Page 1

1
Part of Thermo Fisher Scientific
Finnpipette® F2
Single Channel
Variable & Fixed Volume
Multichannel
Instructions for Use
Bedienungsanleitung
Guide d´utilisation
Instruccions de uso
取扱説明書
Page 2

2
This product complies with the European Union Directive 98/79/EC, and it is marked with
CE-symbol. If the pipette is used according to this directive, the user shall read the additional
information at www.thermo.com/finnpipette or contact the manufacturer.
Product specifications are subject to change without prior notice. Finnpipette® and Finntip®
are registered trademarks of Thermo Fisher Scientific Oy.
Dieses Produkt entspricht der Richtlinie 98/79/EG der Europäischen Union und ist mit dem
CE-Symbol gekennzeichnet. Wird die Pipette entsprechend dieser Richtlinie verwendet,
muss der Anwender die zusätzlichen Informationen auf www.thermo.com/finnpipette
lesen oder den Hersteller kontaktieren.
Wir behalten uns das Recht auf unangekündigte Änderungen der Produktspezifikationen vor.
Finnpipette® und Finntip® sind eingetragene Warenzeichen der Fa. Thermo Fisher Scientific Oy.
Ce produit est conforme à la directive de l’Union européenne 98/79/CE et porte le marquage
CE. Si la pipette est utilisée selon cette directive, l’utilisateur est tenu de contacter le fabricant
ou de lire les informations supplémentaires données sur www.thermo.com/finnpipette.
Les spécifications du produit sont sujettes à modification sans avis préalable. Finnpipette®
et Finntip® sont des marques déposées de Thermo Fisher Scientific Oy.
Este producto cumple la Directiva de la Unión Europea 98/79/CE y presenta el símbolo CE. Si
la pipeta se usa de acuerdo con esta Directiva, el usuario debe leer la información adicional
presente en www.thermo.com/finnpipette o ponerse en contacto con el fabricante.
Las especificaciones del producto pueden cambiar sin previo aviso. Finnpipette® y Finntip
®
son marcas registradas de Thermo Fisher Scientific Oy.
本製品は、欧州連合指令98/79/ECに準拠し、CEマークが表示されています。
ピペットをこの指令に準拠して使用する場合は、弊社ホームページ www.thermo.
com/finnpipette にある追加情報をお読みいただき、または弊社まで
ご連絡くださ
い。製品仕様は事前の予告なく変更されることがあります。 フィンピペット®とフィン
チップ®は、サーモフィッシャーサイエンティフィックの登録商標です。
Page 3

3
CONTENTS
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 4
PIPETTE OPERATION 5
PIPETTING TECHNIQUES 5
CALIBRATION AND ADJUSTMENT 6
MAINTENANCE 8
TROUBLE SHOOTING 11
PACKAGE 11
SPARE PARTS 49-55
English
INHALT
PRODUKTBESCHREIBUNG 12
PIPETTENFUNKTION 13
PIPETTIERMETHODEN 13
KALIBRIERUNG UND JUSTIERUNG 15
WARTUNG 17
FEHLERBEHEBUNG 20
PACKUNG 20
ERSATZTEILE UND ZUBEHÖR 49-55
Deutsch
SOMMAIRE
DESCRIPTION DU PRODUIT 21
UTILISATION DE LA PIPETTE 22
MéTHODES DE PIPETAGE 22
CALIBRAGE 24
ENTRETIEN 26
EN CAS DE PROBLEME 29
CONDITIONNEMENT 29
PIèCES DéTACHéES 49-55
Français
CONTENIDO
DESCRIPCIÓN DEL PRODUCTO 30
USO DE LA PIPETA 31
TéCNICAS DE PIPETEO 31
CALIBRACIÓN Y AJUSTE 33
MANTENIMIENTO 35
PAQUETE 38
SOLUCIÓN DE PROBLEMAS 38
PIEZAS DE RECAMBIO 49-55
Español
目次
製品について 39
ピペットの操作 40
ピペッティングテクニック 40
キャリブレーション 41
メンテナンス 43
トラブルシューティング 46
パッケージ 47
保証規定 47
部品及び付属品 49-55
日
本
語
Page 4

4
Product description
The Finnpipette F2 is a continuously adjustable, general purpose micropipette for sampling and
dispensing accurate liquid volumes.
It operates on an air displacement principle (i.e. an air interface) and uses detachable, disposable
tips.
The adjusted delivery volume is displayed digitally on a readout window in the handle.
The eleven different models of Finnpipette F2 pipettes cover a volume range from 0,2 µl to 10 ml.
Order No. Volume Range Finntip
4642010 0,2 µl to 2 µl Flex 10
4642020 0,5 µl to 5 µl Flex 10
4642030 1 µl to 10 µl Flex 10
4642040 1 µl to 10 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642050 2 µl to 20 µl 50
4642060 2 µl to 20 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642070 10 µl to 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642080 20 µl to 200 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642090 100 µl to 1000 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4642100 0,5 ml to 5 ml 5 ml
4642110 1 ml to 10 ml 10 ml, Flex 10 ml Ext
The thirteen different models of Finnpipette F2 Fixed Volume pipettes cover a volume range
from 1 µl to 10 ml.
Order No. Volume Range Finntip
4652000 1 µl Flex 10
4652010 5 µl Flex 10
4652020 10 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652030 25 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652040 50 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652050 100 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652060 250 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652070 500 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652080 1000 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652090 2000 µl 5 ml
4652100 3000 µl 5 ml
4652110 5000 µl 5 ml
4652120 10000 µl 10 ml
The ten different models of Finnpipette F2 Multichannel pipettes cover a volume range from
1 µl to 300 µl.
Order No. Channel Volume Range Finntip
4662000 8 1 µl to 10 µl Flex 10
4662010 8 5 µl to 50 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662020 8 10 µl to 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662030 8 30 µl to 300 µl 300, Flex 300
4662040 12 1 µl to 10 µl Flex 10
4662050 12 5 µl to 50 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662060 12 10 µl to 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662070 12 30 µl to 300 µl 300, Flex 300
4662080 16 1 µl to 10 µl Flex 10 (384)
4662090 16 5 µl to 50 µl 50
English
Page 5
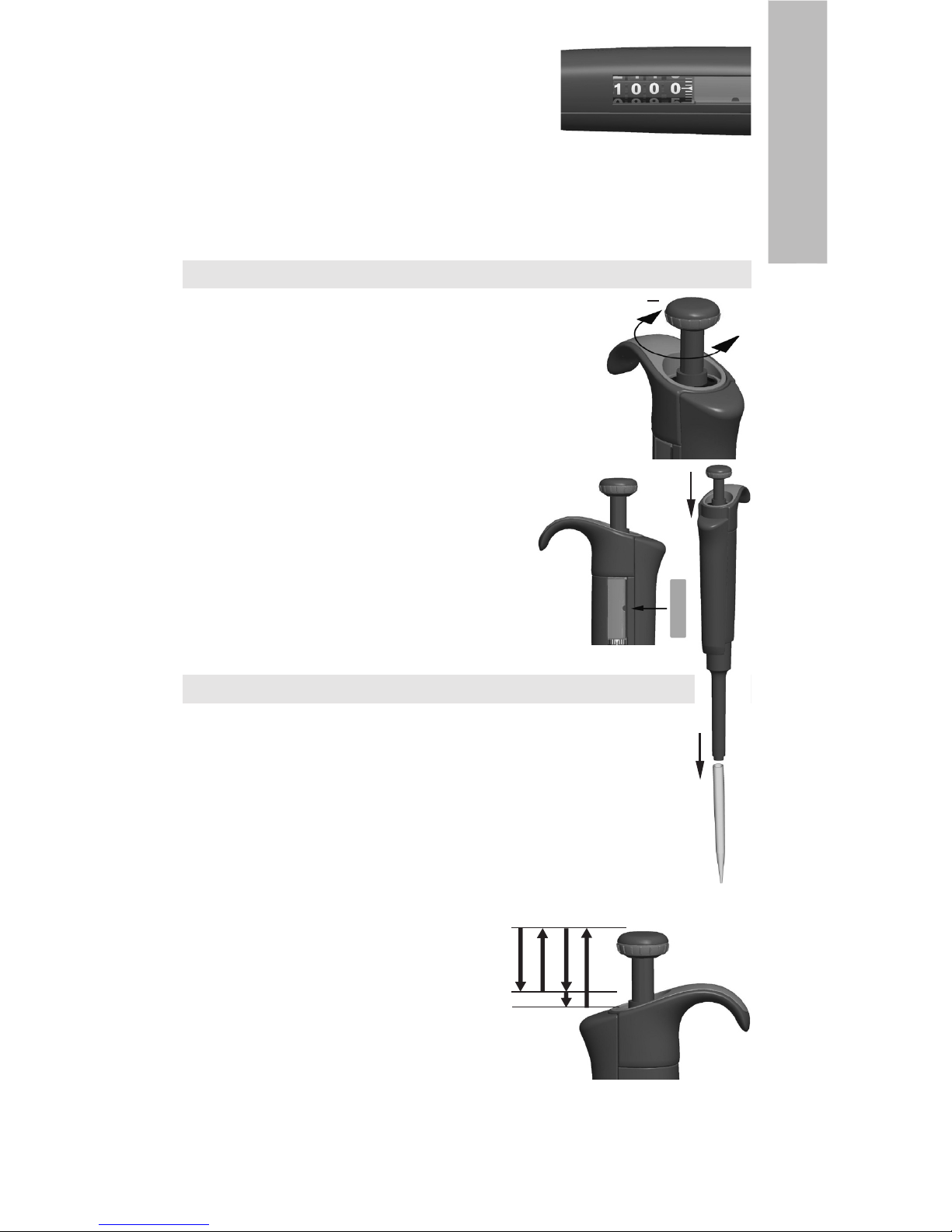
5
English
Digital display
The adjusted delivery volume is clearly indicated in the large
digital display on the handle.
Raw materials
The Finnpipette F2 is made of mechanically durable and chemically resistant materials.
Description of tips
Finntips are recommended for use with the Finnpipette F2.
They are made of virgin natural colour polypropylene, generally regarded as the only
contamination free material suitable for tips. Finntips are also autoclavable (121°C).
Pipette operation
Setting the delivery volume
1. Set the delivery volume using the push button on the top of
the pipette. To increase the delivery volume, turn the push
button counterclockwise. To decrease the delivery volume,
turn it clockwise.
2. Make sure that the desired delivery volume clicks into place.
3. Do not set volumes outside the pipette´s specified volume range.
Using excessive force to turn the push button outside the range
may jam the mechanism and eventually damage the pipette.
Safety Label
You can mark the pipette application, your initials, the
calibration date, etc. on the safety label. Remove the old
label with a sharp needle. Mark the new label with a pencil
and slide the label back in place.
Tip ejection
To help eliminate the risk of contamination, each pipette
is fitted with a tip ejector system. To release the tip, point
the pipette at suitable waste receptacle and press the tip ejector with your thumb.
Pipetting techniques
Push and release the push button slowly at all times particularly when working with
high viscosity liquids. Never allow the push button to snap back.
Make sure that the tip is firmly attached to the tip cone. Check for foreign
particles in the tip.
Before you begin your actual pipetting work, fill and empty the tip 2-3 times with
the solution that you will be pipetting. Hold the pipette in an upright position while
aspirating liquid. The grippy should rest on your index finger. Make sure that the tips,
pipette and solution are at the same temperature.
Forward technique
Fill a clean reagent reservoir with the liquid to be dispensed.
1 Depress the push button to the first stop.
2. Dip the tip under the surface of the liquid in the
reservoir to a depth of about 1 cm and slowly
release the push button. Withdraw the tip from
the liquid touching it against the edge of the
reservoir to remove excess liquid.
3. Deliver the liquid by gently depressing the push
button to the first stop. After a delay of about
one second, continue to depress the push button
all the way to the second stop. This action will empty the tip.
4. Release the push button to the ready position. If necessary, change the tip and continue
pipetting.
1 2 3 4
+
Page 6
6
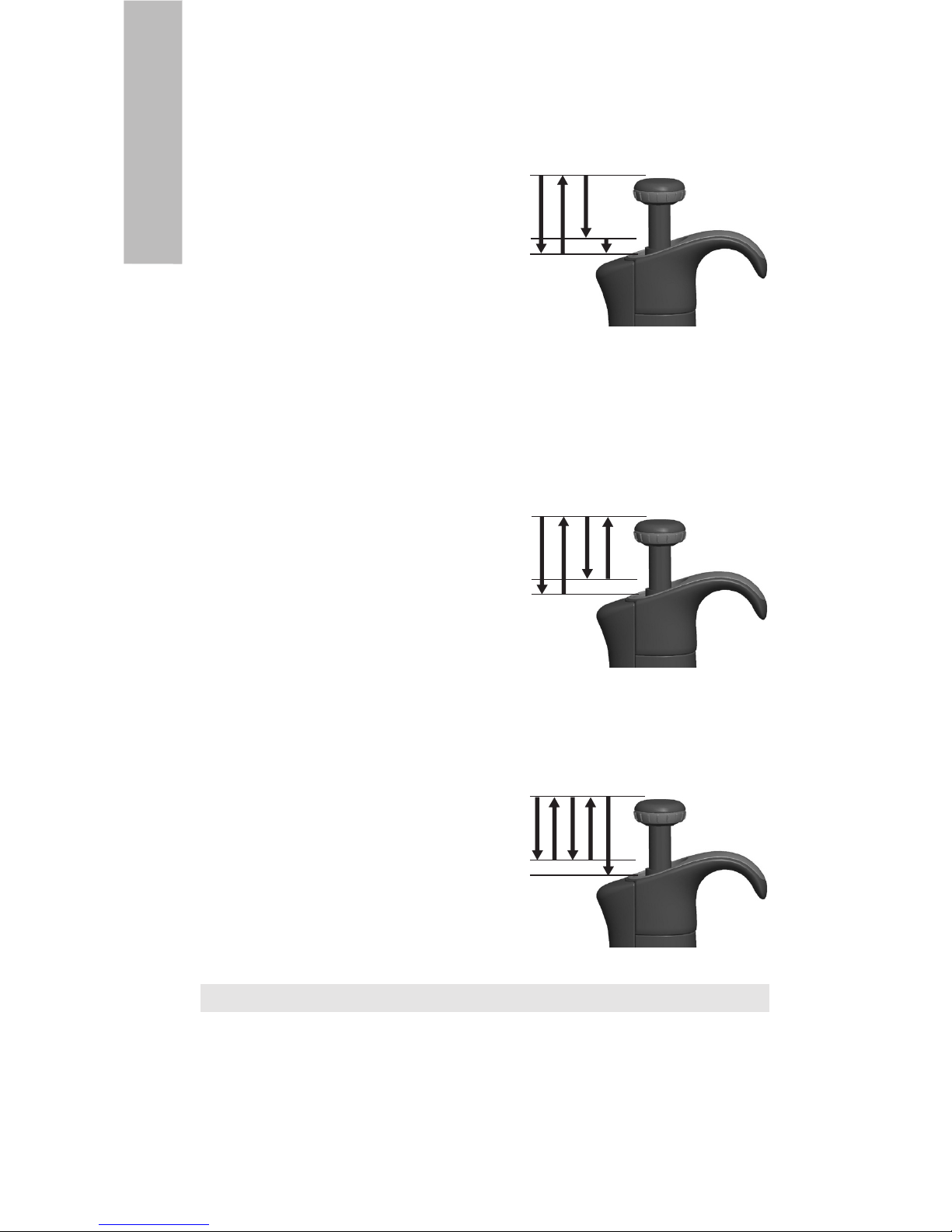
Reverse technique
The reverse technique is suitable for dispensing liquids that have a high viscosity or a tendency
to foam easily. The technique is also recommended for dispensing very small volumes. Fill a
clean reagent reservoir with the liquid to be dispensed.
1. Depress the push button all the way to the second stop.
2. Dip the tip under the surface of the liquid in the
reservoir to a depth of about 1 cm, and slowly
release the push button. This action will fill the
tip. Withdraw the tip from the liquid touching
it against the edge of the reservoir to remove
excess liquid.
3. Deliver the preset volume by gently depressing
the push button to the first stop. Hold the push
button at the first stop. Some liquid will remain
in the tip and this should not be included in
the delivery.
4. The remaining liquid should either be discarded with the tip or pipetted back into the
container.
Repetitive technique
The repetitive technique offers a rapid and simple procedure for repeated delivery of the same
volume. Fill a clean reagent reservoir with the liquid to be dispensed.
1. Depress the push button all the way to the second stop.
2. Dip the tip under the surface of the liquid in the
reservoir to a depth of about 1 cm, and slowly re
lease the push button. This action will fill the tip.
Withdraw the tipfrom the liquid touching against
the edge of the reservoir to remove excess liquid.
3. Deliver the preset volume by gently depressing
the push button to the first stop. Hold the push
button at the first stop. Some liquid will remain
in the tip and this should not be included in
the delivery.
4. Continue pipetting by repeating steps 2 and 3.
Pipetting of heterogeneous samples
(deproteinization in blood glucose determination, for example)
Use steps 1 and 2 of the forward technique to fill the tip with blood.
Wipe the tip carefully with a dry clean tissue.
1. Immerse the tip into the reagent and depress the
push button to the first stop, making sure the tip
is well below the surface.
2. Release the push button slowly to the ready
position.
This will fill the tip. Keep the tip in the solution.
3. Depress the push button to the first stop and
release slowly. Keep repeating this procedure
until the interior wall of the tip is clear.
4. Finally, depress the push button all the way to the second stop to completely empty the tip.
Calibration and adjustment
All Finnpipettes are factory calibrated and adjusted to give the volumes as specified with
distilled
or deionized water using the forward pipetting technique. It should be noted that the use of other
pipetting techniques may affect the calibration results. The pipettes are constructed to permit
re-adjustment for other pipetting techniques or liquids of different temperature and viscosity.
Device requirements and test conditions
An analytical balance must be used. The scale graduation value of the balance should be chosen
according to the selected test volume of the pipette:
1 2 3 4 5
English
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
Page 7

7
Volume range readable graduation
under 10 µl 0.00 1 mg
10-100 µl 0.01 mg
above 100 µl 0.1 mg
Test liquid: Water, distilled or deionized, “grade 3” water conforming ISO 3696. Tests are done
in a draft-free room at a constant (±0.5°C) temperature of water, pipette and air between 15°C
to 30°C. The relative humidity must be above 50%. Especially with volumes under 50 µl the
air humidity should be as high as possible to reduce the effect of evaporation loss. Special
accessories, such as the evaporation trap, are recommended.
Procedure to check calibration
The pipette is checked with the maximum volume (nominal volume) and with the minimum volume.
A new tip is first pre-wetted 3-5 times and a series of ten pipettings is done with both volumes.
A pipette is always adjusted for delivery (Ex) of the selected volume. Use of forward pipetting
technique is recommended. The maximum permissible errors are designed for forward method.
Procedure:
1. Do 10 pipettings with the minimum volume.
2. Do 10 pipettings with the maximum volume.
3. Calculate the inaccuracy (A) and imprecision (cv) of both series.
4. Compare the results to the limits in the Table 1.
If the calculated results are within the selected limits, the adjustment of the pipette is correct.
TABLE 1: Maximum permissible errors according ISO8655
Range Volume Inaccuracy Imprecision
µl µl % s.d. µl cv%
0,2-2 µl 2 ±0.080 ±4 0.040 2.0
0.2 ±0.080 ±40 0.040 20.0
0,5-5 µl 5 ±0.125 ±2.5 0.075 1.5
0.5 ±0.125 ±25 0.075 15
1-10 µl 10 ±0.120 ±1.2 0.080 0.8
1 ±0.120 ±12 0.080 8.0
2-20 µl 20 ±0.20 ±1.0 0.10 0.5
2 ±0.20 ±10.0 0.10 5.0
10-100 µl 100 ±0.80 ±0.8 0.30 0.3
10 ±0.80 ±8.0 0.30 3.0
20-200 µl 200 ±1.60 ±0.8 0.60 0.3
20 ±1.60 ±8.0 0.60 3.0
100-1000 µl 1000 ±8.0 ±0.8 3.0 0.3
100 ±8.0 ±8.0 3.0 3.0
0,5-5 ml 5000 ±40.0 ±0.8 15.0 0.3
500 ±40.0 ±8.0 15.0 3.0
1-10 ml 10000 ±60.0 ±0.6 30.0 0.3
1000 ±60.0 ±6.0 30.0 3.0
Fixed Volume Inaccuracy Imprecision
µl µl % s.d.µl cv%
1 ±0.04 ±4.0 0.04 4.0
5 ±0.07 ±1.4 0.07 1.4
10 ±0.09 ±0.9 0.08 0.8
25 ±0.15 ±0.6 0.13 0.5
50 ±0.3 ±0.6 0.2 0.4
100 ±0.4 ±0.4 0.3 0.3
250 ±1.0 ±0.4 0.8 0.3
500 ±1.5 ±0.3 1.5 0.3
1000 ±3.0 ±0.3 0.3 0.3
2000 ±6.0 ±0.3 4.0 0.2
3000 ±9.0 ±0.3 6.0 0.2
5000 ±15.0 ±0.3 10.0 0.2
10000 ±30.0 ±0.3 20.0 0.2
English
Page 8

8
Range Channel Volume Inaccuracy Imprecision
µl µl % s.d.µl cv%
1-10 µl 8, 12, 16 10 ±0.24 ±2.4 0.16 1.6
1 ±0.24 ±24 0.16 16
5-50 µl 8, 12, 16 50 ±1.0 ±2.0 0.4 0.8
5 ±1.0 ±20 0.4 8.0
10-100 µl 8, 12 100 ±0.80 ±0.8 0.30 0.3
10 ±0.80 ±8.0 0.30 3.0
30-300 µl 8, 12 300 ±8.0 ±2.7 3.0 1.0
30 ±8.0 ±26.7 3.0 10.0
Adjustment
Adjustment is done with the service tool.
1. Place the service tool into the openings of the
calibration nut at the top of the handle.
2. Turn the service tool clockwise to increase, or
counterclockwise to decrease the volume.
3. After adjustment check the calibration according
to the instructions above.
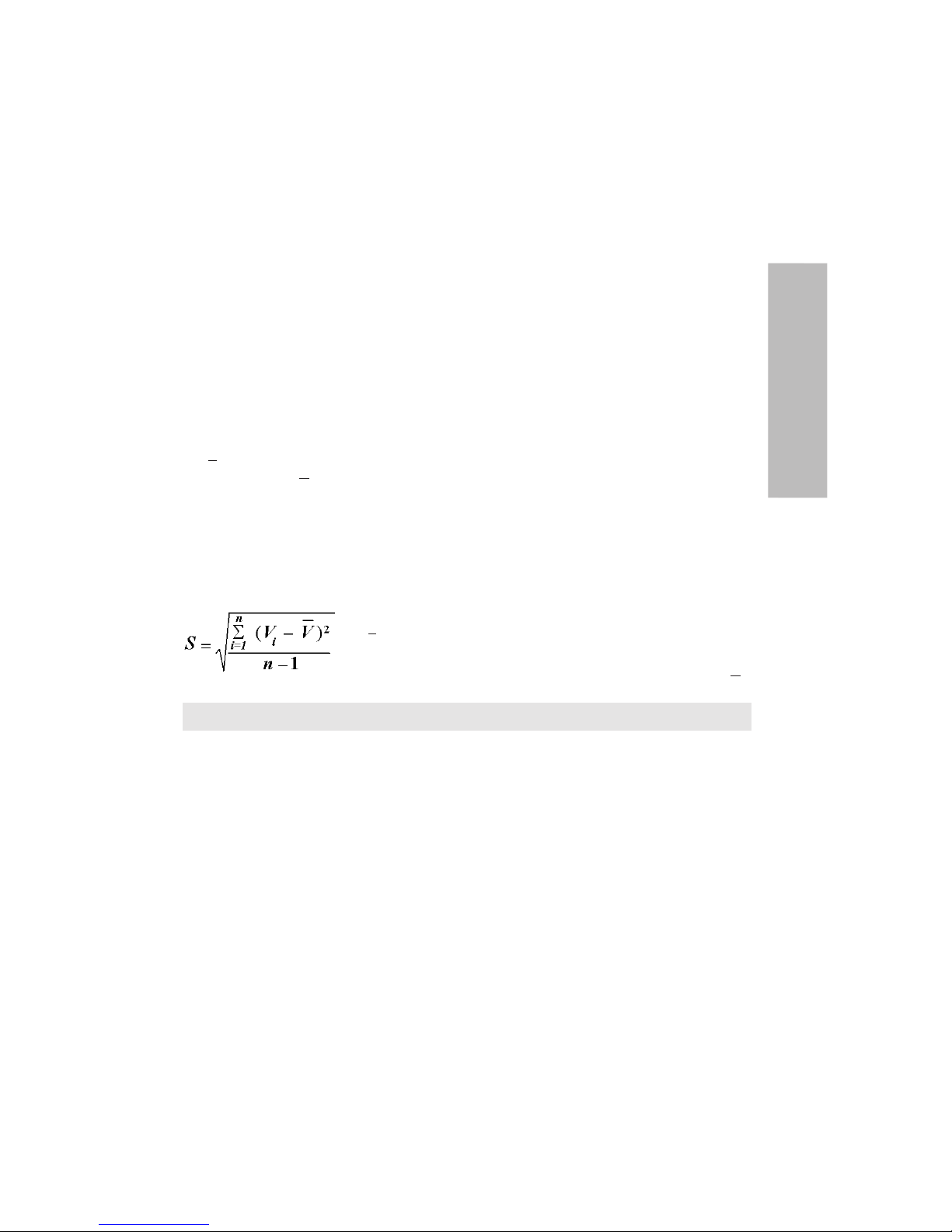
Formulas for calculating results
Conversion of mass to volume
V = (w + e) x Z V = volume (µl)
w = weight (mg)
e = evaporation loss (mg)
Z = conversion factor for mg/µl conversion
Evaporation loss can be significant with low volumes. To determine mass loss, dispense water
to the weighing vessel, note the reading and start a stopwatch. See how much the reading
decreases during 30 seconds (e.g. 6 mg = 0.2 mg/s).
Compare this to the pipetting time from taring to reading. Typically pipetting time might be 10
seconds and the mass loss is 2 mg (10 s x 0.2 mg/s) in this example. If an evaporation trap or lid
on the vessel is used the correction of evaporation is usually unnecessary.
The factor Z is for converting the weight of the water to volume at test temperature and pressure.
A typical value is 1.0032 µl/mg at 22°C and 95 kPa. See the conversion table on page 48.
Inaccuracy (systematic error)
Inaccuracy is the difference between the dispensed volume and the selected volume of a pipette.
A = V - V0 A = inaccuracy
V = mean volume
V
0
= nominal volume
Inaccuracy can be expressed as a relative value: A% = 100% x A / V
0
Imprecision (random error)
Imprecision refers to the repeatability of the pipettings. It is expressed as standard deviation (s)
or coefficient of variation (cv)
s = standards deviation
v = mean volume
n = number of measurements
Standard deviation can be expressed as a relative value (CV)
CV = 100% x S / V
Maintenance
When the Finnpipette F2 is not in use, make sure it is stored in an upright position. We
recommend a Finnpipette stand for this purpose.
The part # refer to exploded views beginning at page 49.
English
+
Page 9
9
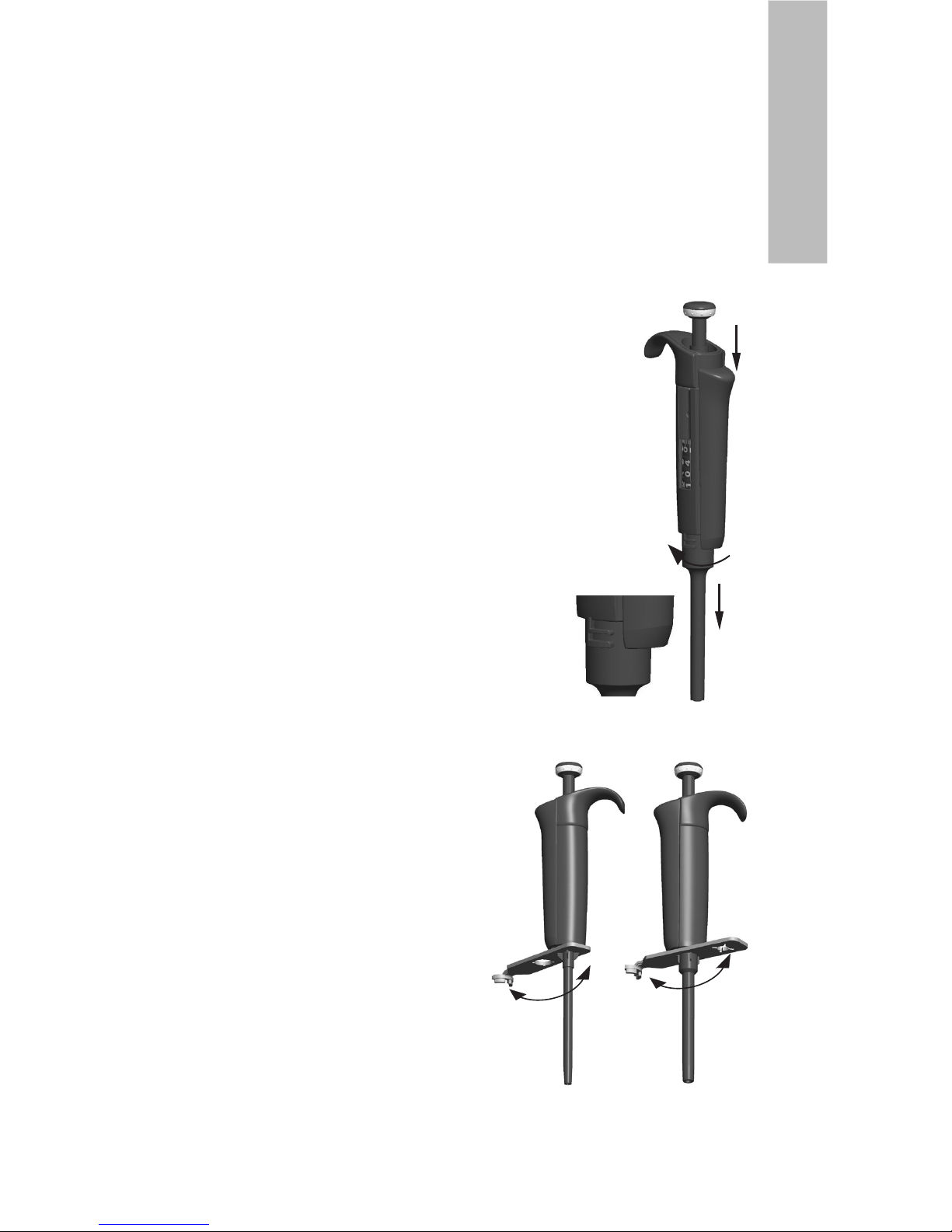
Short-term service
The pipette should be checked at the beginning of each day for dust and dirt on the outside
surfaces of the pipette.
Particular attention should be paid to the tip cone. No other solvents except 70 % ethanol should
be used to clean the pipette.
Long-term service, single channel pipettes
If the pipette is used daily it should be checked every three months. The servicing procedure
starts with the disassembly of the pipette.
1-1000 µl pipettes
1. Press the tip ejector.
2. Rotate the tip ejector 11 counterclockwise and pull it out.
3. Turn out the tip cone counterclockwise with the service tool.
4. Pull out the piston and other parts. Push out with piston the rest of the
piston assembly. Then turn the tip cone upside down and tap all parts
from tip cone. Remember keep all parts in order on table for reassembly.
5. Clean the piston, the piston spring and the O-rings with a dry
napless cloth.
6. Check the tip cone for foreign particles.
7. Grease the cleaned parts with the lubricant that comes with the pipette.
8. Reassemble the pipette components.
0.2-2µl, 0.5-5µl & 1-10 µl: First, slide spring 22, o-ring support 23 and
o-ring 24 on the tube 21. With the 0.2-2µl model insert the tube 27 into
the tube 21. Then slide the spring 13, spring support 16 and tubes 17
and 18, bigger o-ring 19 and smaller o-ring 20 back on the piston.
Compress the spring with fingers by pressing piston and spring support
16 against each other and slide the tube 21 with rest of the parts on the
piston. Hold the spring compressed and carefully slide the entire
assembly
into the tip cone and release the spring.
2-20 µl: Slide the spring 13, spring support 16 and tubes 17
and 18, bigger o-ring 19 and smaller o-ring 20 back on the
piston. Compress the spring with fingers by pressing piston
and spring support 16 against each other and slide the
bigger o-ring 19, smaller o-ring 20, spring support 21 and
the spring
22 (smaller diameter against spring support 21) on
the piston.
Hold the spring compressed and carefully slide
the entire assembly into the tip cone and release the spring.
10-100 µl & 20-200 µl: Slide the spring 13,
spring support 16 and o-ring 17 back on the
piston. Slide the entire assembly into the
tip cone.
100-1000µl: Put the o-ring 17 and support ring
16 to the tip cone. Slide the spring 13 on the
piston and slide the entire assembly into the
tip cone.
9. All: Put the spring 15 and support 14 on top
of the tip cone and carefully insert the tip
cone assembly to the handle and turn it tight
by hand.
10. Reassemble the tip ejector.
English
1
3
2
1-200µl
200-1000µl
Page 10

10
0.5-5ml & 1-10 ml pipettes
1. Press the tip ejector.
2. Rotate the tip ejector 10 counterclockwise to open it.
3. Disassemble the lower part of the tip ejector 14
(snap fitting).
4. Turn the cylinder 13 counterclockwise
and pull out the tip cone assembly.
5. Remove the cylinder 13 by pressing
the snaps fittings of the cylinder.
5. Clean and regrease the O-ring
12 and cylinder 13.
7. Assemble the parts in the opposite
order of disassembly.
Long-term service, multichannel pipettes
If the pipette is used daily it should be checked and lubricated
every three months.
1. Place the servico tool head#1 between ring 15 and ejector 23. Push the tool
until the partssnap from each other.
2. Check that the ejector lever is in up position and pull down the tip ejector part of the module.
Place the service tool head#2 in the hole of adapter tube 46.
3. Open the upper end of the tip ejector slightly and remove the tip ejector.
4. Screw out the module of the handle.
5. Pull out the module spring 19 and clip 22.
6. Press the spring 13 and remove the locking pieces 12 from the groove. Remove the
spring 13.
7. Take off the locking claws 44 and 45 and pull out the adapter tube and tube 43.
8. Use a screwdriver to remove the four screws in the module cover and lift off the cover.
9. Remove the piston bar and clean the pistons and tip cones with a dry nap–free cloth.
10. If needed, service the tip cones:
16-channel 1-10µl: The tip cones cannot be serviced, please replace if necessary.
30-300 µl, 10-100µl & 5-50 µl: Open the tip cone by carefully releasing the cover ring from
its snap joint with the screwdriver. Remove all the parts from the tip cone. Clean all the
parts. If needed, replace the o-rings. Take one piston. Slide the spring 33, cover ring 32
(larger hole), spring 34, support ring 35, (o–ring 37 bigger 5-50µl) and o–ring 36 (smaller)
onto the piston. Grease the o–ring with the lubricant provided in the pipette package. Slide
all the parts into the tip cone and close the snap joint of the cover ring.
1–10 µl: Open the tip cone by carefully releasing the cover ring from its snap joint with
the screwdriver. Remove all the parts from the tip cone. Clean all the parts. If needed,
replace the o-rings. Take one piston. Slide spring 33, cover ring 32 (larger hole), support 35,
o–ring 36 (bigger), o–ring 37 (smaller) and o–ring support 38 onto the piston. Then slide
spring 39, spring support 40 (sharp edges first) and o–ring 41 onto the o–ring sup port 38.
Grease the o–rings with the lubricant provided in the pipette package. Slide all the parts
into the tip cone and close the snap joint of the cover ring.
11. Install the piston bar with pistons and tip cones in the cover and close the cover with the
four screws. Insert the clip 22.
12. Place the adapter tube and tube 43 on the neck of the module and insert the locking claws
44 and 45. Insert the module spring 19.
13. Insert spring 13 and locking pieces 12 to the piston rod 16.
14. Place the tip ejector on the module. Push the spring 19 inside tip ejector parts and close
the upper end of the ejector and keep closed with fingers.
15. Screw the module in the handle and tighten with service tool head#2.
16. Push the tip ejector lever down, until you hear a “click”.
English
1
2
3
Page 11

11
English
Defect
Leakage
Inaccurate
dispensing
Inaccurate
dispensing with
certain liquids
Possible reason
Tip incorrectly attached
Foreign particlesbetween tip and
tip cone
Foreign particles between the
piston, the O-ring and the cylinder
Insufficient amount of grease on
cylinder and O-ring
O-ring damaged
Incorrect operation
Tip incorrectly attached
Calibration altered: caused by
misuse, for example
Unsuitable calibration
High viscosity liquids may require
recalibration
Solution
Attach firmly
Clean tip cones attach new tips
Clean and grease O-ring and
cylinder.
Grease accordingly
Change the O-ring
Follow instructions carefully
Attach firmly
Recalibrate according to
instructions
Recalibrate with the liquids
in question
CAUTION!
The Finnpipette is designed to allow easy in-lab service. If you would prefer to
have us or your local representative service your pipette, please make sure that
the pipette has been decontaminated before you send it to us.
Please note that the postal authorities in your country may prohibit or restrict the
shipment of contaminated material by mail.
Service Instructions for Multichannel Pipette Tip Cones
To ensure even performance between all channels in a multichannel pipette, all tip cones have
to be changed at the same time, if any of them needs to be changed. Don’t mix tip cones of
different packages, because one bag contains a matched set of tip cones.
Sterilization
The entire pipette can be sterilized by autoclaving it at 121°C (252°F) (minimum 20 minutes).
No special preparations are needed for autoclaving. You can use steam sterilization bags if
needed.
After autoclaving the pipette must be cooled to room temperature for at least two hours. Before
pipetting, make sure that the pipette is dry. We recommend that you check the calibration after
every sterilization cycle to achieve the best possible accuracy.
Trouble shooting
The table below lists possible problems and their solutions.
Package
The Finnpipette F2 is shipped in a specially designed package containing the following items:
1. The Finnpipette
2. Service tool
3. Multichannel service tool
4. Finntip sample
5. Tube of grease
6. Instruction manual
7. Calibration certificate
8. Shelf hanger
9. Two stickers
Page 12
12
Produktbeschreibung
Finnpipette F2 ist eine stufenlos einstellbare Mehrzweck-Mikropipette zur Entnahme und
Ausgabe genauer Flüssigkeitsmengen.
Sie funktioniert auf der Basis des Luftverdrängungsprinzips (d. h. einer Luftschnittstelle) und
verwendet abnehmbare Einwegspitzen.
Das einstellbare Ablaufvolumen wird in einer digitalen Anzeige am Griff dargestellt.
Die elf Pipettenmodelle von Finnpipette F2 umfassen einen Volumenbereich von 0,2 µl bis
10 ml.
Bestellnr. Volumen Finntip
4642010 0,2 µl bis 2 µl Flex 10
4642020 0,5 µl bis 5 µl Flex 10
4642030 1 µl bis 10 µl Flex 10
4642040 1 µl bis 10 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642050 2 µl bis 20 µl 50
4642060 2 µl bis 20 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642070 10 µl bis 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642080 20 µl bis 200 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642090 100 µl bis 1000 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4642100 0,5 ml bis 5 ml 5 ml
4642110 1 ml bis 10 ml 10 ml, Flex 10 ml Ext
Die dreizehn Pipettenmodelle von Finnpipette F2 Fixed Volume umfassen einen Volumenbereich
von 1 µl bis 10 ml.
Bestellnr. Volumen Finntip
4652000 1 µl Flex 10
4652010 5 µl Flex 10
4652020 10 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652030 25 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652040 50 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652050 100 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652060 250 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652070 500 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652080 1000 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652090 2000 µl 5 ml
4652100 3000 µl 5 ml
4652110 5000 µl 5 ml
4652120 10000 µl 10 ml
Die zehn Pipettenmodelle von Finnpipette F2 Multichannel umfassen einen Volumenbereich von
1 µl bis 300 µl.
Bestellnr. Channel Volume Range Finntip
4662000 8 1 µl bis 10 µl Flex 10
4662010 8 5 µl bis 50 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662020 8 10 µl bis 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662030 8 30 µl bis 300 µl 300, Flex 300
4662040 12 1 µl bis 10 µl Flex 10
4662050 12 5 µl bis 50 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662060 12 10 µl bis 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662070 12 30 µl bis 300 µl 300, Flex 300
4662080 16 1 µl bis 10 µl Flex 10 (384)
4662090 16 5 µl bis 50 µl 50
Deutsch
Page 13

13
Digitalanzeige
Die einstellbare Ablaufmenge ist in der großen digitalen
Anzeige am Griff zu sehen.
Materialien
Die Finnpipette F2 wird aus mechanisch dauerhaften und
chemisch beständigen Materialien hergestellt.
Beschreibung der Spitzen
Für die Verwendung mit der Finnpipette F2 werden Finntips empfohlen.
Sie bestehen aus neuem, naturfarbenem Polypropylen, dem allgemein einzigen nicht
kontaminierenden Material, das für Spitzen geeignet ist. Finntips sind ebenfalls autoklavierbar
(121°C).
Pipettenfunktion
Einstellen der Ablaufmenge
1. Die Ablaufmenge wird mit dem Bedienungsknopf am oberen
Ende der Pipette eingestellt. Um die Ablaufmenge zu
erhöhen, drehen Sie den Bedienungsknopf gegen den
Uhrzeigersinn. Um die Ablaufmenge zu verringern, drehen
Sie den Bedienungsknopf im Uhrzeigersinn.
2. Achten Sie darauf, dass die gewünschte Ziffernanzeige einrastet.
3. Stellen Sie keine Mengen außerhalb des spezifizierten
Volumenbereichs der Pipette ein. Durch das
gewaltsame Drehen des Bedienungsknopfes
außerhalb des Bereichs kann der Mechanismus
beschädigt und die Pipette unbrauchbar werden.
Sicherheitsetikette
Sie können den Verwendungszweck der Pipette, Ihre
Initialen, das Kalibrierungsdatum etc. auf der
Sicherheitsetikette angeben. Entfernen Sie die alte Etikette
mit einer spitzen Nadel. Beschriften Sie die neue Etikette
mit einem Stift und schieben Sie sie an ihren Platz.
Auswerfen der Spitze
Um die Gefahr einer Kontamination auszuschließen, ist jede Pipette mit einem SpitzenAuswurfsystem ausgestattet.
Um die Spitze zu lösen, halten Sie die Pipette über einen geeigneten Abfallbehälter
und drücken Sie den Spitzenauswerfer mit dem Daumen nach unten.
Pipettiermethoden
Das Drücken und Loslassen des Bedienungsknopfes muss stets langsam erfolgen,
insbesondere wenn mit hochviskosen Flüssigkeiten gearbeitet wird. Achten Sie
darauf, dass der Bedienungsknopf nie zurückschnappt.
Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Spitze fest in der Spitzenhalterung sitzt. Kontrollieren
Sie die Spitze auf Fremdkörper.
Bevor Sie mit dem Pipettieren beginnen, füllen und entleeren Sie die Spitze 2 - 3 Mal mit
der Lösung, die Sie pipettieren wollen. Halten Sie die Pipette beim Ansaugen der Flüssigkeit
senkrecht. Ihr Zeigefinger sollte auf dem griffigen Bereich liegen. Achten Sie darauf, dass die
Spitze, die Pipette und die Lösung dieselbe Temperatur aufweisen.
Vorwärtsmethode
Füllen Sie ein sauberes Reagenzglas mit der Flüssigkeit, die pipettiert werden soll.
1. Drücken Sie den Bedienungsknopf bis zum ersten Anschlag.
2. Tauchen Sie die Spitze ca. 1 cm unter die Oberfläche der Flüssigkeit im Reagenzglas und
lassen Sie den Bedienungsknopf langsam los. Nehmen Sie die Spitze aus der Flüssigkeit,
wobei Sie überschüssige Flüssigkeit am Rand des Glases abstreifen.
Deutsch
+
Page 14

14
3. Gießen Sie die Flüssigkeit aus, indem Sie den
Bedienungsknopf sanft bis zum ersten Anschlag
drücken. Drücken Sie nach etwa einer Sekunde
den Bedienungsknopf bis zum zweiten Anschlag
ganz hinunter. Dadurch wird die Spitze entleert.
4. Lassen Sie den Bedienungsknopf in die
Ausgangsposition zurückgleiten. Wechseln Sie
nötigenfalls die Spitze und fahren Sie mit dem
Pipettieren fort.
Rückwärtsmethode
Die Rückwärtsmethode ist geeignet für Flüssigkeiten, die eine hohe Viskosität aufweisen
oder leicht schäumen. Diese Methode wird auch empfohlen, wenn nur sehr kleine Mengen
verteilt werden sollen. Füllen Sie ein sauberes Reagenzglas mit der Flüssigkeit, die pipettiert
werden soll.
1. Drücken Sie den Bedienungsknopf ganz bis zum
zweiten Anschlag hinunter.
2. Tauchen Sie die Spitze ca. 1 cm unter die
Oberfläche der Flüssigkeit im Reagenzglas und
lassen Sie den Bedienungsknopf langsam los.
Dadurch wird die Spitze gefüllt. Nehmen Sie die
Spitze aus der Flüssigkeit, wobei Sie
überschüssige Flüssigkeit am Rand des
Glases abstreifen.
3. Gießen Sie die voreingestellte Menge aus, indem
Sie den Bedienungsknopf sanft bis zum ersten Anschlag drücken. Halten Sie den
Bedienungsknopf am ersten Anschlag. Etwas Flüssigkeit verbleibt in der Spitze, die nicht
ausgegossen werden darf.
4. Die restliche Flüssigkeit wird entweder mit der Spitze entsorgt oder zurück in den
Flüssigkeitsbehälter gegossen.
Wiederholungsmethode
Die Wiederholungsmethode bietet eine rasche und einfache Möglichkeit, dasselbe Volumen
mehrmals zu dosieren. Füllen Sie ein sauberes Reagenzglas mit der Flüssigkeit, die pipettiert
werden soll.
1. Drücken Sie den Bedienungsknopf ganz bis zum
zweiten Anschlag hinunter.
2. Tauchen Sie die Spitze ca. 1 cm unter die
Oberfläche der Flüssigkeit im Reagenzglas und
lassen Sie den Bedienungsknopf langsam los.
Dadurch wird die Spitze gefüllt. Nehmen Sie die
Spitze aus der Flüssigkeit, wobei Sie überschüssige
Flüssigkeit am Rand des Glases abstreifen.
3. Gießen Sie die voreingestellte Menge aus, indem
Sie den Bedienungsknopf sanft bis zum ersten Anschlag drücken. Halten Sie den
Bedienungsknopf am ersten Anschlag. Etwas Flüssigkeit verbleibt in der Spitze, die nicht
ausgegossen werden darf.
4. Fahren Sie mit dem Pipettieren fort, indem Sie die Schritte 2 und 3 wiederholen.
Pipettieren von heterogenen Proben
(z. B. Deproteinisation bei der Bestimmung des Blutzuckers)
Befolgen Sie Schritt 1 und 2 der Vorwärtsmethode, um
die Spitze mit Blut zu füllen.
Wischen Sie die Spitze sorgfältig mit einem trockenen,
sauberen Tuch ab.
1. Tauchen Sie die Spitze in das Reagenzglas ein
und drücken Sie den Bedienungsknopf bis
zum ersten Anschlag. Achten Sie dabei darauf,
dass die Spitze unter der Oberfläche der
Flüssigkeit eingetaucht ist.
Deutsch
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
Page 15

15
Deutsch
2. Lassen Sie den Bedienungsknopf langsam in die Ausgangsposition zurückgleiten.
Dadurch wird die Spitze gefüllt. Halten Sie die Spitze weiterhin in der Lösung.
3. Drücken Sie den Bedienungsknopf bis zum ersten Anschlag und lassen Sie ihn langsam
aus. Wiederholen Sie diesen Vorgang, bis die Innenwand der Spitze klar ist.
4. Drücken Sie schließlich den Bedienungsknopf ganz hinunter bis zum zweiten Anschlag,
um die Spitze vollständig zu entleeren.
Kalibrierung und Justierung
Alle Finnpipetten werden im Werk auf die spezifizierten Mengen an destilliertem oder
vollentsalztem Wasser bei Verwendung der Vorwärtsmethode kalibriert und justiert.
Beachten Sie, dass die Verwendung anderer Pipettiermethoden die Kalibrierungsergebnisse
beeinflussen können. Die Pipetten sind so konzipiert, dass eine erneute Justierung für andere
Pipetiermethoden oder Flüssigkeiten vorgenommen werden kann, die eine unterschiedliche
Temperatur und Viskosität aufweisen.
Erforderliche Geräte und Prüfbedingungen
Zur Überprüfung wird eine Analysenwaage benötigt. Der Skalenwert der Waage muss
entsprechend der gewählten Testmenge der Pipette gewählt werden:
Menge Skala
unter 10 µl 0,001 mg
10-100 µl 0,01 mg
über 100 µl 0,1 mg
Testflüssigkeit: Destilliertes oder vollentsalztes Wasser der Klasse 3 gemäß ISO 3696. Die
Überprüfung wird in einem zugluftfreien Raum bei einer konstanten Temperatur von 15°C bis
30°C (±0,5°C) des Wassers, der Pipette und der Luft durchgeführt. Die relative Luftfeuchtigkeit
muss über 50% liegen. Insbesondere bei Mengen unter 50 µl sollte die Luftfeuchtigkeit möglichst
hoch sein, um Verdunstungsverluste zu vermeiden. Die Verwendung von Spezialzubehör, z.B.
eines Verdunstungsschutzes, wird empfohlen.
Prüfen der Kalibrierung
Die Pipette wird mit der Höchstmenge (Nennvolumen) und der Mindestmenge geprüft. Zuerst
wird eine neue Spitze drei- bis fünfmal mit Flüssigkeit durchspült. Dann wird mit beiden Mengen
eine Serie von zehn Pipettierungen durchgeführt. Eine Pipette ist stets auf den Ablauf (Ex) der
gewählten Menge justiert. Die Verwendung der Vorwärtsmethode wird empfohlen. Die maximal
zulässigen Abweichungen beziehen sich auf die Vorwärtsmethode.
Vorgang:
1. Nehmen Sie 10 Pipettierungen mit der Mindestmenge vor.
2. Nehmen Sie 10 Pipettierungen mit der Höchstmenge vor.
3. Berechnen Sie die Ungenauigkeit (A) und die Unpräzision (cv) beider Serien.
4. Vergleichen Sie die Ergebnisse mit den Fehlergrenzen in Tabelle 1.
Wenn sich die berechneten Werte innerhalb der festgelegten Fehlergrenzen befinden, ist die
Kalibrierung der Pipette korrekt.
TABELLE 1: Maximal zulässige Abweichungen gemäß ISO 8655
Page 16

16
Deutsch
Bereich Volumen Ungenauigkeit Unpräzision
µl µl % s.d. µl cv%
0,2-2 µl 2 ±0.080 ±4 0.040 2.0
0.2 ±0.080 ±40 0.040 20.0
0,5-5 µl 5 ±0.125 ±2.5 0.075 1.5
0.5 ±0.125 ±25 0.075 15
1-10 µl 10 ±0.120 ±1.2 0.080 0.8
1 ±0.120 ±12 0.080 8.0
2-20 µl 20 ±0.20 ±1.0 0.10 0.5
2 ±0.20 ±10.0 0.10 5.0
10-100 µl 100 ±0.80 ±0.8 0.30 0.3
10 ±0.80 ±8.0 0.30 3.0
20-200 µl 200 ±1.60 ±0.8 0.60 0.3
20 ±1.60 ±8.0 0.60 3.0
100-1000 µl 1000 ±8.0 ±0.8 3.0 0.3
100 ±8.0 ±8.0 3.0 3.0
0,5-5 ml 5000 ±40.0 ±0.8 15.0 0.3
500 ±40.0 ±8.0 15.0 3.0
1-10 ml 10000 ±60.0 ±0.6 30.0 0.3
1000 ±60.0 ±6.0 30.0 3.0
Fixed Volume Ungenauigkeit Unpräzision
µl µl % s.d.µl cv%
1 ±0.04 ±4.0 0.04 4.0
5 ±0.07 ±1.4 0.07 1.4
10 ±0.09 ±0.9 0.08 0.8
25 ±0.15 ±0.6 0.13 0.5
50 ±0.3 ±0.6 0.2 0.4
100 ±0.4 ±0.4 0.3 0.3
250 ±1.0 ±0.4 0.8 0.3
500 ±1.5 ±0.3 1.5 0.3
1000 ±3.0 ±0.3 0.3 0.3
2000 ±6.0 ±0.3 4.0 0.2
3000 ±9.0 ±0.3 6.0 0.2
5000 ±15.0 ±0.3 10.0 0.2
10000 ±30.0 ±0.3 20.0 0.2
Bereich Kanal Volumen Ungenauigkeit Unpräzision
µl µl % s.d.µl cv%
1-10 µl 8, 12, 16 10 ±0.24 ±2.4 0.16 1.6
1 ±0.24 ±24 0.16 16
5-50 µl 8, 12, 16 50 ±1.0 ±2.0 0.4 0.8
5 ±1.0 ±20 0.4 8.0
10-100 µl 8, 12 100 ±0.80 ±0.8 0.30 0.3
10 ±0.80 ±8.0 0.30 3.0
30-300 µl 8, 12 300 ±8.0 ±2.7 3.0 1.0
30 ±8.0 ±26.7 3.0 10.0
Justierung
Zur Justierung wird das mitgelieferte Werkzeug verwendet.
1. Stecken Sie das Werkzeug in die Öffnungen der
Eichungsschraube am oberen Ende des Griffs.
2. Drehen Sie das Werkzeug im Uhrzeigersinn, um
die Menge zu erhöhen, oder gegen den
Uhrzeigersinn, um die Menge zu verringern.
3. Überprüfen Sie nach der Justierung die
Kalibrierung gemäß der oben beschriebenen
Anleitung.
+
Page 17
17
Deutsch
Formeln zum Berechnen von Werten
Umrechnung von Masse in Volumen
V = (w + e) x Z V = Volumen (µl)
w = Gewicht (mg)
e = Verdunstungsverlust (mg)
Z = Umrechnungsfaktor für mg/µl-Konversion
Verdunstungsverluste können bei kleinen Mengen ausschlaggebend sein. Um den Volumenverlust
zu bestimmen, leeren Sie Wasser in die Waagschale, notieren Sie den Anzeigewert und starten
Sie eine Stoppuhr. Stellen Sie fest, um wie viel der angezeigte Wert während 30 Sekunden
abnimmt (z.B. 6 mg = 0,2 mg/s).
Vergleichen Sie dies mit der Pipettierzeit vom Austarieren bis zum Ablesen. Normalerweise
beträgt die Pipettierzeit 10 Sekunden. Der Volumensverlust beträgt in diesem Fall deshalb 2 mg
(10 s x 0,2 mg/s). Wird ein Verdunstungsschutz oder Deckel für das Gefäß verwendet, ist ein
Korrigieren der Verdampfungsmenge normalerweise nicht nötig.
Der Faktor Z dient zur Umrechnung des Gewichts von Wasser auf sein Volumen bei
Prüftemperatur und Prüfdruck. Ein typischer Wert ist 1,0032 µl/mg bei 22°C und 95 kPa. Siehe
die Umwandlungstabelle auf Seite 48.
Ungenauigkeit (systematischer Fehler)
Ungenauigkeit bezeichnet die Differenz zwischen der abgegebenen Menge und dem gewählten
Volumen einer Pipette.
A = V - V0 A = Ungenauigkeit
V = Mittleres Volumen
V
0
= Nennvolumen
Ungenauigkeit kann als relativer Wert dargestellt werden: A% = 100% x A / V
0
Unpräzision (statistischer Fehler)
Unpräzision bezieht sich auf die Wiederholbarkeit der Pipettierung. Sie wird als
Standardabweichung (s) oder Variationskoeffizient (cv) angegeben.
s = Standardabweichung
v = Mittleres Volumen
n = Anzahl der Messungen
Die Standardabweichung kann als relativer Wert dargestellt werden (CV) CV = 100% x S / V
Wartung
Wenn die Finnpipette F2 nicht in Verwendung ist, muss sie in senkrechter Position aufbewahrt
werden. Wir empfehlen dafür eine Finnpipette-Halterung.
Die angegebenen Teilenummern beziehen sich auf die Explosionszeichnungen ab Seite 49.
Kurzfristige Wartung
Die Außenfläche der Pipette sollte täglich vor Gebrauch auf Staub und Schmutz kontrolliert
werden.
Insbesondere der Spitzenkegel sollte gründlich untersucht werden. Zur Reinigung der Pipette
darf ausschließlich 70% Ethylalkohol verwendet werden.
Langfristige Wartung, Einzelkanalpipetten
Falls die Pipette täglich verwendet wird, sollte sie alle sechs Monate gewartet werden. Die
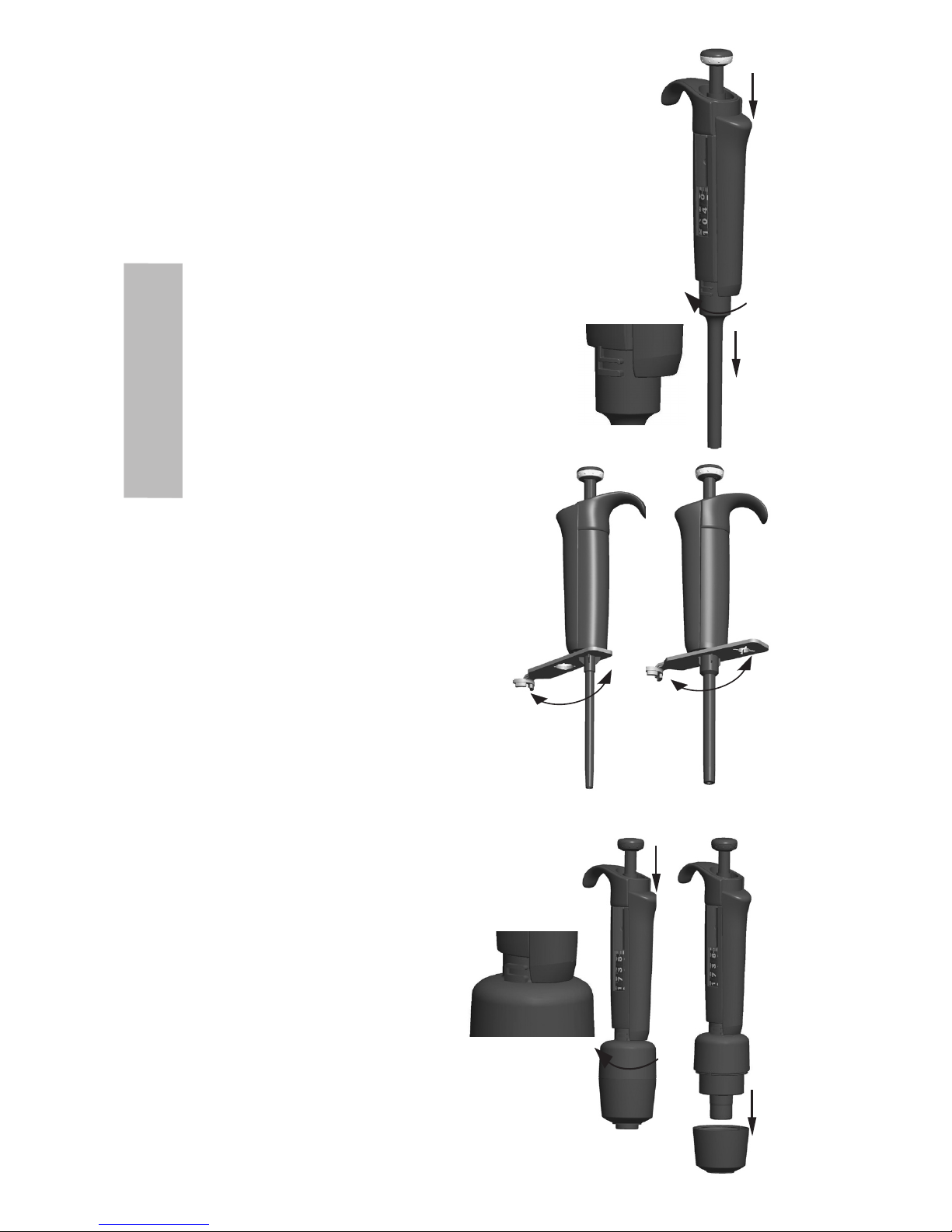
Wartung beginnt mit dem Zerlegen der Pipette.
Pipetten von 1-1000 µl:
1. Drücken Sie auf den Spitzenauswerfer.
2. Drehen Sie den Spitzenauswerfer 11 gegen den Uhrzeigersinn und ziehen Sie ihn heraus.
3. Drehen Sie den Spitzenkegel mit Hilfe des Wartungswerkzeugs gegen den Uhrzeigersinn.
4. Ziehen Sie den Kolben und die übrigen Teile heraus. Drücken Sie mit dem Kolben die
übrigen Teile der Kolbenbaugruppe heraus. Drehen Sie danach den Spitzenkegel um und
klopfen Sie leicht auf ihn, so dass die in ihm befindlichen Teile herausrutschen. Bewahren
Sie die Teile so auf dem Arbeitstisch auf, dass Sie sie beim Wiedereinbau in der richtigen
Reihenfolge griffbereit haben.
Page 18
18
Deutsch
5. Reinigen Sie den Kolben, die Kolbenfeder und die O-Ringe mit einem
trockenen, fusselfreien Tuch.
6. Kontrollieren Sie den Spitzenkegel auf Fremdkörper.
7. Schmieren Sie die gesäuberten Teile mit dem Schmiermittel, das mit
der Pipette geliefert wird.
8. Bauen Sie danach die Pipettenkomponenten wieder zusammen.
0,2-2 µl, 0,5-5 µl & 1-10 µl: Schieben Sie zuerst die Feder 22, die
O-Ring-Stütze 23 und den O-Ring 24 auf die Röhre 21. 0,2-2 µl-Modell:
Schieben Sie die Röhre 27 in die Röhre 21. Schieben Sie danach die
Feder 13, die Federstütze 16, die Röhren 17 und 18, den größeren O-Ring
19 sowie den kleineren O-Ring 20 wieder auf den Kolben.
Drücken Sie die Feder mit den Fingern zusammen, indem Sie den Kolben
und die Federstütze 16 gegeneinander drücken, und schieben Sie auch
die Röhre 21 auf den Kolben. Halten Sie die Feder gedrückt und
schieben Sie die ganze Baugruppe vorsichtig in den
Spitzenkegel. Lassen Sie danach die Feder los.
2-20 µl: Schieben Sie die Feder 13, die Federstütze 16,
die Röhren 17 und 18, den größeren O-Ring 19 sowie
den kleineren O-Ring 20 wieder auf den Kolben. Drücken
Sie die Feder mit den Fingern zusammen, indem Sie
den Kolben und die Federstütze 16 gegeneinander
drücken, und schieben Sie den größeren O-Ring 19,
den kleineren O-Ring 20, die Federstütze 21
und die Feder 22 (den kleineren Durchmesser
der Federstütze 21 zugewandt) auf den Kolben.
Halten Sie die Feder gedrückt und schieben Sie
die ganze Baugruppe vorsichtig in den
Spitzenkegel. Danach können Sie die Feder
loslassen.
10-100 µl und 20-200 µl: Schieben Sie die
Feder 13, die Federstütze 16 und den O-Ring
17 wieder auf den Kolben. Schieben Sie die
ganze Baugruppe in den Spitzenkegel.
100-1000 µl: Schieben den O-Ring 17 und den
Stützring 16 in den Spitzenkegel. Schieben Sie
die Feder 13 auf den Kolben und danach die
ganze Baugruppe in den Spitzenkegel.
9. Alle: Schieben Sie die Feder 15 und die Stütze
14 auf den Spitzenkegel. Setzen Sie danach
die Spitzenkegelbaugruppe vorsichtig in den
Griff ein und drehen Sie sie von Hand, bis
sie fest sitzt.
10. Bauen Sie den Spitzenauswerfer wieder ein.
Pipetten von 0,5-5 ml und 1-10 ml
1. Drücken Sie auf den Spitzenauswerfer.
2. Öffnen Sie den Spitzenauswerfer 10,
indem Sie ihn gegen den Uhrzeigersinn
drehen.
3. Nehmen Sie das Unterteil des
Spitzenauswerfers 14 auseinander
(Einschnapphalterung).
4. Drehen Sie den Zylinder 13 gegen
den Uhrzeigersinn und ziehen Sie die
Spitzenkegelbaugruppe heraus.
5. Entfernen Sie den Zylinder, indem Sie auf dessen
Einschnapphalterung drücken.
6. O-Ring 12 und Zylinder 13 reinigen und schmieren.
7. Bauen Sie die Teile in umgekehrter Reihenfolge wieder ein.
1
3
2
1-200µl
200-1000µl
1
2
3
Page 19

19
Deutsch
Langfristige Wartung, Mehrkanalpipetten
Falls die Pipette täglich verwendet wird, sollte sie alle drei Monate überprüft und geschmiert
werden.
1. Stecken Sie den Wartungswerkzeugkopf #1 zwischen Ring 15 und Auswerfer 23. Drücken
Sie das Werkzeug, bis sich die Teile voneinander lösen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, dass der Auswerferhebel in der oberen Position ist, und ziehen Sie den
Auswerferbreich des Moduls nach unten.
Stecken Sie den Werkzeugkopf #2 in das Loch der Adapterröhre 46.
3. Öffnen Sie das untere Ende des Spitzenauswerfers ein kleines Stück weit und nehmen
Sie den Auswerfer heraus.
4. Schrauben Sie das Modul aus dem Griff.
5. Ziehen Sie die Modulfeder 19 und die Klemme 22 heraus.
6. Drücken Sie die Feder 13 und lösen Sie die Arretierungen 12 aus der Nut. Entfernen Sie die
Feder 13.
7. Entfernen Sie die Arretierungskrallen 44 und 45 und ziehen Sie die Adapterröhre sowie
die Röhre 43 heraus
8. Lösen Sie mit einem Schraubenzieher die vier Schrauben der Modulabdeckung und
entfernen Sie die Abdeckung.
9. Entfernen Sie die Kolbenstange und reinigen Sie Kolben und Spitzenkegel mit einem
trockenen, fusselfreien Tuch.
10. Warten Sie bei Bedarf die Spitzenkegel:
16 Kanäle, 1-10 µl: Die Wartung der Spitzenkegel ist nicht möglich. Bitte ersetzen Sie
verschlissene Kegel durch neue.
30-300 µl, 10-100 µl & 5-50 µl: Öffnen Sie den Spitzenkegel, indem Sie den Schutzring
vorsichtig mit einem Schraubenzieher aus der Einschnapphalterung lösen. Nehmen Sie alle
Teile aus dem Spitzenkegel. Säubern Sie sämtliche Teile. Wechseln Sie bei Bedarf die
O-Ringe aus. Nehmen Sie einen Kolben. Schieben Sie die Feder 33, den Schutzring
32 (größeres Loch), die Feder 34, den Stützring 35, den O-Ring 37 (größer, 5-50µl) und den
O-Ring 36 (kleiner) auf den Kolben. Schmieren Sie den O-Ring mit dem Schmiermittel, das
mit der Pipette geliefert wird. Schieben Sie alle Teile in den Spitzenkegel und schließen
Sie die Einschnapphalterung des Schutzrings.
1-10 µl: Öffnen Sie den Spitzenkegel, indem Sie den Schutzring vorsichtig mit einem
Schraubenzieher aus der Einschnapphalterung lösen. Nehmen Sie alle Teile aus dem
Spitzenkegel. Säubern Sie sämtliche Teile. Wechseln Sie bei Bedarf die O-Ringe aus.
Nehmen Sie einen Kolben. Schieben Sie die Feder 33, den Schutzring 32 (größeres Loch),
die Stütze 35, den O-Ring 36 (größer), den O-Ring 37 (kleiner) sowie die O-Ringstütze 38
auf den Kolben. Schieben Sie danach die Feder 39, die Federstütze 40 (scharfe Kante
zuerst) und den O-Ring 41 auf die O-Ringstütze 38. Schmieren Sie die O-Ringe mit dem
Schmiermittel, das mit der Pipette geliefert wird. Schieben Sie alle Teile in den
Spitzenkegel und schließen Sie die Einschnapphalterung des Schutzrings.
11. Setzen Sie Kolbenstange, Kolben und Spitzenkegel in die Abdeckung ein und befestigen
Sie diese mit den vier Schrauben. Setzen Sie die Klemme 22 ein.
12. Setzen Sie die Adapterröhre und die Röhre 43 auf den Hals des Moduls und bringen Sie die
Arretierungskrallen 44 und 45 an. Setzen Sie die Modulfeder 19 ein.
13. Setzen Sie die Feder 13 und die Arretierungen 12 in die Kolbenstange 16 ein.
14. Setzen Sie den Spitzenauswerfer auf das Modul. Schieben Sie die Feder 19 in den
Spitzenauswerfer. Schließen Sie das obere Ende des Auswerfers und halten Sie es mit
den Fingern zusammen.
15. Schrauben Sie das Modul in den Griff und ziehen Sie es mit Werkzeugkopf #2 fest an.
16. Drücken Sie den Spitzenauswerferhebel nach unten, bis Sie ein Klickgeräusch hören.
Wartung der Spitzenkegel von Mehrkanalpipetten
Um die gleichmäßige Funktion aller Kanäle der Mehrkanalpipette sicherzustellen, müssen stets
alle Spitzenkegel gleichzeitig ausgetauscht werden. Verwenden Sie keinesfalls eine Kombination
von Spitzenkegeln aus verschiedenen Packungen, da die in einer Packung enthaltenen Kegel
jeweils genau aufeinander abgestimmt sind.
Page 20

20
Deutsch
ACHTUNG!
Die Finnpipette wurde konzipiert um eine einfache Verwendung im Labor zu
gewährleisten. Wenn Sie uns oder dem Vertreter vor Ort Ihre Pipette zukommen
lassen wollen, stellen Sie bitte sicher, dass die Pipette dekontaminiert wurde,
bevor Sie sie versenden.
Beachten Sie bitte, dass die Postbehörden in Ihrem Land den Transport von
verunreinigtem Material auf dem Postweg untersagen oder inschränken
könnten.
Packungsinhalt
Die Finnpipette F2 wird in einer speziell konzipierten Verpackung transportiert und enthält die
folgenden Bestandteile:
1. Die Finnpipette
2. Wartungswerkzeug
3. Wartungswerkzeug für Mehrkanalpipetten
4. Finntip-Probe
5. Schmiermittel
6. Bedienungsanleitung
7. Kalibierungszertifikat
8. Aufhängevorrichtung
9. Zwei Aufkleber
Fehler
Undichtigkeit
Ungenaue
Ausgabe
Ungenaue
Ausgabe bei
manchen
Flüssigkeiten
Mögliche Ursache
Spitze nicht ordnungsgemäß befestigt
Fremdkörper zwischen Spitze und
Spitzenhalterung
Fremdkörper zwischen Kolben, O-Ring
und Zylinder
Zu wenig Schmiermittel auf Zylinder
und O-Ring
O-Ring beschädigt
Falsche Handhabung
Spitze nicht ordnungsgemäß befestigt
Geänderte Kalibierung:
verursacht durch z. B. falsche
Verwendung
Ungeeignete Kalibrierungsmethode
Hochviskose Flüssigkeiten könnten
neue Kalibrierung erfordern
Lösung
Ordnungsgemäß befestigen
Spitzenhalterung reinigen und
neue Spitze anbringen
O-Ring und Zylinder reinigen
und schmieren.
Ordnungsgemäß schmieren
O-Ring auswechseln
Anleitung genau befolgen
Ordnungsgemäß befestigen
Gemäß Anleitung neu
kalibrieren
Für manche Flüssigkeiten neu
kalibrieren.
Sterilisieren
Das Spitzenkegelmodul kann sterilisiert werden, indem es bei 121°C 20 Minuten lang autoklaviert
wird. Nötigenfalls können Dampfsterilisationstaschen verwendet werden.
Das Herausnehmen des Moduls aus der Pipette und das Wiedereinsetzen sind im Abschnitt
Wartung beschrieben. Nach dem Autoklavieren muss das Modul mindestens zwei Stunden lang
auf Raumtemperatur abgekühlt werden. Achten Sie vor dem Pipettieren darauf, dass das Modul
trocken ist. Wir empfehlen, nach jedem Sterilisationsdurchgang die Kalibrierung zu prüfen.
Fehlerbehebung
Die unten stehende Tabelle listet mögliche Probleme und Lösungsvorschläge auf.
Page 21

21
Description du produit
La Finnpipette F2 est une micropipette polyvalente à volume variable pour l’échantillonnage et
la distribution de volumes liquides précis de.
Elle fonctionne selon le principe du déplacement d’air (volume d’air entre piston et liquide) et
utilise des cônes jetables.
Le volume sélectionné apparaît sur un écran numérique situé sur le corps de la pipette.
Les onze modèles de Finnpipette F2 couvrent une gamme de 0,2 µl à 10 ml.
Référence Plage de volumes Embout Finntip
4642010 0,2 µl à 2 µl Flex 10
4642020 0,5 µl à 5 µl Flex 10
4642030 1 µl à 10 µl Flex 10
4642040 1 µl à 10 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642050 2 µl à 20 µl 50
4642060 2 µl à 20 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642070 10 µl à 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642080 20 µl à 200 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642090 100 µl à 1000 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4642100 0,5 ml à 5 ml 5 ml
4642110 1 ml à 10 ml 10 ml, Flex 10 ml Ext
Les treize modèles de Finnpipette F2 Fixed Volume couvrent une gamme de 1 µl à 10 ml.
Référence Plage de volumes Embout Finntip
4652000 1 µl Flex 10
4652010 5 µl Flex 10
4652020 10 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652030 25 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652040 50 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652050 100 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652060 250 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652070 500 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652080 1000 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652090 2000 µl 5 ml
4652100 3000 µl 5 ml
4652110 5000 µl 5 ml
4652120 10000 µl 10 ml
Les dix modèles différents de Finnpipette F2 Multiconduit couvrent une gamme de 1 µl à
300 ml.
Référence Conduit Plage de volumes Embout Finntip
4662000 8 1 µl à 10 µl Flex 10
4662010 8 5 µl à 50 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662020 8 10 µl à 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662030 8 30 µl à 300 µl 300, Flex 300
4662040 12 1 µl à 10 µl Flex 10
4662050 12 5 µl à 50 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662060 12 10 µl à 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662070 12 30 µl à 300 µl 300, Flex 300
4662080 16 1 µl à 10 µl Flex 10 (384)
4662090 16 5 µl à 50 µl 50
Français
Page 22

22
Affichage numérique
Le volume sélectionné est indiqué indiqué sur l’écran
numérique de la poignée.
Matériaux de fabrication
La Finnpipette F2 est fabriquée à partir de matériaux à haute résistance mécanique et
chimique.
Description des cônes
Il est recommandé d’utiliser les cônes Finntip avec les Finnpipettes F2.
Ces cônes sont en polypropylène incolore, de haute qualité, seule matière considérée comme
non contaminante. Les Finntip sont également autoclavables (121°C).
Utilisation de la pipette
Réglage du volume à pipeter
1. Régler le volume souhaité à l’aide du bouton-poussoir situé sur le
haut de la pipette. Pour augmenter le volume, tourner le bouton
dans le sens inverse des aiguilles d’une montre. Pour diminuer le
volume, le tourner dans le sens des aiguilles d’une montre.
2. S’assurer que les chiffres correspondants au volume désiré
sont correctement affichés sur l’écran numérique.
3. Ne pas afficher un volume hors de la gamme spécifiée pour
la pipette.
Pour ne pas endommager le mécanisme de la pipette
ni altérer sa précision, éviter de forcer sur le bouton poussoir.
Étiquette de sécurité
L’étiquette de sécurité permet d’inscrire l’application de la
pipette, les initiales de l’utilisateur, la date du calibrage,
etc. Retirer l’ancienne étiquette à l’aide d’un objet pointu.
Utiliser un crayon pour écrire sur la nouvelle étiquette, puis
insérer l’étiquette dans son logement.
Éjection des cônes
Pour éliminer tout risque de contamination, chaque pipette est munie d’un dispositif
d’éjection des cônes.
Pour éjecter le cône, diriger la pipette vers un réceptacle adapté et appuyer sur
l’éjecteur avec le pouce.
Méthodes de pipetage
Manier toujours le bouton-poussoir avec douceur, surtout avec des liquides à forte
viscosité. Ne jamais relâcher le bouton-poussoir brusquement.
S’assurer que le cône est fermement emboîté sur l’embase porte-cône. Vérifier que
le cône est propre.
Humidifier le cône avec la solution à pipeter avant de procéder au pipetage définitif
(en remplissant et vidant 2 ou 3 fois le cône). Tenir la pipette en position verticale durant la
manipulation. Le Grip-index doit reposer sur l’index de l’utilisateur. La température de la pipette
et du cône doit être identique à celle de la solution.
Méthode directe
Remplir un réservoir propre avec le liquide à pipeter.
1. Appuyer sur le bouton-poussoir jusqu’au
premier cran.
2. Plonger d’environ 1 cm le cône dans le liquide
puis relâcher lentement le bouton-poussoir.
Retirer le cône en l’appliquant contre la paro du
réservoir afin d’éliminer le liquide en excès.
Français
1 2 3 4
+
Page 23

23
3. Distribuer le liquide en appuyant doucement sur le bouton-poussoir jusqu’au premier cran.
Marquer un temps d’arrêt d’environ une seconde, puis appuyer jusqu’au deuxième cran.
Cette action videra complètement le cône.
4. Relâcher le bouton jusqu’à sa position de repos. Changer le cône si nécessaire, puis
continuer le pipetage.
Méthode inverse
La méthode inverse convient pour pipeter des liquides à forte viscosité ou ayant tendance à
mousser facilement. Cette méthode est également recommandée pour les faibles volumes.
Remplir un réservoir propre avec le liquide à pipeter.
1. Enfoncer le bouton-poussoir jusqu’au deuxième cran.
2. Plonger d’environ 1 cm le cône dans le liquide
puis relâcher délicatement le bouton-poussoir.
Le cône se remplira. Retirer le cône en
l’appliquant contre la paroi du réservoir afin
d’éliminer le liquide en excès.
3. Distribuer le volume prélevé en enfonçant
délicatement le bouton jusqu’au premier cran.
Maintenir le bouton-poussoir dans cette position.
Une partie du liquide doit rester dans le cône et
ne sera pas distribuée.
4. Le liquide restant est éliminé avec le cône ou reversé dans le réservoir.
Méthode répétitive
La méthode répétitive est une méthode simple et rapide pour la distribution répétée d’un même
liquide. Remplir un réservoir propre avec le liquide à distribuer.
1. Enfoncer le bouton-poussoir jusqu’au deuxième cran.
2. Plonger d’environ 1 cm e cône dans le liquide
puis relâcher lentemen le bouton-poussoir.
Le cône se remplira.
3. Distribuer le volume prélevé en appuyant
lentement le bouton jusqu’au premier cran.
Maintenir le bouton-poussoir dans cette position.
Une partie du liquide doit rester dans le cône et
ne sera pas distribuée.
4. Continuez le pipetage en répétant les étapes 2 et 3.
Pipetage de sang total
(ex. déprotéinisation du sang pour dosage de glucose)
Pour prélever l’échantillon de sang, suivre les étapes 1 et 2 de la méthode directe.
Essuyer soigneusement le cône à l’aide d’un mouchoir en papier propre et sec.
1. Plonger le cône dans le réactif et enfoncer le
bouton-poussoir jusqu’au premier cran, en
s’assurant que la pointe est bien dans le liquide.
2. Relâcher délicatement le bouton-poussoir
jusqu’à sa position de repos.
Le cône se remplira. Ne pas sortir le cône de
la solution.
3. Enfoncer le bouton-poussoir jusqu’au premier
cran puis le relâcher lentement. Répéter cette
opération jusqu’à ce que l’intérieur du cône soit
propre.
4. Enfin, enfoncer le bouton-poussoir jusqu’au deuxième cran pour vider complètement
le cône.
Français
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
Page 24

24
Calibrage
Toutes les Finnpipette sont réglées et calibrées en usine avec de l’eau distillée ou déionisée,
selon la méthode de pipetage direct. Les pipettes sont conçues de sorte à pouvoir utiliser des
liquides de différentes températures et viscosités.
Matériel et conditions de test
Utiliser une balance analytique. Les spécifications de la balance doivent être choisies en fonction
du volume contrôlé de la pipette :
Volumes Sensibilité de la balance
inférieurs à 10 µl 0,001 mg
10-100 µl 0,01 mg
supérieurs à 100 µl 0,1 mg
Liquide test : eau distillée ou déionisée, grade 3, conforme à la norme ISO 3696. Les tests
doivent être effectués dans une pièce climatisée avec une température d’eau, de pipette et d’air
constante (±0,5°C) située entre 20°C et 25°C. L’humidité relative doit être supérieure à 50 %.
Pour les volumes inférieurs à 50 µl en particulier, l’humidité de l’air doit être la plus élevée
possible pour réduire la perte par évaporation. Des accessoires spécifiques, tels qu’un piège à
évaporation, sont recommandés.
Procédure de vérification du calibrage
La pipette est vérifiée au volume maximum (volume nominal) et au volume minimum. Chaque
nouveau cône est d’abord pré-humidifié 3 à 5 fois, et une série de dix pipetages est réalisée pour
chacun des deux volumes. Une pipette est toujours réglée pour distribuer le volume sélectionné.
L’utilisation de la méthode de pipetage directe est recommandée. Les erreurs tolérables
maximales sont fournies pour la méthode de pipetage directe.
Procédure :
1. Effectuer 10 pipetages au volume minimum.
2. Effectuer 10 pipetages au volume maximum.
3. Calculer la justesse (E) et la répétabilité (cv) des deux séries.
4. Comparer les résultats aux tolérances du tableau 1.
Si les résultats calculés se trouvent dans les limites de tolérance sélectionnées, c’est que le
réglage de la pipette est correct.
TABLEAU 1 : Erreurs tolérables maximales, selon la norme ISO 8655
Gamme Volumes Erreur de justesse Erreur de répétabilité
µl µl % s.d. µl cv%
0,2-2 µl 2 ±0.080 ±4 0.040 2.0
0.2 ±0.080 ±40 0.040 20.0
0,5-5 µl 5 ±0.125 ±2.5 0.075 1.5
0.5 ±0.125 ±25 0.075 15
1-10 µl 10 ±0.120 ±1.2 0.080 0.8
1 ±0.120 ±12 0.080 8.0
2-20 µl 20 ±0.20 ±1.0 0.10 0.5
2 ±0.20 ±10.0 0.10 5.0
10-100 µl 100 ±0.80 ±0.8 0.30 0.3
10 ±0.80 ±8.0 0.30 3.0
20-200 µl 200 ±1.60 ±0.8 0.60 0.3
20 ±1.60 ±8.0 0.60 3.0
100-1000 µl 1000 ±8.0 ±0.8 3.0 0.3
100 ±8.0 ±8.0 3.0 3.0
0,5-5 ml 5000 ±40.0 ±0.8 15.0 0.3
500 ±40.0 ±8.0 15.0 3.0
1-10 ml 10000 ±60.0 ±0.6 30.0 0.3
1000 ±60.0 ±6.0 30.0 3.0
Français
Page 25

25
Fixed Volume Erreur de justesse Erreur de répétabilité
µl µl % s.d.µl cv%
1 ±0.04 ±4.0 0.04 4.0
5 ±0.07 ±1.4 0.07 1.4
10 ±0.09 ±0.9 0.08 0.8
25 ±0.15 ±0.6 0.13 0.5
50 ±0.3 ±0.6 0.2 0.4
100 ±0.4 ±0.4 0.3 0.3
250 ±1.0 ±0.4 0.8 0.3
500 ±1.5 ±0.3 1.5 0.3
1000 ±3.0 ±0.3 0.3 0.3
2000 ±6.0 ±0.3 4.0 0.2
3000 ±9.0 ±0.3 6.0 0.2
5000 ±15.0 ±0.3 10.0 0.2
10000 ±30.0 ±0.3 20.0 0.2
Gamme Conduit Volumes Erreur de justesse Erreur de répétabilité
µl µl % s.d.µl cv%
1-10 µl 8, 12, 16 10 ±0.24 ±2.4 0.16 1.6
1 ±0.24 ±24 0.16 16
5-50 µl 8, 12, 16 50 ±1.0 ±2.0 0.4 0.8
5 ±1.0 ±20 0.4 8.0
10-100 µl 8, 12 100 ±0.80 ±0.8 0.30 0.3
10 ±0.80 ±8.0 0.30 3.0
30-300 µl 8, 12 300 ±8.0 ±2.7 3.0 1.0
30 ±8.0 ±26.7 3.0 10.0
Réglage
Le réglage doit être effectué à l’aide de la clé de calibrage fournie dans le coffret.
1. Placer la clé dans les crans de la
bague de calibrage située au-dessous du bouton-
poussoir.
2. Tourner la clé dans le sens des aiguilles d’une
montre pour augmenter le volume ou dans le sens
contraire pour le diminuer.
3. Une fois le réglage terminé, vérifier à nouveau le
calibrage en suivant les instructions données
ci-dessus.
Calculs
Conversion des poids en volume
V = (w + e) x Z V = volume (µl)
w = poids (mg)
e = perte par évaporation (mg)
Z = facteur de conversion pour mg/µl
La perte par évaporation peut être importante avec les micro-volumes. Pour déterminer la
perte de masse, verser de l’eau dans un bécher ou une fiole, noter le poids et déclencher un
chronomètre. Noter le poids indiqué au bout de 30 secondes (ex. 6 mg = 0,2 mg/s).
Comparer ce résultat avec le temps de pipetage entre le tarage et la lecture du poids. Dans cet
exemple, le temps de pipetage devrait être de 10 secondes et la perte de masse serait donc de
2 mg (10 s x 0,2 mg/s). En utilisant un piège à évaporation ou un couvercle sur bécher ou la fiole,
l’erreur due à l’évaporation est négligeable et n’est donc pas prise en compte.
Le facteur Z permet de convertir le poids de l’eau en volume, à la température et à la pression
de contrôle. Z est égal à 1,0032 µl/mg à 22°C et 95 kPa. Se référer à la table de conversion
page 48.
Français
+
Page 26

26
Erreur de justesse (erreur systématique)
La erreur de justesse correspond à la différence entre les volumes distribué et le volume
sélectionné de la pipette.
E = V - V0 E = erreur de justesse
V = volume moyen
V
0
= volume nominal
La erreur de justesse peut être exprimée en valeur relative : E% = 100% x E / V
0
Erreur de répétabilité (erreur aléatoire)
Erreur de répétabilité des pipetages est exprimée par la déviation standard (s) ou le coefficient
de variation (cv).
s = déviation standard
v = volume moyen
n = nombre de mesures
La déviation standard peut être exprimé en valeur relative (CV) : CV = 100% x S / V
Entretien
Lorsque la Finnpipette F2 n’est pas utilisée, elle doit être rangée en position verticale. Pour cela,
utiliser un porte-pipettes Finnpipette.
Le numéro des pièces fait référence aux vues explosées présentées à partir de la page 49.
Entretien à court terme
Il est recommandé de vérifier avant chaque utilisation la propreté extérieure de la pipette.
Une attention toute particulière doit être accordée à l’embase. Pour le nettoyage de la pipette,
utiliser uniquement une solution d’éthanol à 70%.
Entretien à long terme, pipettes monocanal
Si la pipette est utilisée quotidiennement, elle doit être vérifiée tous les trois mois. La procédure
d’entretien commence par le démontage de la pipette.
Pipettes 1-1000 µl
1. Appuyer sur l’éjecteur d’embout.
2. Tourner l’éjecteur d’embout 11 dans le sens inverse des aiguilles d’une
montre et le sortir.
3. Tourner l’embout dans le sens inverse des aiguilles d’une montre à l’aide
de la clé d’entretien.
4. Sortir le piston et les autres pièces. Sortir à l’aide du piston le reste du
mécanisme.
Retourner l’embase et la tapoter pour faire sortir toutes les pièces.
Maintenir toutes les pièces en ordre sur une table en vue du remontage.
5. Nettoyer le piston, le ressort du piston et les joints toriques avec un
chiffon sec sans peluche.
6. Nettoyer l’embase de toute particule étrangère.
7. Lubrifier les pièces nettoyées en utilisant la graisse fournie avec
la pipette.
8. Remonter les pièces de la pipette.
0,2-2 µl, 0,5-5 µl et 1-10 µl : Tout d’abord, faire glisser le
ressort 22, le support de joint torique 23 et le joint torique
24 sur le tube 21. Sur le modèle 0,2-2 ul, introduire le tube
27 dans le tube 21. Puis remettre en place le ressort 13,
le support de ressort 16 et les tubes 17 et 18, le gros joint
torique 19 et le petit joint torique 20 en les faisant glisser
sur le piston.
Comprimer le ressort avec les doigts en serrant le piston et le support de ressort 16 l’un
contre l’autre, et faire glisser le tube 21 avec le reste des pièces sur le piston. Tenir le
ressort serré et faire glisser soigneusement l’ensemble sur l’embase et libérer le ressort.
Français
1
3
2
Page 27

27
2-20 µl : Remettre en place le ressort 13, le
support de ressort 16 et les tubes 17 et 18, le
gros joint torique 19 et le petit joint torique 20
en les faisant glisser sur le piston. Comprimer
le ressort avec vos doigts en serrant le piston
et le support de ressort 16 l’un contre l’autre,
et faire glisser le gros joint torique 19, le petit
joint torique 20, le support de ressort 21 et le
ressort 22 (petit diamètre contre le support de
ressort 21) sur le piston. Tenir le ressort serré et
faire glisser soigneusement l’ensemble sur
l’embase et libérer le ressort.
10-100 µl et 20-200 µl : Remettre le ressort 13,
le support de ressort 16 et le joint torique 17
sur le piston en les faisant glisser. Faire glisser
l’ensemble dans l’embase.
100-1000 µl : Mettre le joint torique 17 et
l’anneau de support 16 sur l’embase. Faire
glisser le ressort 13 sur le piston et faire glisser
l’ensemble sur l’embase.
9. Tous modèles : Mettre le ressort 15 et le support 14 sur
l’embase, insérer soigneusement l’embase dans la
poignée et verrouiller le tout à la main.
10. Remonter l’éjecteur d’embout.
Pipettes 0,5-5 ml et 1-10 ml
1. Appuyer sur l’éjecteur d’embout.
2. Tourner l’éjecteur d’embout 10 dans
le sens inverse des aiguilles d’une
montre pour l’ouvrir.
3. Démonter la partie inférieure de
l’éjecteur d’embout 14 (clips de fixation).
4. Tourner le cylindre 13 dans le sens inverse des aiguilles
d’une montre et sortir l’embase.
5. Retirer le cylindre 13 en appuyant sur ses clips de fixation.
6. Nettoyer et lubrifier le joint torique 12 et le cylindre 13.
7. Remonter les pièces dans le sens inverse du démontage.
Entretien à long terme, pipettes multicanal
Si la pipette est utilisée quotidiennement, elle doit être vérifiée et lubrifiée tous les trois mois.
1. Mettre la tête de la clé d’entretien n°1 entre la bague 15 et l’éjecteur 23. Pousser la clé
jusqu’à ce que les pièces se désenclenchent les unes des autres.
2. Vérifier que le levier de l’éjecteur est en position verticale et tirer vers le bas la pièce de
l’éjecteur d’embout du module.
Placer la tête de la clé d’entretien n°2 dans le trou du tube de l’adaptateur 46.
3. Ouvrir légèrement l’extrémité supérieure de l’éjecteur d’embout et enlever l’éjecteur
d’embout.
4. Dévisser le module de la poignée.
5. Extraire le ressort du module 19 et le clip 22.
6. Appuyer sur le ressort 13 et enlever les pièces de fixation 12 de la gorge. Enlever le
ressort 13.
7. Enlever les pattes de fixation 44 et 45 et extraire le tube de l’adaptateur ainsi que le
tube 43.
8. Utiliser un tournevis pour enlever les quatre vis du couvercle du module et soulever le
couvercle pour l’ôter.
9. Enlever la barre du piston et nettoyer les pistons ainsi que les embases à l’aide d’un
chiffon sec sans peluche.
10. Si nécessaire, faire l’entretien des embases :
1-200µl
200-1000µl
1
2
3
Français
Page 28

28
16 canaux 1-10 µl: Il est impossible de faire l’entretien des embases ; les remplacer
si nécessaire.
30-300 µl, 10-100 µl et 5-50 µl : Ouvrir l’embase en enlevant soigneusement la bague
du couvercle de son joint à pression à l’aide du tournevis. Enlever toutes les pièces de
l’embase. Nettoyer toutes les pièces. Si nécessaire, remplacer les joints toriques. Prendre
un piston. Faire glisser le ressort 33, la bague du couvercle 32 (le trou le plus grand), le
ressort 34, la bague de support 35, (le gros joint torique 37 5-50 µl) et le joint torique 36 (le
petit) sur le piston. Graisser le joint torique à l’aide du lubrifiant fourni avec la pipette.
Glisser toutes les pièces dans l’embase et fermer le joint à pression de la bague
du couvercle.
1–10 µl : Ouvrir l’embase en enlevant soigneusement la bague du couvercle de son joint à
pression à l’aide du tournevis. Enlever toutes les pièces de l’embase. Nettoyer toutes les
pièces. Si nécessaire, remplacer les joints toriques. Prendre un piston. Faire glisser le
ressort 33, la bague du couvercle 32 (le trou le plus grand), le support 35, le joint torique
36 (le plus grand), le joint torique 37 (le plus petit) et le support de joint torique 38 sur le
piston. Glisser ensuite le ressort 39, le support de ressort 40 (les arêtes vives d’abord) et le
joint torique 41 sur le support de joint torique 38. Graisser les joints toriques à l’aide du
lubrifiant fourni avec la pipette. Glisser toutes les pièces dans l’embase et fermer le joint à
pression de la bague du couvercle.
11. Monter la barre du piston avec les pistons et les embases dans le couvercle et fermer le
couvercle en resserrant les quatre vis. Insérer le clip 22.
12. Placer le tube de l’adaptateur et le tube 43 sur le collet du module et insérer les pattes de
fixation 44 et 45. Insérer le ressort du module 19.
13. Insérer le ressort 13 et les pièces de fixation 12 sur la tige du piston 16.
14. Placer l’éjecteur d’embout sur le module. Pousser le ressort 19 dans les pièces de
l’éjecteur d’embout, fermer l’extrémité supérieure de l’éjecteur et la maintenir fermée
avec les doigts.
15. Visser le module dans la poignée et le resserrer à l’aide de la tête de la clé d’entretien
n° 2.
16. Pousser le levier de l’éjecteur d’embout vers le bas jusqu’à ce que vous entendiez un clic.
Instructions d’entretien des embases de pipettes multicanal
Pour que les performances des différents canaux d’une pipette multicanal soient homogènes, il
faut remplacer toutes les embases en même temps en cas de remplacement de l’une d’elles. Il
ne faut pas mélanger les embases de différents emballages parce que chaque paquet contient
un assortiment d’embases.
Stérilisation
Le module porte-cône peut être stérilisé par autoclavage à 121°C. Le module porte-cône peut
être stérilisé par autoclavage à 121°C (252°F) pendant 20 minutes. Si nécessaire, des sacs de
stérilisation à vapeur peuvent être utilisés.
Retirer et remonter le module sur la pipette, comme décrit à la section Entretien. Après
l’autoclavage, le module doit être refroidi à température ambiante pendant au moins deux
heures. Avant de pipeter, s’assurer que le module est sec. Un contrôle de l’étalonnage est
recommandé après chaque cycle de stérilisation.
Français
ATTENTION !
Les Finnpipettes sont conçues pour permettre un entretien facile en laboratoire.
Toutefois, si vous préférez que nous ou notre représentant local se charge de
l’entretien de vos pipettes, assurez-vous que vous les avez décontaminées avant
de nous les envoyer.
Remarque: les services postaux de certains pays peuvent interdire ou restreindre
l’envoi par courrier de matériels contaminés.
Page 29

29
Problème
Fuite
Volume incorrect
Volume
incorrect
avec certains
liquides
Cause probable
Cône mal emboîté
Poussières ou cristaux entre le cône
et l’embase
Piston, joint torique et cylindre
encrassés
Cylindre et joint torique
insuffisamment lubrifiés
Joint torique endommagé
Utilisation incorrecte
Cône mal emboîté
Calibrage modifié: causé par une
mauvaise utilisation par exemple
Calibrage inadapté.
Les liquides très visqueux peuvent
demander un recalibrage.
Solution
Bien vérifier la mise en place
du cône
Nettoyer l’embase et remettre
un nouveau cône
Nettoyer et graisser le joint
torique et le cylindre.
Graisser en conséquence
Remplacer le joint torique
Suivre attentivement les
instructions
Bien vérifier la mise en place
du cône
Recalibrer en respectant les
instructions
Recalibrer en fonction du
liquide utilisé.
Conditionnement
La Finnpipette F2 est livrée dans un emballage spécial contenant les éléments suivants :
1. Finnpipette
2. Clé d’entretien
3. Clé d’entretien multicanal
4. Échantillon Finntip
5. Tube de graisse
6. Guide d’utilisation
7. Certificat de calibrage
8. Porte-pipettes
9. Deux autocollants
Français
En cas de probleme
Le tableau ci-dessous donne une liste des problèmes éventuels et des solutions à apporter.
Page 30

30
Descripción del producto
La Finnpipette F2 es una micropipeta ajustable progresivamente y de propósito general, para el
muestreo y la dispensación de volúmenes de líquido exactos.
Su funcionamiento se basa en el principio de desplazamiento de aire (es decir, en medio aéreo)
y utiliza puntas separables y desechables.
El volumen de dispensación seleccionado se muestra digitalmente en una ventana de lectura
que se encuentra en el mango.
Los once modelos distintos de las pipetas Finnpipette F2 permiten trabajar con volúmenes
diferentes, abarcando un rango de 0,2 µl a 10 ml.
Nº de pedido Rango volumétrico Finntip
4642010 0,2 µl a 2 µl Flex 10
4642020 0,5 µl a 5 µl Flex 10
4642030 1 µl a 10 µl Flex 10
4642040 1 µl a 10 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642050 2 µl a 20 µl 50
4642060 2 µl a 20 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642070 10 µl a 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642080 20 µl a 200 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4642090 100 µl a 1000 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4642100 0,5 ml a 5 ml 5 ml
4642110 1 ml a 10 ml 10 ml, Flex 10 ml Ext
Los trece modelos distintos de las pipetas Finnpipette F2 de volumen fijo permiten trabajar con
volúmenes diferentes, abarcando un rango de 1 µl a 10 ml.
Nº de pedido Rango volumétrico Finntip
4652000 1 µl Flex 10
4652010 5 µl Flex 10
4652020 10 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652030 25 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652040 50 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652050 100 µl 250 Universal, 300, 200 Ext, Flex 300
4652060 250 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652070 500 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652080 1000 µl 1000, Flex 1000
4652090 2000 µl 5 ml
4652100 3000 µl 5 ml
4652110 5000 µl 5 ml
4652120 10000 µl 10 ml
Los diez modelos de pipetas Finnpipette F2 Multicanal permiten trabajar con volúmenes
diferentes, abarcando un rango de 1 µl a 300 µl.
Nº de pedido Canal Rango volumétrico Finntip
4662000 8 1 µl a 10 µl Flex 10
4662010 8 5 µl a 50 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662020 8 10 µl a 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662030 8 30 µl a 300 µl 300, Flex 300
4662040 12 1 µl a 10 µl Flex 10
4662050 12 5 µl a 50 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662060 12 10 µl a 100 µl 250 Universal, 200 Ext
4662070 12 30 µl a 300 µl 300, Flex 300
4662080 16 1 µl a 10 µl Flex 10 (384)
4662090 16 5 µl a 50 µl 50
Español
Page 31

31
Español
Pantalla digital
El volumen de dispensación seleccionado aparece
claramente indicado en la pantalla digital de gran tamaño
que se encuentra en el mango.
Materiales
La Finnpipette F2 está fabricada con materiales mecánicamente duraderos y químicamente
resistentes.
Descripción de las puntas
Se recomienda el uso de puntas Finntip con las pipetas Finnpipette F2.
Las puntas Finntip se fabrican con polipropileno virgen de color natural que, por regla general,
se considera el único material sin contaminar apropiado para las puntas. Asimismo, las Finntip
se pueden introducir en el autoclave (121 °C).
Uso de la pipeta
Selección del volumen de dispensación
1. Determine el volumen de dispensación con el pulsador que se
encuentra en la parte superior de la pipeta. Para aumentar el
volumen de dispensación, gire el pulsador en el sentido contrario
a las agujas del reloj. Para disminuirlo, gírelo en la dirección
opuesta.
2. Asegúrese de que el volumen de dispensación es el deseado.
3. No ajuste volúmenes que estén fuera del rango volumétrico
especificado para la pipeta.
Si fuerza el pulsador excesivamente para superar
dicho rango, puede atascar el mecanismo y, con el
tiempo, estropear la pipeta.
Etiqueta de seguridad
Puede usar la etiqueta de seguridad para indicar la
aplicación de la pipeta, sus iniciales, la fecha de
calibración, etc. Retire la etiqueta anterior con una aguja
afilada. Marque la nueva etiqueta con un lápiz y vuelva a
introducirla en su posición.
Expulsión de la punta
Para evitar el riesgo de contaminación, cada pipeta viene equipada con un sistema
de expulsión de puntas. Para soltar la punta, dirija la pipeta a un contenedor para
residuos y presione el expulsor con el dedo pulgar.
Técnicas de pipeteo
Presione y suelte el pulsador lentamente y de forma continua, especialmente cuando
trabaje con líquidos muy viscosos. Nunca suelte el pulsador de forma brusca.
Asegúrese de que la punta se encuentra firmemente ajustada en el cono portapuntas.
Compruebe que no haya partículas extrañas en la punta.
Antes de empezar, llene la punta con la sustancia que va a pipetear y vacíela,
repitiendo esta acción 2 ó 3 veces. Sostenga la pipeta en posición vertical mientras se
aspira el líquido. El agarre de la pipeta debe apoyarse en el dedo índice. Asegúrese de
que las puntas, la pipeta y la solución se encuentran a la misma temperatura.
Técnica directa
Llene un frasco de reactivos limpio con el líquido con el que va a trabajar.
1. Presione el pulsador hasta la primera posición.
2. Sumerja la punta aproximadamente 1 cm bajo la superficie del líquido y suelte el pulsador
lentamente. Saque la punta, retirando el exceso de líquido del borde del frasco de la
dispensación para eliminar el exceso de líquido.
+
Page 32

32
3. Descargue el líquido presionando ligeramente el
pulsador hasta la primera posición. Transcurrido
aproximadamente un segundo, vuelva a
presionar el pulsador hasta la segunda posición
para vaciar la punta. Esta acción vaciará
la punta.
4. Suelte el pulsador para que vuelva a la posición
inicial. Si es necesario, cambie la punta y siga
pipeteando.
Técnica inversa
Se recomienda esta técnica para el pipeteo de líquidos muy viscosos o con tendencia a formar
espuma fácilmente. Asimismo, resulta apropiada para el trabajo con volúmenes reducidos.
Llene un frasco de reactivos limpio con el líquido con el que va a trabajar.
1. Presione el pulsador hasta la segunda posición.
2. Sumerja la punta aproximadamente 1 cm bajo la
superficie del líquido y suelte el pulsador
lentamente. Mantenga el pulsador en este
punto. Saque la punta, retirando el exceso de
líquido del borde del frasco de la dispensación
para eliminar el exceso de líquido.
3. Descargue el volumen ajustado presionando
ligeramente el pulsador hasta la primera
posición. Mantenga el pulsador en este punto.
El líquido que quede en la punta no debe incluirse en la dispensación.
4. Deseche el líquido restante junto con la punta, o bien, devuélvalo al frasco.
Técnica repetitiva
La técnica repetitiva ofrece un modo rápido y sencillo para la dispensación repetida del mismo
volumen. Llene un frasco de reactivos limpio con el líquido con el que va a trabajar.
1. Presione el pulsador completamente hasta la
segunda posición.
2. Sumerja la punta aproximadamente 1 cm bajo la
superficie del líquido y suelte el pulsador
lentamente. Mantenga el pulsador en este punto.
Saque la punta, retirando el exceso de líquido del
borde del frasco de la dispensación para eliminar
el exceso de líquido.
3. Descargue el volumen ajustado presionando
ligeramente el pulsador hasta la primera posición.
Mantenga el pulsador en este punto. El líquido que quede en la punta no debe incluirse
en la dispensación.
4. Repita los pasos 2 y 3 para seguir pipeteando.
Pipeteo de muestras heterogéneas
(desproteinización en una determinación de glucosa en sangre, por ejemplo)
Siga los pasos 1 y 2 de la técnica directa para llenar la punta de sangre.
Limpie cuidadosamente la punta con un pañuelito limpio y seco.
1. Sumerja la punta en el reactivo y presione el
pulsador hasta la primera posición.
Compruebe que la punta se encuentra debajo de
la superficie.
2. Suelte el pulsador lentamente para que vuelva a
la posición inicial.
Esto llenará la punta. Mantenga la punta
sumergida dentro de la solución.
3. Presione el pulsador hasta la primera posición y
suéltelo lentamente. Repita este proceso hasta que
la pared interior de la punta quede limpia.
4. Por último, presione el pulsador hasta la segunda posición para vaciar la punta completamente.
Español
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
Page 33

33
Español
Calibración y ajuste
Todas las pipetas Finnpipette se distribuyen ajustadas y calibradas de fábrica para trabajar
dentro de los volúmenes especificados con agua destilada o desionizada y con la técnica directa.
Recuerde que el uso de otras técnicas de pipeteo puede afectar al resultado de la calibración.
Las pipetas se diseñan para permitir el reajuste para otras técnicas de pipeteo u otros líquidos
con temperaturas y viscosidades diferentes.
Requisitos de los dispositivos y condiciones del ensayo
Debe utilizar una balanza de laboratorio. Determine el valor de sensibilidad de la escala de la
balanza en función del volumen de ensayo seleccionado de la pipeta:
Rango volumétrico Sensibilidad
Menos de 10 µl 0,001 mg
10-100 µl 0,01 mg
Más de 100 µl 0,1 mg
Líquido de ensayo: agua, destilada o desionizada, agua de “grado 3” conforme a la norma ISO
3696. Los ensayos se deben realizar en una habitación sin corrientes de aire, manteniendo el
agua, la pipeta y el aire a una temperatura constante (±0,5 °C) entre los 15 °C y 30 °C. La
humedad relativa debe ser superior al 50%. La humedad del aire, especialmente cuando se
trabaja con volúmenes inferiores a 50 µl, debe ser lo más elevada posible para reducir el efecto
de la pérdida por evaporación. Se recomienda el uso de accesorios especiales, tales como el
concentrador de evaporación.
Procedimiento de comprobación de la calibración
Se debe comprobar el volumen máximo (volumen nominal) y el volumen mínimo de la pipeta.
Humedezca de 3 a 5 veces una nueva punta antes de usarla y realice una serie de diez
repeticiones a cada volumen. Las pipetas se ajustan siempre para dispensar (Ex) el volumen
seleccionado. Se recomienda utilizar la técnica directa de pipeteo. El número máximo permitido
de errores se ha diseñado para la técnica directa.
Procedimiento:
1. Realice 10 repeticiones al volumen mínimo.
2. Realice 10 repeticiones al volumen máximo.
3. Calcule la inexactitud (A) y la imprecisión (cv) de cada serie.
4. Compare los resultados con los límites de la Tabla 1.
Si los resultados calculados están dentro de los límites seleccionados, el ajuste de la pipeta
es correcto.
TABLA 1: errores máximos permitidos según ISO8655
Rango Volumen Inexactitud Imprecisión
µl µl % s.d. µl cv%
0,2-2 µl 2 ±0.080 ±4 0.040 2.0
0.2 ±0.080 ±40 0.040 20.0
0,5-5 µl 5 ±0.125 ±2.5 0.075 1.5
0.5 ±0.125 ±25 0.075 15
1-10 µl 10 ±0.120 ±1.2 0.080 0.8
1 ±0.120 ±12 0.080 8.0
2-20 µl 20 ±0.20 ±1.0 0.10 0.5
2 ±0.20 ±10.0 0.10 5.0
10-100 µl 100 ±0.80 ±0.8 0.30 0.3
10 ±0.80 ±8.0 0.30 3.0
20-200 µl 200 ±1.60 ±0.8 0.60 0.3
20 ±1.60 ±8.0 0.60 3.0
100-1000 µl 1000 ±8.0 ±0.8 3.0 0.3
100 ±8.0 ±8.0 3.0 3.0
0,5-5 ml 5000 ±40.0 ±0.8 15.0 0.3
500 ±40.0 ±8.0 15.0 3.0
1-10 ml 10000 ±60.0 ±0.6 30.0 0.3
1000 ±60.0 ±6.0 30.0 3.0
Page 34

34
Fixed Volume Inexactitud Imprecisión
µl µl % s.d.µl cv%
1 ±0.04 ±4.0 0.04 4.0
5 ±0.07 ±1.4 0.07 1.4
10 ±0.09 ±0.9 0.08 0.8
25 ±0.15 ±0.6 0.13 0.5
50 ±0.3 ±0.6 0.2 0.4
100 ±0.4 ±0.4 0.3 0.3
250 ±1.0 ±0.4 0.8 0.3
500 ±1.5 ±0.3 1.5 0.3
1000 ±3.0 ±0.3 0.3 0.3
2000 ±6.0 ±0.3 4.0 0.2
3000 ±9.0 ±0.3 6.0 0.2
5000 ±15.0 ±0.3 10.0 0.2
10000 ±30.0 ±0.3 20.0 0.2
Rango Canal Volumen Inexactitud Imprecisión
µl µl % s.d.µl cv%
1-10 µl 8, 12, 16 10 ±0.24 ±2.4 0.16 1.6
1 ±0.24 ±24 0.16 16
5-50 µl 8, 12, 16 50 ±1.0 ±2.0 0.4 0.8
5 ±1.0 ±20 0.4 8.0
10-100 µl 8, 12 100 ±0.80 ±0.8 0.30 0.3
10 ±0.80 ±8.0 0.30 3.0
30-300 µl 8, 12 300 ±8.0 ±2.7 3.0 1.0
30 ±8.0 ±26.7 3.0 10.0
Ajuste
El ajuste se realiza con la herramienta de servicio.
1. Inserte la herramienta de servicio en las aberturas
de la tuerca de calibración que se encuentra en la
parte superior del mango.
2. Gire la herramienta de servicio en el sentido de
las agujas del reloj para aumentar el volumen o
en la dirección opuesta para disminuirlo.
3. Una vez ajustado el volumen, compruebe la
calibración siguiendo las instrucciones descritas
anteriormente.
Fórmulas para el cálculo de los resultados
Conversión de masa a volumen
V = (w + e) x Z V = volumen (µl)
w = peso (mg.)
e = pérdida por evaporación (mg.)
Z = factor de conversión para la conversión mg/µl
La pérdida por evaporación puede ser un factor relevante cuando se trabaja con volúmenes
reducidos. Para determinar la pérdida de masa, llene de agua el recipiente a pesar, observe la
lectura obtenida y ponga en marcha un cronómetro. Compruebe cómo disminuyen los valores al
cabo de 30 segundos (p. ej., 6 mg = 0,2 mg/s).
Compare esta lectura con el tiempo de pipeteo transcurrido entre la acción y la lectura.
Normalmente, el tiempo de pipeteo es de 10 segundos y la pérdida de masa de 2 mg (10 s x 0,2
mg/s) en este ejemplo. Si cubre el recipiente con un concentrador de evaporación o una tapa, no
es preciso por lo general que corrija la evaporación.
El factor Z se utiliza para convertir el peso del agua en volumen a una temperatura y presión
de ensayo. Un valor típico es 1,0032 µl/mg a 22 °C y 95 kPa. Consulte la tabla de conversiones
de la página 48.
Español
+
Page 35

35
Español
Inexactitud (error sistemático)
La inexactitud es la diferencia entre el volumen dispensado y el volumen seleccionado de una
pipeta.
A = V - V0 A = Inexactitud
V = Volumen medio
V
0
= Volumen nominal
La inexactitud se puede expresar como un valor relativo: A% = 100% x A / V
0
Imprecisión (error aleatorio)
La imprecisión hace referencia a la repetibilidad del pipeteo. Se expresa en forma de desviación
estándar (s) o como coeficiente de variación (cv)
s = Desviación estándar
v = Volumen medio
n = Número de mediciones
La desviación estándar se puede expresar como un valor relativo (CV) CV = 100% x S / V
Mantenimiento
Guarde la pipeta Finnpipette F2 cuando no se utilice y asegúrese de que se encuentra en
posición vertical. Se recomienda para este propósito el uso del soporte especial para pipetas
Finnpipette.
La referencia se refiere a las vistas de detalle del principio de la página 49.
Mantenimiento a corto plazo
Compruebe al comienzo de cada día que no haya polvo ni suciedad en las superficies externas
de la pipeta.
Preste especial atención al cono portapuntas. Utilice exclusivamente etanol al 70% para limpiar
la pipeta (no utilice otro tipo de disolvente).
Mantenimiento a largo plazo, pipetas monocanal
Si la pipeta se utiliza diariamente, debe verificarla cada tres meses. El servicio de mantenimiento
empieza por desmontar la pipeta.
Pipetas de 1-1.000 µl
1. Pulse el expulsor.
2. Gire el expulsor 11 en el sentido contrario a las agujas del reloj y tire de
él hacia fuera.
3. Gire hacia fuera el cono portapuntas en el sentido contrario a las
agujas del reloj con ayuda de la herramienta de servicio.
4. Tire del émbolo y las demás piezas hacia fuera. Presione hacia fuera el
émbolo con el resto del conjunto de émbolo. A continuación, invierta el
cono portapuntas y golpee suavemente todas las piezas para retirarlas
del cono portapuntas. Recuerde que debe conservar todas las piezas en
orden sobre la mesa, para el montaje posterior.
5. Limpie el émbolo, el muelle del émbolo y las juntas tóricas con un paño
seco sin hilos.
6. Compruebe que el cono portapuntas no contenga partículas extrañas.
7. Engrase las partes limpias con el lubricante que viene con la pipeta.
8. Vuelva a montar los componentes de la pipeta.
0,2-2 µl, 0,5-5 µl y 1-10 µl: Deslice primero el muelle 22, el soporte 23
para junta tórica y la junta tórica 24 en el tubo 21. En el
modelo para 0,2-2 µl, inserte el tubo 27 en el tubo 21. A
continuación, deslice de nuevo en el émbolo el muelle 13,
el soporte 16 para muelle y los tubos 17 y 18, la junta
tórica mayor 19 y la junta tórica menor 20.
Comprima el muelle con los dedos presionando el émbolo
y el soporte 16 para muelle uno contra otro y deslice el tubo
21 con el resto de las partes del émbolo. Mantenga comprimido el
muelle y deslice cuidadosamente todo el conjunto hacia el interior del cono portapuntas,
liberando a continuación el muelle.
1
3
2
Page 36

36
2-20 µl: Deslice el muelle 13, el soporte 16
para muelle y los tubos 17 y 18, la junta tórica
mayor 19 y la junta tórica menor 20 de nuevo
en el émbolo. Comprima el muelle con los
dedos presionando el émbolo y el soporte 16
para muelle uno contra otro y deslice la junta
tórica mayor 19, la junta tórica menor 20,
el soporte 21 para muelle y el muelle 22 (con
el diámetro menos apoyado contra el soporte
21 para muelle) en el émbolo. Mantenga
comprimido el muelle y deslice
cuidadosamente todo el conjunto hacia el
interior del cono portapuntas, liberando
a continuación el muelle.
10-100 µl y 20-200 µl: Deslice el muelle 13, el
soporte 16 para muelle y la junta tórica 17 de
nuevo en el émbolo. Deslice todo el conjunto
hacia el interior del cono portapuntas.
100-1.000 µl: Coloque la junta tórica 17 y el
anillo de soporte 16 en el cono portapuntas.
Deslice el muelle 13 en el émbolo y deslice todo el conjunto en el cono portapuntas.
9. Todas: Coloque el muelle 15 y el soporte 14 en la parte
superior del cono portapuntas e inserte cuidadosamente
el conjunto de cono portapuntas en el mango, girándolo
y apretándolo a continuación con la mano.
10. Vuelva a montar el expulsor.
Pipetas de 0,5-5 ml y 1-10 ml
1. Pulse el expulsor.
2. Gire el expulsor 10 en el sentido
contrario a las agujas del reloj
para abrirlo.
3. Desmonte la parte inferior del
expulsor 14 (ajuste a presión).
4. Gire el cilindro 13 en el sentido contrario a las agujas del
reloj y tire del conjunto de cono portapuntas hacia fuera.
5. Retire el cilindro 13 presionando los ajustes a presión
del cilindro.
6. Limpie y reengrase la junta tórica 12 y el cilindro 13.
7. Monte las piezas en el orden opuesto al del desmontaje.
Mantenimiento a largo plazo, pipetas multicanal
Si la pipeta se utiliza diariamente, debe verificarla y lubricarla cada tres meses.
1. Coloque el cabezal nº 1 de la herramienta de servicio entre el anillo 15 y el expulsor 23.
Presione la herramienta hasta que las piezas se separen con un chasquido.
2. Compruebe que la palanca del expulsor esté en posición vertical y tire hacia abajo de
la parte de expulsor de puntas del módulo.
Coloque el cabezal nº 2 de la herramienta de servicio en el orificio del tubo adaptador 46.
3. Abra levemente el extremo superior del expulsor de puntas y retire el expulsor de puntas.
4. Desatornille y retire el módulo del mango.
5. Tire del muelle de módulo 19 y del clip 22 hacia fuera.
6. Presione el muelle 13 y retire las piezas de bloqueo 12 de la ranura. Retire el muelle 13.
7. Retire las garras de bloqueo 44 y 45 y tire del tubo adaptador y del tubo 43 hacia fuera.
8. Utilice un destornillador para retirar los cuatro tornillos de la cubierta del módulo y levante
la cubierta para separarla.
9. Retire la barra de los émbolos y limpie los émbolos y los conos portapuntas con un paño
seco sin hilos.
10. En caso necesario, mantenga los conos portapuntas:
Español
1-200µl
200-1000µl
1
2
3
Page 37

37
Español
16 canales y 1-10 µl: Los conos portapuntas no admiten mantenimiento. Sustitúyalos
en caso necesario.
30-300 µl, 10-100 µl y 5-50 µl: Abra con cuidado el cono portapuntas liberando el anillo
de la cubierta de su punto de unión por presión, con ayuda de un destornillador. Retire
todas las piezas del cono portapuntas. Limpie todas las piezas. En caso necesario,
sustituya las juntas tóricas. Tome un émbolo. Deslice el muelle 33, el anillo de cubierta 32
(orificio mayor), el muelle 34, el anillo de soporte 35, (junta tórica 37 mayor en 5-50 µl) y la
junta tórica 36 (menor) sobre el émbolo. Engrase la junta tórica con el lubricante incluido
con la pipeta. Deslice todas las piezas hacia el interior del cono portapuntas y cierre la
unión por presión del anillo de la cubierta.
1–10 µl: Abra con cuidado el cono portapuntas liberando el anillo de la cubierta de su
punto de unión por presión, con ayuda de un destornillador. Retire todas las piezas del
cono portapuntas. Limpie todas las piezas. En caso necesario, sustituya las juntas tóricas.
Tome un émbolo. Deslice el muelle 33, el anillo de la cubierta 32 (orificio mayor), el apoyo
35, la junta tórica 36 (mayor), la junta tórica 37 (menor) y el apoyo de junta tórica 38 sobre
el émbolo. A continuación, deslice el muelle 39, el apoyo de muelle 40 (con los bordes
afilados por delante) y la junta tórica 41 sobre el apoyo de junta tórica 38. Engrase las
juntas tóricas con el lubricante incluido con la pipeta. Deslice todas las piezas hacia el
interior del cono portapuntas y cierre la unión por presión del anillo de la cubierta.
11. Instale la barra de émbolos con los émbolos y conos portapuntas en la cubierta y cierre la
cubierta con los cuatro tornillos. Inserte el clip 22.
12. Coloque el tubo adaptador y el tubo 43 en el cuello del módulo e inserte las garras de
bloqueo 44 y 45. Inserte el muelle de módulo 19.
13. Inserte el muelle 13 y las piezas de bloqueo 12 en el vástago de émbolo 16.
14. Coloque el expulsor de puntas en el módulo. Presione el muelle 19 dentro de las piezas del
expulsor y cierre el extremo superior del expulsor, manteniéndolo cerrado con los dedos.
15. Atornille el módulo al mango y apriete con el cabezal nº 2 de la herramienta de servicio.
16. Presione hacia abajo la palanca del expulsor de puntas hasta que escuche un “clic”.
Instrucciones de mantenimiento para los conos portapuntas de las
pipetas multicanal
Para garantizar un comportamiento uniforme de todos los canales de una pipeta multicanal,
es necesario cambiar todos los conos portapuntas a la vez si resultase necesario sustituir
cualquiera de ellos. No mezcle conos portapuntas de paquetes diferentes, dado que cada bolsa
contiene un conjunto calibrado de conos portapuntas.
Esterilización
Para esterilizar el cono portapuntas, introdúzcalo en el autoclave a 121°C. Para esterilizar el
cono portapuntas, introdúzcalo en el autoclave a 121°C (252 °F) durante unos 20 minutos. Puede
utilizar bolsas para la esterilización con vapor cuando sea necesario.
Retire y fije el módulo de nuevo a la pipeta tal y como se describe en la sección Mantenimiento.
Una vez esterilizado en el autoclave, deje enfriar el módulo a temperatura ambiente durante dos
horas como mínimo. Antes de pipetear, compruebe que el módulo está seco. Es aconsejable que
compruebe la calibración cada vez que termine el ciclo de esterilización.
ADVERTENCIA
El mantenimiento de la pipeta Finnpipette se puede llevar a cabo fácilmente en
el laboratorio. Si desea que nosotros o su representante local realicemos este
servicio, envíenos la pipeta, asegurándose de descontaminarla previamente.
Tenga en cuenta que las autoridades del servicio de correos de su país pueden
prohibir o limitar el envío de materiales contaminados.
Page 38

38
Defecto
Goteo
Dispensación
errónea
Dispensación
errónea con
determinados
líquidos
Posible causa
Colocación incorrecta de la punta.
Presencia de partículas extrañas entre
la punta y el cono portapuntas.
Presencia de partículas extrañas entre
el émbolo, la junta tórica y el cilindro.
Cantidad insuficiente de lubricante
en el cilindro y la junta tórica.
La junta tórica está dañada.
Manejo incorrecto.
Colocación incorrecta de la punta.
Cambios en la calibración:
causados por un mal uso, por ejemplo,
una calibración inapropiada.
Puede que deba volver a calibrar la
pipeta para trabajar con líquidos
muy viscosos.
Solución
Coloque la punta firmemente.
Limpie los conos portapuntas y
coloque puntas nuevas.
Limpie y lubrique la junta tórica
y el cilindro.
Lubrique los componentes
correctamente.
Cambie la junta tórica.
Siga las instrucciones
atentamente.
Coloque la punta firmemente.
Vuelva a calibrar la pipeta
siguiendo las instrucciones.
Vuelva a calibrar la pipeta con
los líquidos con los que va a
trabajar.
Paquete
La pipeta Finnpipette F2 se suministra en un paquete de diseño especial que incluye los
siguientes elementos:
1. Pipeta Finnpipette
2. Herramienta de servicio
3. Herramienta de servicio multicanal
4. Punta Finntip de muestra
5. Tubo de grasa
6. Manual de instrucciones
7. Certificado de calibración
8. Colgador para estante
9. Dos adhesivos
Solución de problemas
En la tabla que aparece a continuación se describen varios problemas que pueden surgir y la
manera de solucionarlos.
Español
Page 39

39
製品について
フィンピペットF2は、液体の量を正確に採取して分注するための連続可変式マイクロピ
ペットです。フィンピペットF2は、空気置換(エアインターフェース)方式(空気界
面)で動作し、取り外し可能な使い捨てチップを採用しています。
分注容量は、ハンドルにあるディスプレイ(表示窓)に表示されます。
フィンピペットF2の シングルチャンネルピペットには11種類のモデルがあり、0,2 µlか
ら10 mlまでの容量範囲に対応しています。
製品番号 容量範囲 フィンチップ
4642010 0,2 µl to 2 µl フレックス10
4642020 0,5 µl to 5 µl フレックス10
4642030 1 µl to 10 µl フレックス10
4642040 1 µl to 10 µl 250ユニバーサル、 200 Ext、フレックス300
4642050 2 µl to 20 µl 50
4642060 2 µl to 20 µl 250ユニバーサル、200 Ext、フレックス300
4642070 10 µl to 100 µl 250ユニバーサル、200 Ext、フレックス300
4642080 20 µl to 200 µl 250ユニバーサル、200 Ext、フレックス300
4642090 100 µl to 1000 µl 1000、フレックス1000
4642100 0,5 ml to 5 ml 5 ml
4642110 1 ml to 10 ml 10 ml、フレックス10 ml Ext
フィンピペットF2の容量固定ピペットには13種類のモデルがあり、1 µlから10 mlまでの
容量範囲に対応しています。
製品番号 容量範囲 フィンチップ
4652000 1 µl フレックス10
4652010 5 µl フレックス10
4652020 10 µl 250ユニバーサル、300、200 Ext、フレックス300
4652030 25 µl 250ユニバーサル、300、200 Ext、フレックス300
4652040 50 µl 250ユニバーサル、300、200 Ext、フレックス300
4652050 100 µl 250ユニバーサル、300、200 Ext、フレックス300
4652060 250 µl 1000、フレックス1000
4652070 500 µl 1000、フレックス1000
4652080 1000 µl 1000、フレックス1000
4652090 2000 µl 5 ml
4652100 3000 µl 5 ml
4652110 5000 µl 5 ml
4652120 10000 µl 10 ml、フレックス10 ml Ext
フィンピペットF2マルチチャンネルには,次の10種類のモデルがあり,1µlから300 µl
までの分注ができます。
製品番号
チャンネル数
容量範囲 フィンチップ
4662000 8 1 µl to 10 µl フレックス10
4662010 8 5 µl to 50 µl 250ユニバーサル、200 Ext
4662020 8 10 µl to 100 µl 250ユニバーサル、200 Ext
4662030 8 30 µl to 300 µl 300、フレックス300
4662040 12 1 µl to 10 µl フレックス10
4662050 12 5 µl to 50 µl 250ユニバーサル、200 Ext
4662060 12 10 µl to 100 µl 250ユニバーサル、200 Ext
4662070 12 30 µl to 300 µl 300、フレックス300
4662080 16 1 µl to 10 µl フレックス10 (384)
4662090 16 5 µl to 50 µl 50
日
本
語
Page 40

40
ディスプレイ
設定した容量は、ハンドルにある大きなデジタルディス
プレイ(表示窓)にはっきり表示されます。
材質
フィンピペットF2は、機械的耐久性と耐薬品性に優れ
た素材を採用しています。
チップ
フィンチップは、フィンピペットF2と組み合わせて使用することをお勧めします。
フィンチップは、コンタミネーションがなく、チップに適した唯一の材質とされる無着色の
ポリプロピレン製です。また、フィンチップはオートクレーブ処理が可能です(121°)。
ピペットの操作
分注容量の設定
1. ピペット上端のプッシュボタンで分注容量をセットします。
分注容量を増やすには、プッシュボタンを反時計回りに回
します。 分注容量を減らすには、プッシュボタンを時計回
りに回します。
2. 設定したい分注容量がカチッと正しい位置にセットされ、
ディスプレイに正しい容量が表示されていることを確認し
てください。
3. ピペットの 容量 規格の範囲外に正しい容量がださい。
規格範囲外までプッシュボタンを無理に回そうとすると、故
障や損傷の原因になることがあります。
安全ラベル
安全ラベルにはピペットの用途、ユーザーのイニシャ
ル、検定日などを記載できます。古いラベルは尖った
針で取り除いてください。新しいラベルを鉛筆で記入
し、元の位置にスライドさせます。
チップイジェクション
コンタミネーション防止のため、各ピペットにチップ
イジェクタシステムを装備しています。ピペットの先
端を廃棄容器に向け、親指でチップイジェクタを押す
と、チップに手を触れずに外すことができます。
ピペッティングテクニック
プッシュボタンの操作は常にゆっくり行い、特に粘性の高い液体を扱うとき
は、ゆっくりと押してゆっくりと離します。プッシュボタンをはじくような
扱いは決してしないでください。
チップをチップコーンにしっかりと装着してください。
チップ内部に異物が入っていないことを確認してください。
分注を始める前に、分注する溶液を2、3回吸排します。溶液を吸引するとき
は、ピペットを垂直に保ち、 人差し指の上にフィンガーレストがかかるよう
に握ってください。 チップ、ピペットおよび溶液が同じ温度であること
を確認してください。
フォワード法
分注する溶液をきれいな容器(リザーバー)に入れます。
1 プッシュボタンを1段目まで押し下げます。
2. チップを容器に入った分注液の液面から約
1cm下まで浸し、プッシュボタンをゆっくり
と離します。チップを溶液から引き上げ、
容器の縁に先端を軽く触れて外側についた余
分な溶液を除きます。
3. プッシュボタンを1段目まで静かに押し下げ、
溶液を分注します。 約1秒待った後、続けて
プッシュボタンを2段目まで押し下げます。
チップから溶液が排出されます。
4. プッシュボタンを離してレディポジションに
戻します。 必要に応じてチップを交換し、
ピペッティングを続けます。
日
本
語
1 2 3 4
+
Page 41

41
リバース法
リバース法は、粘性の高い液体や泡立ちやすい溶液の分注に適しています。また、微量
分注にもお勧めします。 分注する溶液をきれいな容器(リザーバー)に入れます。
1. プッシュボタンを2段目まで押し下げます。
2. チップを容器に入った分注液の液面から約
1cm下まで浸し、プッシュボタンをゆっくり
と離します。チップが溶液で満たされます。
チップを溶液から引き上げ、容器の縁に先端
を軽く触れて外側についた余分な溶液を除き
ます。
3.
プッシュボタンを1段目まで静かに押し下げ、
設定した容量の溶液を分注します。プッシ
ュボタンは、必ず1段目までで止めてくだ
さい。チップの中に少量の溶液が残りますが、
これは分注しません。
4. チップ内に残った溶液を、廃棄するか元の容器に戻します。
リピート法
リピート法は、同じ溶液を同じ容量だけ、繰り返しすばやく分注するのに適しています。
分注する溶液をきれいな容器(リザーバー)に入れます。
1. プッシュボタンを2段目まで押し下げます。
2. チップを容器に入った分注液の液面から約
1cm下まで浸し、プッシュボタンをゆっくり
と離します。チップが溶液で満たされます。
チップを溶液から引き上げ、容器の縁に先端
を
軽く触れて外側についた余分な溶液を除き
ます。
3. プッシュボタンを1段目まで静かに押し下
げ、設定した容量の溶液を分注します。
プッシュボタンは、必ず1段目までで止めて
ください。チップの中に少量の溶液が残
りますが、これは 分注しません。
4. 手順2と3を繰り返して分注を続けます。
不均質サンプルの分注
(血糖値測定時の除蛋白操作など)
フォワード法の手順1と2に従って、チップに血液を吸引します。
乾いたきれいなティッシュペーパーでチップを慎重に拭いてください。
1. 分注済みの試薬の中にチップを浸し、プッシ
ュボタンを1段目まで押し下げます。チップ
の先端が試薬の液面より十分下にあることを
常に確認してください。
2. プッシュボタンをゆっくりと離してレディポ
ジションに戻します。
チップの中に試薬が入ってきます。チップの
先端を試薬に浸したままにしておきます。
3. プッシュボタンを1段目まで押し下げ、再び
ゆっくりと離します。チップの内壁がきれい
になるまで この手順を繰り返します。
4. 最後に、プッシュボタンを2段目まで押し下げてチップから試薬を完全に排出します。
キャリブレーション
フィンピペットはすべて、蒸留水またはイオン交換水を使用し、フォワード法により工
場出荷時にキャリブレーションを行っています。これ以外の分注法では、較正結果が異
なる場合があります。フィンピペットは、フォワード法以外で分注する場合や、温度や
粘性の異なる液体を扱う場合、容易に検定および容量調整を行うことができます。
使用機器と検定条件
分析用天秤が必要です。天秤の感量は、ピペットの検定容量に合わせて選択してくださ
い。
検定容量 感量
10 µl未満 0.00 1 mg
10-100 µl 0.01 mg
100 µl超 0.1 mg
日
本
語
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
Page 42

42
検定液は、蒸留水またはイオン交換水(ISO 3696「grade 3」に準拠するもの)を使用し
ます。 通風がなく、ピペット、チップ、検定液、室温が15~30℃で安定(±0.5℃)し
た状態で検定を行ってください。相対湿度は、50%以上必要です。特に50µl以下の容量
では、できるだけ湿度が高い方が蒸発の影響を防ぐことができます。エヴァポレーショ
ントラップなどのアクセサリを使用することもお勧めします。
検定
ピペットは、最大容量(通常容量)と最小容量で検定します。新しいチップを装着し、
検定液の吸排を3~5回行った後、それぞれの容量について10回ずつピペッティングを行
います。ピペットは、常に選択した容量を分注(Ex)するように調整します。フォワー
ド分注法の使用をお勧めします。最大許容誤差は、フォワード法に合わせて定められて
います。
手順:
1. 最小容量で10回ピペッティングし、天秤でそれぞれの重量を測定します。
2. 最大容量で10回ピペッティングし、天秤でそれぞれの重量を測定します。
3. それぞれの容量について、誤差(A)と不精密度(cv)を計算します。
4. 結果を表1の規格と比較します。
計算結果が選択した容量の規格値の範囲内ならば、ピペットが正常に調整されていま
す。
表1:誤差の最大許容範囲(ISO8655適合)
範囲 検定容量 不正確度 不精密度
µl µl % s.d. µl cv%
0,2-2 µl 2 ±0.080 ±4 0.040 2.0
0.2 ±0.080 ±40 0.040 20.0
0,5-5 µl 5 ±0.125 ±2.5 0.075 1.5
0.5 ±0.125 ±25 0.075 15
1-10 µl 10 ±0.120 ±1.2 0.080 0.8
1 ±0.120 ±12 0.080 8.0
2-20 µl 20 ±0.20 ±1.0 0.10 0.5
2 ±0.20 ±10.0 0.10 5.0
10-100 µl 100 ±0.80 ±0.8 0.30 0.3
10 ±0.80 ±8.0 0.30 3.0
20-200 µl 200 ±1.60 ±0.8 0.60 0.3
20 ±1.60 ±8.0 0.60 3.0
100-1000 µl 1000 ±8.0 ±0.8 3.0 0.3
100 ±8.0 ±8.0 3.0 3.0
0,5-5 ml 5000 ±40.0 ±0.8 15.0 0.3
500 ±40.0 ±8.0 15.0 3.0
1-10 ml 10000 ±60.0 ±0.6 30.0 0.3
1000 ±60.0 ±6.0 30.0 3.0
固定容量 不正確度 不精密度
µl µl % s.d.µl cv%
1 ±0.04 ±4.0 0.04 4.0
5 ±0.07 ±1.4 0.07 1.4
10 ±0.09 ±0.9 0.08 0.8
25 ±0.15 ±0.6 0.13 0.5
50 ±0.3 ±0.6 0.2 0.4
100 ±0.4 ±0.4 0.3 0.3
250 ±1.0 ±0.4 0.8 0.3
500 ±1.5 ±0.3 1.5 0.3
1000 ±3.0 ±0.3 0.3 0.3
2000 ±6.0 ±0.3 4.0 0.2
3000 ±9.0 ±0.3 6.0 0.2
5000 ±15.0 ±0.3 10.0 0.2
10000 ±30.0 ±0.3 20.0 0.2
日
本
語
Page 43

43
範囲
チャンネル数
検定容量 不正確度 不精密度
µl µl % s.d.µl cv%
1-10 µl 8, 12, 16 10 ±0.24 ±2.4 0.16 1.6
1 ±0.24 ±24 0.16 16
5-50 µl 8, 12, 16 50 ±1.0 ±2.0 0.4 0.8
5 ±1.0 ±20 0.4 8.0
10-100 µl 8, 12 100 ±0.80 ±0.8 0.30 0.3
10 ±0.80 ±8.0 0.30 3.0
30-300 µl 8, 12 300 ±8.0 ±2.7 3.0 1.0
30 ±8.0 ±26.7 3.0 10.0
調整
調整には、サービスツールを使用します。
1. サービスツールを、ハンドル上端にあるキャ
リブレーションナットの開口部に差し込みます。
2. サービスツールを時計回りに回すと分注容量
が増し、反時計回りに回すと分注容量が減
ります。
3. 調整後に、上の手順に従って再度検定を行い、
規格に適合するかどうかを確認してください。
計算式
重量から容量への変換
V = (w + e) x Z V =容量(µl)
w = 重量(mg)
e = 蒸発量(mg)
Z = 変換係数(µl/mg変換)
蒸発量は、特に微量の検定で問題になることがあります。蒸発量を調べるには、検定液
を測定容器に分注し、天秤で重量を読み取って記録し、直ちにストップウォッチを押し
ます。読み取り値が30秒でどのくらい減少するか(例えば6 mg = 0.2 mg/秒)を調べま
す。読み取った重量を風袋消去から読み取りまでにかかるピペッティング時間と比較し
ます。1回のピペッティング(風袋消去-分注-読み取り)に10秒かかるとすると、この
例では、蒸発量は2 mg(10s x 0.2mg/秒)になります。エヴァポレーショントラップや
容器のふたなどを使用する場合は、通常、蒸発に関する補正は必要ありません。
変換係数Zは、検定時の温度および気圧での水の重量を容量に換算するための係数で
す。例えば、22℃、95kPaの場合は、1.0032µl/mgです。詳しくは、48ページの変換係数
表を参照してください。
不正確度(システム誤差)
不正確度は、実際に分注された容量と設定した分注容量との差異です。
A = V - V
0
A = 不正確度
V = 分注容量の平均値
V
0
= 設定した分注容量
不正確度は、以下の相対値として表すことができます。 A% = 100% x A / V
0
不精密度(ランダム誤差)
不精密度は、ピペッティングの再現性を表します。不精密度は、標準偏差(s)または
変動係数(cv)で表します。
s = 標準偏差
V = 分注容量の平均値
n = 測定回数
標準偏差は、以下の相対値(CV)として表すことができます。
CV = 100% x S / V
メンテナンス
Finnpipette F2 を使用していないときは、必ずまっすぐ立てた状態で保管してくださ
い。このためには Finnpipette スタンドのご使用をお勧めします。
部品番号は、49ページから始まる分解図を参照するためのものです。
日
本
語
+
Page 44

44
短期点検
毎日、ピペットを使い始める前に、外側の表面に埃や汚れが付着していないことを確認
してください。
チップコーンには特に注意を払う必要があります。ピペットの洗浄には、70%エタノー
ル以外の溶剤は使用しないでください。
長期点検、シングルチャンネルピペット
日常的にピペットをご使用の場合、3ヵ月ごとに点検を行う必要があります。点検作業
はピペットの分解から開始します。
1-1000 µL のピペット
1. チップイジェクタを押します。
2. チップイジェクタ(11)を時計と反対方向に回し、引き出します。
3. サービスツールでチップコーンを時計と反対方向に回します。
4. ピストンおよびその他のパーツを引き出します。ピストンとともに
ピストンアセンブリの残りのパーツを押し出します。次にチップコ
ーンを上下逆さまにし、軽く叩いてチップコーンからすべての部品
を出します。組み立て直すときのためにすべての部品をテーブルの
上にきちんと並べておくことを忘れないでください。
5. けばのない乾いた布でピストン、ピストンスプリングおよびOリ
ングをきれいに拭きます。
6. チップコーンに異物が入っていないことを確認します。
7. きれいに拭いたパーツに、ピペットに付属しているグリースを塗
ります。
8. ピペットのパーうを元通りに組み立てます。
0.2-2 µL、0.5-5 µL および 1-10 µL:まず、スプリング
(22)、Oリングサポート(23)およびOリング(24)をチュ
ーブ(21)に装着します。 0.2-2 µLモデルについては、チュ
ーブ(27)をチューブ(21)に挿入します。次に
スプリング(13)、スプリングサポート(16)とチュ
ーブ(17および18)、大きい方のOリング(19)と小
さい方のOリング(20)をピストンに装着します。
ピストンとスプリングサポート(16)を指で挟んで押
して、スプリングを圧縮し、チューブ(21)を残りの
部品とともにピストンに装着します。スプリングを
圧縮した状態のまま、アセンブリ全体をチップコーンの中に注意深
く装着し、スプリングを緩めます。
2-20 µl:スプリング(13)、スプリング
サポート(16)とチューブ(17および18)、
大きい方のOリング(19)および小さい方
のOリング(20)をピストンに元通りに装
着します。ピストンとスプリングサポート
(16)を指で挟んで押してスプリングを圧
縮し、大きい方のOリング(19)、小さい
方のOリング(20)、スプリングサポート
(21)およびスプリング(22)(スプリン
グサポート(21)より直径が小さい)をピ
ストンに装着します。スプリングを圧縮し
た状態のまま、アセンブリ全体をチップコ
ーンの中に注意深く装着し、スプリングを
緩めます。
10-100 µl および 20-200 µl:スプリ
ング(13)、スプリングサポート(16)お
よびOリング(17)をピストンに 元通りに
装着します。アセンブリ全体をチップコー
ンの中に押し入れます。
100-1000 µL:Oリング(17)とサポート
リング(16)をチップコーンに取り付け
ます。スプリング(13)をピストンに装
着し、組立部全体をチップコーンの中に押し入れます。
9. すべてのタイプ:スプリング(15)およびサポート(14)をチップコーンの上に
置き、チップコーンアセンブリをハンドルにそっと挿入して、手でしっかりと回し
ます。
10. チップイジェクタを元通りに組み立てます。
日
本
語
1
3
2
1-200µl
200-1000µl
Page 45

45
0.5-5 ml および 1-10 ml のピペット
1. チップイジェクタを押し下げます。
2. チップイジェクタ(10)を時計と反対方向に回
して開けます。
3. チップイジェクタの下部(14)(留め金)
を分解します。
4. シリンダー(13)を時計と反対方
向に回し、チップコーンアセンブ
リを引き出します。
5. シリンダーの留め金を押して、
シリンダー(13)を外します。
6. Oリング(12)およびシリンダー
(13)をきれいに拭き、グリース
を塗ります。
7. 分解の逆の手順でパーツを組み立てます。
長期点検、マルチチャンネルピペット
日常的にピペットをご使用の場合、3ヵ月ごとに点検し、
グリースを塗る必要があります。
1. サービスツールのヘッドNO.1をリング(15)とイジェクタ(23)の間
に差し入れます。これらの部品がパチンと外れるまでツールを押します。
2. イジェクタレバーが上がった状態であることを確認し、モジュールのチップイジ
ェクタ部を引き下げます。
サービスツールのヘッドNO.2をアダプタチューブ(46)の穴に差し入れます。
3. チップイジェクタの上端をわずかに開き、チップイジェクタを外します。
4. ハンドルのモジュールのねじを外します。
5. モジュールスプリング(19)およびクリップ(22)を引き出します。
6. スプリング(13)を押し下げて、固定用パーツ(12)を溝から外します。スプリン
グ(13)を外します。
7. 固定ヅメ(44および45)を外し、アダプタチューブとチューブ(43)を引き出し
ます。
8. ドライバーを使ってモジュールカバーの4本のねじを外し、カバーを外します。
9. ピストンバーを外し、けばのない乾いた布でピストンとチップコーンをきれいに
拭きます。
10. 必要に応じてチップコーンを点検します。
16チャンネルの 1-10 µL:チップコーンの点検はできません。必要に応じて交
換してください。
30-300 µL、10-100 µL および 5-50 µL:ドライバーを使ってカバーリングをス
ナップジョイントから注意深く外し、チップコーンを開きます。チップコーンから
すべての部品を外します。すべてのパーツをきれいに拭きます。必要に応じてOリ
ングを交換します。ピストンを1つ取ります。スプリング(33)、カバーリング
(32)(穴の大きいもの)、スプリング(34)、サポートリング(35)、(5-50µl
の場合:大きい方の Oリング(37))およびOリング(36)(小さい方)をピスト
ンに装着します。ピペットのパッケージに付属しているグリースをOリングに塗
ります。すべてのパーツをチップコーンに押し入れて、カバーリングのスナップ
ジョイントを閉じます。
1–10 µL:ドライバーを使ってカバーリングをスナップジョイントから注意深く
外し、チップコーンを開きます。チップコーンからすべてのパーツを外します。す
べてのパーツをきれいに拭きます。必要に応じてOリングを交換します。ピストン
を1つ取ります。スプリング(33)、カバーリング(32)(穴の大きなもの)、サポ
ート(35)、大きい方のOリング(36)、小さい方のOリング(37)およびOリン
グサポート(38)をピストンに装着します。次に、スプリング(39)、スプリング
サポート(40)(尖った側から)およびOリング(41)をOリングサポート(38)
に装着します。 ピペットのパッケージに付属しているグリースをOリングに塗り
ます。すべてのパーツをチップコーンに押し入れて、カバーリングのスナップジョ
イントを閉じます。
11. ピストンとチップコーンとともにピストンバーをカバーの中に取り付けて、4本の
ねじで カバーを閉じます。クリップ(22)を挿入します。
12. アダプタチューブとチューブ(43)をモジュールのネックの部分に置き、固定ヅメ
(44および45)を挿入します。モジュールスプリング(19)を挿入します。
13. スプリング(13)と固定用パーツ(12)をピストン棒(16)に挿入します。
14. チップイジェクタをモジュールの上に置きます。スプリング(19)をチップイジェ
クタに押し入れ、イジェクタの上端部を指で覆って閉じた状態にします。
15.サービスツールのヘッドNO.2を使ってモジュールをハンドルの中にねじ止めします。
16. チップイジェクタのレバーをカチッという音がするまで押し下げます。
1
2
3
日
本
語
Page 46

46
原因
チップが正しく装着されていない
チップコーンとチップの間に異物が
ある
ピストン,O-リング及びシリンダの間
に異物がある
グリース切れ
O-リングの磨耗
操作が正しく行われていない
チップが正しく装着されていない
キャリブレーションのずれ(誤操作な
どのため)
不適切なキャリブレーション
(粘性の高い液体はその液体でキャリ
ブレーションを行う必要がある)
症状
液漏れ
分注精度が
悪い
特定の液体の
分注精度が
悪い
対処方法
チップをしっかり装着
する
チップコーンをきれいに
し,新しいチップを装着
する
ピストン、O-リングとシ
リンダをきれいにし,グ
リースを塗る
O-リング,シリンダ,プ
ストンにグリースを塗る
O-リングを交換する
取扱説明書にしたがって
注意深く操作する
チップをしっかり装着
する
取扱説明書にしたがって
キャリブレーションを
行う
分注する液体を使用して
キャリブレーションを
行う
日
本
語
マルチチャンネルピペット用チップコーンの点検について
マルチチャンネルピペットのすべてのチャンネルで均一な性能を実現するため、いずれ
かのチップコーンを交換する必要が生じた場合、すべてのチップコーンを同時に交換す
る必要があります。交換用パーツのパッケージにはセットされたチップコーンが入って
いるため、別のパッケージのチップコーンを混ぜて使用しないでください。
滅菌
フィンピペットF2は121℃で20分間オートクレーブ滅菌することができます。必要に応
じて滅菌バッグをご使用ください。
オートクレーブ滅菌後は,ピペットが室温に戻るまで少なくとも2時間冷却してくださ
い。ピペットを使う前に,ピペットが乾いているかどうかを確認してください。滅菌後
は,毎回キャリブレーションを実施することをお勧めします
トラブルシューティング
注意!
フィンピペットは,ユーザーの皆様自身で簡単にメンテナンスしていただけるよう
に設計されています。
修理や検定のために販売元へ返をされる場合には,返送前に必ず汚染除去/消毒を行
ってください。
Page 47

47
日
本
語
パッケージ
Finnpipette F2 は、専用パッケージに入れてお届けします。パッケージ内容は以下の
とおりです:
1. Finnpipette F2
2. サービスツール
3. マルチチャンネルサービスツール
4. Finntip (サンプル)
5. チューブ入グリース
6. 取扱説明書
7. 検定証明書兼保証書
8. シェルフハンガー
9. シール2枚
保証規定
万一,故障,不具合が生じた場合には,下記の規定に従って修理させていただきます。
ご購入いただきました販売店または下記の輸入販売元にお申し付けください。
保証期間 ご購入の日から3年間 (但し,Web登録した場合は5年間。
保証登録URL: www.thermofisher.co.jp/finn/w )
保証書 同封の「Finnpipette Warranty Certificate(英文)」が保
証書となります。
紛失しないよう大切に保管してください。
無償修理の範囲 以下の条件を満たす場合は,無償で修理いたします。
1. 保証期間内であること。
2. 保証書(Finnpipette Warranty Certificate, 英文)
の添付があること。
3. 本取扱説明書にしたがい,通常の用法でご使用の場合。
4. フィンピペットに,純正フィンチップを組合せてご使用の
場合。
5. その他製造上,材質上の欠陥が原因と認められた場合。
有償修理の範囲 以下の場合の修理は,保証期間内であっても,有償と
させていただきます。
1. 誤った使用が原因の故障または損傷。
2. 不当な修理改造による故障または損傷。
3. 納品後の移動,輸送あるいは落下が原因の場合。
4. 火災,天災地変その他不可抗力の災害による場合。
5. 過度の使用が原因の摩耗,損傷。
6. O-リング等の消耗部品の摩耗。
7. キャリブレーションまたはクリーニングを依頼される場合。
8. 物理的損傷または化学薬品による損傷。
9. 保証書(Finnpipette Warranty Certificate, 英文)
の添付がない場合。
輸入販売元 サーモフィッシャーサイエンティフィック株式会社
ラボプロダクツ事業本部
〒221-0022 横浜市神奈川区守屋町3-9 C棟
問合せ先 フィンピペットサービス
TEL 045-453-9227 FAX 045-453-9228
Page 48

48
Temperature Air pressure
°C kPa
80 85 90 95 100 101,3 105
15,0 1,0017 1,0018 1,0019 1,0019 1,0020 1,0020 1,0020
15,5 1,0018 1,0019 1,0019 1,0020 1,0020 1,0020 1,0021
16,0 1,0019 1,0020 1,0020 1,0021 1,0021 1,0021 1,0022
16,5 1,0020 1,0020 1,0021 1,0021 1,0022 1,0022 1,0022
17,0 1,0021 1,0021 1,0022 1,0022 1,0023 1,0023 1,0023
17,5 1,0022 1,0022 1,0023 1,0023 1,0024 1,0024 1,0024
18,0 1,0022 1,0023 1,0023 1,0024 1,0025 1,0025 1,0025
18,5 1,0023 1,0024 1,0024 1,0025 1,0025 1,0026 1,0026
19,0 1,0024 1,0025 1,0025 1,0026 1,0026 1,0027 1,0027
19,5 1,0025 1,0026 1,0026 1,0027 1,0027 1,0028 1,0028
20,0 1,0026 1,0027 1,0027 1,0028 1,0028 1,0029 1,0029
20,5 1,0027 1,0028 1,0028 1,0029 1,0029 1,0030 1,0030
21,0 1,0028 1,0029 1,0029 1,0030 1,0031 1,0031 1,0031
21,5 1,0030 1,0030 1,0031 1,0031 1,0032 1,0032 1,0032
22,0 1,0031 1,0031 1,0032 1,0032 1,0033 1,0033 1,0033
22,5 1,0032 1,0032 1,0033 1,0033 1,0034 1,0034 1,0034
23,0 1,0033 1,0033 1,0034 1,0034 1,0035 1,0035 1,0036
23,5 1,0034 1,0035 1,0035 1,0036 1,0036 1,0036 1,0037
24,0 1,0035 1,0036 1,0036 1,0037 1,0037 1,0038 1,0038
24,5 1,0037 1,0037 1,0038 1,0038 1,0039 1,0039 1,0039
25,0 1,0038 1,0038 1,0039 1,0039 1,0040 1,0040 1,0040
25,5 1,0039 1,0040 1,0040 1,0041 1,0041 1,0041 1,0042
26,0 1,0040 1,0041 1,0041 1,0042 1,0042 1,0043 1,0043
26,5 1,0042 1,0042 1,0043 1,0043 1,0044 1,0044 1,0044
27,0 1,0043 1,0044 1,0044 1,0045 1,0045 1,0045 1,0046
27,5 1,0045 1,0045 1,0046 1,0046 1,0047 1,0047 1,0047
28,0 1,0046 1,0046 1,0047 1,0047 1,0048 1,0048 1,0048
28,5 1,0047 1,0048 1,0048 1,0049 1,0049 1,0050 1,0050
29,0 1,0049 1,0049 1,0050 1,0050 1,0051 1,0051 1,0051
29,5 1,0050 1,0051 1,0051 1,0052 1,0052 1,0052 1,0053
30,0 1,0052 1,0052 1,0053 1,0053 1,0054 1,0054 1,0054
Conversion table
Value of the conversion factor Z (µl/mg), as a function of temperature and pressure, for
distilled water.
Umrechnungstabelle
Wert des Umrechnungsfaktors Z (µl/mg) als eine Funktion von Temperatur und Druck für
destilliertes Wasser.
Table de conversion
Valeur du facteur de conversion Z (µl/mg), comme fonction de la température et de la pression,
pour de l’eau distillée.
Tabla de conversiones
Valor del factor de conversión Z (µl/mg), como función de temperatura y presión, para el
agua destilada.
変換係数表
変換係数 Z (μl/mg)は温度と気圧の関数になります。蒸留水の場合の値を表に示します。
Page 49

49
Spare parts
Ersatzteile
Pieces detachees
Piezas de recambio
パーツ及び付属品
1-10 ml
6-10 ml Fixed
1 µl - 10 ml
1. 1062800
2. 2211810 Fixed
1 -300 µl MCP
4. 1062930
1-10 ml 2211670
6-10 ml Fixed 2211920
2. 2211590
3. 2211100
3. 2211250 10ml
0,5-5 ml 2211660
2-5 ml Fixed 2211910
2. 2211580
3. 2211090
3. 2211240 5ml
3. 2211230 3ml
3. 2211220 2ml
2
3
10
11
12
13
14
0,5-5 ml
2-5 ml Fixed
10
11
12
13
14
1
4
Page 50

50
12
14
15
13
11
10
17
16
100-1000µl
250 µl Fixed
500 µl Fixed
1000µl Fixed
2211640
2. 2211570
3. 2211080
3. 2211190 250µl
3. 2211200 500µl
3. 2211210 1000µl
20-200µl 2211630
2. 2211550
3. 2211070
10-100µl
25 µl Fixed
50 µl Fixed
100 µl Fixed
2211620
2. 2211550
3. 2211060
3. 2211160 25µl
3. 2211170 50µl
3. 2211180 100µl
20-200µl 10-100µl
25 / 50 / 100µl
Fixed
12
14
15
13
11
10
17
16
12
14
15
13
11
10
17
16
100-1000µl
250 / 500 / 1000µl
Fixed
Page 51

51
2-20µl / 2-20µl Micro
2-20µl
2211610
2-20 µl Micro
2211600
2. 2211550
2. 2211560 Micro
3. 2211050
3. 2211040 Micro
1-10µl
10 µl Fixed
2211540
1-10 µl Micro
2211510
2. 2211550
2. 2211520 Micro
3. 2211030
3. 2211020 Micro
3. 2211150 10µl
1-10µl / 1-10µl Micro
10µl Fixed
12
13
12
13
11
10
11
10
14
15
17
16
18
19
21
20
22
14
15
17
16
18
19
21
20
22
23
24
Page 52

52
0,5-5 µl
5 µl Fixed
0,5-5 µl / 5 µl
Fixed
2211900
2. 2211520
3. 2211010
3. 2211140 5µl
0,2-2 µl / 1 µl
Fixed
2211890
2. 2211520
3. 2211000
3. 2211130 1µl
12
13
12
13
11
10
11
10
14
15
17
16
18
19
21
20
22
14
15
17
16
18
19
21
20
22
23
24
0,2-2 µl
1 µl Fixed
23
24
27
28
Page 53

53
1-10µl 8-ch 2211260
1-10µl 12-ch 2211270
2. 2211520
3. 2211020
10-100µl 8-ch 2211300
10-100µl 12-ch 2211310
2. 2211550
3. 2211060
15
12
13
19
40
32
17
16
18
39
31
35
33
36
37
38
41
30
46
21
21
22
23
24
42
44
43
45
32
31
30
35
34
36
10-100µl
33
Page 54

54
5-50µl 8-ch 2211280
5-50µl 12-ch 2211290
2. 2211560
3. 2211110
30-300µl 8-ch 2211320
30-300µl 12-ch 2211330
2. 2211680
3. 2211120
30-300µl
33
30
31
32
34
35
36
37
42
21
21
22
23
42
33
31
32
34
30
35
36
15
12
13
19
17
16
18
46
44
43
45
Page 55

55
1-10µl 16-ch 2211340
2. 2211800
3. 2211830
5-50µl 16-ch 2211350
2. 2211560
3. 2211110
15
12
13
19
33
17
16
46
30
31
34
37
32
35
36
45
43
44
21
21
22
24
42
18
23
1-10µl
31
37
42
33
Page 56

56
Finntip (sterile and non-sterile) Finntip Filter (sterile)
10 Micro
10 Flex micro
10 Flex micro 384
50 Micro
250 univ
200 ext
200 Flex
300
300 Flex
1000 Ext
1000
1000 Flex
5 ml
10ml
10ml Flex Ext
10 Micro
10 Univ
20 Univ
10 Flex micro
30 Univ
50 Micro
100 Ext
100 Univ
200 Ext
200 Flex
200 Univ
300
300 Flex
1000 Ext
1000
1000 Flex
5 ml
10ml
10ml Flex Ext
FP F2 0.2 - 2 µl
• • • •
• • •
FP F2 0.5 - 5 µl
• • • •
• • •
FP F2 1 - 10 µl micro
• • • •
• • •
FP F2 1 - 10 µl
• • • • •
• • • • • •
FP F2 2 - 20 µl micro
•
• •
FP F2 2 - 20 µl
• • • • •
• • • • • •
FP F2 10 - 100 µl
• • • • •
• • • • •
FP F2 20 - 200 µl
• • • • •
• • •
FP F2 100 - 1000 µl
• • •
• •
FP F2 0.5 - 5 ml
• •
FP F2 1 - 10 ml
• •
• •
Page 57

57
FP F2 Fixed Volume 1 µl
• • • •
• • •
FP F2 Fixed Volume 5 µl
• • • •
• • •
FP F2 Fixed Volume 10 µl
• • • • •
• • • • • •
FP F2 Fixed Volume 25 µl
• • • • •
• • • • • •
FP F2 Fixed Volume 50 µl
• • • • •
• • • • •
FP F2 Fixed Volume 100 µl
• • • • •
• • • • •
FP F2 Fixed Volume 250 µl
• • •
FP F2 Fixed Volume 500 µl
• • •
FP F2 Fixed Volume 1000 µl
• • •
FP F2 Fixed Volume 2000 µl
•
FP F2 Fixed Volume 3000 µl
•
FP F2 Fixed Volume 5000 µl
•
FP F2 Fixed Volume 10000 µl
• •
FP F2 8-Ch 1-10
• • • •
• • •
FP F2 12-Ch 1-10
• • • •
• • •
FP F2 8-Ch 5-50
• • • • •
FP F2 12-Ch 5-50
• • • • •
FP F2 8-Ch 10-100
• • • • •
FP F2 12-Ch 10-100
• • • • •
FP F2 8-Ch 30-300
• •
FP F2 12-Ch 30-300
• •
FP F2 16-Ch 1-10
• •
FP F2 16-Ch 5-50
•
Page 58

58
Tip Ordering Information
Bestellinformation: Pipettenspitzen
Renseignements pour commander des cônes
Información para pedidos del portapuntas
チップの注文について
Code Finntip Volume Qty
* 9400300 10 Micro 0,2-10 µl 10x96/rack
9400303 10 Micro sterile 0,2-10 µl 10x96/rack
* 9400370 50 Micro 0,2-50 µl 10x384/rack
9400373 50 Micro sterile 0,2-50 µl 10x384/rack
9400130 200 Ext 5-200 µl 10x96/rack
9400133 200 Ext sterile 5-200 µl 10x96/rack
* 9400260 250 Univ. 0,5-250 µl 10x96/rack
9400263 250 Univ. sterile 0,5-250 µl 10x96/rack
* 9401250 300 5-300 µl 10x96/rack
9401253 300 sterile 5-300 µl 10x96/rack
* 94060510 Flex 300 0,5-300 µl 10x96/rack
94060513 Flex 300 sterile 0,5-300 µl 10x96/rack
* 9401110 1000 100-1000 µl 10x96/rack
9401113 1000 sterile 100-1000 µl 10x96/rack
94060810 Flex 1200 100-1200 µl 10x96/rack
94060813 Flex 1200 sterile 100-1200 µl 10x96/rack
* 9402070 5 ml 1-5 ml 5x54/rack
9402073 5 ml sterile 1-5 ml 5x54/rack
* 9402160 10 ml 2-10 ml 5x24/rack
9402163 10 ml sterile 2-10 ml 5x24/rack
* Also available in bags
Code Finntip Filter Volume Qty
94052000 10 Micro sterile 0,2-10 µl 10x96/rack
94052020 20 Micro sterile 0,5-20 µl 10x384/rack
94052060 50 Micro sterile 0,2-50 µl 10x384/rack
94052100 10 sterile 0,5-10 µl 10x96/rack
94052150 20 sterile 0,5-20 µl 10x96/rack
94052160 30 sterile 0,5-30 µl 10x96/rack
94052200 100 µl sterile 0,5-100 µl 10x96/rack
94052310 100 µl Ext sterile 5-100 µl 10x96/rack
94052300 200 µl sterile 0,5-200 µl 10x96/rack
94052320 200 µl Ext sterile 5-200 µl 10x96/rack
94052350 300 µl sterile 5-300 µl 10x96/rack
94052410 1000 µl sterile 100-1000 µl 10x96/rack
94052430 1000 µl Ext sterile 100-1000 µl 5x96/rack
94052550 5 ml sterile 1-5 ml 5x54/rack
94052600 10 ml sterile 2-10 ml 5x24/rack
Page 59

59
Page 60

60
Thermo Fisher Scientific Oy
Ratastie 2, P.O.Box 100
FI-01621 Vantaa
Finland
info.pipettes@thermofisher.com
www.thermo.com/finnpipette
1508700
©
2008 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...