Page 1

User’s Guide
TPS40003 Based 5–A Converter in
Less Than One Square Inch
User’ s Gu ide
Page 2

EVM IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments (TI) provides the enclosed product(s) under the following conditions:
This evaluation kit being sold by TI is intended for use for ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT OR EVALUATION
PURPOSES ONLY and is not considered by TI to be fit for commercial use. As such, the goods being provided
may not be complete in terms of required design-, marketing-, and/or manufacturing-related protective
considerations, including product safety measures typically found in the end product incorporating the goods.
As a prototype, this product does not fall within the scope of the European Union directive on electromagnetic
compatibility and therefore may not meet the technical requirements of the directive.
Should this evaluation kit not meet the specifications indicated in the EVM User’s Guide, the kit may be returned
within 30 days from the date of delivery for a full refund. THE FOREGOING WARRANTY IS THE EXCLUSIVE
WARRANTY MADE BY SELLER TO BUYER AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED,
IMPLIED, OR S TA TUTOR Y, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
The user assumes all responsibility and liability for proper and safe handling of the goods. Further, the user
indemnifies TI from all claims arising from the handling or use of the goods. Please be aware that the products
received may not be regulatory compliant or agency certified (FCC, UL, CE, etc.). Due to the open construction
of the product, it is the user’s responsibility to take any and all appropriate precautions with regard to electrostatic
discharge.
EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT OF THE INDEMNITY SET FORTH ABOVE, NEITHER PARTY SHALL BE LIABLE
TO THE OTHER FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
TI currently deals with a variety of customers for products, and therefore our arrangement with the user is not
exclusive.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance, customer product design, software performance, or
infringement of patents or services described herein.
Please read the EVM User’s Guide and, specifically, the EVM Warnings and Restrictions notice in the EVM
User’s Guide prior to handling the product. This notice contains important safety information about temperatures
and voltages. For further safety concerns, please contact the TI application engineer.
Persons handling the product must have electronics training and observe good laboratory practice standards.
No license is granted under any patent right or other intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any
machine, process, or combination in which such TI products or services might be or are used.
Mailing Address:
Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303
Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2003, Texas Instruments Incorporated
2
Page 3

DYNAMIC WARNINGS AND RESTRICTIONS
It is important to operate this EVM within the input voltage range of 0 V to 5.5 V.
Exceeding the specified input range may cause unexpected operation and/or irreversible damage to the EVM.
If there are questions concerning the input range, please contact a TI field representative prior to connecting
the input power.
Applying loads outside of the specified output range may result in unintended operation and/or possible
permanent damage to the EVM. Please consult the EVM User’s Guide prior to connecting any load to the EVM
output. If there is uncertainty as to the load specification, please contact a TI field representative.
During normal operation, some circuit components may have case temperatures greater than 50°C. The EVM
is designed to operate properly with certain components above 50°C as long as the input and output ranges are
maintained. These components include but are not limited to linear regulators, switching transistors, pass
transistors, and current sense resistors. These types of devices can be identified using the EVM schematic
located in the EVM User’s Guide. When placing measurement probes near these devices during operation,
please be aware that these devices may be very warm to the touch.
Mailing Address:
Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303
Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2003, Texas Instruments Incorporated
3
Page 4

SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
r
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square
Inch
Mark Dennis Systems Powe
Contents
1 Introduction 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Features 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Schematic 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Design Procedure 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 PowerPAD Packaging 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Test Results/Performance Data 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 PCB Layout 15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 List of Material 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 Introduction
The TPS40002 and the TPS40003 are voltage-mode, synchronous buck PWM controllers that utilize TI’s
proprietary Predictive Gate Drive technology to wring maximum efficiency from step-down converters. These
controllers provide a bootstrap charging circuit to allow the use of an N-channel MOSFET as the topside buck
switch to reduce conduction losses and increase silicon device utilization. Predictive Gate Drive technology
controls the delay from main switch turn-off to synchronous rectifier turn-on and also the delay from rectifier
turn-off to main switch turn-on. This allows minimization of the losses in the MOSFET body diodes by reducing
conduction and reverse recovery time. This user’s guide provides details on a 5-A buck converter that converts
3.3 V down to a 1.2-V level utilizing the TPS40003 controller, with less than one square inch board area.
A schematic for the board is shown in Figure 1. A list of material is provided in the final section.
2 Features
The specification for this board is as follows:
D V
D V
D 0 A ≤ I
D Efficiency > 90% with a load of 2 A
D Output voltage ripple < 2% V
D Physical size < 1 square inch circuit area
= 3.0 V to 3.6 V
IN
= 1.2 V ± 3%
OUT
≤ 5 A
OUT
OUT
4
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
Page 5
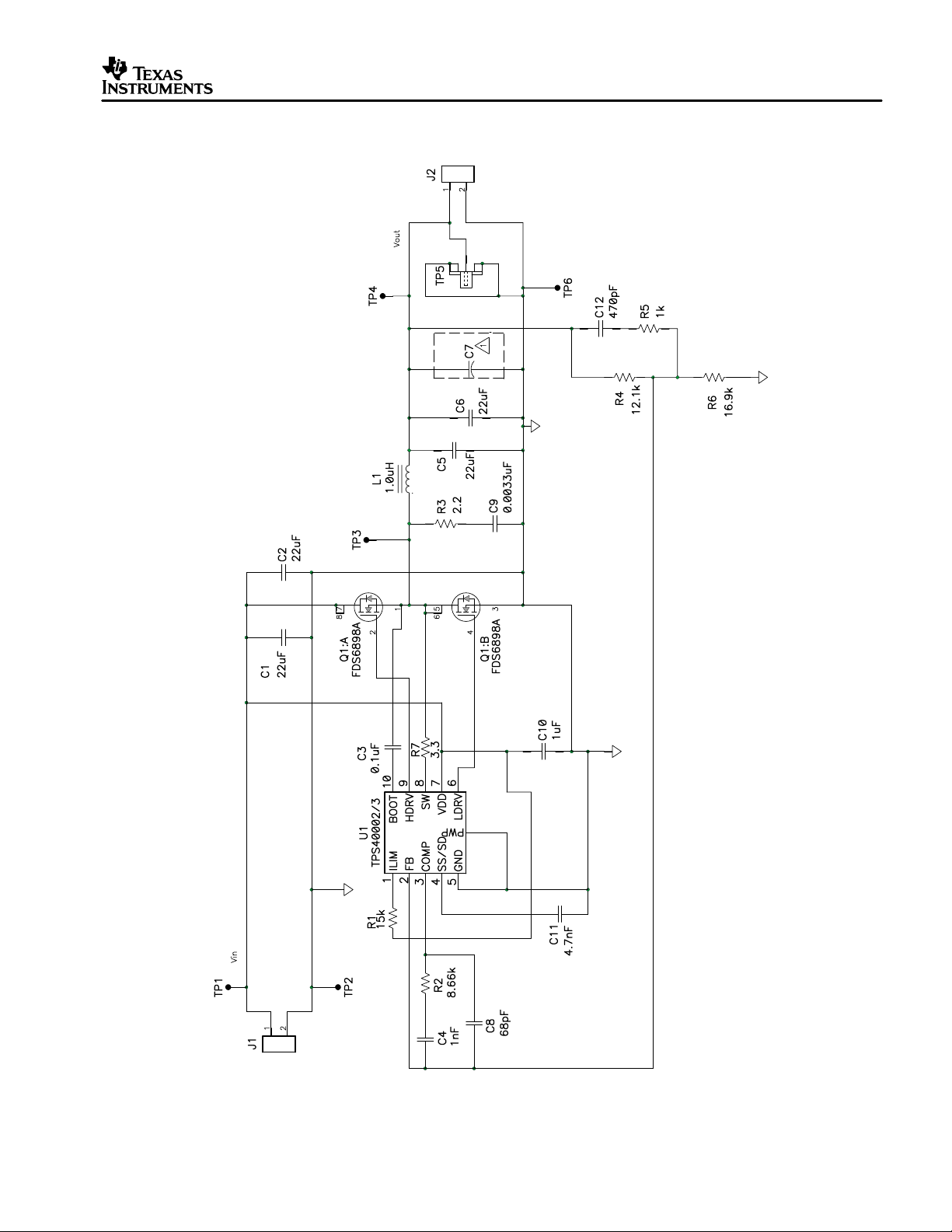
3 Schematic
SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
+
Figure 1. Application Diagram for the TPS40002/3
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
5
Page 6

SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
4 Design Procedure
4.1 TPS4000X Family Device Selection
The TPS4000X family of devices offers four selections to encompass the frequency and output current mode
choices. The TPS40003 is selected for the following reasons. First, the internal oscillator components set a fixed
switching frequency of 600 kHz. This allows minimally sized filter components in this compact design. The other
choice related to the TPS4000X family involves the selection of Discontinuous Current Mode (DCM) operation
or Continuous Current Mode (CCM) operation at lighter loads. In this design the TPS40003 is selected to keep
the current continuous all the way to zero load, to provide robust control characteristics.
4.2 Inductance Value
The output inductor value is selected to set the ripple current to a value most suited to overall circuit functionality.
The inductor value is calculated in equation (1).
L +
where I
V
f I
RIPPLE
OUT
RIPPLE
ȡ
ȧ
Ȣ
is chosen to be 25% of I
1 *
V
OUT
V
IN(max)
ȣ
+
ȧ
600 kHz 1.25 A
Ȥ
OUT
1.2 V
, or 1.25 A. A common value of 1 µH is selected.
ǒ
1 *
1.2 V
3.6 V
Ǔ
+ 1.07 mH
4.3 Input Capacitor Selection
Bulk input capacitor selection is based on allowable input voltage ripple and required RMS current carrying
capability. In typical buck converter applications, the converter is fed from an upstream power converter with
its own output capacitance. In this converter, onboard capacitance is provided to supply the current required
during the top MOSFET on-time while keeping ripple within acceptable limits. For this power level, input voltage
ripple of 150 mV is reasonable, and a conservative minimum value of capacitance is calculated in equation (2).
I Dt
C +
To meet this requirement with the lowest size and cost, a single 22 µF, X5R ceramic capacitor might be
considered. Although these capacitors have an extremely small resistance a typical datasheet indicates that
the part undergoes a 30°C temperature rise with 2 A
nearly 2 A
current derating. These capacitors function as power bypass components and should be located near the
MOSFET package, to keep the high frequency current flow in a tight loop. The low impedance characteristics
of the dual ceramic capacitors help to reduce noise on the V
MOSFET current sense is referenced to this point, so noise at the device must be kept to a low level.
DV
RMS
5A 606 ns
+
of current, so for a conservative design two capacitors are selected to allow for conservative
0.15 V
+ 20 mF
current at 500 kHz. With V
RMS
supply of the device. Specifically , the high side
DD
= 3.0 V our circuit requires
IN
(1)
(2)
6
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
Page 7

SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
4.4 Output Capacitor Selection
Selection of the output capacitor is based on many application variables, including function, cost, size, and
availability. The minimum allowable output capacitance is determined by the amount of inductor ripple current
and the allowable output ripple in equation (3).
I
C
OUT(min)
In this design, C
capacitive component of the ripple voltage. In addition, the voltage component due to the capacitor ESR must
be considered in equation (4).
+
OUT(min)
V
ESR
For compactness while maintaining transient response capability, two 22-µF ceramic capacitors are fitted in
parallel. The total ESR of these capacitors is below 3 mΩ, and contributes only a few mV to the output voltage
ripple.
Cout
v
I
RIPPLE
8 f V
is 22 µF with V
RIPPLE
RIPPLE
RIPPLE
0.012 V
+
1.25 A
+
8 600 kHz 12 mV
RIPPLE
+ 9.6 mW
1.25 A
= 12 mV to allow for some margin. However, this only af fects the
+ 22 mF
4.5 MOSFET Selection
The small physical size of this design requires the use of a single SO-8 package which contains dual N-channel
MOSFETs. MOSFETs with an R
amount at full load.
of 18 mΩ are selected to keep the conduction losses to a manageable
DS(on)
4.6 Short Circuit Protection
The TPS40003 implements short circuit protection by comparing the voltage across the topside MOSFET while
it is on to a voltage dropped from VDD by R
tolerances in the current source and variations in the power MOSFET on-voltage versus temperature, the short
circuit level can protect against gross overcurrent conditions only, and should be set higher than rated load. In
this particular case, R
R
+ R1 +
LIM
is selected as:
LIM
2.5 I
OUT
0.018 W
15 mA
due to an internal current source of 15 µA inside pin 1. Due to
LIM
+ 15 kW
(3)
(4)
(5)
For this design, R
tolerances over temperature and output current ripple. The high currents that are switched under short circuit
conditions may cause SW pin 8 to be driven below ground several volts, possibly injecting substrate current
which can cause improper operation of the device. A 3.3-Ω resistor has been placed in series with this pin to
limit its excursion to safe levels.
= 15 kΩ, and the factor of 2.5 in the equation accounts for the variations in component
LIM
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
7
Page 8

SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
4.7 Compensation Design
The TPS40003 uses voltage mode control in conjunction with a high frequency error amplifier. For the fastest
transient response, the loop crossover frequency is set at 1/10 f
corner frequency f
The feedback compensation network is implemented to provide two zeroes and three poles. The first pole is
placed at the origin to improve dc regulation.
is situated at 24 kHz, and the output capacitor ESR zero is far higher at approximately 1MHz.
C
, or 60 kHz. The power circuit L-C double pole
S
The first zero is placed at approximately 2/3 f
f
+
z1
2 p R
The second zero is selected at fC,
f
+
z2
2 p
The two poles are placed at approximately 300 kHz, which is one-half the switching frequency,
f
+
p1
2 p R
and
f
+
p2
2 p R
1
C
2
ǒ
R4) R
1
2
1
C
5
4
1
Ǔ
C
ǒ
5
C
4 C8
C
4
12
)C
12
Ǔ
8
, 18 kHz,
C
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
8
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
Page 9

SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
Figure 2 shows the plots for the closed loop gain and phase with VIN = 3.3 V and I
frequency of 60 kHz the phase margin is approximately 51 degrees.
40
30
20
10
0
Gain – db
–10
–20
–30
–40
100
GAIN AND PHASE MARGIN
I
= 4.4 A
LOAD
VI = 3.3 V
1000 10000 1000000
vs
FREQUENCY
Gain
Frequency – Hz
Phase
100000
150
100
50
0
–50
–100
–150
= 4.4 A. At the crossover
OUT
Phase – degrees
Figure 2.
4.8 Snubber Component Selection
The switch node where Q1 and L1 come together is very noisy. An R–C network fitted between this node and
ground can help reduce ringing and voltage overshoot on Q1:B. This ringing noise should be minimized to
prevent it from confusing the control circuitry which is monitoring this node for current limit and Predictive Gate
Drive.
As a starting point, the snubber capacitor, C9, is generally chosen to be 5 to 8 times larger than the parasitic
capacitance at the node, which is primarily C
R3 is empirically determined to be 2.2 Ω, which minimizes the ringing and overshoot at the switch node. With
low input voltages the power loss, 1/2×C×V
of Q1:B. Since COS is 440 pF for Q1:B, C9 is chosen to be 3.3 nF.
OS
2
×f , is relatively small at 24 mW.
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
9
Page 10

SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
5 PowerPAD Packaging
The TPS4000X family is available in the DGQ version of TI’s PowerP AD thermally enhanced package. In the
PowerPAD, a thermally conductive epoxy is utilized to attach the integrated circuit die to the leadframe die
pad, which is exposed on the bottom of the completed package. The leadframe die pad can be soldered to the
PCB using standard solder flow techniques when maximum heat dissipation is required. However, depending
on power dissipation requirements, the PowerPAD may not need to soldered to the PCB.
The PowerPAD package helps to keep the junction temperature rise relatively low even with the power
dissipation inherent in the onboard MOSFET drivers. This power loss is proportional to switching frequency,
drive voltage, and the gate charge needed to enhance the N-channel MOSFETs. Effective heat removal allows
the use of ultra small packaging while maintaining high component reliability.
To effectively remove heat from the PowerPAD package, a thermal land should be provided directly
underneath the package whether the package needs to be soldered or not. This thermal land usually has vias
that help to s p r ead heat to internal copper layers and/or the opposite side of the PCB. The vias should not have
thermal reli e f s t h a t are often used on ground planes, because this reduces the copper area which transfers heat.
Additionally, the vias should be small enough so that the holes are effectively plugged when plated. This
prevents the solder from wicking away from the connection between the PCB surface and the bottom of the part.
A typical construction utilizes a few vias of 0.013” diameter plated with 1 ounce copper in the land under the
TPS40003. A typical layout pattern is shown in Figure 2, but does not show the copper land which would
encompass the vias above and below the device.
2.92mm
0.5mm
(0.0197”)
(0.115”)
Minimum
PowerPad ”Y”
1.7mm
(0.068”)
0.28mm
(0.011”)
1.40mm
(0.055”)
Miminum
PowerPad ”X”
1.3mm
(0.050”)
Via Dia.
0.33mm
(0.013”)
Figure 3. PowerPAD PCB Layout Guidelines
The Texas Instrument document, PowerPAD Thermally Enhanced Package Application Report (SLMA002)
should be consulted for more information on the PowerPAD package. This report offers in-depth information
on the package, assembly and rework techniques, and illustrative examples of the thermal performance of the
PowerPAD package.
10
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
Page 11

6 Test Results/Performance Data
The test setup is shown in figure 4
DC Power
Supply
SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
Input wires 18 gauge
or larger short as feasible
CIN = 470 µF or larger, 6.3 V or higher,
low ESR AIEA or OSCON capacitor.
Place within 2 inches of J1.
TP2
GND
SLUP182
J1
TP6
C
IN
+
VIN
TP5
J2
DVM1
(+)
(–)
TP1
TP3
SCOPE
VOUTGND
TP4
DVM2
(+)
Output wires 18 gauge
or larger short as feasible
Resistive load: 0.5 Ω, ≥ 5 W
Active Load: set for 2.4 A
(–)
(–)
LOAD
(+)
Figure 4.
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
11
Page 12

SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
Typical efficiency curves are shown in Figure 5 for an input of 3.3 V.
EFFICIENCY
OUTPUT CURRENT
100
95
90
85
80
75
Efficiency – %
70
65
60
55
50
0123456
I
OUT
vs
– Output Current – A
Figure 5.
Figure 6 shows the switch node during typical operation at full load. Note that there is very minimal body diode
conduction in the bottom MOSFET. This is a result of using the predictive delay control implementation. This
technique is able to dynamically change the delays in the MOSFET drive circuit to account for variations in line,
load, and between devices.
TYPICAL SWITCH NODE WAVEFORM
2 V/div
12
t – Time – 250 ns/div
Figure 6.
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
Page 13

SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
Circuit operation with an output short circuit is shown in Figure 7. After each restart into a short circuit the pulses
terminate for a period of approximately 6 ms. This causes the input power to collapse to minuscule levels, and
the circuit is protected.
SHORT CIRCUIT OPERATION
2 V/div
t – Time – 1 ms/div
Figure 7.
Figure 8 shows the output voltage ripple which is approximately half the 24-mV limit.
OUTPUT VOLTAGE RIPPLE
10 mV/div
t – Time – 500 ns/div
Figure 8.
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
13
Page 14

SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
Figure 9 shows the startup waveforms with an input voltage of 3.3 V and a load of 0.3 Ω. Note that the output
is held low until V
(pin 4) goes above 0.12 V, and then the output comes up smoothly under closed loop
SS
softstart control.
STARTUP WAVEFORM
1 V/div
500 mV/div
500 mV/div
t – Time – 200 µs/div
Figure 9.
Figure 10 shows the transient response for a fast load step from 1 A to 2 A.
TRANSIENT RESPONSE
50 mV/div
t – Time – 20 µs/div
Figure 10.
14
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
Page 15

SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
7 PCB Layout
Figures 11 through13 show the top copper layer, the bottom copper layer , and top assembly layer, of SLUP182.
Figure 12
Figure 13
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
15
Page 16

SLUU130A – September 2002 – Revised February 2003
8 List of Material
Table 1 lists the components used in this design. With minor component tweaks this design could be modified
to meet a wide range of applications.
Reference Qty Description Manufacturer Part Number
Capacitor
Terminal Block J1, J2 2 2 pin, 15 A, 5.1 mm OST ED1609
Inductor L1 1 SMT, 1.0 µH, 8.5 A, 10 mΩ Vishay IHLP–2525CZ–01
MOSFET Q1 1 Dual N–channel, 20 V, 9.4 A, 18 mΩ Fairchild FDS6898A
Resistor
JACK TP1, TP3, TP4, 5 Test point, red Farnell 240–345
JACK TP2, TP6 2 Test point, black Farnell 240–333
Adaptor TP5 1 3.5-mm probe clip (or 131–5031–00) Tektronix 131–4244–00
Device U1 1 Syncronous buck controller, 600 kHz TI TPS40003DGQ
C1, C2, C5, C6 4 Ceramic, 22 µF, 6.3 V, X5R, 20%, 1210 Panasonic ECJ–4YB0J226M
C10 1 Ceramic, 0.001 µF, 10 V, X5R, 10%, 805 Panasonic ECJ–2YB1A105K
C11 1 Ceramic, 0.0047 µF, 50 V, X7R, 10% Vishay VJ0603Y472KXAAT
C12 1 Ceramic, 470 pF, 50 V, X7R, 10% Vishay VJ0603Y471KXAAT
C3 1 Ceramic, 0.1 µF, 50 V, X5R, 10% Vishay VJ0805Y104KXAAT
C4 1 Ceramic, 0.001 µF, 50 V, X7R, 10% Vishay VJ0603Y102KXAAT
C8 1 Ceramic, 68 pF, 50 V, NPO, 10% Vishay VJ0603A680KXAAT
C9 1 Ceramic, 0.0033 µF, 50 V, X7R, 10% Vishay VJ0805Y332KXAAT
R1 1 Chip, 15 kΩ, 1/16W, 1% Std Std
R2 1 Chip, 8.66 kΩ, 1/16 W, 1% Std Std
R3 1 Chip, 2.2 Ω, 1/10 W, 5% Std Std
R4 1 Chip, 12.1 kΩ, 1/16 W, 1% Std Std
R5 1 Chip, 1 kΩ, 1/16 W, 1% Std Std
R6 1 Chip, 16.9 Ω, 1/16 W, 1% Std Std
R7 1 Chip, 3.3 Ω, 1/16 W, 5%, 603 Std Std
16
TPS40003-Based 5-A Converter in Less Than One Square Inch
Page 17

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications,
enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue
any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing
orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms
and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty . Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI
deems necessary to support this warranty . Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all
parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for
their products and applications using TI components. T o minimize the risks associated with customer products
and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right,
copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process
in which TI products or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third–party products or services
does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof.
Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property
of the third party , or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without
alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction
of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for
such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that
product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and
is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Mailing Address:
Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303
Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2003, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...