TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
D
Universal Serial Bus (USB) Version 1.1
Compliant
D
Integrated USB Transceivers
D
3.3-V Low Power ASIC Logic
D
Two Power Source Modes
– Self-powered Mode Supporting Seven
Downstream Ports
– Bus-powered Mode Supporting Four
Downstream Ports
D
All Downstream Ports Support Full-Speed
and Low-Speed Operations
D
Power Switching and Overcurrent
Reporting is Provided Per Port or Ganged
D
Supports Suspend and Resume Operations
D
Suspend Status Terminal Avaliable for
External Logic Power Down
D
Supports Custom Vendor ID and Product ID
With External Serial EEPROM
D
3-State EEPROM Interface to Allow
EEPROM Sharing
D
Push-Pull Outputs for PWRON Eliminate
the Need for External Pullup Resistors
D
Noise Filtering on OVRCUR Provides
Immunity to Voltage Spikes
D
Supports 6-MHz Operation Through Crystal
Input or 48-MHz Input Clock
D
New Functional Pins Introduced to Reduce
the Board Material Cost
– 3 LED Indicator Control Outputs
Enable Visualized Monitoring of 6
Different Hub/Port Status (HUBCFG,
PORTPWR, PORTDIS)
– Output Pin Available to Disable
External Pullup Resistor on DP0 for 15
ms After Reset or After Change on
BUSPWR
and Enable Easy
Implementation of On-Board Bus/Self
Power Dynamic Switching Circuitry
D
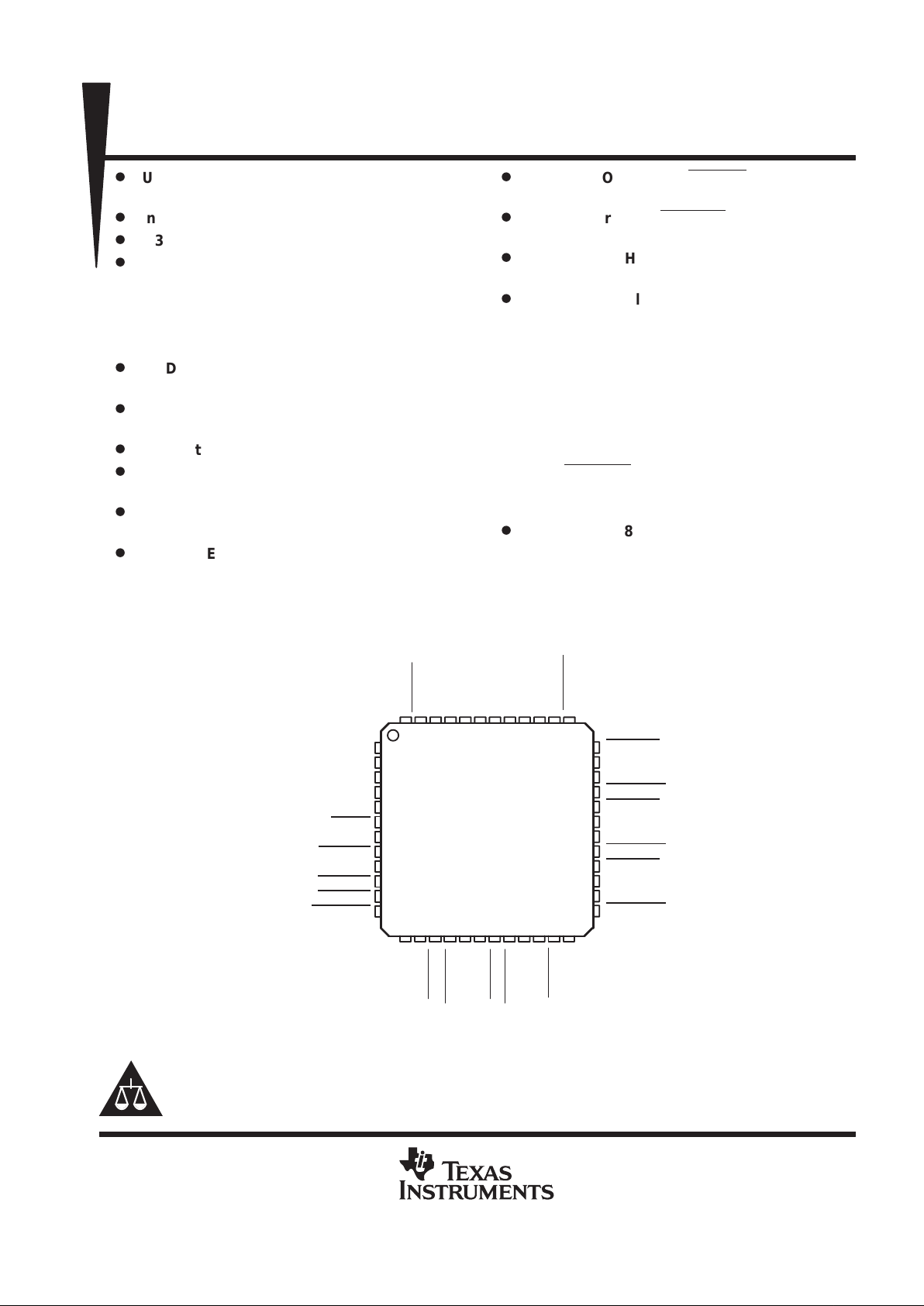
Available in 48-Pin LQFP† Package
EXTMEM
OVRCUR3
OVRCUR2
PWRON7
DP6
DM6
OVRCUR6
PWRON6
DP5
DM5
OVRCUR5
PWRON5
DP4
DM4
OVRCUR4
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
SUSPND
DP0PUR
DP0
DM0
GND
RESET
EECLK
EEDATA/GANGED
V
CC
BUSPWR
PWRON1
OVRCUR1
HUBCFG
DM7
MODEVXTAL1/CLK48
XTAL2
DP3
PWRON4
GND
DM2
DP2
PWRON3
DM3
OVRCUR7
GND
PORTPWR
DP1
DM1
PT PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
393837
46
4443424140
474845
202122
23
13141516172418
19
DP7
PORTDIS
PWRON2
CC
NC – No internal connection
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Copyright 1997, Texas Instruments Incorporated
JEDEC descriptor S–PQFP–G for low-profile quad flatpack (LQFP)

TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
description
The TUSB2077A hub is a 3.3-V CMOS device that provides up to seven down stream ports in compliance with
the USB version 1.1 specification. Because this device is implemented with a digital state machine instead of
a microcontroller, no software programming is required. Fully compliant USB transceivers are integrated into
the ASIC for all upstream and downstream ports. The downstream ports support both full-speed and low-speed
devices by automatically setting the slew rate according to the speed of the device attached to the ports. The
configuration of the BUSPWR
terminal selects either the bus-powered or the self-powered mode. The
introduction of the DP0 pull-up resistor disable pin, DP0PUR, makes it much easier to implement an on-board
bus/self-power dynamic-switching circuitry. The three LED indicator control output pins also enable the
implementation of visualized status monitoring of the hub and its downstream ports. With these new function
pins, the end equipment vendor can considerably reduce the total board cost while adding additional product
value.
The EXTMEM (Pin 47) enables or disables the optional EEPROM interface. When EXTMEM is high, the vendor
and product IDs (VID and PID) use defaults, such that the message displayed during enumeration is
General
Purpose USB Hub
. For this configuration, pin 8 functions as the GANGED input pin and the EECLK (Pin 7) is
unused. If custom VID and PID descriptors are desired, the EXTMEM
must be tied low (EXTMEM = 0) and a
SGS Thompson M93C46 or equivalent EEPROM must be used to store the programmable VID, PID and
GANGED value. For this configuration, pin 7 and pin 8 function as the EEPROM interface signals with pin 7 as
EECLK and pin 8 as EEDATA respectively.
The TUSB2077A supports both bus-powered and self-powered modes. External power management devices
such as the TPS2044 are required to control the 5 V-power source switching (on/of f) to the downstream ports
and detect over-current condition from the downstream ports individually or ganged. Outputs from external
power devices provide over-current inputs to the TUSB2077A OVRCUR pins in case of an over-current
condition, the corresponding PWRON
pins will be disabled by the TUSB2077A. In the ganged mode, all
PWRON signals transitions simultaneously , and any OVRCUR input can be used. In the nonganged mode, the
PWROR outputs and OVRCUR inputs operate on a per port basis.
The TUSB2077A provides the flexibility of using either a 6-MHz or a 48-MHz clock. The logic level of the MODE
terminal controls the selection of the clock source. When MODE is low, the output of the internal APLL circuitry
is selected to drive the internal core of the chip. When MODE is high, the XT AL1 input is selected as the input
clock source and the APLL circuitry is powered down and bypassed. The internal oscillator cell is also powered
down while MODE is high. For 6-MHz operation, TUSB2077A requires a 6-MHz clock signal on XT AL1 pin (with
XT AL2 for a crystal) from which its internal APLL circuitry generates a 48 MHz internal clock to sample the data
from the upstream port. For 48-MHz operation, the clock cannot be generated with a crystal, using the XT AL2
output, since the internal oscillator cell only supports fundamental frequency . If low power suspend and resume
are desired, a passive crystal or resonator must be used, although the hub supports the flexibility of using any
device that generates a 6-MHz clock. Because most oscillators cannot be stopped while power is on, their use
prohibits low-power suspend, which depends on disabling the clock. When the oscillator is used, by connecting
its output to XTAL1 terminal and leaving XTAL2 terminal open, its TTL output level can not exceed 3.6 V. If a
6 MHz oscillator is used, it must be stopped at logic low whenever SUSPND is high. For crystal or resonator
implementations, the XT AL1 terminal is the input and the XTAL2 terminal is used as the feedback path. A sample
crystal tuning circuit is shown in Figure 7.
TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
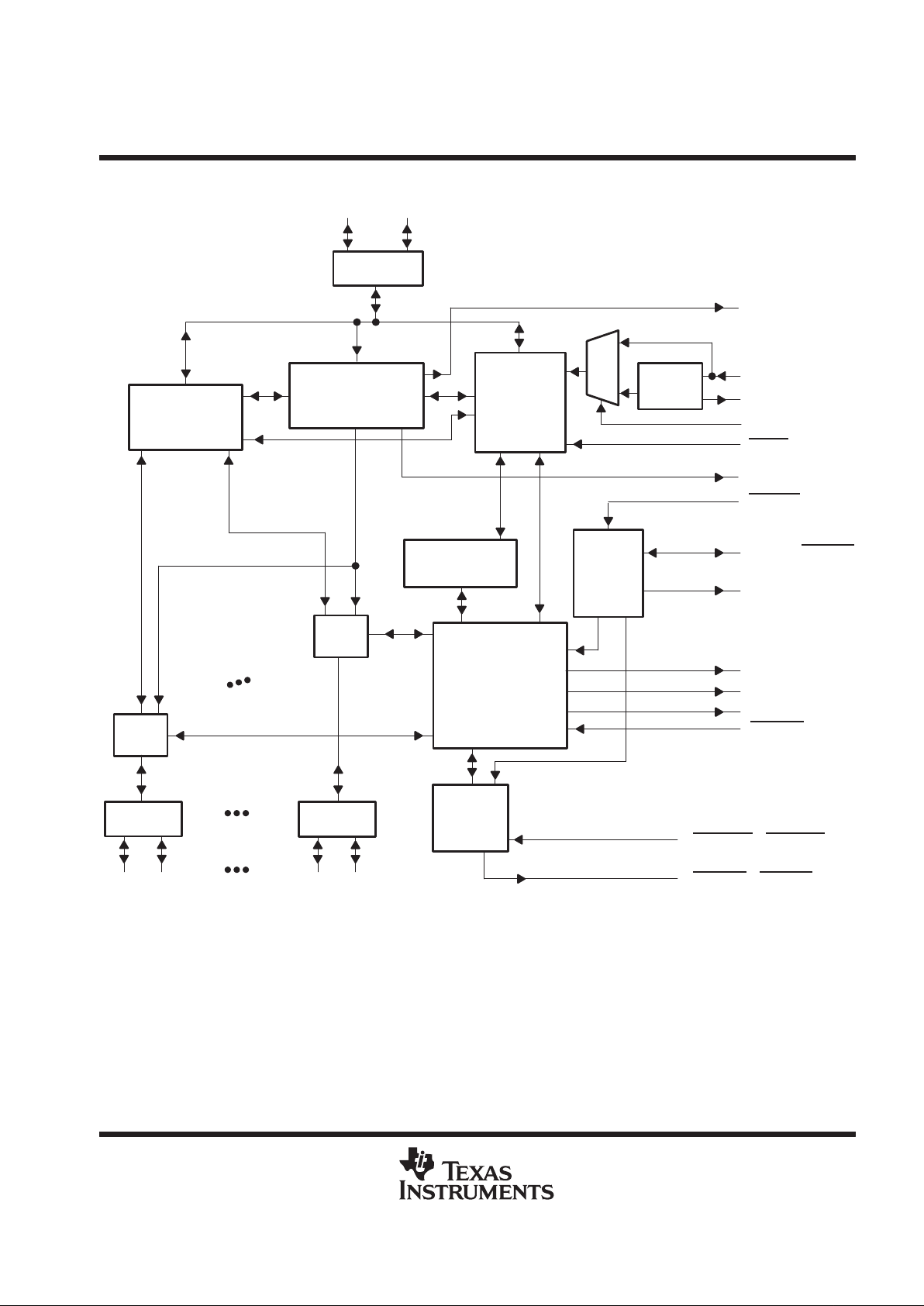
functional block diagram
45
6
47
8
7
Hub Repeater
Suspend/Resume
Logic and
Frame Timer
SIE
SIE Interface
Logic
Port 1
Logic
Hub/Device
Command
Decoder
Hub
Power
Logic
OVRCUR1 – OVRCUR7
PWRON1 – PWRON7
XTAL1/CLK 48
OSC/PLL
DP0 DM0
34
USB
Transceiver
DP7 DM7
DP1 DM1
14 13
12, 16, 20, 25, 29, 33, 37
11, 15, 19, 23,28, 32, 36
RESET
USB
Transceiver
Serial
EEPROM
Interface
EXTMEM
EEDATA/GANGED
EECLK
USB
Transceiver
39 38
Port 4
Logic
10
BUSPWR
1
SUSPND
41
PORTPWR
42
PORTDIS
40
HUBCFG
MODE
M
U
X
44
XTAL2
1
0
48
2
DP0PUR
TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
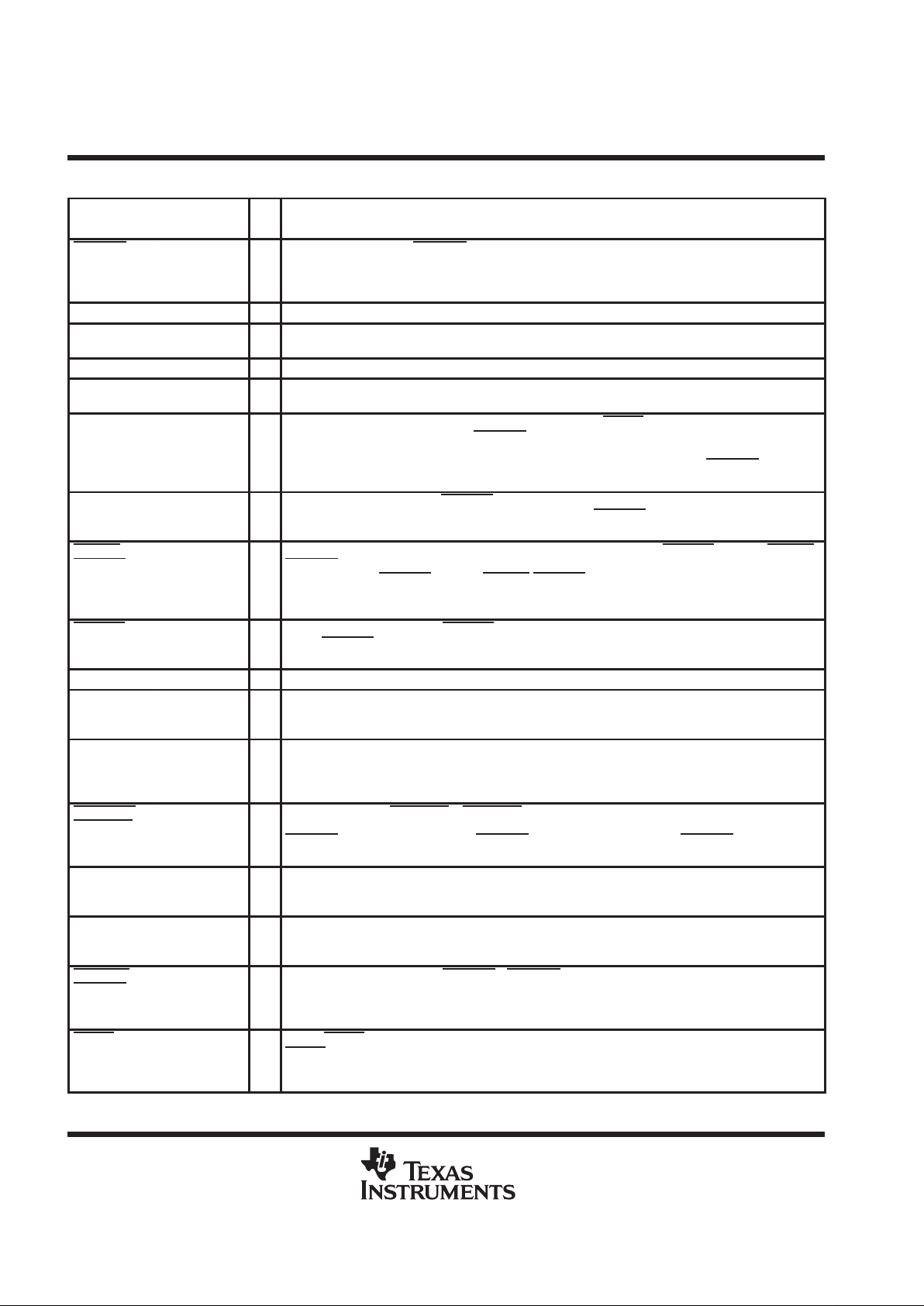
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
I/O
DESCRIPTION
BUSPWR 10 I Power source indicator. BUSPWR is an active low input that indicates whether the downstream ports
source their power from the USB cable or a local power supply. For the bus-power mode, this pin should
be pulled low, and for the self–powered mode, this pin should be pulled to 3.3 V . Input must not change
dynamically during operation.
DM0 4 I/O Root port USB differential data minus. DM0 paired with DP0 constitutes the upstream USB port.
DM1 – DM7 13, 17, 21, 26,
30, 34, 38
I/O USB differential data minus. DM1 – DM7 paired with DP1 – DP7 support up to seven downstream USB
ports.
DP0 3 I/O Root port USB differential data plus. DP0 paired with DM0 constitutes the upstream USB port.
DP1 – DP7 14, 18, 22, 27,
31, 35, 39
I/O USB differential data plus. DP1 – DP7 paired with DM1 – DM7 support up to seven downstream USB
ports.
DP0PUR 2 O Pull-up resistor connection. When a system reset happens (RESET being driven to low, but not USB
reset) or any logic level change on BUSPWR terminal, DP0PUR output is inactive (floating) until the
internal counter reaches a 15 ms time period. After the counter expires, DP0PUR is driven to the V
CC
(3.3 V) level thereafter until the next system reset event occurs or there is a BUSPWR
logic level
change.
EECLK 7 O EEPROM serial clock. When EXTMEM is high, the EEPROM interface is disabled. The EECLK pin is
disabled and should be left floating (unconnected). When EXTMEM is low, EECLK acts as a 3-state
serial clock output to the EEPROM with a 100 µA internal pulldown.
EEDATA/
GANGED
8 I/O EEPROM serial data/power management mode indicator. When EXTMEM is low, EEDATA/
GANGED acts as a serial data I/O for the EEPROM and is internally pulled down with a 100 µA
pulldown. When EXTMEM
is high, EEDATA/GANGED selects between gang or per port power
over–current detection for the downstream ports. This standard TTL input must not change dynamically
during operation.
EXTMEM 47 I EEPROM read enable. When EXTMEM is high, the serial EEPROM interface of the device is disabled.
When EXTMEM
is low, terminals 7 and 8 are configured as the clock and data pins of the serial
EEPROM interface, respectively.
GND 5, 24, 43 Ground. GND terminals must be tied to ground for proper operation.
HUBCFG
†
40 O Hub configured. Used to control LED indicator. When the hub is configured, HUBCFG is high, which
can be used to turn on a green LED. When the hub is not configured, HUBCFG is low, which can be
used to turn on a red LED.
MODE 48 I Mode select. When MODE is low, the APLL output clock is selected as the clock source to drive the
internal core of the chip and 6-MHz crystal or oscillator can used. When MODE is high, the clock on
XTAL1/CLK48 is selected as the clock source and 48-MHz oscillator or other on-board clock source
can be used.
OVRCUR1 –
OVRCUR7
12, 16, 20, 25,
29, 33, 37
I Over-current input. OVRCUR1 – OVRCUR7 are active low. For per-port over current detection, one
over-current input is available for each of the seven downstream ports. In the ganged mode, any
OVRCUR
input may be used and all OVRCUR pins should be tied together. OVRCUR pins have noise
filtering logic.
PORTPWR
†
41 O Any port powered. Used to control LED indicator. When any port is powered on, PORTPWR is high,
which can be used to turn on a green LED. When all ports are off, PORTPWR is low , which can be used
to turn on a red LED.
PORTDIS
†
42 O No ports disabled. PORTDIS is used for LED indicator control. When no port is disabled, PORTDIS is
high, which can be used to turn on a green LED. When any port is disabled, PORTDIS is low, which
can be used to turn on a red LED.
PWRON1 –
PWRON7
11, 15, 19, 23,
28, 32, 36
O Power-on/-off control signals. PWRON1 – PWRON7 are active low, push-pull outputs that enables the
external power switch device. Push-pull outputs eliminate the pull-up resistors which are required by
for open-drain outputs. However, the external power switches that connect to these pins must be able
to operate with 3.3-V inputs because these outputs cannot drive 5-V signals.
RESET 6 I Reset. RESET is an active low TTL input with hysteresis and must be asserted at power up. When
RESET is asserted, all logic is initialized. Generally, a reset with a pulse width between 100 µs and 1
ms is recommended after 3.3-V VCC reaching its 90%. The clock signal must be active during the last
60 µs of the reset window.
TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
5
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
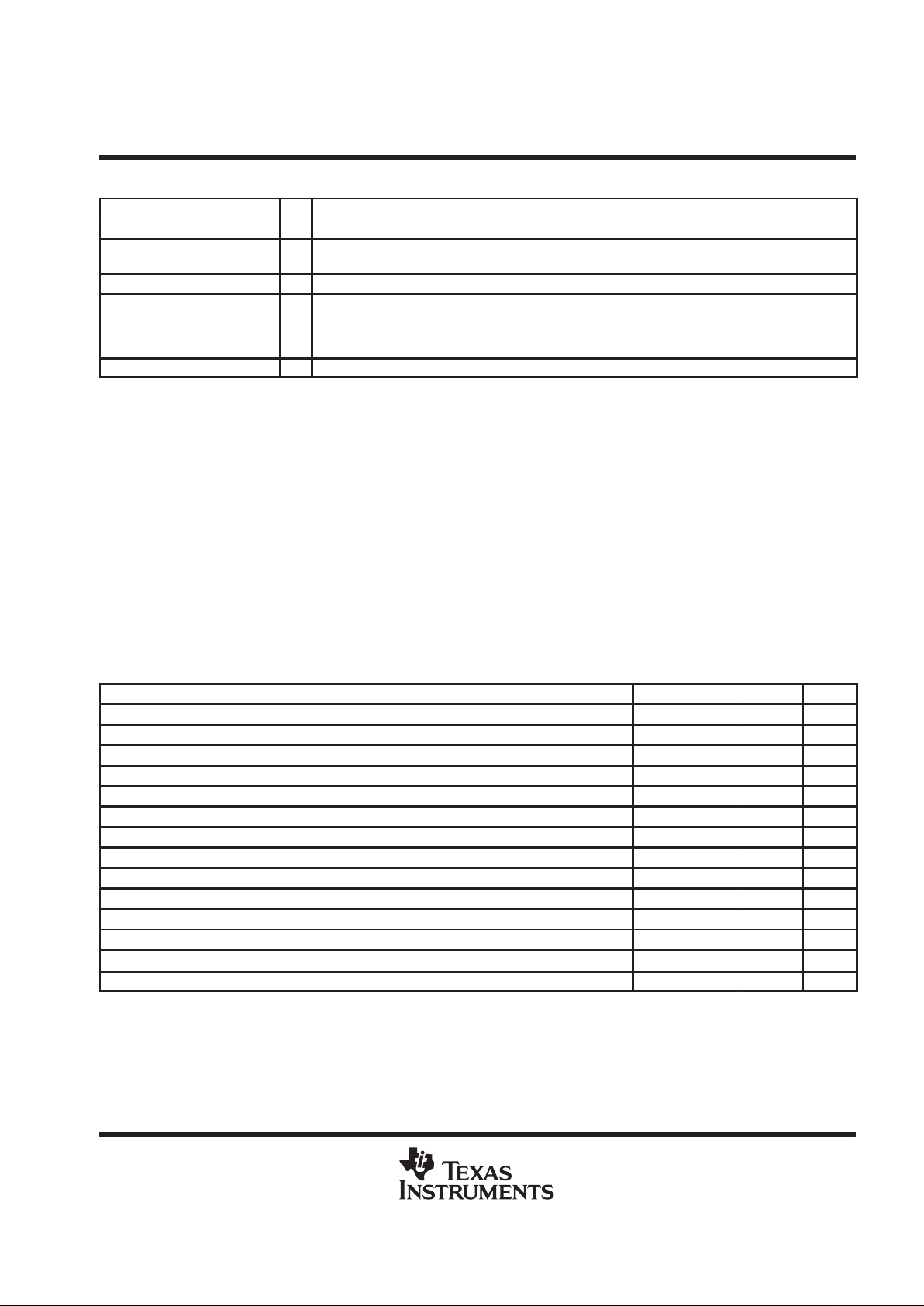
Terminal Functions (Continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
I/O
DESCRIPTION
SUSPND 1 O Suspend status. SUSPND is an active high output available for external logic power down operations.
During the SUSPEND mode, SUSPND is high. SUSPND is low for normal operation.
V
CC
9, 46 3.3-V supply voltage.
XTAL1/CLK48 45 I Crystal 1/48-MHz Clock Input. When MODE is low, XTAL1/CLK48 is a 6-MHz crystal input with 50%
duty cycle. An internal APLL generates the 48-MHz and 12-MHz clocks used internally by the ASIC
logic. When MODE is high, XTAL1/CLK48 acts as the input of the 48 MHz clock and the internal APLL
logic is bypassed.
XTAL2 44 O Crystal 2. XTAL2 is a 6-MHz crystal output. This terminal should be left open when using an oscillator.
†
All LED control are 3-stated during low-power suspend.
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
†
Supply voltage range, VCC (see Note 1) –0.5 V to 3.6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input voltgage range, VI –0.5 V to VCC + 0.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output voltage range, VO –0.5 V to VCC + 0.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input clamp current, I
IK
, (VI < 0 V or VI > VCC) ±20 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output clamp current, IOK, (VO < 0 V or V
O
> VCC) ±20 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
stg
–65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range, TA 0°C to 70°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTE 1: All voltage levels are with respect to GND.
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, V
CC
3 3.3 3.6 V
Input voltage, TTL/LVCMOS‡, V
I
0 V
CC
V
Output voltage, TTL/LVCMOS§, V
O
0 V
CC
V
High-level input voltage, signal-ended receiver, V
IH(REC)
2 V
CC
V
Low-level input voltage, signal-ended receiver, V
IL(REC)
0.8 V
High-level input voltage, TTL/LVCMOS‡, V
IH(TTL)
2 V
CC
V
Low-level input voltage, TTL/LVCMOS‡, V
IL(TTL)
0 0.8 V
Operating free-air temperature, T
A
0 70 °C
External series, differential driver resistor, R
(DRV)
22 Ω
Operating (DC differential driver) high speed mode, f
(OPRH)
12 Mb/s
Operating (DC differential driver) low speed mode, f
(OPRL)
1.5 Mb/s
Common mode, input range, differential receiver , V
(ICR)
0.8 2.5 V
Input transition times (tr and tf), TTL/LVCMOS‡ 0 25 ns
Junction temperature range, T
J
¶
0 115 °C
‡
Applies for input and bidirectional buffers
§
Applies for output and bidirectional buffers
¶
These junction temperatures reflect simulated conditions. Absolute maximum junction temperature is 150°C. The customer is responsible for
verifying junction temperature.

TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of operating free-air temperature and supply
voltage (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT
TTL/LVCMOS IOH = –4 mA VCC –
0.5
V
OH
High-level output voltage
R
(DRV)
= 15 kΩ, to GND 2.8
V
USB data lines
IOH = –12 mA (without R
(DRV)
) VCC –
0.5
TTL/LVCMOS IOL = 4 mA 0.5
V
OL
Low-level output voltage
R
(DRV)
= 1.5 k Ω to 3.6 V 0.3
V
USB data lines
IOL = 12 mA (without R
(DRV)
) 0.5
TTL/LVCMOS 1.8 V
V
IT+
Positi
ve input threshold voltage
Single-ended
0.8 V ≤ V
ICR
≤ 2.5 V 1.8 V
TTL/LVCMOS 0.8 V
V
IT–
N
egative-input threshold voltage
Single-ended
0.8 V ≤ V
ICR
≤ 2.5 V 1 V
TTL/LVCMOS 0.3 0.7 V
V
hys
I
nput hysteresis†
(V
T+
–
VT–)
Single-ended 0.8 V ≤ V
ICR
≤ 2.5 V 300 500 mV
p
p
TTL/LVCMOS V = VCC or GND‡ ±10 µA
IOZHigh-impedance output current
USB data lines 0 V ≤ VO ≤ V
CC
±10 µA
I
IL
Low-level input current TTL/LVCMOS VI = GND –1 µA
I
IH
High-level input current TTL/LVCMOS VI = V
CC
1 µA
z
o(DRV)
Driver output impedance USB data lines Static VOH or V
OL
7.1 19.9 Ω
V
ID
Differential input voltage USB data lines 0.8 V ≤ V
ICR
≤ 2.5 V 0.2 V
p
pp
Normal operation 40 mA
ICCInput supply current
Suspend mode 1 µA
†
Applies for input buffers with hysteresis
‡
Applies for open drain buffers
differential driver switching characteristics over recommended ranges of operating free-air
temperature and supply voltage, C
L
= 50 pF (unless otherwise noted)
full speed mode
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT
t
r
Transition rise time for DPor DM See Figure 1 and Figure 2 4 20 ns
t
f
Transition fall time for DPor DM See Figure 1 and Figure 2 4 20 ns
t
(RFM
Rise/fall time matching
§
(tr/tf) × 100 90% 110%
V
O(CRS)
Signal crossover output voltage
§
1.3 2.0 V
§
Charicterized only. Limits are approved by design and are not production tested.
low speed mode
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT
t
r
Transition rise time for DPor DM
§
CL = 200 pF to 600 pF, See Figure 1 and Figure 2 75 300 ns
t
f
Transition fall time for DPor DM
§
CL = 200 pF to 600 pF, See Figure 1 and Figure 2 75 300 ns
t
(RFM)
Rise/fall time matching
§
(tr/tf) × 100 80% 120%
V
O(CRS)
Signal crossover output voltage
§
CL = 200 pF to 600 pF 1.3 2.0 V
§
Charicterized only. Limits are approved by design and are not production tested.

TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
7
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
C
L
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
C
L
Full
Low
V(
TERM)
= V
CC
1.5 kΩ
DP
DM
22 Ω
22 Ω
Characterization
measurement point
Figure 1. Differential Driver Switching Load
90%
10%
t
r
90%
10%
V
OH
V
OL
DM
DP
t
f
90%
10%
t
r
10%
t
f
90%
NOTE: The tr/tf ratio is measured as t
r(DP)/tf(DM)
and t
r(DM)/tf(DP)
at each crossover point.
Figure 2. Differential Driver Timing Waveforms
0.5
0
012
– Differential Receiver Input Sensitivity – V
1
1.5
34
V
ID
V
ICR
– Common Mode Input Range – V
0.8
3.6
0.2
1.3
2.5
Figure 3. Differential Receiver Input Sensitivity vs. Common Mode Input Range
V
hys
V
IT+
V
IT–
V
CC
V
IH
V
IL
0 V
Logic high
Logic low
Figure 4. Single-Ended Receiver Input Signal Parameter Definitions

TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
A major advantage of USB is the ability to connect 127 functions configured in up to six logical layers (tiers) to
a single personal computer (see Figure 5)
PC
With Root Hub
Monitor
With 4-Port Hub (Self-Powered)
Keyboard
With 4-Port Hub
(Bus-Powered)
Printer
With 4-Port Hub
(Self-Powered)
Modem Telephone
Mouse
Left
Speaker
Right
Speaker
Digital
Scanner
Scanner
Figure 5. USB Tiered Configuration Example
Another advantage of USB is that all peripherals are connected using a standardized four wire cable that
provides both communication and power distribution. The power configurations are bus-powered and
self-powered modes. The maximum current that may be drawn from the USB 5-V line during power up is 100
mA. For the bus-powered mode, a hub can draw a maximum of 500 mA from the 5-V line of the USB cable. A
bus-powered hub must always be connected downstream to a self-powered hub unless it is the only hub
connected to the PC and there are no high-powered functions connected downstream. In the self-powered
mode, the hub is connected to an external power supply and can supply up to 500 mA to each downstream port.
High-powered functions may draw a maximum of 500 mA from each downstream port and may only be
connected downstream to self-powered hubs. Per the USB specification, in the bus-powered mode, each
downstream port can provide a maximum of 100 mA of current, and in the self-powered mode, each
downstream port can provide a maximum of 500 mA of current.
Both bus-powered and self-powered hubs require over-current protection for all downstream ports. The two
types of protection are individual port management (individual port basis) or ganged port management (multiple
port basis). Individual port management requires power management devices for each individual downstream
port, but adds robustness to the USB system because, in the event of an over-current condition, the USB host
only powers down the port that has the condition. The ganged configuration uses fewer power management
devices and thus has lower system costs, but in the event of an over-current condition on any of the downstream
ports, all the ganged ports are disabled by the USB host.
Using a combination of the BUSPWR and EEDA T A/GANGED
inputs, the TUSB2077A supports four modes of
power management: bus-powered hub with either individual port power management or ganged port power
management, and the self-powered hub with either individual port power management or ganged port power
management. Texas Instruments supplies the complete hub solution because we offer this TUSB2077A, the
TUSB2046 (4-port) and the TUSB2140B (4-port with I
2
C) hubs along with the power management chips needed
to implement a fully USB Specification 1.1 compliant system.

TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
9
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
The following sections provide block diagram examples of how to implement the TUSB2077A device. Please
note, even though no resistors are shown, pullup, pulldown and series resistors must still be used to properly
implement this device.
Figure 6 is a block diagram example of how to connect the external EEPROM if a custom Product ID and Vendor
ID are desired.
Figure 7 is an example of how to generate the 6-MHz clock signal. Figure 8 shows the EEPROM Read Operation
Timing Diagram. Figures 9, 10, and 11 illustrate how to connect the TUSB2077A device for different power
source and port power management combinations.
1 kΩ
DP0
DM0
EEDATA
TUSB2077A USB Hub
System
Power-On Reset
Regulator
Power
Switching
OVRCUR1
–
OVRCUR7
PWRON1 –
PWRON7
EECLK
RESET
XTAL1
EXTMEM
V
CC
GND
DP1 – DP7
DM1 – DM7
GND
V
bus
5 V GND
XTAL2
USB Data lines
and Power to
Downstream
Ports
Bus or Local Power
6-MHz Clock
Signal
7
7
7
7
45
44
6
3
4
8
7
9, 46
5, 24, 43
14, 18, 22, 27, 31, 35, 39
12, 16, 20, 25, 29, 33, 37
13, 17, 21, 26, 30, 34, 38
11, 15, 19, 23, 28, 32, 36
5
8
6
2
4
3
ORG
V
CC
V
SS
D
Q
C
S
1
EEPROM
3.3 V
47
Figure 6. Typical Application of the TUSB2077A USB Hub
XTAL1 XTAL2
NOTE A: Figure 7 assumes a 6 MHz fundamental crystal that is parallel loaded. The component values of C1, C2 and Rd were determined
using a crystal from Fox Electronics– part number HC49U–6.00MHz30\50\0 ±70\20 which means ±30 ppm at 25°C and 50 ppm from
0°C to 70°C. The characteristics for the crystal are load capacitance (CL) of 20 pF , maximum shunt capacitance (Co) of 7 pF and the
maximum ESR of 50 Ω. In order to insure enough negative resistance, use C1 = C2 = 27 pF . The resistor Rd is used to trim the gain,
and Rd = 1.5 kΩ
is recommended.
R
d
C2C1
C
L
Figure 7. Crystal Tuning Circuit

TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
programming the EEPROM
An SGS Thompson M93C46 EEPROM or equivalent is used for storing the programmable VID and PID. When
the EEPROM interface is enabled (EXTMEM
= 0), the EECLK and EEDA TA are internally pulled down (100 µA)
inside the TUSB2077A. The internal pulldowns are disabled when the EEPROM interface is disabled
(EXTMEM
= 1).
The EEPROM is programmed with the three 16-bit locations as shown in Table 1. Connecting pin 6 of the
EEPROM high (ORG = 1) organizes the EEPROM memory into 64×16 bit words.
T able 1. EEPROM Memory Map
ADDRESS D15 D14 D13 D12–D8 D7–D0
00000 0
GANGED 00000 00000 00000000
00001 VID High-byte VID Low-byte
00010 PID High-byte PID Low-byte
XXXXXXXX
The D and Q signals of the EEPROM must be tied together using a 1 kΩ resistor with the common I/O operations
forming a single-wire bus. After system power-on reset, the TUSB2077A performs a one-time access read
operation from the EEPROM if the EXTMEM pin is pulled low and the chip select(s) of the EEPROM is
connected to the system power-on reset. Initially , the EEDATA pin will be driven by the TUSB2077A to send a
start bit (1) which is followed by the read instruction (10) and the starting-word address (00000). Once the read
instruction is received, the instruction and address are decoded by the EEPROM, which then sends the data
to the output shift register. At this point, the hub stops driving the EEDATA pin and the EEPROM starts driving.
A dummy (0) bit is then output and the first three 16-bit words in the EEPROM are output with the most significant
bit (MSB) first.
The output data changes are triggered by the rising edge of the clock provided by the TUSB2077A on the EECLK
pin. The
SGS-Thompson M936C46
EEPROM is recommended because it advances to the next memory
location by automatically incrementing the address internally. Any EEPROM used must have the automatic
internal address advance function. After reading the three words of data from the EEPROM, the TUSB2077A
puts the EEPROM interface into a high-impedance condition (pulled down internally) to allow other logic to share
the EEPROM. The EEPROM read operation is summarized in Figure 8. For more details on EEPROM
operation, refer to
SGS-Thompson Microelectronics M93C46 Serial Microwire Bus EEPROM
data sheet.

TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
• 11
6 Bit Address (000000)Start Read OP Code(10) 48 Data Bits Don’t Care
D15 D14 D0 XX
A5 A1
A0 Dummy
Bit
MSB of The
First Word
Other
Data Bits
LSB of
Third Word
MSB of
Fourth Word
EEPROM Driving Data LineHub Driving Data Line
3-Stated
With Internal
Pulldown
S
C
D
Figure 8. EEPROM Read Operation Timing Diagram
Other
Address
Bits

TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
bus-powered hub, ganged port power management
When used in bus-powered mode, the TUSB2077A supports up to four downstream ports by controlling a
TPS2041 device which is capable of supplying 100 mA of current to each downstream port. Bus-powered hubs
must implement power switching to ensure current demand is held below 100 mA when the hub is hot-plugged
into the system. Utliizing the TPS2041 for ganged power management provides over-current protection for the
downstream ports. The SN75240 transient suppressors reduce inrush current and voltage spikes on the data
lines. The OVRCUR
signals should be tied together for a ganged operation.
†
TPS2041 and SN75240 are Texas Instruments devices.
‡
120 µF per hub is the minimum required per the USB specification, version 1.1. However, TI recommends a 100 µF low ESR tantulum capacitor
per port for immunity to voltage droop.
§
LDO is a 5 V to 3.3 V voltage regulator. TPS76333 from Texas Instruments can be used.
DP1
DM1
DP2
DM2
DP3
DM3
DP4
PWRON1
PWRON2
PWRON3
PWRON4
OVRCUR1
OVRCUR2
OVRCUR3
OVRCUR4
DM4
DP0
DM0
V
CC
XTAL1
XTAL2
EXTMEM
RESET
SN75240
†
EN IN
OC
OUT
D +
D –
5 V
GND
D +
D –
5 V
D +
D –
5 V
D +
D –
5 V
Downstream
Ports
TUSB2077A
TPS2041
†
ABC
D
100 µF
‡
SN75240
†
ABC
D
GND
GND
GND
1 µF
100 µF
‡
100 µF
‡
100 µF
‡
5 V
3.3 V
GND
D +
D –
Upstream
Port
3.3 V LDO
§
SN75240
†
A
B
5 V
GND
C
D
4.7 µF
0.1 µF
4.7 µF
GND
Ferrite Beads
Ferrite Beads
Ferrite Beads
Ferrite Beads
EEDATA/GANGED
6-MHz Clock
Signal
BUSPWR
System
Power-On Reset
OUT
OUT
IN
3.3 V
1.5 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
DP5–DP7
DM5–DM7
PWRON5–7
OVRCUR5–7
NC
3.3 V
MODE
DP0PUR
Figure 9. TUSB2077A Bus-Powered Hub, Ganged Port Power Management Application

TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
13
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
self-powered hub, individual port power management
In a self-powered configuration, the TUSB2077A can be implemented for individual port-power management
when used with two TPS2044 because it is capable of supplying 500 mA of current to each downstream port
and can provide current limiting on a per port basis. When the hub detects a fault on a downstream port, power
is removed from only the port with the fault and the remaining ports continue to operate normally . Self-powered
hubs are required to implement over-current protection and report overcurrent conditions. The SN75240
transient suppressors reduce inrush current and voltage spikes on the data lines.
Figure 10. TUSB2077A Self-Powered Hub, Individual Port-Power Management Application
6-MHz Clock
Signal
BUSPWR
DP1
DM1
DP2
DM2
DP6
DM6
DP7
PWRON1
PWRON2
PWRON6
PWRON7
OVRCUR1
OVRCUR2
DM7
DP0
DM0
V
CC
GND
XTAL1
XTAL2
EXTMEM
RESET
5 V
3.3 V
GND
D +
D –
Upstream
Port
3.3 V LDO
§
SN75240
†
EN1
OC1
D +
D –
5 V
GND
D +
D –
5 V
D +
D –
5 V
D +
D –
5 V
Downstream
Ports
5-V Board Power
Supply
TUSB2077A
TPS2044
†
ABC
D
100 µF
‡
SN75240
†
ABC
D
GND
GND
GND
100 µF
‡
100 µF
‡
100 µF
‡
†
TPS2042 and SN75240 are Texas Instruments devices. T wo TPS2042 devices can be substituted for
the TPS2044.
‡
120 µF per hub is the minimum required per the USB specification, version 1.1. However, TI recommends a 100 µF low ESR tantulum capacitor
per port for immunity to voltage droop.
SN75240
†
A
B
5 V
GND
C
D
4.7 µF
0.1 µF
4.7 µF
EN2
EN3
EN4
OC2
OC3
OC4
OUT4
OUT3
OUT2
OUT1
EEDATA/GANGED
System
Power-On Reset
IN1
0.1 µF
IN2
§
LDO is a 5 V to 3.3 V voltage regulator. TPS76333 from Texas Instruments can be used.
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
1.5 kΩ
3.3 V
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
3.3 V
OVRCUR6
OVRCUR7
MODE
DP0PUR

TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
14
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
self-powered hub, ganged port power management
The TUSB2077 can also be implemented for ganged port power management in a self-powered configuration.
The implementation is very similar to the bus-powered example with the exception that a self-powered port
supplies 500 mA of current to each downstream port. The over-current protection can be provided by a TPS2044
quad device or a TPS2024 single power switch.
6-MHz Clock
Signal
Figure 11. TUSB2077A Self-Powered Hub, Ganged Port Power Management Application
†
TPS2044, TPS2042, and SN75240 are Texas Instruments devices.
The TPS2024 can be substituted for the TPS2044.
‡
120 µF per hub is the minimum required per the USB specification, version 1.1. However, TI recommends a 100 µF low ESR tantulum capacitor
per port for immunity to voltage droop.
§
LDO is a 5 V to 3.3 V voltage regulator. TPS76333 from Texas Instruments can be used.
DP1
DM1
DP2
DM2
PWRON1
PWRON7
OVRCUR1
OVRCUR7
GND
XTAL1
XTAL2
EXTMEM
RESET
TPS2044
†
IN1EN1
OUT1
D +
D –
5 V
GND
D +
D –
5 V
Downstream
Ports
OC1
TUSB2077A
D63
DM6
DP7
DM7
SN75240
†
ABC
D
100 µF
‡
GND
100 µF
‡
DP0
DM0
V
CC
5 V
3.3 V
GND
D +
D –
Upstream
Port
3.3 V LDO
§
SN75240
†
A
B
5 V
GND
C
D
4.7 µF
0.1 µF
4.7 µF
Ferrite Beads
5 V Board Power
Supply
Ferrite Beads
0.1 µF
D +
D –
5 V
GND
D +
D –
5 V
GND
100 µF
‡
Ferrite Beads
SN75240
†
ABC
D
100 µF
‡
BUSPWR
3.3 V
Ferrite Beads
EEDATA/GANGED
System
Power-On Reset
EN2
EN3
EN4
OC2
OC3
OC4
OUT2
OUT3
OUT4
IN2
1.5 kΩ
3.3 V
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
15 kΩ
MODE
DP0PUR

TUSB2077A
7-PORT HUB FOR THE UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS
WITH OPTIONAL SERIAL EEPROM INTERFACE
SLLS414 – MARCH 2000
15
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
MECHANICAL DATA
PT (S-PQFP-G48) PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK
4040052/B 03/95
0,13 NOM
0,17
0,27
25
24
SQ
12
13
36
37
6,80
7,20
1
48
5,50 TYP
0,25
0,45
0,75
0,05 MIN
SQ
9,20
8,80
1,35
1,45
1,60 MAX
Gage Plane
Seating Plane
0,10
0°–7°
0,50
M
0,08
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Falls within JEDEC MO-136
D. This may also be a thermally enhanced plastic package with leads connected to the die pads.

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
Customers are responsible for their applications using TI components.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...