Page 1

2.00
IEC 870-5-103 Communication Protocol User Guide
PRON NA60-CB0
PRON NA60-CB0
Version
Page: 1 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 2

2.00
PRON NA60-CB0
Contents
Contents ........................................................................................................................................................................ 2
1 IEC 870-5-103 Protocol ........................................................................................................................................ 3
8.1
Physical Layer .............................................................................................................................................. 3
8.1.1 Electrical Interface ................................................................................................................................... 3
8.1.2 Optical Interface ....................................................................................................................................... 3
8.1.3 Transmission speed ................................................................................................................................. 3
8.2
Link Layer ..................................................................................................................................................... 3
8.3
Application Layer .......................................................................................................................................... 4
8.3.1 Transmission mode for application data .................................................................................................. 4
8.3.2 Common address of ASDU ...................................................................................................................... 4
8.3.3 Selection of standard information numbers in monitor direction .............................................................. 4
8.3.4 Selection of standard information numbers in control direction ............................................................... 7
8.3.5 Basic application functions ....................................................................................................................... 7
8.3.6 Miscellaneous .......................................................................................................................................... 8
2 IEC60870-5-103 INTERFACE .............................................................................................................................. 8
2.1
Physical connection and link layer ............................................................................................................... 8
2.2
Initialisation ................................................................................................................................................... 9
2.3
Time synchronisation ................................................................................................................................... 9
2.4
Spontaneous events ..................................................................................................................................... 9
2.5
General interrogation .................................................................................................................................... 9
2.6
Cyclic measurements ................................................................................................................................... 9
2.7
Commands ................................................................................................................................................. 10
2.8
Disturbance records ................................................................................................................................... 10
2.9
Blocking of monitor direction ...................................................................................................................... 10
2.10 Acronyms.................................................................................................................................................... 10
2.11 List of events produced by the relay .......................................................................................................... 11
2.12 List of data contained in General Interrogation .......................................................................................... 13
2.13 Cyclic measurements ................................................................................................................................. 14
2.14 List of the supported commands ................................................................................................................ 15
Version
Page: 2 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 3

2.00
Introduction
This Protocol Manual is for use with Thytronic Protective Relays, such as the DMC, NTG and PRO-N series that
support the IEC 870-5-103 communication protocol.
PRON NA60-CB0
1 IEC 870-5-103 Protocol
The pages in this section have been extracted from the 60870-5-103 © IEC:1997, pages 159 to 171.
The section numbers below have been purposely retained from that document for reference.
8 INTEROPERABILITY
8.1 Physical Layer
8.1.1 Electrical Interface
EIA RS-485
Number of loads ……32…………. For one protection equipment
NOTE - EIA RS-485 standard defines unit loads so that 32 of them can be operated on one line. For detailed
information refer to clause 3 of EIA RS-485 standard.
8.1.2 Optical Interface
Glass fibre
Plastic fibre
F-SMA type connector
BFOC/2,5 type connector
8.1.3 Transmission speed
1 200 bit/s
9 600 bit/s
2 400 bit/s
19 200 bit/s
8.2 Link Layer
There are no choices for the link layer.
4 800 bit/s
38 400 bit/s
57 600 bit/s
Version
Page: 3 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 4

2.00
PRON NA60-CB0
8.3 Application Layer
8.3.1 Transmission mode for application data
Mode 1 (least significant octet first), as defined in 4.10 of IEC 60870-5-4, is used exclusively in this companion
standard.
8.3.2 Common address of ASDU
One C
8.3.3 Selection of standard information numbers in monitor direction
8.3.3.1 System functions in monitor direction
INF Semantics
OMMON ADDRESS
More than one C
<0> End of general interrogation
<0> Time synchronization
of ASDU (identical with station address)
OMMON ADDRESS
of ASDU
<2> Reset FCB
<3> Reset CU
<4> Start/restart
<5> Power on
8.3.3.2 Status indications in monitor direction
INF Semantics
<16> Auto-recloser active
<17> Teleprotection active
<18> Protection active
<19> LED reset
<20> Monitor direction blocked
<21> Test mode
<22> Local parameter setting
<23> Characteristic 1
<24> Characteristic 2
<25> Characteristic 3
<26> Characteristic 4
<27> Auxiliary input 1
<28> Auxiliary input 2
<29> Auxiliary input 3
<30> Auxiliary input 4
Version
Page: 4 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 5

2.00
8.3.3.3 Supervision indications in monitor direction
INF Semantics
<32> Measurand supervision I
<33> Measurand supervision V
<35> Phase sequence supervision
<36> Trip circuit supervision
<37> I>> back-up operation
<38> VT fuse failure
<39> Teleprotection disturbed
<46> Group warning
<47> Group alarm
8.3.3.4 Earth fault indications in monitor direction
INF Semantics
<48> Earth fault L
1
PRON NA60-CB0
<49> Earth fault L
<50> Earth fault L
<51> Earth fault forward, i.e. line
<52> Earth fault reverse, i.e. busbar
8.3.3.5 Fault indications in monitor direction
INF Semantics
<64> Start /pick-up L
<65> Start /pick-up L
<66> Start /pick-up L
<67> Start /pick-up N
<68> General trip
<69> Trip L
<70> Trip L
<71> Trip L
<72> Trip I>> (back-up operation)
<73> Fault location X in ohms
<74> Fault forward/line
<75> Fault reverse/busbar
<76> Teleprotection signal transmitted
<77> Teleprotection signal received
<78> Zone 1
<79> Zone 2
<80> Zone 3
<81> Zone 4
1
2
3
2
3
1
2
3
Version
Page: 5 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 6

2.00
<82> Zone 5
<83> Zone 6
<84> General start/pick-up
<85> Breaker failure
<86> Trip measuring system L
<87> Trip measuring system L
<88> Trip measuring system L
<89> Trip measuring system E
<90> Trip I>
<91> Trip I>>
<92> Trip IN>
<93> Trip IN>>
8.3.3.6 Auto-reclosure indications in monitor direction
INF Semantics
<128> CB 'on' by AR
1
2
3
PRON NA60-CB0
<129> CB 'on' by long-time AR
<130> AR blocked
8.3.3.7 Measurands in monitor direction
INF Semantics
<144> Measurand I
<145> Measurands I, V
<146> Measurands I, V, P, Q
<147> Measurands IN, V
<148> Measurands I
8.3.3.8 Generic functions in monitor direction
INF Semantics
<240> Read headings of all defined groups
<241> Read values or attributes of all entries of one group
<243> Read directory of a single entry
<244> Read value or attribute of a single entry
<245> End of general interrogation of generic data
L1,2,3
EN
, V
L1,2,3
, P, Q, f
<249> Write entry with confirmation
<250> Write entry with execution
<251> Write entry aborted
Version
Page: 6 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 7

2.00
8.3.4 Selection of standard information numbers in control direction
8.3.4.1 System functions in control direction
INF Semantics
<0> Initiation of general interrogation
<0> Time synchronization
8.3.4.2 General commands in control direction
INF Semantics
<16> Auto-recloser on/off
<17> Teleprotection on/off
<18> Protection on/off
<19> LED reset
<23> Activate characteristic 1
<24> Activate characteristic 2
<25> Activate characteristic 3
PRON NA60-CB0
<26> Activate characteristic 4
8.3.4.3 Generic functions in control direction
INF Semantics
<240> Read headings of all defined groups
<241> Read values or attributes of all entries in one group
<243> Read directory of a single entry
<244> Read value or attribute of a single entry
<245> General interrogation of generic data
<248> Write entry
<249> Write entry with confirmation
<250> Write entry with execution
<251> Write entry abort
8.3.5 Basic application functions
Test mode
Blocking of monitor direction
Disturbance data
Generic services
Private data
Version
Page: 7 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 8

2.00
PRON NA60-CB0
8.3.6 Miscellaneous
Measurands are transmitted with ASDU 3. As defined in 7.2.6.8, the maximum MVAL can
either be 1,2 or 2,4 times the rated value. No different rating shall be used in ASDU 3, i.e., for
each measurand there is only one choice.
Measurand Max. MVAL = rated value times
1,2 or 2,4
Current L
Current L
Current L
Voltage L
Voltage L
Voltage L
Active power P
1
2
3
1-E
2-E
3-E
Reactive power Q
Frequency f
Voltage L1 - L
2
2 IEC60870-5-103 INTERFACE
The following IEC60870-5-103 facilities are supported by this interface:
1. Initialisation
2. Time Synchronisation
3. Event Record Extraction
4. General Interrogation
5. Cyclic Measurements
6. General Commands
2.1 Physical connection and link layer
Connection is available for IEC60870-5-103 through the rear RS485 port. It is possible to select both the relay
address and baud rate using the front panel interface. Following a change, a reset command is required to reestablish communications.
The parameters of the communication are the following :
• Even Parity
• 8 Data bits
• 1 stop bit
• Data rate 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400 or 57600 bauds
Version
Page: 8 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 9

2.00
PRON NA60-CB0
2.2 Initialisation
Whenever the relay has been powered up, or if the communication parameters have been changed a reset
command is required to initialise the communications. The relay will respond to either of the two reset commands
(Reset CU or Reset FCB), the difference being that the Reset CU will clear any unsent messages in the relay's
transmit buffer.
The relay will respond to the reset command with an identification message ASDU 5, the Cause Of Transmission
COT of this response will be either Reset CU or Reset FCB depending on the nature of the reset command.
The following information will be contained in the data section of this ASDU:
Internal Software ID: internal Firmware ID
ASCII ID: Relay model
2.3 Time synchronisation
The relay time and date can be set using the time synchronisation feature of the IEC60870-5-103 protocol. The
relay will correct for the transmission delay as specified in IEC60870-5-103.
2.4 Spontaneous events
The events created by the relay will be passed using the standard function type/information numbers to the
IEC60870-5-103 master station. Private codes are not used, thus any events that cannot be passed using the
standardised messages will not be sent.
Events are categorised using the following information:
• Common Address
• Function Type
• Information number
The common address is used to differentiate in circumstances where the relay produces more events of a certain
type than can be passed using the standardised messages.
For example if the relay produces starts and trips for three stages of overcurrent only two stages can be passed
using the standardised messages.
Using the different common address for two of the overcurrent stages allows each stage to be indicated.
2.5 General interrogation
The GI request can be used to read the status of the relay, the function numbers, information numbers and
common address offsets that will be returned during the GI cycle are indicated in 2.11.
2.6 Cyclic measurements
The relay will produce measured values using ASDU 3 on a cyclical basis, this can be read from the relay using a
Class 2 poll (note ADSU 9 is not used).
It should be noted that the measurands transmitted by the relay are sent as a proportion of either 1.2 or 2.4 times
the rated value of the analogue value. The selection of either 1.2 or 2.4 for a particular value is indicated in 2.11.
Version
Page: 9 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 10

2.00
PRON NA60-CB0
2.7 Commands
A list of the supported commands is contained in 2.11. The relay will respond to other commands with an ASDU 1,
with a cause of transmission (COT) of negative acknowledgement of a command.
2.8 Disturbance records
The relay does not support the exchange of disturbance data through the mechanism defined in the IEC60870-5103 standard.
2.9 Blocking of monitor direction
The relay does not support a facility to block messages in the Monitor direction.
2.10 Acronyms
FUN: Function Type
INF: Information Number
TYPE: Type of ASDU
COT: Cause of Transmission
BIDI: Bidirectional event
Version
Page: 10 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 11

2.00
LIST OF FAULTS
DSC
TYP
2.11 List of events produced by the relay
Two kinds of ASDU can be generated for the events :
Type ASDU 1 (time-tagged message)
Type ASDU 2 (Time-tagged message with relative time)
NORMALIZE
FACTOR
Trip I>
Trip I>>
Trip I>>>
Trip IE>
Trip IE>>
Trip IE>>>
Trip U<
Trip U<<
Trip U>
Trip U>>
Trip UE>
Trip UE>>
Trip Dth>
Trip IPD>
Trip IPD>>
Trip IPD>>>
Trip IPD>>>>
Trip IED>
Trip IED>>
Trip IED>>>
Trip IED>>>>
Alarm ThAL1
Trip Th>1
Alarm ThAL2
Trip Th>2
Alarm ThAL3
Trip Th>3
Alarm ThAL4
Trip Th>4
Alarm ThAL5
Trip Th>5
Alarm ThAL6
Trip Th>6
Alarm ThAL7
Trip Th>7
Alarm ThAL8
Trip Th>8
Trip 74TCS
Trip BF
NAME
TRIP_IM - - 160 90 2 1 - 3
TRIP_IMM - - 160 91 2 1 - 3
TRIP_IMMM - - 160 94 2 1 - 3
TRIP_INM - - 162 92 2 1 - 3
TRIP_INMM - - 162 93 2 1 - 3
TRIP_INMMM - - 162 96 2 1 - 3
TRIP_IM - - 165 90 2 1 - 3
TRIP_IMM - - 165 91 2 1 - 3
TRIP_IM - - 166 90 2 1 - 3
TRIP_IMM - - 166 91 2 1 - 3
TRIP_INM - - 167 92 2 1 - 3
TRIP_INMM - - 167 93 2 1 - 3
TRIP_IM - - 168 90 2 1 - 3
TRIP_IM - - 163 90 2 1 - 3
TRIP_IMM - - 163 91 2 1 - 3
TRIP_IMMM - - 163 94 2 1 - 3
TRIP_IMMMM - - 163 95 2 1 - 3
TRIP_INM - - 164 92 2 1 - 3
TRIP_INMM - - 164 93 2 1 - 3
TRIP_INMMM - - 164 96 2 1 - 3
TRIP_INMMMM - - 164 97 2 1 - 3
ALARM_PT1 - - 178 198 2 1 - 3
TRIP_PT1 - - 178 199 2 1 - 3
ALARM_PT2 - - 178 200 2 1 - 3
TRIP_PT2 - - 178 201 2 1 - 3
ALARM_PT3 - - 178 202 2 1 - 3
TRIP_PT3 - - 178 203 2 1 - 3
ALARM_PT4 - - 178 204 2 1 - 3
TRIP_PT4 - - 178 205 2 1 - 3
ALARM_PT5 - - 178 206 2 1 - 3
TRIP_PT5 - - 178 207 2 1 - 3
ALARM_PT6 - - 178 208 2 1 - 3
TRIP_PT6 - - 178 209 2 1 - 3
ALARM_PT7 - - 178 210 2 1 - 3
TRIP_PT7 - - 178 211 2 1 - 3
ALARM_PT8 - - 178 212 2 1 - 3
TRIP_PT8 - - 178 213 2 1 - 3
TC_SUPERVISION - - 255 36 1 1 X 3
BF - - 255 85 2 1 - 3
RATED
VALUE
PRON NA60-CB0
FUN INF
E
COT BIDI
CAA
Version
Page: 11 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 12

2.00
LIST OF FAULTS
DSC
TYP
IN1
IN2
IN3
IN4
IN5
IN6
IN7
IN8
IN9
IN10
IN11
IN12
IN13
IN14
IN15
IN16
IN17
IN18
IN19
IN20
IN21
IN22
IN23
IN24
IN25
IN26
IN27
IN28
IN29
IN30
IN31
IN32
IN33
IN34
IN35
IN36
IN37
IN38
IN39
IN40
IN41
IN42
General start I>
General trip I>
NAME
AUX_INPUT_1 - - 255 27 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_2 - - 255 28 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_3 - - 255 29 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_4 - - 255 30 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_5 - - 255 160 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_6 - - 255 161 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_7 - - 255 162 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_8 - - 255 163 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_9 - - 255 164 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_10 - - 255 165 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_11 - - 255 166 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_12 - - 255 167 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_13 - - 255 168 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_14 - - 255 169 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_15 - - 255 170 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_16 - - 255 171 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_17 - - 255 172 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_18 - - 255 173 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_19 - - 255 174 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_20 - - 255 175 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_21 - - 255 176 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_22 - - 255 177 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_23 - - 255 178 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_24 - - 255 179 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_25 - - 255 180 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_26 - - 255 181 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_27 - - 255 182 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_28 - - 255 183 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_29 - - 255 184 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_30 - - 255 185 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_31 - - 255 186 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_32 - - 255 187 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_33 - - 255 188 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_34 - - 255 189 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_35 - - 255 190 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_36 - - 255 191 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_37 - - 255 192 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_38 - - 255 193 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_39 - - 255 194 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_40 - - 255 195 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_41 - - 255 196 1 1 X 3
AUX_INPUT_42 - - 255 197 1 1 X 3
GEN_START - - 255 84 2 1 X 3
GEN_TRIP - - 255 68 2 1 - 3
NORMALIZE
FACTOR
RATED
VALUE
PRON NA60-CB0
FUN INF
E
COT BIDI
CAA
Version
Page: 12 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 13

2.00
LIST OF DATA
DSC
RATED
PRON NA60-CB0
2.12 List of data contained in General Interrogation
CONTAINED IN GI
NORMALIZE
FACTOR
VALUE FUN INF
TYPE
COT
CAA
IN1
IN2
IN3
IN4
Trip 74TCS
General start I>
IN5
IN6
IN7
IN8
IN9
IN10
IN11
IN12
IN13
IN14
IN15
IN16
IN17
IN18
IN19
IN20
IN21
IN22
IN23
IN24
IN25
IN26
IN27
IN28
IN29
IN30
IN31
IN32
IN33
IN34
IN35
IN36
IN37
IN38
IN39
IN40
IN41
IN42
NAME
AUX_INPUT_1 - - 255 27 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_2 - - 255 28 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_3 - - 255 29 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_4 - - 255 30 1 9 3
TC_SUPERVISION - - 255 36 1 9 3
GEN_START - - 255 84 2 9 3
AUX_INPUT_5 - - 255 160 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_6 - - 255 161 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_7 - - 255 162 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_8 - - 255 163 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_9 - - 255 164 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_10 - - 255 165 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_11 - - 255 166 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_12 - - 255 167 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_13 - - 255 168 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_14 - - 255 169 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_15 - - 255 170 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_16 - - 255 171 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_17 - - 255 172 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_18 - - 255 173 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_19 - - 255 174 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_20 - - 255 175 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_21 - - 255 176 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_22 - - 255 177 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_23 - - 255 178 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_24 - - 255 179 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_25 - - 255 180 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_26 - - 255 181 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_27 - - 255 182 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_28 - - 255 183 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_29 - - 255 184 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_30 - - 255 185 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_31 - - 255 186 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_32 - - 255 187 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_33 - - 255 188 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_34 - - 255 189 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_35 - - 255 190 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_36 - - 255 191 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_37 - - 255 192 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_38 - - 255 193 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_39 - - 255 194 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_40 - - 255 195 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_41 - - 255 196 1 9 3
AUX_INPUT_42 - - 255 197 1 9 3
Version
Page: 13 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 14
2.00
LIST OF CYCLIC
DSC
RATED
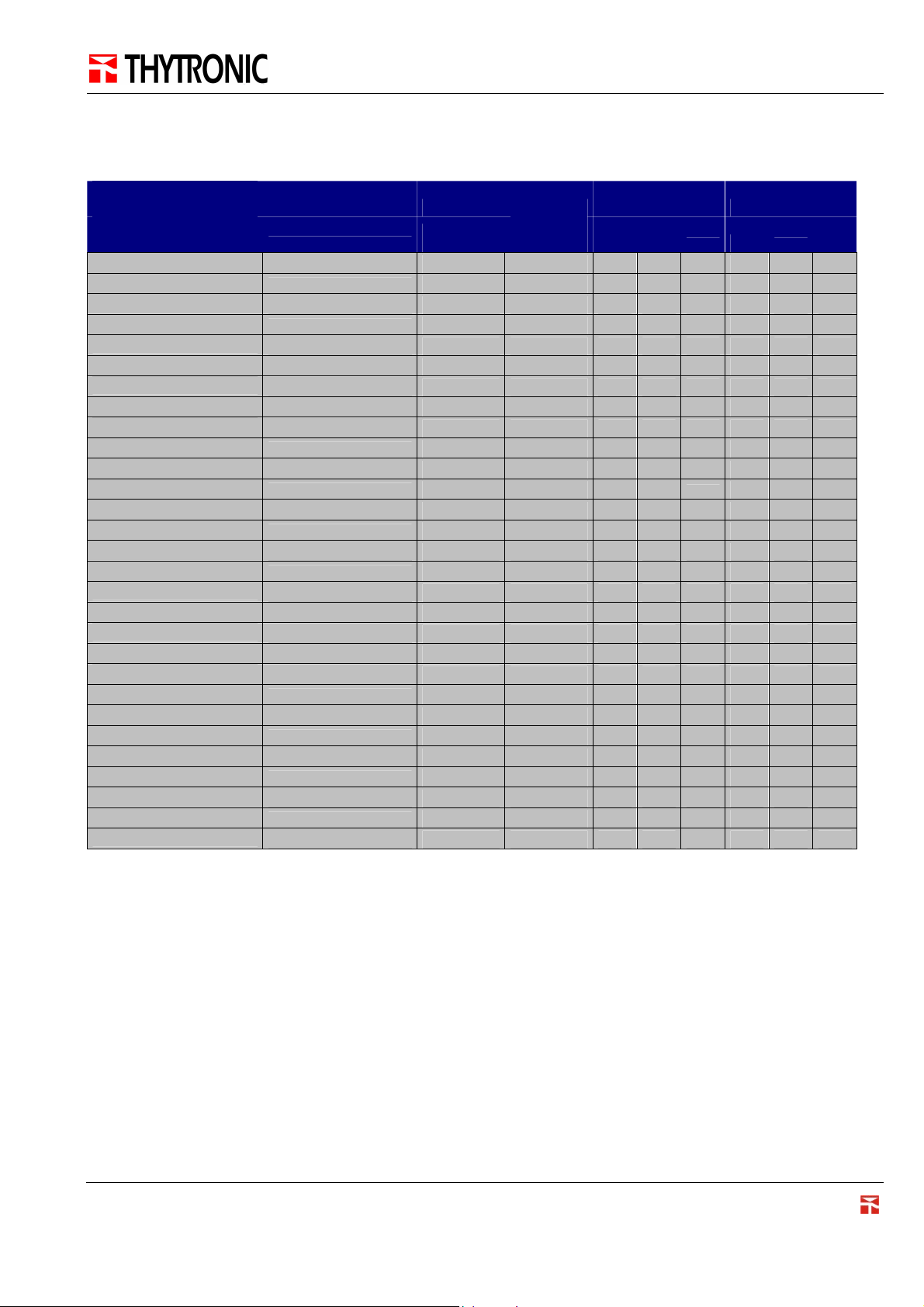
2.13 Cyclic measurements
PRON NA60-CB0
MEASUREMENTS
f
IL1
IL2
IL3
IE
UL1
UL2
UL3
UE
DTheta
U12
U23
U31
UEC
Alpha1
Alpha2
Alpha3
PhiE
PhiEC
P
Q
T1
T2
T3
T4
T5
T6
T7
T8
NAME
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET1
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
MEASURAND_SET2
NORMALIZE
FACTOR
VALUE FUN INF
TYPE
COT
CAA
1,2 50Hz 169 149 9 , 1 2 3
2,4 In 169 149 9 , 2 2 3
2,4 In 169 149 9 , 3 2 3
2,4 In 169 149 9 , 4 2 3
2,4 IEn 169 149 9 , 5 2 3
2,4 En 169 149 9 , 6 2 3
2,4 En 169 149 9 , 7 2 3
2,4 En 169 149 9 , 8 2 3
2,4 UEn 169 149 9 , 9 2 3
2,4 DThetaB 169 149
2,4 Un 169 149
2,4 Un 169 149
2,4 Un 169 149
2,4 UECn 169 149
2,4 180° 169 149
2,4 180° 169 149
9 , 10
9 , 11
9 , 12
9 , 13
9 , 14
9 , 15
9 , 16
2 3
2 3
2 3
2 3
2 3
2 3
2 3
2,4 180° 169 150 9 , 1 2 3
2,4 180° 169 150 9 , 2 2 3
2,4 180° 169 150 9 , 3 2 3
2,4 Pn 169 150 9 , 4 2 3
2,4 Qn 169 150 9 , 5 2 3
2,4 100^C 169 150 9 , 6 2 3
2,4 100^C 169 150 9 , 7 2 3
2,4 100^C 169 150 9 , 8 2 3
2,4 100^C 169 150 9 , 9 2 3
2,4 100^C 169 150
2,4 100^C 169 150
2,4 100^C 169 150
2,4 100^C 169 150
9 , 10
9 , 11
9 , 12
9 , 13
2 3
2 3
2 3
2 3
Version
Page: 14 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
Page 15

2.00
LIST OF COMMANDS
DSC
RATED
2.14 List of the supported commands
NORMALIZE
FACTOR
LED_RESET
OPEN_CB
CLOSE_CB
NAME
- - - 254 19 20 20 3
- - - 254 32 20 20 3
- - - 254 33 20 20 3
PRON NA60-CB0
VALUE FUN INF
TYPE
COT
CAA
Version
Page: 15 of 15
PRON NA60-CB0 IEC 870-5-103
 Loading...
Loading...