
1.1 Features
The Toshiba T200/T200CS Pen Computer uses extensive Large Scale Integration (LSI), and
Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) technology to provide minimum size
and weight, low power usage and high reliability. These computers include the following:
❑ Microprocessor
The T200/T200CS uses an SL Enhanced Intel 486DX2-40 microprocessor that
operates at 40 MHz and 3.3 volts.
❑ Math co-processor
The T200/T200CS has a math co-processor stored in the i486DX2 microprocessor.
❑ Cache memory
The T200/T200CS has an 8 KB cache memory stored in the i486DX2 microprocessor.
❑ Disk storage
The T200/T200CS has an internal 1.8-inch IDE 80 Megabyte (MB) Hard Disk Drive
(HDD).
❑ Memory
The T200/T200CS comes standard with 4 MB of CMOS RAM. This includes 640
KB of conventional memory and 3,328 KB of extended memory, which can be utilized
as expanded memory compatible with Lotus/Intel/Microsoft Expanded Memory
Specifications (LIM-EMS).
❑ Display screen
The T200 has a 9.5-inch high resolution monochrome Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
which displays 640x480 pixels with a 16-level gray scale, and an electromagnetic
derivative tablet (transreflective).
The T200CS has a 9.5-inch high resolution Supertwist Nematic (STN) color LCD
which displays 640x480 pixels and 256 colors, and an electromagnetic derivative
tablet.
The T200/T200CS internal display controller supports Video Graphics Array (VGA)
on the internal/external display and Super VGA (SVGA) on the external display.
❑ Batteries
The T200/T200CS has three different batteries: a main battery, a backup battery, and
a Real Time Clock (RTC) battery.
T200/T200CS 1-1

❑ Exp. memory slot
An optional 4, 8, or 16 MB memory card can be installed in the memory slot.
❑ PC card slot (Type II, Type III)
The T200/T200CS has two PC card slots which support Personal Computer Memory
Card International Association (PCMCIA) standard version release 2.0 and MiNC
Toshiba modem card.
❑ FDD port
An optional external 3.5-inch Floppy Disk Drive (FDD) supports 2HD (1.44 Mbytes)
floppy disks and 2DD (720 Kbytes) floppy disks.
❑ Printer port
The T200/T200CS's Centronics-compatible printer interface port can be connected to
the printer through a parallel printer cable.
❑ Serial port
The T200/T200CS has one 9-pin serial interface port.
❑ Ext. keyboard port
The T200/T200CS has an external keyboard interface port for connection with a PS/2compatible keyboard.
❑ Ext. monitor port
The T200/T200CS has an external monitor interface port for connection with an
analog VGA or SVGA display.
❑ 72-pin Expansion port
The T200/T200CS has a 72-pin Expansion port which enables connection of a 72-pin
Expansion connector. The Expansion port allows connection of a PS/2 keyboard,
external monitor, printer, serial I/O and optional 3.5-inch FDD.
❑ Stylus
The T200/T200CS has one cordless stylus (pen), which is used to enter information
into the computer. The stylus does not need batteries.
1-2 T200/T200CS
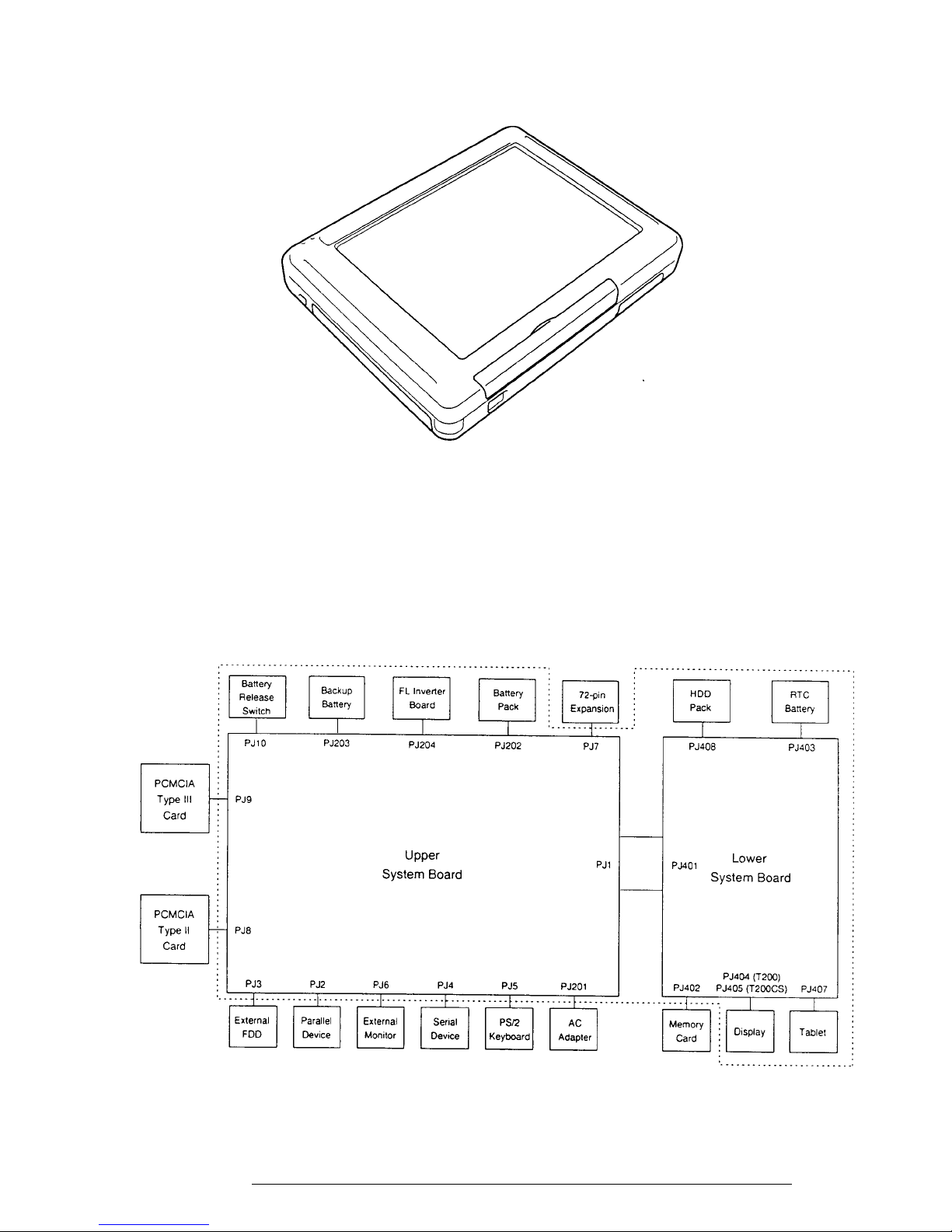
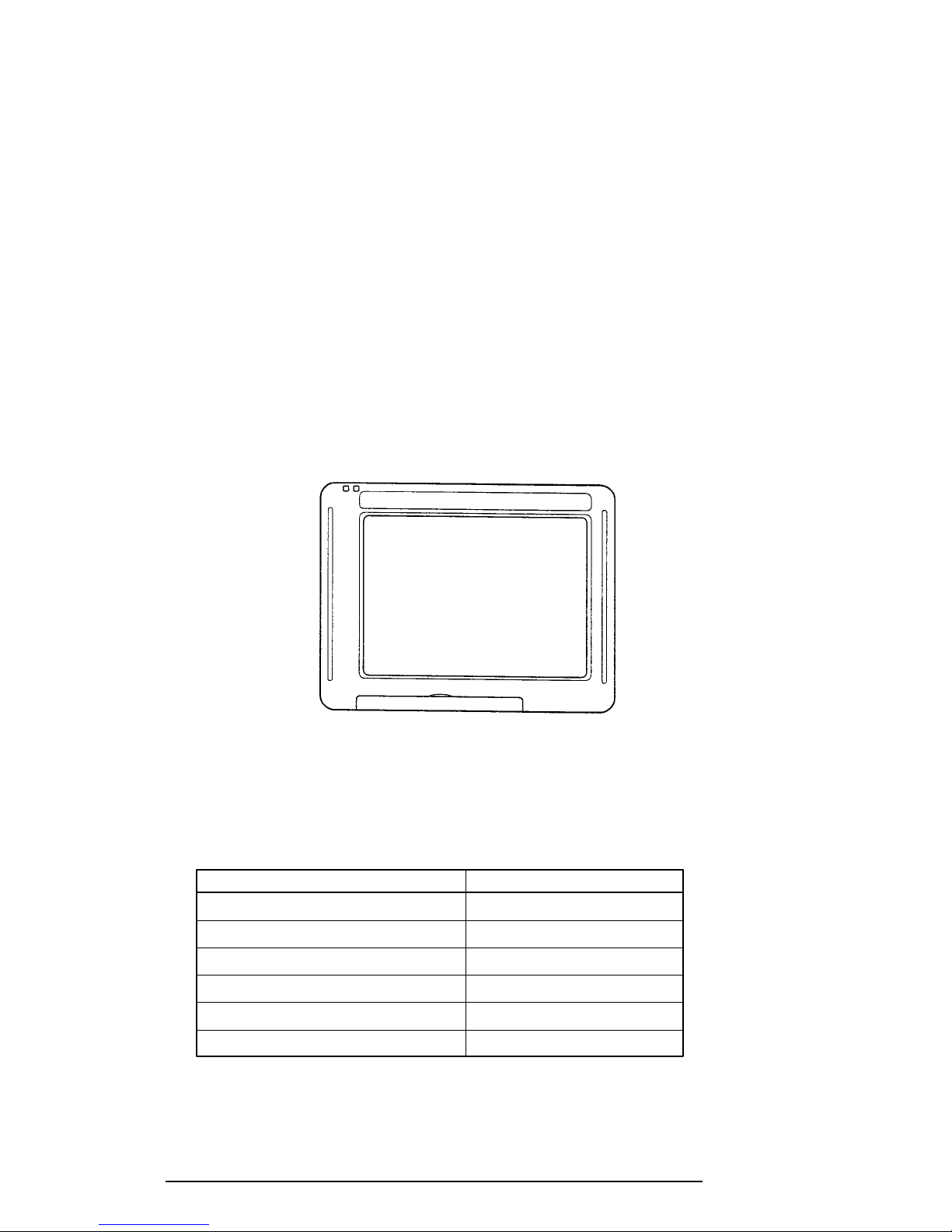
The T200/T200CS Pen Computer is shown in Figure 1-1. Its system configuration is shown
in Figure 1-2.
Figure 1-1 T200/T200CS Pen Computer
Figure 1-2 T200/T200CS System Unit Configuration
T200/T200CS 1-3
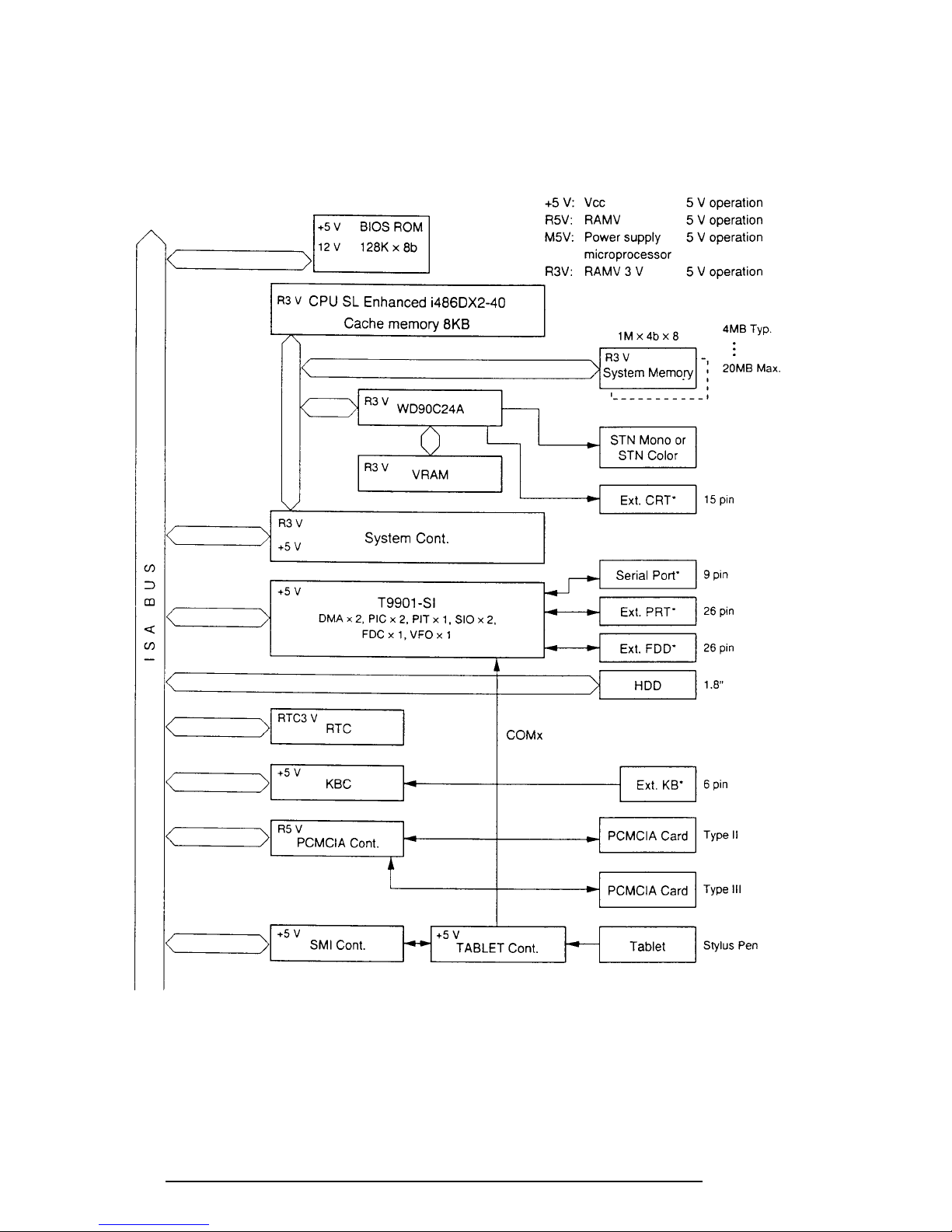
1.2 System Unit Block Diagram
Figure 1-3 is a block diagram of the computer's system unit.
* These port signals also output to the 72-pin Expansion port.
1-4 T200/T200CS
Figure 1-3 Block Diagram

The computer's system board is composed of the following major components:
❑ SL Enhanced i486DX2-40
❑ Super Integration (SI) T9901, which stores the following components:
• Two Direct Memory Access Controllers (DMAC): 82C37
• Two Programmable Interrupt Controllers (PIC): 82C59
• One Programmable Interval Timer (PIT): 82C54
• One Floppy Disk Controller (FDC): TC8565
• Two Serial Input/Output Controllers (SIO): TC8570
• One Variable Frequency Oscillator (VFO): TC8568
• One I/O Controller
• One Printer Port Controller
• One Speaker Controller
❑ A Real Time Clock (RTC)
One T9934 chip with 128 bytes of memory is used. Fourteen bytes of memory are
used for the calendar and clock and the remaining 114 bytes for system configuration
data.
OSC (X2) generates 32.768 KHz for RTC.
❑ A Keyboard Controller (KBC)
One 80C42 chip is used. This KBC includes the keyboard interface controller and
controls the external keyboard.
❑ The following memories:
Standard RAM: 4 MB
Cache memory: 8 KB (inside CPU)
BIOS ROM: 128 KB (96 KB are used)
This ROM contains Initial Reliability Test (IRT),
Basic Input/Output System (BIOS), and video BIOS.
Video RAM: 256 KB
Optional memory cards expand memory to a maximum of 20 MB.
VGA display controller (WD90C24A)
❑
This controller controls internal VGA display and external SVGA compatible display.
❑ Clock Generator receives 14.31818 MHz (X3) and generates the following frequen-
cies:
• 20 MHz for the CPU (CPU operates at 40MHz.)
• 14.7477 MHz for the COM
• 24 MHz for the FDC and VFO
• 16 MHz is used for the System Controller GA
• 14.31818 MHz is used for the T9901 (SI)
T200/T200CS 1-5

❑ Gate Arrays
System Controller Gate Array
This gate array has the following functions:
• CPU Controller
• Memory Controller
-DRAM Controller
-Compatible Bus Interface Controller
• SMI Controller
• VL Bus Controller
• Bus Controller
-Compatible Bus Interface Controller
-Compatible Access Controller
-DMA Controller
-I/O Controller
• Address Latch Controller
-32-Bit to 16-Bit Controller
-Address Latch
-DMA Address Generator
-Refresh Address Generator
• I/O Register
-Compatible I/O Port
-Saving the data of the Register (in resume) Controller
-Toshiba Special Register
• Processing Speed Controller
• Data Bus Change Controller
• Data Latch
PCMCIA Controller Gate Array
This gate array has the following functions:
• Memory Card Controller
-PCMCIA IC Card Controller
-Toshiba Modem Card Controller
1-6 T200/T200CS

SMI Controller Gate Array
This gate array has the following functions:
• Tablet Controller
-Tablet Microprocessor Communication Controller
-SMI Controller
• Others
-Contrast Adjust PWM Controller
T200/T200CS 1-7
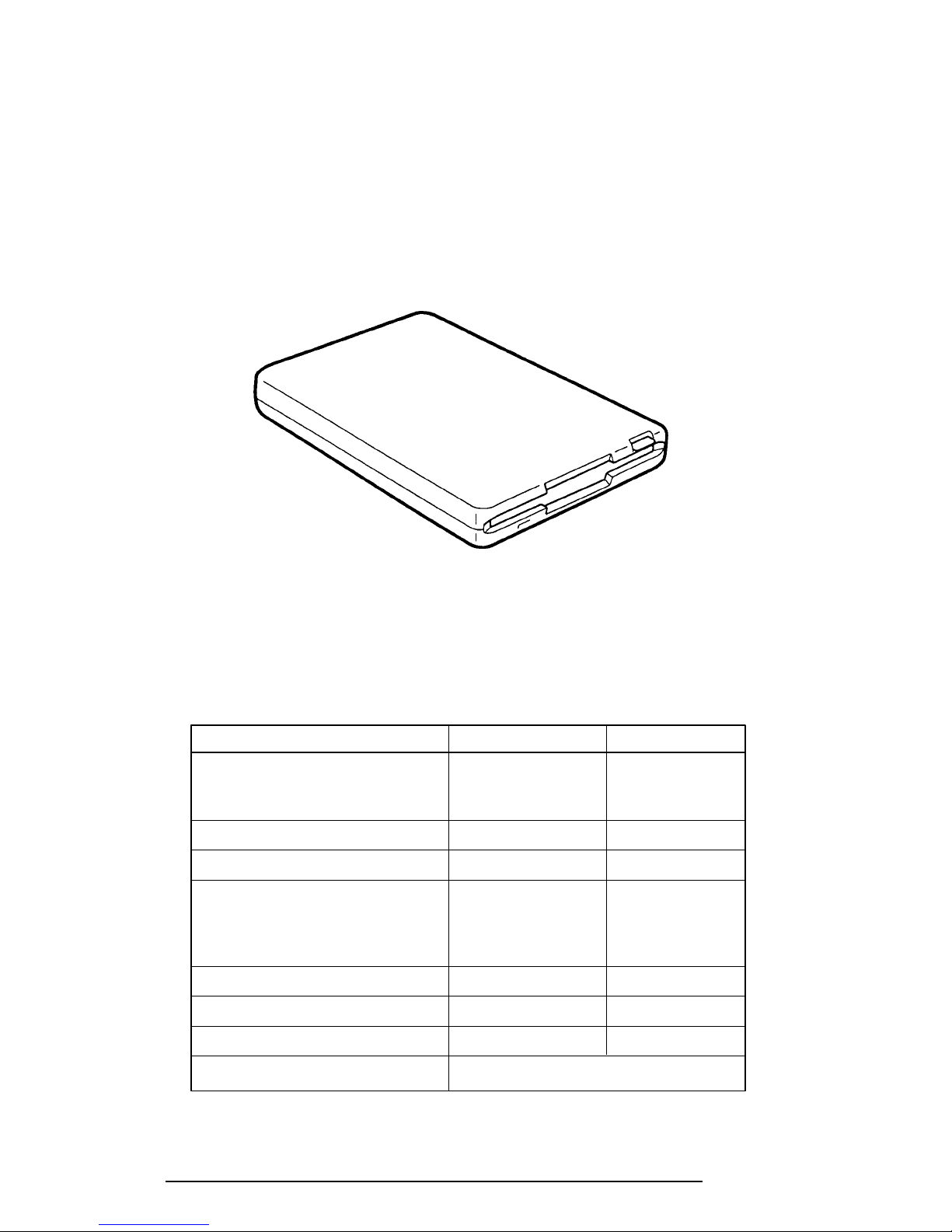
1.3 Optional External 3.5-inch Floppy Disk Drive
The computer's optional 3.5-inch Floppy Disk Drive (FDD) is a thin, high-performance
reliable drive that supports 720-KB (formatted) 2DD and 1.44-MB (formatted) 2HD 3.5-inch
floppy disks.
The computer's FDD is shown in Figure 1-4. The specifications for the FDD are provided in
Table 1-1.
Figure 1-4 3.5-Inch FDD
Table 1-1 3.5-Inch FDD Specifications
Item 2-MB mode 1-MB mode
Storage capacity (KB)
Unformatted 2,000 1,000
Formatted 1,474 737
Number of heads 2 2
Number of cylinders 80 80
Access time (ms)
Track to track 3 3
Average 181 181
Head settling time 15 15
Recording track density (tpi) 135 135
Data transfer rate (Kbps) 500 250
Rotation speed (rpm) 300 300
Recording method Modified Frequency Modulation (MFM)
1-8 T200/T200CS
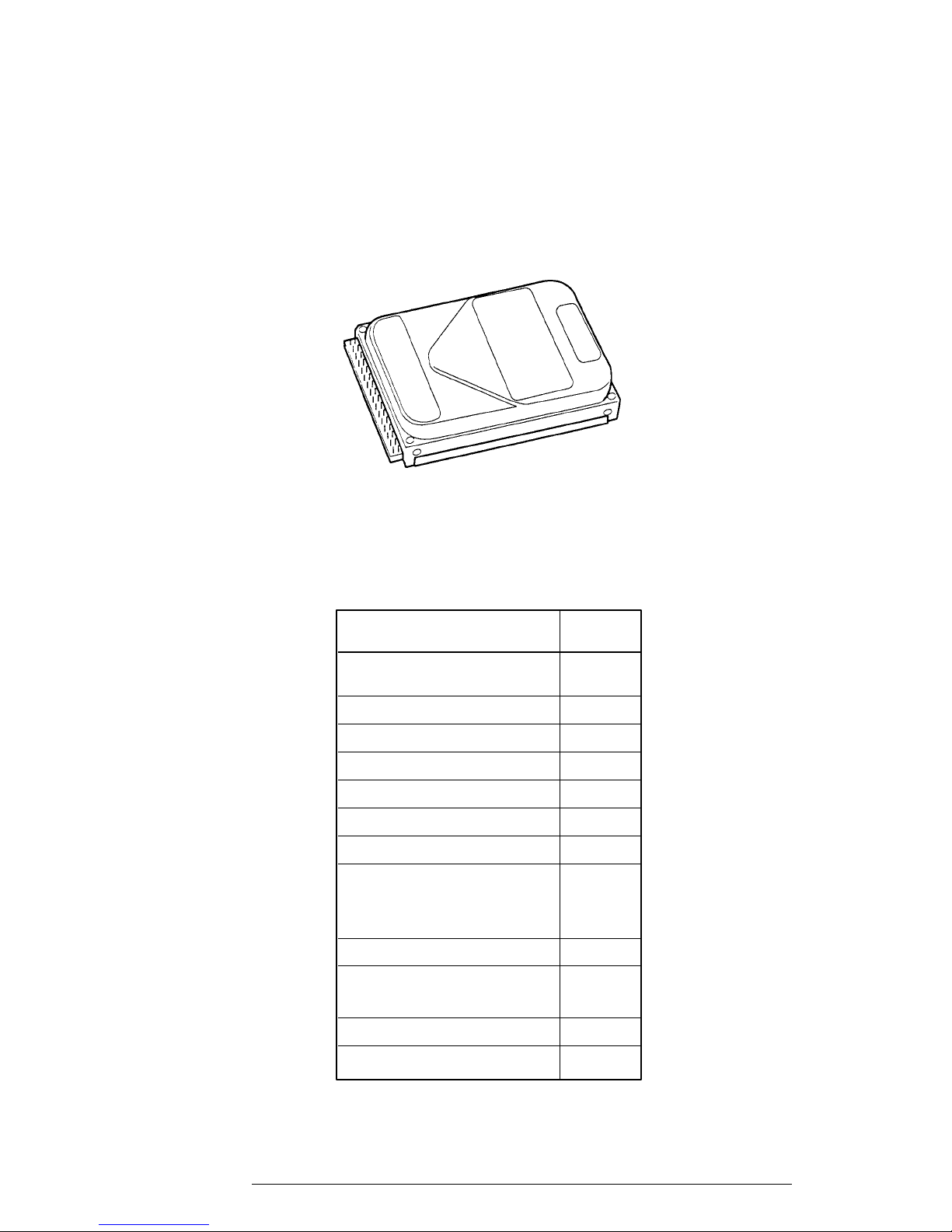
1.4 1.8-inch Hard Disk Drive
The computer’s 80-MB (formatted) Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a random access non-volatile
storage device. It has a non-removable 1.8-inch magnetic disk and mini-winchester type
magnetic heads.
The HDD is shown in Figure 1-5. Specifications for the HDD are provided in Table 1-2.
Figure 1-5 1.8-Inch HDD
Table 1-2 1.8-Inch HDD Specifications
Item 80 MB
(ZA1094)
Storage capacity (MB)
Formatted 85.0
Number of disks 2
Data heads 3
Data surfaces 3
Tracks per surface 2,750
Sectors per track 20
Bytes per sector 512
Access time (ms)
Track to track 8
Average 18
Maximum 35
Rotation speed (rpm) 3,571
Data transfer rate (bps)
To/from media 2.5M
Interleave 1:1
T200/T200CS 1-9
Recording method 1-7 RLL
1.5 Monochrome LCD
The monochrome LCD is composed of an LCD module, a Fluorescent Lamp (FL), and an FL
inverter board.
1.5.1 Monochrome LCD Module
The computer's monochrome LCD supports 640 x 480 pixels with a video controller and 16
levels of gray. The video controller includes the functions of the VGA and SVGA for external
display.
The LCD receives vertical and horizontal synchronizing signals, 8-bit data signals (4-bit upper
block data signal and 4-bit lower block data signal), and shift clock for data transmission. All
signals are CMOS-level compatible.
The sidelit LCD is shown in Figure 1-6 and its specifications are provided in Table 1-3.
Figure 1-6 Monochrome LCD
Table 1-3 Monochrome LCD Specifications
Item Specifications
Number of dots (dots) 640 x 480
Dot pitch (mm) 0.27 (W) x 0.27 (H)
Display area (mm) 196 (W) x 147.6 (H)
Contrast 10:1 (typically)
FL current (mA) 5.5 (r.m.s.)
FL frequency (KHz) 39
1-10 T200/T200CS
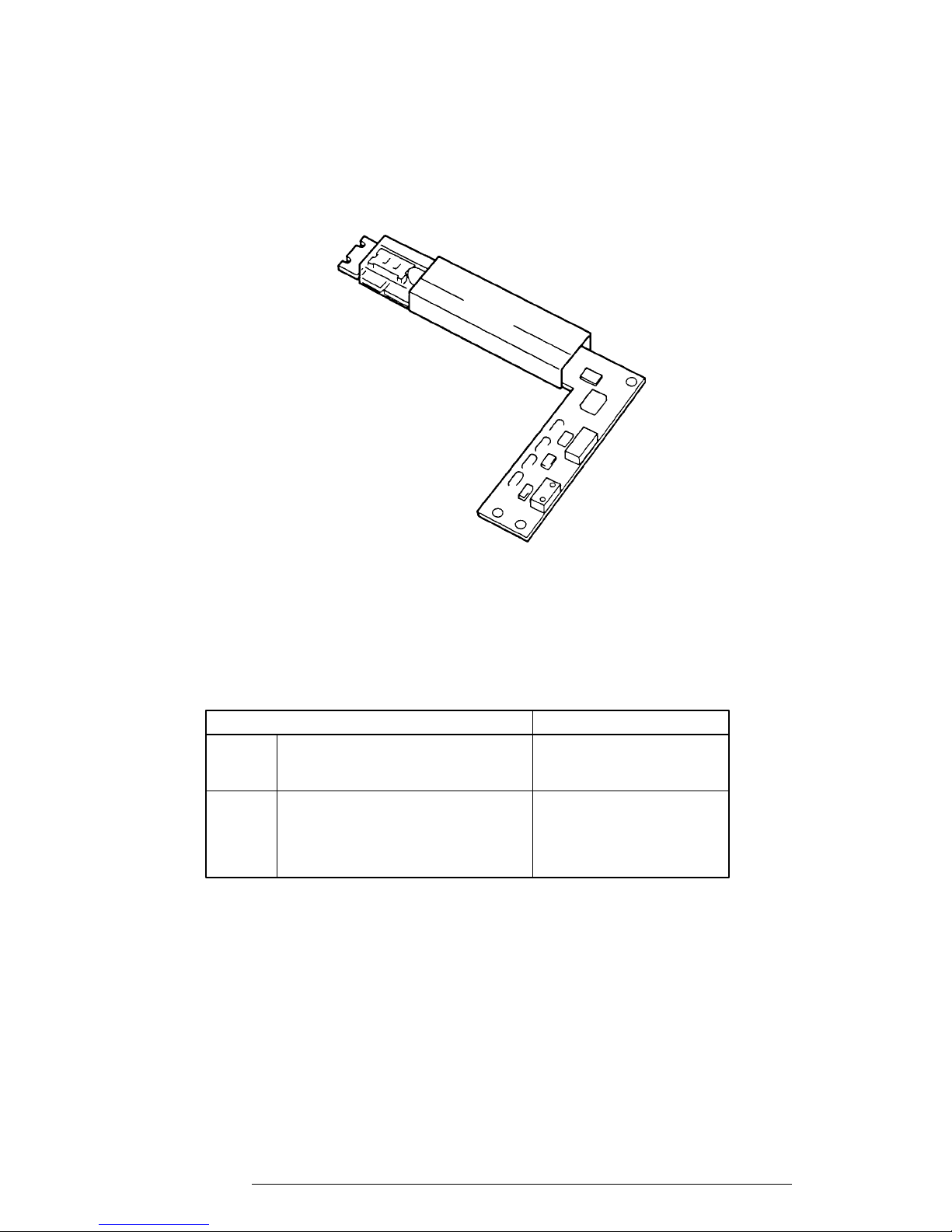
1.5.2 Monochrome LCD Fluorescent Lamp (FL) Inverter Board
The FL inverter board supplies the high-frequency current needed to illuminate the LCD's FL.
The FL inverter board is shown in Figure 1-7 and its specifications are provided in Table 1-4.
Figure 1-7 Monochrome LCD FL Inverter Board
Table 1-4 Monochrome LCD FL Inverter Board Specifications
Item Specifications
Input Voltage (VDC) 5
Power (W) 2.7
Output Voltage (VAC) 1,100 (r.m.s)
Current (mA) 5.5 (r.m.s)
Frequency (KHz) 39
T200/T200CS 1-11

1.6 STN Color LCD
The STN Color Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) contains an LCD module, a Fluorescent Lamp
(FL), and an FL inverter board.
1.6.1 STN Color LCD Module
The computer's STN color LCD supports 640x480 pixels with a video controller. This video
controller includes the functions of VGA and SVGA for external display.
The LCD receives vertical and horizontal synchronizing signals, 16-bit data signal (8-bit upper
block data signal, 8-bit lower block data signal), display enable signal, and shift clock for data
transmission. All signals are CMOS-level compatible.
The STN LCD is shown in Figure 1-8. The LCD specifications are provided in Table 1-5.
Figure 1-8 STN Color LCD
Table 1-5 STN Color LCD Specifications
Item Specifications
Number of Dots (dots) 640x480
Dot pitch (mm) 0.3(W)x0.3(H)
Display area (mm) 195 (W)x147 (H)
Contrast 18:1 (Typically)
FL current (mA) 6.0 (r.m.s.)
FL frequency (KHz) 47
1-12 T200/T200CS
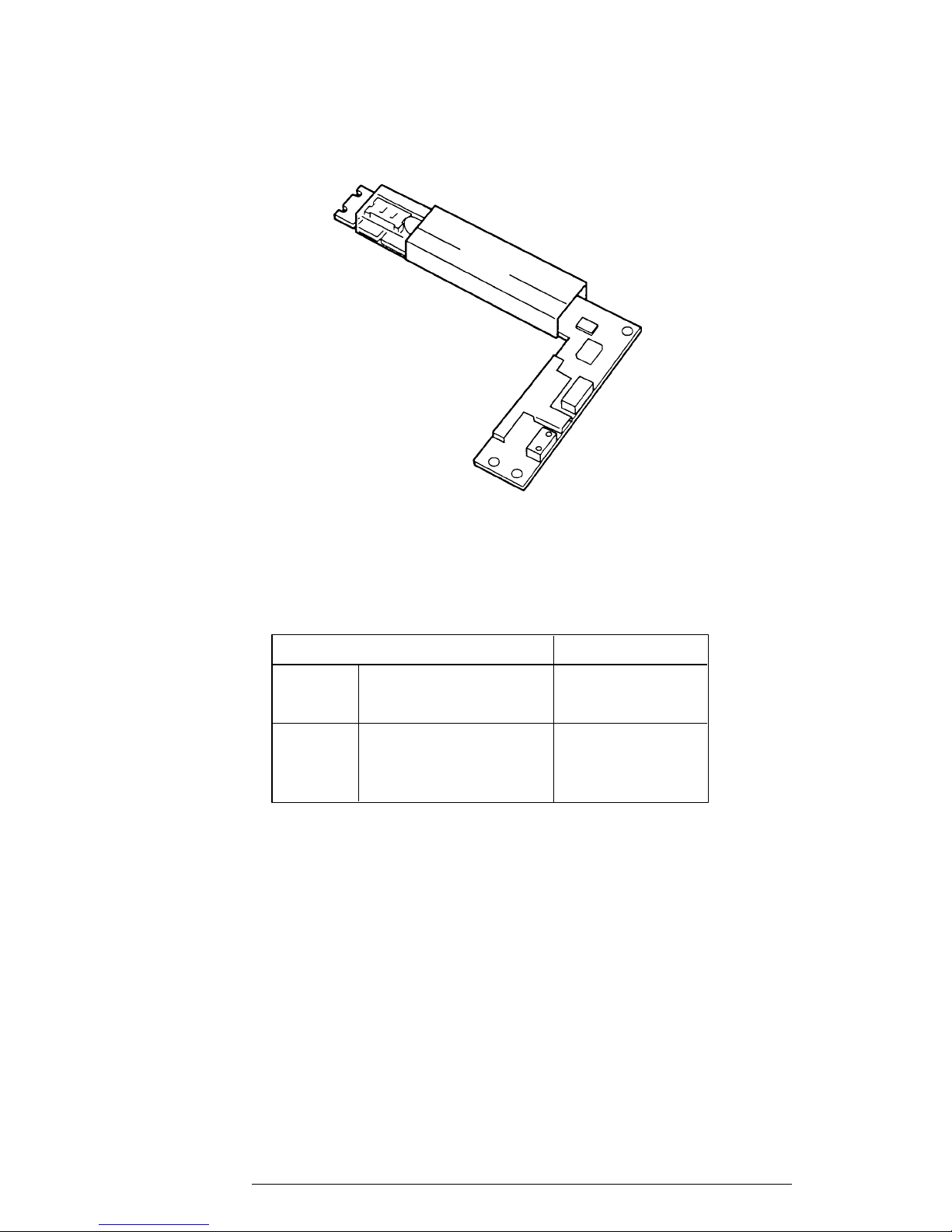
1.6.2 STN Color LCD Fluorescent Lamp (FL) Inverter Board
The FL inverter board supplies high frequency current to light the LCD’s Fluorescent Lamp.
The FL inverter board is shown in Figure 1-9 and its specifications are described in Table 1-6.
Figure 1-9 STN Color LCD FL Inverter Board
Table 1-6 STN Color LCD FL Inverter Board Specifications
Item Specifications
Input Voltage (VDC) 5
Power (W) 4
Output Voltage (VAC) 1,100 (r.m.s.)
Current (mA) 6.0 (r.m.s.)
Frequency (KHz) 47
T200/T200CS 1-13
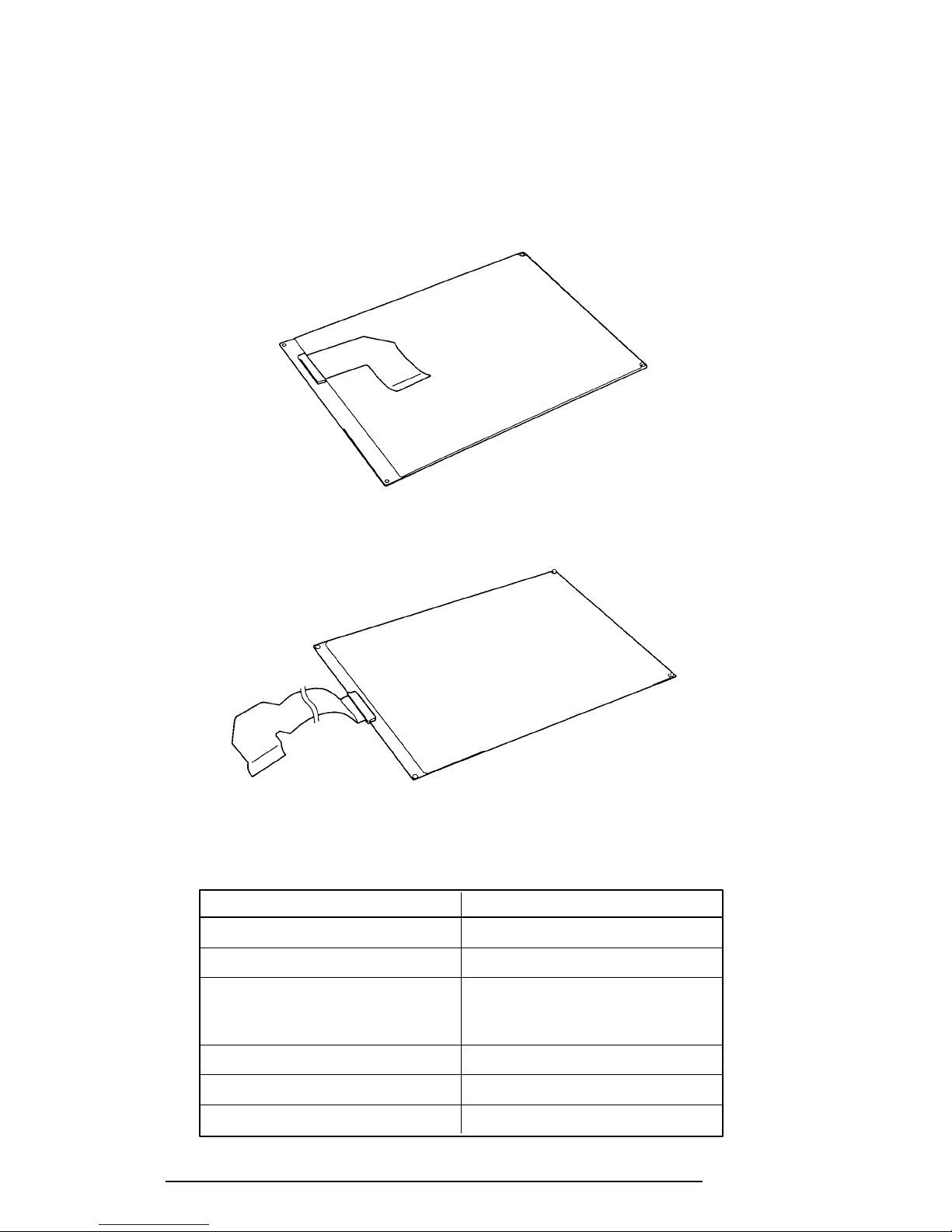
1.7 Tablet
The tablet is the internal digitizer, which also acts as the interface between the stylus and the
computer.
The tablets are shown in Figures 1-10 and 1-11 and their specifications are provided in Table
1-7.
Figure 1-10 T200 Tablet
Item Specifications
Material Electromagnetic derivative
Voltage (VDC) 5V
Current (mA) 30 (In use)
Resolution (mm) 0.1
Precision (mm) ±0.4
Data transfer (point/sec) 205
1-14 T200/T200CS
Figure 1-11 T200CS Tablet
Table 1-7 Tablet Specifications
23 (In suspend)
5.2 (In sleep)
1.8 Power Supply
The power supply supplies five kinds of voltages to the computer's system board. The
computer's power supply has one microprocessor and it operates at 500 Hz. It contains the
following functions:
1. Determines if the AC adapter or battery is connected to the computer.
2. Detects DC output and circuit malfunctions.
3. Controls the LED icon and speaker.
4. Turns the battery charging system on and off and detects a fully charged
battery.
5. Determines if the power can be turned on and off.
6. Provides more accurate detection of a low battery.
7. Calculates the remaining battery capacity.
The power supply output rating is specified in Table 1-8.
Table 1-8 Power Supply Output Rating
DC Regulation Maximum
Use for Name voltage tolerance current Ripple
System logic, FDD, HDD VCC +5 ±5 1,720 100
RS-232C, Flash ROM 12V +12 ±5 120 240
RAM, CPU B3V +3.3 ±5 1243 100
RS-232C -9V -9 15 15 150
(V) (%) (mA) (mV)
T200/T200CS 1-15
1.9 Batteries
The computer has three types of batteries:
❑ Main battery pack
❑ Backup battery
❑ Real Time Clock (RTC) battery
Battery specifications are provided in Table 1-9.
Table 1-9 Battery Specifications
Battery name Material Output voltage Capacity
Main battery pack Lithium-Ion 10.8 V 3,000 mAH
Backup battery Nickel Metal Hydride 3.6 V 120 mAH
RTC battery Lithium-Vanadium 3.0 V 50 mAH
1.9.1 Main Battery
The removable main battery pack is the primary power source when the AC adapter is not
attached. The main battery recharges the backup battery when system power is on. The
backup and main battery maintain the state of the computer system when AutoResume is
enabled. The main battery is shown in Figure 1-12.
1-16 T200/T200CS
Figure 1-12 Main Battery

❏ Battery Indicator
The battery indicator is located on the top cover of the computer. The indicator shows the
status of the removable battery pack, power supply, and AC adapter. The status of each can
be determined by color:
Orange The battery is being charged or an AC adapter is attached.
Green The battery is fully charged. (An AC adapter is attached.)
No light The AC adapter is disconnected from the computer or is connected, but
cannot charge the battery for one of the following reasons:
❏ The battery is extremely hot. Allow the computer and the battery to
reach room temperature before attempting to charge the battery.
❏ The battery is almost fully discharged and will not begin
charging until a few minutes after the AC adapter is connected.
❏ The AC adapter is not receiving power.
T200/T200CS 1-17
1.9.2 Battery Charging Control
Battery charging is controlled by a power supply microprocessor mounted on the power
supply. The microprocessor turns charging on or off and detects a full charge when the AC
adapter and main battery pack are attached to the computer. The system charges the main
battery pack using quick or trickle charge.
❏ Quick Battery Charge
When the AC adapter is attached, there are two types of charge: quick charge when the
system is powered off and trickle charge when powered on. Table 1-10 gives quick charging
time requirements.
Table 1-10 Time Required For Quick Charges
Charge Charging time
Quick charge About 3 hours
(power off)
Quick charge About 8 hours
(power on)
If one of the following occurs, the battery quick charge process stops.
1. The battery becomes fully charged.
2. The AC adapter or battery is removed.
3. The battery or AC adapter output voltage is abnormal.
4. The charge current is abnormal.
❏ Trickle Battery Charge
When the main battery is fully charged and the AC adapter is attached, the power supply
microprocessor changes quick charge to trickle charge.
1-18 T200/T200CS
1.9.3 Backup Battery
The backup battery maintains data for AutoResume. The power source used to back up
AutoResume data is determined according to the following priority:
AC adapter > Main battery > Backup battery
The backup battery is charged by the main battery or AC adapter when the system is powered
on. Table 1-11 shows the charging time and data preservation period of the backup battery.
Table 1-11 Backup Battery Charging/Data Preservation Time
Time
Charging Time Power On 10 H
Power Off 10 H
(with AC Adapter or main battery)
Power Off Doesn’t charge
(Without AC Adapter and main battery)
Data preservation period (full charge) 8 H
1.9.4 RTC Battery
The RTC battery provides power to keep the current date, time, and other setup information
in memory while the computer is turned off. Table 1-12 shows the charging time and data
preservation period of the RTC battery.
Table 1-12 RTC Battery Charging/Data Preservation Time
Time
Charging Time Power On 48 H
Power Off Doesn’t charge
Data preservation period (full charge) 1 month
T200/T200CS 1-19
1.10 Stylus
The stylus is used to enter information into the computer by writing directly onto the screen.
You can write letters or numerals to enter data, draw gestures to enter commands, or tap to
select from menus.
The stylus is shown in Figure 1-13.
Figure 1-13 The Stylus
1-20 T200/T200CS

2.1 Troubleshooting
Chapter 2 describes how to determine if a Field Replaceable Unit (FRU) is causing a malfunction. FRUs covered are:
1. System Board
2. Floppy Disk Drive
3. Hard Disk Drive
4. Display Module
5. Tablet
Diagnostics Disk operations are described in Chapter 3 and detailed replacement procedures
are given in Chapter 4.
The following tools are necessary for troubleshooting:
1. T200/T200CS Diagnostics Disk
2. Phillips-head screwdriver (2 mm)
3. 2DD or 2HD formatted work disk for FDD testing
4. Printer port LED
5. RS-232-C wraparound connector
6. Printer wraparound connector
7. Multimeter
8. Parallel cable (standard equipment)
9. External PS/2-type keyboard
10. Optional external 3.5-inch FDD
T200/T200CS 2-1

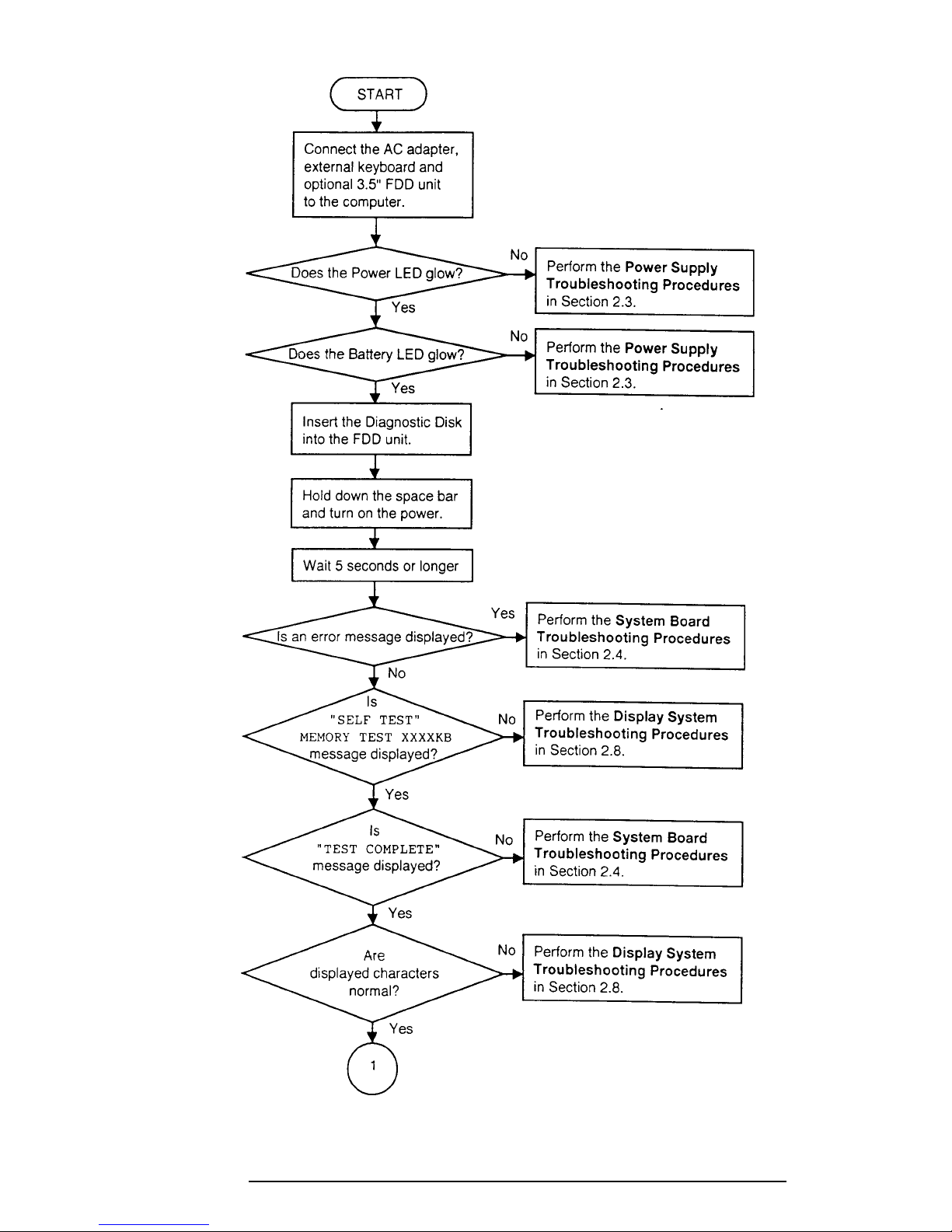
2.2 Troubleshooting Flowchart
Use the flowchart in Figure 2-1 as a guide to determine which procedures to execute. Before
going through the flowchart steps, verify the following:
❑ Ask the user if a password is registered, and if it is, ask him or her to enter the pass-
word. If the user has forgotten the password, connect the printer port wraparound
board (F31PRT), then turn the POWER switch on. The computer will skip the password function.
❑ Make sure all optional equipment is disconnected.
2-2 T200/T200CS
T200/T200CS 2-3
Figure 2-1 Troubleshooting Flowchart (1/2)
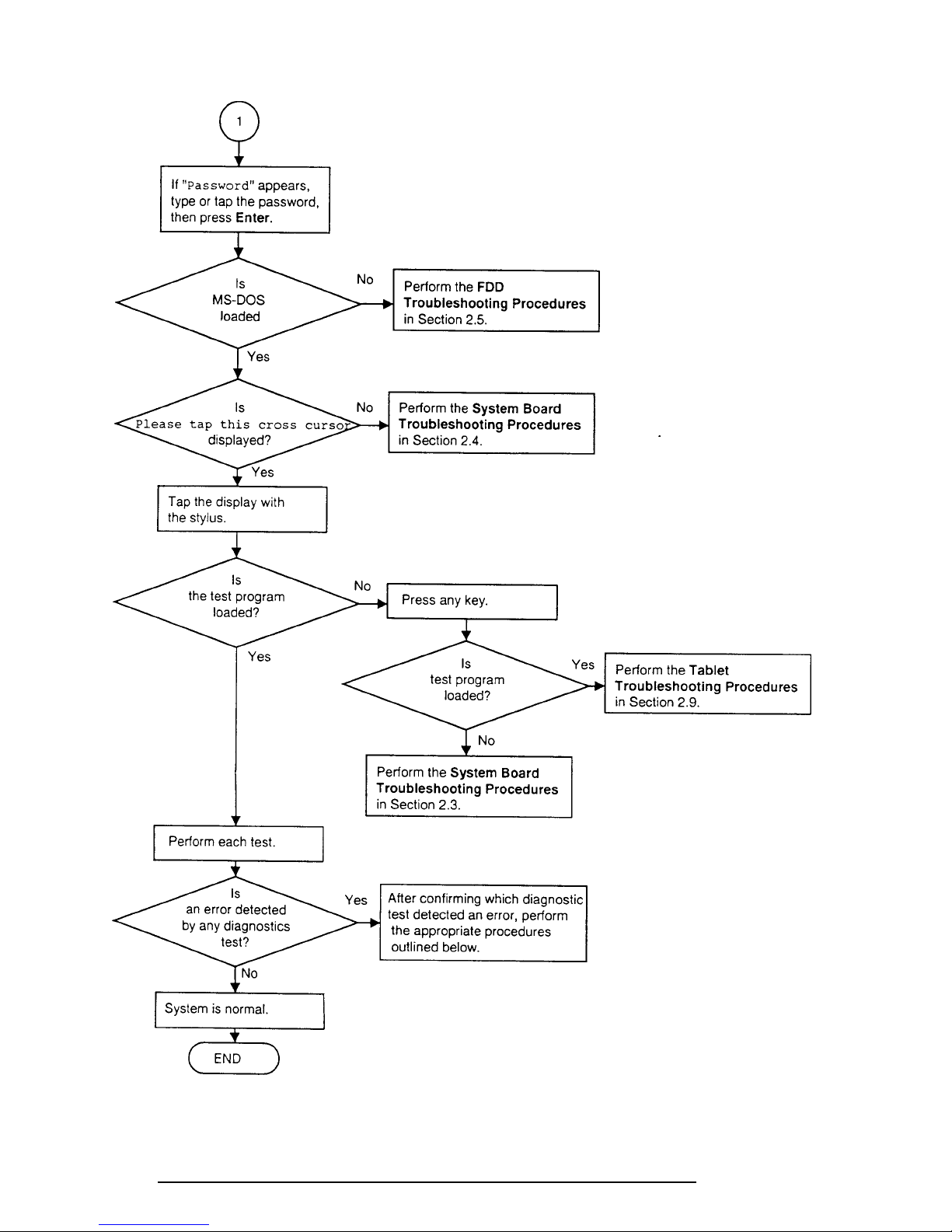
Figure 2-1 Troubleshooting Flowchart (2/2)
2-4 T200/T200CS

If the diagnostics program cannot detect an error, the problem may be intermittent. The
Running Test program should be executed several times to isolate the problem. Check the
Log Utilities function to confirm which diagnostic test detected an error(s), then perform the
appropriate procedures as follows:
1. If an error is detected on the system test, memory test, display test, ASYNC test,
printer test, or real timer test, perform the system board troubleshooting procedures in Section 2.4.
2. If an error is detected on the keyboard test, perform the keyboard troubleshooting
procedures in Section 2.7.
3. If an error is detected on the floppy disk test, perform the floppy disk drive
troubleshooting procedures in Section 2.5.
4. If an error is detected on the hard disk test, perform the hard disk drive troubleshooting procedures in Section 2.6.
5. If an error is detected on the tablet test, perform the tablet troubleshooting procedures in Section 2.9.
T200/T200CS 2-5

2.3 Power Supply Troubleshooting
The power supply controls many functions and components. To determine if the power
supply is functioning properly, start with Procedure 1 and continue as instructed. The procedures described in this section are:
Procedure 1: Power LED Indicator Check
Procedure 2: Battery LED Indicator Check
Procedure 3: PCB Replacement Check
2-6 T200/T200CS

Procedure 1 Power LED Indicator Check
The AC adapter converts AC to DC power and contains a charging circuit for charging the
batteries. The adapter connects to the Power socket connector on the back side of the computer. When the AC adapter is connected and power is off, the AC adapter charges the
batteries.
The Power LED displays whether or not the AC adapter is connected and supplying power.
❑ When the Power LED is green, the AC adapter is connected and supplying power to
the computer.
❑ If the Power LED does not light, the AC adapter is not supplying power to the com-
puter or the AC adapter is not attached to the computer, go to Check 1.
❑ If the Power LED is flashing orange, the AC adapter voltage supply is abnormal or the
power supply is not functioning properly, go to Check 2.
If any of the above indicator conditions are abnormal, make sure the Power LED indicator
lights are not burned out before performing the following checks:
Check 1 Make sure the correct AC adapter cable is firmly plugged into the Power socket
on the back of the computer.
Check 2 If the Power LED flashes orange when the AC adapter is connected, its voltage
output is abnormal. Connect a new AC adapter and turn the computer on again to
verify the indicator condition. If the problem still exists, perform Check 3.
Check 3 The battery pack may be malfunctioning. Replace the battery pack with a new one
and turn the computer on again. If the problem persists, perform Check 4.
Check 4 Place the computer in an environment between –20°C and 70°C until at ambient
temperature. Repeat the steps which caused abnormal operation. If the same
problem persists, perform Procedure 3.
T200/T200CS 2-7

Procedure 2 Battery LED Indicator Check
The battery LED indicator shows battery charging status. The LED, identified by a battery
icon on the front of the computer, glows orange when the AC adapter is charging the battery
pack.
❑ If the Battery LED indicator glows green, the AC adapter is connected and the battery
is fully charged.
❑ If the Battery LED indicator glows orange, the AC adapter is connected and the
battery is being charged.
❑ If the Battery LED indicator does not glow, go to Check 1.
Check 1 Make sure the AC adapter cable and AC cord are firmly plugged into the Power
socket and wall outlet. If connected correctly, go to Check 2.
Check 2 Make sure the battery pack is installed correctly. Go to Check 3 if it is.
Check 3 Remove the battery pack and check that the battery terminal is clean and not bent.
❑ If the terminal appears dirty, clean gently with a cotton swab dipped in
alcohol.
❑ If the terminal looks bent or damaged, replace the upper system board.
❑ If the battery terminal is clean and not bent, go to Check 4.
Check 4 Connect a new AC adapter. If the Battery LED indicator still does not glow, go
to Check 5.
Check 5 Install a new battery pack. If the Battery LED indicator still does not glow, go to
Procedure 3.
2-8 T200/T200CS

Procedure 3 PCB Replacement Check
The power supply is mounted on the upper system board. The upper system board may be
damaged. Disassemble the computer following the steps described in Chapter 4, Replacement
Procedures, then perform the following checks.
Check 1 Replace the upper system board with a new one and restart the system. If the
problem still exists, go to Check 2.
Check 2 Replace the lower system board with a new one and restart the system. If the
problem persists, other FRUs may be damaged.
T200/T200CS 2-9

2.4 System Board Troubleshooting
This section describes how to determine if the system board is defective or not functioning
properly. Start with Procedure 1 and continue as instructed. The procedures provided are:
Procedure 1: Message Check
Procedure 2: Printer Port LED Check on Boot Mode
Procedure 3: Printer Port LED Check on Resume Mode
Procedure 4: Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
Procedure 5: Connection and Replacement Check
2-10 T200/T200CS

Procedure 1 Message Check
When power is turned on while the space bar is held down, the system performs the Initial
Reliability Test (IRT) resident in BIOS ROM. IRT tests and initializes each IC on the system
board.
❑ If an error message is shown on the display, perform Check 1.
❑ If there is no error message, go to Procedure 2.
❑ If the test program is properly loaded, go to Procedure 3.
Check 1 If one of the following error messages is displayed on the screen, tap the display or
press the F1 key as instructed. These errors occur when the system configuration
preserved in RTC memory (CMOS-type memory) is not the same as the actual
configuration or when data is lost.
Tapping the display or pressing the F1 key as instructed causes the SETUP menu
to appear. If error message (b) appears often when power is turned on, replace
the RTC battery. If any other error message is displayed, perform Check 2.
(a) *** Error in CMOS. Bad HDD type ***
Check system. Then tap any point on the screen
with the stylus or press [F1] key.
(b) *** Error in CMOS. Bad battery ***
Check system. Then tap any point on the screen
with the stylus or press [F1] key.
(c) *** Error in CMOS. Bad check sum ***
Check system. Then tap any point on the screen
with the stylus or press [F1] key.
(d) *** Error in CMOS. Bad memory configuration ***
Check system. Then tap any point on the screen
with the stylus or press [F1] key.
(e) *** Error in CMOS. Bad time function ***
Check system. Then tap any point on the screen
with the stylus or press [F1] key.
Check 2 If the following error message is displayed, tap the display or press any key as the
message instructs.
WARNING: RESUME FAILURE.
TAP ANY POINT ON SCREEN WITH STYLUS PEN OR PRESS
ANY KEY TO CONTINUE.
The error message appears when data stored in RAM under the resume function is
lost because the battery is discharged or the system board is damaged. Go to
Procedure 2.
If any other message appears, perform Check 3.
T200/T200CS 2-11

Check 3 The IRT checks the system board. When the IRT detects an error, the system
stops or an error message appears.
❑ If one of the following error messages; (1) through (17), (19), (20), (25) or
(26), is displayed, replace the system board.
❑ If error message (18) is displayed, go to the Keyboard Troubleshooting
Procedures in Section 2.7.
❑ If error message (21) or (22) is displayed, go to the HDD Troubleshooting
Procedures in Section 2.6.
❑ If error message (23) or (24) is displayed, go to the FDD Troubleshooting
Procedures in Section 2.5.
(1) CPU ERROR
(2) SYSTEM ROM CHECK SUM ERROR
(3) PIT ERROR
(4) MEMORY REFRESH ERROR
(5) TIMER OUT ERROR
(6) FIRST 64KB MEMORY ERROR
(7) FIRST 64KB MEMORY PARITY ERROR
(8) VRAM ERROR
(9) KBC ERROR
(10) SYSTEM MEMORY ERROR
(11) SYSTEM MEMORY PARITY ERROR
(12) EXTENDED MEMORY ERROR
(13) EXTENDED MEMORY PARITY ERROR
(14) DMA PAGE REGISTER ERROR
(15) DMAC #1 ERROR
(16) DMAC #2 ERROR
(17) PIC #1 ERROR
(18) PIC #2 ERROR
(19) KEYBOARD ERROR
(20) HDC ERROR
(21) HDD #0 ERROR
(22) HDD #1 ERROR
(23) NO FDD ERROR
(24) FDC ERROR
(25) TIMER INTERRUPT ERROR
(26) RTC UPDATE ERROR
2-12 T200/T200CS

Procedure 2 Printer Port LED Check on Boot Mode
The printer port LED displays IRT and test status by turning lights on and off as an eight-digit
binary value for boot mode. Figure 2-2 shows the printer port LED.
NOTE: When performing this check, the Power-up Mode option in the SETUP program must be set to boot mode.
Figure 2-2 Printer Port LED
To use the printer port LED, follow these steps:
1. Turn on the computer's power, then set to boot mode.
2. Turn off the computer's power.
3. Connect the parallel cable (standard equipment) to the PRT port.
4. Plug the printer port LED into the computer's parallel cable.
5. Connect the external keyboard to the KB port.
6. Hold down the space bar and turn on the computer's power.
7. Read the LED status from left to right.
8. Convert the status from binary to hexadecimal notation.
9. If final LED status is FFh (normal status), go to Procedure 3.
10. If final LED status matches any of the test status values in Table 2-1, perform
Check 1.
NOTE: If an error condition is detected by the IRT, the printer port LED displays an
error code after the IRT ends. For example, when the printer port LED displays 1F
and halts, the IRT has already completed display initialization. In this instance, the
IRT indicated an error was detected during system memory test.
T200/T200CS 2-13

Table 2-1 Printer Port LED Boot Mode Error Status (1/2)
Error status Test item Message
System test 01H Test start
02H PIT test end
03H SM-RAM stack enable
04H CMOS test end
05H KBC initialization, self-test-
skip-request-test and
tablet initialization end
06H DRAM size test end
07H System BIOS ROM/RAM
copy end
08H Display control end
09H Test end
0AH∗ First 64KB memory test FIRST 64KB MEMORY ERROR
0BH** System memory -
initialization
0CH System initialization 0DH Interrupt vector -
initialization
18H PIC initialization -
1FH Display initialization CRTC ERROR
VRAM ERROR
READ DATA = XXXXXXXXH
WRITE DATA = XXXXXXXXH
25H System memory test SYSTEM MEMORY ERROR
ADDRESS = XXXXXXXXH
READ DATA = XXXXXXXXH
WRITE DATA = XXXXXXXXH
SYSTEM MEMORY PARITY ERROR
ADDRESS = XXXX0000H - XXXXFFFFH
30H (Error) Extended memory test EXTENDED MEMORY ERROR
33H (Normal) ADDRESS = XXXXXXXXH
READ DATA = XXXXXXXXH
WRITE DATA = XXXXXXXXH
EXTENDED MEMORY PARITY ERROR
ADDRESS = XXXX0000H - XXXXFFFFH
40H* DMA page register test DMA PAGE REGISTER ERROR
READ DATA = XXH
WRITE DATA = XXH
41H* DMAC test DMAC #1 ERROR
READ DATA = XXXXH
WRITE DATA = XXXXH
42H DMAC initialization -
2-14 T200/T200CS
DMAC #2 ERROR
READ DATA = XXXXH
WRITE DATA = XXXXH

Table 2-1 Printer Port LED Boot Mode Error Status (2/2)
Error status Test item Message
4AH* PIC test PIC #1 ERROR
READ DATA = XXH
WRITE DATA = XXH
PIC #2 ERROR
READ DATA = XXH
WRITE DATA = XXH
50H Mouse initialization 55H KBC initialization KBC ERROR
5AH Boot password1 -
(checks for access right)
60H HDD initialization HDC ERROR
HDC #0 ERROR
HDC #1 ERROR
65H FDD initialization NO FDD ERROR
FDD ERROR
70H Printer test 80H RS-232-C test 90H Timer initialization TIMER INTERRUPT ERROR
RTC UPDATE ERROR
A0H NDP initialization A6H Expansion I/O ROM C0H Boot password2 -
(checks for no access right)
FEH Pre-boot setup FFH Expansion system ROM -
NOTES:
* These error codes are not displayed on hot boot mode.
** This error code is not displayed on cold boot mode.
Check 1 If any of the following error codes are displayed, go to Procedure 5.
01h, 02h, 03h, 04h, 05h, 06h, 07h, 08h, 09h, 0Ah, 0Bh, 0Ch, 0Dh, 18h, 1Fh,
25h, 30h, 33h, 40h, 41h, 42h, 4Ah, 50h, 55h, 5Ah, 60h, 65h, 70h, 80h, 90h,
A0h, A6h, C0h, FEh
Check 2 If error code 5Ah is displayed, go to the HDD Troubleshooting Procedures in
Section 2.6.
Check 3 If error code 60h is displayed, go to the FDD Troubleshooting Procedures in
Section 2.5.
T200/T200CS 2-15

Procedure 3 Printer Port LED Check on Resume Mode
The printer port LED displays IRT and test status by turning lights on and off as an eight-digit
binary value for resume mode.
NOTE: When performing this check, the Power-up option in the SETUP program
must be set to resume mode.
To use the printer port LED, follow these steps:
1. Turn on the computer's power, then set to resume mode.
2. Turn off the computer's power.
3. Connect the parallel cable (standard equipment) to the PRT port.
4. Plug the printer port LED into the parallel cable.
5. Connect the external keyboard to the KB port.
6. Turn on the computer's power.
7. Read the LED status from left to right.
.
8. Convert the status from binary to hexadecimal notation.
9. If final LED status is FFh (normal status), go to Procedure 3.
10. If final LED status matches any of the test status values in Table 2-2, perform
Check 1.
Table 2-2 Printer Port LED Resume Mode Error Status
Error status Meaning of status
00H RAM BIOS error
F0H Press the reset switch.
F1H Suspend process error (The system will suspend while FDD is accessed, etc.)
F2H The system has optional ROM, or optional card (CGA, MDA).
F4H Backup RAM checksum error
F5H Main memory checksum error
F6H Video RAM checksum error
F7H Extended memory checksum error
F8H Backup RAM checksum error
F9H Main memory checksum error
FAH Video RAM checksum error
FBH Extended memory checksum error
FDH Card modem error (Card modem will be removed while system is in resume, etc.)
FEH Password error (The password will be erased before it is suspended.)
2-16 T200/T200CS

Procedure 4 Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
Execute the following tests from the Diagnostic Test Menu. Refer to Chapter 3, Tests and
Diagnostics, for more information on how to perform the tests.
1. System test
2. Memory test
3. Printer test
4. ASYNC test
5. Real Timer test
6. PCMCIA test
7. Tablet test
8. NDP test
If an error is detected during the tests, go to Procedure 5.
T200/T200CS 2-17

Procedure 5 Connection and Replacement Check
The system board(s) may be disconnected or damaged. Disassemble the computer following
the steps described in Chapter 4, Replacement Procedures, and check the connection between
the upper system board and lower system board, and other components. After checking the
connection, perform the following checks.
If the IRT test (Boot mode) detects any of the following codes, go to Check 1.
FFH (first), 01H, 04H, 06H, 07H, 08H, 0BH, 0CH, 0DH, 18H, 30H, 33H, 40H,
41H, 42H, 4AH, 50H, 5AH, 60H, 65H, 70H, 80H, 90H, A0H, C0H, FEH
If the IRT test (Boot mode) detects any of the following codes, go to Check 2.
02H, 03H, 05H, 09H, 0AH, 1FH, 55H, A6H
If the IRT test (Resume mode) detects any of the following codes, go to Check 1.
00H, F0H, F1H, F2H, F6H, FAH, FDH
If the IRT test (Resume mode) detects any of the following codes, go to Check 2.
F4H, F5H, F7H, F8H, F9H, FBH, FEH
If any of the following diagnostic tests detects an error, go to Check 1.
System test
NDP test
Printer test
Async test
PCMCIA test
If any of the following diagnostic tests detects an error, go to Check 2.
Memory test
Real Timer test
Tablet test
Check 1 Replace the upper system board with a new one. If the problem still exists, replace
the lower system board with a new one. Refer to Chapter 4 for instructions on
how to remove and replace the upper and lower system boards.
Check 2 Replace the lower system board with a new one. If the problem still exists, replace
the upper system board with a new one. Refer to Chapter 4 for instructions on
how to remove and replace the upper and lower system boards.
2-18 T200/T200CS

2.5 Floppy Disk Drive Troubleshooting
This section describes how to determine if the computer's optional external 3.5-inch floppy
disk drive is functioning properly. If the test program can be loaded, go to Procedure 3.
Otherwise, perform the steps below starting with Procedure 1 and continue as required.
Procedure 1: Functioning External FDD Check
Procedure 2: FDD Connection Check
Procedure 3: Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
Procedure 1 Functioning External FDD Check
Connect a functioning external 3.5-inch FDD to the computer's FDD port. Check the FDD
operation. If the FDD is operating properly, the user's FDD is malfunctioning. If the FDD
does not operate properly, go to Procedure 2.
Procedure 2 FDD Connection Check
Make sure the external 3.5-inch FDD cable is firmly connected to the FDD port. If this cable
is disconnected, connect it to the FDD port. If the FDD is not functioning properly, replace
the upper system board with a new one and re-start the system. If the problem still exists,
replace the lower system board.
T200/T200CS 2-19

Procedure 3 Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
The FDD Diagnostic Test program is stored on the T200/T200CS Diagnostics Disk. Run the
diagnostic program. Refer to Chapter 3, Tests and Diagnostics, for more information about
the diagnostics test procedures.
FDD test error codes and their status names are listed in Table 2-3. Verify that the floppy
disk in the FDD is formatted correctly and the write protect tab is disabled. If any other
errors occur while the FDD diagnostics test is executing, go to Check 1.
Table 2-3 Floppy Disk Drive Error Code and Status
Code Status
01h Bad command
02h Address mark not found
03h Write protected
04h Record not found
06h Media removed
08h DMA overrun error
09h DMA boundary error
10h CRC error
20h FDC error
40h Seek error
60h FDD not drive error
80h Time out error
EEh Write buffer error
FFh Data compare error
Check 1 If the following message is displayed, disable the write protect tab on the floppy
disk. If any other message appears, perform Check 2.
Write protected
Check 2 Replace the upper system board with a new one and re-start the system. If the
problem still exists, replace the lower system board.
2-20 T200/T200CS

2.6 Hard Disk Drive Troubleshooting
To determine if the HDD is functioning properly, perform the procedures below starting with
Procedure 1 and continue as instructed.
Procedure 1: Partition Check
Procedure 2: Message Check
Procedure 3: Format Check
Procedure 4: Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
CAUTION: The contents of the hard disk will be erased when the HDD troubleshooting procedures are executed. Transfer the contents of the hard disk to a floppy disk(s)
using the Toshiba MS-DOS BACKUP command. Refer to the Toshiba MS-DOS
Manual for more information about how to perform the BACKUP command.
Procedure 1 Partition Check
Insert the Toshiba MS-DOS system disk and turn on the computer, then perform the following checks:
Check 1 Type C: and press Enter. Go to Check 2 if the drive will not change to C. Go to
Procedure 2 if the drive changes to C.
Check 2 Type FDISK and press Enter. Choose Display Partition Information from the
FDISK menu. If drive C is listed, go to Check 3. If drive C is not listed, return to
the FDISK menu and choose the option to create a DOS partition on drive C.
Then recheck the system. If the problem still exists, go to Procedure 2.
Check 3 If drive C is listed as active in the FDISK menu, go to Check 4. If drive C is not
listed as active, return to the FDISK menu and choose the option to set the active
partition for drive C. Then recheck the system. If the problem still exists, go to
Procedure 2.
Check 4 Remove the system disk from the FDD and cold boot the computer. If the prob-
lem still exists, go to Procedure 2. Otherwise, the HDD is operating normally.
T200/T200CS 2-21

Procedure 2 Message Check
When the HDD does not function properly, some of the following error messages may appear
on the display. Start with Check 1 below and perform other checks as instructed.
Check 1 If any of the following messages appear, perform Check 2. If the following mes-
sages do not appear, perform Check 4:
HDC ERROR
(After 5 seconds this message will disappear.)
or
HDD #0 ERROR
(After 5 seconds this message will disappear.)
or
HDD #1 ERROR
(After 5 seconds this message will disappear.)
Check 2 If either of the following messages appears, perform Procedure 3. If the following
messages do not appear, perform Check 3.
Insert system disk in drive
Press any key when ready .....
or
Non-System disk or disk error
Replace and press any key
Check 3 Using the Toshiba MS-DOS system disk, install a system program on the hard disk
using the SYS command.
If the following message appears on the display, the system program has been
transferred to the HDD. Restart the computer. If the error message still appears,
perform Check 4.
System transferred
Check 4 The HDD is connected to the system board. Disassemble the computer as de-
scribed in Chapter 4, Replacement Procedures. If the HDD is disconnected, reattach it to the system board and return to Procedure 1. If the HDD is firmly
connected to the system board, perform Procedure 3.
2-22 T200/T200CS

Procedure 3 Format Check
The HDD is formatted using the low-level format program and the MS-DOS FORMAT
program. To format the HDD, start with Check 1 below and perform other steps as required.
Check 1 Using the Toshiba MS-DOS system disk, partition the hard disk using the FDISK
command. Format the hard disk using FORMAT C:/S/U to transfer the system
program to the HDD. If the following message appears on the display, the HDD
is formatted.
Format complete
If any other error message appears on the display, refer to the Toshiba MS-DOS
Manual for more information and perform Check 2.
Check 2 Using the T200/T200CS Diagnostic Disk, format the HDD with a low-level
format option. Refer to Chapter 3, Tests and Diagnostics, for more information
about the diagnostic program.
If the following message appears on the display, the HDD low-level format is
complete. Partition and format the HDD using the MS-DOS FORMAT command.
Format complete
If the HDD cannot be formatted using the Test and Diagnostic program, go to
Procedure 4.
T200/T200CS 2-23

Procedure 4 Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
The HDD test program is stored on the T200/T200CS Diagnostics Disk. Perform all of the
HDD tests in the Hard Disk Drive Test. Refer to Chapter 3, Tests and Diagnostics, for more
information about the HDD test program.
If an error is detected during the HDD test, an error code and status will be displayed; perform Check 1. Error codes and status are listed in Table 2-4. If an error code is not
generated, the HDD is operating properly.
Table 2-4 Hard Disk Drive Error Code and Status
Code Status
01h Bad command
02h Address mark not found
04h Record not found
05h HDC not reset error
07h Drive not initialized
08h HDC overrun (DRQ)
09h DMA boundary error
0Ah Bad sector
0Bh Bad track error
10h ECC error
11h ECC recover enable
20h HDC error
40h Seek error
80h Time out error
AAh Drive not ready
BBh Undefined error
CCh Write fault
E0h Status error
EEh Access time out error
FFh Data compare error
Check 1 Replace the HDD unit following the instructions in Chapter 4, Replacement
Procedures. If the HDD is still not functioning properly, perform Check 2.
Check 2 Replace the lower system board following the instructions in Chapter 4, Replace-
ment Procedures. If the problem still exists, replace the upper system board.
2-24 T200/T200CS

2.7 Keyboard Troubleshooting
To determine if the keyboard is functioning properly, perform the following procedures. Start
with Procedure 1 and continue as instructed.
Procedure 1: Functioning Keyboard Check
Procedure 2: External Keyboard Connection Check
Procedure 3: Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
Procedure 1 Functioning Keyboard Check
Connect a functioning keyboard to the computer's KB port. Check the keyboard's functions.
If the keyboard is functioning properly, the user's keyboard is malfunctioning. If the keyboard
is not functioning properly, go to Procedure 2.
Procedure 2 External Keyboard Connection Check
Make sure the external keyboard cable is firmly connected to the KB port. If this cable is
disconnected or loose, connect it to the KB port. If the external keyboard still does not
function properly, go to Procedure 3.
Procedure 3 Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
Execute the Keyboard Test in the Diagnostic Program. Refer to Chapter 3, Tests and
Diagnostics, for more information on how to perform the test program.
If an error occurs, replace the upper system board with a new one and re-start the system. If
the problem still exists, replace the lower system board.
T200/T200CS 2-25

2.8 Display Troubleshooting
This section describes how to determine if the display is functioning properly. Start with
Procedure 1 and continue as instructed.
Procedure 1: Brightness and Contrast Control Check
Procedure 2: External CRT Check
Procedure 3: Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
Procedure 4: Connector Check
Procedure 5: Replacement Check
Use the checklist below to determine which procedure to begin with:
❑ Display is dark
: Go to Procedure 1
❑ Backlight does not light.
Characters are not displayed.
Abnormal lines are displayed.
Some pixels do not light.
If the backlight lights but no characters are displayed.
: Go to Procedure 4
❑ Any other problem.
: Go to Procedure 3
Procedure 1 Brightness and Contrast Control Check
Change the brightness and contrast by tapping the adjust point of the display with the stylus.
If the brightness and contrast do not change, go to Procedure 4.
Procedure 2 External CRT Check
Connect the external CRT to the computer's external monitor port, then boot the computer.
If the external CRT works correctly, the internal LCD display may be damaged. Go to Procedure 4.
If the external CRT appears to have the same problem as the internal LCD, the display controller may be damaged. Go to Procedure 3.
2-26 T200/T200CS

Procedure 3 Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
The Display Test program is stored on the T200/T200CS Diagnostic Disk. This program
checks the display controller on the system board. After loading Toshiba MS-DOS, run the
Diagnostic Program. Refer to Chapter 3, Tests and Diagnostics, for details.
If an error is detected, go to Procedure 4. If an error is not detected, the display is functioning properly.
T200/T200CS 2-27

Procedure 4 Connector Check
The display system has an LCD panel, FL unit, tablet, and FL inverter board. These components are connected to the system board.
Disassemble the display unit and check the cable connections shown in Figures 2-3 and 2-4.
Refer to Chapter 4, Replacement Procedures, for more information about how to disassemble
the computer.
If any of these cables is not connected, firmly re-connect it and repeat Procedures 1, 2, and 3.
If the problem still exists, perform Procedure 5.
Figure 2-3 T200 Display Connection
Figure 2-4 T200CS Display Connection
2-28 T200/T200CS

Procedure 5 Replacement Check
The FL inverter board, display module, and system board are connected to the display circuits.
Any of these components may be damaged. Refer to Chapter 4, Replacement Procedures, for
disassembly instructions and then perform the following checks:
❑ If the FL does not light, perform Check 1.
❑ If characters are not displayed clearly, perform Check 1.
❑ If some screen functions do not operate properly, perform Check 1.
Check 1 Replace the display module and test the display again. If the problem persists,
perform Check 2.
Check 2 Replace the FL inverter board and test the display again. If the problem persists,
perform Check 3.
Check 3 Replace the display cable and test the display again. If the problem persists,
perform Check 4.
Check 4 The upper system board may be damaged. Replace the upper system board and
test the display again. If the problem persists, perform Check 5.
Check 5 The lower system board may be damaged. Replace the lower system board.
T200/T200CS 2-29

2.9 Tablet Troubleshooting
To determine if the tablet is functioning properly, perform the following procedures. Before
diagnosing the tablet, however, try using it. If the writing does not feel right, replace the
stylus tip. If it still has trouble, start with Procedure 1.
Procedure 1: Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
Procedure 2: Connector and Replacement Check
Procedure 1 Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
Execute the Tablet Test of the Diagnostic Program. Refer to Chapter 3, Tests and Diagnostics, for more information on how to perform the test program.
If an error occurs, go to Procedure 2.
Procedure 2: Connector and Replacement Check
The tablet is connected to the system board by a cable. This cable may be disconnected or
damaged. Disassemble the computer as described in Chapter 4, Replacement Procedures, and
perform the following checks:
Check 1 Make sure the tablet cable is not damaged and is connected to the lower system
board. If this cable is damaged, replace it with a new one. If the cable is disconnected, firmly re-connect it. Perform Procedure 1 again. If the tablet is still not
functioning properly, perform Check 2.
Check 2 The tablet may be damaged. Replace the tablet with a new one. Refer to Chapter
4, Replacement Procedures, for more information. If the tablet is still not functioning properly, perform Check 3.
Check 3 The lower system board may be damaged. Replace the lower system board. Refer
to the instructions in Chapter 4, Replacement Procedures for more information. If
the tablet is still not functioning, replace the upper system board.
2-30 T200/T200CS

3.1 The Diagnostic Test
This chapter explains how to use the T200/T200CS's Diagnostic Test program to test hardware module functions. The Diagnostics Test Program is stored on the Diagnostic Disk. The
Diagnostic Test consists of 20 programs grouped into the Service Program Module (DIAGNOSTICS MENU) and Test Program Module (DIAGNOSTIC TESTS).
The DIAGNOSTICS MENU consists of the following eight functions:
❑ DIAGNOSTIC TEST
❑ HARD DISK FORMAT
❑ HEAD CLEANING
❑ LOG UTILITIES
❑ RUNNING TEST
❑ FDD UTILITIES
❑ SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
❑ SETUP
The DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu contains the following twelve functional tests:
❑ SYSTEM TEST
❑ MEMORY TEST
❑ KEYBOARD TEST
❑ DISPLAY TEST
❑ FLOPPY DISK TEST
❑ PRINTER TEST
❑ ASYNC TEST
❑ HARD DISK TEST
❑ REAL TIMER TEST
❑ PCMCIA TEST
❑ TABLET TEST
❑ NDP TEST
The following equipment is needed to perform some test programs.
❑ T200/T200CS Diagnostics Disk (all tests)
❑ Optional external 3.5-inch FDD
❑ Formatted working disk for the floppy disk drive test
❑ Cleaning kit to clean floppy disk drive heads (Head Cleaning)
❑ Printer wraparound connector for the printer wraparound (Printer) test
❑ RS-232C wraparound connector for the RS-232C port wraparound (ASYNC) test
❑ Parallel cable for the printer wraparound (Printer) test
❑ External PS/2 type keyboard (Keyboard test)
❑ PCMCIA wraparound connector for the I/O card (PCMCIA) test
❑ Stylus
The following sections detail DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu tests. Refer to sections 3.18
through 3.24 for detailed information on the other Service Program Module functions.
T200, T200CS 3-1

3.2 Executing the Diagnostic Test
To start the Diagnostic Test Program follow the steps below. The Diagnostic Test Program
can be executed with either the stylus or an optional keyboard.
1. Connect an optional 3.5-inch floppy disk drive.
2. Connect an external keyboard (Keyboard Test), RS-232C wraparound connector
(Async Test), parallel cable (Printer Test), PCMCIA wraparound connector
(PCMCIA Test), and printer wraparound connector (Printer Test) to each port.
3. Insert the Diagnostic disk and turn on the computer.
4. A cross-hair cursor will appear. Tap the cursor or press Enter.
The following menu will appear:
TOSHIBA Personal Computer XXXXX DIAGNOSTICS
Version 1.XX (C) Copyright TOSHIBA Corp. 19XX
DIAGNOSTICS MENU :
1 - DIAGNOSTIC TEST
2 - HARD DISK FORMAT
3 4 - HEAD CLEANING
5 - LOG UTILITIES
6 - RUNNING TEST
7 - FDD UTILITIES
8 - SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
9 - EXIT TO MS-DOS
0 - SETUP
Break Break
0 A
1 B
2 C
3 D
4 E
5 F
6
7 Up-Aw
8 Dn-Aw
9 R-Aw
R L-Aw
BS Esc
↑ ↓ → ← : Select items Enter : Specify Esc : Exit
NOTES: • To use the stylus, tap the appropriate number or command in the
menu at right. "Up-Aw" is up arrow, "Dn-Aw" is down arrow, "R-Aw'"
is right arrow, "L-Aw" is left arrow, "Esc" is escape and "BS" is back
space.
• To use a keyboard, set the highlight bar to the desired test, and press
Enter.
• To exit the menu, tap or press Esc. If a test program is in progress,
tap "Break" or press Ctrl+Break to exit the test program.
3-2 T200, T200CS
Enter Enter

5. To execute the DIAGNOSTIC TEST MENU from the DIAGNOSTICS MENU,
move the highlight bar to 1, then tap or press Enter. The following DIAGNOSTIC TEST MENU will appear:
TOSHIBA Personal Computer XXXXX DIAGNOSTICS
Version 1.XX (C) Copyright TOSHIBA Corp. 19XX
DIAGNOSTICS TEST MENU :
1 - SYSTEM TEST
2 - MEMORY FORMAT
3 - KEYBOARD TEST
4 - DISPLAY TEST
5 - FLOPPY DISK TEST
6 - PRINTER TEST
7 - ASYNC TEST
8 - HARD DISK TEST
9 - REAL TIMER TEST
10 - PCMCIA TEST
11 TABLET TEST
12 - NDP TEST
88 - ERROR RETRY COUNT SET : ( FDD & HDD )
99 - EXIT TO DIAGNOSTICS MENU
Break Break
0 A
1 B
2 C
3 D
4 E
5 F
6
7 Up-Aw
8 Dn-Aw
9 R-Aw
R L-Aw
BS Esc
↑ ↓ → ← : Select items Enter : Specify Esc : Exit
Enter Enter
Refer to sections 3.4 through 3.15 for detailed descriptions of Diagnostic Tests 1
through 12. Function 88 sets the floppy disk drive and hard disk drive error retry
count. Function 99 exits the submenus of the Diagnostic Test and returns to the
DIAGNOSTICS MENU.
T200, T200CS 3-3

6. Move the highlight bar to the option you want to execute and tap or press Enter.
When you select SYSTEM TEST, the following message will appear:
SYSTEM TEST TTSSDSS
SUB TEST : XX
PASS COUNT : XXXXX ERROR COUNT: XXXXX
WRITE DATA : XX READ DATA : XX
ADDRESS : XXXXX STATUS : XXX
error status name
SUB-TEST MENU :
01 - ROM checksumum
02 - HW status
03 - Version check
99 - Exit to DIAGNOSTIC TEST MENU
Break Break
0 A
1 B
2 C
3 D
4 E
5 F
6
7 Up-Aw
8 Dn-Aw
9 R-Aw
R L-Aw
BS Esc
↑ ↓ → ← : Select items Enter : Specify Esc : Exit
Enter Enter
3-4 T200, T200CS

7. Move the highlight bar to the desired option from the subtest menu and tap or
press Enter. The following message will appear:
TEST LOOP : YES NO
Selecting YES increases the pass counter by one each time the test cycle ends and
restarts.
Selecting NO returns the sub-test menu to the main menu after the test is complete.
8. After making the Test Loop selection, the following message will appear:
ERROR STOP: YES NO
Selecting YES stops the test program when an error is found and displays the
operation guide on the right side of the display screen as shown below:
ERROR STATUS NAME [[ HALT OPERATION ]]
1: Test end
2: Continue
3: Retry
These three selections have the following functions:
1: Terminates the test program and exits to the subtest menu.
2: Continues the test.
3: Restarts the test from the beginning.
Selecting NO keeps the test running even if an error is found.
9. Move the highlight bar to the desired option and tap or press Enter.
Table 3-1 in Section 3.3 describes the function of each test on the subtest menu.
Table 3-3 in Section 3.16 describes the error codes and error status for each error.
T200, T200CS 3-5

3.3 Subtest Names
Table 3-1 lists subtest names for each test program in the DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu.
Table 3-1 Subtest Names (1/2)
No. Test name Subtest No. Subtest item
1 SYSTEM 01 ROM checksum
02 H/W status
03 Version check
2 MEMORY 01 RAM constant data
02 RAM address pattern data
03 RAM refresh
04 Protected mode
05 Memory module
06 Backup memory
07 Cache memory
3 KEYBOARD 01 Pressed key code display
4 DISPLAY 01 VRAM read/write
02 Character attributes
03 Character set
04 80x25/30 Character display
05 320x200 Graphics display
06 640x200 Graphics display
07 640x350/400/480 Graphics display
08 Display page
09 “H” pattern display/Border color
10 DAC pallet
11 VGA color graphics display
5 FDD 01 Sequential read
02 Sequential read/write
03 Random address/data
04 Write specified address
05 Read specified address
6 PRINTER 01 Ripple pattern
02 Function
03 Wraparound
3-6 T200, T200CS

Table 3-1 Subtest Names (2/2)
No. Test name Subtest No. Subtest item
7 ASYNC 01 Wraparound (board)
02 Board (#1) <=> board (#2)
03 Point to point (send)
04 Point to point (receive)
05 Interrupt test
8 HDD 01 Sequential read
02 Address uniqueness
03 Random address/data
04 Cross talk & peak shift
05 Write/read/compare (CE)
06 Write specified address
07 Read specified address
08 ECC circuit
09 Sequential write
10 W-R-C specified address
9 REAL TIMER 01 Real time
02 Backup memory
03 Real time carry
10 PCMCIA 01 I/O card test (PCMCIA)
11 TABLET 01 TABLET ADJUST
02 9POINT test
03 CURSOR MOVING test
04 WRITE DOT test
12 NDP 01 NDP test
T200, T200CS 3-7

3.4 System Test
To execute the System Test, select 1 from the DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu and tap or press
Enter. The system test contains three subtests. Select a subtest and tap or press Enter.
Subtest 01 ROM checksum
ROM checksum tests the system board from address F0000h to FFFFFh
(64KB).
Subtest 02 H/W status
This test reads and displays hardware status as shown below:
76543210
H/W status = 10001000
Bit7 ... =
Bit6 ... CPU clock = 40MHz
Bit5 ... Notch signal = 2HD
Bit4 ... FDD type = 2MB
Bit3 ... =
Bit2 ... Drive A/B = Ext. = B
Bit1 ... External FDD = OFF
Bit0 ... Internal FDD = 2HD
Table 3-2 lists hardware bit status for each bit tested. Press Enter to return to
the Subtest Menu.
Table 3-2 Hardware Bit Status
Bit H/W status 1 0
7 Reserved — —
6 CPU clock speed 20 MHz 40 MHz
5 Media type 2DD 2HD
4 FDD type 1.6 MB 2 MB
3 Reserved — —
2 Drive A/B Ext. = A Ext. = B
1 External FDD ON OFF
0 Internal FDD 2DD 2HD
3-8 T200, T200CS

Subtest 03 Version check
This subtest checks versions for the following items:
❑ BIOS ROM
❑ BOOT ROM
❑ KBC version
❑ PS microprocessor
The subtest compares the items to test program reference data. When the read
information is lower than the reference data, the speaker sounds, and the
following screen image is displayed. Press the S key to exit. The display is
unchanged if the read information is higher.
ROM-BIOS = V1.00 : OK V1.10
ROM(BOOT) = V1.00 : OK V1.00
KBC Version = V1.26 : NG V1.00
PS Micom Version = V1.35 : OK V1.35
Reference data
Current data
T200, T200CS 3-9

3.5 Memory Test
To execute the Memory Test, select 2 from the DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu and tap or press
Enter. Select a subtest to execute and tap or press Enter.
Subtest 01 RAM constant data (real mode)
This subtest writes constant data to conventional memory (0 to 640 KB), then
reads the new data and compares the result with original data.
Constant data is FFFFh, AAAAh, 5555h, and 0000h.
Subtest 02 RAM address pattern data (real mode)
This subtest writes address pattern data created by the exclusive-ORing
(XORing) to the address segment and address offset in conventional memory
(program end to 640 KB), then reads the new data and compares the result
with original data.
Subtest 03 RAM refresh (real mode)
This subtest writes a 256-byte unit of constant data to conventional memory (0
to 640 KB) then reads the new data and compares the result with original data.
Constant data is AAAAh and 5555h.
NOTE: There is a short delay between write and read operations, depending on
data size.
Subtest 04 Protected mode
This subtest writes constant data and address data to extended memory (from
100000h to the maximum address) then reads new data and compares the
result with original data.
3-10 T200, T200CS

Subtest 05 Memory module
NOTE: To execute this subtest, an optional memory card must be installed in the
computer.
This subtest functions the same as subtest 04 but is used for testing an optional
memory card. Memory module capacity is 2, 4, 8, or 16 MB.
After selecting subtest 05, the following message will appear:
Extended memory size (1:2 MB,2:4 MB,3:8 MB,4:16 MB) ?
Select the number corresponding to the installed memory card.
Subtest 06 Backup Memory
This subtest writes constant data to memory from address C8000h to CFFFFh,
then reads new data and compares the result with original data.
Constant data is 0000h, 5555h, AAAAh, and FFFFh.
Subtest 07 Cache memory
To test cache memory, a pass-through write-read comparison of ‘5A’ data is
run repeatedly to a test area ('7000':'Program' size to '7000':='7FFF' (32 KB))
to check hit-miss ratio (on/off status). One test takes 3 seconds.
Number of miss hit < Number of hit → OK
Number of miss hit > Number of hit → Fail
T200, T200CS 3-11

3.6 Keyboard Test
To execute the Keyboard Test, select 3 from the DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu, tap or press
Enter, and follow the directions displayed on the screen. Subtest 01 tests keyboard actions.
Tap or press Enter to select the subtest.
Subtest 01 Pressed key code display
When a key is pressed, the scan code, character code, and key top name are
displayed on the screen in the format shown below. The Ins, Caps Lock,
Num Lock, Scroll Lock, Alt, Ctrl, Left Shift, and Right Shift keys are
displayed in reverse screen mode when pressed. Scan codes, character codes,
and key top names are shown in Appendix E.
KEYBOARD TEST IN PROGRESS 301000
Scan code =
Character code =
Keytop =
Ins Lock Caps Lock Num Lock Scroll Lock
Alt Ctrl Left Shift Right Shift
PRESS [Enter] KEY
3-12 T200, T200CS

3.7 Display Test
To execute the Display Test, select 4 from the DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu and tap or press
Enter. Eleven subtests test the display in various modes. Select a subtest and tap or press
Enter.
NOTE: In the Display Test, the screen does not display "Break" or "Enter." Tap
the upper right corner of the screen to enter "Break" or the lower right corner to enter
"Enter."
Subtest 01 VRAM Read/Write
This subtest writes constant data FFFFh, AAAAh, 5555h, 0000h and address
data to video RAM (1MB). (CGA (B8000H ~ BFFFFH: 32KB) and VGA
(A0000H ~ AFFFFH:64KB*4*4)). This data is then read from the video
RAM and compared to original data.
Subtest 02 Character Attributes (mode 1, 13h)
This subtest displays four character attribute modes; normal, intensified,
reverse, and blinking. The character attribute modes display foreground and
intensified color (16 colors or 16-level gray scale) using black, blue, red,
magenta, green, cyan, yellow, and white from the color display. The following
display appears when the subtest is executed.
CHARACTER ATTRIBUTES
NEXT LINE SHOWS NORMAL DISPLAY.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
NEXT LINE SHOWS INTENSIFIED DISPLAY.
IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
NEXT LINE SHOWS REVERSE DISPLAY. RRR
R RRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRR
NEXT LINE SHOWS BLINKING DISPLAY
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
00 08 ; BLACK
01 09 ; BLUE
04 0C ; RED
05 0D ; MAGENTA
02 0A ; GREEN
03 0B ; CYAN
06 0E ; YELLOW
07 0F ; WHITE
PRESS [Enter] KEY
T200, T200CS 3-13

Pressing Enter causes 16 colors or gray scales of mode 13h to appear in the
320x200 graphics mode as shown below:
320*200 GRAPHICS DISPLAY [ 13 ]
BLACK
BLUE
GREEN
CYAN
RED
MAGENTA
BROWN
WHITE
GRAY
LIGHT BLUE
LIGHT GREEN
LIGHT CYAN
LIGHT RED
LIGHT MAGENTA
YELLOW
INTENSE WHITE
PRESS [Enter] KEY
Pressing Enter toggles between the two displays.
To exit to the DISPLAY TEST menu, press Ctrl + Break.
Subtest 03 Character Set
In this subtest, the character set (address 00h to FFh) is displayed in the 40x25
character mode as shown below.
PRESS [Enter] KEY
To exit to the DISPLAY TEST menu, press Ctrl + Break.
3-14 T200, T200CS

Subtest 04 80x25/30 Character Display (mode 3, 12)
In this subtest, the character string is displayed shifting one character to the right,
line by line in the 80x25 and 80x30 character modes as shown below.
80*XX CHARACTER DISPLAY
012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567
!”#$%&’()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklm
!”#$%&’()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmn
“#$%&’()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmno
#$%&’()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnop
$%&’()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopq
%&’()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqr
&’()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrs
‘()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrst
()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstu
)*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuv
*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvw
+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwx
,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxy
-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{
/0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|
0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}
123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~
23456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~∆
3456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~∆
456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~∆Çü
PRESS[ENTER]KEY
Pressing Enter toggles between tests. To exit to the DISPLAY TEST menu, press
Ctrl + Break.
Subtest 05 320x200 Graphics Display (mode 4,D)
This subtest displays two color sets for the color display in 320x200 dot graphics
mode 4 and D. One example is shown below:
320*200 GRAPHICS DISPLAY
COLOR SET X : [X]
GREEN RED BROWN
CYAN MAGENTA WHITE
PRESS [Enter] KEY
Pressing Enter toggles between tests. To exit to the DISPLAY TEST menu, press
Ctrl + Break.
T200, T200CS 3-15

Subtest 06 640x200 Graphics Display (mode 6, E)
This subtest displays even, odd, and all dots in 640x200 dot graphics mode 6 and E
as shown below:
640*200 GRAPHICS DISPLAY : [x]
EVEN DOTS ODD DOTS ALL DOTS
DRIVEN DRIVEN DRIVEN
PRESS [ENTER] KEY
To exit to the DISPLAY TEST menu, press Ctrl + Break.
Subtest 07 640x350/400/480 Graphics Display (mode 10, 74, 12)
This subtest displays even, odd, and all dots in 640x350, 640x400 and 640x480
dot graphics mode 10, 74, 12 as shown below:
640*XXX GRAPHICS DISPLAY
EVEN DOTS ODD DOTS ALL DOTS
DRIVEN DRIVEN DRIVEN
PRESS [ENTER] KEY
Press Enter to change displayed image size. To exit to the DISPLAY TEST
menu, press Ctrl + Break.
3-16 T200, T200CS

Subtest 08 Display Page
This subtest confirms that pages can be changed in order from 0 through 7 in 40x25
character mode.
DISPLAY PAGE 0
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Press Ctrl + Break to exit after test completion and return to the DISPLAY
TEST menu.
Subtest 09 H Pattern Display/Border Color
This subtest displays 2000 H characters on the entire screen, as shown below.
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
Pressing Enter displays the following message:
Setting the color CRT (1:yes/2:no)
If an external CRT is connected to the computer, choose 1 to display the following
message:
[Border color test (press [Enter] key 7 times)]
Press Enter to execute the border color test.
To exit to the DISPLAY TEST menu, press Ctrl + Break.
T200, T200CS 3-17

Subtest 10 DAC Pallet
This subtest writes the ‘2A’ and ‘15’ data to 6 bits of 256x3 (RGB), then reads
new data and compares the result with original data.
[ DAC pallet W-R-CMP test ] = (about 5 seconds)
[ Processor latch test ]
Processor latch test (1:256 times, 2:endless) ?
To exit, press Ctrl + Break. Then press Enter.
Subtest 11 VGA color graphics display
This subtest displays eight screens. The first screen shows many colors (mode 13)
at once. The next three display 64 shades (mode 13) of red, green, and blue
successively. Next, a single screen displays many colors (mode 5F). The last three
display 256 shades of red, green and blue.
Press Enter to change the display. Press Ctrl + Break to exit.
3-18 T200, T200CS

3.8 Floppy Disk Test
CAUTION: Before running the floppy disk test, prepare a formatted work disk. Remove the Diagnostics Disk and insert a work disk into the FDD. The contents of the
floppy disk will be erased.
To execute the Floppy Disk Test, select 5 from the DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu, tap or press
Enter, and follow the directions displayed on the screen. Five subtests test the internal floppy disk
drive. The following messages will appear after the Floppy Disk Test is selected. Answer each
question with an appropriate response to execute the test.
1. Select the test drive number of the floppy disk drive to be tested and tap or press
Enter.
Test drive number select : FDD#1 FDD#2 FDD1&2
2. Select the media type of the floppy disk to be tested, and tap or press Enter.
Media in drive #X mode : 2DD 2D, 2D-2HD 2HD
3. Select the track to start the test on and tap or press Enter. Tapping or pressing
Enter alone sets the start track to zero.
Test start track (Enter:0/dd:00-79) ?
4. The floppy disk test menu will appear after the start track number is selected. Select a
subtest number and tap or press Enter. The following message will appear during the
test.
FLOPPY DISK XXXXXXX
SUB-TEST : XX
PASS COUNT : XXXXX ERROR COUNT : XXXXX
WRITE DATA : XX READ DATA : XX
ADDRESS : XXXXXX STATUS : XXX
The first three digits in the ADDRESS number indicate the cylinder being tested. The
fourth indicates the head, and the last two indicate the sector being tested.
The first digit in the STATUS number indicates the drive being tested and the last two
indicate the error status code as explained in Table 3-3.
T200, T200CS 3-19

Subtest 01 Sequential Read
This subtest performs a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) that continuously reads
all tracks on a floppy disk. The following tracks are read according to the media
type in the FDD:
Double-sided, double-density (2D): Tracks 0 to 39.
Double-sided, double-density, double-track (2DD) and double-sided,
high-density, double-track (2HD): Tracks 0 to 79.
A start track is specified when the FDD test is started from the Diagnostic Test
Menu. Refer to step 3 at the beginning of this section to set the start track.
Subtest 02 Sequential Read/Write
This subtest continuously writes data pattern B5ADADh to all the specified tracks
selected in subtest 01. Data is then read and compared to the original data.
Subtest 03 Random Address/Data
This subtest writes random data to random addresses on all tracks defined in
subtest 01. Data is then read and compared to the original data.
Subtest 04 Write Specified Address
This subtest writes specified data to a specified track, head, and address.
When this subtest is selected, the following prompts appear on the screen in succession.
TEST DATA ??
TRACK NO ??
HEAD NO ??
Subtest 05 Read Specified Address
This subtest reads data from a specified track, head, and address.
When this subtest is selected, the following prompts appear on the screen in succession.
TRACK NO ??
HEAD NO ?
3-20 T200, T200CS

3.9 Printer Test
To execute the Printer Test, select 6 from the DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu, tap or press
Enter, and follow the directions displayed on the screen. Three subtests test printer output.
NOTE: An IBM-compatible printer with a parallel cable must be connected to the
system to execute this test.
The following message will appear when the printer test is selected:
channel#1 = XXXXh
channel#2 = XXXXh
channel#3 = XXXXh
Select the channel number (1-3) ?
The printer I/O port address is specified by the XXXXh number. The T200/T200CS supports
three printer channels. Select the appropriate printer channel number, and tap or press Enter
to execute a subtest.
Subtest 01 Ripple Pattern
This subtest prints characters for codes 20h through 7Eh line-by-line while
shifting one character to the left at the beginning of each new line.
!"#$%£'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmno
!"#$%£'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnop
"#$%£'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopq
#$%£'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqr
$%£'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrs
%£'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrst
£'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstu
'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuv
()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvw
)*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwx
*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxy
T200, T200CS 3-21

Subtest 02 Function
This subtest is for IBM-compatible printers, and tests the following functions:
Normal print
Double-width print
Compressed print
Emphasized print
Double-strike print
All characters print
This subtest prints the various print types shown below:
PRINTER TEST
1. THIS LINE SHOWS NORMAL PRINT.
2. THIS LINE SHOWS DOUBLE-WIDTH PRINT.
3. THIS LINE SHOWS COMPRESSED PRINT.
4. THIS LINE SHOWS EMPHASIZED PRINT.
5. THIS LINE SHOWS DOUBLE-STRIKE PRINT.
6. ALL CHARACTERS PRINT
!”#$%&’()*+,./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmn
opqrstuvwxyz{|}~
Subtest 03 Wraparound
NOTE: To execute this subtest, a printer wraparound connector with a parallel
cable must be connected to the computer printer port. The printer wraparound
connector (34M741986G01) wiring diagram is shown in Appendix F.
This subtest checks output and bidirectional modes of the data control and
status lines through the printer wraparound connector.
3-22 T200, T200CS

3.10 Async Test
To execute the Async Test, select 7 from the DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu, tap or press
Enter, and follow the directions displayed on the screen. Five subtests test asynchronous
communication functions. Move the highlight bar to a subtest and press Enter.
Subtests 01 through 04 require the following data format:
Method: Asynchronous
Speed: 9600BPS
Data: 8 bits and one parity bit (EVEN)
Data pattern: 20h to 7Eh
The following message will appear at the bottom of the screen when subtests 01, 03, and 04
are selected:
Channel#1 = XXXXh
Channel#2 = XXXXh
Channel#3 = XXXXh
Select the Channel number (1/2/3) ?
The serial I/O port address is specified by the XXXXh number. Select the serial port channel
number and press Enter to start the subtest.
Subtest 01 Wraparound (board)
NOTE: An RS-232C wraparound connector(34M741621G01) must be connected
to the RS-232C port by a parallel cable to execute this subtest. The wraparound
connector wiring diagram is shown in Appendix F.
This subtest checks the data send/receive function through the wraparound
connector.
Subtest 02 Board (#1) <=> board (#2)
NOTE: To execute this subtest, an RS-232C cable (9-pin to 9-pin) must be connected to boards 1 and 2. The RS-232C direct cable wiring diagram is shown in
Appendix F.
This subtest checks the data send/receive function through the RS-232C direct
cable.
T200, T200CS 3-23

Subtest 03 Point to point (Send)
NOTE: To execute this subtest, two machines must be connected by a parallel
cable to the RS-232C ports. One machine should be set as “send”(subtest
03) and the other as "receive" (subtest 04). The wiring diagram for the RS232C direct cable is shown in Appendix F.
This subtest sends 20h through 7Eh data to the receive side, then receives the
sent data and compares it to the original data.
Subtest 04 Point to point (Receive)
This subtest is used with subtest 03. This subtest receives data from the send
side, then sends the received data.
Subtest 05 Interrupt Test
This subtest checks the Interrupt Request Level of IRQ 4, 3 and 5 from the
send side.
3-24 T200, T200CS

3.11 Hard Disk Test
To execute the Hard Disk Test, select 8 from the DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu, tap or press
Enter, and follow the directions displayed on the screen. Ten subtests test the HDD func-
tions. The following messages will appear after the hard disk test is selected. Answer each
question with an appropriate response.
CAUTION: The contents of the hard disk will be erased when subtest 02, 03, 04, 05,
06, 08, 09, or 10 is executed. Before running the test, transfer the contents of the hard
disk to a floppy disk(s).
After the hard disk test is completed, set the partition. Refer to the customer's operating system documentation for details on partitioning the disk .
1. When the hard disk test is selected, the following message will appear:
Test drive number select : HDD#1 HDD#2 HDD1&2
2. Select the HDD number to be tested and tap or press Enter. The following mes-
sage will appear:
HDC F/W error retry : YES NO
3. This message is used to select the retry operation when the hard disk controller
detects an error. Select 1 or 2 and tap or press Enter. The following message
will appear:
Data compare error dump : NO YES
4. This message is used to select the error dump operation when a data compare
error is detected. Select 1 or 2 and tap or press Enter. The following message
will appear:
Detail status display : NO YES
5. This message is used to select HDD status for display or non-display. The HDD
status is described in section 3.17. Select 1 or 2 and tap or press Enter.
6. The Hard Disk Test message will appear after a response to the Detail Status
prompt. Select a subtest to execute and tap or press Enter. The following message will appear during each subtest.
HARD DISK TEST XXXXXXX
SUB-TEST : XX
PASS COUNT : XXXXX ERROR COUNT : XXXXX
WRITE DATA : XX READ DATA : XX
ADDRESS : XXXXXX STATUS : XXX
T200, T200CS 3-25

The first three digits of the ADDRESS indicate the cylinder being tested, the
fourth digit indicates the head, and the last two digits indicate the sector.
The first digit of the STATUS number indicates the drive being tested, and the last
two digits indicate the error status code as explained in Table 3-3.
Subtest 01 Sequential Read
This subtest is a sequential reading of all HDD tracks starting at 0. When all
tracks have been read, the test starts at the last track and reads sequentially
back to track 0.
Subtest 02 Address Uniqueness
This subtest writes unique address data to each sector track-by-track. The
data written to each sector is then read and compared with the original data.
There are three ways the HDD can be read:
• Forward sequential
• Reverse sequential
• Random
Subtest 03 Random Address/Data
This subtest writes random data to random addresses on the HDD cylinder,
head, and sector. This data is then read and compared to the original data.
Subtest 04 Cross Talk & Peak Shift
This subtest writes eight types of worst pattern data (shown below) to a
cylinder, then reads the data from cylinder to cylinder.
Worst pattern data Cylinder
‘B5ADAD’ 0 cylinder
‘4A5252’ 1 cylinder
‘EB6DB6’ 2 cylinder
‘149249’ 3 cylinder
’63B63B’ 4 cylinder
‘9C49C4’ 5 cylinder
‘2DB6DB’ 6 cylinder
‘D24924’ 7 cylinder
Subtest 05 Write /read/compare (CE)
This subtest writes B5ADADh worst pattern data to the CE cylinder on the
HDD, then reads the data and compares it with the original data.
3-26 T200, T200CS

Subtest 06 Write specified address
This subtest writes specified data to a specified cylinder and head.
Subtest 07 Read specified address
This subtest reads data written to a specified HDD cylinder and head.
Subtest 08 ECC circuit
This subtest checks the Error Check and Correction (ECC) circuit functions of
a specified HDD cylinder and head.
Subtest 09 Sequential write
This subtest writes specified 2-byte data to all HDD cylinders.
Subtest 10 W-R-C specified address
This subtest writes data to a specified HDD cylinder and head, then reads the
data and compares it to the original data.
T200, T200CS 3-27

3.12 Real Timer Test
To execute the Real Timer Test, select 9 from the DIAGNOSTIC TESTS menu, tap or press
Enter, and follow the directions on the screen. Three subtests test the real timer functions.
Select a subtest and tap or press Enter.
Subtest 01 Real Time
A new date and time can be input during this subtest. To execute this subtest
follow these steps:
1. Select subtest 01 and the following message will appear:
Current date : XX-XX-XXXX
Current time : XX:XX:XX
Enter new date:
PRESS [ENTER] KEY TO EXIT TEST
2. If the current date is not correct, input the correct date at the “Enter new
date” prompt and press Enter. The following prompt will appear:
Enter new time :
3. If the current time is not correct, input the correct time in 24-hour format.
Pressing Enter toggles between the time and date. To exit, press Ctrl +
Break
.
Subtest 02 Backup Memory
This subtest performs the following backup memory check:
Writes 1-bit of “on” data to address 01h through 80h
Writes 1-bit of “off” data to address FEh through 7Fh
Writes the data pattern AAh through 55h to the RTC 50-byte memory
(address 0Eh to 7Fh)
The subtest then reads and compares this data with original data.
To exit, press Ctrl + Break.
3-28 T200, T200CS

Subtest 03 Real Time Carry
CAUTION: When this subtest is executed, the current date and time are
erased.
This subtest checks real time clock increments, verifying the date and time are
displayed in the following format:
Current date : 12-31-1992
Current time : 23:59:58
Pressing Enter displays the following
Current date : 01-01-1993
Current time : 00:00:00
PRESS [Enter] KEY TO EXIT TEST
Press Ctrl + Break to exit.
T200, T200CS 3-29

3.13 PCMCIA Test
NOTE: The PCMCIA wraparound card is required to execute this subtest.
Subtest 01 I/O Card Test (PCMCIA)
This test checks the following signal lines of the PCMCIA slot:
❑ Address line
❑ REG#, CE#1, CE#2 line
❑ Data line
❑ Speaker line
❑ Wait line
❑ BSY#, BVD1 line
This subtest is executed in the following order:
Sub# Address Good Bad Contents
01 00001 nn xx Address line
00001 nn xx REG#, CE#1, CE#2
02 00002 ww rr Data line
03 00003 –– –– Speaker line
04 00004 40, 80 xx Wait line (40<xx<80)
05 00005 nn xx Other lines (BSY#, BVD1)
nn=A0, 90, 80, 00
ww=write data, rr=read data
nn=21, 00
3-30 T200, T200CS

3.14 Tablet Test
To execute the Tablet Test, select 11 from the DIAGNOSTIC TEST MENU, and tap or
press Enter. The tablet test contains four subtests that test the computer's tablet functions.
Subtest 01 TABLET ADJUST
This test displays the coordinates of the screen matrix when the pen is tapped
on the screen and a key on the optional keyboard is pressed simultaneously.
After testing coordinates, press Enter to display a cross-hair cursor. Tap the
cursor at the center to complete the test.
Subtest 02 9 POINT test
This test checks the screen matrix addresses. Nine cross-hair cursors appear.
Tap each cursor. If the tapped position corresponds to the cursor coordinate,
the cursor disappears. When all cursors are cleared, the test is over.
Subtest 03 CURSOR MOVING test
This test checks the address and the stylus's switch. A cross-hair cursor appears. Tap and move the cursor. The cursor's address will appear on the right
side of the display. The stylus switch's on/off status is also displayed.
Subtest 04 WRITE DOT test
This test draws a line. Tap and move the stylus on the screen to draw a line.
T200, T200CS 3-31

3-32 T200, T200CS

3.15 NDP Test
To execute the NDP test, select 12 from the DIAGNOSTIC TEST MENU, and tap or press
Enter. The NDP test contains one subtest that tests the computer's NDP functions.
Subtest 01 NDP
This test checks the following functions of NDP:
❑ Control word
❑ Status word
❑ Bus
❑ Addition
❑ Multiplication
Press Ctrl + Break to exit.
T200, T200CS 3-33

3.16 Error Codes and Error Status Names
Table 3-3 lists error codes and error status names for the Diagnostic Test.
Table 3-3 Error Codes and Error Status Names (1/2)
Device name Error code Error status name
(COMMON) FF Data Compare Error
SYSTEM 01 ROM Checksum Error
Memory 01 Parity Error
02 Protected Mode Not Changed
14 Memory Read/Write Error
DD Cache Memory Error
Keyboard 02 IPS Interface Error
03 Interface Error
04 Retransmit Error
FDD 01 Bad Command
02 Address Mark Not Found
03 Write Protected
04 Record Not Found
06 Media Removed
08 DMA Overrun Error
09 DMA Boundary Error
10 CRC Error
20 FDC Error
40 Seek Error
60 FDD Not Drive Error
80 Time Out Error
EE Write Buffer Error
Printer 01 Time Out
08 Fault
10 Select Line
20 Out Of Paper
40 Power Off
80 Busy Line
ASYNC 01 DSR Off Time Out
02 CTS Off Time Out
04 RX-READY Time Out
08 TX-BUFFER Full Time Out
10 Parity Error
20 Framing Error
40 Overrun Error
80 Line Status Error
88 Modem Status Error
3-34 T200, T200CS

Table 3-3 Error Codes and Error Status Names (2/2)
Device name Error code Error status name
HDD 01 Bad Command Error
02 Address Mark Not Found
04 Record Not Found
05 HDC Not Reset Error
07 Drive Not Initialized
08 HDC Overrun (DRQ)
09 DMA Boundary Error
0A Bad Sector
0B Bad Track Error
10 ECC Error
11 ECC Recover Enable
20 HDC Error
40 Seek Error
80 Time Out Error
AA Drive Not Ready
BB Undefined Error
CC Write Fault
E0 Status Error
EE Access Time Out Error
NDP 01 No CO-PROCESSOR
02 Control Word Error
03 Status Word Error
04 Bus Error
05 Addition Error
06 Multiply Error
PCMCIA C1 Address Line Error
C2 REG# Line Error
C3 CE#1 Line Error
C4 CE#2 Line Error
C5 Data Line Error
C6 Wait Line Error
C7 BSY# Line Error
C8 BVD1 Line Error
CD No PCMCIA
TABLET 01 Tablet I/F Error
T200, T200CS 3-35

3.17 Hard Disk Test Detail Status
When an error occurs in the hard disk test, the following message is displayed:
HDC status = XXXXXXXX
Detailed information about the hard disk test error is displayed on the screen by an eight-digit
number. The first four digits represent the hard disk controller (HDC) error status number;
the last four digits are not used.
HDC error status is composed of two bytes; the first byte displays the contents of the HDC
status register in hexadecimal form, and the second displays the HDC error register.
The contents of the HDC status register and error register are described in Tables 3-4 and 35, respectively.
Table 3-4 Hard Disk Controller Status Register Contents
Bit Name Description
7 BSY “0” --- HDC is busy.
(Busy) “1” --- HDC is ready.
6 DRDY “0” --- Hard disk drive is not ready to accept any command.
(Drive ready) “1” --- Hard disk drive is ready.
5 DWF “0” --- DWF error is not detected.
(Drive write fault) “1” --- Write fault condition occurred.
4 DSC “0” --- The hard disk drive heads are not settled over a track.
(Drive seek “1” --- The hard disk drive heads are settled over a track.
complete)
3 DRQ “0” --- Drive is not ready for data transfer.
(Data request) “1” --- Drive is ready for data transfer.
2 CORR “0” --- Other
(Corrected data) “1” --- Correctable data error was corrected.
1 IDX “0” --- Other
(Index) “1” --- Index is sensed.
0 ERR “0” --- Other
(Error) “1” --- The previous command was terminated with some error.
Bit Name Description
3-36 T200, T200CS
Table 3-5 Error Register Contents

7 BBK1 “0” Other
(Bad block “1” A bad block mark was detected.
mark)
6 UNC “0”There is no uncorrectable data error.
(Uncorrectable) “1” Uncorrectable data error has been detected.
5 —— Not used
4 IDNF “0”Other
(Identification) “1” There was no ID field in the requested sector.
3 —— Not used
2 ABRT “0” Other
(Abort) “1” Illegal command error or a drive status error occurred.
1 TK00 “0” The hard disk found track 0 during a recalibrate command.
(Track 0) “1” The hard disk could not find track 0 during a recalibrate command.
0 —— Not used.
T200, T200CS 3-37

3.18 Hard Disk Format
This function performs a low-level (physical) hard disk format and also executes the following:
1. All track FORMAT
2. Good track FORMAT
3. Bad track FORMAT
4. Bad track CHECK
CAUTION: The hard disk will be erased when this program is executed. Before executing, transfer hard disk contents onto a floppy disk(s).
3.18.1 Function Description
1. All track FORMAT
This option performs a low-level format of all hard disk tracks as listed in Table 36 below.
NOTE: Before executing the All Track FORMAT option, check for bad tracks using
the Bad Track CHECK option, or display a list of bad tracks on the HDD.
Table 3-6 Hard Disk Formatting Sequence
80 MB
Items (ZA1094)
Sector sequences 1:1
Cylinders 0 to 2749
Heads 0 to 2
Sectors 1 to 20
Sector length (bps) 512
3-38 T200, T200CS

2. Good track FORMAT
This option formats a specified cylinder and track as a good track. If a good track
is formatted as a bad track, use this option to change the track to a good track.
3. Bad track FORMAT
This option formats a specified cylinder and track as a bad track. If a bad track is
detected, use this option to label it as a bad track.
4. Bad track CHECK
This option searches for bad tracks by reading data to all tracks. A list of bad
tracks is displayed when the program is complete. If an error other than a bad
track is detected, the program is terminated.
3.18.2 Operations
CAUTION: After the hard disk is formatted, set the partition. Refer to the customer's
operating system documentation for details on partitioning the disk.
Select 2 from the DIAGNOSTIC MENU and tap or press Enter to display the following
menu:
DIAGNOSTICS - HARD DISK FORMAT : VX.XX
1 - All track FORMAT
2 - Good track FORMAT
3 - Bad track FORMAT
4 - Bad track CHECK
9 - Exit to DIAGNOSTICS MENU
1. All track FORMAT
Tap or press 1 to select “All track FORMAT,” and format the entire disk.
[All track FORMAT]
Drive : #1 = HDD #2 = Non
Cylinder : XXXX
T200, T200CS 3-39

Head : XX
Sector : XX
<<< Model name = >>>
3-40 T200, T200CS

The following prompts display at the bottom of the screen in succession:
Drive number select (1:#1,2:#2) ?
(a) Select a drive number and tap or press Enter. The following message
appears:
Interleave number (1/1 ~ 8) ?
(b) Select an interleave number (1 ~ 8) and tap or press Enter. Tab or press
Enter only to select 1.
(c) Bad Track Register
Next, the Bad Track Register prompt appears. Enter the bad track cylinder
and head numbers and tap or press Enter. If there are no bad tracks, tap or
press Enter only to execute All Track Format as described in Item (d)
below.
[ WARNING : Current DISK data will be
completely destroyed ]
Press Bad cylinder number (dddd)] key ?
Press Bad head number (dd)] key ?
Enter the cylinder and head number in the format above in decimal notation.
Repeat for each bad track to format.
After entering the bad tracks, tap or press Enter to execute the format.
(d) All Track Format
All tracks are formatted as good tracks except those registered as bad tracks
in Item (c) above, or identified as bad tracks in the Track Verification function described in Item (e) below.
(e) Track Verification
A check is made of all tracks, and if an ECC, ECC-correctable, or recordnot-found track error is detected, the track is formatted as a bad track .
T200, T200CS 3-41

2. Good track FORMAT
If a good track has been erroneously formatted as a bad track, use this subtest to
reformat it as a good track. Enter the drive, interleave, cylinder, and head numbers
as indicated in the screen prompt shown below.
Drive number select (1:#1, 2:#2) ?
Interleave number (1 / 1 - 8) ?
Press [Cylinder number (dddd)] ?
Press [Head number (dd)] ?
Tap or press Enter to return to the Hard Disk Format menu.
3. Bad track FORMAT
To format a track as a bad track, enter the drive, interleave, cylinder, and head
numbers as indicated in the screen prompts shown below.
Drive number select (1:#1, 2:#2) ?
Interleave number (1 / 1 - 8) ?
Press [Cylinder number (dddd)] ?
Press [Head number (dd)] ?
Tap or press Enter to return to the Hard Disk Format menu.
4. Bad track CHECK
This subtest reads the entire disk and displays a bad track list. The test is terminated in case of a bad track check error. To initiate the subtest, enter the drive
number at the prompt shown below.
Drive number select (1:#1, 2:#2) ?
Bad tracks are displayed in the format shown below.
[[cylinder, head = 0123 03]]
Tap or press Enter to return to the Hard Disk Format menu.
3-42 T200, T200CS

3.19 Head Cleaning
3.19.1 Function Description
This function cleans FDD heads by executing a series of head load/seek and read operations.
A cleaning kit is required.
3.19.2 Operations
1. Select 4 from the DIAGNOSTIC MENU and tap or press Enter to display the
following messages:
DIAGNOSTICS - FLOPPY DISK HEAD CLEANING : VX.XX
Mount cleaning disk(s) on drive(s).
Press any key when ready.
2. Remove the Diagnostics Disk from the FDD, insert the cleaning disk, and tap or
press Enter.
3. When the cleaning start message appears, the FDD head cleaning has begun.
4. The display returns to the DIAGNOSTIC MENU when the program is completed.
T200, T200CS 3-43

3.20 Log Utilities
3.20.1 Function Description
This function logs error information generated while a test is in progress and stores the results
in RAM. Data can be stored on a floppy disk or output to a printer. If power is turned off,
the error information will be lost. Error information is displayed in the following order:
1. Error count (CNT)
2. Test name (TS-NAME)
3. Subtest number (TS-NAME)
4. Pass count (PASS)
5. Error status (STS)
6. FDD/HDD or memory address (ADDR)
7. Write data (WD)
8. Read data (RD)
9. HDC status (HSTS)
10. Error status name ( ERROR STATUS NAME)
3.20.2 Operations
1. Select 5 in the DIAGNOSTIC MENU and tap or press Enter to log error infor-
mation into RAM or to a floppy disk. Error information is displayed in the
following format:
XXXXX ERRORS
CNT TS-NAME PASS STS ADDR WD RD HSTS [STATUS NAME]
001 FDD 02 0000 103 00001 00 00 FDD-WRITE PROTECTED
001 FDD 01 0000 180 00001 00 00 FDD-TIME OUT ERROR
Address
Error status
Pass count HDC status
Subtest number Read data
Test name Write data
Error count Error status name
[[1:Next,2:Prev,3:Exit,4:Clear,5:Print,6:FD Log Read,7:FD Log Write]]
3-44 T200, T200CS

2. Error information on the screen can be manipulated by the following number keys:
1 scrolls the display to the next page.
2 scrolls the display to the previous page.
3 returns to the Diagnostic Menu.
4 erases all error log information in RAM.
5 outputs the error log information to a printer.
6 reads log information from a floppy disk.
7 writes log information to a floppy disk.
3. In the case of “error retry OK,” a capital “R” will be placed at the beginning of the
error status, but not added to the error count.
T200, T200CS 3-45

3.22 Floppy Disk Drive Utilities
3.22.1 Function Description
This function formats the FDD, copies the floppy disk, and displays the dump list for both the
FDD and HDD.
1. FORMAT
NOTE: This program is only for testing a floppy disk drive. The option is different
from the operating system's FORMAT command.
The program can format a 5.25-inch or 3.5-inch floppy disk in the following formats:
(a) 2D: Double-sided, double-density, 48/67.5 TPI, MFM mode, 512 bytes, 9
sectors/track.
(b) 2DD: Double-sided, double-density, double-track, 96/135 TPI, MFM mode,
512 bytes, 9 sectors/track.
(c) 2HD: Double-sided, high-density, double-track, 96/135 TPI, MFM mode,
512 bytes, 18 sectors/track.
2. COPY
This program copies data from a source floppy disk to a target floppy disk.
3. DUMP
This program displays floppy disk (both 3.5-inch and 5.25-inch) contents and
designated hard disk sectors.
3.22.2 Operations
1. Select 7 from the DIAGNOSTIC MENU and tap or press Enter to display the
following message:
[ FDD UTILITIES ]
1 - FORMAT
2 - COPY
3 - DUMP
9 - EXIT TO DIAGNOSTICS MENU
3-46 T200, T200CS

2. FORMAT program
(a) Select FORMAT to display the following message:
DIAGNOSTICS - FLOPPY DISK FORMAT : VX.XX
Drive number select (1:A, 2:B) ?
(b) Select a drive number to display the following message:
Type select (0:2DD-2DD,1:2D-2D,2:2D-2HD,3:2HD-2HD) ?
(c) Select a media/drive type number and press Enter to display a message
similar to the one below:
Warning : Disk data will be destroyed.
Insert work disk into drive A:
Tap Enter key when ready.
(d) Remove the Diagnostics Disk from the FDD, insert the work disk, and tap
Enter or press any key.
The following message will be displayed when the FDD format is executed:
[ FDD TYPE ] : TRACK = XXX
[ FDD TYPE ] : HEAD = X
[ FDD TYPE ] : SECTOR = XX
Format start
[[track, head = XXX X]]
After the floppy disk is formatted, the following message will appear:
Format complete
Another format (1:Yes/2:No) ?
(e) Type 1 to display the message from step (c) above. Type 2 to return to the
DIAGNOSTIC MENU.
3. COPY program
(a) Select COPY to display the following message:
FLOPPY DISK FORMAT & COPY : VX.XX
Type select (0:2DD-2DD,1:2D-2D,2:2D-2HD,3:2HD-2HD) ?
(b) Select a media/drive type number to display a message similar to the one
below:
Insert source disk into drive A:
Tap Enter key when ready.
T200, T200CS 3-47

(c) Remove the Diagnostics Disk from the FDD, insert the source disk, and tap
Enter or press any key. The following message indicates the program has
started.
[ FDD TYPE ] : TRACK = XXX
[ FDD TYPE ] : HEAD = X
[ FDD TYPE ] : SECTOR = XX
Copy start
[[ track, head = XXX X ]]
Insert target disk into drive A:
Tap Enter key when ready.
(d) Remove the source disk from the FDD, insert a formatted work disk, and tap
Enter or press any key. The [[ track, head = XXX X ]] message will appear
and copying to the target disk will begin. If data cannot all be copied in one
operation, the message from step (b) is displayed again. After the floppy
disk has been copied, the following message will appear:
Copy complete
Another copy (1:Yes/2:No) ?
(e) To copy another disk, type 1 and the message from step (a) will be displayed
again. Enter 2 to return to the DIAGNOSTIC MENU.
4. DUMP program
(a) Select dump to display the following message:
DIAGNOSTICS-HARD DISK & FLOPPY DISK DUMP : VX.XX
Drive type select (1:FDD, 2:HDD) ?
(b) Select a format type number. If 2 is selected, the display will go to step (e).
Select FDD number (1:A, 2:B) ?
(c) Select a drive number and the following message will be displayed:
Format type select (0:2DD, 1:2D, 2:2HD) ?
(d) Select a media type number and the following message will appear:
Insert source disk into drive A:
Press Enter key when ready.
3-48 T200, T200CS

(e) Insert a source disk and press any key and the following message will appear:
—— Max. address ——
[Track ] = 0079
[ Head ] = 01
[Sector] = 09
Track number ??
(f) Set a track number to dump. The system will access the disk and dump a
list.
T200, T200CS 3-49

3.23 System Configuration
3.23.1 Function Description
The System Configuration program contains the following information:
1. BIOS ROM version
2. Boot ROM version
3. KBC version
4. Base memory size
5. Number of floppy disk drives
6. Number of ASYNC ports
7. Number of hard disk drives
8. Number of printer ports
9. Extended Memory Size
10. PS Micom Version
11. Math Co-processor
3.23.2 Operations
Select 8 from the DIAGNOSTIC MENU and tap or press Enter to display the system configuration menu:
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION :
* - BIOS ROM VERSION = VX.XX
* - BOOT ROM VERSION = VX.XX
* - KBC VERSION = VX.XX
* - 639KB MEMORY
* - 1 FLOPPY DISK DRIVE(S)
* - 1 ASYNC ADAPTER
* - 1 HARD DISK DRIVE(S)
* - 1 PRINTER ADAPTER
* - XXXXXKB EXTENDED MEMORY
* - PS MICOM VERSION = VX.XX
* - 1 MATH CO-PROCESSOR
Press [Enter] Key
Tap or press Enter to return to the DIAGNOSTIC MENU.
3-50 T200, T200CS
 Loading...
Loading...