Page 1
InstallatIon manual
ExplorEr
®
727
Page 2

EXPLORER®727
Including 19" Rack Version
Installation manual
Document number: 98-126844-D
Release date: September 8, 2011
Page 3

Disclaimer
Any responsibility or liability for loss or damage in connection with the use of this
product and the accompanying documentation is disclaimed by Thrane & Thrane. The
information in this manual is provided for information purposes only, is subject to
change without notice and may contain errors or inaccuracies.
Manuals issued by Thrane & Thrane are periodically revised and updated. Anyone
relying on this information should acquire the most current version e.g. from thrane.com
or from the distributor.
Thrane & Thrane is not responsible for the content or accuracy of any translations or
reproductions, in whole or in part, of this manual from any other source.
Copyright © 2011 Thrane & Thrane A/S. All rights reserved.
Trademark acknowledgements
• Thrane & Thrane is a registered trademark of Thrane & Thrane A/S in the European
Union and the United States.
• EXPLORER is a registered trademark of Thrane & Thrane A/S in the European Union
and the United States.
• Windows and Outlook are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and other countries.
• Inmarsat is a registered trademark of International Maritime Satellite Organisation
(IMSO) and is licensed by IMSO to Inmarsat Limited and Inmarsat Ventures plc.
• Inmarsat’s product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of Inmarsat.
• Other product and company names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or
trade names of their respective owners.
Company web site
thrane.com
Page 4
iii
Safety summary 1
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all
phases of operation, service and repair of this equipment. Failure to comply
with these precautions or with specific warnings elsewhere in this manual
violates safety standards of design, manufacture and intended use of the
equipment. Thrane & Thrane A/S assumes no liability for the customer's
failure to comply with these requirements.
Observe marked areas
Under extreme heat conditions do not touch
areas of the terminal or antenna that are
marked with this symbol, as it may result in
injury.
Microwave radiation hazards
During transmission the antenna in this system
radiates Microwave Power.This radiation may
be hazardous to humans close to the antenna.
When the system is powered, make sure that
nobody gets closer than the recommended
minimum safety distance.
The minimum safety distance is 1 m to the side and above the antenna when
the EXPLORER 727 is powered. The safety distance of 1 m does not apply
directly below the antenna, as the radiation forms a hemisphere above the
antenna.
Service
User access to the interior of the system units is prohibited. Only a
technician authorized by Thrane & Thrane A/S may perform service - failure
to comply with this rule will void the warranty.
Do not service or adjust alone
Do not attempt internal service or adjustments unless another person,
capable of rendering first aid resuscitation, is present.
Page 5
iv
Power supply
The voltage range is 10.5 - 32 V DC; 14 A - 5.5 A. Be aware of high start-up
peak current: 20 A@24 V, 5 ms.
Do not operate in an explosive atmosphere
Do not operate the equipment in the presence of flammable gases or fumes.
Operation of any electrical equipment in such an environment constitutes a
definite safety hazard.
Keep away from live circuits
Operating personnel must not remove equipment covers. Component
replacement and internal adjustment must be made by qualified
maintenance personnel. Do not replace components with the power cable
connected. Under certain conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even
with the power cable removed. To avoid injuries, always disconnect power
and discharge circuits before touching them.
Install and use the antenna with care
Thrane & Thrane assumes no liability for any damage caused by the antenna
falling off the vehicle or stressing the mounting base. It is the responsibility
of the customer to ensure a safe and correct installation of the antenna. The
instructions in the Installation manual are only guidelines.
Note the following safety guidelines for mounting the antenna with
magnetic mounts:
Under normal driving circumstances the magnetic force of the magnetic
mount kit for the antenna should be sufficient to hold the antenna. However,
the magnets may not be able to hold the antenna in place, if:
• the vehicle is involved in an accident,
• the magnets are not mounted properly,
Caution! Do not place your fingers underneath the antenna when
placing the antenna on the vehicle!
The magnetic force is very powerful and your fingers
may be hurt if they are caught between the antenna and
the mounting surface.
Page 6
v
• the roof is not plain or made of a material that will not stick properly to
the magnets,
• the speed of the vehicle is too high and/or
• the road is very bumpy.
We recommend mounting the antenna on the roof rails or directly on the
roof instead of using the magnetic mount kit. Make sure that all mounting
bolts and nuts are secured properly, and that the material of the mounting
surface is strong enough to hold the antenna during the intended use.
Page 7

vi
About the manual 2
Intended readers
This is an installation manual for the EXPLORER 727 system,
intended for installers of the system and service personnel.
Personnel installing or servicing the system must be properly
trained and authorized by Thrane & Thrane. It is important that
you observe all safety requirements listed in the beginning of this
manual, and install the system according to the guidelines in this
manual.
Manual overview
Note that this manual does not cover general use of the system nor
does it cover how to use the IP handset that comes with the
system. For this information, refer to the user manual for this
system and the user manual for the IP handset, both listed in the
next section.
This manual has the following chapters:
• System units contains a short description of each main unit in
the system.
• Installing the system describes where to place the system units,
how to mount them, distance to other equipment etc.
• Connecting power explains how to connect the terminal to
power and gives recommendations for cables.
• Hardware interfaces describes each interface on the terminal
and shows pin-out for the connectors.
• Starting up the system explains how to insert the SIM card,
power up the system and enter the PIN. It also gives a short
overview of how to use the system.
• Troubl eshootin g describes the function of the Reset button and
the light indicators on the terminal. It also describes event
messages that may appear in the web interface.
Page 8

vii
Related documents
The below list shows the documents related to this manual and to
the EXPLORER 727 system.
Title and description
Document
number
EXPLORER 727 Including 19" Rack Version
User Manual
Explains how to set up and use the
EXPLORER 727 system.
98-126882
EXPLORER 727 Quick Guide
A short guide to the most important functions
of the EXPLORER 727 system.
98-126881
EXPLORER 727 Getting Started
Explains how to start up your EXPLORER 727
system and make the first call or data session.
TT98-126880
Thrane IP Handset, User Manual
Explains the features and functions of the
Thrane IP Handset. The IP handset works as a
standard IP handset, but also serves as a user
interface for the EXPLORER 727 system.
98-126059
Page 9

viii
Typography
In this manual, typography is used as indicated below:
Bold is used for the following purposes:
• To emphasize words.
Example: “Do not touch the antenna”.
• To indicate what the user should select in the user interface.
Example: “Select SETTINGS > LAN”.
Italic is used to emphasize the paragraph title in cross-references.
Example: “For further information, see Connecting Cables on
page...”.
Page 10

ix
Table of contents
Chapter 1 System units
1.1 Introduction ............................................................... 1
1.2 EXPLORER 727 terminal ............................................. 1
1.3 Antenna .....................................................................3
1.4 Thrane IP Handset & Cradle .......................................4
Chapter 2 Installing the system
2.1 Unpacking .................................................................7
2.2 Placing the antenna ...................................................8
2.3 Installing the antenna ................................................9
2.4 Placing the terminal .................................................17
2.5 Installing the EXPLORER 727 terminal .......................19
2.6 Installing the 19” Rack Terminal ...............................23
Chapter 3 Connecting power
3.1 Power source ...........................................................27
3.2 Power cable selection ..............................................28
3.3 Connecting power ....................................................34
Chapter 4 Hardware interfaces
4.1 The connector panel ................................................39
4.2 Antenna interface on terminal .................................40
4.3 DC power input .........................................................41
4.4 19” rack version only: Terminal block .......................43
4.5 Analogue Phone/Fax interface .................................44
Page 11

Table of contents
x
4.6 ISDN interface ..........................................................45
4.7 LAN interface ...........................................................47
4.8 Discrete I/O interface ............................................... 50
Chapter 5 Starting up the system
5.1 Using the SIM card ...................................................55
5.2 Powering the system ................................................57
5.3 Entering the SIM PIN for the terminal ..................... 60
5.4 Operating the system ...............................................63
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
6.1 Reset button ............................................................65
6.2 Status signalling ..................................................... 68
6.3 Logging of events .....................................................73
App. A Part numbers
A.1 System units ............................................................75
A.2 Spare parts ..............................................................75
App. B Technical specifications
B.1 Overview ..................................................................77
B.2 EXPLORER 727antenna .............................................78
B.3 EXPLORER 727 terminal ...........................................82
Glossary ......................................................................................... 91
Index .........................................................................................95
Page 12

1
Chapter 1
1111
System units
System units 1
1.1 Introduction
The basic system consists of three units: The terminal, the antenna and the IP
handset with cradle.
1.2 EXPLORER 727 terminal
The terminal is the central unit in the system. It contains all user interfaces
and handles all communication between the BGAN antenna and the local
communication units (phones, computers etc.).
The terminal comes in two versions, one designed for wall or desktop
installation, and one designed for installation in a 19” rack.
Below is the terminal for wall or desktop installation.
Page 13

Chapter 1: System units
2 EXPLORER 727 terminal
Below is the 19” rack version of the terminal.
The terminal supplies 23.0 - 30.0 V DC to the antenna through a single coaxial
cable.
The DC input for the terminal is designed for both 24 V DC and 12 V DC power
supply.
Page 14

Chapter 1: System units
Antenna 3
1111
System units
1.3 Antenna
The EXPLORER 727 antenna is a mechanical tracking antenna, consisting of a
2-axis stabilized antenna with RF-unit, antenna control unit and GPS antenna.
The antenna is dedicated to the Inmarsat BGAN (Broadband Global Area
Network) system and is designed for roof mounting on a vehicle. All
communication between the antenna and terminal passes through a single
coaxial cable.
Page 15

Chapter 1: System units
4 Thrane IP Handset & Cradle
1.4 Thrane IP Handset & Cradle
1.4.1 Thrane IP Handset
Besides the normal functions of an IP handset, the Thrane IP handset also
provides a user interface for the EXPLORER 727 system. The IP handset
connects to the LAN interface of the terminal, and is power supplied with
Power over Ethernet (PoE) through the LAN interface.
For further information on the IP handset, refer to the user manual for the
Thrane IP Handset.
Page 16

Chapter 1: System units
Thrane IP Handset & Cradle 5
1111
System units
1.4.2 Thrane IP Cradle
The IP cradle serves as a holder for the IP handset. It is power supplied from
the terminal using Power over Ethernet (PoE). The cradle connects to the
handset with a coil cord and to the terminal with a standard LAN cable.
Page 17

Chapter 1: System units
6 Thrane IP Handset & Cradle
Page 18
7
Chapter 2
2222
Installing the system
Installing the system 2
2.1 Unpacking
Unpack your EXPLORER 727 system and check that the following items are
present:
• TT-3736A EXPLORER 727 terminal or
TT-3736A-T19 EXPLORER 727 19" Rack Terminal
• TT-3053B EXPLORER 727 antenna
• TT-3670A Thrane IP Handset & Cradle, wired
• Basic cable support kit including an I/O connector, or
for 19” rack version: Strain Relief Bracket
•Power cable
• Antenna cable
•LAN cable
• Installation manual (this manual)
• Getting Started kit including:
• Getting Started leaflet
•Quick Guide
•EXPLORER727 CD
including electronic versions of User manual, Installation manual,
Quick Guide and Getting Started guide.
Inspect all units and parts for possible transport damage.
Note
For information on how to install the IP handset and cradle, refer to
the user manual for the handset.
Page 19
Chapter 2: Installing the system
8 Placing the antenna
2.2 Placing the antenna
2.2.1 Obstructions
Obstructions can cause signal degradation.
The amount of degradation depends on the size of the obstruction and the
distance from the antenna. As a rule of thumb any obstruction that covers an
angle of less than 3° at the antenna has limited effect. The table below gives a
guideline for obstruction sizes that will cause limited degradation.
2.2.2 Radiation hazard
The EXPLORER 727 antenna radiates up to 18 dBW EIRP. This translates to a
minimum safety distance of 1 m from the antenna while it is transmitting. Note
that the safety distance applies to a hemisphere above the antenna. The
antenna does not radiate power directly below the antenna.
2.2.3 Interference
Do not place the antenna close to interfering signal sources or receivers. We
recommend that no other antennas are located within three meters of the
antenna. If other equipment is installed near the EXPLORER 727 we
recommend testing the total system by operating all equipment
simultaneously and verifying that there is no interference.
Distance of Obstruction Size of Obstruction
3m 16cm
5m 26cm
10 m 52 cm
20 m 104 cm
Page 20
Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the antenna 9
2222
Installing the system
2.3 Installing the antenna
2.3.1 Antenna cables
Guidelines
A coaxial cable for connection between the antenna and terminal is delivered
with the system. If you need a different cable, make sure that the cable meets
the requirements. Preferably choose one of the cable types in Recommended
antenna cables below.
The maximum allowed RF-loss in the antenna cable is 20 dB at 1660 MHz. This
is to ensure the performance of the system.
Recommended antenna cables
The table below shows recommended cable types and maximum cable lengths
for EXPLORER 727.
Check in the data sheet from the cable supplier that both the RF- attenuation
and the DC-resistance are kept within the maximum specified values:
• Antenna cable RF-attenuation at 1660 MHz: max. 20 dB incl. connector.
Caution! It is the responsibility of the customer to ensure a safe
installation! See guidelines in the Safety summary on
page iii.
Cable Type Absolute maximum length
RG-223_U-01 14 m
RG-214_U-01 50 m
S-10162-B-11 92 m
Page 21

Chapter 2: Installing the system
10 Installing the antenna
• Antenna cable modem-attenuation at 54 MHz: max. 4 dB.
Antenna cable modem-attenuation at 36 MHz: max. 3 dB.
• Antenna cable loop DC-resistance max: 0.6 .
Also ensure that the specified minimum bending radius is respected. If this is
not the case, the loss in the cable will increase. Check the instructions from
the cable supplier. The bending radius for the coax cable delivered with the
system is min. 110 mm.
2.3.2 Important mounting notes
Line of sight
Place the antenna with free line of sight in all directions to ensure proper
reception of the satellite signal. Do not place the antenna close to large
objects that may block the signal.
After installing and starting up the EXPLORER 727, we recommend checking
the signal strength while driving the vehicle in a 360° circle to ensure a clear
line of sight in all directions.
Condensation
In some cases there will be condensation inside the antenna. Gaskets in the
bottom of the EXPLORER 727 antenna are designed to lead any water away
from the antenna.
Make sure these draining gaskets are not blocked.
See the drawing in Mounting the antenna fixed on the vehicle roof on page 16.
Important
Make sure there is always a distance of min. 10 mm between
any part of the antenna bottom and the mounting surface. Use
10 mm spacers (or higher if necessary) at each bolt.
Page 22

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the antenna 11
2222
Installing the system
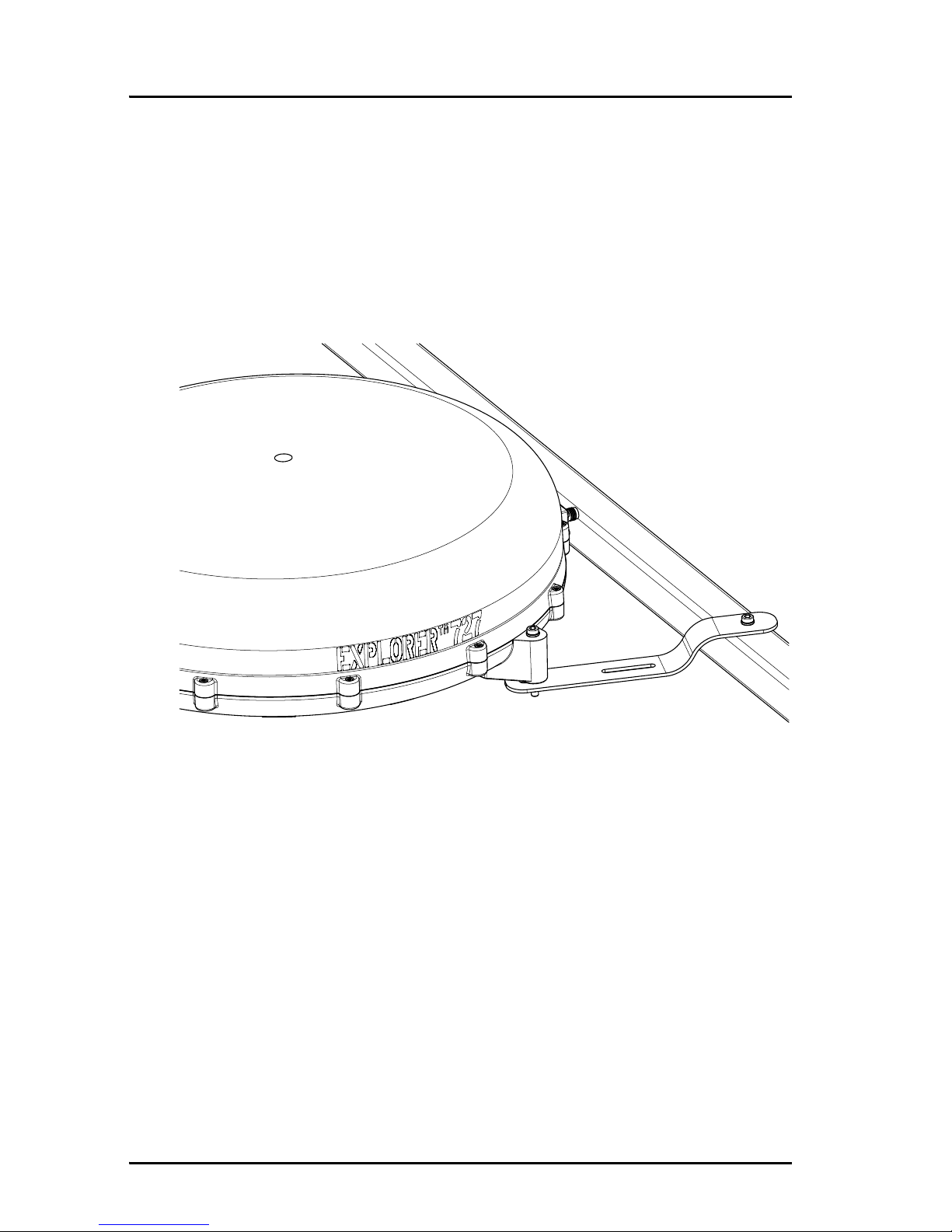
2.3.3 Mounting the antenna
The antenna can now be installed on the roof of the vehicle with three
stainless steel bolts. You may choose between these methods:
• Attach the antenna to the roof rails on your vehicle using the dedicated
mounting brackets delivered with your EXPLORER 727 system.
• Attach the antenna using the magnetic mount kit from Thrane & Thrane.
Mount the magnetic feet on the antenna and the magnetic force will keep
the antenna fixed to the vehicle roof. Note that this method requires a
vehicle roof made of magnetizable material.
• Mount the antenna directly on the roof of the vehicle. This method requires
that you drill holes in the roof of the car. Remember to leave min. 10 mm
space between the antenna and the roof.
Refer to the Safety summary on page iii.
Page 23
Chapter 2: Installing the system
12 Installing the antenna
2.3.4 Mounting the antenna on the roof rails on the vehicle
Overview
Using the dedicated brackets from the roof rail mount kit available from
Thrane & Thrane you can attach the antenna to the roof rails on your vehicle.
Installing the antenna on the roof rails
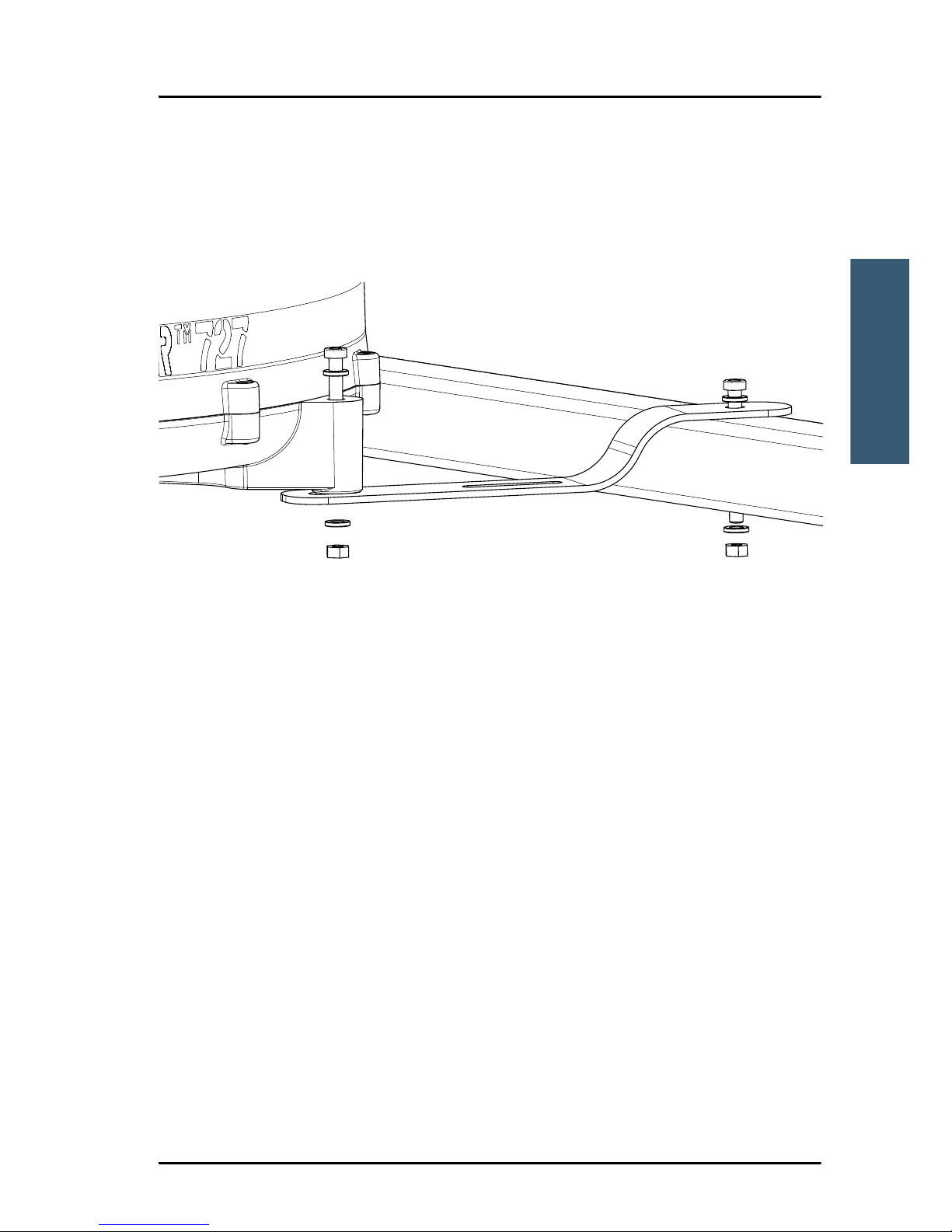
Do as follows:
1. Mount the brackets from the roof rail mount kit on the 3 “legs” of the
antenna, using the bolts, nuts and washers from the kit.
2. Drill 3 holes in the roof rails, matching the position of the 3 brackets.
Page 24
Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the antenna 13
2222
Installing the system
3. Mount the antenna with the brackets onto the roof rails of the vehicle,
placing the bolts, nuts and washers from the kit as shown on the drawing.
4. Tighten all bolts and nuts firmly to secure the antenna to the roof rails.
Torque for the bolts on the antenna: 7.5 Nm.
Torque for the bolts on the roof rails: 8.5 Nm.
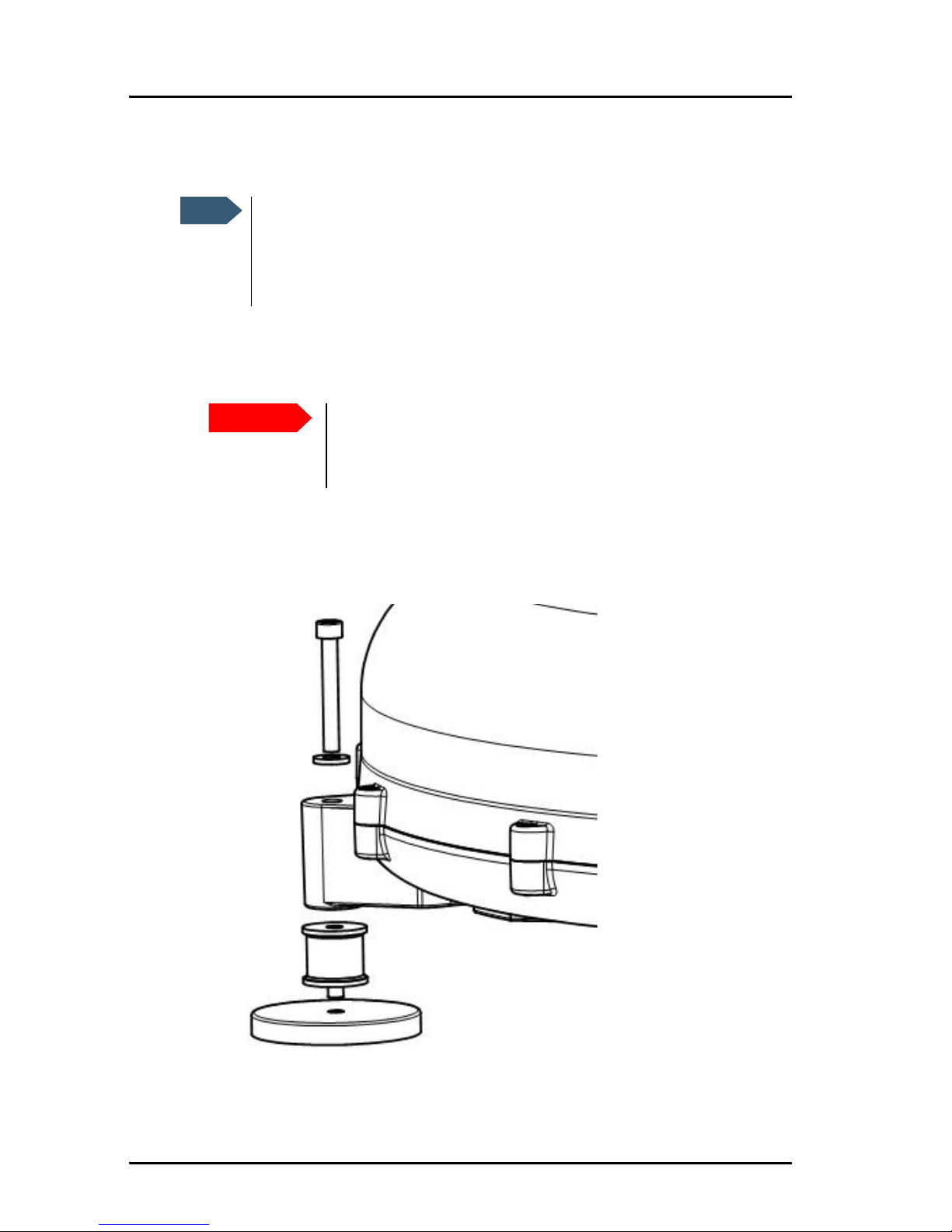
2.3.5 Magnetic mount
Overview
For temporary use – or to avoid drilling holes – you may use the Magnetic
Mount installation kit available from Thrane & Thrane.
The Magnet Mount kit consists of 3 individual high intensity magnets with
rubber coating. Each magnet has an adhesive force of at least 420 N and is
mounted with a stainless steel M5 centre bolt.
Page 25
Chapter 2: Installing the system
14 Installing the antenna
Installing the magnetic mount kit
To use the magnetic mounts, do as follows:
1. First attach the magnets to the antenna.
There are 3 “legs” on the antenna. Place one magnet under each leg as
shown on the drawing on the next page.
2. Tighten the bolts with 7.5 Nm torque.
Note
Make sure the roof of the vehicle is made of a magnetizable
material. Wipe the surface clean before placing the antenna on the
roof, in order to make a better connection between the magnets and
the roof and to avoid scratches in the surface.
Important
The antenna must have a clearance of 10 mm above the
base plane. If the base plane is curved, it may be necessary
to place extra spacers to ensure the clearance of 10 mm.
Page 26

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the antenna 15
2222
Installing the system
3. Place the antenna with magnets on the roof of the car. Remember that the
magnets only work on a roof made of magnetizable material!
4. Connect the antenna cable between the terminal and the antenna.
Refer to Antenna cables on page 9.
Detaching the antenna
Grab the antenna near one of the magnets and lift it. When one magnet is
loose, the other two are easier to “break off”. In some situations the magnetic
force may be so great that it is necessary to unscrew the antenna first and
remove the magnets separately.
Page 27
Chapter 2: Installing the system
16 Installing the antenna
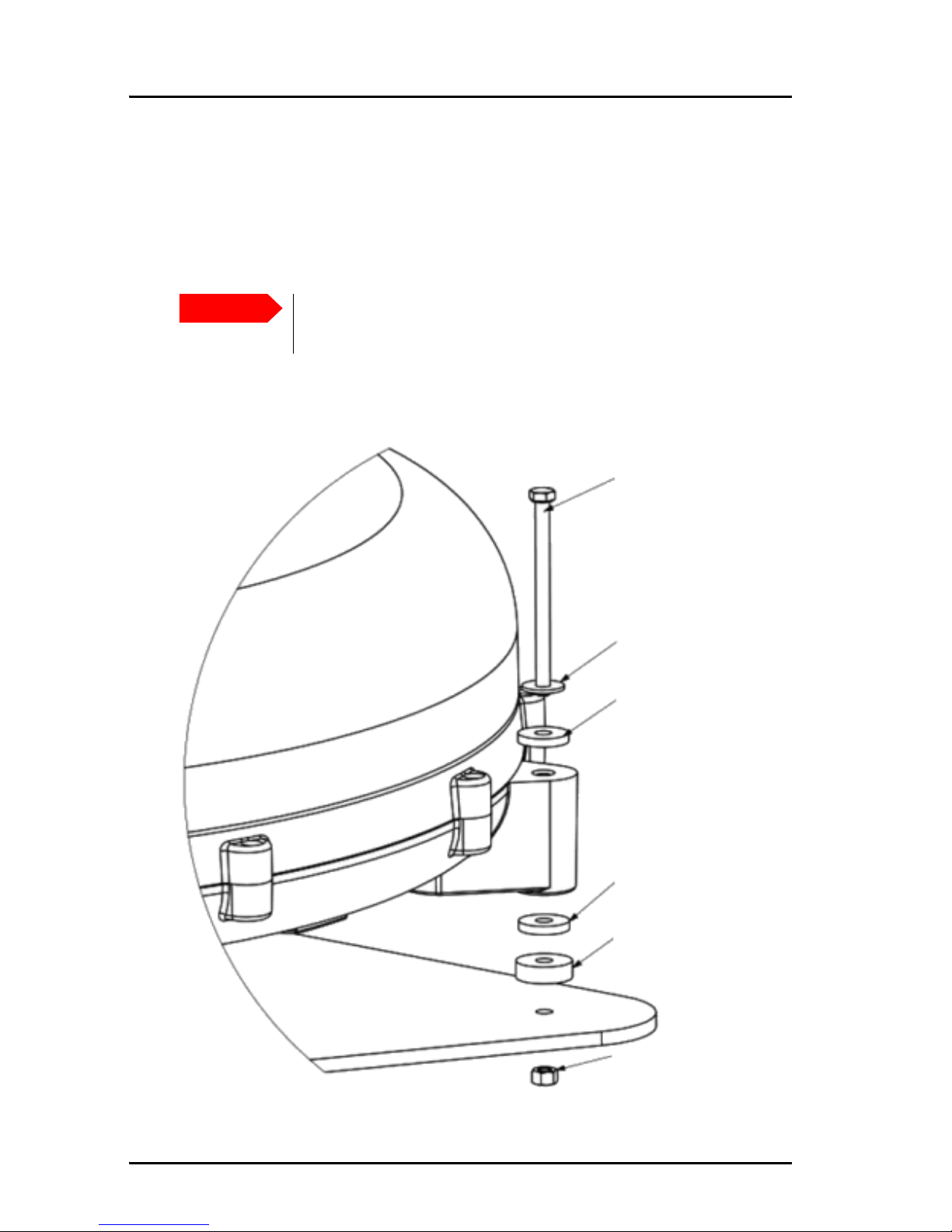
2.3.6 Mounting the antenna fixed on the vehicle roof
The antenna may be fixed on the roof of your car, using three M5 bolts,
spacers and rubber washers. This solution requires that you drill three holes
in the roof of the car.
Mounting accessories are included with the antenna.
Note the individual position of washers and spacers.
Important
There must always be a clearance of min. 10 mm between the
bottom of the antenna and the mounting surface.
M5 bolt
M5 washer
Rubber washer
Spacer - min. 10 mm
M5 nut
Rubber washer
Page 28

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Placing the terminal 17
2222
Installing the system
2.4 Placing the terminal
2.4.1 Overview
Because the terminal comes in two versions, the following description
contains
• one section for the EXPLORER 727 terminal and
• one section for the EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal
2.4.2 Where to place the EXPLORER 727 terminal
General
The terminal is designed for installation inside a vehicle. It is not suited for
outdoor installation.
Temperature conditions
The terminal must be placed in a ventilated area with free space around all
sides of the unit, except the bottom side.
Ambient temperature range is –25°C to +55°C.
If the terminal is installed in a location where the ambient temperature may
exceed 45°C, we recommend placing the terminal where unintentional contact
is avoided. If the maximum ambient temperature does not exceed 45°C, the
terminal can be placed in a public area.
Page 29

Chapter 2: Installing the system
18 Placing the terminal
2.4.3 Where to place the EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal
General
The terminal is designed for installation inside a vehicle. It is not suited for
outdoor installation.
Temperature conditions
Ambient temperature range is –25°C to +55°C.
Note
If you install other equipment close to the terminal in the rack, first
make sure the equipment can withstand the heat that may be
dissipated from the EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal. In max.
ambient temperature the surface of the terminal may reach a
temperature close to 70°C.
Page 30
Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the EXPLORER 727 terminal 19
2222
Installing the system
2.5 Installing the EXPLORER 727 terminal
2.5.1 Overview
Because the terminal comes in two versions, there are two sections describing
installation of the terminal:
• one section for the EXPLORER 727 terminal (this section) and
• one section for the EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal (Installing the
terminal on page 25).
2.5.2 Mounting the Basic cable support
The Basic cable support comes with the terminal as part of the delivery.
When mounted on the terminal the Basic cable support offers a number of
holders to which you can secure the cables from the terminal, using cable
strips.
Page 31

Chapter 2: Installing the system
20 Installing the EXPLORER 727 terminal
To mount the Basic cable support, do as follows:
1. Remove the two rubber washers from the bottom of the terminal at the
connector panel end. The threaded bushings underneath the rubber
washers are used for mounting the cable support.
Page 32

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the EXPLORER 727 terminal 21
2222
Installing the system
2. Fasten the Basic cable support to the terminal using two M4 x 6 mm
countersunk screws.
3. Install the terminal as described in the next section.
Page 33

Chapter 2: Installing the system
22 Installing the EXPLORER 727 terminal
2.5.3 Installing the terminal
Do as follows to mount the terminal:
1. Insert four screws through the mounting holes and into the mounting
surface.
2. Connect all cables.
If you use the cable support, secure the cables to the cable support using
cable strips.
Page 34

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the 19” Rack Terminal 23
2222
Installing the system
2.6 Installing the 19” Rack Terminal
2.6.1 Overview
Because the terminal comes in two versions, there are two sections describing
installation of the terminal:
• one section for the EXPLORER 727 terminal (the previous section) and
• one section for the EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal (this section)
2.6.2 Mounting the Strain Relief Bracket
The Strain Relief Bracket comes with the terminal as part of the delivery.
When mounted on the terminal the Strain Relief Bracket offers a number of
holders to which you can secure the cables from the terminal, using cable
strips.
To mount the Strain Relief Bracket, do as follows:
1. Unscrew the two screws in the connector panel.
Page 35

Chapter 2: Installing the system
24 Installing the 19” Rack Terminal
2. Fasten the Strain Relief Bracket to the terminal with the screws from step 1
3. Install the terminal as described in Installing the terminal on page 25.
Page 36

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the 19” Rack Terminal 25
2222
Installing the system
2.6.3 Installing the terminal
To install the terminal, do as follows:
1. Slide the terminal into a 1U space in a 19” rack.
2. Mount two screws in each side through the holes in the front and fasten
the screws to the rack.
3. Connect all cables.
Note
In order to make the power switch on the front of the terminal
functional, remember to connect the green and orange wires
from the DC cable to the terminal block as described in the next
chapter, Connecting power.
Page 37

Chapter 2: Installing the system
26 Installing the 19” Rack Terminal
Page 38

27
Chapter 3
3333
Connecting power
Connecting power 3
3.1 Power source
The 12 or 24 V DC supply of the vehicle provides power for the terminal.
Note that the maximum allowed source impedance is much lower for a 12 V DC
supply than for a 24 V DC supply. Also, the total output power available for
Power over Ethernet is limited when the power supply is 12 V DC.
Be aware of high start-up peak current: 20 A at 24 V, 5 ms.
The terminal is equipped with an internal 20 A Fuse, so no external fuse is
necessary in order to protect the terminal. However, in order to avoid short
circuit in the power cable/connector, the DC outlet of the vehicle should be
protected by a 30 A fuse or circuit breaker.
Note
Do not use the cigarette lighter socket in the vehicle to supply power
for the EXPLORER 727. Connect directly to the 12 or 24 V supply
instead.
Page 39

Chapter 3: Connecting power
28 Power cable selection
3.2 Power cable selection
3.2.1 Source impedance
The length of the power cable depends on the type of cable used and the
source impedance of the DC power installation in the vehicle.
The maximum allowed source impedance depends on the usage of the power
range of the terminal DC input (10.5 - 32 V DC; 14 A - 5.5 A).
Select a power outlet from the DC system and measure the source impedance
of the installation as described in the next section.
For further recommendations on power cable selection, see Power cable
recommendations on page 30.
3.2.2 Measuring the source impedance
Select a power outlet from the 24 V DC or 12 V DC system, and measure the
source impedance of the installation as described below.
1. Measure the voltage without load (R.var disconnected).
2. Set the current to e.g. 1 A by adjusting R.var.
3. Measure the corresponding voltage change.
Note
If the total impedance is higher than the limits stated in this section,
the terminal may become unstable and start to on/off oscillate.
The total impedance is made up of the source impedance of the
vehicle power supply plus the impedance of connected cables
including connectors and joints where cables are extended.
Page 40

Chapter 3: Connecting power
Power cable selection 29
3333
Connecting power
Example: 1 A and 50 mV. Source impedance: 50 mV/1 Amp = 50 m.
A
V
Ship Installations
Battery 24 VDC
BDU Power
outlet
R.var
Power outlet
for terminal
Vehicle installations
Battery 12/24 V DC
Page 41

Chapter 3: Connecting power
30 Power cable selection
3.2.3 Power cable recommendations
Overview
The terminal is delivered with a power cable, which can be extended
according to the recommendations in this section.
• When extending the power cable, positive and negative supply wires must
be installed closely together side by side to keep cable inductance low.
• Ensure that cable inductance for the selected cable at the desired length is
below the 50 H requirement.
The power cable contains the following wires:
Color of wire in
power cable
Pin number in
connector
Function
Red A1 Vin+
Black A2 Vin-
Black 1 not connected
Green 2 Remote on/off
Brown 3 not connected
Red 4 not connected
Orange 5 Remote on/off
Page 42

Chapter 3: Connecting power
Power cable selection 31
3333
Connecting power
The power cable for the EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal is split in two, so
that the Remote on/off wires are ready to connect to the front power switch.
For information on how to connect to the front power switch, see 19” rack
version only: Connecting to the power switch on the front on page 35.
The remote on/off wires can be used to connect to:
• The front power switch on the 19” rack version of the terminal, or
• a remote switch
For information on how to connect to a remote switch, see Connecting a
Remote on/off switch on page 37.
Note
It doesn’t matter which remote on/off wire connects to which
terminal on the remote switch or the front power switch.
Page 43

Chapter 3: Connecting power
32 Power cable selection
Calculating the maximum power cable extension
For 24 V DC operation, the total impedance must be max. 500 m, including
the source impedance in the vehicle installation.
For 12 V DC operation, the total impedance must be max. 85 m, including
the source impedance in the vehicle installation.
The total impedance is made up of the following:
• the source impedance in the vehicle installation
• the cable impedance of the supplied power cable, including the impedance
in the joint of the two cables. In the following example, the impedance of
the cable and joint is set to 50 m (6 m power cable). Note that if the cable
length or type is changed, the impedance will change accordingly.
• the extension cable impedance.
To calculate the maximum cable extension, do as follows:
1. First measure the source impedance in the vehicle installation as shown in
Measuring the source impedance on page 28.
2. Then find the resistance per meter for the cable type you are going to use.
For 4 mm
2
/AWG 11, the value is 4 m/m at 20°C
For 1.5 mm
2
/AWG 15, the value is 10 m/m at 20°C
For other cable types, refer to the data sheet for the cable.
3. Calculate the maximum allowed impedance in the extension cable as
follows:
Max. allowed impedance in extension cable = max. total impedance (measured source impedance + impedance of the supplied cable).
4. Then calculate the max. extension cable length as follows:
Max. impedance in extension cable (from step 3)
Max. length = 0.5 x impedance/meter (from step 2)
The length is multiplied by 0.5 above because there are two conductors in
the cable.
Page 44

Chapter 3: Connecting power
Power cable selection 33
3333
Connecting power
Example:
Vehicle supply voltage: 12 V DC
Vehicle source impedance (measured): 15 m
Extension cable type: 4 mm
2
(AWG 11)
Max. cable extension =
In this case, the power cable can be extended with up to 2.5 m.
If you need a longer cable, you can double the maximum allowed length by
connecting two cables instead of one, or you can use a cable with a larger
diameter.
Note
The following example may not be applicable to your installation!
For example, the source impedance of the vehicle power supply
varies depending on the type of battery and the temperature.
05
85m 15 50m+–
4m m
-----------------------------------------------------------
25m=
Page 45

Chapter 3: Connecting power
34 Connecting power
3.3 Connecting power
3.3.1 Connecting the power cable
To connect the power cable
Do as follows to connect the power cable:
1. Connect the red (+) and black (-) wires of the power cable to the DC supply
according to the recommendations in the previous sections.
2. Connect the D-sub connector on the power cable to the DC input connector
on the terminal.
If you need a remote on/off function, you may use one of the following
options:
• Connect the Remote on/off wires in the power cable to a remote switch.
Note that this is not possible if you are using the front switch on an
EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal! For further information, see
Connecting a Remote on/off switch on page 37.
• Connect the ignition pins in the I/O connector to the ignition of your
vehicle. For further information, see Connecting to the ignition on
page 36.
For information on pin-out, see DC power input on page 41.
For specifications of the DC input on the terminal, see EXPLORER 727 terminal
on page 82.
Page 46

Chapter 3: Connecting power
Connecting power 35
3333
Connecting power
19” rack version only: Connecting to the power switch on the front
The EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal has a power switch on the front in
addition to the switch in the connector panel.
The power cable included in the delivery is prepared for connection to the
front switch. It has two separate wires (one green, one orange), which can be
connected to the terminal block.
Page 47

Chapter 3: Connecting power
36 Connecting power
If you want to use the power switch on the front of the terminal to switch the
terminal on and off, connect the remote on/off pins in the DC connector to the
terminal block in the connector panel as follows:
1. Press with a small screwdriver at one of the two terminals in the terminal
block to open the terminal. Then insert the end of the green wire into the
terminal and remove the screwdriver.
2. Press with a screwdriver on the other terminal in the terminal block and
insert the end of the orange wire into the terminal.
3.3.2 Connecting to the ignition
The terminal has an ignition function. When this function is used, the terminal
switches on/off when you start/stop the engine of your vehicle (provided the
power switch on the terminal is on; on the 19” rack version both power
switches must be on).
To implement the ignition function, connect the appropriate pin in the I/O
connector to the ignition key switch:
Note
It doesn’t matter which remote on/off wire connects to which
terminal in the terminal block.
TerminalsDC Input connector
Note
You must set up the ignition function in the terminal. For details,
see the user manual for your EXPLORER 727 system.
Page 48

Chapter 3: Connecting power
Connecting power 37
3333
Connecting power
• Active high (default): Connect pin 5 to Ground. Connect pin 8 to “high”
(10.5-32 V DC) when the ignition is on.
• Active low: Connect pin 8 to positive DC voltage (10.5-32 V DC). Connect
pin 5 to Ground (< 1.2 V DC) when the ignition is on.
For pin-out and default functions, see Discrete I/O interface on page 50.
For information on the standby current when the ignition power is off, see
Standby current on page 84 in the general specifications.
3.3.3 Connecting a Remote on/off switch
The terminal has a remote on/off function. When the terminal power switch is
in the “on” position you can remote-control the power function.
By installing a switch that can short-circuit the
“Remote on/off” pins (2 and 5) in the power
connector you can power the terminal on or off
with this remote switch.
When pins 2 and 5 are not short-circuited and
valid input power is present, the terminal is
powered on, provided the Power switch is in the
“on” position.
For pin-out for the power connector and a
description of the wire colours in the power cable, see Pin-out on page 42.
For information on the standby current when the remote on/off switch is off,
refer to Standby current on page 84 in the General specifications (including 19”
rack version).
Note
The remote on/off function is not available if you have connected the
front power switch on an EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal.
pin 2
pin 5
Page 49

Chapter 3: Connecting power
38 Connecting power
Page 50

39
Chapter 4
4444
Hardware interfaces
Hardware interfaces 4
4.1 The connector panel
The connector panel is placed at one end of the terminal and has the following
connectors:
• 1 L-Band connector (not currently used)
• 1 Antenna connector (TNC)
• 2 Phone/Fax connectors (Port 1 is closest to the antenna connector)
• 1 ISDN connector
• 4 LAN connectors with Power over Ethernet (PoE)
• 1 DC power input connector for connection to 10.5-32 V DC, with optional
remote on/off
• 1 Input/Output connector with 5 inputs/outputs for external control or
signalling
• 1 ground stud with wing nut
• 19” rack version only: 1 terminal block with 2 terminals for connection to
front power switch
For information on how to connect to a specific interface, see the next
sections.
Phone/Fax 1 Phone/Fax 2
Page 51

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
40 Antenna interface on terminal
4.2 Antenna interface on terminal
4.2.1 Overview
The antenna interface on the terminal connects to the TT-3053B antenna in
the EXPLORER 727 system.
The antenna connector on the terminal is a TNC female connector placed in
the connector panel.
For information on cables and how to install and connect the antenna, see
Installing the antenna on page 9.
4.2.2 Pin-out
The below drawing shows the TNC female connector in the terminal.
Signal
GND
Page 52

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
DC power input 41
4444
Hardware interfaces
4.3 DC power input
4.3.1 Overview
The DC power input for the terminal is a 10.5 - 32 V DC; 14 A - 5.5 A input with
a remote on/off function. The input is protected against reverse polarity.
The power connector is a D-sub connector placed in the connector panel.
For information on power recommendations and how to connect, see
Connecting power on page 27.
For EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal: To be able to use the power switch on
the front panel of the terminal you must connect the remote on/off pins in the
DC connector to the terminal block in the right side of the connector panel. For
further information, see 19” rack version only: Connecting to the power switch
on the front on page 35.
Important
On the EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal, do not connect power
to the terminal block in the right side of the connector panel!
The terminal block is only for connection of the remote on/off
signal.
Page 53

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
42 DC power input
4.3.2 Pin-out
The power connector is a Mixed D-Sub connector 7W2, control pin male/
power pin male. The below table shows the pin-out for the connector and the
colours of the corresponding wires.
Pin
number
Pin function
Color of wire in
power cable
A1 Vin+ Red
A2 Vin- Black
1 not connected (Black)
2 Remote on/off Green
3 not connected (Brown)
4 not connected (Red)
5 Remote on/off Orange
2 1
5 4 3
A2 A1
Mixed D-Sub connector,
7W2, male
Page 54

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
19” rack version only: Terminal block 43
4444
Hardware interfaces
4.4 19” rack version only: Terminal block
The terminal block in the connector panel is used to connect the remote on/off
pins from the DC connector to the power switch in the front of the terminal.
For information on how to connect, see 19” rack version only: Connecting to
the power switch on the front on page 35.
Important
Do not connect power to the terminal block!
Connection for power switch on front panel
Page 55

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
44 Analogue Phone/Fax interface
4.5 Analogue Phone/Fax interface
4.5.1 Overview
The terminal has two RJ-11 ports, which can be used for connection of
analogue phones or fax machines.
4.5.2 Pin-out
The Phone/Fax connectors are RJ-11, 6/4 female connectors. The table and
figure below show the connector outline and pin assignments.
Phone/Fax 2
Phone/Fax 1
Pin number Pin function
1-
2 not connected
3Tip
4Ring
5 not connected
6-
123456
RJ-11 female connector
Page 56

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
ISDN interface 45
4444
Hardware interfaces
4.6 ISDN interface
4.6.1 Overview
The terminal has one ISDN connector for connecting an ISDN phone or an
ISDN modem. The ISDN interface supports 56/64 kbps data rate. It is
configured as the network side, i.e. Rx is an input and Tx is an output.
Page 57

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
46 ISDN interface
4.6.2 Pin-out
The figure and table below show the connector outline and pin assignments.
Pin number Pin function
1 not connected
2 not connected
3 Rx+ (c) input
4 Tx+ (d) output
5 Tx- (e) output
6 Rx- (f) input
7 not connected
8 not connected
RJ-45 female connector
Page 58

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
LAN interface 47
4444
Hardware interfaces
4.7 LAN interface
4.7.1 Overview
The terminal has four Ethernet LAN ports with Power over Ethernet (PoE). The
standard for the Ethernet ports is IEEE 802.3af, and the connectors are RJ-45
connectors.
4.7.2 Power over Ethernet (PoE)
One power supply powers all four interfaces with a floating 48 V DC supply
(44 - 57 V DC). Therefore, the interfaces are not galvanically separated from
each other. All Tx signals are DC connected to the Positive PoE Voltage and all
Rx signals to the Negative PoE Voltage.
The total output power from all 4 interfaces is
• 64 W at 24 V DC power supply
• 32 W at 12 V DC power supply.
All interfaces can support devices of power class 1, 2 and 3 (4, 7 and 15.4 Watt),
as long as the total power consumption does not exceed the above limits. If
the limits are exceeded, the LAN ports are prioritized so that LAN port 1 has the
highest priority. For example, if all ports are used and the total power
consumption is too high, port 4 is shut down.
Page 59

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
48 LAN interface
In case of power hold-up (failure on input power), PoE will be turned off.
4.7.3 Pin-out
The figure and table below show the connector outline and pin assignments.
4.7.4 Connecting the Thrane IP handset
To connect the Thrane IP Handset to the terminal, do as follows:
Connect the cable from the IP cradle to one of the LAN connectors on the
terminal, preferably port 1. In case of insufficient power to the LAN PoE the
LAN ports are prioritized, so that port 1 is the last to be shut down.
Pin number Pin function
1TxD+ input
(positive PoE)
2TxD-input
(positive PoE)
3RxD+ output
(negative PoE)
4 not connected
5 not connected
6RxD- output
(negative PoE)
7 not connected
8 not connected
RJ-45 female connector
Page 60

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
LAN interface 49
4444
Hardware interfaces
Note that the handset and terminal must be set up to be able to communicate
with each other. For further information, refer to the user manual for the
handset.
The maximum length of the cable between IP cradle and terminal is 80 m.
Note
If you insert a switch or similar between the cradle and the terminal,
make sure that it conforms to the industry standard IEEE 802.3 af
(using data pairs).
Page 61

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
50 Discrete I/O interface
4.8 Discrete I/O interface
4.8.1 Overview
The terminal has an I/O connector with 5 configurable inputs/outputs.
The connector is a WieCon Type 8513S connector. A mating I/O connector is
included in the delivery.
Page 62

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
Discrete I/O interface 51
4444
Hardware interfaces
4.8.2 Pin-out
The figure and table below show the connector outline and pin assignments.
Pin number Connection Default configuration
a
a. The default functions of the I/O pins are described in the next section.
1 GPIO 1 Ringer output
2 GPIO 2 Warning/Error output
3 GPIO 3 Mute output
4 GPIO 4 Radio silence input
5 GPIO 5 Ignition input
6 Chassis GND Chassis GND
7 DC out 9-15 V DC, 50 mA
8 DC in (ignition input)
12345678
WieCon Type 8513S connector
Page 63

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
52 Discrete I/O interface
4.8.3 Default configuration of I/O pins
The built-in web interface of the terminal offers a page for configuring the I/O
pins.
The functions of the I/O pins are as follows:
Pin 1: Ringer output.
Pin 1 acts as a built-in switch in the terminal. You can configure Pin 1 to be
Normally closed or Normally open.
• Normally closed (default):
The internal switch at pin 1 is normally closed (pin 1 is connected to
ground). When the terminal is notified of an incoming call from the
satellite interface, the switch opens (no connection to ground). When the
call is answered, or the caller gives up and releases the call, the switch is
closed again.
• Normally Open:
The internal switch at pin 1 is normally open (no connection to ground).
When the terminal is notified of an incoming call from the satellite
interface, the switch is closed (pin 1 is connected to ground). When the call
is answered, or the caller gives up and releases the call, the switch is
opened again.
Pin 2: Warning/Error output.
Pin 2 acts as a built-in switch in the terminal. Pin 2 can be used to provide an
external signal that indicates active warning/error condition(s). You can
configure pin 2 to be Normally closed or Normally open.
• Normally Closed (default):
The internal switch at pin 2 is normally closed (pin 2 is connected to
ground). When an alarm occurs, the switch opens (no connection to
ground). The switch is closed again when all warnings/errors are cleared.
• Normally Open:
The internal switch at pin 2 is normally open (no connection to ground).
When an alarm occurs, the switch is closed (connected to ground). The
switch is opened again when all warnings/errors are cleared.
Note
Do not use the Ringer output if you have enabled Local exchange.
For information on Local exchange, refer to the User manual.
Page 64

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
Discrete I/O interface 53
4444
Hardware interfaces
Pin 3: Mute output.
Pin 3 acts as a built-in switch in the terminal. Pin 3 can be used to provide an
external signal that is active during a phone call. The signal can be used to
mute external equipment. You can configure pin 3 to Normally closed or
Normally open.
• Normally Closed (default):
The internal switch at pin 3 is normally closed (pin 3 is connected to
ground). During phone calls, the switch opens (no connection to ground).
When the call is ended, the switch is closed again (connected to ground).
•Normally Open:
The internal switch at pin 3 is normally open (no connection to ground).
The switch is closed (connected to ground) during phone calls. When the
call is ended, the switch opens again (no connection to ground).
Pin 4: Radio silence input.
Activation of this pin causes the system to assume radio silence, i.e. to stop all
transmission from the system. The terminal gracefully closes all open
connections, and deregisters from the BGAN network. No transmission is
allowed until the pin is deactivated. You can configure pin 4 to Active low or
Active high.
• Active low (default): Connect pin 4 to ground (< 1.2 V DC) when it should be
activated.
• Active high: Connect pin 4 to ground (< 1.2 V DC). When it should be
activated, disconnect it from ground.
Pin 5/8: Ignition input.
The ignition function can be used to turn on/off the terminal by means of an
external signal. The external signal that triggers the ignition function can be
either positive DC voltage or ground. The ignition function uses pin 5 together
with pin 8 (DC in). Connect the appropriate pin to the ignition switch as
follows:
• Active high (default): Connect pin 5 permanently to Ground. Connect pin 8
to positive DC voltage (10.5-32 V DC) when the ignition is on. To switch off,
disconnect pin 8 from the positive DC voltage.
• Active low: Connect pin 8 permanently to positive DC voltage (10.5-32 V
DC). Connect pin 5 to Ground (< 1.2 V DC) when the ignition is on. To switch
off, disconnect pin 5 from ground.
Page 65

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
54 Discrete I/O interface
Pin 6: Ground.
(Non-configurable) Pin 6 can be used as an external connection to ground.
Pin 6 is connected to Ground inside the terminal.
Pin 7: DC output.
(Non-configurable) Pin 7 can be used as a DC output. The voltage on pin 7 is
9-15 V and the output can supply up to 50 mA. Pin 7 can be used as power
supply to a relay, ringer or similar.
For information on how to configure the I/O pins, see the user manual for the
EXPLORER 727 system.
Page 66

55
Chapter 5
555
Starting up the system
Starting up the system 5
5.1 Using the SIM card
5.1.1 Inserting the SIM card
The SIM card is provided by your Airtime Provider. Insert the SIM card as
follows:
1. Open the SIM cover in the left
side of the connector panel.
2. Insert the SIM card into the SIM
slot.
Place the card with the chip
side facing up as shown.
3. Press gently until it clicks.
4. Slide the lock in front of the SIM
card.
5. Close the cover for the SIM slot.
Page 67

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
56 Using the SIM card
5.1.2 Removing the SIM card
Remove the SIM card as follows:
1. Open the SIM cover in the left
side of the connector panel.
2. Slide the lock aside.
Note
When the SIM card is removed, you cannot use the BGAN menu of
the IP handset nor make calls or start data sessions.
Only emergency calls are allowed, and only if permitted by the
network.
However, if you have an administrator user name and password, you
can upload software using the web interface without having a SIM
card. For further information, see the user manual for the
EXPLORER 727 system.
Page 68

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
Powering the system 57
555
Starting up the system
3. Gently push the SIM card and
let it pop out.
4. Remove the SIM card and
close the cover for the SIM
slot.
5.2 Powering the system
5.2.1 Switching the terminal on
Using the power switch
To switch on the terminal, use the On/Off switch in the connector panel. It
normally takes one or two seconds for the terminal to switch on.
Note
If you have the 19” rack version of the EXPLORER 727 terminal, you
can use the on/off switch in the front panel. See the next section 19”
rack terminal: Using the front power switch.
Page 69

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
58 Powering the system
19” rack terminal: Using the front power switch
If you have the 19” rack version of the EXPLORER 727 terminal, flip the switch
in the front panel to “1” to switch on the terminal.
It normally takes one or two seconds for the terminal to switch on.
Note
To be able to use the power switch on the front panel, you must
leave the On/Off switch in the connector panel in the On position.
Caution! When the system is powered on, stay clear of the
antenna! The antenna emits radio frequency energy, not
only when the system is used. Always keep a minimum
distance of 1 m from the EXPLORER 727 antenna.
Must be On when
front panel switch is used
Page 70

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
Powering the system 59
555
Starting up the system
Using the ignition system
If you have connected the ignition system of your vehicle to the I/O connector,
you may leave the power switch in the “on” position and the terminal will
switch on/off when you start/stop the engine of your vehicle.
When the engine is stopped the terminal is in standby mode, meaning that
only the primary parts of the system are kept alive. The standby current is max.
15 mA when the ignition is off. For information on how to connect to the
ignition, refer to Connecting to the ignition on page 36.
You must set up the ignition function in the web interface. For further
information, see the user manual for the EXPLORER 727 system.
Using a remote on/off switch
If an external switch is connected to the remote on/off pins in the DC
connector, you may leave the power switch in the connector panel in the “on”
position and use the remote switch to turn the terminal on and off. When the
remote switch is off, the terminal is off. However, if you leave the power switch
on the terminal in the “on” position, you can always switch the terminal back
on with the remote switch. The standby current when the remote switch is off
is max. 2 mA. For further information on how to connect a remote on/off
switch, see Connecting a Remote on/off switch on page 37.
Note
If you have the 19” rack version of the terminal, you must leave both
power switches in the “on” position to make use of the ignition
function.
Note
In some cases, the system may reboot after power-on because of the
high start-up current.
Note
In the 19” rack version of the terminal the remote on/off function is
normally not available, because it is used for the front switch.
Page 71

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
60 Entering the SIM PIN for the terminal
5.2.2 Switching the terminal off
To switch off the terminal, change the position of the power switch again.
To switch off the 19” rack version of the terminal, set the power switch in the
front to 0 and leave the On/Off switch in the connector panel in the On
position.
To switch off using the Ignition function, leave the On/Off switch in the
connector panel in the On position and turn off the ignition.
5.3 Entering the SIM PIN for the terminal
5.3.1 Overview
If your SIM card requires a PIN, you have to enter a PIN to use the system. You
can enter the PIN using a standard or ISDN phone, the IP handset or the web
interface.
For information on how to connect the handset or computer you are going to
use, refer to the user manual.
5.3.2 Entering the PIN using a phone or IP handset
To enter the PIN
If you have a phone connected to the terminal, you can use it to enter the PIN
at start up.
Do as follows:
• For an analogue or ISDN phone:
Pick up the phone. When the terminal is waiting for a PIN, you will hear 2
Note
Wait at least 5 seconds after power off, before trying to power on the
system again.
Page 72

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
Entering the SIM PIN for the terminal 61
555
Starting up the system
beeps - pause - 2 beeps - etc.
Dial <PIN> followed by #.
When you hear a “busy” tone or a dialing tone, the PIN has been accepted
and you can hang up or dial a number.
• For an IP handset:
Select the BGAN menu, select ENTER PIN and enter the user name and
password for the terminal. Then enter the PIN for the terminal.
Wrong PIN
Analogue phone or ISDN phone:
If, instead of the busy tone or dialing tone, you continue to hear 2 beeps pause - 2 beeps - etc., it means the PIN was not accepted. Check that you have
the correct PIN and try again.
If a wrong PIN has been entered three times, you will hear 3 beeps - pause - 3
beeps - etc. This means you have to enter the PUK (PIN Unblocking Key)
provided with your SIM card.
After entering the PUK, you must enter a new PIN of your own choice (4 to 8
digits long).
Dial the following:
<PUK> * <New PIN> * <New PIN> followed by # or off-hook key.
Example: If the PUK is 87654321 and the new PIN is 1234, dial
87654321 * 1234 * 1234 followed by # or off-hook key.
If you enter 10 wrong PUKs, the SIM card will no longer be functional. Contact
your Airtime Provider for a new SIM card.
IP handset:
After having entered the user name and password for the terminal you have 3
attempts to enter the terminal PIN, before you are asked to enter the PUK (Pin
Unblocking Key). The PUK is supplied with your terminal SIM card.
Note
The ENTER PIN menu item is only available if your SIM card
requires a PIN, and the PIN has not yet been entered and
accepted in the terminal.
Page 73

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
62 Entering the SIM PIN for the terminal
Enter the PUK followed by a new PIN of your own choice. The PIN must be
from 4 to 8 digits long.
If you enter a wrong PUK 10 times, the SIM card will no longer be functional,
and you have to contact your BGAN Airtime Provider for a new SIM card.
5.3.3 Entering the PIN using the web interface
If your SIM card requires a PIN and the PIN has not yet been entered when
you start up the web interface, the start-up page will be the PIN page. Enter
the PIN and click OK.
For further information on the web interface, see the user manual for your
EXPLORER.
Page 74

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
Operating the system 63
555
Starting up the system
5.4 Operating the system
5.4.1 General use
The user manual for the EXPLORER 727 system describes general use of the
system and all the functions of the web interface. It also contains a brief
description of how to use the Thrane IP Handset with the terminal.
5.4.2 User interfaces
Overview
The main user interfaces for operation of the system are
• the built-in web interface using a computer with an Internet browser
• the Thrane IP Handset
Built-in web interface
The built-in web interface is used for easy configuration and daily use. You
access the web interface from a computer connected to the terminal, using an
Internet browser. No installation of software is needed.
An Administrator password is required to access advanced configuration of
the system. From factory, the Administrator User name is admin and the
Administrator password is 1234.
For further information on the web interface, refer to the user manual for the
EXPLORER 727 system.
Page 75

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
64 Operating the system
IP handset
Apart from the standard functions of an IP handset, the Thrane IP Handset
contains a display menu for the EXPLORER 727 system. For further information
on the Thrane IP Handset, refer to the user manual for the IP handset.
Page 76

65
Chapter 6
666
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting 6
6.1 Reset button
6.1.1 How to access the Reset button
The terminal has a Reset button placed next to the SIM slot behind the SIM
cover. The functions of this button is described in the next section.
To press the Reset button, use a pointed device.
Page 77

Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
66 Reset button
6.1.2 Functions of the Reset button
The Reset button on the terminal has the following functions:
Action Function
With the terminal
running, press the
Reset button
normally.
The terminal IP address and IP netmask are
temporarily set to the default value (default IP
address: 192.168.0.1).
With this function, even if the IP address has been
changed and you do not remember the new IP
address, you can still access the web interface and
see your current configuration. The default value is
not saved in the configuration, but is only valid until
next reboot.
With the terminal
running, press
and hold the Reset
button for 30
seconds, until the
Power indicator
on the terminal is
flashing orange.
The terminal restores factory settings and reboots the
system.
Page 78

Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
Reset button 67
666
Troubleshooting
While the terminal
is booting, press
and hold the Reset
button.
For service use only!
The bootloader initiates software upload. This
firmware upload procedure is only to be used if the
other procedures fail due to missing or corrupted
firmware.
This setup uploads software to the terminal from a
TFTP server via the LAN connection. The procedure is
as follows:
1. Activate or install a TFTP server on a PC.
2. Locate the correct software image (xxx.dl) for the
terminal and place it in the TFTP server directory.
3. Rename the image to ttexp.dl.
4. Reconfigure the PC LAN interface to use the static
address 192.168.0.2/255.255.255.0.
5. Power off the terminal.
6. Connect the PC LAN Interface to the terminal.
7. Press and hold down the Reset button.
8. Keep the Reset button pressed while powering on
the terminal, and through the next step.
9. Monitor the TFTP server window. When the
upload starts you can release the Reset button.
10. When the TFTP upload finishes the terminal boots
up using the new image.
Action Function
Page 79

Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
68 Status signalling
6.2 Status signalling
6.2.1 Overview
The EXPLORER 727 system uses event messages and light indicators to display
the status of the system.
6.2.2 Light indicators
Overview
The terminal has a number of light indicators, placed in the LED panel of the
terminal:
• a green/orange Power indicator,
• a green/red/orange Terminal indicator,
• a green/red/orange Antenna indicator,
• a green Message indicator and
• 3 LAN indicators for each LAN interface, showing Activity (Green),
Link/Speed (Green/Yellow) and PoE (Green/Red).
Page 80

Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
Status signalling 69
666
Troubleshooting
General status indicator functions
Power indicator
Terminal indicator
Behaviour Meaning
Steady green Power OK.
Flashing green The terminal is powering up.
Flashing orange The terminal is shutting down.
Off No power.
Behaviour Meaning
Steady green Ready. BGAN registration completed.
Flashing green Please wait - process in progress.
BGAN registration ongoing.
Orange Warning - temporary malfunction. User action is
required.
Page 81

Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
70 Status signalling
Antenna indicator
Message indicator
Red Critical error.
Check the event log. If the problem is in the
EXPLORER 727 system and you cannot solve it,
contact your distributor and return the unit for
repair.
Behaviour Meaning
Steady green Tracking. The antenna is ready for use.
Flashing green Please wait - process in progress.
Slow flashing: The antenna is starting up
Rapid flashing: Sky scan
Orange Warning - temporary malfunction. User action is
required.
Red Critical error.
Check the event log in the web interface. If the
problem is in the EXPLORER 727 system and you
cannot solve it, contact your distributor and return
the unit for repair.
Behaviour Meaning
Flashing green A new SMS message has arrived.
Off No new messages, or the unit is off.
Behaviour Meaning
Page 82

Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
Status signalling 71
666
Troubleshooting
LAN indicator functions
Activity indicator
Link/Speed indicator
PoE indicator
Behaviour Meaning
Flashing green The LAN port is active.
Behaviour Meaning
Green Link speed is 100 Mbps.
Yellow Link speed is 10 Mbps.
Off The link is down.
Behaviour Meaning
Green The terminal is supplying power to the LAN port.
Red The connected device requires more power than
the terminal can supply to the LAN port.
Off The terminal is not supplying power to the port.
Page 83

Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
72 Status signalling
6.2.3 Event messages
Display of event messages
The terminal can detect events during
• POST (Power On Self Test)
- a self test performed at every power-up,
• PAST (Person Activated Self Test)
- a self test performed when you click the Self test button under Help desk
in the web interface, or
• CM (Continuous Monitoring)
- continuous monitoring while the system is in operation.
When the terminal detects an event that requires your action, it issues an
event message.
When your terminal issues an
event message, the Terminal
indicator or the Antenna
indicator in the LED panel on
top of the terminal signals the
event, according to the tables
Terminal indicator and Antenna
indicator in the previous
section.
You can see the active event messages in the web interface by clicking the
warning symbol in the icon bar at the top in the web interface.
All events are logged in the event log. For information on the event log, see
Event log on page 73.
Page 84

Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
Logging of events 73
666
Troubleshooting
6.3 Logging of events
6.3.1 Diagnostic report
The diagnostic report contains information relevant for the service personnel
during troubleshooting. When contacting Thrane & Thrane A/S for support,
please include a diagnostic report.
To generate the diagnostic report, access the web interface and select Help
Desk. Then click Generate report.
6.3.2 Event log
The event log holds information of all registered events in the terminal or
antenna that are also shown in the Antenna and Terminal LEDs on the
terminal.
The log includes the time of the occurrence, a short description, location of the
error etc. This information can help troubleshooting errors in the system. You
can see the event log in the web interface. For further information on the web
interface, see the user manual for the EXPLORER 727 system.
Page 85

Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
74 Logging of events
Page 86

75
Appendix A
AAAA
Part numbers
Part numbers A
A.1 System units
A.1.1 TT-3722A EXPLORER 727 system
A.1.2 TT-3670A Thrane IP Handset & Cradle, wired
A.2 Spare parts
For information on available spare parts, do as follows:
1. Log on to the Thrane & Thrane Extranet.
2. Select eShop from the menu.
-or click this link http://shop.thrane.com. You may be asked to enter your user
name and password for the Extranet.
Item Part number
EXPLORER 727 antenna 403053B
EXPLORER 727 terminal or
EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal
403736A or
403736A-T19
Item Part number
Thrane IP Handset, wired 403672A
Thrane IP Cradle, wired 403674A
Page 87

Appendix A: Part numbers
76 Spare parts
Page 88

77
Appendix B
BBBB
Technical specifications
Technical specifications B
B.1 Overview
This chapter contains specifications for the EXPLORER 727 system including
the terminal and antenna.
Note
For specifications and outline drawings for the Thrane IP Handset,
refer to the manual for the IP handset.
Page 89

Appendix B: Technical specifications
78 EXPLORER 727antenna
B.2 EXPLORER 727antenna
B.2.1 General specifications
Item Specification
Type BGAN Class 10, land-vehicular mechanical
tracking antenna
Polarization RHCP
Rx Freq. Band
Tx Freq. Band
GPS
1525.0 - 1559.0 MHz
1626.5 - 1660.5 MHz
1575.42 MHz
Channel Spacing 1.25 kHz
Antenna element Gain (RX-band, min.): 12.7 dBi
Gain (TX-band, min.): 13.26 dBi
G/T G/T -12.5 dBK
EIRP Min. EIRP: 8 dBW
Max. EIRP: 18 dBW
Return loss Better than -10 dB/50
Page 90

Appendix B: Technical specifications
EXPLORER 727antenna 79
BBBB
Technical specifications
B.2.2 Environmental specifications
Cable losses RF attenuation:
at 1660 MHz: max. 20 dB
at 54 MHz: max. 4 dB
at 36 MHz: max. 3 dB
DC resistance (loop): max. 0.6
Max. cable length, terminal to antenna:
• RG-223_U-01: 14 meter
• RG-214_U-01: 50 meter
•S-07262-BD: 70 meter
• S-10162-B-11: 92 meter
Antenna power
supply
23.0 - 30.0 V DC, 47 W max. continuous (without
cable loss). Measured at ATB input.
Total antenna weight 6 kg
Antenna dimensions 151.5 mm x Ø477 mm
Item Specification
Item Specification
Water and dust IP-56 dust and water jet proof.
Ambient Temperature Operational: -25° to +55°C
Storage: -40° to +80°C
Operating humidity 100%, condensing
Page 91

Appendix B: Technical specifications
80 EXPLORER 727antenna
Rain Up to 100 mm/h, 0.5-4.5 droplets at 200 km/h
Ice, survival Up to 25 mm of ice (non-operational)
Wind Normal operation with relative average wind
velocity up to 200 km/h (56 m/s, 108 knots).
Vibration, operational Random spectrum 1.05 g rms x 3 axes:
5 to 20 Hz: 0.02 g
2
/Hz
20 to 150 Hz: -3 dB/octave
Vibration, nonoperational
Random spectrum 1.7 g rms 2 h x 3 axes 6 h total):
5 to 20 Hz: 0.05 g
2
/Hz
20 to 150 Hz: -3 dB/octave
Vehicle motion
a
Turning rate: 60°/s
Turning acceleration: 50°/s
2
Induced acceleration: 0.5 g
Velocity: Max. 200 km/h see note below!
Shock Half sine, 20 g/11 ms
Solar radiation 1120 W/m
2
according to MIL-STD-810F 505.4
Air Pressure, transport 4572 m AMSL MIL-SPEC 810E 500.4
a. Note that these specifications only apply for the antenna alone. The values will
differ depending on the mounting method. Especially when the antenna is
mounted with brackets or magnetic mount the max. velocity can be lower.
Item Specification
Page 92

Appendix B: Technical specifications
EXPLORER 727antenna 81
BBBB
Technical specifications
B.2.3 Antenna outline dimensions
A: 3 pcs. ø6.0 mm
TNC-(V) connector
Page 93

Appendix B: Technical specifications
82 EXPLORER 727 terminal
B.3 EXPLORER 727 terminal
B.3.1 General specifications (including 19” rack version)
Item Specification
Weight EXPLORER 727 terminal: 2.5 kg (5.5 lbs)
EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal: 5 kg (11 lbs)
Dimensions EXPLORER 727 terminal:
264.5 mm x 273 mm x 42.5 mm
(10.4” x 10.7” x 1.7”)
EXPLORER 727 19” Rack Terminal:
342.3 mm x 482.6 mm x 43.65 mm
(13.5” x 19” x 1.7”)
Global services
Voice
Data
Standard IP
Streaming IP
SMS
4 kbps AMBE+2 or 3.1 KHz Audio
64 kbps UDI
492/42 kbps
In Standard (on-the-move) mode: 32, 64, 128, 256 kbps
In Standard (on-the-move) mode: 32, 64, 128, 176 kbps
and BGAN X-Stream (from a minimum of 384 kbps up to
approximately 450 kbps)
Up to 160 characters
Page 94

Appendix B: Technical specifications
EXPLORER 727 terminal 83
BBBB
Technical specifications
Antenna interface One connector, TNC-female
1525 to 1559 MHz: -94 dBm to -64 dBm
1626.5 to 1660.5 MHz: -9 dBm to +11 dBm
Power supply: 23.0 - 30.0 V DC
2-wire telephone
interface
Two connectors: RJ-11 female. 600 ITU-T Rec. G.473,
standard DTMF telephone.
Supported cable length: up to 100 meters.
ISDN interface One connector: RJ-45 female.
Conforms with CCITT I.430, ETSI ETS300012, ANSI T1.605.
LAN interface Four connectors: RJ-45 female. Conforms with IEEE 802.3
af, 10/100 Mbps.
Supported cable length: up to 100 m
PoE (max. 15.4 W) on each port,
Total PoE power: 64 W at 24 V operation, 32 W at 12 V.
Item Specification
Page 95

Appendix B: Technical specifications
84 EXPLORER 727 terminal
I/O interface
Output:
Open switch hold-off
voltage
Open circuit
resistance
Closed switch
voltage
Input:
Input resistance
Voltage
Voltage High
Voltage Low
One connector with 5 configurable inputs/outputs.
Open collector, Short circuit protected at 1.5 A and reverse
polarization protected.
max. 32 V
min. 130 K
max. 1 V DC at 50 mA
min. 130 K
Max. 32 V
Min. 2.2 V
Max. 1.2 V
L-Band output Not currently used
One connector: SMA female.
Rx output, 1525 - 1559 MHz: -105 dBm to -80 dBm
Power Input Connector: Mixed D-Sub 7W2
Nominal 12/24 VDC (10.5 - 32 V DC; 14 A - 5.5 A)
Max. source impedance: 85 m at 12 V, 500 m at 24 V
Maximum 20 A at 24 V, 5 ms (start up)
Standby current Ignition function, off: max. 15 mA
Remote on/off in DC connector, off: max. 2 mA
Ambient
temperature
Operational: -25° to +55°C
Storage: -40° to +80°C
Relative Humidity 95% non-condensing at +40°C
Item Specification
Page 96

Appendix B: Technical specifications
EXPLORER 727 terminal 85
BBBB
Technical specifications
B.3.2 Outline dimensions, EXPLORER 727 terminal
Connector panel and bottom view, including Basic cable support.
250
200
Ø4.5 x 6 mm (2 pcs.)
M4 x 6 mm (4 pcs.)
252
191.5
42.5
Ø6 x 6 mm (4 pcs.)
Basic cable support
Page 97

Appendix B: Technical specifications
86 EXPLORER 727 terminal
Side view and top view, including Basic cable support.
264.5
231
273
366.5
9.75
Page 98

Appendix B: Technical specifications
EXPLORER 727 terminal 87
BBBB
Technical specifications
End view with serial number label and heat label.
Weight: 2.5 kg.
Dimensions are in mm.
Page 99

Appendix B: Technical specifications
88 EXPLORER 727 terminal
B.3.3 Outline dimensions, 19” Rack Terminal
Front and top view, including Basic cable support.
43.65
429
342.3
482.6
Page 100

Appendix B: Technical specifications
EXPLORER 727 terminal 89
BBBB
Technical specifications
Connector panel, side view and perspective views, including Basic cable
support.
Weight: 5 kg.
Dimensions are in mm.
441
98.7
 Loading...
Loading...