Page 1
查询DEM-VSP2232Y供应商
VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
CCD SIGNAL PROCESSOR
FOR DIGITAL CAMERAS
FEATURES
CCD Signal Processing
D
– Correlated Double Sampling (CDS)
– Programmable Black Level Clamping
D Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA)
– –6-dB to 42-dB Gain Ranging
D 10-Bit Digital Data Output
– Up to 36-MHz Conversion Rate
– No Missing Codes
D 76-dB Signal-to-Noise Ratio
D Portable Operation
– Low Voltage: 2.7 V to 3.6 V
– Low Power: 130 mW (typ) at 3.0 V
– Standby Mode: 6 mW
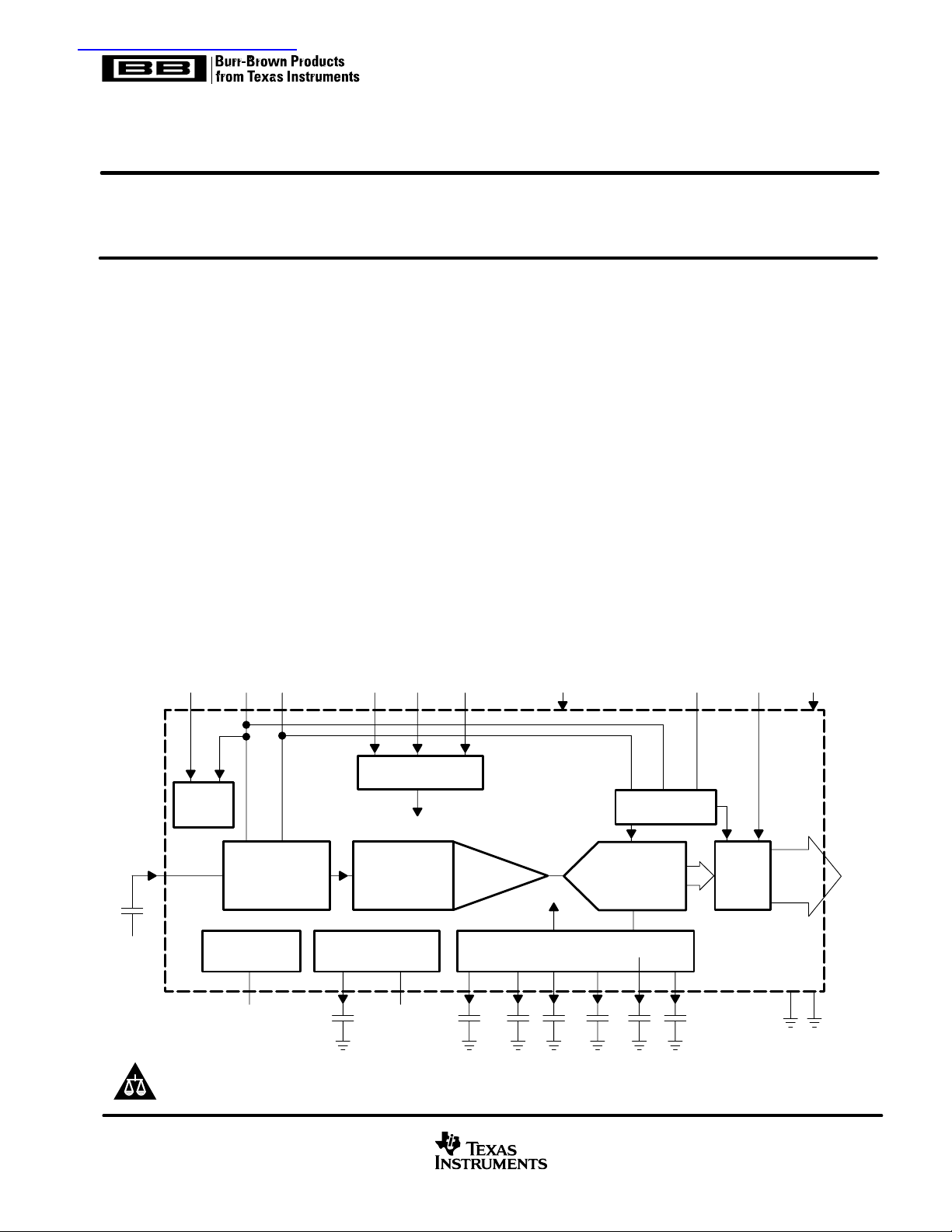
VSP2232 block diagram
CLPDM SHP SHD SLOAD SCLK SDATA RESET ADCCK DRV
DESCRIPTION
The VSP2232 is a complete mixed-signal processing IC
for digital cameras that provides signal conditioning and
analog-to-digital conversion for the output of a CCD
array. The primary CCD channel provides correlated
double sampling (CDS) to extract the video information
from the pixels, a –6-dB to 42-dB gain with digital control
for varying illumination conditions, and black level
clamping for an accurate black level reference.
Input signal clamping and offset correction of the input
CDS is also performed. The stable gain control is linear
in dB. Additionally, the black level is quickly recovered
after gain change.
The VSP2232Y is pin-to-pin compatible with the
VSP2262Y (12-bit 20 MHz) one-chip product.
The VSP2232Y is available in a 48-pin LQFP package
and operates from a single 3-V/3.3-V supply.
DDVCC
Input
Clamp
Correlated
Double
Sampling (CDS)
CCD
Output
Signal
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Preblanking
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
Optical Black (OB)
Level Clamping
Serial Interface
Programmable
Gain Amplifier
(PGA)
–6 to 42 dB
Reference Voltage Generator
www.ti.com
Analog-to-Digital
Timing Control
Output
Converter
Copyright 2001, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Latch
12-Bit
Digital
Output
B(0–11)
GNDADRVGNDREFPCMREFNBYPMBYPBYPP2CPLOBCOBPBLK
1
Page 2
VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
PACKAGE/ORDERING INFORMATION
PRODUCT
VSP2232Y 48-pin LQFP ZZ340 0_C to 85_C VSP2232Y VSP2232Y 250 pcs. Tray
VSP2232Y 48-pin LQFP ZZ340 0_C to 85_C VSP2232Y VSP2232Y/2K Tape and Reel
†
This package is available taped and reeled. To order this packaging option, add an R suffix to the part number (e.g., VSP2232CDR.
PACKAGE
PACKAGE OUTLINE
NUMBER
DEMO BOARD ORDERING INFORMATION
PRODUCT
VSP2232Y DEM-VSP2232Y
pin assignments
48-PIN LQFP PACKAGE
SPECIFIED
TEMPERATURE RANGE
ORDERING NUMBER
(TOP VIEW)
PACKAGE
MARKING
ORDERING
NUMBER
†
TRANSPORT
MEDIA
CC
GNDA
GNDA
35 34 33 32 3136 30
CM
37
REFP
REFN
GNDA
GNDA
RESET
SLOAD
SDATA
SCLK
V
CC
NC
NC
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
1
23
B1
B2
B0(LSB)
NC – No internal connection
VCCV
BYPM
BYP
5678
4
B4B5B6B7B8
B3
BYPP2
CCDIN
28 27 2629
9
CC
COBVGNDA
10 11 12
B9
GNDA
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
B10
B11(MSB)
V
CC
CLPDM
SHD
SHP
CLPOB
PBLK
V
CC
GNDA
ADCCK
GNDA
DRVGND
DRV
DD
2
www.ti.com
Page 3
†
VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
ADCCK 16 DI Master clock, See Note 1
B0(LSB) 1 DO A/D converter output, Bit 0 (LSB)
B1 2 DO A/D converter output, Bit 1
B2 3 DO A/D converter output, Bit 2
B3 4 DO A/D converter output, Bit 3
B4 5 DO A/D converter output, Bit 4
B5 6 DO A/D converter output, Bit 5
B6 7 DO A/D converter output, Bit 6
B7 8 DO A/D converter output, Bit 7
B8 9 DO A/D converter output, Bit 8
B9 10 DO A/D converter output, Bit 9
B10 11 DO A/D converter output, Bit 10
B11(MSB) 12 DO A/D converter output, Bit 11 (MSB)
BYP 31 AO Internal reference C (bypass to ground), See Note 2
BYPM 32 AO Internal reference N (bypass to ground), See Note 3
BYPP2 29 AO Internal reference P (bypass to ground), See Note 3
CCDIN 30 AI CCD signal input
CLPDM 23 DI Dummy pixel clamp pulse (Default = Active low), See Note 4
CLPOB 20 DI Optical black clamp pulse (Default = Active low), See Note 4
CM 37 AO A/D converter common mode voltage (bypass to ground), See Note 2
COB 28 AO Optical black clamp loop reference (bypass to ground), See Note 5
DRV
DD
DRVGND 14 P Digital ground. Exclusively for digital output
GNDA 15, 17, 25, 26, 35, 36,
NC 43, 44 Should be left open
PBLK 19 DI Preblanking
REFN 39 AO A/D converter negative reference (bypass to ground), See Note 2
REFP 38 AO A/D converter positive reference (bypass to ground), See Note 2
RESET 45 DI Asynchronous system reset (active low)
SCLK 48 DI Clock for serial data shift (triggered at the rising edge)
SDATA 47 DI Serial data input
SHP 21 DI CDS reference level sampling pulse (Default = Active low), See Note 4
SHD 22 DI CDS Data level sampling pulse (Default = Active low), See Note 4
†
Designators in TYPE Column: P–power supply and ground, DI–digital input, DO–digital output, AI–analog input, AO–analog output
NOTES: 1. There are two options to drive the A/D converter:
a). External drive mode: The master clock (ADCCK) drives A/D converter directly.
b). Internal drive mode: The clock internally generated by on-chip timing control circuit using SHP and SHD signals drives A/D
converter.
2. BYP, CM, REFN, and REFP should be connected to ground using a bypass capacitor (0.1 µF). Refer to voltage reference for details.
3. BYPM, BYPP2 should be connected to ground using a bypass capacitor with a recommend value of 200 pF to 600 pF. However,
this depends on the application environment. Refer to voltage reference for details.
4. Refer to serial interface for details.
5. COB should be connected to ground using a bypass capacitor with a recommend value of 0.1 µF to 0.22 µF. However , this depends
on the application environment. Refer to optical black level clamp loop for details.
13 P Power supply. Exclusively for digital output
41, 42
TYPE
P Analog ground
High = Normal operation mode
Low = Preblanking mode: Digital output all zero
DESCRIPTION
www.ti.com
3
Page 4
VSP2232
†
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
SLOAD 46 DI Serial data latch signal (triggered at the rising edge)
V
CC
†
Designators in TYPE column: P–power supply and ground, DI–digital input, DO–digital output, AI–aAnalog input, AO–analog output
18, 24, 27, 33, 34, 40 P Analog power supply
TYPE
DESCRIPTION
detailed description
introduction
The VSP2232 is a complete mixed-signal IC that contains all of the key features associated with the processing
of the CCD imager output signal in a video camera, a digital still camera, a security camera, or similar
applications. A simplified block diagram is shown on the front page of this data sheet. The VSP2232 includes
a correlated double sampler (CDS), a programmable gain amplifier (PGA), an analog-to-digital converter
(ADC), an input clamp, an optical black (OB) level clamp loop, a serial interface, a timing control, and a reference
voltage generator. W e recommend an off-chip emitter follower buffer between the CCD output and the VSP2232
CCDIN input. The PGA gain control, the clock polarity setting, and the operation mode choosing can be made
through the serial interface. All parameters are reset to the default value when the RESET pin goes to low
asynchronously from the clocks.
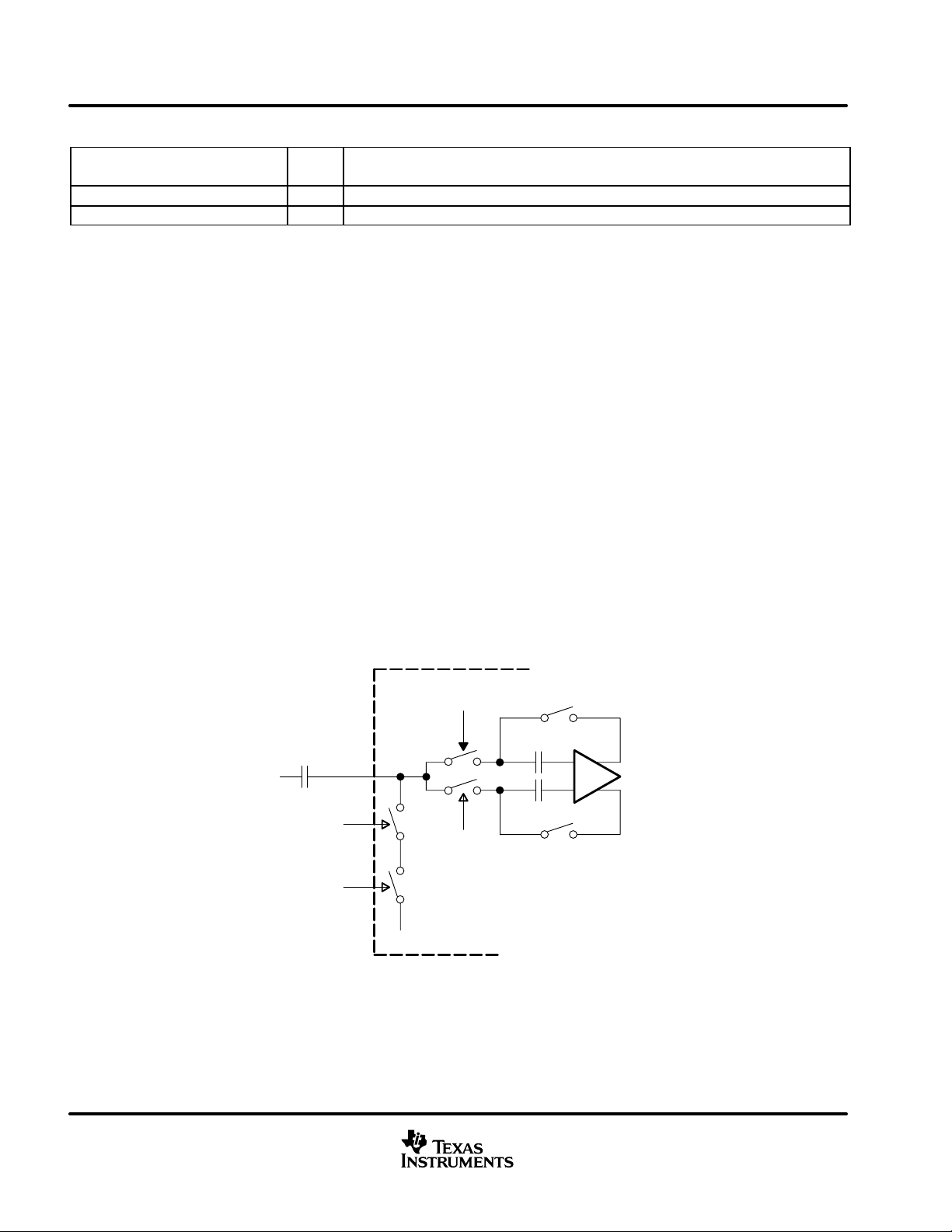
correlated double sampler (CDS)
The output signal of a CCD imager is sampled twice during one pixel period, one at the reference interval and
the other at the data interval.
Subtracting these two samples, extracts the video information of the pixel as well as removes any noise that
is common—or correlated—to both the intervals.
Thus, a CDS is very important to reduce the reset noise and the low frequency noises that are present on the
CCD output signal. Figure 1 shows the simplified block diagram of the CDS and input clamp.
VSP2232
SHP
C
= 5 pF
(1)
= 5 pF
+
OPA
_
CCD
Output
C
IN
CLPDM
SHP
CCDIN
SHD
REFN (1.25 V)
C
(2)
Figure 1. Simplified Block Diagram of CDS and Input Clamp
The CDS is driven through an off-chip coupling capacitor (C
). AC coupling is strongly recommended because
IN
the DC level of the CCD output signal is usually too high (several volts) for the CDS to work properly . A 0.1-µF
capacitor is recommended for C
, however, it depends on the application environment.
IN
4
www.ti.com
Page 5

SLAS320 – MAY 2001
correlated double sampler (CDS) (continued)
Also, an off-chip emitter follower buffer is recommended that can drive more than 10 pF, because the 5 pF of
the sampling capacitor and a few pF of stray capacitance can be seen at the input pin. The analog input signal
range at the CCDIN pin is 1 V
1.5 V.
The reference level is sampled during SHP active period, and the voltage level is held on the sampling capacitor
C
at the trailing edge of SHP. The data level is sampled during SHD active period, and the voltage level is
(1)
held on the sampling capacitor C
the subtraction of these two levels.
The active polarity of SHP/SHD (active high or active low) can be chosen through the serial interface, refer to
serial interface for details. The default value of SHP/SHD is active low . However , right after power on, this value
is unknown. For this reason, it must be set to the appropriate value by using the serial interface, or reset to the
default value by the RESET pin. The description and the timing diagrams in this data sheet are all based on the
polarity of active low (default value).
input clamp and dummy pixel clamp
The buffered CCD output is capacitively coupled to the VSP2232. The purpose of the input clamp is to restore
the dc component of the input signal that was lost with the ac-coupling and establish the desired dc bias point
for the CDS. Figure 1 shows the simplified block diagram of the input clamp. The input level is clamped to the
internal reference voltage REFN (1.25 V) during the dummy pixel interval. More specifically , when both CLPDM
and SHP are active, then the dummy clamp function becomes active. If the dummy pixels and/or the CLPDM
pulse are not available in your system, the CLPOB pulse can be used in place of CLPDM as long as the clamping
takes place during black pixels. In this case, both CPLDM pin (actives as same timing as CLPOB) and SHP
become active during the optical black pixel interval, then the dummy clamp function becomes active.
, and the appropriate common mode voltage for the CDS is around 0.5 V to
P–P
at the trailing edge of SHD. Then, the switched-capacitor amplifier performs
(2)
VSP2232
The active polarity of CLPDM and SHP (active high or active low) can be chosen through the serial interface,
refer to serial interface for details. The default value of CLPDM and SHP is active low. However , right after power
on, this value is unknown. For this reason, it must be set to the appropriate value by using the serial interface,
or reset to the default value by the RESET pin. The description and timing diagrams in this data sheet are all
based on the polarity of active low (default value).
high performance analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
The analog-to-digital converter (ADC) utilizes a fully differential and pipelined architecture. This ADC is well
suited for low voltage operation, low power consumption requirement, and high-speed applications. It assures
10-bit resolution of the output data with no missing code. The VSP2232 includes the reference voltage generator
for the ADC. REFP (positive reference, pin 38), REFN (negative reference, pin 39), and CM (common-mode
voltage, pin 37) should be bypassed to the ground with a 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor. Do not use this voltage
anywhere else in the system because it affects the stability of these reference levels, and then causes ADC
performance degradation. These are analog output pins, so do not apply voltage from the outside.
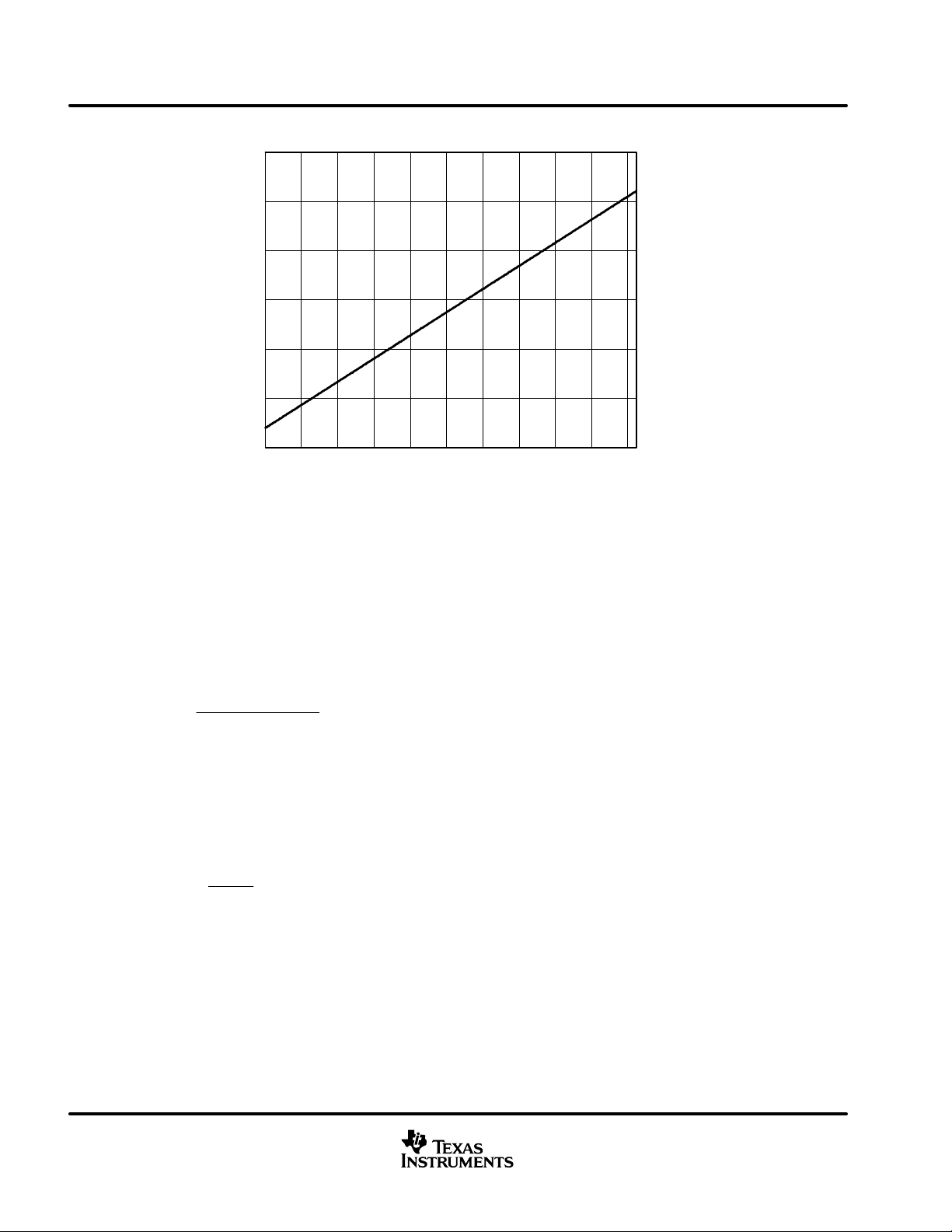
programmable gain amplifier (PGA)
Figure 2 shows the characteristics of the PGA gain. The PGA provides a gain range of –6 dB to 42 dB, which
is linear in dB. The gain is controlled by a digital code with 10-bit resolution, and it can be settle through the serial
interface, refer to the serial interface section for details. The default value of the gain control code is 128 (PGA
gain = 0 dB). However, right after power on, this value is unknown. For this reason, it must be set to the
appropriate value by using the serial interface, or reset to the default value by the RESET pin.
www.ti.com
5
Page 6
VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
programmable gain amplifier (PGA) (continued)
50
40
30
20
Gain – dB
10
0
–10
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
0
Input Code for Gain Control (0 to 1023)
Figure 2. Characteristics of PGA Gain
optical black (OB) level clamp loop
T o extract the video information correctly , the CCD signal must be referenced to a well-established optical black
(OB) level. The VSP2232 has an autocalibration loop to establish the OB level using the optical black pixel
output from the CCD imager. The input signal level of the OB pixels is identified as the real OB level and the
loop should be closed during this period while CLPOB is active. During the effective pixel interval, the reference
level of the CCD output signal is clamped to the OB level by the OB level clamp loop. T o determine the loop-time
constant, an off-chip capacitor is required, and should be connected to the COB (pin 28). The time constant T
is given in equation 1.
T +
ǒ
16384 I
C
(min)
Ǔ
Where:
C is the capacitor value connected to COB, I
is the minimum current (0.15 µA) of the control DAC in the
(min)
OB level clamp loop, and 0.15 µA is equivalent to 1 LSB of the DAC output current. When C is 0.1 µF , then the
time constant T is 40.7 µs. Also, the slew rate (SR) is given in equation 2.
I
SR +
(max)
C
(1)
(2)
Where:
C is the capacitor value connected to COB. I
is the maximum current (153 µA) of the control DAC in the
(max)
OB level clamp loop, and 153 µA is equivalent to 1023 LSB of the DAC output current.
Generally , the OB level clamping at high-speed causes clamp noise (or white streak noise). However, the noise
will decrease by increasing the capacitor size. On the other hand, a larger capacitor requires a much longer time
to restore from the standby mode, or right after the power goes on. Therefore, we recommend a 0.1-µF to
0.22-µF capcitor. However, it depends on the application environment, and making careful adjustments using
the cut-and-try method is recommended.
6
www.ti.com
Page 7

SLAS320 – MAY 2001
optical black (OB) level clamp loop (continued)
The OB clamp level (the pedestal level) is programmable through the serial interface, refer to serial interface
for details. Table 1 shows the relationship between the input code and the OB clamp level.
The active polarity of CLPOB (active high or active low) can be chosen through the serial interface, refer to serial
interface for details. The default value of CLPOB is active low.
However, right after power on, this value is unknown. For this reason, it must be set to the appropriate value
by using the serial interface, or reset to the default value by the RESET pin. The description and the timing
diagrams in this data sheet are all based on the polarity of active low (default value).
Table 1. Programmable OB Clamp Level
INPUT CODE OB CLAMP LEVEL, LSBs of 12-Bits
0000 2 LSB
0001 18 LSB
0010 34 LSB
0011 50 LSB
0100 66 LSB
0101 82 LSB
0110 98 LSB
0111 114 LSB
1000 (Default) 130 LSB
1001 146 LSB
1010 162 LSB
1011 178 LSB
1100 194 LSB
1101 210 LSB
1110 226 LSB
1111 242 LSB
VSP2232
preblanking and data latency
Some CCDs have large transient output signals during blanking intervals. Such signals may exceed the
VSP2232’s 1-V
input signal range and would overdrive the VSP2232 into saturation. Recovery time from
P–P
the saturation could be substantial. T o avoid this, the VSP2232 has an input blanking (or preblanking) function.
When PBLK goes to low, the CCDIN input is disconnected from the internal CDS stage and large transients are
prevented from passing through. The VSP2232’s digital outputs will go to all zeros at the 11th rising edge of
ADCCK from just after PBLK set to low to accommodate the clock latency of the VSP2232. In this mode, the
digital output data comes out at the rising edge of ADCCK with a delay of 1 1 clock cycles (data latency is 11).
In the normal operation mode, it is different from the preblanking mode. The digital output data comes out at
the rising edge of ADCCK with a delay of nine clock cycles (data latency is 9).
In order to keep stable and accurate OB clamp level, CLPOB should not be activated during PBLK active period.
Since CCDIN input is disconnected from the internal circuit, even if the autocalibration loop should be closed
while CLPOB is active. Then the OB clamp level is different from the actual OB level established by the CCD
imager output. The missed OB clamp level would affect the picture quality.
If the input voltage is higher than the supply rail by 0.3 V or lower than the ground rail by 0.3 V, the protection
diodes will be turned on to prevent the input voltage from going further. Such a high swing signal may cause
a device damage to the VSP2232 and should be avoided.
www.ti.com
7
Page 8

VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
detailed description (continued)
standby mode
For the purpose of power saving, the VSP2232 can be set into the standby mode (or power down mode) through
the serial interface when the VSP2232 is not in use. Refer to serial interface for details. In this mode, all the
function blocks are disabled and the digital outputs will go to all zeros. The consumption current will drop to
2 mA. As all the bypass capacitors will discharge during this mode, a substantial time (usually of the order of
200 ms to 300 ms) is required to restore from the standby mode.
voltage reference
All the reference voltages and bias currents needed in the VSP2232 are generated by its internal bandgap
circuitry. The CDS and the ADC use three reference voltages, REFP (positive reference, pin 38), REFN
(negative reference, pin 39), and CM (common-mode voltage, pin 37). All of REFP, REFN, and CM should be
heavily decoupled with appropriate capacitors (for example: 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor). Do not use these
voltages anywhere else in the system because it affects the stability of these reference levels, and causes ADC
performance degradation. These are analog output pins, so do not apply the voltage from the outside.
BYPP2 (pin 29), BYP (pin 31), and BYPM (pin 32) are also reference voltages to be used in the analog circuit.
BYP should be connected to the ground with a 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor . The capacitor value for BYPP2 and
BYPM affects the step response. We consider , for many applications, 200 pF to 600 pF is the reasonable value.
However, it depends on the application environment, and making careful adjustments using the cut-and-try
method is recommended. All of BYPP2, BYP, and BYPM should be heavily decoupled with appropriate
capacitors. Do not use these voltages anywhere else in the system because it affects the stability of these
reference levels, and causes the performance degradation. These are analog output pins, so do not apply the
voltage from the outside.
additional output delay control
The VSP2232 can control delay time of the output data by register setting through the serial interface. In some
cases, the transition of the output data affects analog performance. Generally, it is avoided by adjusting the
timing of the ADCCK. In case ADCCK timing cannot be adjusted, this output delay control is effective to reduce
the influence of transient noise. Refer to serial interface for details.
serial interface
The serial interface has a 2-byte shift register and various parallel registers to control all the digitally
programmable features of the VSP2232. Writing to these registers is controlled by four signals (SLOAD, SCLK,
SDATA, and RESET). To enable the shift register, SLOAD must be pulled low. SDATA is the serial data input
and the SCLK is the shift clock. The data at SDATA is taken into the shift register at the rising edge of SCLK.
The data length should be 2 bytes. After the 2-byte shift operation, the data in the shift register will be transferred
to the parallel latch at the rising edge of SLOAD. In addition to the parallel latch, there are several registers
dedicated to the specific features of the device and they are synchronized with the ADCCK clock. It takes five
or six clock cycles for the data in the parallel latch to be written to those registers. Thus, to complete the data
updates, it has to wait five or six clock cycles after the parallel latching by the rising edge of SLOAD.
The serial interface data format is shown in T able 2. TEST is the flag for the test mode (Burr-Brown proprietary
only), A0 to A2 is the address for the various registers, and D0 to D11 is the data or the operand field.
8
www.ti.com
Page 9

VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
Table 2. Serial Interface Data Format
MSB LSB
REGISTERS TEST A2 A1 A0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Configuration 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 C8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 C0
PGA gain 0 0 0 1 0 0 G9 G8 G7 G6 G5 G4 G3 G2 G1 G0
OB clamp level 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 O3 O2 O1 O0
Clock polarity 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 P2 P1 P0
Output delay 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 J1 J0
Reserved 0 1 0 1 x x x x x x x x x x x x
Reserved 0 1 1 0 x x x x x x x x x x x x
Reserved 0 1 1 1 x x x x x x x x x x x x
Reserved 1 x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
x = Don’t care
C0 : Operation Mode, Normal/Standby
Serial interface and registers are always active, independently from the operation mode
C0 = 0 Normal operation, C0 = 1 Standby
C8 : A/D Converter Drive Mode, Internal/External
Internal drive mode: The clock is internally generated by SHP and SHP drives the A/D converter
External drive mode: The master clock (ADCCK) drives the A/D converter
C8 = 0 Internal drive mode, C8 = 1 External drive mode
G[9:0] : Characteristics of PGA Gain (see Figure 2)
J[1:0] : Additional Output Delay Control
Controls additional output data delay time
J1 = 0, J0 = 0 Additional Delay = 0 ns
J1 = 0, J0 = 1 Additional Delay = 5 ns (typ)
J1 = 1, J0 = 0 Additional Delay = 10 ns (typ)
J1 = 1, J0 = 1 Additional Delay = 13 ns (typ)
O[3:0] : Programmable OB Clamp Level (see Table 1)
P[2:0] : Clock Polarity
P0 = Polarity for CLPDM (P0 = 0 active low, P0 = 1 active high)
P1 = for CLPOB (P0 = 0 active low, P0 = 1 active high)
P2 = for SHP/SHD (P0 = 0 active low , P0 = 1 active high)
Right after power on, these values are unknown. They must be set to the appropriate value using the serial
interface, or reset to the default value by the RESET pin.
Default values are:
C0 = 0 : Normal operation mode
C8 = 0 : A/D converter internal drive mode
G[9:0] = 0010000000 : PGA gain = 0 dB
J[1:0] = 00 : Additional output delay = 0 ns
O[3:0] = 1000 : OB clamp level = 32 LSB
P[2:0] = 000 : CLPDM, CLPOB, SHP/SHD are all active low (see Note 6)
NOTE 6: The description and the timing diagrams in this data sheet are all based on the polarity of active low (default value).
www.ti.com
9
Page 10

VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
timing
VSP2232 has two options to drive the on-chip A/D converter. The internal drive mode and the external drive
mode can be selected by accessing the configuration register via the serial interface. The internal drive mode,
the drive clock for the A/D converter, is generated by the on-chip timing control circuit automatically, based on
the SHP and SHD signals. The external drive mode is the master clock (ADCCK) and drives the on-chip A/D
converter directly . The digital data output is synchronized with the master clock (ADCCK) and it is independent
from the drive mode.
The CDS and the ADC are operated by SHP/SHD and their derivative timing clocks generated by the on-chip
timing generator. The digital output data is synchronized with ADCCK. The timing relationship among the CCD
signal, SHP/SHD, ADCCK, and the output data is shown in the VSP2232 CDS timing specifications. CLPOB
is used to activate the black-level clamp loop during the OB pixel interval, and CLPDM is used to activate the
input clamping during the dummy pixel interval. If the CLPDM pulse is not available in your system, the CLPOB
pulse can be used in place of CLPDM as long as the clamping takes place during black pixels, refer to input
clamp and dummy pixel clamp for details. The clock polarities of SHP/SHD, CLPOB, and CLPDM can be
independently set through the serial interface, refer to serial interface section for details. The description and
the timing diagrams in this data sheet are all based on the polarity of active low (default value). In order to keep
a stable and accurate OB clamp level, it is recommended that CLPOB should not be activated during the PBLK
active period. Refer to preblanking and data latency for details. In the standby mode, ADCCK, SHP, SHD,
CLPOB, and CLPDM are internally masked and pulled high.
power supply, grounding, and device decoupling recommendations
The VSP2232 incorporates a very high-precision and high-speed analog-to-digital converter and analog
circuitry that are vulnerable to any extraneous noise from the rails or elsewhere. For this reason, although the
VSP2232 has analog and digital supply pins, it should be treated as an analog component and all supply pins
except for DRV
should be powered by only the analog supply of the system. This will ensure the most
DD
consistent results, since digital power lines often carry high levels of wide band noise that would otherwise be
coupled into the device and degrade the achievable performance.
Proper grounding, short lead length, and the use of ground planes are also very important for high frequency
designs. Multilayer PC boards are recommended for the best performance since they offer distinct advantages
like minimizing ground impedance, separation of signal layers by ground layers, etc. It is highly recommended
that the analog and digital ground pins of the VSP2232 be joined together at the IC and be connected only to
the analog ground of the system. The driver stage of the digital outputs (B(1 1:0]) is supplied through a dedicated
supply pin (DRV
) and should be separated from the other supply pins completely, or at least with a ferrite
DD
bead. It is also recommended to keep the capacitive loading on the output data lines as low as possible (typically
less than 15 pF). Larger capacitive loads demand higher charging current due to surges that can feed back into
the analog portion of the VSP2232 and affect the performance.
If possible, external buffers or latches should be used which provide the added benefit of isolating the VSP2232
from any digital noise activities on the data lines. In addition, resistors in series with each data line may help
in minimizing the surge current. V alues in the range of 100 Ω to 200 Ω will limit the instantaneous current to the
output stage and has to provide for recharging the parasitic capacitance’s as the output levels change from
low-to-high or high-to-low. Because of the high operation speed, the converter also generates high frequency
current transients and noises that are fed back into the supply and reference lines. This requires the supply and
reference pins to be sufficiently bypassed. In most cases, a 0.1-µF ceramic-chip capacitor is adequate to
decouple the reference pins. Supply pins should be decoupled to the ground plane with a parallel combination
of tantalum (1 µF to 22 µF) and ceramic (0.1 µF) capacitors. The effectiveness of the decoupling largely depends
on the proximity to the individual pin. DRV
should be decoupled to the proximity of DRVGND. Special
DD
attention must be paid to the bypassing of COB, BYPP2, and BYPM since these capacitor values determine
important analog performance of the device.
10
www.ti.com
Page 11

VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage (V
Supply voltage differences (among V
, DRVDD) 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CC
) ±0.1 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CC
†
Ground voltage differences (among GNDA) ±0.1 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Digital input voltage –0.3 V to 5.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Analog input voltage –0.3 V to V
CC
+ 0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input current (any pins except supplies) ±10 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating temperature, T
Storage temperature, T
stg
Junction temperature, T
A
J
–25°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
–55°C to 125°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature (soldering) 260°C, 5 sec. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Package temperature (IR Reflow, Peak) 235°C, 10 sec. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
electrical characteristics, all specifications at TA = 25°C, VCC = DRVDD = 3 V, conversion rate
(f
(ADCCK)
V
IT+
V
IT–
I
IH
I
IL
V
OH
V
OL
) = 36 MHz, no load unless otherwise noted
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Resolution 12 Bits
Max conversion rate 36 MHz
Digital inputs
Logic family TTL
Low-to-high threshold voltage 1.9
High-to-low threshold voltage 0.9
High-level input current VIN = 3 V ±20
Low-level input current VIN = 0 V ±20
ADCCK clock duty cycle 50%
Input capacitance 5 pF
Max input voltage –0.3 5.3 V
Digital inputs
Logic family CMOS
Logic coding
High-level output voltage IOH = –2 mA 2.4
Low-level output voltage IOL = 2 mA 0.4
J[1:0] = 00 0 ns
Additional output data delay
p
J[1:0] = 01 5 ns
J[1:0] = 10
J[1:0] = 11 13 ns
Straight
binary
10 ns
V
µA
V
reference
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Positive reference voltage 1.75 V
Negative reference voltage 1.25 V
www.ti.com
11
Page 12

VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
electrical characteristics, all specifications at TA = 25°C, VCC = DRVDD = 3 V, conversion rate
(f
(ADCCK)
power supply
V
CC
P
D
temperature range
T
A
T
stg
analog input (CCDIN)
Input signal level for full-scale out PGA gain = 0 dB 900 mV
Input capacitance 15 pF
Input limit –0.3 3.3 V
) = 36 MHz, no load unless otherwise noted (continued)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, DRV
Power dissipation
Operation temperature –25 85 °C
Storage temperature –55 125 °C
Thermal resistance θ
DD
Normal operation mode:
VCC = DRVDD = 2.7 V,
f
(ADCCK)
Standby mode: f
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
JA
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
48-pin LQFP 100 °C/W
= 36 MHz, No load
(ADCCK)
= Not applied 6
2.7 3 3.6 V
130
mW
transfer characteristics
PARAMETER
DNL Differential nonlinearity PGA gain = 0 dB ±0.5 LSB
INL Integral nonlinearity PGA gain = 0 dB ±2 LSB
No missing codes Assured
Step response settling time Full-scale step input 1 pixel
Overload recovery time Step input from 1.8 V to 0 V 2 pixels
Data latency 9(fixed)
SNR Signal-to-noise ratio (see Note 7)
CCD offset correction range –180 200 mV
NOTE 7: SNR = 20 log (full-scale voltage/rms noise)
Grounded input cap, PGA gain = 0 dB 76
Grounded input cap, Gain = 24 dB
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Clock
cycles
52
CDS
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Reference sample settling time
Data sample settling time
Within 1 LSB, driver impedance = 50 Ω
6.9
6.9
input clamp
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Clamp-on resistance 400
Clamp level 1.25 V
dB
ns
Ω
12
www.ti.com
Page 13

VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
electrical characteristics, all specifications at TA = 25°C, VCC = DRVDD = 3 V, conversion rate
(fADCCK) = 36 MHz, no load unless otherwise noted (continued)
programmable gain amplifier (PGA)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Gain control resolution 10 Bits
Maximum gain Gain code = 1111111111 42 dB
High gain Gain code = 1101001000 34 dB
Medium gain Gain code = 1000100000 20 dB
Low gain Gain code = 0010000000 0 dB
Minimum gain Gain code = 0000000000 –6 dB
Gain control error ±0.5 dB
optical black clamp loop
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Control DAC resolution 10 Bits
Optical black clamp level
Minimum output current for control DAC
Maximum output current for control DAC
Loop time constant C
SR Slew rate
Programmable range of clamp level 2 242 LSB
OBCLP level at CODE = 1000
COB pin
= 0.1 µF 40.7 µs
(COB)
C
= 0.1 µF,
(COB)
Output current from control DAC is saturated
130 LSB
±0.15
±153
1530 V/s
µA
www.ti.com
13
Page 14

VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
timing specifications
N+2 N+3
t
(CKP)
t
(CKP)
t
(CKP)
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
N–7
Clock
cycles
t
N+1
s
t
(OD)
t
(ADC)
t
s
t
w(P)
t
p(D–P)
N
t
w(D)
PARAMETER
t
(ADC)
CCDD
Output
Signal
SHP
See Note 1
t
p(P–D)
SHD
See Note 1
t
(INHIBIT)
ADCCK
t
(HOLD)
B(0–11)
t
(CKP)
t
(ADC)
t
w(P)
t
w(D)
t
p(P–D)
t
p(D–P)
t
s
t
(Inhibit)
t
(Hold)
t
(OD)
DL Data latency, normal operation mode 9(fixed)
NOTES: 8. The description and the timing diagrams in this data sheet are all based on the polarity of active low (default value). The active polarity
9. Output hold time is specified at additonal output delay = 0 ns. Refer to serial interface section for detail.
N–11 N–10 N–9N–8
Clock period 27.7 ns
ADCCK high/low pulse width 13.8 ns
SHP pulse width 6.9 ns
SHD pulse width 6.9 ns
SHP trailing edge to SHD leading edge (see Note 8) 4 ns
SHD trailing edge to SHP leading edge (see Note 8) 8 ns
Sampling delay 3 ns
Inhibited clock period 12 ns
Output hold time (see Note 9) 2 ns
Output delay 27.7 ns
(active low or active high) can be chosen through the serial interface, refer to serial interface for details.
14
Figure 3. VSP2232 CDS Timing Specifications—A/D Converter Internal Drive Mode
www.ti.com
Page 15

timing specifications (continued)
VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
N+2 N+3
t
(CKP)
t
(CKP)
t
(CKP)
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Clock
cycles
t
(ADC)
N+1
t
s
t
(OD)
t
t
(ADC)
s
t
w(P)
t
p(D–P)
t
(AP)
N
t
(HOLD)
t
w(D)
PARAMETER
CCDD
Output
Signal
SHP
See Note 1
t
p(P–D)
SHD
See Note 1
ADCCK
B(0–9)
t
(CKP)
t
(ADC)
t
w(P)
t
w(D)
t
p(P–D)
t
p(D–P)
t
s
t
(AP)
t
(Hold)
t
(OD)
DL Data latency, normal operation mode 9(fixed)
NOTES: 8. The description and the timing diagrams in this data sheet are all based on the polarity of active low (default value). The active polarity
9. Output hold time is specified at additonal output delay = 0 ns. Refer to serial interface section for detail.
N–11 N–10 N–9N–8N–7
Clock period 27.7 ns
ADCCK pulse duty rate 45% 50% 55%
SHP pulse width 6.9 ns
SHD pulse width 6.9 ns
SHP trailing edge to SHD leading edge (see Note 8) 1 ns
SHD trailing edge to SHP leading edge (see Note 8) 6 ns
Sampling delay 3 ns
ADCCK leading edge to SHP trailing edge 0 1.5 ns
Output hold time (see Note 9) 2 ns
Output delay 27.7 ns
(active low or active high) can be chosen through the serial interface, refer to serial interface for details.
Figure 4. VSP2232 CDS Timing Specifications—A/D Converter External Drive Mode
www.ti.com
15
Page 16

VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
timing specifications (continued)
t
SLOAD
SCLK
t
(DS)
(XS)
t
(CKH)
t
(DH)
t
(CKL)
t
(CKP)
t
(XH)
SDATA
t
(CKP)
t
(CKH)
t
(CKL)
t
su
t
h
t
(XS)
t
(XH)
NOTES: 10. It is effective for the data shift operation at the rising edges of SCLK during SLOAD is low period. 2 bytes of data input are loaded
Clock period 100 ns
Clock high pulse width 40 ns
Clock low pulse width 40 ns
Data setup time 30 ns
Data hold time 30 ns
SLOAD to SCLK setup time 30 ns
SCLK to SLOAD hold time 30 ns
to the parallel latch in the VSP2232 at the rising edge of SLOAD.
11. When the input serial data is longer than 2 bytes (16 bits), the last 2 bytes become effective and the former bits are lost.
MSB LSB
2-Bytes
PARAMETER
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Figure 5. VSP2232 Serial Interface Timing Specification
16
www.ti.com
Page 17

MECHANICAL DATA
PT (S-PQFP-G48) PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK
VSP2232
SLAS320 – MAY 2001
37
48
0,50
1,45
1,35
36
0,27
0,17
25
24
13
1
5,50 TYP
7,20
SQ
6,80
9,20
SQ
8,80
12
0,08
M
0,05 MIN
0,13 NOM
Gage Plane
0,25
0°–ā7°
1,60 MAX
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Falls within JEDEC MS-026
D. This may also be a thermally enhanced plastic package with leads conected to the die pads.
Seating Plane
0,10
0,75
0,45
4040052/C 11/96
www.ti.com
17
Page 18

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
30-Mar-2005
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
VSP2232Y ACTIVE LQFP PT 48 250 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
VSP2232Y/2K ACTIVE LQFP PT 48 2000 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS) or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
(3)
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
Addendum-Page 1
Page 19

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications,
enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue
any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing
orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms
and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI
deems necessary to support this warranty . Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all
parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for
their products and applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products
and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right,
copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process
in which TI products or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third-party products or services
does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof.
Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property
of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without
alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction
of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for
such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that
product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and
is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application
solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Interface interface.ti.com Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303 Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2005, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...