
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
DIGITAL STORAGE OSCILLOSCOPE
DCS-9700 SERIES
DCS-9730
DCS-9730D
DCS-9720
DCS-9720D
DCS-9710
DCS-9710D
DCS-9707
DCS-9707D
B71-0206-11

■ About a trademark, a registered trademark
A company name and the brand name mentioned in this instruction
manual are the trademark or the registered trademark of each
company or group in each country and region.
■ About this instruction manual
When copying the part or all of contents of this instruction manual,
seek the copyright holder.
In addition, the specifications of the product and the contents of
this instruction manual are subject to change without notice for
improvement. Please check to our website for the latest version.
■ About export
When export or ship the product to overseas, please confirm laws
and regulations about the export.

Table of Contents
USING THE PRODUCT SAFELY...................................................Ⅰ-Ⅴ
1. GETTING STARTED ................................................................... 1
1-1. Main Features ...................................................................... 1
1-2. Accessories .......................................................................... 3
1-3. Panel Overview .................................................................... 4
1-3-1. Front Panel ........................................................................................ 4
1-3-2. Rear Panel ...................................................................................... 10
1-3-3. Display............................................................................................. 12
1-4. Set Up ............................................................................... 14
1-4-1. Tilt Stand ......................................................................................... 14
1-4-2. Module Installation .......................................................................... 15
1-4-3. Software Installation ........................................................................ 16
1-4-4. Power Up ......................................................................................... 16
1-4-5. First Time Use ................................................................................. 17
1-4-6. How to Use This Manual ................................................................. 19
2. QUICK REFERENCE ................................................................ 24
2-1. Menu Tree / Operation Shortcuts ......................................... 24
2-1-1. Convention ...................................................................................... 24
2-1-2. Acquire Key ..................................................................................... 25
2-1-3. Acquire Key – Segments ................................................................. 25
2-1-4. Autoset Key ..................................................................................... 26
2-1-5. CH1 ~ 4 Key .................................................................................... 26
2-1-6. Cursor Key ...................................................................................... 26
2-1-7. Display Key ..................................................................................... 27
2-1-8. Help Key .......................................................................................... 27
2-1-9. Math Key ......................................................................................... 28
2-1-10. Measure Key ................................................................................. 29
2-1-11. Hardcopy Key ................................................................................ 30
2-1-12. Run/Stop Key ................................................................................ 30
2-1-13. REF Key ........................................................................................ 30
2-1-14. Save/Recall Key ............................................................................ 31
2-1-15. Test Key ........................................................................................ 32
2-1-16. Test Key – Go-NoGo ..................................................................... 32
2-1-17. Trigger Type Menu ........................................................................ 33
2-1-18. Trigger Edge Menu ........................................................................ 33
2-1-19. Trigger Delay Menu ....................................................................... 33
2-1-20. Trigger Pulse Width Menu ............................................................. 34
2-1-21. Trigger Video Menu ....................................................................... 34
2-1-22. Trigger Pulse Runt Menu ............................................................... 34
2-1-23. Trigger Rise & Fall Menu ............................................................... 35
2-1-24. Trigger Timeout Menu ................................................................... 35
2-1-25. Utility Key ...................................................................................... 36
2-1-26. Utility Key – I/O .............................................................................. 37
2-1-27. Utility Key – File Utilities ................................................................ 37
2-1-28. Utility Key – Wave Generator - Demo Outputs .............................. 38
2-1-29. Search - Edge ............................................................................... 38

2-1-30. Search – Pulse Width .................................................................... 39
2-1-31. Search - Runt ................................................................................ 39
2-1-32. Search – Rise/Fall Time ................................................................ 40
2-1-33. Zoom Key ...................................................................................... 40
2-1-34. Option Key ..................................................................................... 41
2-2. Default Settings .................................................................. 42
2-3. Built-in Help ....................................................................... 43
3. MEASUREMENT ...................................................................... 44
3-1. Basic Measurement ............................................................ 44
3-1-1. Channel Activation .......................................................................... 44
3-1-2. Autoset ............................................................................................ 45
3-1-3. Run/Stop ......................................................................................... 46
3-1-4. Horizontal Position/Scale................................................................. 47
3-1-5. Vertical Position/Scale ..................................................................... 48
3-2. Automatic Measurement ...................................................... 49
3-2-1. Measurement Items ......................................................................... 49
3-2-2. Add Measurement ........................................................................... 53
3-2-3. Remove Measurement .................................................................... 54
3-2-4. Gated mode ..................................................................................... 54
3-2-5. Display All mode .............................................................................. 55
3-2-6. High Low Function ........................................................................... 56
3-2-7. Statistics .......................................................................................... 57
3-3. Cursor Measurement .......................................................... 59
3-3-1. Use Horizontal Cursors ................................................................... 59
3-3-2. Use Vertical Cursors ....................................................................... 61
3-4. Math Operation ................................................................... 64
3-4-1. Overview ......................................................................................... 64
3-4-2. Addition/Subtraction/Multiplication/Division ..................................... 65
3-4-3. FFT .................................................................................................. 66
3-4-4. Advanced Math ............................................................................... 68
3-4-5. Edit F(x) ........................................................................................... 69
4. CONFIGURATION .................................................................... 70
4-1. Acquisition ......................................................................... 70
4-1-1. Select Acquisition Mode .................................................................. 70
4-1-2. Digital Filter ..................................................................................... 71
4-1-3. Show Waveform in XY Mode ........................................................... 72
4-1-4. Set the Sampling Mode ................................................................... 74
4-1-5. Set the Record Length..................................................................... 75
4-2. Segmented Memory Acquisition ........................................... 76
4-2-1. Segments Display ........................................................................... 76
4-2-2. Set the Number of Segments .......................................................... 76
4-2-3. Run Segmented Memory................................................................. 77
4-2-4. Navigate Segmented Memory ......................................................... 78
4-2-5. Segment Measurement ................................................................... 78
4-2-6. Display All ........................................................................................ 79
4-2-7. Automatic Measurement.................................................................. 80
4-2-8. Segment Info ................................................................................... 82
4-3. Display ............................................................................... 82

4-3-1. Display Waveform as Dots or Vectors ............................................. 82
4-3-2. Set the Level of Persistence ............................................................ 83
4-3-3. Set the Intensity Level ..................................................................... 83
4-3-4. Set the Waveform Intensity Type .................................................... 84
4-3-5. Select Display Graticule .................................................................. 85
4-3-6. Freeze the Waveform (Run/Stop) .................................................... 85
4-3-7. Turn Off Menu ................................................................................. 86
4-4. Horizontal View .................................................................. 87
4-4-1. Move Waveform Position Horizontally ............................................. 87
4-4-2. Select Horizontal Scale ................................................................... 87
4-4-3. Select Waveform Update Mode ....................................................... 88
4-4-4. Zoom Waveform Horizontally .......................................................... 89
4-5. Vertical View (Channel) ....................................................... 91
4-5-1. Move Waveform Position Vertically ................................................. 91
4-5-2. Select Vertical Scale ....................................................................... 91
4-5-3. Select Coupling Mode ..................................................................... 91
4-5-4. Input Impedance .............................................................................. 92
4-5-5. Invert Waveform Vertically ............................................................... 92
4-5-6. Limit Bandwidth ............................................................................... 93
4-5-7. Expand by Ground/Center ............................................................... 93
4-5-8. Select Probe Type ........................................................................... 94
4-5-9. Select Probe Attenuation Level ....................................................... 94
4-5-10. Set the Deskew ............................................................................. 95
4-6. Trigger ............................................................................... 95
4-6-1. Trigger Type Overview .................................................................... 95
4-6-2. Trigger Parameter Overview ........................................................... 97
4-6-3. Setup Holdoff Level ....................................................................... 100
4-6-4. Setup Trigger Mode ....................................................................... 101
4-6-5. Using the Edge Trigger.................................................................. 101
4-6-6. Using Advanced Delay Trigger ...................................................... 102
4-6-7. Using Pulse Width (glitch) Trigger ................................................. 103
4-6-8. Using Video Trigger ....................................................................... 104
4-6-9. Pulse Runt trigger .......................................................................... 105
4-6-10. Using Rise and Fall (slope) Trigger ............................................. 106
4-6-11. Using the Timeout Trigger ........................................................... 107
4-7. Search .............................................................................. 108
4-7-1. Configuring Search Events ............................................................ 108
4-7-2. Copying Search Event To/From Trigger Events ............................ 109
4-7-3. Search Event Navigation ............................................................... 110
4-7-4. Save Search Marks ....................................................................... 110
4-7-5. Setting/Clearing Single Search Events .......................................... 111
4-7-6. Play / Pause .................................................................................. 111
4-8. System Info / Language / Clock .......................................... 113
4-8-1. Select Menu Language.................................................................. 113
4-8-2. View System Information ............................................................... 113
4-8-3. Erase Memory ............................................................................... 114
4-8-4. Turn the Buzzer On/Off ................................................................. 115
4-8-5. Set Date and Time ........................................................................ 115

4-8-6. Demo Outputs ............................................................................... 116
5. OPTIONAL SOFTWARE and APPS. ......................................... 118
5-1. Applications ....................................................................... 118
5-1-1. Overview ....................................................................................... 118
5-1-2. Running Applications ..................................................................... 118
5-1-3. Uninstalling Applications................................................................ 118
5-1-4. Using Go-NoGo ............................................................................. 119
5-2. Optional Software .............................................................. 123
5-2-1. Activating Optional Software ......................................................... 123
5-2-2. Running Optional Software ............................................................ 123
5-2-3. Uninstalling Optional Software ...................................................... 124
6. SAVE/RECALL ........................................................................ 125
6-1. File Format/Utility .............................................................. 125
6-1-1. Image File Format ......................................................................... 125
6-1-2. Waveform File Format ................................................................... 125
6-1-3. Spreadsheet File Format ............................................................... 125
6-1-4. Setup File Format .......................................................................... 128
6-2. Create/Edit Labels ............................................................. 129
6-3. Save ................................................................................. 131
6-3-1. File Type/Source/Destination ........................................................ 131
6-3-2. Save Image ................................................................................... 132
6-3-3. Save Waveform ............................................................................. 133
6-3-4. Save Setup .................................................................................... 134
6-4. Recall ............................................................................... 135
6-4-1. File Type/Source/Destination ........................................................ 135
6-4-2. Recall Default Panel Setting .......................................................... 136
6-4-3. Recall Waveform ........................................................................... 137
6-4-4. Recall Setup .................................................................................. 138
6-5. Reference Waveforms ........................................................ 139
6-5-1. Recall and Display Reference Waveforms .................................... 139
7. FILE UTILITIES ...................................................................... 141
7-1. File Navigation .................................................................. 141
7-2. Create Folder .................................................................... 143
7-3. Rename File ...................................................................... 144
7-4. Delete File ........................................................................ 145
7-5. Copy File to USB ............................................................... 145
8. HARDCOPY KEY .................................................................... 147
8-1. Printer I/O Configuration .................................................... 147
8-2. Print Output ....................................................................... 148
8-3. Save - Hardcopy Key ......................................................... 148
9. REMOTE CONTROL CONFIG .................................................. 150
9-1. Configure USB Interface .................................................... 150
9-2. Configure RS-232C Interface ............................................. 151
9-3. Configure the Ethernet Interface ......................................... 152
9-4. Configure Socket Server .................................................... 154
9-5. Configure GP-IB ................................................................ 155
9-6. USB/RS-232C Functionality Check ..................................... 156
9-7. Socket Server Functionality Check ..................................... 157

9-8. GP-IB Functionality Check ................................................. 159
9-9. Web Server Overview ........................................................ 161
10. MAINTENANCE .................................................................... 163
10-1. How to use SPC function .................................................. 163
10-2. Vertical Accuracy Calibration ............................................ 164
10-3. Probe Compensation ........................................................ 165
11. APPENDIX ............................................................................ 167
11-1. DCS-9700 Specifications .................................................. 167
11-1-1. Model-specific ............................................................................. 167
11-1-2. Common-specific ......................................................................... 167
11-2. Probe Specifications ........................................................ 171
11-2-1. GTP-070B-4 ................................................................................ 171
11-2-2. GTP-150A-2 ................................................................................ 171
11-2-3. GTP-250A-2 ................................................................................ 172
11-2-4. GTP-350A-2 ................................................................................ 172
11-3. DCS-9700 Dimensions .................................................... 173
11-4. FAQ................................................................................. 174
I
USING THE PRODUCT SAFELY
■ Preface
To use the product safely, read this instruction manual to the end.
Before using this product, understand how to correctly use it.
If you read this manual but you do not understand how to use it, please
ask us or your local dealer. After you read this manual, save it so that
you can read it, anytime as requied.
■ Pictorial indication
This instruction manual and product show the warning and caution items
required to safely use the product. The following pictorial indication and
warning character indication are provided.
<Pictorial indication>
Some part of this product or the instruction
manual may shows this pictorial indication. In
this case, if the product is incorrectly used in that
part, a serious danger may be brought about on
the user’s body or the product.
To use the part with this pictorial indication, be
sure to refer to this instruction manual.
WARNING
!
If you use the product, ignoring this indication,
you may get killed or seriously injured. This
indication shows that the warning item to avoid
the danger is provided.
CAUTION
!
If you incorrectly use the product, ignoring this
indication, you may get slightly injured or the
product may be damaged. This indication shows
that the caution item to avoid the danger is
provided.
Please be informed that we are not responsible for any damages to the user
or to the third person, arising from malfunctions or other failures due to
wrong use of the product or incorrect operation, except such responsibility
for damages as required by law.
II
USING THE PRODUCT SAFELY
WARNING
!
CAUTION
!
■ Do not remove the product’s covers and panels
Never remove the product’s covers and panels for any purpose.
Otherwise, the user’s electric shock or fire may be incurred.
■ Warning on using the product
Warning items given below are to avoid danger to user’s body and life and
avoid the damage or deterioration of the product.
Use the product, observing the following warning and caution items.
■ Warning items on power supply
● Power supply voltage
The rated power supply voltages of the product are 100, 120, 220
and 240VAC. The rated power supply voltage for each product
should be confirmed by reading the label attached on the back of
the product or by the “rated” column shown in this instruction manual.
The specification of power cord attached to the products is rated to
125VAC for all products which are designed to be used in the
areas where commercial power supply voltage is not higher than
125VAC. Accordingly, you must change the power cord if you want
to use the product at the power supply voltage higher than 125VAC.
If you use the product without changing power cord to 250VAC
rated one, electric shock or fire may be caused.
When you used the product equipped with power supply voltage
switching system, please refer to the corresponding chapter in the
instruction manuals of each product.
● Power cord
(Important) The attached power cord set can be used for this
device only.
If the attached power cord is damaged, stop using the product and
call us or your local dealer. If the power cord is used without the
damage being removed, an electric shock or fire may be caused.
● Protective fuse
If an input protective fuse is blown, the product does not operate. For a
product with external fuse holder, the fuse may be replaced. As for
how to replace the fuse, refer to the corresponding chapter in this
instruction manual.
If no fuse replacement procedures are indicated, the user is not
permitted to replace it. In such case, keep the case closed and
consult us or your local dealer. If the fuse is incorrectly replaced, a
fire may occur.

III
USING THE PRODUCT SAFELY
■ Warning item on Grounding
If the product has the GND terminal on the front or rear panel surface,
be sure to ground the product to safely use it.
■ Warnings on Installation environment
● Operating temperature and humidity
Use the product within the operating temperature indicated in the
“rating” temperature column. If the product is used with the vents of
the product blocked or in high ambient temperatures, a fire may occur.
Use the product within the operating humidity indicated in the “rating”
humidity column. Watch out for condensation by a sharp humidity
change such as transfer to a room with a different humidity. Also, do
not operate the product with wet hands. Otherwise, an electric shock
or fire may occur.
● Use in gas
Use in and around a place where an inflammable or explosive gas or
steam is generated or stored may result in an explosion and fire. Do
not operate the product in such an environment.
Also, use in and around a place where a corrosive gas is generated or
spreading causes a serious damage to the product. Do not operate
the product in such an environment.
● Installation place
Avoid installing the product on inclined places or on places subject to
vibration. Otherwise, the product may slip or fall down to cause
damages or injury accidents.
■ Do not let foreign matter in
Do not insert metal and inflammable materials into the product from its
vent and spill water on it. Otherwise, electric shock or fire may occur.
■ Warning item on abnormality while in use
In abnormal situations, such as “smoke”, “fire”, “abnormal smell” or
“irregular noise” occur from the product while in use, stop using the
product, turn off the switch, and remove the power cord plug from the
outlet. After confirming that no other devices catch fire, ask us or your
local dealer.
IV
USING THE PRODUCT SAFELY
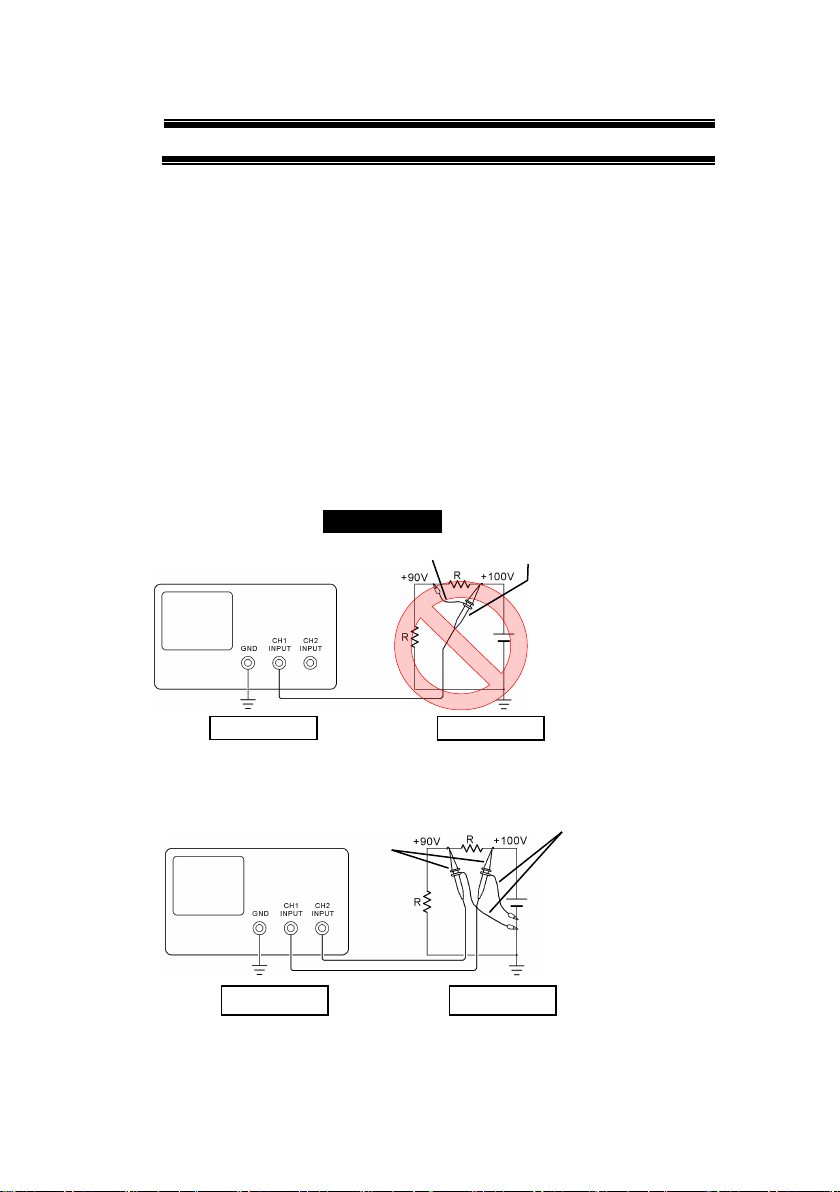
■ Warning Item for the Measurement
● When you measure a part of a high voltage, be careful not to touch a
hand to a measurement part directly. There is a risk of an electric shock.
● Be sure to connect the probe or the cable and the ground side of the input
connector to the ground potential (ground) of the substance measured.
Since the chassis of this instrument is connected to the ground of the
input block, connecting the earth lead of the probe to the potential
floating from the ground potential may result in the following:
⚫ Electric shock
⚫ A high current flows and damages the substance measured, this
instrument, and other connected device.
The following parts are connected to the chassis:
⚫ Probe for each channel and ground side of the input BNC connector
⚫ Grounding conductor of the accessory 3-core power cord
⚫ Ground pin for an interface signal
“Bad example” Prohibition
When measuring the floating potential, a differential method of
measurement is recommended ( refer to the figure below ).
“Good example”
At connecting as Bad
Example, +90V and chassis
are shorted, and damages
substance a measured.
Therefore do not make such
connection.
If the instrument is not
grounded, a potential of the
chassis is +90V.
Ground a chassis, in order to
prevent an electric shock
accident.
Setting of panel switches of an
oscilloscope
CH2 INV: ON (CH2 inverted)
ADD : ON (CH1+CH2)
Grounding
Oscilloscope
Earth Lead
Probe
Grounding
Oscilloscope
Grounding
Grounding
Earth Lead
Probe

V
USING THE PRODUCT SAFELY
■ Input / Output terminals
Maximum input to terminal is specified to prevent the product
from being damaged. Do not supply input, exceeding the
specifications that are indicated in the "Rating" column in the
instruction manual of the product.
Also, do not supply power to the output terminals from the
outside.
Otherwise, a product failure is caused.
■ Calibration
Although the performance and specifications of the product are
checked under strict quality control during shipment from the factory,
they may be deviated more or less by deterioration of parts due to their
aging or others.
It is recommended to periodically calibrate the product so that it is used
with its performance and specifications stable.
For consultation about the product calibration, ask us or your local
dealer.
■ Daily Maintenance
When you clean off the dirt of the product covers, panels, and
knobs, avoid solvents such as thinner and benzene. Otherwise, the
paint may peel off or resin surface may be affected.
To wipe off the covers, panels, and knobs, use a soft cloth with neutral
detergent in it. During cleaning, be careful that water, detergent, or
other foreign matters do not get into the product.
If a liquid or metal gets into the product, an electric shock and fire are
caused. During cleaning, remove the power cord plug from the outlet.
Use the product correctly and safely, observing the above warning and
caution items. Because the instruction manual indicates caution items even
in individual items, observe those caution items to correctly use the product.
If you have questions or comments about the instruction manual, ask us or
E-Mail us.

1
1. GETTING STARTED
The Getting started chapter introduces the oscilloscope’s main
features, appearance, and set up procedure.
1-1. Main Features
Model name
Frequency
bandwidth
Input
channels
Real-time
Sampling Rate
DCS-9707
70MHz
4
2GSa/s
DCS-9710
100MHz
4
2GSa/s
DCS-9720
200MHz
4
2GSa/s
DCS-9730
300MHz
4
2GSa/s
DCS-9707D
70MHz
2
2GSa/s
DCS-9710D
100MHz
2
2GSa/s
DCS-9720D
200MHz
2
2GSa/s
DCS-9730D
300MHz
2
2GSa/s
Note
This instruction manual has been described as the
4ch model. In 2ch model, Can't set the ch3 and ch4.

2
Features
• 8 inch TFT SVGA display.
• All models feature a real-time sampling rate of
2GSa/s and an equivalent time sampling rate of
100GSa/s.
• Deep memory: 2M points record length.
• Waveform capture rate of 80,000 waveforms
per second.
• Vertical sensitivity: 1mV/div~10V/div.
• Logic Analyzer module (optional): Adds 8 or 16
channel digital inputs and serial bus (I2C, SPI,
UART) and parallel bus triggering.
• DDS Function Generator module (optional).
• Segmented Memory: Optimizes the acquisition
memory to selectively capture only the
important signal details. Up to 2048 successive
waveform segments can be captured with a
time-tag resolution of 8ns. Segmented memory
can be used for both analog and digital
channels.
• Enhanced Search: Allows the scope to search
for a number of different signal events.
• On-screen Help.
• 64 MB internal flash disk.
Interface
• USB host port: front and rear panel, for storage
devices.
• USB device port: rear panel, for remote control
or printing.
• Demo output
• GP-IB (optional)
• RS-232C port.
• Calibration output
• SVGA output and Ethernet port (optional)

3
1-2. Accessories
Standard
Accessories
Part number
Description
Power cord
N/A
region dependent
Passive
probe
GTP-070B-4
70MHz(DCS-9707 / DCS-9707D)
GTP-150B-4
150MHz(DCS-9710 / DCS-9710D)
GTP-250A-2
250MHz(DCS-9720 / DCS-9720D)
GTP-350A-2
350MHz(DCS-9730 / DCS-9730D)
Options
Option Number
Description
DS2-LAN
Ethernet & SVGA output
DS2-GPIB
GP-IB Interface
DS2-FGN
DDS Function Generator
DS2-08LA
8-Channel Logic Analyzer card with
8-Channel Logic Analyzer Probe
(GTL-08LA)
DS2-16LA
16-Channel Logic Analyzer card
with 16-Channel Logic Analyzer
Probe (GTL-16A)
Optional
Accessories
Part number
Description
GTL-110
Test lead, BNC to BNC heads
GTL-232
RS-232C cable, 9-pin Female to
9-pin Female, Null modem for PC
GTL-246
USB cable USB2.0A-B type cable
GTL-08LA
8Ch Logic Analyzer Testing Probe
GTL-16LA
16Ch Logic Analyzer Testing Probe
Drivers
USB driver
for Windows PC
LabVIEW driver
4
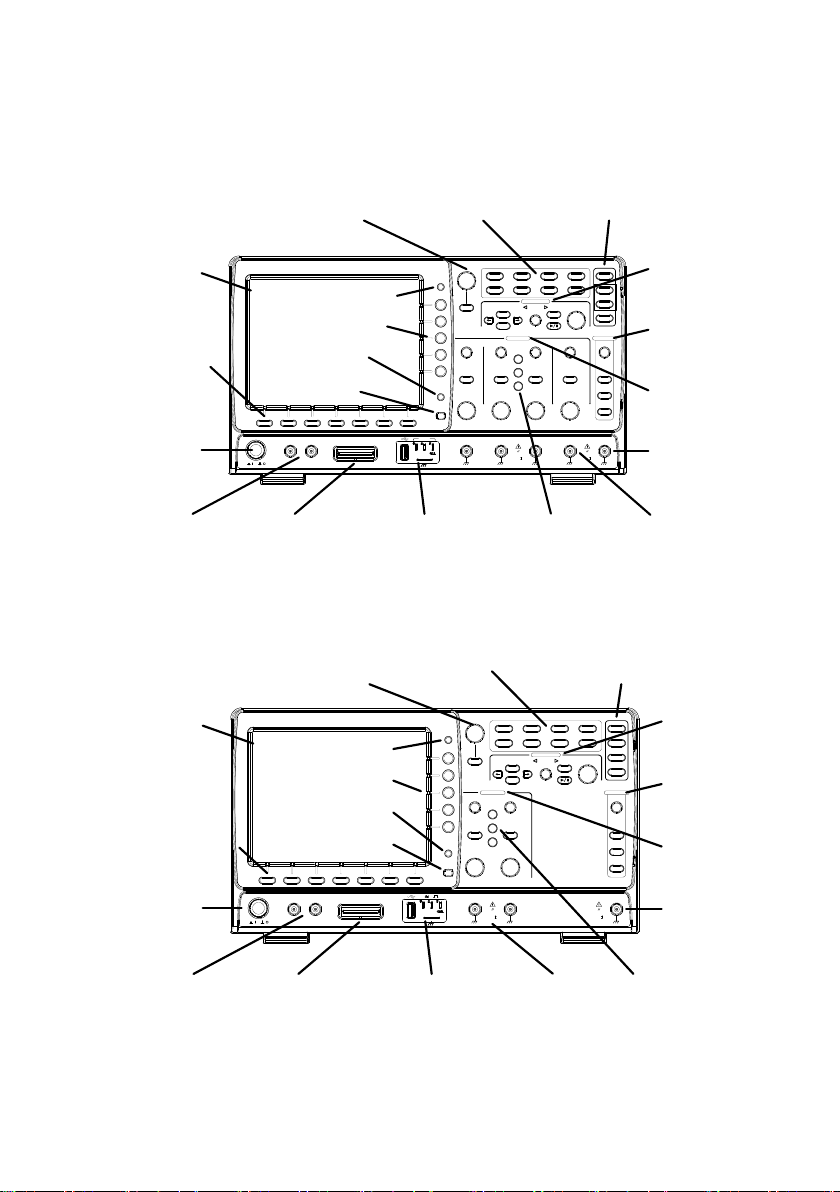
1-3. Panel Overview
1-3-1. Front Panel
4ch Model
POWER
CH1 CH2
POSITION TIME/DIV
POSITIONPOSITION
VOLTS/DIV VOLTS/DIV
Autoset
Menu
50 %
Force-Trig
Select
TRIGGER
HORIZONTAL
VARIABLE
Measure Cursor
Display Help Save/ Recall Utility
Acquire
Single
Run/Stop
Search
Set/Clear
CH3 CH4
POSITION POSITION
VOLTS/DIV VOLTS/DIV
VERTICAL
M
R
B
Test
CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 EXT TRIG
CAT
MW 16pF
300Vpk MAX.
1
CAT
MW 16 pF
300Vpk MAX.
Hardcopy
Option
Menu Off
LEVEL
Zoom
MATH
REF
Demo
Logic Analyzer
1
BUS
/
GEN 1 GEN 2
Default
LCD
Variable knob
and Select
key
Autoset, Run/Stop,
Single and Default
settings
CH1~CH4
input
Trigger
controls
Function
keys
USB Host port ,
Demo and
Ground terminals
Function
Generator
output 1&2
Power
button
Hardcopy Key
Option
key
Math,
Reference
and Bus
keys
Bottom
menu
keys
Horizontal
controls
Menu key
Vertical
controls
Logic
Analyzer
input
EXT
trigger
Side menu keys
2ch Model
CH1 CH2
POSITION TIME/DIV
POSITIONPOSITION
VOLTS/DIV VOLTS/DIV
Autoset
Menu
50 %
Force-Trig
Select
TRIGGER
HORIZONTAL
VARIABLE
Measure Cursor
Display Help Save/ Recall Utility
Acquire
Single
Run/Stop
LEVEL
Search
Set/Clear
VERTICAL
Test
POWER
2V
Hardcopy
Option
Menu Off
Zoom
CAT
M 16pF
300Vpk MAX.
1
CAT
MW 16 pF
300Vpk MAX.
1
M
R
B
MATH
REF
BUS
Default
Logic Analyzer
GEN 1 GEN 2 CH1 CH2 EXT TRIG
-
2
W
LCD
Variable knob
and Select
key
Autoset, Run/Stop,Single
And Default Settings
Math,
Reference
and Bus keys
Trigger
controls
Function
keys
USB Host port,
Demo and
Ground terminals
Function
Generator
output
1&2
Power
button
Hardcopy key
Option key
CH1~CH
2
input
Bottom
menu
keys
Horizontal
controls
Menu
key
Vertical
controls
Logic
Analyzer
input
EXT
trigger
Side menu keys
5
LCD Display
8” SVGA TFT color LCD. 800 x 600 resolution,
wide angle view display.
Menu Off Key
Menu Off
Use the Menu Off key to hide the
onscreen menu system.
Option Key
Option
The Option key is used to access
any installed options, such the
Logic Analyzer option.
Menu Keys
The Side menu and Bottom menu keys are used to
make selections from the soft-menus on the LCD
user interface.
To choose menu items, use the 7 Bottom menu
keys located on the bottom of the display panel.
To select a variable or option from a menu, use the
Side menu keys on the side of the panel. See page
19 for details.
Hardcopy
Option
Menu Off
Side menu keys
Bottom menu keys
Hardcopy Key
Hardcopy
The Hardcopy key is a quick-save
or quick-print key, depending on its
configuration. For more
information see pages 148(save)
or 148(print).
Variable Knob
and Select Key
Select
VARIABLE
The Variable knob is used to
increase/decrease values or to
move between parameters.
The Select key is used to make
selections.
6
Function Keys
The Function keys are used to enter and configure
different functions on the DCS-9700 .
Measure
Measure
Configures and runs automatic
measurements.
Cursor
Cursor
Configures and runs cursor
measurements.
Test
Test
Configures and runs applications.
Acquire
Acquire
Configures the acquisition mode,
including Segmented Memory
acquisition.
Display
Display
Configures the display settings.
Help
Help
Shows the Help menu.
Save/Recall
Save/Recall
Used to save and recall
waveforms, images, panel
settings.
Utility
Utility
Configures the Hardcopy key,
display time, language, calibration
and Demo outputs. It also
accesses the file utilities menu.
Autoset
Autoset
Press the Autoset key to
automatically set the trigger,
horizontal scale and vertical scale.
Run/Stop Key
Run/Stop
Press to Freeze (Stop) or continue
(Run) signal acquisition (page 46).
The run stop key is also used to
run or stop Segmented Memory
acquisition (page 77).
Single
Single
Sets the acquisition mode to single
triggering mode.
Default Setup
Default
Resets the oscilloscope to the
default settings.
Horizontal
Controls
The horizontal controls are used to change the
position of the cursor, set the time base settings,
zoom into the waveforms and search for events*.
Horizontal
Position
POSITION
The Position knob is used to
position the waveforms
horizontally on the display screen.
7
TIME/DIV
Knob
TIME/DIV
The Time/Div knob is used to
change the horizontal scale.
Zoom
Zoom
Press Zoom in combination with
the horizontal Position knob.
Play/Pause
The Play/Pause key allows you to
view each search event in
succession – to effectively “play”
through each search event.
Search
Search
The Search key accesses the
search function menu to set the
search type, source and threshold.
Search Arrows
Use the arrow keys to navigate the
search events.
Set/Clear
Set/Clear
Use the Set/Clear key to set or
clear points of interest when using
the search function.
Trigger Controls
The trigger controls are used to control the trigger
level and options.
Level Knob
LEVEL
Used to set the trigger level.
Trigger Menu
Key
Menu
Used to bring up the trigger menu.
50% Key
50 %
Sets the trigger level to the half
way point (50%).
Force - Trig
Force-Trig
Press to force an immediate
trigger of the waveform.
Vertical
POSITION
POSITION
Sets the vertical position of the
waveform.
Channel Menu
Key
CH1
Press the CH1~4 key to set and
configure the channel.
8
VOLTS/DIV
Knob
VOLTS/DIV
Sets the vertical scale of the
channel.
External Trigger
Input
EXT TRIG
Accepts external trigger signals
(page 95).
Input impedance: 1MΩ
Voltage input: ±15V(peak), EXT
trigger capacitance:16pF.
Math Key
M
MATH
Use the math key to set and
configure math functions.
Reference Key
R
REF
Press the Reference key to set or
remove reference waveforms.
BUS Key
B
BUS
The Bus key is used for parallel
and serial bus (UART, I2C and
SPI) configuration. Serial bus and
parallel bus functionality is
included with the Logic Analyzer
options (DS2-08LA/DS2-16LA).
Channel Inputs
CH1
Accepts input signals.
Input impedance: 1MΩ.
USB Host Port
Demo
TypeA, 1.1/2.0 compatible. Used
for data transfer.
Ground Terminal
Demo
Accepts the DUT ground lead for
common ground.

9
Demo and
Probe
Compensation
Outputs
Demo
The Demo outputs are
multifunction outputs that can be
configured for probe
compensation, as a trigger output
or as a basic waveform generator
for demonstration purposes. (FM
signal, UART, I2C, SPI).
By default, the 3 Demo outputs are
configured as:
1: Trigger output
2: FM waveform
3: Probe Compensation signal
CAL (Demo 3) outputs a 2Vp-p,
square wave signal for probe
compensation.
Please see page 116 for details.
Logic Analyzer
Port
Logic Analyzer
The Logic Analyzer port is used to
connect to a Logic Analyzer probe.
This port only functions if the
optional logic analyzer module is
installed.
Function
Generator
Output
GEN 1
GEN 2
The function generator outputs are
used with an optional function
generator module.
Power Switch
POWER
Used to turn the power on/off.
: ON
: OFF
10
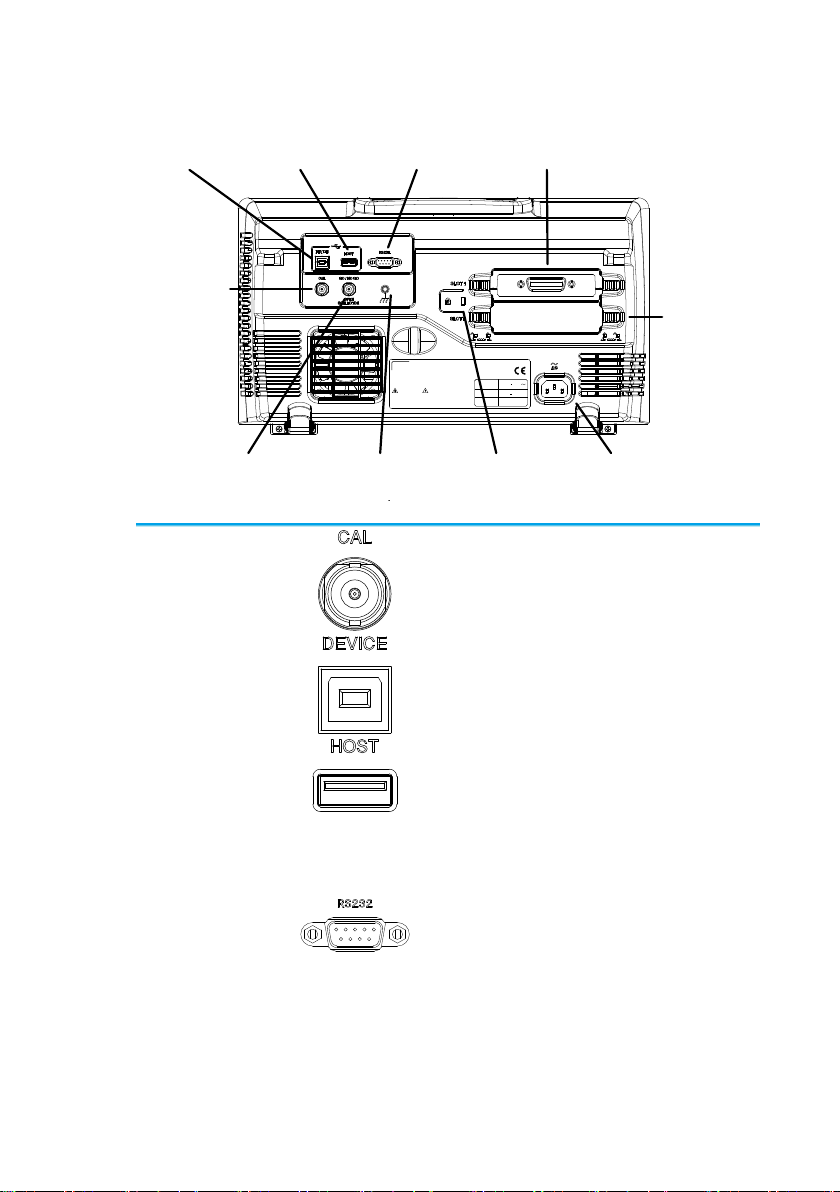
1-3-2. Rear Panel
LINE VOLTAGE
AC 100 240V
RANGE
FREQUENCY 50 60Hz
POWER MAX. 55W 80VA
CAUTION
TO AVOID ELECTRIC SHOCK THE POWER CORD PROTECTIVE GROUNDING
DO NOT REMOVE COVERS. REFER SERVICING TO QUALIFIED PERSONNEL.
CONDUCTOR MUST BE CONNECTED TO GROUND.
Ser. No. Label
Calibration
output
RS-232C
port Module Slot 1
Module
Slot 2
Key
lock
Power input
socket
Ground
strap
Go/No Go
output
USB Host
port
USB Device
port
Calibration
Output
Outputs the signal for vertical scale
accuracy calibration (page 164).
USB Device Port
The USB Device port is used for
remote control.
USB Host Port
The USB Host port is used to data
transfer.
Note: Only one rear panel USB port
can be used at a time. Inserting a
USB flash drive into the USB Host
Port will disable the USB Device
Port.
RS-232C Port
Used for RS-232C-based remote
control.
11
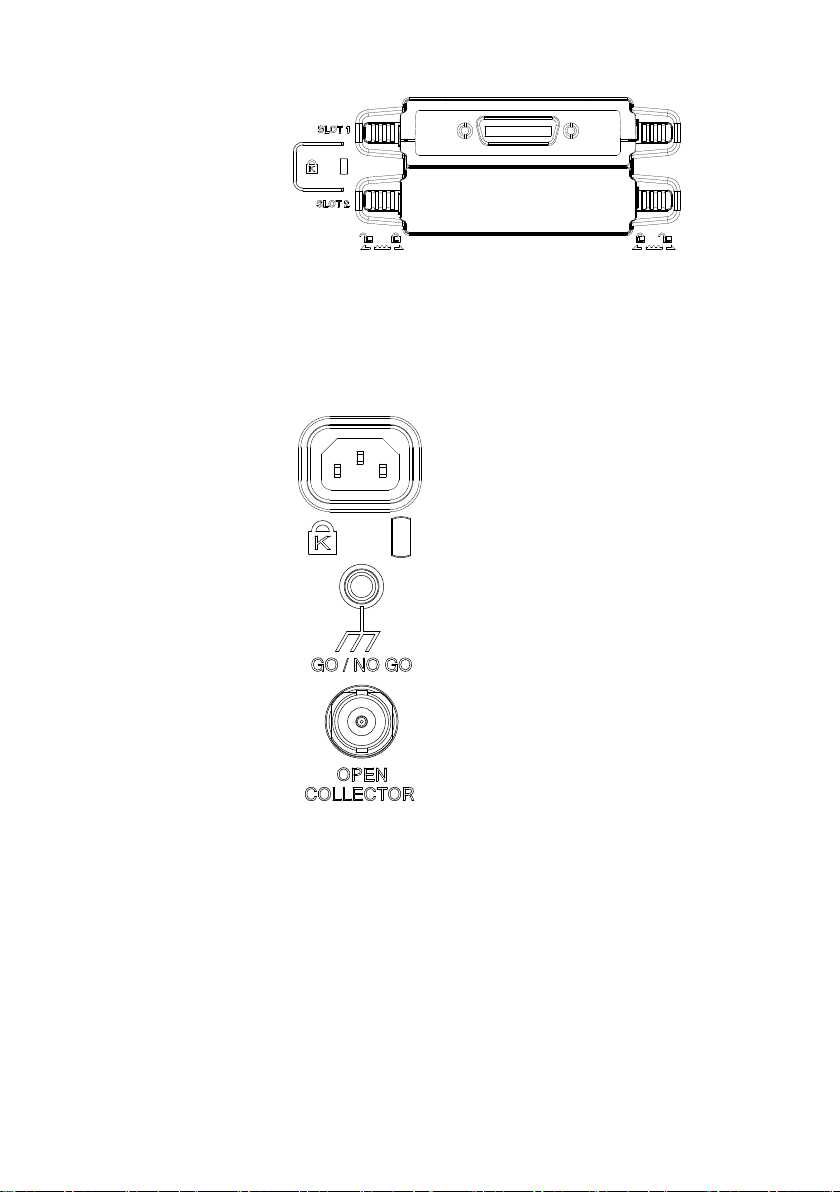
Module Slots
The module slots are used to install the optional
modules:
DS2-LAN
DS2-GPIB
DS2-08LA
DS2-16LA
DS2-FGN
: Ethernet and SVGA
: GP-IB
: 8 channel logic analyzer
: 16 channel logic analyzer
:Function generator
Power Input
Socket
Power cord socket accepts AC
mains, 100 ~ 240V, 50/60Hz.
For power up sequence, see page
16.
Security Slot
Kensington security slot
compatible.
Ground Strap
Connector
For use with a grounding strap.
Go-No Go
Output
Outputs Go-No Go test results
(page 119) as a 500us pulse
signal.

12
1-3-3. Display
Memory bar
Digital
waveforms
Analog
Waveforms
Bus
Channel status Horizontal status
Trigger
configuration
Waveform
frequency
Date and time
Trigger position
Acquisition modeTrigger Status
Trigger level
Channel
Indicators
Analog
Waveforms
Shows the analog input signal waveforms.
Channel 1: Yellow
Channel 2: Blue
Channel 3: Pink
Channel 4: Green
Bus Waveforms
Shows the bus waveforms for either parallel or
serial buses. The values are displayed in hex or
binary.
Digital
Waveforms
Shows the digital channel waveforms. There can
be up to 16 digital channels.
Channel
Indicators
The channel indicators show the zero volt level of
the signal waveform for each activated channel.
Any active channel is shown with a solid color.
Analog channel indicator
Bus indicator(B)
Digital channel indicator
Reference waveform indicator
Math indicator
Trigger Position
Shows the position of the trigger.
Horizontal
Status
Shows the horizontal scale and position.
Date and Time
Current date and time (page 115).
Trigger Level
Shows the trigger level on the
graticule.

13
Memory Bar
The ratio and the position of the
displayed waveform compared with
the internal memory (page 87).
Trigger Status
Triggered.
Pre-trigger.
Not triggered, display not updated.
Trigger stopped. Also appears in
Run/Stop (page 46).
Roll mode.
Auto trigger mode.
For trigger details, see page 95.
Acquisition
Mode
Normal mode
Peak detect mode
Average mode
For acquisition details, see page 70.
Signal
Frequency
Shows the trigger source
frequency.
Indicates the frequency is
less than 2Hz (lower
frequency limit).
Trigger
Configuration
Trigger source, slope,
voltage, coupling.
Horizontal
Status
Horizontal scale,
horizontal position.
For trigger details, see page 95.
Channel Status
Channel 1, DC coupling,
2V/Div.
For channel details, see page 91.
14
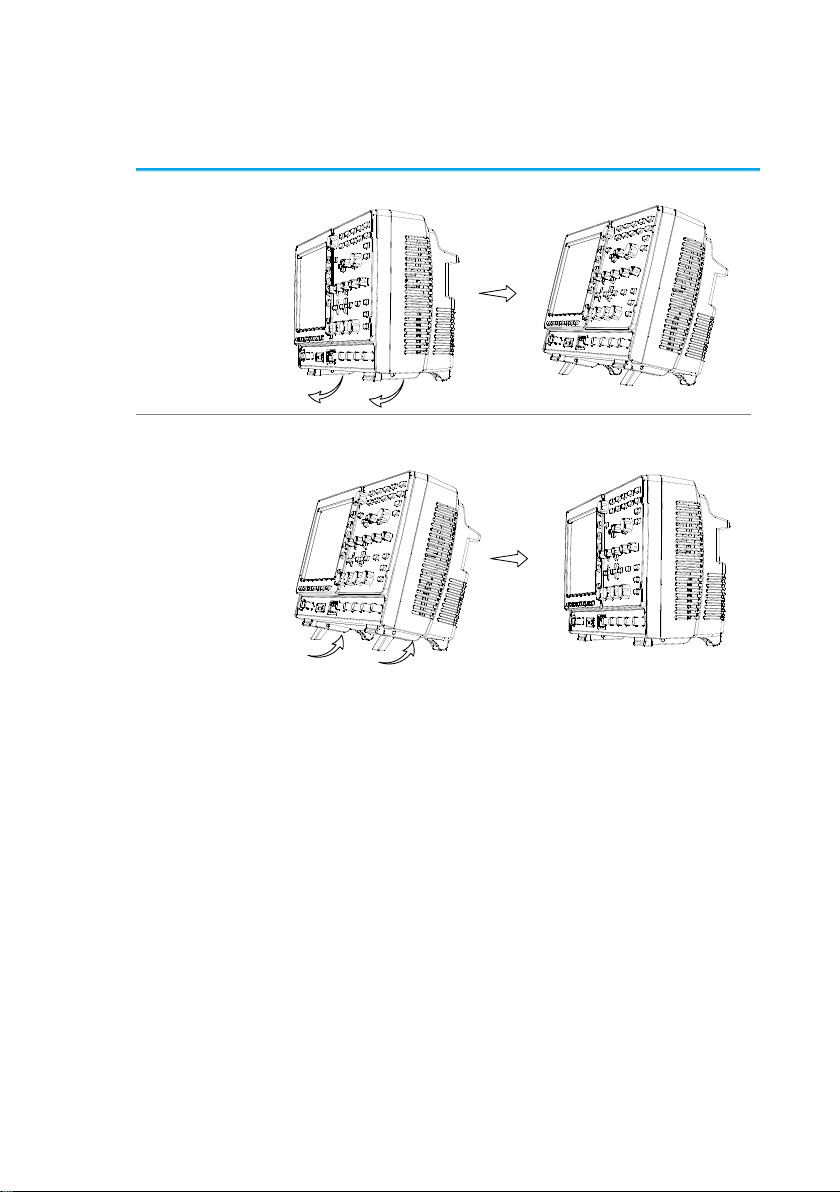
1-4. Set Up
1-4-1. Tilt Stand
Tilt
To tilt, pull the legs forward, as shown below.
Stand
To stand the scope upright, push the legs back
under the casing as shown below.
15
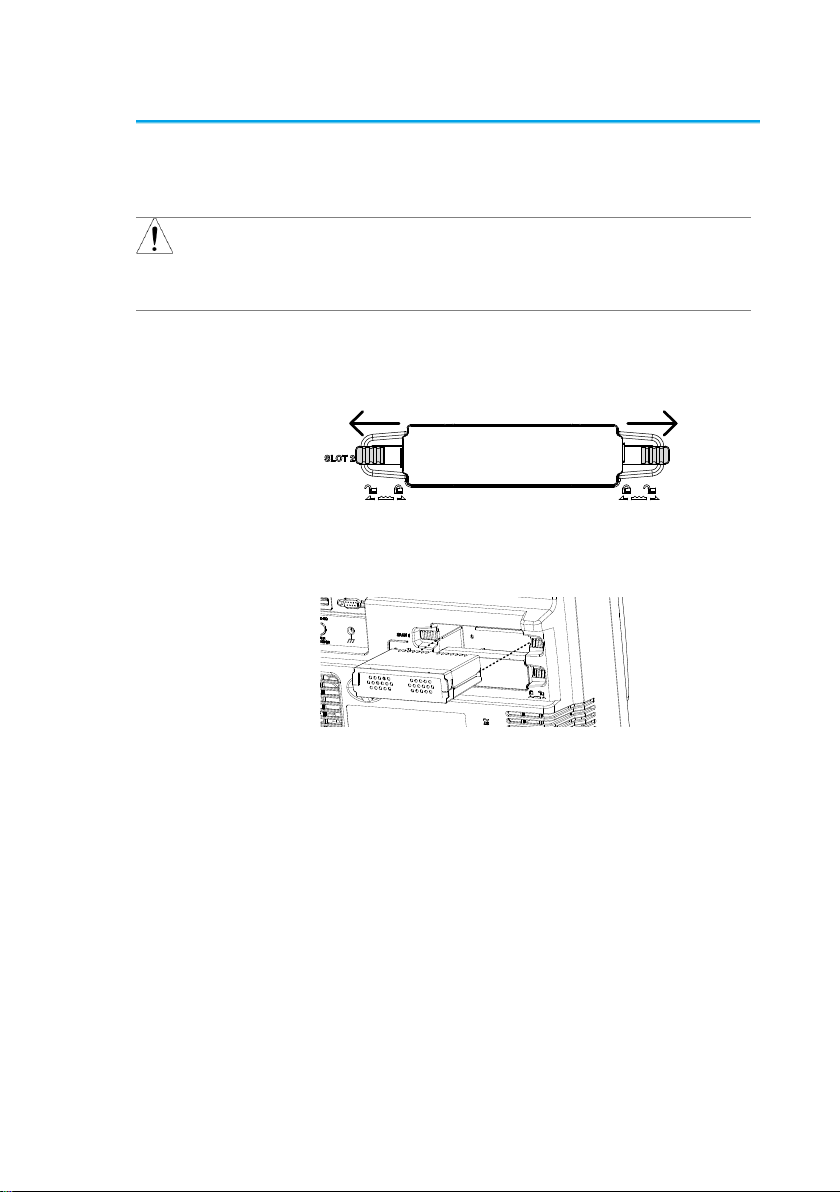
1-4-2. Module Installation
Background
The DCS-9700 has a number of optional modules
that can be installed into the module slots on the
rear panel. These modules must be installed
before power up.
Note
The modules are not hot-swappable. Please
ensure the power is off before connecting or
disconnecting any of the modules from the rear
panel.
Steps
1. Make sure the power is turned off before
installing any of the optional modules.
2. Slide the tabs holding the module cover to the
unlock position and then remove
3. Install the optional module. Be sure to make
sure that the groves on the module line-up to
the slots in the module bay.
4. Slide the tabs back into the lock position.
16
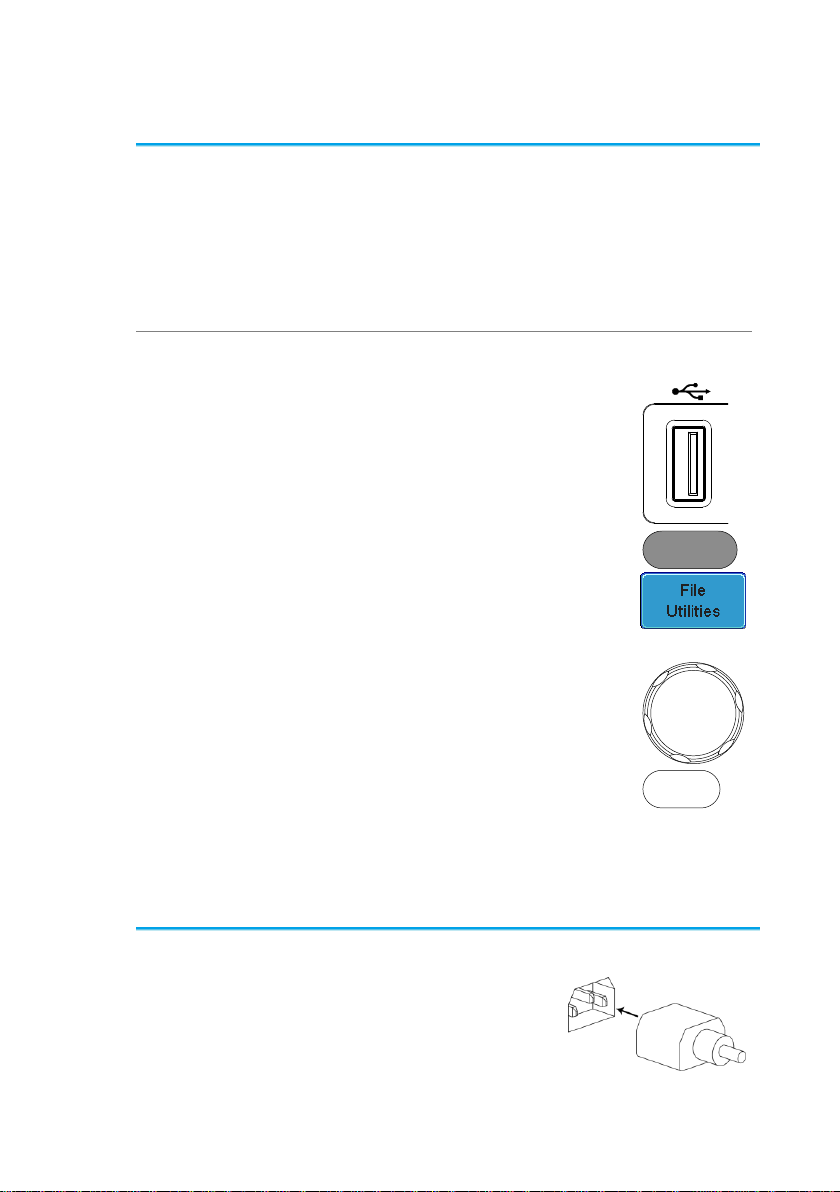
1-4-3. Software Installation
Background
The DCS-9700 has optional software packages to
expand the functionality of the standard DCS9700 .An activation key is required to activate any
optional software. A different activation key is
required for each optional software package.
For the latest files and information regarding the
optional software packages, see our website or
contact your nearest distributor.
Steps
1. Install any hardware modules if needed. See
page 15 for installation details.
Panel Operation
2. Insert the USB serial key for the
desired option into the front panel
USB A port.
Demo
3. Press the Utility key then the File
Utilities soft-key.
Utility
4. Navigate to the desired file in the
USB file path.
When the desired installation file
has been found, press the Select
key to start the installation.
VARIABLE
Select
5. The installation will complete in a few seconds.
When finished a pop-up message will appear
asking you to restart the DCS-9700.
6. Restart the DCS-9700.
1-4-4. Power Up
Requirements
The DCS-9700 accepts line voltages of 100 ~
240V at 50 or 60Hz.
Step
1. Connect the power cord to
the rear panel socket.
17
2. Press the POWER key.
The display becomes
active in ~ 30 seconds.
: ON
: OFF
POWER
Note
The DCS-9700 recovers the state right before the
power is turned OFF. The default settings can be
recovered by pressing the Default key on the front
panel. For details, see page 136.
1-4-5. First Time Use
Background
This section describes how to connect a signal,
adjust the scale, and compensate the probe.
Before operating the DCS-9700 in a new
environment, run these steps to make sure the
instrument performs at its full potential.
1. Power On
Follow the procedures on the previous page.
2. Set the Date
and Time
Set the date and time.
Page 115
3. Reset System
Reset the system by recalling the
factory settings. Press the Default key
on the front panel. For details, see
page 136.
Default
4. Install Optional
modules
There are a number of optional
hardware modules that can be
installed, such as the optional function
generator.
Page 15
5. Install Optional
Software
Optional software packages may also
need to be installed.
Page 16
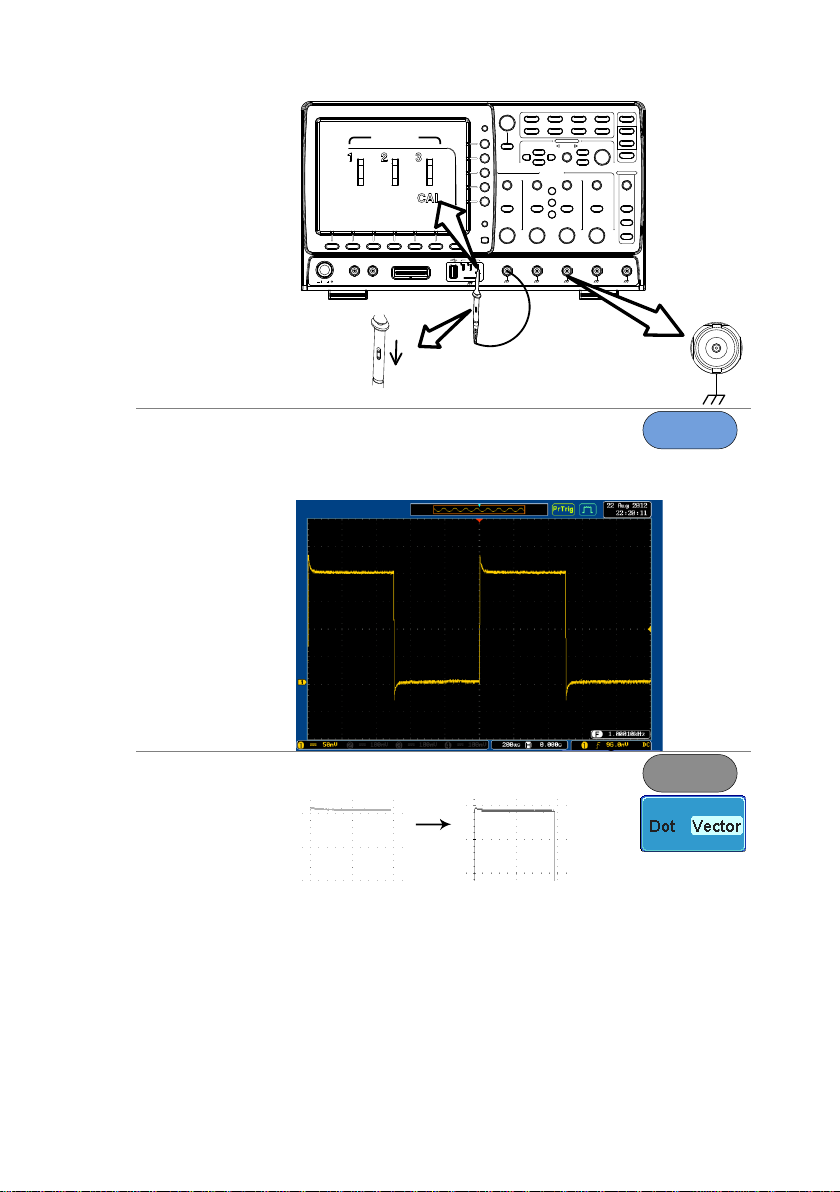
6. Connect
Probe
Connect the probe to the Channel 1 input and to
the CAL signal output (Demo 3 output). This
output provides a 2Vp-p, 1kHz square wave for
signal compensation by default.
Set the probe attenuation to x10 if the probe has
adjustable attenuation.
18
POSITION
CH1
Demo
x1
x10
X
10
X
1
CH1
Demo
6. Capture
Signal (Autoset)
Press the Autoset key. A square
waveform appears on the center of
the screen. For Autoset details, see
page 45.
Autoset
7. Select Vector
Waveform
Press the Display key, and set the
display to Vector on the bottom menu.
Display

19
8. Compensate
Probe
Turn the adjustment point on the probe to make
the square waveform edge flat.
Under
Compensation
Normal
Over
Compensation
9. Start
Operation
Continue with the other operations.
Measurement: page 44
Configuration: page 70
Save/Recall: page 125
File Utilities: page 141
Apps.: page 118
Hardcopy key: page 147
Remote Control: page
150
Maintenance: page 163
1-4-6. How to Use This Manual
Background
This section describes the conventions used in
this manual to operate the DCS-9700.
Throughout the manual any reference to pressing
a menu key refers to the keys directly below or
beside any menu icons or parameters.
When the user manual says to “toggle” a value or
parameter, press the corresponding menu item.
Pressing the item will toggle the value or
parameter.
Active parameters are highlighted for each menu
item. For example in the example below, Coupling
is currently set to DC.
If a menu item can be toggled from one value or
parameter to another, the available options will be
visible, with the current option highlighted. In the
example below the slope can be toggled from a
rising slope to a falling slope or either slop.

20
Menu item
Parameter
Menu item
Active
parameter
Optional
parameters
Menu item
Selecting a
Menu Item,
Parameter or
Variable
When the user manual says to “select” a value
from one of the side menu parameters, first press
the corresponding menu key and use the Variable
knob to either scroll through a parameter list or to
increase or decrease a variable.
Example 1
1
2
3
1. Press a bottom menu key to
access the side menu.
2. Press a side menu key to either
set a parameter or to access a sub
menu.
3. If accessing a sub menu or setting
a variable parameter, use the
Variable knob to scroll through
menu items or variables. Use the
Select key to confirm and exit.
VARIABLE
Select
4. Press the same bottom menu key
again to reduce the side menu.

21
Example 2
For some variables, a circular arrow icon indicates
that the variable for that menu key can be edited
with the Variable knob.
1
1. Press the desired menu key to select it. The
circular arrow will become highlighted.
2. Use the Variable knob to edit the value.
Toggling a Menu
Parameter
1
1. Press the bottom menu key
to toggle the parameter.
Reduce Side
Menu
1

22
1. To reduce the side menu, press the
corresponding bottom menu that brought up
the side menu.
For example: Press the Source soft-key to
reduce the Source menu.
Reduce Lower
Menu
1. Press the relevant function
key again to reduce the
bottom menu. For example:
press the Trigger Menu key
to reduce the trigger menu.
TIME/DIV
Autoset
Menu
50 %
Force-Trig
TRIGGER
Acquire
Single
Run/Stop
POSITION
Test
MW16pF
LEVEL
Zoom
1
Default
1
Remove All
Menus

23
1. Press the Menu Off key to
reduce the side menu, press
again to reduce the bottom
menu.
CH1 CH2
POSITION
TIME/DIV
POSITION
POSITION
VOLTS/DIV VOLTS/DIV
Autoset
Menu
50 %
Force-Trig
Select
TRIGGER
HORIZONTAL
VARIABLE
Measure Cursor
Display Help Save/Recall Utility
Acquire
Single
Run/Stop
Search
Set/Clear
CH3 CH4
POSITION
POSITION
VOLTS/DIV VOLTS/DIV
VERTICAL
M
R
B
Test
CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 EXT TRIG
MW16pF
1
MW16pF
Hardcopy
Option
Menu Off
LEVEL
Zoom
MATH
REF
Demo
1
BUS
Visual Persistence Oscilloscope
Default
1
Remove
On-Screen
Messages
2. The Menu Off key can also
be used to remove any on
screen messages.
CH1 CH2
POSITION
TIME/DIV
POSITION
POSITION
VOLTS/DIV VOLTS/DIV
Autoset
Menu
50 %
Force-Trig
Select
TRIGGER
HORIZONTAL
VARIABLE
Measure Cursor
Display Help Save/Recall Utility
Acquire
Single
Run/Stop
Search
Set/Clear
CH3 CH4
POSITION
POSITION
VOLTS/DIV VOLTS/DIV
VERTICAL
M
R
B
Test
CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 EXT TRIG
MW16pF
1
MW16pF
Hardcopy
Option
Menu Off
LEVEL
Zoom
MATH
REF
Demo
1
BUS
Visual Persistence Oscilloscope
Default
1

24
2. QUICK REFERENCE
This chapter describes the DCS-9700 menu tree, shortcuts to
major operations, built-in Help access, and default factory
settings. Use them as a handy reference to get a quick access to
the functionality.
2-1. Menu Tree / Operation Shortcuts
2-1-1. Convention
For all menu trees, the bottom menu keys are
shown as grey icons and side menu keys are
shown in white. All menu tree operations are
shown in order from top to bottom.
Below is an example of the menu tree operation for
the trigger source menu and a comparison to the
operation on the DSO screen.
Menu Tree
Type
Edge
Source Coupling Slope Level Mode Holdoff
CH1~ CH4
EXT
AC Line
EXT Probe
Volt
Current
DC
AC
0.00V~ XX.XV
Set to TTL
1.4V
Set to ECL
-1.3V
Set to 50%
Auto
Normal
00.0ns~
Xxx.xxns
Set to
Minimum
EXT Probe
On
Off
Alternate
1
2
3
1mX ~ 1kX
Attenuation
Off
HF
LF
Reject
On
Off
Noise Reject
On Screen
Menu
1 2
3

25
2-1-2. Acquire Key
Sets the acquisition mode.
Segments
Goes to the Segments menu
Reset H
Position to 0s
XY ET
Sample rate
XXXMSPS
OFF(YT)
Triggered
XY
ET
Sin(x)/x
Mode
Sample
Peak Detect
2,4,8,16,32,64,
128,256
Average
Off, 1% ~ 49%
of sample rate,
Off
Digital Filter
Record
Length
Auto
Short
Acquire
Segments
2-1-3. Acquire Key – Segments
Setup the Segmented Memory function.
Segmented
Select
Segments
Analyze
Segments
Save
Segmented
Segments
Stop
Run
On
Off
Display All
1~2048
Current Seg
Segment
Time
Go Back
On
Off
1~2048
Num of Segs
Set to Maximum
Set to Minimum
Segments
Measure
Segments
Info
CH1~CH4
D0~D15
From
Select
Segmented
To File
DSXXX.CSV
Save Now
File Utilities
Sements Info
Turns on the segments information
overlay.
Segments
Measure
File Utilties
Goes to the File Utilities menu
1~2048
Start
1~2048
End
Set to Minimum
Set to Maximum
Go Back
Off
Plot Source
1~2048
Select
1~20
Divided
Off
1~2048
Select
Save Meas.
to File
CH1~CH4
Source

26
2-1-4. Autoset Key
Automatically finds the signal and sets the horizontal and vertical
scale.
Undo AutosetMode
Fit Screen
AC Priority
Autoset
2-1-5. CH1 ~ 4 Key
Set the channel input parameters.
Voltage
Current
Probe
Impedence Invert Bandwidth Expand by
Position/
Set to 0
xxxV
Probe
On
Off
Coupling
AC
DC
GND
Full
20MHz
100MHz
200MHz
1MΩ
1mX ~ 1kX
Set to 10X
Attenuation
-50ns~50ns
Set to 0s
Deskew
Ground
Center
CH1
2-1-6. Cursor Key
Set cursor positions.
V CursorH Cursor H Unit
Set Cursor
Positions As
100%
Set Cursor
Positions As
100%
S
Hz
%
˚
V Unit
Base
%
Activates menu
item
Activates menu
item
Cursor

27
2-1-7. Display Key
Set the display properties.
Dot Vector Persistence
Dot
Vector
Clear
Persistence
100ms~10s
Infinite
VPO Off
Time
Intensity
0%~100%
Waveform Intensity
10%~100%
Graticule Intensity
Waveform
Gray
Color
Graticule
Full
Grid
Cross Hair
Frame
Display
2-1-8. Help Key
Turn help mode On/Off.
Help

28
2-1-9. Math Key
Standard math and FFT functions.
FFT
Math
CH1~CH4
Ref1~Ref4
Source 1
XXDiv
Position
+
×
÷
Operator
CH1~CH4
Ref1~Ref4
Source 2
XX~XXV
Unit/Div
Advanced
Math
d/dt
∫dt
√
Operator
CH1~CH4
Ref1~Ref4
f(x)
Source
Edit f(x)
XXDiv
Position
XX~XX
Unit/Div
Hanning
Rectangular
Hamming
Blackman
Window
1X
X.XXXMHz
Zoom
CH1~CH4
Ref1~Ref4
f(x)
Source 1
dBV RMS
Linear RMS
Vertical
XXdB
XXDiv
Vertical
M
MATH
+
×
÷
Operator
CH1~CH4
Source 2
Go Back
CH1~CH4
Source 2

29
2-1-10. Measure Key
Display automatic measurements either individually or as
voltage/current, time or delay measurement groups.
Remove
Measurement
Gating Display All
Off
(Full Record)
Add
Measurement
Pk-Pk
Max
Min
Amplitude
High
Low
Mean
Cycle Mean
RMS
Cycle RMS
Area
Cycle Area
ROVShoot
FOVShoot
RPREShoot
FPREShoot
V/I
Frequency
Period
RiseTime
FallTime
+Width
-Width
Dutycycle
+Pulses
-Pulses
+Edges
-Edges
Time
FRR
FRF
FFR
FFF
LRR
LRF
LFR
LFF
Phase
Delay
Screen
Between
Cursors
CH1~CH4
Math
D0~D15
Source 1
High-Low
Auto
High-Low:
Histogram (best
for pulses)
High-Low:
Min-Max
(all other
waveforms)
Set to
Defaults
CH1~CH4
Math
Source 2
Select
Measurement
Remove
Measurement
CH1~CH4
Math
D0~D15
Source
OFF
Statistics
On
Off
Statistics
Samples: 2~XX
Mean & Std Dev
Reset Statistics
Measure

30
2-1-11. Hardcopy Key
Hardcopy
Print screen images or save a waveform, screen
image or setup (depending on the assigned
function).
2-1-12. Run/Stop Key
Run/Stop
Run/stop signal acquisition.
2-1-13. REF Key
R
REF
R2ON/OFF R3ON/OFF R4ON/OFFR1ON/OFF
Vertical scale
Vertical position
Vertical
Horizontal scale
Horizontal position
Horizontal
Edit Labels
Ref Details
Save To File
Goes to the Save Waveform
menu (Save/Recall)
Goes to the Edit Labels menu
(Save/Recall)
Vertical scale
Vertical position
Vertical
Horizontal scale
Horizontal position
Horizontal
Vertical scale
Vertical position
Vertical
Horizontal scale
Horizontal position
Horizontal
Vertical scale
Vertical position
Vertical
Horizontal scale
Horizontal position
Horizontal

31
2-1-14. Save/Recall Key
Save and recall images, waveforms and panel setups. Edit labels for
reference and setup files.
Save Waveform Save Setup
Recall
Waveform
Recall
Setup
Edit File
Label
Edit Label
Save Image
Png
Bmp
File Format
On
Off
Ink Saver
Save Now
File Utilites
Set1~Set20
Filename.set
CH1~CH4
Ref1~4
Set1~20
Label For
ACK
AD0
ADDR
ANALOG
BIT
CAS
CLK
CLOCK
CLR
COUNT
DATA
DTACK
ENABLE
HALT
INT
IN
IRQ
LATCH
LOAD
NMI
User Preset
Edit Character
CH1~CH4
Math
Ref1~4
D0~D15
All Displayed
From
Ref 1 ~ Ref4
Wave1~20
Lsf
Detail Csv
Fast Csv
LM Detail Csv
LM Fast Csv
To
To File
Save Now
File Utilites
Save Now
File Utilites
To File
To
Ref1~Ref4
To
Wave1~20
Lsf
Fast Csv
From
From File
Recall Now
File Utilites
Edit Label
Set1~Set20
Filename.set
From File
From
Recall Now
File Utilites
Goes to the File Utilities menuFile Utilites
Goes to the Keypad menuEdit Character
Goes to the Edit label menuEdit Label
On
Off
Label Display
Save/Recall

32
2-1-15. Test Key
Use the Go-NoGo application as well as other optional software.
APP.
Go-NoGo
Go-NoGo
Goes to the Go-NoGo menu
Unistall
Test
2-1-16. Test Key – Go-NoGo
NG When Violating
Compare
Source
Reference
Mode
Enable
GoNo
CH1
Enter Stop
Exit
Break
Go Back
Break
Stop Beep
Continue
Continue Beep
Go Back
Break
CH2
CH3
CH4
Go Back
Break
Auto
Tolerance
Maximum
Position
Minimum
Position
Save
Operation
Go Back
Break
Disable

33
2-1-17. Trigger Type Menu
Menu
Type
Pulse Runt
Rise & Fall
Bus
Logic
Others
Edge
Delay
Pulse Width
Video
Goes to the Edge Trigger menu
Goes to the Pulse Width Trigger
menu
Goes to the Video Trigger menu
Goes to the Pulse Runt Trigger menu
Goes to the Rise and Fall menu
Goes to the Bus menu
Goes to the Logic menu
2-1-18. Trigger Edge Menu
Type
Edge
Source Coupling Slope Level Mode Holdoff
CH1~ CH4
EXT
AC Line
D0~D15
EXT Probe
Volt
Current
DC
AC
-XX~XXV
Set to TTL
1.4V
Set to ECL
-1.3V
Set to 50%
Auto
Normal
10.0ns~
10.0s
Set to
Minimum
EXT Probe
Off
HF
LF
Reject
On
Off
Noise Reject
On
Off
Alternate
1mX ~ 1kX
Attenuation
2-1-19. Trigger Delay Menu
DC
AC
Off
HF
LF
Reject
On
Off
Noise Reject
Type
Delay
Source Coupling Slope Level Delay Mode / Holdoff
-XX~XXV
Set to TTL
1.4V
Set to ECL
-1.3V
Set to 50%
10.0ns ~ 10.0s
Auto
Normal
Holdoff
10.00ns ~ 10.0s
Set to
Minimum
Time
1~65535
Event Holdoff
Set to
Minimum

34
2-1-20. Trigger Pulse Width Menu
Type
Pulse Width
Source Polarity When Threshold Mode Holdoff
CH1~ CH4
EXT
AC Line
D0~D15
>
<
=
≠
-XX~XXV
Set to TTL
1.4V
Set to ECL
-1.3V
Set to 50%
Auto
Normal
10.0ns ~ 10.0s
> 10.0ns~10.0S
EXT Probe
Volt
Current
EXT Probe
Set to
Minimum
On
Off
Alternate
1mX ~ 1kX
Attenuation
2-1-21. Trigger Video Menu
Type
Video
Source Standard Trigger On Polarity Mode Holdoff
CH1~ CH4
NTSC
PAL
SECAM
1~XXXX
Auto
Normal
All Fields
All Lines
EXT Probe
Volt
Current
EXT Probe
Field 1
1~XXXX
Field 2
10.0ns ~ 10.0s
Set to
Minimum
On
Off
Alternate
1mX ~ 1kX
Attenuation
2-1-22. Trigger Pulse Runt Menu
Type
Pulse Runt
Source Polarity Mode Holdoff
Auto
Normal
EXT Probe
Volt
Current
When
>
<
=
≠
10.0ns~10.0s
Threshold
Set to TTL
1.4V
Set to ECL
-1.3V
-XX~XXV
-XX~XXV
10.0ns~10.0s
Set to
Minimum
On
Off
Alternate
CH1~ CH4
1mX ~ 1kX
Attenuation

35
2-1-23. Trigger Rise & Fall Menu
Type
Rise & Fall
Source Mode Holdoff
Auto
Normal
When
>
<
=
≠
10.0ns~10.0s
Threshold
Set to TTL
1.4V
Set to ECL
-1.3V
-XX~XXV
-XX~XXV
Slope
High
Low
10.0ns~10.0s
Set to
Minimum
EXT Probe
Volt
Current
On
Off
Alternate
CH1~ CH4
1mX ~ 1kX
Attenuation
2-1-24. Trigger Timeout Menu
Type
Timeout
Source Timer
10.0ns~10.0s
Trigger
When
EXT Probe
Volt
Current
CH1~ CH4,
D0~D15, AC
Line
1mX ~ 1kX
Attenuation
DC
AC
Off
HF
LF
Reject
On
Off
Noise Reject
Coupling
Stays High
Stays Low
Either
Level
-XX~XXV
Set to TTL
1.4V
Set to ECL
-1.3V
Set to 50%
Mode / Holdoff
Auto
Normal
Holdoff
10.00ns ~ 10.0s
Holdoff
Set to
Minimum

36
2-1-25. Utility Key
System
Data &
Time
Hardcopy
File Utilities
I/OLanguage
English
Trad. Chinese
Simp. Chinese
Korean
Japanese
Polish
French
Spanish
Russian
German
Ethernet
RS-232C
System
Info
SPC
On
Off
Ink Saver
Print
Save
Function
Create Folder
Rename
Delete
More 1 of 2
2XXX
Year
Jan~Dec
01~31
Month Day
0~59
0~59
Hour Minute
Save Now
USB Device
Bmp
Png
File Format
Erase Memory
Image
Waveform
Setup
All
Assign Save To
Socket Server
More 1 of 2
Ethernet
RS-232C
USB Device
Port
Goes to the I/O USB Device
Port menu
Goes to the I/O Ethernet menu
Goes to the I/O RS232 menu
Socket Server
Create Folder
Goes to the I/O Socket Server
menu
Goes to the File Utilities
Rename
Goes to the File Utilities
SPC
Start
Abort
On
Off
Buzzer
0~30
GPIB
Demo Output
Analog
UART
I2C
SPI
Demo Mode
Demo 1*
Demo 2*
Demo 1~3*
See Wave Gener
Self Cal
Factory Setting
Self Cal
Option
Uninstall
More
2 of 2
Goes back to System menu
Goes to Uninstall menu
Goes to the Self Cal menu
Goes to the Factory menu
Goes to the Self Cal menu
Utility
Port
Demo 3*
* Demo 1, Demo 2, Demo 3 outputs depend on the Demo Output
settings.

37
2-1-26. Utility Key – I/O
I/O
USB Device
Port
Ethernet
RS-232C
Go Back
Save Now
On
Off
DHCP/BOOTP
2400, 4800,
9600, 19200,
38400, 57600,
115200
Baud Rate
1, 2
Stop Bit
Odd
Even
None
Parity
Back Space
Save Now
Socket Server
On
Off
Server
Current Port
3000
0 to 65535
Select Port
Set Port
Computer
Printer
2-1-27. Utility Key – File Utilities
File Utilities Create Folder
Rename
Delete
Keypad
Enter Character
Back Space
Editing
Completed
Cancel
Keypad
Enter Character
Back Space
Editing
Completed
Cancel
Copy To USB

38
2-1-28. Utility Key – Wave Generator - Demo Outputs
Demo Output
Analog
UART
I2C
SPI
Demo Mode
Demo 1
SCLK
Demo 1
SCLK
Demo 1
Tx
Demo 1
Trigger Output
Demo 3
MOSI
Demo 3
Probe Comp.
Demo 3
Probe Comp.
Demo 3
Probe Comp.
Demo 2
SS
Demo 2
SDA
Demo 2
Rx
Demo 2
FM
1~200kHz
Default
1kHz
Frequency
5~95%
Dutycycle
2-1-29. Search - Edge
Set the Search Function for edge events.
Search
On
Off
Search
Save All
Marks
Clear All
Marks
Copy Trigger
Settings To
Search
Copy Search
Settings To
Trigger
Search Type
Edge
Pulse Width
Runt
Rise/Fall Time
Logic
Bus
Search
Slope Threshold
-XX~XXV
Set to TTL
1.4V
Set to ECL
-1.3V
Set to 50%
Search
Source
CH1~ CH4
D0~D15

39
2-1-30. Search – Pulse Width
Set the Search Function for pulse width events.
Edge
Pulse Width
Runt
Rise/Fall Time
Logic
Bus
Search
Search
On
Off
Search
Save All
Marks
Clear All
Marks
Copy Trigger
Settings To
Search
Copy Search
Settings To
Trigger
Search Type
Polarity
When
>
<
=
≠
10.0ns~10.0S
Threshold
-XX~XXV
Set to TTL
1.4V
Set to ECL
-1.3V
Set to 50%
Source
CH1~ CH4
D0~D15
Search
2-1-31. Search - Runt
Set the Search function for runt events.
Edge
Pulse Width
Runt
Rise/Fall Time
Logic
Bus
Search
Polarity When
>
<
=
≠
10.0ns~10.0S
Threshold
Set to TTL
1.4V
Set to ECL
-1.3V
-XX~XXV
-XX~XXV
Search
On
Off
Search
Save All
Marks
Clear All
Marks
Copy Trigger
Settings To
Search
Copy Search
Settings To
Trigger
Search Type
Search
Source
CH1~ CH4
D0~D15

40
2-1-32. Search – Rise/Fall Time
Set the Search function for rise and fall time events.
Edge
Pulse Width
Runt
Rise/Fall Time
Logic
Bus
Search
Slope When
>
<
=
≠
10.0ns~10.0s
Threshold
Set to TTL
1.4V
Set to ECL
-1.3V
-XX~XXV
-XX~XXV
High
Low
Search
On
Off
Search
Save All
Marks
Clear All
Marks
Copy Trigger
Settings To
Search
Copy Search
Settings To
Trigger
Search Type
Source
CH1~ CH4
Search
*The source bus is determined from the bus trigger settings.
2-1-33. Zoom Key
H Position/
Set to 0
Zoom Position/
Set to 0
Zoom Position
Reset Zoom &
H POS to 0s
XXXXmsXXXXms
Fine
Coarse
Zoom

41
2-1-34. Option Key
Accesses the functions in the Option menu.
Function
Generator
I/O
Logic
Analyzer
Option
Logic
Analyzer
Function
Generator
Goes to the Logic Analyzer menu
Goes to the Function Generator menu
I/O
Goes to the options I/O menu
*Note: Any option that is not installed will be grayed-out.

42
2-2. Default Settings
The default factory installed settings can be
recalled at any time by pressing the Default key.
Default
Acquire
Mode: Sample
XY: OFF
Interpolation: Sin(x)/x
Sample rate: 2GSPS
Record Length: Auto
Display
Mode: Vector
Persistence: 240ms
Waveform intensity: 50%
Graticule intensity: 50%
Waveform visuals: Gray
Graticule: full
Channel
Scale: 100mV/Div
CH1: On
Coupling: DC
Impedance: 1MΩ
Invert: Off
Bandwidth: full
Expand: By ground
Position: 0.00V
Probe: voltage
Probe attenuation: 1x
Deskew: 0s
Cursor
Horizontal cursor: Off
Vertical Cursor: Off
Measure
Source: CH1
Gating: Screen
Display: Off
High-Low: Auto
Statistics: Off
Mean & Std Dev
Samples: 2
Horizontal
Scale: 10us/Div
Position: 0.000s
Math
Source1: CH1
Operator: +
Source2: CH2
Position: 0.00 Div
Unit/Div: 200mV
Math Off
Test
App: Go-NoGo
Trigger
Type: Edge
Source: CH1
Coupling: DC
Alternate: Off
Rejection: Off
Noise Rejection: Off
Slope: Positive
Level: 0.00V
Mode: Auto
Holdoff: 10.0ns
Utility
Hardcopy: Save
Ink Saver: Off
Assign Save To: Image
File Format: Bmp
Search
Search: Off
Segments
Segments: Off

43
2-3. Built-in Help
The Help key accesses a context sensitive help menu. The help
menu contains information on how to use the front panel keys.
Panel Operation
1. Press the Help key. The
display changes to Help
mode.
Help
2. Use the Variable knob to scroll up and down
through the Help contents. Press Select to view
the help on the selected item.
Example: Help
on the Display
key
Home Key
Press the Home key to return to
the main help screen.
Go Back
Press the Back key to go to the
previous menu page.
Exit
Press the Help key again or
press the Exit key to exit the
Help mode.
Help

44
3. MEASUREMENT
3-1. Basic Measurement
This section describes the basic operations required in capturing
and viewing the input signal. For more detailed operations, see the
following chapters.
• Cursor Measurement → from page 59
• Configuration → from page 70
Before operating the oscilloscope, please see the Getting Started.
3-1-1. Channel Activation
Activate
Channel
To activate an input channel,
press a channel key.
When activated, the channel
key will light up. The
corresponding channel menu
will also appear.
CH1CH1
Each channel is associated with the color shown
beside the VOLTS/DIV dial: CH1: yellow, CH2:
blue, CH3: pink and CH4: green.
When a channel is activated, it is shown above the
bottom menu system.
CH1 CH3CH2 CH4
De-activate
Channel
To de-activate a channel, press
the corresponding channel key
again. If the channel menu is
not open, press the channel
key twice (the first press shows
the Channel menu).
CH1CH1
Default Setup
To activate the default state,
press Default.
Default

45
3-1-2. Autoset
Background
The Autoset function automatically configures the
panel settings to position the input signal to the
best viewing condition.
The DCS-9700 automatically configures the
following parameters.
• Horizontal scale
• Vertical scale
• Trigger source channel
There are two operating modes for the Autoset
function: Fit Screen Mode and AC Priority Mode.
Fit Screen Mode will fit the waveform to the best
scale, including any DC components (offset). AC
priority mode will scale the waveform to the screen
by removing any DC component.
Panel Operation
1. Connect the input signal to the
DCS-9700 and press the Autoset
key.
Autoset
2. The waveform appears in the center of the
display.
Before
After
3. To undo Autoset, press Undo
Autoset from the bottom menu.
Change modes
1. Choose between Fit Screen
Mode and AC Priority Mode from
the bottom menu.
2. Press the Autoset key again to
use Autoset in the new mode.
Autoset

46
Fit Screen Mode
AC Priority
Limitation
Autoset does not work in the following situations.
• Input signal frequency is less than 20Hz
• Input signal amplitude is less than 30mV
Note
The Autoset key (page 45) does NOT automatically
activate the channels to which input signals are
connected.
3-1-3. Run/Stop
Background
By default, the waveform on the display is
constantly updated (Run mode). Freezing the
waveform by stopping signal acquisition (Stop
mode) allows flexible observation and analysis. To
enter Stop mode, two methods are available:
pressing the Run/Stop key or using the Single
Trigger mode.
Stop mode icon
When in Stop mode, the Stop icon
appears at the top of the display.
Triggered icon
Freeze
Waveform by
Run/Stop Key
Press the Run/Stop key once.
The Run/Stop key turns red.
The waveform and signal
acquisition freezes.
Stop:
Run/Stop Run/Stop
To unfreeze, press the
Run/Stop key again. The
Run/Stop key turns green
again.
Run:
Run/Stop Run/Stop

47
Freeze
Waveform by
Single Trigger
Mode
Press the Single key to go into
the Single Trigger mode. The
Single key turns bright white.
In the Single Trigger mode, the
scope will be put into the pretrigger mode until the scope
encounters the next trigger
point. After the scope has
triggered, it will remain in Stop
mode, until the Single key is
pressed again or the Run/Stop
key is pressed.
Single Single
Waveform
Operation
The waveform can be moved or scaled in both Run
and Stop mode, but in different manners. For
details, see page 87 (Horizontal position/scale) and
page 91 (Vertical position/scale).
3-1-4. Horizontal Position/Scale
For more detailed configuration, see page 87.
Set Horizontal
Position
The horizontal position knob
moves the waveform left and
right.
POSITION
As the waveform moves, the display bar on the top
of the display indicates the portion of the waveform
currently shown on the display and the position of
the horizontal marker on the waveform.
Position
Indicator
The horizontal position is shown at the bottom of
the display grid to the right of H icon.
Select
Horizontal Scale
To select the timebase (scale),
turn the TIME/DIV knob; left
(slow) or right (fast).
TIME/DIV
Range
1ns/div ~ 100s/div, 1-2-5 increments
The Time/Division rate is displayed to the left of the
H icon at the bottom of the screen.

48
Display bar
The display bar indicates how much
of the waveform is displayed on the
screen at any given time. Changes to
timebase will be reflected on the
display bar.
Fast
Medium
Slow
Stop mode
In the Stop mode, the waveform size
changes according to the scale.
Note
The Sample rate changes according to the
time/division and record length. See page 75.
3-1-5. Vertical Position/Scale
For more detailed configuration, see page 91.
Set Vertical
Position
To move the waveform up or
down, turn the vertical position
knob for each channel.
POSITION
As the waveform moves, the vertical position of the
cursor appears on the display.
Run/Stop
mode
The waveform can be moved
vertically in both Run and Stop
mode.
Select Vertical
Scale
To change the vertical scale,
turn the VOLTS/DIV knob; left
(down) or right (up).
VOLTS/DIV
Range
1mV/div ~ 10V/div
1-2-5 increments

49
The vertical scale indicator for
each channel on the bottom of
the display changes
accordingly.
3-2. Automatic Measurement
The automatic measurement function measures and updates major
items for Voltage/Current, Time, and Delay type measurements.
Measurements can be made with both the analog channels and the
digital channels*, however the digital channels are only limited to a
select number of time measurements. *Logic analyzer option
needed for digital channels.
3-2-1. Measurement Items
V/I Measurements
Time Meas.
Delay Meas.
Overview
FPREShoot
RPREShoot
FOVShoot
ROVShoot
Cycle Area
Area
Cycle RMS
RMS
Cycle Mean
Mean
Low
High
Amplitude
Min
Max
Pk-Pk
Frequency*
Dutycycle*
-Width*
+Width*
FallTime
RiseTime
Period*
-Edges
+Edges
-Pulses
+Pulses
FRR
FRF
FFR
Phase
LFF
LFR
LRF
LRR
FFF
*The logic analyzer option is needed to use the
digital channels for these automatic measurements.

50
Voltage/Curren
t Measurement
Pk-Pk
(peak to
peak)
Difference between positive
and negative peak.
(=max − min)
Max
Positive peak.
Min Negative peak.
Amplitude
Difference between the
global high and value and the
global low value, measured
over the entire waveform or
gated region. (=high − low)
High
Global high voltage. See
page 56 for details.
Low
Global low voltage. See page
56 for details.
Mean
The arithmetic mean value is
calculated for all data
samples as specified by the
Gating option.
Cycle Mean
The arithmetic mean value is
calculated for all data
samples within the first cycle
found in the gated region.
RMS
The root mean square of all
data samples specified by
the Gating option.
Cycle RMS
The root mean square value
is calculated for all data
samples within the first cycle
found in the gated region.
Area
Measures the positive area
of the waveform and
subtracts it from the negative
area. The ground level
determines the division
between positive and
negative areas.
Cycle Area
The Summation based on all
data samples within the first
cycle found in the gated
region.

51
ROVShoot
Rise overshoot
FOVShoot
Fall overshoot
RPREShoot
Rise preshoot
FPREShoot
Fall preshoot
Time
Measurement
Frequency
Frequency of the waveform.
Period
Waveform cycle time.
(=1/Freq)
RiseTime
The time required for the
leading edge of the first pulse
to rise from the low reference
value to the high reference
value.
FallTime
The time required for the
falling edge of the first pulse
to fall from the high reference
value to the low reference
value.
+Width
Positive pulse width.
–Width
Negative pulse width.
Duty Cycle
Ratio of signal pulse
compared with whole cycle.
=100x (Pulse Width/Cycle)
+Pulses
Measures the number of
positive pulses.
-Pulses
Measures the number of
negative pulses.
+Edges
Measures the number of
positive edges.
-Edges
Measures the number of
negative edges.
Delay
Measurement
FRR
Time between:
Source 1 first rising edge and
Source 2 first rising edge.
FRF
Time between:
Source 1 first rising edge and
Source 2 first falling edge.

52
FFR
Time between:
Source 1 first falling edge
and Source 2 first rising
edge.
FFF
Time between:
Source 1 first falling edge
and Source 2 first falling
edge.
LRR
Time between:
Source 1 first rising edge and
Source 2 last rising edge.
LRF
Time between:
Source 1 first rising edge and
Source 2 last falling edge.
LFR
Time between:
Source 1 first falling edge
and Source 2 last rising
edge.
LFF
Time between:
Source 1 first falling edge
and Source 2 last falling
edge.
Phase
The phase difference of two
signals, calculated in
degrees.
360x
t2
t1
Note
The in-built help system can be used to see detailed
automatic measurement definitions.

53
3-2-2. Add Measurement
The Add Measurement function allows you to add up to eight
automatic measurement items on the bottom of the screen from any
channel source.
Add
Measurement
Item
1. Press the Measure key.
Measure
2. Press Add Measurement from the
bottom menu.
3. Choose either a V/I, Time or Delay
measurement from the side menu
and choose the type of
measurement you wish to add.
V/I
(Voltage/
Current)
Pk-Pk, Max, Min, Amplitude, High,
Low, Mean, Cycle Mean, RMS,
Cycle RMS, Area, Cycle Area,
ROVShoot, FOVShoot,
RPREShoot, FPREShoot
Time
Frequency, Period, RiseTime,
FallTime, +Width, –Width, Duty
Cycle, +Pulses, -Pulses, +Edges, Edges
Delay
FRR, FRF, FFR, FFF, LRR, LRF,
LFR, LFF, Phase
4. All measurements will be displayed in a window
on the bottom of the screen. The channel
number and channel color indicate the
measurement source.
For the analog inputs: yellow = CH1,
blue = CH2, pink = CH3, green = CH4.
Choose a
Source
The channel source for measurement items can be
set either before or when selecting a measurement
item.

54
1. To set the source, press either the
Source1 or Source2 key from the
side menu and choose the source.
Source 2 is only applicable for
delay measurements.
Range
CH1~ CH4, Math*, D0~D15**
*The math source cannot include any digital
(D0~D15) inputs.
**Only available with the Logic Analyzer option.
3-2-3. Remove Measurement
Individual measurements can be removed at any time using the
Remove Measurement function.
Remove
Measurement
Item
1. Press the Measure key.
Measure
2. Press Remove Measurement from
the bottom menu.
3. Press Select Measurement and
select the item that you want to
remove from the measurement list.
Remove All
Items
Press Remove All to remove all the
measurement items.
3-2-4. Gated mode
Some automatic measurements can be limited to a “gated” area
between cursors. Gating is useful for measuring a magnified
waveform or when using a fast time base. The Gated mode has
three possible configurations: Off (Full Record), Screen and
Between Cursors.
Set Gating Mode
1. Press the Measure key.
Measure
2. Press Gating from the bottom
menu.

55
3. Choose one of the gating modes
from the side menu: Off (full
record), Screen, Between Cursors
Cursors On
Screen
If Between Cursors is selected, the
cursor positions can be edited by
using the cursor menu.
Page 59
3-2-5. Display All mode
Display All mode shows and updates all items from Voltage and
Time type measurements.
View
Measurement
Results
1. Press the Measure key.
Measure
2. Press Display All from the bottom
menu.
3. Press Source from the side menu
and choose a measurement
source.
Range
CH1~CH4, Math, D0~D15
4. The results of Voltage and Time type
measurements appear on the display.
Remove
Measurements
To remove the measurement results,
press OFF.

56
Delay
Measurements
Delay type measurement is not available in this
mode as only one channel is used as the source.
Use the Individual measurement mode (page 53)
instead.
Digital Channels
Only Frequency, Period, +Width, -Width and Duty
Cycle measurements are supported for digital
channels.
3-2-6. High Low Function
Background
The High-Low function is used to select the
method for determining the value of the High-Low
measurement values.
Auto
Automatically chooses the best
high-low setting for each waveform
when measuring.
Histogram
Uses histograms to determine the
high-low values. This mode
ignores any preshoot and
overshoot values. This mode is
particularly useful for pulse-type
waveforms
low
high
Min-max
Sets the high-low values as the
measured minimum or maximum
measured values.
low
high
Set High-Low
1. Press the Measure key.
Measure
2. Press High-Low from the bottom
menu.

57
3. Select the type of High-Low settings from the
side menu.
High-Low Settings:
Histogram, Min-Max, Auto
Restore Default
High-Low
Settings
To return to the default High-Low
settings, press Set to Defaults.
3-2-7. Statistics
Background
The Statistics function can be used to view a
number of statistics for the selected automatic
measurements. The following information is
displayed with the Statistics function:
Value
Currently measured value
Mean
The mean value is calculated from
a number of automatic
measurement results. The number
of samples used to determine the
mean can be user-defined.
Min
The minimum value observed from
a series of measured results for
the selected automatic
measurement items.
Max
The maximum value observed
from a series of measured results
for the selected automatic
measurement items.

58
Standard
Deviation
The variance of the currently
measured value from the mean.
The standard deviation equals the
squared root of the variance value.
Measuring the standard deviation
can, for example, determine the
severity of jitter in a signal.
The number of samples used to
determine the standard deviation
can be user-defined.
Set High-Low
1. Press the Measure key.
Measure
2. Select at least one automatic
measurement.
Page 53
3. Set the number of samples to be
used in the mean and standard
deviation calculations.
Samples:
2~1000
4. Press Statistics from the bottom
menu and turn the Statistics
function on.
5. The statistics will appear at the bottom of the
display in a table.
Reset Statistics
To reset the statistics calculations,
press Reset Statistics.

59
3-3. Cursor Measurement
Horizontal or vertical cursors are used to show the position and
values of waveform measurements and math operation results.
These results cover voltage, time, frequency and other math
operations. When the cursors (horizontal, vertical or both) are
activated, they will be shown on the main display unless turned off.
(page 86).
3-3-1. Use Horizontal Cursors
Panel Operation/
Range
1. Press the Cursor key once.
Cursor
2. Press H Cursor from the bottom
menu if it is not already selected.
3. When the H Cursor is selected,
repeatedly pressing the H Cursor
key or the Select key will toggle
which cursor is selected.
OR
Select
Range
Description
Left cursor ( ) movable, right
cursor position fixed
Right cursor ( ) movable, left
cursor position fixed
Left and right cursor ( + )
movable together
4. The cursor position
information appears on the
top left hand side of the
screen
Cursor
Hor. position, Voltage/Current
Cursor
Hor. position, Voltage/Current
Delta (difference between cursors)
dV/dt or dI/dt
5. Use the Variable knob to move the
movable cursor(s) left or right.
VARIABLE

60
Select Units
6. To change the units of the
horizontal position, press H Unit.
Units
S, Hz, % (ratio), ˚(phase)
Phase or Ratio
Reference
7. To set the 0% and 100% ratio or
the 0˚ and 360˚ phase references
for the current cursor positions,
press Set Cursor Positions As
100%.
Example
Horizontal
cursors
FFT
FFT cursors use different vertical
units. For FFT details, see page
66.
Cursor
Hor. position, dB/Voltage
Cursor
Hor. Position, dB/Voltage
Delta (difference between cursors)
dV/dt or d/dt
Example
Horizontal
cursors
XY Mode
XY mode cursors measure a number of X by Y
measurements.

61
Cursor
Time, rectangular, polar coordinates, product, ratio.
Cursor
Time, rectangular, polar coordinates, product, ratio.
Delta (difference between cursors)
Example
Horizontal
cursors
3-3-2. Use Vertical Cursors
Panel Operation/
Range
1. Press the Cursor key twice.
Cursor
x2
2. Press V Cursor from the bottom
menu if it is not already selected.
3. When the V Cursor is selected,
repeatedly pressing the V Cursor
key or the Select key will toggle
which vertical cursor is selected.
OR
Select

62
Range
Upper cursor movable, lower cursor
position fixed
Lower cursor movable, upper cursor
position fixed
Upper and lower cursor movable
together
4. The cursor position
information appears on the
top left hand side of the
screen.
,
Time: cursor 1, cursor 2
,
Voltage/Current: cursor1, cursor2
Delta (difference between cursors)
dV/dt or dI/dt
5. Use the Variable knob to move the
cursor(s) up or down.
VARIABLE
Select Units
6. To change the units of the vertical
position, press V Unit.
Units
Base (source wave units), % (ratio)
Base or Ratio
Reference
7. To set the 0% and 100% ratio
references for the current cursor
position, press Set Cursor
Positions As 100%.
Example
Horizontal
cursors
Vertical
cursors
FFT
FFT has different content. For
FFT details, see page 66.

63
,
Frequency/Time: cursor1, cursor2
,
dB/V: cursor1, cursor2
Delta (difference between cursors)
d/dt
Example
Horizontal
cursors
Vertical
cursors
XY Mode
XY mode cursors measure a number of X by Y
measurements.
Cursor
Rectangular, polar co-ordinates,
product, ratio.
Cursor
Rectangular, polar co-ordinates,
product, ratio.
Delta (difference between cursors)

64
Example
Horizontal
cursors
Vertical
cursors
3-4. Math Operation
3-4-1. Overview
Background
Math operation runs addition, subtraction,
multiplication, division, FFT, or certain advanced
math functions for waveform manipulations using
the input signals or reference waveforms (Ref1~4)
and shows the result on the display. The resulted
waveform characteristics can be measured using
the cursors.
Addition (+)
Adds the amplitude of two signals.
Source
CH1~4, Ref1~4
Subtraction (–)
Extracts the amplitude difference between two
signals.
Source
CH1~4, Ref1~4
Multiplication (×)
Multiplies the amplitude of two signals.
Source
CH1~4, Ref1~4
Division (÷)
Divides the amplitude of two signals.
Source
CH1~4, Ref1~4
FFT
Runs FFT calculations on a signal. Four types of
FFT windows are available: Hanning, Hamming,
Rectangular, and Blackman.
Source
CH1~4, Ref1~4, f(x)
d/dt
Differentiate the source waveform.
Source
CH1~4, Ref1~4, f(x)
∫dt
Integrate the source waveform with respect to time.
Source
CH1~4, Ref1~4, f(x)
√
Performs a square root calculation.
Source
CH1~4, Ref1~4, f(x)
Hanning FFT
Window
Frequency
resolution
Good

65
Amplitude resolution
Not good
Suitable for....
Frequency measurement on
periodic waveforms
Hamming FFT
Window
Frequency
resolution
Good
Amplitude resolution
Not good
Suitable for....
Frequency measurement on
periodic waveforms
Rectangular FFT
Window
Frequency
resolution
Very good
Amplitude resolution
Bad
Suitable for....
Single-shot phenomenon (this
mode is the same as having
no window at all)
Blackman FFT
Window
Frequency
resolution
Bad
Amplitude resolution
Very good
Suitable for....
Amplitude measurement on
periodic waveforms
3-4-2. Addition/Subtraction/Multiplication/Division
Panel Operation
1. Press the Math key.
M
MATH
2. Press the Math key on the lower
bezel.
3. Select Source 1 from the side
menu
Range
CH1~4, Ref~4
4. Press Operator to choose the math
operation.
Range
+, -, ×, ÷
5. Select Source 2 from the side
menu.
Range
CH1~4, Ref~4
6. The math measurement result appears on the
display. The vertical scale of the math waveform
appears at the bottom of the screen.
From left: Math function, source1, operator,
source2, Unit/div

66
Example
Math
Source 2
Source 1
Position and
Unit
To move the math waveform vertically,
press the Position key from the side
menu and use the Variable knob to set
the position.
Range
–12.00 Div ~ +12.00 Div
To change the unit/div settings, press
Unit/div, then use the Variable knob to
change the unit/div.
The units that are displayed depend
on which operator has been selected,
and whether the probe for the
selected channel has been set to
voltage or current.
Operator:
Unit/div:
Multiplication
Division
Addition/Subtraction
VV, AA or W
V/V, A/A
V or A
Turn Off Math
To turn off the Math result from the
display, press the Math key again.
M
MATH
3-4-3. FFT
Panel Operation
1. Press the Math key.
M
MATH
2. Press FFT from the bottom menu.
3. Select the Source from the side
menu.
Range
CH1~4, Ref~4, f(x)*
*the f(x) source is set in the advanced math
function, page 69.

67
4. Press the Vertical Units key from
the side menu to select the vertical
units used.
Range
Linear RMS, dBV RMS
5. Press the Window key from the
side menu and select the window
type.
Range
Hanning, Hamming, Rectangular,
and Blackman.
6. The FFT result appears. For FFT, the horizontal
scale changes from time to frequency, and the
vertical scale from voltage/current to dB/RMS.
Source
Math
Position and
Scale
To move the FFT waveform vertically,
press Vertical until the Div parameter
is highlighted and then use the
Variable knob.
Range
–12.00 Div ~ +12.00 Div
To select the vertical scale of the FFT
waveform, press Vertical until the dB
or voltage parameters are highlighted
and then use the Variable knob.
Range
2mV~1kV RMS, 1~20 dB
Zoom and Offset
To zoom into the FFT waveform, press
Zoom until the x times parameter is
highlighted and then use the Variable
knob.
Range
1x ~ 20x
To horizontally offset the FFT
waveform, press Zoom until the
frequency parameter is highlighted
and then use the Variable knob.

68
Clear FFT
To clear the FFT result from the
display, press the Math key again.
M
MATH
3-4-4. Advanced Math
Background
The advanced math function is used to perform a
number of advanced math functions such as
differentiation or integration of a source waveform.
The f(x) source function (as used in the FFT
function) can also be set from the advanced menu.
Panel Operation
1. Press the Math key.
M
MATH
2. Press Advanced Math from the
bottom menu.
3. Select the Operator from the side
menu.
Range
d/dt, ∫dt, √
4. Select the Source from the side
menu.
Range
CH1~4, Ref~4, f(x)*
*the f(x) source is set with the Edit F(x)
function, page 69.
5. The math result appears. For the
differential/integral operations, the unit/div scale
changes accordingly.
Advanced Math
Source
Position and
Unit
To move the math waveform vertically,
press Position and use the Variable
knob.
Range
–12.00 Div ~ +12.00 Div

69
To select the vertical scale of the math
waveform, press Unit/div and use the
Variable knob.
Clear Advanced
Math
To clear the advanced math result
from the display, press the Math key
again.
M
MATH
3-4-5. Edit F(x)
Background
The f(x) source is a user-defined math function that
can be used as a source waveform for the FFT or
advanced math functions. The f(x) source
waveform is created by the addition, subtraction,
multiplication or division of two input waveforms.
Panel Operation
1. Press the Math key.
M
MATH
2. Press Advanced Math from the
bottom menu.
3. Press the Edit f(x) key to edit the
f(x) waveform.
4. Select Source 1 from the side
menu
Range
CH1~4
5. Press Operator to choose the math
operation.
Range
+, -, ×, ÷
6. Select Source 2 from the side
menu.
Range
CH1~4
7. The f(x) source waveform is now
set, press Go Back to return to the
Advanced Math menu.

70
4. CONFIGURATION
4-1. Acquisition
The Acquisition process samples the analog input signals and
converts them into digital format for internal processing.
4-1-1. Select Acquisition Mode
Background
The acquisition mode determines how the samples
are used to reconstruct a waveform.
Sample
This is the default acquisition
mode. Every sample from each
acquisition is used.
Peak detect
Only the minimum and maximum
value pairs for each acquisition
interval (bucket) are used. This
mode is useful for catching
abnormal glitches in the signal.
Average
Multiple acquired data is
averaged. This mode is useful for
drawing a noise-free waveform. To
select the average number, use
the Variable knob.
Average number: 2, 4, 8, 16, 32,
64, 128, 256
Panel Operation
1. Press the Acquire key.
Acquire
2. To set the Acquisition mode, press
Mode on the bottom menu.
3. Select an acquisition mode from
the side menu.
4. If Average was chosen, set the
number of samples to be used for
the average function.
Mode
Sample, Peak
Detect, Average
Average
sample
2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64,
128, 256

71
Example
Sample
Peak Detect
Average (256 times)
4-1-2. Digital Filter
Background
The digital filter function can remove unwanted
components, such as noise, from the desired
signal.
The filtering only functions during continuous
acquisition using either the Sample or Peak detect
mode.
The cut-off frequency range and step resolution of
the digital filter is expressed as a fraction of the
underlying sample rate, as shown below.
Range
Resolution
1% ~ 49% of sample rate, Off
1% of sample rate
Panel Operation
1. Press the Acquire key.
Acquire
2. Press Mode on the bottom menu.
3. Set the acquisition mode to
Sample or Peak Detect.

72
4. Press Digital Filter and set the
digital frequency using the Variable
knob.
Turn the Variable knob fully
anticlockwise to turn the digital
filter off.
4-1-3. Show Waveform in XY Mode
Background
The XY mode maps the input of channel 1 to the
input of channel 2. the input of channel 3 can be
mapped to the input of channel 4. This mode is
useful for observing the phase relationship
between waveforms.
Reference waveforms can also be used in XY
mode. Ref1 is mapped to Ref2 and Ref3 is
mapped to Ref4. Using the reference waveforms is
the same as using the channel input waveforms.
Connection
1. Connect the signals to
Channel 1 (X-axis) and
Channel 2 (Y-axis) or
Channel 3 (X2-axis) and
Channel 4 (Y2-axis).
CH3CH2CH1 CH4
YX X2 Y2
2. Make sure a channel pair is active
(CH1&CH2 or CH3&CH4). Press
the Channel key if necessary. A
channel is active if the channel key
is lit.
CH1CH1
CH2CH2
Panel Operation
1. Press the Acquire menu key.
Acquire
2. Press XY from the bottom menu.
3. Choose Triggered XY from the side
menu.

73
X-Y mode is split into two windows. The top
window shows the signals over the full time range.
The bottom window shows XY mode.
To move the X Y waveform position, use the
vertical position knob: Channel 1 knob moves the
X Y waveform horizontally, Channel 2 knob moves
the X Y waveform vertically. Similarly, the X2 and
Y2 axis can be positioned using the channel 3 and
channel 4 vertical position knobs.
POSITION
CH1
POSITION
CH2
The horizontal position knob and Time/Div knob
can still be used under the XY mode.
Turn Off XY
Mode
To turn off XY mode, choose OFF (YT)
mode.
XY Mode
Cursors can be used with XY mode.
See the Cursor chapter for details.
Page 59

74
4-1-4. Set the Sampling Mode
Background
The DCS-9700 has two types of sampling modes:
ET (Equivalent Time) and Sin(x)/x interpolation.
Equivalent time sampling is able to achieve a
sample rate of 100GSa/s when sampling periodic
waveforms. Sin(x)/x interpolation uses a sinc
interpolation formula to reconstruct a continuous
signal between sampled points.
Sin(x)/x
One sample of data is used to
reconstruct a single waveform.
Sin(x)/x sampling should be used
when the time base is relatively
slow or if single shot events need to
be captured.
Equivalenttime sampling
Sampled data is accumulated a
number of times to reconstruct a
single waveform. This increases the
sampling rate, but can only be used
for repetitive signals. This mode is
usually used when the time base is
too fast for real-time sampling.
Panel Operation
1. Press the Acquire key.
Acquire
2. Press the ET/sin(x)/x key on the
bottom menu to toggle between
equivalent time sampling (ET) and
sin(x)/x interpolation.
The sampling rate will be shown on the bottom
right-hand corner.
Sample
rate
Sampling
mode

75
4-1-5. Set the Record Length
Background
The number of samples that can be stored is set
by the record length. Record length is important in
an oscilloscope as it allows longer waveforms to be
recorded and/or allows higher sampling rates to be
achieved when equivalent time sampling is used.
There are two record length settings, Auto and
Short. The Auto setting will set the record length to
maximum record length available, dependent on
the scope settings. The Short setting will set the
record length to 1k.
The maximum record length for the DCS-9700
depends on the number of active channels, which
channels are active, and whether the normal or
single shot triggering mode is used. The table
below describes the record lengths that are
available for each triggering mode.
Channel Setting
Trigger Mode
Single
Normal
Auto
CH1 on
2M
1M
1M
CH2 on
2M
1M
1M
CH3 on
2M
1M
1M
CH4 on
2M
1M
1M
CH1, CH3 on
2M
1M
1M
CH1, CH4 on
2M
1M
1M
CH2, CH3 on
2M
1M
1M
CH2, CH4 on
2M
1M
1M
CH1, CH2 on
1M
500k
500k
CH3, CH4 on
1M
500k
500k
CH1, CH2, CH3 on
1M
500k
500k
CH1, CH2, CH4 on
1M
500k
500k
CH2, CH3, CH4 on
1M
500k
500k
CH1, CH3, CH4 on
1M
500k
500k
CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4 on
1M
500k
500k
Panel Operation
1. Press the Acquire key.
Acquire
2. Press the Record Length key on
the bottom menu and choose Auto
or Short mode.
Note
The sampling rate may also be changed when the
record length is changed.

76
4-2. Segmented Memory Acquisition
The advanced segmented memory utility allows the scope memory
to be divided into different segments. Each time the scope is
triggered, it only acquires data for one segment of memory at a time.
This allows you to use the full potential of the scope one segment at
a time. This effectively allows you to capture intermittent signal
events while ignoring signal inactivity.
The Advanced Segment Memory Utility is applicable for both analog
and digital channels.
4-2-1. Segments Display
Run/Stop Indicator
Progress Indicator
Progress Indicator
Indicates the number of
segments that have to been
captured relative to the set
number of segments.
Run/Stop Indicator
Stop: The segments have finished
acquiring or have been stopped.
Run: The scope is currently acquiring
segments.
4-2-2. Set the Number of Segments
Note
Before the Segment function can be used, set the
trigger settings as appropriate for the signal you
wish to use.
Panel Operation
1. Press the Acquire key.
Acquire

77
2. Press Segments on the bottom
menu.
3. Press Select Segments and set the
number of segments from the side
menu.
Logic Type
Threshold
Num of Seg
1~2048
Set to Maximum
Sets to 0 segments
Set to Minimum
Sets to 2048 segments
4-2-3. Run Segmented Memory
Background
Before the Segmented Memory function can be
used, set the trigger settings as appropriate for the
signal you wish to use. See page 95 for configuring
the trigger settings.
Run Segments
1. Toggle Segments On from the bottom menu.
Note
The first time Segmented memory is turned on the
segments will automatically be run. Each segment
will be automatically captured. The progress of
capturing the segments is shown at the top of the
display.
2. Run the segments by pressing the
Segments Run key.
Alternatively, press the Run/Stop
key.
Note that the Segments Run key
changes to Segments Stop.
or
Run/Stop
3. The scope will automatically start
acquiring segments. The progress
of the segmented memory capture
is shown in the Progress Indicator.
The Run Indicator will be shown
when in the Run mode.

78
4. When the scope has finished
acquiring segments, press the
Segments Stop key from the
bottom menu.
Alternatively, press the Run/Stop
key again.
The Stop Indicator will be shown
when in the Stop mode.
or
Run/Stop
The scope is now ready to navigate or analyze the
acquired segments.
4-2-4. Navigate Segmented Memory
Background
After the segmented memory acquisitions have
been captured you can navigate through each
segment one at a time.
Operation
1. Press Select Segments from the
bottom menu. This key will be
available in the Stop mode.
2. To navigate to the segment of
interest, press Current Seg from
the side menu and use the Variable
knob to scroll to the segment of
interest.
Alternatively, the Set to Minimum
and Set to Maximum keys can be
used to jump to the first and last
segment respectively.
3. The position in time of the selected
segment relative to the time of the
first segment is shown in the
Segments Time key.
4-2-5. Segment Measurement
Background
The Segmented memory function can be used in
conjunction with the automatic measurements in
the Measurement menu. Please note that digital
channels are not supported for measurement using
segments.
Display All
The Display All function will show
all the acquired segments
simultaneously.

79
Segments
Measure
This function will either perform
statistics calculation on the
segments or tabulate a list of the
measurement results.
Segments
Info
Provides configuration information
common for all the acquired
memory segments.
4-2-6. Display All
Operation
1. Press Analyze Segments from the
bottom menu.
Note: This key will only be
available in the Stop mode.
2. Press Display All
3. The display will show all the acquired segments
on the display simultaneously. The currently
selected segment will be superimposed over
the top for reference purposes.
Example

80
4-2-7. Automatic Measurement
Note
To use automatic measurements with the
segmented memory, automatic measurements
must first be selected from the Measure menu
before a segment is run. Digital channels cannot
be used with this function.
Setup
Press the Measure key and select
any single source measurement
from the Add Measurement menu.
See the user manual for details on
how to add automatic
measurements.
Measure
Operation
1. Press Analyze Segments from the
Segments menu.
Note: This key will only be
available in the Stop mode.
2. Press Segments Measure.
3. Select either the
statistics or the
measurement list from
the side menu.
Statistics
List
4. The statistics table or measurement list appears
on the display.
Note that the more segments that you have, the
longer it will take to calculate the statistics or list
the measurement results.
5. For statistic
measurements, press Plot
Source to choose which
automatic measurement to
use for the statistics
calculations.
6. For the measurement list, press
Source and select the source
channel for measurement.
Range
CH1 ~ CH4

81
Statistics
Results
This function will bin the measurement results of
the selected automatic measurement into a userdefined number of bins. This allows you to easily
view statistics for a large number of segments.
Setup
1. To select the number of bins for the
statistics, press Divided by and
select the number of bins with the
Variable knob.
2. Press Select and use the Variable
knob to view the measurement
results for each bin.
Example:
Statistics
Statistics of currently
selected bin
Select cursor
Bin count
Measurement
List
Puts all the measurement results for a segment in
a list. All the currently selected automatic
measurement results are listed.
Setup
1. Press Select and use the variable
knob to scroll through each
segment.
Example:
Measurement
List
Select
cursor
Measurement results
Measurement types

82
4-2-8. Segment Info
Operation
1. Press Analyze Segments from the
bottom menu.
Note: This key will only be
available in the Stop mode.
2. Press Segments Info.
3. A table showing all general setting information
for the segmented memory acquisitions is
shown on the display.
Info:
Sample rate, Record length,
Horizontal, Vertical
4-3. Display
The Display menu defines how the waveforms and parameters
appear on the main LCD display.
4-3-1. Display Waveform as Dots or Vectors
Background
When the waveform is displayed on screen, it can
be displayed as dots or vectors.
Panel Operation
1. Press the Display menu key.
Display
2. Press Dot Vector to toggle between
Dot and Vector mode.
Range
Dots
Only the sampled dots are
displayed.
Vectors
Both the sampled dots and the
connecting line are displayed.
Example:
Vectors (square wave)
Dots (square wave)

83
4-3-2. Set the Level of Persistence
Background
The persistence function allows the DCS-9700 to
mimic the trace of a traditional analog oscilloscope.
A waveform trace can be configured to “persist” for
designated amount of time.
Panel Operation
1. Press the Display menu key.
Display
2. To set the persistence time, press
the Persistence menu button on
the bottom bezel.
3. Use the Variable knob to select a
persistence time.
Time
16ms~10s, Infinite, Off
Clear
To clear persistence, press Clear
Persistence.
4-3-3. Set the Intensity Level
Background
The intensity level of a signal can also be set to
mimic the intensity of an analog oscilloscope by
setting the digital intensity level.
Panel Operation
1. Press the Display menu key.
Display
2. Press Intensity from the bottom
menu.
Waveform
Intensity
3. To set the waveform intensity, press Waveform
Intensity and edit the intensity.
Range
0~100%
Graticule
Intensity
4. To set the graticule intensity, press Graticule
Intensity from the side menu and edit the
intensity value.
Range
10~100%

84
Example
Waveform Intensity 0%
Waveform Intensity 100%
Graticule Intensity 10%
Graticule Intensity 100%
4-3-4. Set the Waveform Intensity Type
Background
The intensity gradient of a signal can be set to
grayscale or color. If intensity is set to color, the
intensity gradient is analogous to a thermal color
gradient where high intensity areas are colored red
and low intensity areas are colored blue.
Panel Operation
1. Press the Display menu key.
Display
2. Press Waveform from the bottom
menu to toggle the intensity type.
Range
Gray, Color

85
Example
4-3-5. Select Display Graticule
Panel Operation
1. Press the Display menu key.
Display
2. Press Graticule from the bottom
menu.
3. From the side menu choose the
graticule display type.
Full: Shows the full grid; X and Y
axis for each division.
Grid: Show the full grid without the
X and Y axis.
Cross Hair: Shows only the center X
and Y frame.
Frame: Shows only the outer frame.
4-3-6. Freeze the Waveform (Run/Stop)
For more details about Run/Stop mode, see page 46.
Panel Operation
1. Press the Run/Stop key. The
Run/Stop key turns red and
waveform acquisition is
paused.
Run/Stop Run/Stop

86
2. The waveform and the trigger
freezes. The trigger indicator on
the top right of the display shows
Stop.
3. To unfreeze the waveform,
press the Run/Stop key
again. The Run/Stop key
turns green again and
acquisition resumes.
Run/Stop Run/Stop
4-3-7. Turn Off Menu
Panel Operation
1. Press the Menu Off key
below the side menu keys to
reduce a menu. The menu
key needs to be pressed
each time to reduce one
menu.
See page 19 for more
information.
Menu Off

87
4-4. Horizontal View
This section describes how to set the horizontal scale, position, and
waveform display mode.
4-4-1. Move Waveform Position Horizontally
Panel Operation
The horizontal position knob moves
the waveform left/right.
POSITION
As the waveform moves, a position indicator on the
on the top of the display indicates the horizontal
position of the waveform in memory.
Reset Horizontal
Position
1. To reset the horizontal position,
press the Acquire key and then
press Reset H Position to 0s from
the bottom menu.
Acquire
Run Mode
In Run mode, the memory bar keeps its relative
position in the memory since the entire memory is
continuously captured and updated.
4-4-2. Select Horizontal Scale
Select
Horizontal Scale
To select the timebase (scale), turn
the TIME/DIV knob; left (slow) or right
(fast).
TIME/DIV
Range
1ns/div ~ 100s/div, 1-2-5 increment
The timebase indicator updates as the TIME/DIV is
adjusted.

88
Horizontal
position
Time base
Run Mode
In Run mode, the memory bar and waveform size
keep their proportion. When the time base
becomes slower, roll mode is activated (if trigger is
set to Auto).
Stop Mode
In Stop mode, the waveform size changes
according to the scale.
4-4-3. Select Waveform Update Mode
Background
The display update mode is switched automatically
or manually according to the timebase and trigger.
Normal
Updates the whole displayed waveform at
once. Automatically selected when the
timebase (sampling rate) is fast.
Timebase
≤50ms/div
Trigger
all modes
Roll Mode
Updates and moves the waveform
gradually from the right side of the display
to the left. Automatically selected when the
timebase (sampling rate) is slow.
Timebase
≥100ms/div
Trigger
all modes
 Loading...
Loading...