Toshiba T1960CT, T1960CS Maintenance Manual

1-1
1.1 Features
The Toshiba T1960CS and T1960CT are two of the lightest and most advanced portable
computers available. Utilizing advanced technology and high-speed components, the
T1960CS/T1960CT offer excellent display legibility, battery operation and IBM PC/AT
compatibility. The T1960 Series of computers consist of the following features:
❑ Microprocessor
The SL Enhanced Intel 486DX2-50 microprocessor operates at 50 MHz, 3.3 Volts.
❑ Math co-processor
A math co-processor is stored in the i486DX2 microprocessor.
❑ Cache memory
8 KB of cache memory is stored in the i486DX2 microprocessor.
❑ Disk storage
The internal 200 Megabyte (MB) Hard Disk Drive (HDD) has an average access time
of 13 milliseconds, while the 320 MB HDD has an average of 12 milliseconds. The
3.5-inch Floppy Disk Drive (FDD) supports 2HD floppy disks (1.44 MB) and 2DD
floppy disks (720 Kbytes).
❑ Memory
The T1960CS/T1960CT comes standard with 4 MB of CMOS Random Access
Memory (RAM) 3.3 Volts. This includes 640 KB of conventional memory and 3,456
KB of extended memory which can be utilized as expanded memory compatible with
the Lotus/Intel/Microsoft Expanded Memory Specifications (LIM-EMS).
❑ STN color LCD (T1960CS)
The high-resolution, Supertwist Nematic (STN) color Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
displays 640x480 pixels with 226,981 colors for both graphics and characters. The
T1960CS internal display controller supports Video Graphics Array (VGA) functions
on the internal display devices.
❑ TFT color LCD (T1960CT)
The high-resolution, Thin Film Transistor (TFT) color LCD displays 640x480 pixels
with 262,144 colors for both graphics and characters. The T1960CT internal display
controller supports VGA functions for internal display and Super VGA (SVGA) for
external display.
T1960CS/T1960CT

1-2
❑ Keyboard
The easy-to-use 82/84-key enhanced keyboard with full-size keys and standard spacing is compatible with IBM standard software.
❑ Batteries
The T1960CS/T1960CT has three different batteries: a main battery, a backup battery,
and a Real Time Clock (RTC) battery.
❑ Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (PCMCIA) card slot
The PCMCIA slot enables you to install a MiNC Toshiba card modem or other
industry-standard PCMCIA release 2.0 card.
❑ Parallel port
The Centronics-compatible parallel interface port serves two purposes: the port can
be used to connect a Centronics-compatible printer or an external 5 1/4" floppy disk
drive.
❑ RS-232-C port
The RS-232-C port is a 9-pin serial interface port.
❑ Mouse port
The 6-pin mouse port on the back supports an IBM PS/2 mouse.
❑ Keyboard port
The 6-pin keyboard port on the back supports an IBM PS/2 keyboard.
❑ Microsoft BallPoint Mouse V2.0 with Quick Port (BPQP) connection
The BPQP2 port is located on the right side of the computer.
❑ RGB port
The 15-pin RGB port on the back supports an external video display.
❑ Memory card slot
The memory card slot enables you to install an optional Toshiba memory card.
T1960CS/T1960CT
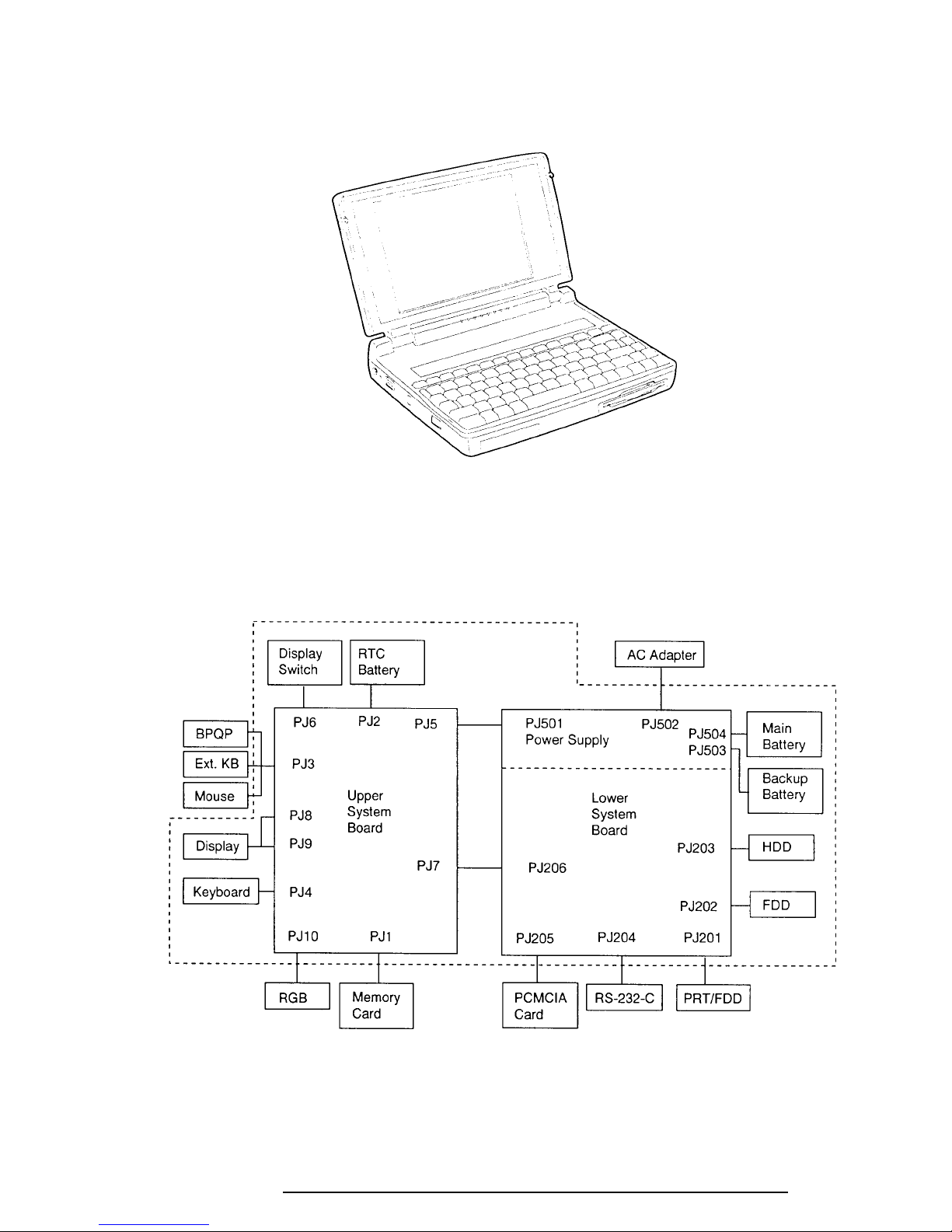
1-3
The T1960CS/T1960CT Personal Computer is shown in Figure 1-1, and its system
configuration is illustrated in Figure 1-2.
Figure 1-1 T1960CS/T1960CT Personal Computer
Figure 1-2 T1960CS/T1960CT System Unit Configuration
T1960CS/T1960CT
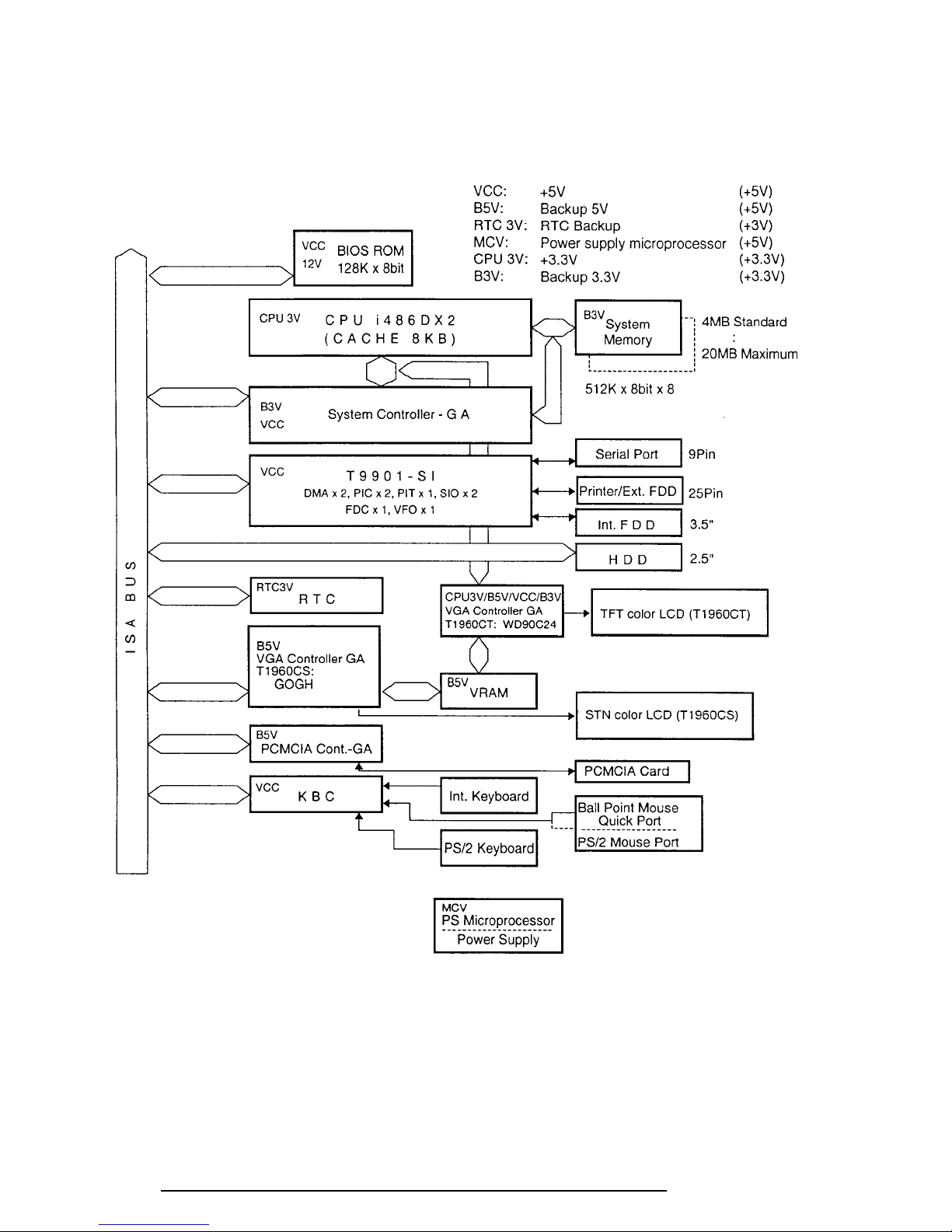
1-4
1.2 System Unit Block Diagram
Figure 1-3 is a block diagram of the T1960CS/T1960CT system unit.
Figure 1-3 T1960CS/T1960CT System Board Block Diagram
T1960CS/T1960CT

1-5
The T1960CS/T1960CT system board is composed of the following major components:
❑ An i486DX2-50 CPU
❑ Super Integration (SI) T9901, which stores the following components:
• Two Direct Memory Access Controllers (DMAC): 82C37
• Two Programmable Interrupt Controllers (PIC): 82C59
• One Programmable Interval Timer (PIT): 82C54
• One Floppy Disk Controller (FDC): TC8565
• One Serial Input/Output Controller (SIO): TC8570
• One Variable Frequency Oscillator (VFO): TC8568
• One I/O Controller
• One Printer Port Controller
• One Speaker Controller
❑ A Real Time Clock (RTC)
A T9934 chip with 128 bytes of memory is used. Fourteen bytes are used for the
calendar and clock, while the remaining 114 bytes are used for the system configuration data.
OSC (X3) generates 32.768 KHz for RTC.
❑ A Keyboard Controller (KBC)
An M37452M4 chip is used.
The KBC, which includes the keyboard scan controller and keyboard interface controller, controls the internal keyboard, external keyboard port, PS/2 mouse port, and Ball
Point Quick Port.
❑ Memory
Standard RAM: 4 MB
Cache memory: 8 KB (inside CPU)
BIOS ROM: 128 KB (96 KB are used)
The ROM contains the Initial Reliability Test (IRT), Basic
Input/Output System (BIOS), and video BIOS.
Video RAM: 256 KB
Optional memory cards expand memory to a maximum of 20 MB.
❑ VGA display controller
T1960CS (GOGH): This controller controls the internal and external VGA compatible display.
T1960CT (WD90C24): This controller controls the internal VGA display and external
SVGA compatible display.
T1960CS/T1960CT

1-6
❑ The Clock Generator receives 14.31818 MHz (X2) and generates the following
frequencies:
• 25 MHz for the CPU (CPU operates at 50MHz.)
• 14.7456 MHz for the COM
• 24 MHz for the FDC and VFO
• 16 MHz is used for GA
• 14.31818 MHz is used for T9901 (SI)
❑ Gate Array
System Controller Gate Array
This gate array has the following functions:
• CPU Controller
• Memory Controller
- DRAM Controller
- Compatible Bus Interface Controller
• SMI Controller
• VL Bus Controller
• Bus Controller
- Compatible Bus Interface Controller
- Compatible Access Controller
- DMAC Controller
- I/O Controller
• Address Latch Controller
- 32-Bit to 16-Bit Controller
- Address Latch
- DMA Address Generator
- Refresh Address Generator
• I/O Register
- Compatible I/O Port
- Saving the data of the Register (in Resume Mode) Controller
- Toshiba Special Register
• 50 MHz/25 MHz Controller
• Data Bus Change Controller
• Data Latch
PCMCIA Controller Gate Array
This gate array has the following functions:
• Memory Card Controller
- PCMCIA IC Card Controller
- Toshiba Modem Card Controller
T1960CS/T1960CT
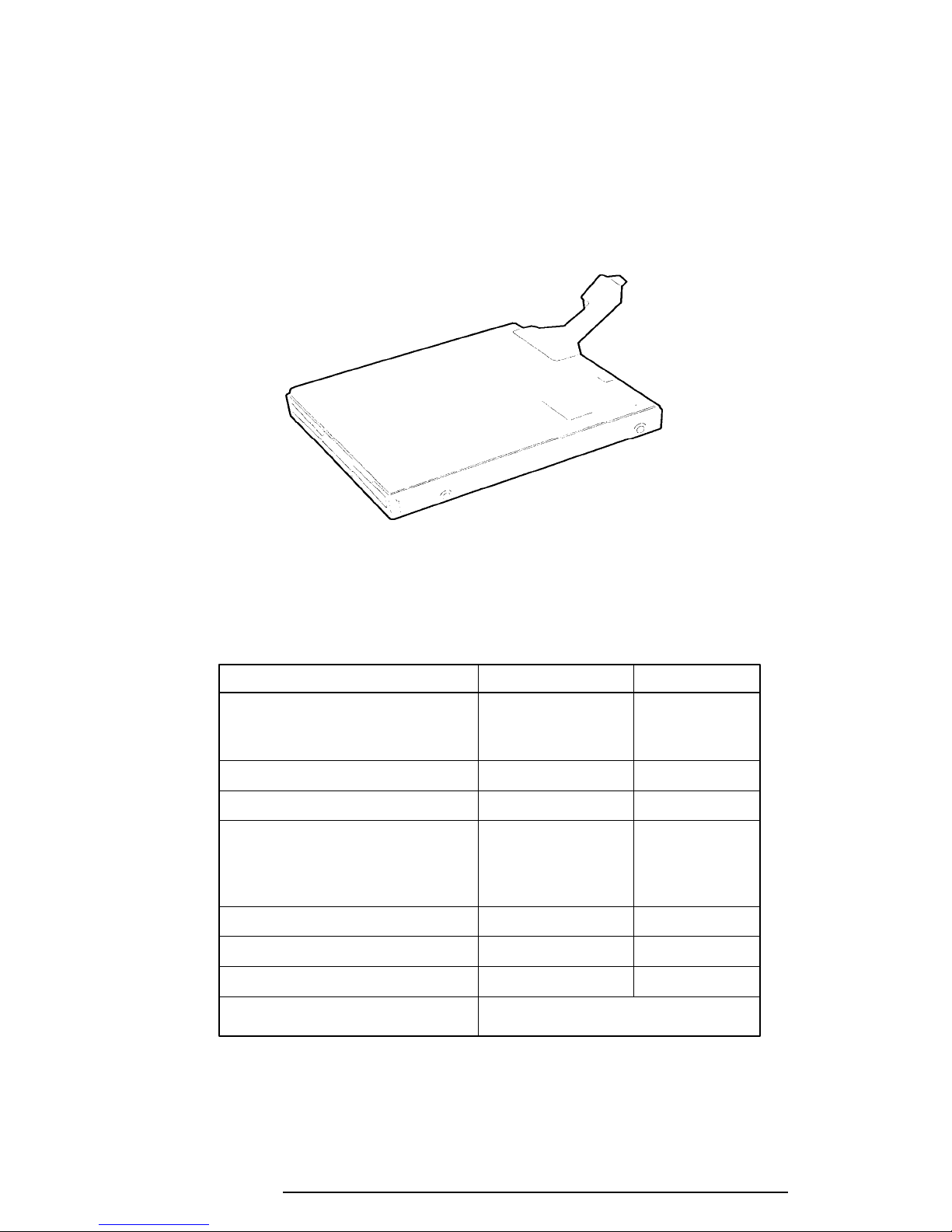
1-7
1.3 3.5-inch Floppy Disk Drive
The T1960CS/T1960CT 3.5-inch Floppy Disk Drive (FDD) is a thin, high-performance
reliable drive that supports 720-KB (formatted) 2DD and 1.44-MB (formatted) 2HD 3.5-inch
floppy disks.
The FDD is shown in Figure 1-4, and its specifications are listed in Table 1-1.
Figure 1-4 3.5-inch FDD
Table 1-1 3.5-inch FDD Specifications
Item 2 MB mode 1 MB mode
Storage capacity (KB)
Unformatted 2,000 1,000
Formatted 1,311 737
Number of heads 2 2
Number of cylinders 80 80
Access time (ms)
Track to track 3 3
Average 181 181
Head settling time 15 15
Recording track density (tpi) 135 135
Data transfer rate (Kbps) 500 250
Rotation speed (rpm) 300 300
Recording method Modified Frequency Modulation (MFM)
T1960CS/T1960CT
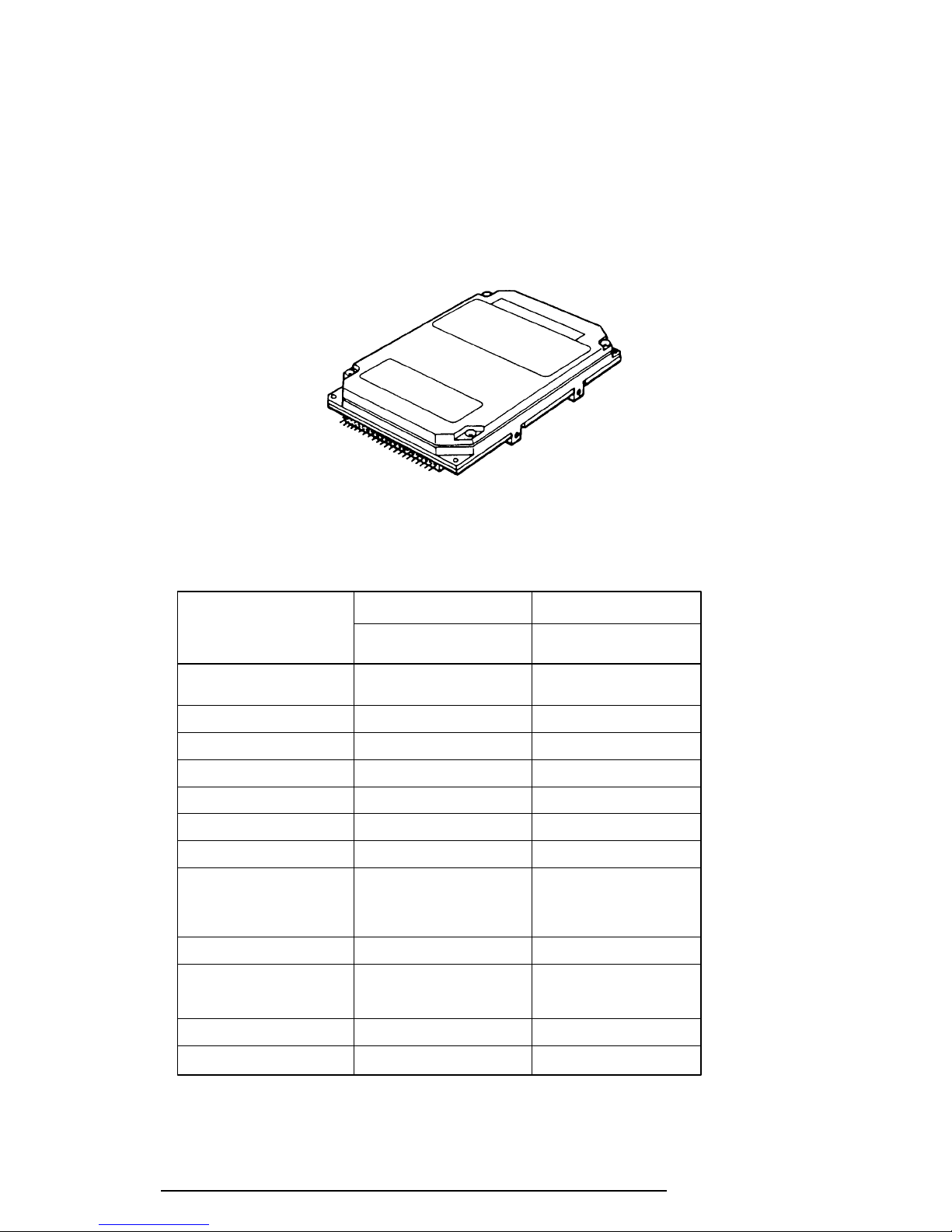
1-8
1.4 2.5-inch Hard Disk Drive
The Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a random access nonvolatile storage device. It has a nonremovable 2.5-inch magnetic disk and mini-winchester type magnetic heads.
The T1960CS/T1960CT supports a 200 and a 320 MB HDD.
The HDD is shown in Figure 1-5, and its specifications are listed in Table 1-2.
Figure 1-5 2.5-inch HDD
Table 1-2 2.5-inch HDD Specifications
Item
Storage capacity (MB)
Formatted 213.0 340.0
Number of disks 2 3
Data heads 4 6
Data surfaces 4 6
Tracks per surface 1,560 1,830
Sectors per track – –
Bytes per sector 512 512
Access time (ms)
Track to track 3 3
Average 13 12
Maximum 25 25
Rotation speed (rpm) 4,000 4,200
Data transfer rate (bps)
To/from media 18.9 to 18.7 to
200MB 320MB
(MK1624FCV) (MK2326FC)
31.6 M 29.6 M
Interleave 1:1 1:1
Recording method 1-7 RLL 1-7 RLL
T1960CS/T1960CT

1-9
1.5 Keyboard
The 82-(USA) or 84-(European) keyboard is mounted on the T1960CS/T1960CT’s system
unit. The keyboard is connected to the keyboard controller on the system board through a
19-pin flat cable. The keyboard is shown in Figure 1-6.
See Appendix F for optional keyboard configurations.
Figure 1-6 Keyboard
T1960CS/T1960CT
1-10
1.6 STN Color LCD (T1960CS)
The STN Color Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) contains an LCD module, a Fluorescent Lamp
(FL), and an FL inverter board.
1.6.1 STN Color LCD Module
The T1960CS STN color LCD is backlit and supports 640x480 pixels with a Video controller. The controller includes the functions of Video Graphics Array (VGA).
The LCD receives vertical and horizontal synchronizing signals, 16-bit data signal, 8-bit upper
block data signal, 8-bit lower block data signal, and shift clock for data transmission. All
signals are CMOS-level compatible.
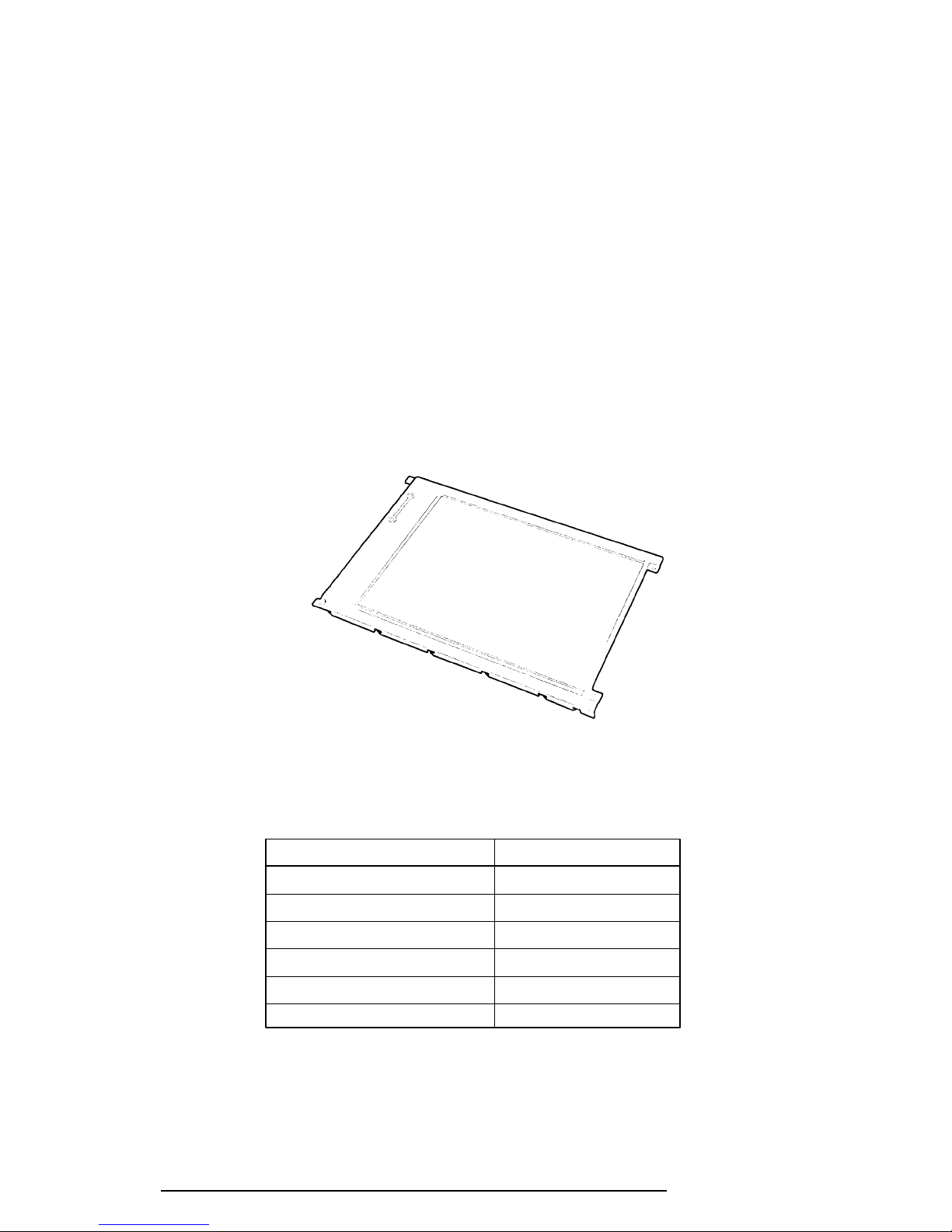
The STN LCD is shown in Figure 1-7, and its specifications are listed in Table 1-3.
Table 1-3 STN Color LCD Specifications
Number of Dots (dots) 640 x 480
Dot pitch (mm) 0.3 (W) x 0.3 (H)
Display area (mm) 195 (W) x 147 (H)
Contrast 18:1 (Typically)
FL current (mA) 5.0 x 2
FL frequency (KHz) 47
Figure 1-7 STN Color LCD
Item Specifications
T1960CS/T1960CT
1-11
1.6.2 STN Color Fluorescent Lamp (FL) Inverter Board
The FL inverter board supplies high frequency current to light the LCD’s Fluorescent Lamp.
Specifications for the FL inverter are listed in Table 1-4.
Table 1-4 STN Color FL Inverter Board Specifications
Item Specifications
Input Voltage (VDC) 5
Power (W) 6
Output Voltage (VAC) 1,000
Current (mA) 5.0 x 2
Frequency (KHz) 42
T1960CS/T1960CT
1-12
1.7 TFT Color LCD (T1960CT)
The TFT Color Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) contains an LCD module, a Fluorescent Lamp
(FL), and an FL inverter board.
1.7.1 TFT Color LCD Module
The T1960CT TFT color LCD supports 640x480 pixels with an internal display controller and
512 colors for graphics and characters. The controller includes the functions of Video Graphics Array (VGA) and Super VGA (SVGA) for external display.
The LCD receives 9-bit data signals, data enable signals, and shift clock for data transmission.
All signals are CMOS-level compatible.
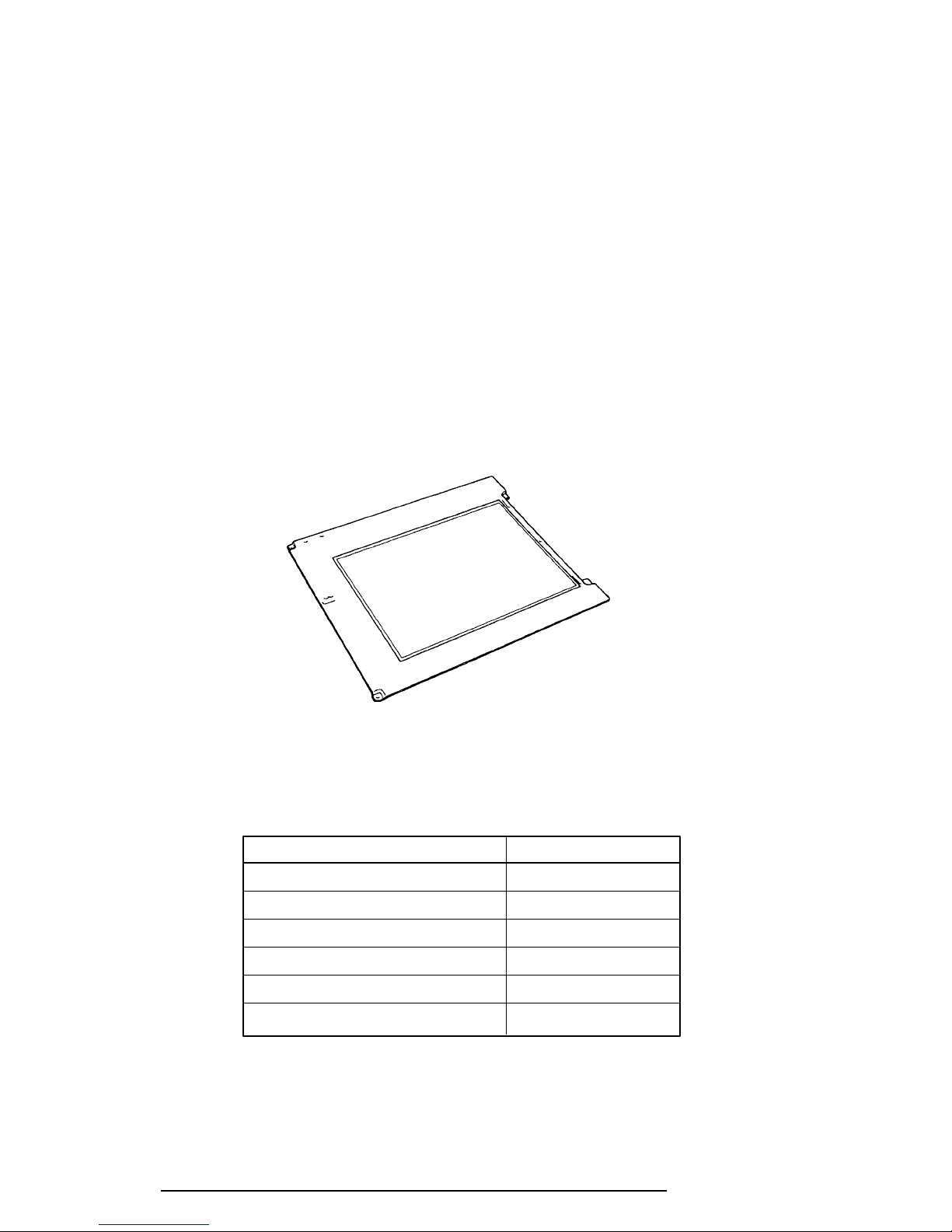
The TFT LCD is shown in Figure 1-8, and its specifications are listed in Table 1-5.
Figure 1-8 TFT Color LCD
Table 1-5 TFT Color LCD Specifications
Item Specifications
Number of dots (dots) 640 x 480
Dot pitch (mm) 0.27 (W) x 0.27 (H)
Display area (mm) 171 (W) x 130 (H)
Contrast 60:1 (minimum)
FL current (mA) 5.0
FL frequency (KHz) 47
T1960CS/T1960CT
1-13
1.7.2 TFT Color Fluorescent Lamp (FL) Inverter Board
The FL inverter board supplies high frequency current to light the LCD’s Fluorescent Lamp.
Specifications for the FL inverter are listed in Table 1-6.
Table 1-6 FL Inverter Board Specifications
Item Specifications
Input Voltage (VDC) 5
Power (W) 3
Output Voltage (VAC) 1,100
Current (mA) 5.0
Frequency (KHz) 47
T1960CS/T1960CT
1-14
1.8 Power Supply
The power supply supplies five kinds of voltages to the T1960CS/T1960CT system board.
The T1960CS/T1960CT power supply board has one microprocessor and operates at 500
KHz. The board performs the following functions:
1. Determines if the AC adapter or battery is connected to the computer.
2. Detects DC output and circuit malfunctions.
3. Controls the LED indicator and speaker.
4. Turns the battery charging system on and off and detects a fully charged battery.
5. Determines if the power can be turned on and off.
6. Provides more accurate detection of a low battery.
7. Calculates the remaining battery capacity.
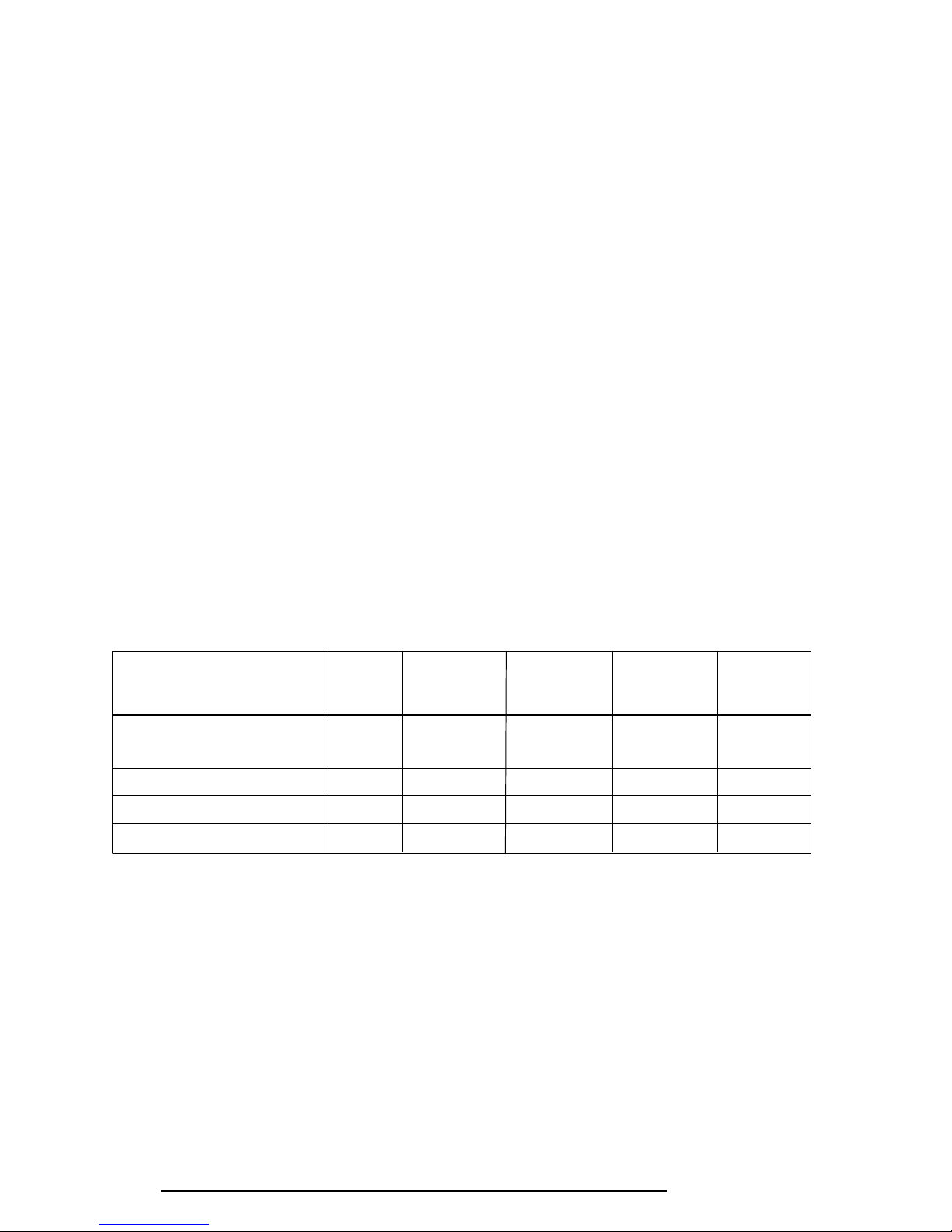
The power supply output rating is specified in Table 1-7.
Table 1-7 Power Supply Output Rating
Use for Name Voltage Tolerance Current Ripple
System logic, FDD, HDD, VCC +5 ±5 3,500 100
Display
RS-232-C Flash ROM 12V +12 ±5 120 240
RAM, CPU B3V +3.3 ±5 755 66
RS-232-C N9V –7 to –12.6 – 10 –
DC Regulation Maximum
(V) (%) (mA) (mV)
T1960CS/T1960CT
1-15
1.9 Batteries
The T1960CS/T1960CT has three types of batteries:
❑ Main battery pack
❑ Backup battery
❑ Real Time Clock (RTC) battery
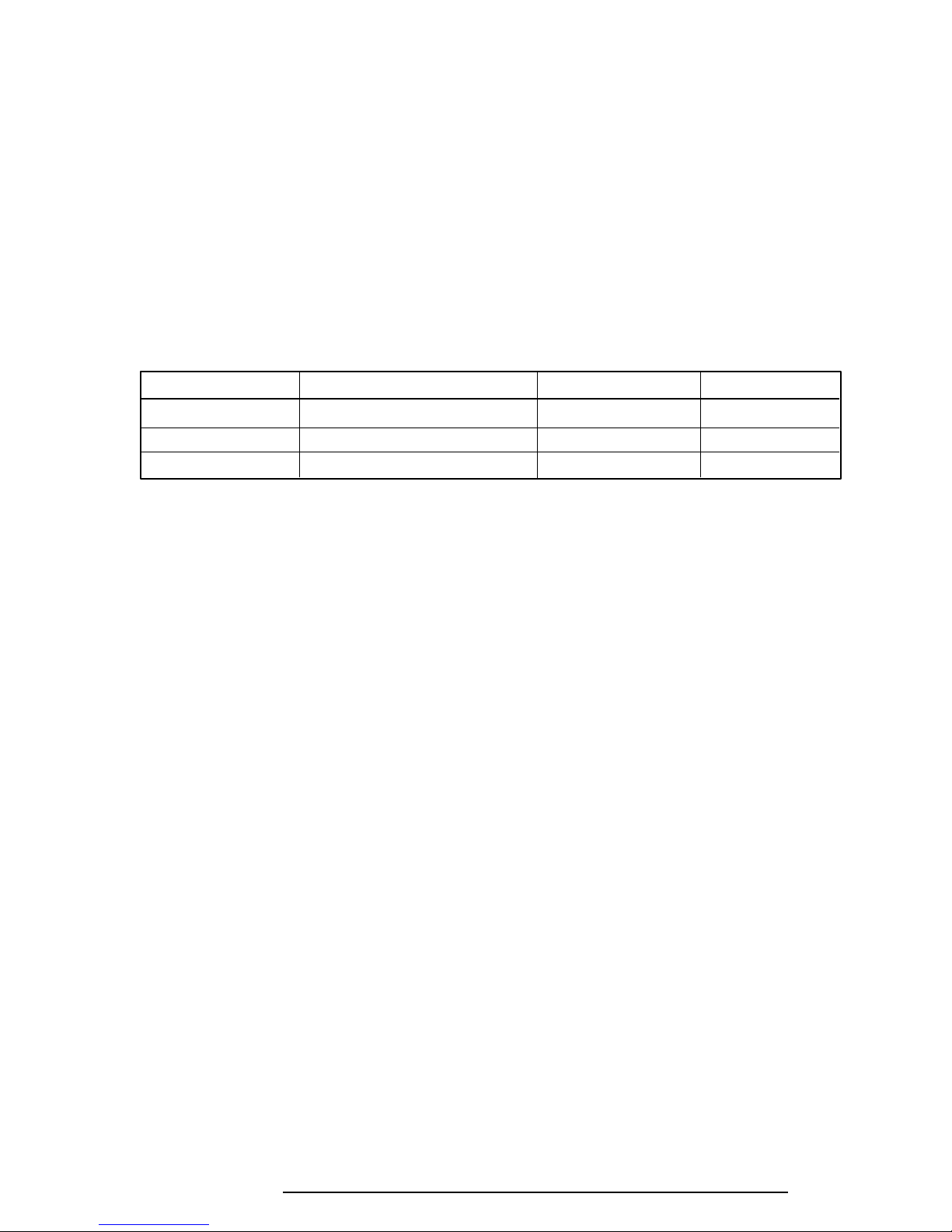
Specifications for these batteries are listed in Table 1-8.
Table 1-8 Battery Specifications
Battery Material Output Voltage Capacity
Main battery Nickel Metal Hydride 12 V 2,400 mAH
Backup battery Nickel Metal Hydride 1.2 V 1,100 mAH
RTC battery Lithium-Vanadium 3.0 V 50 mAH
1.9.1 Main Battery
The removable main battery pack is the computer’s main power source when the AC adapter
is not attached. The main battery recharges the backup battery when the system’s power is
on. The backup and main battery maintain the state of the computer when you enable
AutoResume.
❏ Battery Indicator
The Battery indicator is located on the top cover of the T1960CS/T1960CT. The indicator
shows the status of the removable battery pack, power supply and AC adapter. The status of
each can be determined by color:
Orange The battery is being charged. (AC adapter is attached.)
Green The battery is fully charged. (AC adapter is attached.)
No light The AC adapter is disconnected from the computer, or the AC
adapter is connected, but it cannot charge the battery for one of the
following reasons:
❍ The battery is extremely hot. Allow the computer and the battery
to reach room temperature before attempting to charge the battery.
❍ The battery is almost fully discharged. The battery will not begin
❍ The AC adapter is not receiving power.
T1960CS/T1960CT
charging immediately in this state, it will begin charging a few
minutes after the AC adapter is connected.
1-16
1.9.2 Battery Charging Control
Battery charging is controlled by a microprocessor that is mounted on the power supply. The
microprocessor controls whether the charge is on or off and detects a full charge when the AC
adapter and battery are attached to the computer. The system charges the battery using quick
charge or trickle charge.
❏ Quick Battery Charge
When the AC adapter is attached, there are two types of charge: quick charge when the
system is powered off and trickle charge when the system is powered on.
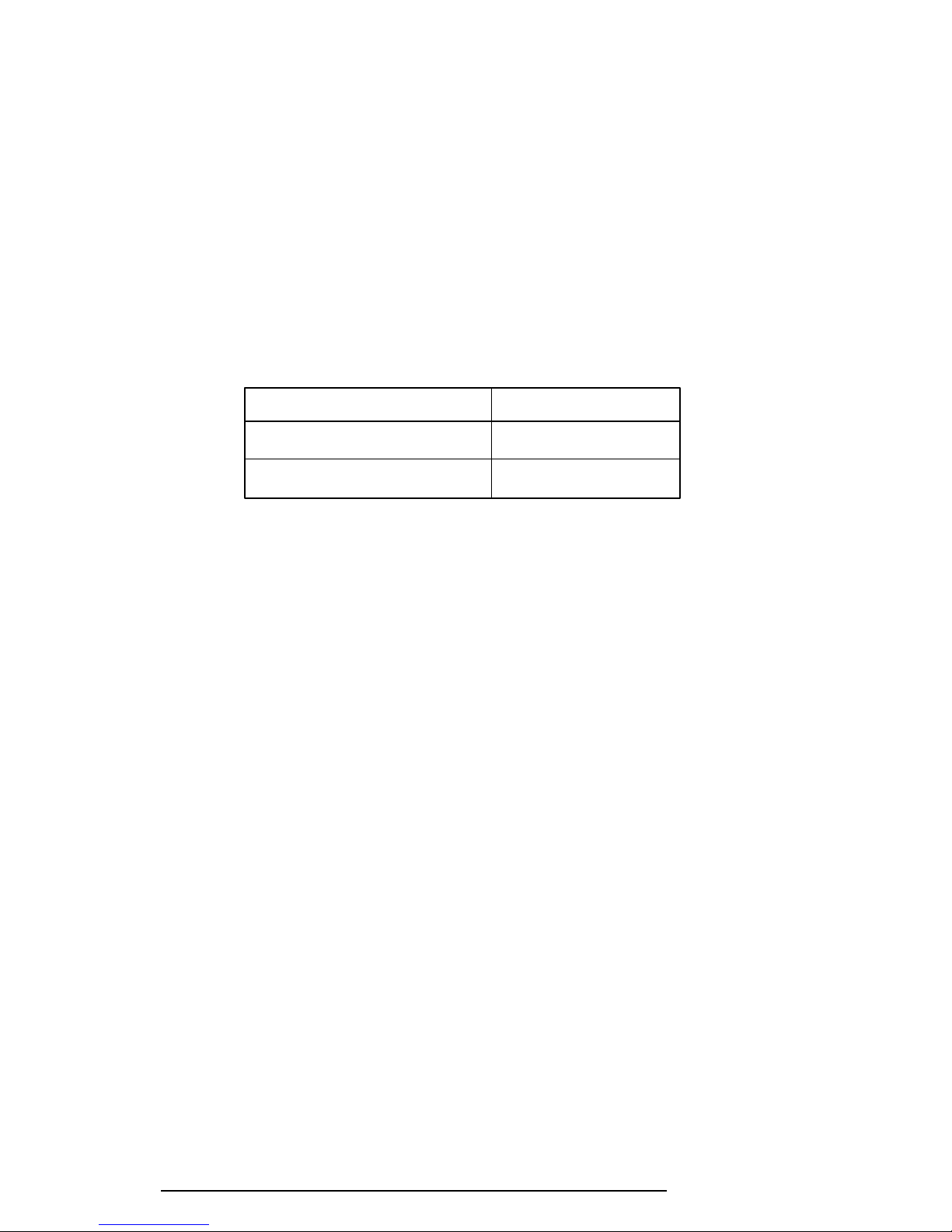
Table 1-9 Time Required for Charges of the Main Battery
Charge Charging Time
Quick charge (power off) About 1.4 hours
Trickle charge (power on) About 48 hours
If one of the following occurs, the battery quick-charge process stops.
1. The battery becomes fully charged
2. The AC adapter or battery is removed.
3. The battery or AC adapter output voltage is abnormal.
4. The charge current is abnormal.
❏ Trickle Battery Charge
When the main battery is fully charged and the AC adapter is attached, the power supply
microprocessor automatically changes quick charge to trickle charge.
T1960CS/T1960CT
1-17
1.9.3 Backup Battery
The backup battery maintains data for AutoResume. The power source used to back up the
AutoResume data is determined according to the following priority:
AC adapter > Main battery > Backup battery
The backup battery is charged by the main battery or AC adapter when the system is powered
on. Table 1-10 shows the charging time and data preservation period of the backup battery.
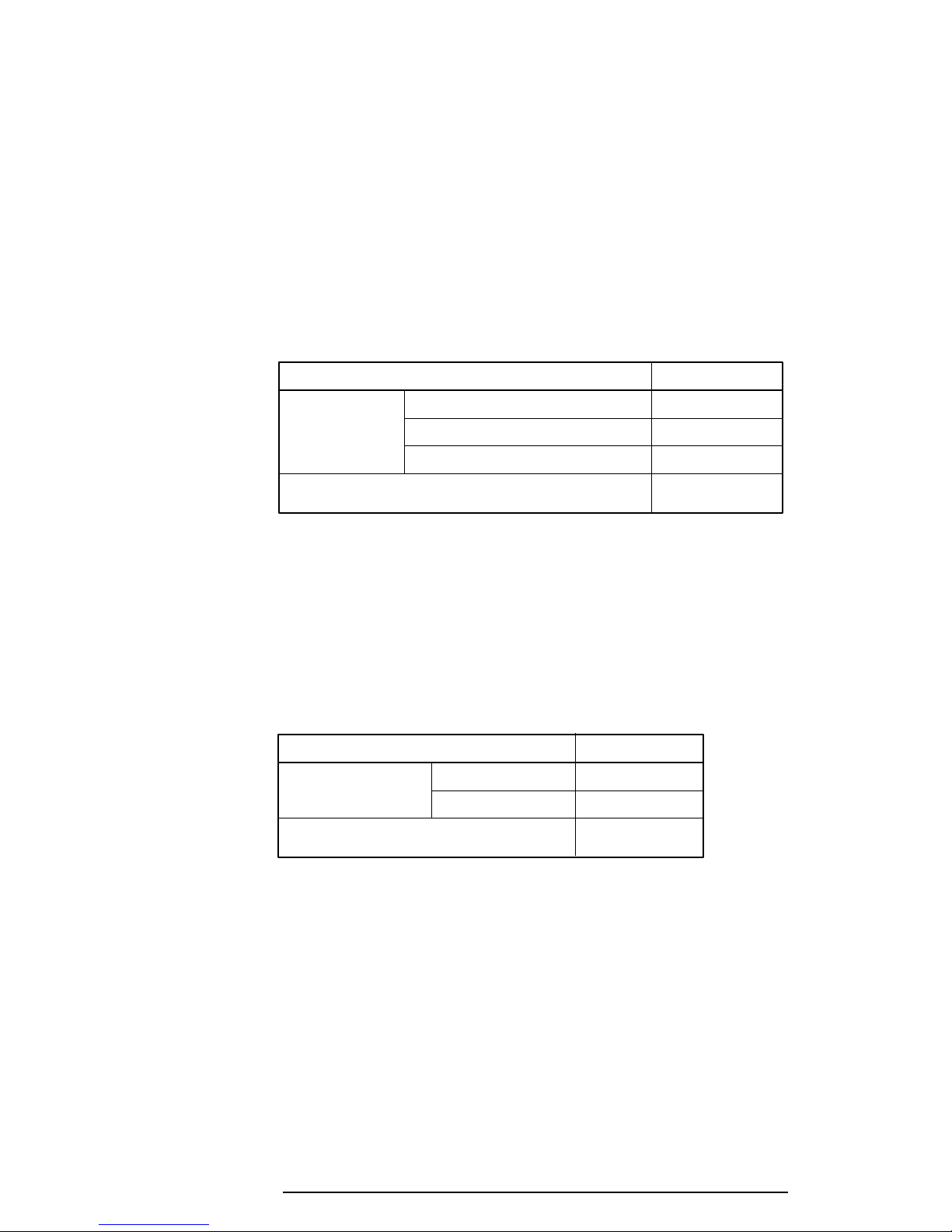
Table 1-10 Backup Battery Charging/Data Preservation Time
Backup Battery Time
Charging Time Power On 16 H
Power Off (with AC Adapter) 60 H
Power Off (Without AC Adapter) Doesn’t charge
Data preservation period (full charge) 8 H
1.9.4 RTC Battery
The RTC battery provides power to keep the current date, time and other setup information in
memory while the computer is turned off. Table 1-11 shows the charging time and data
preservation period of the RTC battery.
Table 1-11 RTC Battery Charging/Data Preservation Time
RTC Battery Time
Charging Time Power On 48 H
Power Off Doesn’t charge
Data preservation period (full charge) 1 month
T1960CS/T1960CT

2-1
2.1 Troubleshooting
Chapter 2 describes how to determine if a Field Replaceable Unit (FRU) in the T1960CS/
T1960CT is causing the computer to malfunction. The FRUs covered are:
1. System Board(s)
2. Floppy Disk Drive
3. Hard Disk Drive
4. Keyboard
5. Display
Diagnostic disk operations are described in Chapter 3, and detailed replacement procedures
are given in Chapter 4.
The following tools are necessary for implementing the troubleshooting procedures:
1. A T1960CS/T1960CT Diagnostics Disk
2. A Phillips-head screwdriver (2 mm)
3. A Toshiba MS-DOS system disk(s)
4. A 2DD or 2HD formatted work disk for testing the floppy disk drive
5. A cleaning kit for troubleshooting the floppy disk drive
6. A printer port LED
7. An RS-232-C wraparound connector
8. A printer wraparound connector
9. A multimeter
10. An external 5.25-inch floppy disk drive
11. An external CRT
T1960CS/T1960CT

2-2
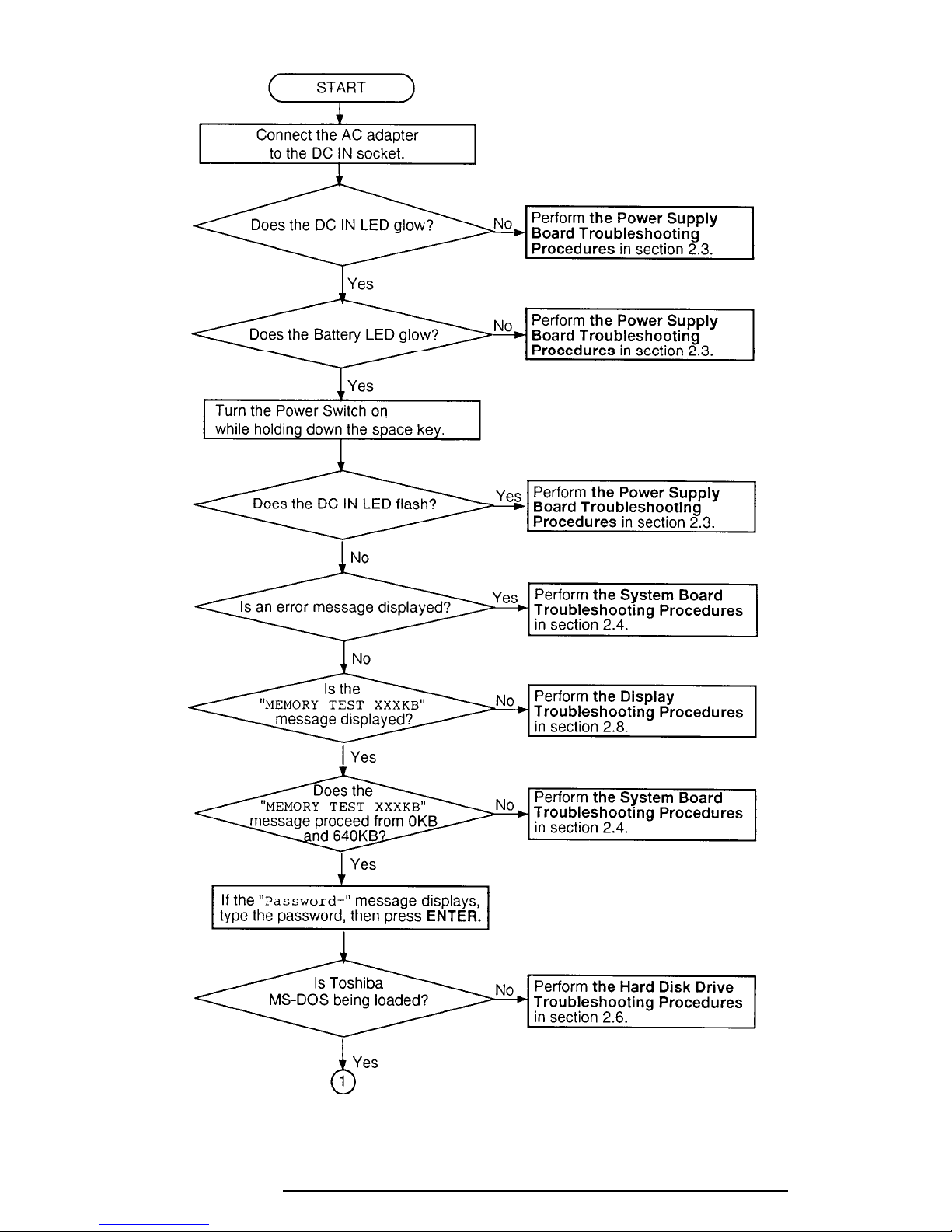
2.2 Troubleshooting Flowchart
Use the flowchart in Figure 2-1 as a guide for determining which troubleshooting procedures
to execute. Before going through the flowchart steps, verify the following:
❑ Ask the user if a password is registered. If one is, ask him or her to enter the pass-
word. If the user has forgotten the password, connect the printer port wraparound
board (F31PRT), then turn the POWER switch on. The computer will override the
password function by erasing the current password.
❑ Verify with the customer that Toshiba MS-DOS is installed on the hard disk. Non-
Toshiba operating systems can cause the computer to malfunction.
❑ Make sure all optional equipment is disconnected from the computer.
❑ Make sure the floppy disk drive is empty.
T1960CS/T1960CT
T1960CS/T1960CT
2-3
Figure 2-1 Troubleshooting Flowchart (1/2)
2-4
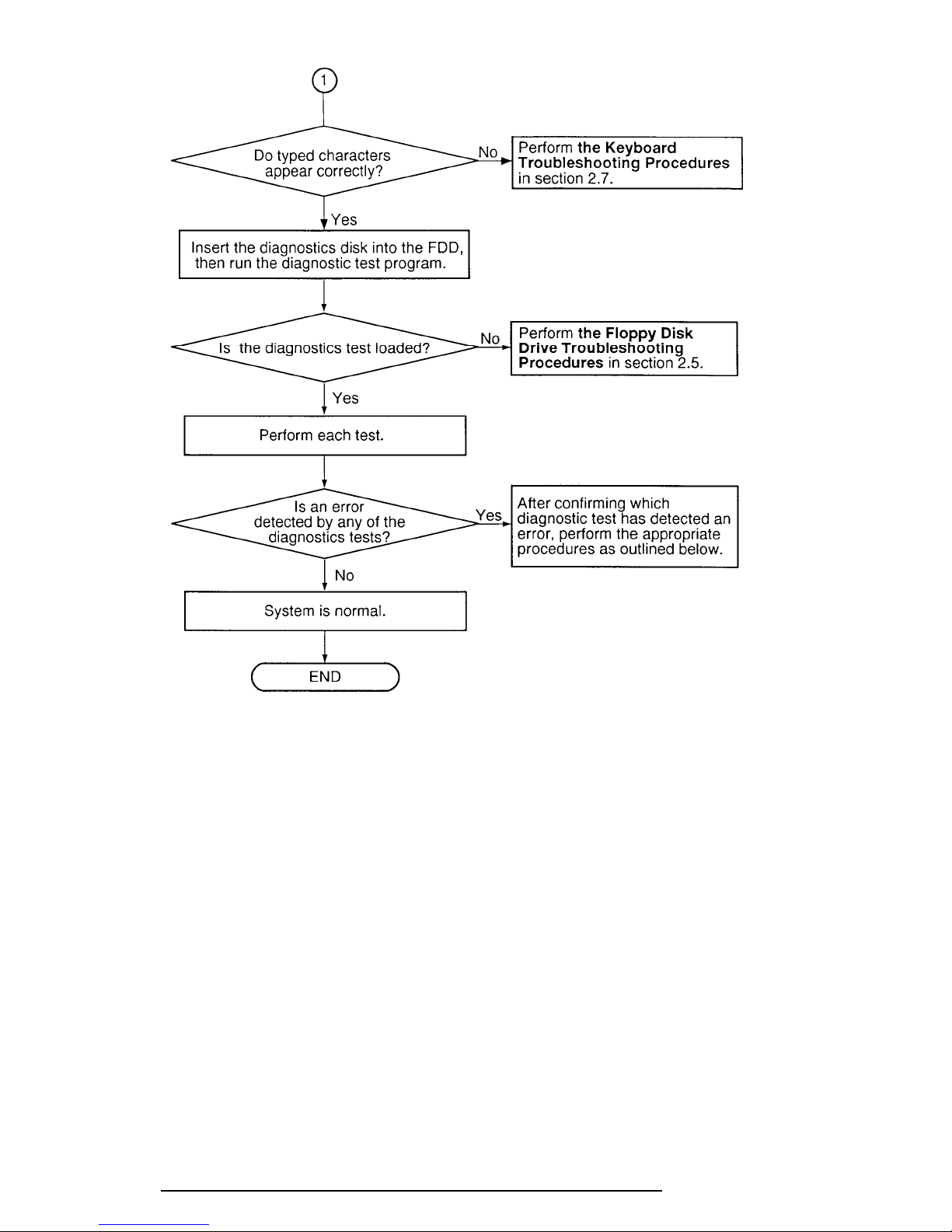
Figure 2-1 Troubleshooting Flowchart (2/2)
If the diagnostics program cannot detect an error, the problem may be intermittent. The
Running Test program should be executed several times to isolate the problem. Check the
Log Utilities function to confirm which diagnostic test detected an error(s), then perform the
appropriate troubleshooting procedures as follows:
1. If an error is detected on the System Test, Memory Test, Display Test, ASYNC
Test, Printer Test, or Real Timer Test, perform the System Board Troubleshooting
Procedures in Section 2.4.
2. If an error is detected on the Keyboard Test, perform the Keyboard Troubleshooting Procedures in Section 2.7.
3. If an error is detected on the Floppy Disk Test, perform the Floppy Disk Drive
Troubleshooting Procedures in Section 2.5.
4. If an error is detected on the Hard Disk Test, perform the Hard Disk Drive
Troubleshooting Procedures in Section 2.6.
T1960CS/T1960CT

2-5
2.3 Power Supply Troubleshooting
The T1960CS/T1960CT’s power supply controls many functions and components in the
computer. To determine if the power supply is functioning properly, start with Procedure 1
and continue with the other Procedures as instructed. The procedures described in this
section include:
Procedure 1: DC IN LED Indicator Check
Procedure 2: Battery LED Indicator Check
Procedure 3: PCB Replacement Check
Procedure 1 DC IN LED Indicator Check
The T1960CS/T1960CT’s AC adapter converts AC power to DC power and contains a
charging circuit which charges the computer’s batteries. The adapter connects to the DC IN
socket connector on the left side of the computer. When the AC adapter is connected to the
computer and the power is turned off, the AC adapter charges the batteries.
The DC IN indicator displays whether or not the AC adapter is connected and supplying
power.
❑ When the DC IN indicator is green, the AC adapter is connected and supplying power
to the computer.
❑ If the DC IN indicator does not light, the AC adapter is not supplying power, or the
AC adapter is not attached to the computer, go to Check 1.
❑ If the DC IN indicator is flashing green, the AC adapter’s voltage supply is abnormal
or the power supply is not functioning properly, go to Check 1.
If any of the above indicator conditions are abnormal, make sure the LED indicator lights are
not burned out before performing the following Checks.
Check 1 Make sure the correct AC adapter’s cable is firmly plugged into the DC IN 1.7 A
socket on the back of the computer.
Check 2 If the DC IN indicator flashes green when the AC adapter is connected, its voltage
output is abnormal. Connect a new AC adapter and turn the computer on again to
verify the indicator condition.
Check 3 The battery pack may be malfunctioning. Replace the battery pack with a new one
and turn the computer on again. If the problem still exists, perform Check 4.
T1960CS/T1960CT

2-6
Check 4 Place the computer in an environment between –20°C and 70°C until it reaches
ambient temperature. Repeat the steps which caused the computer to malfunction.
If the same problem still appears, perform Procedure 3.
Procedure 2 Battery LED Indicator Check
The Battery LED indicator shows the battery charging status. The LED, identified by a
battery icon on the front of the computer, glows orange when the AC adapter is charging the
computer’s battery pack.
❑ If the Battery LED indicator glows green, the AC adapter is connected and the battery
is fully charged.
❑ If the indicator glows orange, the AC adapter is connected and the battery is being
charged.
❑ If the indicator does not glow, go to Check 1.
Check 1 Make sure the AC adapter’s cable and AC cord are firmly plugged into the DC IN
socket and wall outlet. If these cables are connected correctly, go to Check 2.
Check 2 Make sure the battery pack is installed in the computer correctly. If it is, go to
Check 3.
Check 3 Remove the battery pack and check that the battery terminal is clean and not bent.
❑ If the terminal appears dirty, clean it gently with a cotton swab dipped in
alcohol.
❑ If the terminal looks bent or damaged, replace the lower system board.
❑ If the battery terminal is clean and not bent, go to Check 4.
Check 4 Connect a new AC adapter. If the Battery LED indicator still does not glow, go
to Check 5.
Check 5 Install a new battery pack. If the Battery LED indicator still does not glow, go to
Procedure 3.
T1960CS/T1960CT

2-7
Procedure 3 PCB Replacement Check
The power supply is mounted on the lower system board (FA2SL*). If either the power
supply or the system board is damaged, refer to Chapter 4 for instructions on how to disassemble the T1960CS/T1960CT, then perform the following checks.
Check 1 Replace the lower system board with a new one and restart the system. If the
problem still exists, go to Check 2.
Check 2 Replace the upper system board with a new one and restart the system. If the
problem still exists, other FRUs may be damaged.
T1960CS/T1960CT

2-8
2.4 System Board Troubleshooting
This section describes how to determine if the system board is defective or not functioning
properly. Start with Procedure 1 and continue with the other procedures as instructed. The
procedures described in this section include:
Procedure 1: Message Check
Procedure 2: Printer Port LED Check on Boot Mode
Procedure 3: Printer Port LED Check on Resume Mode
Procedure 4: Diagnostic Test Program Execution Check
Procedure 5: Replacement Check
T1960CS/T1960CT

2-9
Procedure 1 Message Check
When the power is turned on, the system performs the Initial Reliability Test (IRT) installed in
the BIOS ROM. The IRT tests each IC on the system board and initializes it.
❑ If an error message displays, perform Check 1.
❑ If there is no error message, go to Procedure 2.
❑ If the Toshiba MS-DOS is properly loaded, go to Procedure 3.
Check 1 If one of the following error messages displays on the screen, press the F1 key as
the message instructs.
(a) *** Error in CMOS. Bad HDD type ***
Check system. Then press [F1] key ......
(b) *** Error in CMOS. Bad battery ***
Check system. Then press [F1] key ......
(c) *** Error in CMOS. Bad check sum ***
Check system. Then press [F1] key ......
(d) *** Error in CMOS. Bad memory size ***
Check system. Then press [F1] key ......
(e) *** Error in CMOS. Bad time function ***
Check system. Then press [F1] key ......
These errors occur when the system configuration preserved in the RTC memory
(CMOS-type memory) is not the same as the actual configuration or when the data
is lost.
If you press the F1 key as the message instructs, the system configuration in the
RTC memory configuration is set to the default setting. If error message (b)
appears often when power is turned on, replace the RTC battery. If any other
error message displays, perform Check 2.
Check 2 If the following error message displays on the screen, press any key as the message
instructs.
WARNING: RESUME FAILURE.
PRESS ANY KEY TO CONTINUE.
This message appears when data stored in RAM under the resume function is lost
because the battery has become discharged or the system board is damaged. Go
to Procedure 3.
If any other message appears, perform Check 3.
T1960CS/T1960CT

2-10
Check 3 The IRT checks the system board. If the IRT detects an error, the system stops or
an error message appears.
❑ If any of the following error messages display, replace the system board:
(1) through (17), (19), (20), (25) or (26).
❑ If error message (18) displays, go to the Keyboard Troubleshooting Proce-
dures in Section 2.7.
❑ If error message (21) or (22) displays, go to the HDD Troubleshooting
Procedures in Section 2.6.
❑ If error message (23) or (24) displays, go to the FDD Troubleshooting
Procedures in Section 2.5.
(1) TIMER CH.2 OUT ERROR
(2) PIT ERROR
(3) MEMORY REFRESH ERROR
(4) FIRST 64KB MEMORY ERROR
(5) RTC ERROR
(6) CRTC ERROR
(7) VRAM ERROR
(8) KBC ERROR
(9) SYSTEM MEMORY ERROR
(10) SYSTEM MEMORY PARITY ERROR
(11) EXTENDED MEMORY ERROR
(12) EXTENDED MEMORY PARITY ERROR
(13) DMA PAGE REGISTER ERROR
(14) DMAC #1 ERROR
(15) DMAC #2 ERROR
(16) PIC #1 ERROR
(17) PIC #2 ERROR
(18) KEYBOARD ERROR
(19) KBC ERROR
(20) HDC ERROR
(21) HDD #0 ERROR
(22) HDD #1 ERROR
(23) NO FDD ERROR
(24) FDD ERROR
(25) TIMER INTERRUPT ERROR
(26) RTC UPDATE ERROR
T1960CS/T1960CT
2-11
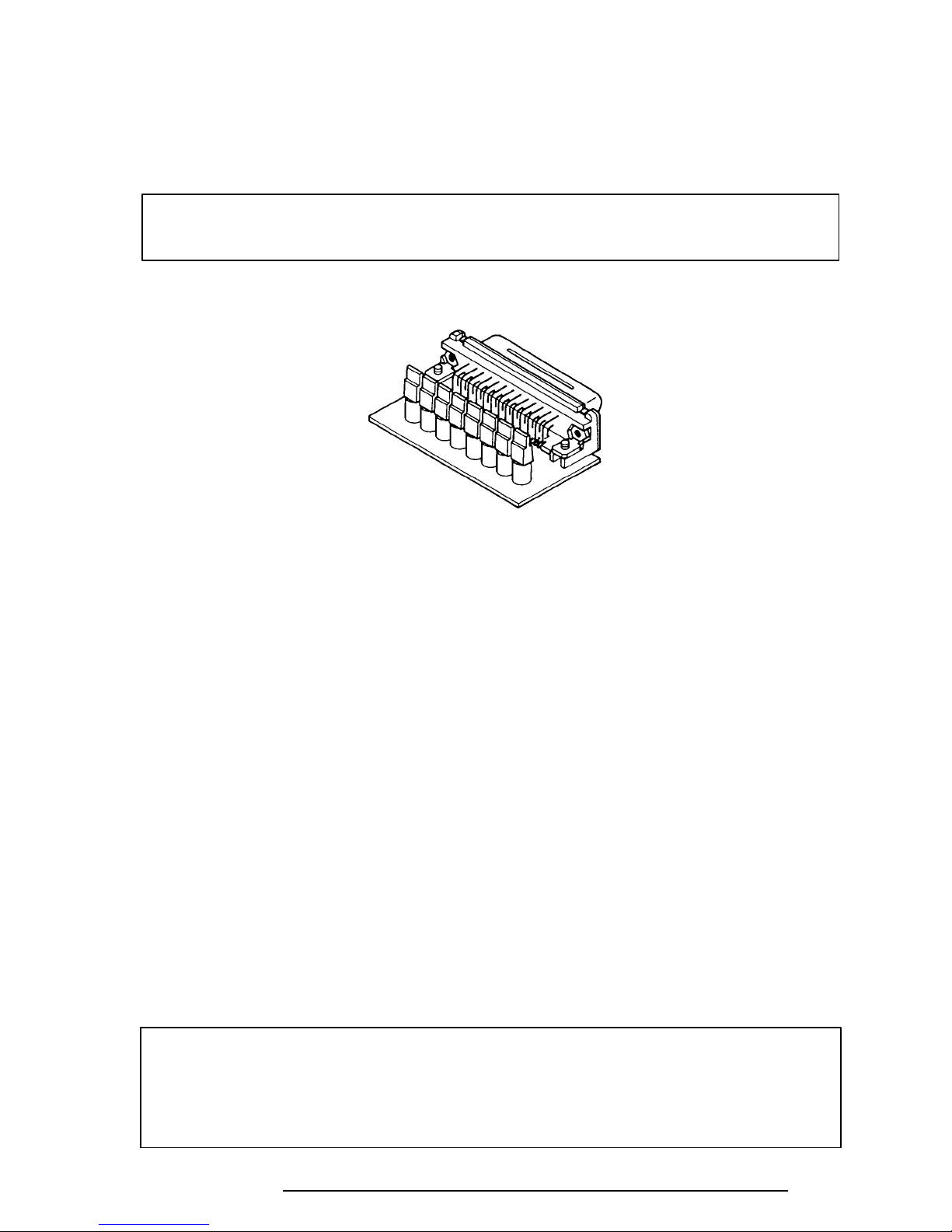
Procedure 2 Printer Port LED Check on Boot Mode
The printer port LED displays the IRT status and test status by turning lights on and off as an
eight-digit binary value for boot mode. Figure 2-2 shows the printer port LED.
NOTE: When you perform this check, the external FDD/PRT option in the SETUP
program must be set to PRT and set to boot mode.
Figure 2-2 Printer Port LED
To use the printer port LED follow these steps:
1. Turn on the T1960CS/T1960CT’s power, then set it to boot mode.
2. Turn off the computer.
3. Plug the printer port LED into the computer’s PRT/FDD connector.
4. Hold down the space bar and turn on the power to the computer.
5. Read the LED status from left to right as you are facing the back of the computer.
6. Convert the status from binary to hexadecimal notation.
7. If the final LED status is FFh (normal status), go to Procedure 3.
8. If the final LED status matches any of the test status values in Table 2-1, perform
Check 1.
NOTE: If an error condition is detected by the IRT test, the printer port LED displays
an error code after the IRT test ends. For example, if the printer port LED displays 22
and halts, the IRT test has already completed the KBC test. In this instance, the IRT
indicates an error has been detected during the system memory test.
T1960CS/T1960CT
2-12
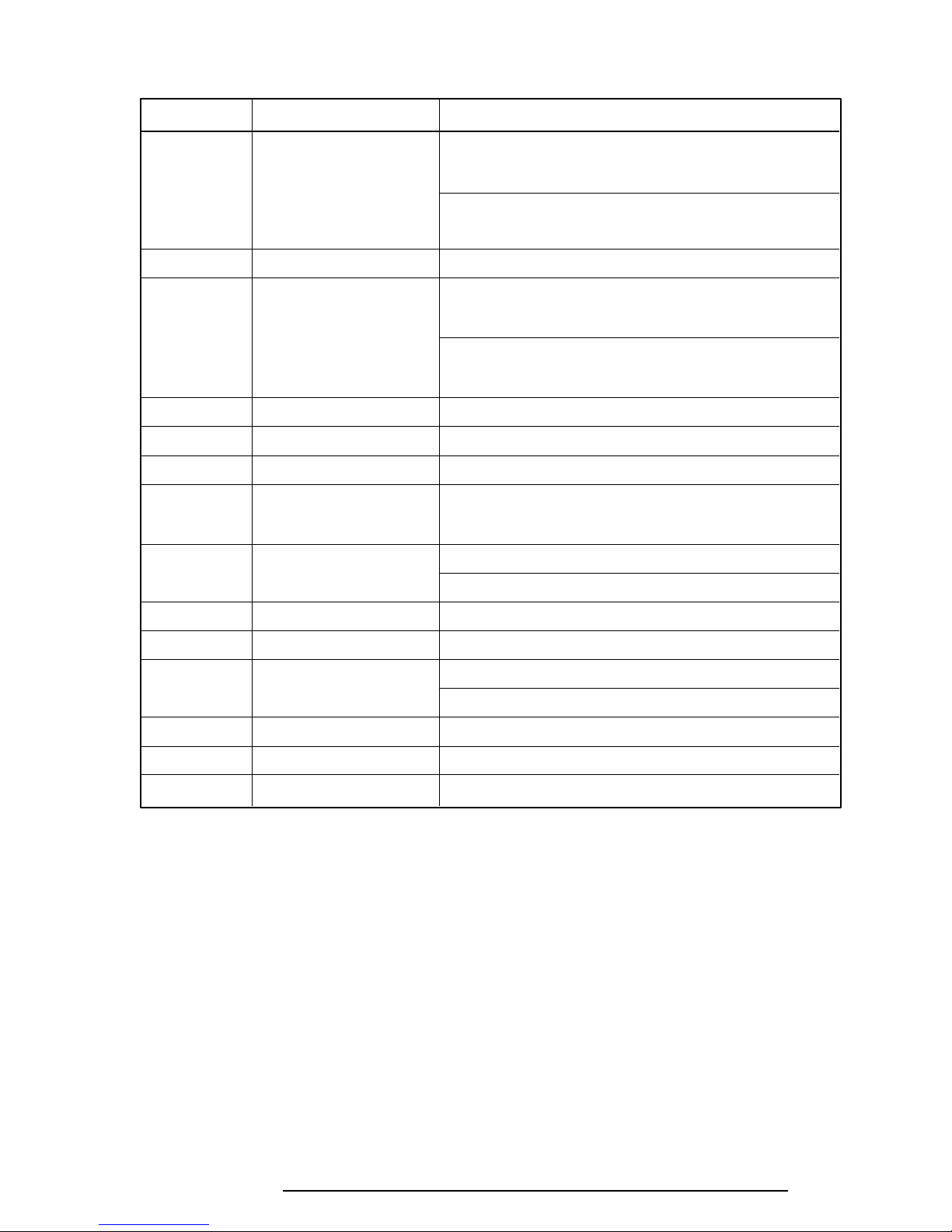
Table 2-1 Printer Port LED Boot Mode Error Statuses (1/2)
Error Status Test Item Message
01H Pre-init for warm start —
test
05H PIT test TIMER CH.2 OUT ERROR
PIT ERROR
READ DATA = XXH
WRITE DATA = XXH
06H PIT initialization —
07H PIT function test MEMORY REFRESH ERROR
0AH First 64KB memory test FIRST 64KB MEMORY ERROR
0BH System memory —
initialization
0DH Interrupt vector —
initialization
15H RTC test RTC ERROR
READ DATA = XXH
WRITE DATA = XXH
16H CMOS RAM test ****Error in CMOS. Bad battery****
****Error in CMOS. Bad check sum****
****Error in CMOS. Bad configuration****
****Error in CMOS. Bad memory size****
****Error in CMOS. Bad HDD type****
****Error in CMOS. Bad time function****
Check system. Then press [F1] key
18H PIC initialization —
1FH Display initialization CRTC ERROR
VRAM ERROR
READ DATA = XXXXXXXXH
WRITE DATA = XXXXXXXXH
22H KBC test KBC ERROR
25H System memory test SYSTEM MEMORY ERROR
ADDRESS = XXXXXXXXH
READ DATA = XXXXXXXXH
WRITE DATA = XXXXXXXXH
SYSTEM MEMORY PARITY ERROR
ADDRESS = XXXX0000H - XXXXFFFFH
30H Extended memory test EXTENDED MEMORY ERROR
ADDRESS = XXXXXXXXH
READ DATA = XXXXXXXXH
WRITE DATA = XXXXXXXXH
EXTENDED MEMORY PARITY ERROR
ADDRESS = XXXX0000H - XXXXFFFFH
40H DMA page register test DMA PAGE REGISTER ERROR
READ DATA = XXH
WRITE DATA = XXH
T1960CS/T1960CT
2-13
Table 2-1 Printer Port LED Boot Mode Error Statuses (2/2)
Error Status Test Item Message
41H DMAC test DMAC #1 ERROR
42H DMAC initialization -
4AH PIC test PIC #1 ERROR
54H Keyboard test KEYBOARD ERROR
55H KBC initialization KBC ERROR
5AH Mouse initialization -
60H HDD initialization HDC ERROR
65H FDD initialization NO FDD ERROR
READ DATA = XXXXH
WRITE DATA = XXXXH
DMAC #2 ERROR
READ DATA = XXXXH
WRITE DATA = XXXXH
READ DATA = XXH
WRITE DATA = XXH
PIC #2 ERROR
READ DATA = XXH
WRITE DATA = XXH
HDC #0 ERROR
HDC #1 ERROR
FDD ERROR
70H Printer test 80H RS-232-C test 90H Timer initialization TIMER INTERRUPT ERROR
RTC UPDATE ERROR
A0H NDP initialization A6H Expansion I/O ROM FFH Expansion system ROM -
Check 1 If any of the following error codes display, go to Procedure 5.
01h, 05h, 06h, 07h, 0Ah, 0Bh, 0Dh, 15h, 16h, 18h, 1Fh, 22h, 25h, 30h, 40h,
41h, 42h, 54h, 55h, 65h, 70h, 80h, 90h, A0h, A6h
Check 2 If error code 4Ah displays, go to the Keyboard Troubleshooting Procedures in
Section 2.7.
Check 3 If error code 5Ah displays, go to the HDD Troubleshooting Procedures in Section
2.6.
Check 4 If error code 60h displays, go to the FDD Troubleshooting Procedures in Section
2.5.
T1960CS/T1960CT
 Loading...
Loading...