
1.1.1.1.1.1.1.1 TOSHIBA
TOSHIBA
Hard Disk Drive Specification
1.8 inch Hard Disk Drive
MK6006GAH/4006GAH/
3006GAL
Rev. 04
REF 360050398
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 1 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
Revision History
1.8 inch Hard Disk Drive MK6006GAH/4006GAH/3006GAL Product Specification
Revision Date
00 2004-07-01 Initial issue
01 2004-08-10
02 2004-10-08
03 2005-02-25
04 2005-09-05
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 2 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
SAFETY
The hard disk drive and product specifications contain essential information for the protection of
users and others from possible injury and property damage and to ensure correct handling.
Please check that you fully understand the definition of the following messages (signs and
graphical symbols) before going on to read the text, and always follow the instructions.
Please describe requirements in the instruction manual of the product in which the drive is
mounted and ensure that users are made thoroughly aware of them.
IMPORTANT MESSAGES
Read this manual and follow its instructions. Signal words such as CAUTION and NOTE,
will be followed by important safety information that must be carefully reviewed.
NOTE
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
・Toshiba Corporation shall not be liable for any damage due to the fault or negligence
of users, fire, earthquake, or other accident beyond the control of Toshiba
Corporation.
・Toshiba Corporation shall not be liable for any incidental or consequential damages
including but not limited to change or loss of stored data, loss of profit, or
interruption of business, which are caused by use or non-usability of the product.
・Toshiba Corporation shall not be liable for any damage result from failure to comply
with the contents in the product specification.
・Toshiba Corporation shall not be liable for any damage based on use of the product
in combination with connection devices, software, or other devices provided by
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which if not avoided, may res ul t
in minor injury or property damage.
Gives you helpful information.
Toshiba Corporation with the product.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
Page 3 of 157
360050398
USAGE RESTRICTIONS
● Since the drive is not designed or manufactured to be used for a system including
equipment (*1) directly linked with human life, etc., Toshiba Corporation shall not
be liable for this type of use.
*1: Equipment directly linked with human life, etc. corresponds to the
following.
−Medical equipment such as life support systems, equipment used in
operations,etc.
● When the drive is to be used for a system including equipment (*2) linked with
human safety or having a serious influence on the safe maintenance of public
function, etc., special consideration (*3) must be given with regard to operation,
maintenance, and management of the system.
*2: A system including equipment linked with human safety or having a
serious influence on the safe maintenance of public function, etc.
corresponds to the following.
−A main equipment control system used in atomic power plants, a safety
protection based system used in atomic facilities, other important
safety lines and systems.
−An operation control system for mass transport, an air-traffic control
system.
*3: Special consideration means that a safety system (fool proof design, fail
safe design, redundancy design, etc.) is established as a result of
adequate consultation with Toshiba engineers.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 4 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

SAFETY
■ Do not disassemble, remodel or repair.
Disassembly, remodeling or repair may cause injury, failure, or data loss.
■ Do not drop.
Dropping may cause injury.
■ Do not touch sharp edges or pins of the drive.
Sharp protrusions etc. may cause injury.
Hold the drive by both sides when carrying it.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 5 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
SAFETY
Observe the following to prevent failure, malfunction or data loss.
NOTE
●Follow the specifications for 6. POWER SUPPLY (page16), 8. ENVIRONMENT (page 22, 24),
etc. when using.
Failure to do so may cause damage to the drive.
●Observe cautions in 7.3 MOUNTING INSTRUCTION (page18) and 9.5 LOAD / UNLOAD
(page28 ) when handling, setting up, or using the drive.
●Take anti-static measures in order to avoid damage to the drive when handling it.
The drive uses parts susceptible to damage due to ESD (electrostatic discharge).
Wear ESD proof wrist strap in accordance with the usage specified when handling a drive that is not in an anti-static
protection bag.
●There is a certain probability of the drive causing failure including data error or data loss.
Take preventive steps such as backing up data etc. without exception in order to prevent loss etc. in cases where data
loss may result in loss or damage.
Please include this in the instruction manual etc. of the system in which this device is used and ensure that users are
made thoroughly aware of it.
●Inserting or pulling out the drive when the power is turned on may cause damage to the drive.
Exchange the drive etc. after the power of HDD is turned off.
●Extreme shock to the drive may cause damage to it, data corruption, etc..
Do not subject the drive to extreme shock such as dropping, upsetting or crashing against other objects.
●Do not touch the top cover since application of force to it may cause damage to the drive.
●Do not stack the drive on another drive or on other parts etc. or stack them on top of it during
storage or transportation.
Shock or weight may cause parts distortion etc..
●Labels and the like attached to the drive are also used as a seal for maintenance of its
performance.
Do not remove them from the drive.
●Attachment of dielectric materials such as metal powder, liquid, etc. to live parts such as printed
circuit board patterns or pins etc. may cause damage to the drive.
Avoid attachment of these materials.
●Do not place objects which generate magnetic fields such as magnets, speakers, etc. near the
drive.
Magnetism may cause damage to the drive or data loss.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 6 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1.
SCOPE........................................................................................................................................................ 11
2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION....................................................................................................................... 11
3. KEY FEATURES....................................................................................................................................... 13
4. BASIC SPECIFICATION.......................................................................................................................... 14
5. PERFORMANCE....................................................................................................................................... 15
6. POWER REQUIREMENTS ...................................................................................................................... 16
6.1 SUPPLY VOLTAGE.....................................................................................................................................16
6.2 POWER CONSUMPTION .............................................................................................................................16
6.3 ENERGY CONSUMPTION EFFICIENCY .......................................................................................................17
7. MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS......................................................................................................... 18
7.1 DIMENSION AND WEIGHT..........................................................................................................................18
7.2 DRIVE ORIENTATION................................................................................................................................18
7.3 MOUNTING INSTRUCTIONS.......................................................................................................................18
7.3.1 Installation ......................................................................................................................................19
8. ENVIRONMENTAL LIMITS.................................................................................................................... 22
8.1 TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY.................................................................................................................22
8.1.1 Temperature....................................................................................................................................22
8.1.2 Humidity..........................................................................................................................................22
8.2 VIBRATION................................................................................................................................................22
8.3 SHOCK......................................................................................................................................................22
8.4 ALTITUDE.................................................................................................................................................24
8.5 ACOUSTICS(SOUND POWER)................................................................................................................24
8.6 SAFETY STANDARDS.................................................................................................................................25
EMC ADAPTABILITY ...........................................................................................................................................26
8.7 MAGNETIC FIELDS ...................................................................................................................................26
9. RELIABILITY............................................................................................................................................ 27
9.1 ERROR RATE.............................................................................................................................................27
9.1.1 Non- Recoverable Error Rate .........................................................................................................27
9.1.2 Seek Error Rate...............................................................................................................................27
9.2 PRODUCT LIFE..........................................................................................................................................27
9.3 REPAIR .....................................................................................................................................................27
9.4 PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE (PM)...........................................................................................................27
9.5 LOAD/UNLOAD..........................................................................................................................................28
10. HOST INTERFACE............................................................................................................................... 29
10.1 CABLING...................................................................................................................................................29
10.1.1 Interface Connector.........................................................................................................................29
10.2 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION ....................................................................................................................30
10.2.1 Cable length and capacitance.........................................................................................................30
10.2.2 DC input/output Characteristics....................................................................................................30
10.3 INTERFACE CONNECTOR...........................................................................................................................31
10.3.1 ATA interface connector .................................................................................................................31
10.3.2 Pin Assignment ...............................................................................................................................32
10.3.3 Signal Treatment ............................................................................................................................33
10.3.4 Series resistance..............................................................................................................................34
10.3.5 Signal Description...........................................................................................................................34
10.4 HOST INTERFACE TIMING.........................................................................................................................36
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 7 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.4.1 Program I/O Write Timing............................................................................................................. 36
10.4.2 Program I/O Read Timing.............................................................................................................. 37
10.4.3 Multiword DMA Write Timing......................................................................................................38
10.4.4 Multiword DMA Read Timing.......................................................................................................39
10.4.5 Ultra DMA Timing ......................................................................................................................... 40
10.4.6 Reset Timing................................................................................................................................... 49
10.5 GROUNDING............................................................................................................................................. 49
10.6 ADDRESS DECODING................................................................................................................................50
10.7 REGISTER DESCRIPTION .......................................................................................................................... 51
10.7.1 Data Register.................................................................................................................................. 51
10.7.2 Error Register................................................................................................................................. 52
10.7.3 Features Register (Write Precompensation Register) ................................................................. 53
10.7.4 Sector Count Register..................................................................................................................... 53
10.7.5 Sector Number Register................................................................................................................. 54
10.7.6 Cylinder Low Registers..................................................................................................................54
10.7.7 Cylinder High Registers.................................................................................................................54
10.7.8 Device/Head Register ..................................................................................................................... 55
10.7.9 Status Register ...............................................................................................................................56
10.7.10 Command Register...................................................................................................................... 57
10.7.11 Alternate Status Register........................................................................................................... 59
10.7.12 Device Control Register.............................................................................................................. 59
10.7.13 Device Address register..............................................................................................................59
10.8 COMMAND DESCRIPTIONS ....................................................................................................................... 60
10.8.1 Nop (00h) ...................................................................................................................................... 61
10.8.2 Recalibrate (1xh) ..........................................................................................................................61
10.8.3 Flush Cache (E7h)........................................................................................................................61
10.8.4 Flush Cache EXT (EAh) ..............................................................................................................61
10.8.5 Read Sector (20h/21h).................................................................................................................. 62
10.8.6 Read Sector EXT (24h) ................................................................................................................ 62
10.8.7 Write Sector (30h/31h)................................................................................................................. 63
10.8.8 Write Sector EXT (34h) ............................................................................................................... 63
10.8.9 Read Verify (40h) .........................................................................................................................65
10.8.10 Read Verify EXT (42h)............................................................................................................. 65
10.8.11 Write Verify (3Ch).................................................................................................................... 66
10.8.12 Format Track (50h) ................................................................................................................ 66
10.8.13 Seek (7xh).................................................................................................................................. 67
10.8.14 Toshiba Specific........................................................................................................................... 67
10.8.15 Execute Diagnostics (90h)........................................................................................................ 68
10.8.16 Initialize Device Parameters (91h) ......................................................................................... 69
10.8.17 Download Microcode (92h).......................................................................................................70
10.8.18 Read Multiple (C4h)................................................................................................................. 71
10.8.19 Read Multiple EXT (29h)......................................................................................................... 72
10.8.20 Write Multiple (C5h)................................................................................................................ 72
10.8.21 Write Multiple EXT (39h)........................................................................................................ 73
10.8.22 Set Multiple Mode (C6h).......................................................................................................... 73
10.8.23 Read DMA (C8h/C9h)............................................................................................................... 74
10.8.24 Read DMA EXT (25h) .............................................................................................................. 74
10.8.25 Write DMA (CAh/CBh) ............................................................................................................75
10.8.26 Write DMA EXT (35h) ............................................................................................................. 75
10.8.27 Power Control (Exh)................................................................................................................. 76
10.8.28 Read Buffer (E4h)..................................................................................................................... 78
10.8.29 Write Buffer (E8h).................................................................................................................... 78
10.8.30 Identify Device (ECh)............................................................................................................... 78
10.8.31 SET MAX (F9h)...........................................................................................................................93
10.8.32 SET MAX ADDRESS EXT (37h) ............................................................................................... 96
10.8.33 Read Native Max Address (F8h) ........................................................................................... 96
10.8.34 Read Native Max Address EXT (27h)................................................................................... 97
10.8.35 Set Features (EFh)................................................................................................................... 98
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 8 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.8.36 SECURITY SET PASSWORD (F1h) .......................................................................................99
10.8.37 SECURITY UNLOCK (F2h)...................................................................................................100
10.8.38 SECURITY ERASE PREPARE (F3h) ...................................................................................100
10.8.39 SECURITY ERASE UNIT (F4h)............................................................................................101
10.8.40 SECURITY FREEZE LOCK (F5h) ........................................................................................101
10.8.41 SECURITY DISABLE PASSWORD (F6h)............................................................................102
10.8.42 SMART Function Set (B0h)......................................................................................................102
10.8.43 Read Log EXT (2Fh) ...............................................................................................................124
10.8.44 Write Log EXT (3Fh) ..............................................................................................................131
10.8.45 Device Configuration (B1h).......................................................................................................132
10.9 SECURITY MODE FEATURE SET..............................................................................................................140
10.9.1 Security mode default setting.......................................................................................................140
10.9.2 Initial setting of the user password .............................................................................................140
10.9.3 Security mode operation from power-on......................................................................................141
10.9.4 Password lost.................................................................................................................................142
10.9.5 Command Table ............................................................................................................................143
10.10 SELF-MONITORING, ANALYSIS AND REPORTING TECHNOLOGY .........................................................144
10.10.1 Attributes...................................................................................................................................144
10.10.2 Attributes values .......................................................................................................................144
10.10.3 SMART function default setting...............................................................................................144
10.11 ADAPTIVE POWER MODE CONTROL ....................................................................................................145
10.11.1 Performance Idle........................................................................................................................145
10.11.2 Active Idle ..................................................................................................................................145
10.11.3 Low Power Idle ..........................................................................................................................145
10.11.4 Transition time..........................................................................................................................145
10.12 RESET .................................................................................................................................................146
10.13 DRIVE0/DRIVE1 CONFIGURATION ......................................................................................................147
10.14 CACHE MEMORY.................................................................................................................................148
10.14.1 Cache Operations.......................................................................................................................148
10.14.2 Notes for write cache.................................................................................................................148
10.15 AUTOMATIC WRITE REALLOCATION ...................................................................................................148
11. PROTOCOL.......................................................................................................................................... 149
11.1 PIO DATA IN COMMANDS........................................................................................................................150
11.2 PIO DATA OUT COMMANDS.....................................................................................................................151
11.3 NON-DATA COMMANDS...........................................................................................................................152
11.4 DMA DATA TRANSFER COMMANDS.........................................................................................................153
11.5 ULTRA DMA...........................................................................................................................................154
11.6 OTHER TIMINGS......................................................................................................................................157
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 9 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
Table of Figures
FIGURE 1 POWER CURRENT TRANSITION..................................................................................................................16
FIGURE 2 MK3006GAL DIMENSIONS................................................................................................................20
FIGURE 3 MK6006GAH/MK4006GAH DIMENSIONS............................................................................21
FIGURE 4 ATA INTERFACE CONNECTOR................................................................................................................................31
FIGURE 5 PASSWORD SET SECURITY MODE POWER-ON FLOW .........................................................................................141
FIGURE 6 USER PASSWORD LOST.......................................................................................................................................142
FIGURE 7 OPTIONAL JUMPER FOR DRIVE0/DRIVE1.........................................................................................................147
ABLE 10.3-1 SIGNAL PIN ASSIGNMENT ................................................................................................................................32
T
TABLE 10.3-2 SIGNAL TREATMENT .......................................................................................................................................33
TABLE 10.6-1 REGISTER MAP................................................................................................................................................50
TABLE 10.6-2 DECODE LOGIC...............................................................................................................................................50
TABLE 10.7-1 DIAGNOSTIC MODE ERROR REGISTER..............................................................................................................53
TABLE 10.7-2 COMMAND CODE............................................................................................................................................58
TABLE 10.8-1 IDENTIFY INFORMATION .................................................................................................................................79
TABLE 10.8-2 IDENTIFY INFORMATION (CONTINUED)...........................................................................................................80
TABLE 10.8-3 IDENTIFY INFORMATION (CONTINUED)...........................................................................................................81
TABLE 10.8-4 IDENTIFY INFORMATION (CONTINUED)...........................................................................................................82
TABLE 10.8-5 IDENTIFY INFORMATION (CONTINUED)...........................................................................................................83
TABLE 10.8-6 SET MAX FEATURES REGISTER VALUES .......................................................................................................93
TABLE 10.8-7 SET MAX SET PASSWORD DATA CONTENT...............................................................................................94
TABLE 10.8-8 DEVICE CONFIGURATION IDENTIFY DATA STRACTURE .................................................................................133
TABLE 10.8-9 DEVICE CONFIGURATION OVERLAY DATA STRACTURE.................................................................................137
TABLE 10.9-1 SECURITY MODE COMMAND ACTIONS ...........................................................................................................143
TABLE 10.12-1 INITIALIZATION OF TASK FILE REGISTERS...................................................................................................146
TABLE 11.6-1 OTHER TIMINGS. ...........................................................................................................................................157
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 10 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

1. SCOPE
This document describes the specifications of the following model, MK3006GAL
/MK4006GAH/MK6006GAH of 1.8- inch type Winchester disk drives.
.
Factory Number
Sales Number
HDD1442 MK3006GAL
HDD1564 MK4006GAH
HDD1544 MK6006GAH
2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MK3006GAL/MK4006GAH/MK6006GAH which is noted hereinafter as
“ MK3006GAL/MK4006GAH/MK6006GAH” or as “ the drive ” comprises a series of intelligent disk
drives .
The drive features an ATA-2 / 3 / 4 / 5 / 6 interface embedded controller that requires a simplified adapter
board for interfacing to an AT or AT compatible bus. The drives employ Winchester technology and a closed
loop servo control system which have made high recording density of 149.6 M bit/mm
2
bit/in
)(MK3006GAL/MK6006GAH), 131.7 M bit/mm2(85.0G bit/in2)(MK4006GAH)and average access time
of 15 msec with highest reliability of 300,000 hours for MTTF (Mean Time to Failure) possible.
The drive is distinctive for its small and light body.
The
MK3006GAL/MK4006GAH/MK6006GAH consists of an HDA (Head Disk Assembly) and a
printed circuit board. The HDA has a sealed module which contains a disk spindle assembly, a head
actuator assembly and an air filtration system. This HDA adopts Winchester technology which enhances
high reliability. The actuator is a rotary voice coil motor which enables high-speed access.
2
(96.5G
The disk is driven directly by a DC spindle motor. Air filtration is provided by a high performance air filtration
system using both breather and circulation filters.
The drive provides a carriage lock mechanism which is activated automatically upon power down in order to
prevent head/media from being damaged when it is not operating or under shipment.
The printed circuit board which is set externally to the HDA and equipped with all the electric circuitry
necessary to operate the drive except the head drivers . The power supply and interface signal connectors
are mounted on the board. Only the head control IC’s are located within the HDA. The circuitry perform the
following functions:
Read/Write, Task File Control, Spindle Motor Control, Seek and Head Positioning Servo Control, Abnormal
Condition Detection and Shock Sensor Control.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 11 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
SAFETY
●There is a certain probability of the drive causing failure including data error or data
loss.
Take preventive steps such as backing up data etc. without exception in order to
■Do not disassemble, remodel or repair.
Disassembly, remodeling or repair may cause injury,
failure, or data loss.
NOTE
prevent loss etc. in cases where data loss may result in loss or damage.
●Do not touch the top cover since application of force to it may cause damage to the
drive.
●Do not stack the drive on another drive or on other parts etc. or stack them on top of
it during storage or transportation.
Shock or weight may cause parts distortion etc..
●Labels and the like attached to the drive are also used as hermetic sealing for
maintenance of its performance.
Do not remove them from the drive.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 12 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

3. KEY FEATURES
• High capacity in smallest size
. 1.8 inch-type 2 platters accommodating formatted capacity of 60.0116GB
(MK6006GAH)/40.000GB(MK4006GAH),
1 platter accommodating formatted capacity of 30.0058GB(MK3006GAL).
. Slim ( MK3006GAL: 5 mm in height, MK6006GAH: 8mm in height) and light (MK3006GAL: 51 gram in
weight, MK6006GAH/MK4006GAH: 62 gram in weight) design.
• Fast access and fast transfer rate
. Quick spin up of Spindle Motor 3 sec.
. Average access time 15 msec enabled by optimized balance of a head actuator assembly and an efficiently
designed magnet of rotary VCM.
. Bus transfer rate up to 100 megabytes per second and disk transfer 283 megabits maximum per
second,(MK3006GAL/MK6006GAH),265 megabits maximum per second. (MK4006GAH)
. Read ahead cache and write cache enhancing system throughput.
• Intelligent Interface
.
ATA-2/ATA-3/ATA-4/ATA-5/ATA-6 interface supported.
.
Ultra100 supported.
.
Quick address conversion in translation mode.
.
Translation mode which enables any drive configuration.
.
LBA (Logical Block Address) mode.
. Multi word DMA, Ultra-DMA modes and Advanced PIO mode supported.
• Data integrity
. Automatic retries and corrections for read errors.
. 520 bits computer generated ECC polynomial with 10 bits symbol 24 burst on-the-fly error correction
capability.
• High reliability
. Powerful self- diagnostic capability.
. Shock detection with shock sensor circuit for high immunity against operating shock up to 4,900 m/s
( 500 G ).
2
. Automatic carriage lock secures heads on the ramp with high immunity against non operating shock up to
14,700 m/s
• Low power consumption
• Supply voltage: 3.3V
2
(1,500G).
. Low power consumption by Adaptive Power Mode Control .
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 13 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
360050398
4. BASIC SPECIFICATION
MODEL MK3006GAL MK6006GAH MK4006GAH
Formatted Capacity
30.0058 60.0116 40.000
( gigabytes )
Number of sectors 58,605,120 117,210,240 78,126,048
Servo design method Sector Servo
Recording method 60/61 ME2PR4+MNP
Recording density
Track / mm (TPI ) 4704 (119.5k) 4331 (110k) typ.
Bit / mm ( BPI ) 31.8k (808k ) max. 29.0k (737k ) max.
Flux change / mm ( FRPI ) 32.3k (821k ) max. 29.5k (750k ) max.
Number of disks 1 2
Number of data heads 2 4
Number of user data cylinders 55,728 38,160
Bytes per sector 512
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 14 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
5. PERFORMANCE
MK3006GAL MK6006GAH MK4006GAH
Access time ( msec ) <*1>
Track to track seek <*2> 3
Average seek <*3> 15
Max. seek <*4> 26
Rotation speed ( RPM ) 4,200 + 0.1%
Average Latency Time ( msec ) 7.14
Internal Transfer rate ( Mbits / sec )
Host Transfer rate ( Mbytes / sec )
Ultra DMA mode 100
PIO mode 16.6
Sector Interleave 1:1
Track skew Yes
Buffer size ( Mbytes ) 2 or 8 2 or 8 2
Cache Read Ahead Cache
Start time <*5>
( Up to Drive Ready)
Recovery time from Stand- by <*5> 3 sec ( Typical )
Command Overhead ( msec ) 1
<*1> Under the condition of normal voltage, 25oC normal temperature and bottom side down.
131.1−283.3 155−265
Write Cache
3.5 sec ( Typical )
20 sec ( Maximum )
20 sec ( Maximum )
<*2> Average time to seek all possible adjacent track without head switching.
<*3> Weighted average time to travel between all possible combination of track calculated as below.
Weighted average access time = [ Sum of P(n)*t(n) ] / [ Sum of P(n) ], n = 1 to N.
Where, N ; Total number of tracks.
P(n); Total number of seek for stroke n [ = 2*(N - n) ].
t(n); Average seek time for stroke n.
Average seek time to seek to stroke n is the average time to 1,000 seeks for stroke n, with random head
switch.
<*4> Average time for 1,000 full stroke seeks with random head switches.
<*5> Typical values are for the condition of normal voltage, 25oC normal temperature and placing bottom
side down. Maximum values are for all conditions specified in this document.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 15 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
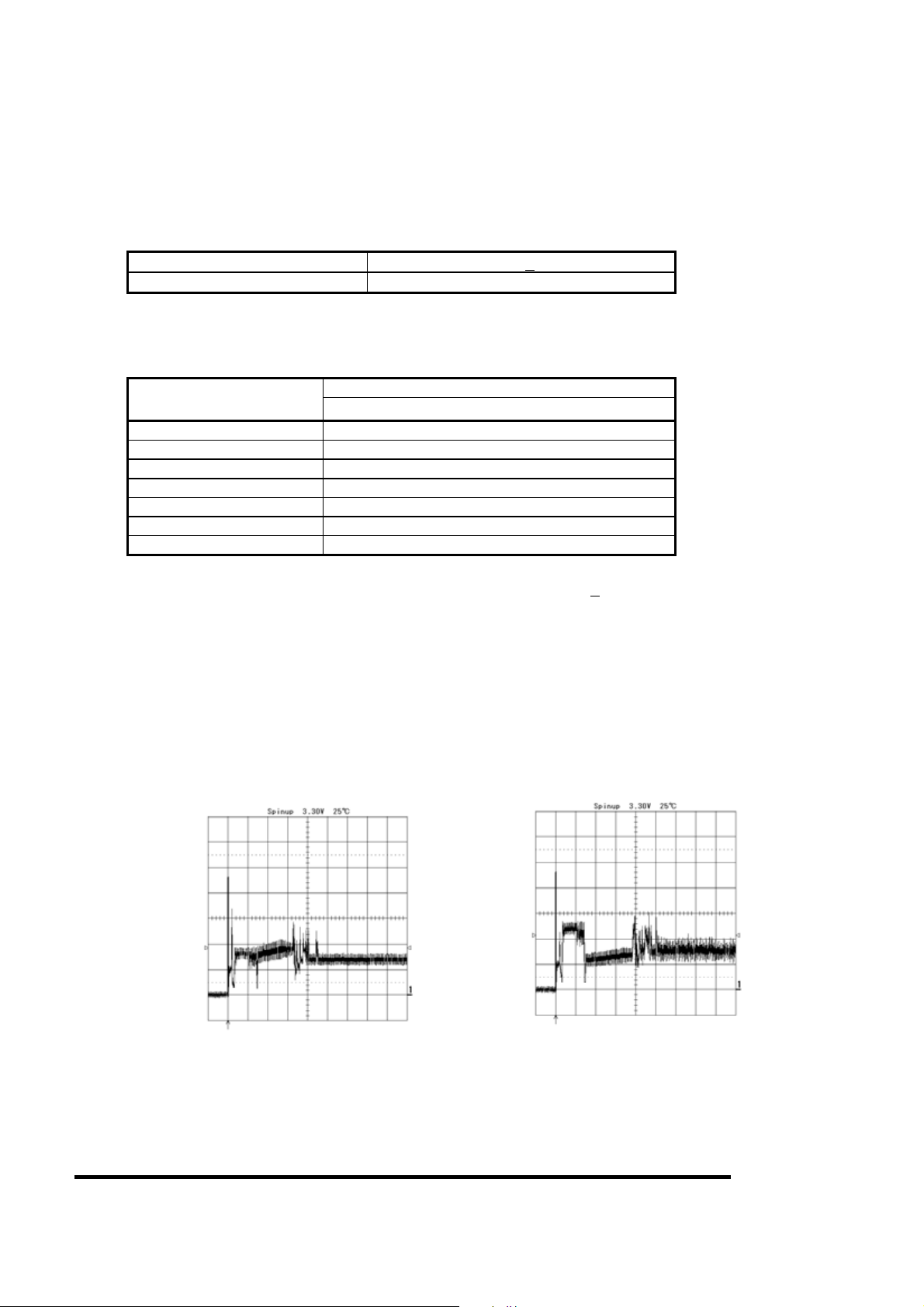
360050398
6. POWER REQUIREMENTS
6.1 Supply Voltage
Allowable voltage 3.3V + 5%
Allowable noise/ripple 70 mV p-p or less
(note 1) When DC power is interrupted,+3.3V voltage drop must be greater than or equal to 0V.
6.2 Power Consumption
Average(note 1)
MK3006GAL/MK6006GAH/MK4006GAH
Start (note 2) 1.8 W Maximum
Seek (note 3) 1.1 W Typical
Read / Write(note 4) 1.1 W Typical
Active idle (note 5 ) 0.4 W Typical
Low power idle (note 6) 0.3 W Typical
Stand- by (note 7) 0.12 W Typical
Sleep 0.07 W Typical
(note 1) Under normal condition ( 25oC, 101.3 kPa ( 1,013 mb ) ) and 3.3V +
(note 2) This is the maximum current value between power on to ready and the maximum value is the RMS(Root
Mean Square) of 10 ms.Dose not include rush current.(more information Figure 1)
(note 3) The seek average current is specified based on three operations per 100 ms.
(note 4) The read/write current is specified based on three operations of 63 sector read/write per 100 ms.
(note 5) Motor is rotating at normal speed but none of Read, Write or Seek is executed.
(note 6) Motor is rotating at normal speed but heads are unloaded on the ramp.
(note 7) Motor is not rotating and heads are unloaded on the ramp.
0%.
0.2A/div
0.5sec/div
MK6006GAH/MK4006GAH
Figure 1
Power Current Transition
0.2A/div
0.5sec/div
MK3006GAL
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 16 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

6.3 Energy Consumption Efficiency
Energy consumption efficiency (W/GB) Classification
Power consumption at Low power idle / Capacity
MK3006GAL
MK4006GAH 0.0075 E
MK6006GAH 0.005 E
Energy consumption efficiency is calculated in accordance with the law regarding efficiency of energy
consumption
:Energy saving law,1979 law number 49.
Calculation of Energy consumption is dividing consumed energy by the capacity.
The consumed energy and capacity shall be measured and specified by the Energy saving low.
0.010
D
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 17 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
360050398
7. MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS
7.1 Dimension and weight
MK3006GAL MK6006GAH/MK4006GAH
Width (mm)
0.15 8.0 + 0.15
Height (mm)
Depth (mm)
Warpage (mm)
Interconnected area
Width (shorter side)
Depth (longer side)
Substrate area
(thickness including warpage)
Weight 51 max. 62 max.
Figure 2 and Figure 3 show an outline of the drive.
5.0 +
5.35 max.
54.0 ±0.2
78.5±0.3
0.15 max.
0.35 max.
8.35 max.
7.2 Drive Orientation
The drive can be installed in all axes (6 directions).
7.3 Mounting Instructions
SAFETY
●Take anti-static measures in order to avoid damage to the drive when handling it.
The drive uses parts susceptible to damage due to ESD (electrostatic discharge).
Wear ESD proof wrist strap in accordance with the usage specified when handling
a drive that is not in an anti-static protection bag.
●Extreme shock to the drive may cause damage to it, data corruption, etc..
Do not subject the drive to extreme shock such as dropping, upsetting or crashing
against other objects.
NOTE
●Do not place objects which generate magnetic fields such as magnets, speakers,
etc. near the drive.
Magnetism may cause damage to the drive or data loss.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 18 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

7.3.1 Installation
1) The drive should be interconnected of mounted carefully on the surface of 0.1mm or less flatness to avoid
excessive distortion.
2) The drive can be easily damaged by shocks. In order to prevent the damege, avoid giving shock to the
drive.
3) Don’t apply any force to the top cover.
4) The drive contains several parts which may be easily damaged by ESD(Electric Static Discharge). Avoid
touching the interface connector pins and surface of PCB.
5) The temperature of top cover and the base must always be kept under 65°C to maintain the required
reliability. (If the drive runs continuousely or spins-up frequently, the temperature of the top cover may rise
to 15°C maximum. If the drive is used in ambient temperature of 50 °C or more, it should be kept where
adequate ventilation is available to keep the temperature of top cover under 65°C)
6) Be careful when removing the drive from the host device. The drive may have heated up during operation.
7) Do not disassemble, modify or repair.
8) A rattle heard when the drive is moved is not a sign of failure.
9) Provision for tying the DC logic ground and the chassis ground together or for separating these ground is
user specific.
Agreeable locations of chassis ground are in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 19 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
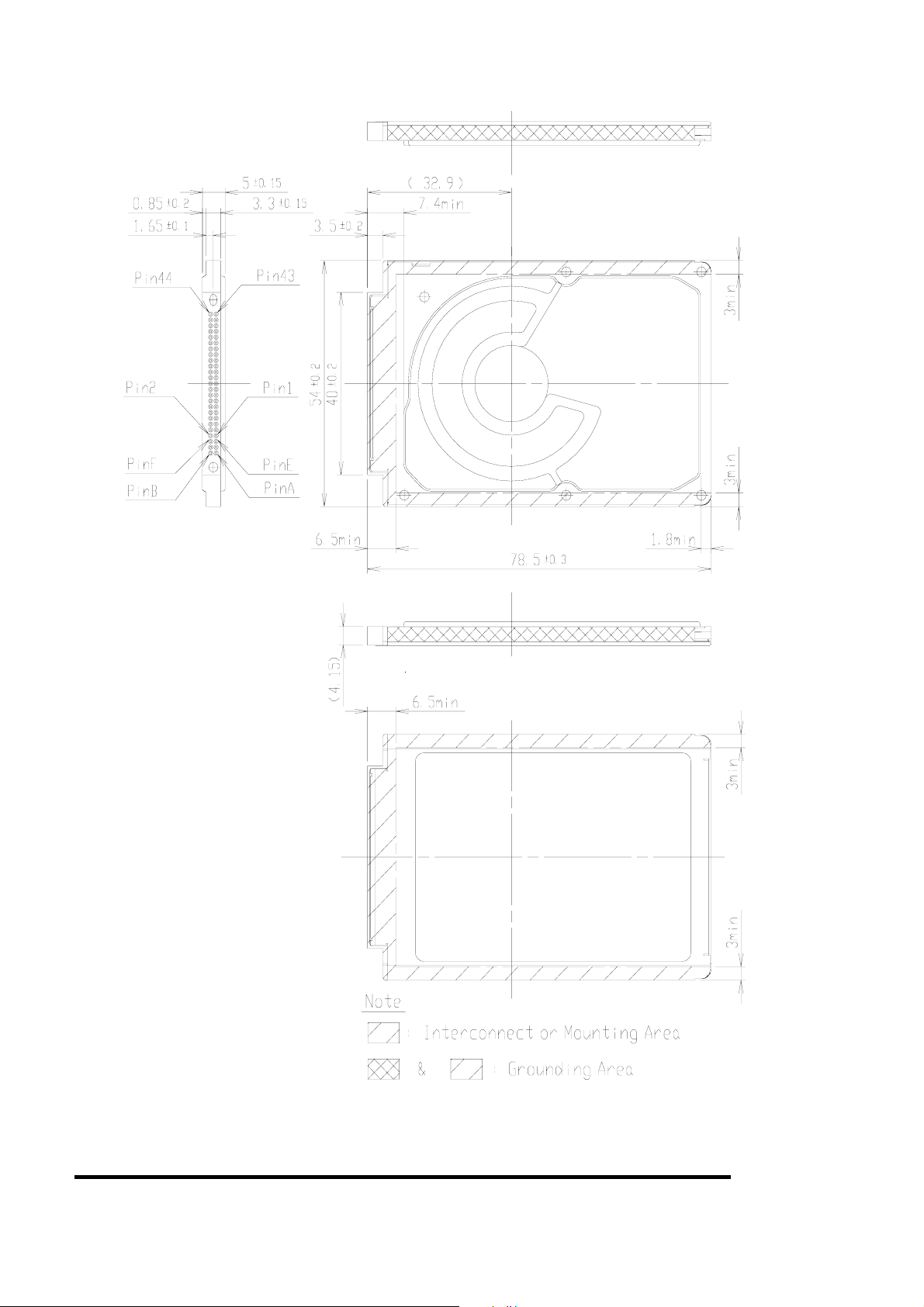
360050398
m
Figure 2
MK3006GAL Dimensions
UNIT: m
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 20 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
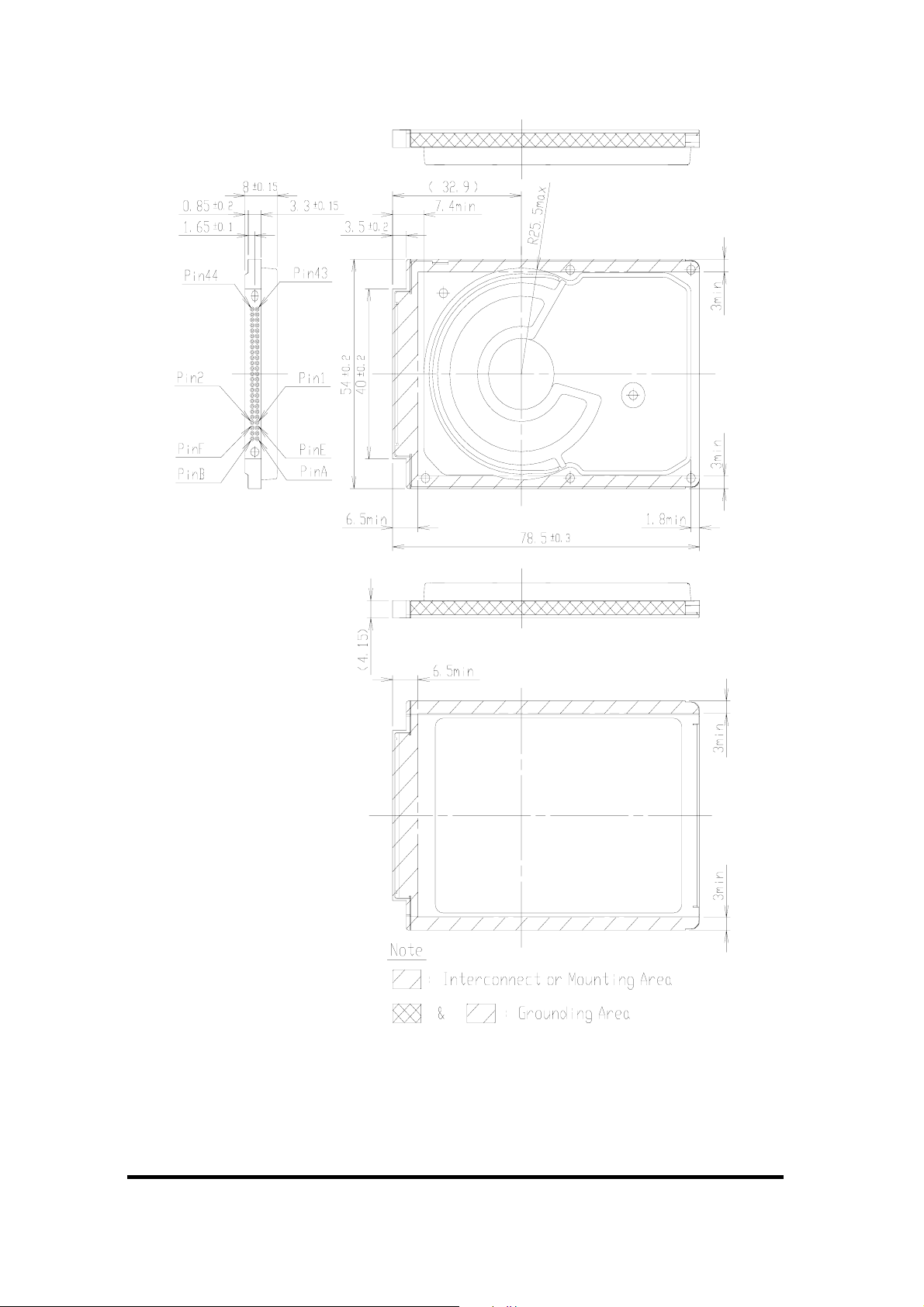
Figure 3
MK6006GAH/MK4006GAH Dimensions
UNIT: mm
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 21 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
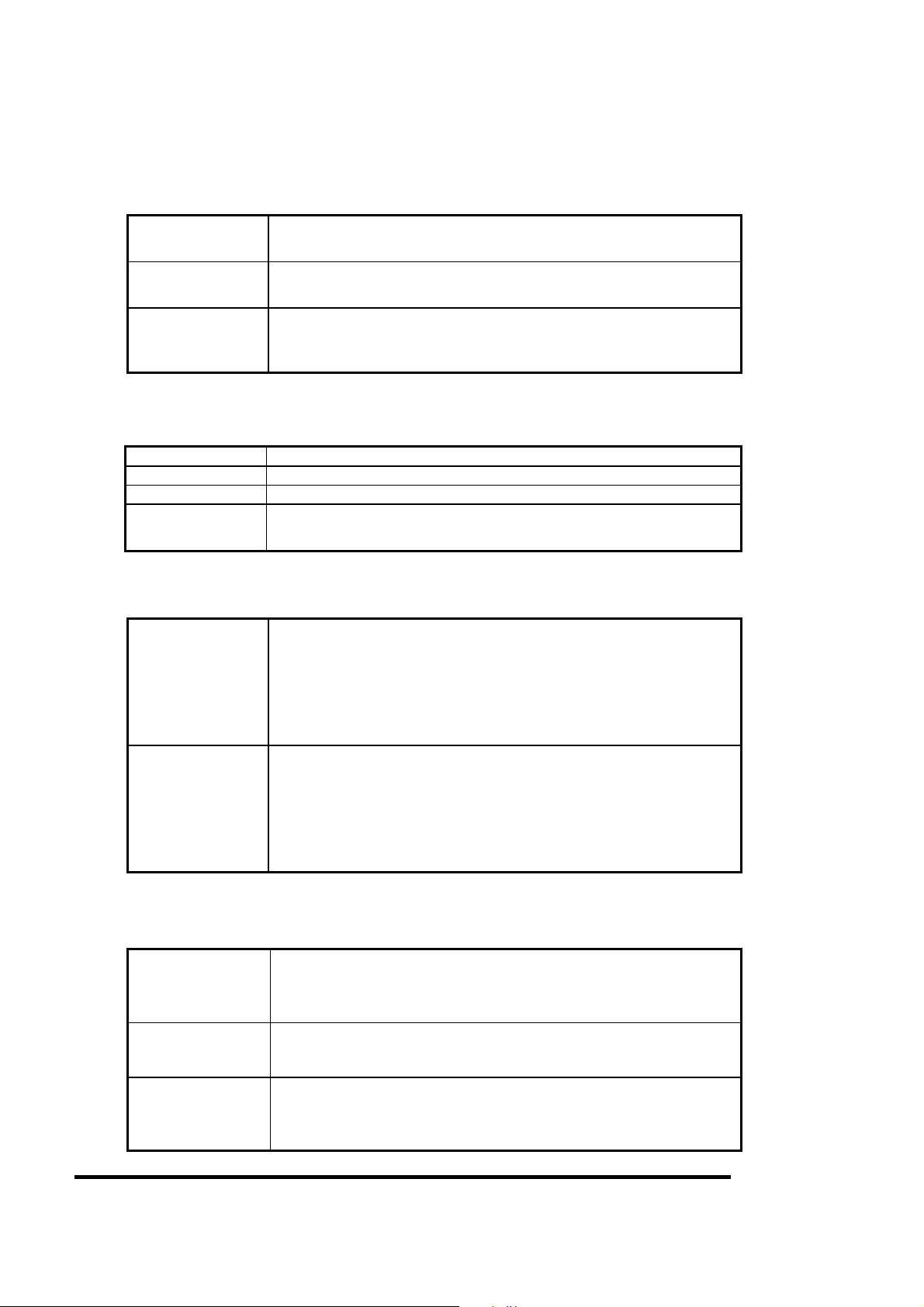
360050398
8. ENVIRONMENTAL LIMITS
8.1 Temperature and Humidity
8.1.1 Temperature
Operating
Non- operating
Under shipment
The temperature of top cover and base must be kept under 65℃ at any moment to maintain the desired reliability.
5oC- 60oC
Gradient 15oC / Hour maximum
- 20oC- 65oC
Gradient 15oC / Hour maximum
- 40oC- 70oC
Gradient 30oC / Hour maximum
( Packed in Toshiba’s original shipping package. )
8.1.2 Humidity
Operating 8%- 90% R.H. ( No condensation. )
Non- operating 8%- 90% R.H. ( No condensation. )
Under shipment 5%- 90% R.H. ( Packed in Toshiba’s original shipping package. )
Max. wet bulb 29o
C (Operating)
40oC (Non- operating)
8.2 Vibration
Operating 4 mm p-p displacement.
5-15 Hz
No unrecoverable error.
19.6 m/s
15- 500 Hz
Sine wave sweeping 1 oct./ minute
No unrecoverable error.
Non operating 10 mm p-p displacement.
5-15 Hz
No unrecoverable error.
49 m/s
15- 500 Hz
Sine wave sweeping 1 oct./ minute
No unrecoverable error.
2
( 2.0G )
2
( 5.0G )
8.3 Shock
Operating 4,900 m/s2 ( 500G )
Non- operating 14,700 m/s2 ( 1500G ) 1 msec half sine wave
Under shipment 70 cm free drop
2 msec half sine wave
Repeated twice maximum / second
No unrecoverable error.
Repeated twice maximum / second
No unrecoverable error.
No unrecoverable error.
Apply shocks in each direction of the drive’s three
mutually perpendicular axes, one axis at a time.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 22 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

( Packed in Toshiba’s original shipping package. )
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 23 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
360050398
8.4 Altitude
Operating - 300 m to 3,000 m
Non operating - 400 m to 15,000 m
8.5 Acoustics(Sound Power)
MK3006GAL MK6006GAH/
MK4006GAH
16dB 18dB For idle mode ( Spindle in rotating ).
Randomly select a track to be sought in such a way thatevery track
has equal probability of being selected.
Seek rate(n
) is defined by the following formura:
s
n
= 0.4 / ( tT = tL )
22dB 24dB
s
t
is published time to seek from one randam track to another
T
without including rotational latency;
t
is the time for the drive to ratate by half a revolution.
L
Measurements are to be taken in accordance with ISO 7779.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 24 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
p
C
/
8.6 Safety Standards
The drive satisfies the following standards .
MK3006GAL MK6006GAH/MK4006GAH
Underwriters Laboratories
Canadian Standard Association
TUV Rheinland
Bureau of Standards,Metrology
and Ins
ection
Ministry of Information and
ommunication
(Note 1) Marks of Ministory of Information and Communication
(UL) 1950
(CSA)C22.2 No.950
EN 60 950
D33003
(Note1)
Made in
Japan
Made in
Philippines
Made in
China
Made in
Indonesia
MK3006GAL MK6006GAH
MK3006GAL
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-05
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
MK3006GAL
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-05
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
MK3006GAL
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-05
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
MK3006GAL
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-05
TOSHIBA CORPORATION /
MK4006GAH
Made in
Japan
Made in
Philippines
Made in
China
Made in
Indonesia
MK4006GAH
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-08
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
MK4006GAH
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-08
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
MK4006GAH
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-08
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
MK4006GAH
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-08
TOSHIBA CORPORATION /
MK6006GAH
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-06
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
MK6006GAH
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-06
MK6006GAH
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-06
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
MK6006GAH
E-H011-04-2071(B)
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
2004-06
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 25 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
360050398
EMC Adaptability
The drive satisfies the following standards .
MK3006GAL MK6006GAH/MK4006GAH
EN5008M1-E1
EN50081-1
EN55024
EN55022 : 1998 Class B
EN61000-3-2 : 1995
EN61000-3-3 : 1995
EN61000-4-2 : 1995
EN61000-4-3 : 1995
ENV50204 : 1995
EN61000-4-4 : 1995
EN61000-4-5 : 1995
EN61000-4-6 : 1996
EN61000-4-11 : 1994
8.7 Magnetic Fields
The disk drive shall work without degradation of the soft error rate under the following Magnetic Flux Density
Limits at the enclosure surface.
MK3006GAL/
MK6006GAH/MK4006GAH
0.6mT(6Gauss)
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 26 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
9. RELIABILITY
A failure is defined as an inability of the drive to perform its specified function described in the requirements
of this document when being operated under the normal conditions or conditions specified in this document.
However , damages caused by operation mistake, mishandling, accidents, system errors and other
damages that can be induced by the customers are not defined as failure.
.
9.1 Error Rate
9.1.1 Non- Recoverable Error Rate
1 error per 10
The defective sectors allocated to the spare locations in the factory are not counted in the error rate.
9.1.2 Seek Error Rate
1 error per 106 seeks
A seek error is a positioning error recoverable by a retry including recalibration.
13
bits read
9.2 Product Life
Approximately 5 years or 20,000 power on hours whichever comes earlier under the following conditions.
- Power on hours (note1) : Less than 333 hours/month
- Operating (note2) : Less than 20% of power on hour
- Number of seek : 1.30 x 10
- Enviroment : Normal ( 25oC, 101.3 kPa ( 1,013 mb ) )
- Do not apply electrical static discharge, vibration and shock to the drive.
- Do not press top cover and bottom PCBA surface of the drive.
- All others condition should be within specification shown in section 6/7/8/9.
(note1) Power on hour includes sleep and standby mode.
(note2) Operating : seeking, writing and reading.
Applicable warranty and warranty period should be covered by the purchase agreement.
6
seeks / month
9.3 Repair
A defective drive should be replaced. Parts and subassemblies should not be repaired individually .
9.4 Preventive Maintenance (PM)
No preventive maintenance is required.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 27 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
9.5 Load/Unload
Be sure to issue and complete the following commands for unloading before cutting off the power
supply.
Following table shows the specification for normal load/unload cycles.
Load/unload cycle (Times) Environment
600,000 Room temperature
300,000 Operational temperature range
Unload is executed by the following commands :
・Standby
・Standby Immediate
・Sleep
・Hard reset
Load/Unload is also executed as one of the idle modes of the drive.
If power is removed from the drive while the heads are over the media an Emergency
Unload will take place. An Emergency Unload is performed by routing the back-EMF
of the spindle motor to the actuator voice coil. An Emergency Unload is mechanically
much more stressful to this drive than a controlled Unload. The minimum number of
Emergency Unloads that can be successfully performed is 20,000. Emergency Unload
should only be performed when it is not possible to perform a controlled Unload.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 28 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
10. HOST INTERFACE
Related Standards
Information technology - AT Attachment Interface with Extensions (ATA-2)
X3T10.279-199x
Information technology - AT Attachment-3 Interface (ATA-3)
X3T10/2008D Revision 6 October 26, 1995
Information technology - AT Attachment with Packet Interface Extension (ATA -4)
T13/1153D Revision 17 October 30, 1997
Information technology - AT Attachment with Packet Interface-5 Interface-5 (ATA-5)
T13/1321D Revision 2 December 13, 1999
Information technology - AT Attachment with Packet Interface-6 (ATA-6)
T13/1410D Revision 3b February 26, 2002
10.1 Cabling
10.1.1 Interface Connector
Drive side
connector
Recommended host side
connector
DDK Ltd, MCD-D50SA-3
DDK Ltd, MCD-D50P*-X
* : B, C, D the difference of connector height
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 29 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
360050398
10.2 Electrical specification
10.2.1 Cable length and capacitance
0.46m MAX 35pF MAX
10.2.2 DC input/output Characteristics
10.2.2.1 Input
item Unit value
voltage high (note 1) V 2.0 to 5.5
low V -0.3 to 0.8
leak current
As non-connected logic voltage, input voltage level is from -0.3V to 0.5V.
(note 1) The max. input range of signal is from -0.3V to 5.5V .
(note 2) Except for signal lines pulled up as shown in Table 10.3.3-1
µA
+ 10 (note 2)
10.2.2.2 Output
item unit value Note
voltage high V 2.4 min. IOH = - 1mA
low V 0.4 max. IOL = 4mA
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 30 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.3 Interface connector
10.3.1 ATA interface connector
UNIT:mm
Figure 4 ATA interface connector
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 31 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.3.2 Pin Assignment
The following table describes all of the pins on the Task File Interface.
Table 10.3-1 Signal pin assignment
PIN No. SIGNALS PIN No. SIGNALS
1 - RESET 2 GROUND
3 DD 7 4 DD 8
5 DD 6 6 DD 9
7 DD 5 8 DD 10
9 DD 4 10 DD 11
11 DD 3 12 DD 12
13 DD 2 14 DD 13
15 DD 1 16 DD 14
17 DD 0 18 DD 15
19 GROUND 20 OPEN
21 DMARQ 22 GROUND
23 - DIOW 24 GROUND
STOP
25 -DIOR 26 GROUND
-DMARDY
HSTROBE
27 IORDY 28 CSEL
-DMARDY
-DSTROBE
29 -DMACK 30 GROUND
31 INTRQ 32 - IOCS16
33 DA 1 34 - PDIAG/-CBLID
35 DA 0 36 DA 2
37 - CS0 38 - CS1
39 - DASP 40 GROUND
41 + 3.3V 42 + 3.3V
43 GROUND 44 RESERVED
Note) Symbol (-) in front of signal name shows negative logic.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 32 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

b
Ω
k
Ω
10.3.3 Signal Treatment
Driver types and requirements for the signal pull- up and down are as follows. Resistor requirement is minimum for the
host. - IO16 is pulled up in the drive with certain valu e so that the Vol is obtained to run with a host that has large value of
pull up resistor. - CS0 and - CS1 are also pulled up for better noise immunity.
Table 10.3-2 Signal treatment
SIGNAL Driven by TYPE By host By drive
- RESET Host TP 10kΩPU
DD 0:15
DMARQ Drive TS 5.6 k
- DIOR Host TS
-DMARDY
HSTROBE
- DIOW Host TS
STOP
IORDY Drive TS 4.7 k ΩPU
-DDMARDY
DSTROBE
CSEL Host GND 10 k Ω PU
- DMACK Host TP
INTRQ Drive TS 10
- IOCS16 Drive OD 1.0 k ΩPU 1.2 k Ω PU
DA 0:2 Host TP
- PDIAG/ Drive TS 10 k Ω PU
- CS0 - CS1 Host TP
- DASP Drive OD 10 k Ω PU
i-direction TS
PD
PD
TP = Totem Pole, TS = Tri-State, PD = Pull Down, PU = Pull-Up, OD = Open Drain
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 33 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.3.4 Series resistance
Each signal has its own series resistance.
SIGNAL SERIAL RESISTANCE VALUE
-DIOR 82Ω
-HDMARDY
HSTROBE
-DIOW 82Ω
STOP
-CS0, -CS1 82Ω
DA0,DA1,DA2 82Ω
-DMACK 82Ω
DMARQ 22Ω
INTRQ 22Ω
IORDY
-DDMARDY
DSTROBE
DD0〜DD15 33Ω
22Ω
10.3.5 Signal Description
SIGNAL DIR. PIN DESCRIPTION
- RESET O (*1) 1 Reset signal from the host system; It shall be active low when system is
powered-up or when voltage fault is detected.
DD 15- 0 I/O 18- 3 16 bit bi- directional data bus between the host system and the drive. All 16 bits
are used for data transfer in the data register. The lower 8 bits, HD0- HD7, are
used for the other register and ECC access.
KEY N/C 20 Pin position 20 has no connection pin, clipped on the drive and plugged on the
cable in order to ensure correct orientation of the cable and to avoid wrong
insertion.
DMARQ I 21 DMA request signal is set by the drive to indicate that the DMA data transfer is
ready. The direction of the data transfer is controlled by write/read strobe signal
(HOST IOW or HOST IOR). This signal is used on a hand shake manner with DMACK.
- DIOW
STOP
- DIOR
-HDMARDY
HSTROBE
IORDY
-DDMARDY
DSTROBE
O 23 Write strobe. The rising clocks data from the host data bus, HD0 through HD15 to
a register or data register of the drive.
Stop signal used by the host after the completion of Ultra DMA Burst.
O 25 Read strobe. When active low, this signal enables data from a register or the data
of the drive onto the host data bus, HD0 through HD15. The rising edge of
-HOST IOR latches on the data on the bus from the drive.
This signal is for reporting the drive that the host system is ready to accept Ultra
DMA data.
Strobe. HSTROBE indicates that the host transfers ULTRA DMA data. The rising
edge and the falling edge of HSTROBE enable the drive to latch the data.
I 27 IORDY reports host that the BUS is available.
-DDMARDY is asserted to indicate that the drive is ready to receive the Ultra DMA
data.
Strobe. DSTROBE is asserted to indicate that the drive transfers Ultra DMA data.
The rising edge and falling edge of DSTROBE enable the host to latch the data.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 34 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

CSEL O 28 If jumper pins B through D are assigned, Master/Slave setting with this pin is valid.
When grounded, the drive recognizes itself as a Master. When not grounded, the
drive recognizes itself as a Slave.
- DMACK O 29 Responding to DMARQ, this signal indicates that the host is ready to receive or
send the data.
INTRQ I 31 Interrupt to the host system, enabled only when the drive is selected and the host
activates the - IEN bit in the Device Control register. When the - IEN bit is inactive
or the drive is not selected, this output is in a high impedance state, whether an
interrupt is set or not.
The interrupt is set when the IRQ bit is set by the drive CPU. IRQ is reset to zero
when host reads the Status register or a write to the command register or when
DRQ is negated.
- IOCS16 I 32 Indication to the host system that the 16 bit data register has been addressed and
that the drive is ready to send or receive a 16 bit data word (open drain).
DA 1 O 33 Address line from the host system to select the registers of the drive.
- PDIAG
/CBLID
DA 0 O 35 Address line from the host system to select the registers of the drive.
DA 2 O 36 Address line from the host system to select the registers of the drive.
- CS0 O 37 Chip select signal generated from the host address bus. This signal is used to
- CS1 O 38 Chip select signal generated from the host address bus. This signal is used to
- DASP I 39 This is a signal from the drive used either to drive an external LED whenever the
RESERVED 27,44 Reserved for future use. No connection.
+ 3.3V 41,42 Power line.
GROUND 2,19
I/O 34 In Master/Slave mode, this signal reports the presence of slave drive to master
drive and enables transmitting of diagnostic result between master drive and slave
drive
select one of the two groups of host accessible registers.
select one of the two groups of host accessible registers.
drive is being accessed, or to report presence of the slave drive to the master
when the drive is in master/slave mode.
Ground between the drive and the host system.
22,24
26,30
40,43
(*1) ‘
I’ is from the drive to the host system, ‘O’ is from the host system to the drive, and ‘I/O’ is bi-directional.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 35 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.4 Host Interface Timing
10.4.1 Program I/O Write Timing
DA2, DA1, DA0
-CS0, -CS1
t
ASW
t
AHW
-DIOW
t
WCY
t
WER
t
WE
DD15∼DD0
t
CICSV
t
DS
t
DH
-IOCS16
t
AICSV
t
t
A
B
IORDY
Transfer mode
Symbol Meaning 0 1 2 3 4
t
Address Setup to -DOW Low (min.) 70 50 30 30 25
ASW
tDS Data Setup to -DOW High (min.) 60 45 30 30 20
t
-DOW Pulse Width (min.) 165 125 100 80 70
WE
t
Data Hold from -DOW High (min.) 30 20 15 10 10
DH
t
ADDR Hold from -DOW High (min.) 20 15 10 10 10
AHW
t
-DOW Inactive (min.) - - - 70 25
WER
t
Write Cycle Time (min.) 600 383 240 180 120
WCY
t
-IOCS16 valid from -CS (max.) 90 50 40 n/a* n/a*
CICSV
t
-IOCS16 valid from address (max.) 90 50 40 n/a* n/a*
AICSV
t
-IOCS16 inactive from address (max.) 60 45 30 n/a* n/a*
AICSI
t
IORDY Setup time (max.) 35 35 35 35 35
A
t
IORDY Pulse Width (max.) 1250 1250 1250 1250 1250
B
t
AICSI
(
*) -IOCS16 shall be specified in ATA-2 specifications. For other modes, this signal is invalid. The Drive
releases -IOCS16 within the time of t
, but how much time it takes to turn to inactive condition is
AICSI
determined by pull up resistance, output impedance and line capacitance.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 36 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.4.2 Program I/O Read Timing
DA2, DA1, DA0
-CS0, -CS1
-DIOR
t
t
ASE
AHE
t
AICSI
t
RDCY
t
RDR
t
RE
DD15∼DD0
t
CICSV
t
DAC
t
RDSE
t
DOH
t
HDTS
-IOCS16
t
AICSV
t
A
t
RD
t
B
IORDY
Transfer mode
Symbol Meaning 0 1 2 3 4
t
Address Setup to -DIOR Low (min.) 70 50 30 30 25
ASE
tRE -DIOR Pulse Width (min.) 165 125 100 80 70
t
-DIOR data setup (min.) 50 35 20 20 20
RDSE
t
Data Hold from -DIOR High (min.) 5 5 5 5 5
DOH
t
Data Tri-state from -DIOR High (max.) 30 30 30 30 30
HDTS
t
ADDR Hold from -DIOR High (min.) 20 15 10 10 10
AHE
t
-DIOR Inactive (min.) - - - 70 25
RDR
t
Read Cycle Time (min.) 600 383 240 180 120
RDCY
t
-IOCS16 valid from -CS (max.) 90 50 40 n/a* n/a*
CICSV
t
-IOCS16 valid from address (max.) 90 50 40 n/a* n/a*
AICSV
t
-IOCS16 inactive from address (max.) 60 45 30 n/a* n/a*
AICSI
t
Read Data Valid to IORDY (min.) 0 0 0 0 0
RD
t
IORDY Setup time (max.) 35 35 35 35 35
A
t
IORDY Pulse Width (max.) 1250 1250 1250 1250 1250
B
*) -IOCS16 is specified in ATA-2 specifications. For other modes, this signal is invalid. Drive releases
(
-IOCS16 within the time of t
, but how long it takes to turn to inactive condition is defined by pull up
AICSI
resistance, output impedance and line capacitance.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 37 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.4.3 Multiword DMA Write Timing
DMARQ
-DMACK
-DIOW
DD15∼DD0
ATA/ATAPI-6 SPECIFICATIONS
t
O
t
I
t
D
t
G
t
K
t
H
t
L
t
J
Transfer mode MODE 0 MODE 1 MODE 2
Symbol Meaning Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max.
t0 Cycle time 480 150 120
tC DMACK to DMARQ delay --- --- -- t
-DIOW 16-bit 215 80 70
D
t
-DIOW data setup 100 30 20
G
t
-DIOW data hold 20 15 10
H
t
DMACK to -DIOW setup 0 0 0
I
t
-DIOW to DMACK hold 20 5 5
J
t
-DIOW negated pulse width 215 50 25
K
t
-DIOW to DMARQ delay 40 40 35
L
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 38 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.4.4 Multiword DMA Read Timing
DMARQ
-DMACK
-DIOR
DD15∼DD0
ATA/ATAPI-6 SPECIFICATIONS
t
O
t
I
t
D
t
E
t
K
t
F
t
L
t
J
t
Z
Transfer mode MODE 0 MODE 1 MODE 2
Symbol Meaning Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max.
t0 Cycle time 480 150 120
tC DMACK to DMARQ delay --- --- -- t
-DIOR 16-bit 215 80 70
D
t
-DIOR data access 150 60 50
E
t
-DIOR data hold 5 5 5
F
t
-DIOR to tristate 20 25 25
Z
t
DMACK to -DIOR setup 0 0 0
I
t
-DIOR to DMACK hold 20 5 5
J
t
-DIOR negated pulse width 50 50 25
K
t
-DIOR to DMARQ delay 120 40 35
L
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 39 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.4.5 Ultra DMA Timing
Initiating an Ultra DMA data in burst
DMARQ
(device)
DMACK-
(host)
STOP
(host)
HDMARDY-
(host)
t
t
t
UI
ACK
ACK
t
t
ENV
ENV
t
ZAD
ZAD
FS
t
FS
t
t
DSTROBE
(device)
DD(15:0)
DA0, DA1, DA2,
CS0-, CS1-
t
t
ACK
ZIORDY
t
AZ
t
ZFS
t
DZFS
t
DVS
t
DVH
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 40 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

Sustained Ultra DMA data in burst
DSTROBE
at dev ice
t
DVH
t
DVHIC
DD(15:0)
at dev ice
DSTROBE
at host
t
CYC
t
2CYC
t
DVH
t
t
DVS
t
DVSIC
DVHIC
t
CYC
t
DVS
t
DVSIC
t
DVH
t
DVHIC
t
2CYC
t
DH
t
DHIC
DD(15:0)
at host
Host pausing an Ultra DMA data in burst
DMARQ
(device)
DMACK-
(host)
STOP
(host)
HDMARDY-
(host)
t
t
DSIC
DS
t
t
DH
DHIC
t
t
DHIC
DH
t
t
DS
DSIC
t
RP
DSTROBE
(device)
DD(15:0)
(device)
t
RFS
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 41 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
Device terminating an Ultra DMA data in burst
DMARQ
(device)
DMACK-
(host)
t
LI
STOP
(host)
t
MLI
t
t
LI
ACK
HDMARDY-
(host)
DSTROBE
(device)
DD(15:0)
DA0, DA1, DA2,
CS0-, CS1-
t
LI
t
SS
t
ZAH
t
AZ
t
CVS
t
ACK
t
t
IORDYZ
CVH
CRC
t
ACK
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 42 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

Host terminating an Ultra DMA data in burst
DMARQ
(device)
t
LI
t
MLI
DMACK-
(host)
STOP
(host)
HDMARDY-
(host)
DSTROBE
(device)
DD(15:0)
DA0, DA1, DA2,
CS0-, CS1-
t
RFS
t
ZAH
t
t
RP
AZ
t
t
MLI
CVS
t
LI
t
ACK
t
ACK
t
IORDYZ
t
CVH
CRC
t
ACK
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 43 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
Initiating an Ultra DMA data out burst
DMARQ
STOP
(host)
(device)
(host)
(host)
t
UI
t
ACK
t
ZIORDY
t
ACK
(device)
DMACK-
(host)
DDMARDY-
HSTROBE
DD(15:0)
t
ENV
t
LI
t
DZFS
t
DVS
t
UI
t
DVH
DA0, DA1, DA2,
CS0-, CS1-
t
ACK
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 44 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

Sustained Ultra DMA data out burst
t
HSTROBE
at host
t
DVH
t
DVHIC
DD(15:0)
at host
HSTROBE
at dev ice
t
DH
t
DHIC
DD(15:0)
at dev ice
CYC
t
2CYC
DH
t
CYC
t
DVS
t
DVSIC
t
t
DS
DSIC
t
DVH
t
DVHIC
t
t
DHIC
DH
t
2CYC
t
DVH
t
DVHIC
t
t
DHIC
t
t
t
DVSIC
t
DS
DSIC
DVS
Device pausing an Ultra DMA data out burst
DMARQ
(device)
DMACK-
(host)
STOP
(host)
DDMARDY
-(device)
HSTROBE
(host)
t
RFS
t
RP
DD(15:0)
(host)
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 45 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
Host terminating an Ultra DMA data out burst
t
LI
DMARQ
(host)
t
SS
(device)
DMACK-
(host)
STOP
t
MLI
t
LI
t
ACK
DDMARDY-
(device)
HSTROBE
(host)
DD(15:0)
(host)
DA0, DA1, DA2,
CS0-, CS1-
t
LI
t
CVS
t
t
ACK
IORDYZ
t
CVH
CRC
t
ACK
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 46 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

Device terminating an Ultra DMA data out burst
DMARQ
(device)
DMACK-
(host)
STOP
(host)
DDMARDY-
(device)
HSTROBE
(host)
DD(15:0)
(host)
DA0, DA1, DA2,
CS0-, CS1-
t
MLI
t
MLI
t
CVS
CRC
t
ACK
t
IORDYZ
t
ACK
t
CVH
t
ACK
t
RFS
t
LI
t
RP
t
LI
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 47 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
ATA/ATAPI specifications
Transfer mode MODE 0 MODE 1 MODE 2 MODE 3 MODE 4 MODE 5
Symbo
l
t
Cycle time
CYC
t
Two cycle time
2CYC
tDS
Data setup time
tDH
Data hold time
t
Data valid setup time
DVS
t
Data valid hold time
DVH
tCS
CRC setup time
tCH
CRC hold time
t
CRC valid setup time
CVS
t
CRC valid hold time
CVH
t
Strobe released to driving
ZFS
t
Data released to driving
DZFS
tFS
First STROBE time
tLI
Limit interlock time
t
Interlock time min.
MLI
tUI
Unlimited interlock
tAZ
Allowed to release
t
Delay time
ZAH
t
Delay time
ZAD
t
Envelope time
ENV
t
Ready to final Strobe
RFS
tRP
Ready to pause
t
Pullup before IORDY
IORDYZ
t
Wait before IORDY
ZIORDY
t
Setup hold for DACK
ACK
tSS
Strobe to DREQ/Stop
Meaning Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max.
112 73 54 39 25 16.8
230 153 115 86 57 38
15.0 10.0 7.0 7.0 5.0 4.0
5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 4.6
70.0 48.0 31.0 20.0 6.7 4.8
6.2 6.2 6.2 6.2 6.2 4.8
15.0 10.0 7.0 7.0 5.0 5.0
5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0
70.0 48.0 31.0 20.0 6.7 10.0
6.2 6.2 6.2 6.2 6.2 10.0
0 0 0 0 0 35
70.0 48.0 31.0 20.0 6.7 25
0 230 0 200 0 170 0 130 0 120 0 90
0 150 0 150 0 150 0 100 0 100 0 75
20 20 20 20 20 20
0 0 0 0 0 0
10 10 10 10 10 10
20 20 20 20 20 20
0 0 0 0 0 0
20 70 20 70 20 70 20 55 20 55 20 50
75 70 60 60 60 50
160 125 100 100 100 85
20 20 20 20 20 20
0 0 0 0 0 0
20 20 20 20 20 20
50 50 50 50 50 50
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 48 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.4.6 Reset Timing
BUSY
- RESE T
t
N
t
M
Symbol Meaning Minimum Maximum Unit Condition
tM
tN
RESET pulse width (Low) 25
RESET inactive to BSY active 400 ns
µs
10.5 Grounding
HDA (Head Disk Assembly) and DC ground(ground pins on interface) are connected electrically each other.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 49 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.6 Address Decoding
The host addresses the drive using programmed I/O. In this method, the required register address should
be placed on the three host address lines, DA2 - DA0. An appropriate chip is selected and a read or write
strode (-DIOR / -DIOW) shall be given to the chip.
The following I/O map shows definitions of all the register addresses and functions for these I/O locations.
The descriptions of each register are shown in the next paragraph.
Table 10.6-1 Register map
Address
- CS0 - CS1 HA2 HA1 HA0 READ REGISTER WRITE REGISTER
0 0 X X X Invalid address Invalid address
0 1 0 0 0 Data register Data register
0 1 0 0 1 Error register Features (Write precompensation)
register
0 1 0 1 0 Sector count Sector count
0 1 0 1 1 Sector number / LBA bit 0- 7 Sector number / LBA bit0-7
0 1 1 0 0 Cylinder low / LBA bit 8- 15 Cylinder low / LBA bit8-15
0 1 1 0 1 Cylinder high / LBA bit16- 23 Cylinder high / LBA bit16-23
0 1 1 1 0 Device head register
/ LBA bit 24- 27
0 1 1 1 1 Status register Command register
1 0 0 X X High impedance Not used
1 0 1 0 X High impedance Not used
1 0 1 1 0 Alt. status register Device control register
1 0 1 1 1 Device address register1 Not used
1 1 X X X High impedance Not used
“X” means “don't care”.
Device head register
/ LBA bit 24-27
The host generates selection of two independent chips on the interface. The selected high order
chip ,-HOST CS1, is valid only when the host is accessing the address of alternate status register, digital
output register , and digital input register respectively. The low order chip, HOST CS0, is used to address all
other registers.
The following table shows the standard decode logic to connect with ISA (Industry Standard Architecture)
bus .
Table 10.6-2 Decode Logic
Register Address Map Decode
1F0-1F7 - CS0 = - ((- A9) (-A3)*(- AEN))
3F6,3F7 - CS1= -
(A9*A8*A7*A6*A5*A*A8*A7*A6*A5*A4*4)*(-A3)*(-
AEN)
170-177 - CS0= - ((- A9)*A8*(- A7)*A6*A5*A4*(- A3)*(- AEN)
376,377 - CS1= - (A9*A8*(- A7)*A6*A5*A4)*(- A3)*(- AEN)
The host data buses 15-8 are valid only when - IOCS16 is active.
• - IOCS16 is asserted when interface address lines match to data register address.
1
ATA-2 Notes: This register is obsolete. A device is not supposed to respond to a read of this address. If a device does
respond, it shall be sure not to drive the DD7 signal to prevent possible conflict with floppy disk implementations.
The drive supports this register to maintain compatibility for ATA-1.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 50 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.7 Register Description
In the following register descriptions, unused write bit should be treated as “don't care”, and unused read
bits should be read as zeros.
10.7.1 Data Register
- CS0 DA2-DA0 : 0 Read / Write
There are seven commands which execute data transfer from/to this register of the sector buffer for Read
and Write operations. The sector table during Format command and the data associated with the Identify
Device command shall also be transferred to this register.
10.7.1.1 Read/Write command
The register provides a high speed 16 bit path into the sector buffer with PIO and DMA.
10.7.1.2 Read/Write Buffer command
This command provides 16 bit path between host and data buffer in the drive.
10.7.1.3 Format command
This command provides a path for the parameter including interleave table in a sector length.
10.7.1.4 Identify Device command
Drive information is transferred during the execution of this command.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 51 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.7.1.5 Security commands
Password information is transferred during the execution of following four commands.
1) Disable password
2) Erase Unit
3) Set Password
4) Unlock
Data in the register and on the media correspond to each other as follows:
A15 - A8 A7 - A0
transfer 1 D2 D1
transfer 2 D4 D3
: : :
: : :
transfer 256 D512 D511 D1 D2 --- D512 E1 --- E4
transfer 257 E1
: E2
: :
transfer 260 E4
DATA REGISTER DATA FLOW ON THE MEDIA
10.7.2 Error Register
- CS0 DA2-DA0 : 1 Read ONLY
10.7.2.1 Operational Mode
The following descriptions are bit definitions for the operational mode including the error information from the
last command. This command is valid only when the ERROR BIT (bit 0) is set.
ICRC UNC MC IDNF MCR ABRT TK0NF AMNF
Bit 7 Interface CRC error was found during the transfer of Ultra DMA. 2
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
2
ATA-2 Notes: Prior to the development of ATA-2 standard, this bit was defined as BBK (Bad Block Detected) -- This bit was used to
indicate that the block mark was detected in the target’s ID field. The mark does not exist when shipping from the factory.The Mark
will be written by FORMAT command. Read or Write commands will not be executed in any data fields marked bad. The drive does
not support this bit.
UNC (Uncorrectable Data Error) – This bit indicates that an uncorrectable error has been encountered in the
data field during a read command.
MC (Media Changed) -- This bit is reserved for use by removable media devices and indicates that new
media is available to the operating system.
IDNF (ID Not Found) --The requested sector could not be found.
MCR (Media Change Requested) is reserved for use by removable media devices and indicates that a
request for media removal has been detected by the device.
ABRT (Aborted Command) -- This bit Indicates that the requested command has been aborted due to the
reason reported in the drive status register (Write Fault, Not Seek Complete, Drive Not Ready, or an invalid
command). The status registers and the error registers may be decoded to identify the cause.
TK0NF (Track 0 Not Found) -- This bit is set to indicate that the track 000 has not been found during a
Recalibrate command.
AMNF (AM Not Found) -- This bit is set to indicate that the required Data AM pattern on read operation has
not been found.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 52 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.7.2.2 Diagnostic Mode
The drive enters diagnostic mode immediately after the power -on or after an Execute Diagnostics
command. Error bit in Status Register shall not be set in these cases. The following table shows bit values
for the diagnostic mode.
Table 10.7-1 Diagnostic mode error register
01 No errors
02 Controller register error
03 Buffer RAM error
04 ECC device error
05 CPU ROM/RAM error
06-7F Reserved
8x Drive1 error (see below)
When two drives are daisy-chained on the interface, the Drive0 has valid error information for diagnostic
mode. When the Drive1 detects an error, 80H and OR value (01〜04) diagnosed by the Drive0 are set to
the code above mentioned.
10.7.3 Features Register (Write Precompensation Register)
- CS0 DA2-DA0 : 1 Write only
Write precompensation is automatically optimized by the drive internally. This register is used with Set
Features command.
10.7.3.1 Smart command
This command is used with the Smart commands to select subcommands.
10.7.4 Sector Count Register
- CS0 DA2-DA0 : 2 Read / Write
10.7.4.1 Disk Access command
The sector count register determines the number of sectors to be read or written for Read, Write, and Verify
commands. A 0 in the sector count register specifies a 256 sector transfer. After normal completion of a
command, the content shall be 0.
During a multi-sector operation, the sector count is decremented and the sector number is incremented. If
an error should occur during multi-sector operation, this command shows the number of remaining sectors
in order to avoid duplicated transfer.
10.7.4.2 Initialize Device Parameters command
This register determines number of sectors per track.
10.7.4.3 Power Control command
This register returns a value in accordance with the operation mode (idle mode or stand-by mode).
10.7.4.4 Set Features Command
If features register for this command is 03h, this register sets the data transfer mode.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 53 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.7.5 Sector Number Register
- CS0 DA2-DA0 : 3 Read / Write
The target logical sector number (starting from 1) for Read, Write, and Verify commands is set in this
register. After completion of a command, it shows the sector number of the last sector transferred to the
host.
The starting sector number is set in this register for multi-sector operations. But when error occurs during
multi-sector transfer, it shows the number of the sector in which the error has been detected. During
multi-sector transfer, the number of the next sector to be transferred will not necessarily be shown.
In LBA mode, this register contains Bits 0 - 7 logical block address. After completion of a command, the
register is updated to reflect the current LBA Bits.
10.7.6 Cylinder Low Registers
- CS0 DA2-DA0 : 4 Read / Write
10.7.6.1 Disk Access command
Lower 8 bits of the starting cylinder number(starting from 0) for Read, Write, Seek, and Verify commands are
contained in these registers. After completion of the command or sector transfer, the current cylinder is
shown in this register.
In LBA mode, Bits 8 - 15 of the target address in logical block address are set in this register. After
completion of a command, the register is updated to reflect the current LBA Bits 0 - 7.
10.7.6.2 SMART commands
This register should be set to 4Fh for SMART commands
10.7.7 Cylinder High Registers
- CS0 DA2-DA0 : 5 Read / Write
10.7.7.1 Disk Access command
The high order bits of the starting cylinder number (starting from 0) for Read, Write, Seek, and Verify
commands are set in this register. After completion of the command or sector transfer, the current cylinder
is shown in this register.
In LBA mode, Bits 16 - 23 of the target address in logical block address are contained in this register. After
completion of the command, it shows the Bits 0 - 7 of the last logical block address.
Cylinder High Cylinder Low
Register Bits 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Cylinder Bits 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 54 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.7.7.2 SMART commands
This register should be set to C2h for SMART commands
10.7.8 Device/Head Register
- CS0 DA2-DA0 : 6 Read / Write
The value of this register is used to select the drive, Drive0 or Drive1, and head. On multiple sector
read/write operation that requires to cross track boundaries, the head select bit will be updated to reflect the
currently selected head number.
1 L 1 DEV HS3 HS2 HS1 HS0
Bit 7 Reserved (recommended to set 1)
Bit 6
Bit 5 Reserved (recommended to set 1)
Bit 4
Bit 3 Bit 0
L (Select LBA mode) L=0: CHS mode. L=1: LBA mode.
DEV (Device Select):
- (Drive0/Drive1 mode) This bit is used to select the drive. DEV= 0 indicates the first fixed disk drive
(Drive0), and DEV= 1 indicates the second (Drive1).
- (Single mode) should be 0. If this is 1, a drive is not selected but 00h shall be returned to status register.
HS3-HS0 (Head Select Bits) -- Bits 3 through 0 determine the required read/write head. Bit 0 is the
least-significant bit. If the L bit is equal to one (LBA Mode), the HS3 through HS0 bits contain bits 27
through 24 of the LBA.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 55 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.7.9 Status Register
-CS0 DA2-DA0:7 Read only
This register contains the command status. The contents of the register are updated at the completion of
each command and whenever the error occurs. The host system reads this register in order to acknowledge
the status and the result of each operation.
When the BSY bit (bit 7) is set, no other bits in the register are valid. And read/write operations of any other
register are negated in order to avoid the returning of the contents of this register instead of the other
resisters’ contents .
If the host reads this register when an interrupt is pending, interrupt request (INTRQ) is cleared in order to
work as Interrupt Acknowledge.
The bits of the status register are defined as below :
BSY DRDY DF DSC DRQ 0 0 ERR
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2 Reserved
Bit 1 Reserved
Bit 0
BSY (Busy) -- This bit is set when Host Reset (HRST) line is activated or Software Reset (SRST) bit in
Device Control register is set or when the COMMAND register is written and until a command is
completed but when Data Request is set to 1, this bit shall be reset. The host shouldn’t write or read any
registers when BSY = 1.
DRDY (Drive ready) -- DRDY=1 when seek complete bit (bit 4) = 1, indicates that the drive is ready to
respond read, write, or seek command. DRDY=0 indicates that read , write and seek are negated. A
command execution shall be interrupted if Not-Ready condition occurs during a command execution and
will be reset until the next command whether the drive condition is Ready or Not Ready. Error bit is set on
this occasion and will be reset just after power on and set again after the drive begins revolving at normal
speed and gets ready to receive a command.
DF (Device Fault) -- DF=1 indicates that the drive has detected a fault condition during the execution of a
Read Write commands; read, write, and seek commands are negated and Error bit is set. DF is set to 1
until the next command, whether the device is in fault condition or not.
3
(Drive Seek Complete) – DSC³= 1 indicates that a seek operation has been completed. DSC³ is set
DSC
to 0 when a command accompanied by a seek operation begins. If a seek is not complete, a command is
terminated and this bit is not changed until the Status Register is read by the host . This bit remains reset
immediately after power on until the drive starts revolving at a nominal speed and gets ready to receive
command.
DRQ (Data Request) -- DRQ=1 indicates that the sector buffer requires 1 sector of data during a Read or
Write command.
ERR (Error) -- ERR = 1 indicates that an error occurred during execution of the previous command . The
cause of the error is reported on the other bit or in the error register. The error bit can be reset by the next
command from the controller. When this bit is set , a multi-sector operation is negated.
3
ATA-2 Notes: Prior to ATA-2 standard, this bit indicated that the device was on track. This bit may be used for other purposes in
future standards. For compatibility the drive supports this bit as ATA-1 specifies. User is recommended not to use this bit.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 56 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.7.10 Command Register
- CS0 DA2-DA0 : 7 Write only
The command register accepts commands for the drive to perform fixed disk operations. Commands are
executed when the TASK FILE is loaded and the command register is written and only when:
The status is not busy (BSY is inactive).
and
DRDY (drive ready) is active.
Any code NOT defined in the following list causes an Aborted Command error. Interrupt request (INTRQ)
is reset when a command is written. The following are acceptable commands to the command register.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 57 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
Table 10.7-2 Command Code
Command Code
Command Name Hex Value PARAMETERS USED
SC SN CY DRV HD FT
Nop 00H X X X O X X
Recalibrate 1xH X X X O X X
Read Sector(s) 20/21H O O O O O X
Read Sector(s) EXT 24h O O O O O X
Read DMA EXT 25H O O O O O X
Read Native Max Address EXT 27H X X X O X X
Read Multiple EXT 29H O O O O O X
Write Sector(s) 30/31H O O O O O X
Write Sector(s) EXT 34H O O O O O X
Write DMA EXT 35H O O O O O X
Set Max Address EXT 37H O O O O O X
Write Multiple EXT 39H O O O O O X
Write Verify 3CH O O O O O X
Read Verify Sector(s) 40/41H O O O O O X
Read Verify Sector(s) EXT 42H O O O O O X
Format Track 50H X X O O O X
Seek 7xH X X O O O X
Execute Diagnostics 90H X X X O X X
Initialize Device Parameters 91H O X X O O X
Download Microcode 92H O O X O X O
SMART B0H X X O O X O
Device Configuration B1H X X X O X O
Read Multiple C4H O O O O O X
Write Multiple C5H O O O O O X
Set Multiple Mode C6H O X X O X X
Read DMA C8/C9H O O O O O X
Write DMA CA/CBH O O O O O X
Power Control Stand-by Immediate E0 / 94H O X X O X X
Idle Immediate E1 / 95H O X X O X X
Stand-by E2 / 96H O X X O X X
Idle E3 / 97H O X X O X X
Check Power Mode E5 / 98H O X X O X X
Sleep E6 / 99H O X X O X X
Read Buffer E4H X X X O X X
Flush Cache E7H X X X O X X
Write Buffer E8H X X X O X X
Flush Cache EXT EAH X X X O X X
Identify Device ECH X X X O X X
Set Features EFH X X X O X O
Security Set Password F1H X X X O X X
Unlock F2H X X X O X X
Erase Prepare F3H X X X O X X
Erase Unit F4H X X X O X X
Freeze F5H X X X O X X
Disable Password F6H X X X O X X
Read Native Max Address F8H X X X O X X
Set Max F9H O O O O O X
Read Sence Data FCH X X X O X O
Note: O and X are defined as follows.
Parameters are defined as follows.
SC = SECTOR COUNT register.
SN = SECTOR NUMBER register.
CY = CYLINDER LOW and CYLINDER HIGH register.
DRV = DRIVE SELECT bit (bit 4 in DRIVE/HEAD register)
HD = HEAD SELECT bits (bit 3-0 in DRIVE/HEAD register)
FT = FEATURES register (WRITE PRECOMPENSATION register)
O = Must contain valid information for this command.
X = Don't care for this command.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 58 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.7.11 Alternate Status Register
- CS1 DA2-DA0 : 6 Read only
This register contains the same information as the status register in the Task File. The only difference is that
this register being read does not imply interrupt acknowledge or doesn’t reset a pending interrupt.
See the description of “ status resister” for definitions of the bit in this register.
10.7.12 Device Control Register
- CS1 DA2-DA0 : 6 Write only
This register contains the following three control bits.
HOB ---- ---- ---- 1 SRST - IEN ----
Bit 7
Bit 6-4 not used
Bit 3 Reserved (recommended to set 1)
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0 not used
HOB (High Order Byte) is defined by the 48-bit Address feature set. A write to any Command register
shall clear the HOB bit to zero.
SRST (Soft Reset) -- SRST= 1 indicates that the drive is held reset and sets BSY bit in Status register.
All internal registers are reset as shown in
interface, this bit will reset both drives simultaneously , regardless of the selection by Device address
bit in DEVICE/HEAD register.
- IEN (Interrupt Enable) -- When -IEN = 0, and the drive is selected by Drive select bit in
DEVICE/HEAD register, the drive interrupt to the host is enabled. When this bit is set, the - INTRQ
pin will be in a high impedance state, whether a pending interrupt is found or not.
Table 10.12-1 . If two drives are daisy chained on the
10.7.13 Device Address register4
- CS1 DA2-DA0 : 7 read only
The device address register is a read-only register used for diagnostic purposes. The followings are definitions of bits for
this register:
RSVD - WTG - HS3 - HS2 - HS1 - HS0 - DS1 - DS0
Bit 7 Reserved -- high impedance
Bit 6
Bit 5 - Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Note) The following facts should be taken into consideration when this resister is in use.
-WG reflects actual write gate in the drive, however, because of address transition or cache operation, there
is no direct connection with the data transferred between host and drive.
-HEAD SELECT represents one’s complement of the binary coded address of currently selected head, but
does not show actual selection of the head.
4
ATA-2 Notes: This register is obsolete. A device is not supposed to respond to a read of this address. If a device does
respond, it shall be sure not to drive the DD7 signal to prevent possible conflict with floppy disk implementations.
The drive supports this register to maintain compatibility for ATA-1.
- WTG (Write Gate) -- This bit is active when a Write to the disk is in progress.
- HS3 to - HS0 (Head Select bits) -- Bit 5 through 2 are one's complement of the binary coded address of
currently selected head which is shown by Head Select bit in SDH register.
- DS1 (Drive Select 1) -- -DS1=0, when Drive1 is selected and active.
- DS0 (Drive Select 0) -- -DS0=0, when single mode or Drive0 in Drive0/Drive1 mode is selected and
active.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 59 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8 Command Descriptions
The drive interprets the commands written in the command register by the host system and executes them.
This table shows the drive’s response to the valid commands written in command-register.
Command
Status register Error register
DRDY DF CORR ERR ICRC UNC IDNF ABRT TK0NF AMNF
CHECK POWER MODE √ √ √ √
EXECUTE DEVICE DIAGNOSTIC √ √ √ See
DEVICE CONFIGRATION RESTORE √ √ √ √
DEVICE CONFIGRATION FRESZE
LOCK
DEVICE CONFIGRATION IDENTIFY √ √ √ √
DEVICE CONFIGRATION SET √ √ √ √
DOWNLOAD MICROCODE √ √ √ √
FLUSH CACHE (EXT) √ √ √ √ √
FORMAT TRACK √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
IDENTIFY DEVICE √ √ √ √
IDLE √ √ √ √
IDLE IMMEDIATE √ √ √ √
INITIALIZE DEVICE PARAMETERS √ √
READ BUFFER √ √ √ √
READ DMA (EXT) √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
READ MULTIPLE (EXT) √ √ √ √ √ √ √
READ NATIVE MAX ADDRESS (EXT) √ √
READ SECTOR(S) (EXT) √ √ √ √ √ √ √
READ VERIFY SECTOR(S) (EXT) √ √ √ √ √ √ √
RECALIBRATE √ √ √ √ √
SECURITY DISABLE PASSWORD √ √ √ √ √
SECURITY ERASE PREPARE √ √ √ √ √
SECURITY ERASE UNIT √ √ √ √ √
SECURITY FREEZE LOCK √ √ √ √ √
SECURITY SET PASSWORD √ √ √ √ √
SECURITY UNLOCK √ √ √ √ √
SEEK √ √ √ √ √
SET FEATURES √ √ √ √
SET MAX ADDRESS (EXT) √ √ √ √
SET MAX SET PASSWORD √ √ √
SET MAX LOCK √ √ √
SET MAX UNLOCK √ √ √
SET MAX FLEEZE LOCK √ √ √
SET MULTIPLE MODE √ √ √ √
SLEEP √ √ √ √
SMART Enable/Disable Attribute
autosave
SMART Enable/Disable Automatic
Off-line
SMART DISABLE OPERATIONS √ √ √ √
SMART ENABLE OPERATIONS √ √ √ √
SMART RETURN STATUS √ √ √ √
SMART Read Attribute Values √ √ √ √ √ √
SMART Read Attribute Thresholds √ √ √ √
SMART Save Attribute Values √ √ √ √
SMART Execute OFF-LINE Immediate √ √ √ √ √
SMART Read Log Sector √ √ √ √ √ √
SMART Write Log Sector √ √ √ √ √
STANDBY √ √ √ √
STANDBY IMMEDIATE √ √ √ √
WRITE BUFFER √ √ √ √
WRITE DMA (EXT) √ √ √ √ √ √
WRITE MULTIPLE (EXT) √ √ √ √ √
WRITE SECTOR(S) (EXT) √ √ √ √ √
WRITE VERIFY √ √ √ √ √
Invalid command code √ √ √ √
√ √ √ √
√ √ √ √
√ √ √ √
Table 10.7-1
√ = valid on this command
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 60 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.8.1 Nop (00h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC no change
FT no change
LBA no change
The Nop command reports the status. The drive terminates the command with aborted error after receiving
this command.
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
REGISTER
10.8.2 Recalibrate5 (1xh)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY 00H
HD no change
SN no change
SC no change
FT no change
LBA 00H
This command will set BSY bit and move the R/W heads on the disk to cylinder 0. At the completion of a
seek , it revises the status, resets BSY and generates an interrupt.
0 0 0 1 X X X X
REGISTER
10.8.3 Flush Cache (E7h)
COMMAND CODE 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1
RESISTER SETTING DR drive no.
This command reports the completion of a Write cache to the host. At the completion of a Write cache,
the drive revises the status, resets BSY and generates an interrupt.
10.8.4 Flush Cache EXT (EAh)
COMMAND CODE 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0
RESISTER SETTING DR drive no.
This command reports the completion of a Write cache to the host. At the completion of a Write cache,
the drive revises the status, resets BSY and generates an interrupt.
5
ATA/ATAPI-4 defines this command as Vendor specific. The drive supports this command to maintain ATA-3, and the previous
models compatibility. User is recommended not to use this command.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 61 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.5 Read Sector (20h/21h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY starting cylinder last possible
HD starting head last possible
SN starting sector last possible
SC no. of sector to read 00H
FT no change
LBA staring address last address
Setting BSY bit, the drive will seek to the target cylinder if the head is not on target track ( implied seek ), select
the head and begin to read the number of sector defined in SC register ( 1-256 ) starting from the target sector.
After finding ID of target sector and having 1 sector of data read into the buffer RAM, the drive sets DRQ in
status register and generates interrupt to report to the host that the drive is ready to transfer the next data.
In case of multi-sector transfer, DRQ bit is reset and BSY is set after 1 sector transfer to prepare for the next
sector transfer.
An uncorrectable data can also be transferred but the subsequent operation will terminate at the cylinder, head,
and sector (or LBA) position in the TASK FILE register. When a sector is ready to be read by the host, an
interrupt is issued. After the last sector is read by the host, no interrupt is issued at the end of a command.
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 X
REGISTER
10.8.6 Read Sector EXT (24h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
LBA
Low
LBA
Mid
LBA
High
SC Current
FT Current
Setting BSY bit, the drive will seek to the target cylinder if the head is not on target track ( implied seek ), select
the head and begin to read the number of sector defined in SC register ( 1-65536 ) starting from the target
sector. After finding ID of target sector and having 1 sector of data read into the buffer RAM, the drive sets DRQ
in status register and generates interrupt to report to the host that the drive is ready to transfer the next data.
In case of multi-sector transfer, DRQ bit is reset and BSY is set after 1 sector transfer to prepare for the next
sector transfer.
An uncorrectable data can also be transferred but the subsequent operation will terminate at the LBA position
in the TASK FILE register. When a sector is ready to be read by the host, an interrupt is issued. After the last
sector is read by the host, no interrupt is issued at the end of a command.
This command is available in LBA addressing only.
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Previous
Previous
0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
LBA(7:0)
LBA(31:24)
LBA(15:8)
LBA(39:32)
LBA(23:16)
LBA(47:40)
sector count(7:0)
sector count(15:8)
reserved
reserved
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
REGISTER
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
00H
00H
no change
no change
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 62 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.8.7 Write Sector (30h/31h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY starting cylinder last possible
HD starting head last possible
SN starting sector start sector
SC no. of sector to write 00H
FT no change
LBA starting address last possible
The drive seeks to the target cylinder and selects the head and begins to write to the number of sectors
defined in SC register (1-256) starting from the target sector. DRQ in status register is set as soon as the
command register is written and the buffer RAM receives the data transferred from the host . After 1 sector
is transferred to the buffer RAM, the drive resets DRQ, sets BSY and begins write operation. In case of
multi-sector transfer, it sets DRQ bit, resets BSY and generates Interrupt to inform host that it is ready to
transfer the next 1 sector of data. The drive will seek to the target cylinder if the head is not on the target
track (implied seek). After transferring the last data in the buffer, it resets BSY and issues an interrupt.
If an error occurs during multi-sector transfer, it will terminate the transfer by setting error information in
status register and error register, without shifting into data transfer mode from the host. CY, HD, SN ( LBA)
registers show the address where error has occurred.
0 0 1 1 0 0 0 X
REGISTER
10.8.8 Write Sector EXT (34h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0
REGISTER
LBA
Low
LBA
Mid
LBA
High
SC Current
FT Current
The drive seeks to the target cylinder and selects the head and begins to write to the number of sectors
defined in SC register (1-65536) starting from the target sector. DRQ in status register is set as soon as
the command register is written and the buffer RAM receives the data transferred from the host . After 1
sector is transferred to the buffer RAM, the drive resets DRQ, sets BSY and begins write operation. In
case of multi-sector transfer, it sets DRQ bit, resets BSY and generates Interrupt to inform host that it is
ready to transfer the next 1 sector of data. The drive will seek to the target cylinder if the head is not on the
target track (implied seek). After transferring the last data in the buffer, it resets BSY and issues an
interrupt.
If an error occurs during multi-sector transfer, it will terminate the transfer by setting error information in
status register and error register, without shifting into data transfer mode from the host. LBA registers show
the address where error has occurred.
This command is available in LBA addressing only.
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Previous
Previous
LBA(7:0)
LBA(31:24)
LBA(15:8)
LBA(39:32)
LBA(23:16)
LBA(47:40)
sector count(7:0)
sector count(15:8)
reserved
reserved
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
00H
00H
no change
no change
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 63 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 64 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.8.9 Read Verify (40h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY starting cylinder last possible
HD starting head last possible
SN starting sector start sector
SC no. of sector to be read 00H
LBA starting address last address
This command is identical to a Read command except that the drive has read the data from the media, and
the DRQ bit is not set and no data is sent to the host. This allows the system to verify the integrity of the
drive. A single interrupt is generated upon completion of a command or when an error occurs.
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
REGISTER
10.8.10 Read Verify EXT (42h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0
REGISTER
LBA
Low
LBA
Mid
LBA
High
SC Current
FT Current
This command is identical to a Read EXT command except that the drive has read the data from the media,
and the DRQ bit is not set and no data is sent to the host. This allows the system to verify the integrity of
the drive. A single interrupt is generated upon completion of a command or when an error occurs.
This command is available in LBA addressing only.
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Previous
Previous
LBA(7:0)
LBA(31:24)
LBA(15:8)
LBA(39:32)
LBA(23:16)
LBA(47:40)
sector count(7:0)
sector count(15:8)
reserved
reserved
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
00H
00H
no change
no change
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 65 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.11 Write Verify6 (3Ch)
COMMAND CODE
0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
REGISTER
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY starting cylinder last possible
HD starting head last possible
SN starting sector start sector
SC no. of sector to be written 00H
LBA starting address last address
This command is all identical to a Write sector command. Read verification is not performed in this
command. A Write verify command transfers the number of sectors (1-256) defined in SC register from the
host to the drive, then the data is written on the media. The starting sector is defined in CY, HD, SN (LBA)
registers.
Upon receipt of the command, the drive sets DRQ until one sector of data is transferred from the host, then
resets DRQ, sets BSY. In case of multi- sector transfer, it sets DRQ, resets BSY and generate an interrupt
to report the host that the host is ready to receive 1 sector of data. The drive will seek to the target track if
the R/W head is not on the target track (implied seek). Reaching the target sector, the command transfers
the sector data from the host to the media. After transferring the last data in the buffer, it sets BSY and
issues an Interrupt.
10.8.12 Format Track 7 (50h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY cylinder to format no change
HD head to format no change
SN 01H
SC 00H
FT no change
The track specified by the task file is formatted with ID and data fields according to the table transferred to
the buffer. This command is rejected in LBA mode with an Aborted command error reported.
DRQ in status register is set as soon as the command register is written, and the buffer RAM receives the
data transferred from the host. After 512 bytes are transferred into the buffer RAM, the drive resets DRQ,
sets BSY and begins format operation. The drive seeks to the target cylinder if the head is not on the target
track ( implied seek ). After completion of the command, it resets BSY and generates an interrupt.
6
ATA/ATAPI-4 defines this command as Vendor specific. The drive supports this command to maintain ATA-3 compatibility. User is
recommended not to use this command.
7
ATA/ATAPI-4 defines this command as Vendor specific. The drive supports this command to maintain ATA-3, and the previous
models compatibility. User is recommended not to use this command.
0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0
REGISTER
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 66 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

Format table consists of the number of sectors ( 16 bits ) per track . Upper byte represents sector number,
and lower byte represents format type.
The drive supports only 00H format type. Intending to maintain compatibility with previous models, the drive
accepts any format type, but the function will not change.
Sector interleave is always set to one regardless of sector sequence in the format table. Data subsequent
to
format table are handled as “Don't care”.
FORMAT TABLE ( FIRST 86 BYTES )
(Ex. 43 logical sector mode)
0001, 0002, 0003, 0004, 0005, 0006, 0007, 0008, 0009, 0013, 0015, 0016, 0017, 0018,.0019,
001A,.......0029, 002A, 002B
DON’T CARE ( 426 BYTES ATTACHED )
0000, 0000, 0000, 0000, 0000, 0000, 0000, 0000, 0000, 0000, 0000, 0000, 0000, ........... 0000, 0000, 0000.
10.8.13 Seek (7xh)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY cylinder to seek no change
HD head to seek no change
SN no change
SC no change
FT no change
LBA address to seek no change
This command moves the R/W heads to the cylinder specified in the task files. The drive sets BSY and
starts seek operation. After the completion of a seek operation, the drive asserts DSC
and return the interrupt.
0 1 1 1 X X X X
REGISTER
8
, negates BSY ,
If CY, HD and SN registers show invalid address, “ID Not Found” error is reported and no seek operation
shall be executed. All commands related to data access possess Implied Seek function and don't need this
command.
10.8.14 Toshiba Specific
COMMAND CODE
These commands are only for factory use. Host must not issue them.
8
ATA-2 Notes: Prior to ATA-2 standard, this bit indicated that the device was on track. This bit may be used for other purposes in
future standards. For compatibility the drive supports this bit as ATA-1 specifies. User is recommended not to use this bit.
1 0 0 0 X X X X
1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0
1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 0 1 X
1 1 1 1 1 1 X X
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 67 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.15 Execute Diagnostics (90h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR OOH
CY OOH
HD OOH
SN O1H
SC O1H
FT
This command enables the drive to execute following self-test and reports the results to the error register
described in Table 10.7.2-1.
(1) ROM checksum test
(2) RAM test
(3) Controller LSI register test
An interrupt is generated at the completion of this command.
When two drives are daisy-chained on the interface, both drives execute the self test and the Drive0 reports
valid error information of the two drives.
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
REGISTER
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 68 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.8.16 Initialize Device Parameters (91h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive number no change
CY no change
HD total number of heads-1 no change
SN number of sector per track no change
SC no change
FT no change
This command specifies the number of sectors per track and the number of heads per cylinder to set head
switching point and cylinder increment point. Specified values affect Number of the current logical heads,
Number of logical sectors per track, which can be read by Identify Device Command.
On issuing this command, the content of CY register shall not be checked. This command will be terminated
with ABORT error when it is issued on a invalid HD or SC register setting ( SC register=0 or the combination
of HD and SC register exceeds the drive parameter.
Any drive access command should accompany correct HD, SN register with heads and sectors within the
number specified for this command. Otherwise, it results in “ID not found” error. If the number of heads
and drives is within the specified number, command gives parameter to convert an address to access into
Logical Block Address (LBA). “ ID Not Found”error also occur when this LBA exceeds the total number of
user addressable sectors. The command does not affect LBA address mode.
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
REGISTER
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 69 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.17 Download Microcode (92h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive number no change
CY 00h
HD no change
SN number of sector(high order) 00h
SC number of sector(low order) 00h
FT subcommand code no change
This command enables the host to alter the device’s microcode. The data transferred using the
DOWNLOAD MICROCODE command is vendor specific.
All transfers shall be an integer multiple of the sector size. The size of the data transfer is determined by the
contents of the Sector Number register and the Sector Count register. The Sector Number register shall be
used to extend the Sector Count register to create a 16-bit sector count value. The Sector Number register
shall be the most significant eight bits and the Sector Count register shall be the least significant eight bits.
A value of zero in both the Sector Number register and the Sector Count register shall specify no data is to
be transferred.This allows transfer sizes from 0 bytes to 33,553,920 bytes, in 512 byte increments.
The Features register shall be used to determine the effect of the DOWNLOAD MICROCODE command.
The values for the Features register are:
− 07h - save downloaded code for immediate and future use.
This feature(07h) is supported. All other values are reserved.
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
REGISTER
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 70 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.8.18 Read Multiple (C4h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive number no change
CY starting cylinder last possible
HD starting head last possible
SN starting sector last possible
SC number of sector to read 00H
FT no change
LBA starting address last possible
The read multiple command performs similarly to the Read Sectors command except for the following
features. Interrupts are not issued on each sector, but on the transfer of each block which contains the
number of sectors defined by a Set Multiple Mode command or the default , if no intervening Set Multiple
command has been issued.
Command execution is identical to the Read Sectors operation except that the number of sectors defined by
a Set Multiple Mode command are transferred without interrupts. DRQ qualification of the transfer is required
only at the start of a data block transfer, not required for the transfer of each sector.
The block count of sectors to be transferred without intervening interrupts is programmed by the Set Multiple
Mode command, which shall be executed prior to the Read Multiple command.
When the Read Multiple command is issued, the Sector Count Register contains the number of required
sectors ( not the number of blocks or the block count ) . If the number of required sectors is not evenly
divisible by the block count, The redundant sectors are transferred during the final partial block transfer. The
partial block transfer shall be for N sectors, where
1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0
REGISTER
N = The redundant sector count ( block count )
If the Read Multiple command is attempted when Read Multiple command are disabled, the Read Multiple
operation shall be rejected with an Aborted Command error.
Disk errors occurred during Read Multiple command are posted at the beginning of the block or partial block
transfer, but DRQ is still set and the data, including corrupted data, shall be transferred as they normally
would .
The contents of the Command Block Registers following the transfer of a data block which has a sector in
error are undefined. The host should retry the transfer as individual requests to obtain valid error
information.
Subsequent blocks or defective blocks are transferred only when the error is a correctable data error. All
other errors after the transfer of the block containing the error terminates the command . Interrupts are
generated when DRQ is set at the beginning of each block or partial block.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 71 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.19 Read Multiple EXT (29h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1
REGISTER
LBA
Low
LBA
Mid
LBA
High
SC Current
FT Current
This command is basically identical to Read Multiple command except register setting.
This command is available in LBA addressing only.
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Previous
Previous
LBA(7:0)
LBA(31:24)
LBA(15:8)
LBA(39:32)
LBA(23:16)
LBA(47:40)
sector count(7:0)
sector count(15:8)
reserved
reserved
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
00H
00H
no change
no change
10.8.20 Write Multiple (C5h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive number no change
CY starting cylinder last possible
HD starting head last possible
SN starting sector start sector
SC number of sector to write 00H
FT no change
LBA starting address last possible
This command performs similarly to the Write Sectors command except for the following features. The Drive
sets BSY immediately upon receipt of the command, and interrupts are not issued on each sector but on
the transfer of each block which contains the number of sectors defined by Set Multiple Mode command or
the default if no intervening Set Multiple command has been issued.
Command execution is identical to the Write Sectors operation except that no interrupt is generated during
the transfer of number of sectors defined by the Set Multiple Mode command but generated for each block.
DRQ qualification of the transfer is required only for each data block, not for each sector.
The block count of sectors to be transferred without programming of intervening interrupts by the Set
Multiple Mode command, which shall be executed prior to the Write Multiple command.
When the Write Multiple command is issued, the host sets the number of sectors ( not the number of blocks
or the block count ) it requests in the Sector Count Register. If the number of required sectors is not evenly
divisible by the block count, the redundant sectors are transferred during the final partial block transfer. The
partial block transfer shall be for N sectors, where
N = The redundant sector count ( block count )
If the Write Multiple command is attempted when Write Multiple command are disabled, the Write Multiple
operation shall be rejected with an Aborted Command error.
Disk errors occurred during Write Multiple command are posted after the attempted disk write of the block or
partial block which are transferred. The Write Multiple command is terminated at the sector in error , even if
it was in the middle of a block. Subsequent blocks are not transferred after an error. Interrupts are generated
for each block or each sector, when DRQ is set .
After the transfer of a data block which contains a sector with error, the contents of the Command Block
Registers are undefined. The host should retry the transfer as individual requests to obtain valid error
information.
1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1
REGISTER
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 72 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.8.21 Write Multiple EXT (39h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1
REGISTER
LBA
Low
LBA
Mid
LBA
High
SC Current
FT Current
This command is basically identical to Write Multiple command except register setting.
This command is available in LBA addressing only.
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Previous
Previous
LBA(7:0)
LBA(31:24)
LBA(15:8)
LBA(39:32)
LBA(23:16)
LBA(47:40)
sector count(7:0)
sector count(15:8)
reserved
reserved
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
00H
00H
no change
no change
10.8.22 Set Multiple Mode (C6h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC The number of sectors / block no change
FT no change
This command enables the drive to perform Read and Write Multiple operations and sets the block count for
these commands.
1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0
REGISTER
The Sector Count Register is loaded with the number of sectors per block. The drive supports 1,2,4,8 or16
sectors per block.
Upon receipt of the command, the drive sets BSY=1 and checks the content of Sector Count Register.
If the Sector Count Register contains a valid value and the block count is supported, the value is loaded for
all subsequent Read Multiple and Write Multiple commands. And these commands are enabled to be
executed. If a block count is not supported , this command shall be terminated with the report of an Aborted
Command error , and Read Multiple and Write Multiple commands are disabled.
If the Sector Count Register contains 0 when the command is issued, Read Multiple and Write Multiple
commands are disabled.
In case of software reset, the result depends on the setting of Set Feature command. If FT=66h, the mode
is not changed. If FT = CCh, the mode reverts to power on default (16 sectors).
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 73 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.23 Read DMA (C8h/C9h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY starting cylinder last possible
HD starting head last possible
SN starting sector last possible
SC no. of sector to read 00H
FT no change
LBA staring address last address
This command is basically identical to Sector command except following features.
• Host initialize the DMA channel before issuing command.
- Data transfer is initiated by DMARQ and handled by the DMA channel in the host.
- Drive issues only one interrupt at the completion of each command to show the status is valid after data
transfer.
During DMA transfer phase, either BSY or DRQ is set to 1.
When a command is completed, CY, HD, SN register (LBA register) shows the sector transferred the latest.
If the drive detects unrecoverable error, the drive terminate the command and CY, HD, SN register (LBA
register) shows the sector where error occurred.
1 1 0 0 1 0 0 X
REGISTER
10.8.24 Read DMA EXT (25h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
LBA
Low
LBA
Mid
LBA
High
SC Current
FT Current
This command is basically identical to Read DMA command except register setting.
This command is available in LBA addressing only.
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Previous
Previous
0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1
LBA(7:0)
LBA(31:24)
LBA(15:8)
LBA(39:32)
LBA(23:16)
LBA(47:40)
sector count(7:0)
sector count(15:8)
reserved
reserved
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
REGISTER
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
00H
00H
no change
no change
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 74 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.8.25 Write DMA (CAh/CBh)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY starting cylinder last possible
HD starting head last possible
SN starting sector last possible
SC no. of sector to write 00H
FT no change
LBA staring address last address
This command is basically identical to Sector command except following differences.
• Host initialize the DMA channel before issuing command.
- Data transfer is initiated by DMARQ and handled by the DMA channel in the host.
- Drive issue only one interrupt at the completion of each command to show the status is valid after data
transfer.
During DMA transfer phase, either BSY or DRQ is set to 1.
When a command is completed, CY, HD, SN register (LBA register) shows the sector transferred the latest.
If the drive detects unrecoverable error, the drive terminates the command and CY, HD, SN register (LBA
register) shows the sector where error has occurred.
1 1 0 0 1 0 1 X
REGISTER
10.8.26 Write DMA EXT (35h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
LBA
Low
LBA
Mid
LBA
High
SC Current
FT Current
This command is basically identical to Write DMA command except register setting.
This command is available in LBA addressing only.
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Previous
Previous
0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1
LBA(7:0)
LBA(31:24)
LBA(15:8)
LBA(39:32)
LBA(23:16)
LBA(47:40)
sector count(7:0)
sector count(15:8)
reserved
reserved
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
REGISTER
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
last address
00H
00H
no change
no change
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 75 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.27 Power Control (Exh)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC shown below 00/FFH (for E5/98 command)
FT no change
Power Control is a group of commands which controls low power mode in the drive. The drive has three
types of power mode:
Idle, Stand-by and Sleep mode
At the completion of disk access, the drive automatically enters the idle mode.
There are two ways to shift to the stand-by mode ( to stop rotation of spindle motor ).
By a command from the host
By internal timer
The internal timer is set by Stand-by or Idle command. If the drive receives disk access command from the
host when it is in stand-by mode , the spindle starts rotating and the drive executes read/write operation.
After power on, the spindle starts rotating and enters the idle mode. During idle or stand-by, READY bit is
set and the drive is ready to receive a command.
1 1 1 0 X X X X
REGISTER
no change (for other command)
To be specific , there are four different sub-commands defined by lower 4 bits of command as follows. The
drive is in the idle mode when it is in default condition after power- on.
10.8.27.1 Stand-by Immediate (E0/94)
SC=X (Don't care)
The drive enters the stand-by mode immediately by this command. If the drive is already in the stand-by
mode, it does no-operation and the stand-by timer doesn’t start .The drive issues an interrupt and reports
the host that the command has been completed before it virtually enters the stand-by mode .
10.8.27.2 Idle Immediate (E1/95)
SC=X
The drive enters the idle mode immediately by this command. If the drive is already in the idle mode, it
does no-operation. If stand-by timer is enabled, timer will start. After the drive enters the idle mode, the
drive issues interrupt to report the host that the command has been completed.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 76 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
10.8.27.3 Stand-by (E2/96)
This command causes the device to enter stand-by mode.
If SC is non-zero then stand-by timer shall be enabled. The value in SC shall be used to determine the time
programmed into the stand-by timer.
If SC is zero then the stand-by timer is disabled.
Value in SC register Setting
0 Time out disabled
1-240 (SC x 5) sec.
241-251 ((value - 240) x 30) min.
252 21 min
253 Period between 8 and 12 hrs
254 Reserved
255 21 min 15 sec.
When the specified time period has passed, the drive enters stand-by mode. If a disk access command is
received during stand-by mode, the spindle starts rotating and the drive executes read/write operation.
After completing the command, the drive reset stand-by timer and the timer starts counting down.
10.8.27.4 Idle (E3/97)
This command causes the device to enter idle mode.
If SC is non-zero then stand-by timer shall be enabled. The value in SC shall be used to determine the time
programmed into the stand-by timer.
If SC is zero then the stand-by timer is disabled.
Value in SC register Setting
0 Time out disabled
1-240 (SC x 5) sec.
241-251 ((value - 240) x 30) min.
252 21 min
253 Period between 8 and 12 hrs
254 Reserved
255 21 min 15 sec.
When the specified time period has expired, the drive enters the stand-by mode. If disk access command
is received during the stand-by mode, the spindle starts rotating and executes read/write operation. After
completing the command, The drive resets stand-by timer and the timer starts counting down.
10.8.27.5 Check Power Mode (E5/98)
SC result value=00 indicates that the drive is in stand-by mode or going into stand-by mode or is shifting
from stand-by mode into idle mode.
SC result value=FFH indicates that the drive is in idle mode.
10.8.27.6 Sleep (E6/99)
When SC=X, the drive enters sleep mode immediately. After entering the sleep mode, the drive issues an
interrupt to report the host that the command has been completed. The drive recovers from sleep mode and
enters stand-by mode by receiving a reset.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 77 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.28 Read Buffer (E4h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC 00H
FT no change
This command transfers a specified sector of data ( 512 bytes) from the 128kB buffer in the drive to the host.
When this command is issued, the drive sets BSY, sets up the buffer for read operation, sets DRQ, resets
BSY, and generates an interrupt. The host reads up to 512 bytes of data from the buffer.
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0
REGISTER
10.8.29 Write Buffer (E8h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC 00H
FT no change
This command transfers a sector of data from the host to the specified 512 bytes of 128kB buffer of the
drive . When this command is issued, the drive will set up the buffer for write operation, and set DRQ. The
host may then write up to 512 bytes of data to the buffer.
1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0
REGISTER
10.8.30 Identify Device (ECh)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC 00H
FT no change
The identify device command requests the drive to transfer parameter information to the host. When the
command is issued, the drive sets BSY, stores the required parameter information in the sector buffer, sets
the DRQ bit, and issues an interrupt. The host may read the parameter information of the sector buffer.
The parameter words in the buffer are arranged as shown in Table 10.8-1 ~ Table 10.8-5.
1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0
REGISTER
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 78 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

Table 10.8-1 Identify Information
WORD DESCRIPTION Hex.
0 General configuration
1 Number of default logical cylinders [1*]
2 Specific configuration C837
3 Number of default logical heads [2*]
4 Reserved 0000
5 Reserved 0000
6 Number of default logical sectors h logical track [3*]
7-9 Reserved
10-19 Serial Number (20 ASCII characters)
20 Reserved 0000
21 Reserved 0000
22 Reserved 0000
23-26 Firmware Revision (8 ASCII characters)
27-46 Controller model # (40 ASCII characters)
47 15-8 80h
48 Reserved 0000
49 Capabilities
50 Capabilities
51 15-8 PIO data transfer cycle timing mode
52 Reserved 0000
53 15-3 Reserved
15 0=ATA device
14-8 Reserved
7 1=Removable cartridge device
6 1=Fixed device
5-3 Reserved
2 Response incomplete
1-0 Reserved
00
7-0
15-14 Reserved
13 1=Standby timer values as specified in ATA/ATAPI-6 specification are
supported
0=Standby timer values are vendor specific
12 Reserved
11 1=IORDY supported
10 1=IORDY can be disabled
9 1=LBA supported
8 1=DMA supported
7-0 Reserved
15 0 (Fixed)
14 1 (Fixed)
13-1 Reserved
0 1= a device specific Standby timer value minimum.
7-0 Reserved
2 1=the fields reported word 88 are valid
0=the fields reported word 88 are not valid
1 1=the fields reported words 64-70 are valid
0=the fields reported words 64-70 are not valid
0 1=the fields reported words 54-58 are valid
= READ/WRITE MULTIPLE command not implemented
H
- FFH = Maximum number of sectors that can be transferred per
01
H
interrupt on READ/WRITE MULTIPLE commands
0=the fields reported words 54-58 are not valid
0040
8010
2F00
4000
0200
0007
54 Number of current cylinders XXXX
55 Number of current heads XXXX
56 Number of current sectors per track XXXX
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 79 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
Table 10.8-2 Identify Information (Continued)
WORD DESCRIPTION Hex.
57-58 Current capacity in sectors
(Number of current cylinders * Number of current heads * Number of current
sectors per track)
59 15-9 Reserved
8 1=Multiple sector setting is valid
7-0 XXh=Current setting for number of sectors that can be transferred per
interrupt on R/W Multiple command
60-61 Total number of user addressable sectors (LBA mode only) [5*]
62 15-0 Reserved XX07
63 15-8 Multiword DMA transfer mode active
7-0 Multiword DMA transfer mode supported
64 15-8 reserved
7-0 Advanced PIO Transfer Modes Supported
bit 7-2 Reserved
bit 1 = 1 PIO MODE 4 supported
bit 0 = 1 PIO MODE 3 supported
65 Minimum Multiword DMA Transfer Cycle Time Per Word (ns) 0078
66 Manufacturer’s Recommended Multiword DMA Transfer Cycle Time 0078
67 Minimum PIO Transfer Cycle Time Without Flow Control (ns) 0078
68 Minimum PIO Transfer Cycle Time With IOCHRDY Flow Control 0078
69-79 Reserved (for future command overlap and queuing) 0000
80 Major version number
0000h or FFFFh = device does not report version
15-7 Reserved for ATA-7~14
6 1=supports ATA/ATAPI-6
5 1=supports ATA/ATAPI-5
4 1=supports ATA/ATAPI-4
3 1=supports ATA-3
2 1=supports ATA-2
1 1=supports ATA-1
0 Reserved
81 Minor version number
0000h or FFFFh = device does not report version
82 Command set supported.
0000h or FFFFh = command set notification not supported
15 Reserved
14 1=NOP command supported
13 1=READ BUFFER command supported
12 1=WRITE BUFFER command supported
11 Reserved
10 1=Host Protected Area feature set supported
9 1=DEVICE RESET command supported
8 1=SERVICE interrupt supported
7 1=release interrupt supported
6 1=look-ahead supported
5 1=write cache supported
4 1=supports PACKET Command feature set
3 1=supports power management feature set
2 1=supports removable feature set
1 1=supports security feature set
0 1=supports SMART feature set
XXXX
01XX
XX07
0003
007E
0000
746B
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 80 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

Table 10.8-3 Identify Information (Continued)
WORD DESCRIPTION Hex.
83 Command set supported.
0000h or FFFFh = command set notification not supported
15 0 (Fixed)
14 1(Fixed)
13 1=FLUSH CACHE EXT command supported
12 1=FLUSH CACHE command supported
11 1=Device Configuration Overlay supported
10 1=48-bit Address feature set supported
9 1=Automatic Acoustic Management feature set supported
8 1=Set MAX security extension supported
7 Reserved
6 1=SET FEATURES subcommand required to spin up after power-up
5 1=Power-Up in Standby feature set supported
4 1=Removable Media Status Notification feature set supported
3 1=Advanced Power Management feature set supported
2 1=CFA feature set supported
1 1=READ / WRITE DMA QUEUED supported
0 1=DOWNLOAD MICROCODE command supported
84 Command set/feature supported extension
15 0 (Fixed)
14 1(Fixed)
13 1(Fixed)
12-6 Reserved
5 1=General Purpose Logging feature set supported
4 1=Reserved
3 1=Media Card Pass Through Command feature set supported
2 1=Media serial number supported
1 1=SMART self-test supported
0 1=SMART error logging supported
85 Command set/feature enabled
15 Reserved
14 1=NOP command enabled
13 1=READ BUFFER command enabled
12 1=WRITE BUFFER command enabled
11 Reserved
10 1=Host Protected Area feature set enabled
9 1=DEVICE RESET command enabled
8 1=SERVICE interrupt enabled
7 1=release interrupt enabled
6 1=look -ahead enabled
5 1=write cache enabled
4 1=PACKET Command feature set supported
3 1=power management feature set enabled
2 1=removable feature set enabled
1 1=Security feature set enabled
0 1=SMART feature enabled
86 Command set/feature enabled
15-14 Reserved
13 1=FLUSH CACHE EXT command supported
12 1=FLUSH CACHE command supported
11 1=Device Configuration Overlay supported
10 1=48-bit Address feature set supported
9 1=Automatic Acoustic Management feature set enabled
8 1=SET MAX security extension enabled by SET MAX SET
PASSWORD
7 Reserved
6 1=SET FEATURES subcommand required to spin-up after power-up
5 1=Power-Up In Standby feature set enabled
4 1=Removable Media Status Notification feature set enabled
3 1=Advanced Power Management feature set enabled
2 1=CFA feature set enabled
1 1=READ / WRITE DMA QUEUED supported
0 1=DOWNLOAD MICROCODE command supported
7D09
6023
XXXX
XX0X
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 81 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
Table 10.8-4 Identify Information (Continued)
WORD DESCRIPTION Hex.
87 Command set/feature default
88 15-8 Ultra DMA transfer mode selected
89 Time required for security erase unit completion 00XX
90 Time required for Enhanced Security erase completion 0000
91 Current Advanced Power Management setting
92 Master Password Revision Code XXXX
93 Hardware reset result. The conetnts of bits 12-0 of this word shall change only
94 Current automatic acoustic management value
95-99 Reserved 0000
100-103 Maximum user LBA for 48-bit Address feature set XXXX
104-126 Reserved 0000
15 0 (Fixed)
14 1 (Fixed)
13 1 (Fixed)
12-6 Reserved
5 1=General Purpose Logging feature set supported
4 Reserved
3 1=Media Card Pass Through Command feature set enabled
2 1=Madia serial number is valid
1 1=SMART self-test supported
7-0 Ultra DMA transfer modes supported
15-8 Reserved
7-0 Current Advanced Power Management setting set by Set Features
Command
during the execution of a hardware reset.
15 0 (Fixed)
14 1 (Fixed)
13 1=device detected CBLID- above V
0=device detected CBLID- below V
12-8 Device 1 hardware reset result. Device 0 shall clear these bits to
zero.
Device 1 shall set these bits as follows :
12 Reserved.
11 0=Device 1 did not assert PDIAG-.
1=Device 1 asserted PDIAG-.
10-9 These bits indicate how Device 1 determined the device
number:
00=Reserved.
01=a jumper was used.
10=the CSEL signal was used.
11=some other method was used or the method is
unknown.
8 1 (Fixed)
7-0 Device 0 hardware reset result. Device 1 shall clear these bit to
zero.
Device 0 shall set these bills as follows:
7 Reserved.
6 0=Device 0 does not respond when Device 1 is selected.
1=Device 0 responds when Device 1 is selected.
5 0=Device 0 did not detect the assertion of DASP-.
1=Device 0 detected the assertion of DASP-.
4 0=Device 0 did not detect the assertion of PDIAG-.
1=Device 0 detected the assertion of PDIAG-.
3 0=Device 0 failed diagnostics.
1=Device 0 passed diagnostics.
2-1 These bits indicate how Device 0 determined the device
number:
00=Reserved.
01=a jumper was used.
10=the CSEL signa was used.
11=some other method was used or the method is
unknown.
0 1 (Fixed)
15-8 Vendor’s recommended acoustic management value
7-0 Current automatic acoustic management value
IH
IL
6023
XX3F
00XX
XXXX
0000
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 82 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

Table 10.8-5 Identify Information (Continued)
WORD DESCRIPTION Hex.
127 Removable Media Status Notification feature set supported
15-2 Reserved
1-0 00=Removable Media Status Notification feature set not supported
01=Removable Media Status Notification feature set supported
10=Reserved
11=Reserved
128 Security status
15-9 Reserved
8 Security level 0=High, 1=Maximum
7-6 Reserved
5 1=Enhanced security erase supported
4 1=Security count expired
3 1=Security frozen
2 1=Security locked
1 1=Security enabled
0 1=Security supported
129-159 Reserved 0000
160 CFA power mode 1
15 Word 160 supported
14 Reserved
13 CFA power mode 1 is required for one or more commands
implemented by the device
12 CFA power mode 1 disabled
11-0 Maximum current in ma
161-175 Reserved 0000
176-205 Current media serial number 0000
206-254 Reserved 0000
255 Integrity word
15-8 Checksum
7-0 Signature
0000
0XXX
0000
XXA5
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 83 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
Word descriptions:
WORD 0: General configuration
bit 15 0=ATA
bit 14-8 Reserved
bit 7 1=Removable cartridge
bit 6 1=Fixed disk drive
bit 5-3 Reserved
bit 2 Response incomplete
bit 1-0 Reserved
The value for this WORD is 0040h.
WORD 1: Logical cylinder number that user can access (in default mode) [*1]
WORD 2: Specific configuration
“37C8” : Device requires SET FEATURES subcommand to spin-up after power-up and IDENTIFY DEVICE
response is incomplete.
“738C” : Device requires SET FEATURES subcommand to spin-up after power-up and IDENTIFY DEVICE
response is complete.
“8C73” : Device does not requires SET FEATURES subcommand to spin-up after power-up and IDENTIFY
DEVICE response is incomplete.
“C837” : Device does not requires SET FEATURES subcommand to spin-up after power-up and IDENTIFY
DEVICE response is complete.
“All other valies” : Reserved
Power-up in Standby feature set is not supported.
The value for this WORD is C837h.
WORD 3: Logical head number that user can access (in default mode) [*2]
WORD 4-5: Reserved
WORD 6: The number of logical sector per track (in default mode) [*3]
Default Values : [*1],[*2],[*3]
Drive Type [*1] : Word 1 [*2] : Word 3 [*3] : Word 6
MK3006GAL
MK4006GAH
MK6006GAH
WORD 7-9: Reserved
WORD 10-19: Serial number
WORD 20-21: Reserved
WORD 22: Reserved
WORD 23-26: Firmware revision ( 8 ASCII characters )
WORD 27-46: Model name (40 ASCII characters)
Drive Type
MK3006GAL
MK4006GAH
MK6006GAH
“_” indicates ASCII space code.
16383 16 63
16383 16 63
16383 16 63
TOSHIBA MK3006GAL_..._
TOSHIBA MK4006GAH_..._
TOSHIBA MK6006GAH_..._
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 84 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

WORD 47:
bit 15 - 8 shall be set to 80h
bit 7 - 0 Maximum number of sectors that can be transferred per interrupt on READ/WRITE MULTIPLE
commands.
The default value for this WORD is 8010h.
WORD 48: Reserved
WORD 49: Capabilities
bit 15-14 0=Reserved
bit 13 1=Standby timer value shall be as specified in ATA-/ ATAPI-6 specification
0=Standby timer value are vendor specific
bit 12 Reserved (For advanced PIO mode support)
bit 11 1=IORDY is supported.
bit 10 1=IORDY function can be disabled.
bit 9 1=LBA supported
bit 8 1=DMA supported
bit 7- 0 Reserved
The value for this WORD is 2F00h.
WORD 50: Capabilities
bit 15 0 (Fixed)
bit 14 1 (Fixed)
bit 13-1 Reserved
bit 0 1=device has a minimum Standby timer value that is device specific.
Standby timer value is set to 5 minutes or more. The value for this WORD is 4000h.
WORD 51: PIO data transfer cycle timing mode
bit 15- 8 PIO data transfer cycle timing mode
bit 7- 0 Reserved
The value returned in Bits 15-8 should fall into one of the mode 0 through mode.
Note: For backwards compatibility with BIOS written before Word 64 was defined for advanced modes, a
device reports in Word 51 the highest original PIO mode (i.e. PIO mode 0, 1, or 2) it can support.
The value for this WORD is 0200h.
WORD 52: Reserved
WORD 53:
bit15- 3 Reserved
bit 2 1= the fields reported in word 88 is valid
bit 1 1= the fields reported in words 64〜70 are valid
bit 0 1= the fields reported in words 54〜58 are valid
If the number of heads and sectors exceed the drive parameter, bit 0 and related WORD 54-58 shall be
cleared to 0. The default value for this WORD is 0007h.
WORD 54: Number of current cylinders defined by INITIALIZE DEVICE PARAMETERS command
WORD 55: Number of current heads defined by INITIALIZE DEVICE PARAMETERS command
WORD 56: Number of current sectors/track defined by INITIALIZE DEVICE PARAMETERS command
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 85 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
WORD 57-58: Total number of sectors calculated by word 54 - 56
bit31-24 by word 58 bit 7- 0
bit23-16 by word 58 bit 15- 8
bit15- 8 by word 57 bit 7- 0
bit 7- 0 by word 57 bit 15- 8
The power on values for each models are.
Drive Type [*4] : Word 57 – 58
MK3006GAL
MK4006GAH
MK6006GAH
16,514,064(FBFC10H)
16,514,064(FBFC10H)
16,514,064(FBFC10H)
WORD 59:
bit15- 9 Reserved
bit 8 1=bit 7- 0 shows number of sectors for multiple sector operation (multiple sector operation is
enabled by SET MULTIPLE command).
bit 7〜0 The number of sectors transferred for XX
=Write / Read multiple command with 1 Interrupt
H
( Current value shall be set by SET MULTIPLE command. The default value is 16 ).
The default value for this WORD is 0110h.
WORD 60-61: Maximum number of sectors that user can access in LBA mode
bit31-24 by word 61 bit 7- 0
bit23-16 by word 61 bit 15- 8
bit15- 8 by word 60 bit 7- 0
bit 7- 0 by word 60 bit 15- 8
The maximum value that shall be placed in this field is 0FFFFFFFh.
The power on values for each models are.
Drive Type [*5] : Word 60 – 61
MK3006GAL
MK4006GAH
MK6006GAH
58,605,120( 037E3E40H )
78,126,048 ( 04A81BE0H )
117,210,240 ( 06FC7C80H )
WORD 62: Reserved
WORD 63: Mode information for multiword DMA
bit15- 8 Active mode
bit 10 1=Mode 2 is active
bit 9 1=Mode 1 is active
bit 8 1=Mode 0 is active
bit 7- 0 Supported mode
bit 2 1=mode 2 is supported
bit 1 1=mode 1 is supported
bit 0 1=mode 0 is supported
Support bit reflects setting by SET FEATURE command.
The default value for this WORD is 0407h and the default figure is mode 2
WORD 64: Mode information for Advanced PIO transfer
bit 7- 0 Supported mode
bit 1 1=mode 4 is supported
bit 0 1=mode 3 is supported
The value for this WORD is 0003h.
WORD 65: Minimum multiword DMA transfer mode cycle time per word (ns)
If this bit is supported, word 53 bit 1 shall be set. The value for this WORD is 0078h (120ns).
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 86 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

WORD 66: Manufacturer recommended multiword DMA transfer cycle time
If the data transfer is requested in a shorter cycle time than this definition, the data transfer may be kept
pending with DMARQ low because data is not ready. The value for this WORD is 0078h (120ns).
WORD 67: Minimum PIO transfer cycle time without flow control (ns)
The Drive can guarantee correct data transfer without flow control in this cycle time or longer. If this bit is
supported, word 53 bit 1 is to be set. The drives which support PIO mode 3 or higher shall support this field
too. This figure shall not be less than 120. The value for this WORD is 0078h (120ns).
WORD 68: Minimum PIO transfer cycle time with IORDY flow control (ns)
If this bit is supported, word 53 bit 1 is to be set. The drive that support PIO mode 3 or higher shall support
this field too. This figure shall not be less than 120. The value for this WORD is 0078h (120ns).
WORD 69-79: Reserved
WORD 80: Major version number
If not 0000h or FFFFh, the device claims compliance with the major version(s) as indicated by bits 1 - 6
being equal to one. Values other than 0000h and FFFFh are bit significant. Since the ATA standards
maintain downward compatibility, a device may set more than one bit .
WORD 81: Minor version number
If an implementor claims that the revision of the standard they used to guide their implementation does not
need to be reported or if the implementation was based upon a standard prior to this revision of the
standard, Word 81 shall be 0000h or FFFFh.
WORD 82: Command sets supported
bit 15 Reserved
bit 14 NOP command supported
bit 13 READ BUFFER command supported
bit 12 WRITE BUFFER command supported
bit 11 Reserved
bit 10 Host Protected Area feature set supported
bit 9 DEVICE RESET command supported
bit 8 SERVICE interrupt supported
bit 7 Release Interrupt supported
bit 6 Look Ahead supported
bit 5 Write Cache supported
bit 4 PACKET feature set supported
bit 3 The Power Management feature set is supported
bit 2 The Removable feature set is supported
bit 1 The security feature set is supported
bit 0 The SMART feature set is supported
The value for this WORD is 746Bh.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
Page 87 of 157

360050398
WORD 83: Features/Command sets supported
bit 15 0 (Fixed)
bit 14 1 (Fixed)
bit 13 1=FLUSH CACHE EXT command supported
bit 12 1=FLUSH CACHE command supported
bit 11 1=Device Configuration Overlay supported
bit 10 1=48-bit Address feature set supported
bit 9 1=Automatic Acoustic Management feature set supported
bit 8 1=Set MAX security extension supported
bit 7 Reserved
bit 6 1=SET FEATURES subcommand required to spin up after power-up
bit 5 1=Power-Up in Standby feature set supported
bit 4 1=Removable Media Status Notification feature set supported
bit 3 Advanced Power Management feature set supported
bit 2 1=CFA feature set supported
bit 1 1=READ / WRITE DMA QUEUED supported
bit 0 1=DOWNLOAD MICROCODE command supported
The value for this WORD is 7D09h.
WORD 84: Features / Command sets supported
bit 15 0 (Fixed)
bit 14 1 (Fixed)
bit 13 1 (Fixed)
bit 12-6 Reserved
bit 5 1=General Purpose Logging feature set supported
bit 4 Reserved
bit 3 1=Media Card Pass Through command feature set supported
bit 2 1=Media serial number supported
bit 1 1=SMART self-test supported
bit 0 1=SMART error logging supported
The value for this WORD is 6023h.
WORD 85: Features / Command sets enable
bit 15 Reserved
bit 14 NOP command enabled
bit 13 READ BUFFER command enabled
bit 12 WRITE BUFFER command enabled
bit 11 Reserved
bit 10 Host Protected Area feature set enabled
bit 9 DEVICE RESET command enabled
bit 8 SERVICE interrupt enabled
bit 7 Release Interrupt enabled
bit 6 Look Ahead enabled
bit 5 Write Cache enabled
bit 4 PACKET feature set supported
bit 3 The Power Management feature set is enabled
bit 2 The Removable feature set is enabled
bit 1 The security feature set is enabled
bit 0 The SMART feature set is enabled
The default value for this WORD is 7468h
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 88 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

A
(
WORD 86: Features / Command sets enabled
bit 15-14 Reserved
bit 13 1=FLUCH CACHE EXT command supported
bit 12 1=FLUSH CACHE command supported
bit 11 1=Device Configuration Overlay supported
bit10 1=48-bit Address feature set supported
bit 9 1=Automatic Acoustic Management feature set enabled
bit 8 1=SET MAX security extension enabled by SET MAX SET PASSWORD
bit 7 Reserved
bit 6 1=SET FEATURES subcommand required to spin-up after power-up
bit 5 1=Power-Up In Standby feature set enabled
bit 4 Removable Media Status Notification feature set enabled
bit 3 Advanced power Management feature set enabled
bit 2 CFA feature set enabled
bit 1 WRITE / READ DMA QUEUED command supported
bit 0 DOWNLOAD MICROCODE supported
The default value for this WORD is 3C09h.
WORD 87: Features / Command sets enabled
bit 15 0 (Fixed)
bit 14 1 (Fixed)
bit 13 1 (Fixed)
bit 12-6 Reserved
bit 5 1=General Purpose Logging feature set supported
bit 4 Reserved
bit 3 1=Media Card Pass Through command feature set enabled
bit 2 1=Media serial number is valid
bit 1 1=SMART self-test supported
bit 0 1=SMART error logging supported
The value for this WORD is 6023h.
WORD 88: Mode information for Ultra DMA
The active mode reflects the command change.
bit 15-8 Active transfer mode
bit 13 1=Mode 5 is active
bit 12 1=Mode 4 is active
bit 11 1=Mode 3 is active
bit 10 1=Mode 2 is active
bit 9 1=Mode 1 is active
bit 8 1=Mode 0 is active
bit 7-0 Supported mode
bit 5 1=Mode 5 is supported
bit 4 1=Mode 4 is supported
bit 3 1=Mode 3 is supported
bit 2 1=Mode 2 is supported
bit 1 1=Mode 1 is supported
bit 0 1=Mode 0 is supported
The default value for this WORD is 003Fh
WORD 89: The time period for Security Erase Unit command completion shall be set.
TIMER
0 Not specified
1-254
255 > 508 minuites
CTUAL VALUE
Timer ×2 ) minuites
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 89 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
WORD 90: Time required for Enhanced Security erase completion
WORD 91: Current Advanced Power Management setting
bit 15-8 Reserved
bit 7-0 Current Advanced Power Management setting set by Set Features Command.
The default value for this WORD is0080h.
WORD 92: Master Password Revision Code
the value of the Master Password Revision Code set when the Master Password was last change. Valid
values are 0001h through FFFEh. A value of 0000h or FFFFh indicates that the Master Password
Revision is not supported.
WORD 93: Hardware configuration test results
bit 15 0 (Fixed)
bit 14 1 (Fixed)
bit 13 1=device detected CBLID- above V
0=device detected CBLID- below V
IH
IL
bit12-8 Device 1 hardware reset result. Device 0 shall clear these bits to zero.
Device 1 shall set these bits as follows :
12 Reserved.
11 0=Device 1 did not assert PDIAG-.
1=Device 1 asserted PDIAG-.
10-9 These bits indicate how Device 1 determined the device number:
00=Reserved.
01=a jumper was used.
10=the CSEL signal was used.
11=some other method was used or the method is unknown.
8 1 (Fixed)
bit 7-0 Device 0 hardware reset result. Device 1 shall clear these bit to zero.
Device 0 shall set these bills as follows:
7 Reserved.
6 0=Device 0 does not respond when Device 1 is selected.
1=Device 0 responds when Device 1 is selected.
5 0=Device 0 did not detect the assertion of DASP-.
1=Device 0 detected the assertion of DASP-.
4 0=Device 0 did not detect the assertion of PDIAG-.
1=Device 0 detected the assertion of PDIAG-.
3 0=Device 0 failed diagnostics.
1=Device 0 passed diagnostics.
2-1 These bits indicate how Device 0 determined the device number:
00=Reserved.
01=a jumper was used.
10=the CSEL signa was used.
11=some other method was used or the method is unknown.
0 1 (Fixed)
WORD 94: Current automatic acoustic management value
bit 15-8 Vendor’s recommended acoustic management value
bit 7-0 Current automatic acoustic management value
This function is not supported. The value for this WORD is 0000h.
WORD 95-99: Reserved
WORD 100-103: Maximum User LBA for 48-bit Address feature set
The value for this WORD is XXXXh.
WORD 104-126: Reserved
WORD 127: Removable Media Status Notification feature set supported
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 90 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

This function is not supported. The value for this WORD is 0000h.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 91 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
WORD 128: Security status
bit 15-9 Reserved
bit 8 the security level.
1=the security level is maximum
0=the security level is high
bit 5 1=the Enhanced security erase unit feature supported
bit 4 the security count has expired.
1=the security count is expired and SECURITY UNLOCK and SECURITY ERASE UNIT are aborted
until receiving a power-on reset or hard reset.
bit 3 security frozen.
1=the drive is in security frozen mode.
bit 2 security locked.
1=the drive is in security locked mode.
bit 1 security enabled.
1=the security is enabled.
bit 0 security supported.
1=security is supported.
WORD 129-159: Reserved
WORD 160: CFA power mode
bit 15 Word 160 supported
bit 14 Reserved
bit 13 CFA power mode 1 is required for one or more commands implemented by the device
bit 12 CFA power mode 1 disabled
bit 11-0 Maximum current in ma
This function is not supported. The value for this WORD is 0000h.
WORD 161-175: Reserved
WORD 176-205: Current media serial number
This function is not supported. The value for this WORD is 0000h.
WORD 206-254: Reserved
WORD 255: Integrity word
The data structure checksum is the two s complement of the sum of all bytes in words 0 through 254 and
the byte consisting of bits 7:0 in word 255. Each byte shall be added with unsigned arismetic, and overflow
shall be ignored. The sum of all 512 bytes is zero when the checksum is correct.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 92 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
10.8.31 SET MAX (F9h)
Individual SET MAX commands are identified by the value placed in the Features register. Table 10.8-6 shows
these Features register values. But regardless of Feature register value, the case this command is immediately
proceded by a Read Native Max ADRESS comamnd, it is interpreted as a Set Max ADDRESS command.
Table 10.8-6 SET MAX Features register values
Value Command
00h Obsolete
01h SET MAX SET PASSWORD
02h SET MAX LOCK
03h SET MAX UNLOCK
04h SET MAX FREEZE LOCK
05h-FFh Reserved
10.8.31.1 Set Max Address
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR DRIVE No. no change
CY Max. cylinder number no change
HD Max. head number no change
SN Max. sector number no change
SC 00H / 01
FT no change
LBA Max. LBA no change
This command specifies the the maximum address in a range of actual drive capacity. The values set in CY,
HD, SN registers indicate the maximum address that can be accessed. In CHS mode, the value of Read Native
Max Address command should be set in HD, SN register. Otherwise, the value shall be ignored and the value of
Read Max Address command will be used. If an LBA bit (DRV / HD register bit 6) is set, the value in LBA mode
shall be set. If the address exceeding the set value is accessed , “ ABORT ERROR “ error will be reported. This
set value affects the values of WORD 1, 54, 57, 58, 60, 61, 100-103 of IDENTIFY DEVICE command.
This command shall be immediately preceded by Read Native Max Address command. Otherwise, it will be
terminated with “ ABORT ERROR ” .
If this command is issued twice with a volatile bit set to 1 after power-up or hardware reset, “ID Not Found
error” will be reported.
If a host protected area has been established by a SET MAX ADDRESS EXT command, this command will be
terminated with “ ABORT ERROR ” .
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
(BITO: reserved bit) no change
H
REGISTER
Volatile bit ( SC register bit 0 ) :
If this command is issued with a volatile bit set to 1, the set value of this command is valid after power-up or
hardware reset.
If this command is issued with a volatile bit cleared to 0, the set value of this command shall be cleared after
hard reset or power-on and the maximam value shall be the last value with a volatile bit set to 1.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 93 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.31.2 Set Max Set Password
F9h with the content of the Features register equal to 01h.
COMMAND CODE
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
REGISTER
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR DRIVE No. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC no change
FT 01
no change
H
LBA no change
This command is not immediately preceded by a READ NATIVE MAX ADDRESS command. If this command is
immediately preceded by a READ NATIVE MAX ADDRESS command, it shall be interpreted as a SET MAX
ADDRESS command.
This command requests a transfer of a single sector of data from the host. Table 10.8-7 defines the content of
this sector of information. The password is retained by the device until the next power cycle. When the device
accepts this command the device is in Set_Max_Unlocked state.
Table 10.8-7 SET MAX SET PASSWORD data content
Word Content
0 Reserved
1-16 Password (32 bytes)
17-255 Reserved
10.8.31.3 Set Max Lock
F9h with the content of the Features register equal to 02h.
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR DRIVE No. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC no change
FT 02
LBA no change
This command is not immediately preceded by a READ NATIVE MAX ADDRESS command. If this command is
immediately preceded by a READ NATIVE MAX ADDRESS command, it shall be interpreted as a SET MAX
ADDRESS command.
The SET MAX LOCK command sets the device into Set_Max_Locked state. After this command is completed
any other SET MAX commands except SET MAX UNLOCK and SET MAX FREEZE LOCK are rejected. The
device remains in this state until a power cycle or the acceptance of a SET MAX UNLOCK or SET MAX
FREEZE LOCK command.
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
no change
H
REGISTER
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 94 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.8.31.4 Set Max Unlock
F9h with the content of the Features register equal to 03h.
COMMAND CODE
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
REGISTER
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR DRIVE No. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC no change
FT 03
no change
H
LBA no change
This command is not immediately preceded by a READ NATIVE MAX ADDRESS command. If this command is
immediately preceded by a READ NATIVE MAX ADDRESS command, it shall be interpreted as a SET MAX
ADDRESS command.
This command requests a transfer of a single sector of data from the hostTable 10.8-7 defines the content of this
sector of information.
The password supplied in the sector of data transferred shall be compared with the stored SET MAX password.
If the password compare fails, then the device returns command aborted and decrements the unlock counter.
On the acceptance of the SET MAX LOCK command, this counter is set to a value of five and shall be
decremented for each password mismatch when SET MAX UNLOCK is issued and the device is locked. When
this counter reaches zero, then the SET MAX UNLOCK command shall return command aborted until a power
cycle.
If the password compare matches, then the device shall make a transition to the Set_Max_Unlocked state and
all SET MAX commands shall be accepted.
10.8.31.5 Set Max Freeze Lock
F9h with the content of the Features register equal to 04h
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR DRIVE No. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC no change
FT 04
LBA no change
A SET MAX SET PASSWORD command shall previously have been successfully completed. This command is
not immediately preceded by a READ NATIVE MAX ADDRESS command. If this command is immediately
preceded by a READ NATIVE MAX ADDRESS command, it is interpreted as a SET MAX ADDRESS command.
The SET MAX FREEZE LOCK command sets the device to Set_Max_Frozen state. After command completion
any subsequent SET MAX commands are rejected.
Commands disabled by SET MAX FREEZE LOCK are:
− SET MAX ADDRESS
− SET MAX SET PASSWORD
− SET MAX LOCK
− SET MAX UNLOCK
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
no change
H
REGISTER
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 95 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.32 SET MAX ADDRESS EXT (37h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
LBA
Low
LBA
Mid
LBA
High
SC Current
FT Current
This command specifies the the maximum address in a range of actual drive capacity. If the address exceeding
the set value is accessed , “ ABORT ERROR “ error will be reported. This set value affects the values of WORD
60, 61, 100-103 of IDENTIFY DEVICE command.
This command shall be immediately preceded by Read Native Max Address EXT command. Otherwise, it will
be terminated with “ ABORT ERROR ” .
If this command is issued twice with a volatile bit set to 1 after power-up or hardware reset, “ID Not Found
error” will be reported.
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Previous
Previous
0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1
Max LBA(7:0)
Max LBA(31:24)
Max LBA(15:8)
Max LBA(39:32)
Max LBA(23:16)
Max LBA(47:40)
00H / 01
reserved
reserved
reserved
H
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
REGISTER
no change
no change
no change
no change
no change
no change
no change
no change
no change
no change
If a host protected area has been established by a SET MAX ADDRESS command, this command will be
terminated with “ ABORT ERROR ” .
Volatile bit ( SC register bit 0 ) :
If this command is issued with a volatile bit set to 1, the set value of this command is valid after power-up or
hardware reset.
If this command is issued with a volatile bit cleared to 0, the set value of this command shall be cleared after
hard reset or power-on and the maximam value shall be the last value with a volatile bit set to 1.
10.8.33 Read Native Max Address (F8h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR DRIVE No. no change
CY maximum cylinder number
HD maximum head number
SN maximum sector number
LBA maximum LBA
This command sets the maximum address in CY, HD, SN register. If LBA ( DRV / HD register bit6 ) is set to 1,
the maximum address shall be LBA value.
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0
REGISTER
If the 48-bit native max address is greater than 268,435,455, the Read Native Max Address command shall
return a maximum value of 268,435,454.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 96 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.8.34 Read Native Max Address EXT (27h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR drive no. no change
LBA
Low
LBA
Mid
LBA
High
SC Current
FT Current
This command sets the maximum address (LBA value).
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Current
Previous
Previous
Previous
0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1
HOB=0
HOB=0
HOB=0
HOB=0
reserved
reserved
HOB=1
HOB=1
HOB=1
HOB=1
HOB=0
HOB=1
REGISTER
Max LBA(7:0)
Max LBA(31:24)
Max LBA(15:8)
Max LBA(39:32)
Max LBA(23:16)
Max LBA(47:40)
no change
no change
no change
no change
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 97 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.35 Set Features (EFh)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR DRIVE No. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC Mode Selection for Data Transfer(*2) no change
FT Features(*1) no change
(*1) Features: FT register defines following selections.
02H Enable write cache feature
03H Select data transfer mode
05H Enable advanced power management
55H Disable read look-ahead feature
66H Disable reverting to power on defaults by soft reset
82H Disable write cache feature
85H Disable advanced power management
AAH Enable read look-ahead feature
CCH Enable reverting to power on defaults by soft reset
others Invalid (reporting with Aborted Command Error)
(*2)Mode selection for data transfer is specified in sector count register. Upper 5 bits show transfer mode
and lower 3 bits show mode figure.
1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1
REGISTER
PIO default transfer mode 00000 000
PIO default transfer mode, disable IORDY 00000 001
PIO flow control transfer mode nnn 00001 nnn
Multiword DMA mode nnn 00100 nnn
Ultra DMA mode nnn 01000 nnn
Reserved 10000 nnn
PIO default mode is mode 4 flow control. DMA default mode is Multiword DMA mode 2.
The level of Advanced Power Management function is set in Sector count register.
C0h-FEh …… Mode0 (Power save up to Low Power Idle)
80h-BFh …… Mode1 (Power save up to Low Power Idle)
01h-7Fh …… Mode2 (Power save up to Standby)
00h,FFh …… Aborted
Transition time of power save is changed dynamically in Mode1 and Mode2 due to Adaptive power control
function. The function level is set to Mode1 when Advanced Power Management function is disabled.
If FT register has any other value, the drive rejects the command with Abort Command error.
Default settings after power on or hard reset are:
Data transfer mode of Multiword DMA mode 2, PIO mode 4 flow control,
4 bytes ECC, look-ahead read enabled, write cache enabled, advanced power management enabled,
READ/WRITE Multiple command enabled (16 sectors)
and reverting to power on defaults by soft reset disabled.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 98 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

10.8.36 SECURITY SET PASSWORD (F1h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR DRIVE No. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC no change
FT no change
This command requests a transfer of a sector of data from the host including the information specified in the
table below. The function of this command is decided by the transferred data.
The revision code field is returned in the IDENTIFY DEVICE word 92. The valid revision codes are 0001h
through FFFEh. A value of 0000h or FFFFh indicated that the Master Password Revision Code is not
supported.
Word Content
0 Control word
Bits 15-9 Reserved
Bits 8 Security level 0=High
1=Maximum
Bits 7-1 Reserved
Bit 0 Identifier 0=set user password
1=set master password
1-16 Password ( 32 bytes )
17 Master Password Revision Code (valid if word 0 bit 0 = 1)
18-255 Reserved
1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1
Security Set Password information
REGISTER
The settings of the identifier and security level bits interact as shown in the table below.
Identifier and security level
Identifier Level Command result
User High The password supplied with the command will be saved as the new user password. The lock
function will be enabled by the next power-on. The drive can then be unlocked by either the
user password or the previously set master password.
Master High This combination will set a master password but will not enable the lock function. The
security level is not changed. Master password revision code set to the value in Master
Password Revision Code field.
User Maximum The password supplied with the command will be saved as the new user password. The lock
function will be enabled by the next power-on. The drive can only be unlocked by the user
password. The master password previously set is still stored in the drive but will not be used
to unlock the drive.
Master Maximum This combination will set a master password but will not enable the lock function. The
security level is not changed. Master password revision code set to the value in Master
Password Revision Code field.
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 99 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved

360050398
10.8.37 SECURITY UNLOCK (F2h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR DRIVE No. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC no change
FT no change
This command requests the host to transfer a sector of data including ones described in the table below .
Word Content
0 Control word
Bit 15-1 Reserved
Bit 0 Identifier 0=compare user password
1-16 Password (32 bytes)
17-255 Reserved
If the Identifier bit is set to master and the drive is in high security level, then the supplied password will be
compared with the stored master password. If the drive is in maximum security level, then the SECURITY
UNLOCK command will be rejected.
If the Identifier bit is set to user, the drive compares the supplied password with the stored user password.
If the drive fails in comparing passwords, then the drive returns an abort error to the host and decrements the
unlock counter. This counter is initially set to five and will be decremented for each mismatched passwords
when SECURITY UNLOCK is issued and the drive is locked. When this counter is zero, SECURITY
UNLOCK and SECURITY ERASE UNIT commands are aborted until the next power-on reset or hard reset.
SECURITY UNLOCK commands issued when the drive is unlocked have no effect on the unlock counter.
1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0
REGISTER
Security Unlock Information
1=compare master password
10.8.38 SECURITY ERASE PREPARE (F3h)
COMMAND CODE
REGISTER SETTING NORMAL COMPLETION
DR DRIVE No. no change
CY no change
HD no change
SN no change
SC no change
FT no change
The SECURITY ERASE PREPARE command must be issued immediately before the SECURITY ERASE
UNIT command to enable the drive erase and unlock. This command can prevent accidental erasure of the
drive.
1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1
REGISTER
Toshiba Corporation Digital Media Network Company
Page 100 of 157
© 2005, Copyright TOSHIBA Corporation All Rights Reserved
 Loading...
Loading...