Page 1

NTDPJTV05
TECHNICAL TRAINING MANUAL
N5SS CHASSIS
PROJECTION TELEVISION
TW40F80
Only the different points from the training manual “N5SS chassis” with its file
No. 026-9506 are described on this manual.
For other parts common with “N5SS chassis”, please refer to the original manual
with its file No. 026-9506.
©1997 TOSHIBA AMERICA CONSUMER PRODUCTS, INC.
NATIONAL SERVICE DIVISION
TRAINING DEPARTMENT
1420-B TOSHIBA DRIVE
LEBANON, TENNESSEE 37087
PHONE: (615)449-2360
FAX: (615)444-7520
www.toshiba.com/tacp
Page 2

Contents Page 1
Contents
SECTION I: OUTLINE................................................................................................6
1. FEATURE....................................................................................................................6
2. MERITS OF BUS SYSTEM...................................................................................... 6
3. SPECIFICATIONS..................................................................................................... 7
4. FRONT VIEW ...........................................................................................................8
5. REAR VIEW...............................................................................................................9
6. REMOTE CONTROL VIEW..................................................................................10
7. CHASSIS LAYOUT.................................................................................................. 11
8. CONSTRUCTION OF CHASSIS........................................................................... 12
SECTION II: TUNER, IF/MTS/S. PRO MODULE ................................................ 13
1. CIRCUIT BLOCK ...................................................................................................13
2. POP TUNER .............................................................................................................17
SECTION III: CHANNEL SELECTION CIRCUIT ............................................... 18
1. OUTLINE OF CHANNEL SELECTION CIRCUIT SYSTEM ..........................18
2. OPERATION OF CHANNEL SELECTION CIRCUIT ...................................... 18
3. MICROCOMPUTER............................................................................................... 19
4. MICROCOMPUTER TERMINAL FUNCTION..................................................20
5. EEPROM (QA02) .....................................................................................................22
6. ON SCREEN FUNCTION....................................................................................... 22
7. SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM................................................................................23
8. LOCAL KEY DETECTION METHOD ................................................................24
9. REMOTE CONTROL CODE ASSIGNMENT ..................................................... 25
10. ENTERING TO SERVICE MODE ...................................................................... 28
11. TEST SIGNAL SELECTION ............................................................................... 28
12. SERVICE ADJUSTMENT .................................................................................... 28
13. FAILURE DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURE ............................................................... 29
14. TROUBLESHOOTING CHART .......................................................................... 32
SECTION IV: DVD SWITCH CIRCUIT .................................................................35
1. DVD SWITCH BLOCK DIAGRAM ......................................................................35
2. OUTLINE..................................................................................................................36
Page 3

Contents Page 2
SECTION V: WAC CIRCUIT .................................................................................... 37
1. OUTLINE..................................................................................................................37
2. CIRCUIT OPERATION ..........................................................................................37
3. BLOCK DIAGRAM ................................................................................................. 42
4. WIDE ASPECT CONVERSION CIRCUIT FAILURE ANALYSIS
PROCEDURES......................................................................................................... 43
SECTION VI: DUAL CIRCUIT ................................................................................ 45
1. OUTLINE..................................................................................................................45
2. PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION............................................................................. 45
3. SYSTEM COMPONENT DIAGRAM OF DUAL UNIT...................................... 46
4. CIRCUIT OPERATION ..........................................................................................47
5. TERMINAL FUNCTION, DESCRIPTION AND BLOCK DIAGRAM OF
MAIN IC.................................................................................................................... 51
SECTION VII: 3-DIMENSION Y/C SEPARATOR CIRCUIT .............................. 58
1. OUTLINE..................................................................................................................58
2. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION ...................................................................................... 58
SECTION VIII: VER TICAL OUTPUT CIRCUIT.................................................. 60
1. OUTLINE..................................................................................................................60
2. V OUTPUT CIRCUIT.............................................................................................. 61
3. PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR V DEFLECTION STOP ................................... 64
4. RASTER POSITION SWITCHING CIRCUIT ....................................................66
SECTION IX: HORIZONTAL DEFLECTION CIRCUIT .................................... 67
1. OUTLINE..................................................................................................................67
2. HORIZONTAL DRIVE CIRCUIT.........................................................................67
3. BASIC OPERATION OF HORIZONTAL DRIVE...............................................67
4. HORIZONTAL OUTPUT CIRCUIT .....................................................................69
5. HIGH VOLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT ....................................................... 76
6. HIGH VOLTAGE CIRCUIT ................................................................................... 78
7. X-RAY PROTECTION CIRCUIT.......................................................................... 80
8. OVER CURRENT PROTECTION CIRCUIT ......................................................81
Page 4

Contents Page 3
SECTION X: DEFLECTION DISTORTION CORRECTION CIRCUIT
(SIDE DPC CIRCUIT)............................................................................................... 82
1. DEFLECTION DISTORTION CORRECTION IC (TA8859CP) ....................... 82
2. DIODE MODULATOR CIRCUIT ......................................................................... 83
3. A CTUAL CIRCUIT.................................................................................................. 84
SECTION XI: DIGITAL CONVERGENCE CIRCUIT ......................................... 87
1. OUTLINE..................................................................................................................87
2. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION ...................................................................................... 87
3. PICTURE ADJUSTMENT ...................................................................................... 89
4. CASE STUDY ...........................................................................................................97
5. TROUBLESHOOTING ........................................................................................... 98
6. CONVERGENCE OUTPUT CIRCUIT................................................................. 99
7. CONVERGENCE TROUBLESHOOTING CHART .........................................101
OVERALL BLOCK DIAGRAM................................................................................102
Page 5

SECTION I: OUTLINE
1. FEATURE
The TW40F80 is a first PJ-TV with a wide screen aspect
ratio of 16:9 we introduce to North U.S.A. markets.
As the basic chassis N5SS chassis is used.
The future of the model TW40F80 is the use of the N5SS
chassis. This chassis introduces a new bus system, developed by the PHILIPS company, called the I2C (or IIC) bus.
IIC stands for Inter-Integrated Circuit control. This bus coordinates the transfer of data and control between ICs inside
the TV. It is a bi-directional serial bus consisting of two lines,
named SDA (Serial D ATA), and SCL (Serial CLOCK). This
bus control system is made possible through the use of digital-to analog converters built into the ICs, allowing them to
be addressed and controlled by strings of digital instructions.
The TW40F80 is a first wide TV with a double window system we introduce to North U.S.A. markets.
The size of the main and sub screens separated in left and
right on the screen is the same as each other. So it is possible
to enjoy two programs or video and TV program at the same
time.
The sub screen is equipped wit 9 screen search function and
this is very convenient convenient to search a program you
desire.
2. MERITS OF BUS SYSTEM
2-1. Improved Serviceability
Most of the adjustments previously made by resetting variable resistors and/or capacitors can be made on the new chassis by operating the remote control and seeing the results on
the TV screen. This allows seeing adjustments to be made
without removing servicing speed and efficiency.
2-2. Reduction of Parts Count
The use of digital-to-analog converters built into the ICs,
allowing them to be controlled by software, has eliminated
or reduced the requirement for many discrete parts such as
potentiometers and trimmers, etc.
2-3. Quality Control
This central control of the adjustment data makes it easier to
understand, analyze, and review the data, thus improving
quality of the product.
Note:
Only the different points from the manual
“N5SS Chassis” with its file No. 026-9506
are described on this manual. For other parts
common with “N5SS Chassis”, please refer
to the original manual with its File No. 026-
9506.
***
5
Page 6
3. SPECIFICATIONS
Model TW56F80TW40F80 TP61F90 TP61F80 TP55F80 TP55F81 TP50F90 TP50F60 TP50F61 TP50F50 TP50F51
CRT 7" 7" 7" 7" 7" 7" 7" 7" 7" 7" 7"
CRT Source Hitach Hitach Hitach Hitach Hitach Hitach Hitach Hitach Hitach Hitach Hitach
Remote H/U Intell Univ Intell Univ Univ Univ Intell Univ Univ. A-Univ A-Univ
RMT Keys 52 key 36 key 52 key 36 key 36 key 36 key 52 key 36 key 36 key 42 key 42 key
GENERALSOUNDPICTURE
PIP 2-TN 2-TN 2-TN 2-TN 2-TN 2-TN 2-TN 2-TN 2-TN 1-TN 1-TN
Dolby Surr ProLgc ProLgc Dy-Sur Dy-Sur Dy-Sur ProLgc
Surround Dsp4Ch ● Dsp4Ch Dsp4Ch Dsp4Ch Dsp4Ch Dsp4Ch ●●●●
SAP ●●●●●●●●●●●
Cyclone
SBS ●●●●●●●●●●●
Audio (W) 28W 28W 28W 28W 28W 28W 28W 28W 28W 28W 28W
Center +20W 20W 20W
Rear +20W 20W 20W 20W 20W 20W
Comb-Filter 3D-Y/C 3D-Y/C 3D-Y/C 3D-Y/C DIG DIG DIG DIG DIG DIG DIG
DQF ●●●●
Scan-Modul ●●●●●●●●●●●
VCC ●●
Black-Expan ●●●●●●●●●●●
Color-D.E ●●●●●●●●●●●
Pic-Prefer ●●●●●●●●●●●
Color-Temp ●●●●●●●●●●●
Flesh-Tone ●●●●●●●●●●●
Nois-Reduce ●●●●●●●●●●●
Hori-Resolu 800 800 800 800 800 800 800 800 800 800 800
C-Chassis
Fav-Channel ●●●●●●●●●●●
Ch-Label ●●●●●●●●●●●
3-Language ●●●●●●●●●●●
Clock ●●●●●●●●●●●
Ch-Lock/Off ●●●●●●●●●●●
C.Caption ●●●●●●●●●●●
OTHERS
EDS ● ●●● ●●●●
New-OSD ●●●●●●●●●
S/Sight ●● ●
S-Video In 1+1 1+1 1+1 1+1 1+1 1+1 1+1 1+1 1+1 1 1
AV-In/Out 1+2/1 1+2/1 1+2/1 1+2/1 1+2/1 1+2/1 1+2/1 1+2/1 1+2/1 2/1 2/1
Front-Term ●●●●●●●●●
A(Var)-Out ●●●●●●●●●●●
2RF-Term ●●●●●●●●●
SPK-Term ●●●●●●●●●●●
TERMINALACCE
PIP Audio ●●
C-Ch-Input ●●●
E/Jack
S/S-Jack ●● ●
IR-B & 75W ●● ●
Adapter ●●●●●●●●●●●
Rod-Antenna
SPK-Box ●●● ●
EZ RMT ●● ●
Cabinet TW56D90 40W30E TP61E90 TP61E80 TP55E80 TP55E81 New New New New New
*
6
Page 7

4. FRONT VIEW
POWER indicator
POWER
POWER button
Press to open
the door.
Behind the door
S-VIDEO VIDEO
IN-VIDEO 3
VIDEO 3 INPUTS DEMO button
AUDIO
L/MCNO R
Note: [No] Owner's manual page.
DEMO
MENU
MENU button
Fig. 1-1
ANT / VIDEO button **
ENTER button
ANT/
VIDEO
ENTER
VOLUME / buttons
/ buttons
VOLUME CHANNEL
CHANNEL / buttons
/ buttons
7
Page 8
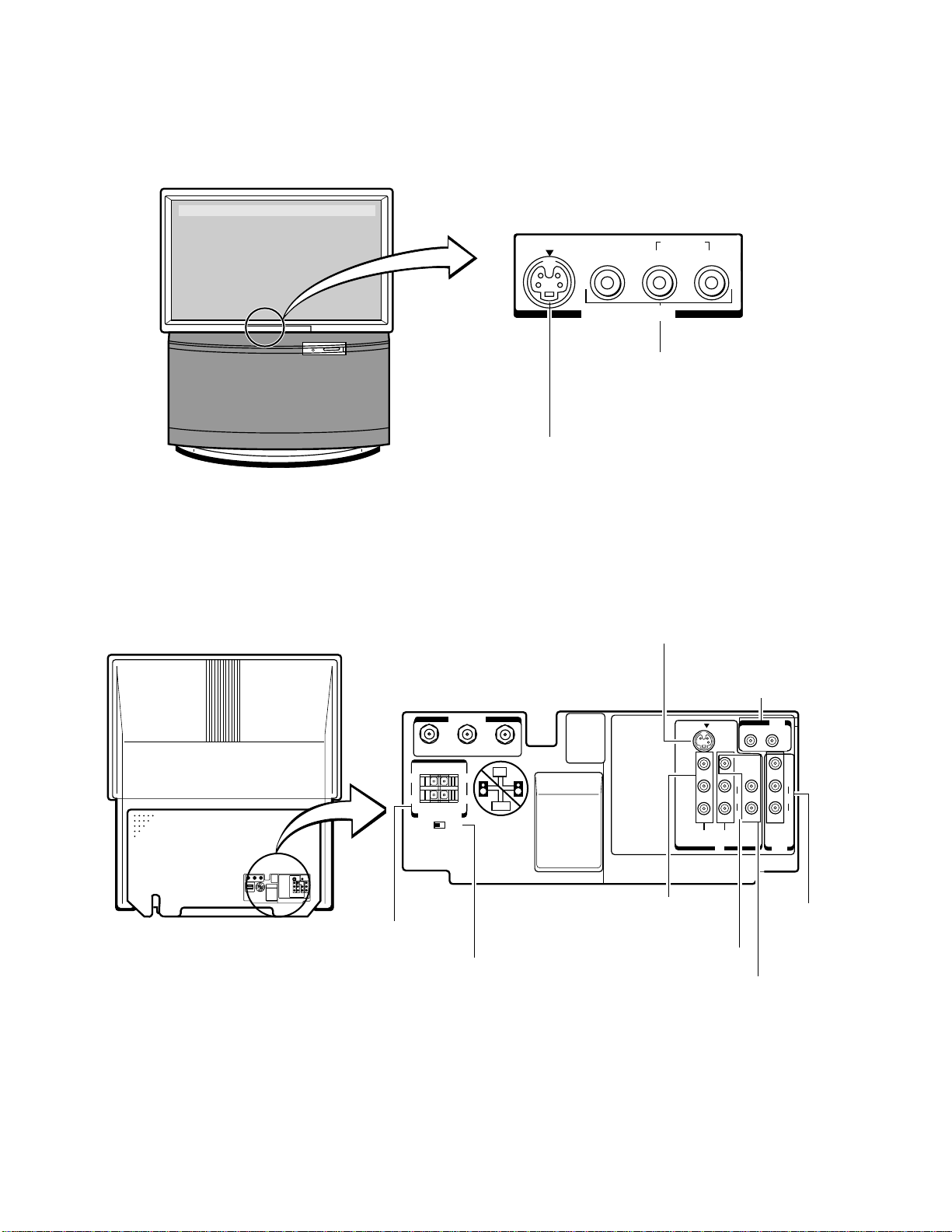
5. REAR VIEW
T
TV front
Fig. 1-2
Behind the door
S-VIDEO VIDEO
L/MCNO R
IN-VIDEO 3
VIDEO / AUDIO INPUT jacks (VIDEO 3)
S-VIDEO INPUT jack (VIDEO 3)
AUDIO
TV rear
(+)
(Ð)
EXT SPEAKER
EXT INT
MAIN SPEAKER
EXTERNAL
SPEAKER
terminal
ANT (75 ½)
(+)
(Ð)
MAIN
SPEAKER
switch
S-VIDEO INPUT jack
(VIDEO 1)
VARIABLE AUDIO
OUTPUT jacks
S-VIDEO
TV
AMP
VIDEO
L
VIDEO
AUDIO
R
VIDEO/AUDIO
VIDEO1
VIDEO2 DVD
N CUT
VIDEO / AUDIO
INPUT jacks
(VIDEO 1)
VIDEO / AUDIO
INPUT jacks
(VIDEO 2)
AMP
VAR
R
L
ACC
Y
C4
VIDEO
L
AUDIO
R
DVD INPUT
AMP
R
VIDEO /
AUDIO
OUTPU
jacks
jacks
Fig. 1-3
8
Page 9
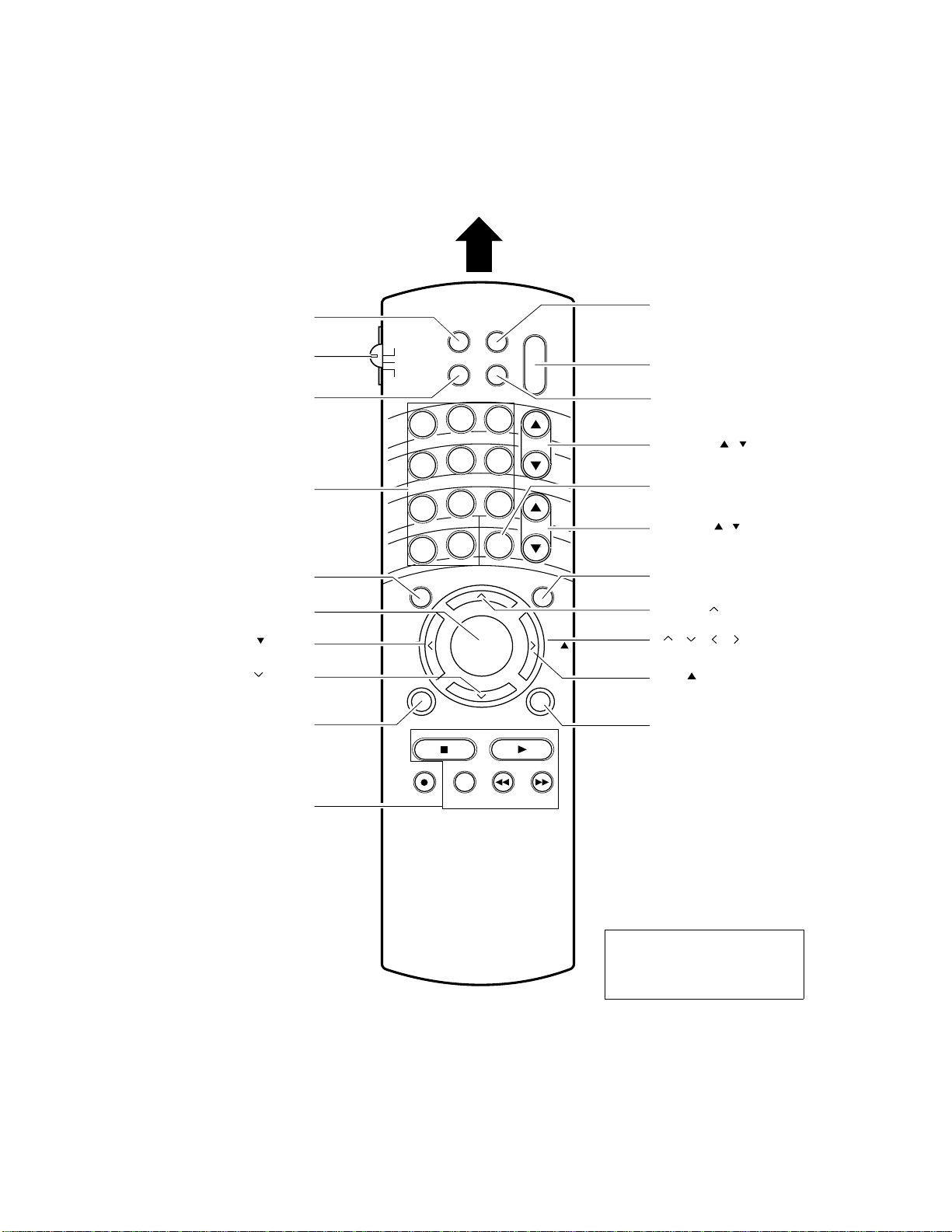
6. REMOTE CONTROL VIEW
Aim at the remote sensor on the TV
TIMER* [ 38, 39 ]
TV / CABLE / VCR switch [ 15 ]
Set to " TV " to control the TV.
TV / VIDEO* [ 55 ]
Channel Number* [ 25 ]
EDS* [ 27 ]
ENTER [ 19 ]
FAN * [ 46 ]
POP CH * [ 40 ]
RESET * [ 33 ]
PIC -SIZE
TV
CABLE
VCR
1
4
7
100
EDS MENU
FAV FAV
STOP SCURCE PLAY POP
REC
RECALL
TV/VIDEO
MUTE
2
3
5
6
8
9
CH RTN
0
ENT
ADV/
POP CH
ENTER
ADV/
POP CH
TV/VCR REW FF
POWER
CH
VOL
¥
EXITRESET
RECALL* [ 26 ]
POWER [ 20 ]
MUTE* [ 26 ]
CHANNEL / [ 25 ]
CH RTN* [ 26 ]
VOLUME / [ 25 ]
MENU [ 18 ]
POP CH * [ 40 ]
///[ 18 ]
FAN * [ 46 ]
EXIT * [ ON ]
Owner's Manual page
(For " TV " and " CABLE " positions)
POP functions* [40]
Note: [No] Owner's Manual page.
CH SEARCH
STILL SWAP
TOSHIBA
* These function do not have
duplicate locations on the TV.
They can be controlled only by
the Remote Control.
Fig. 1-4
9
Page 10
7. CHASSIS LAYOUT
330
242
6pcs
CHIP SINGLE FACED
:AUDIO LIVE
14
(chip)
242
: DIGITAL
10
139
242
2pcs
CONVER
CHIP DOUBLE FACED
160
:SIARSIGHT
15
:DUAL
11
1pcs
2pcs
CHIP DOUBLE FACED
126
CHIP DOUBLE FACED
139
: STARSIGHT
15
- 1: NEW OSD
2pcs
242
:DOLBY PRO
16
TW56F80 ONLY
CHIP DOUBLE FACED
:WAC
13
7
113
: AUTOLIVE
: MAIN
1
242
:3D Y/C
12
2pcs
CHIP DOUBLE FACED
155
189
4pcs
:MAC
13
FACED
CHIP DOUBLE
139
14
- 6
: DUAL
11
YCS
12
16
SURR
FRO.
-2:
PRO
DOLBY
7
- 1 : A/V
4
- 2 : SPEAKER
4
STARSIGHT
N.OSD
FDS
3DYC
COHB
F.SUR
DSP
DOLBY
2
TUNER
3DYC
4CH
PRO
2
PC BOARD
249
249
330
2pcs
-1: NEW OSD7-2: FRONT SURROUND
: NEW OSD/
FRONT SURROUND
7
7
165
1pcs
-1: A.V4-2: SPEAKER
: AV.EXT SPK
4
4
165
1pc
: MAIN
1
294
- 4 : FRONT-LED
5
TW56F80 ONLY
249
330
330
: SW DVD
8
CRT-1pcs
:
5
4pcs
165
-5: FRONT CON5-6: SVH
5
ÐD( R )
ÐD( G )
ÐD( B )
D/FRONT/SHV
-1: CRT
-2: CRT
-3: CRT
-4: FRONT LED
5
5
5
5
249
1pc
: DEFELECTION
2
294
- 5 : FRONT-CON
5
249
: POWER S.S
9
249
: POWER 1
6
330
: CONV / POWER2
3
FOCUS PACK
- 6 : SVM
5
2pcs
TW56F80 ONLY
249
: DEFLECTION
2
REAR ANP
(TW56F80 ONLY)
1pc
: SW DVD
8
CENTER AMP
(TW56F80 ONLY)
To CRT
4
- 3 : DPC
J-BOX
Fig. 1-5
F.B.T
165
1pc
: CONVERTER/POWER 2
PACK
To FOCUS
: POWER 1
6
3
294
CRT-D(B)
:
-3
5
: DIGITAL
CONVER
10
CRT-D(G)
:
-2
5
(TW56F80 ONLY)
POWER STARSIGHT
9
CRT-D(R)
:
-1
5
MODE1
TW40F80
TW56F80
10
Page 11
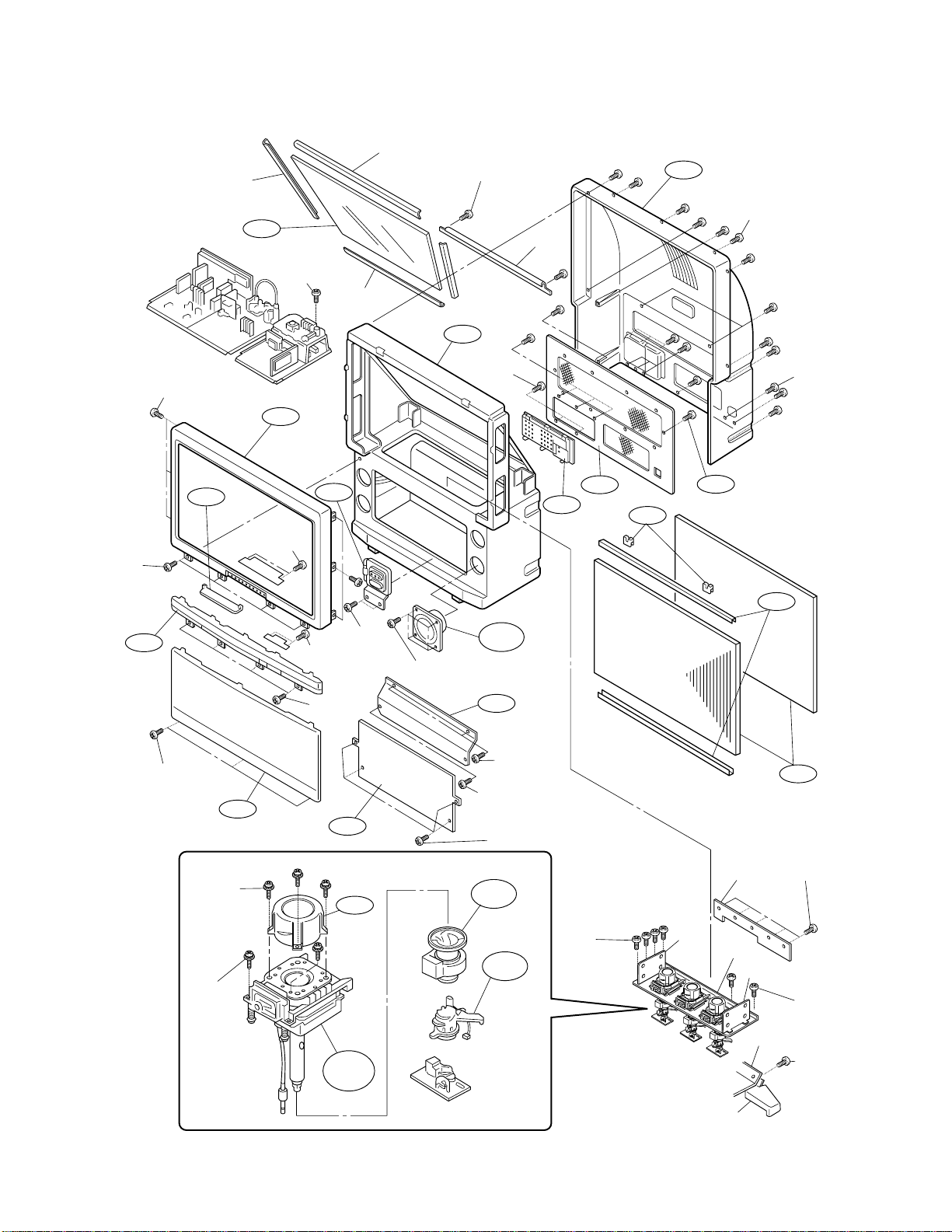
8. CONSTRUCTION OF CHASSIS
A
4
502
PMM 4x16
pcs
A512
BIDT2
4x12 6pcs
A902
A110B
2pcs
K601
BRT TBS 4x16
A201
A520
PP 5x18
4pcs
A521
2pcs
Z410
A110A
A110
A101
A505
BIDT2
4x12 2pcs
A517
PBI 4X16
8pcs
A126
B202
A351
A127
A401
A353
A522
BIDT2
4X12 18pcs
A128
A517
A205
A516
PMS 3.8x28
3pcs
A202
A511
PP4x14
4pcs
A510
BRBTB
5x16
4pcs
PMM 4x16
2pcs
A506
BRB TBS
4x16 4pcs
A515
PMM 4X16
4pcs
A102
K103
V901R
V902G
V903B
A501
BTA 4x16 16pcs
W661~
W664
A106
A508
BIDT2
4x12 2pcs
A523
PMM 4x16
2pcs
A509
BTA 4x16 4pcs
L462~
L464
L472~
L474
A503
PMM
4x16
8pcs
A105
A107
A104
A105
A104
K511
A519
BIDT2
4x12
5pcs
A508
BIDT2
4x12
4pcs
A513
BIDT2
4x12
Fig. 1-6
11
A108
Page 12
SECTION II: TUNER, IF/MTS/S. PRO MODULE
1. CIRCUIT BLOCK
IF/MTS/S.PRO Module MVUS34S
EL466L
Tuner
RF AGC
1-1. Outline
(1) RF signals sent from an antenna are converted into in-
termediate frequency band signals (video: 45.75 MHz,
audio: 41.25 MHz) in the tuner. (Hereafter, these signals are called IF signals.)
(2) The IF signals are band-limited in passing through a
SAW filter.
(3) The IF signals band-limited are detected in the VIF
circuit to develop video and AFT signals.
(4) The band-limited IF signals are detected in the SIF cir-
cuit and the detected output is demodulated by the audio multiplexer, developing R and L channel outputs.
These outputs are fed to the A/V switch circuit.
(5) A sound processor (S.PRO.) is provided.
SAW
Filter
AFT output
Fig. 2-1 Block diagram
VIF/SIF
Circuit
TP12
Video output
SIF
output
To A/V switch circuit
Sound
Multiplex
Circuit
TV
R-OUTTVL-OUT
C-IN
S.PRO Circuit
R-IN L-IN
R-OUT
L-OUT
C-OUT
(L+R)
-OUT
(5) VIF/SIF circuit uses PLL sync detection system to
improve performances shown below:
• Telop buzz in video over modulation
• DP, DG characteristics (video high-fidelity reproduction)
• Cross color characteristic (coloring phenomenon
at color less high frequency signal objects)
(6) HIC SBX1637A-22 is used in the audio multiplexer
circuit to minimize the size with increased performance.
(7) As a sound control processor, TA1217N is used. I2C-
bus data control the DAC inside the IC to perform
switching of the audio multiplexer modes.
1-2. Major Features
(1) The VIF/SIF circuit is fabricated into a small module
by using chip parts considerably.
(2) As the tuner, EL466L that which contains an inte grated
PLL circuit is employed.
(3) Wide band double SAW filter F1802R used.
(4) FS (frequency synthesizer) type channel selection sys-
tem employed.
12
Page 13

1-3. Audio Multiplex Demodulation Circuit
The sound multiplex composite signal FM-detected in the
PIF circuit enters pin 12 of HIC (hybrid IC) in passing
through the separation adjustment VR RV2 and amplified.
After the amplification, the signal is split into two: one enters a de-emphasis circuit, and only the main signal with the
L-R signal and a SAP signal removed enters the matrix circuit. At the same time, the other passes through various filters and trap circuits, and the L-R signal is AM-demodulated, and the SAP is FM-demodulated.
MVUS34S
Then, both are fed to the matrix circuit. At the same time,
each of the stereo pilot signal fH and the SAP pilot signal
5fH is also demodulated to obtain an identification volta ge.
With the identification voltage thus obtained and the user
control voltage are used to control the matrix.
The audio signals obtained by demodulating the sound multiplex signal develop at pin 10 and 11 of HIC and develop
the terminals of 12 and 14 of the module.
MPX
Out
9
Monitor the input
pin for multiplex
sound IC
Table 2-1 Matrix for broadcasting conditions and
reception mode
Broad- Switching
casted mode
Stereo STE R L
SAP R L
MONO L+R L+R
Mono STE L+R L+R – –
SAP L+R L+R – –
MONO L+R L+R – –
Stereo STE R L
+ SAP SAP SAP
SAP MONO L+R L+R
Mono STE L+R L+R –
+ SAP SAP SAP –
SAP MONO L+R L+R –
Output OSD display
12 pin 14 pin
(R) (L)
10
Stereo 0V
Other 5V
Fig. 2-2 Block diagram of MVUS34S
Stereo SAP
•
•
•
••
••
••
11
SAP 0V
Other 5V
–
–
–
•
•
•
TV
R-Out
TV waveform detection
output (R)
: Available, – : Not available
•
DAC-out1
(SURR ON/OFF)
12 13 14
OFF 0V
ON 9V
To AV select circuit
Note:
Of the mode selection voltages, switching voltages for STE,
SAP, MONO do not output outside the module.
They are used inside the module to control the BUS.
TV
L-Out
TV waveform detection
output (L)
DAC-out2
(RFSW)
15
RF1 0V
RF2 9V
13
Page 14
1-4. A.PRO Section (Audio Processor)
The S.PRO section has following functions.
(1) Woofer processing (L+R output)
(2) High band, low band, balance control
(3) Sound volume control, cyclone level control
(4) Cyclone ON/OFF
TA1217N
All these processing are carried out according to the BUS
signals sent from a microcomputer.
Fig. 2-3 shows a block diagram of the A.PRO IC.
Lin
Rin
Cin
Win
SDA
SCL
56
36
I C
Center
LEVEL
Woofer
LEVEL
2
7
31 24
D/A
CONV
VOLUME
23
30 9
BALANCE
22 19
I/O
28
8
L out
26
R out
25
C out
18
W out
10
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
SAP Ident.
STE Ident.
1272922 32
34
30
2
3
20
21
TONE CONTROL
LPF
4
R-in C-in L-in
From From From
A/V Dolby A/V
SCL SDA W-out O-out L-out
to Q670 to Q640 to Q670 to Q670
Via QS101
Fig. 2-3 A.PRO block diagram
14
Page 15
Configuration of the audio circuit and signal flow are given
in Fig. 2-4
A/V PCB
VIF+MTS+S.PRO
MODULE
R
L
12
EQ
14
ER
ICV01
R
6
MOTHER
TV
L
7
CHILD
29
L
R
31
TV
FOR POP
IF MODULE
AUDIO
VIDEO 1
VIDEO 2
OR
DVD
VIDEO 3
(FRONT INPUT)
R L
R L
R L
2
L
L
11
VIDEO 1
13
R
3
L
VIDEO 2
9
R
L
15
VIDEO 3
17
R
PIP
OUTPUT
VARIABLE
AUDIO OUTPUT
TERMINAL
1
R
VIDEO
OUTPUT
TERMINAL
35
R
37
L
L
R
AS
AR
AI
AJ
L
PIP OUT
(AUDIO)
R
FRONT
SURROUND
UNIT
(TW40F80 NOT USE)
VIF+MTS+A.PRO
MODULE
R OUT
16
R
W OUT
18
L
L OUT
Q601
25
22
24
R
2511
+
L
+
7
R
L
Fig. 2-4
15
Page 16
2. POP TUNER
Label
Name
Lot No.
1
15
TUNER
SECTION
RF AGC
SAW
FILTER
AFT
OUTPUT
VIF/SIF
CIRCUIT
VIDEO
OUTPUT
AUDIO
OUTPUT
Fig. 2-5
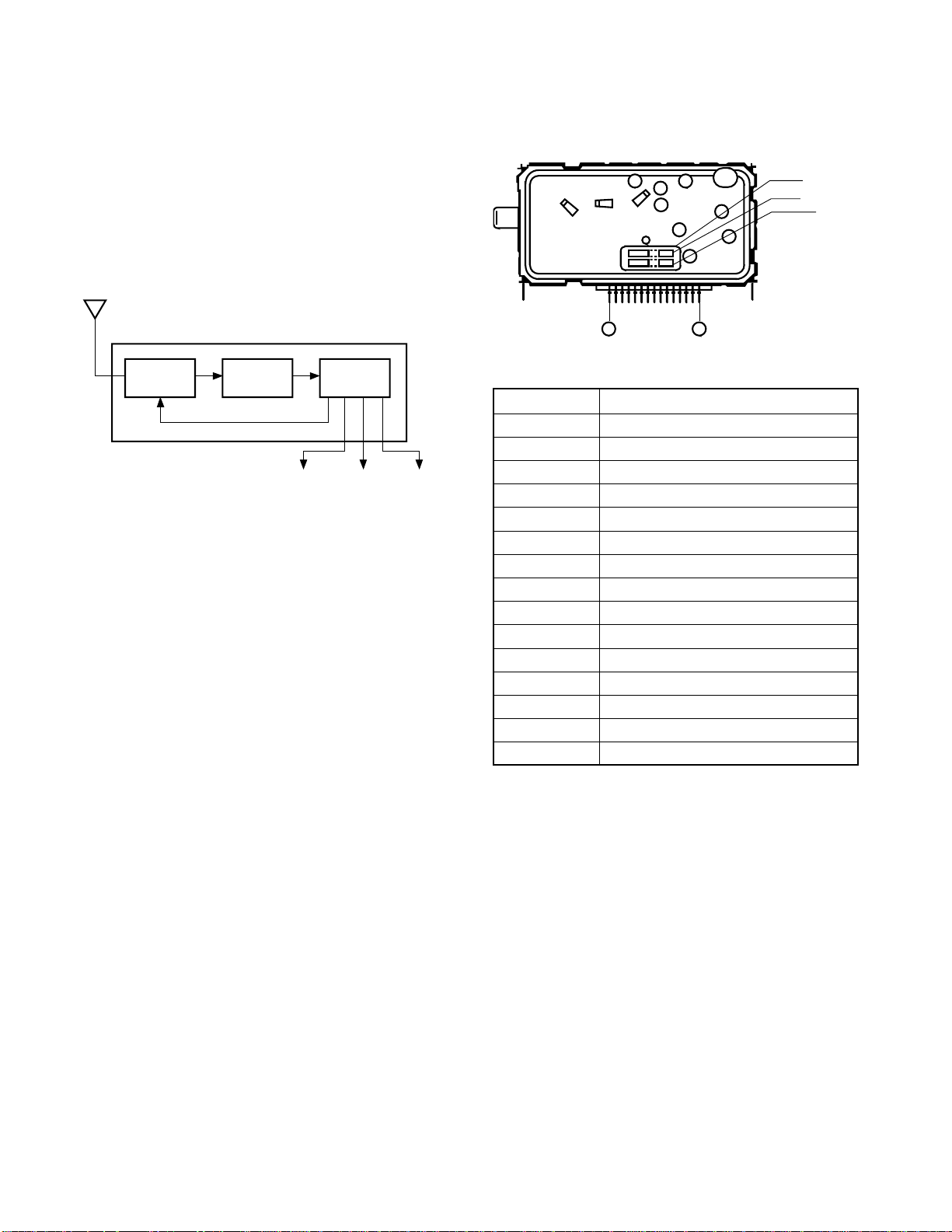
2-1. Outline
The POP tuner (EL922L) consists of a tuner and an IF block
integrated into one unit. The tuner receives RF signals induced on an antenna and develops an AFT output, video
output, and audio output.
The tuner has receive channels of 181 as in the tuner for the
main screen and it is also controlled through the I2C-bus.
As the IC for the IF, a PLL complete sync detection plus
audio inter carrier system are employed.
Terminal No. Name
1NC
2 32V
3 S-CLOCK
4 S-DATA
5NC
6 ADDRESS
75V
8 RF AGC
99V
10 AUDIO
11 GND
12 AFT
13 NC
14 GND
15 VIDEO
Fig. 2-6 Tuner terminal layout
16
Page 17

SECTION III: CHANNEL SELECTION CIRCUIT
1. OUTLINE OF CHANNEL SELECTION CIRCUIT SYSTEM
The channel selection circuit in the N5SS chassis employs
a bus system which performs a central control by connecting a channel selection microcomputer to a control IC in
each circuit block through control lines called a bus. In the
bus system which controls each IC, the I2C bus system (two
line bus system) developed by Philips Co. Ltd. in the Netherlands has been employed.
The ICs controlled by the I2C bus system are: IC for V/C/D
signal processing (Q501), IC for A/V switching (QV01), IC f or
non volatile memory (QA02), Main and sub U/V tuners (H001,
HY01), IC for deflection distortion correction (Q302), IC for
POP and Double Window signal pr ocessing (QY03), IC for
closed caption control (QM01), IC for WAC control (QX01),
IC for 3D-YCS (QZ01), IC for AUTOLIVE (QK06).
Differences from N5SS chassis are as follows;
1. On-screen function inside microcomputer is used. Separate IC is not used for on-screen.
2. The microcomputer does not have the closed caption
function, but controls separate IC for closed caption.
3. The system uses two channels of I2C bus. One is only
for non-volatile memory.
2. OPERATION OF CHANNEL SELECTION CIRCUIT
T oshiba made 8 bit microcomputer TLCS-870 series for TV
receiver, TMP87CS38N-3320 is employed for QA01.
With this microcomputer, each IC and circuit shown below
are controlled.
(1) CONTROL OF VIDEO/CHROMA/DEF SIGNAL
PROCESS IC (Q501 Toshiba TA1222AN)
• Adjustments for uni-color, brightness, tint, color
gain, sharpness and PIP uni-color
• Setting of adjustment memory values for subbrightness, sub-color and sub-tint, etc.
• Setting of memory values for video parameters such
as white balance (RGB cutoff, GB drive) and
gcorrection, etc.
• Setting of video parameters of video modes (Standard, Movie, Memory)
(2) CONTROL OF A/V SWITCH IC (QV01 Toshiba
TA1218N)
• Performs source switching for main screen and sub
screen
• Performs source switching for TV and three video
inputs
(3) CONTROL OF NON-VOLATILE MEMORY IC
(QA02 Microchip 24LC08BI/P)
• Memorizes data for video and audio signal adjustment values, volume and woofer adjustment values, external input status, etc.
• Memorizes adjustment data for white balance (RGB
cutoff, GB drive), sub-brightness, sub color, sub
tint, etc.
• Memorizes deflection distortion correction value
data adjusted for each unit.
(4) CONTROL OF U/V TUNER UNIT (H001 Toshiba
ELA12L, HY01 Toshiba EL922L)
• A desired channel can be tuned by transferring a
channel selection frequency data (divided ratio data)
to the I2C bus type frequency synthesizer equipped
in the tuner, and by setting a band switch data which
selects the UHF or VHF band.
(5) CONTROL OF DEFLECTION DISTORTION COR-
RECTION IC (Q302 Toshiba TA8859P)
• Sets adjustment memory value for vertical amplitude, linearity, horizontal amplitude, parabola, corner, trapezoid distortion.
(6) CONTROL OF POP & Double W indow SIGN AL PRO-
CESS IC (QY03 Toshiba TC9092AF, QY91 Sony
CXP85116B-514Q)
• Controls ON/OFF and 9 pictures serch of POP.
(7) CONTROL OF CLOSED CAPTION/EDS (QM01
Motorola XC144144P)
• Controls Closed Caption/EDS.
(8) CONTROL OF WAC (QX01 Toshiba TC9097F)
• Controls Wide Aspect.
(9) CONTROL OF 3D-YCS (QZ01 Toshiba TC9086F)
• Controls ON/OFF of 3 Dimension Y/C separator.
(10) CONTROL OF VERTICAL AMPLITUDE (QK06
Toshiba TMP87CM36N)
• Controls Wide Mode.
(11) CONTROL OF OSD (Do not I2C BUS) (QR60 Fujitsu
MB90091)
• Controls of OSD Menu.
17
Page 18

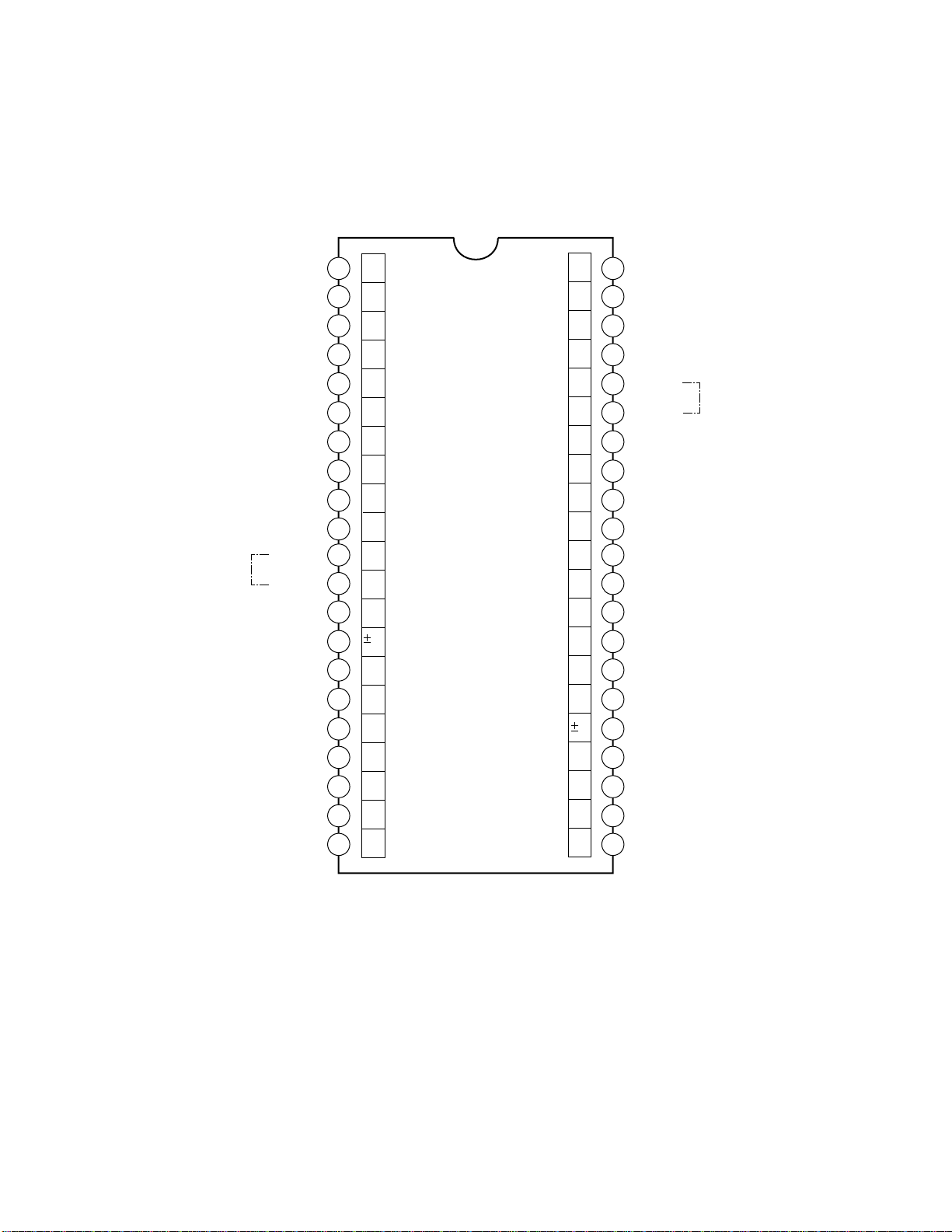
3. MICROCOMPUTER
Microcomputer TMP87CS38N-3320 has 60k byte of ROM
capacity and equipped with OSD function inside.
The specification is as follow.
• Type name : TMP87CS38N-3320
• ROM : 60k byte
• RAM : 2k byte
• Processing speed : 0.5m s (at 8MHz with Shortest command)
• Package : 42 pin shrink DIP
•I2C-BUS : two channels
• PWM : 14 bit x 1, 7 bit x 9
• ADC : 8 bit x 6 (Successive comparison system, Conver sion time 20ms)
IIC device controls through I2C bus. (Timing chart : See Fig.
3-1)
• LED uses big current port for output only.
• For clock oscillation, 8MHz ceramic oscillator is used.
•I2C has two channels. One is for EPROM only.
• Self diagnosis function which utilizes ACK function of
I2C is equipped
• Function indication is added to service mode.
• Remote control operation is equipped, and the control
by set no touch is possible. (Bus connector in the conventional bus chassis is deleted.)
• Substantial self diagnosis function
(1) B/W composite video signal generating function
(micom inside, green crossbar added)
(2) Generating function of audio signal equivalent to
1kHz (micom inside)
(3) Detecting function of power protection circuit opera-
tion
(4) Detecting function of abnormality in IIC bus line
(5) Functions of LED blink indication and OSD indica-
tion
(6) Block diagnosis function which uses new VCD and
AV SW
SDA
SCL
Start
condition
1 - 7
Address
8
R/W
Approx.180µS
9
Ack Data
1 - 7
Fig. 3-1
18
9
8
Ack
1 - 7
Some device may have no data,
or may have data with several
bytes continuing.
8
DATA Ack
9
Stop
condition
Page 19
4. MICROCOMPUTER TERMINAL FUNCTION
S
TMP87CS38N3320 (QA01)
IIC
-BUS
GND
BAL
REM OUT
MUTE
SP MUTE
NC
POWER
LED
SSRST
DVD CONT
SCL0
SDA0
SYNC VCD
PIPRST
AFT2
AFT1
KEY-A
KEY-B
SGV
SGA
GND
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
GND
I
P40 (PWM0)
O
P41 (PWM1)
O
P42 (PWM2)
O
P43 (PWM3)
O
P44 (PWM4)
O
P45 (PWM5)
O
P46 (PWM6)
O
P47 (PWM7)
I
P50 (PWM8/TC2)
O
P51 (SCL1)
IO
P52 (SDA1)
I
P53 (AINO/TC1)
0
P54 (AIN1)
I
P55 (AIN2)
I
P56 (AIN3)
I
P60 (AIN4)
I
P61 (AIN5)
O
P62
O
P63
VSS
VDD
P57
P32
P57
SDA0
SCL0
(TC3)P31
(RXIN)P30
P20
RESET
XOUT
XIN
TEST
0SC2
0SC1
VD
OSD RESET
DATA
BUSY
CS
CLK
I
I
I
IO
O
I
I
I
I
O
I
I
O
I
I
0
O
I
O
O
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
VDD
ACP
SS VD
2
I C STOP
SDA1
SCL1
SYNC AV1
RMT IN
EXT SP
RESET
XOUT
XIN
GND
0SC1
0SC2
VSYNC
OSD RESET
DATA
BUSY
CS
CLK
IIC BU
Fig. 3-2
19
Page 20
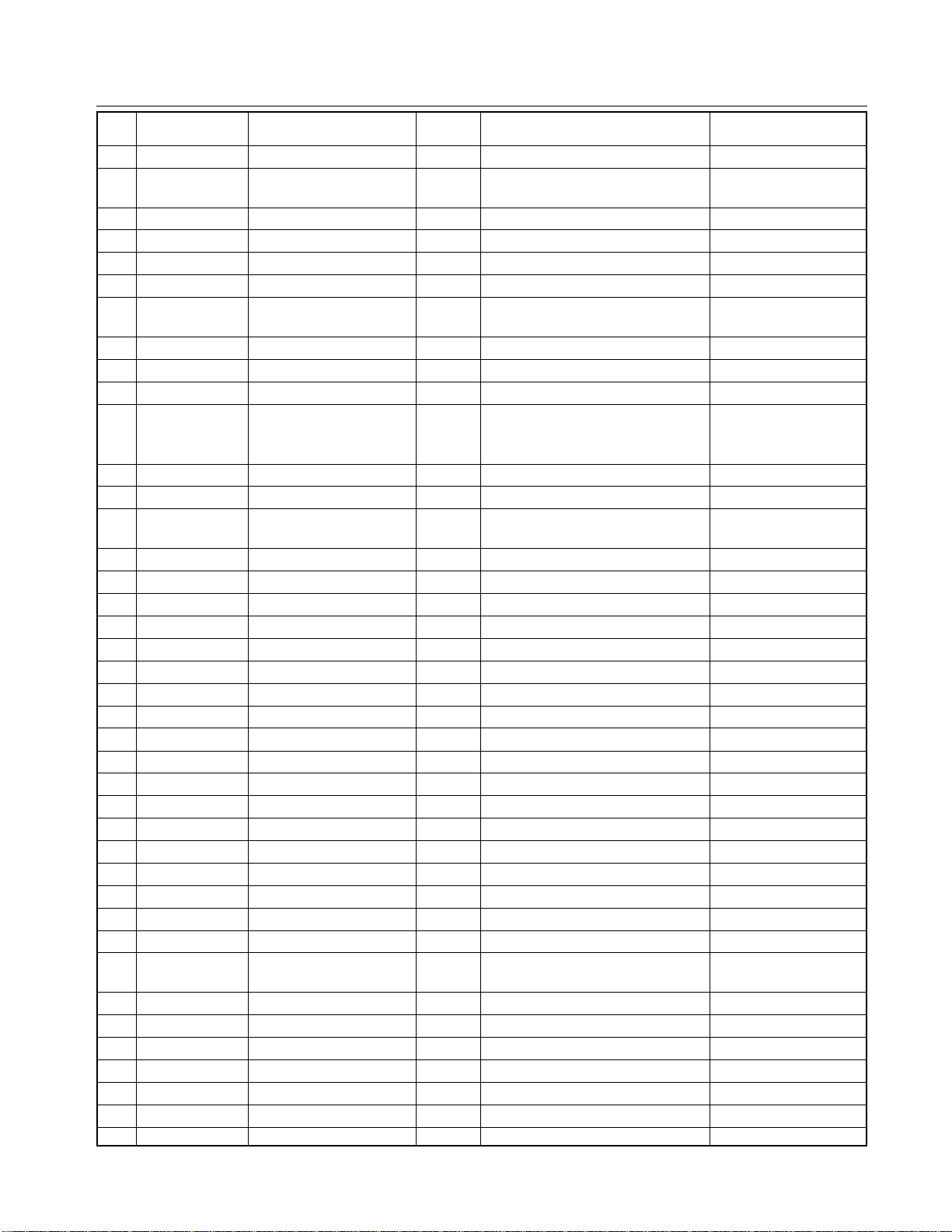
<< MICROCOMPUTER TERMINAL NAME AND OPERATION LOGIC >>
No. Terminal Name Function In/Out Logic Remarks
1 GND 0V
2 BAL INPUT BALANCE Out PWM out
3 REM OUT REMOTE CONTROL Out Remote control output
SIGNAL OUT
4 MUTE SOUND MUTE OUT Out Sound mute output
5 SP MUTE SPEAKER MUTE Out In muting = H
6 DEF POW Out
7 POWER POWER ON/OFF OUT Out Power control In ON = H
8 LED POWER LED OUTPUT Out Power LED on-control
LED lighting = L
9 SS RST STARSIGHT RESET Out Reset = L 0V
10 DVD CONT DVD CONTROL Out DVD = L, Other = H 0V
11 SCL0 IIC BUS CLOCK OUT Out IIC bus clock output 0
12 SDA0 IIC BUS DATA IN/OUT In/Out IIC bus data input/output 0
13 SYNC VCD H SYNC INPUT In Main picture H. sync signal input
14 PIP RST PIP RESET Out Reset = L
15 AFT2 IN In Sub tuner AFT S-curve input
16 AFT1 UV MAIN S-CURVE In Main tuner AFT S-curve
SIGNAL signal input
17 KEY A LOCAL KEY INPUT In Local key detection: 0 to 5V
18 KEY B LOCAL KEY INPUT In Local key detection: 0 to 5V
19 SGV TEST SIGNAL OUT Out Test signal output In normal = L 0V
20 SGA TEST AUDIO OUT Out Test audio output In normal = L 0V
21 VSS POWER GROUNDING — 0V: Gounding voltage 0V
22 CLK CLOCK OSD Out At display on: Pulse
23 CS CHIP SELECT Out At display on: Pulse
24 BUSY BUSY OSD In At display on: Pulse
25 DATA DATA OSD Out At display on: Pulse
26 OSD RESET RESET OSD Out Reset = L
27 VSYNC In VSYNC Pulse
28 OSC1 DISPLAY CLOCK Out 4.5MHz Pulse
29 OSC2 DISPLAY CLOCK In Pulse
30 TEST TEST MODE In GND fixed 0V
31 XIN SYSTEM CLOCK In System clock input 8MHz pulse
32 XOUT SYSTEM CLOCK Out System clock output 8MHz 8MHz pulse
33 RESET SYSTEM RESET In System reset input (In reset = L) 5V
34 EXT SP EXTERNAL SPEAKER In EXTERNAL = L, INT = H
35 RMT IN REMOTE CONTROL In In remote control pulse input = L In reception of
SIGNAL INPUT remote pulse
36 SYNC AV1 HSYNC INPUT In External H. sync signal input Pulse
37 SCL1 IIC BUS CLOCK OUT Out IIC bus clock output 1 Pulse
38 SDA1 IIC BUS DATA IN/OUT In/Out IIC bus data input/output 1 Pulse
39 I2C STP IIC BUS STOP In STOP = L
40 SS VD STARSIGHT VD In VSYNC for Starsight Pulse
41 ACP NSYNC INPUT In AC pulse input
42 VDD POWER — 5V 5V
20
Page 21

5. EEPROM (QA02)
EEPROM (Non vola tile memory) has function which, in spite
of power-off, memor izes the such condition as channel selecting data, last memory status, user control and digital processor data. The capacity of EEPROM is 8k bits.
EEPROM(QA02)
A0
1
Device adress
GND
A1
A2
Vss
2
3
4
6. ON SCREEN FUNCTION
The OSD system of TW40F80 employs the external OSD
IC (QR60, MB90091) to obtain high quality OSD.
Type name is 24LC08BI/P or ST24C08CB6, and those are
the same in pin allocation and function, and are exchangeable each other. This IC controls through I2C bus. The po wer
supply of EEPROM and MICOM is common. Pin function
of EEPROM is shown in Fig. 3-3.
Vcc + 5V
8
NC
7
SCL
6
SDA
5
I2C-BUS line
Fig. 3-3
QR60 is controlled by the microprocessor QA01 with the
exclusive control signals of CLK, DATA, CS, BUSY, RESET.
CLK
CS
BUSY
DATA
OSD RESET
22
23
24
25
26
VIDEO
(YM)
Fig. 3-4
54
56
58
55
16
64
SCLK
SCS
TRE
SIN
RESET
VOB2
QR60 MB90091QA01 Microprocessor
R OUT
G OUT
B OUT
59
60
61
21
Page 22
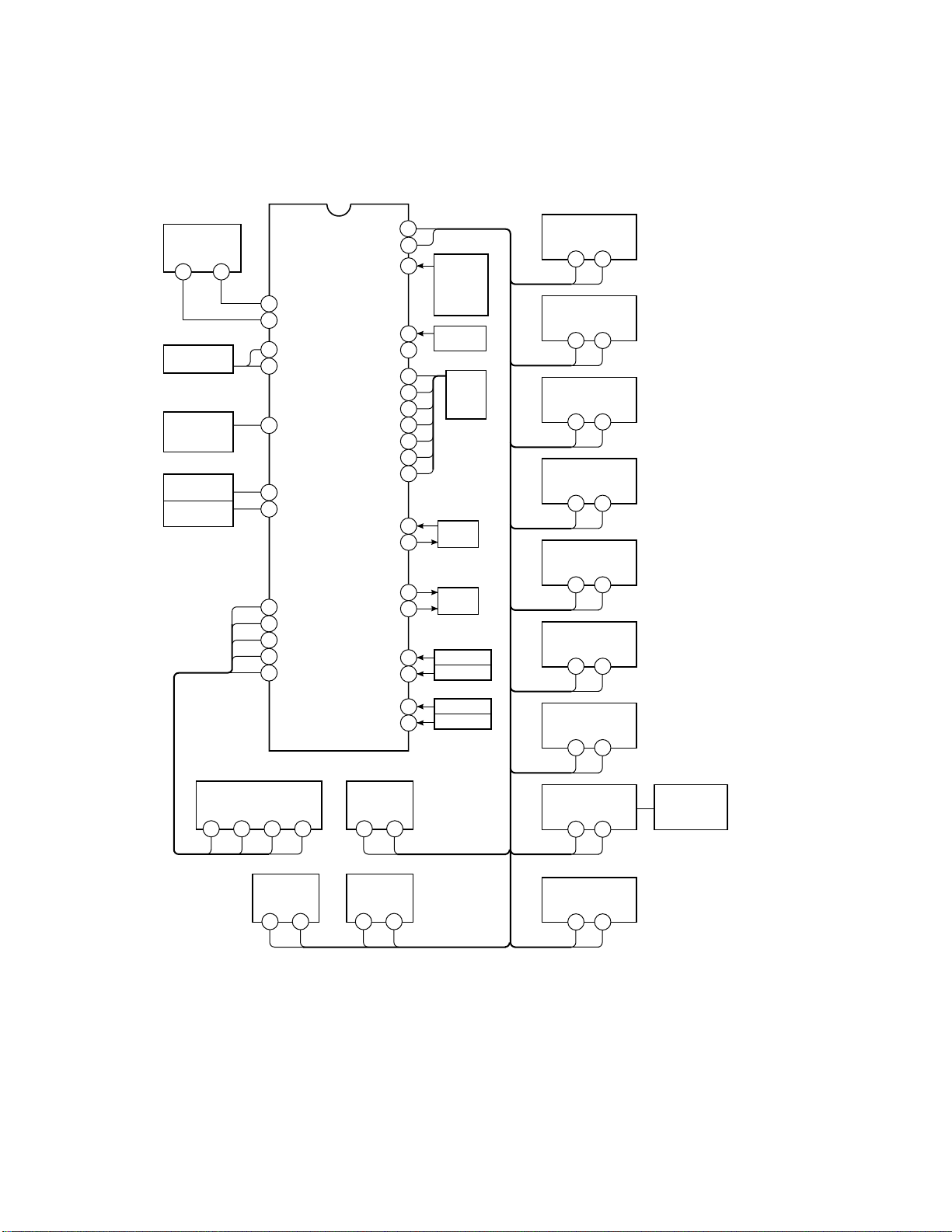
7. SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM
QA01
TMP87CS38N-XXXX
QA02
Memory
24LC08BI/P
SDA SCL
5
V.sync
pulse
Remote
controller
output
Audio mute
Speaker
mute
QR60
OSD
MB90091
CLK
54
6
DATA
55
SCL 0
11
SDA 0
12
INT4
40
VSYNC
27
RMT OUT
3
MUTE
4
SP MUTE
5
DATA
25
CLK
22
CS
23
BUSY
24
RESET
26
CS BUSY
5856
SDA 1
SCL 1
RMT
KEY-A
KEY-B
RST
VDD
GND
VSS
POWER
ACP
LED
XIN
XOUT
SGV
SGA
SYNC-AV1
AFT1 IN
SYNC-AV2
AFT2 IN
QH30
C/C,EDS
XC144144P
SDA SCL
14
38
17
32
20
16
15
37
35
18
33
42
1
21
7
41
8
31
19
Main screen
36
Sub screen
13
2
Remote
controller
light
receiving
unit
Key
switch
Power
supply
circuit
8MHz
Clock
Signal
output
Sync det.
AFT det.
Sync det.
AFT det.
SDA SCL
SDA SCL
SDA SCL
2827
SDA SCL
2021
SDA SCL
25
24
SDA SCL
1920
SDA SCL
HO01
HY01
Q501
HO02
QV01
QZ01
QY91
Main U/V tuner
ELA12L
Sub U/V tuner
EL922L
VCD
TA1222AN
IF/MPX/A.PRO
MVUS5345
AV SW
TA1218N
DPC unit
DATA CLK
YCS
TC9086F
DUAL microprocessor
POP
TC9092F
QY03
QX01
WAC
TC9097F
SDA SCL
60
59
Q701
CONVER
T7K64
SDA SCL
44
43
Fig. 3-5
22
AUTO LIVE
SDA SCL
39
40
QK06
Page 23
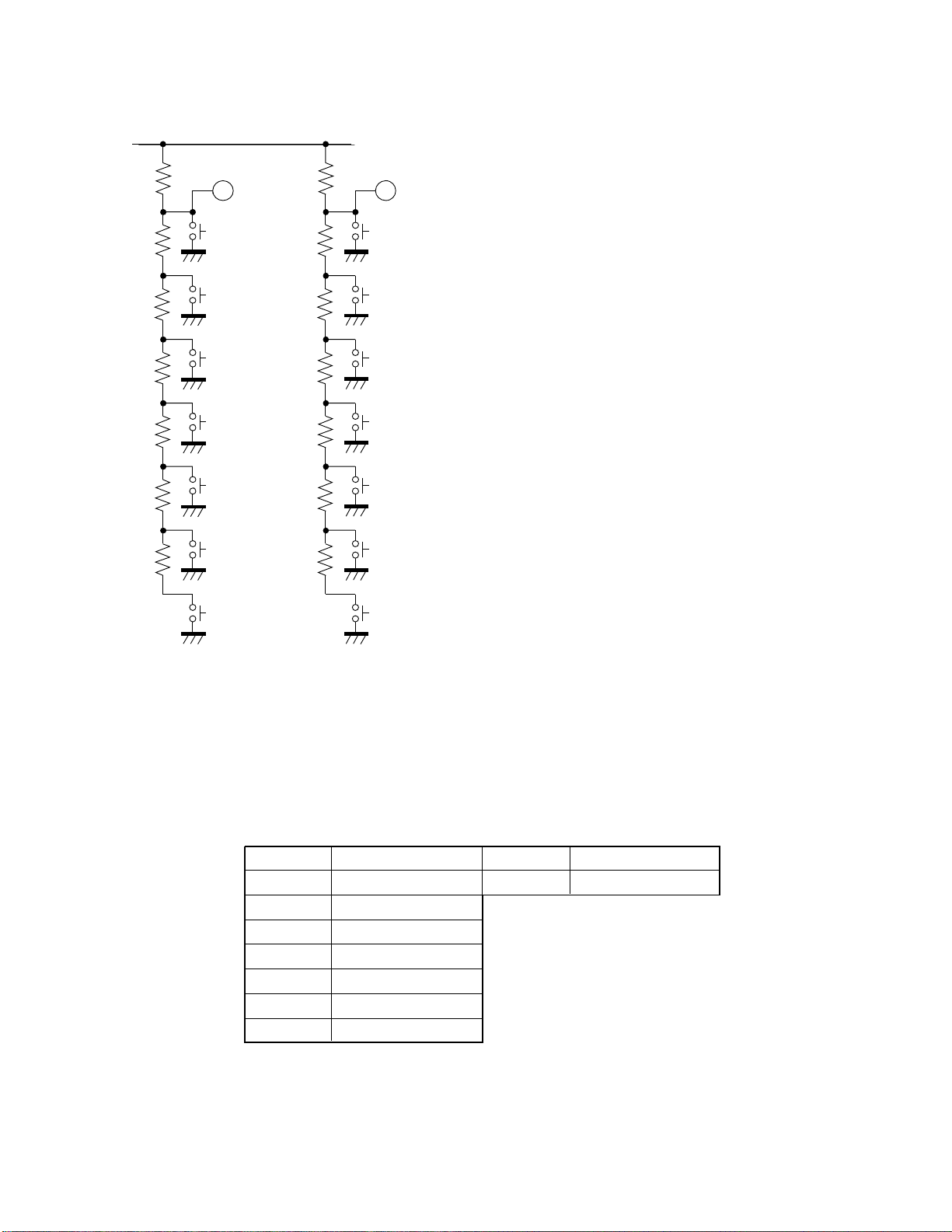
8. LOCAL KEY DETECTION METHOD
17
SA08
SA06
SA05
SA07
18
SA01
SA02
SA03
SA04
Local key detection in the N5SS chassis is carried out by
using analog like method which detects a voltage appears at
local key input terminals (pins 17 and 18) of the microcomputer when a key is pushed. With this method using two
local key input terminals (pins 17 and 18), key detection up
to maximum 14 keys will be carried out.
The circuit diagram shown left is the local key circuit. As
can be seen from the diagram, when one of keys among SA01 to SA-08 is pressed, each of two input terminals (pins 17
and 18) developes a voltage VIN corresponding to the key
pressed. (The voltage measurement and key identification
are carried out by an A/D con v erter inside the microprocessor and the software.
Fig. 3-6 Local key assignment
Key No. Function Key No. Function
SA-02 POWER SA-01
SA-03 CH UP
SA-04 CH DN
SA-05 VOL UP
SA-06 VOL DN
SA-07 ANT/VIDEO, ADV
SA-08 MENU
Table 3-1 Local key assignment
DEMO START/STOP
23
Page 24
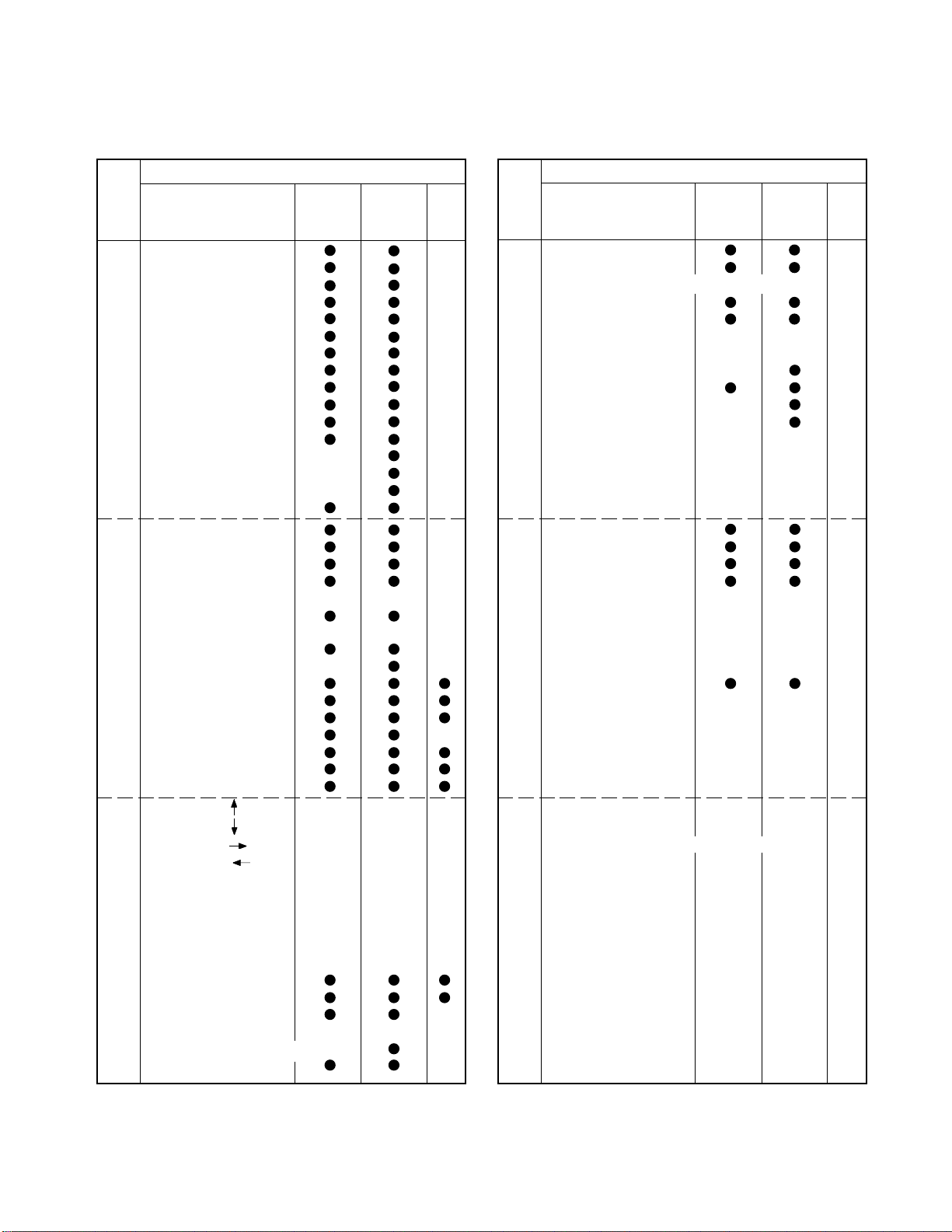
9. REMOTE CONTROL CODE ASSIGNMENT
Custom codes are 40-BFH (TV set for North U.S.A.)
Code
00H 0 Channel
01H 1 Channel
02H 2 Channel
03H 3 Channel
04H 4 Channel
05H 5 Channel
06H 6 Channel
07H 6 Channel
08H 8 Channel
09H 8 Channel
0AH 100 Channel
0BH ANT 1/2
0CH RESET
0DH AUDIO
0EH PICTURE/FUNC
0FH TV/VIDEO
10H MUTE
11H CHANNEL SEARCH
12H POWER
13H MTS
14H ADD/ERASE
15H TIMER/CLOCK
16H AUTO PROGRAM
17H CHANNEL RETURN
18H DSP/SUR (TV/CATV)
19H CONTROL UP
1AH VOLUME UP
1BH CHANNEL UP
1CH RECALL
1DH CONTROL DOWN
1EH VOLUME DOWN
1FH CHANNEL DOWN
40H PIP LOCATE
41H PIP LOCATE
42H PIP LOCATE
43H PIP LOCATE
44H CARVER
45H SURROUND UP
46H SURROUND DOWN
47H VOCAL ZOOM
48H CHANNEL LOCK
49H
4AH PIP CHANNEL UP
4BH PIP CHANNEL DOWN
4CH PIP STILL/RELEASE
PIP ZOOM, ZOOM SIZE
4DH
4EH PIP LOCATE (CH SEARCH)
4FH PIP SOURCE
Function to remote
Applicable
control
Applicable Conti-
to TV set nuity
Custom codes are 40-BFH (TV set for North U.S.A.)
Code
Function to remote
Applicable
control
50H PIP STILL
51H PIP ON/OFF
52H Do not use. Old type core power ON
53H PIP SWAP
54H PIC SIZE
55H DSP F/R
56H WIDE/SCROLL
57H CAPTION
58H EXIT
59H CYCLONE, SBS
5AH SET UP
5BH OPTION
5CH SUB WOOFER UP
SUB WOOFER DOWN
5DH
5EH
5FH
80H MENU
81H EDS
82H ADV UP
83H ADV DWN
84H
85H GUIDE
86H THEME
87H LIST
88H PIP CONTROL
89H ENTER/TUNE
8AH PAGE UP
8BH DATA UP
8CH PAGE DN
8DH DATA DN
8EH CANCEL
8FH REC
90H
91H
92H Do not use. Old type core power ON
93H
94H
95H
96H
97H NOISE CLEAN
98H
99H
9AH PIP VOLUME UP
9BH
9CH PIP CONTROL
9DH
9EH PIP VOLUME DOWN
9FH
Applicable Conti-
to TV set nu ity
24
Page 25
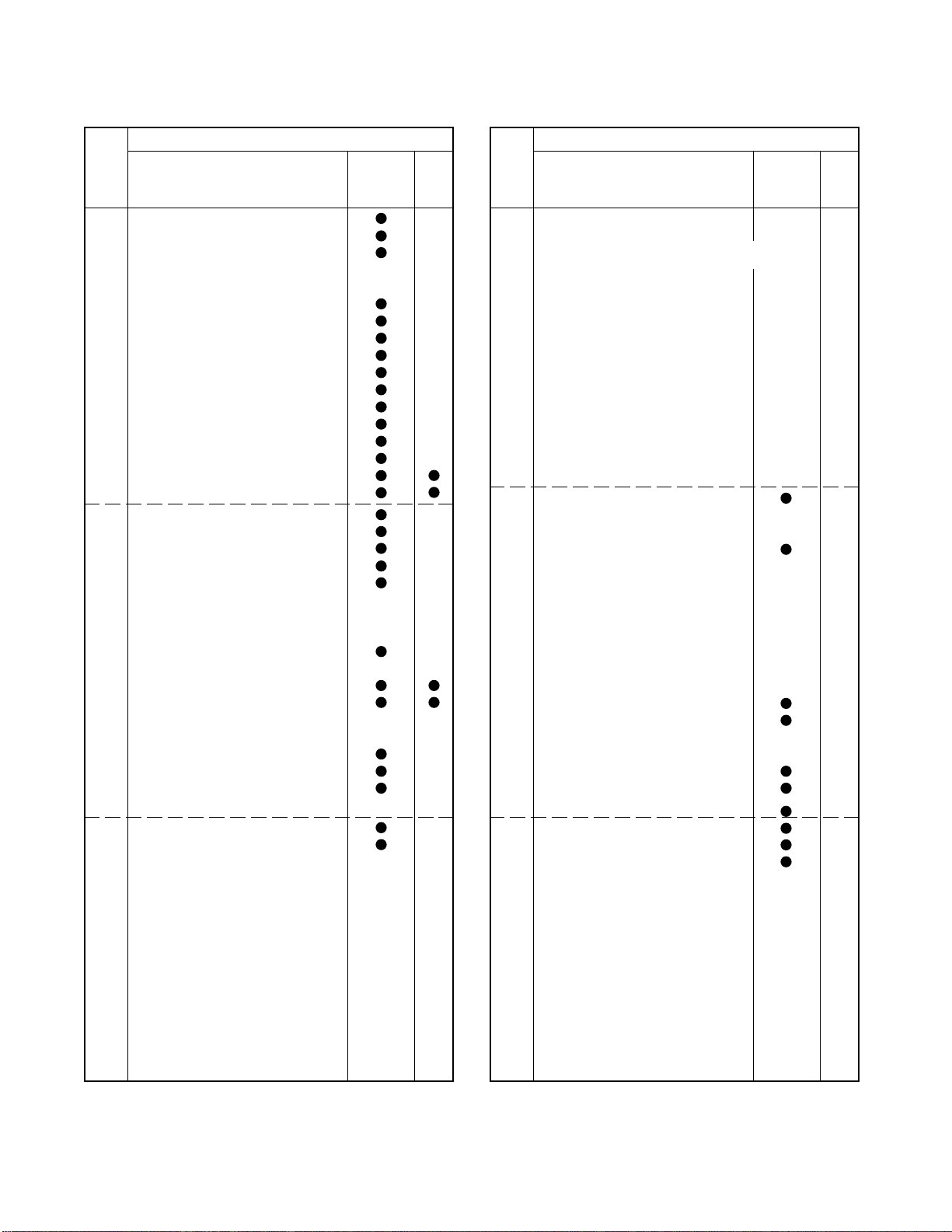
Custom codes are 40-BFH (TV set for North U.S.A.)
Custom codes are 40-BFH (TV set for North U.S.A.)
Code Applicable Conti-
A0H SUB-BRIGHT ADJUSTMENT
A1H G. DRIVE ADJUSTMENT
A2H B. DRIVE ADJUSTMENT
A3H
CUTOFF DRIVE 40H INITIALIZING,
A4H
HORIZONTAL ONE LINE
A5H R. CUTOFF ADJUSTMENT
A6H G. CUTOFF ADJUSTMENT
A7H B. CUTOFF ADJUSTMENT
A8H
MEMORY ALL AREA INITIALIZE
A9H PIP BRIGHT ADJUSTMENT
AAH SUB CONTRAST ADJUSTMENT
ABH
HOR, VER PICTURE POSITON ADJUSTMENT
ACH SUB COLOR ADJUSTMENT
ADH SUB TINT ADJUSTMNET
AEH ADJUSTMENT-UP
AFH ADJUSTMENT-DOWN
B0H
HORIZONTAL ONE LINE: SERVICE
B1H DSP ON/OFF
B2H TEXT-1
B3H
TV/PIP VIDEO CHANGE-OVER
B4H CAPTION-1
B5H
B6H
B7H TV/CABLE CHANGE-OVER IN
SAME TIME ON MAN AND SUB
B8H HOTEL SETTING MENU
B9H DATA 4 TIMES SPEED UP
BAH DATA 4 TIMES SPEED DOWN
CHANGE-OVER OF HOTEL/NORMAL
BBH
BCH PIP CENTER
BDH M MODE
BEH CAPTON OFF
BFH ALL CHANNEL PRESET
C0H
C1H DIRECT WIDE 1
C2H DIRECT FULL
C3H
C4H
C5H
C6H
C7H
C8H
C9H
CAH
CBH
CCH
CDH
CEH
CFH
Function
to TV set nuty
Code Applicable Conti-
D0H
D1H
D2H Do not use. Old type core power ON
D3H
D4H
D5H
D6H
D7H PIP VIDEO ADJ.
D8H STILL, FRAME ADVANCE
D9H
DAH SPEED
DBH
DCH ZOOM
DDH
DEH
DFH
E0H
E1H
E2H
E3H
E4H
E5H
E6H
E7H
E8H
E9H
EAH
EBH
ECH TEST TONE
EDH DOLBY
EEH
EFH DPC
E0H
E1H
F2H SCROOL
F3H
F4H
F5H
F6H
F7H
F8H
F9H
FAH
FBH
FCH
FDH
FEH
FFH
Function
PINCUTION/EW CORER (PARA/CNR)
VERTICAL S-CUVE CORRECTION/
VERTICAL M-CURVE
CORRECTION (VSC/FVC)
HORIZONTAL WIDTH (WID/PARA)
TRAPEZOIDE CORRECTION (TRAP)
3 DIMENTIONAL Y/C SEPARATION
STANDARD (HEIGHT LINEARITY) (VLIN/HIT)
WIDE (HEIGHT ® LINEARITY) (VLIN)
WIDE 1, 2, 3
to TV set nuty
25
Page 26
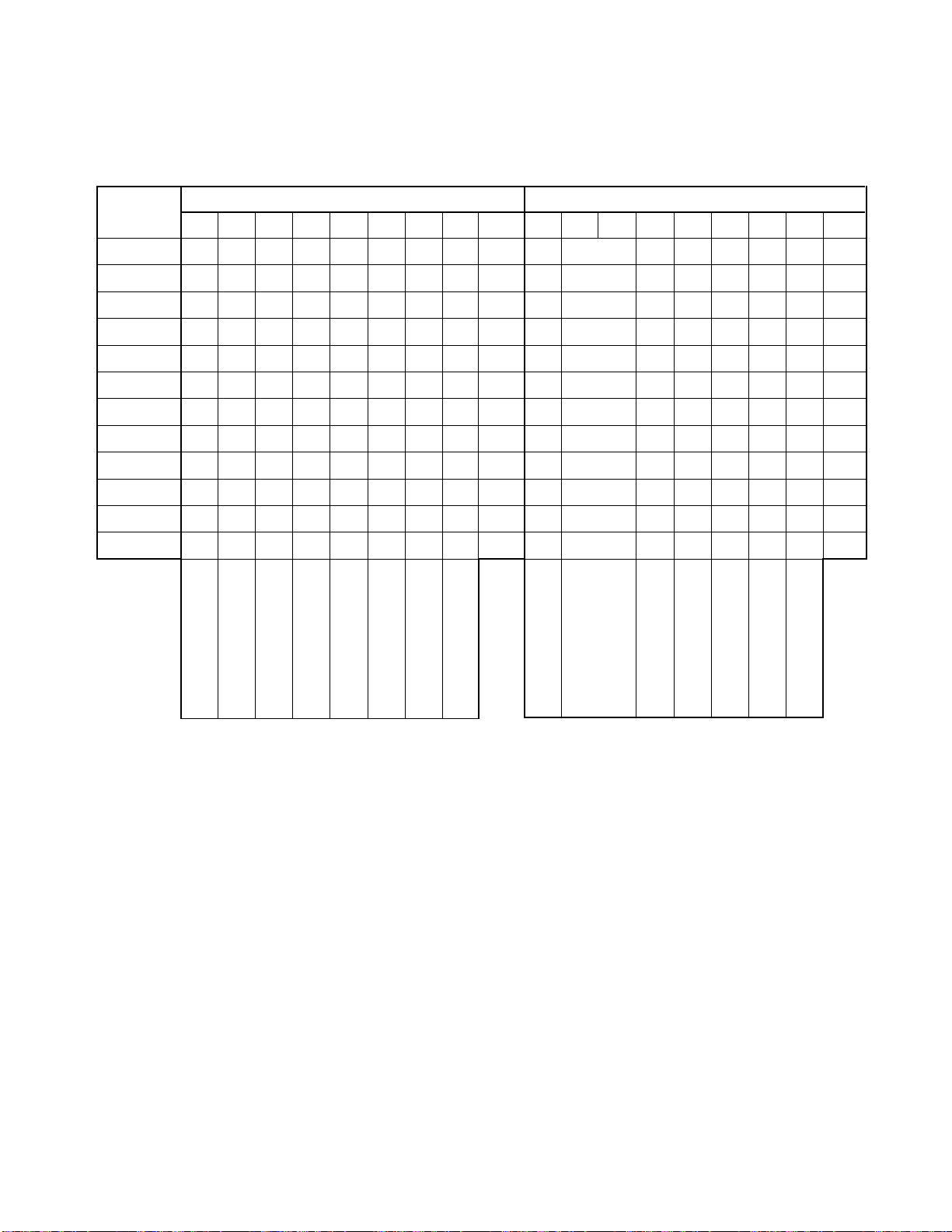
9-1. Optional Setting for Each Model
OPT0 OPT1
MODELS
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
HEX
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
HEX
CN35F90
CN35F95
CX35F70
TW56F80
TW40F80
TP61F90
TP61F80
TP55F80
TP55F81
TP50F90
TP50F60
TP50F61
0
*
0
*
1
*
0
*
1
*
0
*
0
*
0
*
0
*
0
*
1
*
1
*
DSP0/SRD1
NOT USED
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
PP0/MP1
0
*
0
*
1
*
0
*
1
*
0
*
1
*
1
*
1
*
0
*
1
*
1
*
SS/0 NONSS/1
NOT USED
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Normal 0/f0 STOP 1
0
*
0
*
1
*
1
*
1
*
1
*
1
*
1
*
1
*
1
*
1
*
1
*
CYC0/SBS1
NOT USED
00H
00H
02H
02H
92H
02H
12H
12H
12H
02H
92H
92H
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MODE:
Fixed
Normal00
STD: 01
HRC:10
1RC: 11
Normal 0/Free run 1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
NON0/CONV1
NON0/3DYC
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
NON0/DOLBY1
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
NOT USED
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
00H
00H
00H
1CH
18H
1CH
18H
10H
10H
14H
10H
10H
NOT USED
• When the character generation is changed from
MB90091-107 TO MB90091-108, D5 bit of OPT0 in
the design data should be set to “1”.
26
Page 27

10. ENTERING TO SERVICE MODE
12. SERVICE ADJUSTMENT
1. PROCEDURE
(1) Press once MUTE key of remote hand unit to indicate
MUTE on screen.
(2) Press again MUTE key of remote hand unit to keep
pressing until the next procedure.
(3) In the status of above (2), wait for disappearing of in-
dication on screen.
(4) In the status of above (3), press MENU (Channel set-
ting) key on TV set.
2. Service mode is not memorized as the last-memory.
3. During service mode, indication S is displayed at upper
right corner on screen.
11. TEST SIGNAL SELECTION
1. In OFF state of test signal, SGA terminal (Pin 20) and
SGV terminal (Pin 21) are kept “L” condition.
2. The function of VIDEO test signal selection is cyclically
changed with VIDEO key (remote unit).
Table 3-2
1. ADJUSTMENT MENU INDICATION ON/OFF :
MENU key (on TV set)
2. During display of adjustment men u, the followings are
effective.
a) Selection of adjustment item :
POS UP/DN key (on TV/remote unit)
b) Adjustment of each item :
VOL UP/ DN key (on TV / remote unit)
c) Direct selection of adjustment item
R CUTOFF : 1 POS (remote unit)
G CUTOFF : 2 POS (remote unit)
B CUTOFF : 3 POS (remote unit)
d) Data setting for PC unit adjustment
SUB CONTRAST : 4 POS (remote unit)
SUB COLOR : 5 POS (remote unit)
SUB TINT : 6 POS (remote unit)
e) Horizontal line ON/OFF : VIDEO (on TV set)
f) Test signal selection : VIDEO (remote unit)
* In service mode, serviceable items are limited.
Test Signal No.
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Name of Pattern
Signal OFF
All black signal + R single color (OSD)
All black signal + G single color (OSD)
All black signal + B single color (OSD)
All black signal
All white signal
W/B
Black cross bar
White cross bar
Black cross hatch
White cross hatch
White cross dot
Black cross dot
H signal (bright area)
H signal (dark area)
Black cross + G signal color
3. Test audio signal ON / OFF: 8 POS (remote unit)
* Test audio signal : 1 kHz
4. Self check display : 9 POS (remote unit)
* Cyclic display (including ON/OFF)
5. Initialization of memory :
CALL (remote unit) + POS UP (on TV set)
6. Initialization of self check data :
CALL (remote unit) + POS DN (on TV set)
7. BUS OFF :
CALL (remote unit) + VOL UP (on TV set)
(3) SGA (audio test signal) output should be square wave
of 1 kHz.
27
Page 28
13. FAILURE DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURE
Model of N5SS chassis is equipped with self diagnosis function inside for trouble shooting.
13-1. Contents to be Confirmed by Customer
Table 3-3
Contents of self diagnosis
A. DISPLAY OF FAILURE INFORMATION IN NO
PICTURE (Condition of display)
1. When power protection circuit operates;
2
2. When I
C-BUS line is shorted;
Power indicator lamp blinks and picture does not come.
1. Power indicator red lamp blinks. (0.5 seconds interval)
2. Power indicator red lamp blinks. (1 seconds interval)
If these indication appears, repairing work is required.
Display items and actual operation
13-2. Contents to be Confirmed in Service Work (Check in self diagnosis mode)
Table 3-4
Contents of self diagnosis
Contents of self diagnosis
< Countermeasure in case that phonomenon always arises >
B. Detection of shortage in BUS line.
C. Check of comunication status in BUS line.
D. Check of signal line by sync signal detection.
E. Indication of part code of microcomputer (QA01).
F. Number of operation of power protection circuit.
Display items and actual operation
NO. 239XXXX
POWER: 000000
BUS LINE: OK
BUS CONT: OK
BLOCK: UV V1 V2
QV01, QV01S
Display items and actual operation
(Example of screen display)
SELF CHECK
Part coce of QA01
Number of operation of
power protection circuit
Short check of bus line
Communication check of
busline
E
F
B
C
D
13-3. Executing Self Diagnosis Function
[CAUTION]
(1) When executing block diagnosis, get the desired input
mode (U/V BS VIDEO1, 2, 3) screen, and then enter
the self diagnosis mode.
(2) When diagnos other input mode, do again diagnosis
operation.
13-3-1. Procedure
(1) Set to service mode.
(2) Pressing “9” key on remote unit displays self diagno-
sis result on screen.
Every pressing changes mode as below.
SERVICE mode SELF DIAGNOSIS mode
(3) To exit from service mode, turn power off.
28
Page 29
13-4. Understanding Self Diagnosis Indication
In case that phenomenon always arises. See Fig. 3-7 .
(Example of screen display)
SELF CHECK
NO. 239XXXX
POWER: 000000
BUS LINE: OK
BUS CONT: OK
BLOCK: UV V1 V2
QV01, QV01S
Part coce of QA01
Number of operation of
power protection circuit
Short check of bus line
Communication check of
busline
Fig. 3-7
E
F
B
C
D
Item
BUS LINE
BUS CONT
BLOCK: UV1
UV2
V1
V2
Table 3-5
Contents
Detection of bus line short
Communication state of bus line
The sync signal part in each video signal
supplied from each block is detected.
Then by checking the existence or non of sync
part, the result of self diagnosis is displayed
on screen. Besides, when “9” key on remote
unit is pressed, diagnosis operation is first
executed once.
Instruction of results
Indication of OK for normal result, NG for abnormal
Indication of OK for normal result
Indication of failure place in abnormality
(Failure place to be indicated)
QA02 NG, H001 NG, Q501 NG, H002 NG, QV01 NG, Q302
NG, QY02 NG, HY01 NG, QD04 NG, QM01 NG, Q701 NG
Note:
The indication of failure place is only one place though
failure places are plural. When repair of a failure place
finishes, the next failure place is indicated. (The order of
priority of indication is left side.)
*Indication by color
• Normal block : Green
• Non diagnosis block : Cyan
29
Page 30

13-4-1. Clearing method of self diagnosis result
In the error count state of screen, press “CHANNEL DOWN”
button on TV set pressing “DISPLAY” button on remote unit.
CAUTION:
All ways keep the following caution, in the state of service
mode screen.
• Do not press “CHANNEL UP” button. This will cause
initialization of memory IC. (Replacement of memory
IC is required.)
• Do not initialize self diagnosis result. This will change
user adjusting contents to factory setting value. (Adjustment is required.)
13-4-2. Method utilizing inner signal
(VIDEO INPUT 1 terminal should be open.)
(1) With service mode screen, press VIDEO button on re-
mote unit. If inner video signal can be received, QV01
and after are normal.
(2) With service mode screen, press “8” button on remote
unit. If sound of 1 kHz can be heard, QV01 and after
are normal.
* By utilizing signal of VIDEO input terminal, each circuit
can be checked. (Composite video signal, audio signal)
White
Yellow
Cyan
Green
Magenta
Red
Blue
(COLOR BAR SIGNAL)
Color elements are positioned in sequence of
high brightness.
30
Page 31

14. TROUBLESHOOTING CHART
14-1. TV does Not Turned ON
TV does not turned on.
Relay sound
YES
NO
Check of voltage at pin 7 of QA01
(DC 5V).
OK
8MHz oscillation waveform
at pin 32 of QA01.
OK
Pulse output at pins 37 and 38 of QA01.
OK
NG
NG
NG
Check power circuit.
Check OSC circuit.
Replace QA01.
Voltage check at pin 32 of QA01
(DC 5V)
OK
NG
Check reset circuit.
Check relay driving circuit.
Replace QA01.
31
Page 32

14-2. No Acception of KEY-IN
Key on TV
Voltage change at pins 17, 18 of
QA01 (5V to 0V).
OK
Replace QA01.
Remote unit key
Pulse input at pin 35 of QA01,
When remote unit key is pressed.
OK
Replace QA01
NG
Check key-in circuit.
NG
Check tuner power circuit.
14-3. No Picture (Snow Noise)
No picture
Voltage at pins of +5V, and 32V.
OK
Check H001. Check tuner power circuit.
NG
32
Page 33

14-4. Memory Circuit Check
Memory circuit check
Voltage check at pin 8 of QA02 (5V).
NG
Pulse input at pins 5 and 6 of QA02
in memorizing operation.
Replace QA02.
Adjust items of TV set adjustment.
14-5. No Indication On Screen
No indication on screen.
Check of RESET at 5V.
OK
NG
OK
Note: Use replacement parts for QA02.
NG
Check power circuit.
Check QA01.
OK
Check of CLK, CS, BUSY, DATA at
pin 22, 23, 24, 25 of QA01.
"H" = 5V or puls?
OK
Check of character signal at pin 59, 60, 61
of QR60 (5V(p-p)).
OK
Check V/C/D circuit.
33
Replace QA01 or QR60 or QR63.
NG
Replace QA01 or QR60.
NG
Replace QR60.
Page 34

SECTION IV: DVD SWITCH CIRCUIT
1. DVD SWITCH BLOCK DIAGRAM
Q501 VCD
TA1222AN
Y
53
52
13
15
Q
51
I
4
Y
5
Q
C
I
Y
6
DVD SWITCH UNIT
QW01 TC4053BP
L
H
L
H
L
H
QV01 AV SW
TA1218N
MAIN
36
Y
C
34
Y
Q (B - Y)
I (R- Y)
ZY01 Y/C SEPARATOR
Sub V.
42
Sub V.
2
I C BUS
WAC UNIT
Sub Y.
Sub C.
DUAL UNIT
Y
Q
I
YC
"L" = Normal
"H" = DVD
QA01
MAICROPROCESSOR
10
DVD CONTROL
2
I C BUS
Y
Q
I
VIDEO2/
Y, Cr,
DVD
Insertion detection
Cb
21
VIDEO3VIDEO
1
Fig. 4-1
34
Page 35

2. OUTLINE
t
In this model, the DVD input terminals are provided in order to receive the color difference signals (Y, Cr, Cb) output from a DVD player.
The luminance (Y) signal input for DVD input uses the
VIDEO input terminal in common with the VIDEO 2 input.
The terminals for color difference signal inputs Cr (R – Y)
and Cb (B – Y) are used exclusively.
Open : at Cb input
Cb input
RV26
75
The input identification for VIDEO 2 and DVD is carried
out by setting pin 21 of QV01 TA1218N (AV SW IC) from
“L” to “H” when the cable is connected to the Cb input terminal with a switch equipped.
The main microprocessor QA01 sets pin 10 of QA01 from
“L” to “H” through I2C bus when pin 21 of AW SW IC
develops “H”.
Cb to DVD SW uni
RV27
10k
RV28 100k
+9v
21
QV01 TA1218N
Fig. 4-2
35
Page 36

SECTION V: WAC CIRCUIT
1. OUTLINE
A wide aspect conversion (hereafter called WAC) process (3/4
compression process in 4:3 mode and 1/2 compression process
on left screen in double window mode) is performed inside the
WAC unit (PB6348) in TW40F80.
Screen modes for TF40F80 contain THEATER WIDE1, THEATER WIDE 2, THEATER WIDE3, FULL, NORMAL and
DOUBLE WINDOW modes. The video signal compression is
carried out only when either the NORMAL or DOUBLE WINDOW mode is selected. In the modes other than the NORMAL
and DOUBLE WINDOW mode, the video signal input to WAC
unit is output without performing any process.
The screen in the DOUBLE WINDOW mode creates a single
screen by superimposing the left screen processed in the WAC
unit on the right screen processed in the DUAL unit.
On the left screen, the video signal sent is time-compressed to 1/
2 in horizontal direction to fit in the left half of the wide screen
with 16:9 aspect ratio. In this case, a black level of DC is attached on the right half of the screen in this circuit. However,
this is superimposed on the right screen, so nothing is visible on
the screen.
In the normal screen, the video signal is 3/4 time-compressed
and side panels in the black level are added on sides of the screen.
2. CIRCUIT OPERATION
2-1. Configuration
The WAC unit consists of a wide aspect conversion IC (QX01,
TC9097F, working as a central device), clock generation IC
(QX02, TA8667F), switch IC (QX03, TC4053BF), and peripheral circuits (LPF, AMP, emitter follower, etc.). The QX01
(TC9097F) contains an A/D con verter , D/A con verter , clamp circuit, VCO circuit, etc. and performs compression process, etc.
inside the IC for analog video signals entered according to controls through IIC bus, thus providing the signal as an analog signal.
2-2. Operation
2-2-1. Signal Flow
Fig. 5-1 shows a block diagram of this circuit. A Y signal entered through pin 6 of PX01 passes a low pass filter an a 6 dB
amplifier, and enters pin 3 of QX01. On the other hand, I and Q
signals enter through pin 4 and 5 of PX01,
and pass a low pass filter and amplifiers in the same way as the
Y signal, and enter pins 1 and 78 of QX01 respectively.
The Y , I and Q signals entered are clamped by built-in clamp
circuit, converted into digital signals by the built-in A/D converter. Mor eover , their read/write operations are rated up by twice
or 3/4 times to perform a compression process of 1/2 or 3/4
times inside the built-in line memory. And then, a black level
signal is added to the open area (right half, or both sides of
screen). Next, the signal is converted to an analog Y, I, and Q
signals by a built-in D/A converter and output from pins 17, 13,
and 9. Parameters of 1/2, 3/4 phase of the video signal, phase of
the side panel, etc. are controlled through I2C bus, control signals of which enters from pins 7 and 8 of PX01.
Thus processed signals are fed to a low pass filter to remove
high frequency noises generated in QX01 and then fed to the
QX03 switching IC. The compressed signal and a not compressed
signal entered from PX01 are directly fed to QX03, and switched
by a signal showing compression/not compression (NCS = output from pin 61 of QX01 and fed to the receive unit through
pins 5, 6, and 7 of PX02.
2-2-2. Clock Generation
The system clock for QX01 is generated by QX02 according to
an H reference signal supplied from pin 3 of PX02 and fed to
QX01 through QX19 and QX40. (The frequency is adjusted to
28.7 ± 0.2 MHz with LX18).
The compressing operation is carried out by setting the write
clock to 1/2 or 3/4 times by the built-in VCO with the reading
clock fed to pin 47 of QX01.
2-2-3. Timing Pulse Generation
Moreover, the WAC unit generates following timing pulses.
(1) VPout
Reference signal entered through pin 2 of PX02 enters pin
3 of QX01, and outputs at pin 8 of PX02 after delayed by
an amount required. The vertical reference signal is output in modes other than the normal and double window
and fed to the vertical circuit. Accordingly, the raster becomes an horizontal one when the unit is disconnected.
(2) HVBLK
This pulse is a timing pulse showing a black extension
mask period in the normal and double window modes. It
outputs at pin 1 of PX02 and enters pin 30 of Q501 in the
receive unit.
36
Page 37

PX02
T
HVBLK
1
VD IN
2
QX18
HD IN
3
GND
4
LX18
ADJ
VP OU
QD
ID
YD
8
7
6
5
QX32
QX31
QX30
QX01
TC9097F
50
VBL
QX02 TA8667F
18
QX19
47
30
VDI
RCK
11
52
VMO
10
51
HRE
ISI
1
LPF
Y WA
12
LPF
17
YSO
QSI
78
QX15
LPF
LX14 etc
I WA
2
QX21
LPF
LX15 etc
QX20
13
ISO
YSI
3
QX13
LPF
LX13 etc
Q WA
5
QX23
LPF
LX16 etc
QX22
9
QSO
IBC
59
QX11
LX12 etc
QX25
LX17 etc
QX24
57
VDP
IBD
60
9
61
NCS
10
11
I TH
1
Q TH
3
Y TH
QX03 TC4053BF
13
AMP
PX01
1
9V-2
2
5V-3
3
GND
AMP
4
I IN
QX29
QX28
5
Q IN
QX27
QX26
AMP
6
Y IN
QX06
QX10
7
SCL 2
8
DA 2
Fig. 5-1 Wide aspect conversion unit block diagram (PB6348)
37
I
Q
Y
Page 38

• Pin Function
80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65
1ISI
VRA2
2
YSI
3
NC
4
VBC
5
VRD2
6
VBD4
7
VDD3(DA2)
8
QSO
9
NC
10
VBD3
11
VSS3(DA2)
12
ISO
13
VRD1
14
NC
15
VDD2(DA1)
16
YSO
17
VBD2
18
VSS2(DA1)
19
VBD1
20
VSS4(VCO1)
21
VBV
22
NC
23
VFL1
24
VSS1(AD)
VBA
QSI
VBM
NC
VRA1
NC
VDD1(AD)
NC
VSS(DIG)
NC
TDI0
TDI1
TDI2
TDI3
TDI4
BCP(TDI5)
SE42(TDI6)
NCS(TDI7)
ACP(TMO0)
VDP(TMO1)
ISL(TMO2)
QSL(TMO3)
SPT(TMO4)
VMO(TMO5)
HRF(TMO6)
VBL(TMO7)
HBL(TMO8)
VSS5(VCO2)
NC
SDA
SCL
NC
NC
RCK
WCK
VDD(DIG)
NC
NC
VFL2
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
VDD4(VCO1)
VLM
VDD(DIG)
HDI
NC
VDI
RESET
NC
NC
TST0
TST1
TST2
NC
25
26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
Fig. 5-2 Pin function of TC9097F (QFP 80 pin)
38
HDF
VSS(DIG)
VDD5(VCO2)
Page 39

Table 5-1 Names and functions of TC9097F
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Name
ISI
VRA2
YSI
NC
VBC
VBD2
VBD4
AVDD
QSO
NC
VBD3
AGND
ISO
VRD1
NC
AVDD
I/O
–
–
–
–
–
–
O
–
–
–
O
–
–
–
Function
I
I
I color signal input
Reference voltage (low level) for AD1, AD2
Y signal input
–
Bias for clamp 1
Reference voltage for DA2, DA3
Bias 2 (high level) for DA2, DA3
Analog power
Q color signal output
–
Bias 2 (low level) for DA2, DA3
Analog ground
I signal output
Reference voltage for DA1
–
Analog power
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
YSO
VBD2
AGND
VBD1
AGND
NC
VFV
VFL1
AVDD
VLM
VDD
HDI
NC
VD1
RESET
NC
NC
O
–
–
–
–
–
I
–
–
–
–
I
–
I
I
–
–
Y signal output
Bias 1 (high level) for DA1
Analog ground
Bias 2 (high level) for DA1
Analog ground
–
Connected to VSS or VDD
Connected to VDD
Analog power
1/2 VDD for line memory
Digital power
Composite sync signal input
–
V sync signal input
Reset input (Normally: High level, Reset: Low level)
–
–
34
35
36
37
TST0
TST1
TST2
NC
I
I
I
–
Test mode setting (normally connected to VSS)
Test mode setting (normally connected to VSS)
Test mode setting (normally connected to VDD)
–
39
Page 40

No.
Name
I/O
Function
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
HDF
GND
AVDD
VFL2
NC
AGND
CKSEL
VDD
WCK
RCK
HBL
NC
VBL
HRF
VMO
SPT
QSL
I
–
–
I
–
–
–
–
–
O
–
–
–
O
–
–
–
Ext. H sync signal input
Digital ground
Analog power
Loop filter for VCO2
–
Analog ground
VDD
Digital power
Ext. clock input (memory write clock)
Ext. clock input (memory read clock)
H blanking signal
V blanking signal
H AFC reference signal
H AFC mask signal
Side panel timing signal
Q signal select pulse
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
NC
ISL
VDP
ACP
SCL
SDA
NCS
SE42
NC
BCP
TD14
TD13
TD12
TD11
TD10
NC
GND
O
–
–
–
–
–
I
–
–
–
–
I
–
I
I
–
–
–
I signal select pulse
V drive pulse
Later stage clamp pulse
I2C SCL signal input
I2C SDA signal input/output
Prefilter switch signal 1
Prefilter switch signal 2
–
Prestage clamp pulse output
Test input (normally connected to VSS)
Test input (normally connected to VSS)
Test input (normally connected to VSS)
Test input (normally connected to VSS)
Test input (normally connected to VSS)
–
Digital ground
72
73
74
75
NC
NC
AVDD
VRA1
I
I
I
–
Analog power
Reference voltage for AD1, AD2
40
Page 41

No.
Name
I/O
Function
76
77
78
79
80
NC
VBM
QSI
VBA
AGND
3. BLOCK DIAGRAM
Y
POST
FILTER
YSO
VDD2(DA1)
VSS2(DA1)
VBD1
VRD1
VBD4
DA1
I
POST
FILTER
ISO
DA2
VBD2
–
–
–
–
I
VRD2
–
Bias for MPX, clamp 2
Q color signal input
Bias for AD1, AD2
Analog ground
Q
POST
FILTER
QSO
VDD3(DA2&3)
VBD3
VSS3(DA2&3)
DA3
HBL(TMO8)
VBL(TMO7)
HRF(TMO6)
VMO(TMO5)
QSL(TMO3)
SPT(TMO4)
ISL(TMO2)
VDP(TMO1)
ACP(TMO0)
SCL
NCS(TDI7)
SE42(TDI6)
BCP(TDI5)
TST
TEST
CIRCUIT
RCK
WCK
TDI
VLM
SDA
C BUS
2
I
DECODER
1/2
LINE MEMORY (624x8)
LINE MEMORY (1248x8)
LINE MEMORY (1248x8)
AD1
CLAMP1
VBA
VBC
VRA2
VSS1(AD)
VDD1(AD)
VRA1
YSI
LINE MEMORY (624x8)
AD2
&
MPX
CLAMP2
VBM
ISI
QSI
HDF
HDI
VDI
TIMING
CONTROLER
1/2
VCO2
1/2
1/2
1/2
1/456
VCO1
VSS(Digital)
VSS(Digital)
VDD(Digital)
VDD(Digital)
VSS4(VCO1)
VSS5(VCO2)
VDD4(VCO1)
VDD5(VCO2)
VFL2
VFL1
SCL
FILTER
FILTER
PRE
Y
FILTER
PRE
PRE
FILTER
FILTER
I
Q
Fig. 5-3 TC9097F system block diagram
41
Page 42

4. WIDE ASPECT CONVERSION CIRCUIT FAILURE ANALYSIS
PROCEDURES
4-1. Left Screen Picture Failure in Normal Mode/Double Window Modes
(No Picture, Sync Distributed)
Picture fallure
(Normal/DW mode)
Super live
mode OK?
Y
LX18 adjustment
OK?
Y
I2C bus pin 7 , 8
of PX01 OK?
Y
Is clock at pin 47
of QX01 OK?
Y
Signals at pins 5 , 6 ,
7 of PX02 OK?
N
N
N
N
N
Y
Output at pins 5 , 6 ,
7 of PX02 OK?
N
Readjustment
I2C bus line check.
Output at pin 3 (HD)
of PX02 OK?
N
Receive circuit check.
Y
Y
Check circuits other
than WAC unit.
Check around
of QX03.
Check around
QX02.
Check receive
circuit.
QX01 input / output
OK?
Y
Check associated
circuit (Tr.etc).
N
Replace
2
PROM OK?
E
END
Replace QX01.
42
Page 43

4-2. Raster Horizontal One
Horizontal one
Output at pin 8
of PX02 OK?
N
Output at pin 2
of PX02 OK?
Y
Is output OK
2
C bus?
at I
Y
Data initlalization OK?
Y
END
4-2-1. Adjustment Method
(1) Disconnect any video inputs
(2) Open RX-40.
(3) Connect frequency counter to QX19 emitter.
(4) Adjust LX18 until frequency reading of “28.7 MHz
± 0.5 MHz” is obtained.
Y
N
N
N
Check V circuit.
Check receive circuit.
Check I2C
bus line.
Replace QX01.
43
Page 44

1. OUTLINE
SECTION VI: DUAL CIRCUIT
DUAL circuit performs the signal process, etc. on the sub
screen and is composed of the followings as shown in Fig. 6-
1.
• Video/color/deflection (V/C/D) process
• On-screen display (OSD) superimposing process
• Sub-screen process, memory
• Main/Sub screen picture superimposing process
• Sub screen control microprocessor
2. PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
DUAL circuit is composed of the following functions.
(1) Double window sub screen 1/2 compression process
(2) Sub screen still process
(3) 9-screen multi-search process
(4) Main/Sub screen superimposing process by YIQ sig-
nal.
• 9-screen multi-search process
The sub screen process IC (TC9092AF) is the IC using the
programmable technology and can realize various functions
such as sub screen 1/2 compression, 9-screen multi-search,
etc. by switching the program.
The 9-screen multi-search process is carried out by selecting
the channel on the right half of the wide screen with 16:9
aspect ratio and the picture images received are projected on
the 9 screens from the upper left screen in order.
The search is carried out by approx. every 2 seconds repeatedly. When the next picture image is searched, the picture
image on the previous screen becomes a still picture. When
the 9 screens are finished projecting (to the picture image on
the right bottom screen), the search operation is carried out
repeatedly from the upper left screen.)
44
Page 45

3. SYSTEM COMPONENT DIAGRAM OF DUAL UNIT
T
2M memory X2
MSM518221-30ZS
From tuner
SY
SC
Video/color/
deflection
process IC
µPC1832GT
Y
R- Y
B- Y
R- Y
B- Y
I
Q
Control
ON-screen
display super
impose
TC4W53F
MC74HC4053F
Y
Sub screen
process IC
I
TC9092AF
Q
2
I
OSD
Sub screen
control microprocessor
CXP85116B-514Q
I2C BUS
From main microprocessor
From tuner
C BUS
SY
SC
Fig. 6-1
Main/Sub
picture
superimpose
MC74HC4053F
YIQ YIQ
Wide aspect
conversion
TC9097F
YIQ
V/C/D IC
TA1222N
To CR
G
B
R
45
Page 46

4. CIRCUIT OPERATION
4-1. Video/Color/Deflection Process Section
The video/color/deflection section is shown in Fig. 6-2.
The luminance signal is supplied from pin Y08 of PY01 and
its frequency bandwidth is limited by the low pass filter (LPF)
and then input to pin 36 of V/C/D IC (VIDEO IN). The Y
signal output from pin 12 of PY01 superimposes the character signal on the video signal by QY49 and QY44, and then
output to the sub screen process section.
QY49 and QY44 work as the analog switches. When the
screen is displayed in DW, the switch operation is not carried out and the same signal as the input signal is output, and
when the 9-screen multi-search process is carried out, the
switch operation is carried out.
The OSD signal superimposes the shade of character signal
by QY49 and the character signal by QY44 on Y signal.
On the other hand, the color signal is supplied from pin Y15
of PY01, limited its frequency bandwidth by the band pass
filter (BPF) and then input to pin 34 of QY01 (COLOR IN).
The color difference signals of the demodulated signal (R –
Y) and ( B – Y) are output from pins 13 and 14 of QY01. In
the same way as the Y signal, the (R – Y) and (B – Y) signals
are superimposed on the character signal with OSD signal
by QY44.
The GBR matrix circuit which converts the Y , R – Y and B –
Y signals into three primary color signal of G, B and R is
used to convert the (R – Y) and (B – Y) signals into I and Q
signals.
In the GBR matrix circuit, each G, B and R output is output
as G – Y, B – Y and R signals when the Y signal is not input.
Then the B – Y signal is converted to Q signal, R – Y to I
signal pseudically by turning the phase by an angle of 33°.
Thus, R – Y and B – Y signals are input to pins 18 and 19 of
QY01, and the output signals from pins 23 and 24 are developed as the I and Q converted signals pseudically. The amplitude of the signals is amplified by 6 dB amplifier of QY23
and the signals are output to the sub screen process section.
Since the sync signal is added to the luminance signal, the
signal is input to pin 39 of QY01 (SYNC SEP IN) and the
sync signals of HD and VD are output to pins 10 and 11 of
QY01. The HD signal is waveshaped by QY42.
The HD signal (WHD1, WHD2) is used as the horizontal
pulse for sub screen write and the VD signal (WVD) is as the
vertical pulse for sub screen write in the sub screen process
section.
In the sub screen microcomputer section, various kinds of
control signals (brightness, density , hue, etc.) are output from
the sub screen control microprocessor QY91 and the signals
are used for the level matching adjustment. So the setting for
the sub screen cannot be made by the user. Furthermore, the
OSD signal for OSD superimposing is output.
The sub screen process IC control program is stored in the
nonvolatile memory of the sub screen control micr oprocessor QY91 in order to control the sub screen process IC
(TC9092AF), and the data is sent via I2C bus.
46
Page 47

Sub screen microprocessor section
QY91 CXP85116B-514Q
PY01
circuit
Signal reception
Y13
Y14
Y08
Y15
SCL
SDA
PIP VIDEO
PIP C
4947SCL2
SDA2
Sub screen control
microprocessor
50SCLP
48SDAP
46BLK
43B
53COL
54TIN
51S.COL
52CON
62fsc SEL
61PAL/NTSC
23.58
L.P.F
B.P.F
Control
QY01 µPC1832GT
V/C/D IC
20 COLOR
21 TINT
37 SUB COL.
38 CONTRAST
41 fsc SELECT
42 PAL/NTSC
39 SYNC SEPA
IN
36 VIDEO IN
34 CHROMA IN
OSD
OSD
I2C BUS(SCL,SDA)
QY49
TC4W53F
OSD
12Y OUT
13R-Y OUT
14B-Y OUT
18R-Y IN
19B-Y IN
23R OUT(I)
24B OUT(Q)
10HD OUT
superimpose
71
5
QY22 MM1031XMR
6dB. Amp
3
3
6dB. Amp
QY23 MM1031XMR
QY42 TC74HC123AF
Waveform
1
1A
shape
QY44
MC74HC4053F
911
12
5
2
1Q
2Q
14
4
15
superimpose
OSD
1
1
13
5
Y
To Sub screen process section
I
Q
WHD2
WHD1
Fig. 6-2
11VD OUT
WVD
47
Page 48

4-2. Sub Screen Process Section
The sub screen process section is shown in Fig. 6-3.
The Y, I and Q signals from the video/color/deflection pro-
cess section are limited in their frequency bandwidth by the
LPF in the prceeding stage and input to pins 6, 13 and 15 of
QY03.
The frequency of 18.5 MHz generated by LY102 is multiplied by 1/2 inside QY03. The Y signal is sampled by 9.25
MHz and the I and Q signals are sampled by 4.63 MHz (1/2
frequency to multiplex) and then the signals are converted
into 8-bit digital signals.
The horizontal sync signal WHD (the signal mixed with
WHD1 and WHD2 by QY43) for writing input to pins 21
and 20 of QY03 and the vertical sync signal WVD for trigger writing on the field memory QY10 and QY11.
Y
L.P.F
6
Y IN
The horizontal sync signal RHD for reading-out and the vertical sync signal R VD for reading out input to pins 75 and 77
of QY03 trigger the reading at 18.0 MHz which is created
by 2/3-multiplying 27.0 MHz developed in LY101and then
output as the analog signal.
The Y, I and Q signals converted for the sub screen are output from pins 95, 100 and 97 of QY03. The output signals
are used for the input signals compressed by 1/2 in the horizontal direction in the double window mode and for the input signal compressed by 1/6 in the horizontal direction and
by 1/3 in the vertical direction in 9-screen multi-search mode.
Then the signals are smoothed by the LPF in the next stage
then input to the main/sub screen superimposing section.
QY03 TC9092AF
Sub screen process IC
Y OUT
95
L.P.F
Y
I
Q
2
C BUS (SCL, SDA)
I
WVD
WHD2
Video/color/deflection process section
WHD1
PY01
Y11
Y12
Y01
RVD
RHD
YS
OR
1
circuit
2
QY43
TC7S32F
L.P.F
L.P.F
4
LY102
LY101
WHD
13
15
79
80
20
21
24
25
77
75
72
73
R-Y IN
B-Y IN
SCL
SDA
FVS
FHS
OSCSI
OSCSO
FVM
FHM
OSCMI
OSCMO
R-Y OUT(I)
B-Y OUT(Q)
YS OUT
MWD 0
MWD15
MRD 0
MRD15
100
97
70
48
32
51
65
L.P.F
L.P.F
QY10, QY11
MSM518221-30ZS
2M
memory
Date in
Date out
YS
I
Q
process section
To Main/Sub pictore superimposing
Signal reception circuit
Fig. 6-3 Sub screen process section
48
Page 49

4-3. Main/Sub Screen Superimposing Section
CY231
CY230
CY232
CY239
CY240
CY238
Y
I
Q
YS
YD
ID
QD
SCP
3
2
1
4
Clump capacitor
Clump capacitor
3
9
1
4
8
2
Analog
SW
5613
QY46
TC74HC4066AF
Analog
SW
QY47
TC74HC4066AF
5613
3
9
1
4
8
2
Waveform
shape
Clump
pulse
Constant voltage
source E
From Sub screen
process section
Signal reception
circuit
Signal reception
circuit
QY48 MC74HC4053
1IY (Y IN)
3 IZ (I IN)
13 IX (Q IN)
11 A
10 B
9C
2OY (Y IN)
5 OZ (I IN)
12 OX (Q IN)
15Y COM (Y OUT)
4Z -COM (I OUT)
14X-COM (Q OUT)
Y05
Y06
Y04
53
51
52
43
42
41
R
G
B
Y
I
Q
YOUT
I
Q
PY01
Q501
To CRT
Main/Sub picture
superimpose
PY02
TA1222N
The main/sub screen superimposing section is shown in Fig.
6-4.
The sub screen Y, I and Q signals sent from the sub screen
process section and the main screen Y, I and Q signals sent
from the digital unit through the receive circuit and etnered
pins 3, 2, and 1 of PY02 are clamped at a same electrical
potential and the former are fed to pins 1, 3, 13 and the latter
fed to pins 2, 5 and 12 of QY48.
The clamp circuit contains a clamp pulse waveshaping SCP
at pin 4 of PY02, analog switches for ever-v oltage source E,
QY46 and QY47 and clamp capacitors CY230 ~ CY232,
CY238 ~ CY240.
QY48 is an analog switch to feed the Y, I and Q signals for
either sub screen or main screen to pins 15, 4 and 14 by the
YS signal voltage fed to pins 9, 10 and 11. When the YS
signal develops high, QY48 selects the signals for the sub
screen and when low, QY48 selects the signals for the main
screen. Consequently, the signals for both the main and sub
screens are superimposed each other.
In normal mode (with only the main screen picture displayed),
the YS signal voltage always goes low and the Y, I and Q
signals from the digital unit are developed at pins 15, 4 and
14 of QY48.
The Y, I and Q signals for the main/sub screens superimposed are developed at pins Y05, Y06 and Y04 of PY01 and
then supplied to the receive circuit.
The Y, I and Q signals for the main/sub screens superimposed inside the receive circuit are entered to pins 53, 51 and
52 of Q501 (TA1222N) and then fed to CRT. The video
signal is processed in Q501 without distinguishing the signals for main and sub screens, so the high picture quality can
be obtained equally for both the screens.
Fig. 6-4 Main/Sub screen superimposing section
49
Page 50
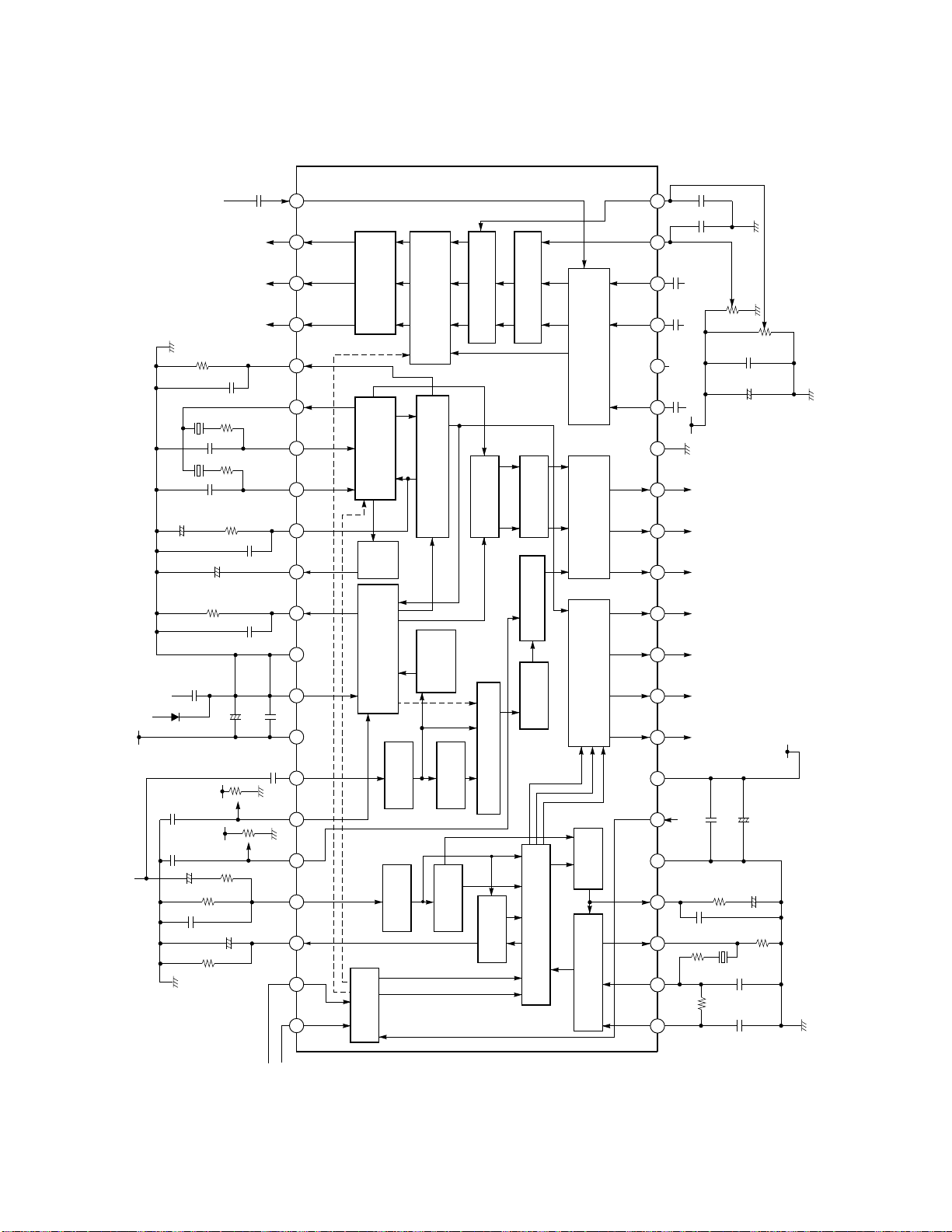
5. TERMINAL FUNCTION, DESCRIPTION AND BLOCK DIAGRAM OF
MAIN IC
3.58MHz
4.43MHz
F
µ
0.47
Ω
6.8K
+
Ω
1M
Ω
1M
Clamp pulse
18
pF
18pF
+
F
µ
1
BGR
F1.8 K
µ
0.22
Ω
1.8 K
Ω
4700pF0.22
F
F
µ
0.1
F
µ
0.1
F
µ
0.22
Ω
F
µ
20k
Tint control
RGB output
VCXO. PAL SW
3.58MHz / 4.43MHz
Filter
fH Adj.
µ
matrix
PAL / NTSC
IDENT D det.
APC killer wave form det.
R-Y, B-Y
demodulation
Color control
L P F
control
Contrast
Y, R-Y, B-Y input clamp
Y, R-Y, B-Y output
0.22
F
µ
0.22
Vcc
Color control
R-Y B-Y
F
µ
0.1
+
F
µ
22
Tint control
Ω
20k
1000pF
Separate
/ color
Separate / composite SW
Vcc
Vcc
F
µ
0.1
control
Sub color
F
Vcc
µ
0.1
Contrast
control
+
F
CVBS
µ
4.7
1500pF
43kΩ
fsc BPF
Separate / Composite SW,
ACC amp., Sub color control
Clamp
Sync. sepa.
Mode SW
fsc
trap
Separate / composite SW
V. filter
+
1
F
µ
22
20kΩ
100Ω
180kΩ
F
µ
0.1
F
µ
20kΩ0.22
41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22
42
3.58 / 4.43
PAL / NTSC
+
H. sync det.
Delay
H / V count
killer output
HD, VD, blanking pulse,
form det.
AFC wave
F
µ
0.015
330Ω
321H VCO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
Killer det. BLK HD VD Y R-Y B-Y
50 / 60
F
µ
0.1
2.2kΩ
8.2kΩ
+
+
500pF
820pF
220pF
Vcc
F
µ
22
F
µ
4.7
2.7kΩ
Fig. 6-5 QY01
mm
mPC1832GT internal block diagram
mm
50
Page 51

t
VCO felter 1
32f
m
1
42
PAL/NTSC SW
VCO felter 1
32f
m
32f
VCO felter 1
m
H.AFC filter
GND (sync)
fv 50/60 SW
Power supply (sync)
Color killer output
Blanking pulse output
HD pulse output
VD pulse output
Y output
R-Y output
B-Y output
GND (video)
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
µPC1832GT
41
fsc SW
40
H. sync det. filter
39
Sync sepa input
38
Contrast control
37
Sab color control
36
Composite video signal inpu
35
Power supply (color)
34
Separati color input
33
GND (color)
32
ACC filter
31
I
. filter
o
30
Color APC filter
29
f
VCO input (4.43MHz)
sc
28
f
VCO input (3.58MHz)
sc
Y input
Power supply (video)
R-Y input
B-Y input
Color control
Tint control
16
17
18
19
20
21
Fig. 6-6 QY01
27
VCO output
f
sc
26
Color killer filter
mm
mPC1832GT pin layout
mm
25
B output
24
G output
23
R output
22
Clamp pulse input
51
Page 52

(DAJA)
YC DELAY
ADJUSTMENT
BETWEEN Y/C
LC
(MAIN)
CLOCK GENERATION
H, V (Main)
FRAME SIGNAL
Ys
GENERATION
Y
(WAKU)
R-Y
DA
FRAME
SIGNAL
B-Y
SW
MULTIPLEX
ELIMINATION
VERTICAL FOLDED
INTERPORATION FILTER
(1H MEMORY (12BIT)) (V)
ELIMINATING
HORIZONTAL
FOLD SIGNAL
FILTER (HFA)
HORIZONTAL
FILTER (HFB)
GENERATION (KGEN)
FILTER FACTOR OPERATION/
INTERPORATION
AD
AD
MPX
CLAMP
CU
(CONTROL UNIT)
(16k BIT + 3k BIT)
PROGRAM DATA MEMORY
C
2
I
(SUB)
CLOCK
GENERATION
INTERFACE
1H MEMORY (11BIT)
TELTEXT DETECTION (J)
DELAY ADJUSTMENT (DAJB)
DATA
DATA
SUB SAMPLE PIT FILLING (C)
(R)
MENT
REARRANGE
(2M BIT)
PICTURE
MEMORY
(W)
MENT
REARRANGE
Y
Sub screen
video input
R-Y
B-Y
LC
H, V (Sub)
C
2
I
Fig. 6-7 QY03 TC9092AF internal block diagram
52
Page 53

50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
MRD1
MRD2
MRD3
MRD4
MRD5
MRD6
MRD7
MRD8
MRD9
MRD10
RMD11
RMD12
MRD13
MRD14
MRD15
RE
RSTR
CKR
CKRI
YSOUT
VSS
OSCMI
OSCMO
VDD
FHM
HFHM
FVM
VSS
SCL
SDA
VDD
MRD0
MWD0
MWD1
MWD2
MWD3
MWD4
MWD5
VSS
MWD7
MWD6
TC9092AF
(TOP VIEW)
MWD8
MWD9
MWD11
MWD10
MWD13
MWD12
MWD15
MWD14
ADVREFC
ADVREFY
RSTW
WE
CKW
VDD
VSS
OSCSO
OSCSI
VDD
NFHS
FHS
FVS
VDD
VSS
ADDVSS
ADDVDD
RYIN
ADBIAS
RYIN
ADVDD
CLAMPC
ADVSS
CLAMPY
ADVSS
YIN
ADVDD
DABIAS2
DABIAS3
DAVSS
30
IE
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
YOUT
DAVDD
DABIAS1
DAVREFY
NC
VDD
TESTAD
TEST1
RESET
ME
PROMRES
PROMCK
PROMDI
VSS
SDAINO
81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96
Fig. 6-8 QY03 TC9092AF pin layout
53
DAVREFC
RYOUT
DAVSS
97 98 99 100
BYOUT
DAVDD
Page 54

Table 6-1 QY03 TC9092AF pin list (No. 1)
No. Pin name I/O Pin function
1 DAVSS D/A GND
2 DABIAS3 D/A bias condenser connection terminal
3 DABIAS2 D/A bias condenser connection terminal
4 ADVDD A/D power supply
5 ADVREFY I A/D Y reference condenser connection terminal
6 YIN I A/D Y input terminal
7 ADVSS A/D GND
8 CLAMPY Y clamp bias condenser connection terminal
9 ADVSS A/D GND
10 CLAMPY C clamp bias condenser connection terminal
11 ADVDD A/D power supply
12 ADVREFC I A/D reference condenser connection terminal
13 RYIN I A/D R – Y input terminal
14 ADBIAS A/D bias condenser connection terminal
15 BYIN I A/D B– Y input terminal
16 ADDVDD A/D digital power supply
17 ADDVSS A/D digital GND
18 VSS Digital GND
19 VDD Digital power supply
20 FVS I Sub screen vertical sync signal input
21 FHS I Sub screen horizontal sync signal input
22 NFHS I Sub screen horizontal sync signal reversing input
23 VDD Digital power supply
24 OSCSI I Oscillator connection terminal sub input
25 OSCSO O Oscillator connection terminal sub output
26 VSS Digital GND
27 VDD Digital power supply
28 CKW O Serial write clock output terminal
29 IE O Input enable output terminal
30 WE O Write enable output terminal
31 RSTW O Reset write output terminal
32 MWD15 O Data output terminal
33 MWD14 O Data output terminal
34 MWD13 O Data output terminal
35 MWD12 O Data output terminal
36 MWD11 O Data output terminal
37 MWD10 O Data output terminal
38 MWD9 O Data output terminal
39 MWD8 O Data output terminal
40 VSS Digital GND
41 MWD7 O Data output terminal
42 MWD6 O Data output terminal
43 MWD5 O Data output terminal
44 MWD4 O Data output terminal
45 MWD3 O Data output terminal
46 MWD2 O Data output terminal
47 MWD1 O Data output terminal
48 MWD0 O Data output terminal
49 VDD Digital power supply
50 MRD0 I Data input terminal
54
Page 55

Table 6-2 QY03 TC9092AF pin list (No. 2)
No. Pin name I/O Pin function
51 MRD1 I Data input terminal
52 MRD2 I Data input terminal
53 MRD3 I Data input terminal
54 MRD4 I Data input terminal
55 MRD5 I Data input terminal
56 MRD6 I Data input terminal
57 MRD7 I Data input terminal
58 MRD8 I Data input terminal
59 MRD9 I Data input terminal
60 MRD10 I Data input terminal
61 MRD11 I Data input terminal
62 MRD12 I Data input terminal
63 MRD13 I Data input terminal
64 MRD14 I Data input terminal
65 MRD15 I Data input terminal
66 RE O Read enable output terminal
67 RSTR O Read reset output terminal
68 CKR O Serial read clock output terminal
69 CKRI I Memory read clock input
70 YSOUT O Ys signal output terminal
71 VSS Digital GND
72 OSCMI I Oscillator connection terminal main input
73 OSCMO O Oscillator connection terminal main output
74 VDD Digital power supply
75 FHM I Main screen horizontal sync signal input
76 NFHM I Main screen horizontal sync signal reversing input
77 FVM I Main screen vertical sync signal input
78 VSS Digital GND
79 SCL I I2C CK input terminal
80 SDA BID I2C data I/O terminal
81 SDAINO O I2C data direction output terminal, Test output terminal
82 VSS Digital GND
83 PROMDI I ROM data input terminal
84 PROMCK O ROM clock output terminal
85 PROMRES O ROM RESET output terminal
86 ME I MEMORY polarity control input terminal
87 RESET I RESET input terminal
88 TEST1 I TEST input terminal
89 TESTAD I AD/DA TEST input terminal
90 VDD Digital power supply
91 NC
92 DAVREFY I D/A Y reference voltage input terminal (4V)
93 DABIAS1 D/A bias condenser connection terminal
94 DAVDD D/A power supply
95 YOUT O D/A Y output terminal
96 DAVSS D/A GND
97 RYOUT O D/A R – Y output terminal
98 DAVREFC I D/A C reference voltage input terminal (3V)
99 DAVDD D/A power supply
100 BYOUT O D/A B – Y output terminal
55
Page 56

Dout (X8) OE RE RSTR SRCK
Data - out
buffer (X8)
71 Word
Sub-register (X8)
71Word
Sub-register (X8)
Data - in
Buffer (X8)
Din (X8) IE WE RSTW SWCK
Serial Read Controller
512 Word serial read register (X8)
Read line buffer
Low-Half (X8)
Write line buffer
Low-Half (X8)
512 Word serial write register (X8)
Serial Write Controller
Read line buffer
High-Half (X8)
256 (X8) 256 (X8)
256K (X8)
Memory
Array
256 (X8) 256 (X8)
Write line buffer
High-Half (X8)
X
De-
coder
Read/Write
and refresh
controller
Clock
oscillator
VB3
Generator
WE
Din0
Din2
Vcc
Din5
Din7
SWCK
NC
OE
Dout6
Dout4
Dout3
Dout1
RSTR
Fig. 6-9 QY10/QY11 M518221-30ZS internal block diagram
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
27
IE
2
Din1
4
Din3
6
Din4
8
Din6
10
RSTW
12
NC
14
RE
16
Dout7
18
Dout5
20
Vss
22
Dout2
24
Dout0
26
SRCK
28
Terminal name Function
SWCK Serial write clock
SRCK Serial read clock
WE Write enable
RE Read enable
IE Input enable
OE Output enable
RSTW Reset write
RSTR Reset read
Din 0 – 7 Data input
Dout 0 – 7 Data output
V
CC
V
SS
Power supply (+5V)
Ground (0V)
NC Not connected
28PIN ZIP
Fig. 6-10 QY10/QY11 M518221-30ZS pin layout
56
Page 57

SECTION VII: 3-DIMENSION Y/C SEPARATOR CIRCUIT
1. OUTLINE
The 3D YC separation circuit uses a comb filter with a frame
memory and ideally separates the Y (luminance) and color
signal for still parts of a picture, thus providing a clean picture without:
(1) Dot interference causing at border areas of color pic-
tures.
(2) Excess color in vertical direction.
Howev er in a moving picture, as the picture mo ves between
the first and second frames, good separation is not obtained.
To prevent this, a motion detection is carried out in the 3D
YC separation (hereafter called YCS) unit (PB6347). When
a picture moving is detected a 2D YC separation using a
line memory is switched in and when not detected or for a
still picture 3D YC separation is switched in, thereby correcting defects both the systems have and performing the
ideal YC separation. The motion detection accuracy and
smoothness of the switching, etc. are controlled through the
IIC bus.
After completion of the Y and S signal separation, a vertical
contour correction is carried out for the Y signal.
2. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
2-1. Configuration
The YCS unit consists of a YC separation IC (QZ01,
TC9086F) which plays major roles, 2 Mbyte field memory
(QZ02, QZ03), clock generation IC (QZ04, TA8667F), and
peripheral circuits (LPF, AMP,emitter followers, etc.).
Of the above circuit blocks, QZ01 (TC9086F) includes an
A/D converter, D/A converter, clamp circuit, 4fsc PLL circuit, 1 line dot countermeasure circuit, vertical contour correction logic circuit, etc. and provides a high separation with
less variations.
2-2. Circuit Description
Fig. 7-1 shows a block diagram of the YCS circuit.
(1) A video signal sent through the AV switching circuit
passes the input terminal (DG) and enters the YCS unit.
(2) The video signal entered is limited in its band width in
passing through an aliasing distortion elimination LPF
consisting of LZ22, etc. , and then enters pin 56 of
QZ01.
(3) At the same time, a fsc (3.58 MHz) signal being oscil-
lated in the video signal color IC (Q501, AN1222AN)
is fed to pin 28 of QZ01 and converted into a 4fsc
(14.32 MHz), a drive clock frequency inside the IC.
(4) The video signal entered pin 56 of QZ01 is processed
inside the IC and a luminance (Y) signal is developed
at pin 48 of QZ01 and the color signal at the pin 51.
(5) The Y signal developed at pin 48 of QZ01 passes a
LPF (LZ20, etc.) which eliminates the clock signal
component, amplified by a 6dB amplifier QZ21, etc.
and comes out from the DC terminal as the Y signal.
(6) At the same time, the color signal developed at pin 51
of QZ01 passes a LPF (LZ21, etc.) which eliminates
the clock component, amplified by 6dB by QZ23, etc.
and comes out from DD terminal through a buffer of
QZ24 as the C signal.
(7) QZ04 is generating a clock signal used to read and
write the digital data between QZ03 and QZ04 based
on the video signal.
(QZ16 emitter: 28.6 MHz ± 0.2 MHz, adjusted by
LZ25.)
57
Page 58

• Terminal description (PZ01)
No.
DH
DC
DE
DD
DB
DG
DA
DF
DI
DJ
PZ01 QZ01 TC9090N
DH
DC
DE
Signal name
Comb through
Y-Comb
9V
C-Comb
GND
V-AV
5V
fsc
SDA1
SCL1
AMP LPF
QZ21 LZ20 etcQZ22
Voltage
Comb through pulse for ED2 ID signal period (V frequency), 5V
2V(p-p)
+9V ± 0.5V
0.6V(p-p) at burst
GND
2V(p-p)
+5V ± 0.5V
0.4V(p-p), 3.58 MHz
IIC bus data, 5V
IIC bus clock, 5V
36
KILL
YOUT
48
DD
DB
DG
DA
DF
DI
DJ
QZ24
QZ06
AMP LPF
QZ23 LZ21 etc
LPF
LZ23 etc
QZ04 TA8667F
QZ14
LZ25
28.6MHz
QZ07
QZ05
QZ16
Fig. 7-1 3-dimension Y/C separator unit block diagram
51
56
28
20
19
8
COUT
CVIN
FS2N
FSC
DATA
SLK
64
100
QZ02
QZ03
58
Page 59

1. OUTLINE
SECTION VIII: VERTICAL OUTPUT CIRCUIT
The sync separation circuit, V pulse circuit, and blanking
circuit are provided inside Q501 (T A1222AN). The sa w tooth
wave generation circuit and amplifier (V driver circuit) are
provided inside Q302 (TA8859AP).
Q302 TA8859AP
MICROPROCESSOR
2
C BUS)
( I
Q501 TA1222AN
V/C/D LSI
SYNC SEP.V PULSE/
BLANKING
WAC
PULSE DELAY
2
C BUS)
( I
SAWTOOTH
WAVE
GENERATOR
CONTROL CIRCUIT
AMP
Q301 (LA7833S) contains the pump up circuit and the output
circuit. V screen position switching function which lowers
the V raster position by flowing an opposite DC current into
the deflection yoke. This circuit is used selecting SUBTITLE
and CINEMA MODE.
Q301 LA7833S
PUMP UP
CIRCUIT
OUTPUT
FEEDBACK
DEFLECTION
YOKE
V-RASTER SHIFT
CIRCUIT
V-BLK
1-1. Theory of Operation
The purpose of the V output circuit is to pro vide a sawtooth
wave signal with good linearity in V period to the deflection
yoke.
When a switch S is opened, an electric charge charged up to
a reference voltage VP discharges in an constant current rate,
and a reference sawtooth voltage generates at point a .
Vp
a
V1
S: Switch
R1 C2 R2
Fig. 8-1
AUTO LIVE
MICROPROCESSOR
This voltage is applied to (+) input (non-inverted input) of
an differential amplifier , A. As the amplification factor of A
is sufficiently high, a deflection current flows so that the
voltage V2 at point c becomes equal to the volta ge at point
a .
Differential
amplifier
A
L
C2
R3
c
V2
Fig. 8-2
59
Page 60

2. V OUTPUT CIRCUIT
2-1. Actual Circuit
C322
Q501
31
R320
R329
C321
15
14
Q302
13
3
6
8
C319
2-2. Sawtooth W av eform Generation
+9V
R301
C314
R330
+35V
7
4
1
Fig. 8-3
D309
R308 C308
D308
6
3
Q301
2
5
C309
C311
D301
R303
L301 R336
R307
R306
R313
C305
R304
C313
C307
L462+L463+L464
C306
R305
2-2-1. Circuit Operation
The sawtooth waveform generation circuit consists of as
shown in Fig. 8-4. When a trigger pulse enters pin 13, it is
differentiated in the waveform shape circuit and only the
falling part is detected by the trigger detection circuit, to the
waveform generation circuit is not susceptible to v ariations
of input pulse width.
5Vp
DC=0V
13
WAVEFORM
SHAPE
TRIGGER
DET.
Fig. 8-4
The pulse generation circuit also works to fix the V ramp
voltage at a reference voltage when the trigger pulse enters,
so it can prevent the sawtooth wave start voltage from
variations by horizontal components, thus improving
interlacing characteristics.
R329
PULSE
GAIN
14
C321 C322 C323
V. LAMP
15 16
+
+9V
AGC
60
Page 61

2-3. V Output
2-3-1. Circuit Operation
The V output circuit consists of a V driver circuit Q302,
Pump-up circuit and output circuit Q301, and external circuit
components.
(1) Q2 amplifies its input fed from pin 4 of Q301, Q3, Q4
output stage connected in a SEPP amplifies the current and supplies a sawtooth waveform current to a
deflection yoke.
+35V
D301 C308
D308
Q301
36
Q3
Q3 turns on for first half of the scanning period and
allows a positive current to f low into the deflection
yoke (Q3 ® DY ® C306 ® R305 ® GND), and Q4
turns on for last half of the scanning period and allows
a negative current to flow into the deflection yoke
(R305 ® C306 ® DY ® Q4). These operations are
shown in Fig. 8-5.
V 3
D309 R308
7
V 7
63V
35V
GND
35V
BIAS
Q2
4
CIRCUIT
Q4
1
(2) In Fig. 8-6 (a), the power Vcc is expressed as a fixed
level, and the positive and negative current flowing
into the deflection yoke is a current (d) = current (b) +
(c) in Fig. 8-6, and the emitter voltage of Q3 and Q4 is
expressed as (e).
Power Vcc
Q3
i1
Vce 1
Fig. 8-5
V 2
2
DY
+
C306
R305
Q3 ON
Q4 ON
GND
63V
GND
GND
(3) Q3 collector loss is i1 x Vce1 and the value is equal to
multiplication of Fig. 8-6 (b) and slanted section of
Fig. 8-6 (e), and Q4 collector loss is equal to multiplication of Fig. 8-6 (c) and dotted section of Fig. 8-6
(e).
GND (b) Q3 Collector current i1
GND (c) Q4 Collector current i2
Q2
Q4
i2
(a) Basic circuit
Fig. 8-6
61
GND (d) Deflection yoke current i1+i2
Vp
Vcc
1/2 Vcc
(e)
GND
Page 62

(4) To decrease the collector loss of Q3, the power supply
voltage is decreased during scanning period as shown
in Fig. 8-7, and VCE1 decreases and the collector loss
of Q3 also decreases.
Q3 Collector loss decreases
by amount of this area
Power supply
for flyback period (Vp)
Power supply
for scanning period
(Vcc)
Scanning period
Flyback period
Fig. 8-7 Output stage power supply voltage
(5) In this way, the circuit which switches power supply
circuit during scanning period and flyback period is
called a pump-up circuit. The purpose of the pump-up
circuit is to return the deflection yoke current rapidly
for a short period (within the flyback period) by applying a high voltage for the flyback period. The basic
operation is shown in Fig. 8-8.
(6) Since pin 7 of a transistor switch inside Q301 is con-
nected to the ground for the scanning period, the power
supply (pin 3) of the output stage shows a voltage of
(VCC – VF), and C308 is charged up to a voltage of
(VCC – VF – VR) for this period.
(7) First half of flyback period
Current flows into L462 + L465 + L464 ® D1 ® C308
® D308 ® VCC (+35V) ® GND ® R305 ® C306
® L462 + L463 + L464 in this order, and the voltage
across these is:
VP = VCC + VF + (VCC – VF – VR) + VF about 63V
is applied to pin 3. In this case, D301 is cut off.
(8) Last half of flyback period
Current flows into VCC ® switch ® D309 ® C308
® Q301 (pin 3) ® Q3 ® L462 + L463 + L464 ®
C306 ® R305 in this order, and a voltage of
VP = VCC – VCE (sat) – VF + (VCC – VF – VR) –
VCE (sat), about 56V is applied to pin 3.
(9) In this way, a power supply voltage of about 35V is
applied to the output stage for the scanning period and
about 63V for flyback period.
Q301
D301 C308
D308
6
Q3
Q4
(a) Scanning period (b) Flyback period
D1
3
D309
Switch
7
L462+L463+L464
2
R308
+
C306
R305
Q301
Q3
Q4
D301 C308
6
D1
Fig. 8-8
D308
3
D309
Switch
7
L462+L463+L464
2
Last half
R308
VR
First half
+
C306
R305
62
Page 63

2-4. V Linearity Characteristic Correction
Volttage Across
R305
Q350 BASE
Q351 Collector
Q340 V
BE
12V-V
BE
(Q341)
2-4-1. S-character Correction
(Up-and Down-ward Extension Correction)
A parabola component developed across C306 is integrated
by R306 and C305, and the voltage is applied to pin 6 of
2-4-2. Up-and Down-ward Linearity Balance
A voltage developed a t pin 2 of Q301 is divided with resistors
R307 and R303, and the voltage is applied to pin 6 of Q301
to improve the linearity balance characteristic.
Q302 to perform S-character correction.
3. PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR V DEFLECTION STOP
Q301
2
L462+L463+L464
R305
C306
Q350
R350
Fig. 8-9
D350
R351
C350
R352
Q351
12V
D353
9V
R354
D354
Q353
BLANKING
CIRCUIT
When the deflection current is not supplied to the deflection
coils, one horizontal line appears on the screen. If this
condition is not continued for a long time, no trouble will
occur in a conventional TV. But in the projection TV, all the
electron beams are directly concentrated at the fluorescent
screen because of no shadow mask used, and burns out the
screen instantly.
T o prevent this, the stop of the V deflection is detected when
the horizontal one line occurs, and the video signals are
blanked out so that the electron beams are not emitted.
When the V deflection circuit is operating normally, a
sawtooth wave voltage is obtained across (R305), so Q350
repeats on-off operation in cycle of V sync. In this case, the
collector voltage of Q35 is set to develop less than (12VVBE (Q351)) with R352 and C350 as shown in Fig. 8-9.
Accordingly, Q351 and Q353 are continuously turned on.
As a result, diode D354 is turned off, giving no influence on
the blanking operation.
Next, when the V deflection stops, the v oltage across (R305)
does not develop, so Q350 turns off, and both the Q351 and
Q353 are turned off. Then, the picture blanking terminal
pin 13 of ICA05 is set to high through R354 and D354
connected to 90V power line, BLANKING CIRCUIT ON
thus cutting off the projection tubes.
Fig. 8-10
63
Page 64

3-1. +35V Over Current Protection Circuit
The over current protection circuit cuts off the power supply
relay when it detects abnormal current increased in the +35V
power line due to failure of the vertical deflection circuit.
3-1-1. Theory of Operation
Fig. 8-11 shows the circuit diagram of the over current
protection circuit. When the load current of the +35V line
increases, the voltage across a resistor of T370 will also
increase.
R370
+35V
R372
R371
When the voltage increases across R370. and the voltage
developed across R371 becomes higher than the Vbs of
Q370, Q370 turns on and a voltage develops across R374
due to the collector current flowing. When this voltage
increases to a value higher than about 7V, Z801 operates,
thus cutting off the power relay . When the circuit operates, a
power LED provided will turn on and off in red.
C303
C310
R327
D302
FBT
pin 6
D421
UZ22BSD
C370
R373
R374
Q370
2SA933SQ
D370
UZ11BSB
C371
Fig. 8-11
R375
To pin 14 (GATE)
of Z801
64
Page 65

4. RASTER POSITION SWITCHING CIRCUIT
)
4-1. Outline
When the vertical screen position adjustment is carried out
on the projection TV, DC current is directly flown in the
vertical deflection yoke and the raster cannot be moved up
and down. (Because the raster is mov ed, the color distortion
may occur.) Accordingly, the vertical screen position
adjustment is carried out by the following method. (Only in
CINEMA and SUBTITLE mode)
V sync pulse output from Q501 sync. separation circuit is
once input to WAC, delayed and then output. The deflection
circuit operates with the delayed sync signal. The screen
upper side position moves up and down by v arying the delay
time. When the vertical position adjustment is carried out
by WAC, the followings must be considered.
WAC becomes “through” except for CINEMA and
SUBTITLE mode.
The phase of the output V sync must not advance from that
of WAC input V sync. If it advances, Vertical jitter may occur
when performing the search operation and the vertical
position adjustment of a VTR.
So, adjust the center of the picture to the center of the screen
in advance under the output V sync delay ed.
T o do this, lower the raster position by flowing a DC current
to the deflection yoke in the CINEMA and SUBTITLE
mode.
The operation above is carried out by the vertical screen
position SW circuit.
4-2. Operation
When CINEMA and SUBTITLE are selected in the screen
mode, a zoom signal is input to the base of Q362 from the
autolive circuit and Q362 turns on. Then, Q363 turns off
and the base of Q364 develops H and Q364 turns on. The
inverted DC current flows into the vertical deflection yoke
from +35V power supply line.V power supply line and then
the raster moves down.
Fig. 8-12
Fig. 8-13
Screen
mask
position
R360
33K
Q362
RN1204
P360
R362
1R5.6K
Q364
2SC2023
R361
12K
Q363
2SC1815Y
+35V
+12V
Raster position
R363
220
D361
S5965G
R364
2R
KETSU
Q367
2SC2023
R365
1R5.6K
Q365
2SC1815Y
R366
R367
12K
33K
Q366
RN1204
Screen
mask
position
Nomal mode (4:3, Full, Dramatic Wide)
65
Mode in which the opposite current
flows into D
(Cinema
Y
Page 66

SECTION IX: HORIZONTAL DEFLECTION CIRCUIT
1. OUTLINE
The H deflection circuit works to deflect a beam from left to
right by flowing a sawtooth wa veform of 15.625 kHz/15.735
kHz into the DY H deflection coil.
2. HORIZONTAL DRIVE CIRCUIT
The H drive circuit works to start the H output circuit by
applying H VCC (Q501 DEF power source) to pin 22 of
Q501 (TA1222N) and a bias to the H drive transistor Q402
at the main power on.
R432 Q430 D431
35V
R433
D430
81
BB80
2-1. Theory of Operation
(1) When the power switch is on, the main power supply
of 125V starts to rise. At the same time, AF power supply 38V also rises.
(2) With 38V line risen, Q430 base voltage which is cre-
ated by dividing the audio power with R433 and D430
also rises. Then, the transistor Q430 turns on and the
H VCC is applied from the audio power line through
R432 and D431 to pin 22 of Q501.
Q501
BB81
81 22
L400
H Vcc
SIGNAL
C431 C430
Fig. 9-1 H drive circuit block diagram
3. BASIC OPERATION OF HORIZONTAL DRIVE
A sufficient current must flow into base of the horizontal
output transistor to rapidly make it into a saturated (ON)
condition or a cut off (OFF) condition. For this purpose, a
drive amplifier is provided between the oscillator circuit and
the output circuit to amplify and to waveshape the pulse voltage.
3-1. Theory of Operation
(1) The horizontal driv e circuit works as a so called switch-
ing circuit which applies a pulse voltage to the output
transistor base and makes the transistor on when the
voltage swings in forward direction and off in reverse
direction.
(2) T o turn on the output transistor completely and to make
the internal impedance low, a sufficiently high, forward drive voltage must be applied to the base and
heavy base current ib must be flown. On the contrary,
to completely turn off the transistor, a suf ficiently high,
reverse voltage must be applied to the base.
(3) When the transistor is on (collector current is maxi-
mum) condition with the sufficiently high forward v oltage applied to the base, the transistor can not be turned
off immediately , if a re ve rse base bias is applied to the
base because minority carriers storaged in the base can
not be reduced to zero instantly. That is, a re v erse cur rent flows through an external circuit and gradually
reduces to zero. The time lag required for the base current to disappear is called a storage time and falling
time.
66
Page 67
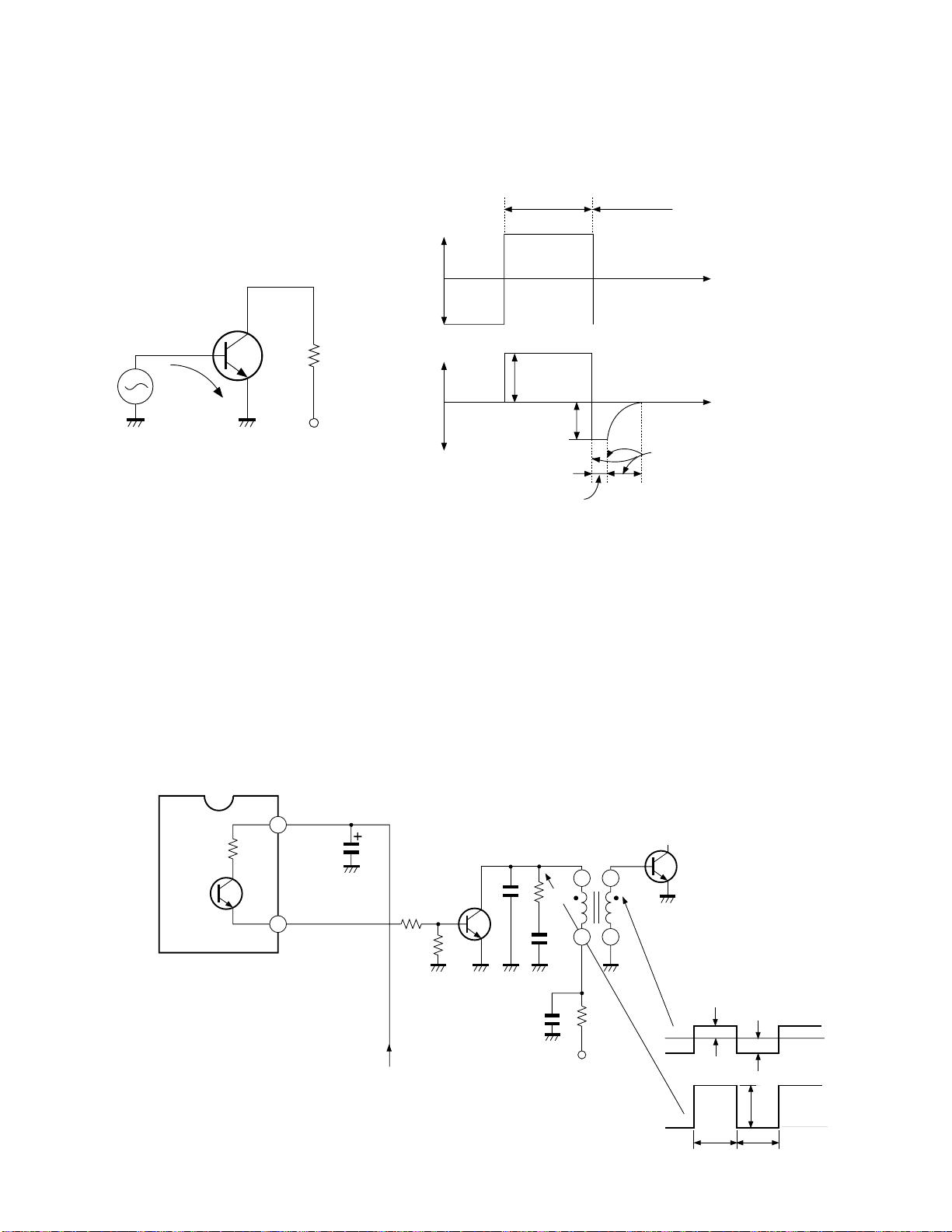
(4) To shorten the storage time and the falling time, a suf-
ficiently high reverse bias voltage must be applied to
allow a heavy reverse current to flow. This operation
also stabilizes operation of the horizontal output transistor.
+
On period OFF period
0
-
+
ib
0
V
(a)
-
Fig. 9-2
3-2. Circuit Description
In the N5SS chassis, the off drive system is employed.
(1) When Q1 inside Q501 is turned on, Q402 base is for-
ward biased through 9V ® pin 22 of Q501 (H. VCC)
® pin 23 of Q501 (H. Out) ® R411/R410 resistor di-
vider, and then, Q402 collector current flows through
125V ® R416 ® T401. In this case, the H output transistor Q404 turns on with the base-emitter reverse biased because of the off drive system employed.
Q501
t Input waveform (b)
Forward
current
t Base current (c)
Reverse
current
Falling
time
Storage
time
(2) On the contrary, when Q1 inside IC501 is off (pin 8 is
0V), base-emitter bias of Q402 becomes 0V and Q402
turns off, and a collector pulse as shown in Fig. 9-3
develops at the collector.
The voltage is stepped down and Q404 is forward biased with this voltage, thus turning on Q404.
(3) In this way, by stepping down the volta ge developed at
primary winding of the drive transformer and by applying it to Q404, a sufficient base current flows into
Q404 base, thereby switching the Q404.
Q1
22
23
H. Vcc
C431
R411
R410
9V
Fig. 9-3
Q402
H drive
transistor
C417
R415
C413
C416
+
+125V
T401
H drive
transistor
1
2
R416
3
Q404
H output
4
transistor
Q402
V1
OFF
V2
0V
VCP
0V
Q402
ON
67
Page 68

4. HORIZONTAL OUTPUT CIRCUIT
10
HV
The horizontal output circuit applies a 15.625 kHz/15.734
kHz sawtooth wave current to the deflection coil with mutual action of the horizontal output transistor and the damper
diode, and deflects the electron beam from left to right in
horizontal direction.
IC501
H. out
Q1
23
R415
TP-33
Q402
H drive
BB81
83
R411
R410
C413
C416
T401
H drive
transformer
C417
+
R416
Q404
H output
(With damper diode)
C463
Resonat
capacitor
C444
D461
To DPC output
5
2
3
1
C467
C440
C464
T461
FBT
S-charactor
capacitor
8
C343
D444
L461
+
Deflection yoke
C418
C423
D443
To High Voltage
Regulator Circuit
(H coil)
L462
R441
L441
L463
L464
H
linearity
coil
SIGNAL DEF/POWER PCB
125V
4-1. Theory of Operation
4-1-1. Operation of Basic Circuit
(1) To perform the horizontal scanning, a 15.625 kHz/
15.735 kHz sawtooth wave current must be flown into
the horizontal deflection coil. Theoretically speaking,
this operation can be made with the circuit shown in
Fig. 9-5 (a) and (b).
(2) As the switching operation of the circuit can be re-
placed with switching operation of a transistor and a
diode, the basic circuit of the horizontal output can be
expressed by the circuit shown in Fig. 9-5 (a). That is,
the transistor can be turned on or off by applying a
pulse across the base emitter. A forward switching current flows for on-period, and a reverse switching current flows through the diode for off-per iod. This switching is automatically carried out. The diode used for
this purpose is called a damper diode.
Fig. 9-4
Diode modulator circuit
(a) H output basic circuit
H output
transistor
(b) H output equivalent circuit
SW1
DCo
Damper
diode
SW2
Resonant
capacitor
Vcc
Co
L
Deflection
yoke
L
68
Vcc
Fig. 9-5
Page 69

A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
t1 t2 t3 t4 t5 t6
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
TR
base voltage
TR
base current
TR
collector
current
D
damper
current (SW2)
Switch
current
(TR, SW1)
Resonant
capacitor
current (Co)
Deflection
current (Lo)
TR
collector
voltage
Description of the basic circuit
1. t1~t2:
A positive pulse is applied to base of the output transistor
from the drive circuit, and a forward base current is flowing.
The output transistor is turned on in sufficient saturation area.
As a result, the collector voltage is almost equal to the ground
voltage and the deflection current increases from zero to a
value in proportionally. (The current reaches maximum at
t2, and a right half of picture is scanned up to this period.)
2. t2:
The base drive voltage rapidly changes to negati v e at t2 and
the base current becomes zero. The output transistor turns
off, collector current reduces to zero, and the deflection current stops to increase.
3. t2~t3:
The drive voltage turns off at t2, but the deflection current
can not reduce to zero immediately because of inherent nature of the coil and continues to flow, gradually decreasing
by charging the resonant capacitor C0. At the same time, the
capacitor voltage or the collector voltage is gradually increases, and reaches maximum voltage when the deflection
current reaches zero at t3. Under this condition, all electromagnetic energy in the deflection coil at t2 is transferred to
the resonant capacitor in a form of electrostatic energy.
4. t3~t4:
Since the charged energy in the resonant capacitor discharges
through the deflection coil, the deflection current increases
in reverse direction, and voltage at the ca pacitor gradually
reduces. That is, the electrostatic energy in the resonant capacitor is converted into a electromagnetic energy in this
process.
5. t4:
When the discharge is completed, the voltage reduces to z ero,
and the deflection current reaches maximum value in reverse direction. The t2~t4 is the horizontal flyback period,
and the electron beam is returned from right end to the left
end on the screen by the deflection current stated above.
The operation for this period is equivalent to a half c y cle of
the resonant phenomenon with L and C0, and the flyback
period is determined by L and C0.
6. t4~t6:
For this period. C0 is charged with the deflection current
having opposite polarity to that of the deflection current
stated in "3.", and when the resonant capacitor voltage exceeds VCC, the damper diode D conducts. The deflection
current decreases along to an exponential function (approximately linear) curve and reaches zero at t6. Here, operation
returns to the state described under "1.", and the one period
of the horizontal scanning completes. For this period a left
half of the screen is scanned.
In this way, in the horizontal deflection scanning, a current
flowing through the damper diode scans the left half of the
screen; the current developed by the horizontal output transistor scans the right half of the screen; and for the flyback
period, both the damper diode and the output transistor are
cut off and the oscillation current of the circuit is used. Using the oscillation current improves eff iciency of the circuit.
That is, about a half of deflection current (one fourth in terms
of power) is sufficient for the horizontal output transistor.
Fig. 9-6
69
Page 70

Amplitude Correction
To vary horizontal amplitude, it is necessary to vary a
sawtooth wave current flo wing into the deflection coil. These
are two methods to vary the current; a method which varies
LH by connecting a variable inductance L in series with the
deflection yoke, and a method which varies power supply
voltage (across S-character capacitor) for the deflection yoke.
As the DPC circuits is used in the this chassis, the later
method which varies the deflection yoke pow er supply voltage by modifying the bus data is used.
t2
t1
θ
θ
2
1
(a) S-character correction (b)
t2 = t1
<
θ
2
θ
1
t2
t1
θ
θ
2
1
t2 > t1
=
θ
2
θ
1
4-1-2. Linearity Correction (LIN)
(1) S-curve Correction (S Capacitor)
Pictures are expanded at left and right ends of the screen
even if a sawtooth current with good linearity flo ws in
the deflection coil when deflection angle of a picture
tube increases. This is because projected image sizes
on the screen are different at screen center area and
the circumference area as shown in Fig. 9-7. To suppress this expansion at the screen circumference, it is
necessary to set the deflection angle q1 to a large value
(rapidly deflecting the electron beam) at the screen
center area, and to set the deflection angle q2 to a small
value (scanning the electron beam slowly) at the circumference area as shown in Fig. 9-7.
In the horizontal output circuit shown in Fig. 9-8, capacitor CS connected in series with the deflection coil
LH is to block DC current. By properly selecting the
value of CS and by generating a parabolic voltage developed by integrating the deflection coild current
across the S capacitor, and by varying the deflection
yoke voltage with the voltage, the scanning speed is
decreased at beginning and end of the scanning, and
increased at center area of the screen. The S curve correction is carried out in this way, thereby obtaining
pictures with good linearity.
TR
Slow deflection
Fig. 9-7
Cs
D Co
Vcc
(a) H output circuit
(b) Sawtooth wave current
(c) Voltage across LH
Fast deflection
L
H
Deflection coil
70
(d) Synthesized current
Fig. 9-8
Page 71

(2) Left-right Asymmetrical Correction (LIN coil)
In the circuit shown in Fig. 9-9 (a), the deflection coil
current iH does not flow straight as shown by a dotted
line in the Fig. 9-9 (b) if the linearity coil does not
exist, by flows as shown by the solid line because of
effect of the diode for a first scanning (screen left side)
and effect of resistance of the deflection coil for later
half period of scanning (screen right side). That is, the
deflection current becomes a sawtooth current with bad
linearity, resulting in reproducing of asymmetrical pictures at left and right sides of the screen (left side expanded, right side compressed).
(a)
TR
(b) Deflection coil current
D Co
iH
L
H
Deflection
coil
Li
Cs
S-character
capacitor
FBT
Vcc
When a horizontal linearity coil L1 with a current characteristic as shown in Fig. 9-9 (c) is used, left side picture will be compressed and right side picture will be
expanded because the inductance is high at the left side
on the screen and low at the right side. The left-right
asymmetrical correction is carried out in this way , and
pictures with good linearity in total are obtained.
(a)
L
H
TR
D Co
Cs
(b) Sawtooth wave current
L
I
L
C
Deflection coil current
(iH)
0
(Left) (Right)
(c) Linearity coil characteristic
Linearity coil characteristic
Inductance
(µH)
(Left) (Right)
Characteristic of D
Fig. 9-9 Linearity coil
Resistance of L
Current (A)
Fig. 9-10
H
71
Page 72

4-2. White Peak Bending Correction Cir cuit
4-2-1. Outline
White peak area in screen picture may sometimes cause bending in picture. See figure below.
In TP48E60 series, correction signal which video ripple in
video output circuit power supply 200V is input to pin 24
(Bending correction terminal) of Q501. This corrects white
peak bending.
Q501
R379
BB91
93
Bending correction
EHT
terminal
Receiving Board
Power, Def board
24
C415
4-2-2. Operation Theory
Fig. 9-11 shows circuit diagram. Video ripple in video output circuit power supply 200V suffers DC cut by C475, and
is inverted in Q470, then input to pin 24 of Q501 via C481.
Pin 24 of Q501 is a bending correction terminal. The voltage which is applied to this terminal, controls phase of video
signal to correct white peak bending.
9V
R481
R483
200V
Bending by white peak
C481 Inversion
Q470
D470
White peak
R482
R484
Fig. 9-11 White peak bending correction circuit
R478
D474
C475
D406
C466
3
T416
72
Page 73

4-3. H Blanking
4-3-1. Outline
The H blanking circuit applies a blanking precisely for the
horizontal flyback period so that undesirable pictures folding does not appear at screen ends.
This unit allows the users to adjust an horizontal amplitude
adjustment, so, picture quality at screen ends will be improved. This is one of the purposes of the blanking circuit.
Q487
ON period
4-3-2. Theory of Operation
The H blanking circuit determines the flyback period precisely from the AFC pulse in the FBT and applies the period
to emitter of the video output stage transistor on the CRT-D
PC board.
4-3-3. Circuit Operation
As can be seen from Fig. 9-12, the flyback period of the
AFC pulse in the FBT starts at a negative side from 0V. To
detects this, the DC component is cut with C493. This is,
C493 is always charged through D487 with a negative side
(about –17V) of the AFC pulse. As a result, a v oltage at point
A in the waveform rises from the ground level. This waveform is sliced in a circuit (R486, D486) to detect the flyback
period. Thus obtained voltage is applied to Q901, Q911, and
Q921 through D904, D914, D927 and cuts off them thereby
blanking the resters.
Q921
0V
Approx.
-17V
AFC Pulse
T461 (FBT)
AFC
10
Fig. 9-12
Point
C493
A
L410
R409
D487
Waveform at
point
R486
D486
Slice level
D486
Q487
R417
+35V
R438
10
10
10
10
6
7
Q489
R906
P904
P903
D927
D914
D904
CRT-D DCB
Deflection/Power PCB
Q488
V blanking
BLUE
CRT/D
Q911
GREEN
CRT/D
RED
CRT/D
Q901
Fig. 9-13
73
Page 74

4-4. 200V Low Voltage Protection
4-4-1. Outline
When the video output power supply 200V is stopped by
some abnormality occurence, the current inside CPT increases abnormally. So the CPT may be damaged. To prevents this, a 200V low voltage protection circuit is provided.
4-4-2. Theory of Operation
Fig. 9-14 shows a connection diagram.
Under a normal condition Q340 is always on because of about
210V supplied from the 200V line. Accordingly Q340 collector is kept at about 6.2V or the zener voltage of D341 and
Q341 is turned off.
If some abnormality occurs and 200V line voltage lowers
by less than about 160V. Q340 turns off and its collector
voltage rises. So Q341 turns on. With Q341 turned on the
voltage at pin 14 of Z801 (expander) exceeds a threshold
voltage and pin 16 of Z80 is high level and mak es the power
relay turn off.
200V
CRT-D Circuit
P405
11
22
Deflection circuit
R879
Z801
GATE
14
C894
R436
PROTECTOR
16
Fig. 9-14
P301
17
DPC circuit
Q340
D315
R389
D340
R391
D341
R346
P350
8
8
17
R390
R392
-12V
Q341
C340
74
Page 75
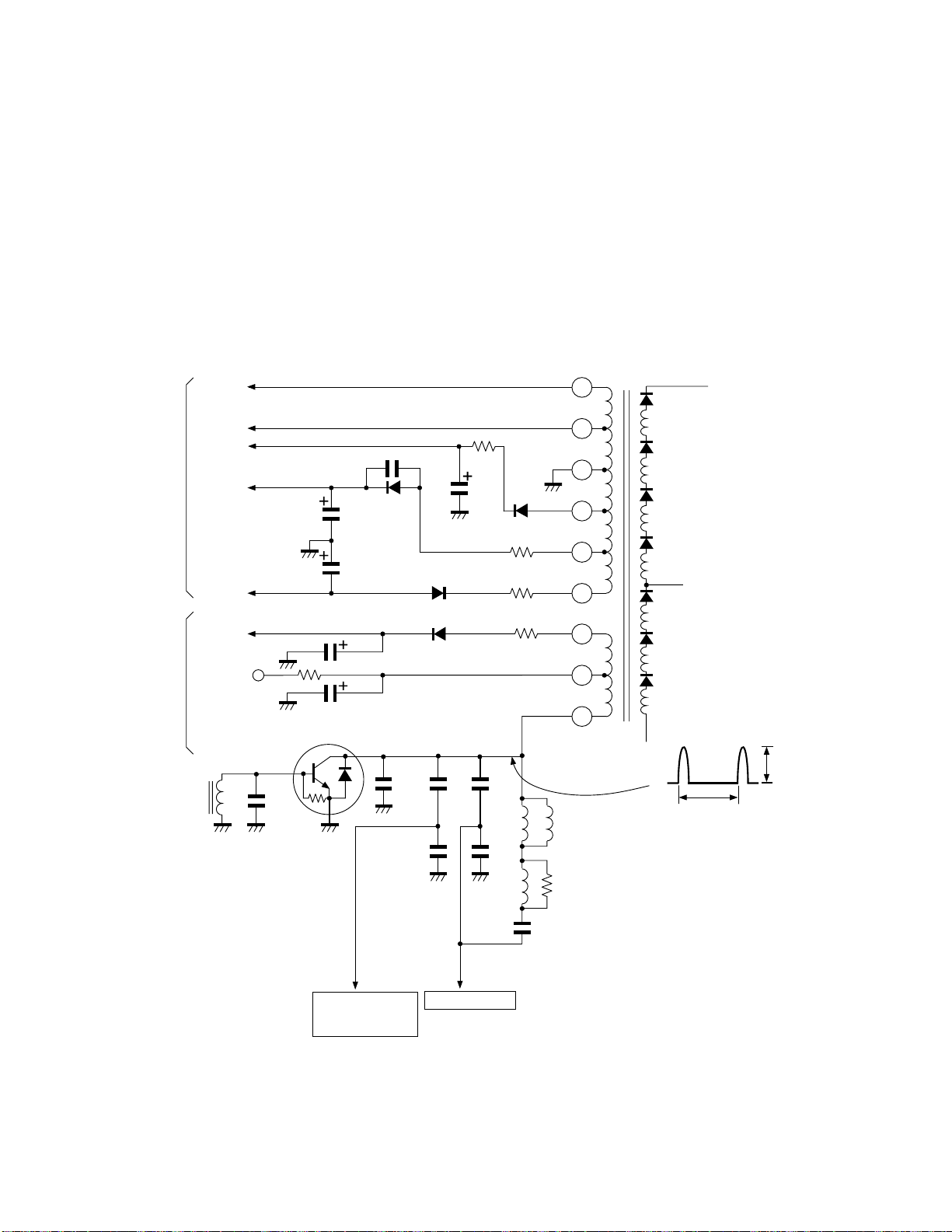
5. HIGH V OLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT
The high voltage generation circuit develops an anode v oltage for the picture tube, focus, screen, CRT heater, video
output (210V) and so on by stepping up the pulse voltage
developed for flyback period of the horizontal output circuit with the FBT, and supplies the power to various circuit.
5-1. Theory of Operation
Auxiliary
winding
Primary
winding
AFC
blanking
Heater
+12V-1
+35V
-27.5V
+210V
+125V
T401
C310
R444
C463
Q404
C460
C446
C448
D302
C440
C303
C418
D460
D406
C443
R448
C447
C444
C467
R327
R469
R443
10
D408
H deflection coil
L462/L463/L464
CRT
anode
9
4
7
6
5
3
2
1
ABL
Focus pack
1H
(15.625kHz)
1040V
(p-p)
REGULATOR
CIRCUIT
DPC CIRCUITHIGH VOLTAGE
Fig. 9-15
75
L441
R441
C423
Page 76

5-1-1. +210V
0
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
E
D
C
B
A
G
F
Primary
Auxiliary
Picture
tube anode
EO
ABL
EH
Pulse
Stacked
pulse of
4 block
1H
15.735KHz
Picture
tube capacitor
For the flyback period, pulses are stacked up to DC +125V
with FBT, and the voltage is rectified by D406 and filtered
by C446.
5-1-2. +35V, 12V
Pin 4 of the FBT is grounded and the shaded area of negative pulse developed for opposite period of the flyback period is rectified, thus developing better regulation power
supply.
5-1-3. –27V
As a power for the DPC circuit, a negative pulse signal is
rectified by D460 and filtered with C460, thus developing
the –27V.
5-1-4. High Voltage
Singular rectification system which uses a harmonics nonresonant type FBT is employed and a better high voltage
regulation is obtained, so amplitude variation of pictures
becomes low.
+125V
0
Fig. 9-16
10
4
7
6
2
1
+35V
For +12V
0
0
Fig. 9-17
Fig. 9-18
5-2. Operation Theory of the Harmonic Non-Resonant System and Tuned Waveforms
The high voltage coil is of film multi-layer winding type
and the coils are isolated into seven blocks. Each bloc k is
connected through a diode.
The basic operation is described in the case of 4 blocks construction for simplification. Positive or ne gativ e pulse determined by stray capacitance of each coil develops at terminal
points ( A , B , C , D , E , F , G ) of each coil as sho wn in Fig. 918, and these pulses are stacked as shown, thus developing
the high voltage.
Moreover, a capacitance between the internal and exter nal
coatings of the picture tube works as a smoothing capacitor .
Focus voltage is obtained at point EO.
76
Page 77

6. HIGH VOLTAGE CIRCUIT
e
6-1. High Voltage Regulator
6-1-1. Outline
Generally, four kinds of methods exist to stabilize a high
voltage in high voltage output circuits using the FBT:
(1) Stabilization by varying the power supply voltage.
(2) Stabilization by v arying L value with a saturable reac-
tance connected in series with the primary winding of
the FBT.
(3) Stabilization by varying equivalent capacitance of the
resonant capacitor C0.
(4) Stabilization by superimposing a DC or pulse (this
varies the high voltage) on a lower voltage side of the
high voltage winding of the FBT.
In this unit, pulse transformer is eliminated and the regulator circuit using the method (3) is employed. The block diagram is shown in Fig. 9-19.
Hotizonal
output
D
Y
Z450
CR-BLOCK
T461
FBT
ANODE
V
V
CP1
CP2
C2
= V
C1 + C
2
C2
= V
C1 + C
2
CP
CP
1
2
C2
V
The V
= V
CP
C1 + C
developed across C2 is DC-clamped with a diode
CP2
CP2
2
3
D1 and the resultant voltage is smoothed with a diode D2
and a capacitor C3. Thus processed voltage is obtained at
the point B . This voltage is used to provide a base current
for the transistor Q1 or to flow the collector current. The
voltage at the point B decreases with the circuit impedance
and finally lowers up to a VCE saturation voltage of Q1.
Then, V
point B . Since the V
V
CP2
the V
is not clamped by D2 with the voltage at the
CP2
is expressed as a sum of V
CP
as shown by equation 3 , V
is decreased. This varies the high voltage.
CP2
decreases by amount
CP
CP1
and
Q1 collector current is controlled by Q1 base current which
is an output of the comparison inverted amplifier. That is,
the Q1 base current is controlled by a voltage obtained by
comparing a detection voltage of the top breeder of the FBT
(9.1V) and a DC voltage of 9V.
125V
PW output
-27V
High voltage Reg.
V.
Ref.
Fig. 9-19 Basic circuit for high voltage regulator
emplyed in the unit
6-1-2. Theory of Operation
Fig. 9-20 shows a basic circuit of the high voltage regulator
used in the unit.
The high voltage regulator circuit splits a resonant capacitor
C0 to C1 and C2. thereby dividing the collector voltage (VCP)
of the H output transistor with C1 and C2.
Here, assume each voltage developed across C1 and C2 as
V
and V
CP1
each relation can be expressed by the above equations
, respectively,
CP1
1 ~ 3 .
77
Horizontal
output
D1
C2
C3
C1 L
D2
Fig. 9-20
Fig. 9-21
Q1
CS
B
H
High voltag
Reg.
output amp
VCP = V
VCP 1
V
CP
FBT
L
P
+B
+ V
CP1
CP2
2
Page 78

6-1-3. Actual
Fig. 9-22 shows the actual circuit used in the unit.
A resonant capacitor C0 is also split into two capacitors C443
and C444 in this circuit. The high voltage regulator cirucits
is structured by splitting the C443 to two capacitors of C443
and C448.
Here, assume a high voltage increases and the detection voltage ED' obtained by dividing the high voltage also increases
in proportional to the high voltage. This makes the voltage
ED increase at pin 7. (The voltage is impedance transformed
by a voltage follower circuit consisting of op amplifier Q483
at pin 7.)
The voltage ED and a 9V reference voltage developed by a
3-terminal regulator Q420 are compared. When the ED increases, the voltage at pin 2 of Q483 differential amplifier
also increases, and the base current IB of the high voltage
transistor Q480 increases.
As a result, Q480 collector current increases and Q480 collector voltage (at the point B ) decreases. Then, a peak value
of V
collector voltage lowered, and the collector voltage V
across C418 is clamped by the diode D443 at the
CP2
CP
of
Q404 (H output transistor) obtained as a sum of the voltage
V
across C443 and V
CP1
across L418 decreases. Then,
CP2
the high voltage also decreases.
When the high voltage lowers, the corrective operation is
carried out in reverse order.
* Resustors R451, R452, R453 and R455 are used to cor-
rect undersirable influence (H amplitude increase at minimum IH) by the H amplidude regulator.
Horizontal
output
D461
Q404
C418
C443
C444
C467
D444
C464
D443
C419
E
D
CR-BLOCK
8
R439
E
C482
Q420
9V-1
'
D
R435
E
H
6
7
FBT
L462
L463
L464
C
S
L461
R463
C440
R466
R461/R469
Q460
R451
B
Q480
R431 R492
-27V
R452
R434
R460
Q462
R454
2
R453
R488
C483
125V
R455
4
3
Q483
R489
R450
R490
R494
Fig. 9-22 Actual high voltage regulator circuit
78
R487
Page 79

7. X-RAY PROTECTION CIRCUIT
7-1. Outline
In case picture tube using high voltage, when high voltage
rises abnormally due to components failure and circuit malfunction, there is possible danger that X-RAY leakage increases to affect human body. To prevent it, X-RAY protection circuit is equipped.
7-2. Operation
Figure 9-23 shows the circuit diagram. Supposing high voltage rises abnormally due to some reason, pulse at pin 9 of
T461 also rises, and detection voltage ED rectified by D471
and C471 in X-RAY protection circuit rises. When ED rises,
emitter voltage of Q464 divided by R459 and R462 becomes
higher than [zener voltage (6.2V) of D458 + Q464 VBE ].
This causes Q464 turns on to supply base current to Q463.
5V
ELAY
R80
Q845
Q846
Z801
R10
Tr6
16
Tr5
R12
R11
15
R9
Tr7
R19
C1
C894
14
Then Q463 turns on. By this Tr6 and Tr6 turn on to make
ON/OFF pulse at pin 7of QA01 in low level, Q846 and Q845
turns off, then relay SR81 turns off. T r6 and Tr7 are in thyristor-connection, and 5V of power holds protection operation until main power switch is turned off. During circuit
operation, power LED near main power switch blinks turn
on and off in red.
Caution:
• To restart TV set, repair failure first.
12V
E
D
R879
R467
Q463
D459
R468
C459
C458
D458
Q464
R458
R459
R462
R472
D471
C471
T461
9
17
Fig. 9-23 X-RAY protection circuit
79
Page 80

8. OVER CURRENT PROTECTION CIRCUIT
8-1. Outline
If main power (125V) current increases abnormally due to
components failure, there is possible danger of the secondary damage like failure getting involved in other part failure, and abnormal heating. T o pre vent this, ov er current protection circuit is equipped, which detects current of main B
line to turn off power relay in abnormal situation.
8-2. Operation
Fig. 9-24 shows over current protection circuit. When the
current of main B line increases abnormally due to the
shortage in load of main B line, voltage drop arises across
R470. By this voltage drop, when base-emitter voltage of Tr8
in protector module (Z801) becomes approx. 0.7V or more,
Tr8 turns on, and the voltage by divided ratio of R15 and R16
is applied to cathode of ZD4. When this voltage becomes
higher than zener voltage of ZD4, ZD4 turns on to supply base
current to base of Tr6 via R14. This causes Tr5 ON and
voltage at pin 16 of Z801 becomes low.
5V
MICON
QA01#7
Therefore, QB30 and Q843 turns off to set SR81 OFF. Tr6
and Tr7 in Z801 are in thyristor-connection, and power 5V1 supplied at pin 15 keeps protection operation for standby
power until main power switch is turned off. During circuit
operation, power LED near main power switch blinks in red.
Caution:
• To restart TV set, repair failure first.
F470
To T461
R471
15
R9
R470
MAIN B
R479
C472
21
RELAY
SR80
Q845
R10
Tr7
16
Q846
Tr6
R12
Tr5
R11
17
Fig. 9-24 Over current protection circuit
80
ZD4
R14
C1
R16
R15
D1
PROTECTOR MODULE
Tr8
Z801
Page 81
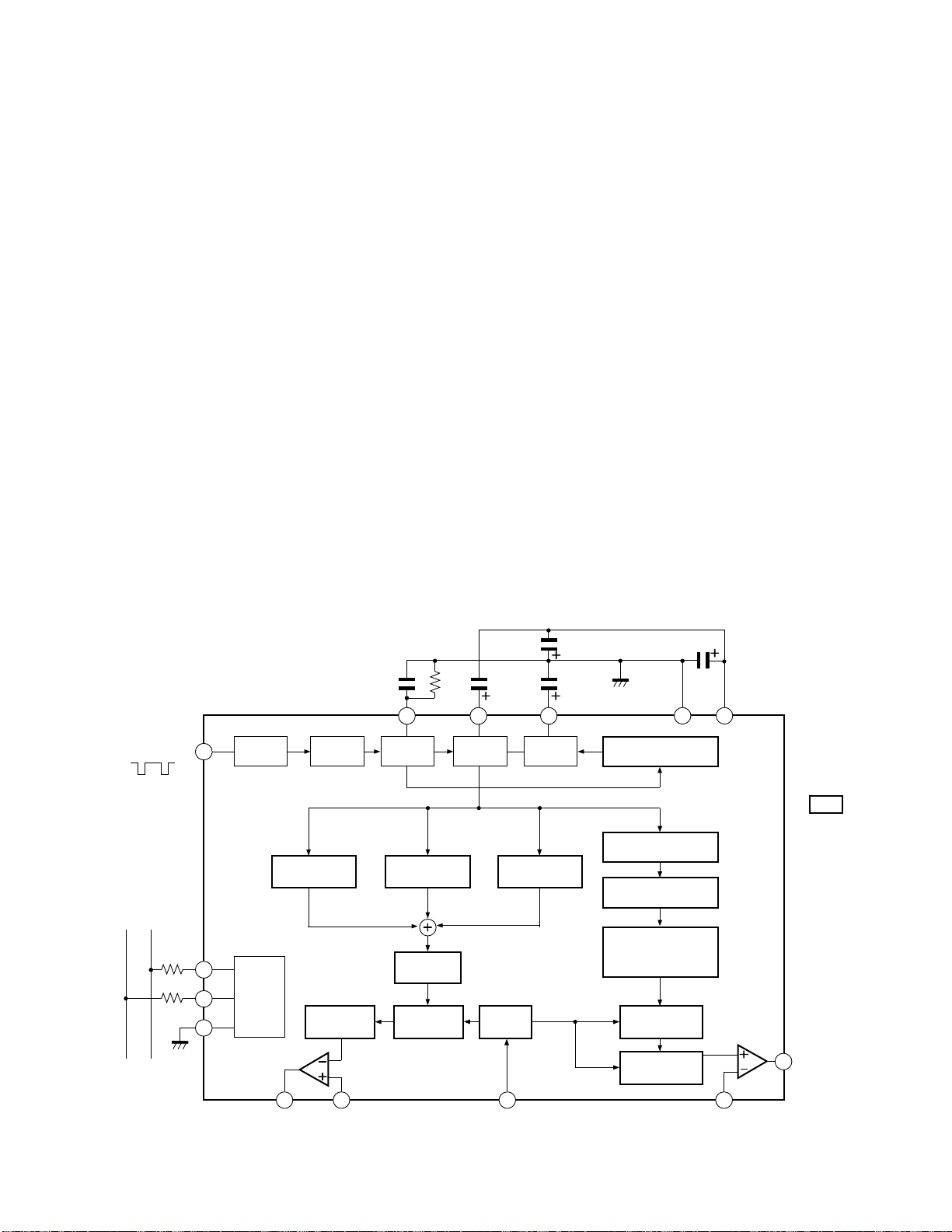
SECTION X: DEFLECTION DISTORTION CORRECTION CIRCUIT
(SIDE DPC CIRCUIT)
1. DEFLECTION DISTORTION CORRECTION IC (TA8859CP)
1-1. Outline
The deflection distortion correction IC (T A8859CP), in combination with a V/C/D IC (TA1222AN) which has a V pulse
output, performs correction for various deflection distortions
and V output through the I2C bus control. All the I2C bus
controls are carried out by a microcomputer and can be controlled with the remote control.
1-2. Functions and Features
The IC has functions of V RAMP voltage generation, V
amplitude automatic switching (50/60 Hz), V linearity correction, V amplification, EHT correction, side pincushion
correction, I2C bus interface, etc. and controls following
items through the I2C bus lines.
(1) V amplitude
(2) V linearity
(3) V S-character correction
(4) V picture position (neutral voltage setting)
(5) V M-character correction
(6) V EHT correction
(7) H amplitude
(8) L and R pin-cushion distortion correction I (entire area)
– Not used for this model.
(9) L and R pin-cushion distortion correction II (corner
portions at top and bottom) – Not used for this model.
(10) H trapezoid distortion correction – Not used for this
model.
(11) H EHT correction
(12) V AGC time constant switching
1-3. Block Diagram
Fig. 10-1 shows a block diagram of the basic circuit.
V. Trigger-in
(Bus Control Signal)
SDA SCL
13
10
12
9
14 15
Waveform
shape
Logic
V drive V. feedback EHT INPUT EW feedback
Trigger
det
V. M-Character
correction
V. screen
position
Puise
Gen.
V. linearity
correction
V. Amplitude
Adj.
V. EHT
correction
V. Rame
H.EHT
input
16 5 3
A G C
V. S-character
correction
168
V. AGC time
constant SW
H. trapezoid distortion
correction
L-R pincushion
distortion correction I
L-R pincushion
distortion correction II
(Top & bottom comer section)
correction
H. Amplitude
H.EHT
Adj.
+9V
control through
bus
2
EW-drive
4
Fig. 10-1
81
Page 82

2. DIODE MODULATOR CIRCUIT
In N5SS, the distortion correction is carried out by the ditigal
convergence circuit. So the component of the diode modulator circuit is the same as that of conventional television,
because it is used only for the horizontal oscillation adjustment.
Fig. 10-2 shows a basic circuit of the diode modulator used
in the N5SS.
A key point in the modulation circuit shown in Fig. 10-2 is
to develop a negative pulse at point B .
In this circuit, a current loop of the resonant circuit for flyback
period is shown by an arrow , and the energy stored in LDY is
transferred to resonant capacitors Cr, Crm in passing thr ough
Cr, Crm, CS when the scanning completes. As a result, a
positive, horizontal pulse as shown in Fig.
10-3 a) will appear at Cr, and the current flows into Crm
with the direction as shown. Then a pulse as shown in F ig.
10-3 b) develops at the point B.
On the other hand, since constant amplitude pulses across
Cr, as shown in Fig . 10-3, are applied to the primary winding, the high voltage of FBT also develops a constant voltage.
When the negative pulse developed at the point B is integrated with Lm and Csm, its average value appears at Csm
as a negative voltage.
By modulating this voltage with Q460, a wav eform of Vm is
obtained as shown in Fig. 10-3 b). As a result, the voltage
VS which is the sum of the power supply voltage VB and the
Vm is applied across the S-curve capacitor CS. The VS becomes as a power source for the deflection yoke as shown in
Fig. 10-4, is applied to the horizontal deflection yoke.
0
a) Waveform at point A
0
b) Waveform at point B
H
OUT
DM
DD
Cr
A
Fig. 10-2
L
DY
Cs
B
Crm
Lm
Vs
Csm
FBT
Q460
Fig. 10-3
V
B
Vm
V
B
VS
0
Fig. 10-4
82
Page 83

3. ACTUAL CIRCUIT
FBT
I
H
V
B
Vm
Csm
C
3
V
S
C
S
Lm
C
2
I
P2
I
Y1
I
Y1
C
1
I
Y
I
P2
I
P1
L
DY
H.
I
P
I
Y2
In the actual circuit, the resonant capacitor is split into two
as shown in Fig. 10-7. One, C440, is inserted between the
collector of the H. OUT transistor and ground and another
C444 inserted between the collector and emitter. In Fig. 105, C440 is expressed as C1 and C444 as C2, and the resonant
current path for the flyback period is shown by arrows.
In a conventional circuit, when brightness of a picture tube
varies, high voltage current varies and the high voltage also
varies. As a result, horizontal amplitude also varies.
However, in this circuit, the horizontal amplitude variation
can be suppressed to near zero if the high voltage current
varies with variation of the high voltage.
When the scanning period completes, the energy stored in
the deflection yoke LDY is transferred to the resonant capacitor in a form of current IY. In this case, the current is
split into two; IY1 passing through C1, C3 and IY2 passing
through C2. In the same way, the energy stored in the pr imary winding of the FBT is transferred to the resonant ca-
V
Fig. 10-5
B
VS
0
Vm
Fig. 10-6
pacitor in the form of IP. In this case, the current (path) is
also split into two; IP1 passing through C1 and IP2 passing
through C2, C3. Concequently, the current differences between IY1 and IP2 (IY1-IP2) passes through C3.
When the high voltage current IH reduces with a dark picture, the current IP in the primary circuit decreases, so I
P1
and IP2 also decrease. Howev er , a current fl owing into (IY1IP2) increases as IP2 decreases. As a result, the pulse developing at the point B increases and the voltage Vm at Csm
also increases as shown in Fig. 10-8. That is, when a dark
picture appears, the voltage across S-curve capacitor CS increases as shown in Fig. 10-8, the high voltage rises, and the
horizontal amplitude is going to decrease. But, as VS increases, the deflection yoke current increases and this works
to increase the horizontal amplitude. Accordingly, if the
brightness of picture changes, the horizontal amplitude is
maintained at a constant value. This is one of the fine features the circuit has.
83
Page 84

3-1. Basic Operation and Current Path
3-1-1. Later Half Scanning Period
When the power is turned on, the power supply voltage V
is applied to CS and Csm, and the CS acts as a power source
for a later half of the scanning period for which the H. OUT
transistor is turned on, and the deflection current IY flows in
the path as shown below.
V
A
FBT
L
DY
H.OUT
I
Y
I
M
D
M
lP
+
Cs
V
B
L
M
I
DC
C
SM
+
3-1-2. First Half Scanning Period
B
When the base drive current decreases and the H. OUT transistor is turned off, each energy stored in LDY, Lm, LP of
FTB is transferred to C1, C2 and C3, respectively, and the
resonant current becomes zero at a center of the flyback period. Then, VA and VB pulses show a maximum amplitude.
V
A
FBT
L
DY
lP
I
I
P1
C
1
V
B
C
I
P2
Y
2
I
Y2
I
M
Cs
V
V
B
L
M
I
DC
C
SM
B
Fig. 10-9
Fig. 10-7
Voltage & current waveform in H period.
I
0
Y
I
V
V
A
0
I
M
0
I
DC
V
B
0
0
Y
A
0
I
M
0
I
DC
V
B
0
C1: IY1+I
C
1
C
2
0
C2: IY2+I
P1
P2
Fig. 10-8
C3: I
-
I
-
I
P2
Y1
C
3
0
M
84
Fig. 10-10
Page 85

3-1-3. Later Half of Flyback Period
D
D
V
A
FBT
I
Y
L
DY
C
S
V
B
V
B
L
M
I
M
C
SM
I
M
D
M
All energy in the coil has been transferred to the resonant
capacitors at the center of the flyback period, and the voltage shows the maximum value. However, during next half
of the flyback period, the energy of the resonat capacitor is
discharged as a rev erse current through respective coil. When
the discharge has been completed, VA and VB becomes zero,
and the deflection current in reverse direction becomes the
V
maximum.
I
I
P1
P2
C
C
1
I
Y1
2
I
Y2
C
3
A
L.O.P.T
L
DY
I
Y
I
M
I
P
C
S
V
B
L
M
I
DC
C
SM
V
B
3-1-4. First Half of Scanning Period
When the flyback period completes, the damper diode D
and the modulation diode DM turn on, and the IY and I
proportionally decrease from the maximum value to zero.
The H. OUT transistor is turned on just preceding at the center
of the scanning period, and repeats the steps 3-1-1 through
3-1-4 stated above.
D
M
Fig. 10-11
Fig. 10-13
Voltage & current waveform in H period.
0
Iy
0
I
Y
V
A
0
V
A
I
M
0
I
DC
I
V
B
0
C1: IY1+I
P1
C
1
C
2
0
C2: IY2+I
P2
0
M
0
I
DC
V
B
0
Fig. 10-14
C
3
C3: I
-
I
-
I
P2
y1
0
Fig. 10-12
M.
85
Page 86

SECTION XI: DIGITAL CONVERGENCE CIRCUIT
1. OUTLINE
The digital convergence circuit develops outputs to correct
screen distortion and perform color matching. The digital
convergence circuit used is of an all digital type and allows
good adjustments in comprise with a conventional analog type
circuit.
Followings are features of the digital convergence circuit.
1) No adjustment controls (volumes)
2) Registration accuracy increased.
3) Space saved
4) Adjustment by a remote control
The data adjusted are classed into 4 screens for each screen
mode. These data are stored on E2PROMs inside the unit.
The memory size used in this case is 4 Kbits per one screen.
Each screen adjustment is carried out by calling the adjustment screen with the remote control unit supplied and the
adjustment is carried out according to the dimensions specified for each screen. The control of the unit is carried out in
the I2C format.
2. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
2-1. Configuration
Fig. 11-1 shows a block diagram. The digital convergence
unit consists of Q701 T7K64 which plays a major role, Q707
PLL circuit which locks a sync entered, Q713 E2PROM to
store the data, and Q703-5 D/A converter which develops a
correction wave form.
The output signal from the Q703 – 705 D/A converter is
amplified and wave form shaped by Q715, Q717 and Q719,
and comes out from the unit.
The clock signal for the PLL is adjusted by L719 to a reference frequency of 32 ± 0.1MHz under no input status.
A test pattern generator is also built inside Q701 and develops R, G, B signals and a Ys switching signal.
2-2. Circuit Description
(1) With the power turned on, the unit is reset and enters
an operation standby status. And a sync signal of the
unit enters external Q707 and Q701. The signal en-
tered Q707 is counted down by a counter inside the
Q701 and this is used as the reference clock. Q701
works in synchronization with the reference clock sig-
nal and the sync signal.
(2) A command is sent from the microcomputer in the unit
and Q701 is set up to load the data in Q713 to the in-
ternal RAM. (8 (horizontal) x 7 (vertical) x 3 (color))
(3) Q701 transfers a serial data specified to Q703 – 705
according to the RAM data. In this case, interpolation
for the RAM data is automatically carried out by a built
-in digital filter inside Q701.
(4) The serial data sent from Q701 are digital-analog con-
verted by Q703 – 705, thus developing the analog type
wave form.
(5) The signals sent from Q703 – 705 are amplified Q715,
Q717, Q719, respectively , and then f iltered in the next
stage to smooth and shape the wave form. Thus pro-
cessed signals are used as H and V correction wave
forms for R, G, and B signals.
86
Page 87

RH
Filter
RV
Filter
GH
Filter
GV
Filter
BH
Filter
BV
Filter
Q715
Test pattern
D/A
R
B
G
Ys
Q703
3
∗
12bit)
∗
8
∗
RAM (8
Q701 T7K64
Q717
D/A
Q704
Q719
Q705
D/A
Counter
DATA
CLK
Q707
HD
VD
32MHz
PLL
Q719
Q713
PROM
2
E
MEMORY
Load
Q767
Main bus line
Save
RESET
R716, C711
M-CON
Fig. 11-1 Block diagram
87
Page 88

3. PICTURE ADJUSTMENT
Four screens for Normal/Full, Theater wide 1, Theater Wide
2, Theater Wide 3 are provided for the adjustments. When
making the adjustments, receive the U/VHF or CABLE
broadcasting signal or the built-in pattern signal of the microprocessor to make a synchronization with the frequency
of the adjusting screen with the unit..
This adjustment program is prepared as the microprocessor
function of the set and it is possible to adjust by the remote
controller attached.
3-1. Outline of the Modification Process of
the Storing Adjustment Data
Set the convergence adjustment screen.
The adjusted data is stored in the memory inside Q713
E2CPROM which is a non-volatile memory.
The RAM data inside Q701 is lost when the power turns
off. So the initial operation status is set by the software command from the microprocessor QA01 every time when the
unit turns on.
The data adjusted manually through the screen by displaying
the adjusting screen on the display is once written on RAM
inside Q701. Adjust each adjusting point and store the modified total data on RAM as correct one into Q713 E2PROM.
The adjustment is carried out for each screen mode, and its
order is as follows; Normal/Full ® Theater Wide 1 ® theater Wide 2 ® Theater Wide 3. (When the adjustment value
is saved after adjusting Normal/Full, the microprocessor calculates the adjustment values for Theater Wide 1, 2 and 3
based on the adjustment value of Normal/Full mode and sets
the values for Theater W ide 1, 2 and 3 to the closed v alues to
require minimum adjustment.)
Normal full distortion
modification
(G screen)
Theater wide 2
distortion modification
(G screen)
Normal full
color matching
(R, B screen)
1. Push "7" key of the remote
controller to save.
2. turn "PIC-SIZE" key of the
remote controller ON
Theater wide 2
color matching
(R, B screen)
1. Push "7" key of the remote
controller to save.
2. turn "PIC-SIZE" key of the
remote controller ON
Theater wide 1
distortion modification
Theater wide 3
distortion modification
Fig. 11-2
(G screen)
(G screen)
Theater wide 1
color matching
(R, B screen)
1. Push "7" key of the remote
controller to save.
2. turn "PIC-SIZE" key of the
remote controller ON
Theater wide 3
color matching
(R, B screen)
1. Push "7" key of the remote
controller to save.
2. turn "PIC-SIZE" key of the
remote controller ON
END
88
Page 89

3-2. Service Mode
3-2-1. Outline
The service mode, one of the functions this unit provides, is
controlled by the microprocessor QA01 and .
This mode is set by the special operation to avoid the easy
operation by the user. Mov e the cursor to between the adjustment points of 8*7/each color and modify the data directly.
Before entering the service mode, perform the center adjustment using the color unmatching adjustment in the user menu.
3-2-2. Entering/Exiting Mode
When the “MUTE” key on the remote controller is pressed,
the screen display appears. Pushing the “MUTE” key again
disappears the screen display.
In this status, when the “MENU” key on the set console is
pushed while pushing the “MUTE” key, S is displayed on
the upper right of the screen. When the “MENU” key is
pressed again, the service data is displayed on the upper left
on the screen.
When “7” key on the remote controller is pressed in this status, the screen changes to display the cross hatch screen (the
first screen described later) and the convergence adjustment
screen appears.
When “7” key is pressed again, the data storing operation is
automatically carried out and the cross hatch + data display
screen (the second screen described later) appears.
When “7” key is pressed furthermore, the display returns to
the initial screen.
+ MENU
+
X
X
Service data display
(original picture)
Remote
"7" key
Note:
When changing the convergence correction data, always be
sure to perform the automatic storing operation. If the power
turns off without carrying out the automatic storing operation, the modified data is lost.
The first picture The second picture
Remote "7" key
+automatic save
Fig. 11-3
Remote
"7" key
89
Page 90

3-2-3. Initial screen
The screen mode is Normal/Full screen mode.
Correction point: Vertical 8 * Horizontal 7 ( ® and - marks
are the adjusting points.)
Primary screen Secandary screen
Y
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
X
1
2
Adjusting point display
X : Horizontal position display
Y : Vertical position display
C : Color display
S : Screen mode display
Cursor (Red) (Blinking)
X:3
Y:2
C:R
S:FULL
3
4
5
(1) First screen:
The initial cross hatch screen appears. The pattern colors are displayed with 3 colors. The cursor color is red
and left blinking.
When the modification is carried out, the last memory
status is displayed.
Cursor mode:
Lighting: Data modification mode
Blinking: Cursor move mode
The display color shows the color which can modify
the data.
6
Screen Center
78
Fig. 11-4
Data display
Screen frame
(2) Second screen
When changing from the first screen to second screen, the
convergence correction waveform is mute for 1 second. The
modified data for this period is sent to Q713 E2PROM from
Q071 RAM and then stored.
The second screen is displayed upper left of the first screen,
so the convergence adjustment cannot be carried out when
the second screen is displayed.
Note:
• The adjusted data is automatically stored when the display changes from the first screen to the second screen.
So be sure to perform this operation after adjustment completes.
• Adjustment should be carried out with a corresponding
signal received.
90
Page 91

3-2-4. Key function of remote control unit
10
2
5
8
0
ADV/
PCB CH
ENTER
ADV/
POP CH
RECALL
MUTE
3
6
9
CH RTN
ENT
POWER
CH
VOL
¥
EXITRESET
100 Key
1
9
2
0 Key
3
ENT Key
4
5 Key
7
8 Key
5
4
6
2 Key
7
6 Key
8
5
3
9
10
4 Key
3 Key
7 Key
Red test pattern ON/OFF
Green test pattern ON/OFF
Blue test pattern ON/OFF
Cursor shift/data change
mode chang over
Cursor down/adjusting point down
Cursor UP/adjusting point UP
Cursor right/adjusting point right
Cursor left/adjusting point left
Cursor color change
Data save
PIC SIZE
TV
6
CABLE
VCR
TV/VIDEO
1
8
4
7
1
2
100
EDS MENU
FAV FAV
STOP SCURCE PLAY PCP
REC
CH SEARCH
TV/VCR REW FF
STILL SWAP
TOSHIBA
Fig. 11-5
91
Page 92

3-2-5. Operation procedure
(1) Set the screen to Normal or Full mode using the PIC-
SIZE key on the remote controller.
(2) Set the unit to the service mode with MUTE + MUTE
+ MENU keys pressed. (Entering to S mode.)
(3) Set the unit to the conver gence adjusting mode by press-
ing the “7” key on the remote controller. (Fist screen)
(4) Select the pattern to display by pressing 100, 0, ENT
on the remote controller.
(Red adjustment; 100 ... ON, 0 ... ON, ENT... OFF)
(Green adjustment; 100 ... OFF, 0 ... ON, ENT... ON)
(Blue adjustment; 100 ... ON, 0 ... OFF, ENT... ON)
(5) Select the color to adjust by pressing “3” key on the
remote controller.
(6) Confirm that the cursor is in the movable status (the
cursor blinking status).
(7) Select the adjusting position by pressing “8”, “4” and
“6”.
3-3. Each Screen Adjustment Method
(8) When the adjusting position is determined, press “5”
key on the remote controller to enter the cursor blinking status.
(9) Set the cursor to the adjusting position by pressing “2”,
“8”, “4” and “6”, and perform the pattern distortion
correction and color matching adjustments.
(10) Press “5” key again and move the cursor. Perform the
adjustment in the same way as described above.
(11) After the adjustment completes, perform the automatic
storing operation by pressing “7” key.
(12) In the same way as described above, adjust WIDE 1,
WIDE 2 and WIDE 3 screens using PIC-SIZE key.
(13) When all of the screen mode adjustment complete,
perform the automatic storing operation by pressing
“7” key.
3-3-1. Normal/Full
2
B
2
B
14xB
2mm
12xA
2mm
Screen frame
40 inches 16:9 Screen size: Horizontal 885mm x Vertical 498mm
Dimension A: 73.5mm Dimension B: 33.2mm
Fig. 11-6
92
Page 93

3-3-2. Theater Wide1
249
213
103.5
Screen
center
0
7.5
115
217.5
249
348.5
298
144
Screen
center
0
10
159
303
348.5
428.5
351
40 inches 16:9 Screen size: Horizontal 885mm x Vertical 498mm
205
66.5
66.5
205
Fig. 11-7
0
351
428.5
605
0
495.5
56 inches 16:9 Screen size: Horizontal 1239mm x Vertical 697mm
289.5
93.5
93.5
289.5
Fig. 11-8
93
495.5
605
Page 94

3-3-3. Theater Wide 2
298.9
256.2
128.1
Screen
center
0
128.1
256.2
298.9
361.8
301.5
180.9
Screen
center
0
180.9
301.5
361.8
435
0
362.5
40 inches 16:9 Screen size: Horizontal 885mm x Vertical 498mm
217.5
72.5
72.5
217.5
Fig. 11-9
362.5
435
618
0
515
56 inches 16:9 Screen size: Horizontal 1239mm x Vertical 697mm
309
103
103
309
Fig. 11-10
94
515
618
Page 95

3-3-4. Theater Wide 3
269.5
231
115.5
Screen
center
0
115.5
231
269.5
379.2
325
162.5
Screen
center
0
162.5
325
379.2
435
0
362.5
40 inches 16:9 Screen size: Horizontal 885mm x Vertical 498mm
217.5
72.5
72.5
217.5
Fig. 11-11
362.5
435
618
0
515
56 inches 16:9 Screen size: Horizontal 1239mm x Vertical 697mm
309
103
103
309
Fig. 11-12
95
515
618
Page 96

4. CASE STUDY
In many cases, a color deviation will be corrected by returning the HIT and WID data for the main deflection side to the
initial values.
Followings are cases which need readjustment of the con ver gence by all means.
4-1. When CRT is Replaced.
When the CRT is replaced, readjustment of the main deflection and color matching will be necessary. Perform the adjustments as follows.
(1) Replace two CRTs, blue and red.
(2) Perform horizontal adjustments for blue and red yokes
to the green CRT. Mount the yokes and velocity modulation coils + alignments so that they closely touches
the CRT without any clearance.
(3) Adjust the red and blue alignments. (refer to item De-
tailed adjustments for alignments)
(4) Perform the center adjustment for the blue CRT center
and the red CRT center to the green CRT center with
the centering magnets.
(5) Adjust the HIT , WID data to obtain the data w hich gives
the most precision to the green.
(6) Perform the color matching in terms of the con vergence
for each screen. In this case, do not move the green.
(7) After completion of the convergence adjustment for
each screen, replace the green CR T . For the green CR T ,
repeat the steps 2-5 to make the color matching in terms
of the convergence by using the red and blue as the
reference.
4-2. When Convergence Unit is Replaced
When replacing the convergence units, all screens must be
adjusted basically. However, performing the adjustment as
shown below will reduce the procedures considerably.
(1) Replace the memory (Q713) for the new unit with the
memory (Q713) for the failure unit. Mount the convergence unit on the set and the screen status before
replacement will be directly reproduced.
(2) Mount the new unit with the old memory installed in
combination on the set, and turn on the set. A screen as
if it is moving vertically or horizontally will appear.
(3) Adjust each center of green, red, and blue with the cen-
tering magnets again.
(4) Check to see color deviation and screen size deviation
among the colors. If deviated, perform the adjustment
for the main deflection and the color matching for the
convergence.
96
Page 97

5. TROUBLESHOOTING
5-1. Adjusting Procedure in Replacing CRT
Cut off
Lens focus
Electrical focus
Yoke horizontal
User convergence enter check
Centering
Convergence adjustment
White balance
End
5-2. Adjusting Procedure in Replacing Convergence Unit/Main Def
User convergence enter check
Centering
Convergence adjustment
End
97
Page 98

6. CONVERGENCE OUTPUT CIRCUIT
6-1. Outline
This circuit current-amplifies digital conv ergence correction
signal at output circuit, and drives by convergence yoke to
perform picture adjustment.
Digital convergence output signal 6ch adjustment is done.
(H-R/G/B) (V-R/G/B)
6-2. Circuit Description
6-2-1. Signal flow
Signal which is corrected by digital conver gence, is output to
P708 (V, H R/G/B);
is input to Q751 (V) R/G/B, and is output to P713, P714 and
P715;
is input to Q752 (H) R/G/B, and is output to P713, P714 and
P715.
6-2-2. Over current protection circuit
All currents of Power supply, -15V, +15V and +30V are detected to protect CONV-OUT IC from damage due to output
short of CONV-OUT.
Current value: Normal ± 15V approx. 700mA
+30V approx. 200mA
Detecting curren ±15V approx. 1.8A
or more
+30V approx. 700mA or more
protecting operation
6-2-4. CONV -OUT m ute
In power-on operation, transistors Q765 and Q766 are made
turned ON, and –15V is applied to pin 3 of CONV-OUT IC.
These cause mute operation on CONV-OUT.
6-2-5. Operation of IC
1) Q764 (TC74HC4050AP)
Sync signal which is input from P711 1 VD, 2 HD, is,
through buffer, supplied to digital convergence P708.
2) 3-terminal source
Q754 (+5V) Q755 (+9V) Q756 (-9V)
Source for digital convergence
3) Q767 (TC4066BP)
P711 4 SDAM, 5 SCLM : microcomputer . Busline, through
Q767, is input to Digital Convergence P709, and is controlled.
4) To adjust from outside of digital conve rgence :
Put adjusting jig into 6P socket of P720. Iscs turns from H to
L, switch of Q767 is changed over. Then busline from microcomputer is cut off.
P720 3 SCLU, 4 SDAU
Controlled by external adjusting jig.
6-2-3. Pump-up source
CONV-OUT IC Q752 (H)
Pin 10 (+15V/H, PV)
Pin 5 (+30V)
By HD input signal, pump-up is done only in horizontal re-
tracing time.
Horizontal correction wafeform
+30V
+15V
0V
-15V
Fig. 11-13
Pump-up
Pump-up source waveform
+30V
+15V
0V
-15V
Horizontal correction waveform
98
Page 99

6-3. Convergence Block Diagram
+12V
NC
PROTECT
+5V-1
RESET
POWER
AC PULSE
GND
(+30V)
R7782
0.82Ω
(PROTECTOR)
P712
1
2
3
P
1
2
3
4
5
(+15V)
R7750
5V-1
D7701 Q757
(-15V)
CONVER
R7765
0.33Ω
D7702
Q771
0.39Ω
+15V
(PUMP UP)
Q770
Q769
(HD)
C7771
YOKE
P713
V
RED
H
Q751
STK392-110
CONV-OUT
10
5
R-V
18
11
G-V
9
B-V
P714
BLUE
V
17
12
8
4
3
MUTE
Q765
H
+
Q752
CONV-OUT
C7765
STK392-110
(H)
(+1501
5
+30V
H.PU)
10
V
R-H
B-H
18
11
G-H
9
P715
GREEN
17
12
8
4
P711
H
-15V
3
MUTE
VD
1
HD
2
2
I CS
3
SDAM
4
SCLM
5
GND
6
DFAI
7
+
Q766
C7766
+5V
Q754
(REGULATER)
+9V
Q755
P708
RV
GV
DIGITAL CONVER
P720
1
GND
2
INCS
3
SCLU
4
SDAU
5
GND
6
GND
VD
(HD)
R
Q767
G
TC4066BP
B
I2CS
SCLV
SDAU
SCLM
SDAM
Q764
-9V
Q756
BH
RH
GH
BV
TC74HC4050
-9V
+9V
+5V
HD
Fig. 11-14
99
Page 100

7. CONVERGENCE TROUBLESHOOTING CHART
Relay turns on
once but immediately
turns off.
Convergence PCB,
pull out of P712.
Check power
supply circuit.
Reray OFF
Proceed to "protection
circuit diagnosis procedures".
Protect 1
Reray ON
Reray OFF
Reray OFF
Reray ON
Relay operation sound
at power on.
Check Q751, Q752
and repair.
Reray OFF
Reray ON
OK
Check screen modes
of picture.
Check P708 R/G/B
correction wave.
OK
No Convergence
correction wave.
Convergence output signals correction wave
Vertical
Q751
(R/G/B)
Horizontal
Q752
(R/G/B)
Pump-up
Check voltage at
±15V+30V pump up.
Are output signals
+30V
0V
-15V
applied to H, Vblk of P711.
Check voltage across
±9V+5V Q754, Q755, Q756.
Check signals of all IC
and associated cirduits.
Fig. 11-6
OK
OK
OK
NG
NG
Check power supply
circuit.
NG
Check DEF PC13.
Check Q754, Q755,
Q756 and repair.
100
 Loading...
Loading...