
TVP5160
NTSC/PAL/SECAM/Component 2x10-Bit Digital Video
Decoder
Data Manual
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Literature Number: SLES135C
February 2005–Revised May 2010

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Contents
1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 9
1.1 Features ...................................................................................................................... 9
1.2 Applications .................................................................................................................. 9
1.3 Description ................................................................................................................... 9
1.4 Related Products .......................................................................................................... 12
1.5 Trademarks ................................................................................................................. 12
1.6 Document Conventions ................................................................................................... 12
1.7 Ordering Information ...................................................................................................... 12
1.8 Functional Block Diagram ................................................................................................ 13
1.9 Terminal Assignments .................................................................................................... 14
2 Functional Description ....................................................................................................... 17
2.1 Analog Processing and A/D Converters ................................................................................ 17
2.1.1 Video Input Switch Control .................................................................................... 18
2.1.2 480p and 576p Component YPbPr ........................................................................... 18
2.1.3 Analog Input Clamping ......................................................................................... 18
2.1.4 Automatic Gain Control ........................................................................................ 18
2.1.5 Analog Video Output ........................................................................................... 18
2.1.6 A/D Converters .................................................................................................. 19
2.2 Digital Video Processing .................................................................................................. 19
2.2.1 2x Decimation Filter ............................................................................................ 19
2.2.2 Composite Processor .......................................................................................... 19
2.2.3 Color Low-Pass Filter .......................................................................................... 19
2.2.4 Y/C Separation .................................................................................................. 20
2.2.5 3D Frame Recursive Noise Reduction ....................................................................... 20
2.2.6 Time Base Corrector ........................................................................................... 20
2.2.7 IF Compensation ............................................................................................... 20
2.2.8 Luminance Processing ......................................................................................... 21
2.2.9 Color Transient Improvement ................................................................................. 21
2.3 Clock Circuits .............................................................................................................. 22
2.4 Real-Time Control (RTC) ................................................................................................. 22
2.5 Output Formatter .......................................................................................................... 23
2.6 Fast Switches for SCART and Digital Overlay ........................................................................ 24
2.7 Discrete Syncs ............................................................................................................. 26
2.8 Embedded Syncs .......................................................................................................... 31
2.9 I
2.10 VBI Data Processor ....................................................................................................... 34
2.11 Powerup, Reset, and Initialization ....................................................................................... 36
2.12 Adjusting External Syncs ................................................................................................. 37
2
C Host Interface .......................................................................................................... 32
2.9.1 Reset and I
2.9.2 I
2
C Operation .................................................................................................... 33
2
C Bus Address Selection ....................................................................... 32
2.9.3 VBUS Access ................................................................................................... 33
2.9.3.1 VBUS Write ......................................................................................... 34
2.9.3.2 VBUS Read ......................................................................................... 34
2.10.1 VBI FIFO and Ancillary Data in Video Stream .............................................................. 35
2.10.2 VBI Raw Data Out .............................................................................................. 36
2 Contents Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
3 Internal Control Registers ................................................................................................... 38
3.1 Register Definitions ........................................................................................................ 43
3.2 VBUS Register Definitions ............................................................................................... 87
4 Typical Application Circuit .................................................................................................. 95
4.1 Typical Application Circuit ................................................................................................ 95
5 Typical Register Programming Sequence ............................................................................. 96
6 Electrical Specifications ..................................................................................................... 97
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings .............................................................................................. 97
6.2 Recommended Operating Conditions .................................................................................. 97
6.3 Crystal Specifications ..................................................................................................... 98
6.4 DC Electrical Characteristics ............................................................................................. 98
6.5 Analog Processing and A/D Converters ................................................................................ 99
6.6 Data Clock, Video Data, Sync Timing .................................................................................. 99
6.7 I
6.8 SDRAM Timing ........................................................................................................... 101
6.9 Example SDRAM Timing Alignment ................................................................................... 102
6.10 Memories Tested ......................................................................................................... 103
6.11 Thermal Specification – WIP ........................................................................................... 103
2
C Host Port Timing ..................................................................................................... 100
7 Designing with PowerPAD™ ............................................................................................. 104
8 Revision History .............................................................................................................. 106
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Contents 3

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
List of Figures
1-1 TVP5160 PNP-Package Terminal Diagram .................................................................................. 15
2-1 Analog Processors and A/D Converters ...................................................................................... 18
2-2 Luminance Edge-Enhancer Peaking Block ................................................................................... 21
2-3 Peaking Filter Frequency Response NTSC/PAL ITU_R BT.601 Sampling............................................... 21
2-4 Reference Clock Configuration................................................................................................. 22
2-5 RTC Timing ....................................................................................................................... 23
2-6 Fast-Switches for SCART and Digital Overlay ............................................................................... 25
2-7 Vertical Synchronization Signals for 525-Line System...................................................................... 28
2-8 Vertical Synchronization Signals for 625-Line System...................................................................... 28
2-9 Horizontal Synchronization Signals for 10-Bit 4:2:2 Mode.................................................................. 29
2-10 Horizontal Synchronization Signals for 20-Bit 4:2:2 Mode.................................................................. 30
2-11 VS Position with Respect to HS for Interlaced Signals...................................................................... 31
2-12 VS Position with Respect to HS for Progressive Signals ................................................................... 31
2-13 VBUS Access..................................................................................................................... 33
2-14 Reset Timing...................................................................................................................... 37
3-1 Teletext Filter Function .......................................................................................................... 80
4-1 Application Example ............................................................................................................. 95
6-1 Clocks, Video Data, and Sync Timing ....................................................................................... 100
6-2 I
6-3 SDRAM Interface Timing ...................................................................................................... 101
6-4 TVP5160 Timing Relationship with K4S161622E-80 SDRAM............................................................ 102
7-1 128-Pin PowerPAD Package.................................................................................................. 105
2
C Host Port Timing............................................................................................................ 100
4 List of Figures Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
List of Tables
1-1 Terminal Functions .............................................................................................................. 15
2-1 Y/C Separation Support by Video Standard.................................................................................. 20
2-2 Output Format .................................................................................................................... 23
2-3 Summary of Line Frequency, Data Rate, and Pixel/Line Counts .......................................................... 24
2-4 Fast-Switch Modes............................................................................................................... 25
2-5 Look-Up Table for Converting from Digital RGB to 10-Bit YCbCr Data................................................... 26
2-6 EAV and SAV Sequence........................................................................................................ 32
2-7 I2C Host Interface Terminal Description ...................................................................................... 32
2-8 I
2-9 Supported VBI System .......................................................................................................... 34
2-10 Ancillary Data Format and Sequence ......................................................................................... 35
2-11 Reset Sequence.................................................................................................................. 36
3-1 I
3-2 VBUS Registers Summary...................................................................................................... 42
3-3 Input/Output Select .............................................................................................................. 43
3-4 Analog Channel and Video Mode Selection.................................................................................. 43
3-5 AFE Gain Control ................................................................................................................ 44
3-6 Video Standard Select .......................................................................................................... 44
3-7 Operation Mode .................................................................................................................. 44
3-8 Autoswitch Mask ................................................................................................................. 45
3-9 Color Killer ........................................................................................................................ 45
3-10 Luminance Processing Control 1 .............................................................................................. 46
3-11 Luminance Processing Control 2 .............................................................................................. 46
3-12 Luminance Processing Control 3 .............................................................................................. 47
3-13 Luminance Brightness .......................................................................................................... 47
3-14 Luminance Contrast ............................................................................................................. 47
3-15 Chrominance Saturation ........................................................................................................ 48
3-16 Chroma Hue ...................................................................................................................... 48
3-17 Chrominance Processing Control 1 ........................................................................................... 49
3-18 Chrominance Processing Control 2 ........................................................................................... 50
3-19 R/Pr Saturation .................................................................................................................. 50
3-20 G/Y Saturation ................................................................................................................... 50
3-21 B/Pb Saturation .................................................................................................................. 51
3-22 G/Y Brightness ................................................................................................................... 51
3-23 AVID Start Pixel .................................................................................................................. 51
3-24 AVID Stop Pixel .................................................................................................................. 52
3-25 HS Start Pixel .................................................................................................................... 52
3-26 HS Stop Pixel .................................................................................................................... 52
3-27 VS Start Line ..................................................................................................................... 52
3-28 VS Stop Line ..................................................................................................................... 53
3-29 VBLK Start Line .................................................................................................................. 53
3-30 VBLK Stop Line .................................................................................................................. 53
3-31 Embedded Sync Offset Control 1 ............................................................................................. 53
3-32 Embedded Sync Offset Control 2 ............................................................................................. 54
3-33 Fast-Switch Control ............................................................................................................. 54
3-34 Fast-Switch Overlay Delay ..................................................................................................... 55
2
C Host Interface Device Addresses.......................................................................................... 32
2
C Registers Summary.......................................................................................................... 38
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated List of Tables 5

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
3-35 Fast-Switch SCART Delay ..................................................................................................... 55
3-36 Overlay Delay .................................................................................................................... 55
3-37 SCART Delay .................................................................................................................... 56
3-38 CTI Control ....................................................................................................................... 56
3-39 Brightness and Contrast Range Extender .................................................................................... 56
3-40 Component Autoswitch Mask .................................................................................................. 57
3-41 Sync Control ..................................................................................................................... 57
3-42 Output Formatter Control 1 ..................................................................................................... 58
3-43 Output Formatter Control 2 ..................................................................................................... 58
3-44 Output Formatter Control 3 ..................................................................................................... 59
3-45 Output Formatter Control 4 ..................................................................................................... 59
3-46 Output Formatter Control 5 ..................................................................................................... 60
3-47 Output Formatter Control 6 ..................................................................................................... 61
3-48 Clear Lost Lock Detect .......................................................................................................... 61
3-49 Status 1 ........................................................................................................................... 62
3-50 Status 2 ........................................................................................................................... 63
3-51 AGC Gain Status ................................................................................................................ 63
3-52 Video Standard Status .......................................................................................................... 64
3-53 GPIO Input 1 ..................................................................................................................... 64
3-54 GPIO Input 2 ..................................................................................................................... 65
3-55 Back End AGC Status 1 ........................................................................................................ 65
3-56 AFE Coarse Gain for CH 1 ..................................................................................................... 65
3-57 AFE Coarse Gain for CH 2 ..................................................................................................... 66
3-58 AFE Coarse Gain for CH 3 ..................................................................................................... 66
3-59 AFE Coarse Gain for CH 4 ..................................................................................................... 66
3-60 AFE Fine Gain for B/Pb ......................................................................................................... 67
3-61 AFE Fine Gain for G/Y/Chroma ............................................................................................... 67
3-62 AFE Fine Gain for R/Pr ......................................................................................................... 67
3-63 AFE Fine Gain for CVBS/Luma ................................................................................................ 68
3-64 656 Version ....................................................................................................................... 68
3-65 SDRAM Control .................................................................................................................. 68
3-66 3DNR Y Noise Sensitivity ...................................................................................................... 69
3-67 3DNR UV Noise Sensitivity .................................................................................................... 69
3-68 3DNR Y Coring Threshold Limit ............................................................................................... 69
3-69 3DNR UV Coring Threshold Limit ............................................................................................. 69
3-70 3DNR Low Noise Limit .......................................................................................................... 69
3-71 "Blue" Screen Y Control ........................................................................................................ 69
3-72 "Blue" Screen Cb Control ....................................................................................................... 69
3-73 "Blue" Screen Cr Control ....................................................................................................... 70
3-74 "Blue" Screen LSB Control ..................................................................................................... 70
3-75 Noise Measurement ............................................................................................................. 70
3-76 3DNR Y Core0 ................................................................................................................... 70
3-77 3DNR UV Core0 ................................................................................................................. 70
3-78 F- and V-Bit Decode Control ................................................................................................... 71
3-79 Back-End AGC Control ......................................................................................................... 72
3-80 AGC Decrement Speed ......................................................................................................... 72
3-81 ROM Version ..................................................................................................................... 72
3-82 AGC White Peak Processing .................................................................................................. 73
www.ti.com
6 List of Tables Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
3-83 F-Bit and V-Bit Control .......................................................................................................... 73
3-84 AGC Increment Speed .......................................................................................................... 74
3-85 AGC Increment Delay ........................................................................................................... 74
3-86 Analog Output Control 1 ........................................................................................................ 74
3-87 Chip ID MSB ..................................................................................................................... 74
3-88 Chip ID LSB ...................................................................................................................... 74
3-89 Color PLL Speed Control ....................................................................................................... 75
3-90 3DYC Luma Coring LSB ........................................................................................................ 75
3-91 3DYC Chroma Coring LSB ..................................................................................................... 75
3-92 3DYC Luma/Chroma Coring MSB ............................................................................................ 75
3-93 3DYC Luma Gain ................................................................................................................ 75
3-94 3DYC Chroma Gain ............................................................................................................. 76
3-95 3DYC Signal Quality Gain ...................................................................................................... 76
3-96 3DYC Signal Quality Coring .................................................................................................... 76
3-97 IF Compensation Control ....................................................................................................... 76
3-98 IF Differential Gain Control ..................................................................................................... 77
3-99 IF Low Frequency Gain Control ............................................................................................... 77
3-100 IF High Frequency Gain Control ............................................................................................... 77
3-101 Weak Signal High Threshold ................................................................................................... 77
3-102 Weak Signal High Threshold ................................................................................................... 77
3-103 Status Request .................................................................................................................. 77
3-104 3DYC NTSC VCR Threshold .................................................................................................. 78
3-105 3DYC PAL VCR Threshold ..................................................................................................... 78
3-106 Vertical Line Count .............................................................................................................. 78
3-107 AGC Decrement Delay ......................................................................................................... 78
3-108 VDP TTX Filter and Mask ...................................................................................................... 79
3-109 VDP TTX Filter Control ......................................................................................................... 79
3-110 VDP FIFO Word Count ......................................................................................................... 80
3-111 VDP FIFO Interrupt Threshold ................................................................................................. 81
3-112 VDP FIFO Reset ................................................................................................................. 81
3-113 VDP FIFO Output Control ...................................................................................................... 81
3-114 VDP Line Number Interrupt .................................................................................................... 81
3-115 VDP Pixel Alignment ............................................................................................................ 82
3-116 VDP Line Start ................................................................................................................... 82
3-117 VDP Line Stop ................................................................................................................... 82
3-118 VDP Global Line Mode ......................................................................................................... 82
3-119 VDP Full Field Enable .......................................................................................................... 83
3-120 VDP Full Field Mode ............................................................................................................ 83
3-121 Interlaced/Progressive Status .................................................................................................. 83
3-122 VBUS Data Access with No VBUS Address Increment .................................................................... 83
3-123 VBUS Data Access with VBUS Address Increment ........................................................................ 83
3-124 VDP FIFO Read Data ........................................................................................................... 84
3-125 VBUS Address ................................................................................................................... 84
3-126 Interrupt Raw Status 0 .......................................................................................................... 84
3-127 Interrupt Raw Status 1 .......................................................................................................... 85
3-128 Interrupt Status 0 ................................................................................................................ 85
3-129 Interrupt Status 1 ................................................................................................................ 86
3-130 Interrupt Mask 0 ................................................................................................................. 86
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated List of Tables 7

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
3-131 Interrupt Mask 1 ................................................................................................................. 86
3-132 Interrupt Clear 0 ................................................................................................................. 87
3-133 Interrupt Clear 1 ................................................................................................................. 87
3-134 VDP Closed Caption Data ...................................................................................................... 88
3-135 VDP WSS/CGMS Data ......................................................................................................... 88
3-136 VDP VITC Data .................................................................................................................. 89
3-137 VDP V-Chip TV Rating Block 1 ................................................................................................ 89
3-138 VDP V-Chip TV Rating Block 2 ................................................................................................ 89
3-139 VDP V-Chip TV Rating Block 3 ................................................................................................ 90
3-140 VDP V-Chip MPAA Rating Data ............................................................................................... 90
3-141 VDP General Line Mode and Line Address .................................................................................. 91
3-142 VDP VPS, Gemstar EPG Data ................................................................................................ 92
3-143 Analog Output Control 2 ........................................................................................................ 93
3-144 Interrupt Configuration .......................................................................................................... 93
3-145 Interrupt Raw Status 1 .......................................................................................................... 93
3-146 Interrupt Status 1 ................................................................................................................ 94
3-147 Interrupt Mask 1 ................................................................................................................. 94
3-148 Interrupt Clear 1 ................................................................................................................. 94
6-1 Memories Tested ............................................................................................................... 103
8-1 Revision History................................................................................................................. 106
www.ti.com
8 List of Tables Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
NTSC/PAL/SECAM/Component 2x10-Bit Digital Video Decoder
Check for Samples: TVP5160
1 Introduction
1.1 Features
1
• Two 11-Bit 60-MSPS Analog-to-Digital (A/D) • Fast Switch 4x Oversampled Input for Digital
Converters With Analog Preprocessors RGB Overlay Switching Between Any CVBS,
(Clamp/AGC) S-Video, or Component Video Input
• Fixed RGB-to-YUV Color Space Conversion • SCART 4x Oversampled Fast Switching
• Robust Sync Detection for Weak and Noisy
Signals as well as VCR
• Supports NTSC (J, M, 4.43), PAL (B, D, G, H, I,
M, N, Nc, 60) and SECAM (B, D, G, K, K1, L) • Chrominance Processor
CVBS, S-Video
• Supports Component Standards 480i, 576i,
480p, and 576p
• Supports ITU-R BT.601 Pixel Sampling
Frequencies
• Supports 3D Y/C Separation, or 2D 5-Line (5H) With Discrete Syncs)
Adaptive Comb and Chroma Trap Filter for
both PAL and NTSC Signals
• Concurrent Temporal, Frame Recursive, Noise
Reduction (3DNR)
• IF Compensation
• Line-Based Time Base Correction (TBC)
Between Component RGB Input and CBVS
Input
• Analog Video Output
• Luminance Processor
• Clock/Timing Processor and Power-Down
Control
• Output Formatter Supports Both ITU-R BT.656
(Embedded Syncs) and ITU-R BT.601 (4:2:2
• I2C Host Port Interface
• VBI Data Processor
• "Blue" Screen (Programmable Color) Output
• Macrovision™ Copy Protection Detection
Circuit (Types 1, 2, and 3) on Both Interlaced
and Progressive Signals
1.2 Applications
• Digital TV
• LCD TV/monitors
• DVD-R
• PVR
• PC video cards
• Video capture/video editing
• Video conferencing
1.3 Description
The TVP5160 device is a high quality, digital video decoder that digitizes and decodes all popular
baseband analog video formats into digital component video. The TVP5160 decoder supports the A/D
conversion of component YPbPr and RGB (SCART) signals, as well as the A/D conversion and decoding
of NTSC, PAL, and SECAM composite and S-Video into component YCbCr. Additionally, component
progressive signals can be digitized. The chip includes two 11-bit, 60-MSPS, A/D converters (ADCs). Prior
to each ADC, each analog channel contains an analog circuit, which clamps the input to a reference
voltage and applies a programmable gain and offset. A total of 12 video input terminals can be configured
to a combination of YPbPr, RGB, CVBS, and S-Video video inputs.
Progressive component signals are sampled at 2× clock frequency (54 MHz) and are then decimated to
the 1× rate. In SCART mode the component inputs and the CVBS inputs are sampled at 54 MHz
1
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas
Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
alternately, then decimated to the 1× rate. Composite or S-Video signals are sampled at 4× the ITU-R
BT.601 clock frequency (54 MHz), line-locked for correct pixel alignment, and are then decimated to the
1× rate. CVBS decoding utilizes advanced 3D Y/C filtering and 2-dimensional complementary 5-line
adaptive comb filtering for both the luma and chroma data paths to reduce both cross-luma and
cross-chroma artifacts. 3D Y/C color separation may be used on both PAL and NTSC video signals. A
chroma trap filter is also available. On CVBS and Y/C inputs, the user can control video characteristics
such as hue, contrast, brightness, and saturation via an I2C host port interface. Furthermore, luma peaking
with programmable gain is included, as well as a patented color transient improvement (CTI) circuit.
Attenuation at higher frequencies or asymmetrical color subcarrier sidebands are compensated using the
IF compensation block. Frame adaptive noise reduction may be applied to reduce temporal noise on
CVBS, S-Video, or component inputs.
3D noise reduction and 3D Y/C separation may be used at the same time or independently.
The TVP5160 decoder uses Texas Instruments' patented technology for locking to weak, noisy, or
unstable signals and can auto-detect between broadcast quality and VCR-style (nonstandard) video
sources.
The TVP5160 decoder generates synchronization, blanking, field, active video window, horizontal and
vertical syncs, clock, genlock (for downstream video encoder synchronization), host CPU interrupt and
programmable logic I/O signals, in addition to digital video outputs.
The TVP5160 decoder includes methods for advanced vertical blanking interval (VBI) data retrieval. The
VBI data processor (VDP) slices and performs error checking on teletext, closed caption, and other VBI
data. A built-in FIFO stores up to 11 lines of teletext data, and, with proper host port synchronization,
full-screen teletext retrieval is possible. The TVP5160 decoder can pass through the output formatter 2×
sampled raw Luma data for host-based VBI processing.
www.ti.com
Digital RGB overlay can be synchronously switched with any video input, with all signals being
oversampled at 4× the pixel rate.
The TVP5160 detailed functionality includes:
• Two high-speed, 60-MSPS, 11-bit, A/D channels with programmable clamp and gain control
The two ADCs can sample CVBS or S-Video at 54 MHz. YPbPr/RGB is multiplexed between the two
ADCs which sample at 54 MHz giving a channel sampling frequency of 27 MHz.
• Supports ITU-R BT.601 pixel sampling frequencies.
Supports ITU-R BT.601 sampling for both interlaced and progressive signals.
• RGB-to-YUV color space conversion for SCART signals
• 3D Y/C separation or 2D 5-line (5H) adaptive comb and chroma trap filter
3-frame NTSC and PAL color separation
• Temporal frame recursive noise reduction (3DNR)
Frame recursive noise reduction can be applied to interlaced CVBS, S-Video, or component inputs for
interlaced signals. Noise reduction can be used at the same time as 3D Y/C separation. Noise
reduction cannot be applied to progressive video signals.
• Line-based time base correction (TBC)
Line based time correction corrects for horizontal phase errors encountered during video decoding up
to ±80 pixels of error. This improves the output video quality from jittery sources such as VCRs. It also
reduces line tearing during video trick modes such as fast forward and rewind.
• IF compensation
Attenuation at higher frequencies or asymmetrical color subcarrier sidebands are compensated using
the IF compensation block
• Fast switch 4× oversampling for digital RGB overlay signals for switching between any CVBS, S-Video,
or component video inputs
The fast switch overlay signals (FSO, DR, DG, DB) are oversampled at 4× the pixel clock frequency.
10 Introduction Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
• SCART 4x oversampled fast switching between component RGB input and CBVS input
• Analog video output
• Supports NTSC (J, M, 4.43), PAL (B, D, G, H, I, M, N, Nc, 60), SECAM (B, D, G, K, K1, L), CVBS, and
• Twelve analog video input terminals for multi-source connection
• User-programmable video output formats
• HS/VS outputs with programmable position, polarity, and width and FID (Field ID) output
• Composite and S-Video processing
• Vertical blank interval data processor
• I2C host port interface
• "Blue" screen output
• Macrovision copy protection detection circuit (types 1, 2, and 3) on both interlaced and progressive
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
The phase of these signals is used to mix the selected video input format and a digital RGB input to
generate an output video stream. This improves the overlay picture quality when the external FSO and
digital RGB signals are generated by an asynchronous source.
The SCART overlay control signal (FSS) is oversampled at 4x the pixel clock frequency. The phase of
this signal is used to mix between the CVBS input and the analog RGB inputs. This improves the
analog overlay picture quality when the external FSS and analog video signals are generated by an
asynchronous source.
Buffered analog output with automatic PGA
S-Video
– 10-bit ITU-R BT.656 4:2:2 YCbCr with embedded syncs
– 20-bit 4:2:2 YCbCr with discrete syncs
– 10-bit 4:2:2 YCbCr with discrete syncs
– 2× sampled raw VBI data in active video during a vertical blanking period
– Sliced VBI data during a horizontal blanking period
– Adaptive 3D/2D Y/C separation using 5-line adaptive comb filter for composite video inputs;
chroma-trap available
– Automatic video standard detection and switching (NTSC/PAL/SECAM/progressive)
– Luma-peaking with programmable gain
– Output data rates either 1× or 2× pixel rate
– Patented architecture for locking to weak, noisy, or unstable signals
– Single 14.31818-MHz reference crystal for all standards (ITU-R.BT601 sampling, interlaced or
progressive)
– Line-locked internal pixel sampling clock generation with horizontal and vertical lock signal outputs
– Certified Macrovision copy protection detection on composite and S-Video inputs (NTSC, PAL)
– Genlock output (RTC) for downstream video encoder synchronization
– Teletext (NABTS, WST)
– Closed caption (CC) and extended data service (XDS)
– Wide screen signaling (WSS)
– Copy generation management system (CGMS)
– Video program system (VPS/PDC)
– Vertical interval time code (VITC)
– EPG video guide 1×/2× (Gemstar)
– V-Chip decoding
– Custom mode
– Register readback of CC, CGMS, WSS, VPS, VITC, V-Chip, EPG 1× and 2× sliced data, CGMS-A
and RC for progressive signals.
signals
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Introduction 11
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Macrovision detection on standard definition signals of types 1, 2, and 3, and to Revision 1.2 for
progressive signals
• Reduced power consumption: 1.8-V digital core, 3.3-V and 1.8-V analog core with power-save and
power-down modes
• 128-TQFP PowerPAD™ package
1.4 Related Products
• TVP5146M2
• TVP5147M1
• TVP5150AM1
• TVP5151
• TVP5154A
• TVP5158
1.5 Trademarks
• TI and PowerPAD are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
• Macrovision is a trademark of Macrovision Corporation.
• Gemstar is a trademark of Gemstar-TV Guide International.
• Other trademarks are the property of their respective owners
www.ti.com
1.6 Document Conventions
Throughout this data manual, several conventions are used to convey information. These conventions are
listed below:
1. To identify a binary number or field, a lower case b follows the numbers. For example: 000b is a 3-bit
binary field.
2. To identify a hexadecimal number or field, a lower case h follows the numbers. For example: 8AFh is a
12-bit hexadecimal field.
3. All other numbers that appear in this document that do not have either a b or h following the number
are assumed to be decimal format.
4. If the signal or terminal name has a bar above the name (for example, RESETB), then this indicates
the logical NOT function. When asserted, this signal is a logic low, 0, or 0b.
5. RSVD indicates that the referenced item is reserved.
1.7 Ordering Information
T
A
0°C to 70°C TVP5160PNP Tray
PACKAGED DEVICES
128-Pin TQFP-PowerPAD
PACKAGE OPTION
12 Introduction Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
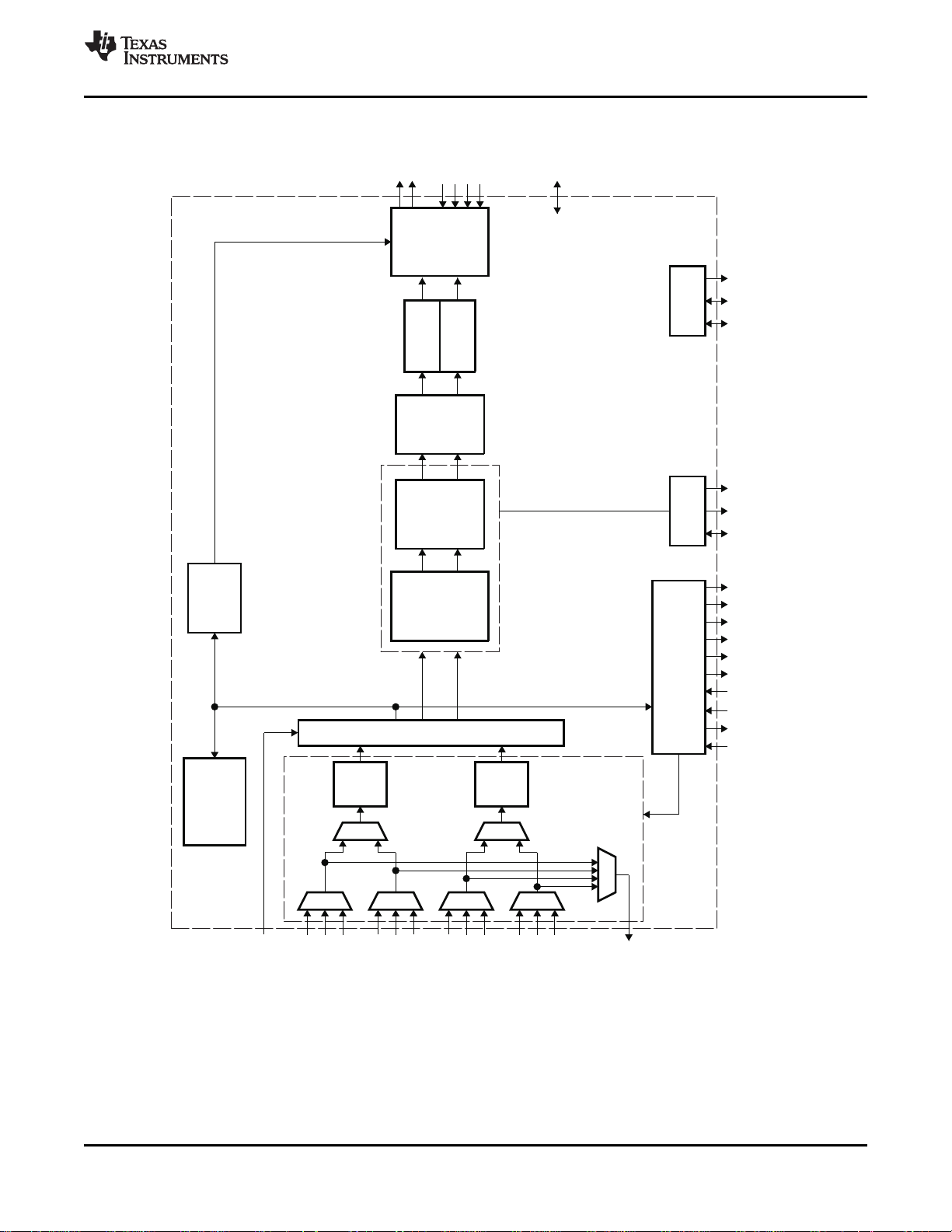
Y/C
Separation
3D/5-line
Adaptive
Comb
Filter
ADC1
MUX
CVBS/Y
C/CbCr
C
Y
Output
Formatter
Y[9:0]
VBI
Data
Slicer
MacroVision
Copy
Protection
Detection
C[9:0]
Host
Interface
Timing Processor
With Sync Detector
Analog Out
CVBS/
Pr/C/R
CVBS/
Y/G
CVBS/
Pb/C/B
CVBS/Y
Analog Front End
Sampling
Clock
GPIO
HS/CS
VS/VBLK
FID
AVID
XIN
XOUT
SCLK
RESETB
GLCO
PWDN
SCL
INTREQ
VI_1
CVBS/
Y/G
VI_2
VI_3
VI_4
VI_5
VI_6
VI_7
VI_8
VI_9
VI_10
VI_11
VI_12
Luma
Processing
3D Noise
Reduction
ADC2
Chroma
Processing
TBC/
IF Comp
DB
DG
DR
FSO
SDA
SDRAM
Interface
Data
Control
Address
C
Y
C
Y
C
Y
FSS
TVP5160
www.ti.com
1.8 Functional Block Diagram
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Introduction 13
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
A33 G ND
Ana log _ o ut
A33 G ND
A33 V D D
PLL 1 8 G N D
PLL 1 8 V D D
XO U T
XIN
D G N D
FSS
VS/V B LK/G P IO
H S/C S /G PIO
FID /G PIO
AV ID /GP IO
C _0 /GP IO
C _1 /GP IO
D G N D
DV D D
C _2 /GP IO
C _3 /GP IO
C _4 /GP IO
C _5 /GP IO
IO G N D
IOVDD
C _6 /GP IO/D R
C _7 /GP IO/D G
C _8 /GP IO/D B
C _9 /GP IO/F S O
D G N D
DV D D
Y_0
Y_1
12 8
12 7
12 6
12 5
12 4
12 3
12 2
12 1
12 0
11 9
11 8
11 7
11 6
11 5
11 4
11 3
11 2
11 1
11 0
10 9
10 8
10 7
10 6
10 5
10 4
10 3
10 2
10 1
10 0
999897
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
PNP PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
Y_2
Y_3
Y_4
IOGND
IOVDD
Y_5
Y_6
Y_7
Y_8
Y_9
DGND
DVDD
SCLK
GLCO/GPIO/I2CA0
GPIO/I2CA1
A3
A2
A1
A0
A10
BA1
IOGND
IOVDD
BA0
RAS
CAS
WE
A4
A5
A6
DGND
DVDD
A33GND
A33VDD
VI_1
VI_2
VI_3
NC
VI_4
VI_5
VI_6
NC
A18VDD
A18GND
A18VDD
A18GND
A18GND
A18VDD
VI_7
VI_8
VI_9
NC
VI_10
VI_11
VI_12
NC
A33VDD
A33GND
A33GND
A33GND
DGND
SCL
SDA
INTREQ
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
DV D D
D G N D
PW D N
R ESETB
IOVDD
IO G N D
D 0
D 1
D 2
D 3
D 4
D 5
D 6
D 7
DV D D
D G N D
D 15
D 14
D 13
D 12
D 11
D 10
D 9
D 8
IOVDD
IO G N D
D Q M
SDR A M _C LK
A11
A9A8A7
33343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263
64
TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
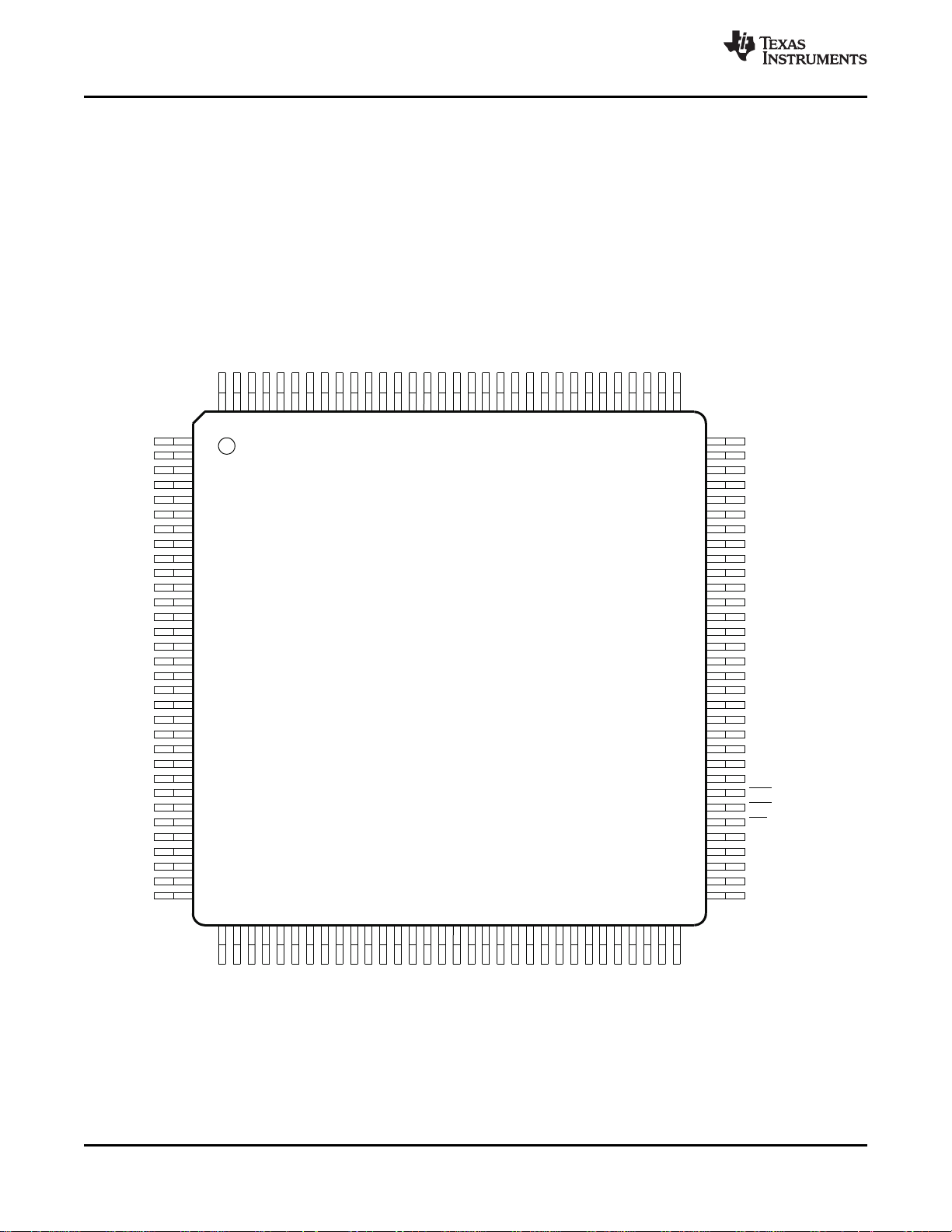
1.9 Terminal Assignments
The TVP5160 video decoder is packaged in a 128-terminal PNP PowerPAD package. Figure 1-1 is the
PNP-package terminal diagram. Table 1-1 gives a description of the terminals.
www.ti.com
PNP PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
Figure 1-1. TVP5160 PNP-Package Terminal Diagram
14 Introduction Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
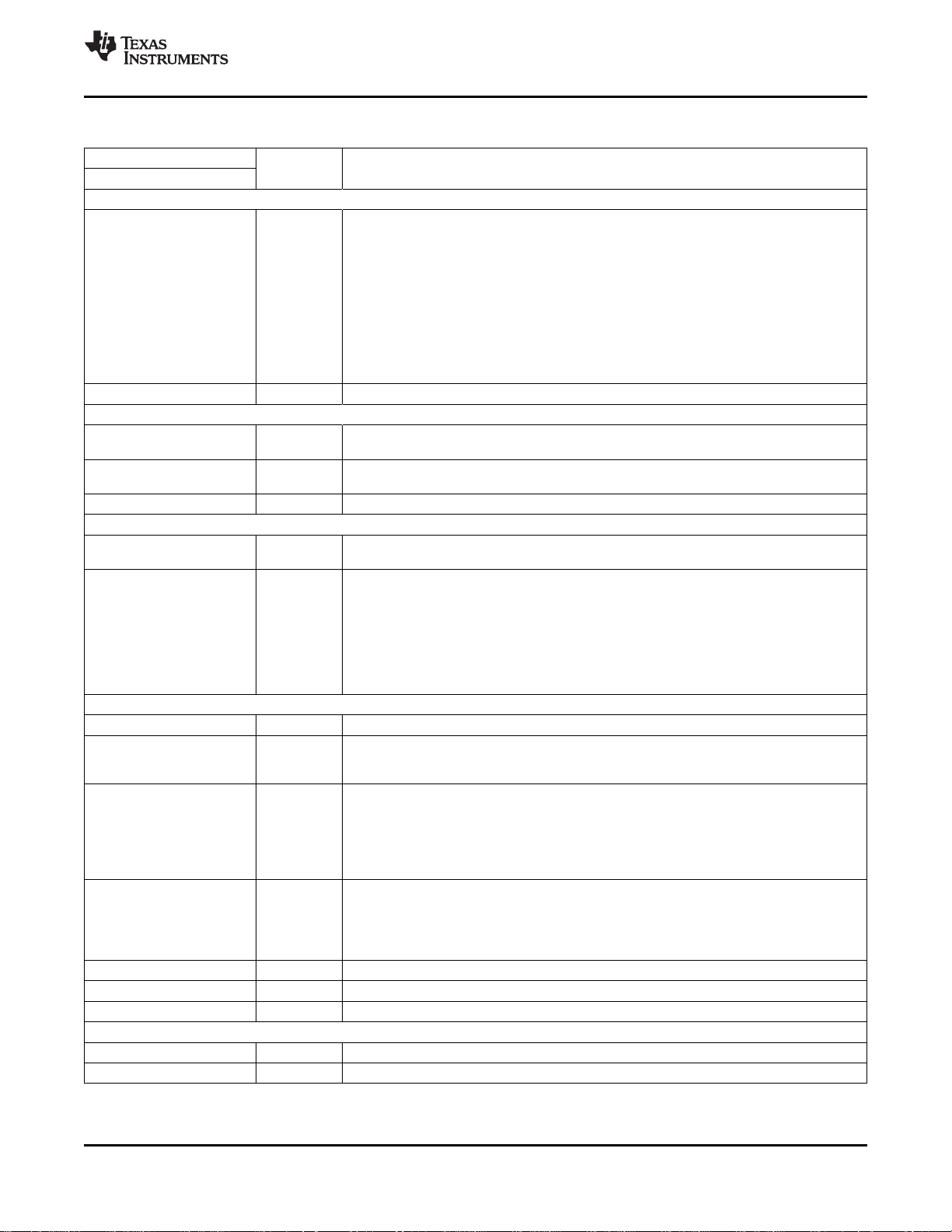
Table 1-1. Terminal Functions
PIN
NAME NO.
Analog Video
VI_1 3 I VI_x: analog video inputs
VI_2 4 Up to 12 composite, 6 S-Video, or 3 component video inputs (or combinations thereof) can
VI_3 5 be
VI_4 7 supported. Also, 4-channel SCART is supported.
VI_5 8 The inputs must be ac-coupled. The recommended coupling capacitor is 0.1 µF.
VI_6 9 The possible input configurations are listed in the input select register 00h.
VI_7 17 Unused inputs must be connected to ground through 0.1-µF capacitors.
VI_8 18
VI_9 19
VI_10 21
VI_11 22
VI_12 23
Analog_out 127 O Unbuffered analog video output
Clock Signals
XIN 121 I External clock reference input. It may connected to external oscillator with 1.8-V compatible
XOUT 122 O External clock reference output. Not connected if XTAL1 is driven by an external
SCLK 84 O Line-locked data output clock
Digital Video
Y[9:0] 87–91, O Digital video output of Y/YCbCr, Y_9 is MSB and Y_0 is LSB. For 8-bit operation, the upper
94–98 8 bits must be connected.
C[9:0] / GPIO 101–104, I/O Digital video output of CbCr, C_9 is MSB and C_0 is LSB. These terminals can be
107–110, programmable general purpose I/O, or as digital overlay controls. For 8-bit operation, the
113, 114 upper 8 bits must be connected.
FSO 101 I Fast-switch overlay between digital RGB and any video input
DB 102 I Digital BLUE input from overlay device
DG 103 I Digital GREEN input from overlay device
DR 104 I Digital RED input from overlay device
Miscellaneous Signals
RESETB 36 I Reset input, active low
PWDN 35 I Power down input
GLCO / 83 I/O
GPIO / I2CA0
GPIO / I2CA1 82 I/O
INTREQ 32 O Interrupt request output (open drain when programmed to be active low)
FSS 119 I SCART fast switch input
NC 6, 10, 20, 24 N/A No internal connection. Connect to AGND through 0.1-µF capacitors for future compatibility.
Host Interface
SDA 31 I/O I2C data bus
SCL 30 I/O I2C clock input
I/O DESCRIPTION
clock signal or 14.31818-MHz crystal oscillator.
single-ended oscillator.
Unused GPIO pins must be either configured as outputs, or tied to either IOVDD or DGND
1 = Power down
0 = Normal mode
Genlock control output (GLCO). Supports the real-time control (RTC) format. This pin can
also be configured as a general-purpose I/O (GPIO).
During power on reset this pin is sampled along with pin 82 (I2CA1) as an input to determine
the I2C address the device will be configured to. A 10-kΩ resistor pulls this either high (to
IOVDD) or low to select between addresses.
Programmable general purpose I/O
During power on reset this pin is sampled along with pin 83 (I2CA0) as an input to determine
the I2C address the device will be configured to. A 10-kΩ resistor pulls this either high (to
IOVDD) or low to select between addresses.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Introduction 15
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
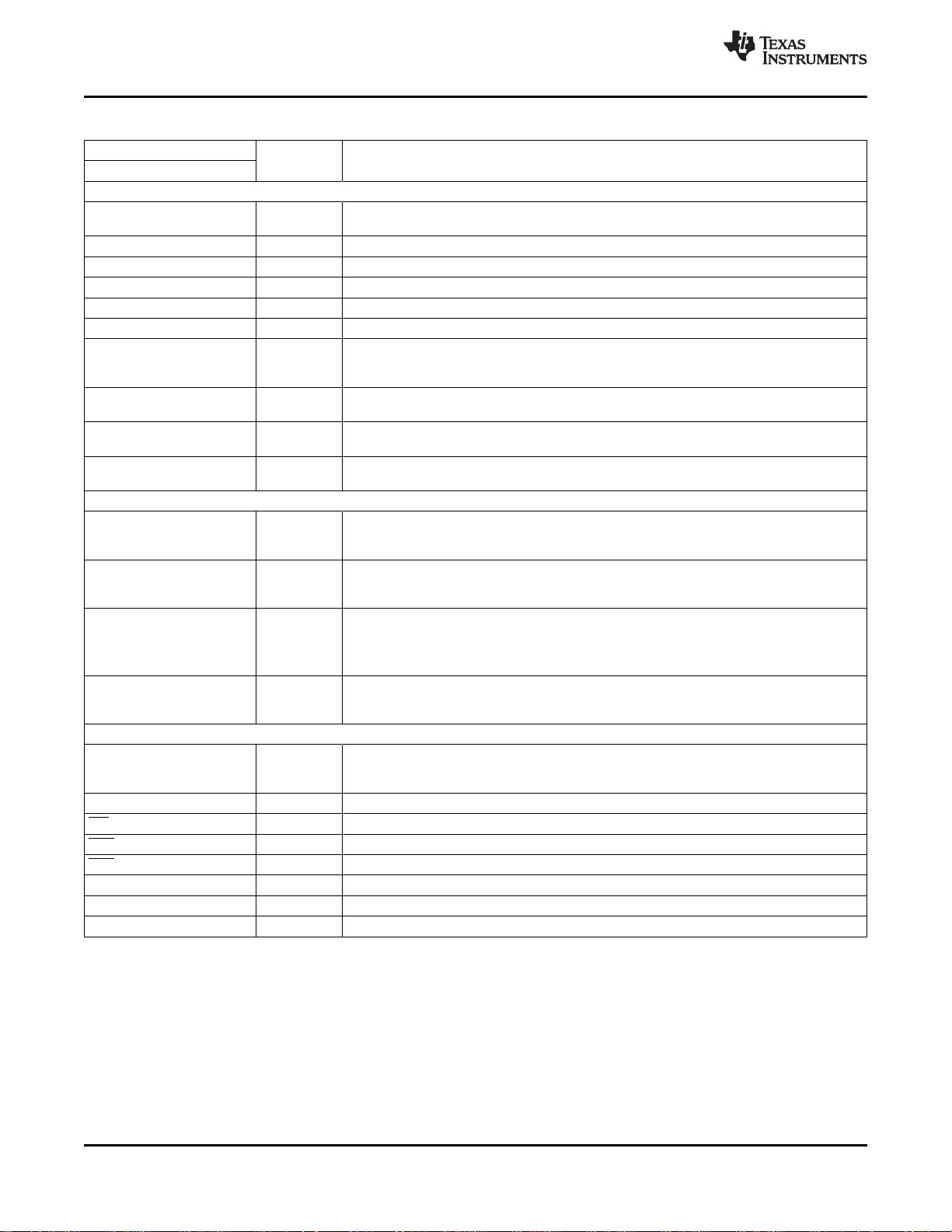
Table 1-1. Terminal Functions (continued)
PIN
NAME NO.
Power Supplies
A33GND 1, 26, 27, P Analog 3.3-V return. Connect to analog ground.
28, 126, 128
A33VDD 2, 25, 125 P Analog power. Connect to analog 3.3-V supply.
A18GND 12, 14, 15 P Analog 1.8-V return. Connect to analog ground.
A18VDD 11, 13, 16 P Analog power. Connect to analog 1.8-V supply.
PLL18GND 124 P Analog power return. Connect to analog ground.
PLL18VDD 123 P Analog power. Connect to analog 1.8-V supply.
DGND 29, 34, 48,66, P Digital return. Connect to digital ground.
86, 100,112,
120
DVDD 33, 47, 65,85, P Digital core power. Connect to 1.8-V supply.
99, 111
IOGND 38, 58, 75,93, P Digital power return. Connect to digital ground.
106
IOVDD 37, 57, 74,92, P Digital I/O power. Connect to digital 3.3-V supply.
105
Sync Signals
HS / CS / 117 I/O Horizontal sync output or digital composite sync output
GPIO Programmable general purpose I/O
VS / VBLK / 118 I/O Vertical sync output. (for modes with dedicated VS) or vertical blanking output
GPIO Programmable general purpose I/O
FID / GPIO 116 I/O
AVID / GPIO 115 I/O Active video indicator
SDRAM Interface
Address[11:0] 61, 77, O SDRAM address bus
62–64,
67–69, 81–78
D[15:0] 49–56, 46–39 I/O SDRAM data bus
WE 70 O SDRAM write enable
CAS 71 O SDRAM CAS enable
RAS 72 O SDRAM RAS enable
DQM 59 O SDRAM input/output mask for data
BA[1:0] 76, 73 O SDRAM bank address
SDRAM_CLK 60 O SDRAM 108-MHz clock
I/O DESCRIPTION
Unused GPIO pins must be either configured as outputs, or tied to either IOVDD or DGND
Unused GPIO pins must be either configured as outputs, or tied to either IOVDD or DGND
Odd/even field indicator
Programmable general purpose I/O This pin must be pulled low through a 10-kΩ resistor for
correct device operation.
Programmable general purpose I/O
Unused GPIO pins must be either configured as outputs, or tied to either IOVDD or DGND
www.ti.com
16 Introduction Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
Clamp
PGA
ADC
ADC1 Out
Line-Locked
Sampling Clock
M
U
X
VI_1
VI_2
VI_3
PGA
Analog_out
M
U
X
Buffer
M
U
X
VI_4
VI_5
VI_6
Clamp
Buffer
PGA
ADC
ADC2 Out
M
U
X
VI_7
VI_8
VI_9
Buffer
M
U
X
VI_10
VI_11
VI_12
Buffer
Clamp
Clamp
TVP5160
www.ti.com
2 Functional Description
2.1 Analog Processing and A/D Converters
Figure 2-1 shows a functional diagram of the analog processors and A/D converters (ADCs). This block
provides the analog interface to all video inputs. It accepts up to 12 inputs and performs source selection,
video clamping, video amplification, A/D conversion, and gain and offset adjustments to center the
digitized video signal. The TVP5160 decoder supports one analog video output.
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Figure 2-1. Analog Processors and A/D Converters
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Functional Description 17
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
2.1.1 Video Input Switch Control
The TVP5160 decoder has two analog channels that accept up to 12 video inputs. The user can configure
the internal analog video switches via I2C. The 12 analog video inputs can be used for different input
configurations, some of which are:
• 12 CVBS video inputs
• 4 S-Video inputs and 2 CVBS inputs
• 3 YPbPr video inputs and 3 CVBS input
• 2 YPbPr video inputs, 2 S-Video inputs, and 2 CVBS inputs
The input selection is performed by the input select register at I2C subaddress 00h.
2.1.2 480p and 576p Component YPbPr
The TVP5160 decoder supports progressive component video inputs. The YPbPr inputs of the TVP5160
decoder may accept 480p or 576p progressive inputs. The Y channel is fed into one ADC while PbPr are
sampled alternatively by the other ADC.
2.1.3 Analog Input Clamping
An internal clamping circuit restores the ac-coupled video signal to a fixed dc level. The clamping circuit
provides line-by-line restoration of the video sync level to a fixed dc reference voltage. The selection
between bottom and mid clamp is performed automatically by the TVP5160 decoder.
www.ti.com
2.1.4 Automatic Gain Control
The TVP5160 decoder utilizes two programmable gain amplifiers (PGAs); one per channel. The PGA can
scale a signal with a voltage input compliance of 0.5 VPPto 2.0 VPPto a full-scale, 11-bit, A/D output code
range. A 4-bit code sets the coarse gain with individual adjustment per channel. Minimum gain
corresponds to a code 0x0 (2.0-VPPfull-scale input, –6 dB gain) while maximum gain corresponds to code
0xF (0.5-VPPfull scale, +6 dB gain). The TVP5160 decoder also has 12-bit fine gain controls for each
channel and applies independently to coarse gain controls. For composite video, the input video signal
amplitude may vary significantly from the nominal level of 1 VPP. The TVP5160 decoder can adjust its
PGA setting automatically: an automatic gain control (AGC) can be enabled and can adjust the signal
amplitude such that the maximum input range of the ADC is reached without clipping. Some nonstandard
video signals contain peak white levels that saturate the ADC. In these cases, the AGC automatically cuts
back gain to avoid clipping. If the AGC is on, then the TVP5160 decoder can read the gain currently being
used.
The TVP5160 AGC comprises the front-end AGC before Y/C separation and the back-end AGC after Y/C
separation. The back-end AGC restores the optimum system gain whenever an amplitude reference, such
as the composite peak (which is only relevant before Y/C separation), forces the front-end AGC to set the
gain too low. The front-end and back-end AGC algorithms can utilize up to four amplitude references: sync
height, color burst amplitude, composite peak, and luma peak.
The specific amplitude references being used by the front-end and back-end AGC algorithms can be
independently controlled using the AGC white peak processing register located at subaddress 74h. The
TVP5160 gain increment speed and gain increment delay can be controlled using the AGC increment
speed register located at subaddress 78h and the AGC increment delay register located at subaddress
79h, respectively.
2.1.5 Analog Video Output
Any one of the analog input signals is available at the analog video output pin. The signal at this pin must
be buffered by a source follower if it drives a 75-Ω resister. The nominal output voltage is 2 VPP, and the
signal can drive a 75-Ω line when buffered. The magnitude is maintained with a PGA in 16 steps
controlled by the TVP5160 decoder.
18 Functional Description Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
2.1.6 A/D Converters
All ADCs have a resolution of 11 bits and can operate up to 60 MSPS. All A/D channels receive an
identical clock from the on-chip, phase-locked loop (PLL) at a frequency between 24 MHz and 60 MHz. All
ADC reference voltages are generated internally.
2.2 Digital Video Processing
This block receives digitized video signals from the ADCs and performs composite processing for CVBS
and S-Video inputs, YCbCr signal enhancements for CVBS and S-Video inputs. It also generates
horizontal and vertical syncs, and other output control signals such as RTC for CVBS and S-Video inputs.
Additionally, it can provide field identification, horizontal and vertical lock, vertical blanking, and active
video window indication signals. The digital data output can be programmed to two formats: 20-bit 4:2:2
with external syncs or 10-bit 4:2:2 with embedded/discrete syncs. The circuit detects pseudo sync pulses,
AGC pulses and color striping in Macrovision-encoded copy protected material. Information present in the
VBI interval can be retrieved and either inserted in the ITU-R.BT656 output as ancillary data or stored in
an internal FIFO for retrieval via the I2C interface.
2.2.1 2x Decimation Filter
All input signals are typically oversampled by a factor of 4 (54 MHz). The A/D outputs first pass through
decimation filters that reduce the data rate to 1× pixel rate. The decimation filter is a half-band filter.
Oversampling and decimation filtering can effectively increase the overall signal-to-noise ratio by 3 dB.
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
2.2.2 Composite Processor
The TVP5160 digital composite video processing circuit receives a digitized composite or S-Video signal
from the ADCs and performs 2D or 3D Y/C separation (bypassed for S-Video input), chroma demodulation
for PAL/NTSC and SECAM, and YUV signal enhancements.
2.2.3 Color Low-Pass Filter
High filter bandwidth preserves sharp color transitions and produces crisp color boundaries. However, for
nonstandard video sources that have asymmetrical U and V side bands, it is desirable to limit the filter
bandwidth to avoid UV crosstalk. The color low-pass filter bandwidth is programmable to enable one of the
three notch filters.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Functional Description 19
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
2.2.4 Y/C Separation
Y/C separation may be done using 3D or 2D adaptive 5-line (5-H delay) comb filters or chroma trap filter
for both NTSC and PAL video standards as shown in Table 2-1. The comb filter can be selectively
bypassed in the luma or chroma path. If the comb filter is bypassed in the luma path, then chroma notch
filters are used. TI's patented adaptive comb filter algorithm reduces artifacts such as hanging dots at
color boundaries. It detects and properly handles false colors in high frequency luminance images such as
a multiburst pattern or circle pattern.
Table 2-1. Y/C Separation Support by Video Standard
Video Standard 2D Y/C 3D Y/C
NTSC-M Yes Yes
NTSC-J Yes Yes
PAL-B, D, G, H, I Yes Yes
PAL-N Yes Yes
PAL-M Yes No
PAL-Nc Yes No
NTSC-4.43, PAL-60 Yes No
SECAM No No
2.2.5 3D Frame Recursive Noise Reduction
www.ti.com
The TI proprietary frame recursive noise reduction or 3DNR reduces the level of noise in CVBS, S-Video,
or component inputs by comparing multiple frames of data and canceling out the resulting noise. The
3DNR utilizes the same frame buffer memory used by the 3DYC. The 3DNR may function concurrently
with 3DYC.
There are various modes of operation for the 3DNR and 3DYC:
MODES OPERATION MEMORY REQUIRED
Mode 0 3DYC + 3DNR 4 MBytes
Mode 1 3DYC only 2 MBytes
Mode 2 2D 5-line CF + 3DNR 2 MBytes
Mode 3 2D only (default None
2.2.6 Time Base Corrector
The time base corrector monitors and corrects for horizontal PLL phase offsets up to ±80 pixels. This
improves video decoder output quality by removing artifacts due to jittery horizontal syncs from broadcast
stations. It also reduces line tearing during VCR trick modes such as fast forward and rewind. 3DYC,
frame recursive noise reduction (3DNR), and time base correction (TBC) can be used simultaneously or
independently. Since TBC does not require any external memory, it can be used in all configurations.
2.2.7 IF Compensation
Attenuation of higher frequencies from the tuners input characteristics or due to channels that are not
correctly tuned can be corrected in the IF compensation block. This block can correct for uneven
sidebands resulting in incorrect and uneven UV demodulation.
20 Functional Description Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
Bandpass
Filter
x
Gain
Peaking
Filter
IN
+
OUT
Delay
Peak
Detector
TVP5160
www.ti.com
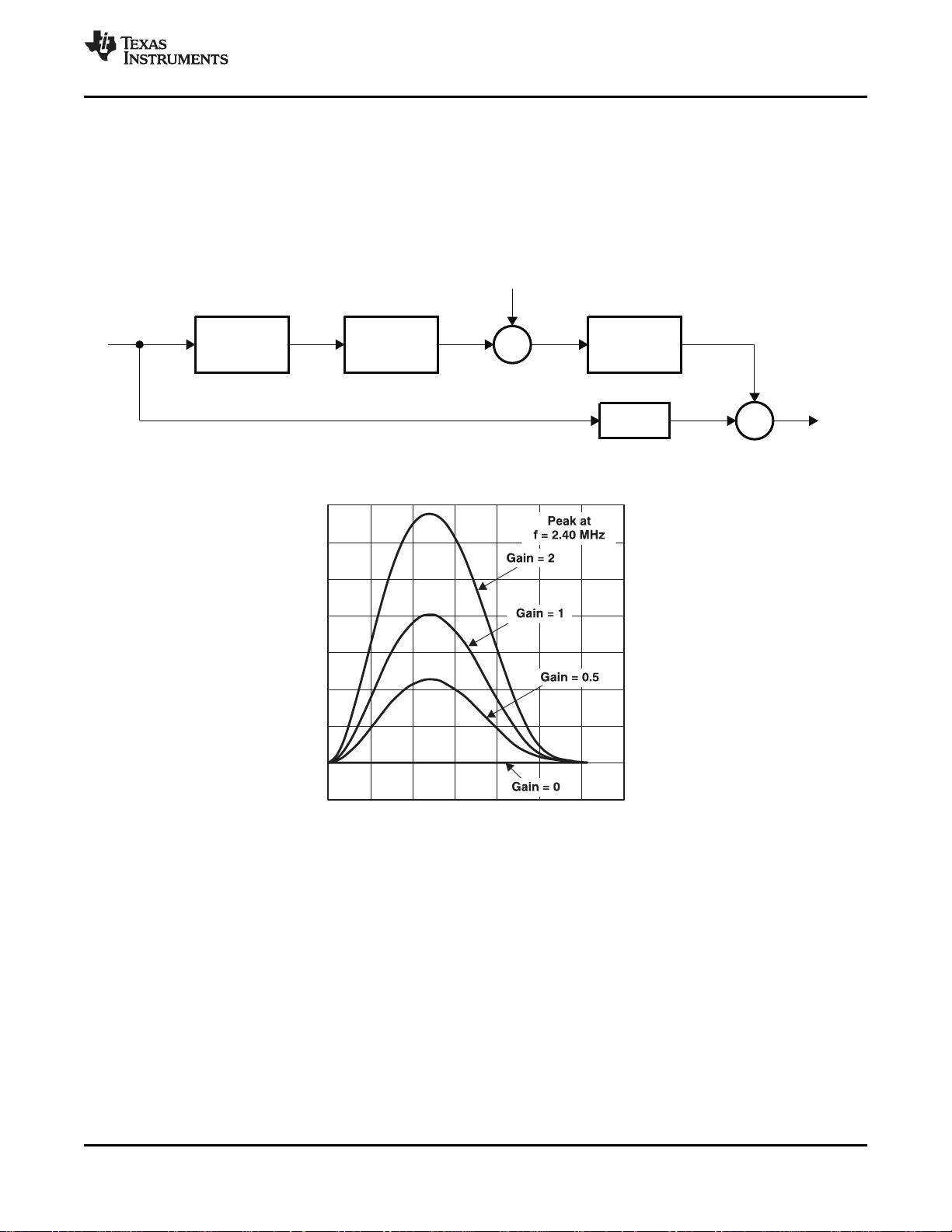
2.2.8 Luminance Processing
The luma component is derived from the composite signal by subtracting the remodulated chroma
information. The luminance signal is then fed to the input of a peaking circuit. Figure 2-2 illustrates the
basic functions of the luminance data path. In the case of S-Video, the luminance signal bypasses the
comb filter or chroma trap filter and is fed to the circuit directly. A peaking filter (edge-enhancer) amplifies
high frequency components of the luminance signal. Figure 2-3 shows the characteristics of the peaking
filter at four different gain settings that are user-programmable by the I2C.
Figure 2-2. Luminance Edge-Enhancer Peaking Block
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Figure 2-3. Peaking Filter Frequency Response NTSC/PAL ITU_R BT.601 Sampling
2.2.9 Color Transient Improvement
Color transient improvement (CTI) enhances horizontal color transients. The color difference signal
transition points are maintained, but the edges are enhanced for signals which have bandwidth limited
color components.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Functional Description 21
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
121
XIN
C
L1
C
L2
XOUT
122
R
TVP5160
121
XIN
XOUT
122
TVP5160
14.31818-MHz
1.8-V Clock
NC
14.31818-MHz
Crystal
33
2
= ×
CTRL
PLL SCLK
F
F F
TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
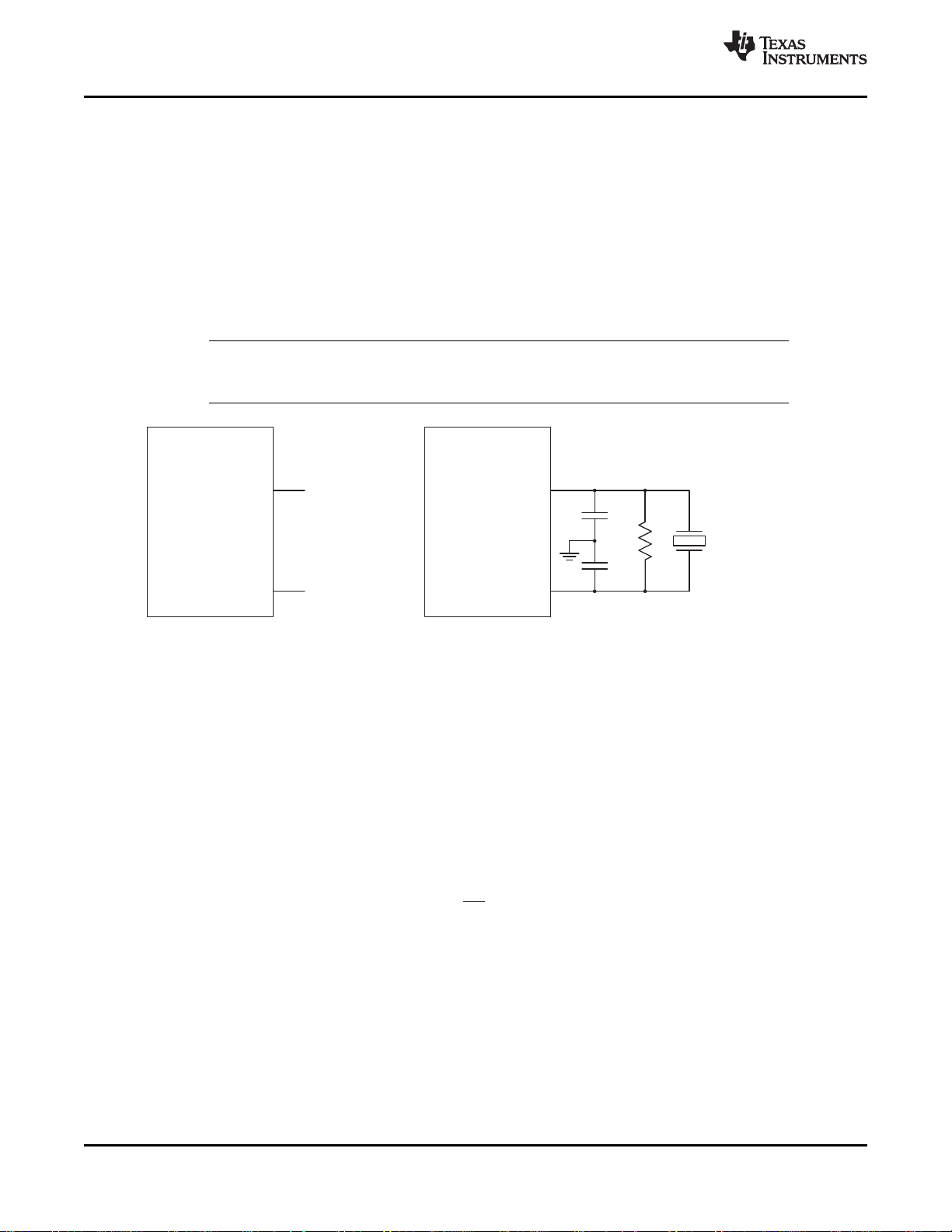
2.3 Clock Circuits
An internal line-locked PLL generates the system and pixel clocks. A 14.31818-MHz clock is required to
drive the PLL. This may be input to the TVP5160 decoder at 1.8-V level on terminal 121 (XIN), or a crystal
of 14.31818-MHz fundamental resonant frequency may be connected across terminals 121 (XIN) and 122
(XOUT). If a parallel resonant circuit is used as shown in Figure 2-4, then the external capacitors must
have following relationship:
CL1= CL2= 2CL– C
where C
STRAY
specified by the crystal manufacturer. Figure 2-4 shows the reference clock configurations. The TVP5160
decoder generates the SCLK signal used for clocking data.
See crystal datasheet for correct loading specifications.
STRAY
is the pin capacitance with respect to ground, and CL is the crystal load capacitance
www.ti.com
NOTE
2.4 Real-Time Control (RTC)
Note: The resistor (R) in parallel with the crystal is recommended to support a wide range of crystal types. A 100-kΩ resistor
may be used for most crystal types.
Figure 2-4. Reference Clock Configuration
Although the TVP5160 decoder is a line-locked system, the color burst information is used to accurately
determine the color subcarrier frequency and phase. This ensures proper operation with nonstandard
video signals that do not follow exactly the required frequency multiple between color subcarrier frequency
and video line frequency. The frequency control word of the internal color subcarrier PLL and the
subcarrier reset bit are transmitted via the terminal 83 (GLCO) for optional use in an end system (for
example, by a video encoder). The frequency control word is a 23-bit binary number. The instantaneous
frequency of the color subcarrier can be calculated from the following equation:
where F
F
SCLK
is the frequency of the subcarrier PLL, F
PLL
is the 2× pixel frequency.
is the 23-bit PLL frequency control word and
CTRL
22 Functional Description Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
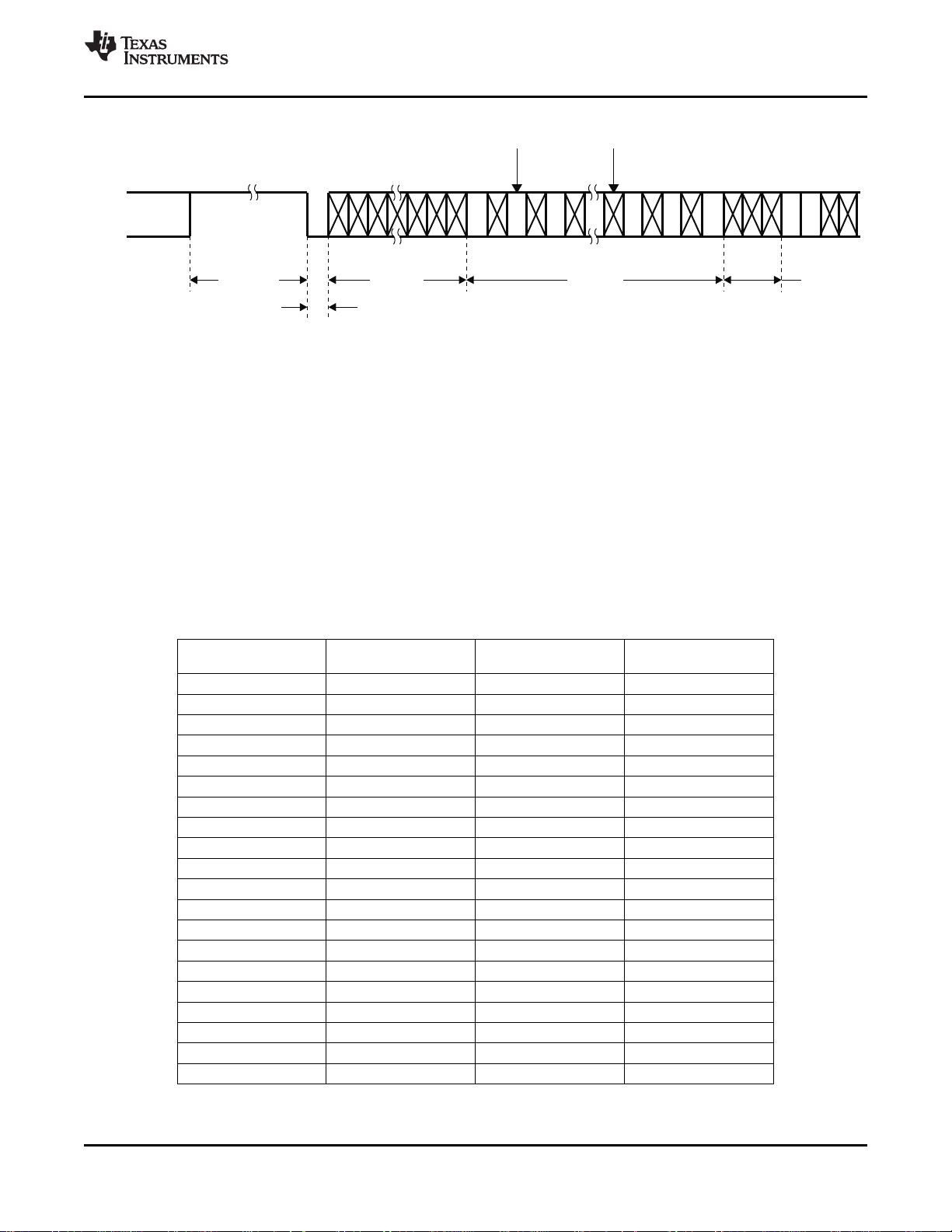
RTC
Mode
45 CLK18 CLK
L
S
B
0
3 CLK
23-Bit Fsc PLL Increment
Start
Bit
1 CLK
RS
M
S
B
22
Reserved
Valid
Sample
Valid
Sample
Valid
Sample
Valid
Sample
128 CLK
128 CLK128 CLK
TVP5160
www.ti.com
RTC: Reset bit (R) is active low 1 = (R-Y) line normal
2.5 Output Formatter
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Figure 2-5. RTC Timing
Sequence bit (S) PAL:
0 = (R-Y) line inverted
NTSC: 1 = no change
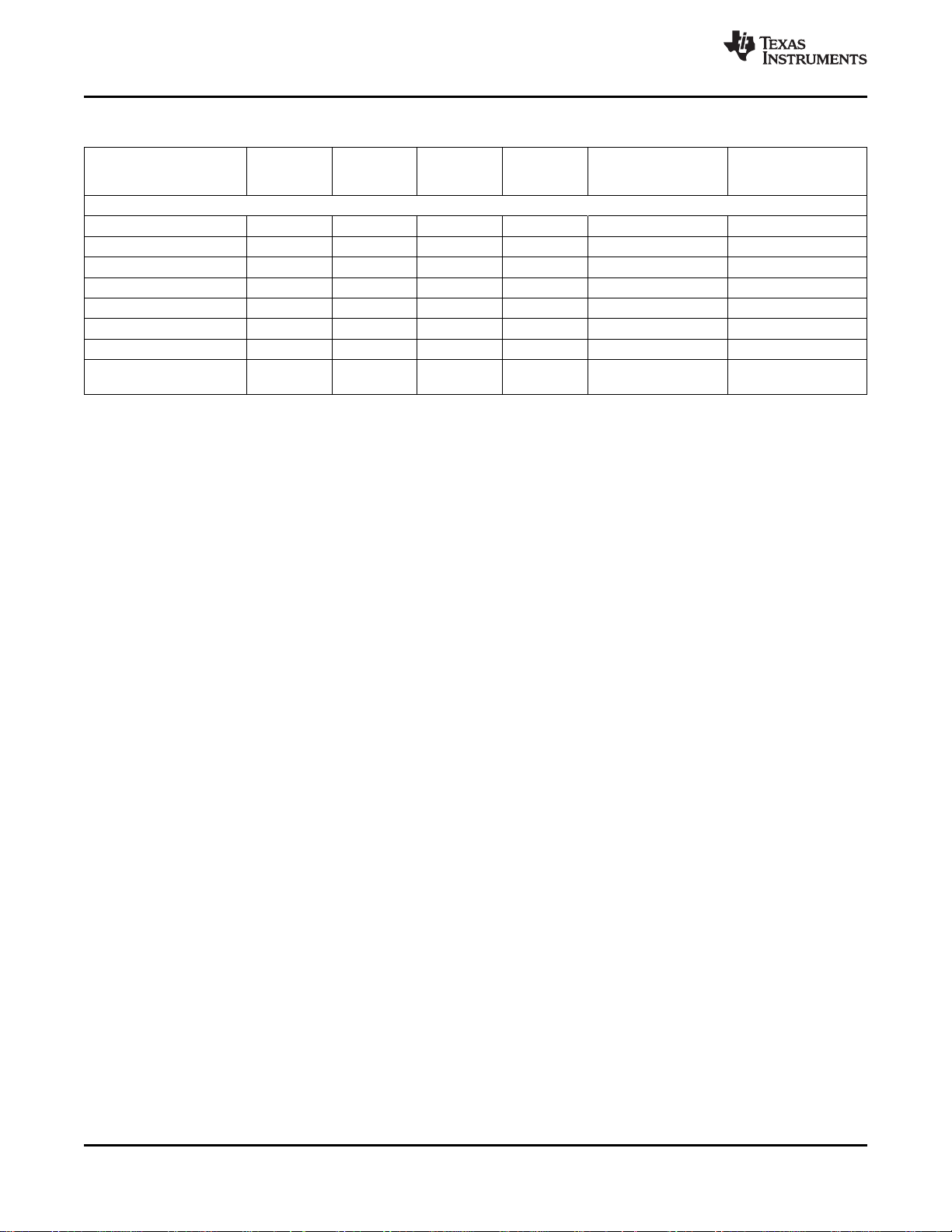
The output formatter sets how the data is formatted for output on the TVP5160 output buses. Table 2-2
shows the available output modes.
Table 2-2. Output Format
TERMINAL TERMINAL ITU-R BT.656 20-BIT 4:2:2
NAME NUMBER 10-Bit 4:2:2 YCbCr YCbCr
Y_9 87 Cb9, Y9, Cr9 Y9
Y_8 88 Cb8, Y8, Cr8 Y8
Y_7 89 Cb7, Y7, Cr7 Y7
Y_6 90 Cb6, Y6, Cr6 Y6
Y_5 91 Cb5, Y5, Cr5 Y5
Y_4 94 Cb4, Y4, Cr4 Y4
Y_3 95 Cb3, Y3, Cr3 Y3
Y_2 96 Cb2, Y2, Cr2 Y2
Y_1 97 Cb1, Y1, Cr1 Y1
Y_0 98 Cb0, Y0,Cr0 Y0
C_9 101 Cb9, Cr9
C_8 102 Cb8, Cr8
C_7 103 Cb7, Cr7
C_6 104 Cb6, Cr6
C_5 107 Cb5, Cr5
C_4 108 Cb4, Cr4
C_3 109 Cb3, Cr3
C_2 110 Cb2, Cr2
C_1 113 Cb1, Cr1
C_0 114 Cb0, Cr0
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Functional Description 23
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 2-3. Summary of Line Frequency, Data Rate, and Pixel/Line Counts
STANDARDS PIXELS SUBCARRIER
ITU-R BT.601 sampling
NTSC-J, M 858 720 525 13.5 3.579545 15.73426
NTSC-4.43 858 720 525 13.5 4.43361875 15.73426
PAL-M 858 720 525 13.5 3.57561149 15.73426
PAL-60 858 720 525 13.5 4.43361875 15.73426
PAL-B, D, G, H, I 864 720 625 13.5 4.43361875 15.625
PAL-N 864 720 625 13.5 4.43361875 15.625
PAL-Nc 864 720 625 13.5 3.58205625 15.625
SECAM 864 720 625 13.5 15.625
PIXELS LINES PER PIXEL FREQ HORIZONTAL
PER LINE FRAME (MHz) LINE RATE (kHz)
ACTIVE COLOR
PER LINE FREQUENCY (MHz)
Dr = 4.406250
Db = 4.250000
The TVP5160 input-to-output processing delay depends on the operating mode and the video standard.
When 3DYC is enabled, the processing delay is approximately 1 frame and 2-1/3 lines. When 3DYC is
disabled, the processing delay is approximately 2-1/3 lines.
www.ti.com
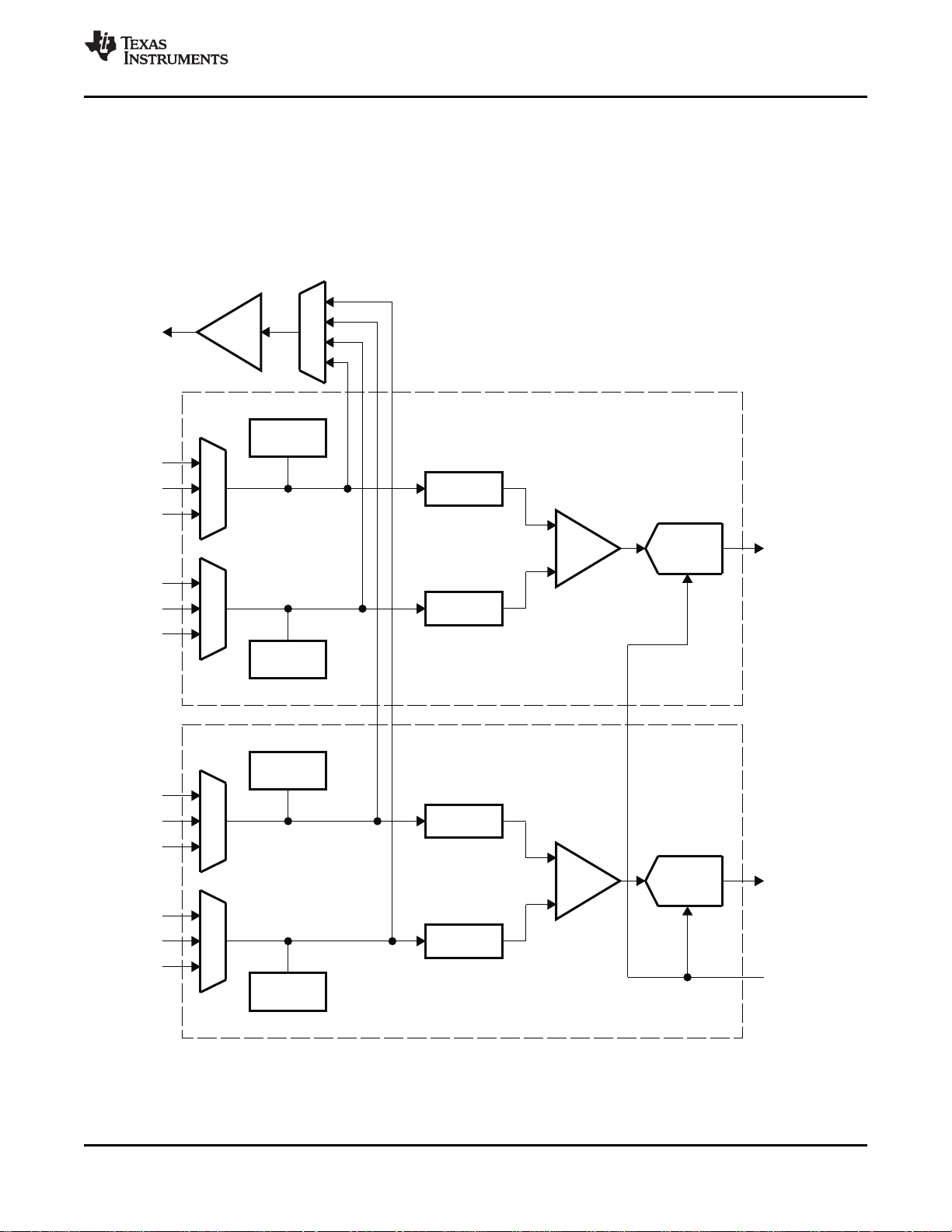
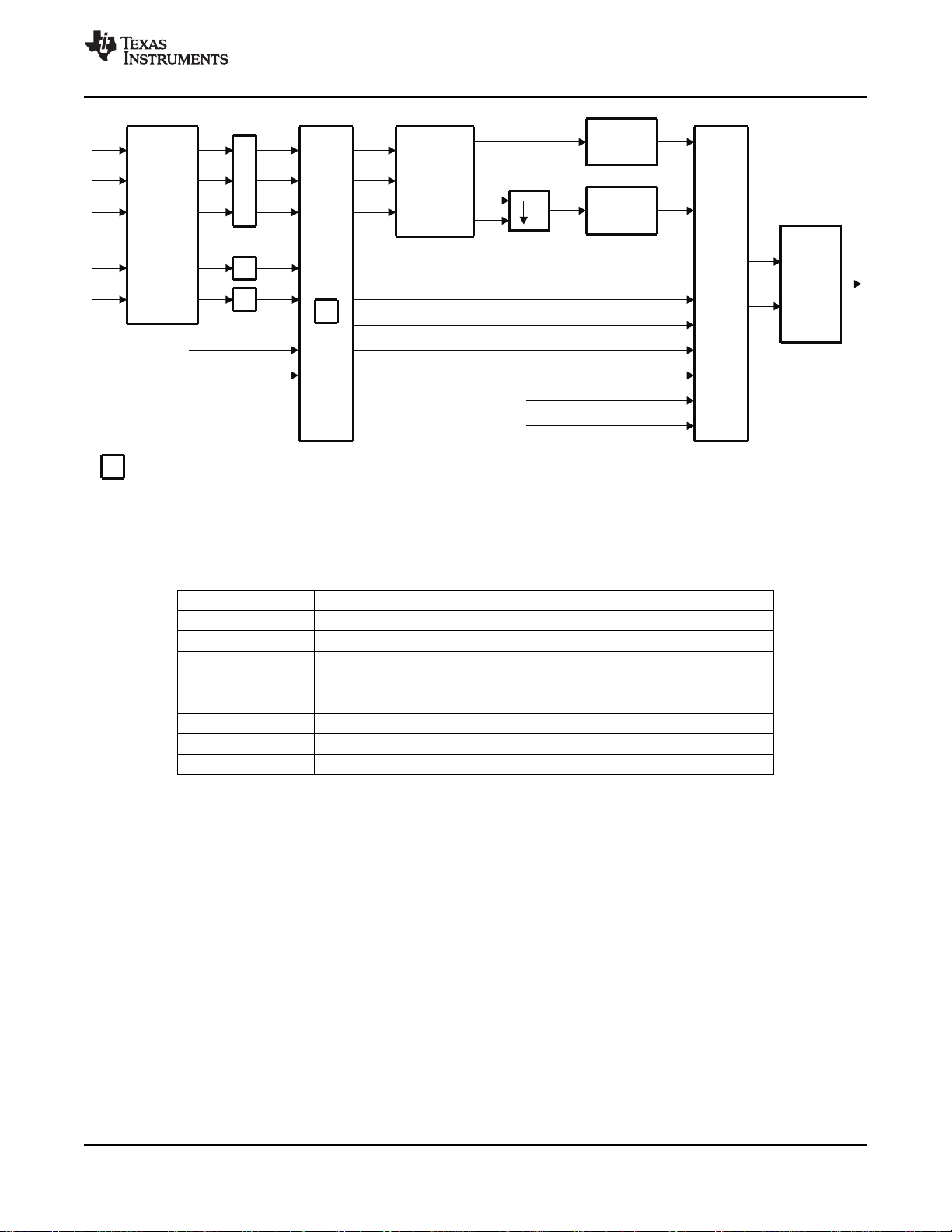
2.6 Fast Switches for SCART and Digital Overlay
The TVP5160 decoder supports the SCART interface used mainly in European audio/video end
equipment to carry mono/stereo audio, composite video, S-Video, and RGB video on the same cable. In
the event that composite video and RGB video are present simultaneously on the video pins assigned to a
SCART interface, the TVP5160 decoder assumes they are pixel synchronous to each other. The timing for
both composite video and RGB video is obtained from the composite source and its derived clock is used
to sample RGB video as well. The fast-switch input pin allows switching between these two input video
sources on a pixel-by-pixel basis. This feature can be used to, for example, overlay RGB graphics for
on-screen display onto decoded CVBS video. The SCART overlay control signals (FSS) are oversampled
at 4× the pixel clock frequency. The phase of this signal is used to mix between the CVBS input and the
analog RGB inputs. This improves the analog overlay picture quality when the external FSS and analog
video signals are generated by an asynchronous source. The TVP5160 decoder has two programmable
delays for component video in order to compensate for composite comb filter delays and two
programmable delays for digital RGB to compensate AFE and decimation filter delays.
If the overlay output is digital supporting 8 colors of data, the TVP5160 decoder can take digital overlay
inputs using terminals C6, C7, and C8. For this mode, output must be the 10-bit ITU-R BT.656 mode.
Figure 2-6 shows the block diagram of two fast-switches.Table 2-4 shows the fast-switch 1 and 2 controls.
24 Functional Description Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
B”
Prog
Delay
Color Space
Conversion
2
Gain
Output
Formatter
U
V
UV
Y
FSS’’’
FSO’’’
SCART/COMP_UV’
SCART/COMP_Y
SCART/COMP_UV
CVBS_SEP_Y
CVBS_SEP_UV
Y’’
UV’’
D
D
= User Prgrammable Delay
4
Oversample
×
R
G
B
FSS
FSO
R’
G’
B’
R”
G”
D
FSS’
FSO’
D
FSS”
FSO”
B’’’
R’’’
G’’’
SCART/COMP_Y’
Gain/Offset
Soft Mix
UV’
Y’
D
TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Figure 2-6. Fast-Switches for SCART and Digital Overlay
Table 2-4. Fast-Switch Modes
MODES DESCRIPTION
000 CVBS ↔ SCART
001 CVBS, S_VIDEO ↔ Digital overlay
010 Component ↔ Digital overlay
011 (CVBS ↔ SCART) ↔ Digital overlay
100 (CVBS ↔ Digital overlay) ↔ SCART
101 CVBS ↔ (SCART ↔ Digital overlay
110 Composite
111 No switching
Fast switching of digital RGB input: closed caption decoder output is digital RGB with blanking signal. The
TVP5160 decoder supports this digital RGB input and can do overlay with composite, S-Video, or
component video.
See TI application note SLEA016, TVP5146 SCART and OSD, for more information on SCART overlay
and digital overlay programming.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Functional Description 25
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
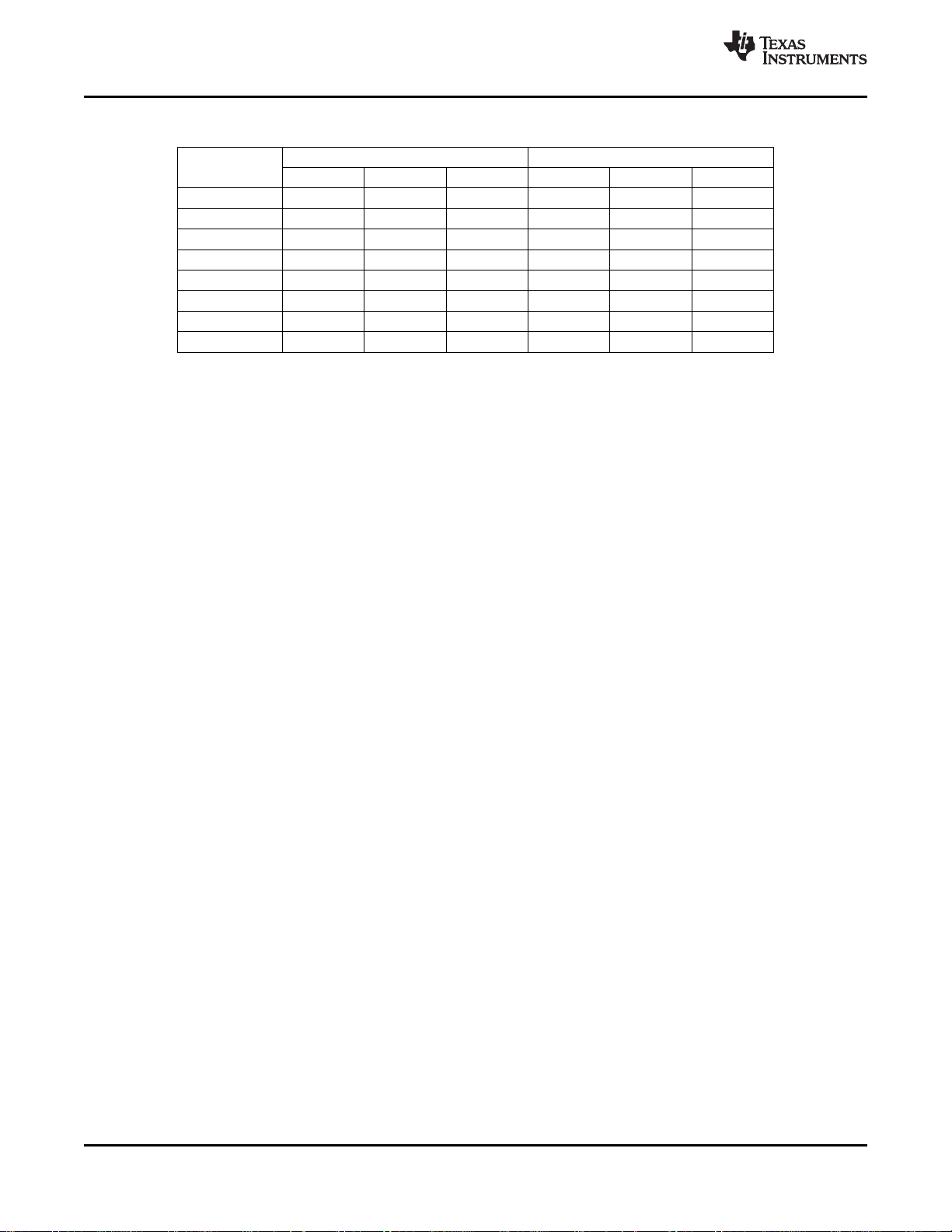
TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 2-5. Look-Up Table for Converting from Digital RGB to 10-Bit YCbCr Data
COLOR
BLACK 0 0 0 64 512 512
BLUE 0 0 1 164 960 440
GREEN 0 1 0 580 216 136
CYAN 0 1 1 680 664 64
RED 1 0 0 324 360 960
MAGENTA 1 0 1 424 808 888
YELLOW 1 1 0 840 64 584
WHITE 1 1 1 940 512 512
DR DG DB Y Cb Cr
2.7 Discrete Syncs
VS, HS, and VBLK are independently software programmable to a 1× pixel count. This allows any
possible alignment to the internal pixel count and line count. The default settings for a 525-line and
625-line video output are given as an example below. FID changes at the same transient time when the
trailing edge of vertical sync occurs. The polarity of FID is programmable by an I2C interface.
www.ti.com
INPUT OUTPUT
26 Functional Description Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
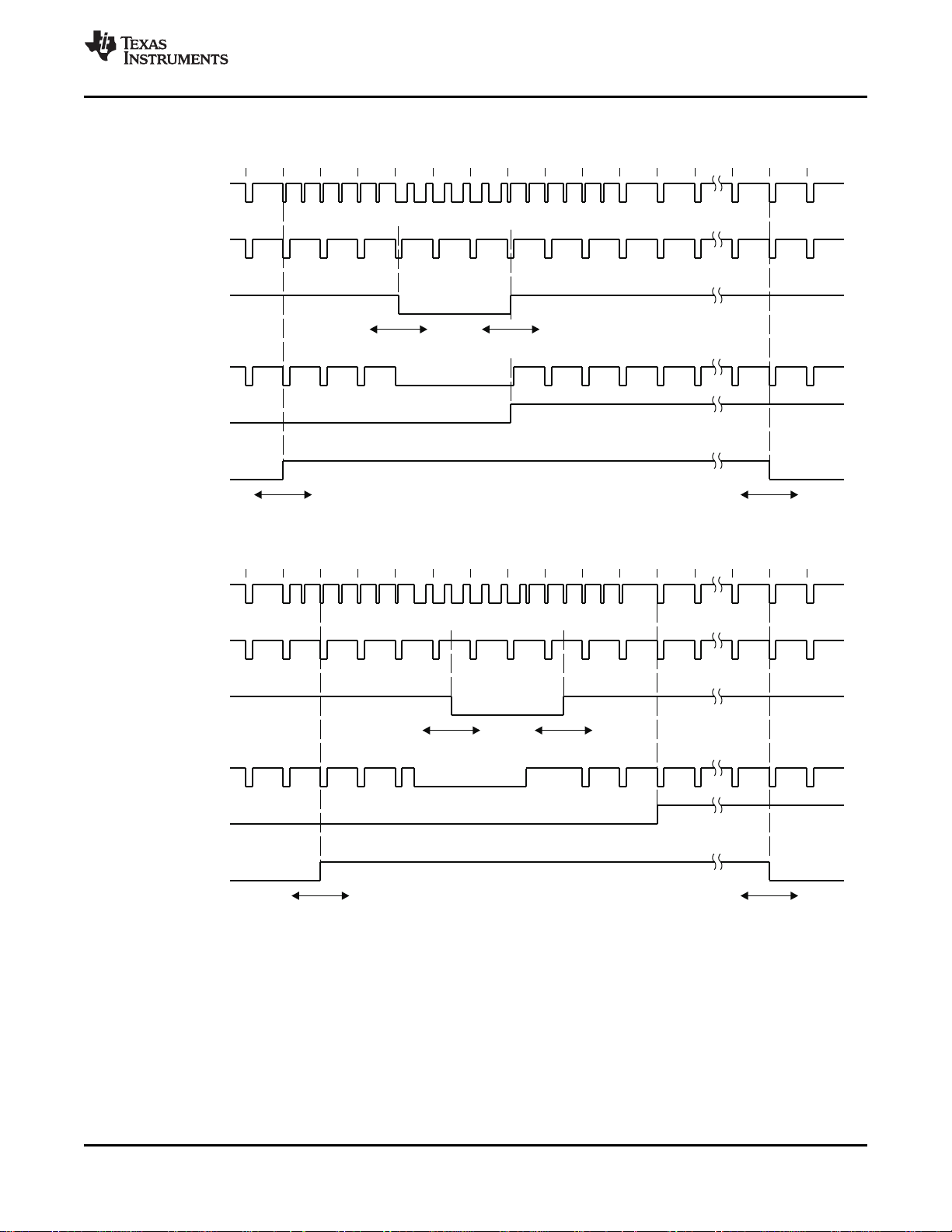
First Field Video
525
VS
VBLK
FID
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 20 21
525-Line
HS
VS Start VS Stop
CS
VBLK Start VBLK Stop
Second Field Video
262
VS
VBLK
FID
263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 283 284
HS
VS Start VS Stop
CS
VBLK Start VBLK Stop
11
TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
NOTE: Line numbering conforms to ITU-R BT.470.
Figure 2-7. Vertical Synchronization Signals for 525-Line System
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Functional Description 27
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
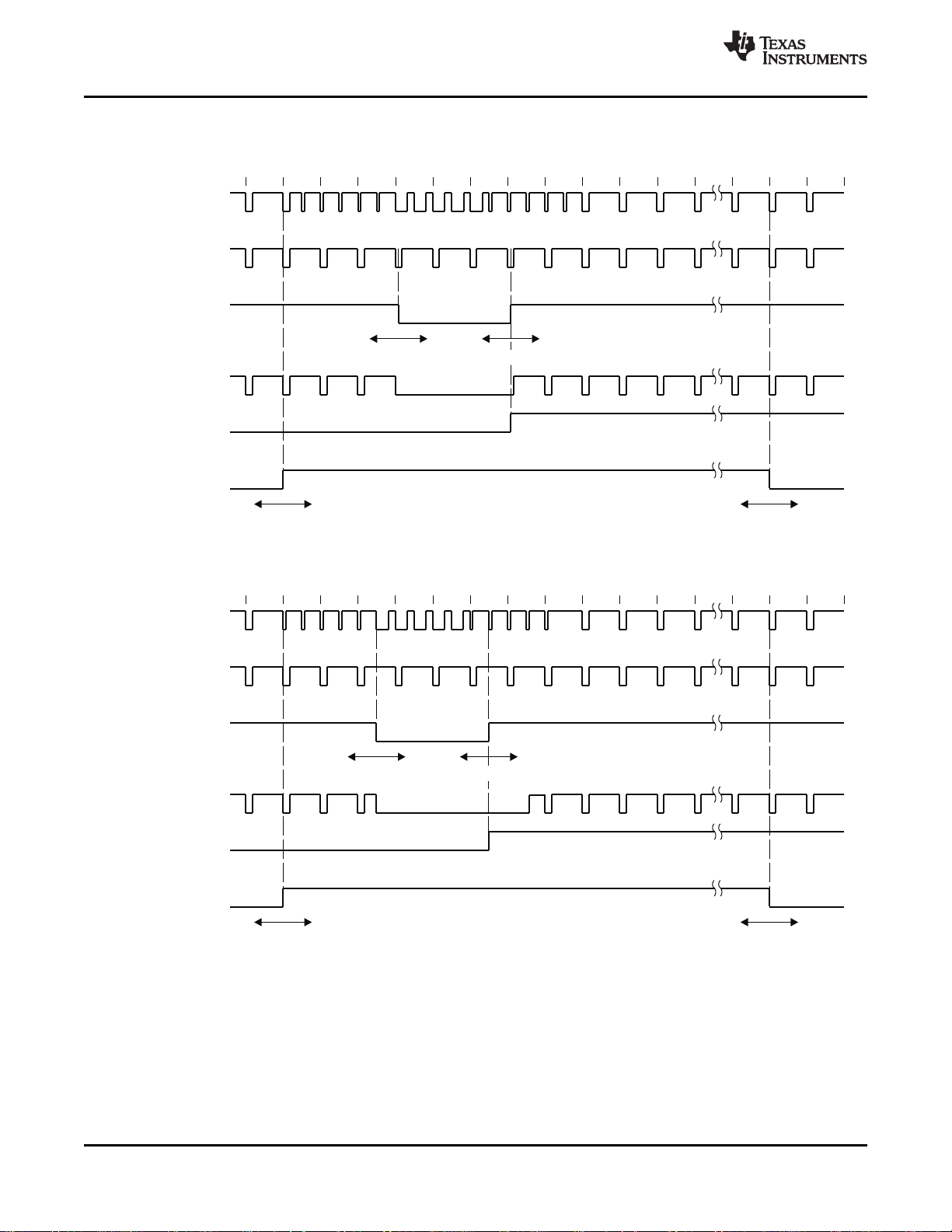
First Field Video
VS
VBLK
FID
625-Line
HS
VS Start VS Stop
CS
VBLK Start VBLK Stop
Second Field Video
310
VS
VBLK
FID
311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 336 337
HS
VS Start VS Stop
CS
VBLK Start VBLK Stop
622 623 624 625 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 23 24 258
338
TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
A. NOTE: Line numbering conforms to ITU-R BT.470.
Figure 2-8. Vertical Synchronization Signals for 625-Line System
ITU-R BT.656 10-bit 4:2:2 Timing with 2× pixel clock reference
28 Functional Description Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
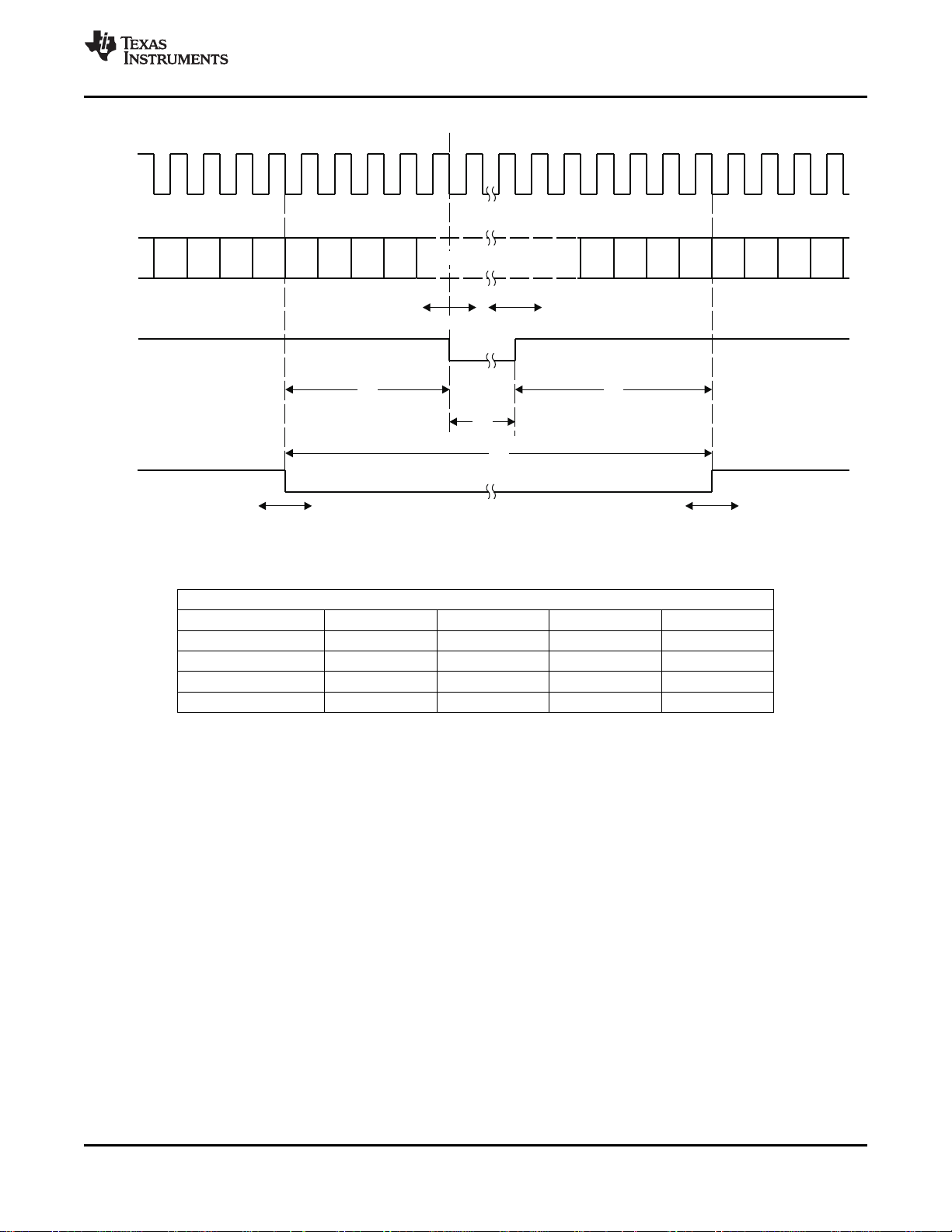
Y[9:0] Cb
SCLK
EAV
1
Y Cr Y
EAV
2
EAV3EAV
4
SAV1SAV2SAV3SAV
4
Cb0 Y0 Cr0 Y1
0
HS Start
Horizontal Blanking
HS
HS Stop
A C
B
AVID
D
AVID Stop AVID Start
TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Figure 2-9. Horizontal Synchronization Signals for 10-Bit 4:2:2 Mode
SCLK = 2× PIXEL CLOCK
MODE A B C D
NTSC 601 106 128 42 276
PAL 601 112 128 48 288
480p 106 128 42 276
576p 112 128 48 288
(1) ITU-R BT.656 10-bit 4:2:2 timing with 2× pixel clock reference 601 = ITU-R BT.601 timin
(1)
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Functional Description 29
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
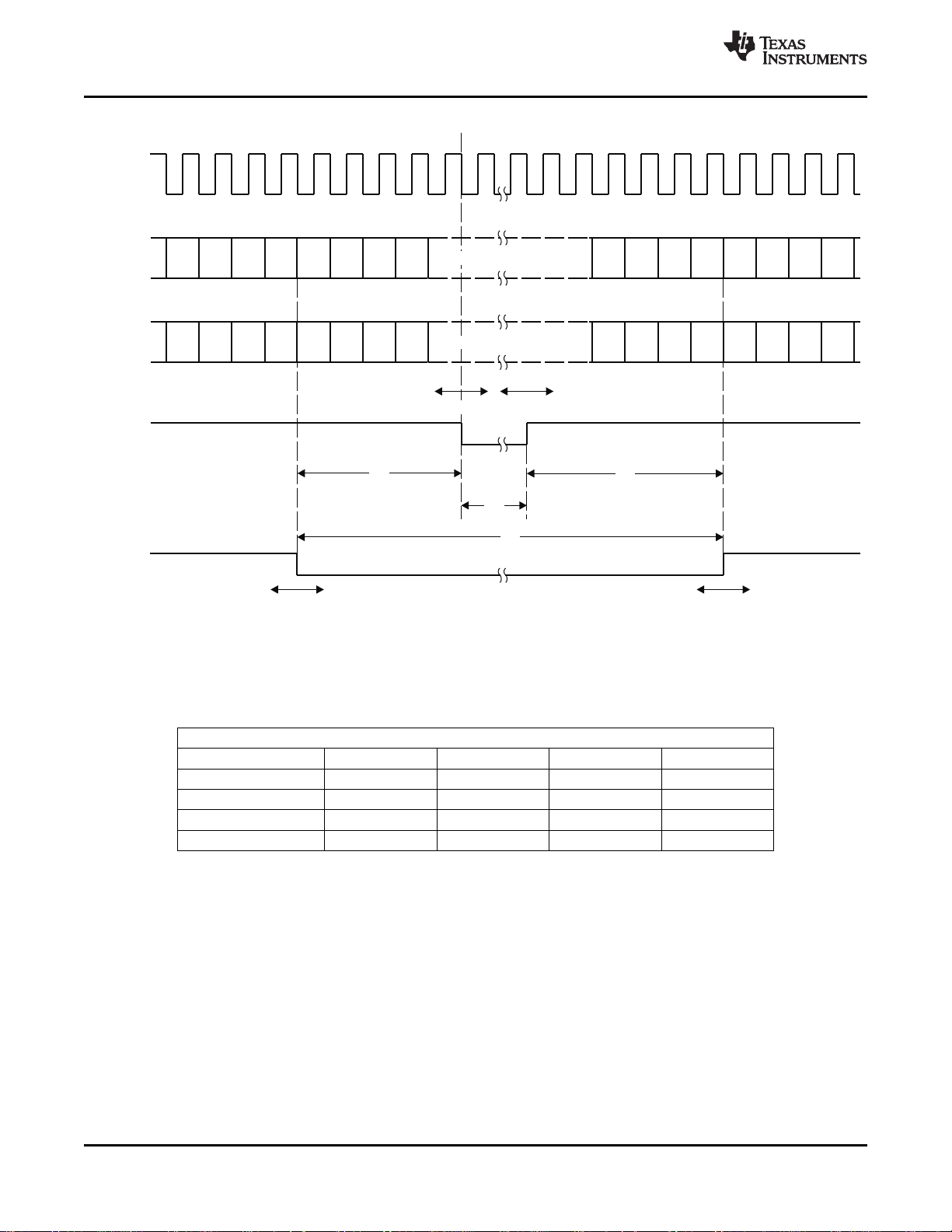
CbCr[9:0] Cb
SCLK
Cr Cb Cr Cb0 Cr0 Cb1 Cr1
0
HS Start
Horizontal Blanking
HS
HS Stop
A C
B
AVID
D
NOTE: AVID rising edge occurs 4 clock cycles early.
Y[9:0]
Y Y Y Y Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3Horizontal Blanking
AVID Stop AVID Start
TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
NOTE: AVID rising edge occurs 4 clock cycles early.
Figure 2-10. Horizontal Synchronization Signals for 20-Bit 4:2:2 Mode
SCLK = 1X PIXEL CLOCK
(1)
MODE A B C D
NTSC 601 53 64 19 138
PAL 601 56 64 22 144
480p 53 64 19 138
576p 56 64 22 144
(1) 20-bit 4:2:2 timing with 1× pixel clock reference 601 = ITU-R BT.601 timing
30 Functional Description Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

First Field B/2
HS
VS
Second Field
HS
VS
B/2
H/2 + B/2 H/2 + B/2
B/2
HS
VS
B/2
TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Figure 2-11. VS Position with Respect to HS for Interlaced Signals
Figure 2-12. VS Position with Respect to HS for Progressive Signals
(1)
MODE
NTSC 601 interlaced 64 858 32 429
PAL 601 interlaced 64 864 32 432
NTSC 601 progressive 858 32
PAL 601 progressive 864 32
(1) 601 = ITU-R BT.601 timing
2.8 Embedded Syncs
Standard with embedded syncs insert SAV and EAV codes into the data stream on the rising and falling
edges of AVID. These codes contain the V and F bits which also define vertical timing. Table 2-6 gives the
format of the SAV and EAV codes.
H equals 1b always indicates EAV. H equals 0b always indicates SAV. The alignment of V and F to the
line and field counter varies depending on the standard.
The P bits are protection bits:
• P3 = V xor H
• P2 = F xor H
• P1 = F xor V
• P0 = F xor V xor H
10-BIT (SCLK= 2× PIXEL CLOCK) 20-BIT (SCLK= 1× PIXEL CLOCK)
B/2 H/2 B/2 H/2
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Functional Description 31
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 2-6. EAV and SAV Sequence
Y9 (MSB) Y8 Y7 Y6 Y5 Y4 Y3 Y2 Y1 Y0
Preamble 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Preamble 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Preamble 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Status 1 F V H P3 P2 P1 P0 0 0
2.9 I2C Host Interface
Communication with the TVP5160 decoder is via an I2C host interface. The I2C standard consists of two
signals, the serial input/output data (SDA) line and input/output clock line (SCL), which carry information
between the devices connected to the bus. A 2-bit control signal (I2CA0/ I2CA1) selects the slave address.
Although an I2C system can be multi-mastered, the TVP5160 decoder can function as a slave device only.
Since SDA and SCL are kept open-drain at logic high output level or when the bus is not driven, the user
must connect SDA and SCL to IOVDD via a pullup resistor on the board. The slave address select,
terminals 83 and 82 (I2CA0 and I2CA1), enables the use of four TVP5160 devices tied to the same I2C bus
since it controls the two least significant bits of the I2C device address.
Table 2-7. I2C Host Interface Terminal Description
SIGNAL TYPE DESCRIPTION
I2CA0 I Slave address selection
I2CA1 I Slave address selection
SCL I/O Input clock line
SDA I/O Input/output data line
2.9.1 Reset and I2C Bus Address Selection
The TVP5160 decoder can respond to four possible chip addresses. The address selection is made at
reset by an externally supplied level on the I2CA0/ I2CA1 pins. The TVP5160 decoder samples the level of
terminals 83 and 82 at power up or at the trailing edge of RESETB and configures the I2C bus address bit
A0/A1. The I2CA0 and I2CA1 terminals have internal pulldown resistors to pull the terminals low to set a
0b.
Table 2-8. I2C Host Interface Device Addresses
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1(I2CA1)
1 0 1 1 1 0 (default) 0 (default) 1/0 B9/B8
1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1/0 BB/BA
1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1/0 BD/BC
1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1/0 BF/BE
(1) To pull up the I2C terminals high, tie to IOVDD via a 2.2-kΩ resistor.
(1)
A0 (I2CA0)
(1)
R/W HEX
32 Functional Description Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

Host
Processor
I C
2
VBUS
Data
I C Registers
2
00h
E0h
E1h
VBUS
Address
E8h
EAh
FFh
VBUS[23:0]
Line Mode
VBUS Registers
00 0000h
FIFO
VPS/Gemstar
VITC
WSS/CGMS
CC
80 051Ch
80 0520h
80 052Ch
80 0600h
80 0700h
90 1904h
FF FFFFh
TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
2.9.2 I2C Operation
Data transfers occur utilizing the following formats.
Read from I2C control registers
S 10111000 ACK subaddress ACK S 10111001 ACK NAK P
receive
data
Write to I2C control registers
S 10111000 ACK subaddress ACK send data ACK P
S = I2C bus start condition
P = I2C bus stop condition
ACK = Acknowledge generated by the slave
NAK = Acknowledge generated by the master, for multiple byte read master will ACK each
byte except the last byte
Subaddress = Subaddress byte
Data = Data byte
I2C bus address = In the example shown, I2CA0/I2CA1 are in default mode. Write (B8h), Read (B9h)
2.9.3 VBUS Access
The TVP5160 decoder has additional internal registers accessible through an indirect access to an
internal 24-bit address wide VBUS. Figure 2-13 shows the VBUS registers access.
Figure 2-13. VBUS Access
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Functional Description 33
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
2.9.3.1 VBUS Write
Single byte
S B8 ACK E8 ACK VA0 ACK VA1 ACK VA2 ACK P
S B8 ACK E0 ACK send data ACK P
Multiple bytes
S B8 ACK E8 ACK VA0 ACK VA1 ACK VA2 ACK P
S B8 ACK E1 ACK send data ACK . . . send data ACK P
2.9.3.2 VBUS Read
Single byte
S B8 ACK E8 ACK VA0 ACK VA1 ACK VA2 ACK P
S B8 ACK E0 ACK S B9 ACK read data NAK P
Multiple bytes
S B8 ACK E8 ACK VA0 ACK VA1 ACK VA2 ACK P
S B8 ACK E1 ACK S B9 ACK read data MACK … read data NAK P
NOTE: Examples use default I2C address
ACK = Acknowledge generated by the slave
MACK = Acknowledge generated by the master
NAK = No Acknowledge generated by the master
www.ti.com
2.10 VBI Data Processor
The TVP5160 VBI data processor (VDP) slices various data services like teletext (WST, NABTS), closed
caption (CC), wide screen signaling (WSS), program delivery control (PDC), vertical interval time code
(VITC), video program system (VPS), copy generation management system (CGMS) data, and electronic
program guide (EPG or Gemstar) 1x/2x. Table 2-9 shows the supported VBI system.
These services are acquired by programming the VDP to enable the reception of one or more VBI data
standard(s) in the vertical blanking interval. The VDP can be programmed on a line-per-line basis to
enable simultaneous reception of different VBI formats, one per line. The results are stored in a FIFO
and/or registers. Because of its high data bandwidth, the teletext results are stored in the FIFO only. The
TVP5160 decoder provides fully decoded V-Chip data to the dedicated registers at subaddresses
800540h through 800543h.
VBI SYSTEM STANDARD LINE NUMBER NUMBER OF BYTES
Teletext WST A SECAM 6–23 (Field 1, 2) 38
Teletext WST B PAL 6–22 (Field 1, 2) 43
Teletext NABTS C NTSC 10–21 (Field 1, 2) 34
Teletext NABTS D NTSC-J 10–21 (Field 1, 2) 35
Closed Caption PAL 22 (Field 1, 2) 2
Closed Caption NTSC 21 (Field 1, 2) 2
WSS-CGMS PAL 23 (Field 1, 2) 14 bits
WSS-CGMS NTSC 20 (Field 1, 2) 20 bits
VITC PAL 6–22 9
VITC NTSC 10–20 9
VPS PAL 16 13
Table 2-9. Supported VBI System
34 Functional Description Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 2-9. Supported VBI System (continued)
VBI SYSTEM STANDARD LINE NUMBER NUMBER OF BYTES
V-Chip (Decoded) NTSC 21 (Field 2) 2
Gemstar EPG 1× NTSC 2
Gemstar EPG 2× NTSC 5 with frame byte
User Any Programmable Programmable
CGMS-A packet A 480p 41 20 bits
CGMS-A packet B 480p 40 16 bytes
2.10.1 VBI FIFO and Ancillary Data in Video Stream
Sliced VBI data can be output as ancillary data in the video stream in ITU-R BT.656 mode. VBI data is
output on the Y[9:2] terminals during the horizontal blanking period following the line from which the data
was retrieved. Table 2-10 shows the header format and sequence of the ancillary data inserted into the
video stream. This format also stores any VBI data into the FIFO. The size of the FIFO is 512 bytes.
Therefore, the FIFO can store up to 9 lines of teletext data according to the WSTB standard.
Table 2-10. Ancillary Data Format and Sequence
BYTE NO. Y7(MSB) Y6 Y5 Y4 Y3 Y2 Y1 Y0 (LSB) DESCRIPTION
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Ancillary data preamble
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
3 NEP EP 0 1 0 DID2 DID1 DID0 Data ID (DID)
4 NEP EP F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 F0 Secondary data ID (SDID)
5 NEP EP N5 N4 N3 N2 N1 N0 Number of 32 bit data (NN)
6 Video line # [7:0] Internal Data ID0 (IDID0)
7 0 0 0 Data error Match #1 Match #2 Video line # [9:8] Internal Data ID1 (IDID1)
8 Sample 1 Data byte 1st word
9 Sample 2 Data byte
10 Sample 3 Data byte
11 Sample 4 Data byte
. . .
. . .
Sample m-1 Data byte Nthword
4N+5 Sample m Data byte
4N+6 CS[7:0] Checksum
4N+7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Fill byte
EP: Even parity for Y5–Y0
NEP: Negated even parity
DID: 91h: Sliced data of VBI lines of first field
53h: Sliced data of line 24 to end of first field
55h: Sliced data of VBI lines of second field
97h: Sliced data of line 24 to end of second field
SDID: This field holds the data format taken from the line mode register bits [5:0] of the
corresponding line.
NN: Number of Dwords beginning with byte 8 through 4N+7. Note this value is the number of
Dwords where each Dword is 4 bytes.
IDID0: Transaction video line number [7:0]
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Functional Description 35
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
IDID1: Bit 0/1 – Transaction video line number [9:8]
Bit 2 – Match 2 flag
Bit 3 – Match 1 flag
Bit 4 – 1b if at least one error was detected in the EDC block. 0b if no error was detected.
CS: Sum of Y7–Y0 of byte 8 through byte 4N+5. For teletext modes, byte 8 is the sync pattern
byte. Byte 9 is Sample 1.
Fill byte: Fill byte makes a multiple of 4 bytes from byte zero to last fill byte
2.10.2 VBI Raw Data Out
The TVP5160 decoder can output raw A/D video data at twice the sampling rate for external VBI slicing.
This is transmitted as an ancillary data block, although a bit differently from the way the sliced VBI data is
transmitted in the FIFO format as described in Section 3.10.1. The samples are transmitted during the
active portion of the line. VBI raw data uses ITU-R BT 656 format having only luma data. The chroma
samples are replaced by luma samples. The TVP5160 decoder inserts a 4-byte preamble 000h 3FFh
3FFh 180h before data start. There is no checksum byte or fill bytes in this mode.
DATA NO. Y9 (MSB) Y8 Y7 Y6 Y5 Y4 Y3 Y2 Y1 Y0 (LSB) DESCRIPTION
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 VBI raw data preamble
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
3 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 Sample 1 2× pixel rate
5 Sample 2
. .
. .
n–1 Sample n–5
N Sample n–4
Luma data
(i.e., NTSC 601: n =
1707)
2.11 Powerup, Reset, and Initialization
No specific power-up sequence is required, but all power supplies must be active and stable within 500
ms of each other. Reset may be low during power-up, but must remain low for at least 1 µs after the
power supplies become stable and the crystal begins to oscillate. Alternately, reset may be asserted any
time after power up and a stable crystal oscillation, and must remain asserted for at least 1 µs. Table 2-11
describes the status of the TVP5160 terminals during and immediately after reset.
200 µs must be allowed after reset before commencing I2C operations if the SCL pin is not monitored
during I2C operations
Table 2-11. Reset Sequence
SIGNAL NAME DURING RESET RESET COMPLETED
Y[9:0], SCLK Input High-impedance
C[9:0]/GPIO Input Input
RESETB, PWDN, SDA, SCL, FSS/GPIO, Input Input
AVID/GPIO, GLCO/GPIO/I2CA0, HS/CS/GPIO,
36 Functional Description Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
VS/VBLK/GPIO, FID/GPIO
INTREQ Input Output (open drain)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

1 sµ
RESET
I C SDA
2
Power
Crystal
200 sµ
TVP5160
www.ti.com
After reset has completed, the following sequence of operations must be completed:
1. Write 01h to VBus register 0xB00060
2. Write 01h to VBus register 0xB00063
3. Write 00h to VBus register 0xB00060
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Figure 2-14. Reset Timing
2.12 Adjusting External Syncs
The TVP5160 decoder stores values for the positions of the external syncs for 2 different modes:
• 525-line with ITU-R BT.601 sampling
• 625-line with ITU-R BT.601 sampling
Once the values are stored, they are retained and restored when the signal switches back into one of
these two modes.
The proper sequence to change the external sync positions is:
• To set NTSC, PAL-M, NTSC 443, PAL 60 (525-line modes):
– Make sure the standard is one of the above 525-line mode formats by forcing the video standard
– Set HS, VS, VBLK, and AVID external syncs (register 16h through 24h)
• To set PAL, PAL-N, SECAM (625-line modes):
– Make sure the standard is one of the above 625-line mode formats by forcing the video standard
– Set HS, VS, VBLK, and AVID external syncs (register 16h through 24h)
Once programmed, the values for each mode are retained when the signal switches back into that or other
compatible video standards.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Functional Description 37
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
3 Internal Control Registers
The TVP5160 decoder is initialized and controlled by a set of internal registers that define the operating
parameters of the entire device. Communication between the external controller and the TVP5160
decoder is through a standard I2C host port interface, as described earlier.
Table 3-1 shows the summary of these registers. Detailed programming information for each register is
described in the following sections. Additional registers are accessible through an indirect procedure
involving access to an internal 24-bit address wide VBUS. Table 3-2 shows the summary of VBUS
registers.
Table 3-1. I2C Registers Summary
REGISTER NAME I2C SUBADDRESS DEFAULT R/W
Input/Output Select 00h 00h R/W
AFE Gain Control 01h 0Fh R/W
Video Standard Select 02h 00h R/W
Operation Mode 03h 00h R/W
Autoswitch Mask 04h 23h R/W
Color Killer 05h 10h R/W
Luminance Processing Control 1 06h 00h R/W
Luminance Processing Control 2 07h 00h R/W
Luminance Processing Control 3 08h 00h R/W
Luminance Brightness 09h 80h R/W
Luminance Contrast 0Ah 80h R/W
Chrominance Saturation 0Bh 80h R/W
Chroma Hue 0Ch 00h R/W
Chrominance Processing Control 1 0Dh 00h R/W
Chrominance Processing Control 2 0Eh 0Ch R/W
Reserved
Pr Contrast 10h 80h R/W
Y Contrast 11h 80h R/W
Pb Contrast 12h 80h R/W
Reserved
G/Y Brightness 14h 80h R/W
Reserved
AVID Start Pixel 16h–17h 55h/5Fh R/W
AVID Stop Pixel 18h–19h 325h/32Fh R/W
HS Start Pixel 1Ah–1Bh 00h/07h R/W
HS Stop Pixel 1Ch–1Dh 40h/47h R/W
VS Start Line 1Eh–1Fh 004h/001h R/W
VS Stop Line 20h–21h 007h/004h R/W
VBLK Start Line 22h–23h 001h/26Fh R/W
VBLK Stop Line 24h–25h 015h/018h R/W
Embedded Sync Offset Control 1 26h 00h R/W
Embedded Sync Offset Control 2 27h 00h R/W
Fast Switch Control 28h C0h R/W
Fast Switch Overlay Delay 29h 17h R/W
Fast Switch SCART Delay 2Ah 1Ch R/W
Overlay Delay 2Bh 12h R/W
(2)
(2)
(2)
0Fh
13h
15h
(1)
(1) R = Read only, W = Write only, R/W = Read and write
(2) Reserved I2C register addresses must not be written to.
38 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-1. I2C Registers Summary (continued)
REGISTER NAME I2C SUBADDRESS DEFAULT R/W
SCART Delay 2Ch 56h R/W
Reserved
CTI Control 2Eh 00h R/W
Brightness and Contrast Range Extender 2Fh 00h R/W
Component Autoswitch Mask 30h 00h R/W
Reserved
Sync Control 32h 00h R/W
Output Formatter 1 33h 40h R/W
Output Formatter 2 34h 00h R/W
Output Formatter 3 35h FFh R/W
Output Formatter 4 36h FFh R/W
Output Formatter 5 37h FFh R/W
Output Formatter 6 38h FFh R/W
Clear Lost Lock Detect 39h 00h R/W
Status 1 3Ah R
Status 2 3Bh R
AGC Gain Status 3Ch–3Dh R
Reserved
Video Standard Status 3Fh R
GPIO Input 1 40h R
GPIO Input 2 41h R
Reserved
Back End AGC Status 44h R
Reserved
AFE Coarse Gain for CH1 46h 20h R/W
AFE Coarse Gain for CH2 47h 20h R/W
AFE Coarse Gain for CH3 48h 20h R/W
AFE Coarse Gain for CH4 49h 20h R/W
AFE Fine Gain for Pb 4Ah–4Bh 900h R/W
AFE Fine Gain for Chroma 4Ch–4Dh 900h R/W
AFE Fine Gain for Pr 4Eh–4Fh 900h R/W
AFE Fine Gain for CVBS_Luma 50h–51h 900h R/W
Reserved
656 Version 57h 00h R/W
Reserved
SDRAM Control 59h 00h R/W
Y Noise Sensitivity 5Ah 80h R/W
UV Noise Sensitivity 5Bh 80h R/W
Y coring threshold 5Ch 80h R/W
UV coring threshold 5Dh 40h R/W
Low Noise Limit 5Eh 40h R/W
"Blue" Screen Y 5Fh 00h R/W
"Blue" Screen Cb 60h 80h R/W
"Blue" Screen Cr 61h 80h R/W
"Blue" Screen LSB 62h 00h R/W
3DNR Noise Measurement LSB 64h R
3DNR Noise Measurement MSB 65h R
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
2Dh
31h
3Eh
42h-43h
45h
52h-56h
58h
(1)
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 39
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-1. I2C Registers Summary (continued)
REGISTER NAME I2C SUBADDRESS DEFAULT R/W
Y Core0 (3DNR) 66h R
UV Core0 (3DNR) 67h R
Reserved
F and V Bit Decode Control 69h 00h R/W
Reserved
Back End AGC Control 6Ch 08h R/W
Reserved
AGC Decrement Speed 6Fh 04h R/W
ROM Version 70h R
Reserved
AGC White Peak Processing 74h 00h R/W
F and V Bit Control 75h 16h R/W
Reserved
AGC Increment Speed 78h 06h R/W
AGC Increment Delay 79h 1Eh R/W
Analog Output Control 1 7Fh 00h R/W
CHIP ID MSB 80h 51h R
CHIP ID LSB 81h 60h R
Reserved
Color PLL Speed Control 83h 09h R/W
3DYC Luma Coring LSB 84h 20h/20h R/W
3DYC Chroma Coring LSB 85h 20h/2Ah R/W
3DYC Chroma/Luma MSBs 86h 00h/00h R/W
3DYC Luma Gain 87h 08h/08h R/W
3DYC Chroma Gain 88h 08h/08h R/W
3DYC Signal Quality Gain 89h 02h/02h R/W
3DYC Signal Quality Coring 8Ah–8Bh 328h/380h R/W
IF Compensation Control 8Dh 00h R/W
IF Differential Gain Control 8Eh 22h R/W
IF Low Frequency Gain Control 8Fh 44h R/W
IF High Frequency Gain Control 90h 00h R/W
Reserved
Weak Signal High Threshold 95h 60h R/W
Weak Signal Low Threshold 96h 50h R/W
Status Request 97h 00h R/W
3DYC NTSC VCR Threshold 98h 10h R/W
3DYC PAL VCR Threshold 99h 20h R/W
Vertical Line Count 9Ah–9Bh 00h R
Reserved
AGC Decrement Delay 9Eh R/W
Reserved
VDP TTX Filter 1 Mask 1 B1h 00h R/W
VDP TTX Filter 1 Mask 2 B2h 00h R/W
VDP TTX Filter 1 Mask 3 B3h 00h R/W
VDP TTX Filter 1 Mask 4 B4h 00h R/W
VDP TTX Filter 1 Mask 5 B5h 00h R/W
VDP TTX Filter 2 Mask 1 B6h 00h R/W
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
68h
6Ah-6Bh
6Eh
71h-73h
76h-77h
82h
91h-94h
9Ch-9Dh
9Fh-B0h
(1)
40 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-1. I2C Registers Summary (continued)
REGISTER NAME I2C SUBADDRESS DEFAULT R/W
VDP TTX Filter 2 Mask 2 B7h 00h R/W
VDP TTX Filter 2 Mask 3 B8h 00h R/W
VDP TTX Filter 2 Mask 4 B9h 00h R/W W
VDP TTX Filter 2 Mask 5 BAh 00h R/W
VDP TTX Filter Control BBh 00h R/W
VDP FIFO Word Count BCh R
VDP FIFO Interrupt Threshold BDh 80h R/W
Reserved BEh
VDP FIFO Reset BFh 00h R/W
VDP FIFO Output Control C0h 00h R/W
VDP Line Number Interrupt C1h 00h R/W
VDP Pixel Alignment C2h–C3h 01Eh R/W
Reserved C4h–D5h
VDP Line Start D6h 06h R/W
VDP Line Stop D7h 1Bh R/W
VDP Global Line Mode D8h FFh R/W
VDP Full Field Enable D9h 00h R/W
VDP Full Field Mode DAh FFh R/W
Interlaced/Progressive Status DBh R
Reserved
VBUS Data Access with No VBUS Address Increment E0h R/W
VBUS Data Access with VBUS Address Increment E1h R/W
VDP FIFO Read Data E2h R
Reserved
VBUS Address Access E8h–EAh 00 0000h R/W
Reserved
Interrupt Raw Status 0 F0h R
Interrupt Raw Status 1 F1h R
Interrupt Status 0 F2h R
Interrupt Status 1 F3h R
Interrupt Mask 0 F4h 00h R/W
Interrupt Mask 1 F5h 00h R/W
Interrupt Clear 0 F6h 00h R/W
Interrupt Clear 1 F7h 00h R/W
Reserved
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
DCh-DFh
E3h-E7h
EBh-EFh
F8h-FFh
(1)
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 41
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-2. VBUS Registers Summary
REGISTER NAME SUBADDRESS DEFAULT R/W
VBUS
Reserved
(2)(3)
00 0000h – 80 051Bh
VDP Closed Caption Data 80 051Ch – 80 051Fh R
VDP WSS/CGMS data 80 0520h – 80 0526h R
Reserved
(2)(3)
80 0527h – 80 052Bh
VDP VITC Data 80 052Ch – 80 0534h R
Reserved
(2)(3)
80 0535h – 80 053Fh
VDP V-Chip Data 80 0540h – 80 0543h R
Reserved
(2)(3)
80 0544h – 80 05FFh
VDP General Line Mode and Address 80 0600h – 80 0611h FFh, 00h R/W
Reserved
(2)(3)
80 0612h – 80 06FFh
VDP VPS/Gemstar EPG Data 80 0700h – 80 070Ch R
Reserved
(2)(3)
80 070Dh – A0 005Dh
Analog Output Control 2 A0 005Eh B2h R/W
Reserved
(2)(3)
A0 005Fh – B0 005Fh
Interrupt Configuration Register B0 0060h 00h R/W
Reserved
(2)(3)
B0 0062h – B0 0064h
Interrupt Mask 1 B0 0065h R
Interrupt Raw Status 1 B0 0069h R
Interrupt Status 1 B0 006Dh R
Interrupt Clear 1 B0 0071h R
Reserved
(2)(3)
B0 0073h – FF FFFFh
(1) R = Read only, W = Write only, R/W = Read and write
(2) Register addresses not shown in the register map summary are reserved and must not be written to.
(3) Writing to or reading from any value labeled "Reserved" register may cause erroneous operation of the TVP5160 decoder. For registers
with reserved bits, a 0b must be written to reserved bit locations unless otherwise stated.
(1)
42 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
3.1 Register Definitions
Table 3-3. Input/Output Select
Subaddress 00h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Input select [7:0]
Twelve input terminals can be configured to support composite, S-Video, and component YPbPr. Only values in Table 3-4 are valid.
NOTE: The video output can be either CVBS, Y, or G.
Table 3-4. Analog Channel and Video Mode Selection
MODE INPUT(S) SELECTED OUTPUT
CVBS VI_1 (default) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 00 VI_1
VI_2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 01 VI_2
VI_3 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 02 VI_3
VI_4 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 04 VI_4
VI_5 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 05 VI_5
VI_6 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 06 VI_6
VI_7 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 08 VI_7
VI_8 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 09 VI_8
VI_9 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0A VI_9
VI_10 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0C VI_10
VI_11 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0D VI_11
VI_12 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0E VI_12
S-Video VI_1(Y), VI_7(C) 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 40 VI_1(Y)
VI_2(Y), VI_8(C) 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 41 VI_2(Y)
VI_3(Y), VI_9(C) 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 42 VI_3(Y)
VI_1(Y), VI_10(C) 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 50 VI_1(Y)
VI_2(Y), VI_11(C) 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 51 VI_2(Y)
VI_3(Y), VI_12(C) 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 52 VI_3(Y)
VI_4(Y), VI_7(C) 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 44 VI_4(Y)
VI_5(Y), VI_8(C) 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 45 VI_5(Y)
VI_6(Y), VI_9(C) 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 46 VI_6(Y)
VI_4(Y), VI_10(C) 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 54 VI_4(Y)
VI_5(Y), VI_11(C) 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 55 VI_5(Y)
VI_6(Y), VI_12(C) 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 56 VI_6(Y)
YPbPr VI_10(Pb), VI_1(Y), VI_7(Pr) 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 90 VI_1(Y)
VI_11(Pb), VI_2(Y), VI_8(Pr) 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 91 VI_2(Y)
VI_12(Pb), VI_3(Y), VI_9(Pr) 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 92 VI_3(Y)
VI_10(Pb), VI_4(Y), VI_7(Pr) 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 94 VI_4(Y)
VI_11(Pb), VI_5(Y), VI_8(Pr) 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 95 VI_5(Y)
VI_12(Pb), VI_6(Y), VI_9(Pr) 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 96 VI_6(Y)
SCART VI_10(B), VI_4(G), VI_7(R), VI_1(CVBS) 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 C0 VI_1(CVBS)
VI_11(B), VI_5(G), VI_8(R), VI_2(CVBS) 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 C1 VI_2(CVBS)
VI_12(B), VI_6(G), VI_9(R), VI_3(CVBS) 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 C2 VI_3(CVBS)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 HEX
INPUT SELECT [7:0]
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 43
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-5. AFE Gain Control
Subaddress 01h
Default 0Fh
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved 1 1 1 AGC
Bit 3: 1b must be written to this bit
Bit 2: 1b must be written to this bit
Bit 1: 1b must be written to this bit
AGC: Controls automatic gain
0 = Manual
1 = Enable auto gain (default)
This setting only affects the analog front-end (AFE). The brightness and contrast controls are not affected by these settings.
Table 3-6. Video Standard Select
Subaddress 01h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Video standard [3:0]
Video standard [3:0]:
CVBS and S-Video Component video
0000 = Autoswitch mode (default) Autoswitch mode (default)
0001 = (M, J) NTSC Interlaced 525 (480i)
0010 = (B, D, G, H, I, N) PAL Interlaced 625 (576i)
0011 = (M) PAL Reserved
0100 = (Combination-N) PAL Reserved
0101 = NTSC 4.43 Reserved
0110 = SECAM Reserved
0111 = PAL 60 Reserved
1000 = Reserved Reserved
1001 = Reserved NTSC Progressive 525 (480p)
1010 = Reserved PAL Progressive 625 (576p)
The user can force the device to operate in a particular video standard mode by writing the appropriate value into this register. Changing
these bits will cause some register settings to be reset to their defaults.
Table 3-7. Operation Mode
Subaddress 01h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Power save
Power save
0 Normal operation (default)
=
1 Power save mode. Reduces the clock speed of the internal processor and switches off the ADCs. I2C interface is active and all
= current operating settings are preserved.
44 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-8. Autoswitch Mask
Subaddress 04h
Default 23h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved PAL 60 SECAM NTSC 4.43 (Nc) PAL (M) PAL PAL (M, J) NTSC
Autoswitch mode mask: Limits the video formats between which autoswitch is possible. See register 30h for masking the progressive
modes.
PAL 60
0 = Autoswitch does not include PAL 60 (default)
1 = Autoswitch includes PAL 60
SECAM
0 = Autoswitch does not include SECAM
1 = Autoswitch includes SECAM (default)
NTSC 4.43
0 = Autoswitch does not include NTSC 4.43 (default)
1 = Autoswitch includes NTSC 4.43
(Nc) PAL
0 = Autoswitch does not include (Nc) PAL (default)
1 = Autoswitch includes (Nc) PAL
(M) PAL
0 = Autoswitch does not include (M) PAL (default)
1 = Autoswitch includes (M) PAL
PAL
0 = Reserved
1 = Autoswitch includes (B, D, G, H, I, N) PAL (default)
(M, J) NTSC
0 = Reserved
1 = Autoswitch includes (M, J) NTSC (default)
Note: Bits 1 and 0 must always be 11b.
Table 3-9. Color Killer
Subaddress 05h
Default 10h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Automatic color killer Color killer threshold [4:0]
Automatic color killer:
00 = Automatic mode (default)
01 = Reserved
10 = Color killer enabled, the UV terminals are forced to a zero color state
11 = Color killer disabled
Color killer threshold [4:0]:
11111 = 31 (maximum)
10000 = 16 (default)
00000 = 0 (minimum)
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 45
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-10. Luminance Processing Control 1
Subaddress 06h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Pedestal Reserved VBI raw Reserved Luminance signal delay [2:0]
Pedestal:
0 = 7.5 IRE pedestal is present on the analog video input signal (default)
1 = Pedestal is not present on the analog video input signal
VBI raw:
0 = Disable (default)
1 = Enable
During the duration of the vertical blanking as defined by VBLK start and stop registers 22h through 25h, the chroma samples are replaced
by luma samples. This feature may be used to support VBI processing performed by an external device during the vertical blanking interval.
In order to use this bit, the output format must be the 10-bit, ITU-R BT.656 mode.
Luminance signal delay [2:0]: Luminance signal delays respect to chroma signal in 1× pixel clock increments.
011 = 3 pixel clocks delay
010 = 2 pixel clocks delay
001 = 1 pixel clock delay
000 = 0 pixel clock delay (default)
111 = –1 pixel clock delay
110 = –2 pixel clocks delay
101 = –3 pixel clocks delay
100 = 0 pixel clock delay
Table 3-11. Luminance Processing Control 2
Subaddress 07h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Luma filter select [1:0] Reserved Peaking gain [1:0] Reserved
Luma filter selected [1:0]:
00 = Luminance adaptive comb enable (default on CVBS and SECAM)
01 = Luminance adaptive comb disable (trap filter selected)
10 = Luma comb/trap filter bypassed (default on S-Video, component mode)
11 = Reserved
Peaking gain [1:0]:
00 = 0 (default)
01 = 0.5
10 = 1
11 = 2
46 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-12. Luminance Processing Control 3
Subaddress 08h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Trap filter select [1:0]
Trap filter select[1:0] selects one of the four trap filters to produce the luminance signal by removing the chrominance signal from the
composite video signal. The stop band of the chroma trap filter is centered at the chroma subcarrier frequency with stopband bandwidth
controlled by the two control bits. Changing this register will trade luma resolution for dot crawl.
Trap filter stop band bandwidth (MHz):
Filter select [1:0] NTSC ITU-R 601 PAL ITU-R 601
00 (default) 1.2129 1.2129
01 0.8701 0.8701
10 0.7183 0.7383
11 0.5010 0.5010
Table 3-13. Luminance Brightness
Subaddress 09h
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Brightness [7:0]
Brightness [7:0]: This register works for CVBS and S-Video luminance. See subaddress 2Fh.
0000 0000 = 0 (dark)
1000 0000 = 128 (default)
1111 1111 = 255 (bright)
For composite and S-Video outputs, the output black level relative to the nominal black level (64 out of 1024) as a function of the
Brightness[7:0] setting is as follows.
Black Level = nominal_black_level + (MB+ 1) × (Brightness[7:0] - 128)
Where MBis the brightness multiplier setting in the Brightness and Contrast Range Extender register at I2C subaddress 2Fh.
Table 3-14. Luminance Contrast
Subaddress 0Ah
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Contrast [7:0]
Contrast [7:0]: This register works for CVBS and S-Video luminance. See subaddress 2Fh.
0000 0000 = 0 (minimum contrast)
1000 0000 = 128 (default)
1111 1111 = 255 (maximum contrast)
For composite and S-Video outputs, the total luminance gain relative to the nominal luminance gain as a function of the Contrast [7:0]
setting is as follows.
Luminance Gain = (nominal_luminance_gain) × [Contrast[7:0] / 64 / (2^MC) + MC- 1]
Where MCis the contrast multiplier setting in the Brightness and Contrast Range Extender register at I2C subaddress 2Fh.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 47
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-15. Chrominance Saturation
Subaddress 0Bh
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Saturation [7:0]
Saturation [7:0]: This register works for CVBS and S-Video chrominance.
0000 0000 = 0 (no color)
1000 0000 = 128 (default)
1111 1111 = 255 (maximum)
For composite and S-Video outputs, the total chrominance gain relative to the nominal chrominance gain as a function of the Saturation
[7:0] setting is as follows.
Chrominance Gain = (nominal_chrominance_gain) × (Saturation[7:0] / 128)
Table 3-16. Chroma Hue
Subaddress 0Ch
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Hue [7:0]
Hue [7:0] (does not apply to a component or SECAM video):
0111 1111 = 180 degrees
0000 0000 = 0 degrees (default)
1000 0000 = –180 degrees
www.ti.com
48 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-17. Chrominance Processing Control 1
Subaddress 0Dh
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
3DYC TBC Reserved Chroma adaptive comb enable 3DNR Automatic color gain control
3DYC, frame recursive noise reduction (3DNR), and time base correction (TBC) can be used simultaneously or independently.
Memory requirements:
3DYC 3DNR Function
0 0 None None
1 0 3DYC only 16 Mbits
0 1 3DNR only 16 Mbits
1 1 3DYC + 3DNR 32 Mbits
Note: The SDRAM configuration register must be programmed before enabling features that require the SDRAM. Failure to do so will
result in incorrect operation of the memory controller
3DYC:
0 = Disable; the 2D adaptive 5-line comb filter is enabled (default)
1 = Enable
3DYC enhances 2D Y/C separation by utilizing temporal-based, or frame-based information. 3DYC requires the use of the frame buffer
memory and can be used simultaneously with 3DNR and TBC.
TBC:
00 = Disable (default)
01 = On
10 = Automatic selection
11 = Automatic selection
Line-based time correction corrects for horizontal phase errors encountered during video decoding up to ±80 pixels of error. TBC can
be used simultaneously with 3DYC and 3DNR. TBC does not require external memory.
Chrominance adaptive comb enable:
0 = Enable (default)
1 = Disable
This bit is effective on composite video only.
3DNR:
0 = Disable (default)
1 = Enable
Frame recursive noise reduction minimizes the amount of noise in interlaced CVBS, S-Video, or component inputs. 3DNR requires the
use of the frame buffer memory and can be used simultaneously with 3DYC and TBC.
Note: Noise reduction can not be used on progressive inputs.
Automatic color gain control (ACGC) [1:0]:
00 = ACGC enabled (default)
01 = Reserved
10 = ACGC disabled, ACGC set to the nominal value
11 = ACGC frozen to the previously set value
External Memory
Required
[1:0]
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 49
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-18. Chrominance Processing Control 2
Subaddress 0Eh
Default 0Ch
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved PAL WCF Chrominance filter select [1:0]
compensation
This register trades chroma bandwidth for less false color.
PAL compensation: This bit has no effect in NTSC and SECAM modes.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled (default)
Wideband chroma LPF filter (WCF):
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled (default)
Chrominance filter select [1:0]:
00 = Disabled (default)
01 = Notch 1
10 = Notch 2
11 = Notch 3
Table 3-19. R/Pr Saturation
Subaddress 10h
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
R/Pr saturation [7:0]
R/Pr saturation [7:0]: This register works only with YPbPr component video. For RGB video, use the AFE gain registers.
0000 0000 = minimum
1000 0000 = default
1111 1111 = maximum
For component video, the total R/Pr gain relative to the nominal R/Pr gain as a function of the R/Pr saturation[7:0] setting is as follows.
R/Pr Gain = (nominal_chrominance_gain) × (R/Pr saturation[7:0] / 128)
www.ti.com
Table 3-20. G/Y Saturation
Subaddress 11h
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
G/Y contrast [7:0]
G/Y contrast [7:0]: This register works only with YPbPr component video. For RGB video, use the AFE gain registers.
0000 0000 = minimum
1000 0000 = default
1111 1111 = maximum
For component video outputs, the total luminance gain relative to the nominal luminance gain as a function of the G/Y contrast[7:0] is
as follows.
G/Y Gain = (nominal_luminance_gain) × (G/Y contrast[7:0] / 128)
50 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-21. B/Pb Saturation
Subaddress 12h
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
B/Pb saturation[7:0]
B/Pb saturation [7:0]: This register works only with YPbPr component video. For RGB video, use the AFE gain registers.
0000 0000 = minimum
1000 0000 = default
1111 1111 = maximum
For component video, the total Pb gain relative to the nominal Pb gain as a function of the B/Pb saturation[7:0] setting is as follows.
B/Pb Gain = (nominal_chrominance_gain) × (B/Pb saturation[7:0] / 128)
Table 3-22. G/Y Brightness
Subaddress 14h
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
G/Y brightness[7:0]
G/Y brightness [7:0]: This register works only with YPbPr component video. For RGB video, use the AFE gain registers.
0000 0000 = minimum
1000 0000 = default
1111 1111 = maximum
For component video, the output black level relative to the nominal black level (64 out of 1024) as a function of G/Y brightness[7:0] is
as follows.
Black Level = nominal_black_level + (G/Y brightness[7:0] - 128)
Table 3-23. AVID Start Pixel
Subaddress 16h–17h
Default 55h/5Fh
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
16h AVID start [7:0]
17h Reserved AVID active Reserved AVID start [9:8]
AVID active
0 = AVID out active in VBLK (default)
1 = AVID out inactive in VBLK
AVID start [9:0]: AVID start pixel number, this is a absolute pixel location from HS start pixel 0.
The TVP5160 decoder updates the AVID start only when the AVID start MSB byte is written to. The AVID start pixel register also
controls the position of the SAV code. If these registers are modified, then the TVP5160 decoder retains the values for each video
standard until the device is reset. The values for a particular video standard must be set by forcing the decoder to the desired video
standard first using register 02h then setting this register. This must be repeated for each video standard where the default values need
to be changed.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 51
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-24. AVID Stop Pixel
Subaddress 18h–19h
Default 325h/32Fh
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
18h AVID stop [7:0]
19h Reserved AVID stop [9:8]
AVID stop [9:0]: AVID stop pixel number. The number of pixels of active video must be an
even number. This is a absolute pixel location from HS start pixel 0.
The TVP5160 decoder updates the AVID stop only when the AVID stop MSB byte is written
to. The AVID stop pixel register also controls the position of the EAV code. If these registers
are modified, then the TVP5160 decoder retains the values for each video standard until the
device is reset. The values for a particular video standard must be set by forcing the decoder
to the desired video standard first using register 02h then setting this register. This must be
repeated for each video standard where the default values need to be changed.
Table 3-25. HS Start Pixel
Subaddress 1Ah–1Bh
Default 000h
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1Ah HS start [7:0]
1Bh Reserved HS start [9:8]
HS start pixel [9:0]: This is an absolute pixel location from HS start pixel 0.
The TVP5160 decoder updates the HS start only when the HS start MSB byte is written to. If these registers are modified, then the
TVP5160 decoder retains the values for each video standard until the device is reset. The values for a particular video standard must be
set by forcing the decoder to the desired video standard first using register 02h then setting this register. This must be repeated for each
video standard where the default values need to be changed.
Table 3-26. HS Stop Pixel
Subaddress 1Ch–1Dh
Default 040h
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1Ch HS stop [7:0]
1Dh Reserved HS stop [9:8]
HS stop [9:0]: This is a absolute pixel location from HS start pixel 0.
The TVP5160 decoder updates the HS stop only when the HS stop MSB byte is written to. If these registers are modified, then the
TVP5160 decoder retains the values for each video standard until the device is reset. The values for a particular video standard must be
set by forcing the decoder to the desired video standard first using register 02h then setting this register. This must be repeated for each
video standard where the default values need to be changed.
Table 3-27. VS Start Line
Subaddress 1Eh–1Fh
Default 004h/001h
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1Eh VS start [7:0]
1Fh Reserved VS start [9:8]
VS start [9:0]: This is a absolute line number.
The TVP5160 decoder updates the VS start only when the VS start MSB byte is written to. If these registers are modified, then the
TVP5160 decoder retains the values for each video standard until the device is reset. The values for a particular video standard must be
set by forcing the decoder to the desired video standard first using register 02h then setting this register. This must be repeated for each
video standard where the default values need to be changed.
52 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-28. VS Stop Line
Subaddress 20h–21h
Default 004h/001h
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
20h VS stop [7:0]
21h Reserved VS stop [9:8]
VS stop [9:0]: This is an absolute line number.
The TVP5160 decoder updates the VS stop only when the VS stop MSB byte is written to. If these registers are modified, then the
TVP5160 decoder retains the values for each video standard until the device is reset. The values for a particular video standard must be
set by forcing the decoder to the desired video standard first using register 02h then setting this register. This must be repeated for each
video standard where the default values need to be changed.
Table 3-29. VBLK Start Line
Subaddress 22h–23h
Default 001h/26Fh
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
22h VBLK start [7:0]
23h Reserved VBLK start [9:8]
VBLK start [9:0]: This is an absolute line number.
The TVP5160 decoder updates the VBLK start line only when the VBLK start MSB byte is written to. If these registers are modified, then
the TVP5160 decoder retains the values for each video standard until the device is reset. The values for a particular video standard must
be set by forcing the decoder to the desired video standard first using register 02h then setting this register. This must be repeated for each
video standard where the default values need to be changed.
Table 3-30. VBLK Stop Line
Subaddress 24h–25h
Default 001h/26Fh
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
24h VBLK stop [7:0]
25h Reserved VBLK stop [9:8]
VBLK stop [9:0]: This is an absolute line number.
The TVP5160 decoder updates the VBLK stop only when the VBLK stop MSB byte is written to. If these registers are modified, then the
TVP5160 decoder retains the values for each video standard until the device is reset. The values for a particular video standard must be
set by forcing the decoder to the desired video standard first using register 02h then setting this register. This must be repeated for each
video standard where the default values need to be changed.
Table 3-31. Embedded Sync Offset Control 1
Subaddress 26h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Offset [7:0]
This register allows the line position of the embedded F bit and V bit signals to be offset from the 656 standard positions. This register is
only applicable to input video signals with standard number of lines.
0111 1111 = 127 lines
...
0000 0001 = 1 line
0000 0000 = 0 line
1111 1111 = –1 line
...
1000 0000 = –128 lines
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 53
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-32. Embedded Sync Offset Control 2
Subaddress 27h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Offset [7:0]
This register allows the line relationship between the embedded F bit and V bit signals to be offset from the 656 standard positions, and
moves F relative to V. This register is only applicable to input video signals with standard number of lines.
0111 1111 = 127 lines
...
0000 0001 = 1 line
0000 0000 = 0 line
1111 1111 = –1 line
...
1000 0000 = –128 lines
Table 3-33. Fast-Switch Control
Subaddress 28h
Default C0h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Mode [2:0] Reserved Polarity FSO Polarity FSS
Mode [2:0]:
000 = CVBS ↔ SCART
001 = CVBS, S_VIDEO ↔ Digital overlay
010 = Component ↔ Digital overlay
011 = (CVBS ↔ SCART) ↔ Digital overlay
100 = (CVBS ↔ Digital overlay) ↔ SCART
101 = CVBS ↔ (SCART ↔ Digital overlay)
110 = Composite (default)
111 = Component
Polarity FSO:
0 = If FSO = 0, then output = YPbPr
If FSO = 1, then output = Digital RGB (default)
1 = If FSO = 0, then output = Digital RGB
If FSO = 1, then output = YPbPr
Polarity FSS:
0 = If FSO = 0, then output = RGB
If FSO = 1, then output = CVBS (4A) (default)
1 = If FSO = 0, then output = CVBS (4A)
If FSO = 1, then output = RGB
See TI application note SLEA016, TVP5146 SCART and OSD, for more information on SCART overlay and digital overlay programming.
54 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-34. Fast-Switch Overlay Delay
Subaddress 29h
Default 17h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved FSO delay [4:0]
Overlay delay [4:0]: Adjusts delay between digital RGB and FSO
11111 = 8 pixel delay
.
.
.
11000 = 1 pixel delay
10111 = 0 delay (default)
10110 = –1 pixel delay
.
.
.
00000 = –23 pixel delay
When SCART mode is active (RGB component) the recommended setting for this register is 1Bh; otherwise, 17h is recommended.
Table 3-35. Fast-Switch SCART Delay
Subaddress 2Ah
Default 1Ch
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved FSS delay [4:0]
FSS delay [4:0]: Adjusts delay between FSS and component RGB
11111 = 3 pixel delay
...
11101 = 1 pixel delay
11100 = 0 delay (default)
11011 = –1 pixel delay
...
00000 = –23 pixel delay
Table 3-36. Overlay Delay
Subaddress 2Bh
Default 12h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Overlay delay [4:0]
Overlay delay[4:0]: Adjusts delay between digital RGB and component video
11111 = 13 pixel delay
....
10011 = 1 pixel delay
10010 = 0 delay (default)
10001 = –1 pixel delay
...
00000 = –18 pixel delay
When SCART mode is active (RGB component) the recommended setting for this register is 16h; otherwise, 12h is recommended.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 55
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-37. SCART Delay
Subaddress 2Ch
Default 56h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved SCART delay [6:0]
This register must be changed in multiples of 2 to maintain the CbCr relationship. SCART delay[6:0]: Adjusts delay between CVBS and
component video.
101 1111 = 9 pixel delay
...
101 0111 = 1 pixel delay
101 0110 = 0 delay (default)
101 0101 = –1 pixel delay
...
000 0000 = –86 pixel delay
Table 3-38. CTI Control
Subaddress 2Eh
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CTI coring [3:0] CTI gain [3:0]
CTI coring [3:0]: 4-bit CTI coring limit control values, unsigned, linear control range from 0 to ±60, step size = 4
1111 = ±60
...
0001 = ±4
0000 = 0 (default)
CTI gain [3:0]: 4-bit CTI gain control values, unsigned, linear control range from 0 to 15/16, step size = 1/16
1111 = 15/16
...
0001 = 1/16
0000 = 0 (default)
Table 3-39. Brightness and Contrast Range Extender
Subaddress 2Fh
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Contrast Brightness multiplier [3:0]
Contrast multiplier [4]: (MC) Increases the contrast control range for composite and S-Video modes.
0 = 2x contrast control range (default), Gain = n/64 – 1 where n is the contrast control and 64 ≤ n ≤ 255
1 = Normal contrast control range, Gain = n/128 where n is the contrast control and 0 ≤ n ≤ 255
Brightness multiplier [3:0]: (MB) Increases the brightness control range for composite and S-Video modes from 1x to 16x.
0h = 1x(default)
1h = 2x
3h = 4x
7h = 8x
Fh = 16x
Note: In general, the brightness multiplier should be set to 0h for 10-bit outputs and 3h for 8-bit outputs
56 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
multiplier
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-40. Component Autoswitch Mask
Subaddress 30h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
576i 480i 576p 480p
Masks the component progressive/interlaced modes from being processed in the autoswitch routines.
480p
0 = Autoswitch does not include 480p progressive modes (default)
1 = Autoswitch includes 480p progressive mode
576p
0 = Autoswitch does not include 576p progressive mode (default)
1 = Autoswitch includes 576p progressive mode
480i
0 = Autoswitch does not include 480i interlaced modes (default)
1 = Autoswitch includes 480i interlaced mode
576i
0 = Autoswitch does not include 576i interlaced mode (default)
1 = Autoswitch includes 576i interlaced mode
Table 3-41. Sync Control
Subaddress 32h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Polarity FID Polarity VS Polarity HS VS/VBLK HS/CS
Polarity FID: determines polarity of FID pin
0 = First field high, second field low (default)
1 = First field low, second field high
Polarity VS: determines polarity of VS pin
0 = Active low (default)
1 = Active high
Polarity HS: determines polarity of HS pin
0 = Active low (default)
1 = Active high
VS/VBLK:
0 = VS pin outputs vertical sync (default)
1 = VS pin outputs vertical blank
HS/CS:
0 = HS pin outputs horizontal sync (default)
1 = HS pin outputs composite sync
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 57
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-42. Output Formatter Control 1
Subaddress 33h
Default 40h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved YCbCr code range CbCr code Reserved Output format [2:0]
YCbCr output code range:
0 = ITU-R BT.601 coding range (Y ranges from 64 to 940, Cb and Cr range from 64 to 960)
1 = Extended coding range (Y, Cb, and Cr range from 4 to 1016) (default)
CbCr code format:
0 = Offset binary code (2s complement + 512) (default)
1 = Straight binary code (2s complement)
Output format [2:0]:
000 = 10-bit 4:2:2 (pixel × 2 rate) with embedded syncs (ITU-R BT.656)
001 = 20-bit 4:2:2 (pixel rate) with discrete syncs
010 = Reserved
011 = 10-bit 4:2:2 with discrete syncs
100 = 20-bit 4:2:2 (pixel rate) with embedded syncs
101–111 = Reserved
Note: 10-bit mode is also used for raw VBI output mode when bit 4 (VBI raw) in the luminance processing control 1 register at subaddress
06h is set.
Table 3-43. Output Formatter Control 2
Subaddress 34h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Data enable "Blue" Screen Output [1:0] Clock polarity SCLK enable
Data enable: Y[9:0] and C[9:0] output enable
0 = Y[9:0] and C[9:0] high-impedance (default)
1 = Y [9:0] and C[9:0] active
"Blue" Screen Output [1:0]:
00 = Normal operation (default)
01 = "Blue" screen out when the TVP5160 decoder detects lost lock (with tuner input but not with VCR)
10 = Force "Blue" screen out
11 = Reserved
Fully programmable color of "blue screen" to support clean input/channel switching. When enabled, in case of lost lock, or when forced, the
decoder waits until the end of the current frame, then switches the output data to a programmable color. Once displaying the "blue screen",
the inputs and or RF channel can be switched without causing snow or noise to be displayed on the digital output data. Once the inputs
have settled, the "blue screen" can be disabled, and the decoder then waits until the end of the current video frame before re-enabling the
video stream data to the output ports.
Clock polarity:
0 = Data clocked out on the falling edge of SCLK (default)
1 = Data clocked out on the rising edge of SCLK
SCLK enable:
0 = SCLK outputs are high-impedance (default)
1 = SCLK outputs are enabled
58 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-44. Output Formatter Control 3
Subaddress 35h
Default FFh
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
GPIO [1:0] AVID [1:0] GLCO [1:0] FID [1:0]
GPIO [1:0]: GPIO pin (pin 82) function select
00 = GPIO is 0b output
01 = GPIO is 1b output
10 = Reserved
11 = GPIO in logic input (default)
AVID [1:0]: AVID pin function select
00 = AVID is 0b output
01 = AVID is 1b output
10 = AVID is active video indicator output
11 = AVID is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
GLCO [1:0]: GLCO pin function select
00 = GLCO is 0b output
01 = GLCO is 1b output
10 = GLCO is genlock output
11 = GLCO is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
FID [1:0]: FID pin function select
00 = FID is 0b output
01 = FID is 1b output
10 = FID is FID output
11 = FID is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
Table 3-45. Output Formatter Control 4
Subaddress 36h
Default FFh
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
VS/VBLK [1:0] HS/CS [1:0] C_1 [1:0] C_0 [1:0]
VS/VBLK [1:0]: VS pin function select
00 = VS is 0b output
01 = VS is 1b output
10 = VS/VBLK is vertical sync or vertical blank output corresponding to bit 1 (VS/VBLK) in the sync control register at subaddress 32h
(see Section 4.1.37)
11 = VS is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
HS/CS [1:0]: HS pin function select
00 = HS is 0b output
01 = HS is 1b output
10 = HS/CS is horizontal sync or composite sync output corresponding to bit 0 (HS/CS) in the sync control register at subaddress 32h
(see Section 4.1.37)
11 = HS is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
C_1 [1:0]: C_1 pin function select
00 = C_1 is 0b output
01 = C_1 is 1b output
10 = Reserved
11 = C_1 is logic input (default)
C_0 [1:0]: C_0 pin function select
00 = C_0 is 0b output
01 = C_0 is 1b output
10 = Reserved
11 = C_0 is logic input (default)
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 59
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-46. Output Formatter Control 5
Subaddress 37h
Default FFh
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
C_5 [1:0] C_4 [1:0] C_3 [1:0] C_2 [1:0]
C_5 [1:0]: C_5 pin function select
00 = C_5 is 0b output
01 = C_5 is 1b output
10 = Reserved
11 = C_5 is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
C_4 [1:0]: C_4 pin function select
00 = C_4 is 0b output
01 = C_4 is 1b output
10 = Reserved
11 = C_4 is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
C_3 [1:0]: C_3 pin function select
00 = C_3 is 0b output
01 = C_3 is 1b output
10 = Reserved
11 = C_3 is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
C_2 [1:0]: C_2 pin function select
00 = C_2 is 0b output
01 = C_2 is 1b output
10 = Reserved
11 = C_2 is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
www.ti.com
60 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-47. Output Formatter Control 6
Subaddress 38h
Default FFh
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
C_9 [1:0] C_8 [1:0] C_7 [1:0] C_6 [1:0]
C_9 [1:0]: C_9 pin function select
00 = C_9 is 0b output
01 = C_9 is 1b output
10 = Reserved
11 = C_9 is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
Note: If overlay is enabled, then C[9] functions as FSO regardless of the setting of register 38h.
C_8 [1:0]: C_8 pin function select
00 = C_8 is 0b output
01 = C_8 is 1b output
10 = Reserved
11 = C_8 is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
C_7 [1:0]: C_7 pin function select
00 = C_7 is 0b output
01 = C_7 is 1b output
10 = Reserved
11 = C_7 is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
C_6 [1:0]: C_6 pin function select
00 = C_6 is 0b output
01 = C_6 is 1b output
10 = Reserved
11 = C_6 is logic input (default). In this mode the pin is used as GPIO.
Table 3-48. Clear Lost Lock Detect
Subaddress 39h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Clear lost lock detect
Clear lost lock detect: Clear bit 4 (lost lock detect) in the status 1 register at subaddress 3Ah
0 = No effect (default)
1 = Clears bit 4 in the status 1 register
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 61
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-49. Status 1
Subaddress 3Ah
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Peak white Line-alternating Field rate Lost lock detect Color Vertical sync Horizontal sync TV/VCR status
detect status status status subcarrier lock lock status lock status
Peak white detect status:
0 = Peak white is not detected
1 = Peak white is detected
Line-alternating status:
0 = Non line-alternating
1 = Line-alternating
Field rate status:
0 = 60 Hz
1 = 50 Hz
Lost lock detect:
0 = No lost lock since this bit was last cleared
1 = Lost lock since this bit was last cleared
Color subcarrier lock status:
0 = Color subcarrier is not locked
1 = Color subcarrier is locked
Vertical sync lock status:
0 = Vertical sync is not locked
1 = Vertical sync is locked
Horizontal sync lock status:
0 = Horizontal sync is not locked
1 = Horizontal sync is locked TV/VCR status: 0 = TV 1 = VCR
status
62 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-50. Status 2
Subaddress 3Bh
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Signal present Weak signal PAL switch Field sequence Color killed Macrovision detection [2:0]
Signal present detection:
0 = Signal not present
1 = Signal present
Weak signal detection:
0 = No weak signal
1 = Weak signal mode
PAL switch polarity of first line of odd field:
0 = PAL switch is 0b
1 = PAL switch is 1b
Field sequence status:
0 = Even field
1 = Odd field
Color killed:
0 = Color killer not active
1 = Color killer activated
Macrovision detection [2:0]:
000 = No copy protection
001 = AGC pulses/pseudo syncs present (Type 1)
010 = 2-line colorstripe only present
011 = AGC pulses/pseudo syncs and 2-line colorstripe present (Type 2)
100 = Reserved
101 = Reserved
110 = 4-line colorstripe only present
111 = AGC pulses/pseudo syncs and 4-line colorstripe present (Type 3)
detection polarity status
Table 3-51. AGC Gain Status
Subaddress 3Ch–3Dh
Read only
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
3Ch Fine Gain [7:0]
3Dh Coarse Gain [3:0] Fine Gain[11:8]
Fine gain [11:0]: This register provides the fine gain value of sync channel.
1111 1111 1111 = 1.9995
1000 0000 0000 = 1
0100 0000 0000 = 0.5
Coarse gain [3:0]: This register provides the coarse gain value of sync channel.
1111 = 2
0101 = 1
0000 = 0.5
These AGC gain status registers are updated automatically by the TVP5160 decoder with AGC on, in manual gain control mode these
register values are not updated by the TVP5160 decoder.
Since this register is a multi-byte register, it is necessary to capture the setting into the register to ensure that the value is not updated
between reading the lower and upper bytes. In order to cause this register to capture the current settings, bit 0 of I2C register 97h (status
request) must be set to 1b. Once the internal processor has updated this register, bit 0 of register 97h is cleared, indicating that both bytes
of the AGC gain status register have been updated and can be read. Either byte may be read first since no further update occurs until bit 0
of 97h is set to 1b again.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 63
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-52. Video Standard Status
Subaddress 3Fh
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Autoswitch Reserved Video standard [3:0]
Autoswitch mode
0 = Single standard set
1 = Autoswitch mode enabled
Video standard [3:0]:
CVBS and S-Video Component Video
0000 = Reserved Reserved
0001 = (M, J) NTSC Interlaced 525 (480i)
0010 = (B, D, G, H, I, N) PAL Interlaced 625 (576i)
0011 = (M) PAL Reserved
0100 = (Combination-N) PAL Reserved
0101 = NTSC 4.43 Reserved
0110 = SECAM Reserved
0111 = PAL 60 Reserved
1000 = Reserved Reserved
1001 = Reserved Progressive 525 (480p)
1010 = Reserved Progressive 625 (576p)
This register contains information about the detected video standard that the device is currently operating. When in autoswitch mode, this
register can be tested to determine which video standard as has been detected.
Table 3-53. GPIO Input 1
Subaddress 40h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
C_7 C_6 C_5 C_4 C_3 C_2 C_1 C_0
C_x input status:
0 = Input is a low
1 = Input is a high
These status bits are only valid when pins are used as input and are updated at every line.
64 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-54. GPIO Input 2
Subaddress 41h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
AVID GPIO GLCO VS HS FID C_9 C_8
AVID input pin status:
0 = Input is a low
1 = Input is a high
GPIO (Pin 82) input pin status:
0 = Input is a low
1 = Input is a high
GLCO input pin status:
0 = Input is a low
1 = Input is a high
VS input pin status:
0 = Input is a low
1 = Input is a high
HS input status:
0 = Input is a low
1 = Input is a high
FID input status:
0 = Input is a low
1 = Input is a high
C_x input status:
0 = Input is a low
1 = Input is a high
These status bits are only valid when pins are used as input and its states updated at every line.
Table 3-55. Back End AGC Status 1
Subaddress 44h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Gain [7:0]
Current back end AGC ratio = Gain/128
Table 3-56. AFE Coarse Gain for CH 1
Subaddress 46h
Default 20h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CGAIN 1 [3:0] Reserved
CGAIN 1 [3:0]: Coarse Gain = 0.5 + (CGAIN 1)/10 where 0 ≤ CGAIN 1 ≤ 15
This register only works in manual gain control mode. When AGC is active, writing to any value is ignored.
1111 = 2
1110 = 1.9
1101 = 1.8
...
0010 = 0.7(default)
0001 = 0.6
0000 = 0.5
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 65
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-57. AFE Coarse Gain for CH 2
Subaddress 47h
Default 20h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CGAIN 2 [3:0] Reserved
CGAIN 2 [3:0]: Coarse Gain = 0.5 + (CGAIN 2)/10 where 0 ≤ CGAIN 2 ≤ 15.
This register only works in manual gain control mode. When AGC is active, writing to any value is ignored.
1111 = 2
1110 = 1.9
1101 = 1.8
...
0010 = 0.7(default)
0001 = 0.6
0000 = 0.5
Table 3-58. AFE Coarse Gain for CH 3
Subaddress 48h
Default 20h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CGAIN 3 [3:0] Reserved
CGAIN 3 [3:0]: Coarse Gain = 0.5 + (CGAIN 3)/10 where 0 ≤ CGAIN 3 ≤ 15.
This register only works in manual gain control mode. When AGC is active, writing to any value is ignored.
1111 = 2
1110 = 1.9
1101 = 1.8
...
0010 = 0.7(default)
0001 = 0.6
0000 = 0.5
www.ti.com
Table 3-59. AFE Coarse Gain for CH 4
Subaddress 49h
Default 20h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CGAIN 4 [3:0] Reserved
CGAIN 4 [3:0]: Coarse Gain = 0.5 + (CGAIN 4)/10 where 0 ≤ CGAIN 4 ≤ 15.
This register only works in manual gain control mode. When AGC is active, writing to any value is ignored.
1111 = 2
1110 = 1.9
1101 = 1.8
...
0010 = 0.7(default)
0001 = 0.6
0000 = 0.5
66 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-60. AFE Fine Gain for B/Pb
Subaddress 4Ah–4Bh
Default 900h
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
4Ah FGAIN 1 [7:0]
4Bh Reserved FGAIN 1 [11:8]
FGAIN 1 [11:0]: This fine gain applies to component B/Pb.
Fine Gain = (1/2048) * FGAIN where 0 ≤ FGAIN 1 ≤ 4095
This register is only updated when the MSB (register 4Bh) is written to.
This register only works in manual gain control mode. When AGC is active, writing to any value is ignored.
1111 1111 1111 = 1.9995
1100 0000 0000 = 1.5
1001 0000 0000 = 1.25 (default)
1000 0000 0000 = 1
0100 0000 0000 = 0.5
0011 1111 1111 to 0000 0000 0000 = Reserved
Table 3-61. AFE Fine Gain for G/Y/Chroma
Subaddress 4Ch–4Dh
Default 900h
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
4Ch FGAIN 2 [7:0]
4Dh Reserved FGAIN 2 [11:8]
FGAIN 2 [11:0]: This gain applies to component G/Y channel or S-Video chroma.
This register is only updated when the MSB (register 4Dh) is written to.
This register only works in manual gain control mode. When AGC is active, writing to any value is ignored.
1111 1111 1111 = 1.9995
1100 0000 0000 = 1.5
1001 0000 0000 = 1.25 (default)
1000 0000 0000 = 1
0100 0000 0000 = 0.5
0011 1111 1111 to 0000 0000 0000 = Reserved
Table 3-62. AFE Fine Gain for R/Pr
Subaddress 4Eh–4Fh
Default 900h
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
4Eh FGAIN 3 [7:0]
4Fh Reserved FGAIN 3 [11:8]
FGAIN 3 [11:0]: This fine gain applies to component R/Pr.
This register is only updated when the MSB (register 4Fh) is written to.
This register only works in manual gain control mode. When AGC is active, writing to any value is ignored.
1111 1111 1111 = 1.9995
1100 0000 0000 = 1.5
1001 0000 0000 = 1.25 (default)
1000 0000 0000 = 1
0100 0000 0000 = 0.5
0011 1111 1111 to 0000 0000 0000 = Reserved
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 67
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-63. AFE Fine Gain for CVBS/Luma
Subaddress 50h–51h
Default 900h
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
50h FGAIN 4 [7:0]
51h Reserved FGAIN 4 [11:8]
FGAIN 4 [11:0]: This fine gain applies to CVBS or S-Video luma (see AFE fine gain for Pb register)
This register is only updated when the MSB (register 51h) is written to.
This register only works in manual gain control mode. When AGC is active, writing to any value is ignored.
1111 1111 1111 = 1.9995
1100 0000 0000 = 1.5
1001 0000 0000 = 1.25 (default)
1000 0000 0000 = 1
0100 0000 0000 = 0.5
0011 1111 1111 to 0000 0000 0000 = Reserved
Table 3-64. 656 Version
Subaddress 57h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved 656 version Reserved
656 version
0 = Timing confirms to ITU-R BT.656-4 specifications (default)
1 = Timing confirms to ITU-R BT.656-3 specifications
www.ti.com
Table 3-65. SDRAM Control
Subaddress 59h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved SDRAM_CLK delay control Enable Configuration[1:0]
Configuration[1:0]
Bit 1 Bit 0 Arrangement
0 0 2 banks × 2048 rows × 256 columns 16 Mbits
0 1 4 banks × 2048 rows × 256 columns 32 Mbits
1 0 2 banks × 4096 rows × 256 columns 32 Mbits
1 1 4 banks × 4096 rows × 256 columns 64 Mbits
Memories with more rows, columns, and/or banks can be used as long as the minimum requirements are met. Additional rows, columns,
and/or banks are ignored and unused by the memory controller.
The memory controller must be configured before enabling 3DYC or 3DNR; otherwise, incorrect operation of the memory controller will
result.
Enable:
0 = SDRAM controller disabled (default)
1 = SDRAM controller enabled
SDRAM_CLK delay control[3:0]
This register changes the delay from the default position of SDRAM_CLK in increments of approximately 0.58 ns.
Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Delay
0 0 0 0 0 (default)
0 0 0 1 0.58 ns
1 0 0 0 1.16 ns
1 1 1 1 9.3 ns
68 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-66. 3DNR Y Noise Sensitivity
Subaddress 5Ah
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Y noise sensitivity[7:0]
Table 3-67. 3DNR UV Noise Sensitivity
Subaddress 5Bh
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
UV noise sensitivity[7:0]
Table 3-68. 3DNR Y Coring Threshold Limit
Subaddress 5Ch
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Y coring threshold [7:0]
Table 3-69. 3DNR UV Coring Threshold Limit
Subaddress 5Dh
Default 40h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
UV coring threshold [7:0]
Table 3-70. 3DNR Low Noise Limit
Subaddress 5Eh
Default 40h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Threshold to indicate when Low Noise Present[7:0]
This register sets a threshold for low noise present.
Table 3-71. "Blue" Screen Y Control
Subaddress 5Fh
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Y value [9:2]
The Y value of the color screen output when enabled by bit 2 or 3 of the output formatter 2 register is programmable using a 10-bit value.
The 8 MSB, bits[9:2], are represented in this register.
The remaining two LSB are found in the "Blue" screen LSB register. The default color screen output is black.
Table 3-72. "Blue" Screen Cb Control
Subaddress 60h
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Cb value [9:2]
The Cb value of the color screen output when enabled by bit 2 or 3 of the output formatter 2 register is programmable using a 10-bit value.
The 8 MSB, bits[9:2], are represented in this register.
The remaining two LSB are found in the "Blue" screen LSB register. The default color screen output is black.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 69
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-73. "Blue" Screen Cr Control
Subaddress 61h
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Cr value [9:2]
The Cr value of the color screen output when enabled by bit 2 or 3 of the output formatter 2 register is programmable using a 10-bit value.
The 8 MSB, bits[9:2], are represented in this register. The remaining two LSB are found in the "Blue" screen LSB register. The default color
screen output is black.
Table 3-74. "Blue" Screen LSB Control
Subaddress 62h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Y value LSB [1:0] Cb value LSB [1:0] Cr value LSB [1:0]
The two LSB for the "Blue" screen Y, Cb, and Cr values are represented in this register.
Table 3-75. Noise Measurement
Subaddress 64h–65h
Read only
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
64h 3DNR Noise Measurement [7:0]
65h 3DNR Noise Measurement [15:8]
3DNR Noise Measurement
Since this register is a double-byte register it is necessary to capture the setting into the register to ensure that the value is not updated
between reading the lower and upper bytes. In order to cause this register to capture the current settings, bit 0 of I2C register 97h (status
request) must be set to 1b. Once the internal processor has updated this register bit 0 of register 97h is cleared, indicating that both bytes
of the noise measurement register have been updated and can be read. Either byte may be read first since no further update will occur until
bit 0 of 97h is set to 1b again.
Table 3-76. 3DNR Y Core0
Subaddress 66h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Y_core0[7:0]
Y Core0
Table 3-77. 3DNR UV Core0
Subaddress 67h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
UV_core0[7:0]
UV Core0
70 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-78. F- and V-Bit Decode Control
Subaddress 69h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
VPLL Adaptive Reserved F-Mode[1:0]
This register only works in manual gain control mode. When AGC is active, writing to any value is ignored.
F-bit control mode
00 = Auto: If lines per frame is standard decode F and V bits as per 656 standard from line count else decode F bit from vsync input
and set V bit = 0b
01 = Decode F and V bits from input syncs
10 = Reserved
11 = Always decode F and V bits from line count (TVP5146 compatible)
This register is used in conjunction with register 75h as indicated below:
REGISTER 69H REGISTER 75H STANDARD LPF NONSTANDARD LPF
BIT 1 BIT 0 BIT 3 BIT 2 F V F V
0 0 0 0 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
0 0 0 1 TVP5160 656 656 Toggle Switch9
0 0 1 0 TVP5160 656 656 Pulse 0
0 0 1 1 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
0 1 0 0 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
0 1 0 1 656 656 Toggle Switch9
0 1 1 0 656 656 Pulse 0
0 1 1 1 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
1 0 0 0 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
1 0 0 1 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
1 0 1 0 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
1 0 1 1 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
1 1 0 0 TVP5146 656 656 Switch
1 1 0 1 TVP5146 656 656 Toggle Switch
1 1 1 0 TVP5146 656 656 Pulse Switch
1 1 1 1 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
656 = ITU-R BT.656 standard
Pulse = Pulses low for 1 line prior to field transition
Switch = V bit switches high before the F-bit transition and low after the F bit transition
Switch9 = V bit switches high 1 line prior to the F-bit transition, then low after 9 lines
Reserved = Not used
MODE
Even = 1
Odd = toggle
Adaptive
0 = Enable F- and V-bit adaptation to detected lines per frame
1 = Disable F- and V-bit adaptation to detected lines per frame
VPLL time constant control:
0 = VPLL adapts time constants to input signal
1 = VPLL time constants fixed
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 71
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-79. Back-End AGC Control
Subaddress 6Ch
Default 08h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved 1 Peak Color Sync
This register allows disabling the back-end AGC when the front-end AGC uses specific amplitude references (sync height, color burst, or
composite peak) to decrement the front-end gain. For example, writing 0x09 to this register disables the back-end AGC whenever the
front-end AGC uses the sync height to decrement the front-end gain.
Sync: Disables back end AGC when the front end AGC uses the sync height as an amplitude reference.
0 = Enabled (default)
1 = Disabled
Color: Disables back end AGC when the front end AGC uses the color burst as an amplitude reference.
0 = Enabled (default)
1 = Disabled
Peak: Disables back end AGC when the front end AGC uses the composite peak as an amplitude reference.
0 = Enabled (default)
1 = Disabled
Table 3-80. AGC Decrement Speed
Subaddress 6Fh
Default 04h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved AGC decrement speed [2:0]
AGC decrement speed: Adjusts gain decrement speed. Only used for composite/luma peaks.
111 = 7 (slowest)
110 = 6 (default)
...
000 = 0 (fastest)
Table 3-81. ROM Version
Subaddress 70h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
ROM version [7:0]
ROM Version [7:0]: ROM revision number
72 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-82. AGC White Peak Processing
Subaddress 74h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Luma peak A Reserved Color burst A Sync height A Luma peak B Composite Color burst B Sync height B
Luma peak A: Use of the luma peak as a video amplitude reference for the back-end feed-forward type AGC algorithm
0 = Enabled (default)
1 = Disabled
Color burst A: Use of the color burst amplitude as a video amplitude reference for the back-end
NOTE: Not available for SECAM, component and B/W video sources.
0 = Enabled (default)
1 = Disabled
Sync height A: Use of the sync height as a video amplitude reference for the back-end feed-forward type AGC algorithm
0 = Enabled (default)
1 = Disabled
Luma peak B: Use of the luma peak as a video amplitude reference for front-end feedback type AGC algorithm
0 = Enabled (default)
1 = Disabled
Composite peak: Use of the composite peak as a video amplitude reference for front-end feedback type AGC algorithm
NOTE: Required for CVBS video sources
0 = Enabled (default)
1 = Disabled
Color burst B: Use of the color burst amplitude as a video amplitude reference for front-end feedback type AGC algorithm
NOTE: Not available for SECAM, component and B/W video sources
0 = Enabled (default)
1 = Disabled
Sync height B: Use of the sync-height as a video amplitude reference for front-end feedback type AGC algorithm
0 = Enabled (default)
1 = Disabled
NOTE: If all 4 bits of the lower nibble are set to 1111b (that is, no amplitude reference selected), then the front-end analog and digital
gains are automatically set to nominal values.
If all 4 bits of the upper nibble are set to 1111b (that is, no amplitude reference selected), then the back-end gain is set automatically to
unity. If the input sync height is greater than 100% and the AGC-adjusted output video amplitude becomes less than 100%, then the
back-end scale factor attempts to increase the contrast in the back-end to restore the video amplitude to 100%.
peak
Table 3-83. F-Bit and V-Bit Control
Subaddress 75h
Default 16h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved 1 F and V [1:0] 1 Reserved
F and V [1:0]
F AND V
(1) F and V control bits are only enabled for F-bit control modes 01 and 10 (see register 69h).
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 73
(1)
00 = Nonstandard even Forced to 1 Switch at field boundary
01 = (default)
10 =
11 = Reserved
LINES PER FRAME F BIT V BIT
Standard ITU-R BT 656 ITU-R BT.656
Nonstandard odd Toggles Switch at field boundary
Standard ITU-R BT 656 ITU-R BT.656
Nonstandard Toggles Switch at field boundary
Standard ITU-R BT 656 ITU-R BT.656
Nonstandard Pulsed mode Switch at field boundary
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-84. AGC Increment Speed
Subaddress 78h
Default 06h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved AGC increment speed [2:0]
AGC increment speed: Adjusts gain increment speed.
111 = 7 (slowest)
110 = 6 (default)
...
000 = 0 (fastest)
Table 3-85. AGC Increment Delay
Subaddress 79h
Default 1Eh
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
AGC increment delay [7:0]
AGC increment delay: Number of frames to delay gain increments
1111 1111 = 255
...
0001 1110 = 30 (default)
...
0000 0000 = 0
www.ti.com
Table 3-86. Analog Output Control 1
Subaddress 7Fh
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved AGC enable Reserved Analog output
AGC enable:
0 = Enabled (default)
1 = Disabled, manual gain mode set (see Section 4.2.10)
Analog output enable:
0 = Analog output is disabled (default)
1 = Analog output is enabled
Table 3-87. Chip ID MSB
Subaddress 80h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CHIP ID MSB[7:0]
CHIP ID MSB[7:0]: This register identifies the MSB of device ID. Value = 51h
Table 3-88. Chip ID LSB
Subaddress 81h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CHIP ID LSB [7:0]
CHIP ID LSB [7:0]: This register identifies the LSB of device ID. Value = 60h
enable
74 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-89. Color PLL Speed Control
Subaddress 83h
Default 09h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Speed[3:0]
Color PLL speed control.
Table 3-90. 3DYC Luma Coring LSB
Subaddress 84h
Default 20h/20h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
3DYC Luma Coring [7:0]
This register contains the lower 8 bits of the 10-bit 3DYC luma coring register. The upper 2
bits are accessed through I2C register 86h.
An inter-frame luma signal difference smaller than the programmed value is assumed to be
noise, resulting in the pixel being recognized as "no motion" hence favoring intra-frame (3D)
comb filtering. The minimum value of 000h favors the 2D comb filter output, whereas the
maximum value of 3FFh favors the 3D comb filter output.
Table 3-91. 3DYC Chroma Coring LSB
Subaddress 85h
Default 20h/2Ah
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
3DYC Chroma Coring [7:0]
This register contains the lower 8 bits of the 10-bit 3DYC chroma coring register. The upper
2 bits are accessed through I2C register 86h.
An inter-frame chroma signal difference smaller than the programmed value is assumed to
be noise, resulting in the pixel being recognized as "no motion" hence favoring intra-frame
(3D) comb filtering. The minimum value of 000h favors the 2D comb filter output whereas the
maximum value of 3FFh favors the 3D comb filter output.
Table 3-92. 3DYC Luma/Chroma Coring MSB
Subaddress 86h
Default 00h/00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Chroma Coring [9:8] Luma Coring [9:8]
This register contains the upper 2 bits of the 10-bit 3DYC luma coring and 3DYC chroma
coring registers. The lower 8 bits are accessed through I2C registers 84h and 85h.
An inter-frame luma signal difference smaller than the programmed value is assumed to be
noise, resulting in the pixel being recognized as "no motion" hence favoring intra-frame (3D)
comb filtering. The minimum value of 000h favors the 2D comb filter output, whereas the
maximum value of 3FFh favors the 3D comb filter output.
Table 3-93. 3DYC Luma Gain
Subaddress 87h
Default 08h/08h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
3DYC luma gain [7:0]
This register contains a 5.3 format gain value used to calculate the luma difference value for luma coring. The gain can vary from 0 to
31.875 in steps of 0.125. The minimum value of 0 favors the 3D comb filter output, whereas the maximum value of 31.875 favors the 2D
comb filter output.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 75
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-94. 3DYC Chroma Gain
Subaddress 88h
Default 08h/08h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
3DYC chroma gain [7:0]
This register contains a 5.3 format gain value used to calculate the chroma difference value
for chroma coring. The gain can vary from 0 to 31.875 in steps of 0.125. The minimum value
of 0 favors the 3D comb filter output, whereas the maximum value of 31.875 favors the 2D
comb filter output.
Table 3-95. 3DYC Signal Quality Gain
Subaddress 89h
Default 02h/02h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
3DYC Signal Quality gain [7:0]
When the input signal quality is not good, for example weak broadcast signals or poor VCR
signals, 3DCY comb filtering is automatically turned off. This register sets the gain, or
sensitivity, to distinguish poor signal quality. A smaller value in this register favors application
of 3DYC, whereas a larger value favors 2DYC.
Table 3-96. 3DYC Signal Quality Coring
Subaddress 8Ah–8Bh
Default 328h/380h
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
8Ah 3DYC Signal Quality Coring [7:0]
8Bh 3DYC Signal Quality Coring [15:8]
When the input signal quality is not good, for example weak broadcast signals or poor VCR
signals, 3DCY comb filtering is automatically turned off. This register sets the coring value
used to distinguish poor signal quality. A larger value in this register favors application of
3DYC, whereas a smaller value favors 2DYC.
www.ti.com
Table 3-97. IF Compensation Control
Subaddress 8Dh
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved U V Comp. IF Enable
Comp:
0 = Crosstalk compensation only. Use if SAW IF stage used.
1 = Crosstalk and low-frequency gain compensation. Use if non-SAW IF stage used.
U: Enable high frequency U gain
0 = Enabled
1 = Disabled
V: Enable high frequency V gain
0 = Enabled
1 = Disabled
IF enable:
0 = IF compensation disabled (default)
1 = IF compensation enabled
76 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-98. IF Differential Gain Control
Subaddress 8Eh
Default 22h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
U differential gain[3:0] V differential gain[3:0]
For low IF stage distortions, use lower settings.
Table 3-99. IF Low Frequency Gain Control
Subaddress 8Fh
Default 44h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
U low frequency gain[3:0] V low frequency gain[3:0]
Table 3-100. IF High Frequency Gain Control
Subaddress 90h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
U high frequency gain[3:0] V high frequency gain[3:0]
Table 3-101. Weak Signal High Threshold
Subaddress 95h
Default 60h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Level [7:0]
This register controls the upper threshold of the noise measurement that determines whether
the input signal is considered a weak signal.
Table 3-102. Weak Signal High Threshold
Subaddress 96h
Default 50h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Level [7:0]
This register controls the lower threshold of the noise measurement that determines whether
the input signal is considered a weak signal.
Table 3-103. Status Request
Subaddress 97h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Capture
Capture:
Setting a 1b in this bit causes the internal processor to capture the current settings of the AGC status, 3DNR noise measurement, and
the vertical line count registers. Since this capture is not immediate, it is necessary to check for completion of the capture by reading
the Capture bit repeatedly after setting it and waiting for it to be cleared by the internal processor. Once the Capture bit is 0b, then the
AGC status, noise measurement, and vertical line counters (3Ch/3Dh, 64h/65h, and 9Ah/9Bh) will have been updated and can be
safely read in any order.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 77
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-104. 3DYC NTSC VCR Threshold
Subaddress 98h
Default 10h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Thresh [7:0]
This register controls how 3DYC is enabled/disabled for VCR modes.
Table 3-105. 3DYC PAL VCR Threshold
Subaddress 99h
Default 20h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Thresh [7:0]
This register controls how 3DYC is enabled/disabled for VCR modes.
Table 3-106. Vertical Line Count
Subaddress 9Ah–9Bh
Read only
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
9Ah Vertical line [7:0]
9Bh Reserved Vertical line [9:8]
Vertical line [9:0] represent the detected a total number of lines from the previous frame. This
can be used with nonstandard video signals such as a VCR in trick mode to synchronize
downstream video circuitry.
Since this register is a double-byte register it is necessary to capture the setting into the
register to ensure that the value is not updated between reading the lower and upper bytes.
In order to cause this register to capture the current settings bit 0 of I2C register 97h (status
request) must be set to a 1b. Once the internal processor has updated this register, bit 0 of
register 97h is cleared, indicating that both bytes of the vertical line count register have been
updated and can be read. Either byte may be read first since no further update will occur
until bit 0 of 97h is set to 1b again.
www.ti.com
Table 3-107. AGC Decrement Delay
Subaddress 9Eh
Default 1Eh
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
AGC decrement delay [7:0]
AGC decrement delay: Number of frames to delay gain decrements
1111 1111 = 255
0001 1110 = 30 (default)
0000 0000 = 0
78 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-108. VDP TTX Filter and Mask
Subaddress B1h B2h B3h B4h B5h B6h B7h B8h B9h BAh
Default 00h 00h 00h 00h 00h 00h 00h 00h 00h 00h
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
B1h Filter 1 Mask 1 Filter 1 Pattern 1
B2h Filter 1 Mask 2 Filter 1 Pattern 2
B3h Filter 1 Mask 3 Filter 1 Pattern 3
B4h Filter 1 Mask 4 Filter 1 Pattern 4
B5h Filter 1 Mask 5 Filter 1 Pattern 5
B6h Filter 2 Mask 1 Filter 2 Pattern 1
B7h Filter 2 Mask 2 Filter 2 Pattern 2
B8h Filter 2 Mask 3 Filter 2 Pattern 3
B9h Filter 2 Mask 4 Filter 2 Pattern 4
BAh Filter 2 Mask 5 Filter 2 Pattern 5
For an NABTS system, the packet prefix consists of five bytes. Each byte contains 4 data bits (D[3:0]) interlaced with 4 Hamming protection
bits (H[3:0]):
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
D[3] H[3] D[2] H[2] D[1] H[1] D[0] H[0]
Only the data portion D[3:0] from each byte is applied to a teletext filter function with corresponding pattern bits P[3:0] and mask bits M[3:0].
The filter ignores hamming protection bits.
For a WST system (PAL or NTSC), the packet prefix consists of two bytes. The two bytes contain three bits of magazine number (M[2:0])
and five bits of row address (R[4:0]), interlaced with eight Hamming protection bits H[7:0]:
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
R[0] H[3] M[2] H[2] M[1] H[1] M[0] H[0]
R[4] H[7] R[3] H[6] R[2] H[5] R[1] H[4]
The mask bits enable filtering using the corresponding bit in the pattern register. For example, a 1b in the LSB of mask 1 means that the
filter module should compare the LSB of nibble 1 in the pattern register to the first data bit on the transaction. If these match, then a true
result is returned. A 0b in a mask bit means that the filter module should ignore that data bit of the transaction. If all 0s are programmed in
the mask bits, the filter matches all patterns returning a true result (default 00h).
Table 3-109. VDP TTX Filter Control
Subaddress BBh
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Filter logic [1:0] Mode TTX filter 2 TTX filter 1
Filter logic [1:0]: Allow different logic to be applied when combining the decision of Filter 1 and Filter 2 as follows:
00 = NOR (default)
01 = NAND
10 = OR
11 = AND
Mode: Indicates which teletext mode is in use:
0 = Teletext filter applies to 2 header bytes (default)
1 = Teletext filter applies to 5 header bytes
TTX filter 2 enable: provides for enabling the teletext filter function within the VDP.
0 = Disable (default)
1 = Enable
TTX filter 1 enable: provides for enabling the teletext filter function within the VDP.
0 = Disable (default)
1 = Enable
If the filter matches or if the filter mask is all 0s, then a true result is returned.
enable enable
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 79
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

1P1[3]
1M1[0]
1M1[1]
1M1[2]
1M1[3]
NIBBLE 1
FILTER 2
FILTER 1
00
01
10
11
PASS 1
Filter 1
Enable
2
Filter Logic
PASS
1P1[2]
1P1[1]
1P1[0]
D1[3]
D1[2]
D1[1]
D1[0]
NIBBLE 2
D2[3:0]
1P2[3:0]
1M2[3:0]
NIBBLE 3
NIBBLE 4
NIBBLE 5
D3[3:0]
1P3[3:0]
1M3[3:0]
D4[3:0]
1P4[3:0]
1M4[3:0]
D5[3:0]
1P5[3:0]
1M5[3:0]
D1..D5
2P1..2P5
2M1..2M5
PASS 2
Filter 2
Enable
TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Figure 3-1. Teletext Filter Function
Table 3-110. VDP FIFO Word Count
Subaddress BCh
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
FIFO word count [7:0]: This register provides the number of words in the FIFO.
Note: 1 word equals 2 bytes.
FIFO word count [7:0]
80 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-111. VDP FIFO Interrupt Threshold
Subaddress BDh
Default 80h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Thresh [7:0]
Threshold [7:0]: This register is programmed to trigger an interrupt when the number of
words in the FIFO exceeds this value.
Note: 1 word equals 2 bytes.
Table 3-112. VDP FIFO Reset
Subaddress BFh
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved FIFO reset
FIFO reset: Writing any data to this register clears the FIFO and VDP data registers. After clearing, this register bit is automatically cleared.
Table 3-113. VDP FIFO Output Control
Subaddress C0h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Host access
Host access enable: This register is programmed to allow the host port access to the FIFO or allowing all VDP data to go out the video
output.
0 = Output FIFO data to the video output Y[9:2] (default)
1 = Allow host port access to the FIFO data
enable
Table 3-114. VDP Line Number Interrupt
Subaddress C1h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Field 1 enable Field 2 enable Line number [5:0]
Field 1 interrupt enable:
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled
Field 2 interrupt enable:
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled
Line number [5:0]: Interrupt line number (default 00h)
This register is programmed to trigger an interrupt when the video line number exceeds this value in bits [5:0]. This interrupt must be
enabled at address F4h.
Note: The line number value of zero or one is invalid and will not generate an interrupt.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 81
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-115. VDP Pixel Alignment
Subaddress C2h–C3h
Default 01Eh
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
C2h Pixel alignment [7:0]
C3h Reserved Pixel alignment [9:0]
Pixel alignment [9:0]: These registers form a 10-bit horizontal pixel position from the falling
edge of horizontal sync, where the VDP controller will initiate the program from one line
standard to the next line standard. For example, the previous line of teletext to the next line
of closed caption. This value must be set so that the switch occurs after the previous
transaction has cleared the delay in the VDP, but early enough to allow the new values to be
programmed before the current settings are required.
The default value is 0x1E and has been tested with every standard supported here. A new
value will only be needed if a custom standard is in use.
Table 3-116. VDP Line Start
Subaddress D6h
Default 06h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
VDP line start [7:0]
VDP line start [7:0]: Sets the VDP line starting address for the global line mode register
This register has to be set properly before enabling the line mode registers. The global line
mode is only active in the region defined by the VDP line start and stop registers.
www.ti.com
Table 3-117. VDP Line Stop
Subaddress D7h
Default 1Bh
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
VDP line stop [7:0]
VDP line stop address [7:0]: Sets the VDP stop line.
Table 3-118. VDP Global Line Mode
Subaddress D8h
Default FFh
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Global line mode [7:0]
Global line mode [7:0]: VDP processing for multiple lines set by VDP start line register D6h
and stop line register D7h.
Global line mode register has the same bits definitions as the line mode register's (see
Table 3-141).
General line mode will have priority over the global line mode.
82 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-119. VDP Full Field Enable
Subaddress D9h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Full field enable
Full field enable:
0 = Disabled full field mode(default)
1 = Enabled full field mode
This register enables the full field mode. In this mode, all lines outside the vertical blank area and all lines in the line mode register
programmed with FFh are sliced with the definition of full field mode register at subaddress DAh. Values other than FFh in the line mode
registers allow a different slice mode for that particular line.
Table 3-120. VDP Full Field Mode
Subaddress DAh
Default FFh
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Full field mode [7:0]
Full field mode [7:0]: This register programs the specific VBI standard for full field mode. It
can be any VBI standard. Individual line settings take priority over the full field register. This
allows each VBI line to be programmed independently but have the remaining lines in full
field mode. The full field mode register has the same bits definition as line mode registers.
(default FFh)
Global line mode will have priority over the full field mode.
Table 3-121. Interlaced/Progressive Status
Subaddress DBh
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Interlaced/progressive detection status:
0 = SD interlaced signal detected
1 = ED/HD signal detected
Table 3-122. VBUS Data Access with No VBUS Address Increment
Subaddress E0h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
VBUS data [7:0]
VBUS data [7:0]: VBUS data register for VBUS single byte read/write transaction.
Table 3-123. VBUS Data Access with VBUS Address Increment
Subaddress E1h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
VBUS data [7:0]
VBUS data [7:0]: VBUS data register for VBUS multi-byte read/write transaction. VBUS
address is auto-incremented after each data byte read/write.
I/P
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 83
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-124. VDP FIFO Read Data
Subaddress E2h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
FIFO Read Data [7:0]
FIFO Read Data [7:0]: This register is provided to access VBI FIFO data through the I2C
interface. All forms of teletext data come directly from the FIFO, while all other forms of VBI
data can be programmed to come from registers or from the FIFO. If the host port reads data
from the FIFO, then bit 0 (host access enable) in the VDP FIFO output control register at
subaddress C0h must be set to 1b.
Table 3-125. VBUS Address
Subaddress E8h E9h EAh
Default 00h 00h 00h
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
E8h VBUS address [7:0]
E9h VBUS address [15:8]
EAh VBUS address [23:16]
VBUS address [23:0]: VBUS is a 24-bit wide internal bus. The user must program the 24-bit
address of the internal register to be accessed via host port indirect access mode.
www.ti.com
Table 3-126. Interrupt Raw Status 0
Subaddress F0h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
FIFO THRS TTX WSS/CGMS VPS/Gemstar VITC CC F2 CC F1 Line
FIFO THRS: FIFO threshold passed, unmasked
0 = Not passed
1 = Passed
TTX: Teletext data available unmasked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
WSS/CGMS: WSS/CGMS data available unmasked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
VPS/Gemstar: VPS/Gemstar data available unmasked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
VITC: VITC data available unmasked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
CC F2: CC field 2 data available unmasked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
CC F1: CC field 1 data available unmasked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
Line: Line number interrupt unmasked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
The host interrupt raw status 0 and 1 registers represent the interrupt status without applying mask bits.
84 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-127. Interrupt Raw Status 1
Subaddress F1h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved FIFO full
FIFO full:
0 = FIFO not full
1 = FIFO was full during write to FIFO
The masked or unmasked status is set in the interrupt mask 1 register at subaddress F5h.
The FIFO full error flag is set when the current line of VBI data can not enter the FIFO. For example, if the FIFO has only 10 bytes left and
teletext is the current VBI line, the FIFO full error flag is set, but no data will be written because the entire teletext line will not fit. However, if
the next VBI line is closed caption requiring only 2 bytes of data plus the header, then this will go into the FIFO even if the full error flag is
set.
Table 3-128. Interrupt Status 0
Subaddress F2h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
FIFO THRS TTX WSS/CGMS VPS/Gemstar VITC CC F2 CC F1 Line
FIFO THRS: FIFO threshold passed, masked
0 = Not passed
1 = Passed
TTX: Teletext data available masked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
WSS/CGMS: WSS/CGMS data available masked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
VPS/Gemstar: VPS/Gemstar data available masked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
VITC: VITC data available masked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
CC F2: CC field 2 data available masked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
CC F1: CC field 1 data available masked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
Line: Line number interrupt masked
0 = Not available
1 = Available
The interrupt status 0 and 1 registers represent the interrupt status after applying mask bits. Therefore, the status bits are the result of a
logical AND between the raw status and mask bits. The external interrupt pin is derived from this register as an OR function of all
nonmasked interrupts in this register.
Reading data from the corresponding register does not clear the status flags automatically. These flags are reset using the corresponding
bits in interrupt clear 0 and 1 registers.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 85
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
Table 3-129. Interrupt Status 1
Subaddress F3h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved FIFO full
FIFO full: Masked status of FIFO
0 = FIFO not full
1 = FIFO was full during write to FIFO, see the interrupt mask 1 register at subaddress F5h
The masked or unmasked status is set in the interrupt mask 1 register.
Table 3-130. Interrupt Mask 0
Subaddress F4h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
FIFO THRS TTX WSS/CGMS VPS/Gemstar VITC CC F2 CC F1 Line
FIFO THRS: FIFO threshold passed mask
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled FIFO_THRES interrupt
TTX: Teletext data available mask
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled TTX available interrupt
WSS/CGMS: WSS/CGMS data available mask
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled WSS/CGMS available interrupt
VPS/Gemstar: VPS/Gemstar data available mask:
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled VPS/Gemstar available interrupt
VITC: VITC data available mask:
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled VITC available interrupt
CC F2: CC field 2 data available mask
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled CC field 2 available interrupt
CC F1: CC field 1 data available mask
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled CC field 1 available interrupt
LINE: Line number interrupt mask
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled Line_INT interrupt
The host interrupt mask 0 and 1 registers can be used by the external processor to mask unnecessary interrupt sources for interrupt status
0 and 1 register bits, and for the external interrupt pin. The external interrupt is generated from all nonmasked interrupt flags.
Table 3-131. Interrupt Mask 1
Subaddress F5h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved FIFO full
FIFO full: FIFO full mask
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled FIFO full interrupt
86 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-132. Interrupt Clear 0
Subaddress F6h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
FIFO THRS TTX WSS/CGMS VPS/Gemstar VITC CC F2 CC F1 Line
FIFO THRS: FIFO threshold passed clear
0 = No effect (default)
1 = Clear FIFO_THRES bit in status register 0 bit 7
TTX: Teletext data available clear
0 = No effect (default)
1 = Clear TTX available bit in status register 0 bit 6
WSS/CGMS: WSS/CGMS data available clear
0 = No effect (default)
1 = Clear WSS/CGMS available bit in status register 0 bit 5
VPS/Gemstar: VPS/Gemstar data available clear
0 = No effect (default)
1 = Clear VPS/Gemstar available bit in status register 0 bit 4
VITC: VITC data available clear
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Clear VITC available bit in status register 0 bit 3
CC F2: CC field 2 data available clear
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Clear CC field 2 available bit in status register 0 bit 2
CC F1: CC field 1 data available clear
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Clear CC field 1 available bit in status register 0 bit 1
LINE: Line number interrupt clear
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Clear Line interrupt available bit in status register 0 bit 0
The host interrupt clear 0 and 1 registers are used by the external processor to clear the interrupt status bits in the host interrupt status 0
and 1 registers. When no nonmasked interrupts remain set in the registers, the external interrupt pin will also become inactive.
Table 3-133. Interrupt Clear 1
Subaddress F7h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved FIFO full
FIFO full: Clear FIFO full flag
0 = No effect (default)
1 = Clear bit 0 (FIFO full flag) in the interrupt status 1 register at subaddress F3h and the interrupt raw status 1 register at subaddress
F1h
3.2 VBUS Register Definitions
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 87
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-134. VDP Closed Caption Data
Subaddress 80 051Ch – 80 051Fh
Read only
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
80 051Ch Closed Caption Field 1 byte 1
80 051Dh Closed Caption Field 1 byte 2
80 051Eh Closed Caption Field 2 byte 1
80 051Fh Closed Caption Field 2 byte 2
These registers contain the closed caption data arranged in bytes per field.
Table 3-135. VDP WSS/CGMS Data
Subaddress 80 0520h – 80 0526h
Read only
WSS/CGMS NTSC
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Byte
80 0520h – – b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0 WSS/CGMS Field 1 Byte 1
80 0521h b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 WSS/CGMS Field 1 Byte 2
80 0522h – – b19 b18 b17 b16 b15 b14 WSS/CGMS Field 1 Byte 3
80 0523h Reserved
80 0524h – – b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0 WSS/CGMS Field 2 Byte 1
80 0525h b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 WSS/CGMS Field 2 Byte 2
80 0526h – – b19 b18 b17 b16 b15 b14 WSS/CGMS Field 2 Byte 3
These registers contain the wide screen signaling data for NTSC.
Bits 0 – 1 represent word 0, aspect ratio
Bits 2 – 5 represent word 1, header code for word 2
Bits 6 – 13 represent word 2, copy control
Bits 14 – 19 represent word 3, CRC
www.ti.com
WSS/CGMS PAL/SECAM
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Byte
80 0520h b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0 WSS/CGMS Field 1 Byte 1
80 0521h – – b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 WSS/CGMS Field 1 Byte 2
80 0522h Reserved
80 0523h Reserved
80 0524h b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0 WSS/CGMS Field 2 Byte 1
80 0525h – – b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 WSS/CGMS Field 2 Byte 2
80 0526h Reserved
These registers contain the wide screen signaling data for PAL/SECAM:
Bits 0 – 3 represent Group 1, Aspect Ratio
Bits 4 – 7 represent Group 2, Enhanced Services
Bits 8 – 10 represent Group 3, Subtitles
Bits 11 – 13 represent Group 4, Others
88 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-136. VDP VITC Data
Subaddress 80 052Ch – 80 0534h
Read only
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
80 052Ch VITC frame byte 1
80 052Dh VITC frame byte 2
80 052Eh VITC seconds byte 1
80 052Fh VITC seconds byte 2
80 0530h VITC minutes byte 1
80 0531h VITC minutes byte 2
80 0532h VITC hours byte 1
80 0533h VITC hours byte 2
80 0534h VITC CRC byte
These registers contain the VITC data.
Table 3-137. VDP V-Chip TV Rating Block 1
Subaddress 80 0540h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved 14-D PG-D Reserved MA-L 14-L PG-L Reserved
TV Parental Guidelines Rating Block 3
14-D: When incoming video program is TV-14-D rated, this bit is set high.
PG-D: When incoming video program is TV-PG-D rated, this bit is set high.
MA-L: When incoming video program is TV-MA-L rated, this bit is set high.
14-L: When incoming video program is TV-14-L rated, this bit is set high.
PG-L: When incoming video program is TV-PG-L rated, this bit is set high.
Table 3-138. VDP V-Chip TV Rating Block 2
Subaddress 80 0541h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved 14-S PG-S Reserved MA-V 14-V PG-V Y7-FV
TV Parental Guidelines Rating Block 2
MA-S: When incoming video program is TV-MA-S rated, this bit is set high.
14-S: When incoming video program is TV-14-S rated, this bit is set high.
PG-S: When incoming video program is TV-PG-S rated, this bit is set high.
MA-V: When incoming video program is TV-MA-V rated, this bit is set high.
14-V: When incoming video program is TV-14-V rated, this bit is set high.
PG-V: When incoming video program is TV-PG-S rated, this bit is set high.
Y7-FV: When incoming video program is TV-Y7-FV rated, this bit is set high.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 89
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-139. VDP V-Chip TV Rating Block 3
Subaddress 80 0542h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
None TV-MA TV-14 TV-PG TV-G TV-Y7 TV-Y None
TV Parental Guidelines Rating Block 1
None: No block intended
TV-MA: When incoming video program is "TV-MA" rated in TV Parental Guidelines Rating, this bit is set high.
TV-14: When incoming video program is "TV-14" rated in TV Parental Guidelines Rating, this bit is set high.
TV-PG: When incoming video program is "TV-PG" rated in TV Parental Guidelines Rating, this bit is set high.
TV-G: When incoming video program is "TV-G" rated in TV Parental Guidelines Rating, this bit is set high.
TV-Y7: When incoming video program is "TV-Y7" rated in TV Parental Guidelines Rating, this bit is set high.
TV-Y: When incoming video program is "TV-G" rated in TV Parental Guidelines Rating, this bit is set high.
Table 3-140. VDP V-Chip MPAA Rating Data
Subaddress 80 0543h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Not Rated X NC-17 R PG-13 PG G NA
MPAA Rating Block (E5h)
Not Rated: When incoming video program is "Not Rated" rated in MPAA Rating, this bit is set high.
X: When incoming video program is "X" rated in MPAA Rating, this bit is set high.
NC-17: When incoming video program is "NC-17" rated in MPAA Rating, this bit is set high.
R: When incoming video program is "R" rated in MPAA Rating, this bit is set high.
PG-13: When incoming video program is "PG-13" rated in MPAA Rating, this bit is set high.
PG: When incoming video program is "PG" rated in MPAA Rating, this bit is set high.
G: When incoming video program is "G" rated in MPAA Rating, this bit is set high.
N/A: When incoming video program is "N/A" rated in MPAA Rating, this bit is set high.
www.ti.com
90 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-141. VDP General Line Mode and Line Address
Subaddress 80 0600h – 80 0611h
(default line mode = FFh, line address = 00h)
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
80 0600h Line address 1
80 0601h Line mode 1
80 0602h Line address 2
80 0603h Line mode 2
80 0604h Line address 3
80 0605h Line mode 3
80 0606h Line address 4
80 0607h Line mode 4
80 0608h Line address 5
80 0609h Line mode 5
80 060Ah Line address 6
80 060Bh Line mode 6
80 060Ch Line address 7
80 060Dh Line mode 7
80 060Eh Line address 8
80 060Fh Line mode 8
80 0610h Line address 9
80 0611h Line mode 9
Line address [7:0]: Line number to process selected line mode register on
Line mode register x [7:0]
Bit 7
0 = Disabled filters
1 = Enabled filters for teletext and CC (Null byte filter) (default)
Bit 6
0 = Send sliced VBI data to registers only
1 = Send sliced VBI data to FIFO and registers, teletext data only goes to FIFO (default)
Bit 5
0 = Allow VBI data with errors in the FIFO
1 = Do not allow VBI data with errors in the FIFO (default)
Bit 4
0 = Disabled error detection and correction
1 = Enabled error detection and correction (teletext only) (default)
Bit 3
0 = Field 1
1 = Field 2 (default)
Bit [2:0]
000 = Teletext (WST625, Chinese Teletext, NABTS 525)
001 = CC (US, European, Japan, China)
010 = WSS/CGMS (525, 625)
011 = VITC
100 = VPS (PAL only), Gemstar EPG (NTSC only)
101 = USER 1
110 = USER 2
111 = Reserved (active video) (default)
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 91
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-142. VDP VPS, Gemstar EPG Data
Subaddress 80 0700h – 80 070Ch
Read only
VPS
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
80 0700h VPS byte 1
80 0701h VPS byte 2
80 0702h VPS byte 3
80 0703h VPS byte 4
80 0704h VPS byte 5
80 0705h VPS byte 6
80 0706h VPS byte 7
80 0707h VPS byte 8
80 0708h VPS byte 9
80 0709h VPS byte 10
80 070Ah VPS byte 11
80 070Bh VPS byte 12
80 070Ch VPS byte 13
These registers contain the entire VPS data line except the clock run-in code and the frame code.
Gemstar EPG
Subaddress 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
80 0700h Gemstar EPG Frame Code
80 0701h Gemstar EPG byte 1
80 0702h Gemstar EPG byte 2
80 0703h Gemstar EPG byte 3
80 0704h Gemstar EPG byte 4
80 0705h Reserved
80 0706h Reserved
80 0707h Reserved
80 0708h Reserved
80 0709h Reserved
80 070Ah Reserved
80 070Bh Reserved
80 070Ch Reserved
www.ti.com
92 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-143. Analog Output Control 2
Subaddress A0 005Eh
Default B2h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Gain[3:0]
Analog output PGA gain [3:0]: These bits are effective when analog output AGC is disabled.
Gain[3:0]
0000 1.30
0001 1.56
0010 (default) 1.82
0011 2.08
0100 2.34
0101 2.60
0110 2.86
0111 3.12
1000 3.38
1001 3.64
1010 3.90
1011 4.16
1100 4.42
1101 4.68
1110 4.94
1111 5.20
Table 3-144. Interrupt Configuration
Subaddress A0 0060h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Polarity Reserved
Polarity: Interrupt pin polarity
0 = Active high (default)
1 = Active low (open drain, a pullup register is required)
Table 3-145. Interrupt Raw Status 1
Subaddress B0 0069h
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved H/V lock Macrovision status changed Standard changed Reserved
H/V lock: unmasked
0 = H/V lock status unchanged
1 = H/V lock status changed
Macrovision status changed: unmasked
0 = Macrovision status unchanged
1 = Macrovision status changed
Standard changed: unmasked
0 = Video standard unchanged
1 = Video standard changed
The masked or unmasked status is set in the interrupt mask 1 register.
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Internal Control Registers 93
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Table 3-146. Interrupt Status 1
Subaddress B0 006Dh
Read only
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved H/V lock Macrovision status changed Standard changed Reserved
H/V lock: H/V lock status changed masked
0 = H/V lock status unchanged
1 = H/V lock status changed
Macrovision status changed: Macrovision status changed masked
0 = Macrovision status not changed
1 = Macrovision status changed
Standard changed: Standard changed masked
0 = Video standard not changed
1 = Video standard changed
The masked or unmasked status is set in the interrupt mask1 register.
Table 3-147. Interrupt Mask 1
Subaddress B0 0065h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved H/V lock Macrovision status changed Standard changed Reserved
H/V lock: H/V lock status changed mask
0 = H/V lock status unchanged (default)
1 = H/V lock status changed
Macrovision status changed: Macrovision status changed mask
0 = Macrovision status unchanged (default)
1 = Macrovision status changed
Standard changed: Standard changed mask
0 = Disabled (default)
1 = Enabled video standard changed
www.ti.com
Table 3-148. Interrupt Clear 1
Subaddress B0 0071h
Default 00h
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved H/V lock Macrovision status changed Standard changed Reserved
H/V lock: Clear H/V lock status changed flag
0 = H/V lock status unchanged
1 = H/V lock status changed
Macrovision status changed: Clear Macrovision status changed flag
0 = No effect (default)
1 = Clear bit 2 (Macrovision status changed) in the interrupt status 1 register at subaddress B0 006Dh and the interrupt raw status 1
register at subaddress B0 0069h
Standard changed: Clear standard changed flag
0 = No effect (default)
1 = Clear bit 1 (video standard changed) in the interrupt status 1 register at subaddress B0 006Dh and the interrupt raw status 1
register at subaddress B0 0069h
94 Internal Control Registers Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
4 Typical Application Circuit
4.1 Typical Application Circuit
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
Figure 4-1. Application Example
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Typical Application Circuit 95
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
5 Typical Register Programming Sequence
Composite Input, Autoswitch, 10-bit ITU-656, 3DYC and 3DNR Enabled
// Address, Data
0xEE, 0x01 // ROM Initialization Procedure - Required
0xEA, 0xB0
0xE9, 0x00
0xE8, 0x63
0xE0, 0x01
0xEE, 0x00
0x00, 0x00 // Input/Output Select - Composite input selected (default)
0x06, 0x40 // Luminance Processing Control 1 - No pedestal present
0x33, 0x40 // Output Formatter Control 1 - 10-bit ITU-656 (default)
0x34, 0x11 // Output Formatter Control 2 - Data and SCLK enabled
0x35, 0x2A // Output Formatter Control 3 - GPIO (pin 82) = 0, GLCO, AVID, and FID enabled
0x36, 0xAF // Output Formatter Control 4 - HS and VS enabled
0x59, 0x07 // SDRAM Control - 64-Mbit SDRAM configured and enabled; must be set before enabling
3DYC
or 3DNR
0x0D, 0x84 // Chrominance Processing Control 1 - 3DYC and 3DNR enabled
480p Progressive Inputs, Autoswitch, 20-bit ITU-656, 3DYC and 3DNR Enabled
// Address, Data
0xEE, 0x01 // ROM Initialization Procedure - Required
0xEA, 0xB0
0xE9, 0x00
0xE8, 0x63
0xE0, 0x01
0xEE, 0x00
0x00, 0x95 // Input/Output Select - Y(VI_5), Pb(VI_11), Pr(VI_8)
0x06, 0x40 // Luminance Processing Control 1 - No pedestal present
0x30, 0x0F // Component Autoswitch Mask - 480i/p and 576i/p enabled in autoswitch
0x33, 0x44 // Output Formatter Control 1 - 20-bit ITU-656
0x34, 0x11 // Output Formatter Control 2 - Data and SCLK enabled
0x35, 0x2A // Output Formatter Control 3 - GPIO (pin 82) = 0, GLCO, AVID, and FID are enabled
0x36, 0xAF // Output Formatter Control 4 - HS and VS enabled
0x59, 0x07 // SDRAM Control - 64-Mbit SDRAM configured and enabled; must be set before enabling
3DYC
or 3DNR
0x0D, 0x84 // Chrominance Processing Control 1 - 3DYC and 3DNR enabled
www.ti.com
96 Typical Register Programming Sequence Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
6 Electrical Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
IOVDD to
IOGND
DVDD to DGND –0.2 2.0 V
A33VDD
A33GND
A18VDD
A18GND
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
VIto DGND Digital input voltage range –0.5 4.5 V
VOto DGND Digital output voltage range –0.5 4.5 V
AINto AGND Analog input voltage range –0.2 2.0 V
T
A
T
stg
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under "Absolute Maximum Ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings
only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under "recommended operating
conditions" is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) CH1_A33VDD, CH2_A33VDD
(3) CH1_A33GND, CH2_A33GND
(4) CH1_A18VDD, CH2_A18VDD, A18VDD, A18VDD_REF, PLL_A18VDD
(5) CH1_A18GND, CH2_A18GND, A18GND
Supply voltage range
to
to
Operating free-air temperature 0 70 °C
Storage temperature –65 150 °C
(1)
MIN MAX UNIT
0.5 4.0 V
–0.3 3.6 V
–0.2 2.0 V
6.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN NOM MAX UNIT
IOVDD Supply voltage, digital 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
DVDD Supply voltage, digital 1.65 1.8 1.95 V
AV
AV
V
I(PP)
V
IH
V
IL
I
OH
I
OL
I
OH
I
OL
I
OH
I
OL
T
A
Analog
out
(1) Exception: 0.7 AVDD18 for XIN terminal
(2) Exception: 0.3 AVDD18 for XIN terminal
(3) Currents out of a terminal are given as a negative number
Supply voltage, analog 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
DD33
Supply voltage, analog 1.65 1.8 1.95 V
DD18
Input voltage, analog (ac-coupling necessary) 0.5 1.0 2.0 V
Input voltage high, digital
Input voltage low, digital
Output current (Y/SD data/SD address/SCLK)
(1)
(2)
(3)
Vout = 2.4 V –8 mA
0.7 IOVDD V
Output current (Y/SD data/SD address/SCLK) Vout = 0.4 V 8 mA
Output current (SDRAM_CLK) Vout = 2.4 V –8 mA
Output current (SDRAM_CLK) Vout = 0.4 V 8 mA
Output current (C) Vout = 2.4 V –4 mA
Output current (C) Vout = 0.4 V 4 mA
Operating free-air temperature 0 70 °C
Output voltage 2.0 2.4 V
0.3
IOVDD
V
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Electrical Specifications 97
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
www.ti.com
6.3 Crystal Specifications
CYSTAL SPECIFICATION MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Frequency 14.31818 MHz
Frequency tolerance
(1)
–50 50 ppm
(1) This number is the required specification for the external crystal/oscillator and is not tested.
6.4 DC Electrical Characteristics
For minimum/maximum values: IOVDD = 3.0 V to 3.6 V, DVDD = 1.65 V to 1.95 V, AV
to 1.95 V, TA= 0°C to 70°C. For typical values: IOVDD = 3.3 V, DVDD = 1.8 V, AV
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
CVBS, 3DYC, 3DNR 28 33
I
DD(IOD)
I
DD(D)
I
DD(33A)
I
DD(18A)
P
TOT
P
SAVE
P
DOWN
I
lkg
C
I
V
OH
V
OL
V
OH
V
OL
V
OH
V
OL
3.3-V IO digital supply current
1.8-V digital supply current mA
3.3-V analog supply current mA
1.8-V analog supply current mA
Total power dissipation, normal
operation
Total power dissipation, power save 180 mW
Total power dissipation, power down 3 mW
Input leakage current
(1)
Input capacitance by design (not tested) 8 pF
Output voltage high
(Y/SD data/SD address/SCLK)
Output voltage low
(Y/SD data/SD address/SCLK)
Output voltage high (SDRAM_CLK) IOH= –8 mA 0.8 IOVDD V
Output voltage LOW (SDRAM_CLK) IOL= 8 mA 0.2 IOVDD V
Output voltage HIGH (C) IOH= –4 mA 0.8 IOVDD V
Output voltage LOW (C) IOL= 4 mA 0.2 IOVDD V
(1)
(1) GLCO and GPIO are bidirectional pins with an internal pulldown resistor during reset. These pins may sink up to 30 µA during reset.
S-Video, 3DNR 23 27
SCART 33 39
480p/525p 52 63
CVBS 159 190
S-Video 156 187
SCART 172 206
480p/525p 205 246
CVBS 18 21
S-Video 31 37
SCART 38 45
480p/525p 35 42
CVBS 80 96
S-Video 136 163
SCART 138 165
480p/525p 138 165
CVBS, 3DYC, 3DNR 582 698
S-Video, 3DNR 704 845
SCART 792 950
480p/525p 904 1085
IOH= –8 mA 0.8 IOVDD V
IOL= 8 mA 0.2 IOVDD V
DD33
= 3.0 V to 3.6 V, AV
DD33
= 3.3 V, AV
DD18
= 1.65 V
DD18
= 1.8 V, TA= 25°C
mA
mW
10 µA
98 Electrical Specifications Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

TVP5160
www.ti.com
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
6.5 Analog Processing and A/D Converters
FS= 60 MSPS for CH1, CH2
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Z
i
C
i
V
i(PP)
ΔG Input gain control range –6.7 dB
DNL Absolute differential nonlinearity AFE only 0.75 LSB
INL Absolute integral nonlinearity AFE only 1 LSB
FR Frequency response Multiburst (60 IRE) –0.9 dB
XTALK Crosstalk 1 MHz dB
SNR Signal-to-noise ratio all channels FIN= 1 MHz, 1.0 V
GM Gain match
NS Noise spectrum –58 dB
DP Differential phase Modulated ramp 0.5 °
DG Differential gain Modulated ramp ±1.5 %
(1) Component inputs only
Input impedance, analog video inputs specified by design (not tested) 200 kΩ
Input capacitance, analog video inputs specified by design (not tested) pF
Input voltage range C
= 0.1 µF 0.50 1.0 V
coupling
Input gain ratio, N = 0 to 15 –7.5% 0.5 +N/10
Input offset control per step 2 4 LSB
(1)
Full scale, 1 MHz 1.5 %
PP
54 dB
Luma ramp (100 kHz to full, tilt
null)
Analog output gain ratio, N = 0 to 15 –8% 1.3 + 0.26xN 8 %
6.6 Data Clock, Video Data, Sync Timing
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Duty cycle SCLK 45 50 55 %
t
1
t
1
t
1
t
2
t
2
t
2
t
3
t
4
t
5
t
6
High time, SCLK @ 13.5 MHz ≥ 50% 37 ns
High time, SCLK @ 27 MHz ≥ 50% 18.5
High time, SCLK @ 54 MHz ≥ 50% 9.25
Low time, SCLK @ 13.5 MHz ≤ 50% 37 ns
Low time, SCLK @ 27 MHz ≤ 50% 18.5
Low time, SCLK @ 54 MHz ≤ 50% 9.25
Fall time, SCLK 90% to 10% 5 ns
Rise time, SCLK 10% to 90% 5 ns
Data valid time To 90%/10% 5 ns
Data hold time To 90%/10% 2.5 ns
Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Electrical Specifications 99
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160

90%
Y, C, AVID,
VS, HS, FID
Valid DataValid Data
SCLK
t
1
t
2
t
6
t
5
t
3
t
4
10%
90%
10%
VC1 (SDA)
t
1
t
6
t
7
t
2
t
8
t
3
t
4
t
6
VC0 (SCL)
Data
Stop Start Stop
t
5
Change
Data
TVP5160
SLES135C–FEBRUARY 2005–REVISED MAY 2010
6.7 I2C Host Port Timing
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
t
1
t
2
t
3
t
4
t
5
t
6
t
7
t
8
C
b
f
12C
(1) Assured by design. Not tested.
Bus free time between STOP and START 1.3 µs
Data hold time 0 0.9 µs
Data setup time 100 ns
Setup time for a (repeated) START condition 0.6 µs
Setup time for a STOP condition 0.6 µs
Hold time (repeated) START condition 0.6 µs
Rise time VC1(SDA) and VC0(SCL) signal specified by design
Fall time VC1(SDA) and VC0(SCL) signal specified by design
Capacitive load for each bus line specified by design
I2C clock frequency 400 kHz
www.ti.com
(1)
(1)
(1)
250 ns
250 ns
400 pF
Figure 6-1. Clocks, Video Data, and Sync Timing
Figure 6-2. I2C Host Port Timing
100 Electrical Specifications Copyright © 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TVP5160
 Loading...
Loading...