Page 1

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
.
.
.
.
.
.
The technical parameters are subject to change without notices.
All rights reserved.
Figures herein are for information only.
Page 2

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
.
Instruction Manual
of
TMP Series
High Performance Vector Control Inverter
TM, control and protect your motors
TM Industry Co.Ltd.
Page 3

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction to TMP Series Inverter ................................................................................ 1
1.1 Product Model Description ............................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Product Nameplate Description ....................................................................................................... 1
1.3 Product Series ................................................................................................................................ 6
1.4 Product Specifications ..................................................................................................................... 8
1.5 Product Component Name ............................................................................................................. 11
1.6 Product Outline, Mounting Dimension, and Weight ................................ .......................................... 11
1.7 Operation Panel Outline and Mounting Dimension .......................................................................... 13
1.8 Pallet Outline and Mounting Dimension .......................................................................................... 14
1.9 Braking Resistor Lectotype ................................................................ ............................................ 15
Chapter 2 Inverter Installation ........................................................................................................ 16
2.1 Environment for Product Installation ............................................................................................... 16
2.2 Mounting Direction and Space ................................................................ ....................................... 16
2.3 Removal and Mounting of Operation Panel and Cover.................................................................... 17
Chapter 3 Wiring of Inverter ................................................................................................ ........... 21
3.1 Connection of the Product and Peripheral Devices ................................................................ ......... 21
3.2 Description of Peripheral Devices for Main Circuit .......................................................................... 22
3.3 Lectotype of mMain Circuit Peripheral Devices ................................ ............................................... 22
3.4 Product Terminal Configuration ...................................................................................................... 24
3.5 Functions of Main Circuit Terminal ................................................................................................. 25
3.6 Attention for Main Circuit Wiring ..................................................................................................... 25
3.7 Terminal Wiring ............................................................................................................................. 28
3.8 Functions of Control Circuit Terminals ............................................................................................ 29
3.9 Lectotype of Control Circuit Peripheral Devices ................................ .............................................. 30
3.10 Description of Jumper Function .................................................................................................... 30
.......................................................................................................................................................... 30
Chapter 4 Using Instructions of Operation Panel .......................................................................... 31
4.1 Introduction to Operation Panel ..................................................................................................... 31
4.2 Descriptions of Indicators .............................................................................................................. 31
4.3 Description of Keys on Operation Panel ......................................................................................... 32
4.4 Keypad Operating Status ............................................................................................................... 33
4.5 Panel Operation Method ................................................................................................................ 34
4.6 Parameter Display ......................................................................................................................... 35
4.7 Motor auto-tuning procedure .......................................................................................................... 36
4.8 Running for the First Time ............................................................................................................. 37
Page 4

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
Chapter 5 List of Parameters ......................................................................................................... 38
5.1 Function Parameter Table .............................................................................................................. 38
Chapter6 Detail Function Introduction ............................................................................................. 56
P0 Basic function parameters .............................................................................................................. 56
P1 Auxiliary function parameters 1 ................................................................................................ ....... 61
P2 Auxiliary function parameters 2 ....................................................................................................... 65
P3 Motor parameters .......................................................................................................................... 70
P4 Dedicatd function for V/F control .................................................................................................. 71
P5 Vector control funtion ..................................................................................................................... 73
P6 I/O I/O output terminal .................................................................................................................... 77
P7 Analog input terminal function......................................................................................................... 90
P8 Analog output terminal ................................................................................................................... 92
P9 Program operating parameters ....................................................................................................... 94
PA PID parameter ................................................................ ............................................................... 97
Pb Traverse function ..........................................................................................................................100
PC Communication and Bus control function ......................................................................................102
Pd Faults and protection parameters ..................................................................................................103
PE Factory reserved ..........................................................................................................................106
PF Factory reserved ..........................................................................................................................106
PH Display function ............................................................................................................................106
Chapter 7 Fault diagnosis and troubleshooting ................................ ..............................................109
7.1 Fault query at fault .......................................................................................................................109
7.2 List of Fault and Alarm Information ................................................................................................109
7.3 Troubleshooting Procedures ......................................................................................................... 114
Chapter 8 Routine Repair and Maintenance .................................................................................... 115
8.1 Routine Maintenance ................................................................................................................... 115
8.2 Periodic Maintenance ................................................................................................ ................... 116
8.3 Component Replacement ............................................................................................................. 116
8.4 Insulation Test .............................................................................................................................. 117
Appendix A Communication Protocol ........................................................................................... 118
Appendix B Control Mode Setting Process ..................................................................................133
Page 5
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
Chapter 1 Introduction to TMP−H Series Inverter
1
Chapter 1 Introduction to TMP Series Inverter
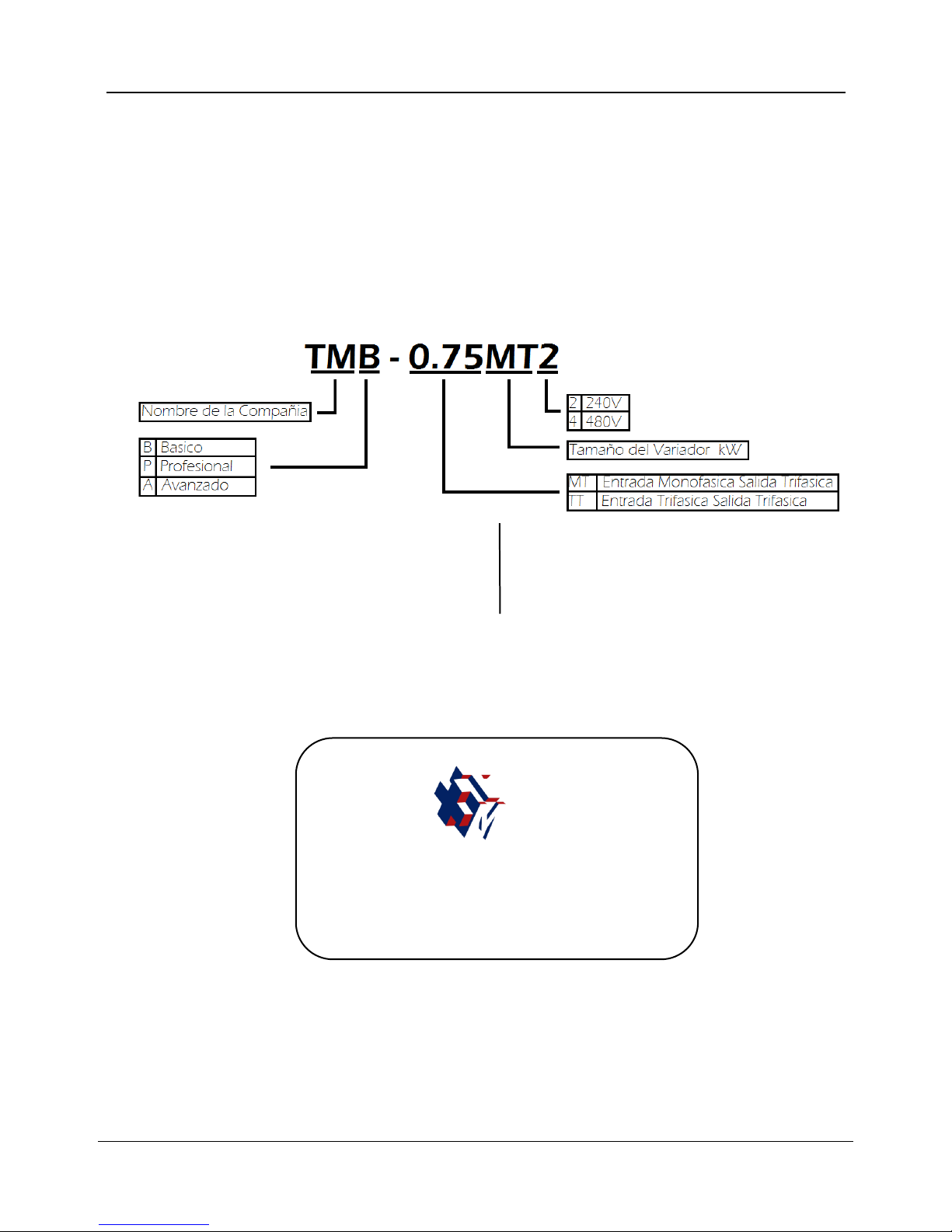
1.1 Product Model Description
The digits and letters in the inverter model field on the nameplate indicate such information as the
product series, power supply class, power class and software/hardware versions.
TM P – 7.5 □ -4
TM Input Voltage class
Inverter Series S2:1AC220V
2:3AC220V
4:3AC380V
Fig. 1-1 Inverter symbol description
1.2 Product Nameplate Description
Fig. 1-2 Inverter Nameplate
MODLE: TMP-7.5TT4
POWER:7.5KW
INPUT: 3PH AC480V 50Hz
Page 6
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
2
Safety Precautions
Description of safety marks:
Danger: The misuse may cause fire, severe injury, even death.
Note: The misuse may cause medium or minor injury and equipment damage.
Use
DangerDanger
This series of inverter is used to control the variable speed operation of three-phase
motor and cannot be used for single-phase motor or other applications. Otherwise,
inverter failure or fire may be caused.
This series of inverter cannot be simply used in the applications directly related to the
human safety, such as the medical equipment.
This series of inverter is produced under strict quality management system. If the
inverter failure may cause severe accident or loss, safety measures, such as
redundancy or bypass, shall be taken.
Goods Arrival Inspection
NoteNote
If the inverter is found to be damaged or lack parts, the inverter cannot be installed.
Otherwise, accident may be caused.
Installation
NoteNote
When handling and installing the product, please hold the product bottom. Do not hold
the enclosure only. Otherwise, your feet may be injured and the inverter may be
damaged because of dropping.
The inverter shall be mounted on the fire retardant surface, such as metal, and kept far
away from the inflammables and heat source.
Keep the drilling scraps from falling into the inside of the inverter during the installation;
otherwise, inverter failure may be caused.
When the inverter is installed inside the cabinet, the electricity control cabinet shall be
equipped with fan and ventilation port. And ducts for radiation shall be constructed in
the cabinet.
Page 7
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
3
Wiring
DangerDanger
The wiring must be conducted by qualified electricians. Otherwise, there exists the risk
of electric shock or inverter damage.
Before wiring, confirm that the power supply is disconnected. Otherwise, there exists the
risk of electric shock or fire.
The grounding terminal PE must be reliably grounded, otherwise, the inverter enclosure
may become live.
Please do not touch the main circuit terminal. The wires of the inverter main circuit
terminals must not contact the enclosure. Otherwise, there exists the risk of electric
shock.
The connecting terminals for the braking resistor are ⊕2/B1 and B2. Please do not
connect terminals other than these two. Otherwise, fire may be caused.
The leakage current of the inverter system is more than 3.5mA, and the specific value of
the leakage current is determined by the use conditions. To ensure the safety, the
inverter and the motor must be grounded.
NoteNote
The three-phase power supply cannot connect to output terminals U/T1, V/T2 and
W/T3, otherwise, the inverter will be damaged.
It is forbidden to connect the output terminal of the inverter to the capacitor or LC/RC
noise filter with phase lead, otherwise, the internal components of the inverter may be
damaged.
Please confirm that the power supply phases, rated voltage are consistent with that of
the nameplate, otherwise, the inverter may be damaged.
Do not perform dielectric strength test on the inverter, otherwise, the inverter may be
damaged.
The wires of the main circuit terminals and the wires of the control circuit terminals shall
be laid separately or in a square-crossing mode, otherwise, the control signal may be
interfered.
The wires of the main circuit terminals shall adopt lugs with insulating sleeves.
The inverter input and output cables with proper sectional area shall be selected
according to the inverter power.
When the length of the cables between the inverter and the motor is more than 100m, it
is suggested to use output reactor to avoid the inverter failure caused by the overcurrent
of the distribution capacitor.
The inverter which equipped with DC reactor must connect with DC reactor between the
terminal of ○,+1、○,+2, otherwise the inverter will not display after power on.
Page 8
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
4
Operation
DangerDanger
Power supply can only be connected after the wiring is completed and the cover is
installed. It is forbidden to remove the cover in live condition; otherwise, there exists the
risk of electric shock.
When auto failure reset function or restart function is set, isolation measures shall be
taken for the mechanical equipment, otherwise, personal injury may be caused.
When the inverter is powered on, even when it is in the stop state, the terminals of the
inverter are still live. Do not touch the inverter terminals; otherwise electric shock may
be caused.
The failure and alarm signal can only be reset after the running command has been cut
off. Otherwise, personal injury may be caused.
NoteNote
Do not start or shut down the inverter by switching on or off the power supply, otherwise,
the inverter may be damaged.
Before operation, please confirm if the motor and equipment are in the allowable use
range, otherwise, the equipment may be damaged.
The heatsink and the braking resistor have high temperature. Please do not touch such
device; otherwise, you may be burnt.
When it is used on lifting equipment, mechanical contracting brake shall also be
equipped.
Please do not change the inverter parameter randomly. Most of the factory set
parameters of the inverter can meet the operating requirement, and the user only needs
to set some necessary parameters. Any random change of the parameter may cause
the damage of the mechanical equipment.
In the applications with industrial frequency and variable frequency switching, the two
contactors for controlling the industrial frequency and variable frequency switching shall
be interlocked.
Maintenance, Inspection
DangerDanger
In the power-on state, please do not touch the inverter terminals; otherwise, there exists
the risk of electric shock.
If cover is to be removed, the power supply must be disconnected first.
Wait for at least 10 minutes after power off or confirm that the CHARGE LED is off
before maintenance and inspection to prevent the harm caused by the residual voltage
of the main circuit electrolytic capacitor to persons.
The components shall be maintained, inspected or replaced by qualified electricians.
Page 9

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
5
NoteNote
The circuit boards have large scale CMOS IC. Please do not touch the board to avoid
the circuit board damage caused by electro static.
Others
DangerDanger
It is forbidden to modify the inverter unauthorizedly; otherwise, personal injury may be
caused.
Page 10
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
6
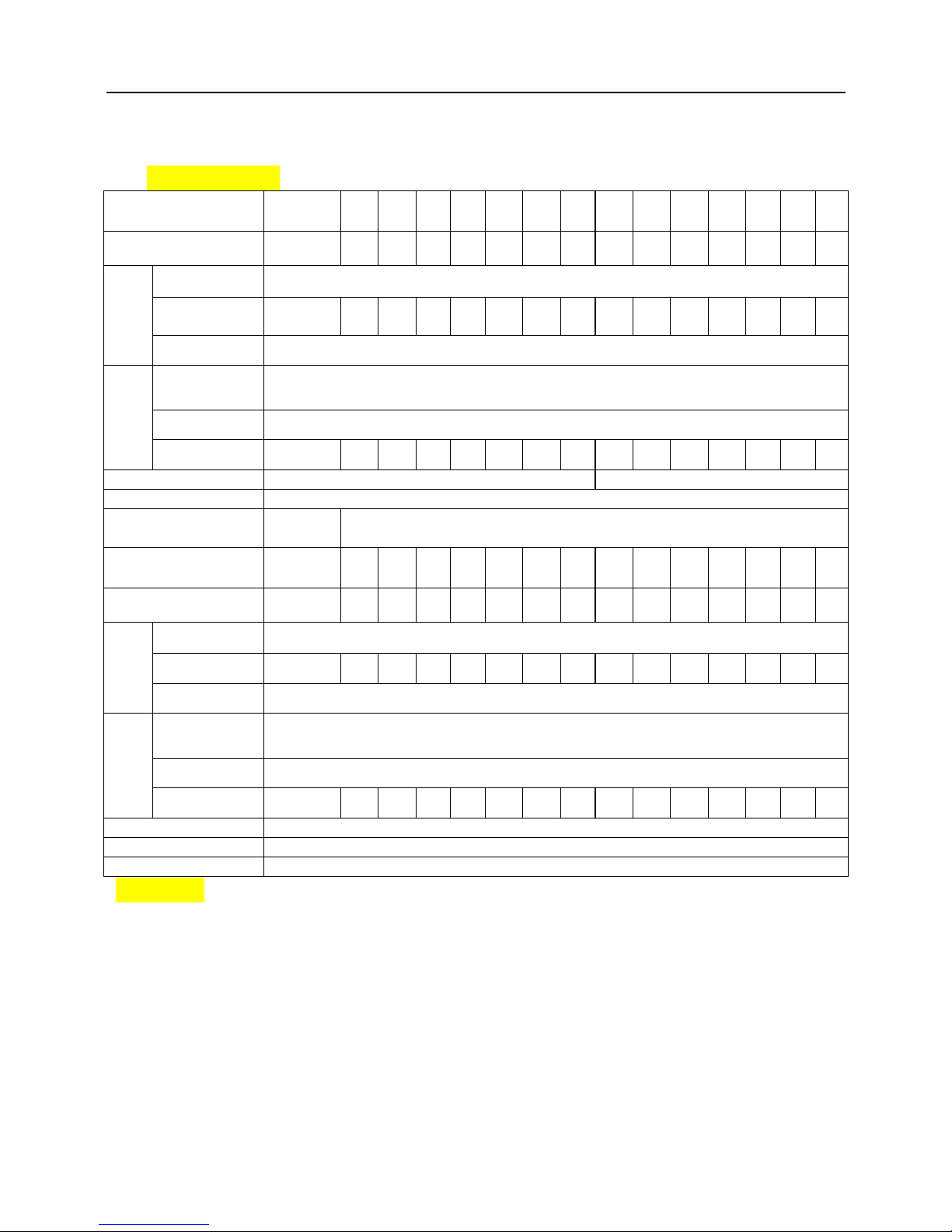
1.3 Product Series
TMP−□□□G-4 Three-phase 400V Constant torque/heavy-duty application
Power (kW)
0.75
1.5
2.2
4.0
5.5
7.5
11
15
18.5
22
30
37
45
55
75
Motor
power (kW)
0.75
1.5
2.2
4.0
5.5
7.5
11
15
18.5
22
30
37
45
55
75
Output
Voltage (V)
Three-phase 0 to rated input voltage
Rated current
(A)
2.5
3.8
5.5 9 13
17
24
30
39
45
60
75
91
112
15
0
Overload
capacity
feature)
Input
Rated
voltage/frequen
cy
Three-phase 380V/480V; 50Hz/60Hz
Allowable
voltage range
323V ~ 528V; Voltage unbalanceness ≤3%; allowable frequency fluctuation: ±5%
Rated current
(A)
3.5
6.2
9.2
14.9
21.5
27.9
39
50.3
60
69.3
86
104
124
150
20
1
Braking unit
Built-in as standard
Built-in as option
Protection class
IP20
Cooling mode
Self-coolin
g
Forced air convection cooling
Power (kW)
90
110
132
160
185
200
220
250
280
315
355
400
450
500
Motor
power (kW)
90
110
132
160
185
200
220
250
280
315
355
400
450
500
Output
Voltage (V)
Three-phase 0 to rated input voltage
Rated current
(A)
176
210
253
304
350
380
426
470
520
600
650
690
775
860
Overload
capacity
feature)
Input
Rated
voltage/frequen
cy
Three-phase 380V/480V; 50Hz/60Hz
Allowable
voltage range
323V ~ 528V; Voltage unbalancedness ≤3%; allowable frequency fluctuation: ±5%
Rated current
(A)
160*
196* 232* 282* 326* 352* 385* 437* 491* 580* 624* 670* 755* 840
*
Braking unit
External braking unit needed
Protection class
IP20
Cooling mode
Forced air convection cooling
*TMP −090G-4 and above products are equipped with external DC reactor as standard.
Page 11

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
7
TMP−□□□P -4 Three-phase 400V Variable torque/light-duty application
Power (kW)
1.5
2.2
4.0
5.5
7.5
11
15
18.5
22
30
37
45
55
75
90
Motor
power (kW)
1.5
2.2
4.0
5.5
7.5
11
15
18.5
22
30
37
45
55
75
90
Output
Voltage (V)
Three-phase 0 to rated input voltage
Rated current (A)
3.3
5.0
7.5
11
17
22
30
37
44
56
72
91
110
142
176
Overload capacity
120% 1 minute, 145% 2 second, interval: 10 minutes (inverse time lag feature)
Input
Rated
voltage/frequency
Three-phase 380V/480V; 50Hz/60Hz
Allowable voltage
fluctuation range
323V ~ 528V; Voltage unbalancedness: ≤3%; allowable frequency fluctuation: ±5%
Rated current (A)
5.6
8.1
13.5
19.5
26
39
50.3
60
69.3
86
104
124
150
190
235
Braking unit
Built-in as standard
Built-in as option
Protection class
IP20
Cooling mode
Self-cooling
Forced air convection cooling
Power (kW)
110
132
160
185
200
220
250
280
315
355
400
450
500
560
Motor
power (kW)
110
132
160
185
200
220
250
280
315
355
400
450
500
560
Output
Voltage (V)
Three-phase 0 to rated input voltage
Rated current (A)
210
253
304
350
380
426
470
520
600
650
690
775
860
950
Overload capacity
115% 1 minute, 160% 0.5 second, interval: 10 minutes (inverse time lag feature)
Input
Rated
voltage/frequency
Three-phase 380V/480V; 50Hz/60Hz
Allowable voltage
range
323V ~ 528V; Voltage unbalancedness ≤3%; allowable frequency fluctuation: ±5%
Rated current (A)
196*
232*
282*
326*
352*
385*
437*
491*
580*
624*
670*
755*
840*
920*
Braking unit
External braking unit needed
Protection class
IP20
Cooling mode
Forced air convection cooling
*TMP−110P-4 and above products are equipped with external DC reactor as standard.
TMP−□□□G-2 Three-phase 200V Constant torque/heavy-duty application
Power (kW)
0.4
0.75
1.5
2.2
Motor
power (kW)
0.4
0.75
1.5
2.2
Output
Voltage (V)
Three-phase 0 to rated input voltage
Rated current (A)
3 5 7.5
10
Overload capacity
150% 1 minute, 180% 10 seconds, 200% 0.5 second, interval: 10 minutes
(inverse time lag feature)
Input
Rated
voltage/frequency
Three-phase or single-phase 200V~240V; 50Hz/60Hz
Allowable voltage
range
180V ~ 260V; Voltage unbalancedness ≤3%; allowable frequency fluctuation: ±5%
Rated current (A)
3.8
5.5
8.3
12
Braking unit
Built-in as standard
Protection class
IP20
Cooling mode
Self-cooling
Forced air convection cooling
Page 12
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
8
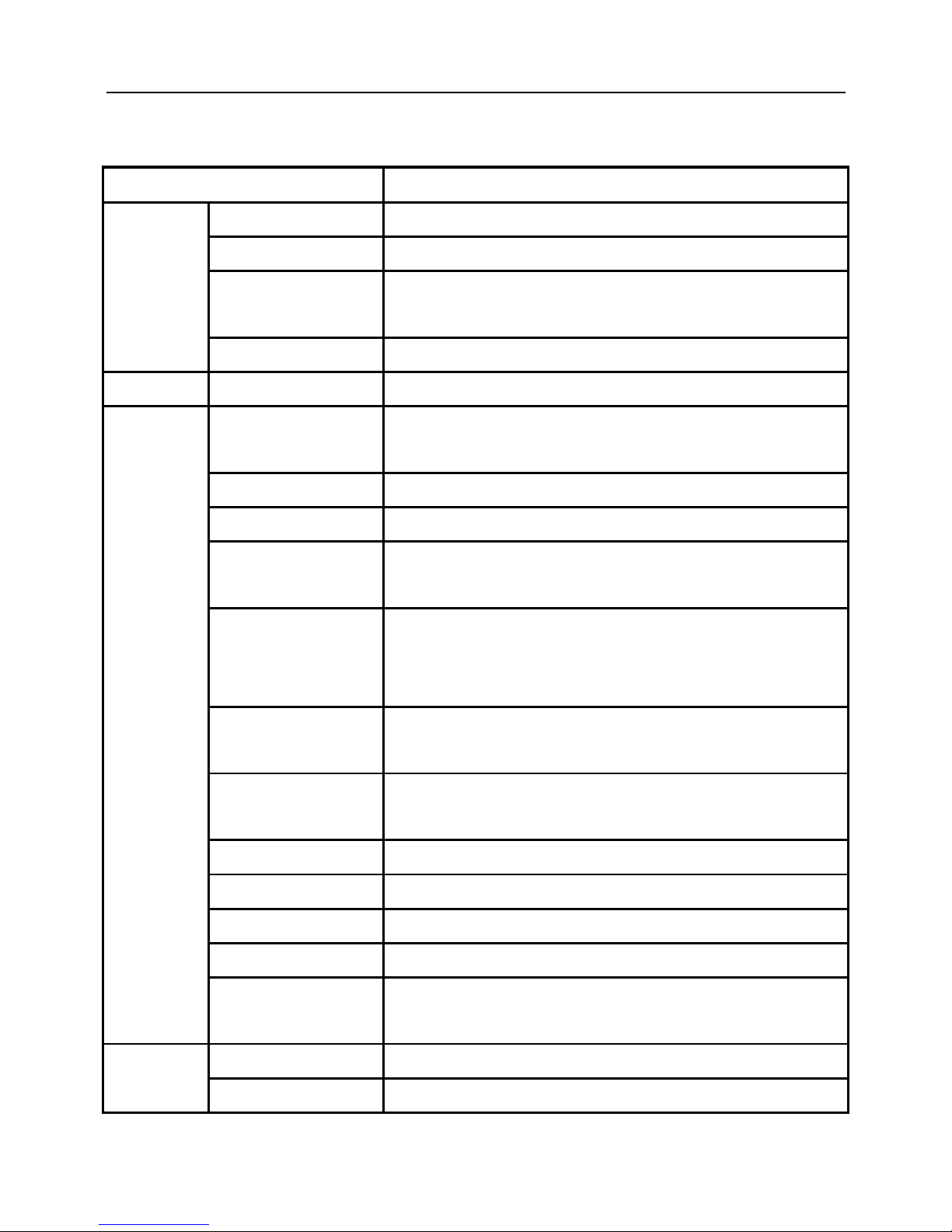
1.4 Product Specifications
Item
Specifications
OUTPUT
Rated Output Voltage
Three phase 380V (Max output voltage is equal to input voltage)
Max continuous current
100% rated output current
Overload ability
150% rated current for 1minutes,
180% rated current for 2 seconds.
Output frequency
0Hz~400Hz
Input
Rated input voltage
Three phase: 380V±20%, 50~60Hz±5%
Control
performance
AVR Function,
When AVR function is enable,output voltage is stable under input voltage
fluctuation
Modulation modes
Optimized space voltage vector PWM modulation
Control mode
Sensorless Vector control; V/F control.
Running command input
modes
Panel control, external terminal control, control by serial port of host computer
Speed setting mode
Ten kinds of main frequencysetting modes, seven kinds of Auxiliary
frequencysetting modes. Several combination kinds of main frequencysetting
modes and Auxiliary frequencysetting modes.
Speed setup resolution
Digital setting: 0.01Hz.
Analog setting: highest frequency×0.1%
Voltage/Frequency
characteristic
Rated voltage: 50-100%,adjustable, Base frequency 50Hz, adjustable, five type
V/F curves
Speed control accuracy
Sensorless vector control: ±0.05% rated speed(25℃±10℃)
Speed control range
vector control: 1:100
Starting torque
vector control: 150% rated torque at 0.5Hz.
Acc/dec characteristic
0.1seconde~3600 seconds
Braking torque
22 kW below: >20% rated torque,
30 kW above: >15% rated torque
Control I/O
Reference voltage output
1 channel, +10V, 50mA
Control voltage output
24V, 100mA
Page 13
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
9
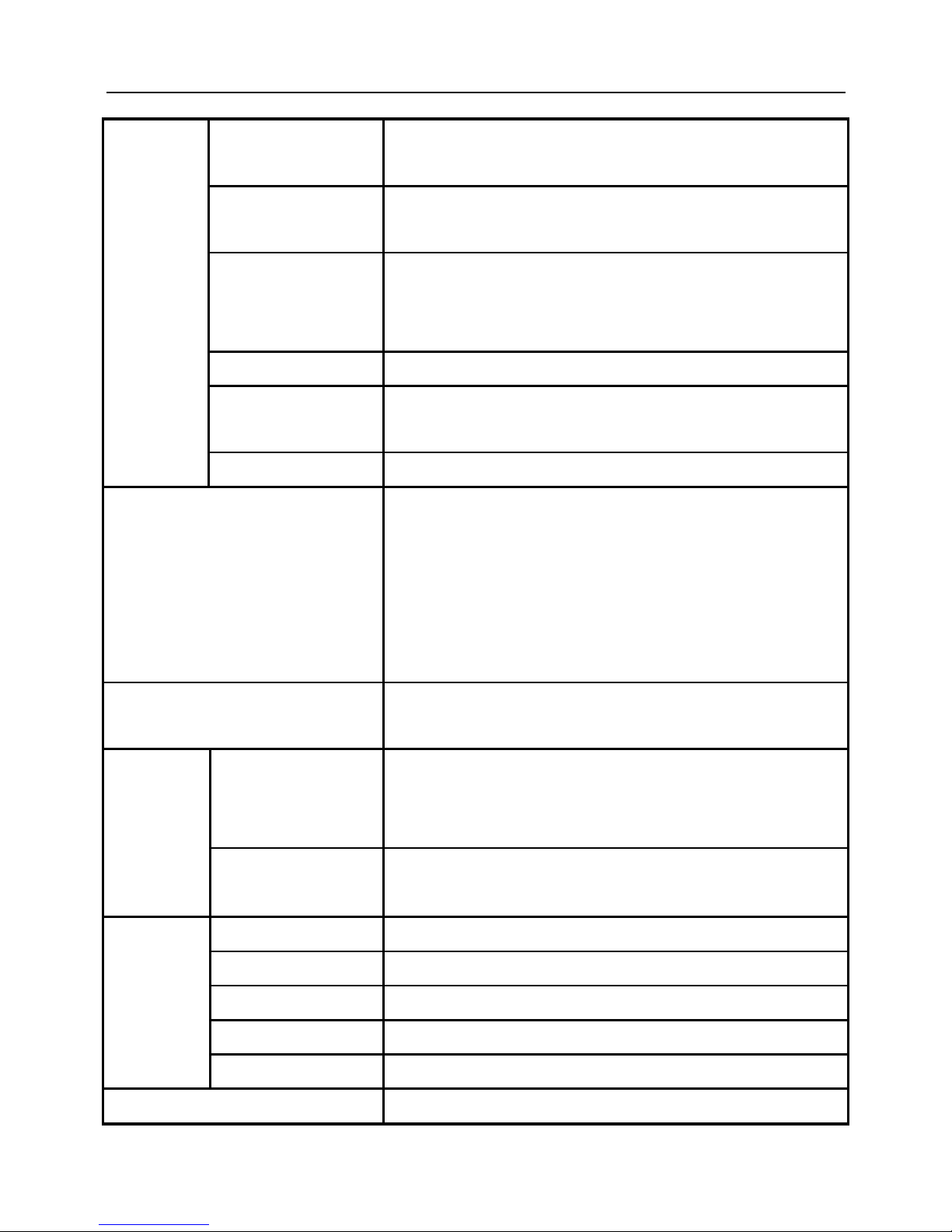
signal
Analog input
1 channel, 0~10V/0~20mA DC,10 bit;
1 channel, 0~10 V DC,10 bit
Analog output
1 channel, 0~10V, output programmable, various output selectable
1 channel, 0~10V/0-2 0mA, output programmable, various output selectable
Programmable terminal
input
7 programmable channels, 27 kinds of functions can be selected, such as Run
forward/reverse, Jog forward/reverse, multi-step speed selection, multi-step
Acc/Dec time, free run to stop, voltage/current switch, etc.
Open collector output
1 channel, 20 optional running states, the maximum output current is 50mA
Programmable relay output
1 channel, 20optional running states, contact capacity: 250V AC /3A or 30V DC
/1A
Serial port
RS-485 port
Standard function
urrent limit, torque boost, speed trace, DC braking, restart after power failure, slip
compensation, auto fault reset, high/low limit frequency, starting frequency, jump
frequency, frequency gain, Carrier frequency adjustment, Acc/Dec mode
selection, voltage meter output, current meter output, multi-frequency operation,
programming operation, traverse operation, PI close loop operation, proportional
control, remote control, FWD/REV dead time, etc.
Protection function
Over voltage, low voltage, over current, current limit, overload, over heat,
electronic thermal overload relay, over voltage stall, data protection, etc.
Display
4-digit display (LED)
15 kinds of parameters, such as frequency setting, output frequency, output
voltage, output current, motor speed, output torque, digital value terminals,
program menu parameters and 33kinds of Fault codes
Indicator (LED)
Parameter unit, RUN/STOP state, etc.
Operating
environment
Environment
Inside, low than 1000m, free from dust, corrosive gas and direct sunlight
Ambient temperature
-10℃~+40 ℃ (bare machine: -10℃~+50℃), 20%~90%RH, no condensing
Vibration
Lower than 0.5g
Storage temperature
-25℃~+65℃
Installation
Wall mounted or surface mounted inside a cabinet
Protection class
IP20
Page 14
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
10
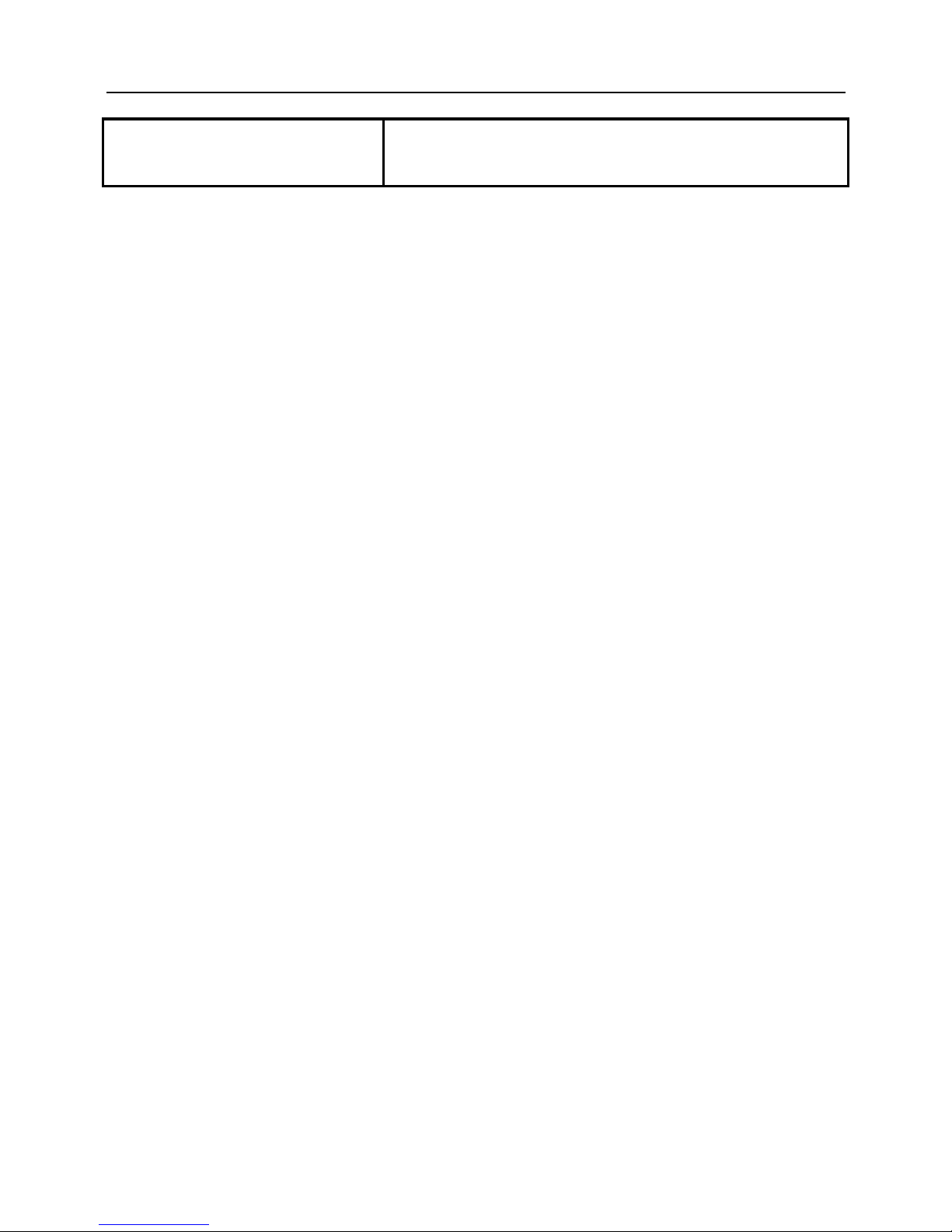
Cooling
0.75 kW and below: enclosed self-cooling,
Others: forced cooling.
Page 15
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
11
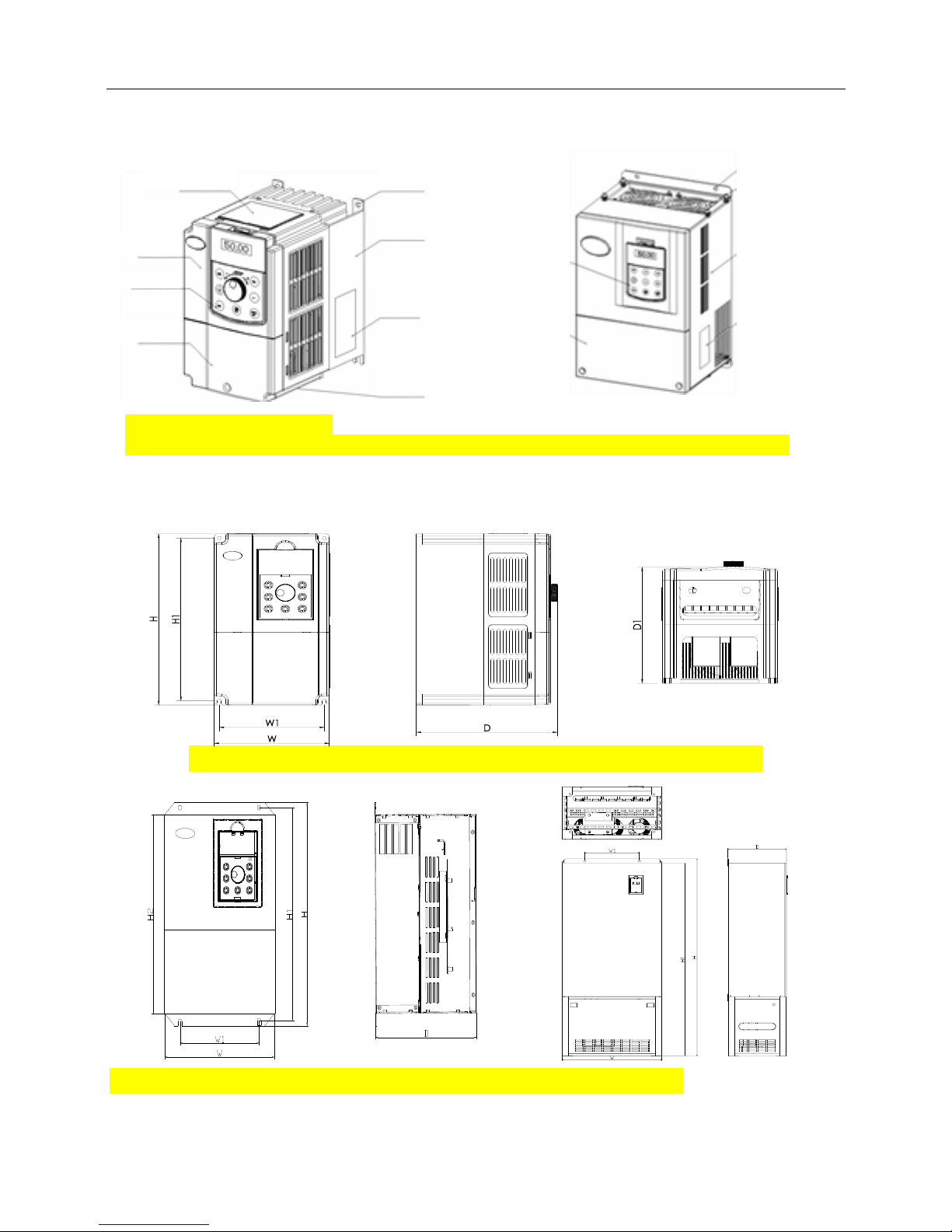
1.5 Product Component Name
TMP−0R4G-2~TMP−2R2G-2
TMP−7R5G-4 and below power class TMP-011G-4 and above power class
Fig.1−3 Product component name
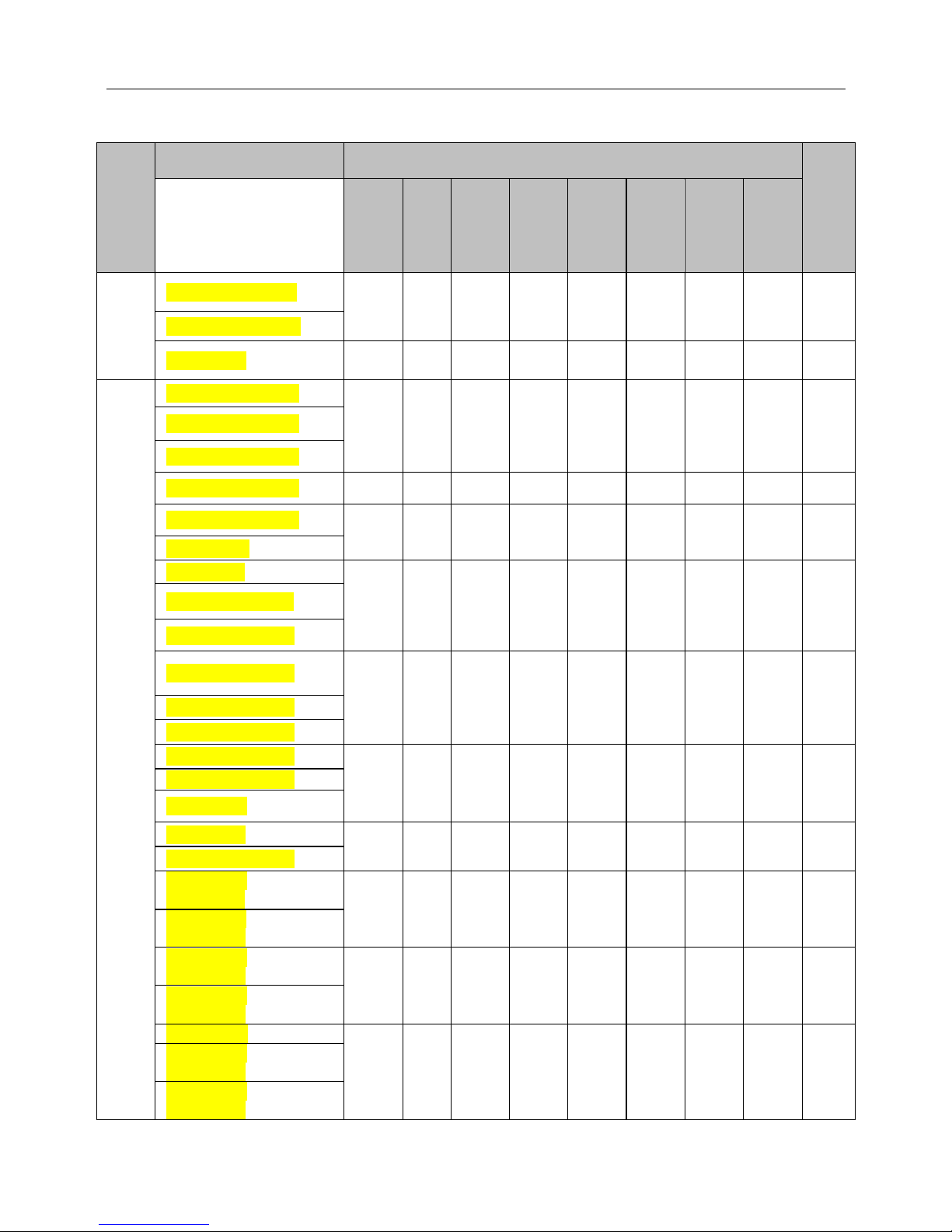
1.6 Product Outline, Mounting Dimension, and Weight
TMP−0R4G-2~TMP−2R2G-2、TMP−0R7G-4~TMP-7R5G-4 and blow power class
TMP-011G-4~ TMP-220G-4 power class TMP-185G-4~TMP-400G-4
Fig.1−4 Product outline and mounting dimension
Nameplate
Dust guard
Upper cover
Operation panel
Lower cover
Heatsink
Mounting hole
Operation panel
Cover
Mounting hole
Cooling fan
Enclosure
Nameplate
Page 16
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
12
Product outline, mounting dimension, and weight
Volta
ge
class
Inverter model
Outline and mounting dimension (mm)
App
roxi
mat
e
weig
ht
(kg)
)
W H D
W1
H1
D1
H2
Moun
ting
hole
diam
eter
220V
TMP-0R4G-2/0R7G-2
118.5
185
159
106.5
174.5
150 5.5
2.0
TMP−1R5G-2/2R2G-2
TMP-3R7G-2
150
258
183.8
136.8
245
175.3 5.5
4.5
400V
TMP−0R7G-4/1R5P-4
118.5
185
159
106.5
174.5
150 5.5
2.0
TMP−1R5G-4/2R2P-4
TMP−2R2G-4/4R0P-4
TMP−4R0G-4/5R5P-4
118.5
195
169
106.5
184.5
160 5.5
3.0
TMP−5R5G-4/7 R5P-4
150
258
183.8
136.8
245
175.3 5.5
4.5
TMP−7R5G-4
TMP−011P-4
210
337
191
150
322.5
298 7 8.5
TMP−011G-4/015P-4
TMP−015G-4/018P-4
TMP−018G-4/022P-4
285
501
230.2
200
482 460 7 17
TMP−022G-4/030P-4
TMP−030G-4/037P-4
TMP−037G-4/045P-4
352
585
274.2
220
559 538
10
25
TMP−045G-4/055P-4
TMP−055G-4
TMP−075P-4
404
680
302.7
300
658 633
10
35
TMP−075G-4/093P-4
TMP−093G-4
TMP−110P-4
485
760
316
325
739 713
12
55
TMP−110G-4
TMP−132P-4
TMP−132G-4
TMP−160P-4
533
830
371.7
325
809 780
12
85
TMP−160G-4
TMP−185P-4
Wall Mounted
638
101
0
374
350
985 950
14
125
TMP−185G-4
TMP−200P-4
TMP−200G-4
TMP−220P-4
Page 17
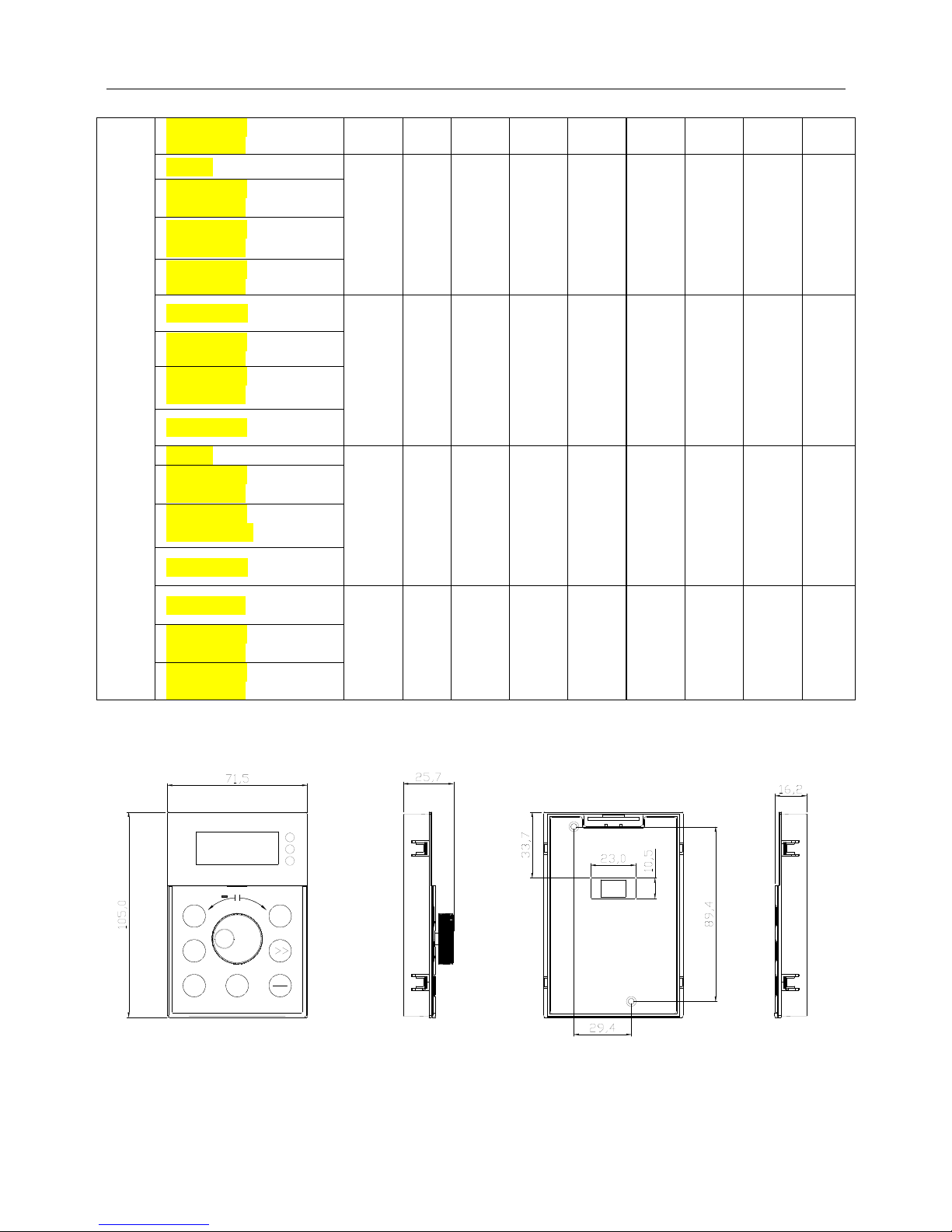
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
13
TMP−220G-4
TMP−250P-4
Cabinet
638
140
2
374
350
1372
14
140
TMP−185G-4
TMP−200P-4
TMP−200G-4
TMP−220P-4
TMP−220G-4
TMP−250P-4
Wall Mounted
700
124
0
460
520
1207.5
1168
14
150
TMP−250G-4
TMP−280P-4
TMP−280G-4
TMP−315P-4
TMP−315G-4
Cabinet
700
162
7
460
520
1592
14
180
TMP−250G-4
TMP−280P-4
TMP−280G-4
TMP−3150P-4
TMP−315G-4
TMP−355P-4
800
177
2
460
520
1737
14
215
TMP−355G-4
TMP−400P-4
TMP−400G-4
TMP−450P-4
1.7 Operation Panel Outline and Mounting Dimension
Shuttle type operation panel (TMP-DP01) Rear view of operation panel
Fig.1−5 Operation panel outline and mounting dimension
SET
MF
JOG
RUN
STOP
+
RST
PRG
5 0.00
Page 18
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
14
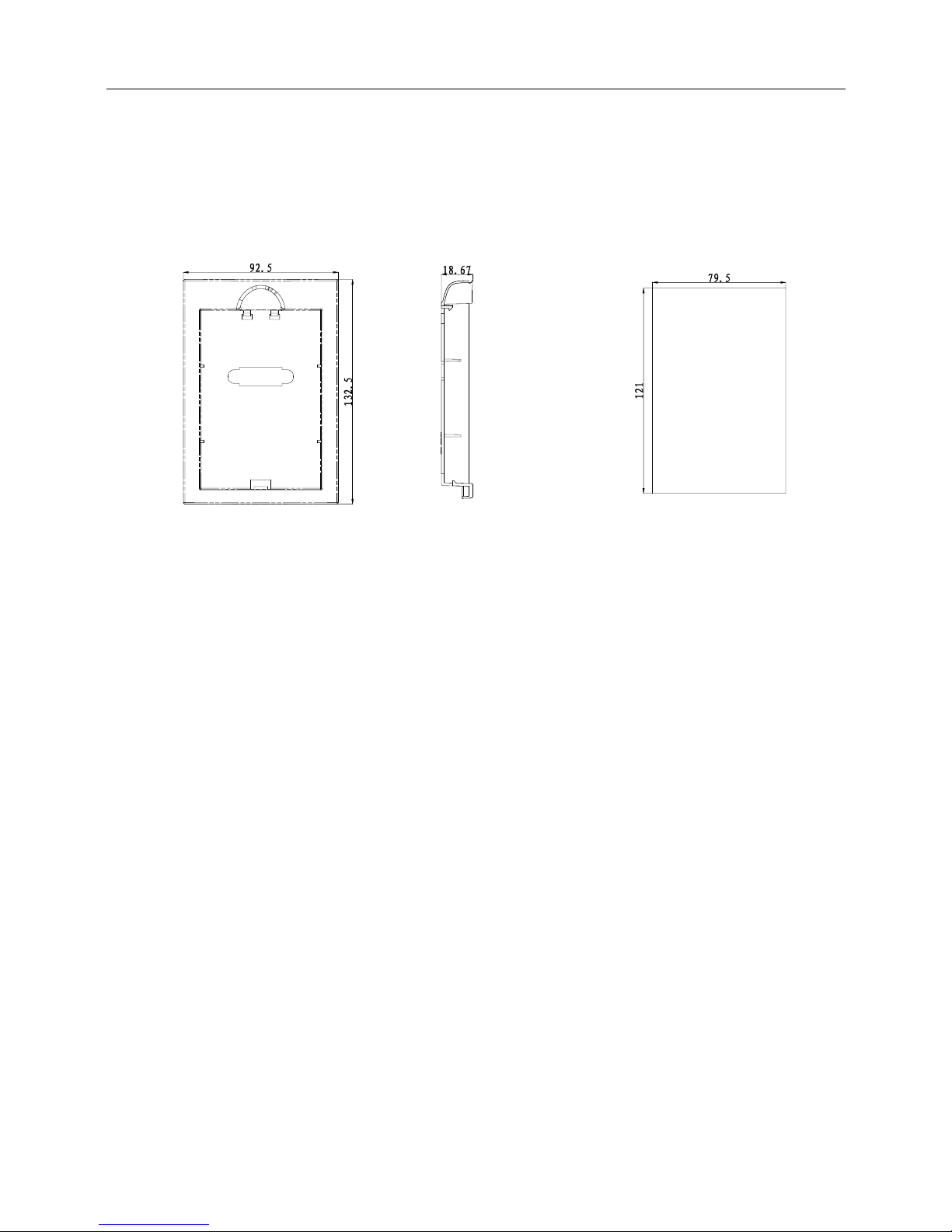
1.8 Pallet Outline and Mounting Dimension
TMP−DP03 is the mounting pallet when the operation panel is to install on the electric control cabinet.
The outline and dimension are as follows:
Pallet(TMP-DP03) Open pore dimension of pallet
Fig.1-6 Pallet outline and mounting dimension
Page 19
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
15
1.9 Braking Resistor Lectotype
Inverter model
Brakin
g unit
Braking resistor unit
Braking torque%
Power
Resis
tor
Qty.
TMP−0R4G-2
Built-
in as
stand
ard
70W
200Ω
1
220
TMP−0R7G-2
70W
200Ω
1
125
TMP−1R5G-2
260W
100Ω
1
125
TMP−2R2G-2
260W
70Ω
1
120
TMP−0R7G-4/1R5P-4
70W
750Ω
1
130
TMP−1R5G-4/2R2P-4
260W
400Ω
1
125
TMP−2R2G-4/4R0P-4
260W
250Ω
1
135
TMP−4R0G-4/5R5P-4
390W
150Ω
1
135
TMP−5R5G-4/7 R5P-4
520W
100Ω
1
135
TMP−7R5G-4/011P-4
780W
75Ω
1
130
TMP−011G-4/015P-4
1040W
50Ω
1
135
TMP−015G-4/018P-4
1560W
40Ω
1
125
TMP−018G-4/022P-4
Built-in as optio n
4800W
32Ω
1
125
TMP−022G-4/030P-4
4800W
27.2Ω
1
125
TMP−030G-4/037P-4
6000W
20Ω
1
125
TMP−037G-4/045P-4
9600W
16Ω
1
125
TMP−045G-4/055P-4
9600W
13.6Ω
1
125
TMP−055G-4/075P-4
6000W
20Ω
2
135
TMP−075G-4/090P-4
9600W
13.6Ω
2
145
Note: The connection mode for multiple braking resistors is parallel connection. For example, the inverter of
TMP-055G-4/075P-4, the braking resistor lectotype: it is suggest to select two 6000W, 20Ω braking resistor
parallel connection, amount to braking resistor is 12000W, 10Ω.
Page 20
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
16
Chapter 2 Inverter Installation
2.1 Environment for Product Installation
Avoid installing the product in the sites with oil mist, metal powder and dust.
Avoid installing the product in the sites with hazardous gas and liquid, and corrosive, combustible
and explosive gas.
Avoid installing the products in salty sites.
Do not install the product in the sites with direct sunlight.
Do not mount the product on the combustible materials, such as wood.
Keep the drilling scraps from falling into the inside of inverter during the installation.
Mount the product vertically in the electric control cabinet, mount the cooling fan or air conditioner
to prevent the ambient temperature from rising to above 45 ºC.
For the sites with adverse environment, it is recommended to mount the inverter heatsink outside
the cabinet.
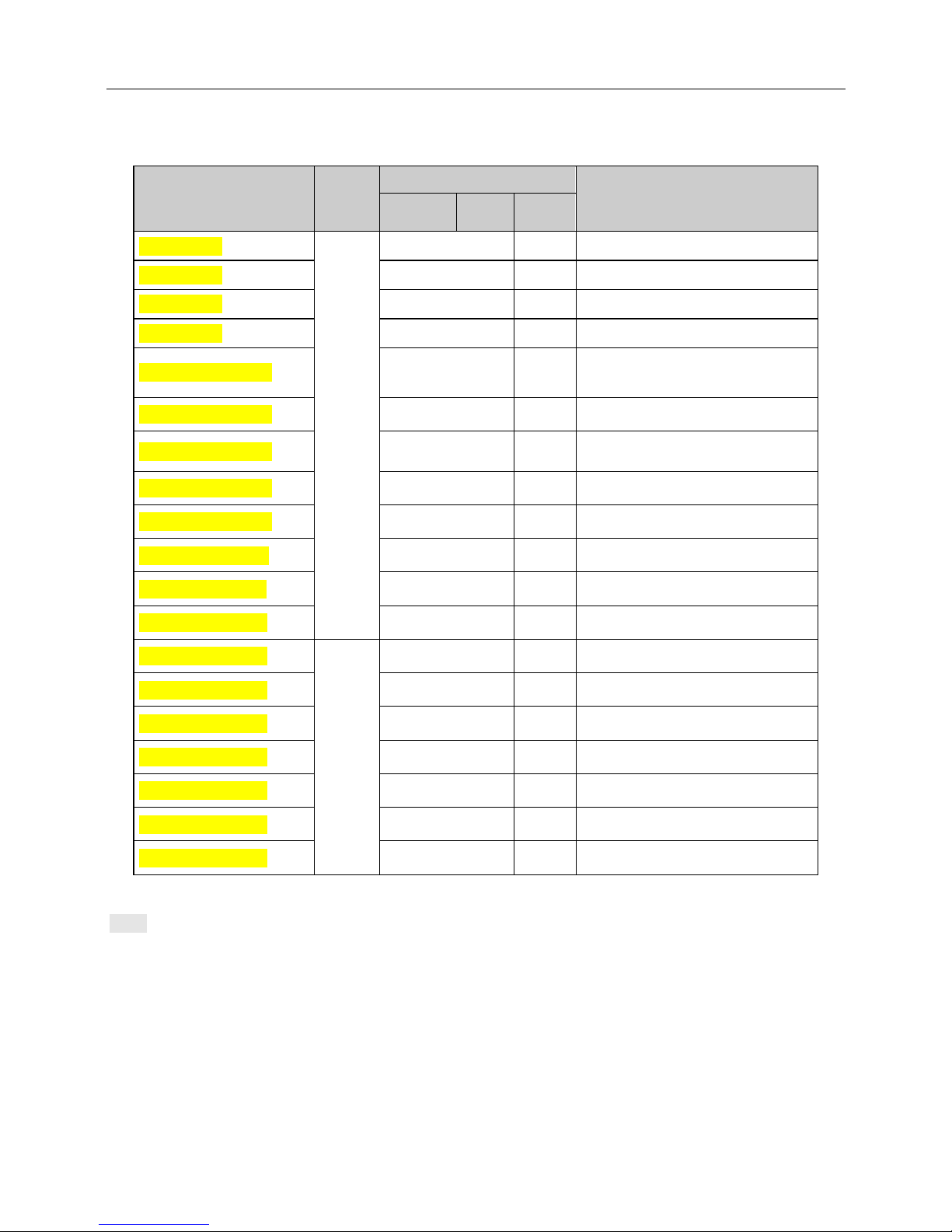
2.2 Mounting Direction and Space
In order not to reduce the inverter cooling effect, the inverter must be mounted vertically, and certain
space must be maintained, as shown in Fig. 2−1 and Fig.2−2.
Fig.2−1 Fig.2−1 Mounting direction and space forTMP-0R4G-2~TMP-2R2G-2 and TMP-0R7G-4/1R5P-4
and below power class
Note:
Air circulation position
Air circulation position
Above 120mm
Above 120mm
Air circulation position
Air circulation position
Above 120mm
Above 120mm
Above 30mm
Above 30mm
Page 21
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
17
When the TMP inverters are mounted side by side in the cabinet, please remove the upper dust
guard and the lower leading board.
2.3 Removal and Mounting of Operation Panel and Cover
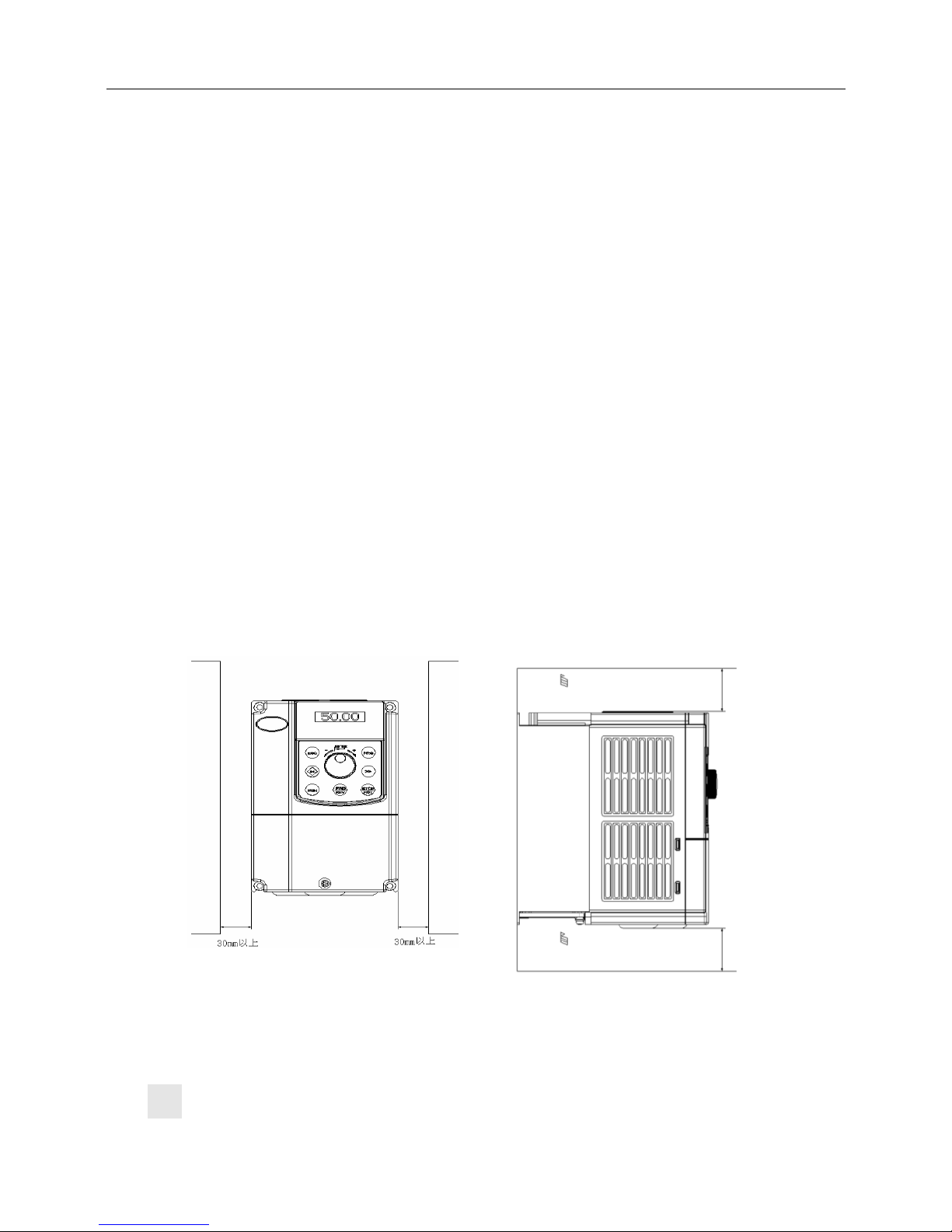
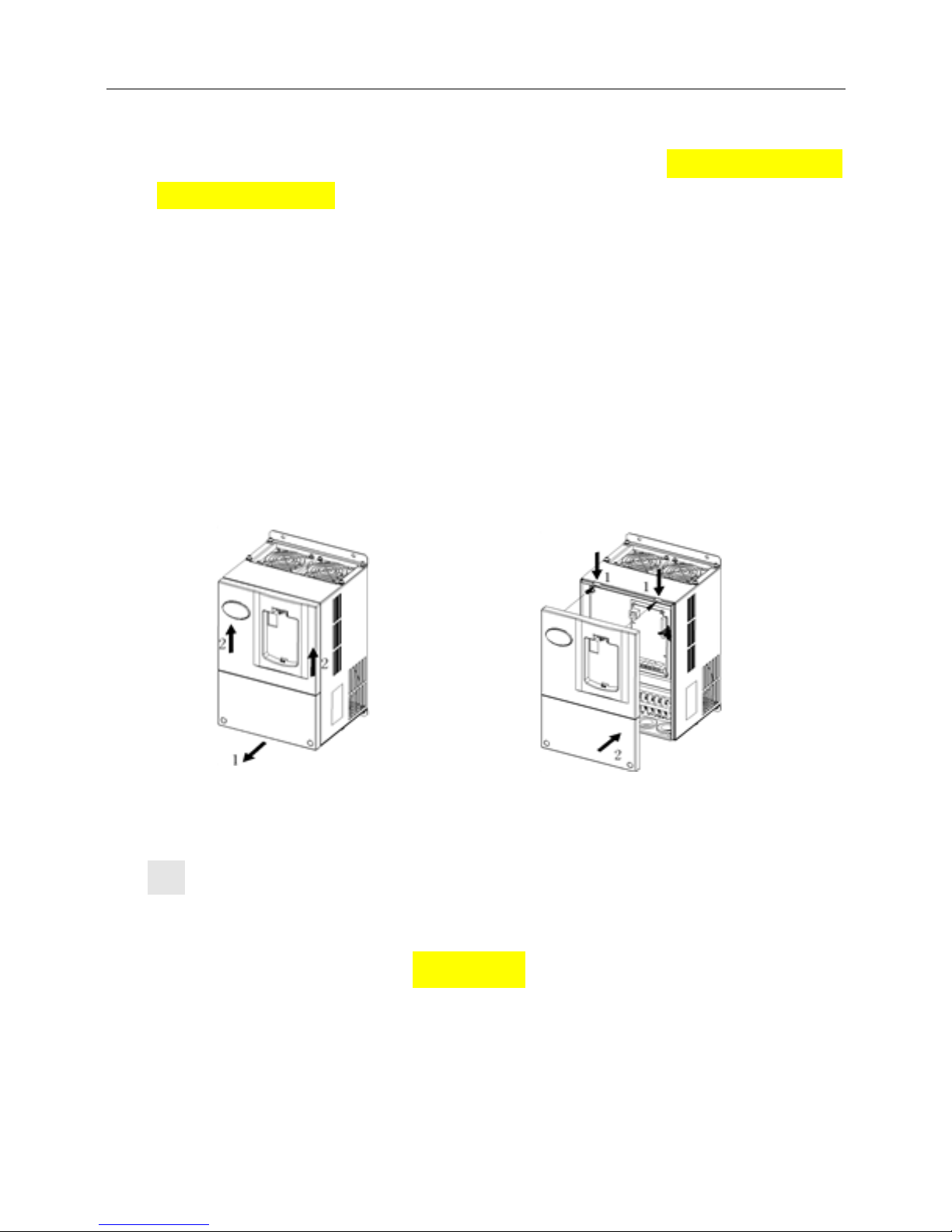
2.3.1 Removal and Mounting of Operation Panel
Removal of operation panel
As shown in Fig. 2−3, the grab on the operation panel forcefully in direction 1, and then lift the panel
body in direction 2.
Mounting of operation panel
As shown in Fig.2−4, align with the lower clamping position of the operation panel in direction 1,
and then press down the operation panel in direction 2, until the “crack” sound is heard.
Do not mount the operation panel in any other direction; otherwise, the operation panel will have
poor contact.
Fig. 2−3 Removal of operation panel Fig.2−4 Mounting of operation panel
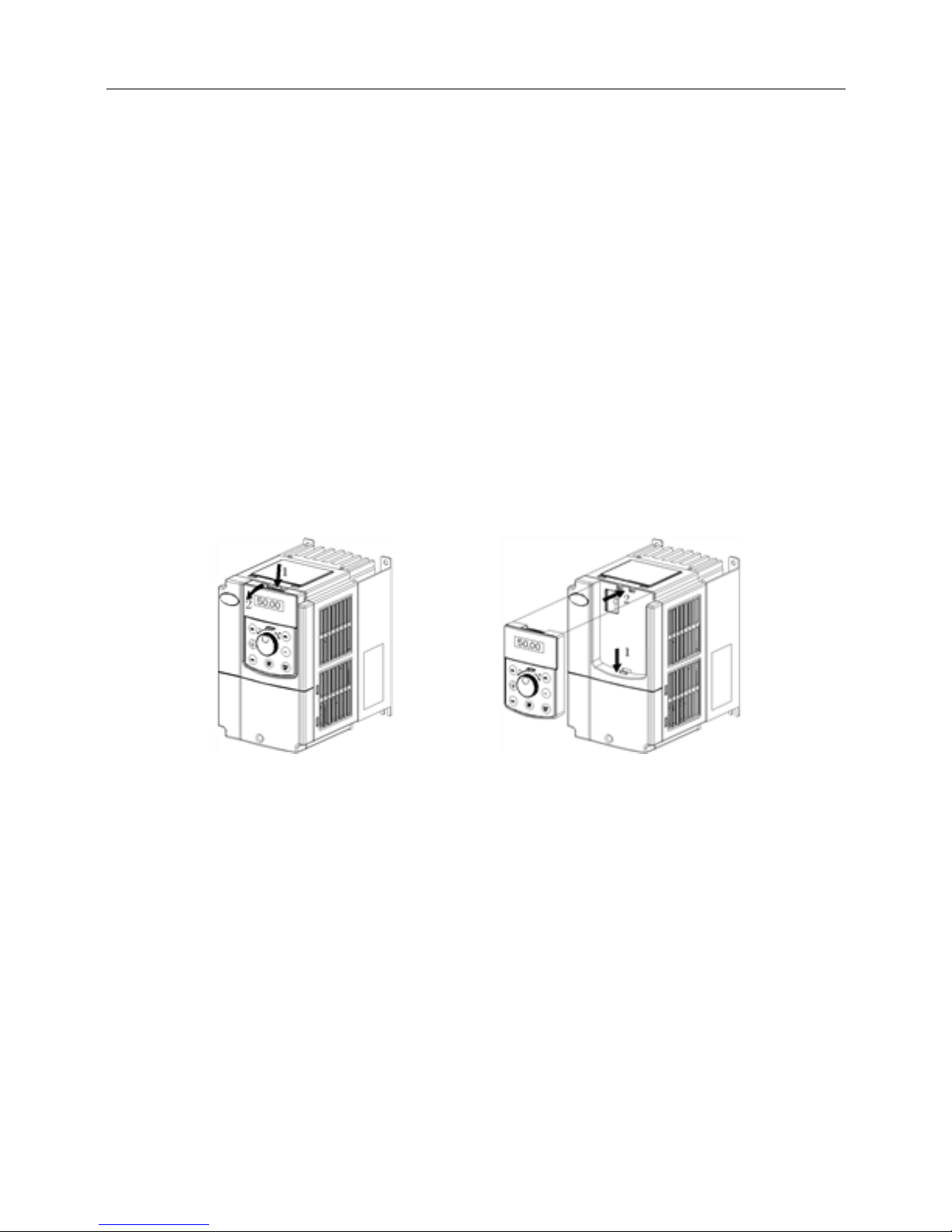
2.3.2 Removal and Mounting of Covers of Inverter with Plastic Enclosure
Removal of operation panel
Please refer to 2.3.1 removal and mounting of operation panel.
Removal of lower cover
After removing the mounting screws of the cover, press the left and right sides of the cover
forcefully in direction 1 and at the same time lift the cover in direction 2, as shown in Fig. 2−5.
Removal of upper cover
As shown in Fig.2−6, press the left and right sides of the cover forcefully in direction 1, and at the
same time lift the cover in direction 2.
Page 22
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
18
Fig.2−5 Removal of lower cover Fig.2−6 Removal of upper cover
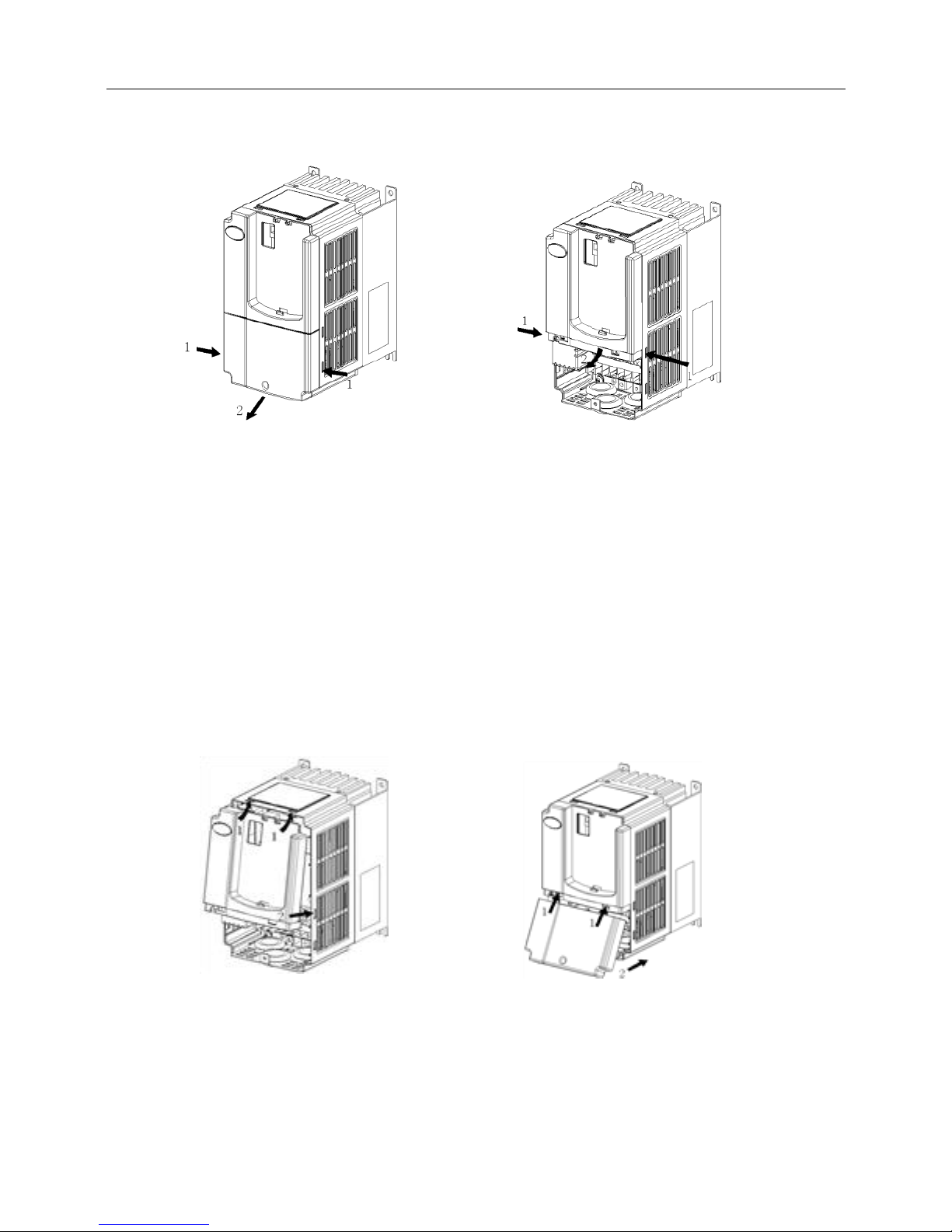
Mounting of upper cover
After the wiring of main circuit terminals and control circuit terminals, insert the upper claw grab of
the upper cover into the groove of the inverter body, as shown in position 1 in Fig.2−7, and then
press the lower part of the upper cover in direction 2 as shown in Fig.2−7, until the “crack” sound is
heard.
Mounting of lower cover
Insert the upper claw grab on the lower cover into the groove of the upper cover, as shown in
position 1 of Fig.2−8, and then press the lower part of the lower cover in direction 2 of Fig.2−8, until
the “crack” sound is heard. Now, tighten the cover screws.
Fig.2−7 Mounting of upper cover Fig.2−8 Mounting of lower cover’
Mounting of operation panel
Please refer to 2.3.1 Removal and mounting of operation panel.
Page 23
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
19
2.3.3 Removal and Mounting of Covers of TMP−011G-4/015P-4 ~
TMP−075G-4/090P-4and Above Power Class Inverter with Sheet-metal Enclosure
Removal of operation panel
Please refer to 2.3.1 Removal and mounting of operation panel.
Removal of cover
Remove the mounting screws on the lower part of the cover, lift the cover in direction 1 as shown in
Fig.2−9, and then take out the cover in direction 2.
Mounting of cover
After the wiring of the main circuit terminals and control circuit terminals, cramp the cover in
direction 1 as shown in Fig.2−10, press down the cover in direction 2 and then tighten the cover
screws.
Fig.2−9 Removal of cover Fig.2−10 Mounting of cover
Mounting of operation panel
Please refer to 2.3.1 Removal and mounting of operation panel.
Note:
Do not directly mount the cover with operation panel on the inverter, otherwise, the operation panel will
have poor contact.
2.3.4 Open and Close of Doors of TMP−090G-4 and Above Power Class Inverter with
Sheet-metal Enclosure
Opening of the door
Press the latch following direction 1 in Fig.2−11 and open the door following direction 2.
Removal of operation panel
Page 24
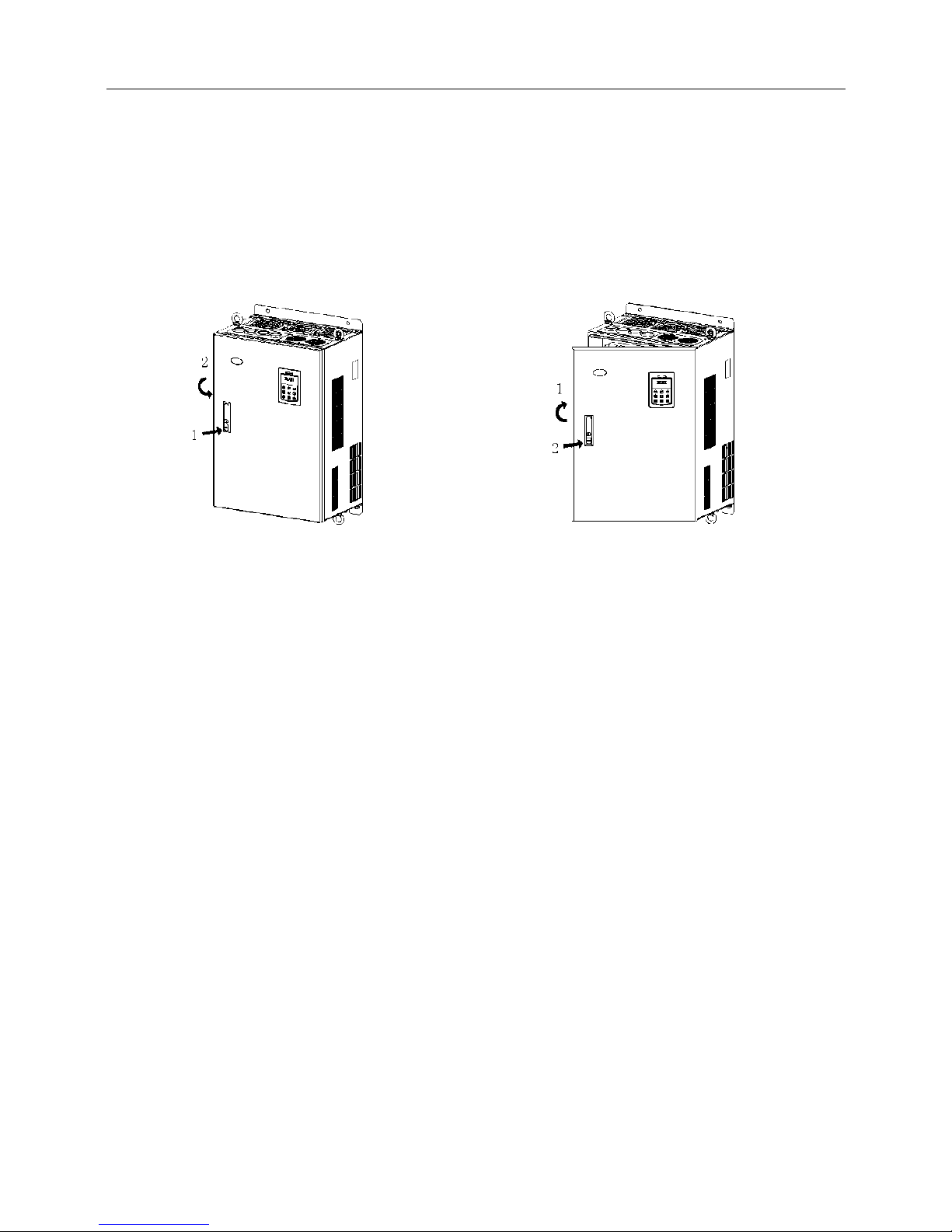
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
20
The operation panel is connected to the control board through the standard network cable and will not
interfere with the open/close of the door. To remove the operation panel, refer to section 2.3.1 Removal
and Mounting of Operation Panel
Mounting of cover
After the wiring operation of main circuit terminals and control circuit terminals is completed, close the
door following direction 1 in Fig.2−12, and then press down the latch following direction 2 to lock the
door.
Fig. 2−11 opening the door Fig. 2−12 closing the door
Page 25

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
21
Chapter 3 Wiring of Inverter
3.1 Connection of the Product and Peripheral Devices
Fig.3−1 Connection diagram of the product and peripheral devices
Power supply
Contactor
Input AC reactor
DC reactor
Inverter
Grounding
Motor
Grounding
Circuit breaker or
leakage circuit breaker
Input noise filter
Output noise filter
Braking resistor
Output AC reactor
Page 26
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
22
3.2 Description of Peripheral Devices for Main Circuit
Circuit breaker
The capacity of the circuit breaker shall be 1.5 ~ 2 time of the rated current of the inverter.
The time features of the circuit breaker shall fully consider the time features of the inverter
overload protection.
Leakage circuit
breaker
Because the inverter output is the high-frequency pulse, there will be high-frequency leakage
current. Special leakage circuit breaker shall be used when installing leakage circuit breaker
at the input end of the inverter.
It is suggested that B type leakage circuit breaker be used, and the leakage current value
shall be set as 300mA.
Contactor
Frequent open and close of contactor will cause inverter failure, so the highest frequency for
the open and close of contactor shall not exceed 10 times/min.
When braking resistor is used, to void the overtemperature damage of the braking resistor,
thermal protection relay with braking resistor overtemperature detection shall be installed to
disconnect the contactor at the contact control power side of the thermal protection relay.
Input AC reactor
or DC reactor
1. The inverter power supply capacity is more than 600kVA or 10 times of the inverter capacity.
2. If there is switch type reactive-load compensation capacitor or load with silicon control at
the same power node, there will be high peak current flowing into input power circuit,
causing the damage of the rectifier components.
3. When the voltage unbalancedness of the three-phase power supply of the inverter
exceeds 3%, the rectifier component will be damaged.
4. It is required that the input power factor of the inverter shall be higher than 90%.
When the above situations occur, install the AC reactor at the input end of the inverter or DC
reactor to the DC reactor terminal.
Input noise filter
The noise input from the power end to the inverter and output from the inverter to the power
end can be reduced.
Thermal protection
relay
Although the inverter has motor overload protection function, when one inverter drives two or
more motors or multi-pole motors, to prevent the motor overtemperature failure, thermal
protection relay shall be installed between the inverter and each motor, and the motor
overload protection parameter P9.16 shall be set as “2” (motor protection disabled).
Output noise filter
When the output end of the inverter is connected with noise filter, the conduction and
radiation interference can be reduced.
Output AC reactor
When the cable connecting the inverter and the motor is longer than 100m, it is suggested to
install AC output reactor to suppress the high-frequency oscillation to avoid the damage to
motor insulation, large leakage current and frequent inverter protective action.
3.3 Lectotype of mMain Circuit Peripheral Devices
Inverter model
Circuit
(A)
(A)
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, ⊕1, ⊕2/B1, B2,
Ө
, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
Grounding terminal PE
Terminal
screw
Tightenin
g torque
(N·m)
Wire
specificatio
n (mm2)
Terminal
screw
Tightening
torque
(N·m)
Wire
specification
(mm2)
TMP−0R4G-2
16
10
M4
1.2~1.5
2.5
M4
1.2~1.5
2.5
TMP−0R7G-2
25
16
M4
1.2~1.5
2.5
M4
1.2~1.5
2.5
TMP−1R5G-2
32
25
M4
1.2~1.5
4
M4
1.2~1.5
2.5
TMP−2R2G-2
40
32
M4
1.2~1.5
6
M4
1.2~1.5
4
TMP−0R7G-4/1R5P-4
10
10
M4
1.2~1.5
2.5
M4
1.2~1.5
2.5
TMP−1R5G-4/2R2P-4
16
10
M4
1.2~1.5
2.5
M4
1.2~1.5
2.5
TMP−2R2G-4/4R0P-4
16
10
M4
1.2~1.5
2.5
M4
1.2~1.5
2.5
TMP−4R0G-4/5R5P-4
25
16
M4
1.2~1.5
4
M4
1.2~1.5
4
TMP−5R5G-4/7 R5P-4
32
25
M4
1.2~1.5
6
M4
1.2~1.5
6
TMP−7R5G-4/011P-4
40
32
M4
1.2~1.5
6
M4
1.2~1.5
6
Page 27
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
23
Inverter model
Circuit
(A)
(A)
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, ⊕1, ⊕2/B1, B2,
Ө
, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
Grounding terminal PE
Terminal
screw
Tightenin
g torque
(N·m)
Wire
specificatio
n (mm2)
Terminal
screw
Tightening
torque
(N·m)
Wire
specification
(mm2)
TMP−011G-4/015P-4
63
40
M5
2.5~3.0
6
M5
2.5~3.0
6
TMP−015G-4/018P-4
63
63
M5
2.5~3.0
6
M5
2.5~3.0
6
TMP−018G-4/022P-4
100
63
M6
4.0~5.0
10
M6
4.0~5.0
10
TMP−022G-4/030P-4
100
100
M6
4.0~5.0
16
M6
4.0~5.0
16
TMP−030G-4/037P-4
125
100
M6
4.0~5.0
25
M6
4.0~5.0
16
TMP−037G-4/045P-4
160
100
M8
9.0~10.0
25
M8
9.0~10.0
16
TMP−045G-4/055P-4
200
125
M8
9.0~10.0
35
M8
9.0~10.0
16
TMP−055G-4/075P-4
315
250
M10
17.6~22.5
50
M10
14.0~15.0
25
TMP−075G-4/090P-4
350
330
M10
17.6~22.5
60
M10
14.0~15.0
35
TMP−093G-4
TMP−110P-4
315
250
M10
17.6~22.5
70
M10
14.0~15.0
35
TMP−110G-4
TMP−132P-4
350
330
M10
17.6~22.5
100
M10
14.0~15.0
50
TMP−132G-4
TMP−160P-4
400
330
M12
31.4~39.2
150
M12
17.6~22.5
75
TMP−160G-4
TMP−185P-4
500
400
M12
31.4~39.2
185
M12
17.6~22.5
50×2
TMP−185G-4
TMP−200P-4
630
500
M12
48.6~59.4
240
M12
31.4~39.2
60×2
TMP−200G-4
TMP−220P-4
630
500
M12
48.6~59.4
240
M12
31.4~39.2
60×2
TMP−220G-4
TMP−250P-4
800
630
M12
48.6~59.4
150×2
M12
31.4~39.2
75×2
TMP−250G-4
TMP−280P-4
1000
630
M12
48.6~59.4
185×2
M12
31.4~39.2
100×2
TMP−280G-4
TMP−315P-4
1000
630
M12
48.6~59.4
185×2
M12
31.4~39.2
100×2
TMP−315G-4
TMP−355P-4
1000
800
M14
48.6~59.4
250×2
M14
31.4~39.2
125×2
TMP−355G-4
TMP−400P-4
1200
800
M14
48.6~59.4
325×2
M14
31.4~39.2
150×2
TMP−400G-4
TMP−450P-4
1500
1000
M14
48.6~59.4
325×2
M14
31.4~39.2
150×2
TMP−450G-4
TMP−500P-4
2000
1500
M14
48.6~59.4
350×2
M14
31.4~39.2
175×2
TMP−500G-4
TMP−560P-4
2000
1500
M14
48.6~59.4
350×2
M14
31.4~39.2
175×2
Page 28

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
24
3.4 Product Terminal Configuration
TMP−0R4-2G~TMP−2R2G-2
TMP−7R5G-4/011P-4 and below power class TMP−7R5G-4/011P-4 and above power class
Fig.3−2 Product terminal configuration
Control circuit
terminal
Main circuit
terminal
Grounding
terminal
Control circuit
terminal
Main circuit
terminal
Grounding
terminal
Page 29

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
25
3.5 Functions of Main Circuit Terminal
3.5.1 TMP−0R4G-2~TMP−2R2G-2 和 TMP−0R7G-4/1R5P-4~TMP−015G-4/018P-4
3.5.2 TMP−018G-4/022P-4~TMP-630G-4
Terminal symbol
Terminal name and function description
R、S、T
Three-phase AC input terminal
⊕1、⊕
2
DC reactor connecting terminal, short circuited with copper bus upon
⊕
2、 Ө
DC power input terminal; DC input terminal of external braking unit
U、V、W
Three-phase AC output terminal
Grounding terminal PE
3.6 Attention for Main Circuit Wiring
3.6.1 Power Supply Wiring
It is forbidden to connect the power cable to the inverter output terminal, otherwise, the internal
components of the inverter will be damaged.
To facilitate the input side overcurrent protection and power failure maintenance, the inverter shall
connect to the power supply through the circuit breaker or leakage circuit breaker and contactor.
Please confirm that the power supply phases, rated voltage are consistent with that of the nameplate,
otherwise, the inverter may be damaged.
3.6.2 Motor Wiring
It is forbidden to short circuit or ground the inverter output terminal, otherwise the internal
components of the inverter will be damaged.
Terminal symbol
Terminal name and function description
R、S、T
Three-phase AC input terminal
⊕
、B
Connecting terminal of braking resistor
⊕
、
Ө
DC power input terminal; DC input terminal of external braking unit
U、V、W
Three-phase AC output terminal
Grounding terminal PE
Page 30
TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
26
Avoid short circuit the output cable and the inverter enclosure, otherwise there exists the danger of
electric shock.
It is forbidden to connect the output terminal of the inverter to the capacitor or LC/RC noise filter with
phase lead, otherwise, the internal components of the inverter may be damaged.
When contactor is installed between the inverter and the motor, it is forbidden to switch on/off the
contactor during the running of the inverter, otherwise, there will be large current flowing into the inverter,
triggering the inverter protection action.
Length of cable between the inverter and motor
If the cable between the inverter and the motor is too long, the higher harmonic leakage current of the
output end will cause adverse impact on the inverter and the peripheral devices. It is suggested that
when the motor cable is longer than 100m, output AC reactor be installed. Refer to the following table for
the carrier frequency setting.
Length of cable between the
inverter and motor
Less than 50m
Less than 100 m
More than 100m
Carrier frequency (PA.00)
Less than 15kHz
Less than 10kHz
Less than 5kHz
3.6.3 Grounding Wiring
The inverter will produce leakage current. The higher the carrier frequency is, the larger the leakage
current will be. The leakage current of the inverter system is more than 3.5mA, and the specific value of
the leakage current is determined by the use conditions. To ensure the safety, the inverter and the motor
must be grounded.
The grounding resistance shall be less than 10ohm. For the grounding wire diameter requirement,
refer to 3.3 lectotype of main circuit peripheral devices.
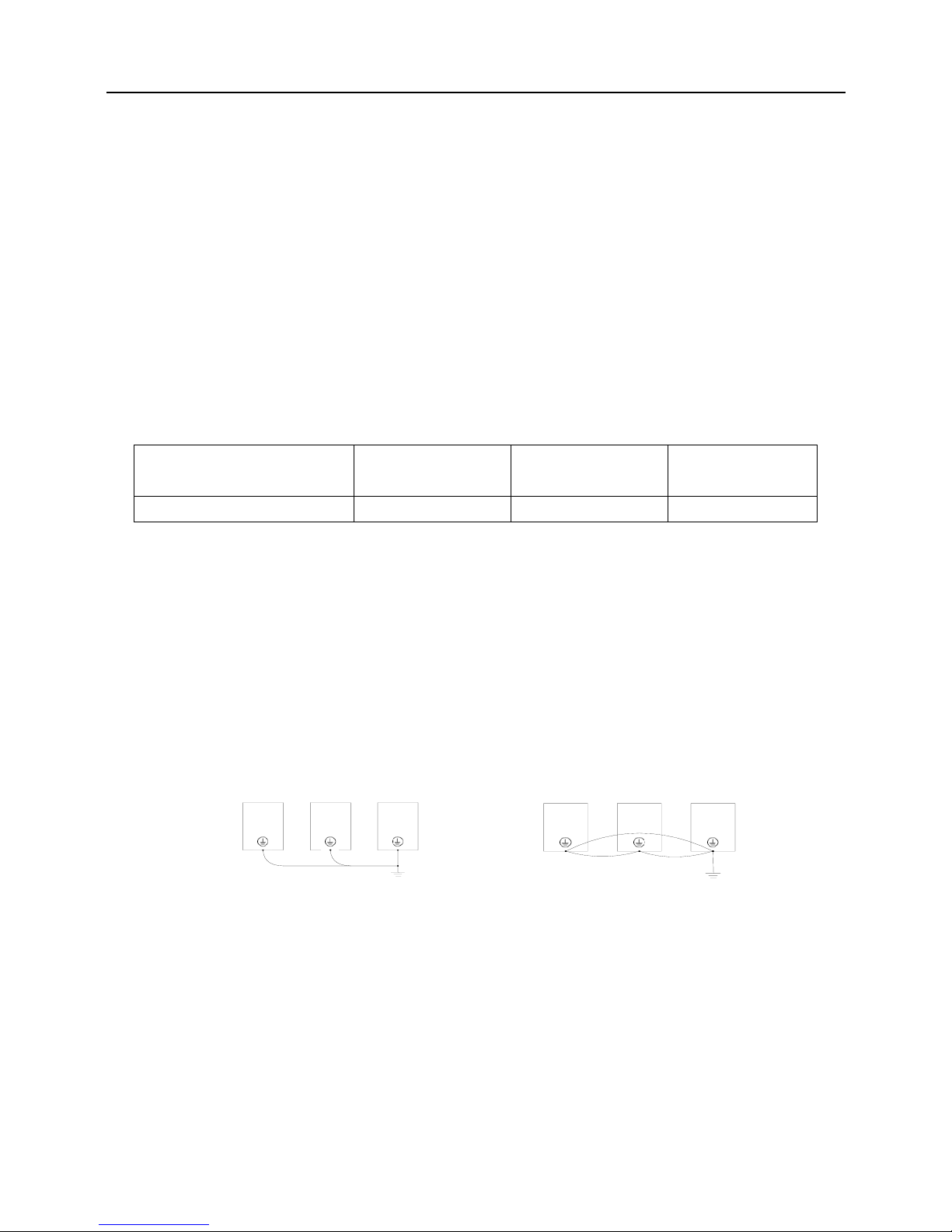
Do not share grounding wire with the welding machine and other power equipment.
In the applications with more than 2 inverters, keep the grounding wire from forming a loop.
Correct Wrong
Fig. 3−3 Grounding wiring
Page 31

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
27
3.6.4 Countermeasures for Conduction and Radiation Interference
Fig.3−4 Noise current illustration
When the input noise filter is installed, the wire connecting the filter to the inverter input power end
shall be as short as possible.
The filter enclosure and mounting cabinet shall be reliably connected in large area to reduce the back
flow impedance of the noise current Ig.
The wire connecting the inverter and the motor shall be as short as possible. The motor cable adopts
4-core cable, with the grounding end grounded at the inverter side, the other end connected to the motor
enclosure. The motor cable shall be sleeved into the metal tube.
The input power wire and output motor wire shall be kept away from each other as long as possible.
The equipment and signal cables vulnerable to influence shall be kept far away from the inverter.
Key signal cables shall adopt shielding cable. It is suggested that the shielding layer shall be
grounded with 360-degree grounding method and sleeved into the metal tube. The signal cable shall be
kept far away from the inverter input wire and output motor wire. If the signal cable must cross the input
wire and output motor wire, they shall be kept orthogonal.
When analog voltage and current signals are adopted for remote frequency setting, twinning
shielding cable shall be used. The shielding layer shall be connected to the grounding terminal PE of the
inverter, and the signal cable shall be no longer than 50m.
The wires of the control circuit terminals RA/RB/RC and other control circuit terminals shall be
separately routed.
It is forbidden to short circuit the shielding layer and other signal cables or equipment.
When the inverter is connected to the inductive load equipment (e.g. electromagnetic contactor, relay
and solenoid valve), surge suppressor must be installed on the load equipment coil, as shown in Fig.3-5.
Fig.3−5 Application of inductive load surge suppressor
Input filter
Inverter
Filtering cable
Input filter
Inverter
Filtering cable
DC 24V AC 220V
AC 220V
感性
负载
感性
负载
感性
负载
压敏
电阻
Inductive
load
Inductive
load
Inductive
load
Piezoresistor
DC 24V AC 220V
AC 220V
感性
负载
感性
负载
感性
负载
压敏
电阻
Inductive
load
Inductive
load
Inductive
load
Piezoresistor
Page 32

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
28
3.7 Terminal Wiring
Braking resistor
B
R
S
T
U
V
W
M
Morotr
Three phase AC
power supply
Circult braker
Power grounding
Mortor grounding
Main circult
X1
X2
X3
X4
X5
X6
X7/DI
CM
+10V
AI1
GND
AI2
485+
485-
GND
(Compatible with pulse input)
Multi function input 1
Analog input reference voltage
(DC 0~10V)
10kΩ
P
P
Analog input
DC 0~10V
DC 0~20mA
Switchable)
(
P
Modbus
communication
RS485
AO1
AO2
GND
A1
+24V
Y1
P
+
-
P
+
-
(DC 0~10V)
DC 0~10V
DC 0~20mA
Switchable)
(
C1
B1
Relay output
250V AC/1A
30V DC/1A
Relay
CM
Analog input/analog output
AI2
V
I
AO2
V
I
485
ON
OFF
P
Shielding
cable
Twisted shielding
cable
Operation panel
interface
CN2
Control circult
Multi function input 2
Multi function input 3
Multi function input 4
Multi function input 5
Multi function input 6
Multi function input 7
485 terminal resistor selecting switch
Analog output 1
Analog output 2
Fig.3−6 Terminal wiring diagram (take TMP−015G-4/018P-4 as an example)
Page 33

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
29
3.8 Functions of Control Circuit Terminals
Type
Terminal
symbol
Terminal function
description
Technical specification
Terminal
485
485+
Positive end of 485
differential signal
Rate: 4800/9600/19200/38400/57600bps
Up to 32 sets of equipment can be paralleled. Relay
shall be used if the number exceeds 32.
Maximum distance: 500m (adopt standard twisted
shielding cable)
485−
Negative end of 485
differential signal
GND
Shielding grounding of 485
communication
Internal isolated with COM
Operation
panel 485
CN2
485 port of operation panel
When used for communication connection with host
The maximum distance is 15m for the communication
connection of operation panel
Digital input
+24V
+24V
24V±10%, internal isolated with GND,
Maximum load: 200mA, with overload and short
circuit protection
X1~X6
Multi-functional input
terminals 1 ~ 6
Input specification: 24VDC,5mA
Frequency range: 0~200Hz
Voltage range: 24V±20%
X7/DI
Multi-functional input or
pulse input
Multi-functional input: same as X1~X6
Pulse input: 0.1Hz~10kHz; voltage range: 24V±20%
CM
+24V grounding
Internal isolated with GND
Digital
outpu
Y1
Open collector output
Voltage range: 24V±20%, maximum input current:
50mA
CM
Open collector output
common end
Internal isolated with GND
Analog
input
+10V
Analog input reference
voltage
10V ±3%, internal isolated with COM,
Maximum output current: 10mA, with short circuit
and overload protection
AI1
Analog input channel 1
0~10V: Input impedance 20kΩ, maximum input
voltage : 15V
Resolution: 10 bits (0.025%)
AI2
Analog input channel 2
0~20mA: Input impedance 500Ω, maximum input
current: 30mA
0~10V: Input impedance 20kΩ, maximum input
voltage : 15V
Resolution: 10 bits (0.025%)
0~20mA or 0~10V analog input can be selected
through jumper.
GND
Analog grounding
Internal isolated with COM
Analog
output
AO1
Analog output 1
0~20mA: allowable output impedance 200~500Ω
0~10V: allowable output impedance ≥10kΩ
Output precision: 2%, resolution: 10 bits (0.1%)
with short circuit protection function,
0~20mA or 0~10V analog output can be selected
through jumper.
AO2
Analog output 2
0~20mA: allowable output impedance 200~500Ω
0~10V: allowable output impedance ≥10kΩ
Output precision: 2%, resolution: 10 bits (0.1%)
with short circuit protection function,
0~20mA or 0~10V analog output can be selected
through jumper.
Page 34

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
30
GND
Analog grounding
Internal isolated with COM
Relay
output
A1/B1/C1
Relay output
A1-B1:Normally open
C1-B1: Normally closed
Contact capacity: 250VAC/1A, 30VDC/1A
Note: ﹡ If the user connects adjustable potentiometer between +10V and GND, the resistance of the
potentiometer shall be no less than 5kΩ,
Note:
1. The arrangement sequence of the control circuit terminals is as follows:
3.9 Lectotype of Control Circuit Peripheral Devices
Terminal number
Terminal
screw
Tightening
torque
(N·m)
Wire
specification
mm2
Wire type
+10V、AI1、AI2、485+、485−、AO1、
AO2、GND
M3
0.5~0.6
0.75
Twinning shielding
cable
+24V、X1、X2、X3、X4、X5、X6、X7/DI、
CM、Y1、CM、A1、B1、C1
M3
0.5~0.6
0.75
Shielding cable
3.10 Description of Jumper Function
Jumper selecting switch in Fig.3-7:
AI2
V
I
AO2
V
I
485
ON
OFF
Name
Function
Leave-factory
AI2
I is the current input (0~20mA), V is the voltage input (0~10V)
0~20mA
AO2
I is the current input (0~20mA), V is the voltage input (0~10V)
0~20mA
485
485 terminal resistor selection: ON: there is 100Ω terminal resistor, OFF: there
is no terminal resistor
There is no terminal
resistor
Page 35

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
31
Chapter 4 Using Instructions of Operation Panel
4.1 Introduction to Operation Panel
Shuttle type operation pane(TMP−DP01) Analog type operation pane(TMP−DP02)
Fig. 4−1 Display unit of operation panel
4.2 Descriptions of Indicators
Symbol of
Name
Meanings
Color
Hz
Frequency indicator
On: Current display parameter is running
frequency
red
A
Current indicator
On: Current display parameter is current
red V Voltage indicator
On: Current display parameter is voltage
red
Hz+A
Rotating speed indicator
On: Current display parameter is rotating
speed
red
A+V
Time indicator
On: Current display parameter is time
red
Hz+A+V
% indicator
On: Current display parameter is rotating
red
No unit indicator
Off: Current display parameter is no unit
−
L/R
Running command
reference mode indicator
On: Running command is given via operation
panel
Off: Running command is given via terminals
Flash: Running command is given via host
computer
red
RUN
Running status indicator
On: Inverter is running
Off: Inverter has stopped
Flash: Inverter is stopping
green
F/R
Run forward indicator
On: In stop status, inverter has run forward
command;
In running status, inverter is running
forward
Flash: Changing from running forward to
running reverse
red
TRIP
Faule/Alarm indicator
ON:Normal condition
Off:Fault condition
Flash:Alarm
red
Page 36

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
32
4.3 Description of Keys on Operation Panel
Symbol
Name
Function
Analog type
Shuttle-type
Programming
key PRG
1、 Switch between program and other states, which includes
parameters display and programming; In menu status, press
this key to return previous menu.
Function
Selection/Save
SET
1、 In program status, press this key to enter next menu.
2、 In menu level 3, press this key to save parameters value.
Increase +
Decrease −
Increase Key
∧
1、 In first level menu, increase function code PX according to edit bit
2、 In second level menu, increase the function code PX YZ data.
3、 In third level menu ,Increase the function code data
Decrease ∨
1、 In first level menu, decrease function code PX according to edit bit
2、 In second level menu, decrease the function PX YZ code data
3、 In third level menu ,decrease the function code data
Shift
>>
1、 In third level menu ,use key >> to shift edit bit of the data
2、 In stop/run status, switch the panel display parameters such
as frequency, current and voltage.
Run Key
RUN
1、 When running command is given via operation panel, the key is
used to control the start of inverter.
2、 After setting the parameter auto tuning,start parameter auto tuning
for inverter startup
Stop/Reset
Key
STOP/RST
1、 When running command is given via operation panel, the key is
used to control the stop of inverter.
2、 When the inverter has fault and has stopped, this key is used as
RESET key to clear the fault alarm.
Multi-function
Key MF
0:Nonfunction;1:Reversal
JOG KEY
JOG
Press this key to start jog operation, release this key to stop the drive.
Page 37

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
33
4.4 Keypad Operating Status
4.4.1 Initialization after power on
When the power is switched on, panel will start 5 seconds’ initiation process. During this
process, LED displays "8.8.8.8.” , and all LED indicators on the panel are in ON state
4.4.2 Stopping State
In stopping state, LED displays default parameters in flashing mode, and the unit
indicator in right side displays the unit of this parameters. In this state, all status
indicators are OFF, press ►► key ,LED displays fault code“n-xx”(xx=00-08),press
SET key to enter and view the parameter; press PRG key to exit; and press ►► key to
scroll through parameters in stopping state.
4.4.3 Running state
In stopping state, after receiving running command, the drive enters running
state. The LED and unit indicator display parameter and its unit respectively.
At this time, running status indicator is ON all the time. Press PRG key to
enter programming menu and view parameter value.
Press ►► key, LED displays running parameter “r-xx” (xx=00~14). Press
SET key to enter and view parameter value; press PRG key to exit this parameter
menu; press ►► key to scroll through monitoring parameters.
4.4.4 Fault alarm state
In stopping, running or programming state, correspondent fault information
will be reported if fault is detected. At this time, LED displays the fault code in
flashing mode. When fault alarm occurs, press PRG key to enter programming
menu and look up the fault log.
When fault alarm occurs, the alarm picture is displayed, and the fault can be
reset by press STOP/RESET key. The drive restores to normal operation upon
clearing the fault, and the fault code is displayed again if the fault has not been
cleared.
Page 38

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
34
4.5 Panel Operation Method
4.5.1 Panel Operation Procedure
Parameter setting method via panel: through three-level menu, users can look
up and modify the function codes very easily.
Three level menu structure: function parameters (first level)→ function
codes(second level)→value of function code(third level). Operation process is
shown in Fig.4-1.
Stop/run
first level
second level
third level
PRG
PRG
SET
PRG
PRG
SET
function codes set
Fig.4-1 Menu Operation Procedure
In the third level menu, user can return second level menu by pressing PRG key or
SET key. The difference is: Parameter settings can be saved in control board if SETkey
is pressed, then LED returns to second level menu and shifts to next function code
automatically; If user presses PRG key, LED returns to second level menu directly, but
the parameters can not be saved and stop at current function code.
4.5.2 Parameter setup
Setting parameters correctly is a premise for actualizingTMP’s performances.
Parameter setting method via panel will be introduced in the following part with rated
power as an example (Change 18.5kW into 7.5kW).
Operation process is shown in Fig.5-2. Press the SHIFT key with single direction
shifting function to shift the flashing bit of parameters (that is modification bit). After
finishing the parameters setup, press the MENU key twice to exit programing state.
Page 39

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
35
50.00
P0
-P0-
P3
-P3-
P3.00
0.4~999.9KW
018.5
018.5
008.5
008.5
007.5
P3.01
50.00
0.4~999.9KW
0.4~999.9KW
0.4~999.9 KW
0.4~999.9 KW
PRG
SET
SET
PRG
SET
stopping state
/ running state
Basic
parameters
Stop monitoring
parameters
motor
parameters
Motor rated power
By three
times
By two
times
Motor rated
voltage
At a time
Stop monitoring
parameters
stopping state
/ running state
Fig 4-2 Procedure of parameter setup
4.6 Parameter Display
In stopping state or running state, various state parameters can be displayed by
LED. The displayed parameters can be decided by PH.00 ~ PH.01 and can be scrolled
through by pressing the SHIFT key. The following is an explanation for the parameters
operation method in stopping and running state.
4.6.1 Switch of Parameter Display in Stopping State
In stopping state, the drive has 9 state parameters which can be scrolled by SHIFT
key, they are: frequency setting, external counting value, digital value input terminal
state, digital value output terminal state, panel potentiometer, analog input AI1, analog
input AI2 and DC bus voltage. Please refer to the explanation of PH.01.
The default value of PH.01 is "preset frequency". If PH.01 value is set to 2, default
display parameter in stopping state will be changed into "DC bus voltage".
User can look up other parameters during stopping state by pressing SHIFT key:
Everytime you press SHIFT key, the next parameter in stopping state will be displayed.
Page 40

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
36
4.6.2 Switch of the running parameters
In running state, maximum 15 running state parameters can be displayed by TMP drive
via SHIFT key.
4.7 Motor auto-tuning procedure
Before selecting vector control mode, user should input motor parameters correctly.
TMP drive can get motor’s standard parameters according to the parameters on
nameplate; In order to get better control performance, you can control the drive to
perform auto-tuning on the motor, so as to get accurate motor parameters.
Parameter tuning can be done through P3.05.
1. Set F0.01 parameter to 0 to select panel running command control mode;
2. According the motor’s name-plat,Set P3.00、P3.01、P3.02、P3.03、P3.04 parameter in proper order。
3. Set P3.05 to1,Slect static auto- tuning,Or set P3.05 to 2,Slect overall auto- tuning ,Press“SET”
key。
4. Press RUN key to start motor auto-tuning, After tuning, the motor stops.
Page 41

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
37
4.8 Running for the First Time
Please follow the procedures to run the inverter for the first time:
P7.10
P7.10
50Hz
FWD
50Hz
REV
5V
10V
AI1
AI2
P7.01=50%
P7.02=0Hz
P7.06=50%
P7.07=0Hz
OR
Note:
◆If fault happens, please judge the fault
causes and clear the fault according to
7.1 Fault and alarm information list.
◆If motor can without connecting the load
rotating auto tuning can be selected
(P3.05=2),otherwise only static auto
tuning can be selected .When enabling
the auto tuning please ensure the motor is
in standstill status .If over voltage or over
current happens in auto tuning process,
you can prolong the acceleration and
deceleration times of P0.16 and P0.17.
Page 42

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
38
Chapter 5 List of Parameters
Meanings of Each Item in Function Code Parameter Table
Item
Mean in gs
Function code
number
The number of function code, such as P0.00
Function code
name
The name of function code, which explains the function code’s meanings.
Function code
selection
Function code parameter setting list
Factory setting
Restore the settings of the function code after the product is delivered (see P0.19).
Order number
The order number of function code
Property
#: This function code can be changed during operation; +: This function code can only be changed
during stopping status; *: The setting of this function code is read-only and cannot be changed.
5.1 Function Parameter Table
Function
code
Name
Description
Factory
setting
Order
number
Property
P0 Group Basic parameter
P0.00
reserved
0
*
P0.01
Running command
selection
0: Keypad control
1: External terminal
2: Commuincation
0
1
+
P0.02
Control mode
0: open loop vector control
1: V/F control
1
2
+
P0.03
Main Frequency
Source
0:Panel setting
1:External analog signal AI1(0~10V)
2 : External analog signal AI2(0~10V) or
0~20mA
3: up/down 1 setting
4: up/down 1 setting
5:Pulse frequency setting
6:Multi Frequency
7:PID
8:Communication setting mode
9:Program run
0
3
+
Page 43

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
39
10:Panel potentiometer setting (0~5V)
P0.04
Main Frequency gain
0.000-9.999
1.000 4 +
P0.05
Zero frequency
source of
multi-speed mode
0:Digital frequency of P0.11
1:External analog signal: AI1
2:External analog signal: AI2
3: Panel potentiometer setting (0~5V)
0
5
+
P0.06
Auxiliary frequency
source
0:External analog signal: AI1(0~10V)
1:External analog signal: AI2(0~10V) or
0~20mA
2: External analog signal:AI1(0~10V)( +/polarity)
3:External analog signal: AI2
AI2(0~10V) or 0~20mA(+/- polarity)
4:pid
0
6
+
P0.07
Auxiliary frequency
range selection
0:Maximum output frequency
1:Main frequency
0
7
+
P0.08
Auxiliary frequency
range
0-100%
100
8
+
P0.09
Setting Frequency
selection
0:Main frequency
1:Auxiliary frequency
2:Main frequency + Auxiliary frequency
3:Main frequency - Auxiliary frequency
4 : switch between Main frequency and
Auxiliary frequency
5:switch between Main frequency and (Main
frequency + Auxiliary frequency)
6:switch between Main frequency and (Main
frequency - Auxiliary frequency)
7 : MAX ( Main frequency , Auxiliary
frequency)
8 : MIN ( Main frequency , Auxiliary
frequency)
9:Traverse operation
0
9
+
P0.10
up/down setting store
selection
0:Store
1:Not Store
0
10
#
Page 44

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
40
P0.11
Digital frequency
setting
0~400.0Hz
50.00
11
#
P0.12
Rotating direction
(Keypad operation)
0: FWD
1: REV
0
12
+
P0.13
Maximum output
frequency
50.00~400.0 Hz
50.00
13
+
P0.14
High frequency limit
0.00~ Maximum output frequency
50.00
14 + P0.15
Low frequency limit
0.00Hz~ High frequency limit
0
15
+
P0.16
Acc time 1
0.1~3600.0s
20.0
16
#
P0.17
Dec time 1
0.1~3600.0s
20.0
17
#
P0.18
Inverter type
select
0:General load mode
1:light load mode (for fan,punp)
0
18
+
P0.19
Parameter
initialization
0: No operation
1: Clear fault information
2: Recover factory setting
Note: After executing 1~2 steps, restores to
zero automatically.
0
19
+
P1 Group Auxiliary function parameters 1
P1.00
Starting mode
0: Start from starting frequency
1: First braking then restart from starting
frequency
2: Speed trace starting
0
20
+
P1.01
Starting frequency
0.50~20.00Hz
0.50
21
+
P1.02
Hold time of Starting
Frequency
0.0~60.0s
0
22 + P1.03
DC injection braking time
at start
0.0~60.0s
0
23
+
P1.04
DC injection braking
current start
0.0~100.0%(motor rated current)
0
24
+
P1.05
Stopping mode
0: Dec-to-stop
0
25
+
Page 45

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
41
1: Dec-to-stop + DC braking
2: Free run to stop
P1.06
Initial frequency of
DC injection braking
0.00~20.00Hz
0
26
+
P1.07
DC injection braking
time
0:No operation
0.1~60.0s
0
27
+
P1.08
DC injection braking
current
0.0~100.0%(motor rated current)
0
28
+
P1.09
Acc/Dec mode
selection
0: Linear mode
1:reserved
0
29 + P1.10
Time of S curve’ s
start part
10.0%~50.0%
20.0%
30
+
P1.11
Time of S curve’ s
rising part
10.0%~80.0%
60.0%
31
+
P1.12
Restart after power
failure
0: disabled
1: enabled
0
32
+
P1.13
Delay time for
restarting after power
failure
0.0~20.0s
2.0
33
+
P1.14
dynamic braking start
voltage
630-710
660
34 P1.15
Rate of dynamic
braking
0:No dynamic braking
1~100%
90
35
#
P1.16
Action on frequency
lower than lower
frequency limit
0:dormancy
1:start, running at lower frequency limit
2:Stop
0
36
+
P1.17
MF key function
0:No operation; 1:reverse rotation
0
37
+
P1.18
Stop/reset Key
function
0:action on keypad control mode
1:action on both keypad and External
terminal
2:action on both keypad and communication
0
38
+
Page 46

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
42
P1.19
Fan control
function
0:always run after power on
1: stop fan after inverter stop running
1
39
+
P2 Group Auxiliary function parameters 2
P2.00
Acc time 2
0.1~3600s
20.0
40
#
P2.01
Dec time 2
0.1~3600s
20.0
41 # P2.02
Acc time 3
0.1~3600s
20.0
42 # P2.03
Dec time 3
0.1~3600s
20.0
43 # P2.04
Acc time 4
0.1~3600s
20.0
44 # P2.05
Dec time 4
0.1~3600s
20.0
45 # P2.06
Jog Acc time
0.1~20.0s
10.0
46 # P2.07
Jog Dec time
0.1~20.0s
10.0
47 # P2.08
Jog frequency
0.50~60.00Hz
5.00
48 # P2.09
Multi-frequency 1
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
49 # P2.10
Multi-frequency 2
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
50 # P2.11
Multi-frequency 3
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
51 # P2.12
Multi-frequency 4
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
52 # P2.13
Multi-frequency 5
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
53 # P2.14
Multi-frequency 6
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
54 # P2.15
Multi-frequency 7
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
55 # P2.16
Multi-frequency 8
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
56 # P2.17
Multi-frequency 9
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
57 # P2.18
Multi-frequency 10
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
58 # P2.19
Multi-frequency 11
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
59 # P2.20
Multi-frequency 12
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
60 # P2.21
Multi-frequency 13
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
61 # P2.22
Multi-frequency 14
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
62 # P2.23
Multi-frequency 15
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
63 # P2.24
Jump frequency 1
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
64 + P2.25
Jump frequency 2
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
65 + P2.26
Jump frequency 3
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
66
+
Page 47

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
43
P2.27
Jump frequency range
0.00~20.00 Hz
0.00
67 + P2.28
FWD/REV dead time
0.0~3600s
0.5
68
+
P2.29
REV prohibited
0: REV enabled
1: REV disabled
0
69
+
P2.30
Carrier frequency
2.0~12.0KHz
3.0
70
+
P2.31
Zero frequency
threshold
0.0~400.0Hz
0.00
71
+
P2.32
Zero frequency
hysteresis
0.0~400.0 Hz
0.00
72
+
P2.33
Droop control
0.00-10.00Hz
0.00
73
+
P3 Group motor parameters
P3.00
Motor rated power
0.4~999.9KW
Drive’s
rated power
74
+
P3.01
Motor rated voltage
0~440V
380V
75
+
P3.02
Motor rated current
0.1~999.9A
Drive’s
rated value
76
+
P3.03
Motor rated frequency
1.00~400.0Hz
50.00
77 + P3.04
Motor rated speed
1~9999RPM
1440
78
+
P3.05
Motor auto-tuning
0:No operation
1:static auto tuning
2:overall auto- tuning
0
79
+
P3.06
Stator resistance
0.001-20.00%
Motor
parameter
80
+
P3.07
Rotor resistance
0.001-20.00%
Motor
parameter
81
+
P3.08
Self inductance
1.000-9.999
Motor
parameter
82
+
P3.09
Leakage inductance
0.001-1.000
Motor
parameter
83
+
P3.10
Exciting current with
0.0~999.9A
Motor
84
+
Page 48

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
44
no load
parameter
P3.11
reserved
85
+
P4Group V/F control
P4.00
V/f control mode
0: Linear V/F
1: Square V/F
2: 1.5 times torque
3: 1.2 times torque
4: User defined V/f
0
86
+
P4.01
Base voltage
0~440V
380
87
+
P4.02
Base frequency
10.00~400.0 Hz
50.00
88 + P4.03
Intermediate voltage 1
0~P4.04
32
89 + P4.04
Intermediate voltage 2
P4.03~100%
50
90
+
P4.05
Intermediate
frequency 1
0~P4.06
16.00
91
+
P4.06
Intermediate
frequency 2
P4.05~400.0Hz
25.00
92
+
P4.07
Torque boost
0.0~20.0% base voltage
3.0
93 + P4.08
Slip compensation
0.0~10.0%(rated speed)
0.00
94
+
P4.09
AVR function
0: disabled
1: enabled
0
95
+
P5 Group VC control
P5.00
ASR proportional gain
1
0.000~6.000
2.000
96
+
P5.01
ASR integration time
1
0.000~9.999
0.500
97
+
P5.02
ASR proportional gain
2
0.000~6.000
1.000
98 + P5.03
ASR integration time
2
0.000~9.999
1.000
99
+
P5.04
ASR switching
00.00~99.99Hz
5.00
100
+
Page 49

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
45
frequency
P5.05
Slip compensation
gain
50.0~200.0%
100.0
101
+
P5.06
Driving torque limit
0~200.0% (motor rated current)
150.0
102
+
P5.07
Braking torque limit
0~200.0% (motor rated current)
150.0
103 + P5.08
reserved
104 + P5.09
reserved
105 + P5.10
reserved
106
+
P6 Group I/O parameters
P6.00
FWD/REV mode
0: Two-line operation mode 1
1: Two-line operation mode 2
2: 3-line operation mode 1
3: 3-line operation mode 2
0
107
+
P6.01
Up/down rate
0.10~99.99Hz/s
1.00
108
#
P6.02
Definition of input
terminal X1
0 No function
1: FWD
2: REV
3: External reset
4: Jog FWD
5: Jog REV
6: Multi-frequency 1
7: Multi-frequency 2
8: Multi-frequency 3
9: Multi-frequency 4
10: Terminals for selecting Acc/Dec time 1
11: Terminals for selecting Acc/Dec time 2
12: Normally open terminal for inputting
external fault
13: Normally close terminal for inputting
external fault
14: Frequency increase command
15: Frequency decrease command
16: Free run to stop
17: Three-wire control
18: switch of speed given mode
19:Reset terminal for program operation
1
109 + P6.03
Definition of input
terminal X2
2
110
+
P6.04
Definition of input
terminal X3
3
111
+
P6.05
Definition of input
terminal X4
4
112 + P6.06
Definition of input
terminal X5
5
113 + P6.07
Definition of input
terminal X6
16
114
+
P6.08
Definition of input
terminal X7
0
115
+
Page 50

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
46
20: Start traverse operation
21:pause traverse operation
22:DC braking command
23:Acc/Dec disabled command
24:switch between panel control mode and
external terminal control mode
25:switch between panel control mode and
communication control mode
26: Counter trig signal
27: Counter reset signal
28: PID dormancy waking up
29:switch between PID positive mode and
negative mode
30:emergence stop
P6.09
Programmable relay 1
0: No function
1: Drive ready
2: Drive running signal 1
3: Drive running signal 1
4: Frequency arriving signal
5: Frequency detection threshold 1
6: Frequency detection threshold 2
7: High limit frequency arriving
8: Low limit frequency arriving
9: Overload signal
10: Over voltage stall
11: Over current stall
12: External stopping command
13: Preset counting value arriving
14: Specified counting value arriving
15: Low voltage lockup signal
16: Overload pre-alarm
17: Drive failure signal
18: Zero speed running
19:end signal of stage of program operation
20:end signal of cycle of program operation
17
116
+
P6.10
Output terminal Y1
definition
1
117
+
P6.11
Frequency arriving
width
0.00~10.00Hz
0.00
118
#
P6.12
FDT1 level
0.00~400.0 Hz
50.00
119
#
Page 51

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
47
P6.13
FDT1 lag
0.00~10.00Hz
0.00
120 # P6.14
FDT2 level
0.00~400.0 Hz
25.00
121 # P6.15
FDT2 lag
0.00~10.00Hz
0.00
122 # P6.16
Preset value arriving
0~9999
0
123
+
P6.17
Specified value
arriving
0~9999
0
124
+
P6.18
Terminal logic
0~255
0
125
+
P7 Group Analog input terminal
P7.00
AI1 Filter time
0.05~5.00s
0.50
126 # P7.01
Minimum AI1
0.0~100.0%
0.0
127
#
P7.02
Frequency
corresponding to
F7.02
0.00~100.0% (Maximum output frequency)
0.00
128
#
P7.03
Maximum AI1
0.0~100.0%
100.0
129
#
P7.04
Frequency
corresponding to
F7.06
0.00~100.0% (Maximum output frequency)
100.0
130
#
P7.05
AI2 filter time
0.05~5.00s
0.50
131 # P7.06
Minimum AI2
0.0~100.0%
0.0
132
#
P7.07
Frequency
corresponding to
F7.11
0.00~100.0% (Maximum output frequency)
0.00
133
#
P7.08
Maximum AI2
0.0~100.0%
100.0
134
#
P7.09
Frequency
corresponding to
F7.08
0.00~100.0% (Maximum output frequency)
100.0
135
#
P7.10
FWD/REV dead time
range
0.0~10.0%
1.0
136 + P7.11
pulse frequency filter
time
0.05~5.00s
0.50
137
#
P7.12
Minimum pulse
frequency
0.0~100.0%
0.0
138
#
Page 52

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
48
P7.13
Frequency
corresponding to
F7.12
0.00~100.0% (Maximum output frequency)
0.00
139
#
P7.14
Maximum pulse
frequency
0.0~100.0%
0.0
140
#
P7.15
Frequency
corresponding to
F7.14
0.00~100.0% (Maximum output frequency)
100.0
141
#
P8 Group Analog output terminal
P8.00
AO1 output selection
0: Running frequency
1: Frequency setting
2: Output current
3: Output voltage
4: Output torque
5: DC Bus Voltage
6: PI reference
7: PI feedback
8: AI1
9:AI2
1 142
#
P8.01
AO2 output selection
1
143
#
P8.02
Minimum AO1
0.0~100.0%
0.0
144
#
P8.03
Minimum value
corresponding to
F8.02
0.0~100.0%
0.0
145
#
P8.04
Maximum AO1
0.0~100.0%
100.0
146
#
P8.05
Maximum value
corresponding to
F8.05
0.0~100.0%
100.0
147
#
P8.06
Minimum AO2
0.0~100.0%
0.0
148
#
P8.07
Minimum value
corresponding to
F8.06
0.0~100.0%
0.0
149
#
P8.08
Maximum AO2
0.0~100.0%
100.0
150 # P8.09
Maximum value
0.0~100.0%
100.0
151
#
Page 53

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
49
corresponding to
F8.08
P9 Group program operating parameters
P9.00
Programming
operation function
0: Single cycle (Stop after a single cycle)
1: Continuous cycle
2: Maintain the final value
0
152
+
P9.01
Time Unit
0:Second
1:Minute
0
153
+
P9.02
Stage 1 timing T1
0~3600.0
0
154 + P9.03
Stage 2 timing T2
0~3600.0
0
155 + P9.04
Stage 3 timing T3
0~3600.0
0
156 + P9.05
Stage 4 timing T4
0~3600.0
0
157 + P9.06
Stage 5 timing T5
0~3600.0
0
158 + P9.07
Stage 6 timing T6
0~3600.0
0
159 + P9.08
Stage 7 timing T7
0~3600.0
0
160 + P9.09
Stage 8 timing T8
0~3600.0
0
161 + P9.10
Stage 9 timing T9
0~3600.0
0
162 + P9.11
Stage 10 timing T10
0~3600.0
0
163 + P9.12
Stage 11 timing T11
0~3600.0
0
164 + P9.13
Stage 12 timing T12
0~3600.0
0
165 + P9.14
Stage 13 timing T13
0~3600.0
0
166 + P9.15
Stage 14 timing T14
0~3600.0
0
167 + P9.16
Stage 15 timing T15
0~3600.0
0
168
+
P9.17
T1 running mode
0:FWD,Acc/Dec time 1
1:FWD,Acc/Dec time 2
2:FWD,Acc/Dec time 3
3:FWD,Acc/Dec time 4
4:REV,Acc/Dec time 1
5:REV,Acc/Dec time 2
6:REV,Acc/Dec time 3
0
169
+
P9.18
T2 running mode
0
170 + P9.19
T3 running mode
0
171 + P9.20
T4 running mode
0
172 + P9.21
T5 running mode
0
173
+
P9.22
T6 running mode
0
174
+
P9.23
T7 running mode
0
175
+
Page 54

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
50
P9.24
T8 running mode
7:REV,Acc/Dec time 4
0
176 + P9.25
T9 running mode
0
177 + P9.26
T10 running mode
0
178
+
P9.27
T11 running mode
0
179
+
P9.28
T12 running mode
0
180 + P9.29
T13 running mode
0
181 + P9.30
T14 running mode
0
182 + P9.31
T15 running mode
0
183
+
P9.32
Record function
0: Disabled
1:Record,not store after power off
2:Record,store after power off
0
184
+
PA Group PID parameters
PA.00
PID control
characteristic
0: Positive characteristic
1: Negative characteristic
0
185
+
PA.01
Reference selection
0: Panel Digital setting
1: External analog signal AI1
2: External analog signal AI2
3:Communication
4: Panel potentiometer setting (0~5V)
0
186
+
PA.02
Feedback channel
selection
0: External analog signal AI1
1: External analog signal AI2
0
187
+
PA.03
Digital setting of
reference
0.00~10.00V
5.00
188
#
PA.04
Minimum reference
0~100%
0
189 + PA.05
Maximum reference
0~150%
100
190 + PA.06
Minimum feedback
0~100%
0
191 + PA.07
Maximum feedback
0~150%
100
192
+
PA.08
Proportional gain
0.00~10.00
1.00
193
#
PA.09
Integration time
0.01~99.99s
0.5
194
#
Page 55

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
51
PA.10
Differential time
0.00, no differentiation
0.01~99.99s
0
195
#
PA.11
Sample cycle
0.01~99.99s
0.1
196
#
PA.12
Error limit
0.0~15.0%
0.0
197
#
PA.13
Level of abnormal
feedback signal
0~100%
50
198
#
PA.14
Detection time of
abnormal feedback
signal
0:No detection
0.1~3600s
0.0
199
#
PA.15
reserved
0 200
+
PA.16
PID Sleep control
0: No sleep function;
1: Internal waking up,
2. External input terminal
0
201
+
PA.17
Delay time of sleepin
0~3600s
0
202
+
PA.18
Sleeping frequency
0.00~400.0Hz
0.00
203
+
PA.19
Delay time of waking
0.0~60.0s
0.0
204 + PA.20
Waking value
0.0~100.0%
100.0
205
+
Pb GROUP Traverse operation parameters
Pb.00
Traverse mode
0: Auto mode
1: Manual mode
0
206 + Pb.01
Preset traverse
frequency
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
207 # Pb.02
Hold time of preset
traverse frequency
0.0~3600s
0.0
208
#
Pb.03
Preset central
frequency
0.00~400.0 Hz
0.00
209
#
Pb.04
Travers amplitude
0.0~50.0% (Pb.03)
0.0
210 # Pb.05
Step frequency
0.0~50.0% (Pb.04)
0.0
211
#
Pb.06
Traverse cycle
0.1~999.9s
10.00
212
#
Pb.07
Rise time of triangular
wave
0.0~100.0% (Pb.06)
50.0
213
#
PC Group 485 communication parameters
PC.00
Baud rate selection
0:1200BPS
3
214
+
Page 56

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
52
1:2400BPS
2:4800BPS
3:9600BPS
4:19200BPS
5:38400BPS
PC.01
Data format
0: 8,N,2 for RTU (MODBUS)
1: 8,E,1 for RTU (MODBUS)
2: 8,O,1 for RTU (MODBUS)
3: 7,N,2 for ASCII (MODBUS)
4: 7,E,1 for ASCII(MODBUS)
5: 7,O,1 for ASCII(MODBUS)
6: 8,N,1 free communication format
7: 8,E,1 free communication format
8: 8,O,1 free communication format
9: 8,N,2 for RTU (MODBUS)MASTER
0
215
+
PC.02
Local address
1~32,0 is the broadcast address
1
216
+
PC.03
Communication
timeout detect
0, No detection
2.0~10.0s
0
217
+
PC.04
Response delay
2~1000ms
218
+
PC.05
EEROM Store
selection
0:Store
1:no store function
0
219
+
Pd Group Faults and protection parameters
Pd.00
Motor overload
protection mode
0: No protection
1: Common motor protection
2: Variable frequency motor protection
1
220
+
Pd.01
Motor overload
protection factor
20.0~150.0%
100.0
221 + Pd.02
Over voltage stall
selection
0: Disabled
1: Enabled
1
222
+
Pd.03
Stall over voltage
point
120.0~150.0%
120.0
223
+
Pd.04
Selection of overload
0: Detect at constant speed and alarm
0
224
+
Page 57

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
53
pre-alarm detection
1: Detect all the time and alarm
Pd.05
Overload detection
threshold
20.0~180.0%
150.0
225
+
Pd.06
Overload pre-alarm
delay
0.0~60.0s
2.0
226
+
Pd.07
Auto current limiting
threshold
20.0~180.0%
150.0
227
+
Pd.08
Frequency decrease
rate during current
limiting
0.00~99.99 Hz/s
0.00
228
+
Pd.09
Action mode of auto
current limiting
0: Disabled
1: Enabled during Acc/Dec, disabled at
constant speed
2: Enabled during Acc/Dec, enabled at constant
speed
1
229
+
Pd.10
Auto reset
0:Disabled
1~5:Times of fault reset
0
230
+
Pd.11
Auto reset interval
2.0~20.0s
2.0
231
+
Pd.12
Relay action in
Auto reset
0:No action
1:action
0
232
Pd.13
Act selection at under
voltage fault
0:No action
1:Act in running state
2:Act in running and stop state
1
233
+
Pd.14
Input phase loss
function
0:Disable
1:Enale
1
234
+
Pd.15
Output phase loss
function
0:Disable
1:Enale
1
235
+
Pd.16
Under Voltage Point
360-440
400
236
+
Pd.17
reserved
237
+
Pd.18
reserved
238
+
Pd.19
reserved
239
+
Page 58

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
54
Pd.20
reserved
240
+
PE Group group Reserve 1
PF group Reserve 2
PH Group Display parameters
PH.00
running display
parameters selection
0: Frequency setting
1: Running frequency
2: Output current
3: Output voltage
4: Bus voltage
5: Overload rate
6: Preset line speed
7: Running line speed
8: Output torque
9: PI reference
10: PI feedback
11: Analog input AI1
12: Analog input AI2
13: I/O status
14: External counting value
1
267
#
PH.01
Display parameters at
stop
0: Frequency setting
1: Preset line speed
2: DC Bus voltage
3: Analog input AI1
4: Analog input AI2
5: I/O status
6: external counting value
7: PI reference
8:PI feedback
0
268
#
PH.02
Line speed factor
0.01~99.99
30.00
269
#
Page 59

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
55
PH.03
Inverter Power
270 * PH.04
heatsink temperature 1
0~100 271
*
PH.05
heatsink temperature 2
0~100 272
*
PH.06
1st fault type
273
*
PH.07
2nd fault type
274
*
PH.08
3rd fault type
275
*
PH.09
Bus voltage at last
fault
276
*
PH.10
Output current at last
fault
277
*
PH.11
Frequency setting at
last fault
278
*
PH.12
Running frequency at
last fault
279
*
PH.13
I/O state at last fault
280
*
PH.14
Total operating time
281
*
PH.15
Software version of
CPU Board
282
*
PH.16
Software version of
Keypad Board
283
*
Page 60

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
56
Chapter6 Detail Function Introduction
P0 Basic function parameters
P0.00 Reservation
P0.01 Running command selection
Setting range: 0, 1, 2
Select physical channel of inverter's running control command, common running commands
include: Start, Stop, FWD and REV;
0: Running command issued by keypad
Running command is issued by pressing the keys on the keypad, such as RUN,
STOP/RESET, JOG, etc.
1: Running command issued by External terminals
Running command is issued by external terminals, such as FWD, REV, JOGF
and JOGR (terminal function must be defined).
2: Running command issued by RS485 serial communication port
Running command can be issued through internal RS485 serial communication port by host.
P0.02 Control mode
Setting range: 0~1
0:Sensorless vector control
That is no speed sensor vector control running mode, which can be used for high performance
variable speed general driving condition.
Note:
a. At the first running when vector control mode is selected, please perform motor
auto-tuning to get accurate parameters of motor. After auto-tuning, motor
parameters will be saved in the internal control board for control operation.
b. To ensure high steady/dynamic control performance, user must set parameters of
speed controller correctly. For parameters setup and adjustment of speed
controller, please refer to explanation of P5 parameter group.
c. If vector control mode is selected, one TMP can only drive one motor. At this
time, motor capacity can be one level higher (full load is forbidden) or lower
than that of the inverter. Difference of capacity between inverter and motor
should not be too large, otherwise, the inverter’s control performance drops or
drive system cannot operate normally.
1:V/F control
When one inverter drives more than one motor, if motor auto-tuning cannot be performed or
the motor's parameters cannot be acquired through other methods, please select V/F control mode.
P0.03 Main Frequency Source
Setting range: 0~10
TMP series inverter has ten kinds of frequency setting mode.
0:Keypad setting,In this mode, present frequency is set by the Shuttle knob on the
panel.
1:External analog signal AI1(0~10V)
Use external analog signal AI1to set the running frequency
2:External analog signal AI2(0~10V or 0-20mA),use S1(AI2) dial switch to determine
Page 61

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
57
voltage/current signal
3:up/down 1 setting
Present frequency is set by terminal defined by up/down function. Frequency setting is held
when the drive stops.
4:up/down 2 setting
Present frequency is set by terminal defined by up/down function. Frequency setting is the
data of P0.11 when the drive stops.
5:Pulse frequency setting
6:Multi Frequency
You need to set relevant parameter of the P6 I/O and P2 ,When choose multi frequency
operational mode
7:PID
8:RS485 setting
Frequency setting is set by host computer via RS485 serial communication command.
9:Program running
When inverter begins running,Need to set P9 parameter.
10: Panel potentiometer setting (0~5V)
P0.04 Main Frequency gain
Setting arrange:0.000~9.999
The main frequency is the product of the setting frequency selected by parameter P0.03 and
this gain.
P0.05 Zero frequency source of
multi-speed mode
Setting arrange:0~2
0:P0.11Digital frequency setting
1:External analog signal AI1 setting
2:External analog signal AI2 setting
3: Panel potentiometer setting (0~5V)
P0.06 assit frequency setting
Setting arrange:0~4
TMP series inverter has ten kinds of assist frequency setting mode
0:External analog signal AI1(0~10V)
1:External analog signal AI2(0~10V or 0-20mA), use S1(AI2) dial switch to determine
voltage/current signal
2:External analog signaAI1(0~10V)with polarity control
3:External analog signaAI2(0~10V or 0-20mA)with polarity control
4:PID
When P0.06=2,3, Polarity control of external analog AI1 and AI22 is shown in Fig. 6-1, and
dead zone of polarity is decided by parameterP7.10.
Page 62

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
58
P7.10
P7.10
50Hz
FWD
50Hz
REV
5V
10V
AI1
AI2
P7.01=50%
P7.02=0Hz
P7.06=50%
P7.07=0Hz
OR
Fig6-1 Polarity control of external analog signa
P0.07 Auxiliary frequency range selection
Setting range:0~1
Selecting the range of the auxiliary frequency
0:Maximum output frequency
1:Main frequency
P0.08 Auxiliary frequency range
Setting range:0~100%
The auxiliary frequency is the product of the setting frequency selected by
parameter P0.07 and this gain.
P0.09 Setting Frequency selection
Setting range:0~9
Select the setting frequency source of the inverter.
0:Main frequency
The setting frequency source of the inverter is determined by the main frequency
of the parameter of P0.03.
1:Auxiliary frequency
The setting frequency source of the inverter is determined by the auxiliary
frequency of the parameter of P0.06.
2:Main frequency + Auxiliary frequency
3:Main frequency - Auxiliary frequency
4:switch between main frequency and auxiliary frequency
The setting frequency source of the inverter can be switched between the main
frequency and auxiliary frequency with the external terminal defined by P6 Group
parameter.
5:switch between Main frequency and (Main frequency + Auxiliary frequency)
Page 63

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
59
The setting frequency source of the inverter can be switched between the main
frequency and (Main frequency + Auxiliary frequency) with the external terminal defined
by P6 Group parameter.
6:switch between Main frequency and (Main frequency - Auxiliary frequency)
The setting frequency source of the inverter can be switched between the main
frequency and (Main frequency - Auxiliary frequency) with the external terminal defined
by P6 Group parameter.
7:MAX(Main frequency,Auxiliary frequency)
The setting frequency source of the inverter is maxium of main frequency and
auxiliary frequency
8:MIN(Main frequency,Auxiliary frequency)
The setting frequency source of the inverter is minium of main frequency and
auxiliary frequency
9:Traverse operation
The setting frequency source of the inverter is determined by traverse operation mode
defined by function code Pb parameter group.
P0.10 up/down setting store selection
Setting range:0、1
0:Store
The initial frequency setting value is the value of parameter P0.11. It can
be changed by the terminal defined with function “Frequency increase command” and
“Frequency decrease command”. When the inverter is power off, the current frequency setting
value is stored.
1:Not Store
The initial frequency setting value is the value of parameter P0.11. It can
be changed by the terminal defined with function “Frequency increase command” and
“Frequency decrease command”. When the inverter is power off, the current frequency setting
value is not stored.
P0.11 digital frequency setting
Setting range: 0.00~High frequency limit
If digital frequency setting via panel is selected, the value of parameter, will be the present
preset frequency.
P0.12 Rotating direction
Setting range: 0, 1
If panel control mode is selected, select the relationship between inverter's actual output
direction and the direction of control command.
0: Same with control command;
1: Opposite to control command
Page 64

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
60
。
P0.13 Maximum output
frequency
Setting range: 50Hz~400.0Hz
P0.14 High frequency limit
Setting range: lower frequency limit ~ Maximum output
frequency
P0.15 Low frequency limit
Setting range: 0.00Hz~Upper frequency limit
The maximum output frequency is the maximum frequency which the inverter is able to
output, shown in Fig. 6-2 as Fmax;
High frequency limit is the maximum frequency which the user is allowed to set, shown in
Fig. 6-2 as Fh;
Low frequency limit is the minimum frequency which the user is allowed to set, shown in
Fig. 6-2 as FL;
Fb in Fig.6-2 is basic running frequency, which is defined as the lowest output frequency
when the inverter outputs the highest voltage in V/F control mode.
f
L
f
H
Output
frequency
f
b
f
max
Output voltage
V
max
Fig.6-2 Frequency limits definition
P0.16 Acc time 1
Setting range: 0.1~3600s
P0.17 Dec time 1
Setting range: 0.1~3600s
Acc time means the time during which the inverter output from zero frequency to the
maximum output frequency, shown in Fig. 6-3 as T1.
Dec time means the time during which the inverter outputs from the maximum output
frequency to zero frequency, shown in Fig. 6-3 as T2.
Fmax
Time
output frequency
T2
T1
Fig 6-3 Definition of Acc/Dec tim
Factory setting of Acc/Dec time: Acc/Dec time 1(P0.16、P0.17)。
Page 65

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
61
Other Acc/Dec time must be selected through control terminals according to different
groups(Please refer to P2 Parameter group)。
When program is running, selection of Acc/Dec time group is setup in function code (Please
refer to P9 Parameter group).
P0.18 Inverter type select
Setting range: 0, 1
0:General –type inverter (for constant torque load)
1:Pump –type inverter (for fan, punp)
Some of the TMP series inverter combine the General-type and Pump-type into one
device. The power of the motor of the General –type inverter is lower than Pump –type inverter.
The default type is General –type inverter. If the user changes the inverter from General –type
inverter to Pump –type inverter, he must do following steps:
1. Setting the parameter to 1.
2.Resetting the parameter P3.02(motor rated current).
P0.19 Parameter initialization
Setting range:0~3
0: No operation
Inverter is in normal parameter read/write state.
1: Clear fault information
The fault information clearing operation will clear all the memorized parameters stored in the
function codes between PH.06~PH.13
2: Recover factory setting
Setup F0.19 to 2 and confirm, inverter will recover all the parameters between P0~P2
and P4~PH to the default factory setting value.
All the setting values of P3 Parameter group will not be influenced when factory setting
value is restored.
3: Parameter locking
When set P0.19 to 3, parameter locking function is enabled. Except this parameter, all
other parameters are read only and can not be modified.
P1 Auxiliary function parameters 1
P1.00 start mode
Setting range: 0~2
0: Start from starting frequency
When inverter begins running, it starts from starting frequency (P1.01) and runs for the
preset time (P1.02) at this frequency according to the setting values of P1.01 and P1.02;
then it enters normal Acc mode according to preset Acc time and Acc/Dec mode
parameters, at last it accelerates to preset frequency.
1: Brake first then start from starting frequency
When inverter begins running, it starts DC injection braking process according to the
preset DC injection braking voltage and time defined in P1.03 and P1.04. It starts from
starting frequency, and runs for the preset time at this frequency; and then enters
normal Acc mode according to preset Acc time and Acc/Dec mode parameters, and at
last accelerates to preset frequency. The process is shown in Fig. 6-4.
Page 66

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
62
Output frequency
stop
Start DC
braking
Start
Frequency
P1.01
Acc process
Dec process
Stop DC braking
Start frequency
P1.06
Run time
Start
Frequency
Hold time
P1.02
Fig. 6-4 Start mode 1 (FWD, REV, Stop and RUN) diagram
2:Speed trace starting
When the inverter begins running, first it detects the motor 's speed and direction, and
then it starts smoothly at the detected speed and direction. Smooth start without
impaction should be performed on rotating motor.
P1.01 Starting frequency
Setting range: 0.00~20.00Hz
P1.02 Hold time of starting frequency
Setting range: 0.00~60.0s
Start frequency: It is the initial frequency when the inverter starts from zero frequency, which
is shown in Fig. 6-4.
In the Acc and Start process, if the preset frequency is lower than the start frequency, inverter's
output frequency becomes zero;
Start frequency holding time: the running time at start frequency in Acc/Start process, which is
shown in Fig. 6-4.
P1.03 DC injection braking time
at start
Setting range: 0.00~60.0s
P1.04 injection braking current
at start
Setting range:0.0~100.0%(inverter rated currente)
DC braking time at start: holding time for output DC injection braking current when the
inverter is in start process.
If DC injection braking time at start is set to 0.0 second, DC injection braking function is
disabled.
DC braking current at start: percentage of braking voltage when the inverter starts in DC
injection braking process.
P1.05 Stop mode selection
Setting range: 0, 1, 2
0: Dec-to-stop mode 1
When the inverter receives stop command, it lowers its output frequency and
decelerates to stop according to the preset Dec time. During Dec process, for inverter
with braking resistor or unit, it will enter dynamic braking.
Page 67

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
63
1: Dec-to-stop mode 2
After the inverter receives stop command, it lowers its output frequency and decelerates
to stop according to the preset Dec time. During Dec process, when output frequency is
equal to the frequency set by P1.06, the inverter starts DC braking according to the DC
braking time and voltage defined by P1.07 and P1.08.
2: Free run to stop
After the inverter receives the stop command, it stops its output immediately; the
motor will decelerate to stop according to its inertia.
P1.06 Initial frequency of DC injection braking
Setting rang: 0.00~20.00Hz
Initial frequency of DC injection braking: It is the frequency when the inverter's output
frequency is decreased to zero along the Dec curve in Dec-to-stop process, which is shown in Fig.
6-4.
In the process of Dec-to-stop, when the preset frequency is lower than the initial frequency
of Stop DC injection braking, the inverter’s output frequency is decreased to zero.
If the running condition has no strict requirements for braking, the initial frequency of DC
injection braking should be set as low as possible.
P1.07 DC injection braking time
Setting range: 0.0, 0.1~60.0s
P1.08 DC injection braking current
Setting range: 0.0~100.0% (inverter’s rated current)
DC injection braking time: the time for maintaining output DC injection braking in inverter's
stopping process.
DC injection braking current: percentage of braking voltage when the inverter stops in DC
injection braking mode.
When the DC injection braking time is set to 0 second., the DC injection braking function is
disabled.
P1.09 Acc/Dec mode selection
Setting range: 0, 1
Acc/Dec modes 0 and 1 are valid in Start, Stop, FWD/REV, Acc and Dec process.
0: linear mode
In Acc/Dec process, the relationship between output frequency and Acc/Dec time is
linear. The output frequency increases or decreases at the constant slope as shown in
Fig. 6-5.
1: S curve mode
In Acc/Dec process, the relationship between output frequency and Acc/Dec time is
nonlinear. The output frequency increases or decreases according to the S curve shown
in Fig. 6-6.
Page 68

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
64
Fmax
T1
Running
time
Output
frequency
T2
Fig. 6-5 linear Acc/Dec
1: S curve mode
In Acc/Dec process, the relationship between output frequency and Acc/Dec time is
nonlinear. The output frequency increases or decreases according to the S curve shown
in Fig. 6-6.
Fig. 6-6 S curve Acc/Dec
P1.10 Time of S curve’ s start part
Setting range: 10.0 ~ 50.0 % (Acc/Dec time)
P1.11 Time of S curve’ s rising part
Setting range: 10.0 ~ 80.0 % (Acc/Dec time)
The function codes of P1.10 and P1.11 define the Acc/Dec parameters of S curve.
S curve start time is shown in Fig. 6-6 as ①, which is the stage when the slope of output
frequency rises gradually.
S curve rise time is shown in Fig. 6-6 as ②, which is the stage when the slope of output
frequency maintains phase.
S curve end time is shown in Fig.6-6 as ③, which is the stage when the slope of output
frequency decreases to zero.
Note:
1. Limit of setting value: S curve start time + S curve rise time≤90% (Acc/Dec time).
Page 69

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
65
2. In Acc/Dec Process, the parameters of S curve are set in symmetry.
P1.12 Restart after power failure
Setting range: 0, 1
0: Disabled;
1: Enabled; Function of restarting after power failure is enabled when the power supply
recovers.
P1.13 Delay time for restarting after power failure
Setting range: 0.0~20.0s
When the power recovers from failures, the time before the inverter restarts is the delay time.
This time is set according to the time needed by other equipment to recover when the power
supply recovers.
P1.14 dynamic braking start voltage
Setting range:630~710V
Setting the start voltage of dynamic braking.
P1.15 Rate of dynamic braking
Setting range: 0.0 ~100.0%
Define duty cycle of dynamic braking.
0: No dynamic braking
1%~100%: In process of dynamic braking, percentage of valid braking time to carrier cycle,
user can modify this value if necessary.
P1.16 Start frequency lower than frequency limit
Setting range:0, 1,2
0:when preset frequency is lower than low frequency limit, the inverter will not start;
1:when preset frequency is lower than low frequency limit, the inverter will start at low
frequency limit;
2:When preset frequency is lower than frequency limit, the inverter stop.
P1.17 MF key function
0:No operation;
1:reverse rotation
P1.18 Stop/reset Key function
Setting range:0、1、2
This parameter decides the “stop” function of STOP/RESET key of the keypad
in different command source.The”Reset”function is usable in all command source.
0:action on keypad control mode
1:action on both keypad and External terminal
2:action on both keypad and communication
P1.19 Fan control function
Setting arrange:0、1
0:Cooling fan always runs after power on
1: Cooling fan stops fan after inverter stop running
P2 Auxiliary function parameters 2
P2.00 ACC time2
Setting arrange:0.1~3600s
P2.01 ACC time2
Setting arrange:0.1~3600s
P2.02 ACC time3
Setting arrange:0.1~3600s
P2.03 ACC time3
Setting arrange:0.1~3600s
Page 70

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
66
P2.04 ACC time4
Setting arrange:0.1~3600s
P2.05 ACC time4
Setting arrange:0.1~3600s
Four Acc/Dec times are defined as following:
Phases of Acc/Dec time
1 2 3
4
Terminal state
X4
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
X5
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
As shown in the table above, in normal operation condition, Acc/Dec time 1 is the default
setting (both terminals X4, X5 are OFF, and Acc/Dec time 1 and 2 are defined by terminal X4 and
X5 respectively).
P2.06 Jog Acc time 1
Setting range: 0.1~20.0s
P2.07 Jog Dec time 1
Setting range: 0.1~20.0s
P2.08 Jog frequency
Setting range: 0, 1~60.00Hz
P2.06~P2.08 define the jog running parameters, which is shown in Fig. 8-7.
In Fig. 6-7, f1 is Jog running frequency (P2.08), t1 is Jog Acc time (P2.06), t3 is Jog Dec
time (P2.07), and t2 is the Jog running time.
Jog running command can be issued through panel, control terminal or host computer.
Fig. 6-7 Jog running parameters
P2.09 Multi-frequency 1
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.10 Multi-frequency 2
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.11 Multi-frequency 3
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.12 Multi-frequency 4
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.13 Multi-frequency 5
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.14 Multi-frequency 6
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.15 Multi-frequency 7
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.16 Multi-frequency 8
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.17 Multi-frequency 9
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.18 Multi-frequency 10
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.19 Multi-frequency 11
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.20 Multi-frequency 12
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.21 Multi-frequency 13
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.22 Multi-frequency 14
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.23 Multi-frequency 15
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
Page 71

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
67
Multi-frequency/speed is set in P2.09~P2.23, which can be used in multi-speed
running and programming state.
There are 15 multi-frequency operation modes, which can be selected through control
terminals.
Assumption:
“1 (ON)” means that control terminal is connected;
“0 (OFF)” means that control terminal is disconnected.
If control terminals of multi-frequency are not set, or all of them are in OFF position,
frequency setting is determined by function code P0.02;
If certain control terminal of multi-frequency is not in OFF position, frequency setting
is determined by function code P2.09~P2.23;
If multi-frequency operation is selected, Starting/stopping the drive is determined by
control mode selection P0.01.
Freque
ncy
Termin
al
1X 2X 3X 4X 5X 6X 7X 8X 9X 10X 11X 12X 13X 14X 15
X
Termin
al 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
Termin
al 2
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1
Termin
al 3
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
Termin
al 4
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
P2.24 Jump frequency 1
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.25 Jump frequency 2
Setting range:0~400.0Hz
P2.26 Jump frequency 3
Setting range:0~400.0Hz
P2.27 Jump frequency range
Setting range:0~20.00Hz
Jump frequency is set to prevent the output frequency of inverter from meeting the
mechanical resonant point of load.
In Jump frequency parameters, set the system's mechanical resonant central frequency, at
most three frequency values can be setup, shown in Fig.6-8.
Page 72

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
68
Output
frequency
Jump frequency 1
Jump range
Jump range
Jump range
Jump frequency 2
Jump frequency
3
Frequency setup signal
Fig. 6-8 Jump frequency and its range
p2.28 FWD/REV dead time
Setting range: 0.1~3600s
FWD/REV dead time: the waiting and holding time before the motor changes its rotating
direction after the inverter's output frequency is decreased to zero. It is the time taken by the motor
to change its rotating direction when the inverter receives REV command during its running
process. The time is shown in Fig. 6-9 as T0.
Running frequency
TO
Running time
Fig. 6-9 FWD/REV dead time
P2.29 REV prohibited
Setting range: 0, 1
When P2.29=0, this function is disabled. In this case, terminal F/R=OFF, Run FWD;
terminal F/R=ON, Run Rev;
When P2.29=1, this function is enabled. In this case, terminal F/R signal is invaid. Mtor can
only run forward, and switching between FWD/REV is not available.
Running mode of routine program is independent of this function.
Page 73

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
69
In traverse operation mode, both FWD and REV running are allowable, but switching
between FWD/REV is prohibited. Setting FWD/REV direction may not be same as actual
direction, which can be defined by changing phase sequence of the output.
P2.30 Carrier frequency adjustment
Setting range:2.0~12.0KHz
Carrier wave frequency can be continuously adjusted within 2.0~12.0KHz.
This function is mainly used to improve system performance, and reduce noise and vibration.
Since TMP series adopts IGBT as power devices, carrier frequency can be higher. Increasing
carrier frequency can bring following benefits: better current waveform, lower noise, which is
especially suitable for applications that need low noise. However, with the increase of carrier
frequency, it also brings some disadvantages, such as increase of power loss on switching
devices, overheat, low efficiency, etc. Since high frequency carrier produces severe radio
interference, please install filter for application with high requirement on EMI. At the same time,
capacitive leakage current increases, and the wrong action of leakage protector and over current
may happen.
Decreasing carrier frequency, the contrary is the case. Motor noise will increase in lower
carrier frequency. Influence of carrier frequency is different for various motors. Therefore,
optimal carrier frequency should be selected according to practical situation. In fact, with the
increase of motor capacity, carrier frequency should decrease. For motor capacity above 37 kW,
2KHz carrier frequency is recommended.
P2.31 Zero frequency threshold
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
P2.32 Zero frequency hysteresis
Setting range: 0~400.0Hz
The above two parameters are to set zero frequency hysteresis control.
Take analog input AI1 for example, see Fig.6-10:
Startup process:
When the Run command is issued, only afterAI1 voltage arrives or exceeds VS-b, does the
drive start and accelerate to the preset frequency in defined Acc time.
Stop process:
During Dec process, when AI1 voltage reduces to VS-b, the drive will not stop until it
reaches VS-a and the corresponding frequency becomes fa, where fa is the threshold of zero
frequency defined by P2.31, and fb, fa is defined by P2.32.
This function can realize dormancy to save energy, in this way, frequent start and stop at
threshold frequency can be avoided.
Page 74

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
70
AI1 Input voltage
FWD
VS-b
VS-a
Vmin
Fmin Fmax
Operating
frequency
Output
frequency
Setting
frequency
Fa
Fb
0
fa: Zero frequency threshold
fb: fa + Zero frequency hysteresis
Fig. 6-10 Zero Frequency Hysteresis
P2.33 Droop control
Setting range:0.00~10.00Hz
When several inverter drives one load, the load of indivial inverter is different due to speed
difference. The inverter with higher speed drives more load. This parameter can decrease the speed
when the load is increased and equalizes the load of inverters.
P3 Motor parameters
P3.00 Motor rated power
Setting range:0.4~999.9kW
P3.01 Motor rated voltage
Setting range:0~440V
P3.02 Motor rated current
Setting range:0.1~999.9A
P3.03 Motor rated frequency
Setting range:1.00~400.0Hz
P3.04 Motor rated speed
Setting range: 1~999 rpm
Note:
In order to ensure motor tuning, please set nameplate parameter of the motor correctly.
In order to ensure high control performance, the motor capacity should match that of the
drive. Generally the motor’s power is allowed to be one grade higher or lower that of the drive.
Note:Before tuning, the parameters on the nameplate of the motor must be input correctly
P3.05 Motor auto-tuning
Setting range: 0, 1,2
Note:Before tuning, the parameters on the nameplate of the motor must be input correctly
(F3.00~F3.04).
0:No operation
Page 75

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
71
1:static auto tuning
If the load can not be unconnected from motor, user can adopt static auto
tuning. First set F3.05 to 1, after confirmation, then press the RUN key on the Keypad, inverter
will perform static auto-tuning functions.
2:overall auto- tuning
First set F3.05 to 2, after confirmation, then press the RUN key on the Keypad, inverter will
perform overall auto-tuning functions. The overall auto- tuning includes static auto tuning and
spinning auto tuning and the load must be unconnected form the motor.
Note:
a. If over-current or over-voltage fault occurs during tuning process, user can adjust
Add/Dec time (P0.16, P0.17) and torque boost (P4.07);
b. Do not start tuning with load on motor;
c. Make sure the motor is in stopping status before tuning, otherwise, the tuning can not be
performed normally;
d. Motor auto-tuning can only be performed in keypad control mode (P0.01=0).
P3.06 Stator resistance
Setting range:0.001-20.00%
P3.07 Rotor resistance
Setting range:0.001-20.00%
P3.08 Self inductance
Setting range:1.000~9.999
P3.09 leakage inductance
Setting range:0.001~1.000
P3.11 Exciting current with no load
Setting range:0.0~999.9A
Factory settings of P3.06~F3.10 are the parameters of motor that rated power matches
the inverter. If user already knows the motor's parameters, just input the motor parameters
directly. However, after successfully performing motor auto-tuning, value of P3.06~P3.10
will be updated automatically.
Resistance and inductance are the relative value of the nomial motor parameters.
Resistance value=(real Resistance value )*(1.732*I)/V*100%;
Inductance value=(real Inductance value )*2*3.14*P*(1.732*I)/V;
In above formular,V is motor rated voltage defined by P3.01 ; I is motor rated current
defined by P3.02 ; Pis the motor rated frequency defined by P3.03.
These parameters are reference parameters for vector control, which will affect control
performance directly.
P3.11 Reservation
P4 Dedicatd function for V/F control
P4.00 V/F curve control mode
Setting range:0~4
0: linear voltage/frequency mode (constant torque load), shown as curve 0 in Fig. 6-11;
1: Square voltage/frequency mode, shown as curve 1 in Fig. 6-11;
2: 1.5 times torque/frequency mode, shown as curve 2 in Fig. 6-11;
3: 1.2 times torque/frequency mode, shown as curve 3 in Fig. 6-11;
Page 76

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
72
4: User defined V/F curve.
Fmax
output voltage
output frequency
0
3
2
1
Fig. 6-11 V/F curve
P4.01 Base voltage
Setting range: 0~440V
P4.02 Base frequency
Setting range: 10.00~ 400.0Hz
Basic V/F characteristic of TMP series is shown in Fig. 6-12. Base Frequency F
BASE
is the
output frequency corresponding to the rated output voltage UN. Its range is 10 to 400Hz.
Generally, F
BASE
should be selected according to rated frequency of the motor. In some special
case, it can be selected according to requirement. In this condition, both motor V/F characteristic
and output torque should be considered.
output Frequency
output voltage
UN
0
FMAXFBASE
Fig. 6-12 Base voltage and frequency
P4.03 Intermediate voltage 1
Setting range:0~P4.04
P4.04 Intermediate voltage 2
Setting range:P4.03~100% (Inverter’s rated voltage)
P4.05 Intermediate frequency 1
Setting range:0~P4.06
P4.06 Intermediate frequency 2
Setting range: P4.05~400.0Hz
P4.07 Torque boost
Setting range:0~20%(Inverter’s rated voltage)
In order to compensate the torque drop at low frequency, the inverter can boost the output
voltage in the low frequency zone, which is shown in Fig. 6-13.
Page 77

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
73
output
voltage
VN
Output
frequency
P4.04
0
P4.05
P4.06
F
P4.03
P4.07
BASE
Fig. 6-13 Torque boost
Note:
Generally, factory setting (2%) can satisfy most applications. If over-current fault occurs
during startup, please increase this parameter from zero gradually until it meets requirement. Pay
attention that large torque boost could damage equipment.
P4.08 Slip compensation
Setting range:0.0~10%(Rated speed P3.04)
In V/F control mode, motor's speed will be decreased with load rising. In order to ensure
the motor's speed be close to synchronous speed in rated load condition, slip compensation can be
done according to the preset frequency.
P4.09 AVR function
Setting range: 0, 1
0: Disabled; 1: Enabled
AVR is auto voltage regulation. When the inverter's input voltage differs with the rated input
voltage, the inverter's output voltage can be stablized by adjusting the width of PWM wave.
This function is disabled when the output voltage is higher than input voltage.
P5 Vector control funtion
P5.00 ASR proportional gain 1
Setting range:0.00~10.00
P5.01 ASR integration time 1
Setting range:0.00~10.00
P5.02 ASR proportional gain 2
Setting range:0.00~10.00
P5.03 ASR integration time 2
Setting range:0.00~10.00
P5.04 ASR switching frequency
Setting range:0.0~99.99Hz
Through P5.00~P5.04, user can set the proportional gain P and integration time I of speed
regulator, so as to change the speed response characteristic.
a. Speed regulator (ASR)'s structure is shown in Fig.6-14, where KP is proportional gain P,
and KI is integration time I.
Page 78

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
74
Speed error
Frequency
instruction
Actual speed
+
-
Torque limit
(P5.07,P5.08)
Given torque current
Fig. 6-14 Simplified block diagram of ASR
If the integral time is set to 0 (P5.01=0, P5.03=0), which means integral function is disabled,
and the speed loop is simply a proportion regulator.
a. Adjustment of proportion gain P and integration time I for speed regulator
Increasing P will fasten system transient response, but system oscillation may occur
given too big P. Decreasing I will fasten transient response, but system oscillation and
overshoot may occur given too small.
Normally, user may tune P first, increase its value as long as no system oscillation
occurs; then adjust I, ensuring fast response without overshoot. Figure 6-15 shows
better speed step response if P, I are set properly. Speed response can be monitored
through analog terminals AO1 and AO2. Refer to P8 parameter group for detail
information.
Reference
speed
Fig. 6-15 Step response with better dynamic performance
)
KiS
1
+(1KP
Page 79

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
75
Note:
a. With improper PI parameters, after accelerating to high speed,
over-voltage during Dec process may occur (Without external braking
resistor or unit), which is caused by regenerative braking after speed
overshoot. To avoid this fault, user can tune PI parameters.
b. Adjustment of PI parameter in high/low speed applications
If system is required to respond quickly both in low and high frequency
operation with load, user may set ASR switching frequency (P5.04).
Normally, when the system runs at low frequency, the transient response
performance can be improved by increasing P and decreasing I. Adjust
ASR parameters following the procedures below:
1. Set appropriate switching frequency P5.04;
2. Tune proportional gain P5.00 and integration time P5.01 for low-speed
application, and ensure no oscillation and good response performance
at low frequency.
3. Next, tune proportional gain P5.02 and integration time P5.03 for
high-speed application, and ensure no oscillation and good response
performance at high frequency.
P5.05 Slip compensation gain
Setting range:50.0~200.0%
P5.05 is used to calculate slip frequency. Setting value 100% means rated slip
frequency corresponds to rated torque current. User may decrease/increase the
settings of P5.05 to adjust the speed control's difference accurately.
Note:
This function is valid to open loop vector control mode. For close loop vector
control mode, F5.05 can be set to 100% for most applications.
Page 80

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
76
P5.06 Torque control
Setting range:0, 1
This function is reserved.
P5.07 Driving torque
lilmit
Setting range:0.0~200.0% (motor’s rated current)
P5.08 Braking torque
limit
Setting range:0.0~200.0%(motor’s rated current)
Torque limiting is used to limit output torque current of speed
regulator'.
Torque limit is the percentage of the motor’s rated current; If the torque limit is
100%, then the torque current limit is the motor's rated current. P5.07 and P5.08
limit the output torque in driving state and braking state respectively, which is
shown in Figure 6-16.
Braking state
Braking state
Power state
Power state
positive
Negative
moment
Output
torque
Motor speedREV
P5.08
P5.07
P5.08
P5.07
Fig. 6-16 Torque limit function
P5.09 Retain
P5.10 Retain
Page 81

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
77
P6 I/O I/O output terminal
P6.00 FWD/REV running
Setting range: 0~3
0:Two-line operation mode 1
FWD
REV
Running
command
0
0
Stop
0
1
FWD
1
0
REV
1
1
Stop
Fig. 6-17 Two-line control mode 1
In Fig. 6-17, terminal X1 is defined as running FWD, and X2 is defined as
running REV.
1:Two-line operation mode 2
FWD
REV
Running
command
0
0
Stop
0
1
Stop
1
0
FWD
1
1
REV
Fig.6-18 Two-line control mode 2
In Fig. 8-18, terminal X1 is defined as running FWD, and X2 is defined as
running REV.
2: Three-wire operation mode 1
K
Running
command
X1(FWD)
X2(REV)
COM
K1
K2
X1(FWD)
X2(REV)
COM
K1
K2
Page 82

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
78
i=3,4,5,6,
Fig. 6-19 Three-wire operation mode 1
3: Three-wire operation mode
i=3,4,5,6
Fig. 6-20 Three-wire operation mode 2
In Fig.6-19 and 8-20, X1 is defined as running FWD, X2 is defined as running
REV, and K is used for selecting running direction;
In Fig. 6-19 and 8-20, STOP is a normally closed button for stopping the
motor. RUN, FWD and REV are normally open buttons for running the motor, and
they are active at pulse edge.
In Fig. 6-19 and 8-20, Xi (I=3~7) is defined as three-wire running control
terminal of X3~X7.
In 3-wire mode, when X3~X7 is not selected, the inverter will report ERR4
fault.
P6.01 Up/down rate
Setting range:0.10~99.99Hz/s
Up/down rate: To define the increase/decrease rate when using up/down
terminal to change reference frequency.
P6.02 Selecting the function of control terminal X1
Setting range: 0~30
P6.03 Selecting the function of control terminal X2
Setting range:0~30
0
FWD
1
REV
STOP
RUN
K
FWD
Xi
REV
COM
FWD
X1(FWD)
Xi
X2(REV)
COM
STOP
REV
Page 83

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
79
P6.04 Selecting the function of control terminal X3
Setting range:0~30
P6.05 Selecting the function of control terminal X4
Setting range:0~30
P6.06 Selecting the function of control terminal X5
Setting range:0~30
P6.07 Selecting the function of control terminal X6
Setting range:0~30
P6.08 Selecting the function of control terminal X7
Setting range:0~30
Control terminals X1~X7 are programmable digital input terminals. X1~X7
can be defined by setting the values of P6.02~P6.08 respectively.
Programmable digital input terminal can be selected as “ no function”
repeatedly (that is, it can be set as 0 at the same time). Function description is
shown below:
Content
Function
Content
Funtion
0
X1~X6: No function (can be selected
repeatedly)
X7: high speed pulse input
16
Free run to stop
1
Run FWD
17
Three-wire control
2
Run Rev
18
Voltage/current switching
3
External reset
19
Input terminal for recording
program operation
4
Jog FWD (JOGF)
20
Start traverse operation
5
Jog REV (JOGR)
21
DC braking command
6
Multi-frequency 1
22
Acc/Dec disabled command
7
Multi-frequency 2
23
Switch between panel control
mode and external terminal
control mode
8
Multi-frequency 3
24
Counter trig signal
9
Multi-frequency 4
25
Counter reset signal
10
Terminals for selecting
26
PID dormancy waking up
Page 84

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
80
Acc/Dec time 1
11
Terminals for selecting
Acc/Dec time 2
27
Counter reset signal
12
Normally open terminal for
inputting external fault
28
PID dormancy waking up
13
Normally close terminal for
inputting external fault
29
switch between PID positive
mode and negative mode
14
Frequency increase
command
30
Emergence stop
15
Frequency decrease
command
Note:
1 0: When X1~X6=0, no function is defined.
2 1~2: input terminals for external operation control
In terminal control mode (P0.01=1), the terminal is used to select
FWD/REV operation.
3. 3: External RESET
If fault alarm occurs, user can reset the inverter by external terminal. This
function is active at rising edge of pulse signal. It has the same function as
STOP/RESET key.
4. 4~5: Terminal for external FWD/REV Jog running control.
In terminal control mode (P0.01=1), this terminal is used to select Jog
operation.
5. 6~9: Multi-frequency terminals
In multi-frequency operation mode, 4 digital input terminals should be
defined as the control terminals. Through the combination of ON/OFF state
of the 4 terminals, up to 15 values can be defined set as preset frequency.
Refer to parameter P2.09~P2.23 for details.
6. 10~11: Acc/Dec time terminals
Page 85

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
81
By combination of the ON/OFF state of Acc/Dec time terminals, user can
select Acc/ Dec time 1~4, refer to parameter P0.16,P0.17 and
P2.00~P2.05 for more details. If this function is not defined, Acc/Dec
time 1 will be the default setting except in simple PLC operation mode.
7 12~13: Normally open terminal for external fault
Fault signal of external equipment can be input via the terminal, which is
convenient for the drive to monitor the fault of external equipment. Once
the drive receives the fault signal, it will display “Er11”. During normal
stop process, this function is disabled. The fault signal has two input
modes, i.e. normally open and normally close.
8. 14~15: Frequency increase/decease command
The running frequency can be set through external terminals, thus the
running frequency can be set remotely. At this time, P0.03 can be set to 2
or 3. When the terminal is ON, the frequency setting value is increased or
decreased at the rate defined by P6.01; when the terminal is OFF,
frequency setting value keeps constant. When these two terminals are ON
at the same time, frequency setting value also keeps constant. Please refer
to P0.03 parameters description.
9. 16: Free run to stop terminal (FRS)
When the function terminal is ON, inverter stops output immediately and
enter stopping state, the motor enters free run to stop state.
10 17: Three-wire control
If F6.00=2 or 3, this terminal is defined as three-wire control terminal
when three-wire control mode is selected. If If F6.00=2 or 3, and none of
X1~X7 is defined as three-wire control terminal, the inverter will report
parameter setting fault ERR4. In this case, user should define “three-wire
control terminal” first, and then define “three-wire control mode”
(P6.00=2 or 3).
11. 18: Switching input signal
If analog setting mode is selected, (P0.09=4 5 or 6), this function is used
to switch reference channel.
Page 86

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
82
If this terminal is OFF, reference signal is decided by settings of panel
potentiometer (P0.09=4 5 OR 6 )
If this terminal is ON, reference signal is decided by settings of VS2.
12. 20: Start traverse operation
If the traverse operation is set to manual start, then traverse function is
enabled if this function is selected. Refer to Pb parameter group for
details.
13. 22: DC braking command
When the inverter is in Dec-to-stop process, and the running frequency is
lower than initial frequency of DC injection braking defined in P1.06, this
function is enabled. When the terminal is ON, DC injection braking is
performed under braking voltage defined in P1.08. DC injection braking
is ended only when the terminal is OFF.
When this function is enabled, parameters of DC injection braking time
are invalid.
14. 23: Acc/Dec disabled command
When the terminal is ON, the inverter temporarily inhibits executing the
Acc/Dec command and runs at current frequency. When the terminal is
OFF, normal Acc/Dec commands can be executed. If there is any control
signal with higher priority input such as external fault signal, the inverter
will exit Acc/Dec inhibit state immediately and execute specified
processing procedures.
15. 24: Switch between panel control mode and external terminal control
mode
This function is used for selecting the physics channel that inputs
inverter’s running control command: Selecting between keypad and
external terminal to input control commands.
Commands input via external terminals include FWD, REV, JOGF, JOGR,
RUN and STOP.
This function is used in conjunction with ON/OFF state and the setting
value of P0.01.
Page 87

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
83
The control logic is shown in the Table below.
F0.01
Terminal state
Source of control command
0
ON
External terminals
0
OFF
Keypad
1
ON
Keypad 1 OFF
External terminals
This function is enabled during running state. User should pay attention to
the drive’s running status after switching.
If the drive is in keypad control mode first, connect the terminal (ON),
there are 2 cases: if running command from external terminal is valid, such as
FWD terminal is ON in two-wire control mode, then the drive’s operation state
will not change; if running command from external terminal is invalid, the drive
will stop running.
16. 25: Switch between panel control mode and external terminal control
mode
This function is used for selecting the physics channel that inputs
inverter’s running control command: Selecting between keypad and
external terminal to input control commands.
Commands input via external terminals include FWD, REV, JOGF, JOGR,
RUN and STOP.
This function is used in conjunction with ON/OFF state and the setting
value of P0.01.
The control logic is shown in the Table below.
P0.01
Terminal state
Source of control command
0
ON
External terminals
0
OFF
Keypad 1 ON
Keypad 1 OFF
External terminals
Page 88

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
84
17 26: Counter trig signal
It is the input terminal of the drive’s internal counter. If the input signal of the
terminal changes from ON to OFF, the counting value is increased by 1.
18. 27: Counter reset signal
This terminal is used to clear the inverter's internal counter, and is used in
conjunction with Function 24 "Counter trig signal".
When the terminal is ON, internal counter is cleared to 0.
19. 28: PID dormancy waking up
i. When PA.17=2 and this terminal is ON, PID control will exit
dormancy state and execute normal PID function.
20.29: switch between PID positive mode and negative mode:
When PA.00 is set to 0,PID positive mode is selected with the terminal is off ;
negative modeis selectedwiththe terminal is on.
21. 30:“Emergence stop”
If the terminal defined with the function is on, the inverter is in emergence
stopstatus( motor free stop)
P6.09 Programmable relay 1
Setting range:0~20
P6.10 Output terminal Y1 definition
Setting range:0~20
Function selection of programmable relay output terminals and open
collector output terminals is shown in the table below.
Content
Function
Content
Function
0
Programmable relay 1: No
operation
Output terminal Y1: No
operation
11
Over voltage stall
1
Drive ready
12
External stopping command
2
Drive running signal1
13
Preset counting value
arriving
3
Drive running signal2
14
Specified counting value
Page 89

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
85
arriving
4
Frequency arriving signal
15
Low voltage lockup signal
5
Frequency detection threshold
1
16
Overload pre-alarm
6
Frequency detection threshold
2
17
Drive failure signal
7
High limit frequency arriving
18
Zero speed running
8
Low limit frequency arriving
19
程序运行阶段完成
9
Overload signal
20
PG cable broken
10
Over current stall
Functions in the table above are described as following:
0 0: No function is defined by programmable relay output terminal 1, and open
collector output terminal Y1. is defined as frequency signal output.
1 1: Drive ready
The drive is in normal waiting state, and terminals output indication signal.
2 2: Drive running signa l
The drive is in running state, and the terminal outputs indication signal.
3 3: Drive running signa2
In run status, when the drive’s output frequency is 0Hz, the terminal does not output
indication signal; when the drive’s output frequency is above 0Hz, the terminal
does output indication signal
4 4: Frequency arriving signal
When the drive’s output frequency arrives preset frequency, the terminal
outputs indication signal.
It is used in conjunction with parameter P6.11.
5 4~5: Frequency detection threshold 1 and 2
When the drive’s output frequency arrives specified value, the terminal
outputs indication signal, which is used in conjunction with parameters
P6.12~P6.15.
Page 90

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
86
FDT
Time(S)
output frequency(Hz
Time(S)
0
T
FDT level - FDT lag
Frequency
detecting
signal
Fig. 6-21 Frequency detection threshold 1 and 2
6 7:High limit frequency arriving
When the drive’s output frequency reaches high limit frequency, the
terminal outputs indication signal.
7 8: Low limit frequency arriving
When the drive’s output frequency reaches low limit frequency, the terminal
outputs indication signal.
8 9: Overload signal
When overload occurs, the terminal outputs indication signal.
9 10: Over current stall
When over current stall occurs in running state, terminal outputs indication
signal.
10 11: Over voltage stall
When over voltage stall occurs in running state, the terminal outputs
indication signal.
11 12: External stopping command
During running process, when external fault signal is received by the digital
input terminals, the drive reports ER11 fault, and the terminal outputs
indication signal at the same time.
Page 91

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
87
12 13: Preset counting value arriving
Set up counting value of the drive’s internal counter. The drive inputs counting
pulses via external terminals Xi (I=1~7), and the drive’s internal counter
counts this signal. When the preset value arrives, Yi outputs an indication
signal. When the next external counting pulse signal arrives, Yi 's output
signal recovers, and the counter restarts to count again at the same time.
13 14: Specified counting value arriving
When Xi inputs external counting pulse signal and the counting value reaches
specified value defined by p6.17 (See Fig. 6-22), Y1 outputs an indication
signal, Y1 does not recover until speicified value arrives.
As shown in Fig. 6-22, if P6.16=5, P6.17=3, when Xi inputs the 3th pulse, Y1
outputs an indication signal. When Xi inputs the 5th pulse, Y1 outputs
specified value arriving signal. Y1 will recover when the 6th pulse arrives.
0 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3
X1
1
Y1
Programmable
relay
Fig. 6-22 Preset counting value arriving and specified counting value
arriving
14 15: Low voltage lockup signal
When DC bus voltage is lower than the low voltage limit, the panel LED
displays “LU”, and the terminal outputs indication signal at the same time.
15 16: Overload pre-alarm
Page 92

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
88
According to PD.04~PD.06 overload pre-alarm setup, when the output current
is higher than the setting value, the terminal outputs indication signal.
16 17: Drive failure signal
When fault occurs, the terminal outputs indication signal
17 18: Zero speed running
When the drive’s running frequency is zero, the terminal outputs indication
signal.
For example, in the following three conditions the terminals output indication
signal:
FWD/REV dead time running period;
The phase when the setup frequency is lower than the start frequency
when the inverter starts from zero frequency;
In Dec process output frequency is lower than initial frequency of DC
injection braking.
18 19:End signal of stage of program operation
In program operation mode, when a stage is finished, the inverter outputs a pulse with width of 250ms.
19 20: End signal of stage of program operation
In program operation mode, when a cycle is finished, the inverter outputs a pulse with width of 250ms.
P6.11 Frequency arriving width (FAR)
Setting range:0.0~10.00Hz
When output terminal function is selected as frequency arriving signal, this
function is used to detect output frequency range. When error between output
frequency and setting value is less than FAR, the terminal outputs indication signal,
as shown in Fig.6-24.
Page 93

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
89
Detection width
Output frequency
Time
Yi
Time
Fig.6-24 FAR and FAR detection width
P6.12 FDT1 level
Setting range: 0.0~400.0Hz
P6.13 FDT1 lag
Setting range: 0.0~10.00Hz
P6.14 FDT2 level
Setting range: 0.0~400.0Hz
P6.15 FDT2 lag
Setting range: 0.0~10.00Hz
If output frequency exceeds certain value, the terminal outputs indication
signal, and this signal is called FDT level.
If output frequency decreases, the terminal continues to outputs indication
signal, until the output frequency is lowered to the FDT signal width and exceeds
certain width, this width is called FDT signal lag, as shown in Fig.6-21 and 6-23.
P6.16 Preset value arriving
Setting range:0~9999
P6.17 Specified value arriving
Setting range:0~9999
For P6.16 and P6.17 function, please refer to definition of terminal function 13,
14.
P6.18 Terminal logic
Setting range:0~255
Page 94

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
90
This parameter defines positive or negative logic of terminals.
Y1
X7
X6
X5
X4
X3
X2
X1
Bit7
Bit6
Bit5
Bit4
Bit3
Bit2
Bit1
Bit0
Note:
a. If bit 0 is set to 0, it means positive logic, and 1 for negative logic. Factory
setting of all terminals are positive logic;
b. In positive logic mode, terminal Xi is enabled if it is connected to the
common terminal, and disabled if disconnected;
In negative logic mode, terminal Xi is disabled if it is connected to the
common terminal, and enabled if disconnected;
In positive logic mode, terminal Yi closes when its output signal is valid;
In negative logic mode, terminal Yi opens when its output signal is valid;
c. Only decimal number can be set to the drive (including display). When
negative logic is selected, conversion from binary code to Hex value is
shown as below:
Setting value =(2*Y1)
7
+(2*X6)5 +(2*X5)
4
+(2*X4)
3
+(2*X3)2+(2*X2)1+X1
For example,
if X6 and X4 select negative logic and others are positive logic, then:
Setting value =(2*0)
6
+(2*1)5 +(2*0)4+(2*1)
3
+(2*0)2+(2*0)1+0=32+8=40
P7 Analog input terminal function
P7.00 AI1 filter time
Setting range: 0.05-5.00S
P7.01 Minimum AI1
0.0-100.0%
P7.02 Frequency corresponding to P7.06
0.00 ~ Maximum frequency
P7.03 Maximum AI1
0.0-100.0%
P7.04 Frequency corresponding to P7.08
0.00 ~ Maximum frequency
P7.05 AI2 filter time
Setting range: 0.05-5.00s
P7.06 Minimum AI2
0.0-100.0%
Page 95

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
91
P7.07 Frequency corresponding to P7.06
0.00 ~ Maximum frequency
P7.08 Maximum AI2
0.0-100.0%
P7.09 Frequency corresponding to P7.09
0.00 ~ Maximum frequency
Reference signal from external input (AI1, AI2) is filtered and amplified, and
then its relationship with frequency setting is shown as curve 1 in Fig. 6-25 or curve
2 in Fig.6-26.
AI2 can input current signal (4~20mA), P7.06 should be set to 20% except that
S1 (AI2) is in “I” position,
P7.10 FWD/REV dead time range
Setting range: 0~10% Maximum input signal
If polarity control is selected (P0.06= 2 or 3), FWD/REV dead time is set by
this parameter. Refer to parameter P0.06 and fig 6-1 for details.
P7.11 AI1 filter time
Setting range: 0.05-5.00S
P7.12 Minimum AI1
0.0-100.0%
P7.13 Frequency corresponding toP7.12
0.00 ~ Maximum frequency
P7.14 Maximum AI1
0.0-100.0%
P7.15 Frequency corresponding to P7.13
0.00 ~ Maximum frequency
Reference signal(AI1) from keypad potentiometer is filtered and amplified, and
then its relationship with frequency setting is shown as curve 1 in Fig. 6-25 or curve
2 in Fig. 6-26.
Page 96

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
92
0
Minimum value
(F7.01)
Hz
Maximum value
corresponding to the
frequency
(F7.04)
Input signal
output frequency
Maximum value
(F7.03)
Minimum value corresponding
to the frequency(F7.02)
Fig. 6-25 curve 1: relationship between reference and frequency setting
0
Minimum
(F7.01)
Hz
Minimum value corresponding to the
frequency(F7.02)
Input signal
output frequency
Maximum value
(F7.03)
Maximum value corresponding to the
frequency(F7.04)
Fig. 6-26 curve 2: relationship between reference and frequency setting
P8 Analog output terminal
P8.00 AO1 output selection
Setting range:0~9
P8.01 AO2 output selection
Setting range:0~9
Inverter's state represented by analog output signal is defined by the function
codes P8.00 and P8.01, as shown below.
Page 97

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
93
P8.00/P8.01
Drive state
Description
0
Running
frequency/speed
0~ highest running frequency/speed
1
Frequency
setting/speed
0~ highest running frequency/speed
2
Output current
0~ 2×rated current
3
Output voltage
0~+200% rated voltage
4
Output torque
-200%~+200% rated torque current
5
PI reference
0~10V
6
PI feedback
0~10V
7
Bus voltage
0-800V
8
Analog input AI1
0-10V
9
Analog input AI2
0-10V
p8.02 Minimum AO1
Setting range:0.00~100.0%
p8.03 Minimum value corresponding to F8.02
Setting range:0.00~100.0%
p8.04 Maximum AO1
Setting range:0.00~100.0%
p8.05 Maximum value corresponding to F8.04
Setting range:0.00~100.0%
This function code is used to setup maximum/minimum value of analog output
signal (0~10V), and the relationship between these values and P8.00 is shown in
Fig. 6-27 and 6-28.
0
Minimum value
(F8.02)
Corresponding to
the maximum
(F8.05)
AO1 Output signal
Output(F8.00)
Maximum value
(F8.04)
Corresponding to the minimum
value(F8.03)
Fig. 6-27 Relationship between maximum/minimum AO1 and F8.00
Page 98

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
94
For example, connect AO1 with a voltage meter (range: 0~5V) to indicate
operating frequency, and the range of operating frequency is 0~50Hz (Maximum
frequency=50Hz), then F8.00=0(=frequency), F8.02=0(=0V), F8.03=0(0Hz),
F8.04=50%(=5V), F8.05=100%(=50Hz).
0
AO1 Output signal
output(F8.00)
Minimum value
(F8.02)
Corresponding to the
minimum value
(F8.03)
Maximum value
(F8.04)
Corresponding to the
maximum
(F8.05)
Fig. 6-28 Relationship between maximum/minimum AO1 and F8.00
P8.06 Minimum AO2
Setting range:0.00~100.0%
P8.07 Minimum value corresponding to F8.06
Setting range:0.00~100.0%
P8.08 Maximum AO2
Setting range:0.00~100.0%
P8.09 Maximum value corresponding to F8.08
Setting range:0.00~100.0%
For more information about P8.02~P8.05, refer to Fig. 6-27 and 6-28. AO2
can output voltage or current signal. To output 4~20mA signal, P8.06 should be set
to 20% except that S2(AO2) is in “I” position.
P9 Program operating parameters
P9 parameter group is function code of programming operation.
Both programming operation and multi-frequency operation are used for
realizing the inverter's variable speed running according to certain regulations.
Page 99

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
95
One cycle of programming operation is shown in Fig. 6-29, f1~f7 and T1~
T7 will be defined in the following function codes.
T2T1 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7
f1
f2
f3
f4
f5
f6
f7
Fig. 6-29 Programming operation
P9.00 Programming operation function
Setting range:0, 1,2
0: Single cycle (Stop after a single cycle)
1: Continuous cycle (Continue cycle operation according to setup phase
parameters)
2: Maintain the final value (maintain the non-zero operating frequency of
last stage after completing one cycle)
P9.01 Programming operation time setting unit
Setting range:0、1
0:second
1:minute
P9.02 Stage timing T1
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.03 Stage timing T2
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.04 Stage timing T3
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.05 Stage timing T4
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.06 Stage timing T5
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.07 Stage timing T6
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.08 Stage timingT7
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.09 Stage timingT8
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
Page 100

TMP High Performance Vector Control Inverter User Manual
96
P9.10 Stage timingT9
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.11 Stage timingT10
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.12 Stage timingT11
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.13 Stage timingT12
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.14 Stage timingT13
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.15 Stage timingT14
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
P9.16 Stage timingT15
Setting range:0.0~3600.0
Parameters P9.02~P9.16 are used to set running time of each stage.
P9.17 T1Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.18 T2Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.19 T3Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.20 T4Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.21 T5Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.22 T6Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.23 T7Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.24 T8Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.25 T9Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.26 T10Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.27 T11Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.28 T12Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.29 T13Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.30 T14Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.31 T15Running mode
Setting range:0~7
P9.17~P9.31 are used to set operating direction and Acc time of each stage:
0 :Run forward Acc/Dec time is 1; 1:Run forward Acc/Dec time is 2; 2 :Run forward
Acc/Dec time is 3; 3:Run forward Acc/Dec time is 4;4 : Run reverse Acc/Dec time is 1; 5 : Run
reverse Acc/Dec time is 2; 6 : Run reverse Acc/Dec time is 3; 7 : Run reverse Acc/Dec time is 4;
 Loading...
Loading...