Page 1

TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
8
VOL
REMT
OUT
IN/
BRG
OUT
AMP
PRE
IN
AMP
PWR
OUT
AUX
MUTE
MUTE
GND
60W
60Hz
120V
COM
DIRECT
25V
70V
UNSWITCHED AC 120V 60Hz
MAX 500W 4A
AC
PROTECT
POWER
PEAK
NORMAL
SIGNAL
MASTER
OFF
TONE DEFEAT
TREBLE
BASS
INPUT 8
INPUT 7
INPUT 6
INPUT 5
INPUT 4
INPUT 3
INPUT 2
INPUT 1
ON
OFF
LOW CUT
OFFONON
PROGRAM
10
MIC
0
TEL
10
10
AUX
10
MODULE
SIGNAL
POWER
ON
OFF
PEAK
HOT
COM
120V 60Hz
120V 50Hz
UNSWITCHED
150W
MAX 500W
CLASS 2 WIRING
PROGRAM
OUTPUT 120W
COM
OUTLET
4A
BREAKER
COM
70V
25V
OUTPUT 1W
RESET
PUSH
HOT
TEL
COM
10
NC
RESET
MUTE
COM
MOH
600
MIC
COM
UNIT
4A
BREAKER
HOT
PUSH
OUTPUT 1W
SENSE
BASS
10
AUX
PREAMP
10
MOH
OUT
MUTE
TREBLE
POWER
IN
MODULE
PAGE
BGM
COM
HOT
INPUT LEVEL
LOW CUT
-20dBV
OFF
ON
INPUT
DC FUSE
DC FUSE
250V 8A
250V 8A
250V 7A
AC FUSE
S.
LISTED
COMMERCIAL
AUDIO EQUIP.
111J
OU
0dBV
NOR
PO
OFF
ON
OUT
IN/
BRG
OUT
AMP
PRE
IN
AMP
PWR
OUTPUT 1W
BASS
10
AUX
PREAMP
MOH
OUT
MUTE
TREBLE
POWER
IN
MODULE
PAGE
BGM
8
VOL
REMT
MUTE
MUTE
GND
60W
60Hz
120V
COM
DIRECT
25V
70V
UNSWITCHED AC 120V 60Hz
MAX 500W 4A
AC
120V 60Hz
MAX 500W
UNSWITCHED
120V 50Hz
150W
DIRECT
4õ 8
MIC
0
UNSWITCHED AC 120V 60Hz
MAX 500W 4A
70V
25V
õ
COM
120V
AC
60Hz
60W
UNIT
BREAKER
4A
PROGRAM
G COM
OUTPUT 120W
COM
4õ
TEL
PUSH
RESET
HOT
25V
CLASS 2 WIRING
NORMAL
INPUT 5
SIGNAL
INPUT 4
LOW CUT
ONONOFF
OFF
POWER
PEAK
ON
OFF
BGM
INPUT 3
TONE DEFEAT
MODULE
0 10
MUTE
MODULE
A0B
PAGE
TREBLE
AUX
- +
PREAMP
POWER
OUT
IN
MOH
10
0
10
4A
G
600
MIC
COM
MOH
COM
õ G
INPUT 2
TREBLE
AUX
10100
SENSE
PUSH
RESET
0
10
BASS
NC
HOT
0
- +
MUTE
OUTPUT 1W
0
INPUT 1
BASS
REMT
VOL
MUTE
1
MUTE
2
GND
PROGRAM
0 10
OUTLET
BREAKER
TEL
HOT
G
COM
OUTPUT 1W
COM
70V
8õ
INPUT 6
INPUT 7
INPUT 8
PWR
AMP
IN
PRE
AMP
OUT
BRG
IN/
OUT
SIGNAL
MASTER
PROTECT
AUX
OUT
PWR
AMP
IN
PRE
AMP
OUT
BRG
IN/
OUT
PEAK
POWER
ON
OFF
POWER
IN
BGM
DC FUSE
250V 8A
DIRECT
4õ 8
UNSWITCHED AC 120V 60Hz
MAX 500W 4A
70V
25V
õ
COM
120V
AC
60Hz
60W
DC FUSE
250V 8A
AC FUSE
250V 7A
MUTE
10
0
A0B
BASS
TREBLE
0
- +
- +
OUTPUT 1W
MOH
PREAMP
OUT
MODULE
PAGE
AUX
R
LISTED
COMMERCIAL
AUDIO EQUIP.
111J
REMT
VOL
MUTE
1
MUTE
2
GND
LOW CUT
INPUT LEVEL
ON
OFF
0dBV
-20dBV
INPUT
HOT
COM
Guide
Page 2

TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Page 3

Table of Contents
Introduction............................................................................................................................................................................1
Chapter 1: Selecting An Amplifier......................................................................................................................2
Sound Sources..........................................................................................................................................2
Speaker Requirements........................................................................................................................2
System Function......................................................................................................................................2
Chapter 2: Amplifier Basics......................................................................................................................................4
Signal Flow..................................................................................................................................................4
Audio Levels...............................................................................................................................................8
Impedance................................................................................................................................................10
Chapter 3: Amplifier/Speaker Matching.....................................................................................................11
Low Impedance Systems................................................................................................................11
High Impedance (70.7/25 Volt) Distributed Line Systems.....................................12
How to Design a High Impedance Distributed System...........................................13
Chapter 4: Wiring..........................................................................................................................................................14
Low Level and Line Level Wiring..............................................................................................14
Twisted Pair Wiring..............................................................................................................15
Shielded and Unshielded Cable.................................................................................15
Balanced and Unbalanced Lines...............................................................................15
Transformer Isolation.........................................................................................................16
Speaker Level Wiring.........................................................................................................................16
Minimizing Line Loss..........................................................................................................16
Troubleshooting Guide...............................................................................................................................................17
Load T roubleshooting......................................................................................................................17
Power Tap to Impedance Conversion Chart....................................................................17
TOA Amplifier Overview............................................................................................................................................18
TOA Amplifier Comparison Chart...............................................................................................................21-22
Appendix A: Wire Size Charts.............................................................................................................................A-1
Appendix B: Power Consumption & Thermal Dissipation...........................................................A-2
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Page 4

TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Welcome to the TOA Amplifier Guide!
TOA has been pro viding complete sound systems sinc e 1934. After our first U.S.sales office was established in 1974, our TA-900 Series mixer/amplifiers quickly gained recognition for their unmatched
combination of flexibility,reliability,and performance. Since that time,T O A has steadily expanded and
improved our line of amplifiers,mixer/amplifiers,and associated electronics. The TOA 900 Series,now
in its 3rd generation of product design,is renowned for its flexible modular architechture ,elegant simplicity of operation,and bulletproof reliability. The new BG-M Series builds further on our tradition by
offering the flexibility of a module port in a package that is remarkably affordable without sacrificing
either performance or reliability. With six distinct series of amplifiers and mixer/amplifiers to choose
from,plus a range of mixers,signal processors,and now network audio,TOA offers the most comprehensive line of audio electronics for systems contractors.
The TOA Amplifier Guide is a sound system design tool aimed at helping system designers,sales staff,
installers and end users select the right amplifiers and accessories for their applications. I t includes a
review of the basic concepts of audio amplification,such as signal flow,levels,and impedance,plus
useful references such as thermal dissipation,power consumption and line loss charts,as well as tips
for troubleshooting (including impedance measurement). Further information on speaker system
design and speaker selection and placement may be found in the TOA Speaker Guide,available for
download at www.toaelectronics.com.
Disclaimer: This design guide does not cover all of the general concepts underlying sound system design
and installation, which would require several hundred pages. This guide is not meant to replace the participation of an experienced consultant or engineer.
References: For more in-depth coverage of sound system design principles,we recommend the following two excellent books:
Sound System Engineering, S econd Edition, Don & Carolyn Davis, 1975, 1987 by Howard Sams & Co.
ISBN:0-672-21857-7
Handbook for Sound Engineers:Third Edition,Glen Ballou,Editor,2001,Butterworth & Heinemann. ISBN:
0-240-80454-6
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Steve Mate,Lucas Marciniak,and Martin Gonzalez in the TOA Product Support Group for
their invaluable support and contributions to this project,and to Geraldine Vargas for designing the
layout. This guide is dedicated to the memory of my late father,whose amp-building projec ts on the
kitchen table gave me a love for the smell of solder,and whose demonstrations of loudspeaker sensitivity gave me a love for the art of sound system design.
David Menasco
Product Application Specialist
TOA Electronics,Inc.
1
Page 5

2
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Chapter 1: Selecting An Amplifier
Amplifiers are the heart of any sound system. In addition to providing the audio power for a system,
amplifiers may also incorporate the input mixing and control functions vital to a system’s operation
(such an amp is called a mixer/amplifier). Selecting the right amplifier or mixer/amplifier for a job
means choosing a set of features and characteristics suited to meet the customer’s needs. The main
characteristics of an amplifier or mixer/amplifier include:The number and type of input channels,the
number of busses (signal paths) and output channels,and the amount of output power per channel.
Dimensions,weight and other basic parameters may also be important,depending on the installation.
Features needed for a job may include: Auto-muting (e.g.voice-over-music),remote volume control,
transformer-isolated inputs/outputs, phantom power, bass/treble controls, multi-level muting, rack
mounting,equalization,or any of a number of other special purpose features.
When selecting an amplifier,there are three key questions to consider:
1. What sound sources will be used?
2. What speakers will it be driving?
3. How does the client or end user need the system to operate?
Answers to these questions will dictate what characteristics and features are needed. Below is a more
detailed look at each question.
Sound Sources
One of the first questions you will need to answer,at least in general, is what sound sources will be
used in the system. Will the system be used with microphones? A CD player? A telephone exchange?
Due to standardization,many sources can be treated similarly — for example,CD and DVD players,
VCRs and computer sound cards all provide unbalanced line level outputs,usually with a similar output level,and thus may be treated the same in the design phase. But it is still important to know how
many such sources you will have,and what other sources may also be used.
Speaker Requirements
Two more key questions when selecting an amplifier is how much power is needed,and what kind of
load (impedance) the speakers will present — and here,the answers will depend on the type of speakers used. It is usually preferable to select the speakers,or at least the general type of speak ers,before
selecting the amplifier. Please refer to the TOA Speaker Guide for information on selection and placement of speakers. Once the type of speakers has been determined,it will be possible to choose an
amplifier with adequate power and an appropriate output impedance. See Chapter 3
“Amplifier/Speaker Matching”for discussions of impedance,power levels,and 70.7V/25V line operation.
System Function
The paramount rule of sound system design is almost too obvious,and yet it is all too often overlooked: it is important to let the system design be guided by the needs of the client or end user,and
the function they need the system to fill. For example,if they need the mic to automatically mute the
music,you will need a mixer/amplifier that includes this feature. O ften,the user won’t be very
Page 6
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
3
specific until after the system is installed and they try to make it work. The designer’s job includes asking enough questions in the beginning to make sure the design will meet the client’s needs. As a
start, imagine yourself in the place of your client, using the system, and asking questions such as
“where will this go?”and “how will this work?” Experience helps a lot in this process,but installers and
designers of all levels of experience can save time and headaches by asking some basic questions at
the outset.
Visit us at
www.toaelectronics.com
to download the
TOA Speaker Design Guide!
Page 7
4
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Chapter 2: Amplifier Basics
Important Concepts: Signal Flow, Level and Impedance
When designing and installing sound systems,mastery of some key concepts helps a great deal. A
basic understanding of signal flow,levels,and impedance can increase your efficiency on the job,and
dramatically reduce the number of costly call-backs.
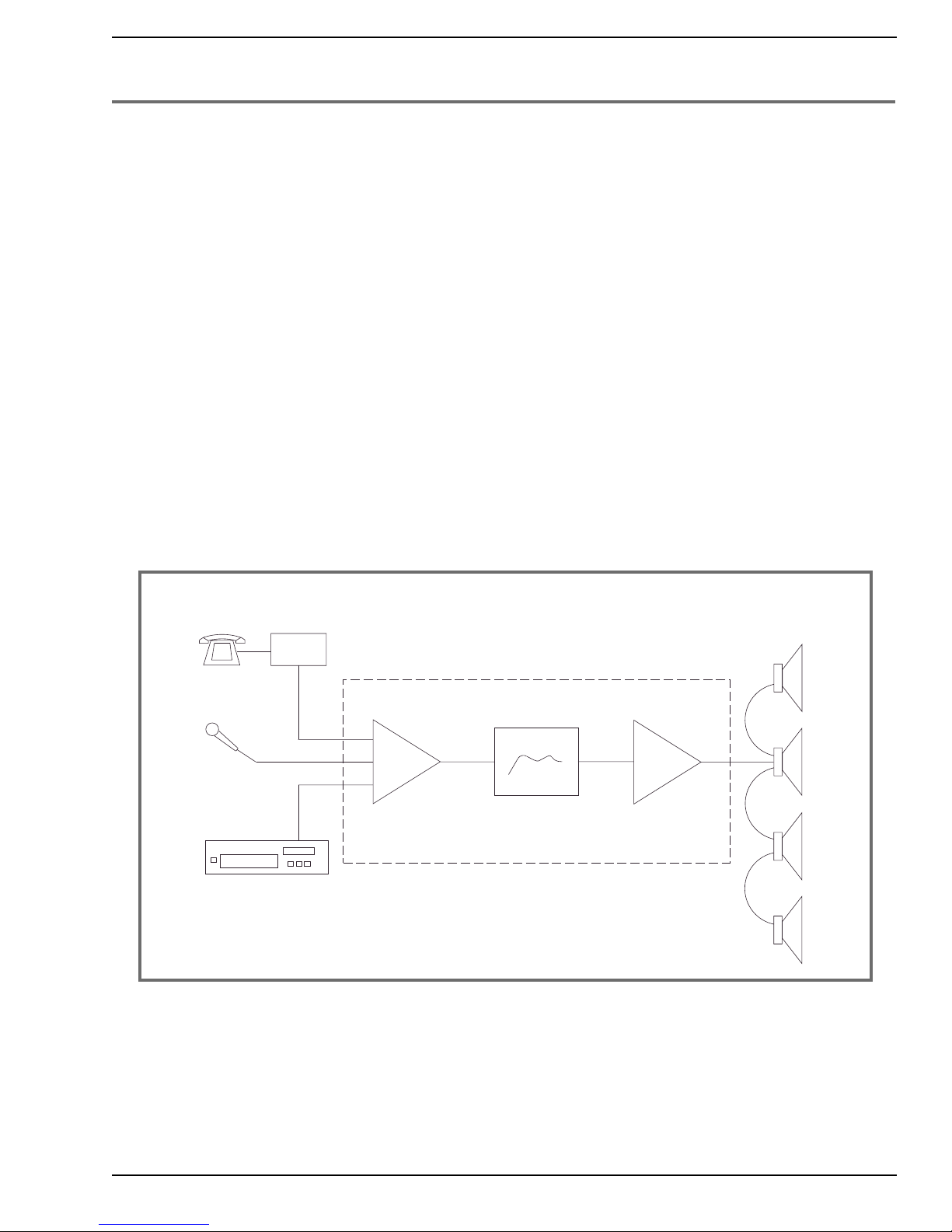
Signal Flow: The Audio Chain
Signal Flow refers to the path of the sound from the source (page announcement,CD player,satellite
receiver,etc.) to the listener. This path can be very simple,using just a single source,a power amplifier,and one or more speakers,or it can be complex,having multiple sources,multiple paths,and multiple destinations,with extra processing stages. A typical paging system signal path will begin with
two or three sources — for example,background music,paging audio from the phone system,and a
microphone (see fig.1). These will be fed into a mixer ,which combines the sources into one single line .
The mixer output may be fed into an equaliz er,compressor or other processor,or directly to an amplifier. The amplifier increases the power of the signal and feeds it to the speakers. In most smaller systems, the mixer and amplifier sections are integrated in one unit, which may include a built-in or
optional processing stage,such as an equalizing module for premium spe ak ers.
Figure 1: Basic System for Paging and Background Music
Sources
PBX
Phone System
Microphone
Mixer
Music Source
Mixer/Amplifier
Σ
Processor
(optional)
Speakers
Amplifier
Page 8
5
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
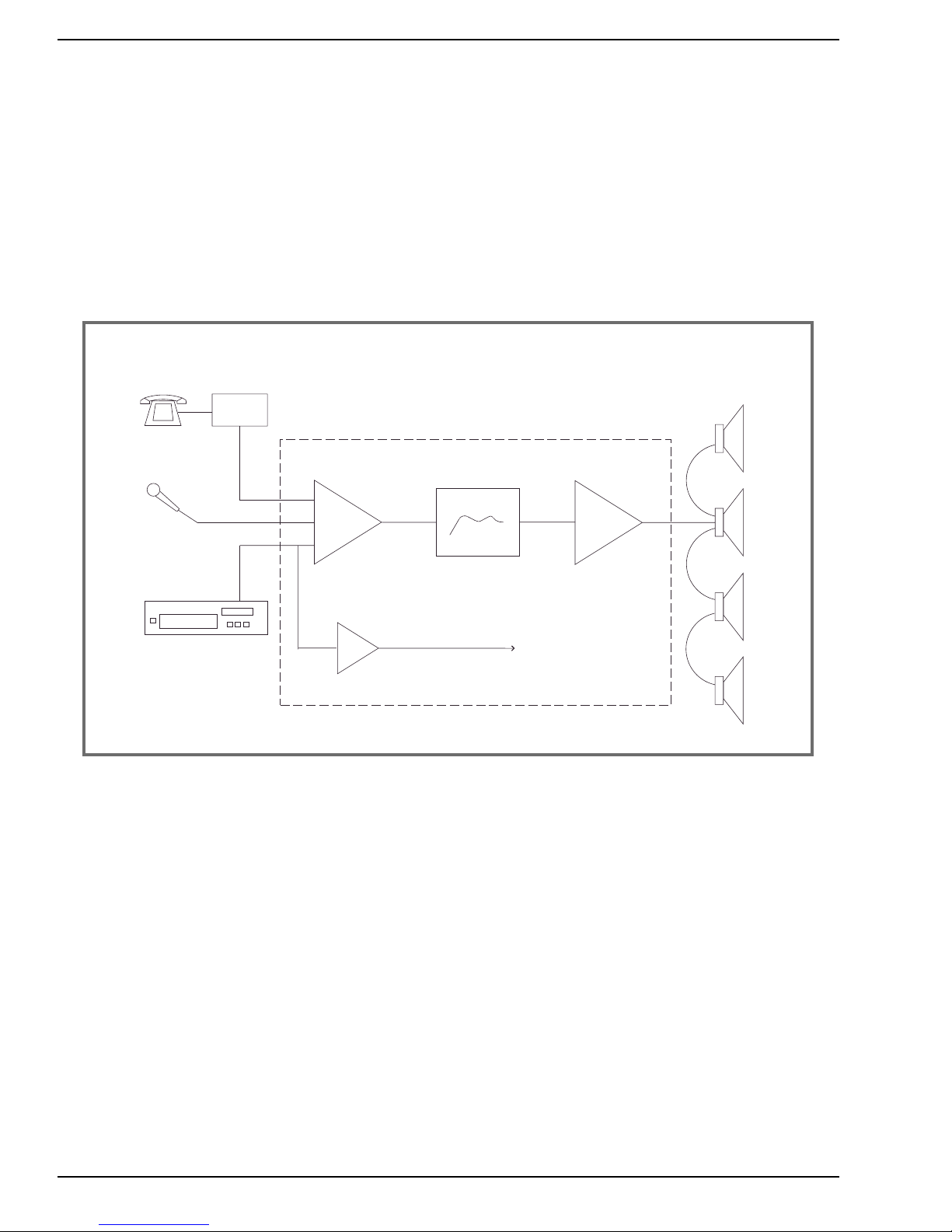
Figure 2: Basic System Plus Music-On-Hold Output
More complex systems include all these same stages — sources,mixing ,processing ,amplification,and
speakers — but may add additional signal paths (called busses) so that some sources or listening
areas can be treated differently. A common addition to the typical paging system is the Music On
Hold (MOH) output bus. This bus is fed from the music input,and not affected by speaker processing
modules or by mute functions used for the overhead paging (see fig.2).TOA 900 Series amplifiers can
provide an MOH output using the T-12S module, which provides for both the music input and the
MOH output. This module also works with the 900 Series mute bus to allow for muting of the music
during paging announcements to the main output,while the separate MOH output is not muted and
receives no page announcement. TOA BG and BG-M Series amplifiers include MOH outputs as standard features.
Zone paging and multimedia systems can use additional signal paths to route sounds to different
areas (see figs.3 and 4). Figure 3 shows a typical 3-zone paging system for central mic and/or telephone paging with background music. Simple contac t closures, provided by the phone system or
contractor, are used to activate the zones in any desired combination, simultaneously muting the
background music in each activated zone. TOA BG-M Series amplifiers offer an especially economical
solution for this type of zone paging system. The background music may be from sources local to
each zone or distributed from the head-end via the MOH output.
In multimedia applications, multiple signal paths can be used to route speech and music or movie
sound to different speakers,allowing precise matching of speaker type for the intended application.
Figure 4 shows a multimedia system for a lecture hall,training room, or multi-media-ready meeting
room. This system provides for stereo playback of music sources and stereo sound for video,using a
pair of speakers which may be located flanking a fixed or retractable screen, alongside distributed
mono speech. The resulting system can provide powerful and moving reproduction of music and
movie soundtracks and clear, intelligible speech. An optional subwoofer for the music feed further
enhances the impact.
Sources
PBX
Phone System
Microphone
Mixer
Music Source
Mixer/Amplifier Speakers
Σ
Processor
(optional)
to Phone System
Music on Hold input
Amplifier
Page 9
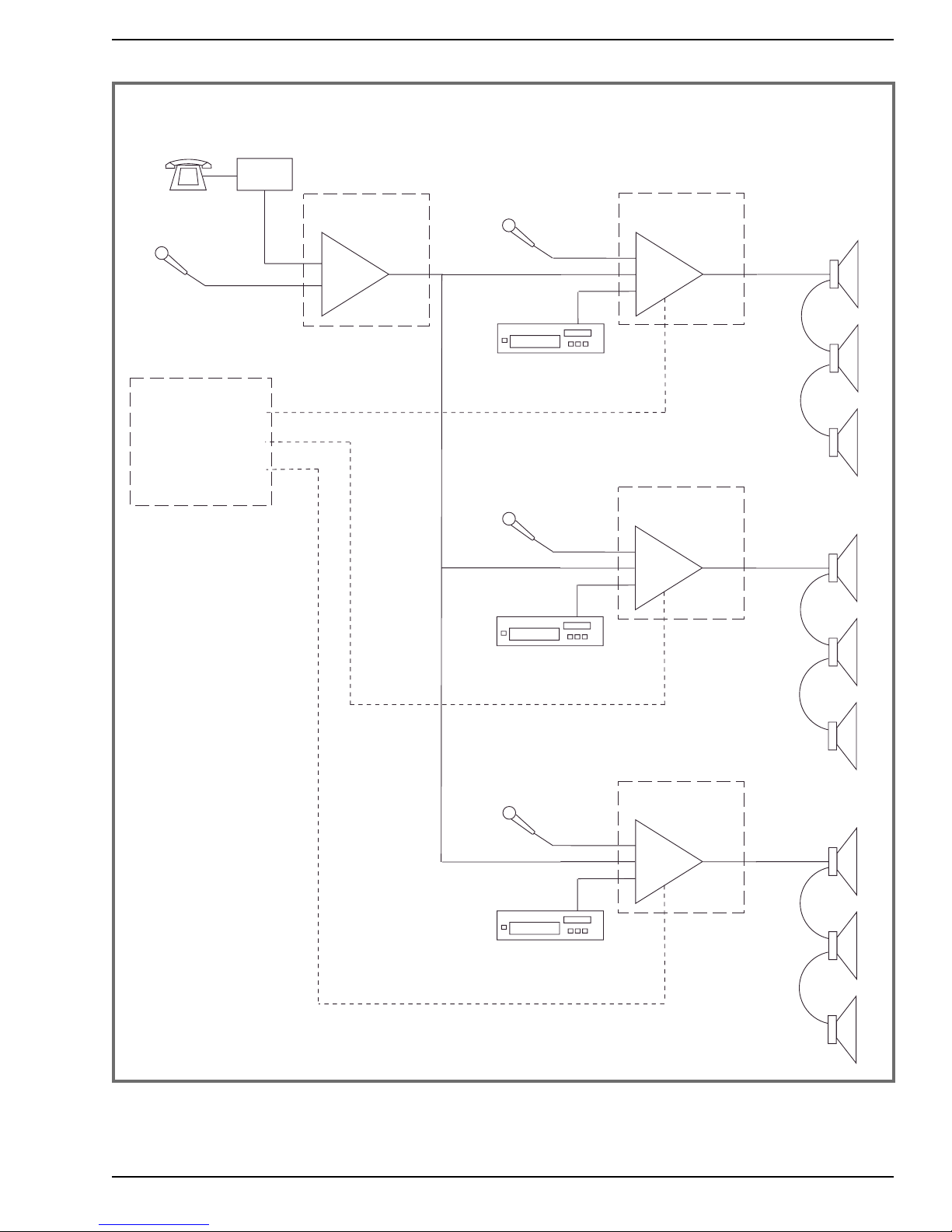
Figure 3: Three-Zone Paging System
6
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Sources
Phone System
Microphone
Dry Contact
Closures
(one pair
per zone)
PBX
BG-M Series
Mixer/Amplifier
Σ
Microphone
To 'Tel' Input
Music Source
Microphone
Local
Local
Speakers
Zone 1
BG-M Series
Mixer/Amplifier
Σ
Mute
Zone 2
BG-M Series
Mixer/Amplifier
To 'Tel' Input
Music Source
Microphone
To 'Tel' Input
Music Source
Local
Σ
Mute
Zone 3
BG-M Series
Mixer/Amplifier
Σ
Mute
Page 10

7
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Figure 4: Multimedia System
Sources
Podium
Microphone
Wireless
Microphone
CD/DVD Player
VHS Player
Mixer/Amplifier
Σ
Σ
Σ
Σ
Speakers
IP-300D
Amplifier
P-924MK2
Amplifier
Audio Cassette
Computer Audio
D-901 Mixer/Processor
P-912MK2
Amplifier
P-906MK2
Amplifier
Page 11

8
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Audio Levels: Voltage, Gain and the Decibel
A basic characteristic of any audio signal is its amplitude,measured electrically in terms of voltage or
acoustically in terms of sound pressure. When assessing the loudness of a signal, the amplitude or
pressure is converted to a decibel value . The decibel scale gives a relative number referenced to a certain voltage or pressure. For example,0 dBV is a popular standard reference for audio levels,and represents one volt. Note that amplitude is expressed as a voltage,while level (or loudness) is expressed
using a dB scale.
When working with audio electronics, levels are commonly divided into three ranges: mic level, line level,
and speaker level. Mic level is the smallest signal.
Microphones and other passive transducers (devices
that convert energy from one form, such as sound, to
another, such as electricity) produce signals ranging
from a few microvolts to a few millivolts. A typical nominal operating level for a microphone output would be
–55 dBV. Line level is hundreds of times greater in voltage terms — typically ranging from several millivolts up
to around 1 volt,with a nominal level of 0 dBV. Speaker
level is the strongest, ranging from a fraction of a volt
(during quiet periods) to several dozen volts depending
on the output rating of the amplifier. Of course,sound
is very dynamic in nature, so whatever the nominal
operating level of your signal is, if you read it with a
meter during operation,you are likely to see large fluctuations from moment to moment within that range.
An important function of amplifiers is providing the
“ gain ”needed to raise signals from mic or line level up to
speaker level. Gain is another word for amplification,
and simply means an increase of the voltage or power.
The opposite of gain is attenuation. Both gain and
attenuation are commonly measured in decibels.
The dBV scale is not the only one used for audio levels.
Another popular reference scale is the dBu,where 0 dBu
represents 0.775 volts. The historical predecessor to
these two scales is the original dBm scale,where 0 dBm
represents one milliwatt, or 0.001 watts. Other scales
you might encounter include dBW (referenced to one
watt) and dBµV (referenced to one microvolt). These
scales are seen mostly in the radio broadcast industry.
Care should be taken not to confuse one scale with
another,especially the common dBV and dBu scales. To
make things especially aggravating,the term for dBu was previously dBv — with a lower-case “v”;so
if you encounter dBv on an old spec sheet,it means dBu,not dBV.
What is RMS Power?
An audio signal is defined by its amplitude
(loudness) and frequency (pitch). When the
sound is represented as a waveform,the amplitude is the vertical dimension, while the frequency is the number of up and down cycles of
the wave per second, with seconds running
from left to right.
Amplifier power ratings are based on the
amplitude of the waveform. Since the peak levels
of a complex waveform (one containing many
frequencies) may occur rarely or frequently, an
averaged value is used, based on the “root
mean square” or RMS method. In this method,
the amplitude is squared (so that all values are
positive), then the resulting values are averaged, and the square root of this average is the
RMS value. For simple sine wave test signals,
the RMS voltage will be 0.707 times the peak
voltage. After calculating RMS voltage, the
RMS power is calculated by squaring the voltage and dividing by the load resistance.
Amplitude
Time
Peak
RMS
Peak
to
Peak
Page 12

Figure 5 shows a simplified block diagram and a level diagram,indicating gain stages inside a mixeramplifier, from mic and line level inputs to 70.7 volt speaker level output. The signal is amplified in
stages,with attenuators (volume controls) between each stage to reduce the o v erall gain when needed .
The mic pre-amp provides 32 to 52 dB of gain,bringing the mic level signal up to a level that can be
matched with other line level sources. The summing amplifier provides additional gain, bringing all
sources up to 0 dBV. The power amplifier serves to boost the power up to a level that can drive a
speaker. It also provides a low output impedance for efficient power transfer. Lastly,the output transformer matches the amplifier to the 70.7 volt line and increases drive v oltage to a maximum rated output of +37 dBV.
9
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Figure 5: Block Diagram and Level Diagram of Mixer/Amplifier
Phone System
Microphone
+40
+20
0 dBV
-20
-40
-60
PBX
B-series
Input Module
M-series
Input Module
B-series Line Input
-18 dBV
M-series Mic Input
-72 dBV to -52 dBV
Matching
Transformer
Mic
Preamp
Gain
Mix Bus
-20 dBV
Input
Level
Bridge
In/
Out
Σ
Summing
Amplifier
Master
Level
A-900MK2 series
Mixer/Amplifier
Pre-Amp
Output
PreAmp
Out
0 dBV
Link
Power
Amp
In
Power
Amplifier
Transformer
Power Amp
70 Volt Output
+37 dBV
Page 13

Impedance
Impedance refers to the way a device reacts to the application of electric current. The device will
exhibit varying amounts of resistance and either capacitance or inductance. For our purposes, the
resistance is most important. In keeping with common practice,when we say “impedance” we will
mean resistance.
Impedance,in this sense,refers to how much resistance
the device presents to the free flow of electricity
through it. At a given drive voltage, the lower the
impedance of the receiving device, the higher will be
the current flow through it. This is impor tant to know
when working with amplifiers, because if the load
impedance presented by the speakers is too low,it may
draw so much current that the amplifier will overwork
itself and deliver distorted sound,overheat — perhaps
even burn out.
Impedance is measured in ohms, named for Georg
Ohm, who first described the set of electrical relationships now known as Ohm’s Law (see fig.6). Every device
will have both an input impedance (also called the load
impedance) and an output impedance (also called the
source impedance). The input impedance of an amplifier
could range from 600 ohms to 10,000 ohms, or even
higher (see side bar). A typical speaker impedance may range from 4 to 16 ohms.
10
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Figure 6
Impedance “Matching”
A common point of confusion is the concept of
“impedance matching.” Transmission line theory
states that the load impedance and source
impedance should be equal, to avoid reflections in the line. But this requirement holds
only when the line is longer than the shortest
wavelength of the signal. For audio frequencies,the line would need to be over 9 miles long
for transmission line theory to apply. When
using solid-state equipment and typical cable
runs of several hundred feet or less, the best
performance is obtained when the load impedance is about 5 to 20 times greater than the
source impedance. So, for example, a 10,000
ohm input is a good “match”for a 600 ohm output.
W x R
R = Resistance in Ohms
W = Power in Watts
V = Electromotive Force in Volts
I = Current in Amperes
2
V
W
W
2
I
V
I
W
I
R =
I x R
W =
I =V =
2
V
R
I2 x R
V x I
V
R
W
V
W
R
Ohm's Law
Page 14

11
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Chapter 3: Amplifier/Speaker Matching
Interfacing between the amplifier and speakers is commonly done in one of two ways. Small systems
with one or two speakers will typically use a direct connection between the speakers and the amp.
This is sometimes called low impedance operation,because the load impedance ranges from 4 to 16
ohms nominal. Systems with more than 2 speakers usually use transformers at the amp and at each
speaker to simplify impedance matching and reduce line loss. These systems are commonly called
distributed line systems,70.7 volt (or 25 volt) systems,or constant voltage systems. In both cases,speakers
should be wired in parallel (plus to plus and minus to minus).
Low Impedance Systems
When matching amplifiers with speakers,there are a couple of important rules to remember. First,low
impedance amplifier outputs are described in terms of the recommended load impedance,i.e.“4 ohm
output”or “8 ohm output”(the actual source impedance of a power amplifier output is seldom specified but is typically less than one ohm). Second: With rare exceptions, when using more than one
speaker,the speakers should be wired in parallel.
Parallel wiring always results in a lo wer load impedance than the individual rating of each speaker. For
example, two 8 ohm speakers in parallel results in a 4 ohm load. Two 16 ohm speakers in parallel
results in an 8 ohm load. The general-purpose equation for calculating the load of multiple speakers
in parallel is shown in Figure 7. But as the above two examples illustrate,you will find that when all
the speakers have the same impedance, the total load will be equal to the rated impedance divided by
the number of speakers.
A commercial-grade speaker without any transformer may have a rated nominal impedance anywhere from 4 ohms to 16 ohms. The most common ratings are 4 ohms,8 ohms or 16 ohms. The most
common recommended load ratings for low impedance amplifier outputs are 4 ohms and 8 ohms.
This means that in most cases,you will be limited to one or two speakers per amp channel when connecting low impedance speakers in parallel.
Figure 7
+
Total Load
+
-
-
Speaker 1
+
-
Speaker 2
+
-
Speaker 3
Total Impedance =
Calculating Speaker Impedance
1
1
R
1
+
R
1
1
+
2
+
R
. . .
3
Page 15

12
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
High Impedance (70.7 Volt / 25 Volt) Distributed Line Systems
In order to overcome the limitations of low impedance speaker systems,most medium-scale installed
sound systems in the United States use either 70.7 volt or 25 volt distributed line systems,also kno wn
as high impedance or constant voltage systems. Often,they will be called simply “70 volt”or “25 volt”
systems.
These systems work by including transformers at the input to each speaker and directly after the
amplifier output (see fig.8). The transformers are used to convert the impedance of each speaker to
a higher value,and to convert the amplifier output impedance to a correspondingly high value. In a
70 volt line system, speaker impedances (with transformers) may range from below 20 ohms to as
high as 10,000 ohms or more. But you won’t need to calculate the load impedance in ohms,because
of how the high impedance approach works.
High impedance (70.7 volt and 25 volt line) systems have three major advantages over low-impedance
systems:
1) System impedance-matching is made much easier — it is simply a matter of adding up speaker
power taps and selecting an amplifier rated for at least that much power plus an allowance for
headroom.
2) Line loss is greatly reduced,especially over long cable runs,resulting in better performance and
reduced cost compared to long low impedance lines.
3) The amplifier output is electrically isolated from the speaker line by the output transformer,pro-
tecting the output stage against a grounded line and thus eliminating a potential source of system failure.
Figure 8: High Impedance Distributed System
Amplifier
Transformer
8 ohms
Step-up
70 volt line
(high impedance)
Step-down
Transformers
8 ohms
8 ohms
8 ohms
8 ohms
Speakers
Page 16

13
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
How To Design A High Impedance Distributed System
In designing a high impedance speaker system, there is no need to calculate the total impedance
from the speaker impedance values,the way you would for a low impedance system. This is because
in high impedance systems (i.e. 70.7 volt and 25 volt line systems), the load impedance rating is
expressed in terms of the amount of power that would be delivered t o it at the rat ed line v oltage . The
rating is given in W atts ,which can simply be added to the other speakers to get the total pow er drawn
by the load. Just add a little extra for headroom (see example below),and you know how much power
is needed. You don’t even have to know Ohm’s Law.
Here’s the process in more detail: You should begin by choosing the type of speakers,how many,and
how much power each one will need in order to reach the desired volume in the listening area.Help
with this can be found in the TOA Speaker Guide. Once you know the type(s) of speaker(s) and how
much power each one will need,determine what is the lowest available transformer tap that will supply at least that much power to the speaker. For example, the SC-615T has 70.7 volt transformer taps at
15, 7.5 and 3.8 watts. To reach your desired level (maximum average level plus headroom for short-term
peaks), you decide you’ll need at least 5 watts at the speaker. In this case, choose the 7.5 watt power tap.
When you have selected the proper power tap f or each speaker,simply add them up and multiply the
total times 1.25. Your amplifier should have at least this much power into the selected line voltage.
For example, the job requires twelve SC-615T horns, each tapped at 7.5 watts, to cover the listening area.
Twelve times 7.5 watts = 90 watts, and 90 watts times 1.25 = 112.5 watts. Your amplifier should have at
least this much power.
Visit us at
www.toaelectronics.com
to download specification sheets,
manuals, CAD data and more!
Page 17

14
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Chapter 4: Wiring
The “audio chain”analogy is an especially good one when talking about wiring. Lik e a chain,a sound
system is only as good as its weakest link. The kinds of cables used and how they are connected can
often be the difference between a great system and a useless one. Most experienced audio professionals can tell stories about contractors who have saved a few pennies on installation and wiring
costs,only to spend costly hours back on site correcting noise or other problems later.
The kind of wire to use will vary depending on the kind of signal it will be carrying,as well as the environment it will be used in. For most commercial installations,wiring will be “jacketed,”meaning that
the insulated conductors will be bundled together, often in twisted pairs, inside an overall jacket for
extra protection.
Low level and Line Level Wiring: Twisting, Shielding, Balancing and Isolating
One of the challenges in sound engineering is to avoid the introduction of unwanted electrical noise
and interference into the system. Unwanted noises enter the system in one (or both) of two ways:
Induced noises can come into the system from sources that are not directly connected,much as radio
waves can be picked up at a distance. In fact,radio waves are one of the main sources of induc ed noise
(this type of noise is called radio frequency interference,or RFI). Induced noises may also be the result
of inductance or capacitance between cable conductors and other conductors nearby (often called
electro-magnetic interference or EMI,andelectro-static interference). Common sources of induced noise
include electric motors,radio transmitters,some t ypes of lighting equipment,digital circuits,all kinds
of power supplies. Indeed,in microphone applications,if you use the wrong cable ,then just about any
circuit where AC current is flowing could be a source of induced noise. The good news is most
induced noises are easy to control by choosing the right type of cable and input/output circuit.
Ground loops come from ground reference mis-matches,which are a function of the power source(s)
used for the sound system. If a mixer/amplifier is plugged into one AC outlet,and the input signal
comes from a source that is plugged into a different outlet elsewhere in the building ,the ground wires
at the two outlets might have slightly different voltage potentials with respect to ground (and more
importantly,with respect to each other). If the signal ground is tied to the AC mains ground,as is commonly the case in unbalanced audio circuits,then connecting the audio cables from the source to the
mixer/amplifier will complete a circuit through which will flow a voltage equal to the potential difference between the two AC mains grounding points. This circuit is called a ground loop. The main
symptom of a ground loop will be a 60 Hz hum in the sound system,often with harmonics above this
at multiples of 60 Hz. There are three ways to alleviate ground loops,or avoid them altogether:
1) Use the same AC outlet for all equipment in the system. This may be impractical, if distances are
great,or even inappropriate if the current draw exceeds the rating of the AC circuit.
2) Use transformer isolation between sound system components (see page 16).
3) Use a “floating”balanced line for the audio signal, so that neither leg of the signal is tied to ground
(see page 16). Often,methods 2 and 3 are combined with the use of transformer-balanced inputs
and outputs.
Page 18

15
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
The two most popular methods to reduce the pickup of induced noises through sound system wiring
are the use of twisted pair wiring,and the use of shielded cable.
Twisted Pair Wiring
Twisted pair wiring is just what it sounds like: two insulated conductors are twisted around each other
over the length of the cable run. The twisting has the effect of rejecting certain t ypes of induced
noise,since each half-turn of the wire exposes it to the noise source with the opposite polarity of the
preceding half-turn. The effect also works in reverse:t wisted pairs generate less noise than pairs run
in “flat,”untwisted wire. This fact helps to reduce the effect of “crosstalk”between pairs when multiple lines carrying similar signals are bundled together. Twisted pairs have been used by telephone
companies for the better part of a century to carry voice communications,and are now the standard
type of cable for Ethernet networking and other data transmission protocols (for example, CAT 5
wiring is simply a set of twisted pairs).
In sound systems,twisted pairs are often used for speaker wiring,especially over longer distance runs.
For other sound system applications,twisted pair wiring is seldom used, except in conjunction with
shielding and balancing (see Balanced and Unbalanced Lines,below). So,while CAT 5 may be the cat’s
meow in data networking, you don’t want to use it for your microphone wiring, or you risk serious
noise problems.
Shielded and Unshielded Cable
Shielded cables are the most common,and a more effective,line of defense against noise pickup in
audio applications. They protect the signal path from noise pickup by surrounding one or more of the
cable’s conductors with another conductor (the shield) that is tied to ground at one or both ends of
the line. Shielded cables should always be used for microphone wiring. They should also be used for
all unbalanced line level wiring,such as the outputs of CD players,tape decks,or many other common
music sources. Standard stereo RCA patch cords are a common example of shielded wiring for unbalanced sources.
Balanced and Unbalanced Lines
The most effective defense against the pickup of induced noise through the wiring is to use a “balanced”circuit for the connection between equipment. This method involves not only using the right
cable,but also having a certain t ype of input and output circuit. In sound systems,balanced circuits,
or balanced lines, are typically run using three conductors — a twisted pair of inner conductors sur-
rounded by a shield conductor. Running a balanced line requires the use of balancing output and
input circuits, which work by splitting the signal into two paths, then inverting the polarit y of one
path,so that each conductor carries a signal that is the exact electrical opposite of the signal on the
other conductor. While the signal is carried by the two conductors in opposite polarity,the noises that
accumulate on the line will have the same polarity on both conductors. When the polarity of the
reversed “low side”conduc tor is reversed again at the receiving end,any noise picked up by the line
will be cancelled out. The combination of this balancing action with the use of shielded cable,and the
twisted inner pair makes this arrangement the best for protecting audio signals from noise pickup.
Page 19

16
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Balanced circuits also protect the system against noise from ground loops. This is because the signal
carried on the balanced pair represents a complete,“floating”or independent circuit, and is not connected to ground as a reference.
Transformer Isolation
Another way of protecting against ground loops is to use a transformer at one or both ends of the line.
The transformer works by converting the signal from electric energy into magnetic energy,then back
to electric energy. Since it is not a direct electrical connection,the transformer does not complete the
circuit that would create the ground loop. But it still passes the audio signal unchanged. Low-cost
transformers should be avoided ,since they can add distortion and limit frequency response. But good
quality transformers have a transparent audio quality and can give a high degree of assurance that
ground loops will not occur. In balanced applications, where the floating circuit already protects
against ground loops,the transformer adds protection against equipment failure that could occur if
one side of the audio pair were shorted to ground. Here again, because it is not a direct connection,
the transformer does not complete the circuit,and the output stage is protected. This is an important
benefit in high powered speaker applications.
Speaker Level Wiring
Noise pickup is not usually a problem for speaker cables,because the voltages used to drive speakers
are much greater than the voltage levels of induced noises. The main concerns for speaker wiring are
adequate durability for the installation environment, adequate spacing from mic- and line-level
wiring to avoid feed-back loops (do not put speaker and mic lines in same conduit),and adequate
wire size to minimize line loss.
Minimizing Line Loss
Line loss occurs in speaker wiring in two ways,both related to the resistance of the wire. First,the wire
will dissipate some of the power as heat. This power is wasted. Second,the wire will increase the total
line resistance,causing the line to draw less power from the amp. This power is not wasted,but is just
unused. Either way,it is best to keep line losses down to a minimum — preferably less than 1 dB.
One of the great benefits of 70.7 volt distributed line systems is that they are not affected by losses
due to speaker line resistance to the same degree that low impedance or 25 volt line systems are. In
most typical installations,if 18 gauge speaker wire is used,line loss will be less than 1 dB. If the total
speaker load on the line is greater than 120 watts,or if the cable runs exceed 200 feet,consider using
heavier gauge wire,as indicated in Appendix A,Table 1. Line losses are greater in 25 volt line systems.
Appendix A,Table 2 shows the wire size to use for a given load and distance on a 25 volt line. An 8
ohm load will be very susceptible to line losses when the cable length exceeds about 100 feet.
Page 20

17
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Troubleshooting Guide
Load Troubleshooting
Shorted speaker lines and mis-matched loads are among the most common causes of sound system
failure. Being attentive to the condition,configuration and installation of the speakers and wiring are
the first line of defense against these common problems. But alas,the best laid plans do sometimes
go awry,and when this happens,the installer/troubleshooter’s best friend is a speaker line impedance
meter such as the TOA ZM-104. Mastering this relatively simple measuring device can save hours of
valuable field service time per job when tracking down existing problems,and most impor tantly,can
help avoid call-backs by identifying mis-matched loads before the system is ever turned on.
When installing a system,it is prudent to check each branch line with the meter before bringing them
together at the amplifier’s output terminals. A final test of the impedance of the full load should be
made before connecting it to the amplifier. If the system is already in place and load problems are
suspected,the process is reversed: First, check the load at the amp. If the impedance is below the
amplifier’s rated impedance (or the effective power tap total is above the amplifier’s rated power output),then check each branch line to see which one (or more) has a lower impedance than it should.
Keep tracing this path,following the lowest impedance (or the impedance farthest below its expected value),until you find the culprit. This may be either an improperly tapped speaker/ transformer,a
speaker without a transformer,a shorted line,or even a shorted speaker voice coil or transformer.
Table 1: Power Tap to Impedance Conversion
Power Tap Impedance (Ohms)
(Watts) 25 V 70 V
0.25 2500 20000
0.5 1250 10000
1 625 5000
2 313 2500
3 208 1667
4 156 1250
5 125 1000
8 78 625
10 63 500
12 52 417
15 42 333
20 31 250
30 21 167
60 10 83
75 8 67
100 6 50
120 5 42
150 4 33
180 3.5 28
200 3.1 25
220 2.8 23
300 2.1 17
400 1.6 13
Page 21

A-706
A-712
A-724
60/120/240 WATT 9-CHANNEL MIXER/AMPLIFIERS
• Flexible mixer/amplifiers for sound reinforcement,paging and background/foreground music distribution
• Six switchable Mic/Line inputs,balanced,with mic trim and switchable 24 VDC phantom power
• Two auxiliary inputs,unbalanced,with dual-RCA jacks
• 900 series module slot accepts 900 series plug-in modules for custom system configurations
• 25 V, 70.7 V and 4 ohm speaker outputs
• Transformer isolation for telephone paging (Input #1)
• User configurable auto-mute function with sensitivity adjustment
• Five-segment LED power meter
• Remote master volume (via 10k ohm pot) and remote turn-on
• Insert jacks for connecting external signal processor
• Protection circuitry prevents potential damage from overloads,short-circuit and overheating
• Five year warranty
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
TOA Amplifier Overview
BG-1015
BG-1030
BG-1060
BG-1120
15/30/60/120 WATT 5-CHANNEL MIXER/AMPLIFIERS
• Compact,flexible mixer/amplifiers for paging,
background/foreground music distribution and
music/messaging-on-hold
• 900 series module slot with Page/BGM switch
accepts most 900 series plug-in modules for custom
system configurations
• 25 V, 70.7 V and 4 / 8 ohm speaker outputs
• Microphone page input,balanced,with 24 VDC
phantom power
• Telephone page input,balanced,transformerisolated with switchable 600/10k ohm input
impedance
• Program input,balanced,with screw terminal
connector
• Auxiliary input,unbalanced,with dual-RCA jacks
for convenient connection of stereo sources
• Music-on-hold (MOH) outputs,600 ohm balanced
0 dBV,and 8 ohm / 1 watt
• Selectable muting modes for versatile priority
paging configurations
• Insert jacks for connecting ex ternal signal processor
• Protection circuitry prevents potential damage
from overloads,short-circuit and overheating
• Five year warranty
BG-M Series
BG-115
BG-130
15/30 WATT 3-CHANNEL MIXER/AMPLIFIERS
• Compactmixer/amplifiers for paging,background/
foreground music distribution and music/messagingon-hold
• 25 V, 70.7 V and 4 / 8 ohm speaker outputs
• Microphone/telephone paging input (switchable),balanced,transformer-isolated,with switchable 600/10k ohm
input impedance
• Program (PGM) input,balanced,screw-terminal connector
• Auxiliary (AUX) input,stereo-summing dual-RCA jacks
• Music-on-hold (MOH) output adjustable from line-level
to 1 W at 8 ohms
• Auto-mute function allows voice-activated paging override of AUX/PGM without interrupting the MOH output
• Protection circuitry prevents potential damage from
overloads,short-circuit and over-heating
• Five year warranty
BG Series
18
700 Series
Page 22

19
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
A-901A
10 WATT 3-CHANNEL MIXER/AMPLIFIER
• Modular design allows fast and easy custom
configurations for unmatched flexibility
• Two module slots accept TOA plug-in modules
• Program input for unbalanced line-level source
• 25 V, 70.7 V and 4 / 8 ohm speaker outputs
• Muting function for priority paging over background music
• Bass and treble controls for program input
• Optional rack-mount kit,model MB-920 (2 RU)
• Five year warranty
M-900MK2
8-CHANNEL MODULAR MIXER
• Modular design allows fast and easy custom configurations for unmatched flexibility
• Eight module slots accept any combination of TOA
plug-in modules
• Balanced,transformer-isolated output with selectable
impedance,screw terminal connector and protective
cover plate
• Dual mute bus permits multiple levels of paging
priority using optional mute-type modules
• Remote master volume terminals for control with
an external 10k ohm linear-taper potentiometer
• Auxiliary output for connecting an external mixer or
recording device
• Bridging input/output for input expansion or system
combining
• Protection circuitry prevents potential damage from
overload,short-circuit or over-heating
• Five year warranty
A-903MK2
A-906MK2
A-912MK2
30/60/120 WATT 8-CHANNEL MIXER/AMPLIFIERS
• Modular design allows fast and easy custom
configurations for unmatched flexibility
• Eight module slots accept any combination of
TOA plug-in modules
• 25 V, 70.7 V and 4 / 8 ohm speaker outputs
• Dual mute bus permits multiple levels of paging
priority using optional mute-type modules
• Remote master volume terminals for control
with an external 10k ohm linear-taper potentiometer
• Low cut switch to limit low frequency response
• Auxiliary output for connecting an external
mixer or recording device
• Insert jacks for connecting external signal
processing
• Bridging input/output for input expansion or
system combining
• Protection circuitry prevents potential damage
from overload,short-circuit and over-heating
• Five year warranty
P-906MK2
P-912MK2
P-924MK2
60/120/240 WATT POWER AMPLIFIERS
• Modular single-channel power amplifiers
• Input module slot accepts most TOA plug-in modules
for custom system configurations
• 25 V, 70.7 V and 4 / 8 ohm speaker outputs
• Direct input for connecting an external mixer or other
source
• Selectable input sensitivity to accommodate high or low
input levels
• Low cut switch to limit low frequency response
• Protection circuitry prevents potential damage from
overload,short-circuit,or over-heating
• Five year warranty
900 Series
Page 23

W-906A
W-912A
60/120 WATT 6-CHANNEL IN-WALL MIXER/
AMPLIFIERS
• Modular design allows fast and easy custom
configurations for unmatched flexibility
• Six module slots accept TOA plug-in modules,
expandable to eight slots with optional kit,
model WE-2
• 25 V, 70.7 V and 4 / 8 ohm speaker outputs
• Flush or surface-mount with optional back
boxes
— BX-9F (flush-mount) and BX-9S
(surface-mount)
• One-octave nine band equalizer
• High and low pass filters
• Compressor prevents overload and distortion
• Muting function for input priority override
• Bridging input/output for input expansion or
system combining
• Protection circuitry prevents potential damage
from overload,short-circuit and over-heating
• Five year warranty
A-503A
A-506A
A-512A
30/60/120 WATT 6-CHANNEL MIXER/AMPLIFIERS
• Integrated mixer/amplifiers for sound reinforcement,
paging and background/foreground music distribution
• 25 V, 70.7 V and 4 ohm transformer-isolated speaker
outputs with screw terminal connector and protective cover plate
• Two low impedance microphone inputs,balanced,
transformer-isolated with XLR-F connectors
(expandable to 4)
• Three auxiliary line inputs,unbalanced with RCA
connectors
• Hi-z mic/phono input (switchable),unbalanced
with RCA/screw terminal connectors
• External mute terminals for switch closure override
of inputs 3-5 with adjustable mute depth
• Insert jacks for connecting external signal processor
• Booster and tape outputs for connecting external
equipment
• +24 VDC input for connection to external power source
• Protection circuitry prevents potential damage from
overload,short-circuit and overheating
• Five year warranty
500 Series
CA-115
CA-130
CA-160
15/30/60 WATT MOBILE MIXER/AMPLIFIERS
• Mobile mixer/amplifiers for remote applications
• 12 VDC powered
• Supports 4 or 8 ohm speaker loads
• Two microphone inputs and one auxiliary
input
• Handheld microphone included
— unidirec-
tional,dynamic-type with talk switch,6’cord
and mounting hardware
• Mounting hardware included
— mounts
under dashboard or into standard DIN-size
console cutout
• Five year warranty
CA Series
IP-300D
IP-450D
IP-600D
300/450/600 WATT DUAL CHANNEL POWER AMPLIFIERS
• Stereo,bridged,and parallel output modes
• Electronically balanced screw-terminal and XLR input
connectors
• Optional input transformer available
— model lT-101
• Precision stepped attenuators,recessable to prevent
accidental setting changes (security covers included)
• Variable-speed fan for quiet,efficient cooling
• Advanced protection circuitry monitors voltage,current and thermal levels to prevent potential damage
from overloads,short circuit,DC offset or over-heating
• In-rush current limiter prevents AC breaker overload
during system turn-on of multiple amplifiers
• Optional transformers for 25 volt / 70.7 volt applications: model MT-300M (200 W), MT-450M (300 W),
MT-600M (400 W)
• Five year warranty
IP Series
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
20
Page 24

21
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
TOA Amplifier Comparison Chart
Model Description Power Total Inputs Input Types Output Channels Main Output Type
A-706 Mixer/Amplifier 60 W 9 1 Module Port,6 Bal.Mic/Line 14 Ω ,25 V,70.7 V,
(Rem.Term.Blk),2 Unbal. Record (Unbal.Line)
A-712 Mixer/Amplifier 120 W “ “ “ “
A-724 Mixer/Amplifier 240 W “ “ “ “
A-503A Mixer/Amplifier 30 W 6
2 Bal.Mic (expandable to 4),1 Unbal.
14 Ω,25 V,70.7 V,
Mic/Phono,1 Unbal.Mic/Line,2 Unbal. Record (Unbal.Line)
A-506A Mixer/Amplifier 60 W “ “ “ “
A-512A Mixer/Amplifier 120 W “ “ “ “
A-901A Mixer/Amplifier 10 W 3
2 Module Ports,
1 4 / 8 Ω,25 V,70.7 V,
1 Unbal.Line (single RCA) Aux (Unbal.Line)
A-903MK2 Mixer/Amplifier 30 W 8
8 Module Ports
1 4 / 8 Ω,25 V,70.7 V,
Aux (Unbal.Line)
A-906MK2 Mixer/Amplifier 60 W “ “ “ “
A-912MK2 Mixer/Amplifier 120 W “ “ “ “
BG-1015 Mixer/Amplifier 15 W + 1 W 5 1 Module Port,1 Bal.Mic, 1 Main,1 MOH 4 Ω,25 V,70.7 V
1 Transformer-Bal.Line ,
1 Active-Bal.Line,1 Unbal.(Dual RCA)
BG-1030 Mixer/Amplifier 30 W + 1 W “ “ “ “
BG-1060 Mixer/Amplifier 60 W + 1 W “ “ “ “
BG-1120 Mixer/Amplifier 120 W + 1 W “ “ “ “
BG-115 Mixer/Amplifier 15 W 3
1 Transformer-Bal.Mic/Line, 1 Main, 1 MOH 4 Ω,25 V,70.7 V
1 Active-Bal.Line,1 Unbal.(Dual RCA)
BG-130 Mixer/Amplifier 30 W “ “ “ “
CA-115 Mobile Mixer/ 15 W 3 2 Lo-Z Unbal.Mic,1 Bal.Line 1 4 / 8 Ω
Amplifier
CA-130 Mobile Mixer/ 30 W “ “ “ “
Amplifier
CA-160 Mobile Mixer/ 60 W “ “ “ “
Amplifier
IP-300D Power Amplifier 300 W/Ch.@ 4 Ω 2 1 Bal.Line per channel (Screw terminals, 2 4 / 8 Ω,
200 W/Ch.@ 8 Ω Female XLR,Male XLR) optional 25/70.7 V
600 W Mono @ 8 Ω using MT-300M
IP-450D Power Amplifier 450 W/Ch.@ 4 Ω “ “ “ 4 / 8 Ω,
300 W/Ch.@ 8 Ω optional 25/70.7 V
900 W Mono @ 8 Ω using MT-450M
IP-600D Power Amplifier 600 W/Ch.@ 4 Ω “
1 Bal.Line per channel (Female XLR, “ 4 / 8 Ω,
400 W/Ch.@ 8 Ω Male XLR,Screw terminals) optional 25/70.7 V
1200 W Mono @ 8 Ω using MT-600M
P-906MK2 Power Amplifier 60 W 1
1 Module Port 1 4 / 8 Ω,25 V,70.7 V
P-912MK2 Power Amplifier 120 W “ “ “ “
P-924MK2 Power Amplifier 240 W at 4 or 8 Ω,“ “ “ “
220 W at 25 or 70.7 V
W-906A In-Wall Mixer/ 60 W 6/8
6 Module Ports,Expandable to 1 4 / 8 Ω,25 V,70.7 V
Amplifier
8 Ports w/ WE-2
W-912A In-Wall Mixer/ 120 W “ “ “ “
Amplifier
Page 25

TOA Amplifier Comparison Chart
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Model MOH Auto-Mute Phantom Insert Additional Features Color Rack Rack-
Output Power* Jacks Space Mount Kit
A-706 Optional, User Yes Yes Selectable mute assign.,5-seg.LED Black 2U MB-25B
using T-02S Configurable meter, remote master vol. & turn on
A-712 ““““ “ “““
A-724 ““““ “ “““
A-503A — — Inputs 1 & Yes
RIAA phono pre-amp input,
Black 2U MB-21B2
2 Only
closure-controlled muting
A-506A —— “ “ “ “““
A-512A —— “ “ “ “““
A-901A Optional, Optional,using Yes Yes
Closure-controlled muting (auto-mute Silver 2U MB-920
using T-12S muting module optional),transformer isolated output
A-903MK2 “ “ “ “ Remote master vol.,bridge in/out Black “ MB-25B
jack**,2 mute busses,low cut filter
A-906MK2 ““““ “ “““
A-912MK2 “ “ “ “ “ “ “ “
BG-1015 Yes User Yes Yes Closure-controlled inputs for zone Black 2U MB-1000
Configurable
applications,user-configurable muting
and buss assignments
BG-1030 ““ ““ “ “““
BG-1060 ““““ “ “““
BG-1120 ““““ “ “““
BG-115 Yes User — —
Selectable 600 / 10k ohm transformer- Black 2U MB-25B-BK (1)
Configurable isolated paging input MB-25B-J (2)
BG-130 “ “ — — “ “ “ “
CA-115 —— ——
12 Volt DC operation for automotive Black (DIN (Mounting
applications,includes handheld PT T mic Chassis) brackets incl.)
CA-130 — — — — “ “ “ “
CA-160 — — — — “ “ “ “
IP-300D —— ——
Stereo,bridge and parallel output modes; Black 2U Built-in
variable-speed fan;precision stepped
attenuators
IP-450D —— —— “ “““
IP-600D —— —— “ “““
P-906MK2 Optional, — Yes — Low-cut filter,high-gain mode, Black 2U MB-25B
using T-12S extensive protection circuitry
P-912MK2 “ — “ — “ “ “ “
P-924MK2 “ — “ — “ “ (3U) MB-35B
W-906A Optional, Optional,using Yes — Wall-mount,10-band equalizer and Silver —
(Backbox: BX-9S
using T-12S
muting modules compressor,bridge in/out connec tion**
or BX-9F)
W-912A “ “ “ — “ “ — “
22
* Mic inputs only
** For expansion and room combining
Page 26

Appendix A: Wire Size Charts
Table 1 Speak er Cable Lengths (ft) and Gauges (AWG) for 70.7 V Line with 1 dB Power Loss
Table 2 Speak er Cable Lengths (ft) and Gauges (AWG) for 25 V Line with 1 dB Power Loss
A-1
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
* Greater than 10,000 feet
** Not recommended,may exceed safe current capacity of wire
70.7 V
Wire Gauge
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
(AWG)
Load Power Load Impedance
Maximum Cable Distance (ft)
(W) (Ω)
10 490 * * * 7,200 4,600 2,800 1,800
15 327 * * 7,600 4,800 3,000 1,920 1,200
20 245 * 9,200 5,600 3,600 2,200 1,400 900
30 163 10,000 6,200 3,800 2,400 1,500 960 600
40 122 7,400 4,600 2,800 1,800 1,100 700 450
60 81 5,000 3,200 1,900 1,200 730 480 **
100 49 2,900 1,820 1,120 720 230 ** **
200 24.5 1,450 910 560 360 110 ** **
400 12.2 730 460 280 180 ** ** **
25 V
Wire Gauge
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
(AWG)
Load Power Load Impedance
Maximum Cable Distance (ft)
(W) (Ω)
10 61 3,700 2,300 1,400 900 575 350 225
15 41 2,500 1,550 950 600 375 240 150
20 31 1,850 1,150 700 450 275 175 113
30 20 1,250 775 475 300 188 120 **
40 15 925 575 350 225 138 ** **
60 10 625 400 238 150 ** ** **
100 6 363 228 140 90 ** ** **
200 3 181 114 70 ** ** ** **
Page 27

A-2
TOA Electronics Amplifier Guide
Appendix B:
Power Consumption and Thermal Dissipation
Model Power Consumption Power Consumption Heat Dissipation
at Rated Output (Watts) at 50% duty cycle (Watts) (BTU / Hr.)
A-503A 60 30 102
A-506A 100 50 171
A-512A 180 90 307
A-706 68 34 116
A-712 110 55 188
A-724 215 108 367
A-901A 30 15 51
A-903MK2 60 30 102
A-906MK2 100 50 171
A-912MK2 180 90 307
BG-115 50 25 85
BG-130 90 45 154
BG-1015 50 25 85
BG-1030 80 40 136
BG-1060 160 80 273
BG-1120 260 130 444
IP-300D 1040 520 1774
IP-450D 1650 825 2815
IP-600D 2080 1040 3548
M-900MK2 18931
P-906MK2 100 50 171
P-912MK2 180 90 307
P-924MK2 360 180 614
W-906A 100 50 171
W-912A 180 90 307
Page 28

www.toaelectronics.com
PROTECT
POWER
PEAK
NORMAL
SIGNAL
MASTER
OFF
TONE DEFEAT
TREBLE
BASS
INPUT 8
INPUT 7
INPUT 6
INPUT 5
INPUT 4
INPUT 3
INPUT 2
INPUT 1
ON
OFF
LOW CUT
OFFONON
8
VOL
REMT
OUT
IN/
BRG
OUT
AMP
PRE
IN
AMP
PWR
OUT
AUX
MUTE
MUTE
GND
60W
60Hz
120V
COM
DIRECT
25V
70V
UNSWITCHED AC 120V 60Hz
MAX 500W 4A
AC
PROGRAM
MIC
0
TEL
10
10
AUX
10
MODULE
SIGNAL
POWER
ON
OFF
PEAK
HOT
COM
120V 60Hz
120V 50Hz
UNSWITCHED
150W
MAX 500W
CLASS 2 WIRING
PROGRAM
OUTPUT 120W
COM
OUTLET
4A
BREAKER
COM
70V
25V
OUTPUT 1W
RESET
PUSH
HOT
TEL
COM
10
NC
RESET
MUTE
COM
MOH
600
MIC
COM
UNIT
4A
BREAKER
HOT
PUSH
OUTPUT 1W
SENSE
BASS
10
AUX
PREAMP
10
MOH
OUT
MUTE
TREBLE
POWER
IN
MODULE
PAGE
BGM
NORMAL
SIGNAL
T
P
OUT
IN/
BRG
OUT
AMP
PRE
IN
AMP
PWR
OUT
COM
HOT
INPUT LEVEL
LOW CUT
-20dBV
OFF
ON
INPUT
DC FUSE
DC FUSE
250V 8A
250V 8A
250V 7A
AC FUSE
.
LISTED
COMMERCIAL
AUDIO EQUIP.
111J
0dBV
8
VOL
REMT
MUTE
MUTE
GND
60W
60Hz
120V
COM
DIRECT
25V
70V
UNSWITCHED AC 120V 60Hz
MAX 500W 4A
AC
TOA Electronics, Inc.
Tel: 800-733-7088
Fax: 800-733-9766
TOA Canada
Corporation
Tel: 905-564-3570
Fax: 905-564-3569
DIRECT
4õ 8
INPUT 1
BASS
UNSWITCHED AC 120V 60Hz
MAX 500W 4A
70V
25V
õ
COM
120V
AC
60Hz
60W
MIC
0
TEL
INPUT 2
TREBLE
REMT
VOL
MUTE
1
MUTE
2
GND
PROGRAM
0 10
INPUT 3
TONE DEFEAT
INPUT 6
POWER
ON
OFF
SIGNAL
INPUT 5
PEAK
INPUT 4
LOW CUT
ONONOFF
OFF
AUX
MODULE
10100
0 10
INPUT 7
INPUT 8
SIGNAL
MASTER
NORMAL
PROTECT
PEAK
POWER
ON
OFF
AUX
OUT
PWR
AMP
IN
PRE
AMP
OUT
BRG
IN/
OUT
120V 60Hz
MAX 500W
UNSWITCHED
120V 50Hz
150W
DC FUSE
250V 8A
AC FUSE
250V 7A
4õ 8
©2004, TOA Electronics, Inc.
Literature Order #: L-AMPGUIDE
DIRECT
UNIT
PUSH
BREAKER
RESET
4A
PROGRAM
G COM
HOT
OUTPUT 120W
COM
4õ
25V
CLASS 2 WIRING
UNSWITCHED AC 120V 60Hz
MAX 500W 4A
70V
25V
õ
COM
120V
AC
60Hz
60W
DC FUSE
250V 8A
SENSE
OUTLET
PUSH
BREAKER
RESET
4A
TEL
MIC
HOT
G
COM
OUTPUT 1W
70V
8õ
NC
COM
G
HOT
MUTE
MOH
COM
COM
600
õ G
REMT
VOL
MUTE
1
MUTE
2
GND
MUTE
MODULE
- +
0
A0B
PAGE
BGM
10
AUX
PREAMP
OUT
R
LISTED
COMMERCIAL
AUDIO EQUIP.
111J
OUT
POWER
IN
INPUT
LOW CUT
ON
OFF
INPUT LEVEL
0dBV
-20dBV
PWR
AMP
IN
PRE
AMP
OUT
BRG
IN/
OUT
HOT
COM
TREBLE
MOH
0
10
BASS
0
- +
OUTPUT 1W
10
0
Guide
 Loading...
Loading...