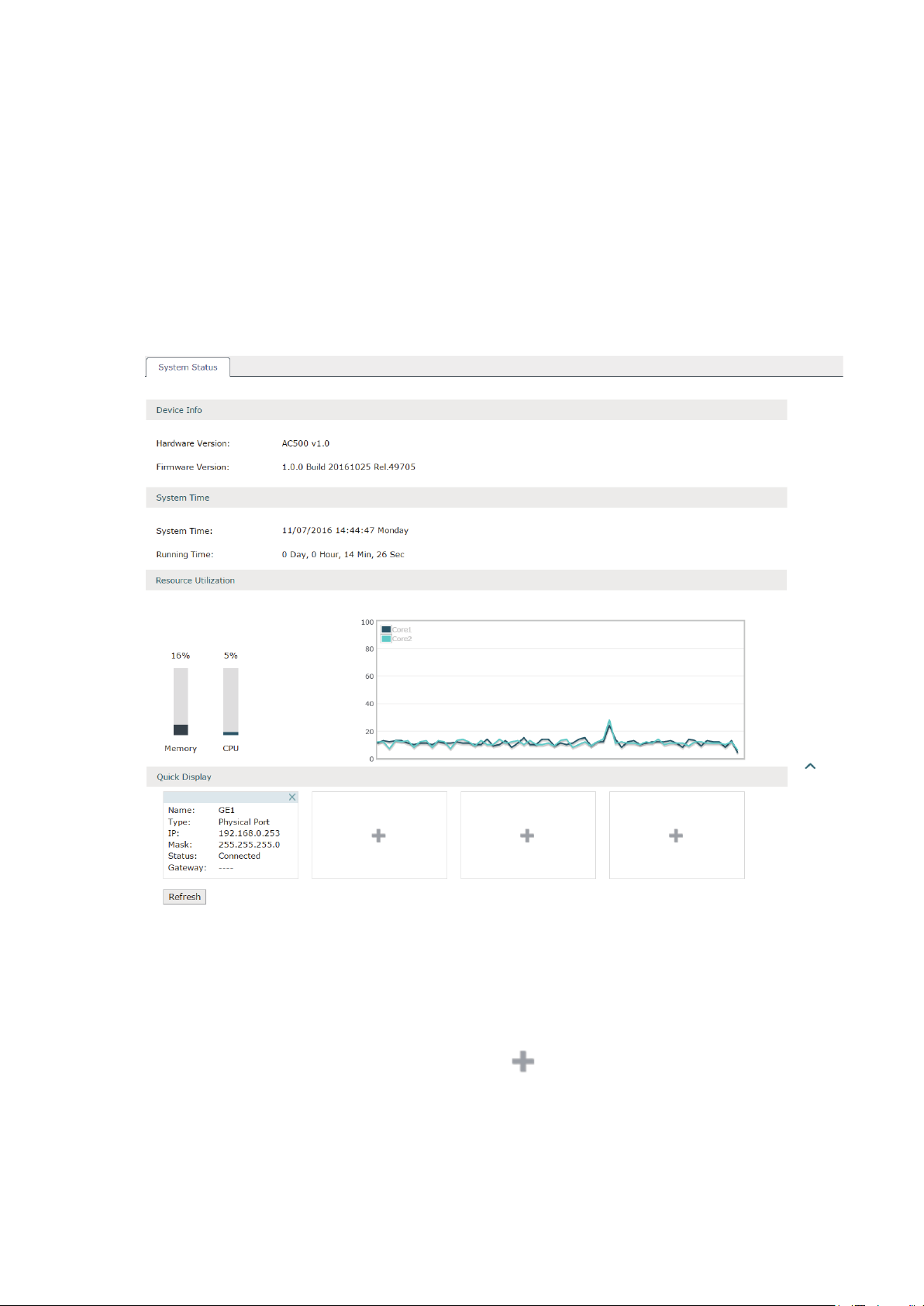
2.1 System Status
Choose the menu Status > System Status > System Status to load the following page.
Figure 2-1 System Status
In the Resource Utilization section, you can monitor the utilization of the memory and
CPU. It is recommended that the CPU utilization should be no more than 50%. The CPU
utilization above 85% indicates that the AC is under a high load and above 95% means AC
is completely loaded. When the CPU utilization keeps at high loads, some functions of the
AC may be abnormal. Please check to find the real reason.
In the Quick Display section, click the button
basic information such as interface name, type and IP address will be shown in this section.
7
to select the desired interface and its
Page 12
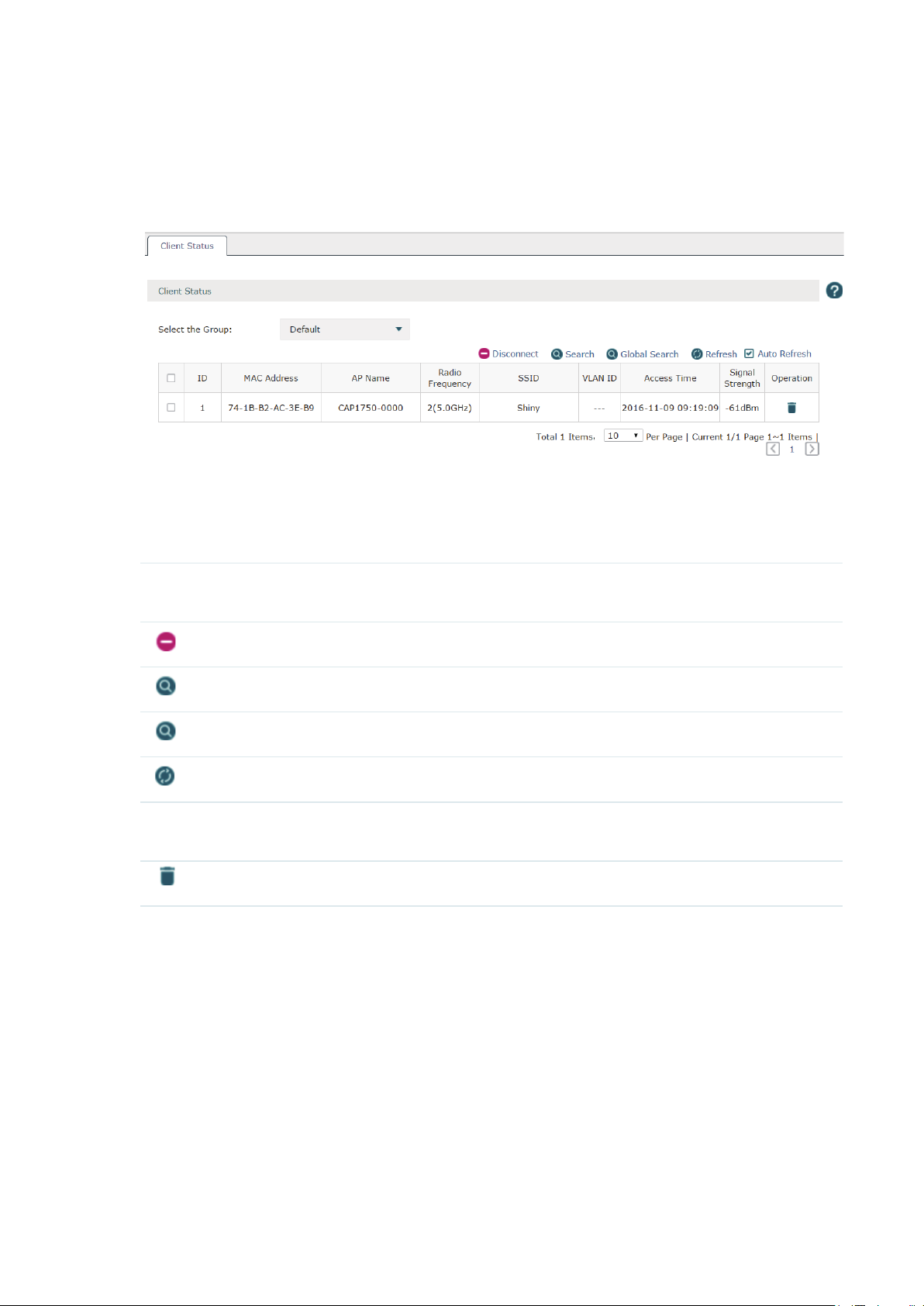
2.2 Client Status
Choose the menu Status > Client Status > Client Status to load the following page.
Figure 2-2 Client Status
You can check the information of the connected clients on this page. Select the desired
clients by checking the boxes in front of the entries. Click the buttons above the list for
additional operations.
Select the Group Select the group from the drop-down list to see the clients' information in the
corresponding group.
Disconnect
Search
Global Search
Refresh
Auto Refresh Check the box to enable the Auto Refresh function. With it enabled, the list will
Disconnect one or more clients from the AP(s).
Search the specified clients in the list.
Search the specified clients globally.
Refresh the list manually.
refresh every few seconds automatically.
Disconnect the client from the AP in this corresponding entry.
8
Page 13

2.3 AP Status
Choose the menu Status > AP Status > AP Status to load the following page.
Figure 2-3 AP Status
The information of the connected CAPs will be displayed in this section.
Select the desired
CAPs by checking the boxes in front of the entries. Click the buttons above the list for
additional operations.
Select the Group Select the group from the drop-down list to see the CAPs' information in the
corresponding group.
LED ON
LED OFF
Reboot
Search
Global Search
Refresh
Auto Refresh Check the box to enable the Auto Refresh function. With it enabled, the list will
Select the corresponding CAPs and click this button to turn on their LEDs.
Select the corresponding CAPs and click this button to turn off their LEDs. For
example, if the CAP's LED disturbs you at night, you can turn off it.
Select the corresponding CAPs and click this button to reboot them.
Search the specified clients in the list.
Search the specified clients globally.
Refresh the list manually.
refresh every few seconds automatically.
It indicates the LED is on. you can click the icon to turn off it.
It indicates the LED is off. you can click the icon to turn on it.
Click this icon to reboot the CAP.
Detail Click Detail to check the information of the radio list and SSID and click
to return.
9
Page 14
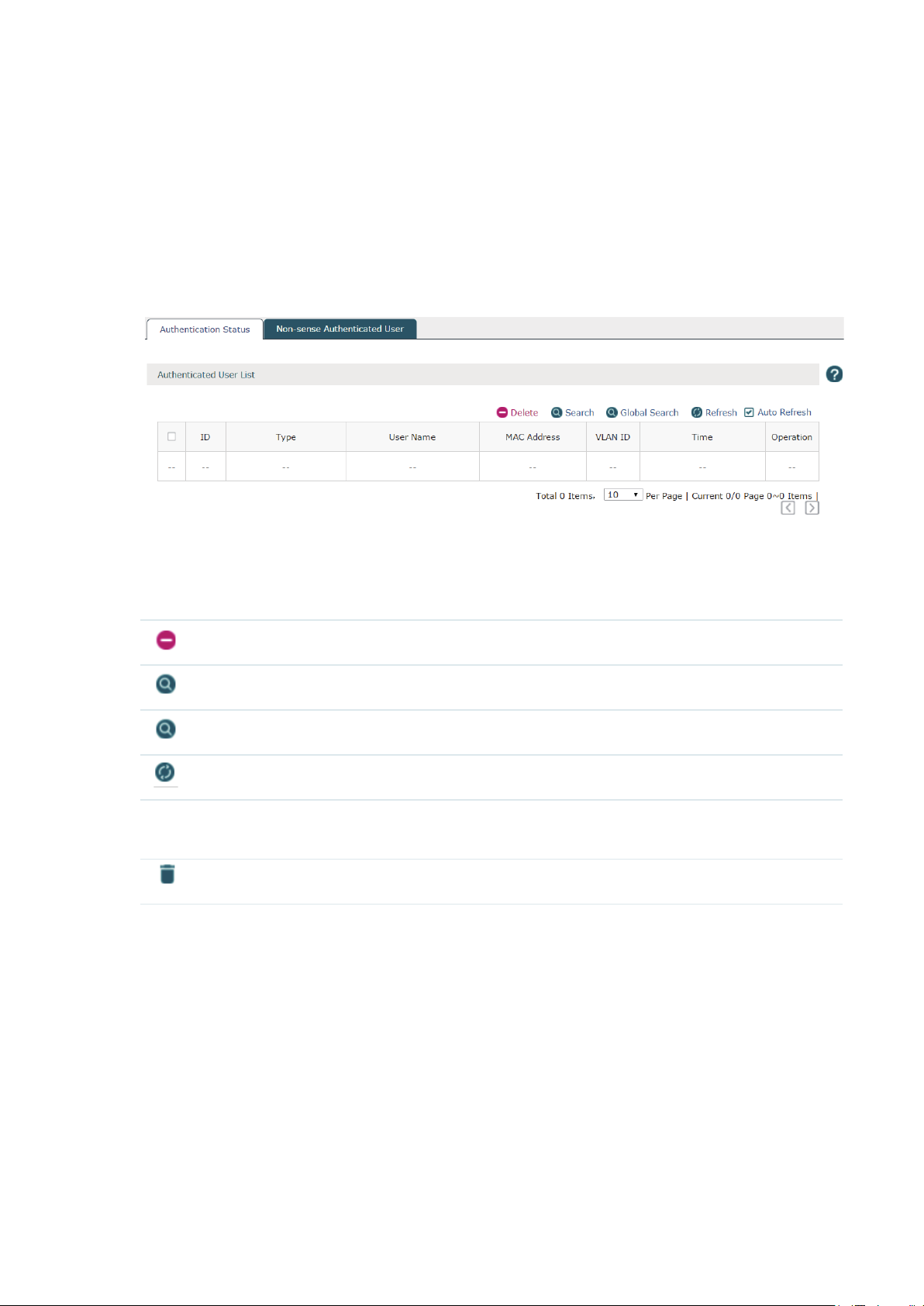
2.4 Authentication Status
2.4.1 Authentication Status
Choose the menu Status > Authentication Status > Authentication Status to load the
following page.
Figure 2-4 Authentication Status
You can check the information of the authentication status on this page. Select the desired
users by checking the boxes in front of the entries. Click the buttons above the list for
additional operations.
Delete
Search
Global Search
Refresh
Auto Refresh Check the box to enable the Auto Refresh function. With it enabled, the list will
Delete the users from the authentication list.
Search the specified users in the list.
Search the specified users globally.
Refresh the list manually.
refresh every few seconds automatically.
Disconnect the client from the AP in this corresponding entry.
10
Page 15

2.4.2 Non-sense Authenticated User
A non-sense authenticated user who has passed the authentication can leave the wireless
network and then join the wireless network again without any re-authentication operation.
Choose the menu Status > Authentication Status > Non-sense Authenticated User to load
the following page.
Figure 2-5 Non-sense Authenticated User
You can check the information of the non-sense authenticated users on this page. Select
the desired users by checking the box in the front of the entries. Click the buttons above
the list for additional operations.
Delete
Search
Global Search
Refresh
Auto Refresh Check the box to enable the Auto Refresh function. With it enabled, the list will
Delete the users from the authentication list.
Search the specified users in the list.
Search the specified users globally.
Refresh the list manually.
refresh every few seconds automatically.
Disconnect the client from the AP in this corresponding entry.
11
Page 16

3
Network
3.1 Interface
Choose the menu Network > Interface > Interface to load the following page. On this page
you can create a logical interface and specify it to a specified VLAN. Please refer to
to set VLANs first.
VLAN
Figure 3-1 Interface
3.3.1
Click to create a new interface. The page will be shown as below.
Figure 3-2 Add an Interface
Interface Name Specify a name for the interface to make it easier to search for and manage.
VLAN Specify a VLAN for the interface.
12
Page 17
Connection Type Select the connection type for the interface. Only static IP is supported at
present.
IP Address Specify an IP address for the interface.
Subnet Mask Specify a subnet mask for the interface.
Default Gateway (Optional) Specify a default gateway for the interface.
MTU Specify the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) for the interface. Its value is
between 576 to 1500 and 1500 by default.
Primary DNS (Optional) Specify the primary DNS server for the interface.
Secondary DNS (Optional) Specify the secondary DNS server for the interface.
MAC Address The MAC address is filled automatically. You can modify it manually.
Description Specify a description for the entry to make it easier to search for and manage.
Click OK to finish the settings.
3.2 DHCP Server
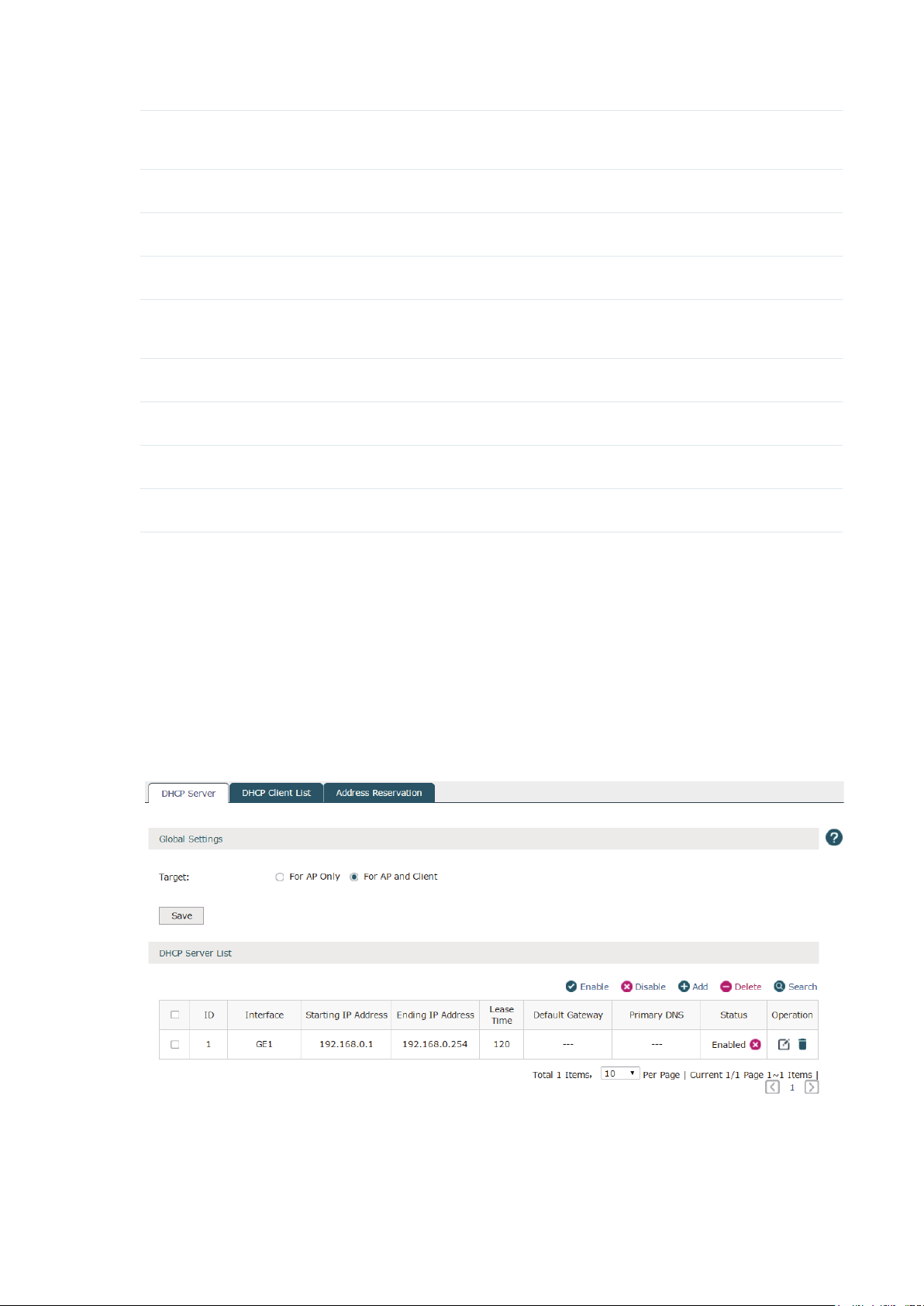
3.2.1 DHCP Server
Choose the menu Network > DHCP Server > DHCP Server to load the following page.
Figure 3-3 DHCP Server
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) allows the wireless controller to assign IP
addresses, subnet masks, default gateways and other IP parameters to CAPs and clients
that request this information. In the global settings you can select that the DHCP server
assigns IP parameters to AP only or both AP and client.
13
Page 18
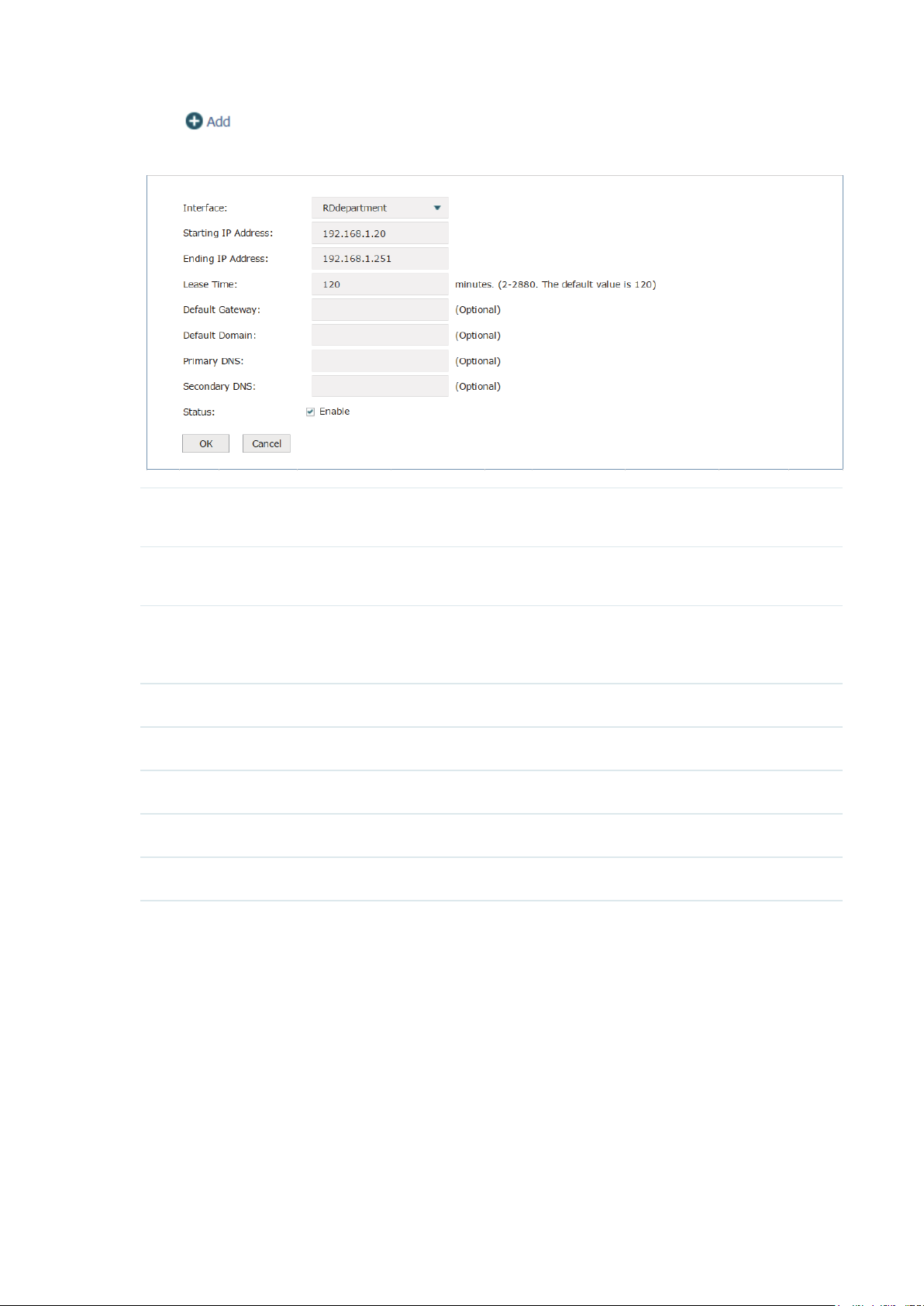
Click to create a DHCP server. The page will be shown as below.
Figure 3-4 Add a DHCP Server
Interface Select the interface which you want to create the DHCP server for. Refer to
Interface
Starting/Ending IP
Address
Lease Time Enter the time duration of the IP address assigned by the DHCP server between
Default Gateway Optional: Specify the IP address of gateway for the server.
Default Domain Optional: Specify the domain of for the server.
Primary DNS Optional: Specify the primary DNS server for the server.
Secondary DNS Optional: Specify the secondary DNS server for the server.
Status Check the box to enable the DHCP service.
Specify the starting IP address and ending IP address of the DHCP server IP
pool. The IP pool should be in the same segment with the interface IP address.
2 and 2880 minutes. The default is 120 minutes. Before the time is up, DHCP
server would not assign this IP address to other APs or clients.
to set the interface first.
Click OK to finish the settings.
3.1
14
Page 19

3.2.2 DHCP Client List
Choose the menu Network > DHCP Server > DHCP Client List to load the following page.
The list displays the information such as the IP address, MAC address and lease time of the
connected clients.
Figure 3-5 DHCP Client List
3.2.3 Address Reservation
Choose the menu Network > DHCP Server > Address Reservation to load the following
page.
Figure 3-6 Address Reservation
If the CAP or client requires a static IP address, you can manually reserve an IP address
for it. Once reserved, the IP address will only be assigned to the same client by the DHCP
server.
15
Page 20
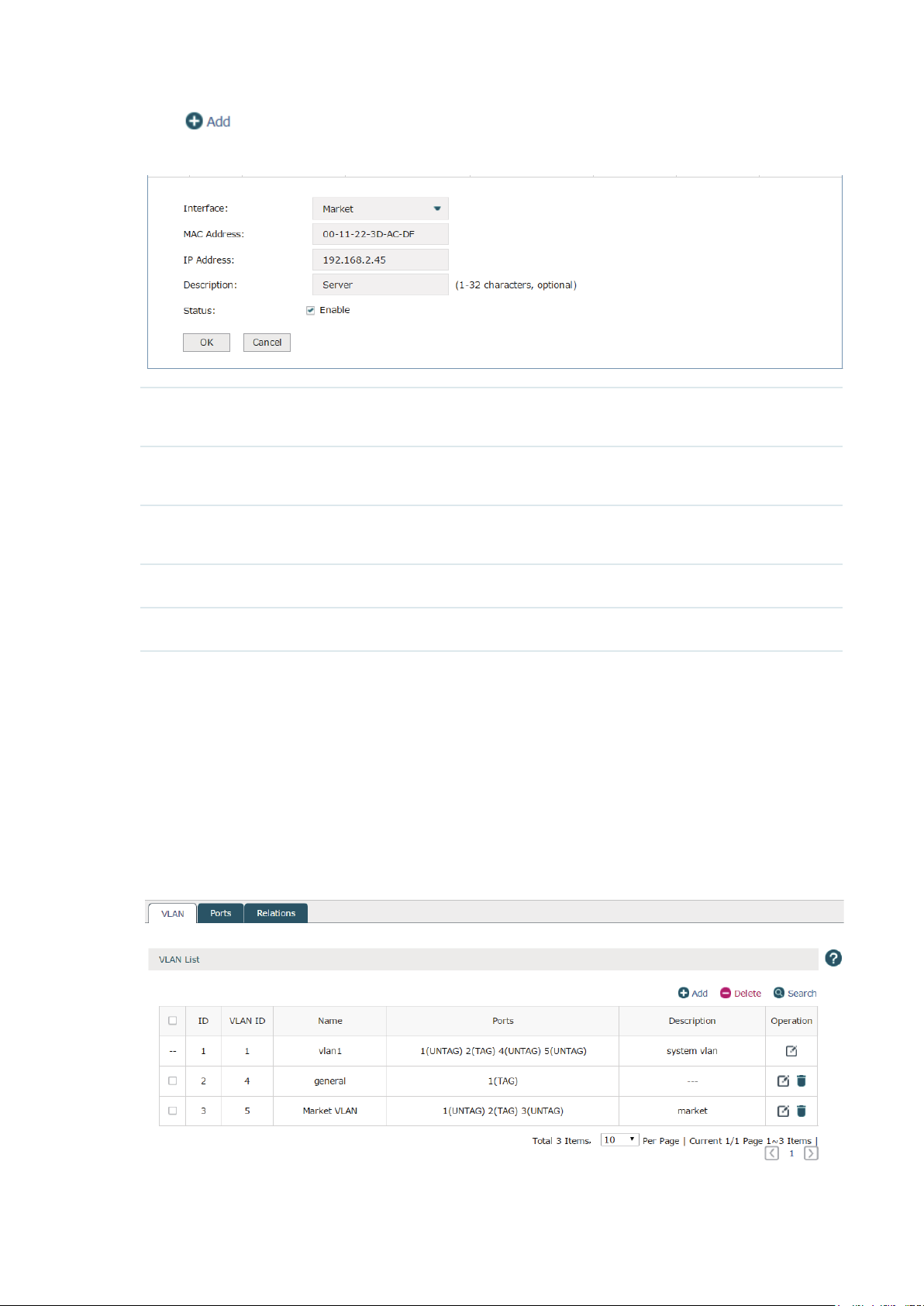
Click to create an IP address reservation.
Figure 3-7 Create an IP Address Reservation
Interface Select the interface which the CAP or client requiring the static IP address
belongs to. Refer to
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of the specified AP or client to which you want to assign
the static IP address.
IP Address Specify a static IP address to the specified AP or client. The IP address should
be in the same segment as the interface.
3.1 Interface
to set the interface first.
Description Specify a description for the entry to make it easier to search for and manage.
Status Check the box to enable the address reservation.
Click OK to finish the settings.
3.3 VLAN
3.3.1 VLAN
Choose the menu Network > VLAN > VLAN to load the following page.
Figure 3-8 VLAN
16
Page 21
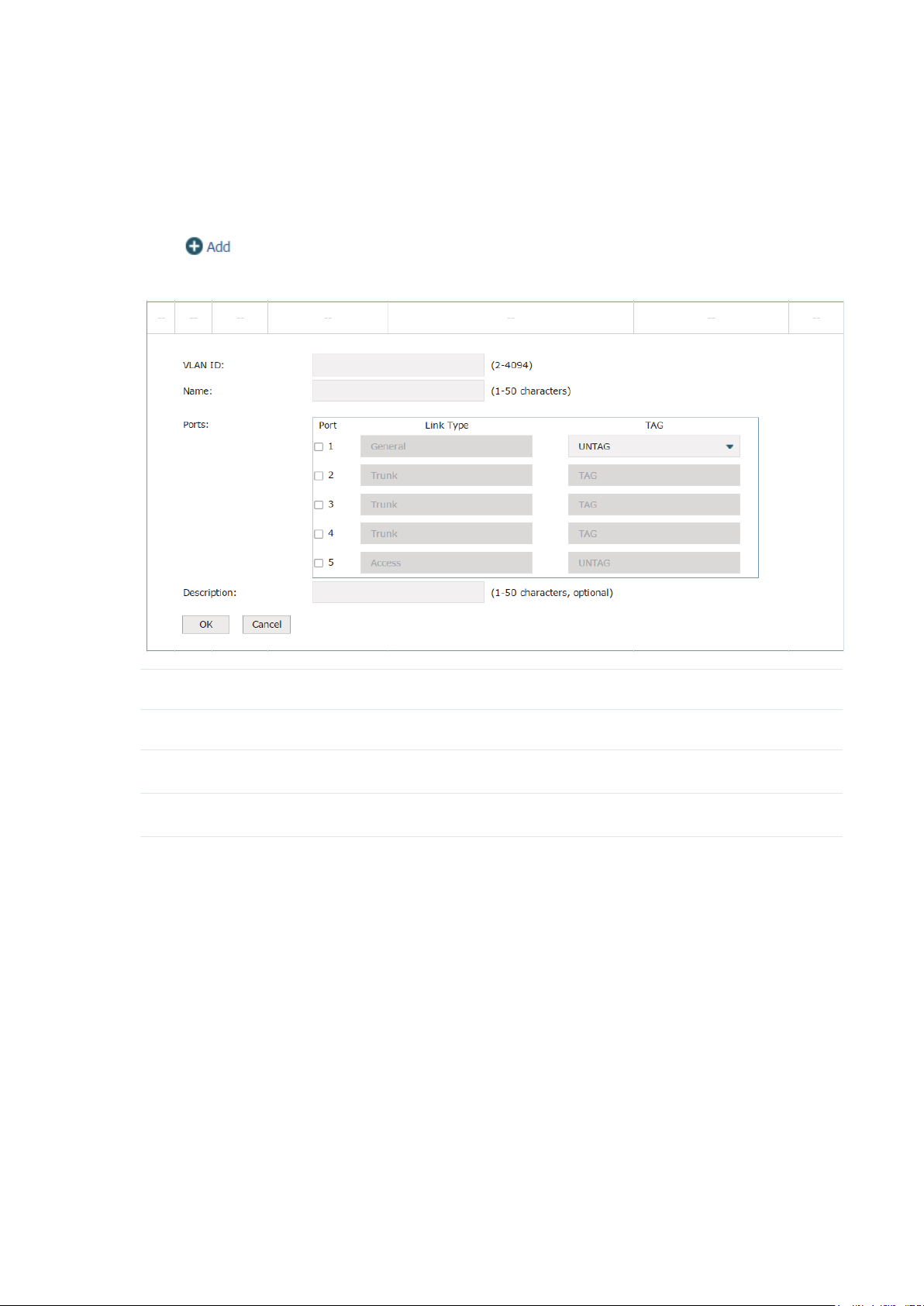
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a network technique that solves broadcasting issues
in local area networks. A local area network is partitioned into several VLANs, and all VLAN
traffic remains within its VLAN. Therefore, you can group and isolate APs and clients to
enhance network security. VLANs group devices logically instead of physically, so devices
in the same VLAN can be located in different places.
Click
Figure 3-9 Create a VLAN
VLAN ID Specify a VLAN ID between 2 to 4094.
to create a VLAN.
Name Specify an easy-to-remember name for the VLAN.
Ports Select the ports that belong to the VLAN.
Description Specify a description for the entry to make it easier to search for and manage.
Click OK to finish the settings.
17
Page 22

3.3.2 Ports
Choose the menu Network > VLAN > Ports to load the following page. Specify the link type
and PVLD for each port. The link type and PVID can not be modified at the same time.
Figure 3-10 Ports
Link Type The ports can be divided into three link types:
Access: The access port can be added in a single VLAN, and the egress rule
of the port is UNTAG. The PVID is same as the current VLAN ID. If the current
VLAN is deleted, the PVID will be set to 1 by default.
Trunk: The trunk port can be added in multiple VLANs. The egress rule of the
port is UNTAG if the arriving packet’s VLAN tag is the same as the port’s PVID,
otherwise the egress rule is TAG. The PVID can be set as the VID number of any
valid VLAN.
General: The general port can be added in multiple VLANs and set various
egress rules according to the different VLANs. The default egress rule is
UNTAG. The PVID can be set as the VID number of any valid VLAN.
PVID Enter the VLAN ID of the port.
Note:
AC50 doesn't include a General port link type.
18
Page 23

3.3.3 Relations
Choose the menu Network > VLAN > Relations to load the following page. This list displays
the relations among ports, link types and VLANs.
Figure 3-11 Relations
19
Page 24
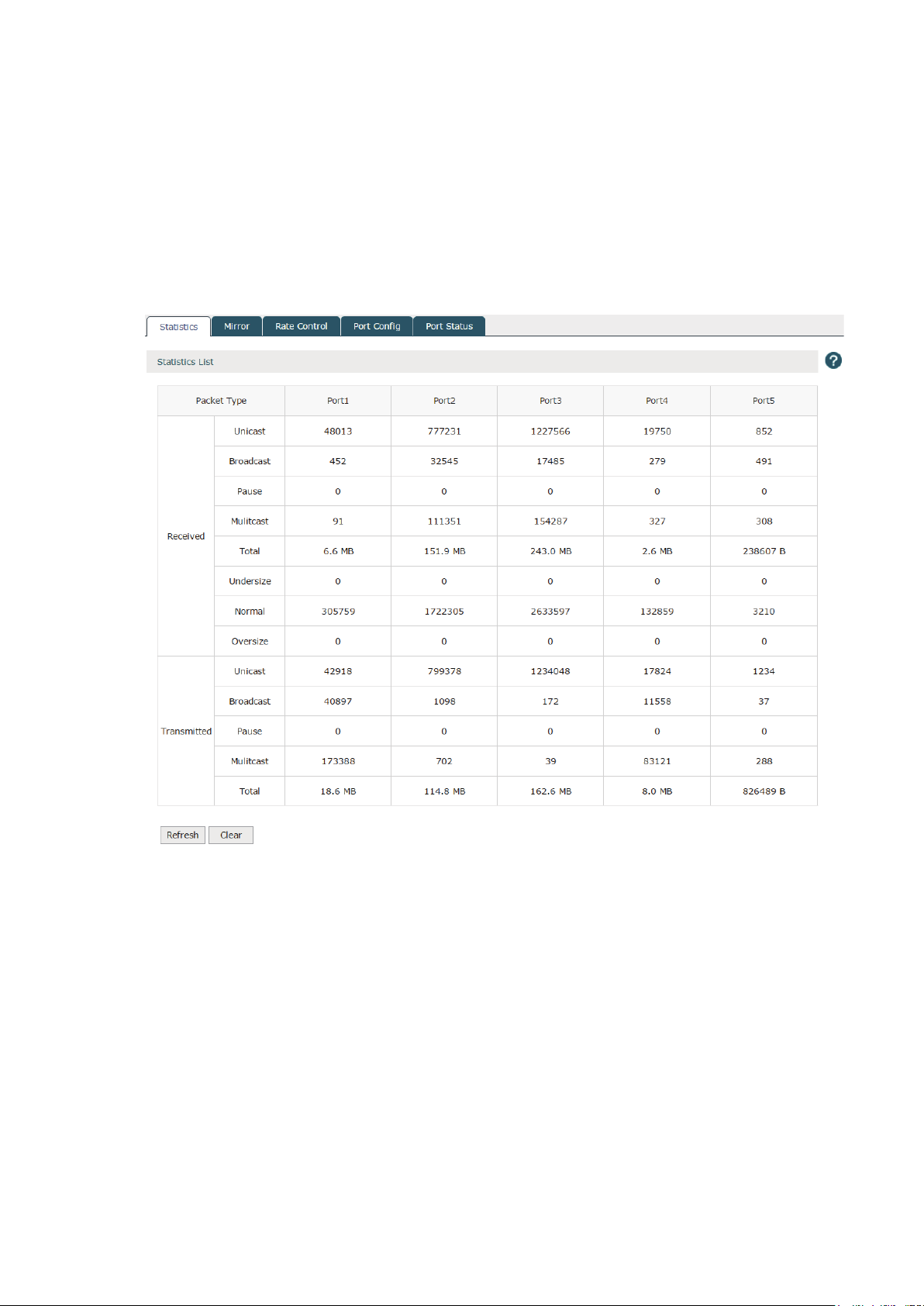
3.4 Switch
3.4.1 Statistics
Choose the menu Network > Switch > Statistics to load the following page. The statistics
list displays the information of data packets received or transmitted by each port.
Figure 3-12 Statistics
20
Page 25
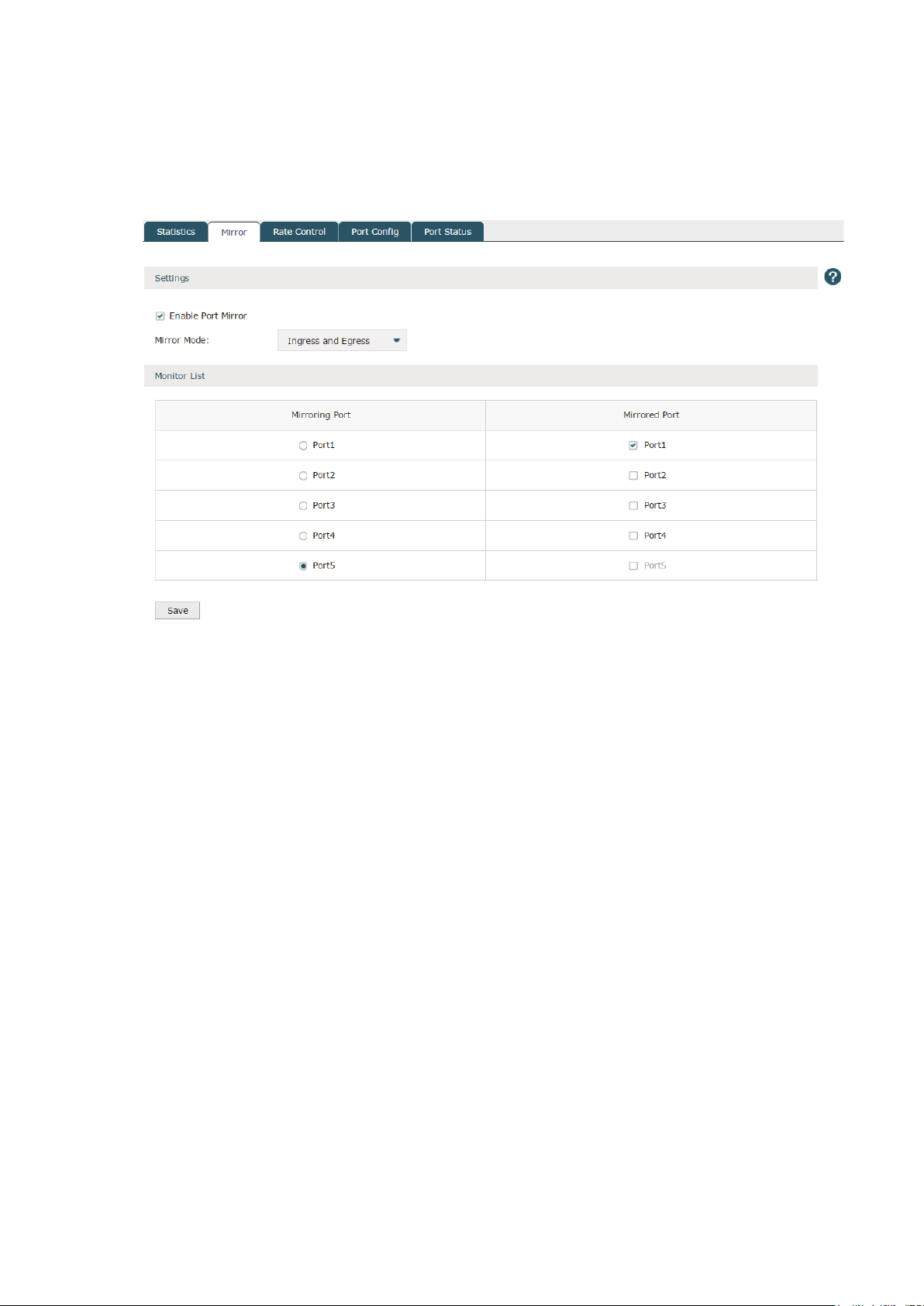
3.4.2 Mirror
Choose the menu Network > Switch > Mirror to load the following page.
Figure 3-13 Mirror
Check the box to enable the Port Mirror function. There are three port mirror modes as
follows.
Ingress and egress: When this mode is selected, both the incoming and outgoing packets
through the mirrored port will be copied to the mirroring port.
Ingress: When this mode is selected, the incoming packets received by the mirrored port
will be copied to the mirroring port.
Egress: When this mode is selected, the outgoing packets sent by the mirrored port will be
copied to the mirroring port.
A port cannot be set as the mirrored port and the mirroring port simultaneously. Only one
mirroring port can be set.
3.4.3 Rate Control
Choose the menu Network > Switch > Rate Control to load the following page. Here
you can control the data transfer rate for each port. Check boxes to manually enter the
corresponding rates.
Note:
The data transfer rate ranges from 1 to 100Mpbs for AC50, and from 1 to 1000Mpbs for AC500.
21
Page 26
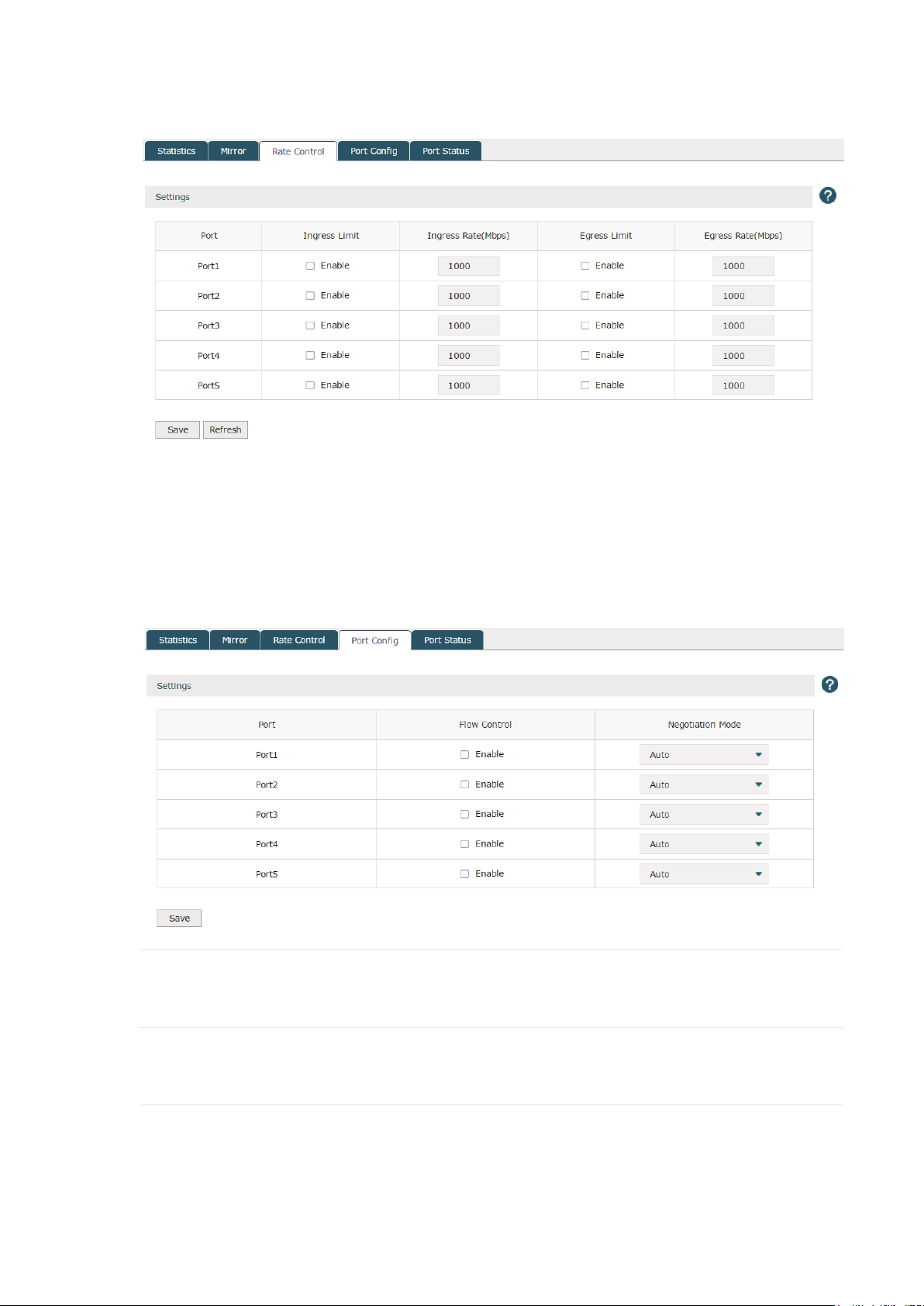
Figure 3-14 Rate Control
Click Save to finish the settings.
3.4.4 Port Config
Choose the menu Network > Switch > Port Config to load the following page.
Figure 3-15 Port Cofig
Flow Control With this option enabled, the device synchronizes the data transmission speed
with the peer device, thus avoiding the packet loss caused by congestion. By
default, it is disabled.
Negotiation Mode Select the Negotiation Mode for the port including auto and duplex mode.
Duplex mode includes 10M Half-duplex, 10M Full-duplex, 100M Half-duplex,
100M Full-duplex and 1000M Full-duplex.
Note:
The AC50 doesn't support 1000M Full-duplex.
22
Page 27
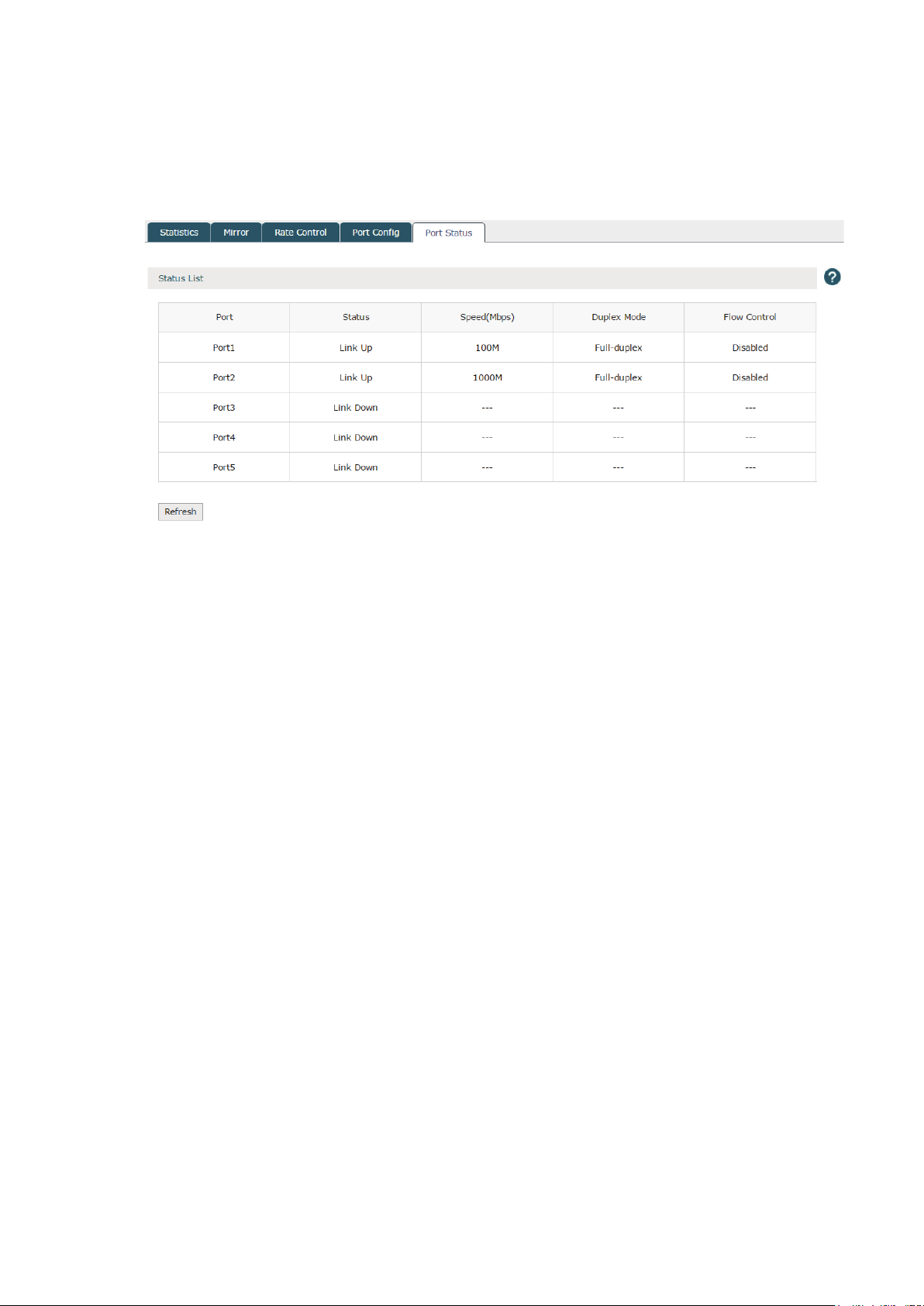
3.4.5 Port Status
Choose the menu Network > Switch > Port Status to load the following page.
Figure 3-16 Port Status
This page displays the connection status, speed, duplex mode and flow control status of
each port.
Disabled: The port is disabled.
Link down: The port is enabled but with physical connection.
Link up: The Port is enabled and connected normally.
Note:
The data transfer rate ranges from 1 to 100Mpbs for AC50, and from 1 to 1000Mpbs for AC500. AC50 doesn't
support 1000M Full-duplex.
23
Page 28

4
AP Control
4.1 AP Settings
Choose the menu AP Control > AP Settings > AP Settings to load the following page.
Figure 4-1 AP Settings
In the global settings, check the Reboot Schedule box and then the Lock to AC
Automatically box to enable the corresponding function. Click Save to complete.
Reboot Schedule With the reboot schedule enabled, all connected APs will reboot at the
specified time.
Reboot Date Select the date to reboot the APs. If you want to reboot the APs everyday,
please select everyday in the list.
Reboot Time Specify the reboot time to reboot the APs in the format of HH/MM/SS.
Lock to AC
Automatically
Click to create a new group. The following figure will be shown. Specify a group
name in the field and click OK.
With the lock to AC automatically enabled, all the APs entries will be locked to
AC automatically once APs connect to the AC. The unlocked AP entries will
disappear when the AC reboots.
24
Page 29
Figure 4-2 Add a group
In the group list, click the numbers at the Group Statistics Information row. The group
information will be shown as below. Click the buttons above the list for additional
operations.
Figure 4-3 Group statistics information
Back to Group List
Move to Other
Group
Lock to AC
Bulk Edit
Search
Intra Group Search
Click this button to return to the group list.
Select the corresponding entries and click this button to move them to your
desired group.
Select the corresponding entries and click this button to lock the APs to the
AC.
Select the corresponding entries and click this button to bulk edit the APs' AP
keep-alive time, client keep-alive time and client idle time. Refer to the following
introduction below the table for details.
Click this button to search the specified AP(s) on the current page.
Click this button to search the specified AP(s) in all the AP entries without the
limitation of groups.
25
Page 30
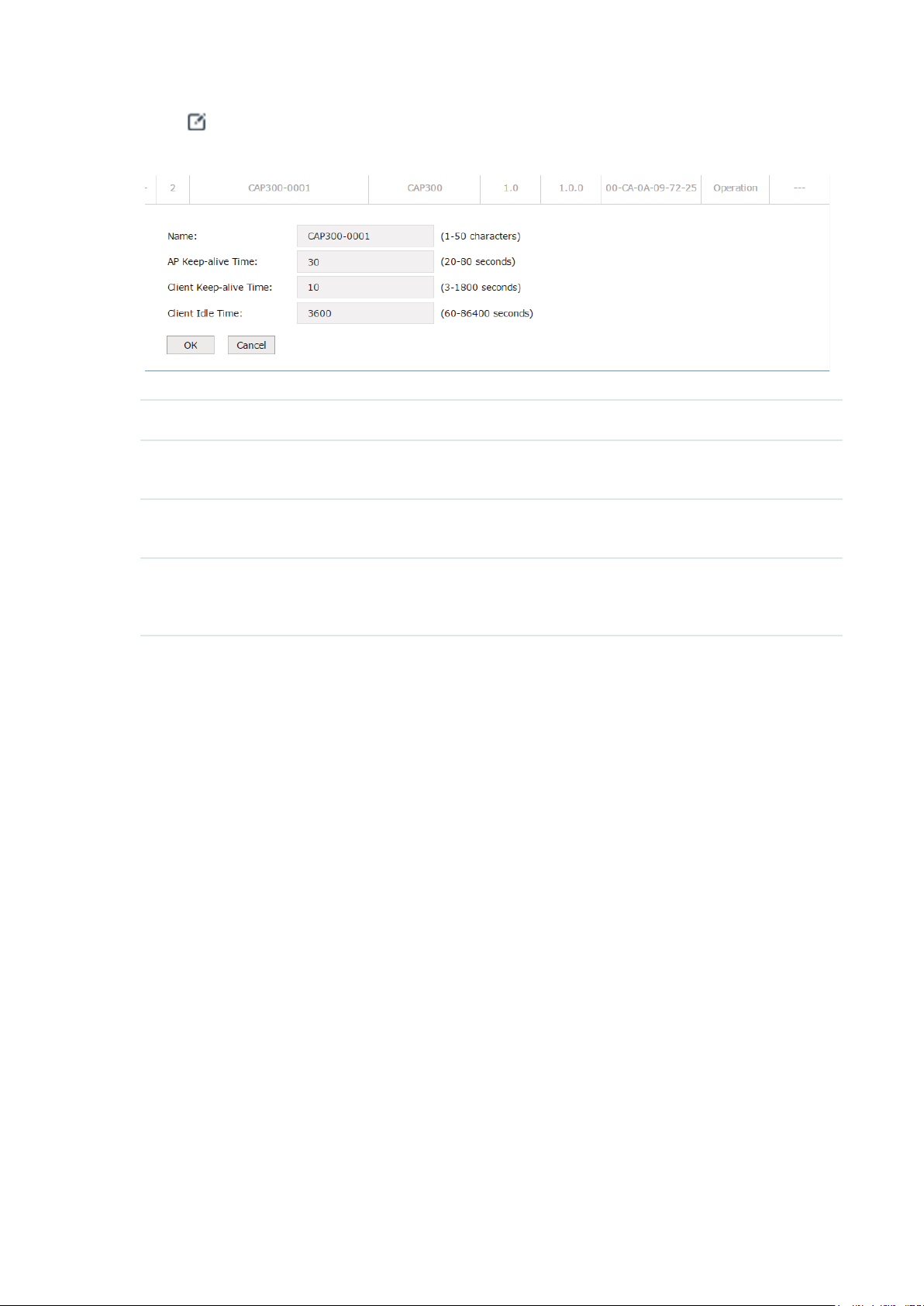
Click at the Operation row of the list. The following figure will be shown.
Figure 4-4 AP Settings
Name Specify the AP's name.
AP Keep-alive Time Specify the time interval for the AP sending echo packets to the AC. AC can
detect whether the AP is online or not by receiving the echo packets.
Client Keep-alive Time Specify the time interval for the client sending heartbeat packets to the AP. APs
can detect whether the client is online or not by receiving heartbeat packets.
Client Idle Time Specify a time interval for the client idle time. The clients will be disconnected
from the AP if there is no data transmission between AP and clients for the
specific time interval.
26
Page 31

4.2 AP Firmware Upgrade
Choose the menu AP Control > AP Firmware Upgrade > AP Firmware Upgrade to load the
following page.
With it enabled, import the correct firmwares and set the starting upgrade time. The
connected APs will start to upgrade at the specified time. If it is disabled, the APs that
haven’t started upgrading will not be upgraded.
Figure 4-5 AP Firmware Upgrade
AP Model Displays the AP model.
Hardware Version Displays the current hardware version.
Firmware Version Displays the imported firmware version.
Upgrade Starting Time After the upgrade file has been imported successfully, specify the upgrade
starting time. With upgrade enabled, the APs of this model will automatically
upgrade using the upgrade file.
Upgrade Process Displays the upgrade process. The format is X/Y/Z, which means there are Z
APs of this model in the system, with Y APs waiting to upgrade and X APs have
upgraded successfully. Click the numbers to check each AP's upgrade status.
Upgrade Failure Displays the number of APs which failed to upgrade. Click the number to check
the detailed log information.
27
Page 32

Upgrade Status Displays the upgrade status of current APs of this model. Click to check the
detailed upgrade information of each AP of this model.
Latest: There is no AP of the current model to be upgraded.
Waiting: APs of the current model are waiting to be upgraded.
Upgrading: Some APs of the current model are upgrading.
Completed: All APs of the current model are upgraded.
Terminated: The upgrade was disabled while the AP was waiting to upgrade.
The AP's upgrade process is terminated. When the upgrade is enabled again,
the status of the AP will change to "Waiting".
Operation Click Import to import the upgrade firmware into the system.
Click Delete to delete the firmware.
Note:
1. Only one model can upgrade at a time.
2. When the AC reboots or the CAPs reboot automatically, the CAPs can only upgrade after ten minutes.
3. The parameter of upgrade process and upgrade failure will be cleared when the AC reboots.
4. The standby link doesn't support upgrade schedule.
4.3 AP Database
Import the AP database file to support the identification and management of new AP
models on this page. When there is an undetected AP model connecting to the AC, the AC
should import the latest AP database to identify the new AP models.
Choose the menu AP Control > AP Database > AP Database to load the following page.
Figure 4-6 AP Settings
Current Version Displays the current version of the AP database.
File Path Click Browse to locate and select the new AP database. Click Upgrade to
import it.
Download the latest AP
database
Click Download the latest AP database. You will be redirected to the TP-Link
download center to download the AP database files. The download center will
update the AP database file.
28
Page 33

4.4 Load Balancing
Load Balancing is applied in the high density wireless environment. It can balance the APs
load and guarantee the reasonable access of the clients to APs. Therefore, the wireless
resources and bandwidth of each AP can be used fairly.
The following example is used to illustrate the working process of load balancing.
Figure 4-7 Topology
Wireless Controller
CAP1
Client number: 20 Client number: 16
Client
CAP2
The client is within the wireless range of CAP1 and CAP2. The client requests to connect to
CAP1 and the following two conditions are met:
1 The client number of CAP1 has reached or exceeded the maximum number that the
load balancing set ( 20 as an example).
2 The client is also in the coverage of other CAPs. And the difference of the connected
client number between CAP1 and one of the other CAPs is greater than the difference
threshold set in load balancing (4 as an example, 20-16≥4).
Due to load balancing, AC will reject the client’s request to connect to CAP1 and instead
connect the client to other CAPs with a smaller load. Thus, the performance of the whole
network is improved.
If the client requests to connect to CAP1 continually, and the request fail number exceeds
the maximum fail number set in load balancing, CAP1 will accept the connecting request of
the client.
If the signal strength of the client is smaller than the RSSI threshold, it will not count to the
total number of clients in load balancing.
29
Page 34

Choose the menu AP Control > Load Balancing > Load Balancing to load the following
page.
Figure 4-8 Load Balancing
Load Balancing Specify whether to enable load balancing.
Mode Load balancing supports session mode only at present. In this mode, each AP
will be assigned an average number of clients by the AC.
Threshold Set the maximum number of clients that are allowed to access the AP. The
client's request to connect to the CAP will be rejected when the threshold and
difference threshold are exceeded.
Difference Threshod Set the maximum difference between the number of clients connected to the
AP with the number of clients connected to other APs. The client's requests
to connect will be rejected when the threshold and difference threshold are
exceeded.
Maximum Fail Number Set the maximum fail number for the client's connection request. When the
client's connection requests fail more than the specified number, the AP will
allow it to connect.
RSSI Threshold Specify the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) threshold. If the signal
strength of the client is lower than the RSSI threshold, it will not count to the
total number of clients for the purpose of load balancing.
30
Page 35

5
5.1 Radio Settings
Radio
Choose the menu Radio > Radio Settings > Radio Settings to load the following page.
Figure 5-1 Radio Settings
On this page, you can specify the radio parameters of multiple or individual CAPs. Select
the entries and click the buttons above the list to change the radio status or bulk edit the
parameters.
Click
at the operation row in the radio list, the following figure will be shown.
31
Page 36

Figure 5-2 Change the Radio Settings
AP Name Displays the name of the AP.
Radio Frequency Displays the radio frequency of the AP to be modified.
Mode Specify the working mode of the wireless network. AP with a frequency band of
2.4GHz supports five wireless modes: 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11b/g,
802.11g/n and 802.11b/g/n. You are recommended to select the 11b/g/n mode,
and all of 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n wireless stations can connect to the AP.
AP with a frequency band of 5GHz supports 802.11a, 802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11a/
n, 802.11n/ac and 802.11a/n/ac modes. You are recommended to select 11a/n/ac
mode, allowing 802.11a, 802.11n and 802.11ac wireless stations to access the AP.
Bandwidth Specify the bandwidth of the wireless network. According to IEEE 802.11n standard,
using higher bandwidth can increase wireless throughput. However, users may
choose lower bandwidth due to the following reasons:
1. Increase the available number of channels within the limited total bandwidth.
2. To avoid interference from overlapping channels occupied by other devices in the
environment.
3. Lower bandwidth can concentrate higher transmit power, increasing stability of
wireless links over long distances.
Channel Specify a channel for the wireless network. If auto is selected, the AP will
automatically choose a suitable channel.
32
Page 37

Transmit Power Specify a transmit power for the wireless network. A larger transmission power than
needed may cause interference to other wireless networks.
Maximum Users Specify the maximum number of clients that can be connected to the AP.
Antenna Specify the antenna type. Only internal antenna is supported at present.
Fragment
Threshold
Beacon Interval Enter a value between 40 and 1000 in milliseconds to determine the duration
Airtime Fairness Specify whether to enable Airtime Fairness feature. With this feature enabled,
RTS Threshold Enter a value between 1 and 2347 to determine the packet size of data transmission
DTIM Period This value indicates the number of beacon intervals between successive Delivery
Specify the fragment threshold for transmitting packets. If the size of the packet
is larger than the fragment threshold, the packet will be fragmented into several
packets. A value that is too low for the fragment threshold may result in poor
wireless performance caused by the excessive packets. The recommended and
default value is 2346 bytes.
between beacon packets that are broadcasted by the AP to synchronize the wireless
network. The default is 100 milliseconds.
each client connected to the AP can get the same amount of time to transmit data,
preventing low-data-rate clients from occupying too much network bandwidth and
improving the network throughput. We recommend that you enable this function
under multirate wireless networks.
through the AP. By default, the RTS (Request to Send) Threshold size is 2346. If the
packet size is greater than the preset threshold, the AP sends Request of Send
frames to a particular receiving station and negotiates the sending of a data frame,
or else the packet will be sent immediately.
Traffic Indication Messages (DTIM) and this number is included in each Beacon
frame. A DTIM is contained in Beacon frames to indicate whether the AP has
buffered broadcast and/or multicast data for the client devices. Following a Beacon
frame containing a DTIM, the access point will release the buffered broadcast and/or
multicast data, if any exists. You can specify a value between 1-255 Beacon Intervals.
The default value is 1, indicating the DTIM Interval is the same as the Beacon Interval.
An excessive DTIM interval may reduce the performance of multicast applications. It
is recommended to keep it as the default.
WMM Specify whether to enable the WMM. With WMM enabled, this device uses the QoS
function to guarantee the transmission of audio and video packets with high priority.
Broadcast Probe
Response
Short GI Specify whether to enable the Short GI. Short GI is used to increase the throughput
Weak Signal
Forbidden
Specify whether to enable the broadcast probe response function. The clients send
broadcast probes to detect the wireless networks nearby. If the function is enabled,
the AP will respond to the broadcast probe to let the clients know of its existence.
With the function disabled, the client cannot find the AP by sending broadcast
probes.
by reducing the guard interval time. It is recommended to enable this function.
Specify whether to enable the weak signal forbidden function. With this function
enabled, the AP will forbid the client with a signal strength lower than a certain value
from connecting.
33
Page 38

Weak Signal
Discard
Click OK to complete the configuration. Click Default Settings to restore the parameters to
the default.
5.2 Rate Settings
Choose the menu Radio > Rate Settings > Rate Settings to load the following page. Specify
the data transmission rate on this page.
Figure 5-3 Rate Settings
Specify whether to enable the weak signal discard function. With this function
enabled, the AP will discard the client with a signal strength lower than a certain
value.
34
Page 39

802.11a Basic Rate: Specify the basic rate set with which the 802.11a clients are
allowed to access the network. At least one rate should be selected from the
rate set. 6Mbps, 12Mbps and 24Mbps are selected by default.
Supported Rate: Specify the supported rate for 802.11a clients. The supported
rate set should not overlap with the basic rate set. 9Mbps 18Mbps, 36Mbps
48Mbps and 54Mbps are selected by default.
Multicast Rate: Specify the multicast rate for the 802.11a multicast packets.
The rate should be selected from the basic rate set. When auto is selected, the
system will select a suitable rate from the basic rate set automatically.
802.11b Basic Rate: Specify the basic rate with which 802.11b clients are allowed to
access the wireless network. At least one rate should be selected in the rate
set. 1Mbps and 2Mbps are selected by default.
Supported Rate: Specify the supported rate for 802.11b clients. The supported
rate should not overlap with the basic rate that has been set. 5.5Mbps and
11Mbps are selected by default.
Multicast Rate: Specify the multicast rate for the 802.11b multicast packets.
The rate should be selected from the basic rate set. When auto is selected, the
system will select a suitable rate from the basic rate set automatically.
802.11g Basic Rate: Specify the basic rate with which the 802.11g clients are allowed to
access the network. At least one rate should be selected in the rate set. 1Mbps,
2Mbps, 5.5 Mbps and 11Mbps are selected by default.
Supported Rate: Specify the supported rate for 802.11g clients. The supported
rate set should not overlap with the basic rate set. 6Mpbs, 9Mbps, 12Mbps,
18Mbps, 24Mbps, 36Mbps, 48Mbps and 54Mbps are selected by default.
Multicast Rate: Specify the multicast rate for the 802.11g multicast packets.
The rate should be selected from the basic rate set. When auto is selected, the
system will select a suitable rate from the basic rate set automatically.
802.11n Basic MCS Index: Specify the basic MCS index for 802.11n clinet. The
maximum MCS index value for 802.11n clients should be equal to or greater
than the basic MCS index value. Otherwise, the clients cannot be allowed to
access the wireless network. The default setting is blank. If a value is selected ,
only 802.11n clients are allowed to access the network.
Supported MCS Index: Specify the support MCS index for the device. The
support MCS index should be equal to or greater than the basic MCS index.
802.11ac Basic MCS Set: Specify the basic MCS set for the device. The 802.11ac clients
should support the number of antennas and MCS index range regulated by the
basic MCS set. Otherwise, the clients cannot access the wireless network.
Supported MCS Set: Specify the support MCS set for the device. The
corresponding number of antennas and MCS index range of the support MCS
set should be equal to or greater than that of basic MCS set.
Note:
For the connected APs enabled with radio, the rate settings won’t take effect until the APs
reboot or their radios are disabled and enabled again.
35
Page 40

5.3 Band Steering
There are clients that only support the 2.4GHz band and clients that support dual band in a
wireless network. If all the clients connect to the 2.4GHz band, the 2.4GHz band will become
very congested, reducing the network performance. With band steering enabled, the AP
would steer the dual band clients to connect to the 5GHz first, which would balance the
band connections and improve the network performance. When enabling band steering,
please ensure the SSIDs of both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands are the same.
The following example is used to illustrate the process of band steering.
Figure 5-4 Band Steering Process
Wireless Controller
Dual-band CAP
2.4GHz SSID: TP-Link
Client Number: 36
Dual-band Client
5GHz SSID: TP-Link
Client Number: 40
The 2.4GHz SSID and 5GHz SSID of the dual-band CAP are set the same. If a 2.4GHz client
or 5GHz client requests to connect to the CAP, the band steering won’t take effect and the
client will connect to the 2.4GHz or 5GHz directly. If a dual band client requests to connect
to the CAP, due to band steering, the CAP will lead the client to connect to the 5GHz band
first.
When the wireless network satisfies the following two conditions:
1 The client number of the 5GHz band reaches or exceeds the maximum client numbers
that are allowed to connect (40 as an example).
2 The difference value in client number of the 2.4GHz band and the 5GHz band
reaches or exceeds the difference threshold set in band steering setting (4 as an
example,40-36≥4)
.
Due to band steering, a new dual band client will be rejected from connecting to the 5GHz
band and be allowed to connect to the 2.4GHz band.
36
Page 41

But if the client repeatedly requests to connect to the 5GHz, and the rejection exceeds the
maximum failure number set in band steering setting, the client will be allowed to connect.
Choose the menu Radio > Band Steering > Band Steering to load the following page.
Check the Enable radio button to enable the band steering function.
Figure 5-5 Band Steering
5GHz Maximum
Connection Threshold
Difference Threshold Specify the maximum difference value between the number of clients
Maximum Failure
Number
Click Save to finish the settings.
5.4 Wi-Fi Roaming
Wi-Fi roaming is a technology that keeps a station connected to the network while the
station is moving from one Access Point to another.
Specify the maximum number of clients that are allowed to connect to the 5GHz
band. When the client number meets the 5GHz maximum connection threshold
and difference threshold, the AP will prevent more APs from connecting to the
5GHz band.
connected to the 5GHz band and the number connected to the 2.4GHz band.
When the client connections meet the 5GHz maximum connection threshold
and the difference threshold, the AP will prevent more APs from connecting to
the 5GHZ band.
Specify the maximum number of failed connection attempts of the client.
If the clients continuously request to connect to the 5GHz band and the number
of failed attempts exceeds the specified number, the CAP will accept the
connection request.
For example, a client can walk through a facility while carrying on a conversation over a WiFi phone. The Wi-Fi radio inside the phone automatically roams from one access point to
another as needed to provide seamless connectivity.
37
Page 42

Choose the menu Radio > Wi-Fi Roaming to load the following page. Configure the two
802.11k options.
Figure 5-6 Wi-Fi Roaming
Neighbor List Choose to whether enable Wi-Fi roaming feature. With this option enabled, Wi-
Fi roaming will take effect on the 2.4GHz band.
Neighbor List Dual
Band
Choose to whether enable Wi-Fi roaming on both of the 2.4GHz and 5GHz
bands.
Note:
Only when Neighbor List is enabled, will Neighbor List Dual Band take eect.
Click Save to finish the settings.
38
Page 43

6
Wireless
6.1 Wireless Service
Choose the menu Radio > Wireless > Wireless Service to load the following page.
Figure 6-1 Wireless Service
Specify and view the wireless service on this page. Click to create a new wireless
service. Click
Figure 6-2 Add a New Wireless Service
Status Specify whether to enable the wireless network.
SSID Specify the SSID (Service Set Identifier) for the wireless network. The SSID
button, you can go into the radio binding page.
should be unique.
Description Specify a description for the entry to make it easier to search for and manage.
39
Page 44

AP Isolation Enable AP isolation to isolate the wireless clients connected to the same AP
so that they cannot communicate with each other. This setting cannot take
effect in other APs; that is, AP isolation cannot isolate the clients connected to
different APs with the same SSIDs.
SSID Broadcast With this option enabled, the AP will broadcast the SSID to the nearby hosts, so
that those hosts can find the wireless network identified by this SSID. With this
option disabled, users must enter the SSID manually to connect to the AP.
Security Specify the security option of the wireless network. If all the clients are allowed
to access the wireless network, please select None. For the safety of the
wireless network, you are suggested to encrypt your wireless network with
password. This device provides three security options: WPA/WPA2 (Wi-Fi
Protected Access) and WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK (WPA Pre-Shared Key). WPAPSK/WPA2-PSK is recommended. Settings vary in different security options as
the details is in the following introduction.
Following is the detailed introduction of security mode: WPA/WPA2 and WPA-PSK/WPA2-
PSK.
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Based on pre-shared key. It is characterized by higher safety and simple settings, which
suits for common households and small business. WPA-PSK has two versions: WPA-PSK
and WPA2-PSK.
Figure 6-3 Security of WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Authentication Type Select one of the following versions:
Auto: Select WPA or WPA2 automatically based on the wireless client's
capability and request.
WPA-PSK: Pre-shared key of WPA.
WPA2-PSK: Pre-shared key of WPA2.
Encryption Select the encryption type, including Auto, TKIP, and AES. The default setting is
Auto, which can select TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) or AES (Advanced
Encryption Standard) automatically based on the wireless station's capability
and request. AES is more secure than TKIP and TKIP is not supported in
802.11n mode. It is recommended to select AES as the encryption type.
Group Key Update
Period
Enter the number of seconds (minimum 30) to control the time interval for the
encryption key automatic renewal.
PSK Password Configure the PSK password with ASCII or Hexadecimal characters. For ASCII,
the length should be between 8 and 63 characters with a combination of
numbers, letters (case-sensitive) and common punctuations. For Hexadecimal,
the length should be 64 characters (case-insensitive, 0-9, a-f, A-F).
40
Page 45

WPA/WPA2
Based on Radius Server, WPA can assign different passwords for different users and it is
much safer than WPA-PSK. However, it has high maintenance costs and is only suitable for
enterprise users. At present, WPA has two versions: WPA and WPA2.
Figure 6-4 Security of WPA/WPA2
Authentication Type Select one of the following versions:
Auto: Select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK automatically based on the wireless
station's capability and request.
WPA: Wi-Fi Protected Access.
WPA2: Version 2 of WPA.
Encryption Select the encryption type, including Auto, TKIP, and AES. The default setting is
Auto, which can select TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) or AES (Advanced
Encryption Standard) automatically based on the wireless station's capability
and request. AES is more secure than TKIP and TKIP is not supported in
802.11n mode. It is recommended to select AES as the encryption type.
Group Key Update
Period
Radius Server IP Enter the IP address of the Radius server.
Radius Port Enter the port number of the Radius server.
Radius Password Enter the share key of the Radius server.
Enter the number of seconds (minimum 30) to control the time interval for the
encryption key automatic renewal.
Click button, you can go into the radio binding page.
41
Page 46

Figure 6-5 Radio Banding
SSID Displays the current wireless network.
Select the Group Select the group to be displayed in the list.
VLAN Binding
Bound
Unbind
Back to Wireless
Enter a VLAN ID into the field and Click
network will be bound to the corresponding VLAN.
Select the desired entries and click this button to bind the service to
corresponding radios. Unlocked APs cannot be bound. Please refer to
Settings
Select the desired entries and click this button to unbind the service in
corresponding radios.
Click this button to return to the wireless service page.
and check the box Lock to AC Automatically.
above the list. The wireless
4.1 AP
42
Page 47

7
Authentication
7.1 MAC Authentication
MAC Authentication is based on VLAN and MAC address. The administrator can preset
MAC Authentication entries to allow or deny the clients with specific MAC addresses
and in specific VLANs to access the network. The clients do not need to install any client
software, nor do any operation during the MAC authentication process.
With this feature configured, when a client tries to access the network, the AP sends
the MAC address and VLAN information of the client to the AC. Based on the preset
MAC Authentication entries, the AC checks whether the client is allowed to access the
network or not. Only the clients allowed to access the network can go for the further portal
authentication process.
As the following diagram shows, we configure Client 1 and Client 2 to the whitelist, and
Client 3 to the blacklist on the AC. When these clients are trying to access the network,
the AC will check the MAC authentication entries. According to these entries, Client 1 and
Client 2 will be allowed to access the network, and Client 3 will be denied to access the
network.
Figure 7-1 Topology for MAC Authentication
Client 1
01-86-FC-75-B1-02
VLAN 2
Internet
AC
PoE Switch
CAP
Client 2
01-86-FC-75-B2-75
VLAN 2
Whitelist of MAC Addresses:
01-86-FC-75-B1-02 VLAN2
01-86-FC-75-B2-75 VLAN2
Blacklist of MAC Address:
01-86-FC-75-B3-34 VLAN 3
Client 3
01-86-FC-75-B3-34
VLAN 3
To configure MAC Authentication, refer to the following steps:
43
Page 48

1 Choose the menu Authentication > MAC Authentication > MAC Address to bind the
MAC addresses and VLANs of the clients to be authenticated.
2 Choose the menu Authentication > MAC Authentication > MAC Authentication to set
MAC authentication rule on the VLANs.
7.1.1 MAC Address
Choose the menu Authentication > MAC Authentication > MAC Address to load the
following page.
Figure 7-2 MAC Address
You can click Backup to back up all the MAC authentication entries in the CSV file which
are in ANSI coding format. This file can be restored to the AC and all MAC addresses can
be added into the MAC address list.
To add multiple MAC address entries at a time:
1 Save the MAC address entries as a CSV file with ANSI coding format in the AC. You can
use the Backup MAC Address function to obtain a CSV file to view the correct format.
2 Click Browse to select the file path, and then click Restore to restore the file.
Note:
Using Excel to open the CSV le may cause some numerical format changes, and the number may be displayed
incorrectly. If you use Excel to edit the CSV le, please set the cell format as text.
In the MAC address list you can view the MAC address entries.
Click
to add a new MAC address entry, as shown in the following figure.
44
Page 49
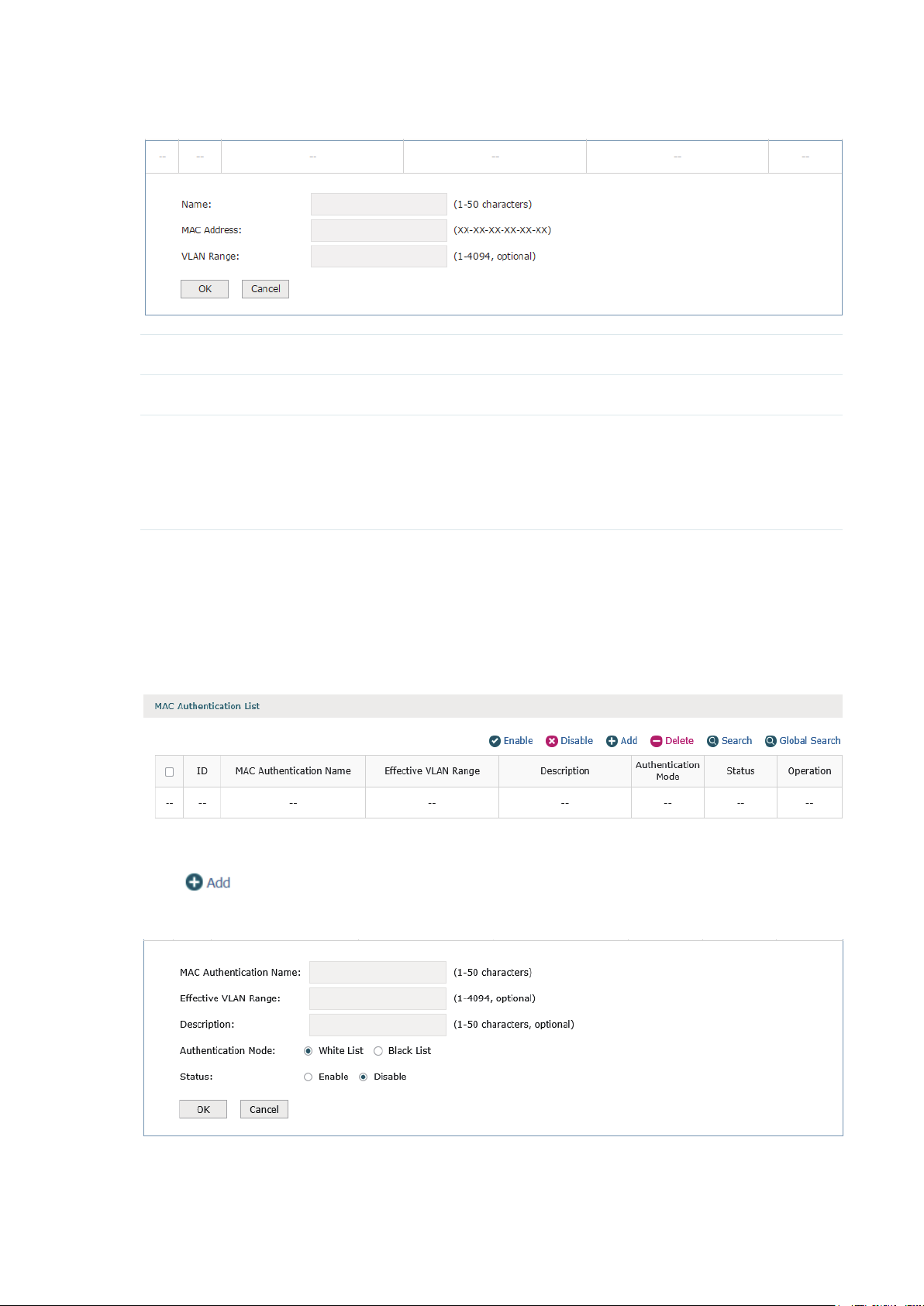
Figure 7-3 Add a new MAC Address Entry
Name Specify the name for the entry.
MAC Address Specify the MAC address of the client.
VLAN Range Specify the VLAN range. The range is 1 to 4094. Number and range are both
supported. The ranges can be seperated by commas. For example:
1
11-20
1,3,5,4090-4094
7.1.2 MAC Authentication
Choose the menu Authentication > MAC Authentication > MAC Authentication to load the
following page.
Figure 7-4 MAC Authentication
Here you can view the MAC Authentication List.
Click
Figure 7-5 Add a MAC Authentication List
to add a new entry.
45
Page 50

MAC Authentication
Name
Effective VLAN Range Specify or check the effective VLAN range of the MAC authentication entry.
Description Specify or check the description of the authentication entry to make it easier to
Authentication Mode Black List: All the MAC addresses in this authentication mode are forbidden to
Status Specify whether to enable this authentication entry.
Specify or check the name of the MAC authentication entry to make it easier to
search for and manage.
The range is 1 to 4094. Number and range are both supported. The ranges can
be seperated by commas. For example:
1
11-20
1,3,5,4090-4094
search for and manage.
access the network.
7.2 Portal Authentication
AC provides several types of portal authentication, including Web Authentication, Onekey
Online, Voucher, SMS, Facebook, Remote Portal.
To provide portal authentication service, two kinds of servers are required: web server
which is used to provide login page for the clients, and authentication server which is used
to authenticate the clients. The web server and authentication server can be the built-in
servers of the AC or the external connected servers. Which kinds of servers are used to
provide portal service is determined by the portal authentication types and your choices.
Figure 7-6 Portal Topology
Web Server (external or built in AC)
Access Device
Authentication Server (external or built in AC)
Web Server
Client
For Web Authentication, Onekey Online, Voucher and SMS, the AC uses its built-in web
server to provide login page for the clients. Before configuring such portal authentication
features, you need to set the login page in the Splash Page module.
For Facebook, the web sever of Facebook is used to provide login page and Facebook
Page for the clients.
For Remote Portal, you need to build a remote portal server on your network to provide
customized login page for the clients.
Authentication Server
46
Page 51

For Web Authentication and Remote Portal, there are two methods to authenticate the
clients: using the built-in authentication server of the AC or using the remote authentication
server on the network. You can configure the remote authentication server in the
Authentication Sever module.
For Onekey Online and Voucher, the AC uses the built-in authentication server to
authentication the clients.
For SMS, the AC uses the authentication server of service provider Twilio to authenticate
the clients.
For Facebook, the AC uses the authentication server of Facebook to authenticate the
clients.
Note:
Before conguring portal authentication, make sure that the IP address of the AC’s interface that manages the
AP and the IP addresses of the clients are routable.
7.2.1 Splash Page
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Splash Page to load the
following page.
Figure 7-7 Splash Page
Here you can upload pictures or use the default template to set the splash pages for
subsequent authentication to meet the requirements of advertisement promotions.
Click
to add a new entry. There are four authentication types of the splash page,
including Web Authentication, Onekey Online, Voucher and SMS.
47
Page 52

Figure 7-8 Add a Splash Page
Page Name Specify the name of the splash page template.
Authenticaiton Type Select the authentication type of the splash page. Options include Web
Authentication, Onekey Online, Voucher and SMS.
Web Authentication: Clients need to enter a username and password to log in,
and can access the network after successful authentication.
Onekey Online: Clients can access the network without entering any
parameters on the login page.
Voucher: Clients need to enter the voucher code to log in, and can access the
network after successful authentication.
SMS: Clients need to enter the verification code received by their mobile
phones to log in, and can access the network after successful authentication.
Page Title Specify the page title for the authentication.
Background Select the background type. Two types are supported: Solid Color selected on
the page and Picture uploaded from your local computer.
Background Color If Solid Color is selected, configure your desired background color through the
color picker or by entering the RGB values manually.
Background Picture If Picture is selected, click the Upload button and a window will pop up. Click
the Browse button and select a background picture. You can drag and scale
the clipping region to edit the picture.
Logo Click the Upload button and a window will pop up. Click the Browse button and
select a logo picture. You can drag and scale the clipping region to edit the
picture.
Logo Position Set the position of the logo picture. The options include Middle, Upper and
Lower.
48
Page 53

Welcome Information Specify the welcome information.
Welcome Information
Color
Copyright Specify the copyright information.
Copyright Information
Color
Description Specify a description for the entry to make it easier to search for and manage.
Input Box Frame Color Select your desired color for the input box border through the color picker or
Button Position Set the position of the login button. The options include Middle, Upper and
Button Color Select your desired login button color through the color picker or by entering
Button Text Color Select your desired text color for the button through the color picker or by
Select your desired text color for the welcome information through the color
picker or by entering the RGB values manually.
Select your desired text color for Copyright information through the color
picker or by entering the RGB values manually.
by entering the RGB values manually.
Lower.
the RGB values manually.
entering the RGB values manually.
On the right side of the page, you can click the buttons Tablet PC, Mobile Phone and PC to
preview the login pages on these kinds of devices.
7.2.2 Web Authentication
In Web Authentication, clients can use the user accounts to pass the authentication.
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Web Authentication to load
the following page.
Figure 7-9 Web Authentication
Here you can view the Web Authentication information and edit the entries.
Click
Authentication Server and Remote Authentication Server.
Local Authentication Server
Select Local Authentication Server as the Authentication Server Type, and the following
the page will appear.
to add a new entry. There are two authentication server types, including Local
49
Page 54

Figure 7-10 Local Authentication Server Page
Status Specify the status of the entry.
SSID Specify the SSIDs of the Web authentication.
Note: The SSIDs abeled "Bound" are being used by other authentication entries.
If these SSIDs are selected, the original configuration will be replaced by the
current configuration.
Splash Page Select the splash page of the Web authentication.
Authenticaiton Server
Type
Success Redirect URL Specify the redirect URL address after successful authentication.
Fail redirect URL Specify the redirect URL address after the authentication failure.
Non-sense
Authentication
Advertisement Specify whether to enable the Advertisement feature. With this feature
Specify the server type of the Web authentication. Here we select Local
Authentication Server.
With this option enabled, the non-sense authenticated users will pass the
authentication automatically when connecting to the wireless network.
enabled, you can add advertisement pictures on the authentication page.
These advertisement pictures will be displayed before the login page appears.
You can also allow users to skip the advertisement by enabling Allow to Skip
Advertisement.
50
Page 55

Description Specify a description for the Web authentication entry to make it easier to
search for and manage.
Note:
When Local Authentication Server is selected, you need to add the login information of the allowed users. For
detailed conguration, refer to
Remote Authentication Sever
7.3 Local User Management
.
Select Remote Authentication Server as the Authentication Server Type, and the following
the page will appear.
Figure 7-11 Remote Authentication Server Page
Status Specify the status of the entry.
SSID Specify the SSIDs that will be enabled with Web authentication.
Note: The SSIDs labeled "Bound" are being used by other authentication
entries. If these SSIDs are selected, the original configuration will be replaced
by the current configuration.
Splash Page Select the splash page of the Web authentication.
51
Page 56

Authenticaiton Server
Type
Specify the server type of the Web authentication. Here we select Remote
Authentication Server.
To configure Radius server, refer to
Authentication Server
.
Authentication Server
Group
Free Authentication
Timeout
Success Redirect URL Specify the redirect URL address after successful authentication.
Fail redirect URL Specify the redirect URL address after the authentication failed.
Non-sense
Authentication
Advertisement Specify whether to enable the Advertisement feature. With this feature enabled,
Select the server group of the Web authentication.
Set the free online duration for the users.
Note: If the remote authentication server is configured with an online time
duration for the users, then the time duration set on the server will take effect
instead of Free Authentication Timeout set here.
If non-sense authentication is enabled, the non-sense authenticated users will
pass the authentication automatically when connecting to the wireless network.
you can add advertisement pictures on the authentication page. These
advertisement pictures will be displayed before the login page appears. The
required parameters are as follows:
Picture Resouce: You can add up to 5 advertisement pictures. When several
pictures are added, they will be played in a loop. There are two picture
resources: Local Upload and External Link.
Advertisement Duriation Time: Specify how long the advertisement will be
displayed for. For this duration, the pictures will be played in a loop. Enter
a value from 1 to 30 seconds. If the duration time is not enough for all the
pictures, the rest will not be displayed.
Photo Carousel Interval: Specify the picture carousel interval. If this value
is set as 5 seconds, the first picture will be displayed for 5 seconds, followed
by the second picture for 5 seconds, and so on. Enter a value from 1 to 10
seconds.
Allow to Skip Advertisement: Specify whether to enable this feature. With this
feature enabled, the user can click the Skip button to skip the advertisement.
Description Specify a description for the Web authentication entry to make it easier to
search for and manage.
52
Page 57

7.2.3 Onekey Online
In Onekey Online Authentication, clients can pass the authentication without entering any
parameters on the login page .
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Onekey Online to load the
following page.
Figure 7-12 Onekey Online
Here you can view the Onekey Online Authentication information and edit the entries.
Click
Figure 7-13 Add a New Onekey Online Entry
to add a new entry.
Configure the related parameters and click OK.
Status Specify whether to turn on the Onekey Online authentication entry.
SSID Specify the SSIDs that will be enabled with Onekey Online authentication.
Note: The SSIDs labeled "Bound" are being used by other authentication
entries. If these SSIDs are selected, the original configuration will be replaced
by the current configuration.
Splash Page Select the splash page of Onekey Online authentication.
Free Authentication
Timeout
Select the free online time for users who have passed onekey online
authentication.
53
Page 58

Advertisement Specify whether to enable the Advertisement feature. With this feature enabled,
you can add advertisement pictures on the authentication page. These
advertisement pictures will be displayed before the login page appears. The
required parameters are as follows:
Picture Resouce: You can add up to 5 advertisement pictures. When several
pictures are added, they will be played in a loop. There are two picture
resources: Local Upload and External Link.
Advertisement Duriation Time: Specify how long the advertisement will be
displayed for. For this duration, the pictures will be played in a loop. Enter
a value from 1 to 30 seconds. If the duration time is not enough for all the
pictures, the rest will not be displayed.
Photo Carousel Interval: Specify the picture carousel interval. If this value
is set as 5 seconds, the first picture will be displayed for 5 seconds, followed
by the second picture for 5 seconds, and so on. Enter a value from 1 to 10
seconds.
Allow to Skip Advertisement: Specify whether to enable this feature. With this
feature enabled, the user can click the Skip button to skip the advertisement.
Description Specify a description for the onekey online authentication entry to make it
7.2.4 Voucher
In Voucher Authentication, you can distribute the voucher codes that are automatically
generated by the AC to the clients. Clients can enter the voucher codes on the login page
to access the network.
Note:
To create voucher codes, refer to
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Voucher to load the following
page.
Figure 7-14 Voucher
easier to search for and manage.
Voucher Management
.
Here you can view the Voucher Authentication information and edit the entries.
54
Page 59

Click to add a new entry.
Figure 7-15 Add a New Voucher Entry
Configure the related parameters and click OK.
Status Specify whether to turn on the Voucher authentication entry.
SSID Specify the SSIDs that will be enabled with Voucher authentication.
Note: The SSIDs labeled "Bound" are being used by other authentication
entries. If these SSIDs are selected, the original configuration will be replaced
by the current configuration.
Splash Page Select the splash page of Onekey Online authentication.
Success Redirect URL Specify the redirect URL address after successful authentication
Fail redirect URL Specify the redirect URL address after the authentication failure.
Non-sense
Authentication
If non-sense authentication is enabled, the non-sense authenticated users will
pass the authentication automatically when connecting to the wireless network.
55
Page 60

Advertisement Specify whether to enable the Advertisement feature. With this feature enabled,
you can add advertisement pictures on the authentication page. These
advertisement pictures will be displayed before the login page appears. The
required parameters are as follows:
Picture Resouce: You can add up to 5 advertisement pictures. When several
pictures are added, they will be played in a loop. There are two picture
resources: Local Upload and External Link.
Advertisement Duration Time: Specify how long the advertisement will be
displayed for. For this duration, the pictures will be played in a loop. Enter
a value from 1 to 30 seconds. If the duration time is not enough for all the
pictures, the rest will not be displayed.
Photo Carousel Interval: Specify the picture carousel interval. If this value
is set as 5 seconds, the first picture will be displayed for 5 seconds, followed
by the second picture for 5 seconds, and so on. Enter a value from 1 to 10
seconds.
Allow to Skip Advertisement: Specify whether to enable this feature. With this
feature enabled, the user can click the Skip button to skip the advertisement.
Description Specify a description for the Voucher entry to make it easier to search for and
7.2.5 SMS
In SMS Authentication, the client can get a verification code using a mobile phone and
enter the code to pass the authentication.
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > SMS to load the following
page.
Figure 7-16 SMS Page
Here you can view the SMS Authentication information and edit the entries.
Click
manage.
to add a new entry.
56
Page 61

Figure 7-17 Add a New SMS Entry
Configure the following parameters. Note that you need to first go to the Twilio website
to register an account and get the following three parameters: Twilio SID, Authentication
Token and Phone Number.
Status Specify whether to turn on the SMS authentication entry.
SSID Specify the SSIDs that will be enabled with SMS authentication.
Note: The SSIDs labeled "Bound" are being used by other authentication
entries. If these SSIDs are selected, the original configuration will be replaced
by the current configuration.
Splash Page Select the splash page of SMS authentication.
Twilio SID Enter the Account SID for Twilio API Credentials.
Authentication Token Enter the Authentication Token for Twilio API Credentials.
Phone Number Enter the phone number that is used to send verification messages to the
clients.
Free Authentication
Timeout
Specify the permitted online time of the clients who have passed SMS
authentication.
57
Page 62

Advertisement Specify whether to enable the Advertisement feature. With this feature enabled,
you can add advertisement pictures on the authentication page. These
advertisement pictures will be displayed before the login page appears. The
required parameters are as follows:
Picture Resouce: You can add up to 5 advertisement pictures. When several
pictures are added, they will be played in a loop. There are two picture
resources: Local Upload and External Link.
Advertisement Duriation Time: Specify how long the advertisement will be
displayed for. For this duration, the pictures will be played in a loop. Enter
a value from 1 to 30 seconds. If the duration time is not enough for all the
pictures, the rest will not be displayed.
Photo Carousel Interval: Specify the picture carousel interval. If this value
is set as 5 seconds, the first picture will be displayed for 5 seconds, followed
by the second picture for 5 seconds, and so on. Enter a value from 1 to 10
seconds.
Allow to Skip Advertisement: Specify whether to enable this feature. With this
feature enabled, the user can click the Skip button to skip the advertisement.
Description Specify a description for the SMS entry to make it easier to search for and
7.2.6 Facebook
In Facebook Authentication, the login page is your own Facebook Page that are bound
to the AC, and you can customize your Facebook Page according to your actual needs.
AC uses the Facebook server to authenticate the clients, and the logged-in clients will be
redirected to your Facebook Page.
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Facebook to load the following
page.
Figure 7-18 Facebook
manage.
Here you can view the Facebook Authentication information and edit the entries.
Click
to add a new entry.
58
Page 63

Figure 7-19 Add a New Facebook Entry
Status Specify whether to turn on the Facebook authentication entry.
SSID Specify the SSIDs that will be enabled with Facebook authentication.
Note: The SSIDs labeled "Bound" are being used by other authentication
entries. If these SSIDs are selected, the original configuration will be replaced
by the current configuration.
Configuration Click this button to specify the Facebook Page. For details, refer to the
following introduction.
Facebook Page Displays the name of the specified Facebook Page.
Description Specify a description for the Facebook entry to make it easier to search for and
manage.
Click the Configuration button and log in to your Facebook account in the pop-up window.
Then configure the Facebook Wi-Fi parameters and click Save Settings.
59
Page 64

Figure 7-20 Facebook Configuration Page
Facebook Page Select a Facebook Page that has been created in advance. Note that a valid
Bypass Mode Select bypass mode. There are two options:
Session Length Select how long the users will have Wi-Fi after they check in.
Terms of Service (Optional) Check the box and specify the terms of service.
7.2.7 Remote Portal
In Remote Portal, you can build your own portal server on the network to provide the
customized login page for clients. In such scenario, your customized server is called as
remote portal server, and AC will be responsible for the communication between the
clients and the remote portal server.
location should be associated with the Facebook Page.
Skip check-in link: Users can directly skip check-in and access the network
without any code.
Require Wi-Fi code: Users need to enter the Wi-Fi code you configured here to
access the network.
60
Page 65

Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Remote Portal to load the
following page.
Figure 7-21 Remote Portal
Here you can view the Remote Portal Authentication information and edit the entries.
Click
to add a new entry. There are two authentication server type: Local
Authentication Server and Remote Authentication Server.
Local Authentication Sever
Select Local Authentication Server as the Authentication Server Type, and the following
page will appear.
Figure 7-22 Local Authentication Server Page
Status Specify whether to turn on the remote portal authentication entry.
Splash Page Enter the splash page name of the remote portal authentication.
61
Page 66

SSID Specify the SSID that will be enabled with Remote Portal authentication.
Note: The SSIDs labeled "Bound" are being used by other authentication
entries. If these SSIDs are selected, the original configuration will be replaced
by the current configuration.
Remote Portal Address Enter the address of the server used for remote portal authentication.
Authenticaiton Server
Type
Success Redirect URL Specify the redirect URL address after successful authentication.
Fail redirect URL Specify the redirect URL address after the authentication failure.
Non-sense
Authentication
Description Specify a description for the remote portal authentication entry to make it
Select the server type used for remote portal authentication.
If non-sense authentication is enabled, the non-sense authenticated users will
pass the authentication automatically when connecting to the wireless network.
easier to search for and manage.
Note:
When Local Authentication Server is selected, you need to add the login information of the allowed clients. For
detailed conguration, refer to
Remote Authentication Sever
7.3 Local User Management
.
Select Remote Authentication Server as the Authentication Server Type, and the following
page will appear.
Note:
To congure the remote Radius server ,
62
Page 67

Figure 7-23 Remote Authentication Server Page
Status Specify whether to turn on the remote portal authentication entry.
Splash Page Enter the splash page name of the remote portal authentication.
VLAN ID Select the VLAN ID used to remote portal authentication.
Remote Portal Address Enter the address of the server used for remote portal authentication.
Authenticaiton Server
Type
Authentication Server
Group
Select the server type used for remote portal authentication.
To configure Radius server, refer to
Select the server group used for remote portal authentication.
63
Authentication Server
.
Page 68

Free Authentication
Timeout
Success Redirect URL Specify the redirect URL address after successful authentication.
Fail redirect URL Specify the redirect URL address after the authentication failure.
Set the free online duration for the users.
Note: If the remote authentication server is configured with an online time
duration for the users, then the time duration set on the server will take effect
instead of Free Authentication Timeout set here.
Non-sense
Authentication
Description Specify a description for the remote portal authentication entry to make it
If non-sense authentication is enabled, the non-sense authenticated users will
pass the authentication automatically when connecting to the wireless network.
easier to search for and manage.
7.3 Local User Management
In Local User Management, you can create and manage local user accounts for the Web
authentication feature. Clients need to use the local user accounts to pass the Web
authentication.
Choose the menu Authentication > User Management > Local User Management to load
the following page.
Figure 7-24 Local User Management
Backup User Information
Click Backup to backup all the local users’ information into a CSV file in ANSI coding format.
This file can be restored to the user’s list.
Restore User Information
Add multiple local user entries at a time:
64
Page 69

1 Save the local user entries as a CSV file with ANSI coding format in the device. You
can use the Backup User Information function to obtain a CSV file to view the correct
format.
2 Click Browse to select the file path, and then click Restore to restore the file.
Note:
Using Excel to open the CSV file may cause some numerical format changes, and the
number may be displayed incorrectly. If you use Excel to edit the CSV file, please set the
cell format as text.
Rule List
Here you can specify and view the local users. Click
to add a new entry. There are
two user types, including Formal User and Free User.
Formal User
You can provide formal users with continuous internet service. When the user’s account
expires, the account will be invalid.
Figure 7-25 Add a Formal User
User Type Specify the user type as formal user.
Username Specify the username. The username should not be the same as any existing
one.
Password Specify the password. Users will be required to enter the username and
password when they attempt to access the network.
65
Page 70

Authentication
Timeout
Authentication Period Specify the authentication period during which the users can log in to the web
Specify the authentication timeout for formal users. After the timeout, the users
need to log in at the web authentication page again to access the network.
authentication page.
MAC Address Binding
Type
Maximum Users Specify the maximum number of users able to use this account to pass the
Rate Limit (Download) Select whether to enable download rate limit. With this option enabled, you can
Rate Limit (Upload) Select whether to enable upload rate limit. With this option enabled, you can
Traffic Limit Select whether to enable traffic limit. With this option enabled, you can specify
Name Specify the user's name (optional).
Telephone Specify the user's telephone number (optional).
There are three types of MAC binding: No binding, Static Binding and Dynamic
Binding.
If dynamic binding is selected, the MAC address of the first user that passes
the authentication will be bound.
If static binding is selected, the MAC address of all users that pass the
authentication will be bound.
authencitation.
specify the limit of download rate.
specify the limit of upload rate.
the total traffic limit in a period of time. Once the limit is reached in one period,
the client cannot access the network until the next period. The period options
include Every Day, Every Week, Every Month and All Authentication Time.
Description Enter a description for the user (optional).
Status Specify whether to enable this account.
Free User
You can provide free users with internet service for a short time (in minutes). The account
can be reused. When the time expires, the user can log in to the authentication page again
and can be re-authenticated.
66
Page 71

Figure 7-26 Add a Free User
User Type Specify the user type as free user.
Username Specify the username. The username should not be the same as any existing
one.
Password Specify the password. Users will be required to enter the username and
password when they attempt to access the network.
Authentication Period Specify the authentication period during which the users can log in to the web
authentication page.
Free Period Specify the free period for the users to be online.
Maximum Users Specify the maximum number of users able to use this account to pass the
authentication.
Rate Limit (Download) Select whether to enable download rate limit. With this option enabled, you can
specify the limit of download rate.
Rate Limit (Upload) Select whether to enable upload rate limit. With this option enabled, you can
specify the limit of upload rate.
Traffic Limit Select whether to enable traffic limit. With this option enabled, you can specify
the total traffic limit in a period of time. Once the limit is reached in one period,
the client cannot access the network until the next period. The period options
include Every Day, Every Week, Every Month and All Authentication Time.
Description Optional: Enter a description for the user.
Status Specify whether to turn on authentication.
67
Page 72

7.4 Voucher Management
You can create voucher codes in batch on the Create Voucher page and manage them
conveniently on the Manage Voucher page.
7.4.1 Create Voucher
Choose the menu Authentication > Voucher Management > Create Voucher to load the
following page.
Figure 7-27 Create Voucher
Specify the parameters of the vouchers to be created and click OK.
Code Length Specify the length of the voucher codes to be created.
Amount Specify the number of voucher codes to be created.
Type Select the type of the voucher codes to be created. There are two types:
Single Use and Multi Use. Single Use allows only one client to pass the
authentication with one voucher code. Multi Use allows several clients to pass
the authentication with one voucher code.
Max Users If Multi Use is selected, specify the maximum number of the clients who can use
the same voucher code to pass the authentication.
Duration Time Specify the permitted online time of clients who have passed the
authentication.
Rate Limit (Download) Select whether to enable download rate limit. With this option enabled, you can
specify the limit of download rate.
Rate Limit (Upload) Select whether to enable upload rate limit. With this option enabled, you can
specify the limit of upload rate.
Traffic Limit Specify the total traffic limit for one voucher. Once the limit is reached, the
client can no longer access the network using the voucher.
68
Page 73

Description Specify a description for the voucher codes to make them easier to search for
7.4.2 Manage Voucher
Choose the menu Authentication > Voucher Management > Manage Voucher to load the
following page.
Figure 7-28 Manage Voucher
The above table displays the information of the current vouchers. You can print and
distribute them to the users. Also, you can manage the vouchers, such as deleting the
vouchers and setting the vouchers to be expired.
and manage.
Code Displays the voucher code. Clients will be required to enter the voucher code
when they attempt to access the network.
Create Time Displays the time when the voucher code is created.
Dscription Displays the description for the voucher code.
Duration Displays the permitted online time of the clients who have passed the
authentication.
Status Displays whether the code is valid or not, and if valid, how many clients are
permitted to pass the authentication.
Operation
: Click this button to print the codes created in the same batch.
: Click this button to delete the voucher code.
: Click this button to set the voucher code to be expired, which means that
the voucher code cannot be used to pass the authentication.
7.5 Authentication Server
AC supports external Radius server. When clients start the authentication process, the
AC will forward user information to the external authentication server, and the server will
authenticate the user. To use this feature, follow the steps below:
69
Page 74

1 Configure the Radius Server. Choose the menu Authentication > Authentication Server
> Radius Server.
2 Configure the Server group. Choose the menu Authentication > Authentication Server
> Authentication Server Group.
7.5.1 Radius Server
Choose the menu Authentication > Authentication Server > Radius Server to load the
following page.
Figure 7-29 Radius Server
Here you can add, edit or delete an external radius server.
Click
Figure 7-30 Add a Radius Serve
to add a new entry.
Server Name Specify a name for the Radius server.
Server Address Specify the address of the server. It should be an IPv4 address or a DNS
domain.
Authentication Port Specify a port for the server to monitor the authentication packets.
70
Page 75

Billing Port Specify a port for the server to monitor the billing packets. 0 means disable the
billing function.
Share Key Specify a shared key for the Radius server.
Retry Count If no reply is received after the client sends a connect request, it will keep
resending the request. Specify the number of times the client is allowed to
resend the request.
Timeout Interval Specify the timeout interval after the client sends a request packet.
NAS IP Address Specify the NAS IP address for the authentication. Generally, it is the address
by which the AC and Radius server communicate. This field can be left empty.
Authentication Type The authentication type includes PAP, CHAP, MSCHAP and MSCHAPv2.
7.5.2 Authentication Server Group
Choose the menu Authentication > Authentication Server > Authentication Server Group
to load the following page.
Figure 7-31 Server Group
Here you can view or edit the server group.
Click
Figure 7-32 Add a Serve Group
Group Name Specify a group name for the authentication server. The group name should not
Authentication Type Select the authentication server type. Only Radius server is supported so far.
to add a new entry.
be the same as the existing one.
71
Page 76

Main Server Select the main server for the group. The main server will have higher priority.
Standby Server Select the standby server for the group. If the main server malfunctions, the
standby server will come into use.
Recovery Time Specify the time interval after the main server malfunctions for reconnection.
Description Specify a description for the authentication server group.
7.6 Authentication Config
7.6.1 Free Authentication Policy
Free authentication policy is used to provide free resources for clients before they pass
the portal authentication.
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Free Authentication Policy to
load the following page.
Figure 7-33 Free Authentication Policy
Here you can view the Free Authentication Policy information and edit the entries. Entry 1
to entry 4 are default free authentication policies and cannot be edited.
72
Page 77

Click to add a new entry. There are two Match Modes, including Five Tuple Type and
URL Type.
Five Tuple Type
Five Tuple Type is configured based on the IP address range, MAC address, VLAN ID,
port and protocol. It is recommended to select Five Tuple Type when there are many
parameters to be configured in the free authentication policy.
Figure 7-34 Five Tuple Type
Strategy Name Specify a name for the free authentication policy entry.
Match Mode Specify a match mode for the free authentication policy.
Source IP Range Specify the source IP address and subnet mask of the free authentication
policy entry.
Source MAC Address Specify the source MAC address of the free authentication policy entry.
Source VLAN Specify the source VLAN ID of the free authentication policy entry.
Source Port Specify the source port range of the free authentication policy entry.
Destination IP Range Specify the destination IP address and subnet mask of the free authentication
policy entry.
Destination Port Specify the destination source MAC address of the free authentication policy
entry.
Protocol Specify the service protocol of the free authentication policy entry.
73
Page 78

Description Specify a description for the free authentication policy entry to make it easier
to search for and manage.
Status Specify whether to turn on the free authentication policy.
URL Type
URL Type is configured based on the URL address, IP address range, MAC address and
VLAN ID. It is recommended to select URL Type when the URL address is already known.
Figure 7-35 URL Type
Strategy Name Specify a name for the free authentication policy entry.
Match Mode Specify a match mode for the free authentication policy.
URL Address Specify the URL address for the URL type of free authentication policy.
Source IP Range Specify the source IP address and subnet mask of the free authentication
policy entry.
Source MAC Address Specify the source MAC address of the free authentication policy entry.
Source VLAN Specify the source VLAN ID of the free authentication policy entry.
Protocol Specify the service protocol of the free authentication policy entry.
Description Specify a description for the free authentication policy entry to make it easier
to search for and manage.
Status Specify whether to turn on the free authentication policy.
Note:
• The empty strategy means all sources are allowed to visit.
74
Page 79

• Only when one of the source port or the destination port is congured, can the protocol take eect.
7.6.2 Authentication Parameters
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Authentication Parameters to
load the following page.
Figure 7-36 Authentication Config
Here you can configure and view the global parameters for the authentication.
Authentication Aging Specify whether to enbale authentication aging. If the authenticated users
leave the wireless network within the aging time, they could reconnect to the
AP without re-authentication. If the leave time is longer than the aging time,
authentication is required again for users to connect to the AP.
Aging Time Enter the aging time within which the users could reconnect to the AP without
authentication.The default value is 5.
Portal Authentication
Port
Specify the service port for portal authenticaiton. The default setting is 8080. It
should not be the same as other occupied service ports.
7.7 Applications
7.7.1 Application for Web Authentication
Network Requirements
A hotel wants to offer customers internet access and push hotel advertisements through
the Web authentication page. The clients can access the network only after passing the
Web authentication.
In this case, the hotel can use the local authentication server to authenticate the clients
and use the advertisement feature to display the advertisement pictures to the clients.
75
Page 80

Clients
CAP CAP
Core Switch
AC
PoE Switch PoE Switch
Router
Internet
Network Topology
Figure 7-37 Network Topology
Configuration Steps
1 Create SSID
Create an SSID for the clients in the Wireless module.
2 Configure the Splash Page
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Splash Page. Click
add a new entry.
Set the Authentication Type as Web Authentication and set the related parameters. Here
you can upload the logo image and a promotional image of the hotel to the device.
to
76
Page 81

Figure 7-38 Splash Page Configurations
3 Configure the Web Authentication
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Web Authentication. Click
to add a new entry.
Enable Web Authentication and set the related parameters.
77
Page 82

Figure 7-39 Web Authentication Configurations
4 Add Authentication Accounts
After Web Authentication configuration, we still need to add user accounts to the device.
In this example, we create accounts to meet the following requirements: Each room is
offered with a free account, and up to three clients are able to use this account to pass the
authentication at the same time. The free time is two hours, and the client needs to restart
the authentication after the time expires.
78
Page 83

Choose the menu Authentication > Local User Management > Local User Management.
Click
to add a new entry.
Set the related parameters as shown below.
Figure 7-40 Add a Free Account
79
Page 84

7.7.2 Application for Onekey Online
Clients
CAP CAP
Core Switch
AC
PoE Switch PoE Switch
Router
Internet
Network Requirements
A hotel wants to offer customers free internet access. Customers can access the internet
without providing any information. In this case, the hotel can use Onekey Online to meet
the requirements.
Network Topology
Figure 7-41 Network Topology
Configuration Steps
1 Create SSID
Create an SSID for the clients in the Wireless module.
2 Configure the Splash Page
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Splash Page. Click
add a new entry. Set the Authentication Type as Onekey Online and set the other related
parameters.
to
80
Page 85

Figure 7-42 Splash Page Configurations
3 Configure Onekey Online
In this case, we set the free online time as 30 minutes, and the client needs to restart the
connection after the time expires.
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Onekey Online. Click
add a new entry. Turn on the Onekey Online and set the related parameters.
Figure 7-43 Onekey Online Configurations
7.7.3 Application for Voucher
Network Requirements
A hotel wants to offer customers internet access. To access the internet, the customers
should provide the correct codes which are got from the hotel to pass the authentication.
to
In this case, the hotel can use the Voucher feature to generate voucher codes and assign
these codes to the clients. AC can use the built-in authentication server to authenticate the
clients.
81
Page 86

Network Topology
Figure 7-44 Network Topology
Internet
Router
Configuration Steps
1 Create SSID
AC
PoE Switch PoE Switch
CAP CAP
Core Switch
Clients
Create an SSID for the clients in the Wireless module.
2 Configure the splash page.
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Splash Page. Click
add a new entry.
Set the Authentication Type as Voucher and set the related parameters.
82
to
Page 87

Figure 7-45 Splash Page Configurations
3 Configure Voucher Authentication
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Voucher. Click
new entry. Turn on the Voucher feature and set the related parameters. Click OK.
Figure 7-46 Voucher Configurations
to add a
83
Page 88

4 Create Vouchers
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Voucher Management >
Create Voucher. Specify the related parameters and click Save.
Figure 7-47 Create Vouchers
5 Print Vouchers
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Voucher Management >
Manage Voucher. Click
Figure 7-48 View Vouchers
to export the voucher codes.
The voucher codes in the table will be exported as the following figure shows. You can print
these codes and give them to your customers.
84
Page 89

Figure 7-49 Print Vouchers
7.7.4 Application for SMS
Network Requirements
A hotel wants to offer customers internet access using the Twilio API service. The
customer needs to get authentication code using a mobile phone and access the network
with the authentication code.
In this case, the hotel can use the SMS feature to authenticate the clients.
85
Page 90
Network Topology
Figure 7-50 Network Topology
Internet
SMS Authentication Server
Router
PoE Switch PoE Switch
Configuration Steps
1 Create SSID
AC
CAP CAP
Core Switch
Clients
Create an SSID for the clients in the Wireless module.
2 Configure the splash page
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Splash Page. Click
add a new entry.
Set the Authentication Type as SMS and set the related parameters.
86
to
Page 91

Figure 7-51 Splash Page Configurations
3 Register an Twilio account
Go to the official website of Twilio and follow the instructions to create an account.
Figure 7-52 Register Account
4 Apply for Twilio Service and get the related information
After successful login to Twilio, you need to buy the service for SMS according to the
instructions on the website. Then get the account information, including ACCOUNT SID,
AUTH TOKEN and Phone number.
87
Page 92

Figure 7-53 Account Infromation_SID and Auth Token
Figure 7-54 Account Infromation_Phone Number
5 Configure the SMS Authentication
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > SMS. Click
to add a new
entry.
Figure 7-55 SMS Authentication Page
Enable SMS and configure the related parameters. You can directly paste the Twilio
account information from the website to this page. Click OK.
7.7.5 Application for Facebook
Network Requirements
A hotel wants to offer customers internet access and push hotel advertisement through
the Facebook Page of the hotel. And The customers will be redirected to the Facebook
Page after checking in.
88
Page 93
In this case, the hotel can use the Facebook authentication feature to authenticate the
clients.
Network Topology
Figure 7-56 Network Topology
Internet
Facebook Servers
Router
AC
PoE Switch PoE Switch
CAP CAP
Configuration Steps
1 Create the Facebook Page
Core Switch
Log in to Facebook and create a Facebook Page with advertisements of the hotel.
2 Create SSID
Create an SSID for the clients in the Wireless module.
3 Configure the Facebook Authentication
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Facebook. Click
a new entry.
89
to add
Page 94

Figure 7-57 Facebook Authentication Page
Click the Configuration button and specify the Facebook Page and the related parameters.
Click Save Settings and close this window.
Figure 7-58 Facebook Configurations
Verify the configuration result and click OK.
90
Page 95

Figure 7-59 Facebook Configuration Result
7.7.6 Application for Remote Portal
Network Requirements
A hotel wants to offer customers internet access and use the remote portal server to push
hotel advertisement through the login page. The clients can access the network only after
pass the authentication.
In this case, the hotel can use the Remote Portal feature. The remote portal server provides
login and authentication page, and the local server of the AC authenticates the clients.
91
Page 96

Network Topology
Figure 7-60 Network Topology
AC
PoE Switch PoE Switch
Internet
Router
Remote Portal Server
Core Switch
CAP CAP
Clients
Configuration Steps
1 Build Remote Portal Server
Build your remote portal server on the network and make sure the connectivity between
the AC and the server.
2 Create SSID
Create an SSID for the clients in the Wireless module.
3 Configure the Remote Portal Authentication
Choose the menu Authentication > Portal Authentication > Remote Portal. Click
to
add a new entry. Enable Remote Portal and set the related parameters.
92
Page 97

Figure 7-61 Web Authentication Configurations
93
Page 98

8
Link Backup
8.1 Dual-link Backup
Choose the menu Link Backup > Dual-link Backup > Dual-link Backup to load the following
page. Check the option to enable the dual-link backup.
Figure 8-1 Dual-link Backup
Enble Check this option to enable the dual-link backup function.
Priority Specify the priority of the AC. The AC with a greater number represents a
higher priority to be selected as the master link. The modification of priority will
result in the reconnection of all CAPs in the master link.
Peer Address Specify the address of the peer AC as the standby link. The CAP will get the
peer address when obtaining the IP address from the DHCP server. You should
enable the DHCP service on the AC.
Click Save to complete the configuration.
Note:
• If the priority and peer address are changed, the CAPs in the standby link should be rebooted to make the
settings take eect. To keep the settings of the master link and standby link consistent, please reboot all
the CAPs in the standby link after the modication of the settings.
• ACs used in the dual-link backup should be the same models.
• With the dual-link backup enabled, please ensure the settings of the master AC and standby AC are
consistent.
• When the CAPs switch to the standby link from the master link, the authenticated wireless clients will expire
and be required to re-authenticate.
94
Page 99

8.2 Application
Scenario
The dual-link backup and the standby AC are applied in the scenario that two ACs are used
to manage wireless networks together.
Topology
Figure 8-2 Topology
AC1
192.168.1.253
Priority: 150
AC2
192.168.0.253
Priority: 100
Internet
Router
Core Switch
PoE Switch PoE Switch
CAP
Configuration
1 Configure the external DHCP server.
DHCP Server
CAP
The external DHCP should support the configuration of the option field. Refer to the
corresponding guide for details of the option settings.
When an AP obtains an IP address from the DHCP server, it also needs the DHCP server
to deliver the IP addresses of the two ACs in the network. You should configure the
following parameters in the DHCP server:
95
Page 100

Enter TP-LINK at the DHCP Option 60 field.
Enter the IP addresses of the two ACs into DHCP Option 138 filed, therefore, the CAPs
in the network can find the two ACs.
Note:
• Before conguring the external DHCP server, please disable the DHCP function of the AC to avoid CAPs
obtaining IP addresses abnormally.
• Please enable DHCP Relay function on the core switch to ensure that the DHCP packets can be
transmitted.
2 Configure the priority
There are several ACs in the network and they can manage all the CAPs normally. If you
want CAPs to be managed by a specified AC, set a higher priority for it. When a new
CAP requests to connect to an AC, the AC with higher priority will be connected first.
The higher value means higher priority.
In the above topology, the priority of AC1 is 150 and AC2 is 100. Therefore the AC
becomes the master controller of the CAPs and all CAPs will connect to AC1 first. AC2
is the standby controller.
3 Configure the standby AC
The standby AC comes into use when the master AC breaks down and cannot work
normally. In this situation, the CAPs will automatically accept the management of the
standby AC.
If you want CAPs to connect to another AC when the master AC malfunctions, please
enter the IP address of the standby AC into the peer address field. Therefore, the
master AC will deliver the IP address of the standby AC to CAPs when assigning IP
addresses. CAPs will be associated with master AC and standby AC at the same time.
When the master AC breaks down, the standby AC becomes the master AC.
96
 Loading...
Loading...