Page 1

Getting started guide
PrimeFlow RNA Assay
Conjugated
antibodies
Flow RNA Flow cytometry
instrument
Page 2

Contents
1. Introduction 3
2. Workflow summary 4
3. Things to consider 6
4. Checklist—what you’ll need 8
5. FAQs 9
6. Ordering information 10
7. Additional resources 10
Page 3
1. Introduction
Label probe
What is the PrimeFlow RNA Assay?
The Invitrogen™ PrimeFlow™ RNA Assay employs
fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with branched-DNA
(bDNA) signal amplification for the simultaneous detection
of up to four RNA targets. This assay can also be used
in combination with immunolabeling of both cell-surface
and intracellular proteins using fluorophore-conjugated
antibodies and detection by flow cytometry. The PrimeFlow
RNA Assay can detect messenger RNA (mRNA), long
noncoding RNA (lncRNA), and microRNA (miRNA).
What is bDNA signal amplification?
bDNA signal amplification is achieved through sequential
hybridization steps with preamplifiers, amplifiers, and
fluorophore-conjugated label probes (Figure 1). A fully
assembled signal amplification “tree” has 400 label-probe
binding sites. When all target-specific oligonucleotides in
the probe set bind to the target RNA transcript, 8,000- to
16,000-fold amplification can be achieved.
The purpose of this guide is to provide all the necessary
information to help you get started with the PrimeFlow RNA
Assay and walk you through the design and workflow of an
experiment using the PrimeFlow RNA Assay.
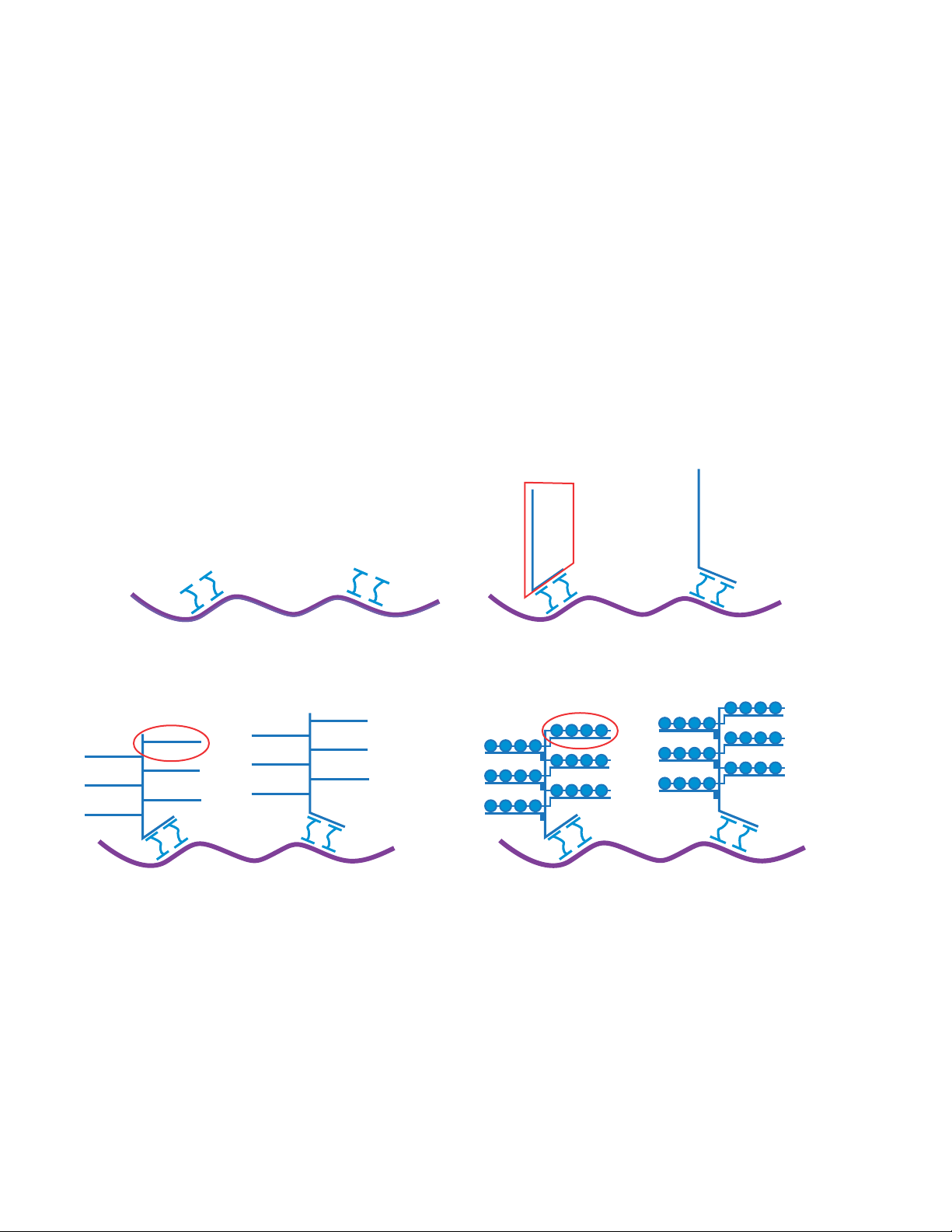
BA
Preamplifier
mRNA
Probe set
C D
Amplifier
Figure 1. Signal amplification by sequential hybridization of oligonucleotides. (A) Gene-specific probe sets are hybridized to target RNA transcripts.
(B) Preamplifier (“trunk”) binds to a probe set. (C) Amplifiers (“branches”) bind to multiple sites on the preamplifier. (D) Fluorophore-conjugated label
probes (“leaves”) bind to multiple sites on the amplifiers.
3
Page 4

2. Workflow summary
Add Label Probes to
cells
Target
Hybridization
Signal
Amplification
Detection
PreAmplifier
Amplifier
Fluorescent Label
Probe
Gene-specific Label
Extenders (LE)
Gene-specific
Blocking Probes (BL)
Hybridization of
Pre-Amplifier and
Amplifier DNA
(Type 1, 4, and 6)
process cells using
a standard Flow
Cytometer Instrument
Add Label Probes to
cells
Incubate cells with
Gene Specific
probe sets
(Type 1, 4 or 6)
Sample
Preparation
Target
Hybridization
Signal
Amplification
Detection
PreAmplifier
Amplifier
Fluorescent Label
Probe
Gene-specific Label
Extenders (LE)
Gene-specific
Blocking Probes (BL)
Hybridization of
Pre-Amplifier and
Amplifier DNA
(Type 1, 4, and 6)
process cells using
a standard Flow
Cytometer Instrument
Target
Hybridization
Signal
Amplification
Detection
PreAmplifier
Fluorescent Label
Gene-specific Label
Target
Hybridization
Signal
Amplification
Detection
PreAmplifier
Fluorescent Label
Probe
Gene-specific Label
Extenders (LE)
PrimeFlow RNA Assay workflow summary
In the PrimeFlow RNA Assay workflow, cells are first labeled
with cell-surface antibodies, fixed and permeabilized, and
then labeled with intracellular antibodies. Next, these cells
are sequentially hybridized with probes specific to the RNA
targets, and hybridized targets are detected after bDNA
signal amplification.
Protocol flowchart
Day 1
Sample preparation Target hybridization
Antibody fixation and permeabilization Target probe hybridization
The PrimeFlow RNA Assay currently oers four unique
amplifications of bDNA structures that allow simultaneous
measurement of up to four dierent RNA targets for
multicolor flow cytometry analysis.
Fix and permeabilize cells in the presence of
Stain cells with antibodies to intracellular antigens
* If using compensation beads provided in the k it, the preparation should be done on day 2.
4
Harvest cells
Prepare single-color
compensation controls*
Stain cells with an eBioscience
Fixable Viability Dye
Stain cells with antibodies to
cell-surface antigens
RNase inhibitors
(optional)
Gene 1
Gene 2
Add target probes to
cell suspension
Incubate at 40°C for 2 hr
Gene-specific
label ex tenders (LE)
Page 5

Detection
Fluorescent Label
Probe
Add Label Probes to
cells
Signal
Amplification
Detection
PreAmplifier
Amplifier
Fluorescent Label
Probe
Hybridization of
Pre-Amplifier and
Amplifier DNA
(Type 1, 4, and 6)
process cells using
a standard Flow
Cytometer Instrument
General precautions on experiments
• Prepare buers (PrimeFlow RNA Fixation Buers 1 and 2,
and RNA Permeabilization Buer with RNase Inhibitors)
each time as necessary for sample preparation. Do not
prepare buer in advance to cover multiple experiments
for dierent days.
• Control the incubator temperature in target hybridization
steps (40 ± 1°C) accurately.
• When diluting and adding antibodies, probes, and
labeling reagents in the sample preparation, target
hybridization, and signal amplification steps, place
the tip directly onto the liquid surface to avoid making
bubbles in the liquid.
Day 2
Signal amplification Detection
• During permeabilization of cells, take precautions to avoid
precipitation after adding PrimeFlow Permeabilization
Buer with RNase Inhibitors to samples by following
these steps:
– Centrifuge > discard supernatant > suspend carefully
in the residual 100 µL volume (using markings on the
tube as a guide and checking to make sure the solution
becomes cloudy as uniformly as possible).
• After the target probe hybridization step, be sure to use
the specialized tube attached to the kit.
Signal amplification Detection and analysis
Add PrimeFlow RNA PreAmp mix to
cell suspension
Incubate at 40°C for 1.5 hr
Add PrimeFlow RNA Amp mix to
cell suspension
Incubate at 40°C for 1.5 hr
Add label probes to
cell suspension
Incubate at 40°C for 1 hr
Perform Attune NxT Flow Cytometer setup,
compensation, and analysis
Process cells using
a flow cytometer
CD8 mRNA Alexa Fluor 647
CD8 PE-Cyanine7
5
Page 6

3. Things to consider
Precisely control the temperature of incubator
The assay is highly dependent on temperature. Ensure
that the incubator holds the temperature at 40 ± 1°C. A
significant reduction in signal will result from temperature
deviations greater than 1°C. To ensure the correct
temperature control in samples, follow the steps for setting
up the Invitrogen™ ViewRNA™ Temperature Validation Kit
(Figure 2).
A CB D
Make a hole through the cap of
a 1.5 mL tube.
Figure 2. Steps for setting up the ViewRNA Temperature Validation Kit.
Select compatible dyes for cell-surface and/or
intracellular labeling of proteins
Compatible dyes
•
• Organic fluorescent dyes (Invitrogen™ FITC, eBioscience™
eFluor™ 450, eFluor™ 506, eFluor™ 660, Alexa Fluor™ 700,
Brilliant™ Violet, Super Bright dyes, etc.)
• Most fluorescent proteins (Invitrogen™ PE, PE-eFluor™
610, PE-Cyanine5, PE-Cyanine5.5, PE-Cyanine7, APC,
APC-eFluor™ 780, etc.)
Incompatible dyes
•
• Invitrogen™ eBioscience™ PerCP-Cyanine 5.5,
PerCP-eFluor™ 710
• Invitrogen™ Qdot™ nanocrystal, eBioscience™ eVolve
dye–conjugated antibodies
Place electric sensor from the
ViewRNA Temperature Validation
Kit through the tube.
Put a tube with a code to the
metal heat block in an incubator.
Make sure you have the right buer for your target
If your target is microRNA, Invitrogen™ PrimeFlow™
microRNA Pretreatment Buer (Cat. No. 88-18006) is
recommended. This reagent helps ensure that you get
improved signal and better sensitivity for miRNA.
Make sure you have V-bottom plates
When the assay is processed in a 96-well plate, V-bottom
plates are recommended; do not use flat-bottom plates.
A modified protocol for the use of polystyrene 96-well
plates is available in Appendix 7 of the PrimeFlow RNA
Assay User Manual.
Make sure you use a swinging-bucket centrifuge
To maximize cell recovery, use a swinging-bucket
centrifuge. Using fixed-angle centrifuge will result in
significant cell loss.
Overview of setup.
6
Page 7

Determine the best probe set for your target
• Four types of probe sets are currently available for
RNA detection
• For multiplex analysis with immunolabeling of both
cell-surface and intracellular proteins, use fluorophoreconjugated antibodies
• Select dierent types of probe sets depending on the
expression level of RNA (Table 1)
Table 1. Probe sets for RNA detection.
Probe type/fluorescent
label Laser Channel
Type 1/Alexa Fluor 647 633 (red) APC, Alexa Fluor 647, eFluor 660 Low
Type 10/Alexa Fluor 568 561 (yellow) PE-Texas Red, PE-eFluor 610, Alexa Fluor 568 Low
Type 4/Alexa Fluor 488 488 (blue) FITC, Alexa Fluor 488 Medium to high
Type 6/Alexa Fluor 750 633 (red) APC-Cy7, APC-eFluor 780, Alexa Fluor 750 Medium to high
Expression level
of detected gene
Set controls to obtain clear results
The following controls are recommended to obtain clear
results. Figure 3 demonstrates an example of control and
sample placement.
Sensitivity
of the probe
• Positive-control probe sets (RPL13A for human, ACTB for
mouse, etc.)
• Negative-control probe sets (samples with the targetspecific probe omitted, or samples labeled with a probe
against a target not expressed in the cells of interest)
Protein RNA
Sample #
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
FVD eFluor
450
CD3-SB600 CD8-PE CD14 -PE-C y7
• Single-color compensation samples
• Fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls
Tbet-Alexa
Fluor 647
CD8-Alexa
Fluor 488
ACTB-Alexa
Fluor 750
Positive control
Single-color
compensation sample
FMO controls
Figure 3. Example of controls that are required for an experiment having a viability marker along with detection of three proteins and three
RNA targets.
7
Page 8

4. Checklist—what you’ll need
Reagents
PrimeFlow RNA Assay Kit
PrimeFlow target probe set
(Find targets at thermofisher.com/primeflow)
Invitrogen™ eBioscience™ Flow Cytometry
Staining Buer
Optional
For protein detection: fluorescently labeled antibodies
(Find at thermofisher.com/antibody)
For viability check: viability marker (fixable viability dyes,
Invitrogen™ LIVE/DEAD™ fixable dyes, etc.)
For microRNA detection: Invitrogen™ PrimeFlow™
microRNA Pretreatment Buer
Controls
Positive-control probe sets (RPL13A for human, ACTB
for mouse, etc.)
Negative-control probe sets (samples with the targetspecific probe omitted, or samples labeled with a
probe against a target not expressed in the cells
of interest)
Instruments
Flow cytometer:
– Three lasers: blue (488 nm), yellow-green (561 nm), and
red (633 nm or similar)
– Detection optics optimized for FITC, PE-eFluor 610 (PE-
Texas Red), APC, and APC-eFluor 780 (APC-Cyanine7)
Incubator:
– Capable of maintaining temperature at 40 ± 1°C
Metal heat block for 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube,
placed inside the validated incubator
ViewRNA Temperature Validation Kit (Cat. No. QV0523)
Swinging-bucket centrifuge with adaptors for 15 mL
conical tubes and 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes
Aspirator system for washing—aspiration rate adjusted
to 0.5 mL/sec; can use in-house vacuum line or
vacuum pump
Optional
For 96-well plate assay: V-bottom shape 96-well plates
Single-color compensation samples
Fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls
8
Page 9

5. Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Q: Which species are compatible with the PrimeFlow
RNA Assay?
Q: When using the PrimeFlow RNA Assay kit with the
PrimeFlow microRNA Pretreatment Buer, can we
combine miRNA and mRNA staining?
Q: Can you detect rare populations in a heterogeneous mix
of cells using the PrimeFlow RNA Assay?
Q: What is the minimum length of targeted sequence
needed to design the probe sets for use with the
PrimeFlow RNA Assay?
Q: When using the PrimeFlow RNA Assay, what is the
sensitivity (limit of detection) for RNA staining?
A: We have tested the PrimeFlow RNA Assay on mouse
and human cells. The assay is expected to work on
other mammalian species and has been reported to
work in some nonmammalian species. However, this
should be determined empirically.
A: Yes, it is possible to perform any combination of miRNA
and mRNA up to a total of four targets.
A: This assay can be used to detect cell populations that
represent greater than 1% of the total cells.
A: For optimal sensitivity, a minimum of 1 kb is
recommended to design target probe sets with sucient
sensitivity for medium- and high-expressing genes. For
low-expressing genes, a minimum of 2 kb of sequence
is recommended.
A: Under fully optimized conditions, we estimate that
10–20 copies can be detected per cell for Type 1 or
Type 10; and about 30 copies per cell for Type 4 or
Type 6. The actual sensitivity may vary depending on the
specific target.
Q: Can you design custom probes?
Q: What can I use the PrimeFlow RNA Assay for?
Q: Is the PrimeFlow RNA Assay compatible with live- and
dead-cell determination?
Q: Is the PrimeFlow RNA Assay compatible with
extracellular and intracellular staining?
A: By request, PrimeFlow probe sets can be designed
and synthesized at no additional cost. Please provide
the following information when ordering: accession
number (including version or GI number) or RNA
sequence for the target of interest, species, gene
name or symbol, PrimeFlow probe set type, and
any special design requirements. Please contact
flowsupport@thermofisher.com for more information.
A: It can be used for the following key application areas:
• Probing mRNA when an antibody to the protein target
is unavailable
• Analyzing mRNA expression at the single-cell level
• Comparing RNA and protein kinetics in the same cell
• Detecting miRNA
• Detecting viral RNA in infected cells
• Verifying single-cell RNA sequencing results
A: Yes.
A: Yes.
9
Page 10

6. Ordering information
Product Quantity Cat. No.
PrimeFlow probe sets
PrimeFlow RNA Assay Kit*
• PrimeFlow RNA Tubes
• PrimeFlow RNA Fixation Buer 1A
• PrimeFlow RNA Fixation Buer 1B
• PrimeFlow RNA Permeabilization Buer (10X)
• PrimeFlow RNA Fixation Buer 2 (8X)
• PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buer
• PrimeFlow RNA Target Probe Diluent
• PrimeFlow RNA PreAmp Mix
• PrimeFlow RNA Amp Mix
• PrimeFlow RNA Label Probe Diluent
• PrimeFlow RNA Storage Buer
• PrimeFlow RNase Inhibitors (100X)
• PrimeFlow Compensation Kit
• IC Fixation Buer
ViewRNA Temperature Validation Kit 1 QV0523
eBioscience Flow Cytometry Staining Buer 200 mL 00-4222-57
Optional: Is your target microRNA? This buer helps ensure you get improved signal and better sensitivity
for miRNA.
PrimeFlow microRNA Pretreatment Buer 100 tests 88-1800 6
Go to step 4 under the ordering information at
thermofisher.com/primeflow
40 tests
100 te sts
88-18005-204
88-18005-210
Optional: Will the assay be processed in a 96-well plate?
PrimeFlow 96-well plate 10 packets 44-170 0 5 -46
* The PrimeFlow RNA A ssay Kit provides a complete bu er system, compensation kit, and reagents for detecting up to four RNA transcripts in mammalian cells optionally labeled with antibodies that recognize
cell-surface or intracellular proteins.
7. Additional resources to help you get started
Resource
• Use our Custom Branched DNA Probe Set Tool at thermofisher.com/custom-bDNA
• Find fluorescently labeled antibodies for protein detection at thermofisher.com/antibody
• Learn more about the Invitrogen™ Attune™ NxT Flow Cytometer at thermofisher.com/attune
• See publications citing the use of the PrimeFlow RNA Assay at thermofisher.com/primeflowpublications
• View webinars about the PrimeFlow RNA Assay at thermofisher.com/primeflow
Find out more at thermofisher.com/primeflow
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Super Bright Polymer Dyes are sold under license from
Becton, Dickinson and Company. Not for resale. © 2019–2021 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. All trademarks
are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific and its subsidiaries unless otherwise specified. Cy is a registered trademark of GE
Healthcare. COL014712 0321
 Loading...
Loading...