Page 1

KAWASAKI FB460V ENGINE MANUAL
Table of Contents – Page 1 of 3
FOREWORD
SECTION 1 - GENERAL INFORMATION
BEFORE SERVICING
PERFORMANCE CURVES
DIMENSIONAL SPECIFICATIONS
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
4-STROKE ENGINE THEORY
CONSTRUCTION (INTERNAL COMPONENT)
FUEL SYSTEM AND OPERATION
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
PRELIMINARY ENGINE CHECKS
TROUBLE SHOOTING
TUNE-UP PROCEDURE
OVERHAUL PROCEDURE
SECTION 2 - I GNITION
IGNITION SYSTEM
SPARK CHECK
FLYWHEEL REMOVAL
FLYWHEEL CHECK
IGNITION COIL CHECK
CONTROL UNIT CHECK
FLYWHEEL INSTALLATION
IGNITION COIL AIR-GAP ADJUSTMENT
FLYWHEEL HOUSING INSTALLATION
SPARK PLUG CHECK AND CLEANING
SECTION 3 - AIR CLEANER
AIR CLEANER SERVICE
AIR CLEANER HOUSING INSPECTION
AIR CLEANER INSTALLATION
SECTION 4 - CARBURETOR
CARBURETOR OPERATION
CARBURETOR REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY
CARBURETOR CLEANING
CARBURETOR INSPECTION
CARBURETOR ASSEMBLY
CARBURETOR INSTALLATION
CARBURETOR ADJUSTMENT
SECTION 5 - GOVERNOR
REMOVAL (GOVERNOR RELATED)
GOVERNOR GEAR DISASSEMBLY
Page 2

KAWASAKI FB460V ENGINE MANUAL
Table of Contents – Page 2 of 3
SECTION 5 - GOVERNOR - continued
GOVERNOR GEAR INSPECTION
GOVERNOR REASSEMBLY
REASSEMBLY (GOVERNOR RELATED)
LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
THROTTLE CABLE INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENT
CHOKE ADJUSTMENT
MAXIMUM SPEED ADJUSTMENT
IDLE SPEED ADJUSTMENT
SECTION 6 - COMPRESSION
COMPRESSION CHECK
CYLINDER HEAD AND HEAD GASKET REMOVAL
CYLINDER HEAD TIGHTENING PROCEDURE
CYLINDER HEAD CHECK AND REPAIR
VALVE AND SPRING REMOVAL
VALVE SPRING INSPECTIO N
TO ANALYZE VALVE
VALVE INSPECTION
VALVE GUIDE CHECK AND REPLACEMENT
VALVE SEAT RECONDITIONING
TAPPET CLEARANCE CHECK AND REPAIR
SECTION 7 - LUBRICATION
LUBRICATION
OIL WARNING SYSTEM
FULL FLOW OIL FILTER (OPTIONAL)
CAPACITIES
OIL RECOMMENDATION
OIL LEVEL CHECK
OIL CHANGE
BREATHER CHECK
OIL PUMP INSPECTION
OIL PUMP INSTALLAT ION
SECTION 8 - PISTON, PISTON RING, AND CON-ROD
PISTON AND CON-ROD REMOVAL
PISTON INSPECTION
PISTON RING THICKNESS INSPECTION
PISTON RING END GAP INSPECTION
PISTON PIN AND PIN HOLE DIA. INSPECT IO N
CON-ROD INSPECTION
PISTON AND CON-ROD ASSEMBLY
PISTON RING INSTALLATION
PISTON AND CON-ROD ASSY INSTALLATION
Page 3

KAWASAKI FB460V ENGINE MANUAL
Table of Contents – Page 3 of 3
SECTION 9--CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT
CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT REMOVAL
CRANKSHAFT INSPECTION
UNDER-SIZE CON-ROD
LINK ROD INSPECTION
BUSHING REPLACEMENT
BALANCE WEIGHT INSPECTION
BALANCER GUIDE INSPECTION
CAMSHAFT INSPECTION
CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT INSTALLATION
CRANKCASE COVER INST ALL AT IO N
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY ADJUSTMENT
SECTION 10--CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEARING
CYLINDER BLOCK INSPECTION AND REPAIR
BALL BEARING REMOVING
BALL BEARING INSPECTION
PLAIN BEARING INSPECTION
BALL BEARING INSTALLATION
OIL SEAL REPLACEMENT (PT O SIDE)
SECTION 11 - ELECTRIC STARTER AND CHARGE
STARTER MOTOR CIRCUIT
STARTER SYSTEM CHECK
STARTER MOTOR CHECK
STARTER SOLENOID TEST
STARTER MOTOR DI SASSEMBLY
STARTER MOTOR INSPECTION
BRUSH HOLDER CHECK
PINION CLUTCH INSPECTION
STARTER MOTOR REASSEMBLY
CHARGING SYSTEM CHECK
TROUBLESHOOTING
SECTION 12 - RECOIL STARTER
RECOIL STARTER DISASSEMBL Y
RECOIL STARTER REASSEMBL Y
RECOIL STARTER INSPECTIO N
Page 4

4-stroke
air-cooled
gasoline engine
Page 5

FOREWORD
This manual
nics in
In order to perform the work efficiently and to
avoid costly mistakes, read the text, thorough-
ly
familiarize yourself with the procedures before
starting work, and then do the work carefully
a
clean area. Whenever special tools or equip-
in
ment are specified, do not use makeshift tools
equipment. Precision measurements can only
be made if the proper instruments are used, and
the use of substitute tools may adversely affect
safe operation.
Whenever you
symbols, heed their instructions!
Always follow safe operating and maintenance
practices.
special instructions or procedures which,
correctly followed, could result
injury, or
CAUTION:
or procedures which,
could result in equipment damage or destruction.
NOTE:
ular interest for more efficient and convenient
operation.
is
designed for use by trained mecha-
a
properly equipped shop.
see
these
WARNING
WARNING:
loss
This identifies special instructions
Indicates message or points
of
This warning
life.
if
not strictly observed,
and
symbol
in
fire,
or
CAUTION
identifies
if
not
personal
of
partic-
The term "Replace" and some abbreviations are
used
as
follows:
-
Replace
MIN
MAX
Ass'y
STD
I
Ilust.
Spec.
PTO
Approx.
Carb.
Con-rod
Cyl.
All rights reserved.
may be reproduced, stored in
or transmitted in any form or by any means,
electronic mechanical photocopying, recording or
otherwise, without the prior written permission
of Engine Division/Kawasaki Heavy Industries,
Ltd.
curacies or omissions in this publication, although
every possible care has been taken to make
complete and accurate
and specifications subject to change without prior
notice or obligation. Illustrations in this publication are intended for reference use only and may
not depict actual model component parts.
usually means replace with a new part.
=
Minimum
=
Maximum
=
Assembly
=
Standard
=
I
llustration
=
Specification(s)
=
Power take off
=
Approximately (Approximate)
=
Carburetor
=
Connecting rod
=
Cylinder
No
part
of
this publication
a
retrieval system,
No
liability can be accepted for any inac-
as
possible. All procedures
it
as
Page 6

TABLE
OF
CONTENTS
/-
Section
GENERAL INFORMATION
Before Servicing
Specifications.
Performance Curves
Dimensional Specifications
Periodic Maintenance
4-Stroke Engine Theory
Construction (Internal Component)
Fuel System and Operation
Electrical System
Preliminary Engine Checks
Trouble Shooting
Tune-up Procedure
Overhaul Procedure
Ignition System
Spark Check
Flywheel Removal
Flywheel Check
Ignition Coil Check
Control Unit Check
Flywheel Installation
Ignition Coil Air-gap Adjustment
Flywheel Housing Installation
Spark Plug Check and Cleaning
.......................
.........................
....................
...................
......................
......................
.....................
....................
Section
IGNITION
........................
..........................
.....................
.......................
....................
....................
1
.....
..................
..............
...............
2
...................
.............
...........
1-1
1-3
1-4
.........
........
..........
1-5
1-7
1-7
1-8
1-9
1-10
1-11
1-13
1-17
1-17
2-1
2.1
2.1
2.2
2-3
2-3
2-3
2-3
2-4
2.4
Section
GOVERNOR
Removal (Governor Related)
Governor Gear Disassembly
Governor Gear Inspection
Governor Reassembly
Reassembly (Governor Related)
Linkage Adjustment
Throttle Cable Installation and
Adjustment
Choke Adjustment
Maximum Speed Adjustment
Idle Speed Adjustment
Compression Check
Cylinder Head and Head Gasket Removal
Cylinder Head Tightening Procedure
Cylinder Head Check and Repair
Valve and Spring Removal
Valve Spring Inspection
To Analyze Valve
Valve Inspection
Valve Guide Check and Replacement
Valve
Seat
Tappet Clearance Check and Repair
..........................
Reconditioning
...................
....................
.....................
Section
COMPRESSION
....................
......................
.......................
5
.............
..............
...............
...........
.............
..................
6
..........
...............
.................
...............
5-1
5-1
5-2
5-2
5-2
5-2
5-3
5-3
5-3
5-3
6-1
...
6-1
.......
.......
........
6-1
6-2
6-2
6-2
6-2
6-2
6-3
6-4
6-6
Section
AlR-CLEANER
Air cleaner Service
Air cleaner Housing Inspection
Air cleaner Installation
Carburetor Operation
Carburetor Removal and Disassembly
Carburetor Cleaning
Carburetor Inspection
Carburetor Assembly
Carburetor Installation
Carburetor Adjustment
.....................
Section
CARBURETOR
....................
3
............
..................
4
...................
..................
...................
..................
.................
3.1
3.1
3.1
4.1
......
4.1
4-2
4.2
4.2
4-3
4-3
LUBRICATION
Lubrication
Oil Warning System
Full Flow Oil Filter
Capacities
Oil Recommendation
Oil Level Check
Oil Change
Breather Check
Oil Pump Inspection
Oil Pump Installation
..........................
.....................
............................
.......................
...........................
........................
Section
....................
...................
....................
7
7-1
7-1
7-1
7-1
7-2
7-2
7-2
7-2
7-3
...................
7-3
Page 7

Section
PISTON. PISTON RING. AND CON-ROD
8
Section
RECOIL STARTER
12
Piston and Con-rod Removal
Piston Inspection
Piston Ring Thickness Inspection
Piston Ring End Gap Inspection
Piston
Con-rod Inspection
Piston and Con-rod Assembly
Piston Ring Installation
Piston and Con-rod Assembly Installation
Crankshaft and Camshaft Removal
Crankshaft Inspection
Under
Link
Bushing Replacement
Balance Weight Inspection
Balancer Guide Inspection
Camshaft Inspection
Crankshaft and Camshaft Installation
Crankcase Cover Installation
Crankshaft End Play
Crankshaft End Play Adjustment
Pin
and Pin Hole Dia . Inspection
CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT
Size
Con-rod
Rod
Inspection
......................
.....................
Section
..................
....................
...................
...................
....................
....................
.............
..........
...........
.............
.................
9
.........
...............
...............
.......
.............
..........
8-1
8.2
8-2
8-3
.....
8-3
8-4
8-5
8-5
...
8-5
9-1
9-1
9-2
9-2
9-2
9-3
9-3
9-3
9-4
9-5
9-5
9-5
Recoil
Recoil Starter Reassembly
Recoil
Starter
Starter
Disassembly
Inspection
...............
...............
................
12-1
12-1
12-2
Section
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEARING
Cylinder Block Inspection and Repair
Ball Bearing Removing
Ball Bearing Inspection
Plain Bearing Inspection
Ball Bearing Installation
Oil
Seal
Replacement
Section
ELECTRIC STARTER AND CHARGE
Starter Motor Circuit
Starter System Check
Starter
Starter Solenoid Test
Starter Motor Diassembly
Starter Motor Inspection
Brush Holder Check
Pinion Clutch Inspection
Starter Motor Reassembly
Charging System Check
Trouble Shooting
Motor Check
......................
....................
....................
10
..................
..................
.................
.................
...................
11
...................
...................
...................
................
................
................
...............
.................
......
10-1
10-2
10-2
10-2
10-3
10-3
11-1
11-1
11-2
11-2
11-3
11-4
11-7
11-7
11-7
11-7
11-9
Page 8

1-1
GENERAL INFORMATION
Section
GENERAL
BEFORE
Before starting to service a engine carefully read
the applicable section to eliminate unnecessary
work. However,
tations;
is
required for successful work. Especially note
the following:
Mechanical
Adjustments
Adjustments shall be made in accordance with
the Periodic Maintenance Chart or whenever
troubleshooting or presence of symptoms indi-
cate
that adjustments may be required.
Edges
Watch for sharp edges, especially during major
engine disassembly and assembly. Protect your
hands with gloves or
lifting the engine or turning
Dirt
Before removal and disassembly, clean the engine.
dirt
Any
parts, will work
of the engine. For the same reason, before install-
a
new part, clean off
ing
Tightening Sequence
Where there
this
Service
must be tightened in the order and method indicated. When installing
or screws, they should
and tightened to
evenly, according to the tightening sequence, to
the specified torque. This
of the part and/or causing
Conversely, when loosening the bolts, nuts, or
screws, loosen
turn and then remove them.
Torque
The torque values given in this
should always be adhered to. Either too
or too much torque may lead to serious damage.
Use
a
good quality, reliable torque wrench.
SERVICING
a
detailed account has limi-
a
certain amount of basic knowledge
Systems:
a
piece of thick cloth when
it
over.
entering the engine, carburetor, or other
as
an abrasive and shorten the life
any
dust or metal fillings.
is
a
tightening sequence indicated in
Manual, 'the bolts, nuts, or screws
a
part with several bolts, nuts,
all
be started in their holes
a
shug fit. Then tighten them
is
to avoid distortion
gas
or oil leakage.
all
of them about
a
quarter of
Service
INFORMATION
Manual
little
a
1
Force
Common sense should dictate how much force
is
necessary in assembly and disassembly.
part seems especially difficult to remove or install,
stop and examine what may be causing the pro-
is
blem. Whenever tapping
using
impact driver for screws (particularly for the removal of screws held by
to avoid damaging the heads.
greases in particular should be used only in certain
applications and may be harmful if used in an application for which they are not intended.
a
wooden or plastic-faced mallet.
Lubricant
Don't use just any oil or grease. Some oils and
Battery Ground
Before performing any disassembly operations
on the equipment, remove the ground
from the battery to prevent the possibility of
accidentally turning the engine over while partially
disassembled.
Lubrication
Engine wear
the engine
surfaces have an adequate lubricative film. During
assembly, oil or grease (whichever
should be applied to any rubbing surfave which
has lost
oil should be cleaned off. Deteriorated grease
has lost
abrasive foreign particles.
Press
A part installed using
seal,
should first be coated with oil on
inner circumference
smoothly.
Oil
Seal, Grease
Replace any oil or grease
with new ones,
seals. A seal
grease
to the
seal,
perature grease, to the lips to reduce rubber-tometal friction.
Gasket,
When in doubt
O-ring, replace
surfaces around the gasket should be free of for-
eign matter and perfectly smooth to avoid oil or
compression leaks.
seals
seal
apply
O-ring
is
generally
is
warming up and before
its
lubricative film. Old grease and dirty
its
lubricative quality and may contain
so
Seal
as
removal generally damages
guide
during installation to avoid damage
lips. Before
a
little
is
lubricant, preferably high tem-
as
to the condition of a gasket or
it.
with a new one. The mating
necessary, tap lightly
a
lacking agent) in order
at
its
maximum while
all
the rubbing
is
more suitable)
a
press or driver, such
its
that
it
will go into place
seals
that were removed
required for certain oil or
a
shaft passes through
If
Use
(-)
lead
as
outer or
an
a
a
a
Page 9

GENERAL INFORMATION
1-2
Liquid
Follow manufacturer's directions for cleaning and
preparing surfaces where these compounds will
used. Apply sparingly. Excessive amounts may
block engine oil passages and cause serious damage.
An example of
commonly, available in North America
Lock'n
Ball Bearing Installation
When installing
which
a
balls and races, and prevents races and balls from
being dented. Press
at
Circlip, Retaining Ring
Renew any circlips and retaining rings that were
removed,
When installing circlips and retaining rings, take
care to compress or expand them only enough
to install them.
High Flash-point Solvent
A high flash-point solvent
reduce fire danger. A commercial solvent com-
monly available in North America
solvent (generic name). Always follow manufac-
turer and container directions regarding the use of
any solvent.
Molybdenum Disulfide
This manual makes reference to molybdenum
disulfide grease in the assembly of certain engine
and chassis parts. Always check manufacturer
recommendations before using such special lubricants.
Engine Rotation
When turning the crankshaft by hand, always turn
it
clockwise, viewed from the front (flywheel end)
of the engine. This will ensure proper adjustments.
Gasket
and Non-permanent Locking Agent
be
a
non-permanent locking agent
is
Loctite
Seal
(Blue).
a
ball bearing, the bearing race
is
affected by friction should be pushed by
suitable driver. This prevents severe stress on the
a
ball bearing until
the stop in the hole or on the shaft.
as
removal weakens and deforms them.
is
recommended to
)
Grease
in the direction of normal rotation; which
it
is
Stoddard
stops
is
The electrical parts should never be struck
as
sharply,
on a hard surface. Such
can damage them.
Do
not disconnect the battery leads or any
other electrical connections when the ignition switch
ning, unless specifically noted.
Never keep the starter engaged
motor will not turn over, or the current may
burn out the starter motor windings.
Never replace
without determining what caused the failure.
If the failure was brought on by some other
item or items, they too must be repaired or
replaced, or the new replacement will fail.
Make sure
clean and tight, and examine wires for signs
of burning, fraying,
connections will affect electrical system ope-
ration.
Measure coil and winding resistance when the
is
part
All the electrical leads are either single-color
or two-color and, with only
must
When soldering or unsoldering connections,
do not use
watts capacity. Use
60/40
wiring.
with a hammer, or allowed to
a
shock to the parts
is
on, or while the engine
if
the starter
a
defective electrical component
all
connectors in the circuit are
etc.
Poor wires and bad
cold
(at
room temperature).
a
few exceptions,
be
connected to leads of the same color.
a
soldering iron of more than
16
gauge
resin core solder when reconnecting
(0.062
is
fall
run-
40
in.)
Electrical
Always minimize shock hazards when working
on electrical equipment. Work in
dry environment with dry hands. For max-
imum shock hazard protection, connect the
equipment ground terminal to an earth ground.
Do
This will burn out the diodes in the electrical
parts.
Always check battery condition before condemning other parts of an electrical system.
A fully charged battery
ing accurate electrical system
Systems:
not reverse the battery lead connections.
is
a
must for conduct-
tests.
a
clean,
Page 10

1-3
GENERAL INFORMATION
SPECI
FlCATlONS
ENGINE MODEL
ENGINE TYPE
NUMBER OF CYLINDER
PISTON DISPLACEMENT
BORE x STROKE
COMPRESSION RATIO
MAX. OUTPUT
MAX. TORQUE
MIN. SPECIFIC FUEL CONSUMPTION RATIO
DIRECTION OF ROTATION
FAST IDLE SPEED SETTING
SLOW IDLE SPEED SETTING
LUBRICATION
BALANCING
THROTTLE CONTROL
CHOKE CONTROL
STARTER
CARBURETOR
IGNITION
CHARGING COIL
RFI
GOVERNOR
OIL FILL AND DIP STICK
OIL DRAIN
COOLING AIR INLET
COOLING SHROUDS
AIR CLEANER
FB460V
Forced Air Cooled, Vertical Shaft, 4-Stroke Gasoline Engine
1
460 cc (28.1 cu.in.)
89 mm x 74 mm (3.50 in. x 2.91 in.)
6.4
:
1
12.5/3,600 r.p.m. (with JX156-K112-01 muffler)
2.78 kg-m/2,300 r.p.m. (20.1 ft-lbs/2,300 r.p.m.)
315 gr/hp-hr (0.694 Ibs/hp-hr)
Counter-Clockwise Facing the PTO Shaft
3,350 r.p.m.
1,400 r.p.m.
Pressurised Lubrication
Reciprocating Weight
Remote Cable
Automatic
Electric Starter or Recoil Starter
Float Type Fixed Main Jet
Transistorized-Fly-Wheel Magneto (Point
12V-13A with Regulator (Electric Starter Model
per Canada and U.S.A. Requirement
Mechanical Governor
Extended Above Engine
with Extention
Rotating Screen with Periphery Blade Protector
Noise Suppresive Layered Sheet
Semi Cyclone Type with Dual Element
Pipe
Less)
LUBRICANT
FUEL
DIMENSION (H x
NET WEIGHT
OPTIONAL PARTS
Specifications and dimensions are subject to change without notice.
W x L)
API Service Classification
At temperatures below 0°C (32°F)
At temperatures above 0°C (32°F)
Regular Grade Leaded or Unleaded Gasoline
(Electric Starter Model) (Recoil Starter Model)
307 mm x 381 mm x 419.5 mm 356 mm x 365 mm x 511 mm
(12.08 in. x 15.00 in. x 16.51 in.) (14.01 in. x 14.37 in. x 20.12 in.
36 kg (79.36
Oil Warning System, Full Flow Oil Filter
Ibs)
:
SD, SE, SE/CC, SF Class
:
SAE 5W-20
:
SAE 30
36 kg (79.36
Ibs)
Page 11
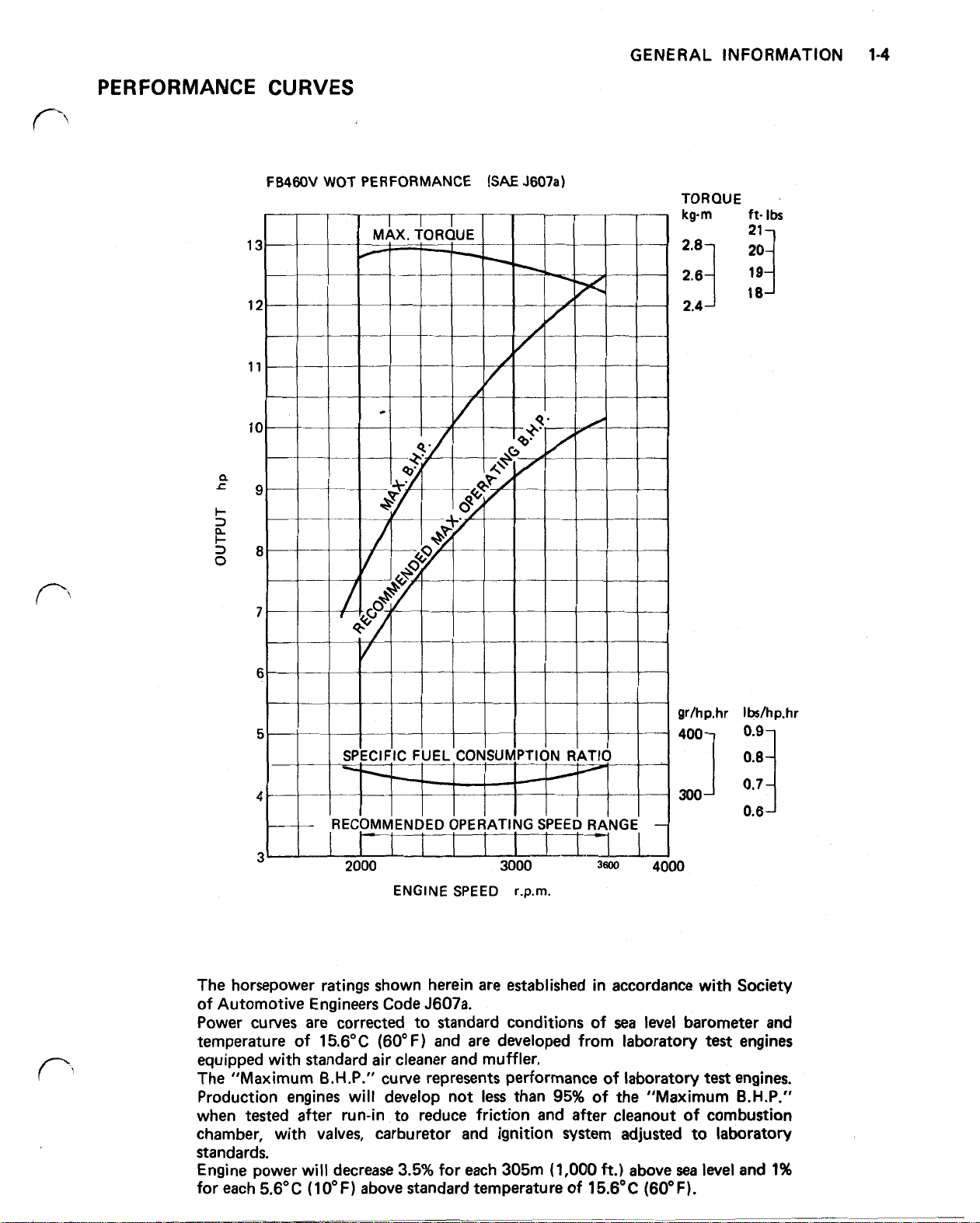
PERFORMANCE CURVES
GENERAL
INFORMATION
1-4
FB46OV
WOT
PERFORMANCE
(SAE
J607a)
TORQUE
kgm
2.6
2.4
ft-
18
Ibs
gr/hp.hr Ibs/hp.hr
300
2000
ENGINE
SPEED
3000
r.p.m.
3600
4000
The horsepower ratings shown herein are established in accordance with Society
of Automotive Engineers Code J607a.
sea
Power curves are corrected to standard conditions of
F)
temperature of 15.6°C (60"
and are developed from laboratory
level barometer and
test
engines
equipped with standard air cleaner and muffler.
The "Maximum
B.H.P."
Production engines will develop not
curve represents performance
less
than 95% of the "Maximum
of
laboratory
test
engines.
B.H.P."
when tested after run-in to reduce friction and after cleanout of combustion
chamber, with
valves,
carburetor and ignition system adjusted to laboratory
standards.
Engine power will decrease
for each 5.6°C (10°F) above standard temperature of 15.6°C
3.5%
for each 305m
(1,000
ft.)
above
(60°F).
sea
level
and 1%
Page 12
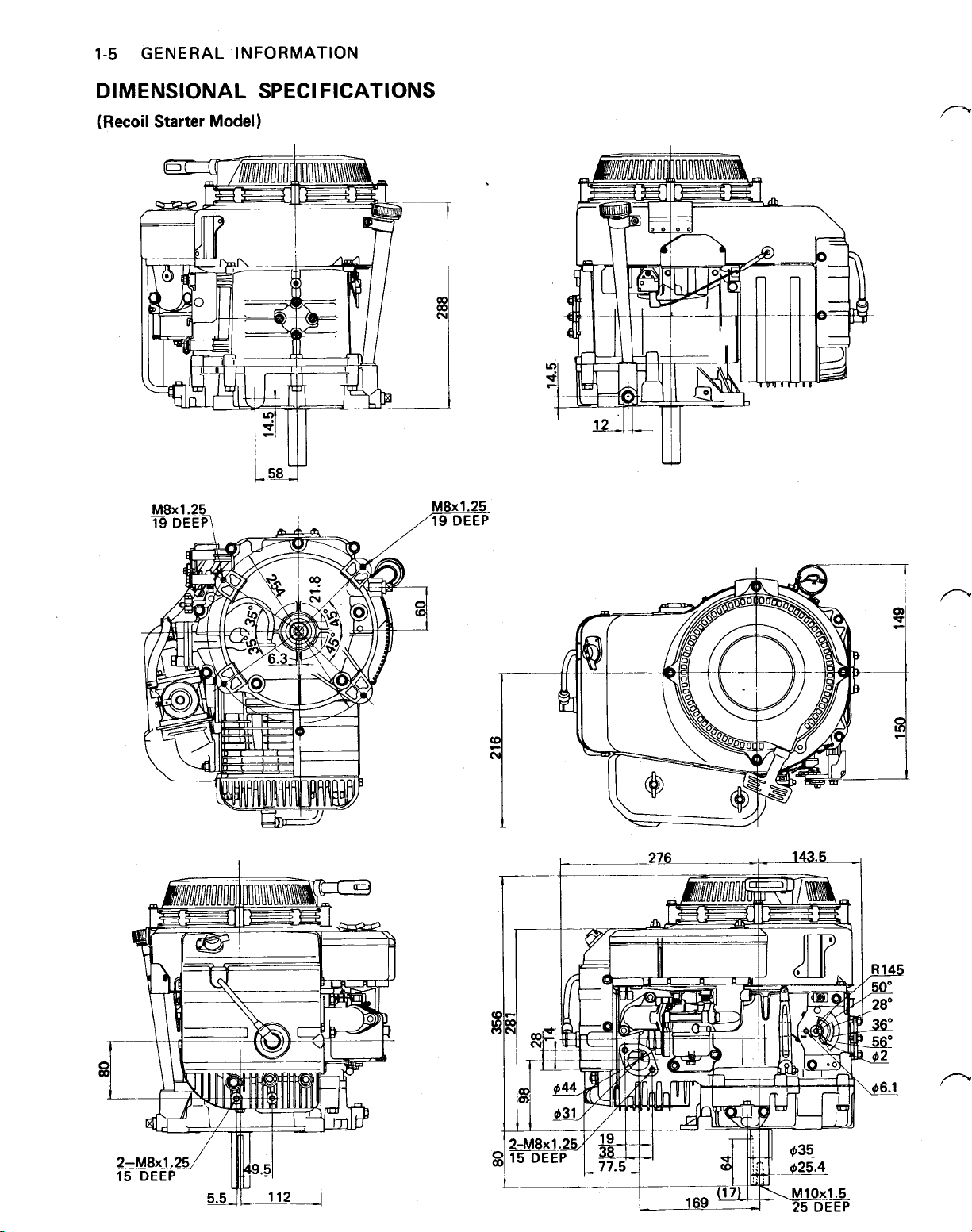
1-5
GENERAL INFORMATION
DIMENSIONAL SPECIFICATIONS
(Recoil Starter Model)
276 143.5
I
Page 13
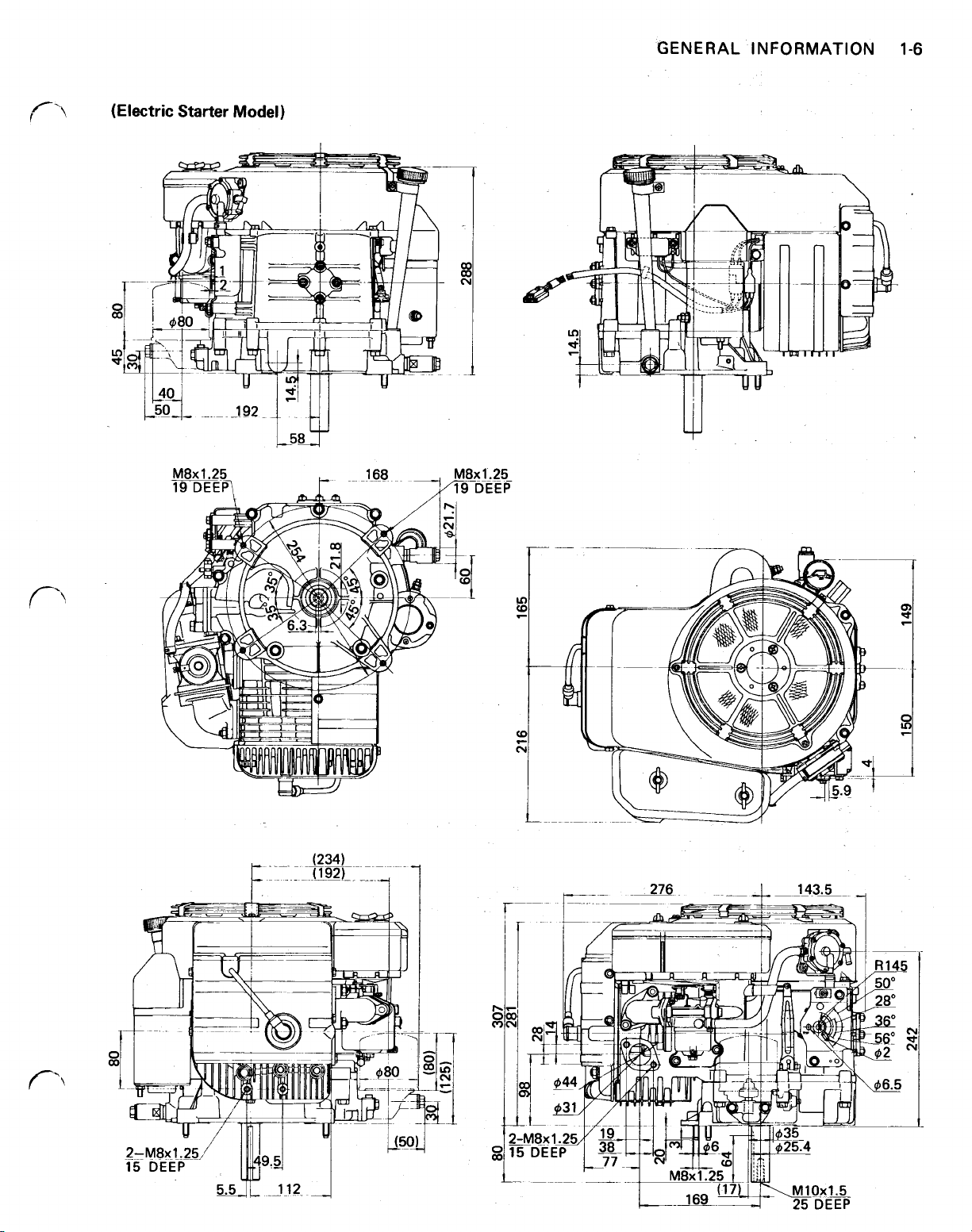
GENERAL INFORMATION
1-6
(Electric
Starter
Model)
Page 14
1-7
GENERAL INFORMATION
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Engine Serial Number
is
The engine serial number
located on the front of the cylinder-head cover above the spark
plug.
Periodic Maintenance
Chart
To ensure satisfactory operation over an extended period of time, the engine requires normal maintenance
at
regular intervals.
The chart below shows periodic inspection and maintenance required and suitable interval designated with
Electric start models only.
5
Perform these operations after the first
Clean the air cleaner element more often when operating under dusty conditions.
hours of use, then
at
the recommended interval.
Fuel
Use regular grade leaded or unleaded.
CAUTION: Gasohol
Don't use additives, such
oil
Don't mix
with gasoline. Always use a clean container.
is
not recommended.
as
carburetor cleaners, de-icers, or moisture-removing liquids in the gasoline.
Engine Oil
Use API classification
at
temperatures below
SF,
SE/CC,
0°C
(32°F). Don't put additives in the oil.
SE
or SD. Use SAE
30
at
temperatures above 0°C (32°F) and SAE 5W-20
4-STROKE ENGINE THEORY
KAWASAKI
and tractors. There are four strokes to one complete power cycle.
Intake Stroke:
1.
Compression Stroke:
2.
Power Stroke:
3.
Exhaust Stroke:
4.
FG
Series engines are of the same basic "4-stroke cycle design"
The piston goes down, creating
gas
draws
through open intake
The piston comes up with both
the
gas
into the space left between the top of the piston and cyl-
inder head.
At this point the magneto sends high tension current to the
spark plug, firing or exploding the compressed
the piston down.
valve
Exhaust
out
all
of the burnt gases, thus completing the power cycle.
opens and the upward stroke of the piston forces
as
used in automobiles, trucks
a
vacuum in the cylinder which
valve
into the space above piston.
valves
closed, highly compressing
gas
and driving
Page 15
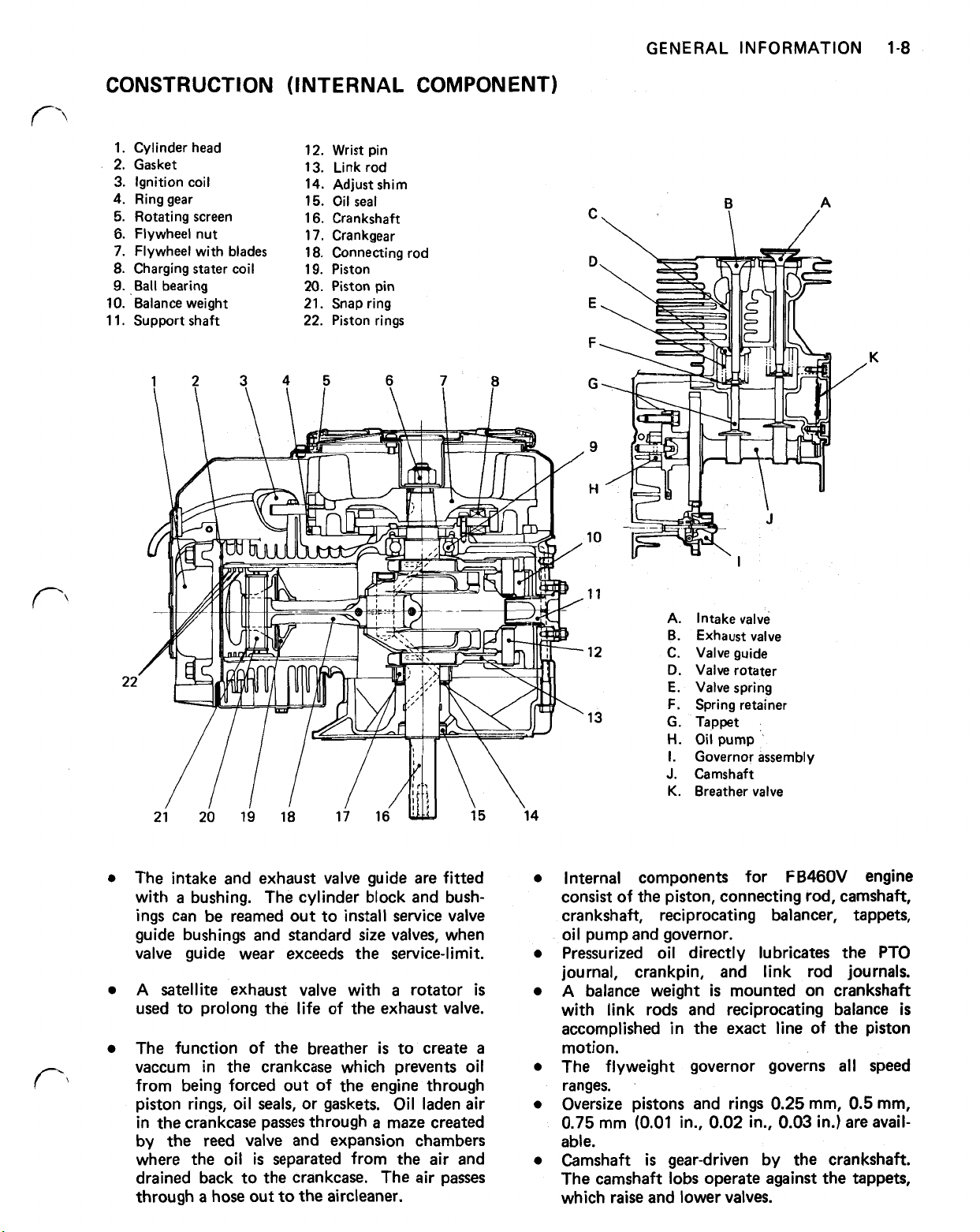
CONSTRUCTION (INTERNAL COMPONENT)
GENERAL INFORMATION
1-8
1. Cylinder head
2. Gasket
3. Ignition coil
4.
Ring gear
5.
Rotating screen
6.
Flywheel nut
7.
Flywheel with blades
8.
Charging stater coil
9. Ball bearing
10. Balance weight
1 1. Support shaft
12. Wrist pin
13. Link rod
14. Adjust shim
15. Oil seal
16. Crankshaft
17.
Crankgear
18. Connecting rod
19. Piston
20.
Piston pin
21. Snap ring
22. Piston rings
\
14
11
A. Intake valve
B.
Exhaust valve
12 C. Valve guide
D.
Valve rotater
E.
Valve spring
F.
13
Spring retainer
G.
Tappet
H.
Oil pump
I.
Governor assembly
J.
Camshaft
K.
Breather valve
The intake and exhaust
a
with
bushing. The cylinder block and bushings can be reamed out to install service
guide bushings and standard
valve
A
guide wear exceeds the service-limit.
satellite
exhaust valve with a rotator
valve
guide are fitted
size
valves,
valve
when
is
used to prolong the life of the exhaust valve.
is
The function of the breather
to create
vaccum in the crankcase which prevents oil
from being forced out of the engine through
piston rings, oil
in the crankcase passes through
seals,
or gaskets. Oil laden air
a
maze created
by the reed valve and expansion chambers
where the oil
is
separated from the air and
drained back to the crankcase. The air passes
a
through
hose out to the aircleaner.
a
Internal components
for
FB460V
engine
consist of the piston, connecting rod, camshaft,
crankshaft, reciprocating balancer, tappets,
oil pump and governor.
Pressurized oil directly lubricates the PTO
journal, crankpin, and link rod journals.
is
A balance weight
with link rods and reciprocating balance
mounted on crankshaft
is
accomplished in the exact line of the piston
motion.
all
The flyweight governor governs
speed
ranges.
0.25
mm,
0.5
Oversize pistons and rings
0.75
mm
(0.01
in.,
0.02
in.,
0.03
in.) are avail-
mm,
able.
is
Camshaft
The camshaft
which
raise
gear-driven by the crankshaft.
lobs
operate against the tappets,
and lower valves.
Page 16
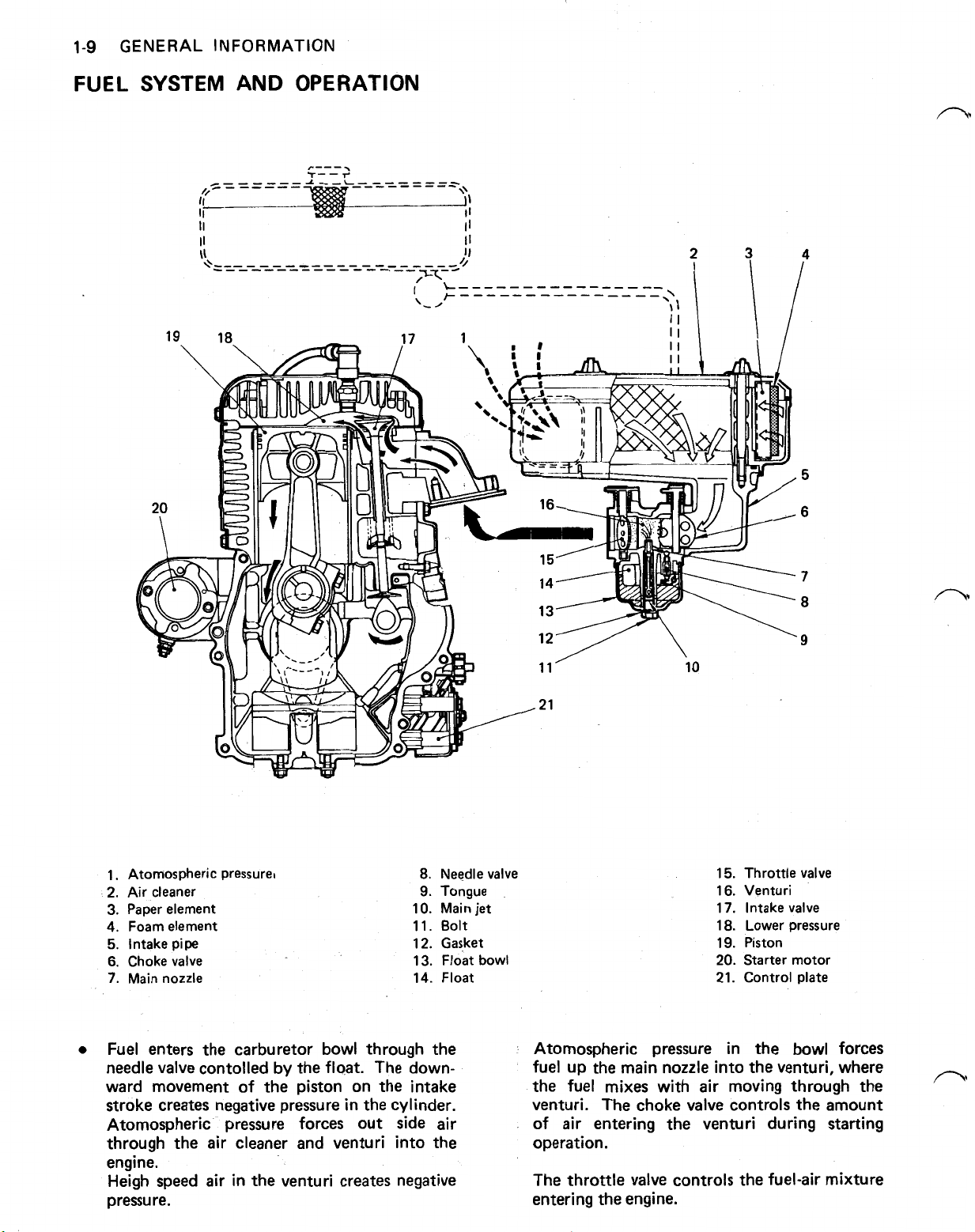
1-9
GENERAL INFORMATION
FUEL SYSTEM
AND
OPERATION
n
8.
1. Atomospheric pressure
2. Air cleaner
3.
Paper element
4. Foam element
5.
Intake pipe
6.
Choke valve
7.
Main nozzle
Needle valve
9.
Tongue
10. Main
11. Bolt
12. Gasket
13. Float bowl
14. Float
Fuel enters the carburetor bowl through the
needle
valve
contolled
by
the float. The downward movement of the piston on the intake
stroke creates negative pressure in the cylinder.
Atomospheric pressure forces out side air
through the air cleaner and venturi into the
engine.
Heigh speed air in the venturi creates negative
pressure.
jet
15. Throttle valve
16. Venturi
17. Intake valve
18. Lower pressure
19. Piston
20. Starter motor
21. Control plate
bowl
Atomospheric pressure in the
forces
fuel up the main nozzle into the venturi, where
the fuel mixes with air moving through the
valve
venturi. The choke
controls the amount
of air entering the venturi during starting
operation.
valve
The throttle
controls the fuel-air mixture
entering the engine.
n
n
Page 17
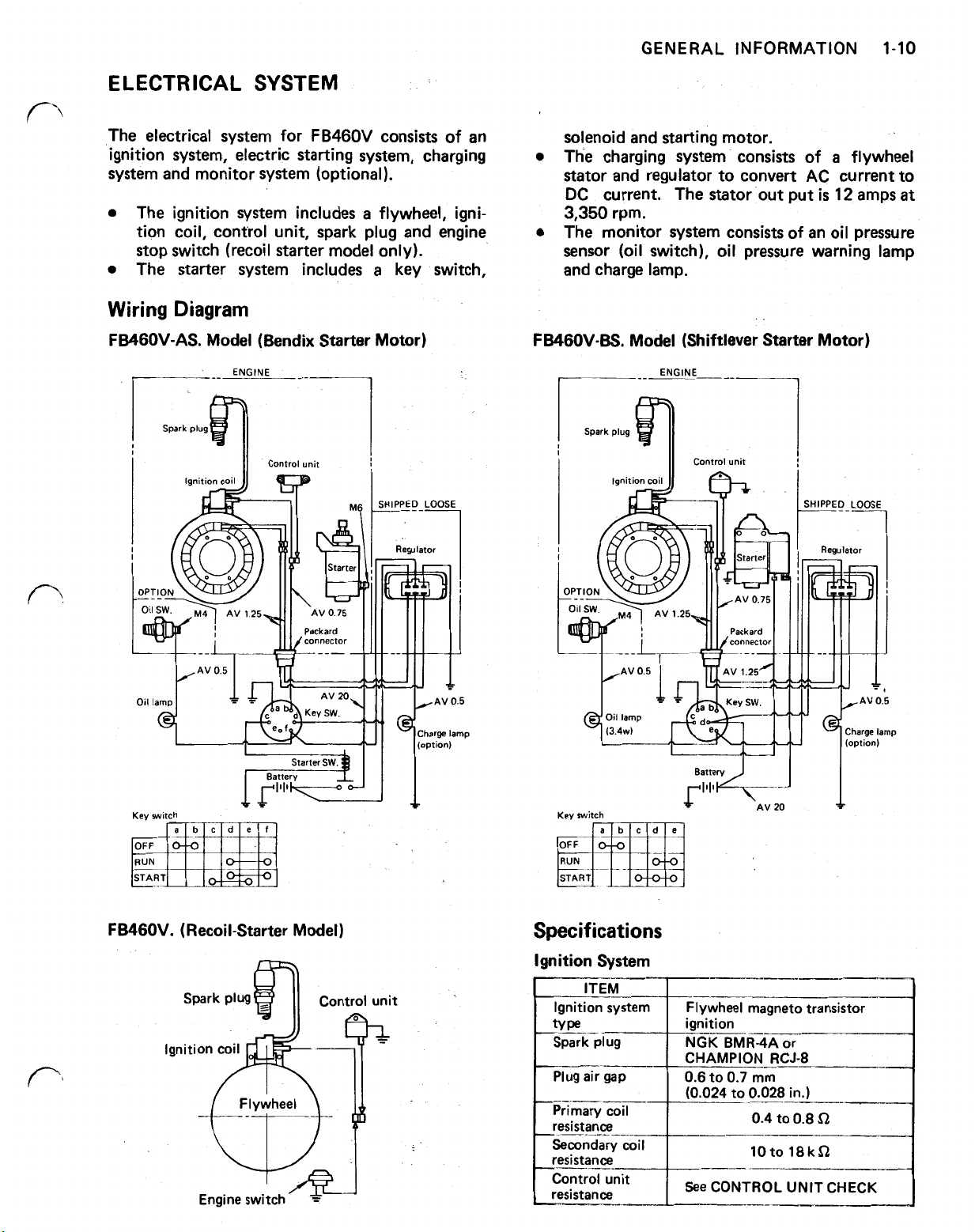
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
1-10
The electrical system for FB460V consists of an
ignition system, electric starting system, charging
system and monitor system (optional).
a
The ignition system includes
flywheel, ignition coil, control unit, spark plug and engine
stop switch (recoil starter model only).
a
The starter system includes
key switch,
Wiring Diagram
FB46OV-AS. Model (Bendix Starter Motor)
ENGINE
solenoid and starting motor.
The charging system consists of
a
flywheel
stator and regulator to convert AC current to
DC
current. The stator out put
3,350
rpm.
is
12
amps
The monitor system consists of an oil pressure
sensor (oil switch), oil pressure warning lamp
and charge lamp.
FB46OV-BS. Model (Shiftlever Starter Motor)
ENGINE
Spark plug
I
Control unit
at
Key
switch
FB460V. (Recoil-Starter Model)
OFF
RUN
START
Specifications
Ignition System
Control unit
I
resistance
~-
ignition
NGK BMR4A or
CHAMPION RCJ-8
0.6
to
0.7
mm
See
CONTROL
UNIT
CHECK
Page 18

1-1 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
Electric Starter System (Bendix-type)
I
ITEM
Battery rating
current
Starter-rating
Brush length 12 mm (0.47 in.) (MINI
Commutator
groove depth
Commutator
diameter
Commutator
Run-out
Current draw
12 V/35 A.H. or more
of
One tenth
12 V
-
0.2 mm
32 mm (1.26 in.) (MINI
0.3 mm (0.012
12 V, 7000 rpm (MINI 60A (MAX)
battery capacity Max charging
0.8
KW
(0.008
in.) (MINI
in.)
(MAX)
Electric Starter System (Shiftlever-type)
Battery rating
Max charging
current
Starter-rating
Brush length
Commutator 0.2 rnm
groove depth
Commutator 27 mm (1.10 in.) (MAX)
diameter
Commutator 0.4 mm (0.016 in.) (MAX)
run-out
Current draw 11.5 V, 6000 rpm (MINI
test
12 A.H.
One-tenth
12 V
6
/
35 A.H. or more
of
-
0.75
mm (0.24 in.) (MIN)
(0.008
I
50A (MAX)
battery capacity
KW
in.) (MIN)
PRELIMINARY
1
A complete diagnosis of engine malfunctions
appears in this section.
However, the majority of engine problems
normally due to ignition or fuel system diffi-
I
culties.
1.
If engine will not start with gasoline in the
tank, remove spark plug and check spark by
cranking engine while having the plug touched
against engine block.
WARNING:
plug in close positions to
as
plug
To
avoid an electric shock, do not hold the plug
itself. Make sure to hold the plug
If there
I
1-1.
the ignition system
I
I
far away
ENGINE
To
avoid fire, do not hold spark
the
as
possible from the plug hole.
CHECKS
plug hole. Keep the
cap.
is
good spark between electrodes,
is
in good condition.
is
Charging System
I
ITEM
Stator output
No-load voltage
Regulator-type
Regulator
resistance
Monitor System
I
Approx. 12 amps-0 rpm
/
34.5 V
12V system, constant voltage,
regulator
See Regulator Inspection
3350 rpm (MIN)
I
1-2.
If there
plug and regap to
0.028 in.). Replace the plug if
is
no or a very weak spark, clean the
0.6
to 0.7mm (0.024 to
it's
electrodes
are of worn.
1-3.
If there
is
still
no spark refer to "IGNITION"
section.
A
2.
If engine
still
fails to start, check the fuel
system for the tank to carburetor to be sure
gas
is
getting to carburetor.
Check carb. adjustments and be sure choke
and throttle controls are working properly.
Refer to Section 4 for carb. information.
Check for
3.
a
plugged air cleaner. Clean or re-
place if necessary.
still
If engine
4.
will not start, or starts but
does not run properly, perform the compres-
test
sion
that follows, and refer to "Diagnose
Malfunction" in this Section.
Page 19

5.
Test compression when engine loses power or
runs erratically and fuel and ignition
adjustments do not correct the problem.
systems
GENERAL INFORMATION
1-12
CAUTION:
engine from starting during compression
6.
Crank engine with electric or recoil starter and
check the compression force.
7.
If
of one or more of following:
8. Use
sion by:
8-1. Remove spark plug and screw compression
gauge into the plug hole securely.
Disconnect spark plug cap
compression
Leaking cyl. head gasket.
Warped cyl. head.
Worn piston rings.
Worn cyl. bore.
Damaged piston.
Burned or warped
Improper
Broken
a
compression gauge and
valve
valve
is
low,
clearance.
springs.
valves.
it
is
usually the result
to
test
prevent
compres-
test.
8-2. Crank engine with electric or recoil starter
and take highest pressure gauge reading.
8-3. Cylinder compression should not be
(55
380 KPa
8-4.
If
compression reading
for carbon built up in combustion chamber.
psi).
is
too high, check
less
than
Page 20
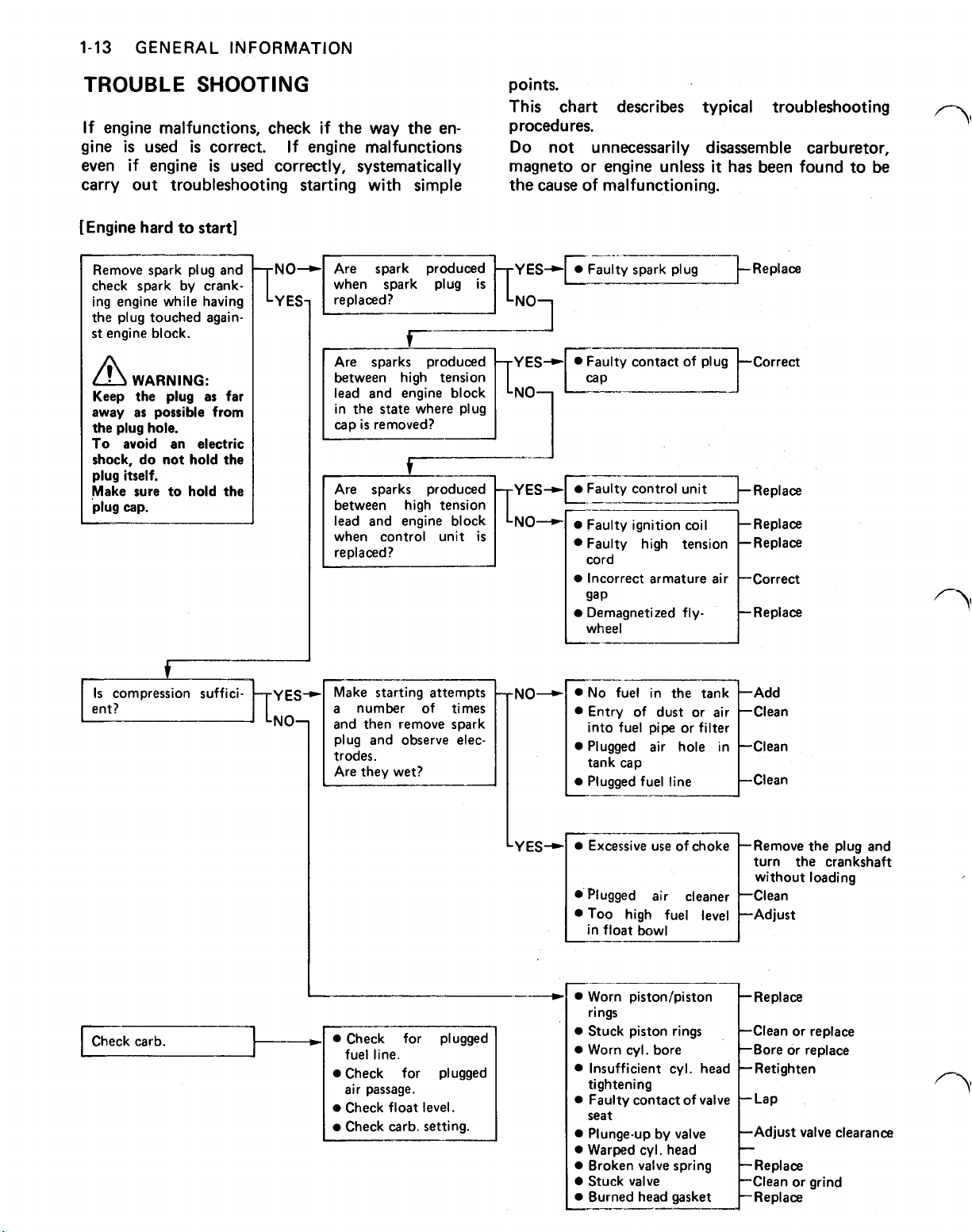
1-13
GENERAL INFORMATION
TROUBLE
SHOOTING
points.
This chart describes typical troubleshooting
If engine malfunctions, check if the way the en- procedures.
is
used
is
gine
even if engine
correct. If engine malfunctions
is
used correctly, systematically magneto or engine unless
Do
not unnecessarily disassemble carburetor,
carry out troubleshooting starting with simple the cause of malfunctioning.
[Engine hard to start]
Remove spark plug and
check spark by crank-
I
ing engine while having
the plug touched again-
st
engine block.
WARNING:
Keep the plug
as
away
the plug hole.
To
shock, do not hold the
plug
,Make sure to hold the
plug cap.
possible
avoid an electric
itself.
as
from
far
between high tension
lead and engine block
in the
state
where plug
Are sparks produced
between high tension
lead and engine block
when control unit
replaced?
is
it
has been found to be
Check carb.
Make starting attempts
number of times
and then remove spark
plug and observe
[odes.
Are they wet?
fuel line.
Check for plugged
air passage.
Check float
level.
elec-
NO-
Y
ES-,
gap
Demagnetized fly- Replace
wheel
into fuel pipe or filter
tank cap
Plugged fuel line Clean
turn the crankshaft
without loading
in float bowl
Worn piston/piston
t
rings
Stuck piston rings Clean or replace
Worn cyl. bore Bore or replace
tightening
seat
Plunge-up by
Warped cyl. head
Broken
Stuck
valve
valve
valve
spring Replace
Replace
Adjust
valve
Clean or grind
Replace
clearance
Page 21
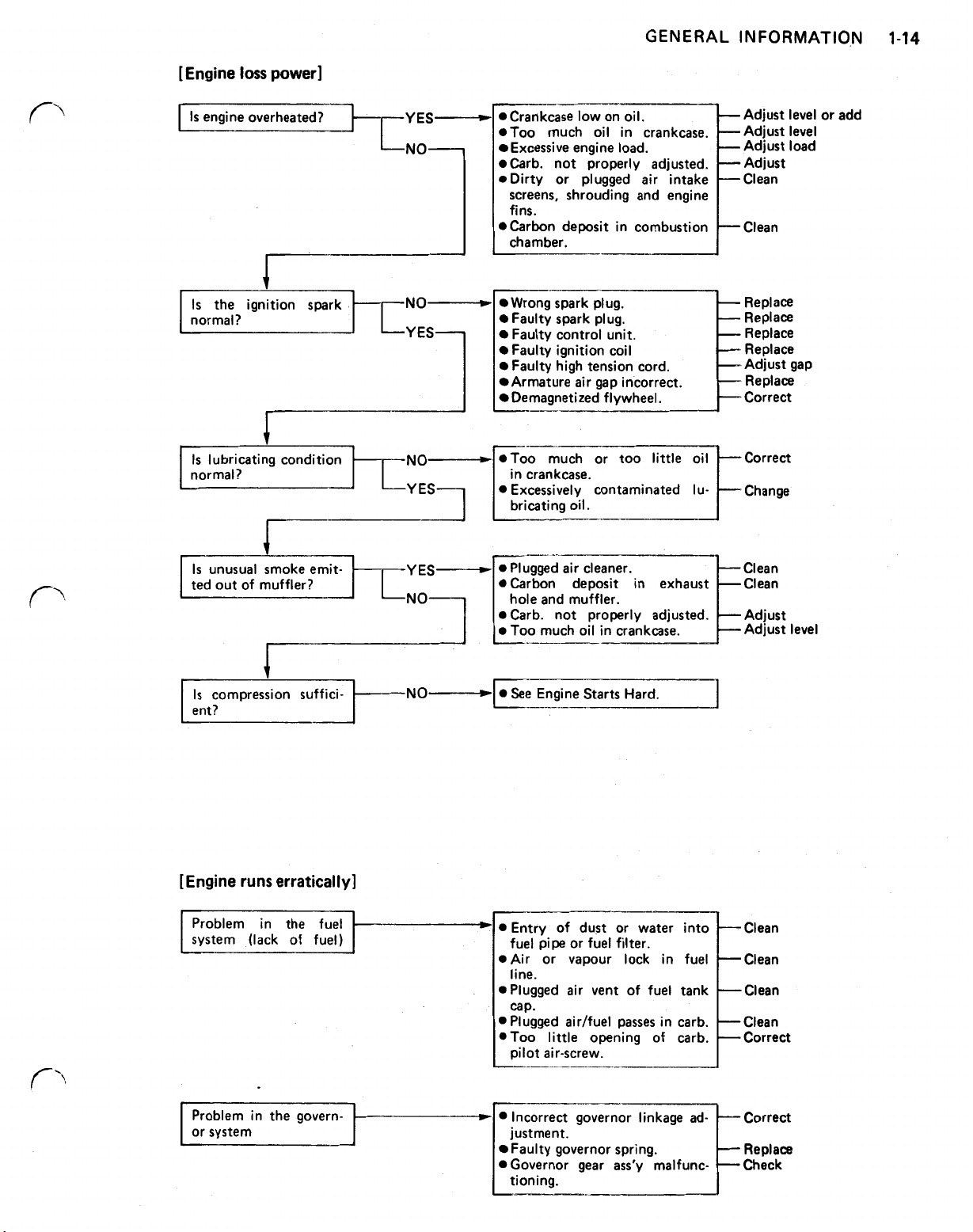
GENERAL
INFORMATION
1-14
[Engine
Is
normal?
Is
normal?
loss
power]
the ignition spark NO-
lubricating condition NO-
Adjust
level
Excessive engine load. Adjust load
screens, shrouding and engine
fins.
chamber.
Wrong spark plug. Replace
Faulty spark plug. Replace
Faulty control unit. Replace
Faulty ignition coil Replace
Faulty high tension cord. Adjust gap
Armature air gap incorrect. Replace
Demagnetized flywheel. Correct
in crankcase.
bricating oil.
or add
Is
unusual smoke emit- YES
ted out of muffler?
Is
compression suffici-
ent?
[Engine runs erratically]
Plugged air cleaner. Clean
@Carbon deposit in
hole and muffler.
not properly
Too
much oil in crankcase. Adjust
-I_--
Hard.
fuel pipe or fuel filter.
level
Problem in the governor system
I
justment.
Faulty governor spring. Replace
tioning.
Page 22
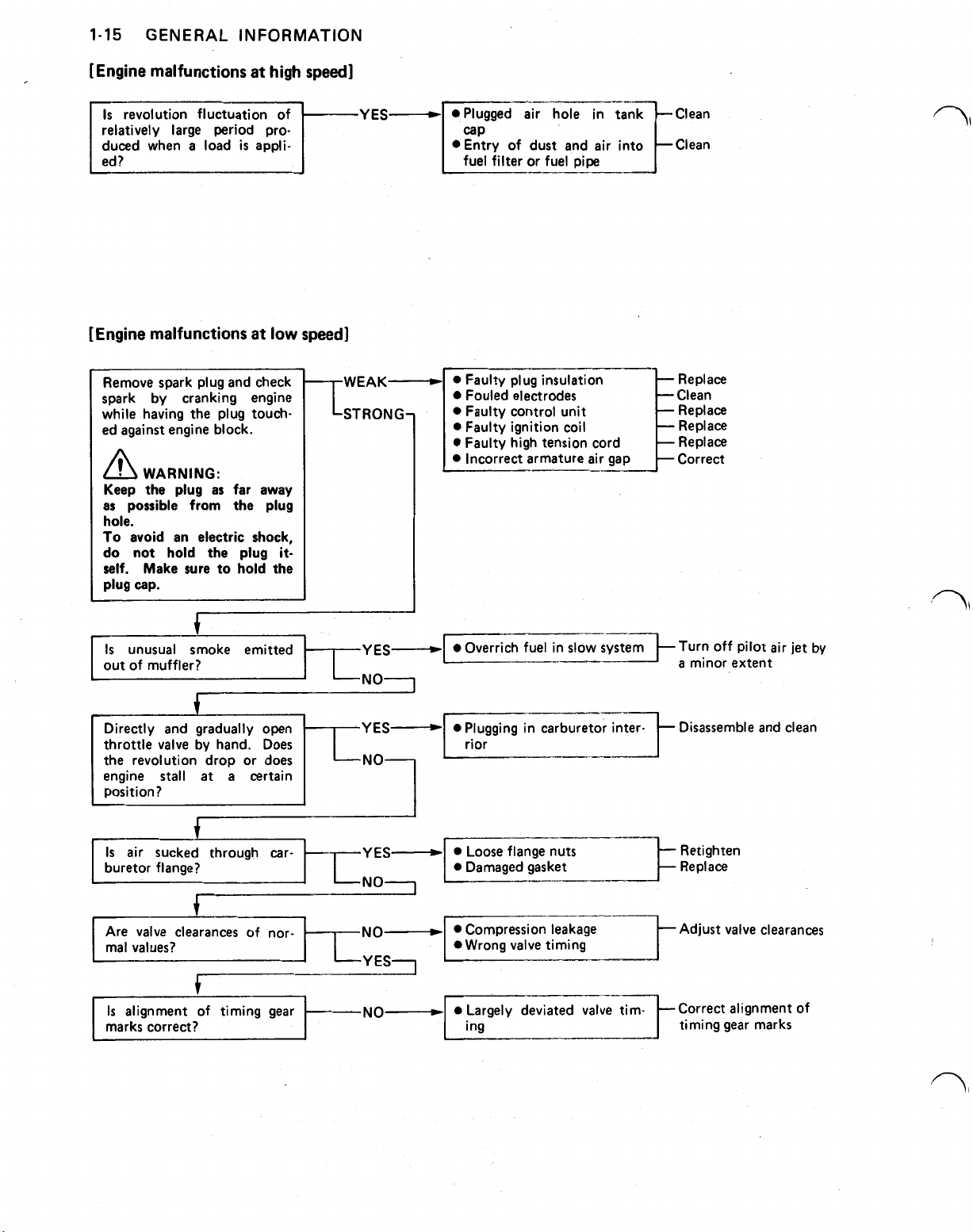
1-15
GENERAL INFORMATION
[Engine malfunctions
Is
revolution fluctuation of
relatively large period produced when
a
[Engine malfunctions
Remove spark plug and check
spark by cranking engine
while having the plug touched against engine block.
WARNING:
Keep the plug
as
possible from the plug
hole.
To
avoid an electric shock,
do not hold the plug
self.
Make sure
plug cap.
load
as
to
at
is
appli-
at
far away
hold the
high
low
it-
speed]
fuel filter or fuel pipe
speed]
Faulty plug insulation Replace
Fouled electrodes Clean
Faulty control unit Replace
Faulty ignition coil Replace
Faulty high tension cord Replace
Incorrect armature air gap Correct
J
t
Is
unusual smoke emitted
out
of
muffler?
Directly and gradually open Disassemble and clean
valve
stall
by hand. Does
at
a
certain
throttle
the revolution drop or does
engine
position?
Is
air sucked through car- Retighten
buretor flange? Damaged gasket Replace
t
Are
valve
mal values?
clearances of nor- Adjust
t
Is
alignment of timing gear
marks correct?
NO
YES
Overrich fuel in
Wrong
valve
timing
Largely deviated
i
ng
slow
system Turn off pilot air
a
minor extent
valve
tim-
timing gear marks
jet
valve
clearances
alignment of
by
Page 23

GENERAL INFORMATION
1-16
[Fuel consumption
compression sufficient?
Is
[Oil consumption
is
excessive]
is
excessive]
YES-
r
High fuel
float chamber (including
overflow)
Delay
High idling
Incomplete opening of
choke
Excessively backed off car-
burator pilot air screw
Stuck piston
Worn cylinder bore
insufficient cyl. head tighteness
Faulty
Plunge-up of
Wrong
Broken
Stuck
Plugged oil ring groove
High oil
Faulty
Worn
guides
Oil leakage along governor
shaft
Oil leakage from oil
Oil leakage from mounting
surface
Oil leakage from drain plug
Clogged breather
Drain-back hole in tappet -Clean
chamber plugged
Incorrect oil viscosity
Worn piston rings
Stuck piston rings
Worn cylinder bore
level
is
ignition timing
R.P.M.
valve
valve
seat
valve
valve
timing -Adjust
valve
spring
valve
level
valve
seat
valve
stems and
in carb.
contact
contact
valve
seal
valve
-Adjust
-Adjust
-Adjust
-Clean or replace
-Bore or replace
-Adjust
-Replace
-Clean
-Clean
-Adjust
-Replace
-Replace
-Replace gasket
-Retighten
-Clean
-Correct
choke
Replace
valve
or
grind
or
Replace
Clean or replace
Bore or replace
Replace
clearance
replace gasket
[Engine runs erratically]
Carb.
not properly adjust-
ed
Spark plug fould, pitted,
or
gapped incorrectly
Carb. flange leaking
ket
Carb. body and throttle
shaft warn
Restricted
Governor mulfunctioning
gas
[Engine backfires]
head gasket.
valve
[Engine knocks]
Stale
fuel
Excessive carbon deposit in Clean
Excessive engine load
Engine overheating
Faulty control unit
engine
at
tank vent
gas-
-Clean
-Adjust
Tighten
Change
Adjust
See low on power
Replace
or adjust
or replace
Page 24

1-17 GENERAL INFORMATION
TUNE-UP PROCEDURE
A "Tune-Up"
ly
be performed on relatively new engines brought
in for minor difficulties. By performing these
steps you will either be sure the engine
tion properly or will know if and what major
repairs should be performed.
The steps are
PROCEDURE and will normally be performed
as
a
part of the complete overhall.
Remove fuel tank, clean tank and
Check oil
Remove air cleaner, check for proper
servicing.
Remove recoil starter, flywheel housing,
and shrouds.
Inspect rope, recoil starter assembly or
pinion clutch (electric starter).
Clean cooling fins and entire engine.
Rock flywheel to check compression.
Remove carb., disassemble and inspect
for wear or damage. Wash in solvent,
replace parts
Set
Inspect inlet and exhaust flange for damaged gaskets.
Check governor linkage, spring, and speed
control lever for damage or wear, also
check adjustment.
Remove flywheel, check for
both flywheel and PTO shaft sides.
Check flywheel key for damage.
Check coil and control unit, inspect
wires for breaks damaged insulation.
Be
Check stop switch and lead.
Install flywheel.
spark.
Remove cyl. head, check gasket, remove
spark plug, and clean carbon, inspect
valves
Install cyl. head, torque to the specified
torque,
the plug if necessary.
Replace oil and fuel, check muffler for
restrictions or damage.
Adjust speed control linkage and cable
if used, for correct operation.
Run and adjust idle (mixture), and MAX
speed.
(see
the steps below) would normal-
is
func-
also
covered in the OVERHAUL
lines.
level
and drain.
as
necessary and assemble.
initial adjustment.
seal
leakage,
sure lead wires do not touch flywheel.
Set
air gap. Check for
for seating.
set
spark plug gap or replace
all
OVERHAUL PROCEDURE
The following overhaul procedure
help you in systematic and sequential method of
repairing
obtained when the repair operations are performed
in the same sequence every time. The exact
procedure will vary according to the engine model
being repaired.
This table can also be used
For detail information on how to perform each
operation refer to the section and page number
listed.
a
Kawasaki FB46OV engine. Efficiency
as
an index.
DISASSEMBLY
Drain engine oil
Air cleaner assy
Muffler ass'y
Carburetor, heat shield plate and
ket. Intake
Carburetor and linkage.
Disassemble carburetor.
Electric starter
Recoil starter
Dip stick and blower housing
Spin flywheel to check compression
Spark plug-adjust
inspect.
Rope starter pulley.
Adjust armature air gap.
Tappet chamber cover and
pipe
connector
Cylinder head and gasket
Check valve-to- tappet clearance
and spring.
Flywheel
_-
Breather
Ignition coil and control unit
Starter motor disassembly
Recoil starter disassembly
Governor control base plate and
governor arm
Crankcase cover
Damaged
Damaged governor gear ass'y
Oil
pump and relief
Camshaft and gear
Tappets
Con-rod and piston
Balance weight support shaft
Crankshaft and balance weight
ass'y
Disassemble crankshaft ass'y
oil
pipe.
I_______-
seal
valve
__
gap,
is
intended to
clean
valve
gas-
and
is
I
I
Page 25

GENERAL INFORMATION
1-18
Section
9
10
6
8
I
Section
2
9
DISASSEMBLY
Crankshaft inspect and check
Cylinder check bore, main bearings,
valve
guides and
Disassemble connecting rod and piston.
Check piston, rings, connecting rod,
piston pin.
Resize
Replace
Reface
Replace main bearings.
Replace oil
Replace governor gear ass'y.
Cylinder head repair
Replace flywheel ring gear.
Replace bushing link rod.
cylinder bore to next over
valve
valves
valve
seats.
R
EPAl
R
guide intake, exhaust.
and
seats
and
seals.
size.
lap.
I
Section
9
8
9
5
7
9
5
6
7
2
REASSEMBLY
Assemble crankshaft, link rod and
balance weight.
Crankshaft ass'y and balance
weight support shaft
Piston, piston pin, rings
Connecting rod sub ass'y
Tappets, camshaft
Governor gear
Crankcase cover
Valves,
Adjust
Tappet chamber cover, breather pipe
connector
Breather reed
lgnition coil
Control unit
Charging stator coil
Flywheel and pulley
Adjust air gap
Check spark.
Cylinder head and gasket
Cylinder head and cylinder cover
Blower housing.
Inlet pipe.
Governor control base
valve
valve
ass’y
springs, retainers
tappet clearance.
valve
and cover
:
armature to flywheel.
Oil
dip stick
plate.
~-
Page 26

2-1
IGNITION
Section
IGNITION
IGNITION
A transistor controlled ignition system
FB46OV.
components.
Ignition coil unit
Control unit (Igniter)
Permanent magnet flywheel
Spark plug
The ignition coil unit
wheel on the cylinder block.
Since the transistor ignition system contains no
mechanical parts, no wear occurs and no periodic
maintenance
Principle of Operation
SYSTEM
is
used for
This system consists of the following
is
mounted outside the
is
required except for the spark plug.
fly-
2
SPARK CHECK
Remove spark plug and check spark by cranking
engine while having the plug touched against
engine block.
the
plug
as
Keep
possible from the plug hole. To avoid an electric
shock do not hold the plug itself. Make sure to
hold the plug cap.
is
If there
ignition system
good spark between electrodes, the
is
in good condition.
far away
as
:
Primary coil
:
Secondary coil
:
Control Resister
CU
:
Control Unit (Igniter)
:
Control Resister
When voltage
)
flows into Transistor
Transistor
large amplified current to flow, during
which the Transistor does not operate
because Resister
As the flywheel continues to rotate, AC
power
(L,
"ON" by high voltage
As soon
the base current
Transistor
Transistor thus the Transistor
turned
is
).
"OFF"
at
point (A)
is
(
)
further generated in the primary coil
Then the Transistor
as
the Transistor
)
)
changes
because of voltage drop
is
turned "ON" and allows
lowers
at
through Resistor
point
its
flow
valtage
:
Transistor
:
Transistor
F
:
Flywheel
SP
:
Spark plug
SW
:
Stop switch
plus, base current
).
Then the
at
point
C.
)
is
turned
(C).
)
is turned "ON",
(R,
)
to
to )
and to
at
point
)
is
(B).
This sudden current change induces high
voltage within the secondary coil
fires the spark plug.
(L,),
which
is
If there
plug and regap to
in.). Replace spark plug if electrodes are worn.
See
"Spark Plug Check and Cleaning" section.
no or very weak spark, clean spark
0.6
to 0.7mm
(0.024
to
0.028
FLYWHEEL REMOVAL
1.
Remove spiral
2.
Disconnect spark plug cap from spark plug.
3.
'Carefully remove the wire out of spiral
CAUTION: Flywheel nut has a left-hand thread.
4.
Place a pry bar against the thick root of the
blades to prevent the blades from breaking off.
case.
(Flywheel housing)
case.
Page 27

6.
Remove flywheel with a flywheel puller
(A).
CAUTION:
deep or
(2)
too
By
using a hammer and bar, strike ring gear
evenly to remove
Do
close.
not cut
it.
flywheel
IGNITION
by
drilling
2-2
too
7.
Remove and inspect flywheel key. Replace the
key if
8.
it
is
bent or sheared.
Inspect crankshaft taper
for
nicks or burrs.
If necessary, finish taper using fine emery
paper.
FLYWHEEL CHECK
CAUTION:
impact weakens magnetic force of
1.
Put flywheel on a wooden surface.
2.
Hold
from flywheel magnet. The metal tool should
be attracted by magnet. If magnetic force
is
weak, replace flywheel.
Do
not
give
impact to magnet,
a
metal tool about 25mm
it.
(1
in.) away
as
drill 5/16 deep (4-6) drill
(3)
Heat a new ring gear
(C),
holes
evenly
to
an extent
that expansion by heating facilitates following
installation.
(4)
With the beveled edge of the gear faced up,
quickly install ring gear, quickly followed
tapping ring gear evenly to insure good seating.
gear
by
New
ring
gear
Page 28

2-3
IGNITION
IGNITION COIL CHECK
1.
Remove two mounting screws and remove
ignition coil.
2.
Remove the plug cap from high tension cord.
3.
Set KAWASAKI multimeter selector switch
a
specified range and connect leads
the chart below,. If meter reading falls within
the values shown in the chart, the coil
tioning properly.
Spark plug lead Primary terminal
Core
as
shown in
is
func-
at
FB460V-BS. Model
BM1129
Terminal Core
Control Unit Resistance
Terminal
Terminal
Case
Case
*Resistance value may vary with individual meters.
*Do
(A)
(A)
(B)
(B)
not use a megger.
ON to ON to
(AS.
Terminal
Terminal
(A)
(A)
BS,
Model)
I
I
Ignition Coil Resistance
Connection
I
coi
I
Secondary
*Resistance value may vary with individual meters.
CONTROL
Unfasten connectors.
1.
2.
Unscrew mounting screws and remove control
unit.
Set
3.
KAWASAKI multimeter selector switch
Rx1
the chart below. If meter reading falls within
the values shown in the chart, the unit
functioning properly.
FB460V-AS. Model
Primary terminal
UNIT
scale and connect leads
White lead
CHECK
I
I
Resistance
0.4
(R
x
10
(R
x
to 0.8
1 Range) core
to 18 Plug lead
1 Range) core coil
as
at
shown in
is
FLYWHEEL INSTALLATION
Be sure the key
To
tighten flywheel nut, reverse the removal steps.
Torque to spec. listed.
Flywheel Nut Tightening Torque
is
in place when installing flywheel.
83 to 88 N-m
(62
to
65
ft-lbs)
IGNITION COIL AlR-GAP
ADJUSTMENT
(1)
Leave ignition coil mounting screws loose
so
the coil can be moved for air gap adjust-
ment.
(2)
Inserting a 0.3mm
thickness gauge (A)
coil
legs
on flywheel rim, move the coil to
adjust AIR GAP.
(3) Tighten mounting screws firmly.
(0.012
in.)
at
each area in between
AIR
GAP-
(Ground lead) (Ground lead)
Page 29

IGNITION
2-4
FLYWHEEL HOUSING
INSTALLATION
1.
Install flywheel housing
protector
NOTE: The air gap
(D)
and tighten screws.
(C)
under screen and flywheel housing
not
less
than 1 mm
adjust the air gap
Adjust washer (A)
Bracket
2.
Install cylinder head cover and tighten screws.
NOTE:
Flywheel Flywheel housing
Push cylinder head cover firmly against
(0.04
(C).
Rotating screen
flywheel housing to eliminate cooling air leakage.
3.
Install dipstick and air cleaner assembly.
(E),
rotating screen
between contour blades
(E)
should
in.).
Use
(B)
Protector
washers
(D)
(A)
Air gap
(B),
(D)
be
to
Electrodes
Spark gap
Shell
Porcelain
Gasket
Terminal
Seating material
Reach
The plug can be cleaned using
a
solvent and
wire brush or other suitable tool.
a
high flash-point
If the spark plug electrodes are burn away or
is
damaged, or if the porcelain
cracked, replace
the plug. Use the following spark plug.
Specified Spark Plug
Spark
plug
NGK
BMR-4A
CHAMPION
RCJ-8
0.6
Gap
to
to
0.7
0.028
mm
in.)
SPARK PLUG CHECK
AND CLEANING
A
spark plug consists of two electrodes
ed from each other by spark gap
is
electrode
plug. The center electrode
connected to shell
is
completely insulated
from the shell.
The high voltage, produced in the secondary coil
is
winding,
causes
applied to the center electrode and
a
spark to jump the gap
electrode. This spark ignites the fuel-air-mixture
starts
and
the combustion process in the cylinder.
Gap between electrodes affects the entire
range of engine performance
accelerating, power and top speed.
Spark plugs must operate within
temperature range to give good performance.
(A)
separat-
(B).
The side
(C)
of the spark
(B)
to the side
-
starting, idling,
a
specific
Spark Plug Gap
(1)
Measure the gap with a wire type thickness
is
gauge. If the gap
the outer electrode with
incorrect, carefully bend
a
needle nose plier
to obtain the correct gap.
Spark Plug Tightening Torque
28
N-m
(20
ft-lbs)
Page 30

3-1
AIR CLEANER
Section
AIR
A properly serviced
parts of the engine from dust particles in the air.
If the air cleaner instructions are not carefully
followed, the dirt and dust which should be
collected in the cleaner, will be drawn into the engine and become
is
very detrimental to engine life; dirt in the oil
forms an abrasive mixture which wears the moving
parts.
The air cleaner on every engine brought in for
check up or repair should be examined and
ed.
An air cleaner element clogged with dirt chokes
the air supply to the engine, resulting in an overly
rich fuel/air mixture and inefficient combustion.
This in turn causes reduced engine power and
overheating due to carbon build-up in combustion chamber.
cleaner removed.
air
cleaner protects the internal
a
part of the oil film, which
Do
not run engine with air
CLEANER
servic-
a
3
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
INSPECTION
1.
Check air cleaner housing for deformation or
other damage. The housing must
and permit only filtered air to reach carburetor. Replace the housing if damaged.
2.
Check no foreign material
air passage.
AIR CLEANER INSTALLATION
1.
Clean elements, housing, cover and other parts.
2.
Elements and housing must be installed cor-
rectly.
3.
Install O-ring, housing, elements cover, washers
and tighten wing bolts.
is
obstructing the
seal
well
AIR CLEANER SERVICE
A FB460V engine
air
cleaner which has dual elements and an element
housing.
Remove two wing bolts and lift off air cleaner
completely.
CAUTION:
or compressed air.
Foam Element
1.
Visually examine element for turn, puncture
and otherwise damaged. Replace element if
necessary.
Wash element in detergent and water and dry
throughly.
Immerse in new engine oil and squeeze out
excess.
Paper Element
2.
Clean element by tapping gently to remove
dust. If very dirty, wash in detergent and
water, and dry throughly. Replace with a new
paper element every
Do
is
equipped with a heavy duty
not clean the element with solvent
300
hours.
1.
Wing bolt
2.
Washers
3.
Cover
4.
Element (Foam)
5.
Element (Paper)
6.
Housing
7.
0-Ring
8.
Element housing
Page 31

CARBURETOR
4-1
CARBURETOR
CARBURETOR OPERATION
1.
In the choke or start position, the choke
is
closed, and the only air entering the engine
enters through opening around the
is
the starting device
engine, the air pressure in the carburetor
reduced
the air passage
fuel
both idle fuel discharge ports and mixes with
the air that passes through the throttle
This makes a very rich fuel mixture required to
start
2.
At idle a relatively small amount of fuel
required to operate the engine. The throttle
almost closed, shutting off the fuel supply
from
orifice,
as
air drawn into the engine. Since
is
is
drawn from the main nozzle and from
a
Cold engine.
all
except the one idle-fuel discharge
so
that the suction created by the
operated to
blocked by the choke valve,
valve.
start
Section
valve
As
the
is
valve.
is
is
4
engine draws fuel only from that orifice.
3.
During intermediate operation, second and
third orifices are uncovered
valve opens, and more fuel
with the air flowing into the engine.
4.
During high speed operation, the throttle
is
fully opened. Air flows through the car-
at
buretor
The venturi, which decreases the air passage
through carburetor, further accelerates the air
flow. This high speed movement of the
decreases the air pressure, and fuel
into
that opens into venturi, mi ing with the air in
the air passage. As the en 'ne load increases,
is
air
through the air jet located in the air horn.
This allows fuel to be metered freely from the
main nozzle and to be facilitated atomization.
high speed.
the
air stream thro gh the main nozzle
automatically bled into
as
the throttle
is
allowed to mix
the
main nozzle
is
valve
air
drawn
Carburetor
Specifications
Main Jet
Pilot Jet
Pilot Screw (Turn out)
Float Valve
Low Idle Speed
Fast Idle Speed
CARBURETOR REMOVAL
AND DISASSEMBLY
WARNING: Gasoline
Avoid fires due to smoking or careless maintenance
practices.
1.
Before removing for repair, check for signs of link rod.
air leakage, or mounting gaskets that are loose,
deteriorated, or otherwise damaged.
is
dangerous. CAUTION:
2.
3.
4.
F
B460V-AS F B46OV-BS
#
47.5 #47.5
1-1/8
1.5 mm (0.059 in.)
3275 to 3425 rpm 3275
Float parallel to carburetor body-to-bowl mating surface.
Do
not bent
Pull carb. free, and gently twist carb. to free
Remove governor link rod and link spring.
Disassemble carb.
I
the
links or stretch.
(See
illust. below).
1
-1/8
1.5 mm (0.059
1350 to 1450 rpm 1350 to 1450 rpm
to
3425 rpm
in.)
Page 32

4-2
CARBURETOR
Disassembly Carburetor (See: Illustration)
Parts should remain in cleaner for 1 or
2.
hours. Remove and rinse with solvent.
NOTE: Rinse carb. body in hot water to
neutralize corrosive action of cleaner on
aluminum.
Dry parts with compressed air.
3.
Be
holes are open. Do not use rags or paper to
dry parts. Lint may plug hole or passages.
CARBURETOR INSPECTION
Inspect carb. body for damage. Flange sealing
1.
surfaces should be smooth and free of burrs
and nicks.
Replace gasket if necessary.
2.
Inspect pilot screw and drain screw for wear
3.
at
the seating surface. Inspect for weak springs.
Inspect main jet, bleed pipe, main nozzle and
4.
pilot screw for damage.
valve
Inspect inlet needle
5.
at
the seating surface.
Inspect clip for damage.
6.
for wear or damage
sure
2
all
Ref.
No.
1
2
5
6
7
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 Gasket
Parts Name
Screw
Throttle valve
Screw 3
Choke valve 4
Screw
Spring
Spring
Pilot screw 8
Pilot jet
Drain screw
Spring
Spring
Ring
Ring
Ref.
No.
16
Float pin
17
Clip
18
Float chamber
19
Choke shaft
20
Throttle shaft
21
Ring
22
Seal
23
Float
24
Main nozzle
25
Main jet
26
27
Washer
Bolt
28
Bleed pipe
29
Spring
30
Parts Name
Needle valve
CARBURETOR CLEANING
CAUTION: Never clean holes or passages with
small drill bits or wire.
1.
Place
cleaner or
and plastic parts in cleaner.
carb. body and carb. parts in PT503
its
equivalent. Do not put gaskets
NOTE: Inspect the other parts of carb. for
wear, damage.
CARBURETOR ASSEMBLY
Reassembly
following points:
1.
Install main nozzle, bleed pipe, and main jet by
turning clockwise into carb. body. Do not
over tighten screws.
2.
Install pilot screw (mixture screw) and spring
finger tight.
3.
Install pilot jet screw by turning
into carb. body. Do not over tighten.
4.
Install float and float pin.
CAUTION:
valve
when adjusting float
5. When carburetor
(A)
adjust float surface angle, bend tang
needle-nose pliers.
is
the reverse of removal. Note the
it
Do
not push on float or, inlet needle
level.
is
upside down, float surface
must be parallel to carb. body
clockwise
(B).
(C)
with
To
Page 33

CARBURETOR 4-3
CARBURETOR ADJUSTMENT
CARBURETOR INSTALLATION
1. Install throttle linkages (A) and choke linkage
(B)
on carburetor.
2.
Install breather connector
(D).
3. Assembly gaskets
carburetor
(D).
4. Install carb. ass'y on inlet pipe
(J).
bolts
(G),
(E),
gasket
(C)
on intake pipe
heat shield plate
(H)
and intake pipe
(I)
with through
(F),
WARNING: Gasoline
Avoid fires due to smoking or careless maintenance
practices.
Adjust Idle Mixture
Air cleaner must be assembled to engine.
1. Turn idle mixture screw
seats,
then back
CAUTION:
The pointed end of
damage.
2.
Start
lever on equipment to "IDLE POSITION".
3. Use
screw (A) to obtain 1,350 to 1,450 rpm by
turning
the screw against carb. body.
4. Adjust idle mixture screw
clockwise (lean) or counterclockwise (rich) to
obtain the peak of idling.
5. Turn idle mixture screw
turn more.
6.
Use a tachometer and readjust throttle stop
screw (A) to obtain and satisfy specified 1,350
to 1,450 rpm idling.
7.
Stop engine.
Do
and allow engine to warm. Move throttle
a
tachometer and adjust throttle stop
it
it
not turn
in or out while holding the end of
is
dangerous.
(B)
in until
out 1-1/8 turns.
the
screw in too far.
valve
seat
is
(B)
(B)
it
just
susceptible to
by turning
back out 1/4
Page 34

5-1
GOVERNOR
Section
5
GOVERNOR
The governor control regulates the engine speed by
changing the governor spring
allowing the governor to control the carb. throttle buretor
at
all
times and maintain any desired speed.
A
FB46OV
flyweight type governor. chamber cover.
If the engine
rated speed, the speed will drop if the load increases even slightly. In responce to the decrease,
governor weights
amount. Their movement
sleeve
the
(5).
direction of the arrow)
valve
in the opening direction.
As
speed increases,
(8),
and the rod turns the
direction. This action/reaction sequence soon
creates
engine to run
while carrying
Dumping the load suddenly will cause
increase in speed. But the interaction of the
engine-governor-carb. protects the engine from carburetor to free throttle linkage
over-revolution and speed soon
level.
engine
(3)
The arm then moves the link rod
is
equipped with a mechanical
is
carrying a load and running
(2)
contact by corresponding
and governor shaft
(7)
it
is
sensed by the governor
a
state
of equilibrium which allows the
at
nearly the same speed
a
slightly greater load.
(1)
tension, thus
at
is
transmitted through
(4)
to the arm
(6)
(in the
which turns the throttle
valve
in the opposite
as
before
a
rapid
settles
at a constant choke linkage
3.
Remove through-bolts
4.
Remove intake pipe
(GI,
heat shield plate
(J).
(D),
gasket
(F)
(E).
5.
Disconnect breather connector from tappet
6.
Remove link spring
(C).
(A)
and gently twist
Remove linkage.
(H),
and gaskets
(B)
car-
and
Low
speed position
High speed position
REMOVAL (GOVERNOR RELATED)
1.
Remove air cleaner assembly. and remove crankcase cover from crankcase.
2.
Loosen clamp and disconnect fuel line from
carburetor.
GOVERNOR GEAR DISASSEMBLY
1.
Unscrew mounting bolts in the order specified
2.
If necessary, remove governor ass’y
a
proper
size
screw driver.
(A)
with
Page 35

GOVERNOR GEAR INSPECTION
1.
Inspect governor gear for worn and damage.
as
Replace
ceed.
an unit, if wear and damage
ex-
GOVERNOR
is
Reassembly
following points:
1.
Install governor lever (A) on governor shaft
(B)
and tighten nut
the reverse of removal. Note the
(C)
finger tight.
5-2
GOVERNOR REASSEMBLY
1.
Install thrust washer
governor ass'y
(A) until inner flange
(B)
of the shaft
CAUTION: The
stuffed into the gear to the shaft.
governor
2.
ass'y
After installed, governor ass'y should rotate
freely on the shaft.
as
sleeve
once removed.
(C)
and stuff into new
(E)
to short stationary shaft
(D)
fitted into groove
shown.
can not
be
installed after
Do
not reuse
2.
The throttle and choke linkages can not
installed on the carburetor after the intake
pipe was installed.
LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
1.
Place throttle lever on dash in "FAST"
tion. (Equipment side)
2.
Loosen nut
governor shaft
3.
Turn governor shaft
travel by inserting needle
and tighten nut
(1),
that holds governor arm to
(2).
(2)
clockwise to the end of
(3)
to shaft end hole
(1).
be
posi-
3.
I
nstall governor gear cover.
4.
Place a new gasket on crankcase cover and put
small amount of grease around oil
5.
Lubricate crankshaft bearing in crankcase
cover with engine oil.
6.
Suitably
gear when installing crankcase cover.
set
the gear to be meshed with cam
seal
lips.
NOTE: The throttle lever on
"FAST" position when adjusting the governor.
4.
Lower and raise throttle lever after adjustment
to be sure linkage
5.
More throttle lever (on dash) up to "FAST"
position. Speed control lever
wide open throttle position [aligned hole
and
(D)],
but not enough to move choke link
(4).
If adjustment
clamp bolt (A) and adjust cable.
6.
Retighten clamp bolt (A).
is
not binding.
the
dash must
(C)
should be
is
necessary, loosen cable
be
in
in
(B)
Page 36

5-3
GOVERNOR
THROTTLE CABLE INSTALLATION
AND ADJUSTMENT
Make sure that the throttle lever and cable on
equipment have the speed control linkages with
engine.
1.
Leave
cable clamp bolt (A) loose.
(B)
Align hole
2.
hole (D) of control plate
a
insert
bolt) through the two holes.
Pull up outer housing
3.
until the inner cable
and tighten the cable clamp bolt.
Remove the
4.
Be
completely when throttle lever on equipment
is
form "CHOKE ADJUSTMENT,, described
below.
(6
sure that carb. choke
moved to "CHOKE" position. If not, per-
of speed control lever
(E)
mm)
0.24
in. dia. pin (or
(F)
(G)
has almost no slack,
6
mm dia. pin.
valve
moving the lever;
of throttle cable
(H)
(C)
a
is
with
6
mm
closed
CHOKE ADJUSTMENT
1.
Align hole (B) of speed control lever
hole (D) of control plate
a
6
mm
insert
dia. bolt) through the two holes.
2.
Turn in choke setting screw (K) until
just begins to touch the tongue of lever
3.
Remove the 6 mm dia. pin
(0.24
(E)
moving the lever;
in.) dia. pin (or
or
bolt.
(C)
a
its
with
6
mm
end
(L).
MAXIMUM SPEED ADJUSTMENT
Start
engine and allow
1.
Align hole
with hole (D) of control plate
the lever; insert
(or
a
6
mm bolt) through the two holes.
2.
Leave two control-plate-tightening-bolts
loose.
3.
Use a tachometer and slide control plate
left
or right to obtain specified
Be
sure that the carb. choke
opened during adjustment.
4.
Tighten two bolts
avoid changing the specified speed.
5.
Adjust choke per procedure previously mentioned.
6.
Remove the 6 mm dia. pin or bolt.
7.
Stop engine.
it
warm.
(B)
of speed control lever
a
(6
mm)
0.24
(I)
securely in a manner to
(E)
by moving
in. dia. pin
3,350
valve
is
IDLE SPEED ADJUSTMENT
Before the following procedure, carb. adjustment
must be performed.
(See
CARBURETOR ADJUSTMENT)
Start engine and allow
1.
Move throttle lever on equipment to farest
IDLE position and leave
2.
Turning throttle stop screw (J) in or out to
obtain specified idling
3.
Stop engine.
it
warm.
it
there.
1,350
to
1,450
(C)
(I)
(E)
rpm.
fully
rpm.
Page 37

COMPRESSION
6-1
Section
COMPRESSION
COMPRESSION CHECK
Before measuring compression pressure;
Be
Check cyl. head to torque.
charged on electric starter models. Start engine
it
and allow
for leaks around cyl. head gasket. Stop engine.
1.
Remove spark plug and screws compression
gauge into the plug hole securely.
2.
Crank engine with recoil or electric starting for
several seconds and take highest pressure gauge
reading. Cylinder compression should not
be
3.
If compression reading
carbon built up in combustion chamber.
Carbon deposits in combustion chamber
should be removed every
of.
4.
If the compression pressure
cified,
Leaking cyl. head gasket.
Warped cyl. head.
Worn piston rings.
Damaged piston.
Worn cyl. bore.
Burned or warped
Improper
Broken
To
practically measured by:
to warm up. During warm up, check
less
than 3 kg/cm²
use, or whenever cyl. head
it
is
usually the result of one or more of:
valves.
valve
clearance.
valve
springs.
a
great extent, compression can also be
sure battery
(43
psi).
is
too high, check for
100
to
is
removed.
is
less
is
fully
200
hours
than spe-
6
torque and maintain positive sealing of the combustion chamber.
1.
Remove cyl. head and
CYLINDER HEAD TIGHTENING
PROCEDURE
CAUTION: Do not use a sealer of any kind on
ket.
1.
Coat head bolts threads with a light film of
oil and install the bolts.
2.
Tighten screws down evenly by hand.
3.
Use a torque wrench and tighten head bolts
in the sequence
torque.
gasket.
as
shown, and to the specified
gas-
*-
Disconnect spark plug cap to
prevent engine starting during compression
Be careful not to get your fingers caught in flywheel fins during
Spin flywheel counter clockwise (flywheel side)
against the compression stroke;
indicates satisfactory compression. Slight or
no rebound indicates poor compression.
test.
a
sharp rebound
test.
CYLINDER HEAD AND
HEAD GASKET REMOVAL
CAUTION: Always note the position of each
cyl. head screw
bled.
A
FB46OV
in the exhaust
so
they may
has 3-heat-resistant high-tension studs
valve
side area to prevent
be
properly reassem-
loss
of
Cylinder Head Tightening Torque
34
to
39
N-m
(25
to
29
L
CAUTION: Do not turn one screw down completely before the others,
cyl. head.
as
ft-lbs)
it
may cause a warped
Page 38

6-2
COMPRESSION
CYLINDER HEAD CHECK
AND REPAl
1.
Clean cyl. head.
WARNING: Be
cleaner
2.
3.
Cyl.
I
4.
is
used.
Check cyl. head flatness by placing cyl. head
on
a
surface plate more than
Use
a
space between surface plate and cyl. head.
Head Warp (MAX)
If cyl. head
replace
R
alert
thickness gauge
0.4
mm
(0.01
is
warped more than specified,
it.
to fire if combustible
at
six points.
(A)
to measure the
5 in.)
I
J
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION
1.
Inspect
springs if necessary.
2.
Measure the free length of springs. If shorter
than specified, replace spring.
Intake
Exhaust 39.0
TO
ANALYZE VALVE
When leaded gasoline
deposits on the exhaust
exhaust
dicates the
Clean the seating face and lap the valve into
the
reface the
CAUTION: Be sure to reset valve-to-tappet
ance after grinding
valve
Valve Spring Free Length
I
gas
seat.
springs for damage. Replace
43.3
leakage past the
valve
is
not seating properly.
If worn severly, grind the
seat
to correct condition.
valve.
mm
mm
is
(MIN)
(1.705 in.)
(1.535 in.)
used,
valve
excessive
are caused by
valve.
valve
lead
This in-
and
clear-
5.
If cyl. head
limit, reface the head surface by rubbing on
emery paper (first:
placed on
6.
Check cyl. head gasket for burn and trace of
gas
leakage. Replace gasket if necessary.
is
warped
a
surface plate.
less
than the specified
No. 200,
then: No. 400)
VALVE AND SPRING REMOVAL
1.
To remove
pressor
over the
spring
2.
Compress spring. Remove retainer by a needle
nose plier. Pull out
sor and
(A),
valve
(B)
and retainer
valve
valves
using a valve spring com-
put screw head of compressor
head and slip lower jaw between
(C).
valve.
spring.
Remove compres-
Valve stem corrosion
in the engine. Moisture in the fuel-air mixture
or combustion
engine when the engine
down.
Valve corrosion can also occur during storage.
Fogging or pouring oil in combustion chamber
before storing helps prevent
Corroded or pitted
and may cause sticking
Replace badly corroded or pitted
Poor engine cooling due to dirt or obstructions
is
a
common cause for overheating an engine
and the
clean cooling fins.
Other causes for
valve guides or
clearance, lean fuel-air mixture and incorrect
or overheated plug.
Use of old or stale gasoline
for sticky
be seen on the
exists, the carburetor may also contain gum
deposits and will require
CAUTION: Always use fresh gasoline and drain
fuel tank, lines and carburetor before storing
equipment.
valves.
gases
Remove flywheel housing and
valve
valves.
is
caused by moisture
can condense inside the
is
stopped and cools
valve
valves
valves.
valves
springs, incorrect
This gummy deposit can
valve.
collect deposits
running hot are worn
is
a
When this condition
a
complete cleaning.
corrosion.
valves.
valve
common cause
VALVE INSPECTION
1.
Remove carbon from
a
stem with
sure carbon
ed.
power-operated wire brush.
is
removed and not merely burnish-
valve
head, face and
Be
Page 39

2.
Check
fects.
sive
valve
Look
faces, heads and stem for defor bent
valve
corrosion causing pits on
stem.
3.
Replace
less than (0.6mm)
valves
with a warped head or with
0.02
stem ends should be ground square before
checking valve-to-tappet clearance.
stems and exces-
valve
in. margin. Valve
face or
COMPRESSION
6-3
Warped Head
Worn
or
Improperly Ground Valve Stems
No
Margin
Valve Stem Bend Check
(1)
Support
valve
in V blocks
stem.
at
each end
of
the
Valve Stem Diameter
If any single measurement
replace the
valve.
VALVE GUIDE
(MIN)
Valve Stem Diameter
7.91
2
mm
(0.31
CHECK
is
15
less
in.)
than MIN,
AND REPLACEMENT
1.
Use valve guide cleaner to clean the inside of
valve guides.
2.
Measure inside diameter of
inside micrometer
at
several points.
valve
guide with
(2)
Position
a
dial gauge perpendicular to the
stem.
(3)
Turn
valve
and read the variation on dial
gauge.
Valve Stem Bend
If
the stem bend
valve.
(MAX)
0.03 mm (0.001 2 in.)
is
greater than MAX, replace
Valve Stem Diameter Check
(1)
Measure the diameter of
at
directions
right angles,
positions on the stem.
valve
at
stem
(A)
four different
in two
Valve Guide
Intake
Replace
MAX.
Reject
Valve Guide Inside Diameter
valve
Size
(MAX)
8.062
mm (0.3174 in.)
8.062
mm (0.3174 in.)
guide if inside diameter exceeds
Page 40

6-4
COMPRESSION
To
Replace Valve Guide
To
Remove Valve Guide:
(1
)
Use
a
valve
guide remover
(A) to replace
guide.
(2)
Fix
valve
guide remover on cylinder with bolts
and nuts.
(3)
Put a coat of engine oil to the remover bolt
threads and screw
at
be seen
(4)
Install thrust washer
valve
it
in until the threads can
guide lower end.
(B)
and nut
hand thread) to the remover bolt.
Draw out
valve
(C)
(left
(4)
Turning the remover bolt, drive new
guide into the hole to proper depth.
Valve Guide Depth h
30
mm
(1.18
in.)
Exhaust
30
mm
(1.18 in.)
valve
(5)
Turn out the bolt to remove
it
is
bushing until
completely removed from
valve
the guide.
To
Install Valve Guide:
(1)
Use
a
valve
guide remover to install
(2)
Apply a coat of engine oil to the outer surface
of
valve
guide (A).
(3)
Install thrust washer
(B)
and new
valve
valve
(A) to the remover bolt and retain them with
(C)
as
nut
shown.
Draw
in
guide
guide.
guide
(5)
Use stanisol or kelosen lubricant to finish
reaming by
(6)
Turn to finish specified reamer (A) clockwise.
(7)
Throughly clean
a
valve
guide reamer.
valve
area before reassembling
engine.
VALVE SEAT RECONDITIONING
1.
Inspect
warped or distorted by beyond recondition-
ing, replace cyl. block.
Pitted or worn
valves
2.
To repair the
then
and
Check the
around with machinist's dye.
valve
seats
to
seats
after refacing.
seats;
30"
to obtain standard
45"
again to finish.
seat
for damage. If
valve
seats
can be refaced. Lap
first use
for good contact
45"
valve
seats
cutter (A)
seat
all
the way
are
width
Page 41

D
COMPRESSION
6-5
Right
CAUTION: Loosen
moved up or down.
Use a center punch to tighten insert
:
Wrong
valve
If
this appears;
seat
can
be
turned
at
three
or
points equally spaced.
Otherwise peen over edge around entire insert.
Valve Lapping
(1)
\
lap
If the
seat
valve
does not make proper contact,
into the
seat
with a vacuum cup
tool.
(2)
STD
Valve Seat Width
I
I
Intake
Exhaust
I
Valve
1
.0
to 1.6 mm
1
.0
to 1.6 mm
Seat
Width
(0.039
(0.039
to 0.063
to 0.063 in.)
in.)
Coat face of
compound.
(3)
Use vacuum cup tool
Rotate
seat.
(4)
Lift
valve
continue lapping operation until an uniform
ring appears around the entire surface of
valve
face.
valve
from
valve
sparingly with a fine lapping
(A),
to grip top of
valve.
in a circular motion to lap to
seat
every 8 to 10s strokes,
:
Valve Sealing Width.
:
Valve
Seat
Angle.
:
Valve Face Angle. In.:
:
Valve Margin. 0.6mm
:
Valve Narrowing Angle. In.: 30°/ Ex.: 30°
3.
Follow
the
valve face
"Valve
seat
contact with the middle point of the center of the
(as
shown).
See
Table.
In.:
45°/
45°/
Lapping" procedure to keep The lapping mark should appear on or near
Ex.:
Ex.:
(0.02
45"
45°
in.) MIN.
(5)
When lapping
is
completed, wash
in solvent to remove lapping compound.
Dry parts thoroughly.
(6)
Note position of lapping mark on
valve
face.
(7)
Check
valve
clearance after lapping.
all
valve
the parts
face.
Page 42

6-6
COMPRESSION
TAPPET CLEARANCE CHECK
AND REPAIR
4.
Install
Reassembly
all
parts related to
is
the reverse
valve
of
removal.
repair.
valve
Since
to-tappet), check the clearances (intake and ex-
haust sides). Make Sure to do this when engine
is
cold.
1.
Insert
cyl. block.
2.
Turn crankshaft until piston
position in compression stroke. Then insert
a
thickness gauge
and tappet to check tappet clearance.
repairs change tappet clearance
valves
in their respective positions in
(A)
between
valve
is
(valve-
at
highest
stemsend
CAUTION: After installing
check retainers are positioned Correctly.
Use
not
valve
molybdenum dissulfied when installing
in cyl. block.
valves
and springs,
DO
Specified Tappet Clearance (Cold)
Tappet Clearance
3.
If the clearance
the end of
tappet clearance.
To
Grind Valve Stem End:
Place
valve
in
valve
the stem end over oil stone back and forth.
is
less
than specified, grind
valve
stem to obtain the specified
lapping guide
(A)
and slide
Page 43

LUBRICATION
7-1
Section
LUBRICATION
LUBRICATION
Oil
has four purposes.
lubricates.
A pressurized lubrication system used on the
FB460V engine pressure-lubricates the crank pin,
PTO main journal and balancer link.
The FB46OV utilizes
pump to pressurize the lubrication system.
is
first drawn through
the inlet (2) and into the pump chamber
pressure
of above
speed). The oil
journal (4) into crankshaft and lubricates the
lower link rod
rod journal
is
passed through a metered orifice in the connect-
ing rod and
piston and prevent ring sticking. The return oil
mists then lubricates the magneto side ball bearing
and others.
is
adjusted by a relief
(3
kg/cm² ) 42.6 psi
is
(5),
(7).
A portion
is
sprayed on the piston to cool the
It
cools, cleans,
a
camshaft driven trochoid
a
filtering screen
valve
at
3,000
then pumped to the PTO main
crank pin
of
(6)
and upper link
oil
at
seals
and
Oil
(1)
then
(3).
Oil
(8)
to a value
rpm (Rated
the crank pin
7
I I
Oil
pressure sensor
FULL FLOW OIL FILTER
The FB46OV can accept an optional car-
oil
tridge type full flow
extend oil change intervals to
hours. (STD intervals:
filter (A) which can
25
hours)
(Optional)
as
mush
as
50
OIL WARNING SYSTEM
(Electric
Starter Model
Triggered by the sensor (A), a warning light
comes on when pressure falls below
kg/cm² ) 4.26 psi lubrication problem.
(See
ELECTRICAL
only)
SYSTEM)
(0.3
CAPACIT
Crankcase
IE
S
1.4
(2.96
Pt
US)
Page 44

7-2
LUBRICATION
OIL RECOMMENDATION
Use
a
high quality detergent engine oil classified
"API
Service
engine oils keep the engine cleaner and delay the
formation of gum and vernish deposits. Nothing
should be added to the recommended oil.
Recommended
Temperature
I
Viscosity SAE 5W-20 SAE 30
OIL
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6. Check oil
LEVEL CHECK
Put engine on a level
Remove dipstick; wipe dipstick with a clean
rag; insert dipstick into filler tube.
Let dipstick cap (A) threads rest on top of
the tube. Do not screw dipstick in.
Remove dipstick to check oil
necessary.
Install and tighten dipstick.
ing equipment.
SF,
SE/CC,
SAE
I
I
SE,
or
SD".
Viscosity Grades
Below Above
0°C
(32°F)
surface.
0°C
I
level.
DO
NOT overfill.
level
and add regularly before operat-
Detergent
(32°F)
Add if
I
BREATHER CHECK
It
is
the breather's function to maintain a vacuum
a
reed
valve"
a
reed
crankcase
valve,
valve
in the crankcase. The breather has
which limits the direction of air flow caused by
the piston movement of up and down. Air can
flow out of the crankcase, but the "one way
blocks the return flow, thus maintaining a vacuum
in the crankcase.
A partial vacuum must be maintained in the crankcase
to prevent oil from being forced out of
at
engine,
The FB460V uses the combination of
and four expansion chambers
breather.
through
chambers where the oil
and drained back to the crankcase. The breather
is
vented through the air cleaner, to prevent dirt
from entering the crankcase.
the piston rings, oil
Oil
laden air in the crankcase passes
a
maze by the reed
seals
and gaskets.
(1
4)
valve
and expansion
is
separated from the air
Full
level
OIL CHANGE
Change oil after first 5 hours of operation. There-
25
after
dirty operating conditions.
1.
2.
3.
4.
.Remove dipstick and refill with new oil up to
5.
hours of operation; more often under
Put engine on a level
Remove oil drain plug, and drain oil while
is
engine
Install drain plug.
no higher than "Full" mark on dipstick.
(See
Install dipstick.
warm.
OI
L LEVEL CHECK)
surface.
1.
Inspect reed
2.
Inspect reed valve seating surface. They must
not have any nicks or burrs.
3.
Inspect reed
and broken.
4.
Check to be sure vent tube
and sealed properly.
valve
for stuck and binding.
valve
for hair crack, distortion
is
not damaged
Page 45

LUBRICATION
7-3
OIL
1.
2.
I
PUMP INSPECTION
Remove crankcase cover from crankcase.
(See
Section
Measure camshaft bearing on oil pump cover
(A) with an inside micrometer
bearing
replaceable.
Bearing Inside Diameter
is
9
:
Crankshaft Removal)
cast
with oil pump cover and
t
(MAX)
20.071
mm
(0.7902
(B).
in.)
is
The
not
OIL
1.
2.
3.
4.
Pump Cover Tightening Torque
PUMP INSTALLATION
Install inner and outer rotors together.
Install oil screen.
Put relief-valve ball on
Install oil pump cover with relief
and tighten cap screws to specified torque.
valve
seat.
valve
spring
Replace pump cover, if inside diameter ex-
MAX.
ceeds
3.
Remove oil pump cover and inspect oil screen
for broken mesh. Replace
4.
Inspect relief ball
have any nicks or burrs.
5.
Measure free length of ball
Free Length of Spring (MIN)
Replace spring if free length
6.
Inspect inner and outer
place rotors if wear or damage
NOTE:
relief
(3).
Do
not unscrew bolts
valve
cover
These bolts are applied locking bond.
valve
19.5
mm
._______-
(2)
and oil induction guide plate
it,
if necessary.
seating, they must not
valve
spring.
(0.768
in.)
is less
than
oil
pump rotors.
is
excessive.
(1)
which tighten
MIN.
I
Re-
17
to
23
N-m
(12
to
17
___--
After installation, the oil pump should rotate
freely in the housing.
5.
Install crankcase cover on block.
(See
Section
9
:
Crankcase Cover Installation)
ft-lbs)
Page 46

8-1
PISTON, PISTON RING, AND CON-ROD
Section
PISTON, PISTON RING, AND
PISTON AND CON-ROD REMOVAL
1.
Remove any carbon
cyl. bore; this will help prevent piston rings
from breaking.
2.
To
remove piston and con-rod from engine,
rotate crankshaft (A) to expose con-rod bolts
(B)
as
shown.
3.
Remove rod bolts and con-rod cap.
Push piston and con-rod out through the top
4.
of cylinder.
or
ridge
at
the top of
To Analyze Piston Ring Wear:
(1)
8
CON-ROD
Rings of the wrong
proper end gap will not conform to the shape
of cylinder. This results in high oil consumption and excessive blow-by.
Ring end gaps should be staggered on piston
during installation. End gaps in alignment can
cause oil consumption and blow-by.
Light scuffing
piston occurs when unusually high friction
and combustion temperatures approach the
melting point of piston material. Probable
causes of this condition one:
Dirty cooling shroud and cyl. head.
Lack of cylinder lubrication.
Improper combustion.
Wrong bearing
Too much oil in crankcase causing fluid
friction.
size
or
rings having im-
or
scoring of both rings and
or
piston clearance.
To
Remove Piston From Con-Rod:
(1)
Remove piston pin snap rings with thin nose
pliers and slide out piston pin.
CAUTION:
Removal weakens and deforms the rings.
(2)
Remove piston rings one
them over (A) ring lands. Use
(A) to prevent damage to rings and piston.
Do
not reuse snap rings once removed.
at a time, by slipping
a
ring expander
(2)
An engine operating
peratures may cause varnish, lacquer
deposits to form in the piston grooves making
the rings stick.
When this happens, excessive oil consumption
and blow-by will occur.
Engine overheating and ring sticking
ly
caused by one
Overloading.
Incorrect ignition timing.
Lean fuel mixture.
Dirty cooling fins.
Incorrect oil.
Low oil supply.
Stale
fuel.
(3)
Vertical scratches across piston rings are due
to an abrasive in engine. Abrasives may be
airborne, may have been left in engine during
or
overhaul
deposits.
When this exists, check for one
Damaged, collapsed
air cleaner.
Loose connection
air cleaner and carb.
Air leak around carburetor-to-cyl. block
ket.
Air leakage around throttle shaft.
Failure to properly clean cyl. bore after
reconditioning engine.
Scratches across oil side rails (A) are due to
abrasive in engine oil.
may be loose lead and carbon
at
abnormally high tem-
or
more of:
or
or
improperly installed
or
damaged gasket between
or
more of:
carbon
is
usual-
/-
gas-
Page 47

In this condition and much use, compression
(B)
rings
Oil
cause increase oil up by pumping action of oil
ring. This results in high oil consumption, increased deposit in combustion chamber and
stick of rings.
will also be worn.
inner spacer wear
(C)
and distorsion may
ring
PISTON, PISTON RING, AND CON-ROD
4.
Visually inspect rings and grooves for uneven
wear or damage. Replace them if uneven wear
or damage are excessive.
5.
Measure piston ring groove width. Use
vernier caliper
piston.
Piston Ring Groove Width (MAX)
at
several points around the
8-2
a
PISTON INSPECTION
No need to proceed with the steps shown if cyl-
is
inder
shows wear or scoring
piston.
1.
2.
CAUTION:
or
3.
CAUTION: Never clean piston head with engine
assembled. Carbon particles will fall between
piston and cylinder, and may cause severe seizure.
to be resigned or visual inspection of piston
-
which require replacing
Remove all deposits from piston.
Clean carbon from piston ring grooves with
ring groove cleaner.
Do
not use a caustic cleaning solution
a
wire brush to clean piston.
Be
sure oil return passages in ring grooves are
open.
a
Ring
Top
If the width of any of the grooves
than MAX
6.
Inspect piston for scoring or fractures
ring lands.
PISTON
I
at
any point, replace piston.
RING
Groove
2.120
rnm
(0.0835
2.095
mm
(0.0825
4.055
rnm
--_-
(0.1596
THICKNESS
INSPECTION
Use
a
micrometer to measure piston ring
at
thickness
several points around rings.
Width
in.)
in.)
in.)
is
I
I
wider
at
Piston Ring Thickness
(MIN)
1.945
1.941
mm
mm
(0.0766
(0.0764
in.)
in.)
Page 48

8-3
PISTON, PISTON RING, AND CON-ROD
NOTE:
ness. Replace oil ring together with compression
rings.
PISTON RING END
1.
2.
NOTE:
square.
3.
Difficult to exactly measure oil ring thick-
GAP
Insert each ring in cyl. bore and check end
gap.
Install ring squarely in the bore to a point
1
approx. (25mm)
cylinder.
Use piston to push
Check ring end gap with feeler gauge (A).
in. down from the top of
INSPECTION
it
in to
be
sure
it
is
Piston Pin Dia.
1.
Measure inside diameter
in piston with an inside micrometer
points.
2.
If inside diameter exceeds MAX, replace pis-
ton.
Piston Pin Hole Dia. (MAX)
(MIN)
20.978
mm
(0.8259 in.)
of
piston pin hole
at
I
several
End
Gap
(MAX)
0.7
mm
(0.028 in.)
mm
(0.028 in.)
is
of rings.
greater than MAX,
4.
If the end gap
replace the entire
of
any ring
set
0.7
PISTON PIN AND PIN HOLE DIA.
INSPECTION
Measure outside diameter
a
with
If piston pin diameter
replace piston pin.
micrometer
at
several points.
of
piston pin (A)
is
msaller than MIN,
21.028
To
Analyze Piston Wear:
Detonation can cause an extensive damage
to piston, cyl. head, gasket or others. Detonation
cessive
bustion chamber. Commonly called carbon
knock, spark knock or timing knock, detonation occurs
mixture ignites spontaneously to interrupt
the normal ignition.
Following
nation:
Lean fuel mixture.
Low octane fuel.
Advanced ignition timing.
Engine lugging.
Build-up of carbon deposits on piston or cyl.
head.
Wrong cyl. head or milling of head increasing
compression ratio.
Poor cooling.
Pre-ignition
mixture prior to regular ignition spark. Preignition causes internal shock, resulting in
pings, vibration, detonation and power
.Severe damage to piston, rings and
results from pre-ignition.
Check following for causes
Internal carbon deposits.
Incorrect spark plug.
Broken ceramic in spark plug.
Sharp edges on combustion chamber.
Poor cooling.
is
temperature and pressure in the com-
is
mm
(0.8279 in.)
abnormal combustion causing ex-
as
the compressed fuel-air
a
list
of possible cause for deto-
is
the ignition of the fuel-air
of
pre-ignition:
I
loss.
valves
Page 49

Check con-rod and piston alignment when
a
piston shows
diagonal wear pattern extend-
ing across the skirt of piston. Contact with
the cyl.
on bottom of skirt
at
left (or
wall
right) and ring lands on right (or left).
at
A cylinder bored
an angle to crankshaft
can also cause improper ring contact with
cylinder.
This condition causes:
Rapid piston wear.
Uneven piston wear.
Excessive oil consumption.
PISTON, PISTON RING, AND CON-ROD
8-4
CON-ROD
1.
Clean and inspect bearing surface on con-rod
INSPECTION
and cap. Replace parts if scored.
2.
Measure inside diameter of the small end of
con-rod
at
several points by a telescoping
gauge.
Small End Inside Dia. (MAX)
Big End Inside Dia. (MAX)
37.066
6.
If inside diameter exceeds MAX, replace con-
mm
(1.4593
in.)
rod.
NOTE: A bent or twisted con-rod must
placed.
be
re-
I
3.
If inside diameter
21.039
mm
(0.8283
is
in.)
greater than specified,
replace con-rod.
4.
Place
con-rod cap over con-rod big end to
align pilot grooves (A) on the cap and rod.
Screw cap bolts and tighten bolts to the
specified torque shown.
Rod Cap Tightening Torque
19
to
20
N-m
----_____
5.
Measure the inside diameter of big end
(14
to
--I--
15
ft-lbs)
several points by a telescoping gauge or inside
micrometer.
at
To Analyze Con-Rod Wear:
Check con-rod and cap for damage or unusual
wear patterns.
Lack of lubrication or improper lubrication
seize
can cause con-rod and cap to
to
shaft.
seize
When rod and cap
to crankshaft, the conrod and piston may both break causing other
internal damage. Inspect the block carefully
before rebuilding engine.
Con-rod and crankshaft damage can result
from:
Engine run low on oil or without oil.
Oil
pump broken or damage.
Oil
hole in con-rod plugged.
Oil
not changed regularly.
Bearing cap installed incorrectly.
crank-
Page 50

8-5
PISTON, PISTON RING, AND CON-ROD
PISTON AND CON-ROD ASSEMBLY
1.
Aligning match mark
with "MADE
install piston over con-rod.
2.
Coat piston pin with a light film of oil. Insert
pin through piston and con-rod.
3.
Install retaining rings in each end of piston
pin bore. Rings should be seated firmly in
retainer grooves in piston.
CAUTION:
Do
not reuse the rings which was
removed. Removal weakens, deforms the rings
and could fall out
and
"
"
on the piston head
IN
JAPAN" on the con-rod,
score
the
cyl. wall.
Marking
(R)
facing
UP
30'
to
45'
Top and upper side rail and gap
Position Ring End Gaps
2nd and lower
TOP
(chrom plated)
Second
Oil
(three piece)
side
PISTON RING INSTALLATION
1.
Be
sure oil return holes are clean and carbon
is
removed from
2.
Use
a
ring expander to install rings
rated.
3.
Make sure rings are installed
Install top and second rings with the mark-
4.
ings facing up.
"TOP" or "Bottom".) After installation,
rings should rotate freely in the grooves.
Space top and second ring end gaps
5.
grees apart.
6.
Space side rail and gaps
respectively.
See
all
grooves.
(Oil
I
Ilust.
ring
as
shown.
steel
rails have no
180°
degrees a part
as
180
illust-
de-
PISTON AND CON-ROD ASSY
INSTALLATION
TO INSTALL RINGS TO PISTON:
1.
Place
the projections (A) on compressor toward
the top of piston.
Push compressor down until
the top of piston. Tighten compressor with
a
2.
3.
ring compressor (B) over piston with
it
is
flush with
wrench
Coat the inside of cyl. bore with
(C),
then loosen slightly.
a
light film
of oil.
Align arrow mark (A) on piston head towards
flywheel end and install con-rod and piston
ass'y through the top of cyl. bore. Push pis-
a
ton into cyl. bore with
hammer handle.
Page 51

4.
Turn crankshaft gently and
in lowest position. Then further insert piston
into cylinder while leading big end bearing
surface to place above crankpin. Turn cyl.
block upside down on bench.
5.
Coat the inside of big end bearing surface
a
and cap screws with
6.
Install rod cap
(B)
align and tighten cap screws
specified torque
light film of oil.
(A)
so
assembly pilot groove
as
shown.
place
(C)
crankpin
to the
PISTON, PISTON RING, AND CON-ROD
8-6
Con-Rod Bolt Tightening Torque
r
CAUTION: Tighten rod screws securely. After
tightening rod screws, con-rod should
move sideway
wrench must
tight cap screws which may result in breakage and/
or scoring of rod.
19
to 20
N-m
(14
to
15
on
crankpin of shaft. A torque
be
used to prevent loose or over-
ft-lbs)
be
able to
Page 52

9-1
CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT
Section
CRANKSHAFT
CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT
REMOVAL
1.
To
remove crankshaft from cyl. block, remove rust or burrs from power take-off shaft
end of crankshaft.
2.
Lightly tapping the both ends near dowel
alternately with
case
cover.
3.
Turn cyl. block upside down on a bench.
4.
Rotate crankshaft until timing marks on
crankshaft gear and cam gear align.
5.
Pull out the camshaft, then remove tappets.
NOTE: Align timing marks to prevent damage
to tappets when removing camshaft. Mark tappets
so
they can
during assembly.
be
a
soft mallet, remove crank-
installed in their original guides
9
AND
PTO Main Journal Dia. (MIN)
Mag. Side Journal Dia. (MIN)
CAMSHAFT
mm
(1.3746
6.
Remove con-rod and piston.
(See
Section
7.
Rotate crankshaft gently until the crank pin
positioned opposite side of cylinder bore.
8.
Remove balancer guide.
9.
Remove crankshaft.
8)
34.945
If journal diameter
crankshaft.
3.
Measure con-rod big-end journal (A)
point with
Con-Rod Big-End Journal Dia. (MIN)
a
36.934
mm
(1.3757 in.)
is
micrometer.
mm
(1.4541 in.)
less
than MIN, replace
at
several
CRANKSHAFT INSPECTION
1.
shaft for scored. Inspect crankshaft gear(s) points with
for cracked, scored or broken teeth.
place parts if necessary. Link Rod Journal Dia. (MIN)
2.
With a micrometer, measure both main journals
at
and
inspect
bearing
surfaces
On
crank-
Re-
several points around journal circumference.
If journal diameter
shaft.
4.
Measure crankshaft link rod journals
a
dial-caliper.
53.951
is
less
mm
(2.12406 in.)
than MIN, replace crank-
at
several
Page 53

CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT
9-2
is
less
If journals diameter
than MIN, replace
crankshaft.
TO
5.
CHECK CRANKSHAFT ALIGNMENT:
Place
crankshaft into an alignment jig, rotate
crankshaft slowly, and measure total indicat-
at
ed runout
locations shown.
Dial indicator
\
Turn crankshaft
Run Out
(TIR)
If total run out exceeds MAX, replace crankshaft.
e
Crankshaft damage can result from:
Engine runs with low oil
Oil
dipper broken
Oil
hole in con-rod plugged.
Oil
not changed regularly.
Bearing cap installed incorrectly.
slowly
(MAX)
0.05
mm
(0.002
or
damaged.
in.)
or
without oil.
3. A-Surface must be concentric and parallel to
each other within 0.005 mm
(0.0002
in.)
full indicator reading.
NOTE: Finish should
be
very smooth; use a super
finishing stone.
LINK ROD INSPECTION
1.
Clean and inspect bearing surfaces on link
rod. If the bearing surface of small end
scored or damaged, replace the rod. Scored
or damaged big end bearing (bushing) must
a
be replaced with
2.
With a micrometer, measure both inside bearing surfaces
at
new bushing.
several points.
is
UNDER-SIZE CON-ROD
1.
Con-rod journal can accept an under-size
con-rod having 36.5 mm (1.437 in.) dia.
grinding
size.
2.
The final finishing diameter should be 36.48
to 36.467 mm (1.4362 to 1.4357 in.).
c
I-
Under
D=
R=
B=
size
36.480
2.30
to
32.3
mm
is
required before using the under-
R
B
dimentional spec.
to
36.467
2.70
MAX (1.272
mm
mm
(1.4362
(0.09
in.
to
MAX)
0.1
1
to
in.)
1.4357
in.)
Re-
Small End Inside Dia. (MAX)
12.059
mm
(0.4748
in.)
If the inside diameter exceeds MAX, replace
the link rod.
Big End (bushing) Inside Dia. (MAX)
r
If
the inside diameter
54.121
mm
(2.13074
in.)
is
greater than MAX,
replace bushing.
BUSHING REPLACEMENT
1.
Place
link rod on a bench plate (4) with radial
oil-groove side up.
2.
With a bearing driver
(2)
as
shown.
NOTE:
the
Do not forget the direction of seam
shell to reinstall new one.
(1),
drive out bushing
of
Page 54

9-3
CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT
3.
1. Bearing driver
2. Big end bushing
3.
Clean the parts in solvent throughly and dry
them. Put
4.
Re-install the bushing using an arbor press
or bearing driver.
5.
Press-in the bushing
flange surface
a
light coat of oil on a new bushing.
0.5
(3).
Link rod
4. Bench plate
mm
(0.02
in.) below
BALANCER GUIDE -INSPECTION
1.
Clean and inspect bearing surface on the shaft
it
for worn or damage, replace
2.
Measure bearing surface diameter
a
point, using
Support Shaft Dia. (MIN)
I
micrometer.
25.927
mm
(1.0208
if necessary.
at
in.)
several
I
BALANCE WEIGHT INSPECTION
1.
Clean and inspect bearing surface of bushing
it,
for worn or damage. Replace
2.
Wrist pins (A) are press fit on weight
strongly, and normally require no mainte-
nance.
3.
With a inside micrometer or telescoping gauge,
measure bearing surface of bushing
if necessary.
(C).
(B)
If shaft diameter
support shaft.
is
less
than MIN, replace
CAMSHAFT INSPECTION
1.
Inspect camshaft for worn or broken teeth.
2.
Measure with a micrometer, camshaft bearing
at
surfaces and camlobes
3.
Replace camshaft if worn
point shown.
or
damaged.
Bushing Inside Dia. (MAX)
26.097
If inside diameter exceeds the MAX replace
bushing.
Bushing can be replaced
as
that of link rod bushing.
NOTE:
on
Align oil hole on bushing and
weight, when installing service bushing.
mm
(1.02744 in.)
as
the same procedure
oil
passage
Page 55

CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT
9-4
Bearing Surface Dia. (MIN)
is
If bearing surface diameter
less
replace camshaft.
Lobe
Height (MIN)
If lobe height
is
less
than MIN for either lobe,
replace camshaft.
CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT
INSTALLATION
1.
Assemble crankshaft, link rods, collares, gear
as
and balance weight
16 17 18
illustrated below.
I
than MIN,
NOTE: Radial oil-grooves of
toward the outside of
balance
weight to crankshaft with oil hole
the
the
crankwebs.
link rods must
Install
be
(7)
facing flywheel side.
2.
Cover key way on flywheel end of crankshaft
a
with
tape to prevent
seal
damage when
installing crankshaft.
3.
Put a light film of oil on crankshaft bearing
surfaces.
4.
Pack preferably high temperature grease
into oil
5.
Put crankpin
seals.
at
bottom dead center of engine.
Install crankshaft carefully.
6.
Align center hole of balance weight and
support shaft hole in crankcase.
7.
Install support shaft, O-ring and nuts.
8.
Install con-rod and piston assembly.
(See
Section
9.
Install tappets in their respective guides from
8)
which they were removed.
NOTE: Push tappets
the way in to
valve
guides
all
to prevent damage to tappets when installing
camshaft.
Install governor shaft and snap pin by properly
the
positioning
as
illustrated.
shaft,
pin and projection-stopper
1.
Crankshaft
2.
Crankcase
3.
Oil
seal
4.
Ball bearing
5.
Collar
6.
Balance weight
7.
Oi
hole
8.
O-ring
9.
Nut
10.
Washer
11.
Support shaft
12.
Stud
13.
Bushing
14.
Wrist pin
15.
Link rod
16.
Crank gear
17.
Collar
18.
Bushing
7
8
1.
Case
cover mounting face
2.
Crankcase
3.
Snap pin
4.
Governor shaft
5.
Stopper (projection)
6.
Governor shaft in crankcase
Page 56

9-5 CRANKSHAFT
AND
CAMSHAFT
Rotate crankshaft until piston
top dead center. Install camshaft with timing
mark (A) aligned with mark
gear.
is
positioned
(B)
on crankshaft
at
CRANKCASE COVER INSTALLATION
Crankcase Cover Tightening Torque
17
to
23
N-m
(12
to
17
ft-lbs)
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
1.
Measure crankshaft end play with a dial in-
dicator.
2.
Install dial indicator (A) on crankshaft
shown. Move crankshaft in and out. End
0.20
play must be 0.09 to
0.0078 in.).
mm (0.035 to
as
1.
Clean gasket surface and put a new gasket
on crankcase cover.
2.
Pack preferably high temperature grease into
oil
seal.
3. Lubricate crankshaft bearing in
with engine oil.
4. Check governor weights closed.
NOTE: To make the installation easier, align oil
pump shaft convex with camshaft end groove.
Be
5.
6. Install crankcase cover and tighten cap screws
sure to suitably
meshed with cam gear when installing crank-
case
cover.
down evenly by hand.
a
torque wrench and tighten screws in the
Use
squence shown, and to the specified torque.
Do not turn one screw down completely before the others,
crankcase cover.
as
set
governor gear to be
it
may cause
case
a
cover
warped
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
ADJUSTMENT
1.
The end play should be 0.09 to
to 0.0078 in.) with the 0.5 mm
gasket placed in-between crankcase cover and
crankcase.
2.
Check end play and adjust if necessary.
3. Measure depth
mounting surface to PTO shaft bearing end
shown.
4. Measure depth (b); from crank gear end to
crankcase gasket surface
5. Calculate (a-b), and
shim(s) from "Adjusting Shim Table" to
correctly adjust end play.
6. Insert the shim(s) to PTO shaft and install
crankcase cover.
sizes
7. Shim
of 1.74 mm (0.0685 in.) to 1.18 mm (0.0464
in.) in 0.07 mm (0.0027 in.) increments
shown.
(thickness) are provided in the range
(a);
from crankcase cover
as
select
0.2
mm (0.0035
(0.02
shown.
appropriately sized
in.)
as
as
Page 57

Gasket Crankshaft
Crankcase
bearing
CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT
9-6
Crankcase cover
Adjustment
Difference in depth
1.92
(0.0755
-___-_-
1.85
(0.0728
1.78
(0.0700
1.71
(0.0673
1.64
(0.0645
1.57
(0.0618
1.50
(0.0590
1.43
(0.0562
1.36
(0.0535
A-0
to
1.99 mm
to
0.0748
to
1.92 mm
to
0.0755
to
1.85 mm
to
0.0728
to
1.78 mm
to
0.0700
to
1.7 mm
to
0.0673
to
1.64 mm
to
0.0645
to
1.57 mm
to
0.0618
to
1.50 mm
to
0.0590
to
1.43 mm
to
0.0562
Shim
:
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
of Shim
92025-2153
92025-2152
92025-2151
92025-2 150
92025-2149
92025-2 148
92025-2 147
92025-2 146
92025-2145
1.74mm
(0.0685
1.67 mm
(0.0657
1.60 mm
(0.0629
1.53mm
(0.0602
1.46 mm
(0.0574
1.39 mm
(0.0547
1.32 mm
(0.0519
1.25 mm
(0.0492
1.18 mm
(0.0464
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
in.)
Page 58

10-1
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEARING
CYLINDER BLOCK
CYLINDER BLOCK INSPECTION
AND REPAl
Visually inspect cyl. block, whenever engine
disassembled, to
ped bolt holes, broken fins, or cyl. wall
Use an inside micrometer, or telescoping gauge
and micrometer to determine the
bore. Measure parallel with crankshaft and
right angles to crankshaft
bottom
If cyl. bore
and/or the out of round,
R
see
of
ring travel.
is
if there are any cracks, strip-
is
scored.
size
at
top, center and
more than the wear tolerance
it
must be resized.
Section
is
of cyl.
at
10
AND
Resize
rized repair shop or by using
honing tool.
hone manufacturer to produce the correct
cyl.
wall finish.
1.
MACHINE THE
the allowance table below.
0.25
mm
0.50
mm
BEARING
cyl. bore can be done by an autho-
a
drill press and
Use
a
stone recommended by the
BORE
89.23
(3.5130
89.48
(3.5228
89.73
(3.5327
first according to
Bore Dia.
to
89.21
to
to
to
to
to
mm
3.5122 in.)
89.46
mm
3.5220 in.)
89.71
mm
3.5319 in.)
Cylinder Bore Wear Tolerance (MAX)
0.076
mm
(0.003 in.)
Out of Round Cylinder Bore (MAX)
0.063
mm
Dia.
(0.0025 in.)
88.980
(3.5031 in.)
MIN
mm
(0.010
(0.03
in.)
in.) over
I
Standard Bore
89.000
(3.5039 in.)
TO
RESIZE
Size
MAX
mm
Bore to Next Oversize:
Always resize to exactly 0.25mm
or 0.50mm (0.02 in.) or 0.75mm
standard
If this
size
as
shown in table.
is
done accurately, the stock oversize rings
and pistons will fit perfectly and proper clearances
will be maintained.
I
I
2.
TO
FINISH THE BORE:
Select
and use
suitable stone (normally driven by a drill
press)
CAUTION: Allow for
size) of
0.006
to 0.008mm
a
shrinkage (from the final
(0.00024
to
0.00031
in.) which will occur when engine cools down.
Final Bore Size Dia.
0.25
mm
0.75
mm
(1)
Clean cylinder
89.250
(3.51378
89.500
(3.52362
89.750
(3.53346
at
to
89.230
to
to
89.480
to
to
89.730
to
mm
3.51299 in.)
mm
3.52283 in.)
mm
3.53268 in.)
top and bottom to remove
burrs and pieces of base and head gasket.
(2) Anchor cyl. block on drill press table before
honing.
(3)
Align center of the cyl. bore to drill press
Set
center.
the press to operate from 200 to
250 rpm.
(4)
Connect drive shaft to hone and
drill press
mm
so
hone can only extend
(3/4
to 1 in.) from the top or bottom
set
stop on
20
to 25
of cylinder.
(5)
Rotate adjusting nut (knob) on hone with
finger or small screw driver until stones contact
at
snugly against cyl. wall
DO
NOT
FORCE.
(6)
Turn stone by hand. If you cannot turn
hone
is
too tight, Loosen hone until
be
turned by hand.
narrowest point.
it
a
I
it,
can
Page 59

CAUTION: Be sure cylinder and hone are centered
and aligned with drive shaft and drill spindle.
(7)
Coat inside of cylinder with honing oil. Start
60
cyl-
degree
drill press. Move hone up and down in
inder spprox.
(8)
Check diameter of cylinder regularly during
honing, using an inside micrometer.
ing,
and remove hone from cylinder.
CAUTION: Finish should have
cross-hatch pattern.
(9)
Clean cylinder thoroughly. Use soap, warm
water and clean rags. Clean cyl. wall for
"white glove" inspection. A clean white rag
should not show soil from the cyl. wall.
(10)
Dry cylinder and coat with engine oil.
20
cycles-per-minute.
Stop drill press before measur-
a
40
to
Do
not use solvent or gasoline.
a
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEARING
Bearing driver Ball bearing Crankcase cover
BALL BEARING INSPECTION
1.
Clean bearing in high flash point solvent
throughly and dry
2.
Spin bearing by hand and check for play.
Replace bearing if
smoothly spin, or has excessive play.
it.
it
is
noisy, or does not
10-2
be
CAUTION: Cylinder must
after honing to eliminate
thoroughly cleaned
all
grit.
BALL BEARING REMOVING
Ball
bearings are press-fit into crankcase and
case
cover.
1.
Remove oil
not be reused once removed.
2.
Place
UP.
3.
Using
as
shown.
seals
on crankcase.
crankcase on a bench with oil
a
bearing driver, drive out bearings
Oil
seal
seal
should
side
AXIAL
RADIAL
PLAIN BEARING INSPECTION
The camshaft bearings and PTO journal bearing
are
cast
with the cyl. block and covers.
Cylinder block and covers should be replaced
if scored or worn.
1.
Measure camshaft bearing on block with an
inside micrometer or telescoping gauge.
Page 60

10-3
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEARING
Camshaft Bearing Inside Dia.
16.068
mm
Replace cyl. block, if inside diameter exceeds
MAX.
2.
Measure PTO and camshaft bearings on covers
with an inside micrometer or telescoping gauge.
PTO
Bearing Inside Dia.
(MAX)
(0.6326 in.)
(MAX)
0.5mm
(0.02 in.)
mm
(1.3804 in.)
Camshaft Bearing Inside Dia.
I
Replace crankcase cover or oil pump cover,
if inside diameter exceeds MAX.
20.071
mm
(MAX)
(0.7902 in.)
I
BALL BEARING INSTALLATION
1.
Clean cylinder/crankcase and the cover in
high flash point solvent throughly and dry.
2.
Put a light coat of oil on bearing surface.
3.
Press-fit ball bearing into cyIinder/crankcase
and the cover with an arbor or bearing driver.
OIL SEAL REPLACEMENT (PTO SIDE)
1.
Remove old oil
with
a
screw-driver or punch from the inside.
2.
Pack preferably high temperature grease into
a
new oil
3.
Press-in oil
lip toward inside of engine. (Dust
outside.)
4.
For flywheel side, press-in oil
with housing.
5.
For PTO side, press-in oil
below outside end most face of PTO bearing.
seal.
seals
by tapping them out
seal
with sharp edge of oil
seal
seal
0.5
to
mm
seal
seal
be flush
(0.02
in.)
lip
Page 61

ELECTRIC STARTER AND CHARGE
11-1
Section
ELECTRIC STARTER
STARTER MOTOR CIRCUIT
The starter motor circuit includes the engine
switch, starter solenoid, battery and starter motor.
is
When the engine switch
(See
position
of current flows through the switch and the
solenoid. This current magnetizes the solenoid
core, which then pull the plunger to
solenoid contacts complete
er motor, and the starter armature rotates. At the
same time plunger pull the shift lever end.
The pinion linkaged to the other end of the lever
on
slides
with flywheel ring gear. As engine fires and
speed up, starter armature
pinion to disengage. The key switch
"I"
to
system.
Starter motors used on
and shift lever type.
CAUTION: Because of
never hold engine switch in START position
starter motor will not turn over, or current may
burn out starter motor windings.
(ON) position, cutting off the cranking
Wiring Diagram),
the armature shaft, engaging the pinion
turned to (START)
a
small amount
it,
closing
a
circuit for the
is
overrun, causing
is
returned
FB46OV
a
large amount of current,
are a Bendix type
start-
if
11
AND
STARTER
MOTOR
STARTER SYSTEM CHECK
If a starting problem occurs, check engine thoroughly to be sure engine
problem.
plug and rotate crankshaft by hand, to be sure
it
rotates freely. Any belt, clutch or other load
of this nature will affect cranking performance.
The Trouble Shooting
you in diagnosing problems.
It
CHARGE
STARTER
SOLENOID
is
not the cause of the
is
a
good practice to remove spark
(1-1
7)
table should aid
IGNITION
SWITCH
Wiring Diagram
Bendix-Type
(FB460V-AS
ENGINE
Model)
Shift
Lever-Type
(FB46OV-BS
Model)
AV
20
Page 62

11-2 ELECTRIC STARTER AND CHARGE
STARTER MOTOR CHECK
A performance
in the following manner.
Needed for the
A tachometer capable of reading 20,000 rpm.
A 12V 32Ah (or more) battery.
An ammeter capable of reading 200 amperes.
test
of starter motor can be made
test
are:
A shorted, open, or grounded armature or
field coil.
A defective
starter
motor switch.
STARTER SOLENOID TEST
WARNING:
and corrosive.
clothing. Handle
ed, flush immediately with
Battery electrolyte
It
is
injurious
it
carefully.
to
If
electrolyte
a
solution of one part
is
eyes,
poisonous
skin and
is
baking soda to four parts water.
1. Connect starter motor, battery and ammeter
as
shown in illust.
(Wiring
diagram
for
performance
A
test)
I
Starter motor should not be loaded. The
test
should be quickly conducted,
is
rating
2.
Insert tachometer in the end of starter motor
and
30 seconds.
activate
starter motor. A starter motor
as
in good condition will be within the follow-
ing spec.
spill-
the
Use the same procedure for starter relay
the Bendix
1.
Disconnect lead (A) to starter motor
Measure the continuity of solenoid when
2.
starter
and shift lever starter.
as
activated.
3.
Set
a
multimeter selector switch to
position and connect leads across the large
terminals.
test
for
shown.
Bendix Type
(FB460V-AS
Model)
Terminal voltage
Starter motor rpm
Current draw (A)
Shift Lever Type
(FB46OV-BS
7,000
Model)
rpm (MIN)
60
A (MAX)
Terminal voltage
Starter motor rpm
Current draw (A)
6,000
rpm (MIN)
50
A (MAX)
If not, check for the following and correct
if necessary:
A binding or seizing condition in the starter
motor bearings.
'Starter motor brushes sticking in brush hold-
ers.
A dirty or worn armature commutator
brushes.
12
v
11.5 V
or
Turn engine switch to START and read the
4.
meter.
If solenoid does not click or if the meter reads
more than continuity, solenoid
Replace
If solenoid makes
it.
a
single clicking sound,
is
the meter read continuity, and pinion
moves outward (shift lever solenoid only),
solenoid and the rest of the starter circuit
are
good.
faulty.
gear
Page 63

ELECTRIC STARTER AND CHARGE
11-3
If solenoid clicks once but the meter does
not read continuity, solenoid
it.
place
If solenoid does not click
at
is
faulty.
all,
proceed with
following.
5.
Disconnect lead
position and connect leads
(BW)
and
set
multimeter to
as
shown.
If the meter does not read close to continuity,
solenoid
faulty. Replace
it.
is
If the meter reads close to continuity, solenoid may be good. Check the voltage to sole-
noid from engine switch.
Set
multimeter selector switch to 25VDC
it
as
position and connect
shown.
Re-
STARTER MOTOR DISASSEMBLY
(Bendix
Type)
2
6.
Turn engine switch to START and read the
meter.
If the meter reads battery voltage, the cir-
is
cuit,
good.
the previous
If the meter reads much
voltage or no voltage
or engine switch
Test engine switch.
7.
Inspect the wiring shown carefully for damaged
8.
or broken wires and replace
If
solenoid would not click in
tests,
it
is
faulty. Replace
less
than battery
at
all, either the wiring
is
faulty.
as
required.
it.
Parts
1
Pinion stopper set
2
Pinion ass'y
Front cover
3
4
Front cover metal
5
Thrust washers
Armature
6
7
Brush holder ass'y
8
Brush
(-)
Name
No.
Parts Name
For disassembly, follow the steps below.
1.
Pinion stopper
2.
Pinion ass'y
3.
Through bolts
4.
Rear
cover
5.
Brush holder ass'y
6.
Brush
7.
Yoke ass'y
8.
Armature
9.
Thrust washers (5)
10.
(10)
Front cover
set
(1
)
(2)
(14)
and screws
(
1
1
)
(7)
and brush springs
(16)
(16)
(11)
(1
(9)
5)
Page 64

11-4
(Shift
ELECTRIC
Lever
Type)
STARTER
AND
CHARGE
Ref,
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Parts Name
Front cover
Washer
Stopper
Snap ring
ass'y
Clutch
Shift lever
Armature
Brush holder
Brush
Ref
No.
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Parts Name
Brush spring
Insulator
Rear cover
Bolt
Solenoid
Nut
Nut
Yoke ass'y
For disassembly, follow the steps below.
1. Nut (16)
2.
Nuts and solenoid (14), (15)
3. Long bolts (13)
4.
Rear cover
5. Insulator
6.
Brush holder and spring
7.
Yoke ass'y
8.
Shift lever
9.
Armature
10.
Washer
11. Stoppers and snap ring
12.
Clutch ass'y (5)
(1
(1
1)
(9),
(6)
(7)
(2)
2)
(17)
(8),
(3),
(4)
(10)
Measure commutator outside diameter
several points around diameter circumference,
a
using
Commutator Outside Dia.
Bendix Type
If outside diameter
vanier caliper.
lever Type
I_--
(MIN)
32
27
is
less
mm
mm
(1.26
(1.10
than
in.)
in.)
(MIN),
armature.
Measure depth of grooves between commutator
segments.
Commutator Groove Depth
Shift lever Type
(MIN)
0.2
0.2
mm
mm
(0.01
(0.01
in.)
in
)
at
replace
STARTER MOTOR INSPECTION
1.
Armature Inspection
Inspect surface of commutator.
If
it
has a scratch or
piece of very fine emery paper (No.5000 to
No.6000).
is
dirty, polish
it
with
a
2.
Segment
3.
Good
4.
0.2
mm
(0.08
5.
Insulating Material
in.) limit
Page 65

If grooves are shallower than (MIN), under cut
insulating material to standard depth using
thin file.
Standard Groove Depth
Bendix Type
Shift lever Type
If
grooves are only dirty, clean them carefully.
Support armature in
as
shaft
pendicular to commutator. Turn armature
slowly and read run-out on dial indicator.
0.5
to
0.8
mm
(0.02
to
0.03
0.5
to
0.6mm
shown. Position dial indicator per-
tail
(0.02
stock
to
0.023
at
each, end of
in.)
in.)
a
ELECTRIC STARTER AND CHARGE
Commutator-to-Shaft Resistance
r
If
resistance
shorted.
Test armature windings for shorts.
Place
armature on a growler.
a
Hold
on top of armature.
is
less
than infinite, armature
thin metal strip
(e.g.,
(52)
hack
saw
11-5
is
blade)
Commutator Run-Out
Bendix Type
Shift lever Type
If run-out
commutator or replace starter motor.
Set
multimeter selector switch to R x
tion and check resistance between each
ment and
Armature Winding Resistance
is
all
(MAX)
0.3
mm
0.4
mm
greater than (MAX), turn down
the others.
(0.012
(0.016
in.)
in.)
posi-
seg-
I
I
Turn on growler and rotate armature .one
complete turn.
If metal strip vibrates, windings are internally
shorted to each other and starter motor must
be replaced.
2.
Brush Length Check
Measure overall length of each brush.
Very
Low
If resistance
ture winding has an open circuit. Replace
starter motor.
Set
multimeter selector switch to
position and measure resistance between commutator and armature shaft.
is
too high or even infinite, arma-
R
x
Page 66

11-6
ELECTRIC STARTER AND CHARGE
Brush Length
Shift
lever Type
If brushes are shorter than (MIN), replace shorted to ground. Replace yoke assembly.
them.
3.
Brush Spring Check position and measure resistance between field
Inspect brush spring for damage. Replace coils‘ terminals (A).
springs if necessary.
If brush spring are able to snap the brushes
firmly into
serviceable. If they cannot, replace them.
Field Coil Check
4.
Bendix-Type Starter Motor
4-
1
Set
tion and measure resistance between field
coils’ terminals
(M
IN) Terminal-to-Ground Resistance
6
mm
(0.24
in.)
place,
multimeter selector switch to R x
they may be considered
(A).
posi-
If resistance
4-2
Shift lever-Type Starter Motor
Set
multimeter selector switch to R x
is
less
than infinite. field coil
is
Terminal-to-Terminal Resistance
Very
Low
If resistance
(no continuity), replace yoke assembly.
Set
multimeter selector switch to R x
position and measure resistance between yoke
(A) and one terminal of each coil
is
greater than indicated above
(52
(B).
1
Terminal-to-Terminal Resistance
Very
Low
If there
If resistance
(no continuity). Replace yoke assembly.
Set
position and measure resistance between yoke
(A)
is
continuity field coil
is
greater than indicated above
multimeter selector switch to R x
and one terminal of each coil
is
still
(B).
good.
Terminal-to-Yoke Resistance
I
If resistance
continuity), replace yoke ass‘y.
Set
multimeter selector switch to R x
position and measure resistance between positibe brush (A) and starter motor yoke
Very
Low
is
greater than indicated above (no
I
1
(B).
Page 67

ELECTRIC STARTER AND CHARGE
11-7
Positive Brush-to-Yoke Resistance
is
less
If resistance
is
horted to ground. Replace entire positive
brush ass’y
(C).
than infinite, positive brush
BRUSH HOLDER CHECK
(Bendix-Type only)
Set
multimeter selector switch to R x
position and measure resistance between
its
base
brush holder (A) and
Positive Brush Holder-to-Ground Resistance
(B).
1
)
If any irregularity
should be replaced.
is
noted, pinion clutch
STARTER MOTOR REASSEMBLY
Reassembly
Note the following points.
Apply multi-purpose
Sliding surface of pinion and shaft’s spline.
Dust
Metal holding shaft
Do not reuse retaining ring on shaft, which
was removed.
Removal weaken and deform the retaining
ring.
Charging System
A charging system produces the current required
to maintain the battery in good
The charging system consist of
magnet, charging coil (stater) and regulator.
The charging coil output current
(changed from AC to DC) and
constant voltage for battery charging.
Rated speed of AC generator
at
lower speeds available output will be re-
duced relatively.
seal
is
the reverse order of disassembly.
glease
lip.
to:
at
front and rear cover.
state
of charge.
a
flywheel
is
is
maintained
is
3,350 rpm, and
rectified
If resistance
holder.
is
less
than infinite, replace brush
PINION CLUTCH INSPECTION
Rotate pinion manually.
While rotating pinion in direction of normal
operation, smoothly reverse the direction of
it
rotation to confirm that
locks.
CHARGING SYSTEM CHECK
Be
sure to perform more basic checks first such
1.
Battery defective or not charged.
2.
Eroded or
3.
Cracked insulation or brocken wires.
4.
Wire grounding out the system.
5.
Defective switch.
Condition Found (Battery Run Down)
Check battery polarity. Negative
battery should be grounded to engine or frame
(equipment), positive
regurator charge lead.
loose
terminals or connections.
(+)
side of battery to
(See
I
Ilustration)
(-)
as;
side of
Page 68

11-8
ELECTRIC STARTER
If the wiring
damaged.
AC generator
CHG
AND
CHARGE
is
reversed, regulator will be
3.4w
monitor
Stater Unregulated Out Put (MIN)
34.5
volts
3,350 rpm
If voltage
is
less
than specified, replace stater.
Regulator Resistance Measurement
all
Remove
Set
multimeter selector switch to R x
the wires from regulator.
position.
Connect tester leads to regulator connecter
terminals using the table below.
The resistance value should be specified.
OHM Meter Readings Connected Between
1
d
Key
SW.
Out Put Test
Start engine and allow
ly.
Set
multimeter selector switch to the 25V DC
position. (Use KAWASAKI multimeter)
Connect meter positive
(+)
positive
terminal, and negative
lead to battery negative
at
Run engine
shoule show
the system
rated
a
minimum of
is
defective and the components
of the system should be checked.
Test Stater Out Put
Start engine and allow
ly.
Disconnect coupler from charging circuit.
Connect voltmeter leads to stater lead ter-
minals on coupler.
Run engine
at
rated
voltage should be
it
to warm up complete-
(+)
(-)
terminal.
RPM
(3,350 rpm), meter
it
to warm up complete-
RPM
(3,350 rpm). Output
as
specified below.
Stater
lead to battery
(-)
12
amps. If not,
meter
CHG
(by
KAWASAKI
monitor
TESTER)
If resistance
is
not
as
specified, replace the
regulator.
NOTE: Resistance value may vary with individual
meters.
Page 69

TROUBLESHOOTING
ELECTRIC STARTER AND CHARGE
11-9
t
Does crankshaft rotate? Does starter rotate?
Yes
and ring gear satisfac- or replace pinion and/
I
Yes
Check
clutch for damage, and run?
replace if necessary.
I
pinion‘s ent starter. Does motor
Inspection
terminals
Is
operating sound pro-
duced out of starter’s
Item
for
->-
Faulty
/Make connection
terminal of independ-
and
No
Remedy
Correct connection or
Check and repair wiring to solenoid switch.
Wiring connection
Repair or replace sole-
noid switch.
Check return spring
for permanent defor-
mation and check pinion for dragging.
Correct meshing of
pinion and ring gear
or ring gear.
Replace motor
(field coil or armature).
(rotation
Is
rotation normal?
Check ignition system
Faulty
Check battery charge Charge or replace the
is
slow) and also check battery
terminals for disconnec- Correct connection or
tion and corrosion, corrosion
Yes
engine
starter
new one?
Inspect interior of engine.
oil
is
satisfac- Change engine oil.
is
replaced with
t
No
Faulty solenoid switch
terminals.
Faulty
If abnormal (Immedi-
ately disconnect cable
from of the
battery.)
‘Motor fails to stop even
Repair or replace start- when key switch
turned to OFF position.
I
I
at
battery
is
Page 70

12-1 RECOIL STARTER
Section
RECOIL
RECOIL STARTER DISASSEMBLY
1. Pull handle out about 10 to 12 inches or until
is
notch (A) in pulley
rope in place with knot
near rope hole. Hold
(B).
12
STARTER
6.
Remove bolt (A) and ratched cover
7.
Remove pawls (A) and spring
(B).
(B).
2. Pry knot out of handle and untie
handle off rope.
3.
While carefully holding rotating parts with one
hand, untie knot
4.
Pull rope in through rope hole (A) in housing
and hold
5.
Allow spring tension slowly to unwind recoil
mechanism.
CAUTION:
the
reel and
it
Do
the
(B)
with the other.
in notch
not
housing. Be careful that spring does not
(B)
in reel
let
the rope wedge between
(C).
it.
Pull
8.
Remove reel.
loose
fly
Turn reel one-quarter turn counterclockwise past
the
Now, slowly lift reel straight up out of housing.
NOTE:
reel
reel
reel may be easily removed.
9.
and injure you.
rest position where no tension can be
There should
when removing reel. If tension
back
into place and gently "wiggle"
If necessary, remove spring.
It
is
under great pressure.
be
no spring tension on
is
felt,
it
felt.
push
until
RECOIL STARTER REASSEMBLY
Assembly
Note the following points.
is
reverse of disassembly.
Page 71

RECOIL STARTER
12-2
If spring was removed,
as
shown. If
starter will not operate properly.
//\WARNING: Spring must
pressure during installation. Wear gloves to avoid
injury.
1.
Lightly
glease
it
spring
it
must be installed Pawls (A) must be installed
is
not installed correctly,
be
put under
(A).
great
as
proper starter operation.
Install coil spring (A), ratched cover
tighten bolt
(C).
shown for
(B)
and
If rope was unwound from reel,
(as
wound clockwise
starter operation.
Set
reel into place
case
catch on tabs
(B)
shown) for correct
so
that slots (A) on spring
on reel.
it
must be
Rotate reel three turns counterclockwise to
preload the spring.
Pull rope in through rope hole in housing
and install handle.
RECOIL STARTER INSPECTION
Disassemble recoil starter.
Immerse only metal parts in
flash-point solvent.
Do
CAUTION:
in solvent
as
Use compressed air to dry cleaned components.
not clean any non-metalic parts
they may
be
damaged.
a
bath of high
Check starter pawls for chips or excessive
wear.
Check starter rope for excessive wear or
fraying.
Check condition of recoil spring and ratched
cover spring.
Inspect springs for breaks, rust, distortion,
or weakened condition.
Page 72

 Loading...
Loading...