TOKO TK15211MTL Datasheet
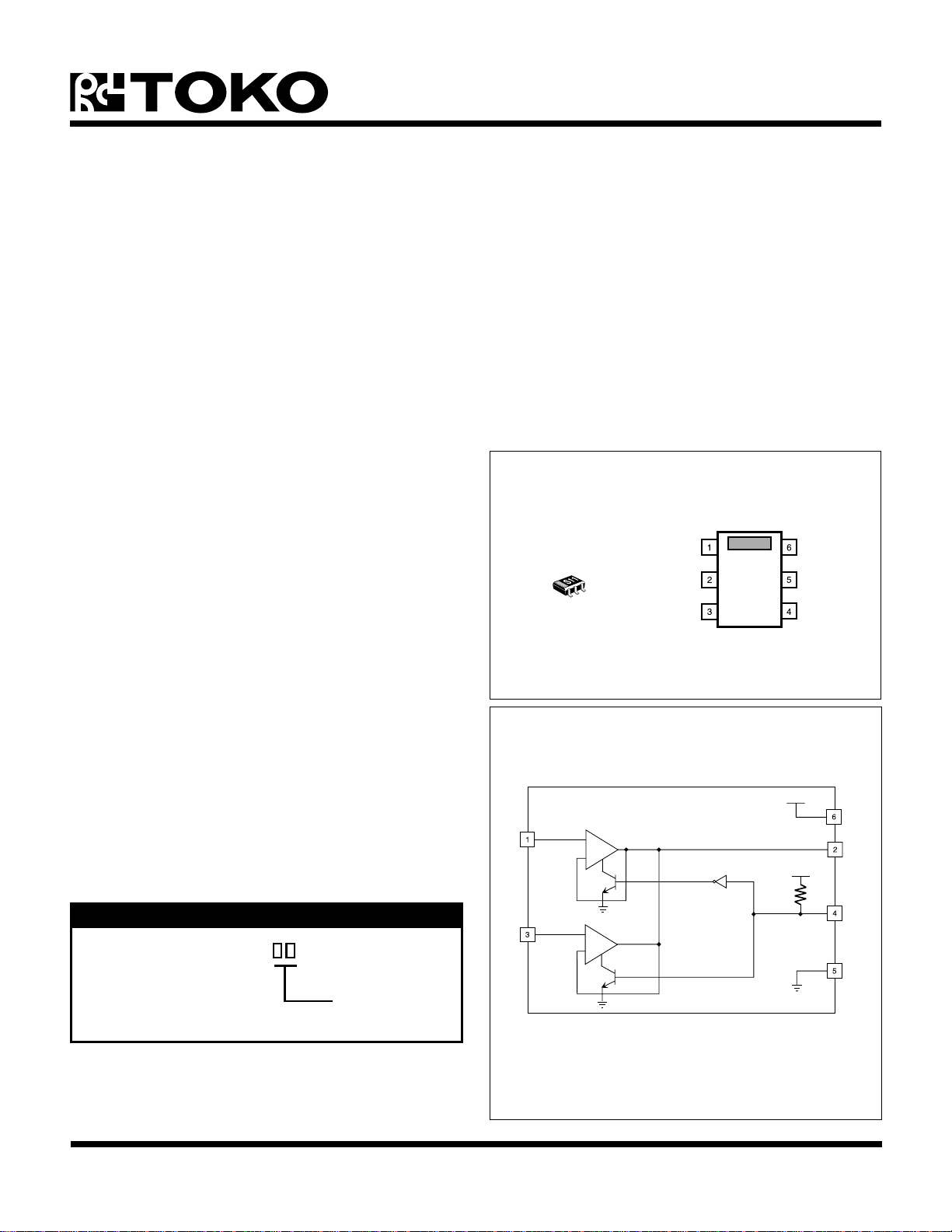
TK15211
Audio Analog Switch
FEATURES
■ Wide Operating Voltage Range (3 to 13 V)
■ Low Distortion (typ. 0.004%)
■ Wide Dynamic Range (typ. 6 V
P-P
)
■ Low Output Impedance (typ. 20 Ω)
■ Protection at Output Terminal.
■ Direct Coupling Possible.
DESCRIPTION
The TK15211M is an Analog Switch IC that was developed
for audio frequency applications. The function of the IC is
to select one output from two input channels. The channel
selection is controlled by a low level. The TK15211M
operates from a single power supply. The input bias
circuitry is provided externally, making the device suitable
for various signal switching applications, especially Hi-Fi
devices. The TK15211M offers a wide operating voltage
range with simple associated circuitry.
APPLICATIONS
■ Audio Systems
■ Radio Cassettes
20P
TK15211
IN A
OUT
IN B
V
CC
GND
KEY
The TK15211M is available in the small SOT23L-6 plastic
surface mount packages.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TK15211M
Tape/Reel Code
TAPE/REEL CODE
TL: Tape Left
IN A
IN B
BLOCK DIAGRAM
+
-
+
-
V
CC
V
CC
OUT
V
CC
KEY
GND
June 1999 TOKO, Inc. Page 1
TK15211
Logic
Key Input
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage ......................................................... 14 V
Operating Voltage Range................................. 3 to 13 V
Power Dissipation (Note 5) ................................ 200 mW
Storage Temperature Range ................... -55 to +150 °C
Operating Temperature Range ...................-20 to +75 °C
CONTROL SECTION
Input Voltage .................................... -0.3 V to VCC +0.3 V
TK15210M ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Test conditions: V
LOBMYSRETEMARAPSNOITIDNOCTSETNIMPYTXAMSTINU
= 8.0 V, T
CC
= 25 °C, unless otherwise specified.
A
ANALOG SWITCH SECTION
Signal Input Voltage ......................... -0.3 V to VCC +0.3 V
Signal Output Current ............................................. 3 mA
Maximum Input Frequency..................................100 kHz
Lead Soldering Temperature ............................... 235 °C
I
CC
tnerruCylppuS 2.26.4Am
NOITCESLORTNOCYEK
V
LI
V
HI
I
)YEK(TUO
tnerruCwolftuODNGotdetcennoc4niP03Aµ
leveLwoLegatloVtupnI1etoN3.0-6.0+V
leveLhgiHegatloVtupnI0.2V
CC
NOITCESHCTIWSGOLANA
DHTnoitrotsiDcinomraHlatoTV
N
L
esioNlaudiseR2etoN01smrVµ
TCklaTssorC
NI
V
NI
3etoN
zHk1=f,smrV1=400.0800.0%
,zHk01=f,smrV1=
08-57-Bd
NYDleveLlangiStupnImumixaM%1.0=DHT,zHk1=f0.2smrV
AVGniaGegatloVzHk02~=f0Bd
V
∆V
I
Z
tnec
egatloV
egatloVlanimreTtuptuO
lanimreTtuptuO-tupnI
tnec
NI
TUO
ecnereffiD
tnerruCsaiBtupnI4etoN5.0Aµ
ecnadepmItuptuOecnadepmICD02
V
TUO
edistuo
morfegatlovylppus=
V
2.0-V
TUO
V
TUO
TUO
41Vm
3.0+V
2.0+V
Ω
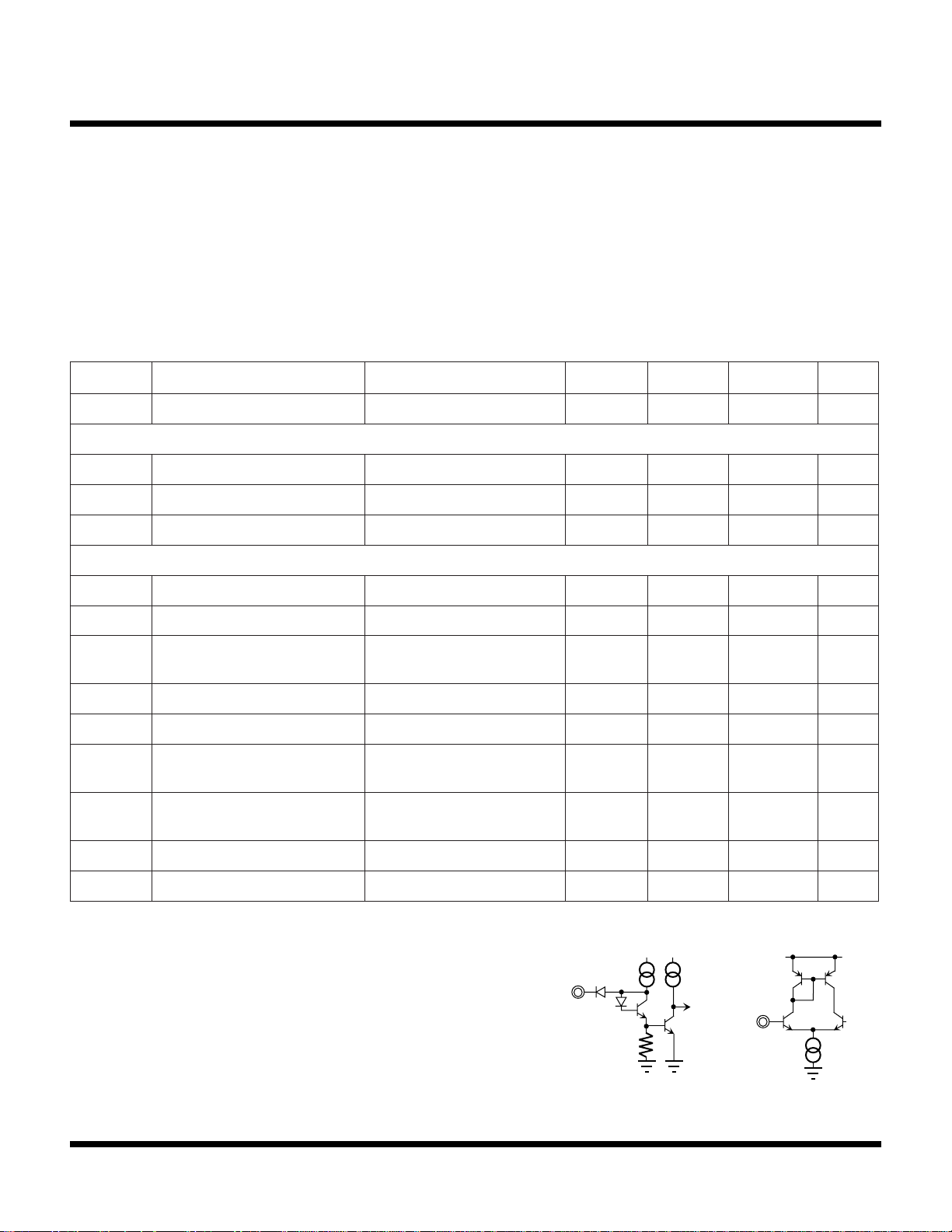
Note 1: The KEY input equivalent circuit is shown to the right in Figure A. When the
control pin is open, the input is pulled up to a high level (approximately 1.4 V).
This applies the channel A input signal to the output. A low level changes the
output to the channel B input signal.
Note 2: This value measured with a capacitor connected between the input terminal
and ground. See Figure 7.
Note 3: This value measured with a 5 kΩ resistor and series capacitor connected
between the input terminal and ground. See Figure 8.
Note 4: The input equivalent circuit is shown to the right in Figure B. The
standard application of the TK15211M is direct coupling with external input
bias.
Note 5: Power dissipation is 200 mW when mounted as recommended.
Derate at 1.6 mW/°C for operation above 25°C.
Page 2 June 1999 TOKO, Inc.
Figure A Figure B
Input
V
CC
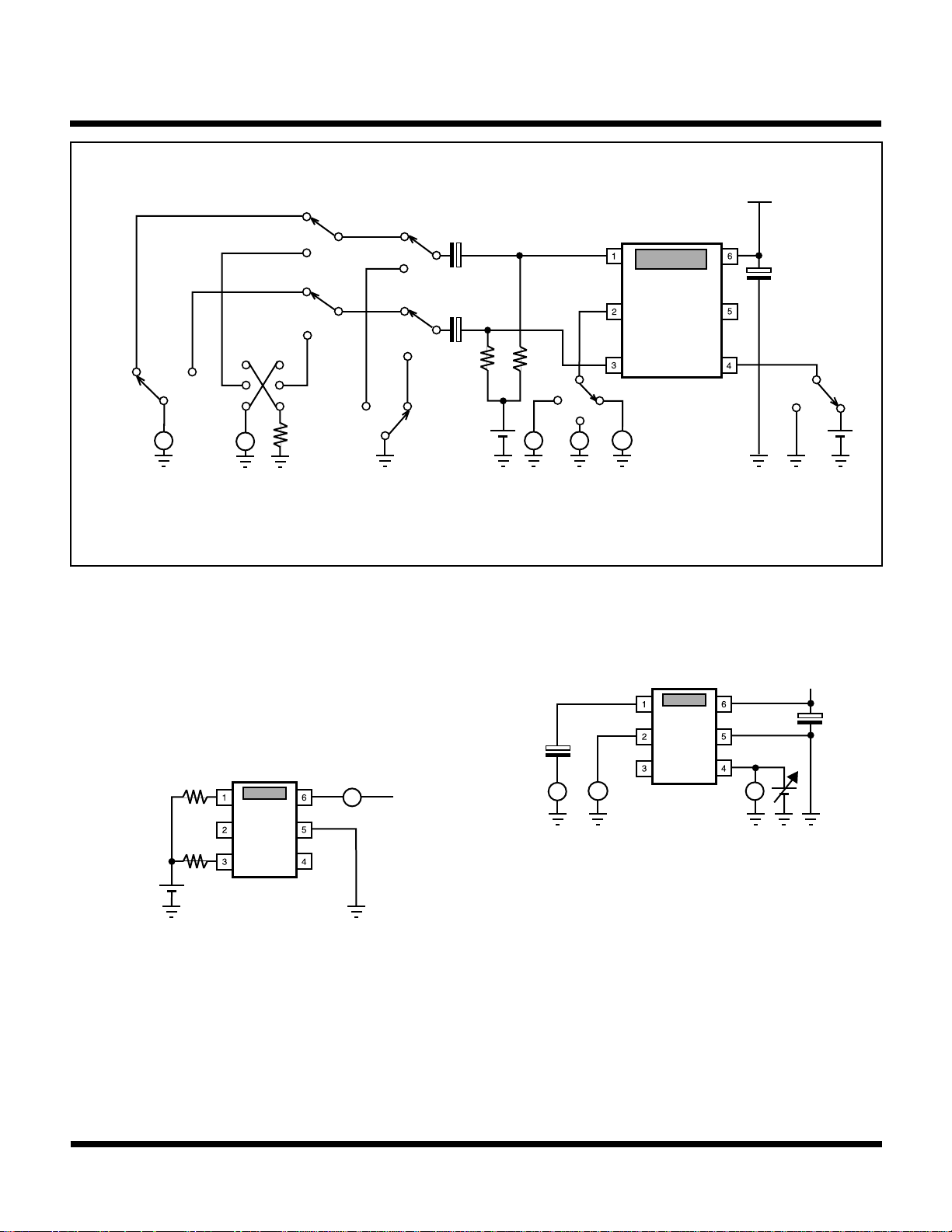
TEST CIRCUITS AND METHODS
TK15211
V
CC
SW9
1 kHz
1 Vrms
2 Vrms
SW6
SW7
SW8
10 kHz
1 Vrms
~
or
~
5 kΩ
SW5
10 µF
SW3
10 µF
SW4
1: The above condition tests the dynamic range measurement for channel A.
2: SW5 is for residual noise measurement.
3: SW8 is for cross talk measurement.
SUPPLY CURRENT (FIGURE 1)
This current is a consumption current with a nonloading
condition.
1) Bias supply to Pin 1 and Pin 3. (This condition is the
same with the other measurements too, omits from
next).
2) Measure the inflow current to Pin 6 from VCC.
This current is the supply current.
+
+
VCC/2
50 kΩ50 kΩ
SW2
V
V
THD
_
~
+
SW1
3) Connect an oscilloscope to Pin 2.
4) Elevate the Pin 4 voltage from 0 V gradually, until the
sine wave appears at the oscilloscope. This voltage is
the threshold level when the wave appears.
+
V
CC
+
50 K
50 K
V
CC
/ 2
V
CC
A
OSC
~
V
Figure 2
KEY INPUT CURRENT (FIGURE 3)
Figure 1
This current means the outflow current with the control
terminal.
1) Measure the current to GND from Pin 4. This current is
CONTROL LOW/HIGH LEVEL (FIGURE 2)
the outflow current.
This level is to measure the threshold level.
1) Input, the VCC to Pin 6. (This condition is the same with
the other measurements, omitted from the next for
simplicity.)
2) Input to Pin 1 with sine wave (1 kHz, 1 Vrms).
June 1999 TOKO, Inc. Page 3

TK15211
V
CC
+
+
~
V
~
THD
TEST CIRCUITS AND METHODS (CONT.)
V
CC
+
A
Figure 3
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION (FIGURE 4)
Use the lower distortion oscillator for this measurement
because distortion of the TK15211 is very low.
1) Pin 4 is the open condition, or high level.
2) Connect a distortion analyzer to Pin 2.
3) Input the sine wave (1 kHz, 1 Vrms) to Pin 1.
4) Measure the distortion of Pin 2. This value is the
distortion of Ach.
5) Next connect Pin 4 to the GND, or low level.
6) Input the same sine wave to Pin 3.
7) Measure in the same way. This value is the distortion
of Bch.
V
CC
+
+
THD
~
Figure 4
6) Calculate Gain = 20 Log (( |V2 - V1| )/V1)
V1<V2 = + Gain, V1>V2 = - Gain
This value is the voltage gain of Ach.
7) Next, connect Pin 4 to the GND, or low level.
8) Input the same sine wave to Pin 3.
9) Measure and calculate in the same way.
This value is the voltage gain of Bch.
V
CC
+
+
~
V1 V2
V~V
~
Figure 5
MAXIMUM INPUT LEVEL (FIGURE 6)
This measurement measures at the output side.
1) Pin 4 is the open condition, or high level.
2) Connect a distortion analyzer and an AC volt meter to
Pin 2.
3) Input a sine wave (1 kHz) to Pin 1 and elevate the voltage
from 0 V gradually until the distortion gets to 0.1% at Pin
2.
4) When the distortion amounts to 0.1%, stop elevating and
measure the AC level of Pin 2.
This value is the maximum input level of Ach.
5) Next, connect Pin 4 to the GND, or low level.
6) Input the same sine wave to Pin 3.
7) Measure in the same way.
This value is the maximum input level of Bch.
VOLTAGE GAIN (FIGURE 5)
This is the output level against input level.
1) Pin 4 is in the open condition, or high level.
2) Connect AC volt meters to Pin 1 and Pin 3.
(Using the same type meter is best)
3) Input sine wave (1 kHz) to Pin 1 (f = optional up to max.
20 kHz, 1 Vrms).
4) Measure the level of Pin 1 and name this V1.
5) Measure the level of Pin 2 and name this V2.
Figure 6
Page 4 June 1999 TOKO, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...