Page 1
User's Guide
SLOU321– August 2011
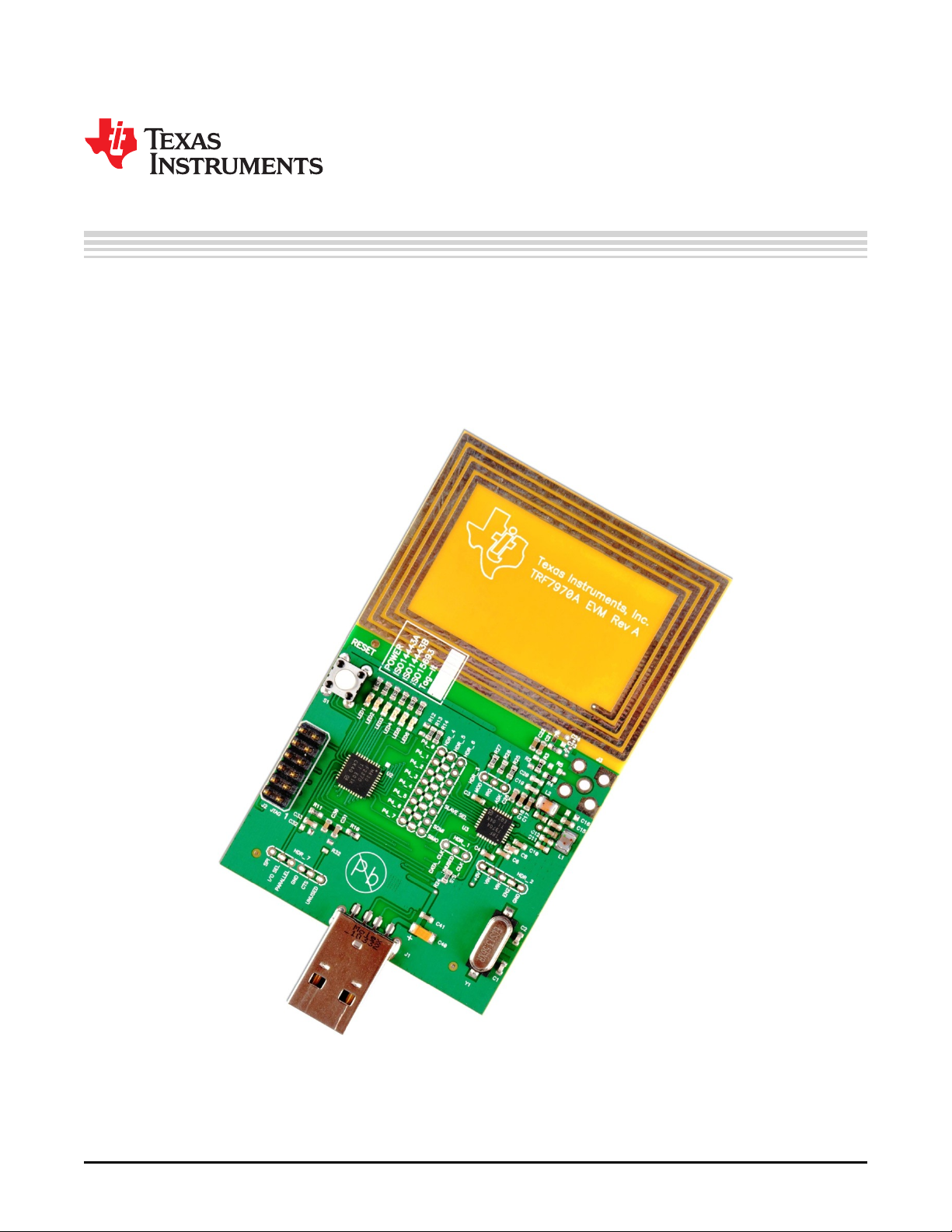
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
The Texas Instruments TRF7970A evaluation module (EVM) is intended to be used by to demonstrate the
capabilities of the TRF7970A and help aid in the development process by providing a working
hardware/firmware reference example for traditional HF (13.56 MHz) RFID and also NFC Forum
operations.
This manual includes a list of EVM features, a brief description of the module, EVM specifications, details
on connecting and using the EVM, and a discussion of the software interface for the EVM.
MSP430, Stellaris, Sitara are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
Cortex, ARM8, ARM9 are trademarks of ARM Corporation.
MIFARE is a trademark of NXP Semiconductors.
FeliCa is a trademark of Sony Corporation.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
Page 2

www.ti.com
Contents
1 TRF7970A EVM Description .............................................................................................. 4
2 Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI ................................................................................ 7
3 Abbreviations ............................................................................................................... 45
4 References ................................................................................................................. 45
List of Figures
1 TRF7970A EVM (Top Side) ............................................................................................... 5
2 TRF7970A EVM GUI Connected ......................................................................................... 7
3 Single Slot Inventory Command (One Tag in Field).................................................................. 10
4 Single Slot Inventory Command (Two Tags in Field/Collision)...................................................... 10
5 Sixteen Slot Inventory Command (Four Tags in Field With No Collision) ......................................... 11
6 Sixteen Slot Inventory Command (Five Tags in Field, Collision in Slot 0)......................................... 12
7 Read Single Block Command Example ................................................................................ 13
8 Write Single Block Command Example ................................................................................ 14
9 Lock Block Command Example ......................................................................................... 15
10 Read Multiple Blocks Command Example............................................................................. 16
11 Stay Quiet Command Example.......................................................................................... 17
12 Select Command Example............................................................................................... 18
13 Reset to Ready Command Example.................................................................................... 19
14 Write AFI Command Example........................................................................................... 20
15 Lock AFI Command Example............................................................................................ 21
16 Write DSFID Command Example ....................................................................................... 22
17 Lock DSFID Command Example........................................................................................ 23
18 Get System Information Command Example.......................................................................... 24
19 Get Multiple Block Security Status Command Example.............................................................. 25
20 Anticollision Command Example for One Type A PICC.............................................................. 27
21 Anticollision Command Example for Two Type A PICCs ............................................................ 28
22 Select Command Example............................................................................................... 29
23 RATS Command Example ............................................................................................... 30
24 REQ_B Command Example ............................................................................................. 31
25 ATTRIB Command Example............................................................................................. 32
26 FeliCa Polling Example................................................................................................... 33
27 Find Tags Tab Example 1................................................................................................ 34
28 Find Tags Tab Example 2................................................................................................ 34
29 Registers Tab .............................................................................................................. 35
30 Setting up TRF7970A EVM as Initiator................................................................................. 36
31 Setting up TRF7970A EVM as Target.................................................................................. 36
32 Demonstration Hardware Configuration Example..................................................................... 37
33 Peer-to-Peer Connection Step........................................................................................... 38
34 NFC Text Message Transfer............................................................................................. 38
35 NFC File Transfer, Select File on Initiator.............................................................................. 39
36 NFC File Transfer, Save File on Target................................................................................ 39
37 NFC File Transfer Progress.............................................................................................. 40
38 Card Emulation Mode..................................................................................................... 41
39 Continuous Write to Registers 0x00 to 0x0B Example............................................................... 42
40 Continuous Read from Registers 0x00 to 0x0B Example............................................................ 42
41 Sending GPIO Control Command....................................................................................... 43
42 Sending Single Slot REQB............................................................................................... 44
2
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 3

www.ti.com
1 Logic Analyzer Connection Points on EVM at HDR_5................................................................. 5
2 Logic Analyzer Connection Points on EVM at HDR_1, HDR_3 and HDR_2 ....................................... 6
3 ISO/IEC 15693 Request Flags (b1 – b4) ................................................................................ 8
4 ISO/IEC 15693 Request Flags (b5 – b8) when Inventory Flag is NOT set ......................................... 8
5 ISO/IEC 15693 Request Flags (b5 – b8) when Inventory Flag is set................................................ 8
6 ISO/IEC 15693 UID Format ............................................................................................... 9
7 Custom Commands Request Format................................................................................... 26
8 Command Codes for GPI/O Controlled Outputs on EVM............................................................ 43
List of Tables
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
3
Page 4

TRF7970A EVM Description
1 TRF7970A EVM Description
The TRF7970A EVM features include:
• Support for:
– ISO15693 standard based transponders
– ISO14443 standard based transponders (Types A and B)
– NFC Forum modes (RFID reader\writer, peer to peer, and card emulation)
• FeliCa™ based transponders (UID read only)
• Standalone polling mode for quick demonstration of transponder detection
• Communication with host software graphical user interface (GUI) via USB VCP
The TRF7970A EVM also has the following hardware features specifically for development purposes:
• MSP430F2370 ultra-low power microcontroller with JTAG connectivity to development environment for
custom firmware development.
• Parallel or SPI connectivity via 0-Ω jumpers
• Logic analyzer/oscilloscope test points for relevant signal observation during code development
• SMA (edge mount and through-hole) pads for connecting customer designed magnetic dipole circuit
NOTE: Onboard antenna circuit should be disconnected by removing R3 beforehand to maintain
50-Ω impedance.
www.ti.com
1.1 Default Configuration
As shipped, the TRF7970A EVM is fully functional as an RFID/NFC Forum reader/writer, NFC Forum
Initiator or NFC Forum Target. To evaluate the TRF7970A beyond the standalone mode, which only
requires that power be applied via the USB connector, the TRF7970A EVM GUI must be used.
The TRF7970A EVM contains components that can be potentially damaged by
electrostatic discharge. Always store and transport the EVM in the supplied
ESD bag when not in use. Always handle the TRF7970A EVM in an ESD
controlled environment. For more information regarding proper ESD handling
procedures see the Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) application report, SSYA008.
1.2 Hardware Description
As shown in Figure 1, the TRF7970A EVM is a self contained development platform which can be used to
independently evaluate/test the performance of the TRF7970A IC, custom firmware, customer designed
magnetic dipole antennas and/or potential transponders for a customer defined RFID/NFC Forum
application. The TRF7970AEVM is configured from the factory in parallel communication mode between
the MSP430F2370 and the TRF7970A via 0-Ω resistors between HDR_4 and HDR_5 pads. On power up,
the preloaded MSP430F2370 firmware also checks the voltage level of P2.3 (pin 15), which is factory
configured at HDR_7 to have I/O_SEL connected to Parallel connection via a 0-Ω resistor. If the user
wants to change to SPI with Slave Select operation, all that is needed is to move all the 0-Ω resistors
connecting HDR_4 and HDR_5 together over so HDR_5 and HDR_6 are connected as well as moving
0-Ω resistor over on HDR_7 so that I/O_SEL and SPI connected instead. The preloaded MSP430
firmware handles either hardware configuration case, parallel or SPI with SS.
CAUTION
4
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 5
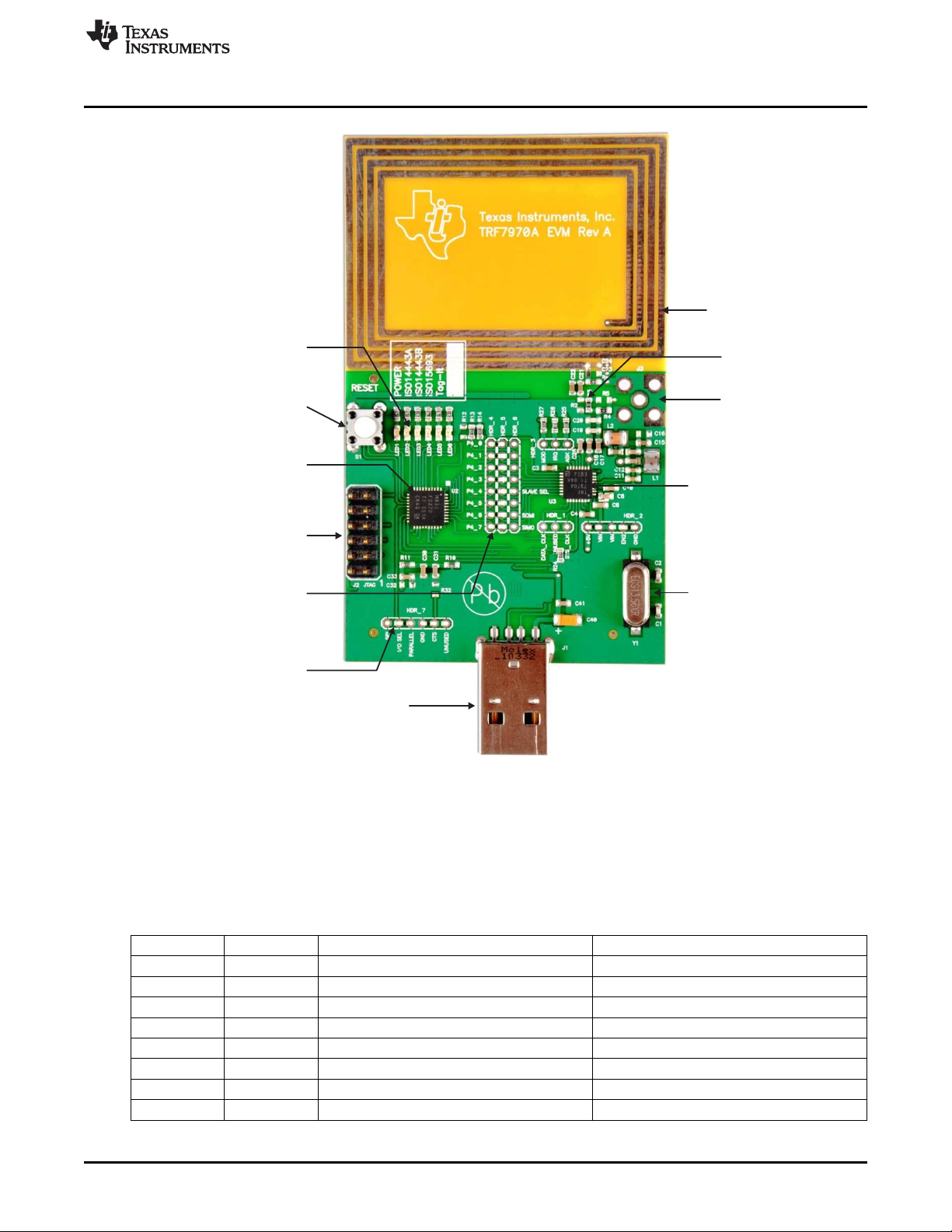
J3 (SMA)
I/O_SEL Jumper
USB Interface
MSP430F2370/TRF7970A
Communication Header
(default configuration shown)
MSP430
JTAG Interface
Reset Switch
MSP430F2370
TRF7970A
13.56-MHz Crystal
PCB Magnetic Dipole
Power and Protocol
LED Indicators
Resistor R3
www.ti.com
TRF7970A EVM Description
If a logic analyzer is to be connected to the TRF7970A EVM, the user can install three-position 2-mm
board headers at positions HDR_1 and HDR_3 for observation of DATA_CLK and IRQ signals. An
8-position 2-mm board header can be installed at position HDR_5 for observation of the parallel or SPI
signals between the MSP430F2370 and the TRF7970A. See the PCBA silkscreen or Table 1 and Table 2
for reference.
HDR_5 Pin Parallel Name SPI With SS Name SPI Without SS Name
P5_7 I/O_7 MOSI MOSI
P5_6 I/O_6 MISO MISO
P5_5 I/O_5
P5_4 I/O_4 Slave Select
P5_3 I/O_3
P5_2 I/O_2 VDD_I/O voltage level (VDD_X on EVM) VDD_I/O voltage level (VDD_X on EVM)
P5_1 I/O_1 GND
P5_0 I/O_0 GND GND
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Table 1. Logic Analyzer Connection Points on EVM at HDR_5
Figure 1. TRF7970A EVM (Top Side)
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
5
Page 6
TRF7970A EVM Description
Table 2. Logic Analyzer Connection Points on EVM at HDR_1, HDR_3 and HDR_2
HDR_3 Pin Parallel Name SPI With SS Name SPI Without SS Name
P2 IRQ IRQ IRQ
HDR_2 Pin Parallel Name SPI With SS Name SPI Without SS Name
P5 GND GND GND
HDR_1 Pin Parallel Name SPI With SS Name SPI Without SS Name
P1 DATA_CLK DATA_CLK DATA_CLK
It is also possible to disconnect the MSP430F2370 from the TRF7970A and utilize the above mentioned
headers to wire in MCU of choice (for example, other members of the MSP430™, Stellaris™ Cortex™-M3,
or Sitara™ ARM8™/ ARM9™ families)
Resistor R3 (0 Ω) makes the electrical connection between the 50-Ω impedance matching circuit from the
TRF7970A to the onboard magnetic dipole antenna circuit, also matched to 50 Ω. When testing
application specific antennas using J3 (SMA port), disconnect or remove R3 to maintain 50-Ω impedance
out from the TRF7970A circuitry to the application specific antenna being tested (see Figure 1).
1.3 Standalone Mode Description
The TRF7970A EVM has a standalone mode in which when power is applied (via the USB connector),
then the preloaded MSP430F2370 firmware initializes the TRF7970A IC for full power operation,
illuminates the power LED, and begins a polling loop for ISO15693, ISO14443A, and ISO14443B
transponders.
When any (or all) of these types of transponders are presented to the onboard antenna, the corresponding
LED is illuminated (see silkscreen or actual TRF7970A PCBA in kit or in Figure 1). The TRF7970A EVM
kit comes with a sample selection of Texas Instruments ISO15693 transponders.
When the TRF7970A EVM is connected to a PC and the TRF7970A EMV GUI is started, the preloaded
MSP430F2370 firmware detects this, stops the polling loop, and turns off any protocol LEDs that were
illuminated to take direct host commands.
www.ti.com
1.4 GUI Software Description
The TRF7970A EVM can be used with the TRF7970A EVM PC GUI to demonstrate the traditional RFID
reader/writer operations as well as NFC Forum Initiator/Target operations. As the EVM enumerates as a
serial port on a PC, the EVM can be used with almost any simple serial terminal based program such as
(but not limited to) HyperTerminal, Docklight, or LabVIEW. Using the TRF7970A EVM with the GUI is
detailed in Section 2.
6
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 7
www.ti.com
2 Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
2.1 USB Driver
The TRF7970A EVM has SiLabs CP2102 USB to UART Bridge IC onboard. The USB driver needs to be
loaded onto the PC being used prior to attempting to start the TRF7970A EVM GUI.
https://www.silabs.com/products/mcu/pages/USBtoUARTbridgeVCPdrivers.aspx
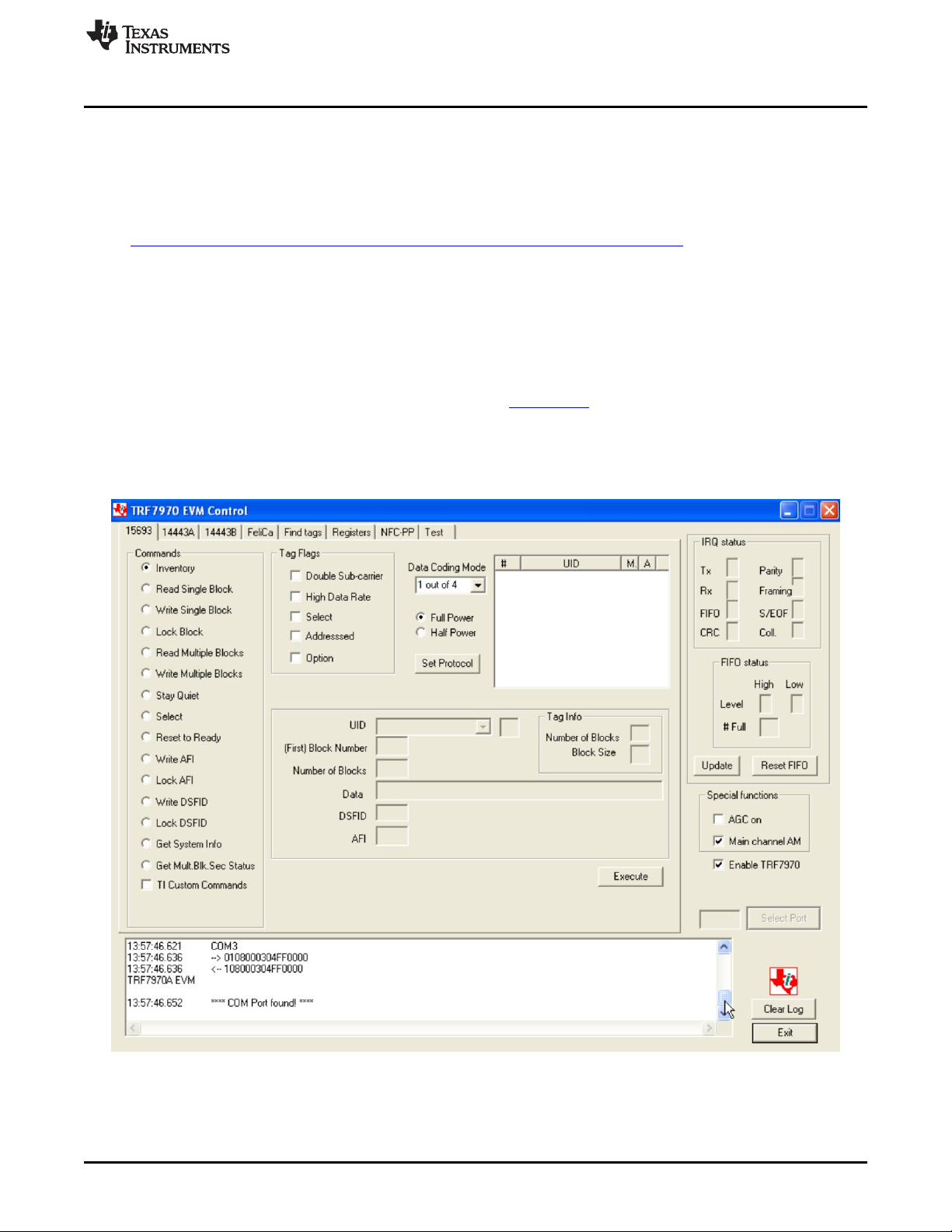
2.2 TRF7970A EVM GUI Startup
The TRF7970A EVM GUI has a COM port auto detect function which is limited to COM ports 1 through
12. This being the case, the user is advised that after plugging in TRF7970A EVM but before starting the
GUI, they check the COM port it enumerated on via Windows Control Panel, System, Hardware Tab,
Device Manager, Ports, Port Properties, Port Settings and ensure it is within this range and also that the
COM port settings are for 115200 bps, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit (115200 8N1).
The TRF7970A EVM GUI should be downloaded from http://ti.com, unzipped into dedicated folder, and
then executable can be launched. Figure 2 shows the first screen the user will see when executable
launches and automatically connects to the TRF7970A EVM.
The user can scroll down in the data log window with the slider bar on the right side to see that the GUI
has connected to the TRF7970A EVM.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 2. TRF7970A EVM GUI Connected
Figure 2 shows TRF7970A EVM connected to COM3 (as example). The EVM and the GUI are now ready
to be used together to demonstrate the RFID reader/writer and NFC Forum operations.
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
7
Page 8
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
2.3 ISO15693 Tab
By default the TRF7970A EVM GUI starts up with the ISO15693 tab selected. The user should set/select
the transponder/tag request flags as appropriate for the given operation (details on this to follow for each
command) and by using the Set Protocol button in the GUI first before executing any commands so that
the TRF7970A register settings match what is being sent out/expected back to/from the transponder(s) in
the field of the EVM antenna. Please note that there are only two mandatory commands in ISO/IEC 15693
standard (Inventory and Stay Quiet). All other available commands are either Optional (as defined by the
ISO/IEC 15693 standard) or Custom (as defined by the transponder IC manufacturer by means of the
framework outlined in ISO/IEC 15693 standard). The user should always use the transponder/tag IC
specific data sheet in conjunction with this guide to ensure settings and commands match what the
transponder is designed to support. To avoid any misunderstanding regarding the transponder/tag request
flags, see Table 3, Table 4, and Table 5 (taken from the ISO/IEC 15693-3 standard).
Bit Flag Name Value Definition
b1 Sub-carrier_flag
b2 Data_rate_flag
b3 Inventory_flag
b4 Protocol Extension_flag
www.ti.com
Table 3. ISO/IEC 15693 Request Flags (b1 – b4)
0 A single sub-carrier shall be used by the VICC
1 Two sub-carriers shall be used by the VICC
0 Low data rate shall be used
1 High data rate shall be used
0 Flags 5 to 8 according to Table 4
1 Flags 5 to 8 according to Table 5
0 No protocol format extension
1 Protocol format is extended. Reserved for Future Use (RFU)
Table 4. ISO/IEC 15693 Request Flags (b5 – b8) when Inventory Flag is NOT set
Bit Flag Name Value Definition
Request shall be executed by any VICC according to the setting of the
0
Address_flag
b5 Select_flag
b6 Address_flag
b7 Option_flag
b8 RFU 0 RFU
Request shall be executed by only the VICC in selected state. The
1 Address_flag shall be set to 0 and the UID field shall not be included in the
request.
Request is not addressed. UID field is not included. It shall be executed by
0
any VICC.
Request is addressed. UID field is included. It shall be executed only by
1
the VICC whose UID matches the UID specified in the request.
Meaning defined by command description. It shall be set to 0 if not
0
otherwise defined by the command.
1 Meaning defined by command description.
Table 5. ISO/IEC 15693 Request Flags (b5 – b8) when Inventory Flag is set
Bit Flag Name Value Definition
b5 AFI_flag
b6 Nb_slots_flag
b7 Option_flag
b8 RFU 0 RFU
0 AFI Field is not present
1 AFI Field is present
0 16 slots
1 1 slot
Meaning defined by command description. It shall be set to 0 if not otherwise
0
defined by the command.
1 Meaning defined by command description.
8
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 9

www.ti.com
2.3.1 Inventory (Command Code 0x01)
The ISO/IEC 15693 Inventory command is used to acquire the factory programmed and permanently
locked 64 bit unique identifier(s) (UIDs) of transponders that are in within the read zone of the TRF7970A
EVM antenna. They are used, as the name implies, to address each VICC uniquely and individually during
the anticollision loop and for one to one exchange between a VCD and a VICC. The format of the UID is
shown in Table 6.
Table 6. ISO/IEC 15693 UID Format
Byte Position MSB LSB
Bits 64 57 56 49 48 1
Hexadecimal Representation 0xE0 IC Serial Number
As shown in Table 6, the ISO/IEC 15693 standard mandates the MSByte of the UID be 0xE0. The
standard also mandates that the IC manufacturing code byte be according to the list shown in
ISO/IEC7816-6. The remaining 48 bits (6 bytes) are to be assigned by the IC manufacturer.
There is a slotted ALOHA style anticollision algorithm used for the inventory sequence and as stated
above, the purpose is to retrieve the UIDs of the tags in the field. This algorithm does not use timeslots
but rather is keyed off nibbles of the UID, starting with the lower half of the LSByte and as collisions are
detected, a mask value is incremented until the collisions seen by the VCD are arbitrated.
As indicated above by bit 6 of Table 5, the Inventory command can be issued either as a single slot
command or a sixteen slot command. If the command is issued as a single slot and there are two or more
transponders in the field only a collision will be indicated and no arbitration will take place. This is useful in
applications where only one transponder is allowed to be in the field at a time as the detection of a
collision would be considered quite useful.
Another technique of pre-sorting transponders that will be present in the field is to pre-program different
AFI values on the transponders, then issue the inventory command (single or sixteen slot) with one of
those values in the AFI field and also indicate that this field is present via the request flags (see Table 5,
bit 5). Only the tags with the corresponding AFI value respond. See Section 2.3.10 and the ISO/IEC
15693-3 Standard for more information.
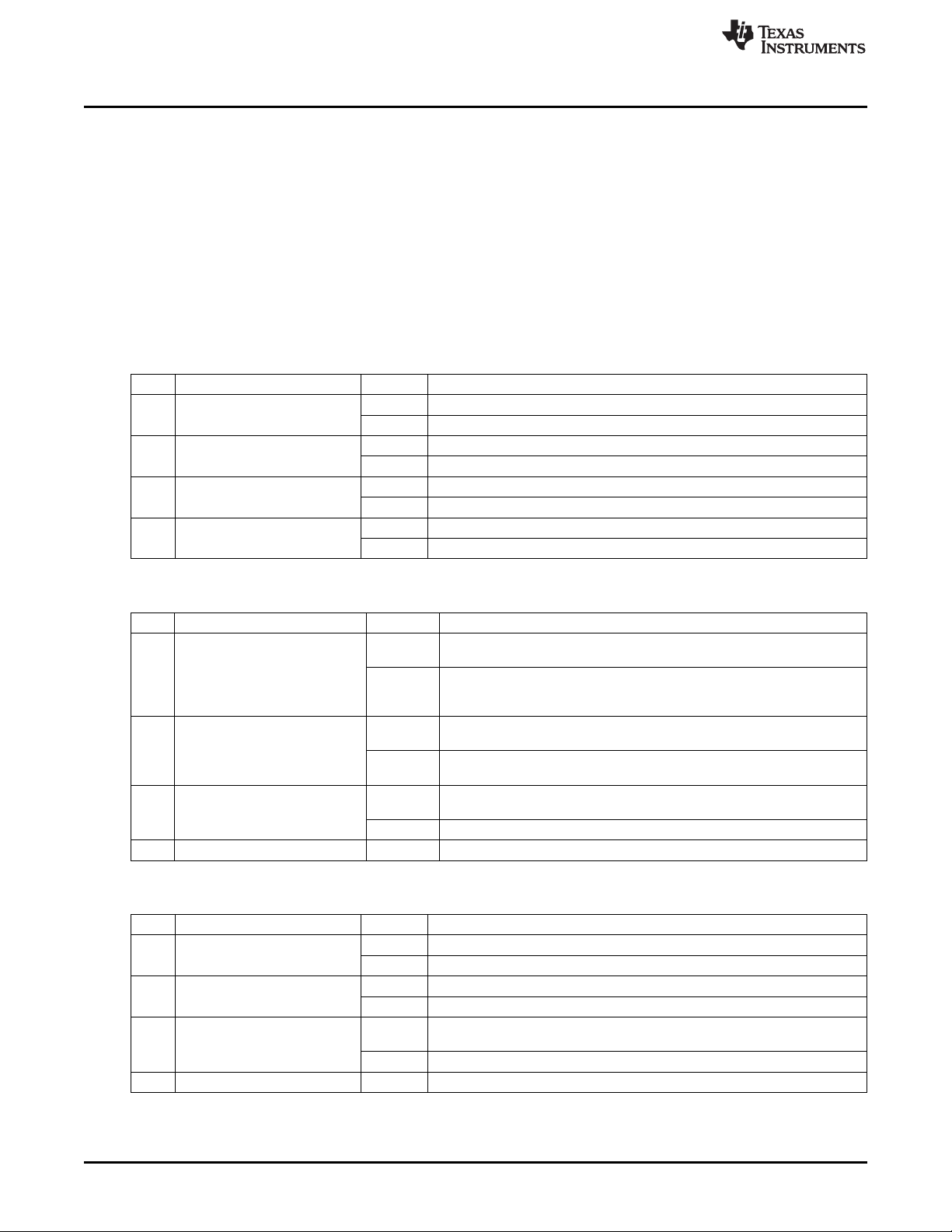
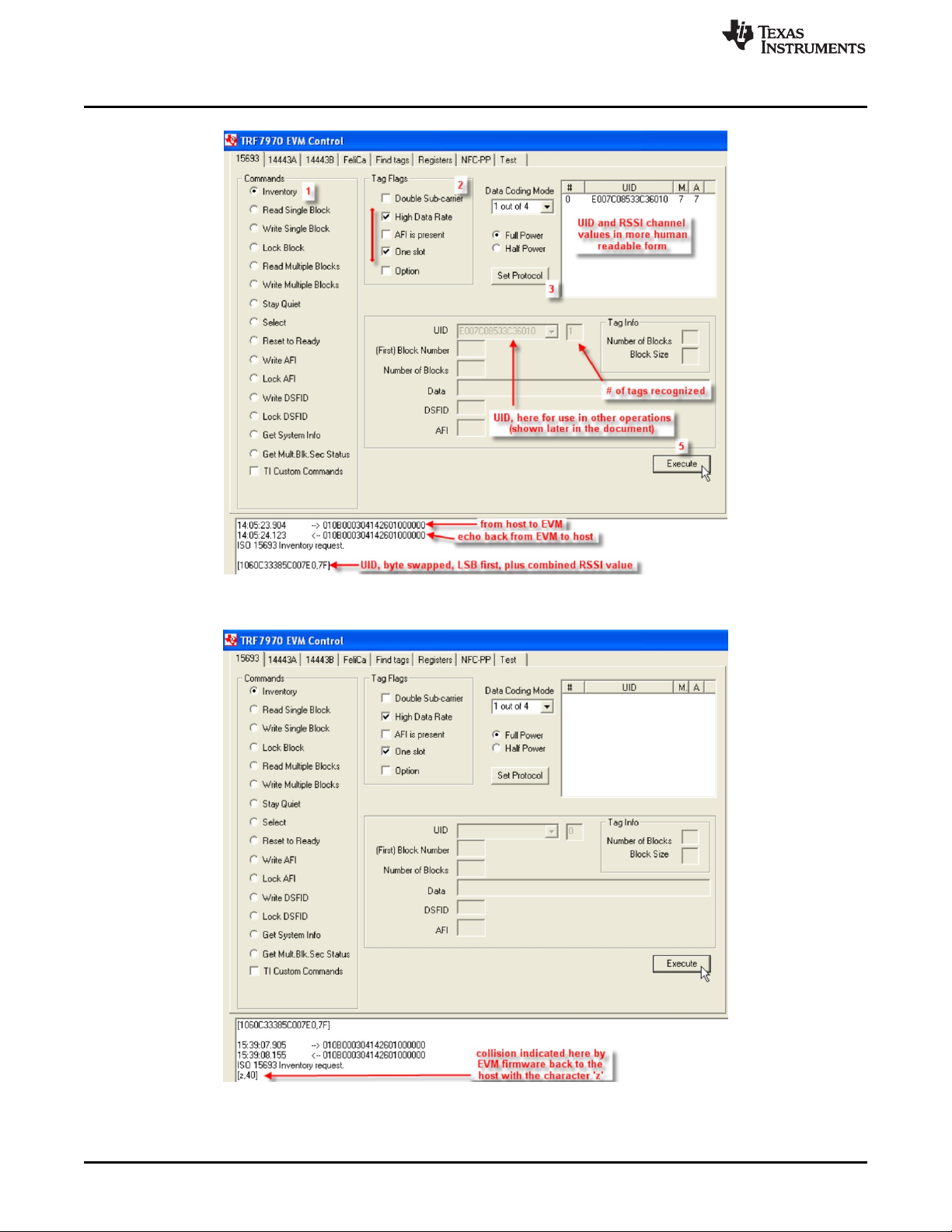
To perform single slot inventory using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for Inventory.
2. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 3 for one example).
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
5. Click Execute.
See Figure 3 and Figure 4 for example results of one tag in field and a collision between two tags,
respectively.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
IC Manufacturing Code
(TI = 0x07)
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
9
Page 10
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
www.ti.com
Figure 3. Single Slot Inventory Command (One Tag in Field)
10
Figure 4. Single Slot Inventory Command (Two Tags in Field/Collision)
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 11

www.ti.com
In time sensitive applications in which the number of tags that are presented to the field should be one at
one time but could be from 1 to n, polling or looking for tags using the single slot method first might be
effective. If a collision is detected, the firmware could then change the tag request flags to sixteen slot
method and then proceed as described here.
To perform sixteen slot Inventory using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for Inventory.
2. Select the Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 5 for one example).
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
5. Click Execute.
See Figure 5 and Figure 6 for example results of multiple tags in the field without and with collisions,
respectively.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
NOTE: For graphics brevity, only four tags are shown.
Figure 5. Sixteen Slot Inventory Command (Four Tags in Field With No Collision)
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
11
Page 12

Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
www.ti.com
NOTE: For graphics brevity, only five tags are shown.
Figure 6. Sixteen Slot Inventory Command (Five Tags in Field, Collision in Slot 0)
12
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 13
www.ti.com
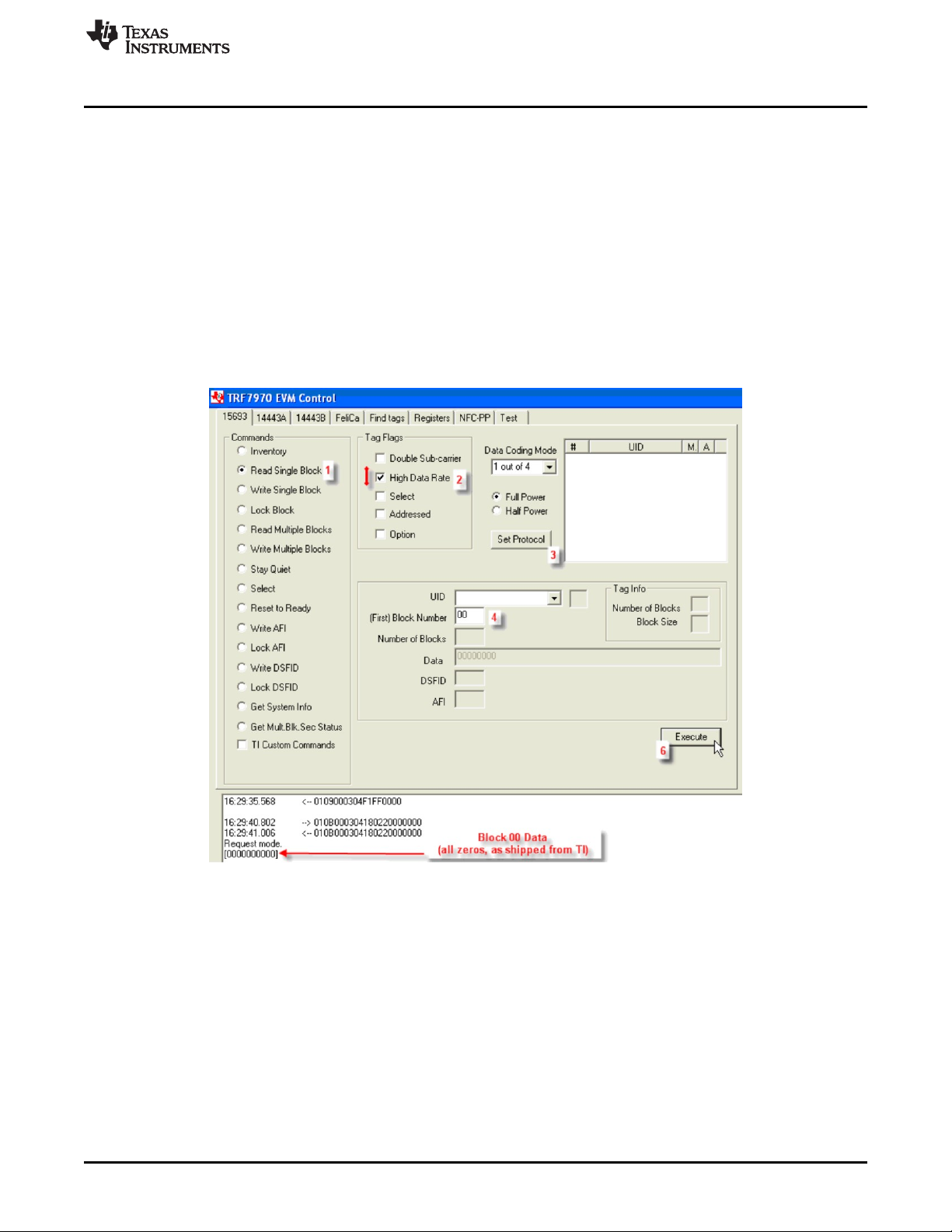
2.3.2 Read Single Block (Command Code 0x20)
The Read Single Block Command is an optional command that requests one block of user memory data
from a VICC, with the block number specified in the request. If the Option_flag is set in the request, the
VICC also will return the block security status. This command can be sent as an addressed or
unaddressed request.
To perform Read Single Block using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for Read Single Block.
2. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 7 for one example).
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Enter the Block number to be read (in hex).
5. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
6. Click Execute.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 7. Read Single Block Command Example
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
13
Page 14
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
2.3.3 Write Single Block (Command Code 0x21)
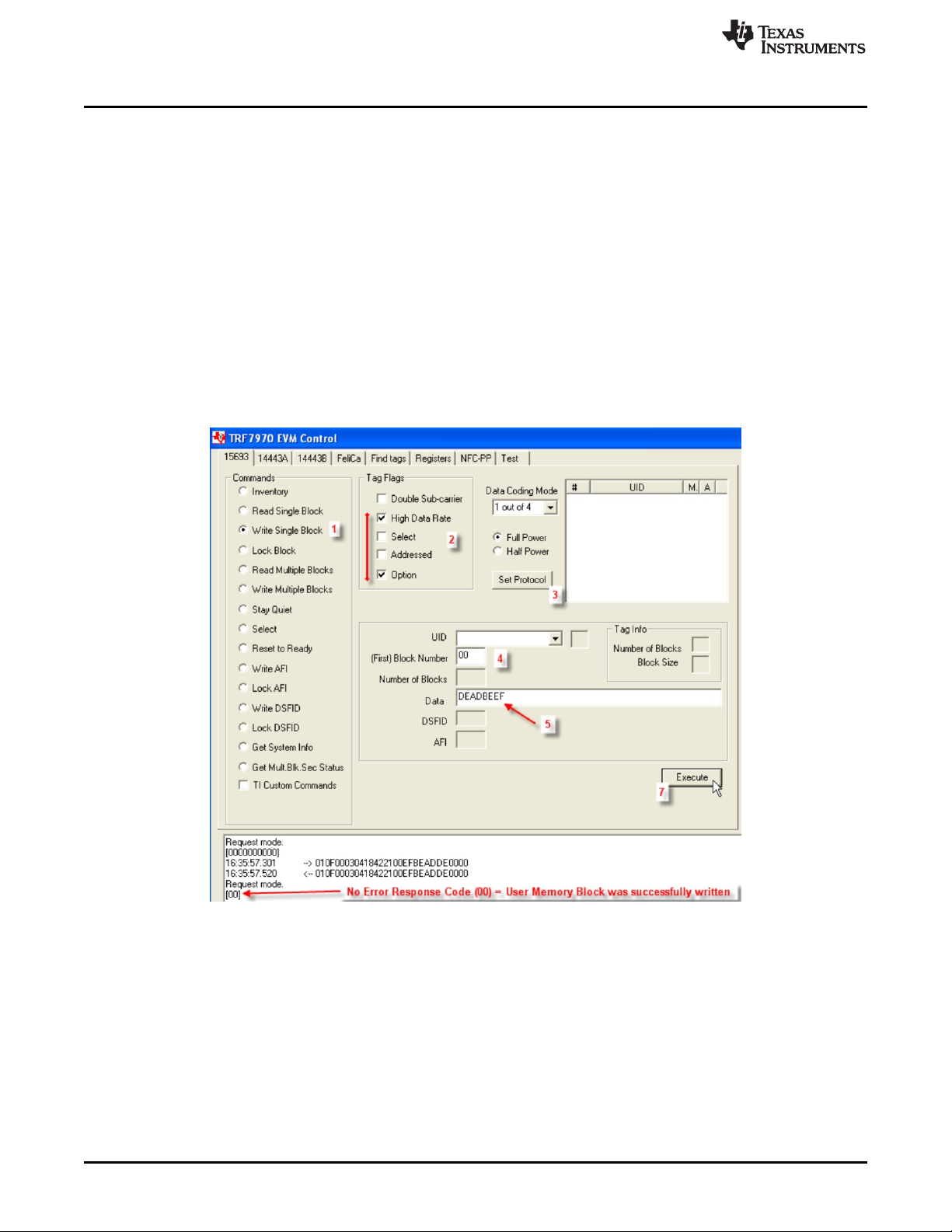
The Write Single Block Command is an optional command that writes one block of user memory data on a
VICC, with the block number and the block data specified in the request. For TI, TI based, and some other
manufacturers' VICCs, the Option_flag must be set in the request. This command can be sent as an
addressed or unaddressed request, and the VICC returns an error/no error response after the write
operation has been completed.
To perform Write Single Block using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for Write Single Block.
2. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 8 for one example, and note use of option flag).
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Enter the Block number to be written (in hex).
5. Enter the Data to be written (in hex).
6. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
7. Click Execute.
www.ti.com
14
Figure 8. Write Single Block Command Example
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 15

www.ti.com
2.3.4 Lock Block (Command Code 0x22)
The Lock Block Command is an optional command that locks one block of user memory data on a VICC,
with the block number specified in the request. For TI, TI based, and some other manufacturers' VICCs,
the Option_flag must be set in the request. This command can be sent as an addressed or unaddressed
request, and the VICC returns an error/no error response after the lock operation has been completed.
To perform Lock Block using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for Lock Block.
2. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 9 for one example, and note use of option flag)
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Enter the Block number to be locked.
5. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
6. Click Execute.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 9. Lock Block Command Example
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
15
Page 16
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
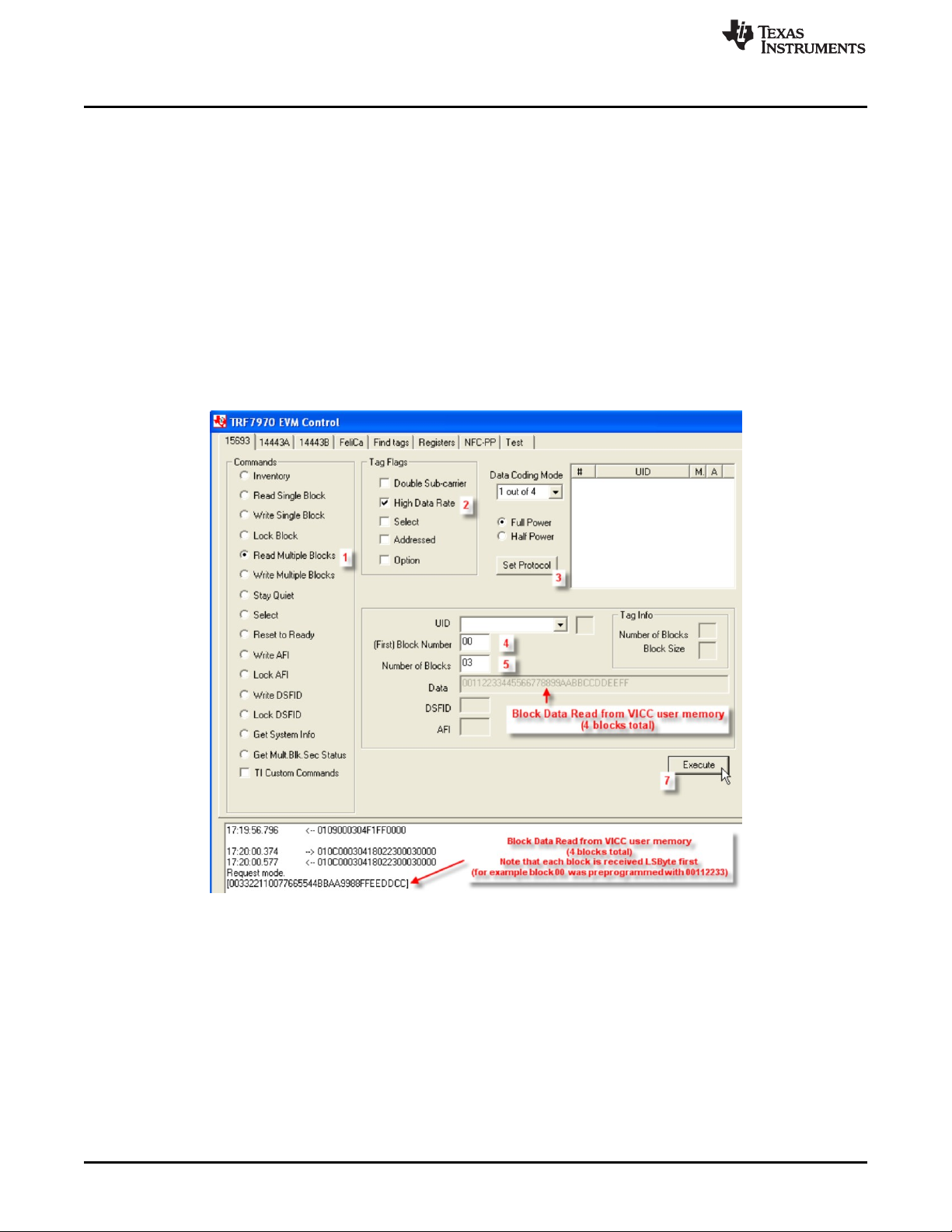
2.3.5 Read Multiple Blocks (Command Code 0x23)
The Read Multiple Blocks command is an optional command that requests more than one block of user
memory data from a VICC at a time, with the first block number and the number of blocks specified in the
request. This command can be sent as an addressed or unaddressed request. If the Option_flag is set in
the request, the VICC also will return the block security status, followed by the block value, sequentially.
To perform Read Multiple Blocks using the GUI (after connecting) the user should:
1. Select the radio button for Read Multiple Blocks
2. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 10 for one example)
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Enter First Block number to be read
5. Enter number of blocks to be read (n-1)
6. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
7. Click Execute
www.ti.com
16
Figure 10. Read Multiple Blocks Command Example
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 17
www.ti.com
2.3.6 Write Multiple Blocks (Command Code 0x24)
This optional command is not currently known to be supported by any ISO/IEC 15693 transponders
available.
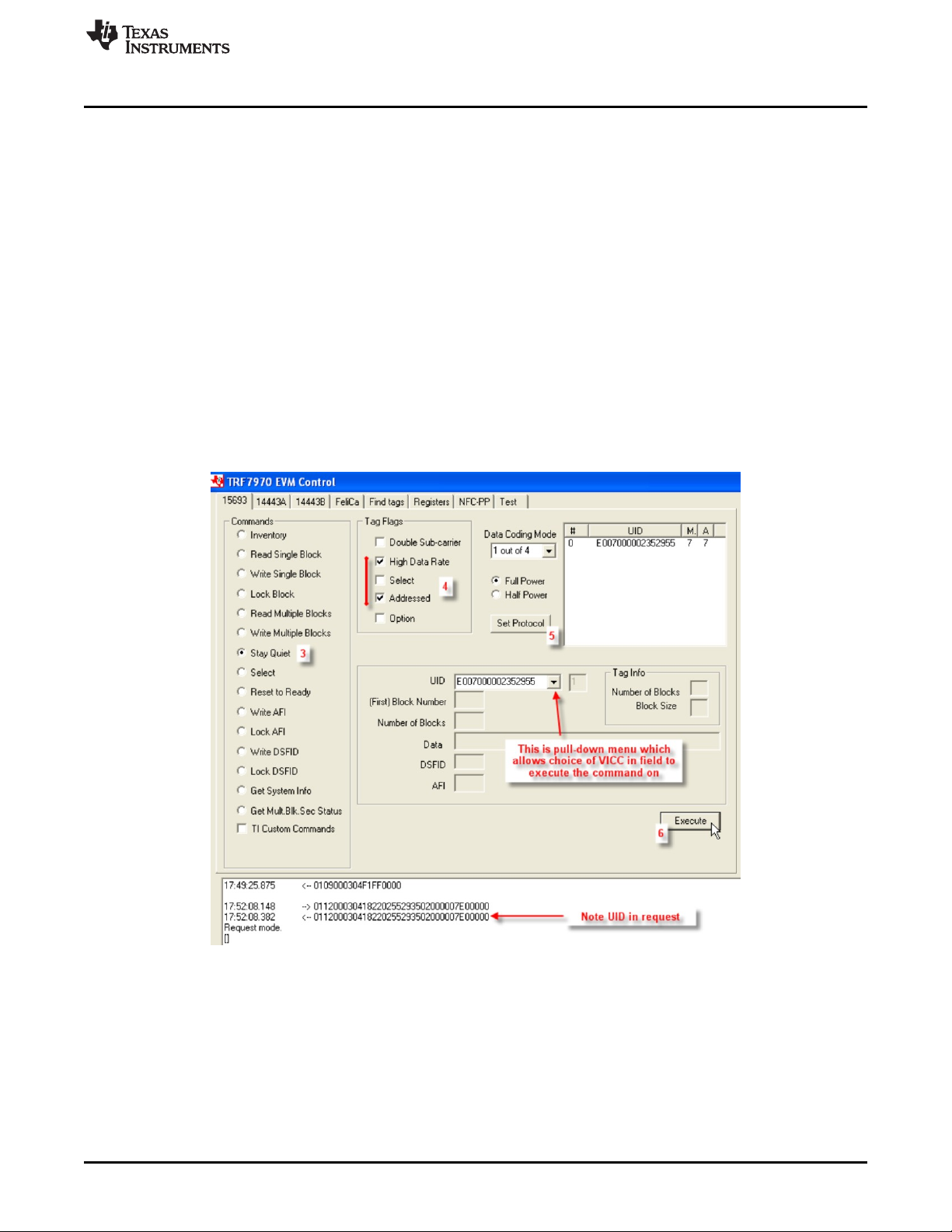
2.3.7 Stay Quiet (Command Code 0x02)
The Stay Quiet command is a mandatory command which instructs the VICC to enter the quiet state. The
command is always issued as an addressed command and of course there is no response to the Stay
Quiet Command. The VICC exits the quiet state when the transponder exits the field, receives a Reset to
Ready command or a Select request.
To perform Stay Quiet command using the GUI:
1. Perform Inventory command (see Section 2.3.1) to obtain UID of VICC
2. Leave tag/transponder in field
3. Select the radio button for Stay Quiet
4. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 11 for one example)
5. Click Set Protocol. (if Data Rate or Sub-carrier Tag Request Flags are changed)
6. Click Execute
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 11. Stay Quiet Command Example
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
17
Page 18
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
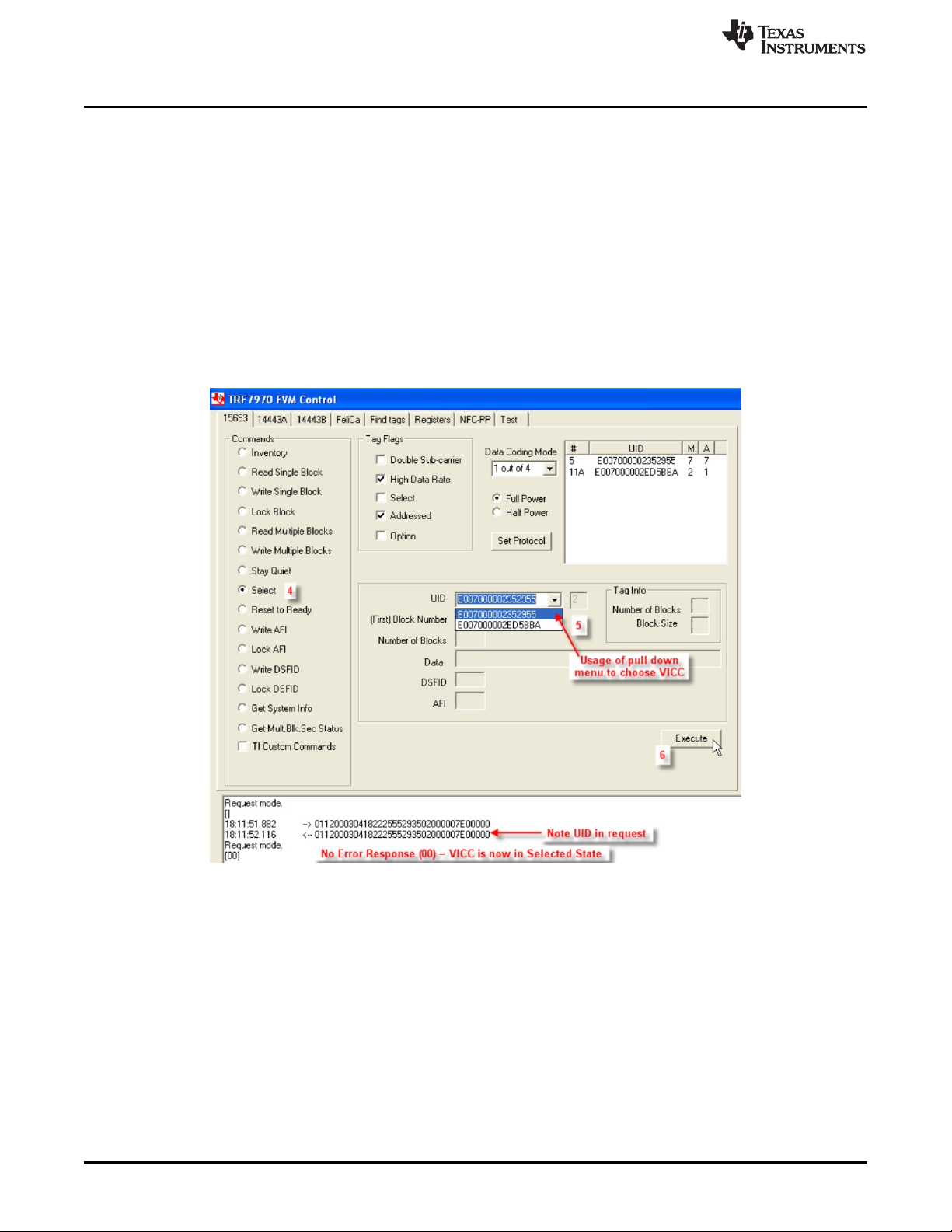
2.3.8 Select (Command Code 0x25)
The Select command is an optional command that is always issued as an addressed command. If the UID
sent as the address in the request matches the UID of the VICC, the VICC will enter the Selected state.
The intention of the Select Command is that only one VICC in the field should be in the Selected state at
any one time.
To perform Select command using the GUI:
1. Perform sixteen slot Inventory command (see Section 2.3.1) to obtain UIDs of VICCs.
2. Leave VICCs in field.
3. Perform Stay Quiet command on each transponder (see Section 2.3.7).
4. Select the radio button for Select.
5. Select from the pulldown menu to choose which one of the tags will be issued the Select Command.
6. Click Execute.
www.ti.com
18
Figure 12. Select Command Example
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 19
www.ti.com
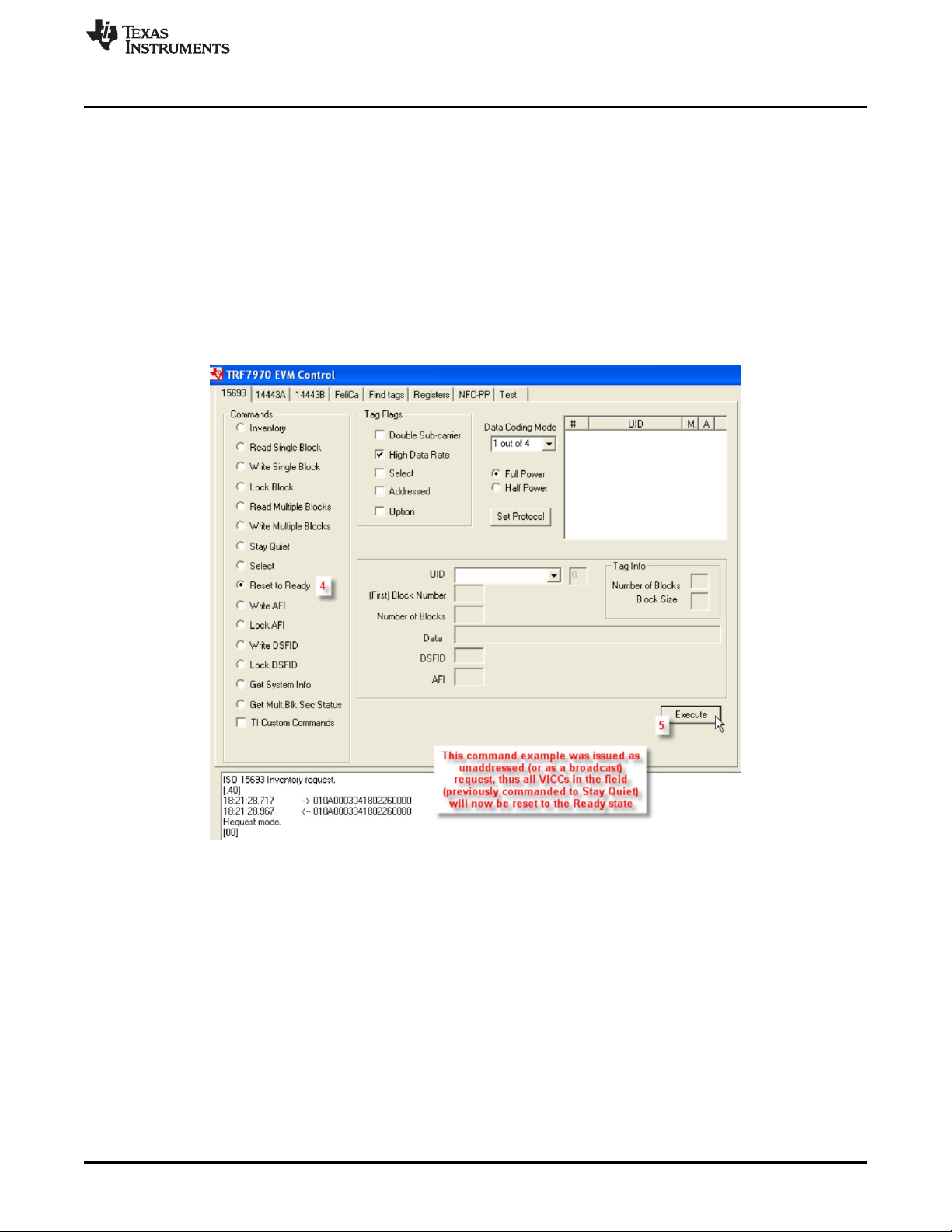
2.3.9 Reset to Ready (Command Code 0x26)
The Reset to Ready Command is an optional command that returns the VICC(s) in the Quiet state to the
Ready state. This command can be sent as an addressed or unaddressed request and the same end
result can also be achieved by turning off the activating field from the VCD or removing the VICC(s) from
the activating field.
To perform Reset to Ready command using the GUI:
1. Perform sixteen slot Inventory command (see Section 2.3.1) to obtain UIDs of VICCs.
2. Leave VICCs in field.
3. Perform Stay Quiet command on each transponder (see Section 2.3.7).
4. Select the radio button for Reset to Ready.
5. Click Execute.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 13. Reset to Ready Command Example
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
19
Page 20
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
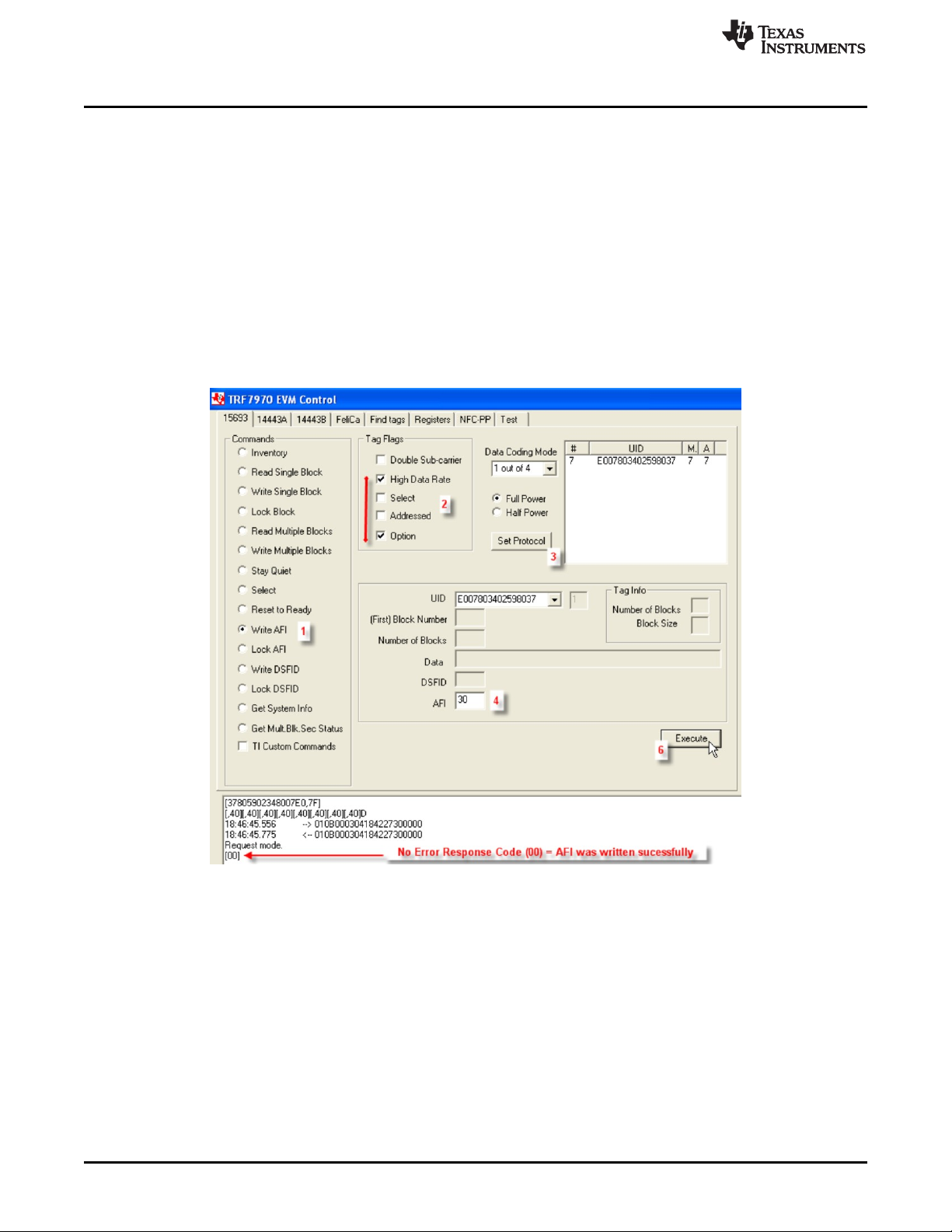
2.3.10 Write AFI (Command Code 0x27)
The Write AFI Command is an optional command that writes a value to the AFI memory block on the
VICC. For TI, TI based, and some other manufacturers' VICCs, the Option_flag must be set in the request.
This command can be sent as an addressed or unaddressed request, and the VICC returns an error/no
error response after the write operation has been completed.
To perform Write AFI using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for Write AFI.
2. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 14 for one example, note use of option flag)
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Enter AFI value to be written (in hex).
5. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
6. Click Execute.
www.ti.com
20
Figure 14. Write AFI Command Example
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 21
www.ti.com
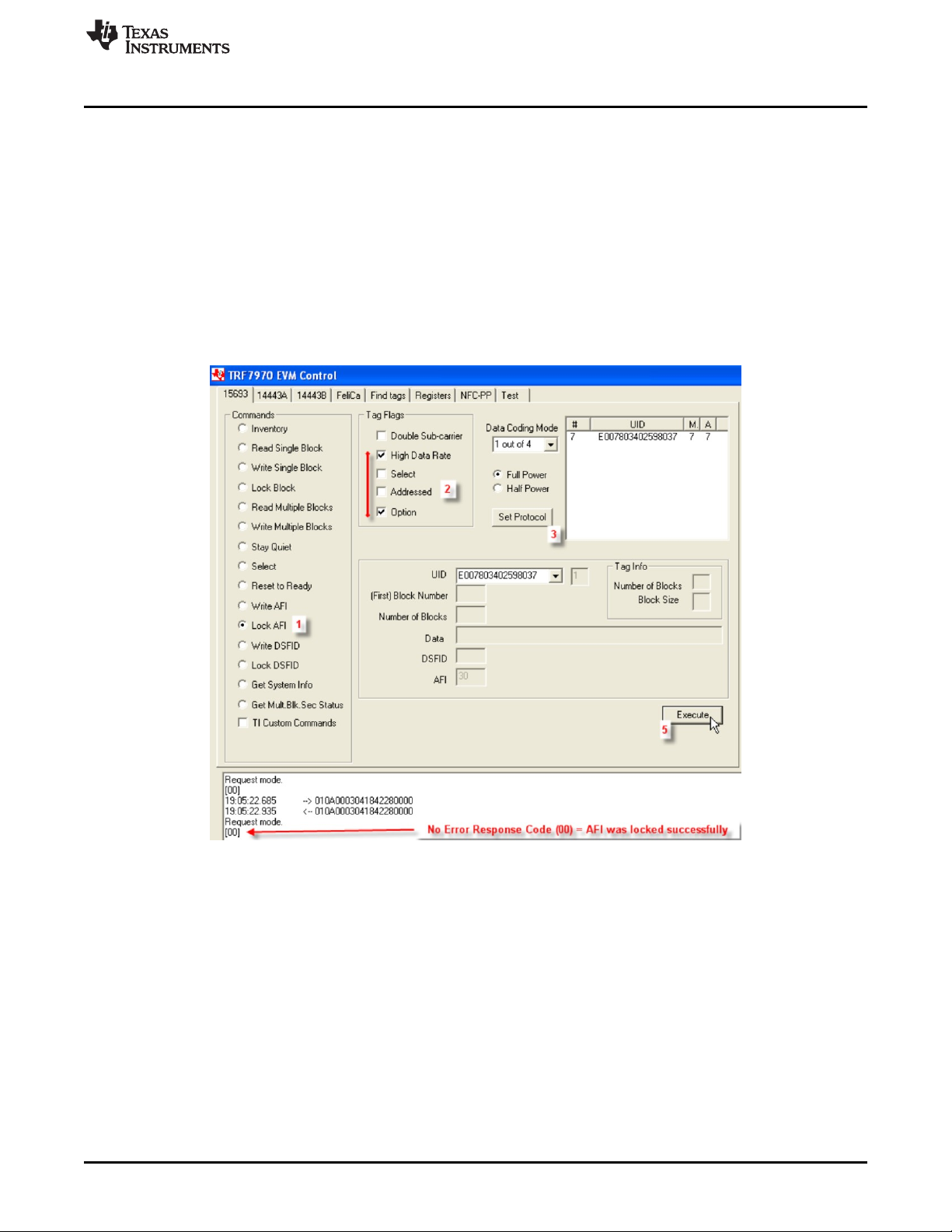
2.3.11 Lock AFI (Command Code 0x28)
The Lock AFI Command is an optional command that locks the value of the AFI memory block on the
VICC. For TI, TI based, and some other manufacturers' VICCs, the Option_flag must be set in the request.
This command can be sent as an addressed or unaddressed request, and the VICC returns an error/no
error response after the lock operation has been completed.
To perform Lock Block using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for Lock AFI.
2. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 15 for one example, note use of option flag).
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
5. Click Execute.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 15. Lock AFI Command Example
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
21
Page 22
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
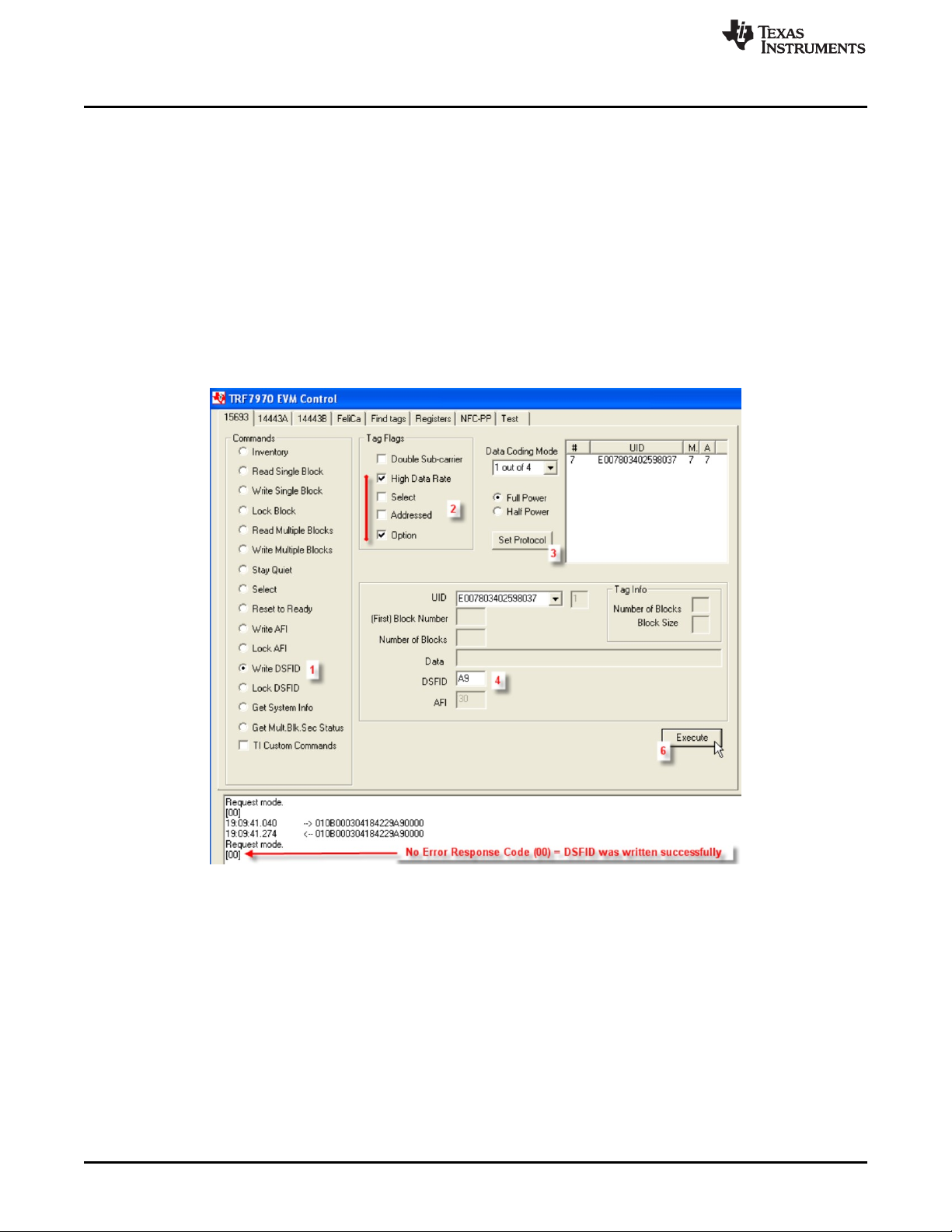
2.3.12 Write DSFID (Command Code 0x29)
The Write DSFID Command is an optional command that writes a value to the DSFID memory block on
the VICC. For TI, TI based, and some other manufacturers' VICCs, the Option_flag must be set in the
request. This command can be sent as an addressed or unaddressed request, and the VICC returns an
error/no error response after the write operation has been completed.
To perform Write DSFID using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for Write DSFID.
2. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 16 for one example, note use of option flag).
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Enter Data to be written (in hex).
5. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
6. Click Execute.
www.ti.com
22
Figure 16. Write DSFID Command Example
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 23
www.ti.com
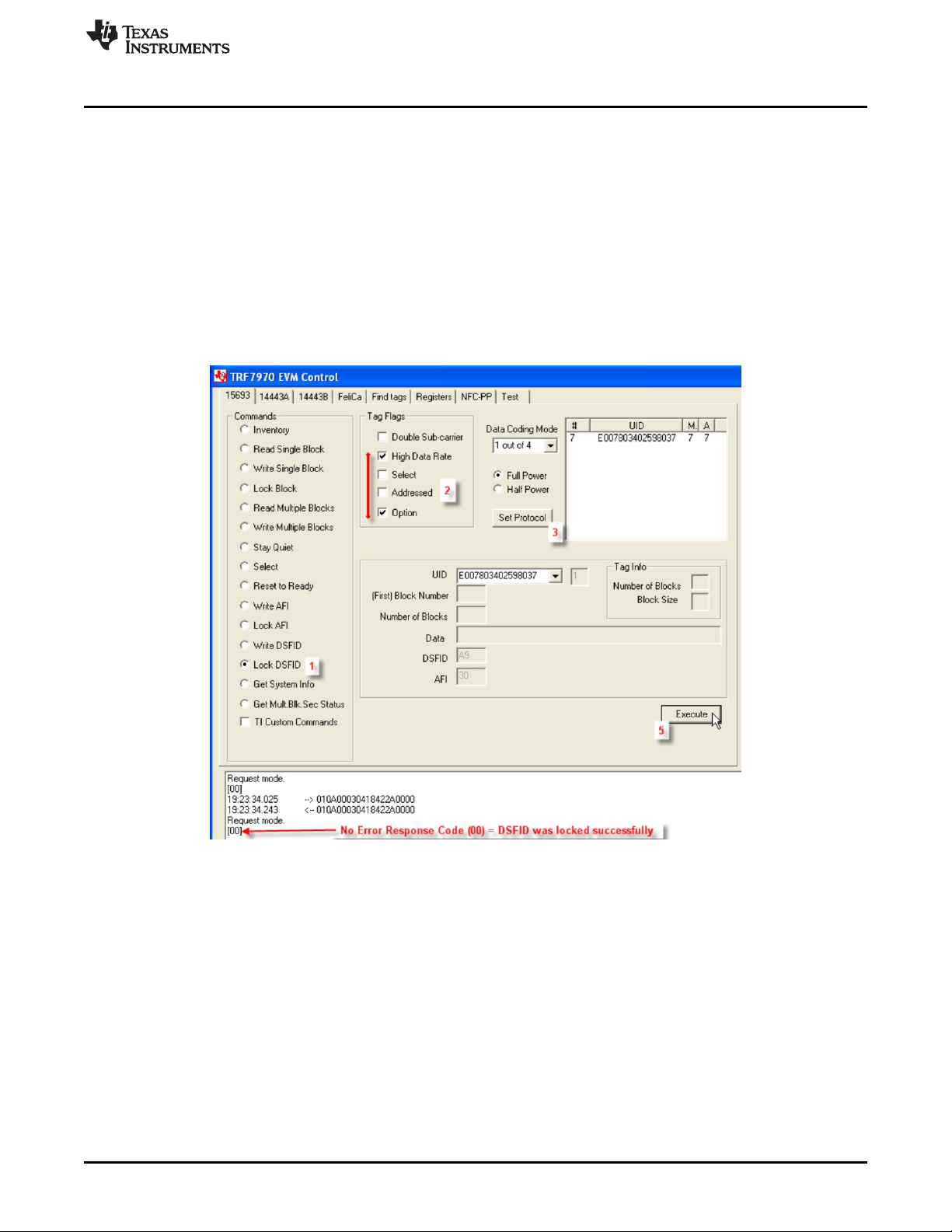
2.3.13 Lock DSFID (Command Code 0x2A)
The Lock DSFID Command is an optional command that locks the value of the DSFID memory block on
the VICC. For TI, TI based, and some other manufacturers' VICCs, the Option_flag must be set in the
request. This command can be sent as an addressed or unaddressed request, and the VICC returns an
error/no error response after the lock operation has been completed.
To perform Lock DSFID using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for Lock DSFID.
2. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 17 for one example, note use of option flag).
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
5. Click Execute.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 17. Lock DSFID Command Example
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
23
Page 24
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
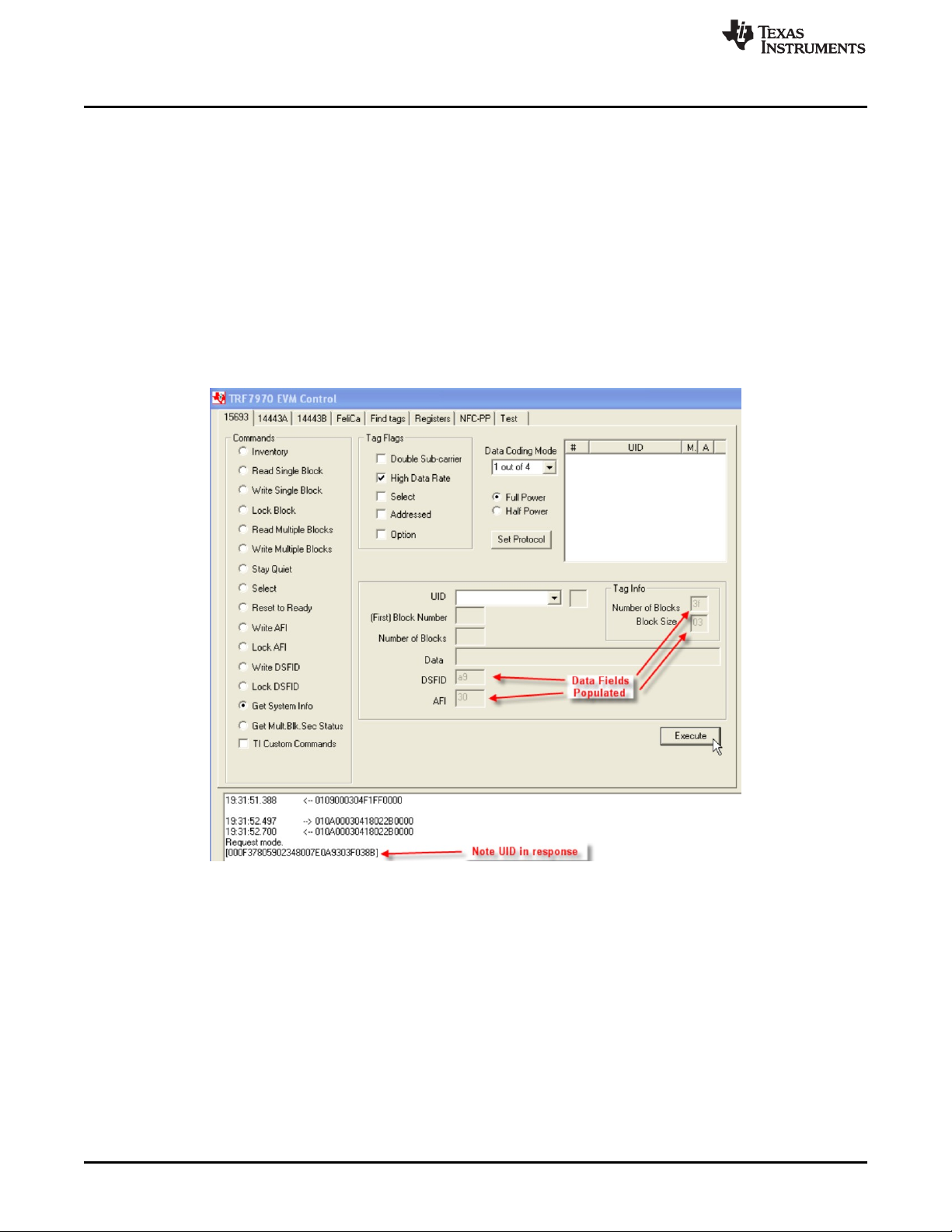
2.3.14 Get System Information (Command Code 0x2B)
The Get System Information Command is an optional command that retrieves the system information
values from the VICC information fields. This command can be sent as addressed or unaddressed
request. These fields are summary of what is and is not supported on the tag, what the user memory size
of the VICC is, and if there is an IC reference field. The IC reference field is defined by the VICC IC
manufacturer.
To perform Get System Information using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for Get System Info.
2. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 18 for one example).
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
5. Click Execute.
www.ti.com
24
Figure 18. Get System Information Command Example
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 25
www.ti.com
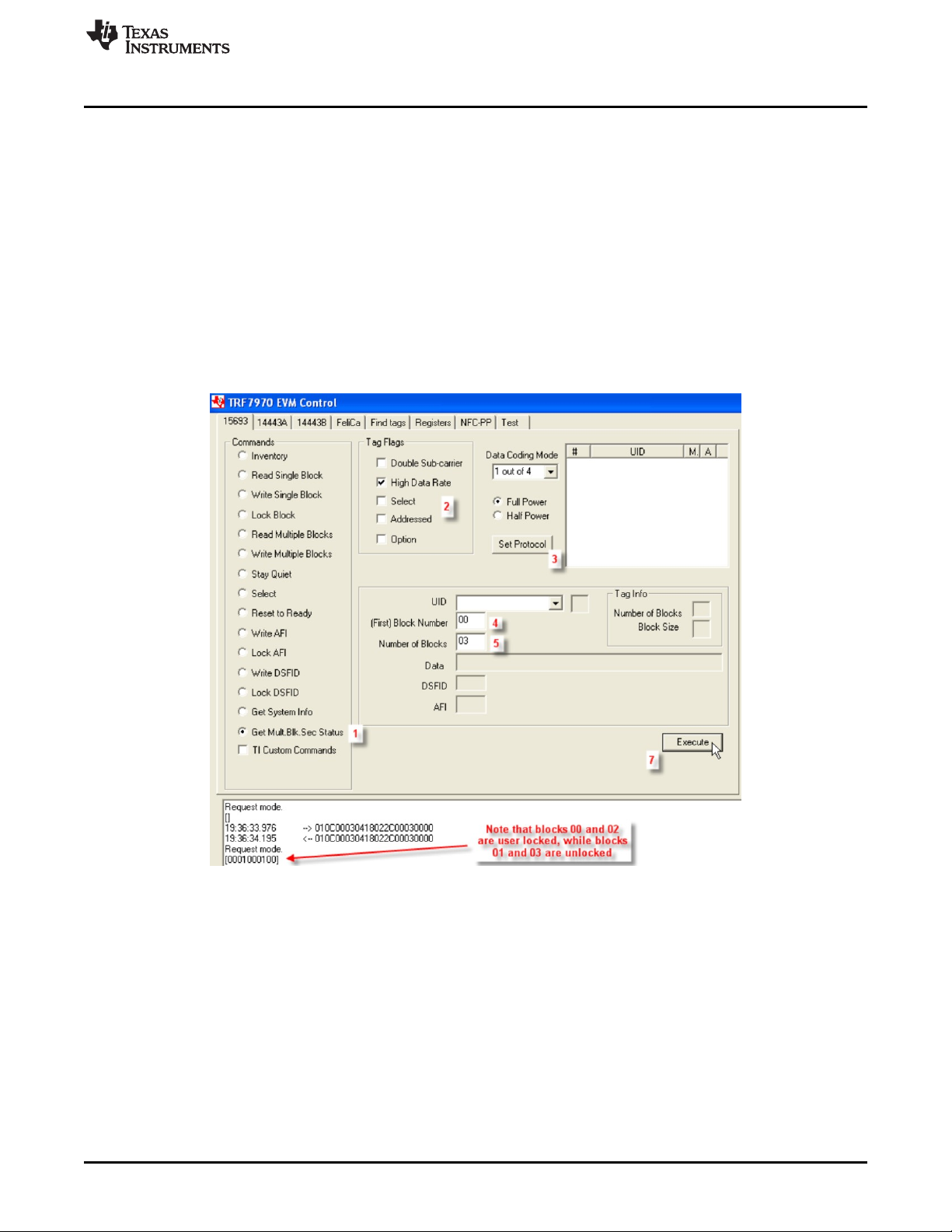
2.3.15 Get Multiple Block Security Status (Command Code 0x2C)
The Get Multiple Block Security Status Command is an optional command that retrieves the block security
status on more than one block at a time, with the first block number and the number of blocks specified in
the request. This command can be sent as addressed or unaddressed request.
To perform Get System Information using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for Get Multiple Block Security Status.
2. Select Tag Flags accordingly (see Figure 19 for one example).
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Type the first block number.
5. Type the number of blocks.
6. Place tags or transponders near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
7. Click Execute.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 19. Get Multiple Block Security Status Command Example
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
25
Page 26

Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
2.3.16 TI Custom Commands
The TRF7970A supports the two custom commands that are outlined in the ISO/IEC 15693 standard and
defined by Texas Instruments. The format outlined in the standard for custom VICC commands is shown
in Table 7. These commands are only supported by TI "Plus" silicon based transponders, which can be
identified by part numbers containing RI-xxx-112A.
Table 7. Custom Commands Request Format
SOF Request Flags Command Custom Request Parameters CRC16 EOF
Custom
Code
1 byte 1 byte
Manufacturer
Code
1 byte Custom defined by IC 2 bytes
(0x07 = TI) manufacturer (handled by TRF7970A)
2.3.16.1 Write Two Blocks (Command Code 0xA2)
When receiving the Write 2 Block Command, the transponder programs the requested blocks with the
data contained in the request and reports the success of the operation in the response.
The addressed pair of blocks must contain one even and one odd block (for example, block numbers 2
and 3 or block numbers 6 and 7). The start block must have the even address (for example, number2,
number4, or number6). If the odd address is used in the start block, the transponder does not execute the
write operation and returns the error code 0xA1.
If one or both of the addressed blocks are locked, the transponder does not execute the write operation
and returns the error code 0xA2.
The transmitted LSB block data are written to the LSB of the even addressed block (bytes 0-3) and the
MSB transmitted data to the odd addressed block (bytes 4-7).
www.ti.com
2.3.16.2 Lock Two Blocks (Command Code 0xA3)
When receiving the Lock_2_Block Command, the Transponder shall lock the addressed blocks and report
the success of the operation in the Response.
The addressed pair of blocks must contain one even and one odd block (for example, block numbers 2
and 3 or block numbers 6 and 7). The start block must have the even address (for example, number2,
number4, or number6). If the odd address is used in the start block, the Transponder does not execute the
Lock Block operation and returns the error code 0xA1.
If one or both of the addressed blocks are locked, the VICC returns the error code 0xA2.
26
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 27
www.ti.com
2.4 ISO14443A Tab
The ISO14443A tab is used to perform Layer 3 and some Layer 4 operations on ISO14443A PICCs, up to
the stage at which transparent data is to be exchanged according to the ISO/IEC144443-4 standard.
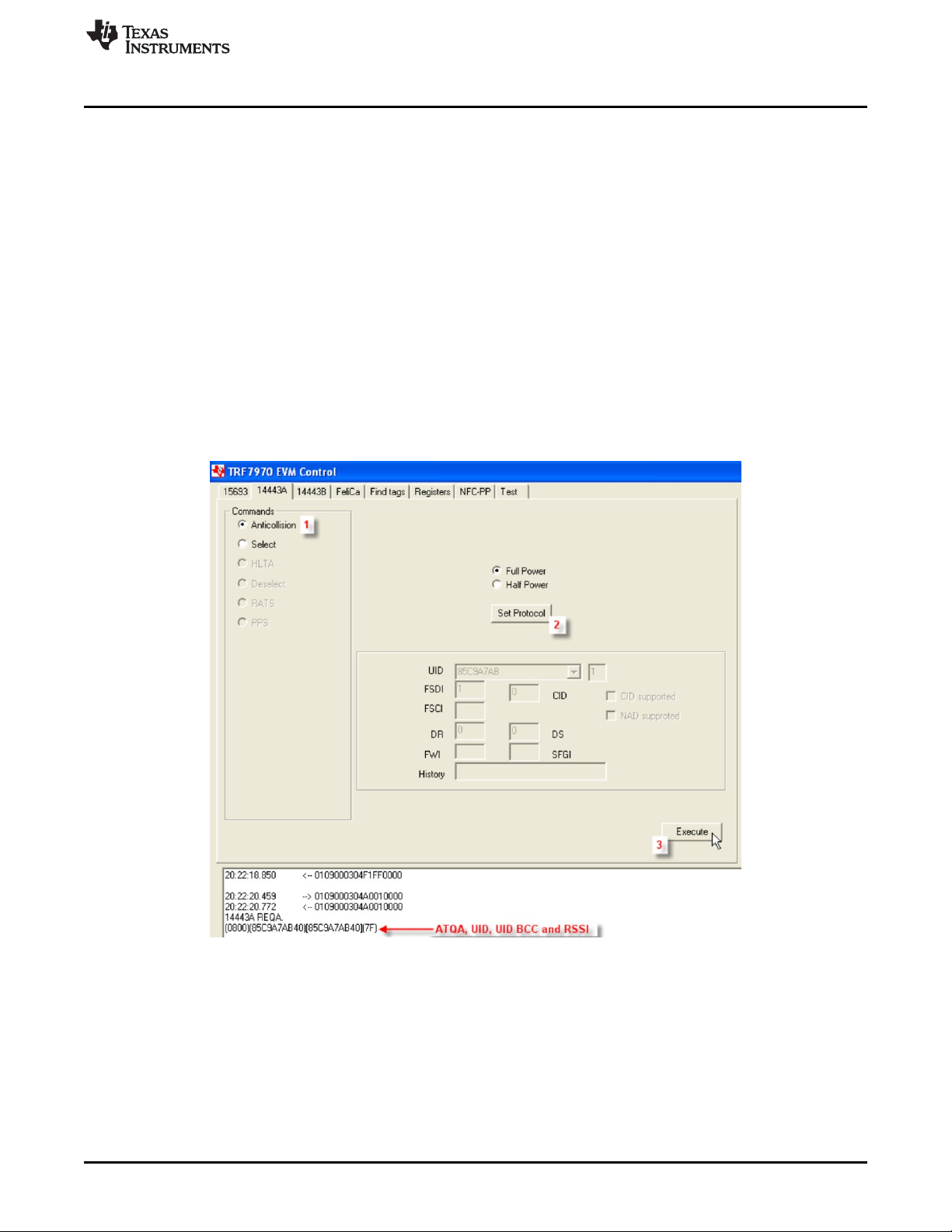
2.4.1 Anticollision
In the TRF7970A EVM GUI, this command performs the anticollision loop as outlined in the
ISO/IEC14443-3 standard as outlined for one PICC (steps 1-5, flowchart for PCD). The TRF7970A EVM
firmware and GUI also have provisions for resolving a collision between two Type A PICCs by using a
special combination command (0xE6) and the Test tab. This section demonstrates the remaining steps
(6-10) for this operation from the previously mentioned flowchart that occur before the select command is
issued.
To perform anticollision loop on one tag using the GUI:
1. Select the radio button for anticollision
2. Click Set Protocol.
3. Place tag or transponder near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
4. Click Execute.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 20. Anticollision Command Example for One Type A PICC
To perform anticollision loop on up to two tags using the GUI:
1. Go to the ISO14443A tab.
2. Click Set Protocol.
3. Go to the Test tab.
4. Type the string E600 in String to Send window (see Figure 21).
5. Place up to two ISO/IEC14443A PICCs near enough to the TRF7970A EVM antenna to be read.
6. Click Send.
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
27
Page 28

Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
www.ti.com
Figure 21. Anticollision Command Example for Two Type A PICCs
28
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 29

www.ti.com
2.4.2 Select, RATS, and PPS
The Select command radio button is automatically selected after the anticollision loop is complete when
using the ISO14443A tab, because this command cannot be issued to a PICC until the UID is obtained.
To issue Select command, leave the PICC in the field and click Execute (see Figure 22).
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 22. Select Command Example
After the Select command request is sent and a valid response is obtained, the GUI automatically selects
the RATS radio button. The user again only needs to select the Execute button to process the command
request (see Figure 23). Then the PPS radio button is automatically selected and is available as example,
but the PICC must support it.
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
29
Page 30

Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
www.ti.com
2.4.3 HLTA and Deselect
These commands are available in the GUI as needed to demonstrate stopping a card from responding
while it remains in the field (HLTA) or to reset a card back to ready state once it has been selected
(Deselect). Select the radio buttons as appropriate and click Execute.
Figure 23. RATS Command Example
30
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 31

www.ti.com
2.5 ISO14443B Tab
The ISO14443B tab is used to perform Layer 3 and into Layer 4 operations on ISO14443B PICCs
according to the ISO/IEC144443-4 standard. After selecting this tab, select the Set Protocol button.
2.5.1 Request (REQ_B)
This command is used to probe the field for ISO/IEC14443B PICCs, and it retrieves the PUPI and other
relevant information needed by the ATTRIB command (see Figure 24).
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 24. REQ_B Command Example
2.5.2 Wake-Up (WupB)
This command is used to bring ISO14443B PICCs out of the HALT state.
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
31
Page 32
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
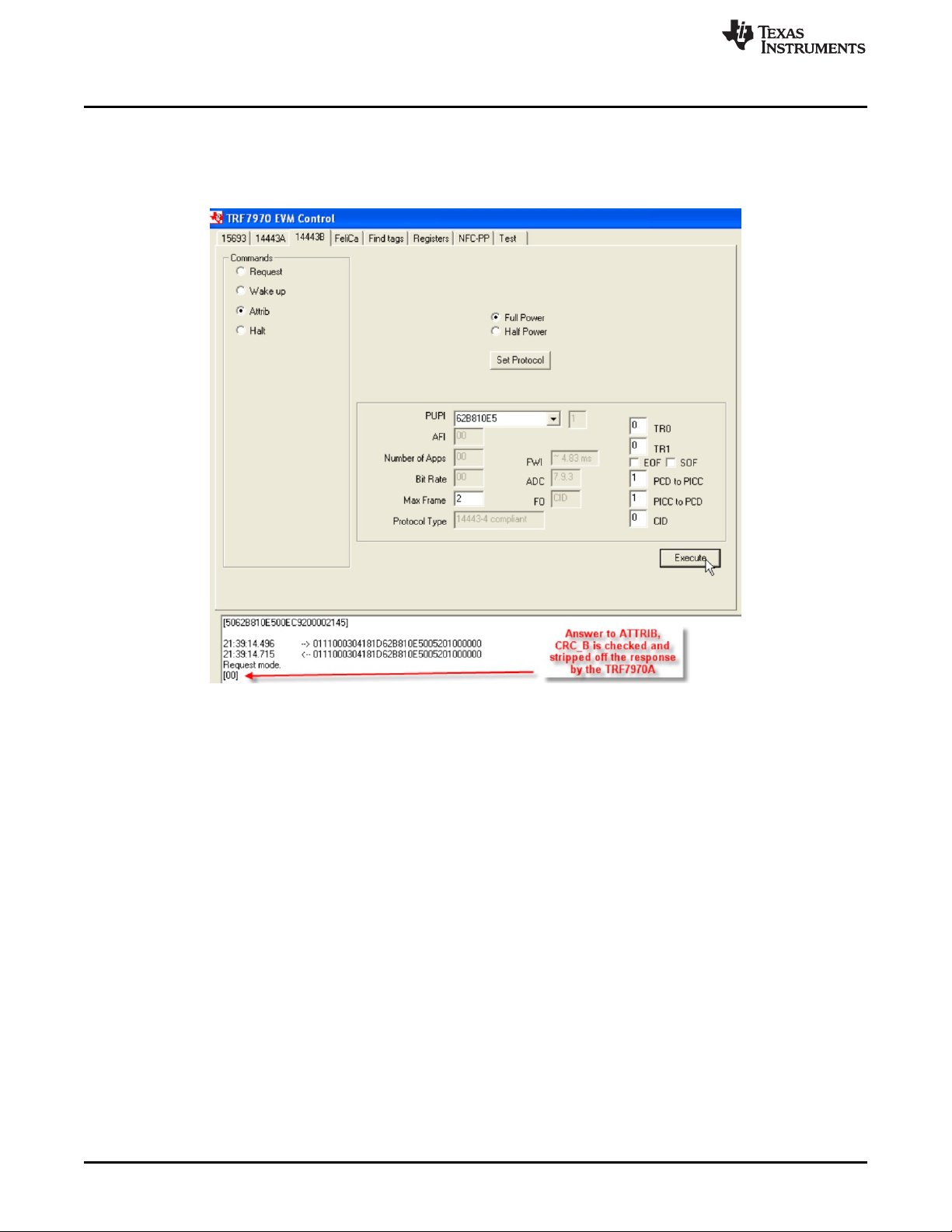
2.5.3 ATTRIB
This command is used to select an ISO14443B PICC and bring it into Layer 4. REQ_B should be sent
before this command so that the TRF7970A system has the information that is required in this command
(see Figure 25).
www.ti.com
2.5.4 Halt
This command is used to halt or stop a card from responding while still in the activation field.
Figure 25. ATTRIB Command Example
32
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 33
www.ti.com
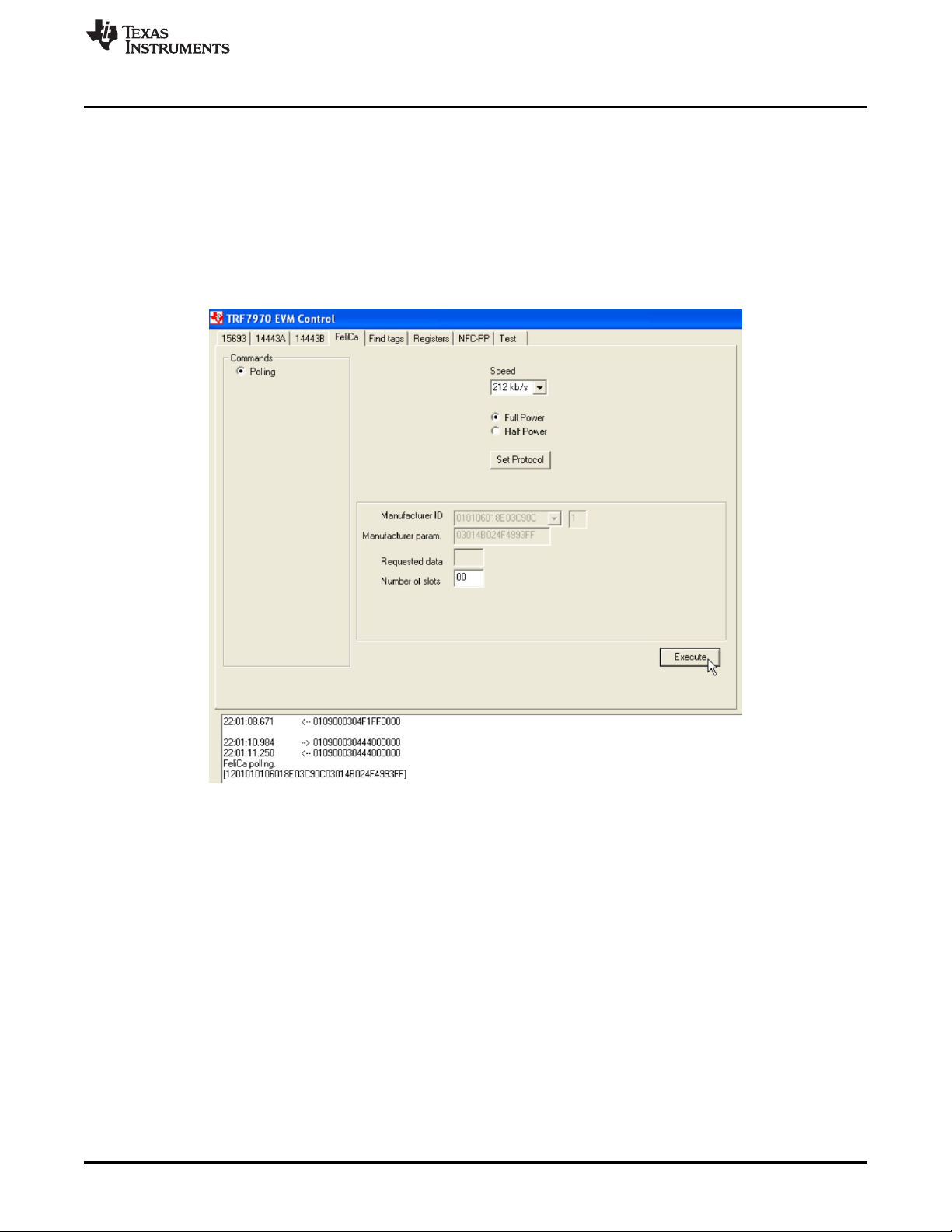
2.6 FeliCa Tab
This tab is used to poll for FeliCa transponders. This transponder technology is from the Sony Corporation
and is primarily used for payment, and it is also included in the NFC Forum specification, just like ISO/IEC
15693 and ISO/IEC 14443 transponders.
2.6.1 Polling
When inside the FeliCa tab, first select the radio button to select the protocol and click Set Protocol, then
click Execute to retrieve the Manufacturer ID and the Manufacturer Parameters from the tag (see
Figure 26). The Polling radio button is automatically selected.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 26. FeliCa Polling Example
2.7 Find Tags Tab
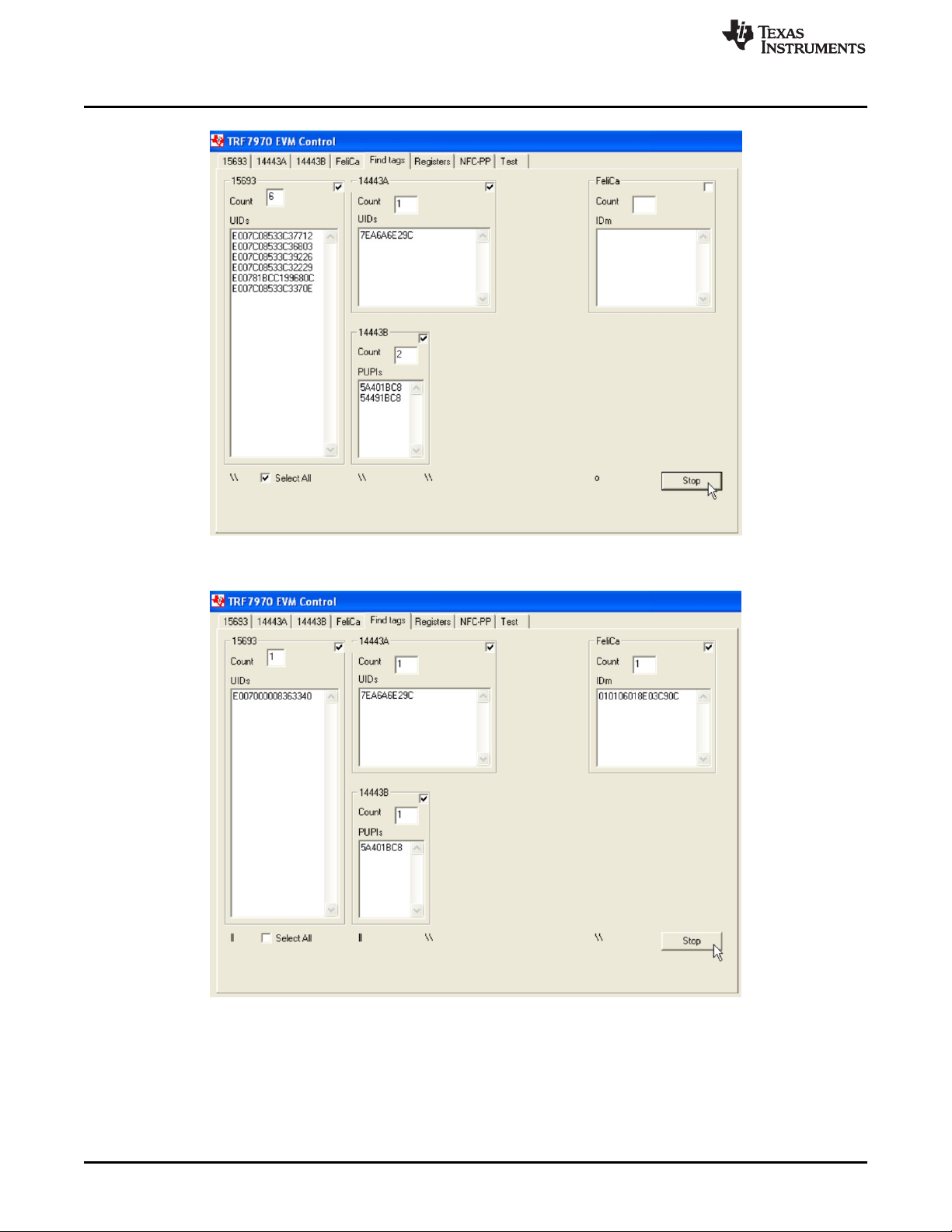
The Find Tags tab is a GUI-controlled version of the standalone mode that the reader defaults to when
powered up but before the TRF7970A EVM GUI is executed. When this tab is selected, all of the
supported protocols are selected to be polled for. Deselect any of the protocols that are not desired and
click Run, which then turns into a Stop button (see Figure 27 and Figure 28). While this tab is useful for
showing the multiprotocol capabilities of the TRF7970A EVM, it must be understood that the EVM antenna
is a certain size and generates a specific magnetic field and also that the transponders are resonant
circuits and can couple with each other, so some appropriate separation between the devices is
recommended. The ISO15693 and ISO14443B transponders are polled for with multiple slot commands,
while the FeliCa and ISO14443A transponders are polled for with single slot style commands only.
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
33
Page 34
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
www.ti.com
Figure 27. Find Tags Tab Example 1
34
Figure 28. Find Tags Tab Example 2
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 35
www.ti.com
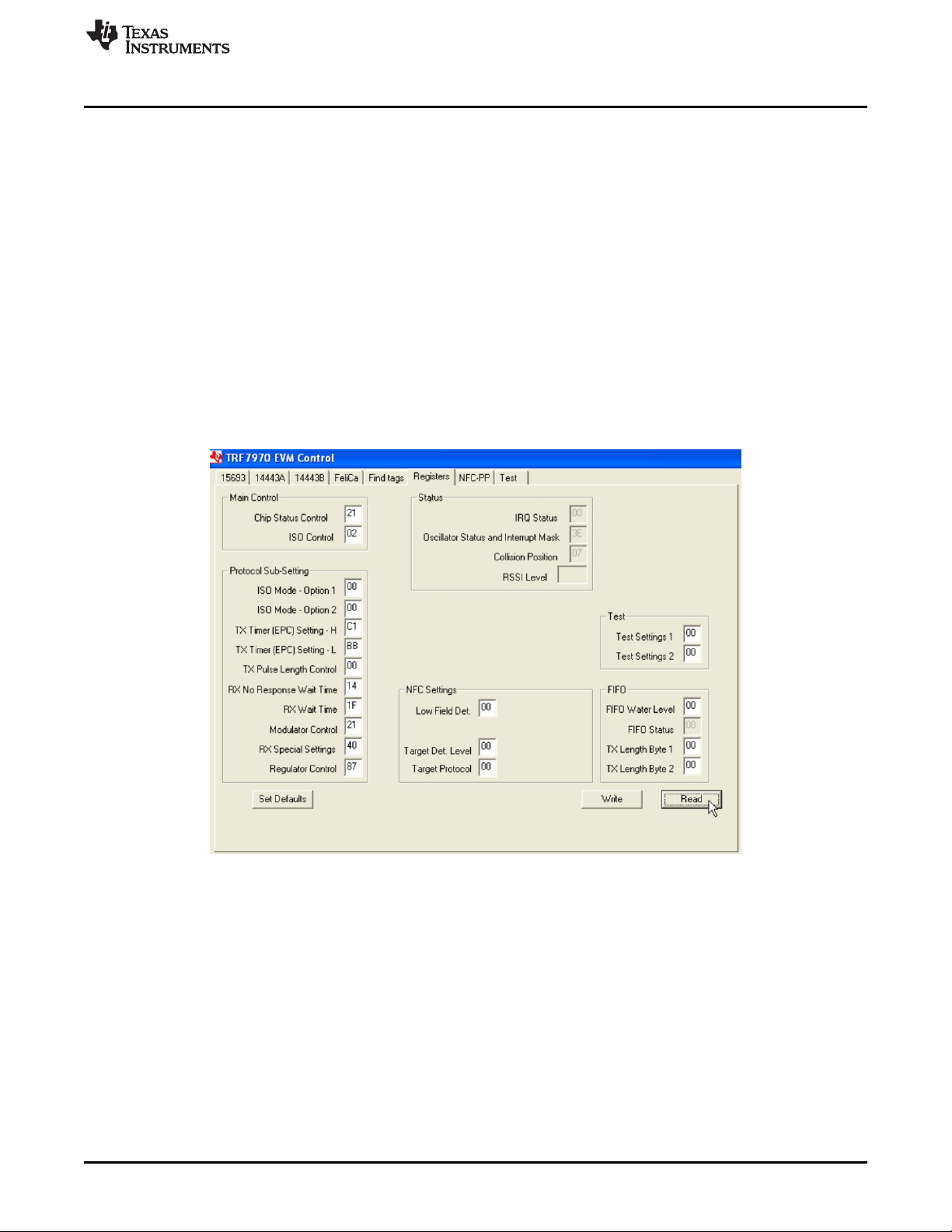
2.8 Registers Tab
The Registers tab is used to retrieve the values in the TRF7970A registers and to directly change the
values of those registers.
Some of the register settings are coded in the TRF7970A EVM firmware for the various protocols
commands; therefore, changes made in the Registers tab can be overwritten when going to a protocol tab
and setting a different protocol. To keep the values that are manually set, go to the Test Tab and check
Expert – keep settings when switching protocols. However, as some register settings are not compatible
or do not make sense when looking across the protocols, these values are coded into the EVM firmware
to provide (at the very least) sustaining performance. For example, the ISO Control Register value cannot
be set to 0x02 (default setting for ISO15693) and still support operation of ISO14443A, ISO14443B, or
FeliCa. See Figure 29 for example of this tab with registers set for default operation.
If the Set Defaults button is clicked, the EVM loses communication with the GUI. This is because the
Modulator and Sys Clock register (register 0x09) value is changed, so the MSP430 is no longer running at
the same clock speed as it was when communications were established. This causes the the UART baud
rate to be off time base, and the communications link is broken. To recover, close the GUI and reset the
TRF7970A EVM either by pressing the reset button on the board or by removing and USB power; next,
reconnect the EVM to USB and restart the GUI.
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 29. Registers Tab
2.9 NFC-PP Tab
This tab is for demonstrating the Near Field Communications (NFC) capabilities of the TRF7970A. It
requires two TRF7970A evaluation modules and two PCs with the TRF7970A EVM GUI loaded. The steps
required to demonstrate these functionalities from an Initiator and a Target perspective are described in
the following sections.
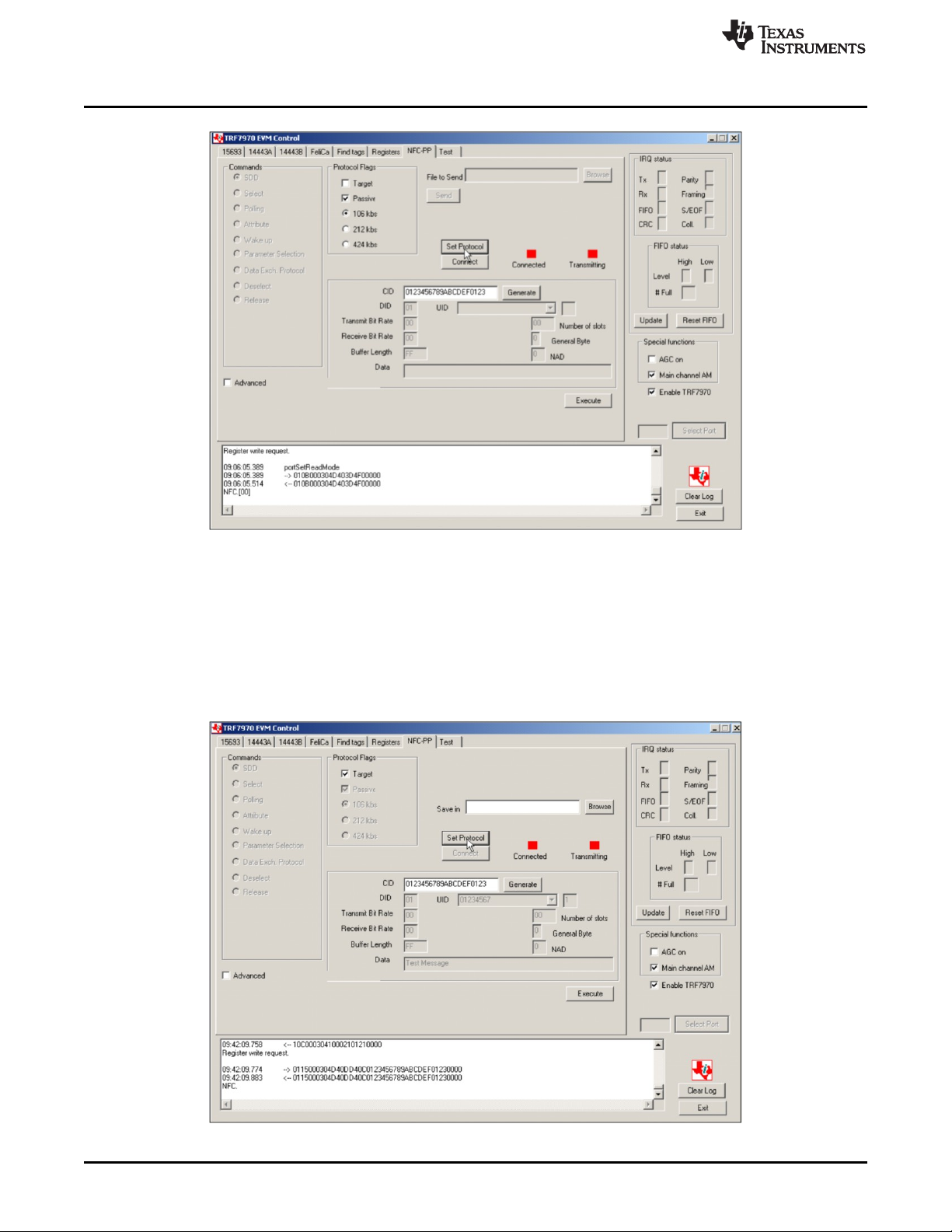
2.9.1 Initiator Setup
To setup the first TRF7970A as an Initiator (Master) (after connecting on the first PC) (see Figure 30):
1. Click the NFC-PP tab.
2. Click Set Protocol.
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
35
Page 36
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
www.ti.com
2.9.2 Target Setup
To set the second TRF7970A as a Target (Slave) (after connecting on the second PC) (see Figure 31):
1. Click the NFC-PP tab.
2. Check the Target Box in the Protocol Flags section of the GUI window.
3. Click Set Protocol.
Figure 30. Setting up TRF7970A EVM as Initiator
36
Figure 31. Setting up TRF7970A EVM as Target
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 37
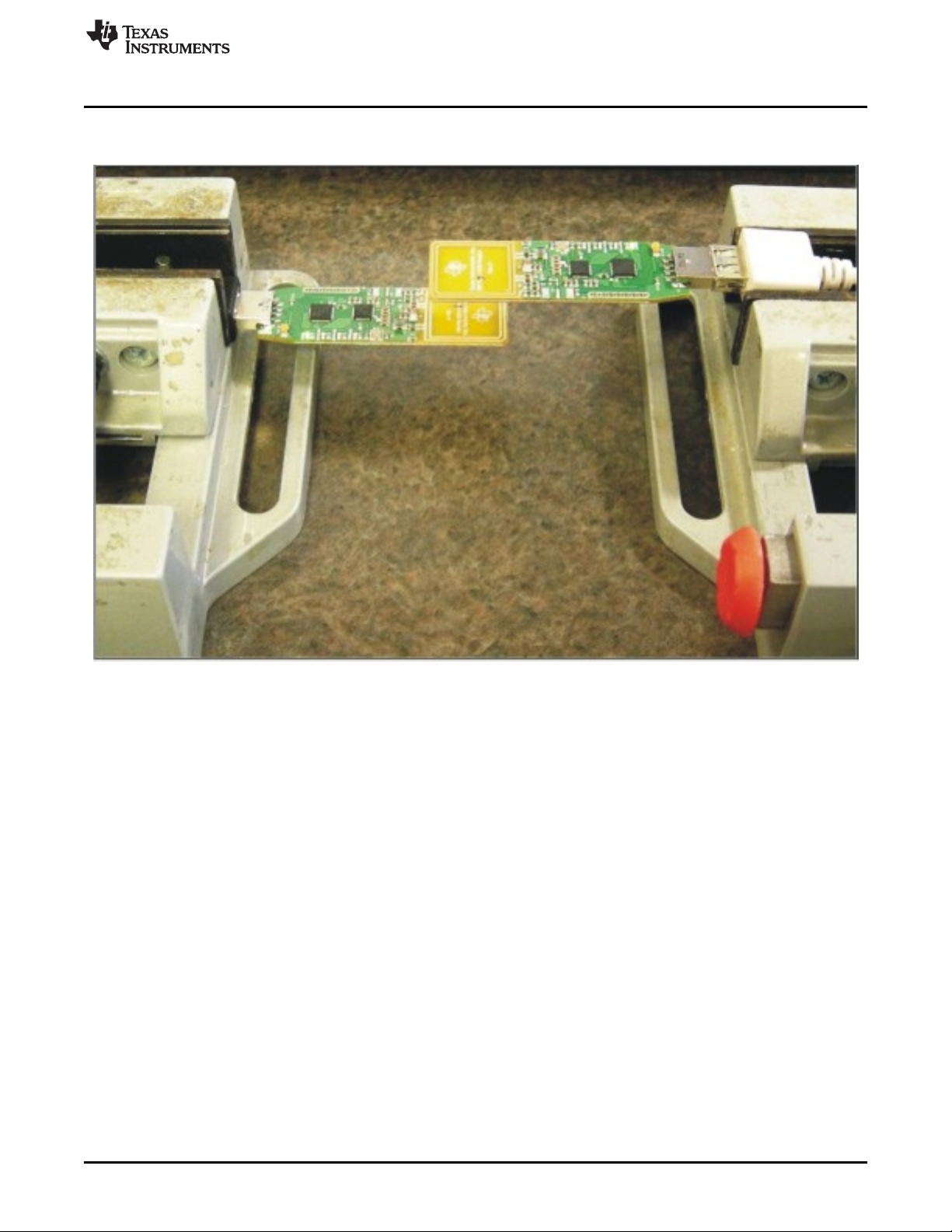
www.ti.com
After setting up the two separate TRF7970A evaluation modules, they should be arranged in a parallel
orientation relative to each other for the best coupling/best performance (see Figure 32).
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 32. Demonstration Hardware Configuration Example
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
37
Page 38
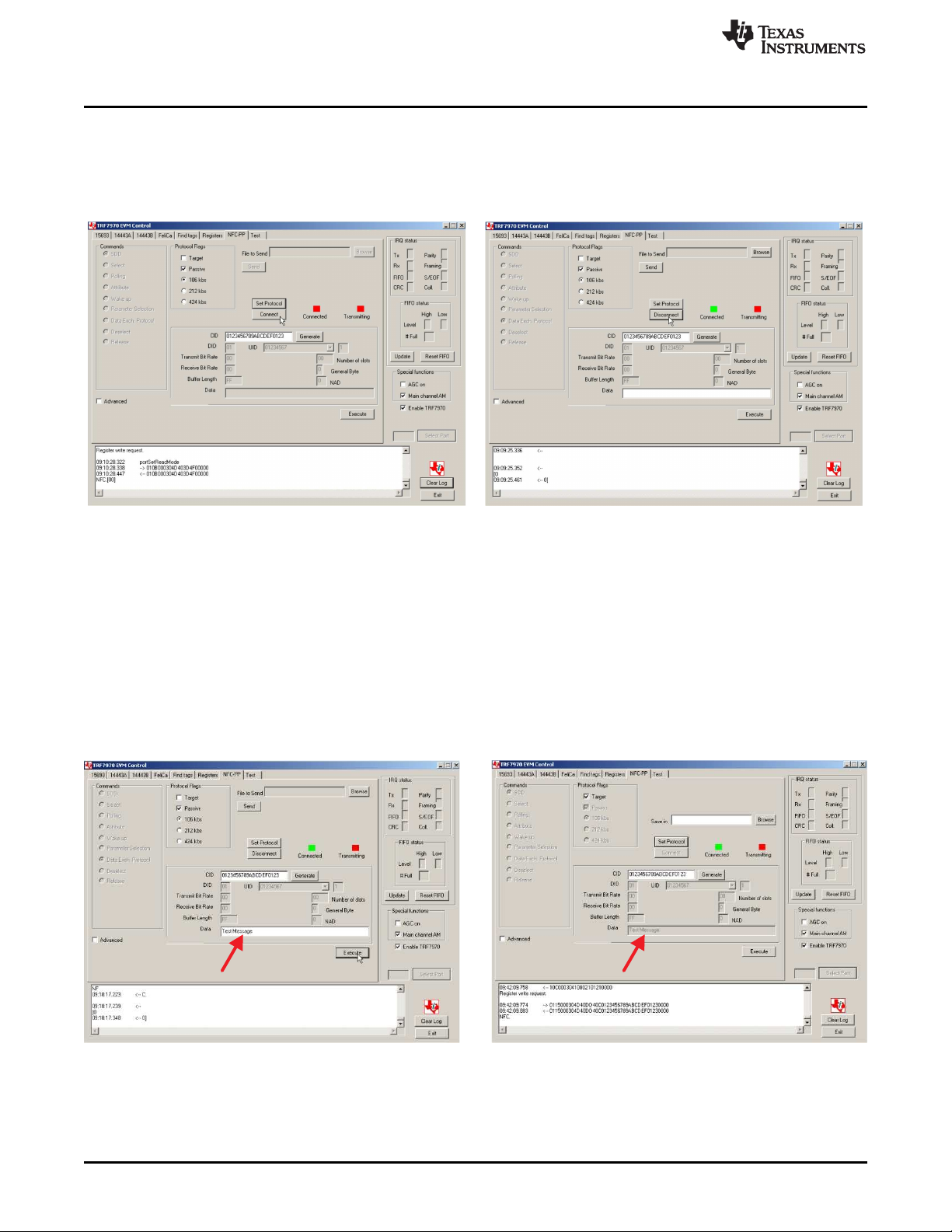
Not Connected (Initiator GUI) Connected (Initiator GUI)
Initiator GUI Window (Message Being Sent) Target GUI Window (Message Received)
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
2.9.3 Peer-to-Peer Connection Step
To connect the two TRF7970A evaluation modules (see Figure 33):
1. In the GUI for the Initiator, click Connect (the button then changes to Disconnect).
2. The Initiator and Target GUI indicators turn green when connection is successful.
www.ti.com
Figure 33. Peer-to-Peer Connection Step
2.9.4 NFC Text Message Transfer
To transfer a text message from the Initiator hardware to the Target hardware for display in the Target
GUI:
1. Perform peer-to-peer connection as described in Section 2.9.3.
2. Type in text to be sent into the Data entry text box.
3. Click Execute.
4. Look at the Target GUI window and observe text message that was sent (see red arrows in Figure 34).
Figure 34. NFC Text Message Transfer
38
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 39

www.ti.com
2.9.5 NFC File Transfer
While still in Initiator and Target modes as described in Section 2.9.3, files can also be transferred. This is
done by selecting a file to be sent from the Initiator side and also a location (a file folder or directory) to
store the file on the Target. Any file format can be transferred (for example, .doc, .xls, .jpg, or .zip). In this
example, a firmware image file (.d43) is used.
1. Select file using the Browse button in the Initiator GUI.
2. Click Open (see Figure 35).
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 35. NFC File Transfer, Select File on Initiator
3. Select file folder or directory using the Browse button in the Target GUI (in this case, a folder called
NFC_File_Transfers was created for the demonstration).
4. Click Open (see Figure 36).
Figure 36. NFC File Transfer, Save File on Target
5. Click Send in the Initiator GUI (a status bar indicates activity) (see Figure 37).
6. When file transfer is complete, the status is reported in the Initiator protocol log window and the file is
available on the Target PC. The Target GUI also indicates activity.
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
39
Page 40
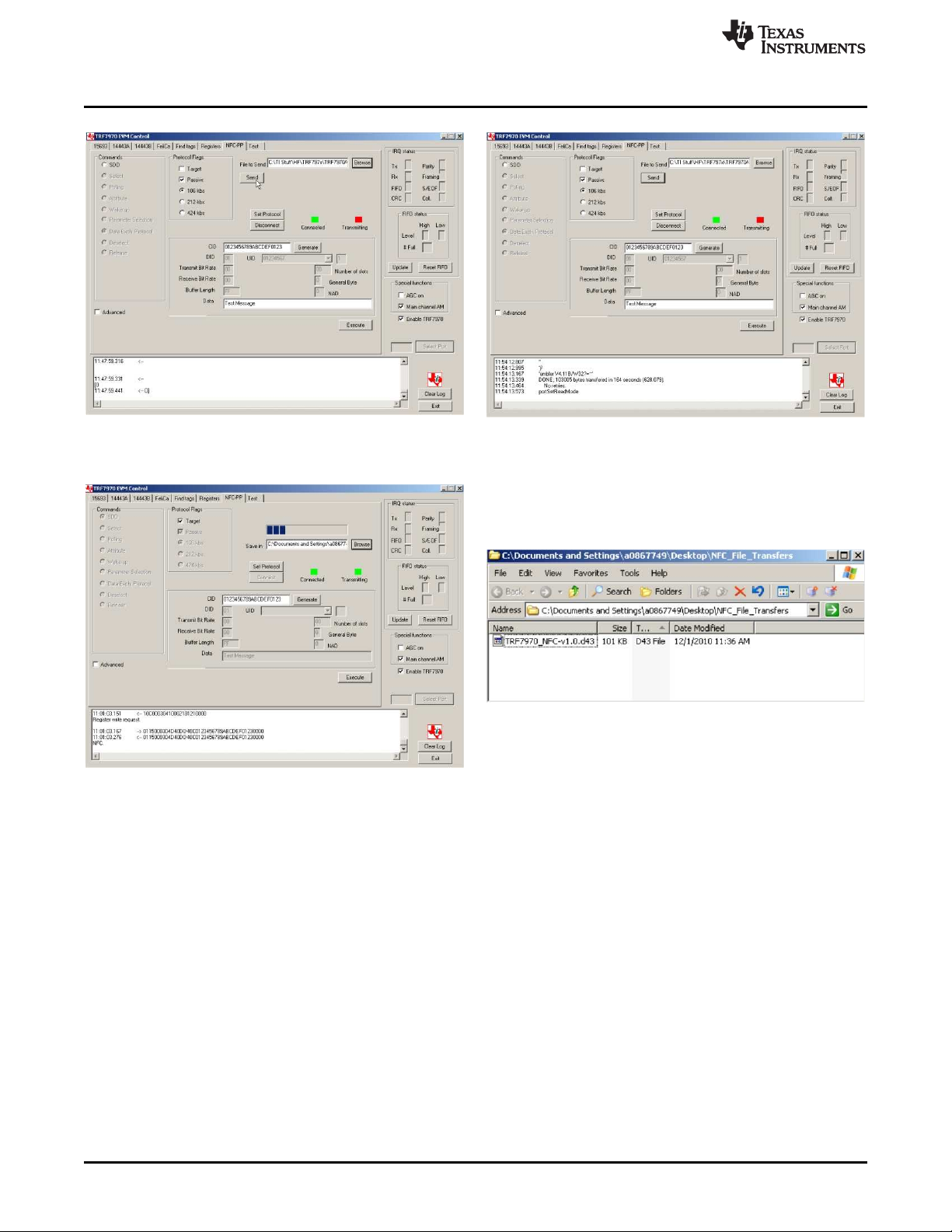
Initiator GUI File Transfer Being Started Initiator GUI File Transfer Complete
Target GUI File Transfer in Progress
Target File Folder Contents After
File Transfer is Complete (File Received)
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
www.ti.com
Figure 37. NFC File Transfer Progress
2.9.6 Card Emulation Mode
For card emulation mode, one TRF7970A EVM should be set up as a Target (see Section 2.9.2). Another
TRF7970A EVM can be used as an RFID reader (in this example, the device is set up and used as an
ISO14443A reader; see Section 2.4).
To use card emulation mode (see Figure 38):
1. On the Initiator reader side, go to the NFC-PP tab.
2. Select the Advanced check box.
3. Click Set Protocol.
4. Click Execute.
5. The SDD and Select commands can now be used.
40
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 41

ISO14443A UID Read
From TRF7970A in Card Emulation Mode
ISO14443A Select Command Response
From TRF7970A in Card Emulation Mode
ISO14443A UID Read
From TRF7970A in Card Emulation Mode
ISO14443A Select Command Response
From TRF7970A in Card Emulation Mode
www.ti.com
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
Figure 38. Card Emulation Mode
2.10 Test Tab
The TRF7970A EVM GUI Test Tab is used to send specific command strings that the firmware supports
but that are not built into the specific protocol tabs in the GUI and to assist in understanding the finer
details of the TRF7970A EVM operations. This tab also allows retrieval of the version number of the
firmware loaded in the MSP430F2370 on the EVM. The following example show how and why test strings
might be used.
Two buttons are available for sending strings: Send and Send Raw. The Send button is used to send
complete strings (including SOF, length, etc.). The Send Raw button prepends and appends those byte
required by the MSP4340F2370 host.c file for a properly concatenated string.
A few examples of when a user would need to utilize these features would be:
1. For observing a read or write continuous to the registers of the TRF7970A during code development
with a logic analyzer. These examples are using the Send button which adds on the necessary bytes
before and after data to send strings are entered. This example is setting up the TRF7970A for full
power out and ISO15693 operation (see Figure 39 and Figure 40).
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
41
Page 42

Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
www.ti.com
Figure 39. Continuous Write to Registers 0x00 to 0x0B Example
42
Figure 40. Continuous Read from Registers 0x00 to 0x0B Example
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 43

www.ti.com
2. To turn on or off the MSP430F2370 GPIO-controlled LEDs on the EVM. These could also be used in
Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
the development environment for other functions such as turning on or off other peripherals, for digital
control of reed relays and switches, etc. (see Table 8 and Figure 41).
Table 8. Command Codes for GPI/O Controlled
Outputs on EVM
LED Number be Sent (Using Send State
2 FB ON
2 FC OFF
3 F9 ON
3 FA OFF
4 F7 ON
4 F8 OFF
5 F5 ON
5 F6 OFF
6 F3 ON
6 F4 OFF
Command Code to
Button in GUI)
Figure 41. Sending GPIO Control Command
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
43
Page 44

Using the TRF7970A EVM With PC GUI
3. To retrieve the PUPI from an ISO14443B tag on which anticollision has been disabled (this is most
often the instance for ISO14443B cards that are being used for payment applications), thus requiring a
single slot REQB to be sent. Notice in Figure 42 that the Send Raw button is used. This could have
also been sent using the Send button with only B000 as the String to send.
www.ti.com
Figure 42. Sending Single Slot REQB
44
TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM) SLOU321– August 2011
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 45

www.ti.com
3 Abbreviations
AFI Application Family Identifier
BCC Block Check Character
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check
DSFID Data Storage Format Identifier
EOF End of Frame
LSB Least Significant Byte
MSB Most Significant Byte
RFU Reserved for Future Use
SOF Start of Frame
UID Unique Identifier
PCD Proximity Coupling Device
PICC Proximity Integrated Circuit Card
PUPI Pseudo Unique PICC Identifier
VCD Vicinity Coupling Device
VICC Vicinity Integrated Circuit Card
4 References
1. TRF7970A Data Sheet (SLOS743)
2. TRF7970A Firmware Description (SLOA157)
3. TRF7970A Firmware Design Hints (SLOA159)
4. TRF7970A NFC BSL Application Note (SLOA160)
5. ISO/IEC 15693 (http://www.iso.org)
6. ISO/IEC 14443 (http://www.iso.org)
7. ISO/IEC18092 (http://www.iso.org)
8. ISO/IEC 21481 (http://www.iso.org)
9. FeliCa™ (http://www.sony.net/Products/felica/)
10. MIFARE™ (http://www.mifare.net/)
Abbreviations
SLOU321– August 2011 TRF7970A Evaluation Module (EVM)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
45
Page 46

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Audio www.ti.com/audio Communications and Telecom www.ti.com/communications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Computers and Peripherals www.ti.com/computers
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Consumer Electronics www.ti.com/consumer-apps
DLP® Products www.dlp.com Energy and Lighting www.ti.com/energy
DSP dsp.ti.com Industrial www.ti.com/industrial
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Medical www.ti.com/medical
Interface interface.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Logic logic.ti.com Space, Avionics and Defense www.ti.com/space-avionics-defense
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Transportation and www.ti.com/automotive
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Video and Imaging www.ti.com/video
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Wireless www.ti.com/wireless-apps
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf
TI E2E Community Home Page e2e.ti.com
Automotive
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 47

EVALUATION BOARD/KIT/MODULE (EVM) ADDITIONAL TERMS
Texas Instruments (TI) provides the enclosed Evaluation Board/Kit/Module (EVM) under the following
conditions:
The user assumes all responsibility and liability for proper and safe handling of the goods. Further, the user
indemnifies TI from all claims arising from the handling or use of the goods.
Should this evaluation board/kit not meet the specifications indicated in the User’s Guide, the board/ kit may
be returned within 30 days from the date of delivery for a full refund. THE FOREGOING LIMITED
WARRANTY IS THE EXCLUSIVE WARRANTY MADE BY SELLER TO BUYER AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL
OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE. EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT OF
THE INDEMNITY SET FORTH ABOVE, NEITHER PARTY SHALL BE LIABLE TO THE OTHER FOR ANY
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
Please read the User's Guide and, specifically, the Warnings and Restrictions notice in the User's Guide
prior to handling the product. This notice contains important safety information about temperatures and
voltages. For additional information on TI's environmental and/or safety programs, please visit
www.ti.com/esh
No license is granted under any patent right or other intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to
any machine, process, or combination in which such TI products or services might be or are used. TI
currently deals with a variety of customers for products, and therefore our arrangement with the user is not
exclusive. TI assumes no liability for applications assistance, customer product design, software
performance, or infringement of patents or services described herein.
As noted in the EVM User’s Guide and/or EVM itself, this EVM and/or accompanying hardware may or may
not be subject to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and Industry Canada (IC) rules.
For EVMs not subject to the above rules, this evaluation board/kit/module is intended for use for
ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT, DEMONSTRATION OR EVALUATION PURPOSES ONLY and is not
considered by TI to be a finished end product fit for general consumer use. It generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and has not been tested for compliance with the limits of computing devices
pursuant to part 15 of FCC or ICES-003 rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against
radio frequency interference. Operation of the equipment may cause interference with radio communications,
in which case the user at his own expense will be required to take whatever measures may be required to
correct this interference.
General Statement for EVMs including a radio
User Power/Frequency Use Obligations:
legally allocated frequency and power limits. Any use of radio frequencies and/or power availability of this
EVM and its development application(s) must comply with local laws governing radio spectrum allocation and
power limits for this evaluation module. It is the user’s sole responsibility to only operate this radio in legally
acceptable frequency space and within legally mandated power limitations. Any exceptions to this is strictly
prohibited and unauthorized by Texas Instruments unless user has obtained appropriate
experimental/development licenses from local regulatory authorities, which is responsibility of user including
its acceptable authorization.
or contact TI.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments Post Office Box 655303 Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
REGULATORY COMPLIANCE INFORMATION
This radio is intended for development/professional use only in
SSZZ027 December 2011
Page 48

For EVMs annotated as FCC – FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION Part 15 Compliant
Caution
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1)
This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the
user's authority to operate the equipment.
FCC Interference Statement for Class A EVM devices
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to
part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses,
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction
manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the
interference at his own expense.
FCC Interference Statement for Class B EVM devices
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
SSZZ027 December 2011
Page 49

For EVMs annotated as IC – INDUSTRY CANADA Compliant
This Class A or B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the
user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Concerning EVMs including radio transmitters
This device complies with Industry Canada licence-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
Concerning EVMs including detachable antennas
Under Industry Canada regulations, this radio transmitter may only operate using an antenna of a type and
maximum (or lesser) gain approved for the transmitter by Industry Canada. To reduce potential radio
interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain should be so chosen that the equivalent
isotropically radiated power (e.i.r.p.) is not more than that necessary for successful communication.
This radio transmitter has been approved by Industry Canada to operate with the antenna types listed in the
user guide with the maximum permissible gain and required antenna impedance for each antenna type
indicated. Antenna types not included in this list, having a gain greater than the maximum gain indicated for
that type, are strictly prohibited for use with this device.
~
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A ou B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Les changements ou les modifications pas expressément approuvés par la partie responsable de la
conformité ont pu vider l’autorité de l'utilisateur pour actionner l'équipement.
Concernant les EVMs avec appareils radio
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio exempts de
licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l'appareil ne doit pas produire de
brouillage, et (2) l'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le
brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
Concernant les EVMs avec antennes détachables
Conformément à la réglementation d'Industrie Canada, le présent émetteur radio peut fonctionner avec une
antenne d'un type et d'un gain maximal (ou inférieur) approuvé pour l'émetteur par Industrie Canada. Dans
le but de réduire les risques de brouillage radioélectrique à l'intention des autres utilisateurs, il faut choisir le
type d'antenne et son gain de sorte que la puissance isotrope rayonnée équivalente (p.i.r.e.) ne dépasse pas
l'intensité nécessaire à l'établissement d'une communication satisfaisante.
Le présent émetteur radio a été approuvé par Industrie Canada pour fonctionner avec les types d'antenne
énumérés dans le manuel d’usage et ayant un gain admissible maximal et l'impédance requise pour chaque
type d'antenne. Les types d'antenne non inclus dans cette liste, ou dont le gain est supérieur au gain
maximal indiqué, sont strictement interdits pour l'exploitation de l'émetteur.
SSZZ027 December 2011
Page 50

【Important Notice for Users of this Product in Japan】
This development kit is NOT certified as Confirming to Technical Regulations of
Radio Law of Japan!
If you use this product in Japan, you are required by Radio Law of Japan to follow the instructions below with
respect to this product:
(1) Use this product in a shielded room or any other test facility as defined in the notification #173
issued by Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications on March 28, 2006, based on Sub-section 1.1 of
Article 6 of the Ministry’s Rule for Enforcement of Radio Law of Japan,
(2) Use this product only after you obtained the license of Test Radio Station as provided in Radio
Law of Japan with respect to this product, or
(3) Use of this product only after you obtained the Technical Regulations Conformity Certification as
provided in Radio Law of Japan with respect to this product.
Also, please do not transfer this product, unless you give the same notice above to the transferee.
Please note that if you could not follow the instructions above, you will be subject to penalties of Radio Law
of Japan.
Texas Instruments Japan Limited
(address) 24-1, Nishi-Shinjuku 6 chome, Shinjukku-ku, Tokyo, Japan
http://www.tij.co.jp
【ご使用にあたっての注意】
本開発キットは技術基準適合証明を受けておりません。
本製品のご使用に際しては、電波法遵守のため、以下のいずれかの措置を取っていただく必要がありますの
でご注意ください。
(1)電波法施行規則第6条第1項第1号に基づく平成18年3月28日総務省告示第173号で定められた
電波暗室等の試験設備でご使用いただく。
(2)実験局の免許を取得後ご使用いただく。
(3)技術基準適合証明を取得後ご使用いただく。
なお、本製品は、上記の「ご使用にあたっての注意」を譲渡先、移転先に通知しない限り、譲渡、移転でき
ないものとします。
上記を遵守頂けない場合は、電波法の罰則が適用される可能性があることをご留意ください。
日本テキサス・インスツルメンツ株式会社
東京都新宿区西新宿6丁目24番1号
西新宿三井ビル
http://www.tij.co.jp
SSZZ027 December 2011
Page 51

EVALUATION BOARD/KIT/MODULE (EVM)
WARNINGS, RESTRICTIONS AND DISCLAIMERS
For Feasibility Evaluation Only, in Laboratory/Development Environments. Unless otherwise indicated,
this EVM is not a finished electrical equipment and not intended for consumer use. It is intended solely for
use for preliminary feasibility evaluation in laboratory/development environments by technically qualified
electronics experts who are familiar with the dangers and application risks associated with handling electrical
mechanical components, systems and subsystems. It should not be used as all or part of a finished end
product.
Your Sole Responsibility and Risk. You acknowledge, represent and agree that:
1. You have unique knowledge concerning Federal, State and local regulatory requirements (including but
not limited to Food and Drug Administration regulations, if applicable) which relate to your products and
which relate to your use (and/or that of your employees, affiliates, contractors or designees) of the EVM
for evaluation, testing and other purposes.
2. You have full and exclusive responsibility to assure the safety and compliance of your products with all
such laws and other applicable regulatory requirements, and also to assure the safety of any activities to
be conducted by you and/or your employees, affiliates, contractors or designees, using the EVM.
Further, you are responsible to assure that any interfaces (electronic and/or mechanical) between the
EVM and any human body are designed with suitable isolation and means to safely limit accessible
leakage currents to minimize the risk of electrical shock hazard.
3. You will employ reasonable safeguards to ensure that your use of the EVM will not result in any property
damage, injury or death, even if the EVM should fail to perform as described or expected.
4. You will take care of proper disposal and recycling of the EVM’s electronic components and packing
materials
Certain Instructions. It is important to operate this EVM within TI’s recommended specifications and
environmental considerations per the user guidelines. Exceeding the specified EVM ratings (including but not
limited to input and output voltage, current, power, and environmental ranges) may cause property damage,
personal injury or death. If there are questions concerning these ratings please contact a TI field
representative prior to connecting interface electronics including input power and intended loads. Any loads
applied outside of the specified output range may result in unintended and/or inaccurate operation and/or
possible permanent damage to the EVM and/or interface electronics. Please consult the EVM User's Guide
prior to connecting any load to the EVM output. If there is uncertainty as to the load specification, please
contact a TI field representative. During normal operation, some circuit components may have case
temperatures greater than 60 C as long as the input and output are maintained at a normal ambient
operating temperature. These components include but are not limited to linear regulators, switching
transistors, pass transistors, and current sense resistors which can be identified using the EVM schematic
located in the EVM User's Guide. When placing measurement probes near these devices during normal
operation, please be aware that these devices may be very warm to the touch. As with all electronic
evaluation tools, only qualified personnel knowledgeable in electronic measurement and diagnostics
normally found in development environments should use these EVMs
Agreement to Defend, Indemnify and Hold Harmless. You agree to defend, indemnify and hold TI, its
licensors and their representatives harmless from and against any and all claims, damages, losses,
expenses, costs and liabilities (collectively, "Claims") arising out of or in connection with any use of the EVM
that is not in accordance with the terms of the agreement. This obligation shall apply whether Claims arise
under law of tort or contract or any other legal theory, and even if the EVM fails to perform as described or
expected.
Safety-Critical or Life-Critical Applications. If you intend to evaluate the components for possible use in
safety critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably be
expected to cause severe personal injury or death, such as devices which are classified as FDA Class III or
similar classification, then you must spe
and Indemnity Agreement.
cifically notify TI of such intent and enter into a separate Assurance
SSZZ027 December 2011
 Loading...
Loading...