
www.ti.com
APPLICATION CIRCUIT
PGND
ROUT-
PV
DD
RHPIN
RLINEIN
RIN
V
DD
LIN
LLINEIN
LHPIN
PV
DD
LOUT-
1
ROUT+
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
VOLUME
SEDIFF
SEMAX
AGND
BYPASS
FADE
SHUTDOWN
LOUT+
PGND
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
C
S
C
i
V
DD
Right HP
Audio Source
C
i
C
i
C
S
C
i
C
i
C
i
C
S
Power Supply
Right Line
Audio Source
Left Line
Audio Source
Left HP
Audio Source
Power Supply
V
DD
100 kΩ
100 kΩ
C
C
In From DAC
or
Potentiometer
(DC Voltage)
C
(BYP)
System
Control
C
C
Right
Speaker
Left
Speaker
Headphone
s
1 kΩ
1 kΩ
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
Volume [Pin 21] - V
DC VOLUME CONTROL
SE Volume,
SEDIFF [Pin 20] = 0 V
SE Volume,
SEDIFF [Pin 20] = 1 V
Volume - dB
BTL Volume
BTL Volume (dB) ∝ Volume (V)
SE Volume (dB) ∝ Volume (V) - SEDIFF
(V)
3-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
WITH ADVANCED DC VOLUME CONTROL
FEATURES DESCRIPTION
• Advanced DC Volume Control With 2-dB
Steps
From -40 dB to 20 dB
– Fade Mode
– Maximum Volume Setting for SE Mode
– Adjustable SE Volume Control
Referenced to BTL Volume Control
• 3 W Into 3- Ω Speakers
• Stereo Input MUX
• Differential Inputs
APPLICATIONS
• Notebook PC
• LCD Monitors
• Pocket PC
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
The TPA6011A4 is a stereo audio power amplifier
that drives 3 W/channel of continuous RMS power
into a 3- Ω load. Advanced dc volume control
minimizes external components and allows BTL
(speaker) volume control and SE (headphone) volume control. Notebook and pocket PCs benefit from
the integrated feature set that minimizes external
components without sacrificing functionality.
To simplify design, the speaker volume level is
adjusted by applying a dc voltage to the VOLUME
terminal. Likewise, the delta between speaker volume
and headphone volume can be adjusted by applying
a dc voltage to the SEDIFF terminal. To avoid an
unexpected high volume level through the
headphones, a third terminal, SEMAX, limits the
headphone volume level when a dc voltage is applied. Finally, to ensure a smooth transition between
active and shutdown modes, a fade mode ramps the
volume up and down.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas
Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
Copyright © 2002–2004, Texas Instruments Incorporated
www.ti.com
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
T
A
40 ° C to 85 ° C TPA6011A4PWP
(1) The PWP package is available taped and reeled. To order a taped
and reeled part, add the suffix R to the part number
(e.g., TPA6011A4PWPR).
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
V
SS
V
I
T
A
T
J
T
stg
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under "absolute maximum ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings
only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under "recommended operating
conditions" is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Supply voltage, VDD, PV
DD
Input voltage -0.3 V to VDD+0.3 V
Continuous total power dissipation See Dissipation Rating Table
Operating free-air temperature range -40 ° C to 85 ° C
Operating junction temperature range -40 ° C to 150 ° C
Storage temperature range -65 ° C to 150 ° C
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds 260 ° C
PACKAGE
24-PIN TSSOP (PWP)
(1)
(1)
UNIT
-0.3 V to 6 V
PACKAGE
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIIONS
V
SS
V
IH
V
IL
T
A
Supply voltage, VDD, PV
High-level input voltage
Low-level input voltage
Operating free-air temperature -40 85 ° C
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
TA≤ 25 ° C DERATING FACTOR TA= 70 ° C TA= 85 ° C
POWER RATING ABOVE TA= 25 ° C POWER RATING POWER RATING
PWP 2.7 mW 21.8 mW/ ° C 1.7 W 1.4 W
DD
SE/ BTL, HP/ LINE, FADE 0.8 × V
SHUTDOWN 2 V
SE/ BTL, HP/ LINE, FADE 0.6 × V
SHUTDOWN 0.8 V
MIN MAX UNIT
4.0 5.5 V
DD
DD
V
V
2
www.ti.com
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
TA= 25 ° C, V
| V
| Output offset voltage (measured differentially)
OO
PSRR Power supply rejection ratio V
| IIH| 1 µA
| IIL| V
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD(SD)
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
TA= 25 ° C, V
P
O
THD+N Total harmonic distortion + noise PO= 1 W, RL= 8 Ω , f = 20 Hz to 20 kHz <0.4%
V
OH
V
OL
V
(Bypass
)
B
OM
Z
I
= PV
DD
= 5.5 V (unless otherwise noted)
DD
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
= 5.5 V, Gain = 0 dB, SE/ BTL = 0 V 30 mV
DD
V
= 5.5 V, Gain = 20 dB, SE/ BTL = 0 V 50 mV
DD
= PV
DD
High-level input current (SE/ BTL, FADE, HP/ LINE, V
SHUTDOWN, SEDIFF, SEMAX, VOLUME) VI= V
Low-level input current (SE/ BTL, FADE, HP/ LINE,
SHUTDOWN, SEDIFF, SEMAX, VOLUME)
Supply current, no load mA
Supply current, max power into a 3- Ω load SHUTDOWN = 2 V, RL= 3 Ω , 1.5 A
DD
DD
V
DD
SHUTDOWN = 2 V
V
DD
SHUTDOWN = 2 V
V
DD
= 4.0 V to 5.5 V -42 -70 dB
DD
= PV
= 5.5 V,
DD
= PV
DD
DD
= PV
= 5.5 V, VI= 0 V 1 µA
DD
= PV
= 5.5 V, SE/ BTL = 0 V,
DD
= PV
= 5.5 V, SE/ BTL = 5.5 V,
DD
= 5 V = PV
, SE/ BTL = 0 V,
DD
6.0 7.5 9.0
3.0 5 6
PO= 2 W, stereo
Supply current, shutdown mode SHUTDOWN = 0.0 V 1 20 µA
= PV
DD
= 5 V, RL= 3 Ω , Gain = 6 dB (unless otherwise noted)
DD
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Output power W
High-level output voltage RL= 8 Ω , Measured between output and V
THD = 1%, f = 1 kHz 2
THD = 10%, f = 1 kHz, V
= 5.5 V 3
DD
DD
700 mV
Low-level output voltage RL= 8 Ω , Measured between output and GND 400 mV
Bypass voltage (Nominally VDD/2) Measured at pin 17, No load, V
= 5.5 V 2.65 2.75 2.85 V
DD
Maximum output power bandwidth THD = 5% >20 kHz
Supply ripple rejection ratio f = 1 kHz, Gain = 0 dB, C
Noise output voltage BTL 36 µV
f = 20 Hz to20 kHz, Gain = 0 dB,
C
= 0.47 µF
(BYP)
= 0.47 µF
(BYP)
BTL -63 dB
SE -57 dB
Input impedance (see Figure 26 ) VOLUME = 5.0 V 14 k Ω
RMS
RMS
3
www.ti.com
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
PGND
ROUT-
PV
DD
RHPIN
RLINEIN
RIN
V
DD
LIN
LLINEIN
LHPIN
PV
DD
LOUT-
ROUT+
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
VOLUME
SEDIFF
SEMAX
AGND
BYPASS
FADE
SHUTDOWN
LOUT+
PGND
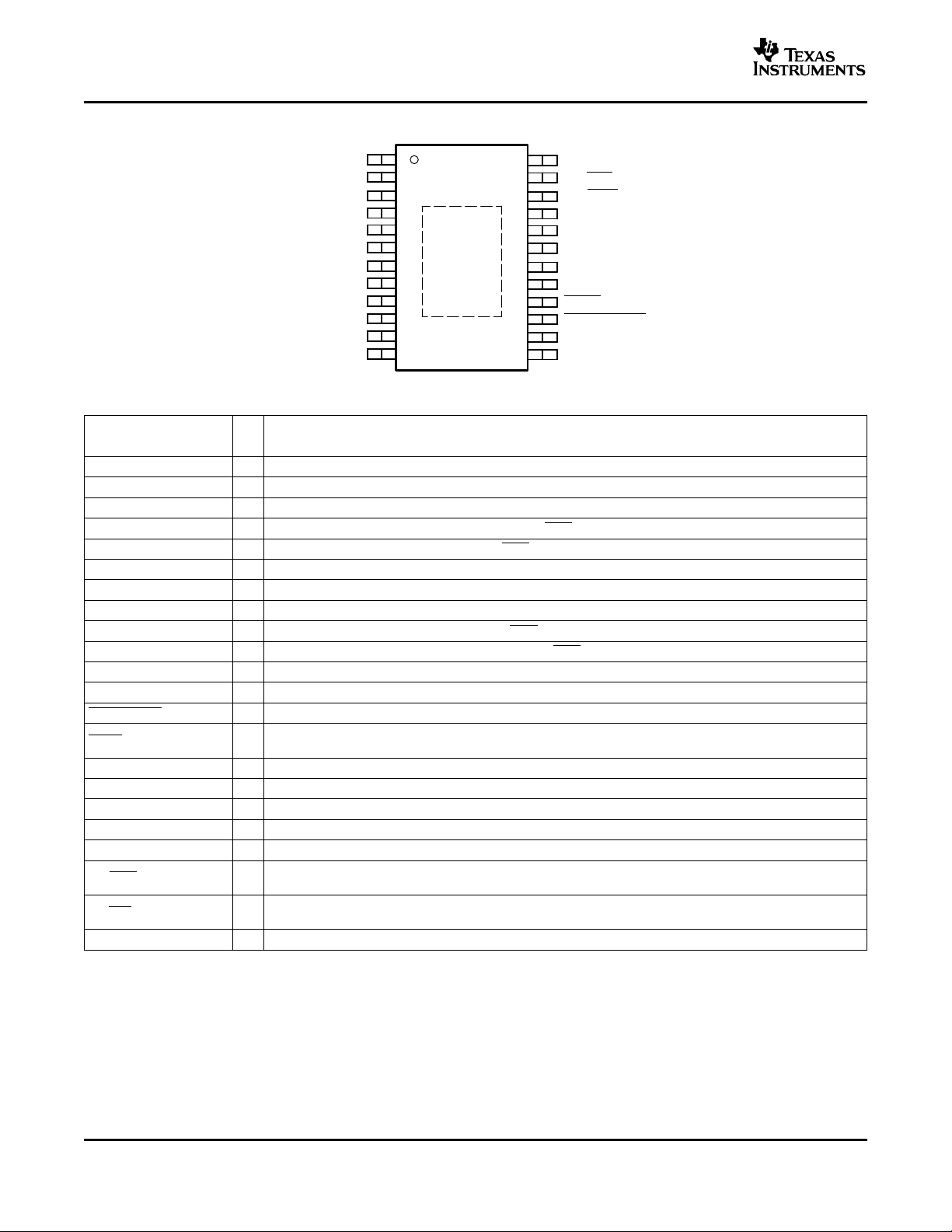
PWP PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
PGND 1, 13 - Power ground
LOUT- 12 O Left channel negative audio output
PV
DD
LHPIN 10 I Left channel headphone input, selected when HP/ LINE is held high
LLINEIN 9 I Left channel line input, selected when HP/ LINE is held low
LIN 8 I Common left channel input for fully differential input. AC ground for single-ended inputs.
V
DD
RIN 6 I Common right channel input for fully differential input. AC ground for single-ended inputs.
RLINEIN 5 I Right channel line input, selected when HP/ LINE is held low
RHPIN 4 I Right channel headphone input, selected when HP/ LINE is held high
ROUT- 2 O Right channel negative audio output
ROUT+ 24 O Right channel positive audio output
SHUTDOWN 15 I Places the amplifier in shutdown mode if a TTL logic low is placed on this terminal
FADE 16 I
BYPASS 17 I Tap to voltage divider for internal midsupply bias generator used for analog reference
AGND 18 - Analog power supply ground
SEMAX 19 I Sets the maximum volume for single ended operation. DC voltage range is 0 to VDD.
SEDIFF 20 I Sets the difference between BTL volume and SE volume. DC voltage range is 0 to VDD.
VOLUME 21 I Terminal for dc volume control. DC voltage range is 0 to VDD.
HP/ LINE 22 I
SE/ BTL 23 I
LOUT+ 14 O Left channel positive audio output.
I/O DESCRIPTION
3, 11 - Supply voltage terminal for power stage
7 - Supply voltage terminal
Places the amplifier in fade mode if a logic low is placed on this terminal; normal operation if a logic high is
placed on this terminal
Input MUX control. When logic high, RHPIN and LHPIN inputs are selected. When logic low, RLINEIN and
LLINEIN inputs are selected.
Output MUX control. When this terminal is high, SE outputs are selected. When this terminal is low, BTL
outputs are selected.
4
www.ti.com
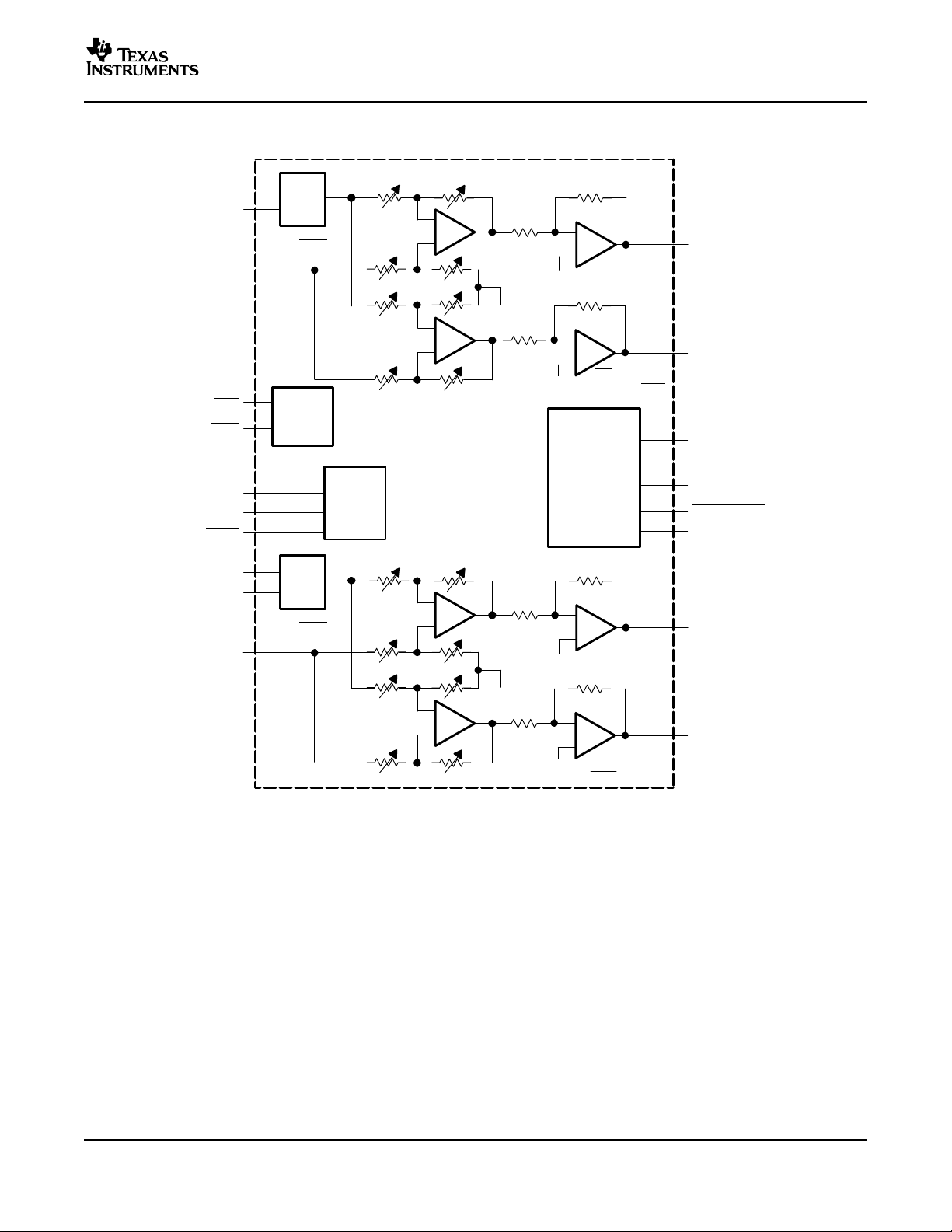
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Power
Management
32-Step
Volume
Control
MUX
Control
R
MUX
RHPIN
ROUT+
SHUTDOWN
ROUT-
PV
DD
PGND
V
DD
BYPASS
AGND
LOUT+
LOUT-
RLINEIN
RIN
HP/LINE
VOLUME
SEDIFF
SEMAX
FADE
_
+
HP/LINE
_
+
_
+
BYP
_
+
BYP
BYP
EN
SE/BTL
L
MUX
_
+
HP/LINE
_
+
_
+
BYP
_
+
BYP
BYP
EN
SE/BTL
SE/BTL
LHPIN
LLINEIN
LIN
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
NOTE: All resistor wipers are adjusted with 32 step volume control.
5
www.ti.com
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
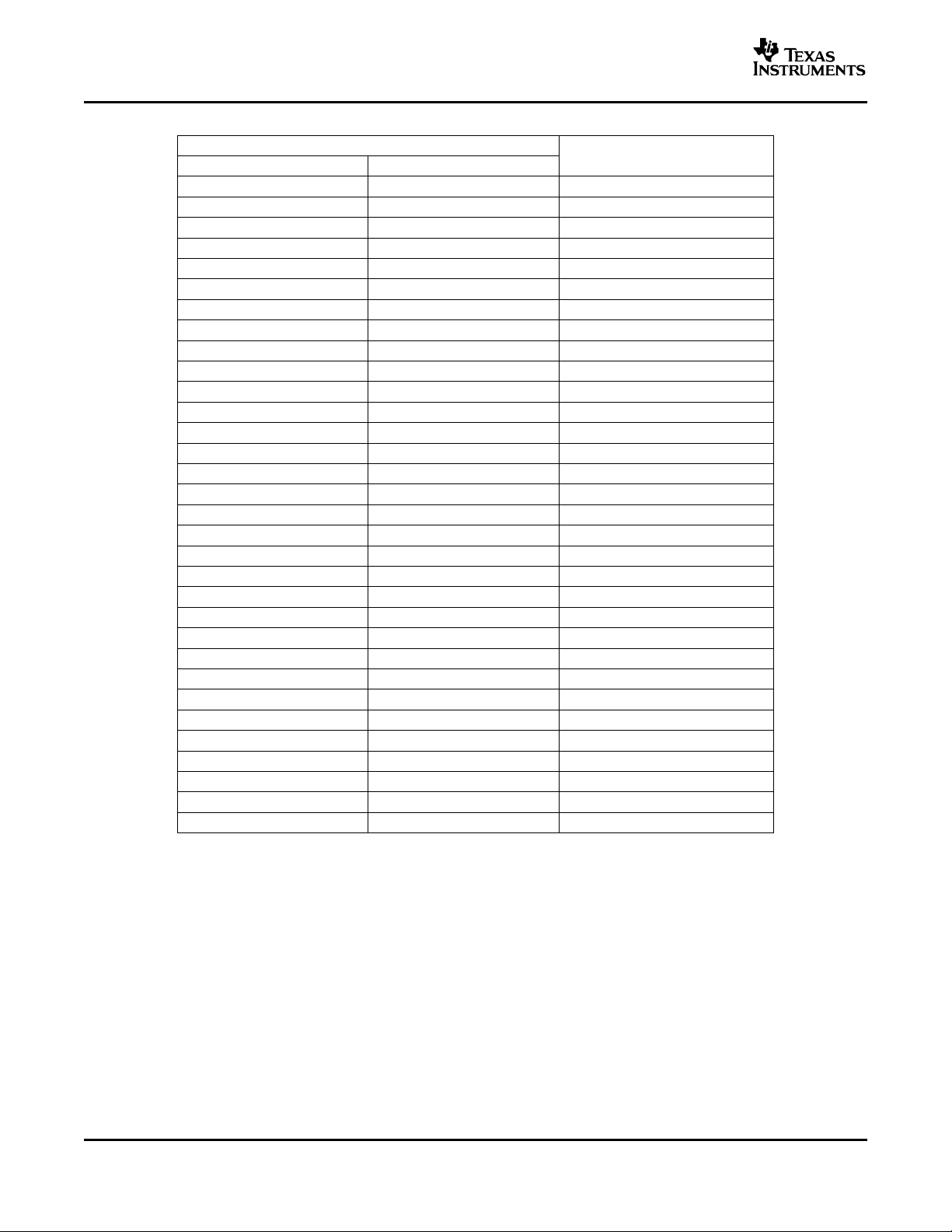
Table 1. DC Volume Control (BTL Mode, V
FROM (V) TO (V)
0.00 0.26 -85
0.33 0.37 -40
0.44 0.48 -38
0.56 0.59 -36
0.67 0.70 -34
0.78 0.82 -32
0.89 0.93 -30
1.01 1.04 -28
1.12 1.16 -26
1.23 1.27 -24
1.35 1.38 -22
1.46 1.49 -20
1.57 1.60 -18
1.68 1.72 -16
1.79 1.83 -14
1.91 1.94 -12
2.02 2.06 -10
2.13 2.17 -8
2.25 2.28 -6
2.36 2.39 -4
2.47 2.50 -2
2.58 2.61 0
2.70 2.73 2
2.81 2.83 4
2.92 2.95 6
3.04 3.06 8
3.15 3.17 10
3.26 3.29 12
3.38 3.40 14
3.49 3.51 16
3.60 3.63 18
3.71 5.00 20
(1) For other values of VDD, scale the voltage values in the table by a factor of VDD/5.
(2) Tested in production. Remaining gain steps are specified by design.
VOLUME (PIN 21)
(1)
= 5 V)
DD
GAIN OF AMPLIFIER
(Typ)
(2)
(2)
(2)
6
www.ti.com
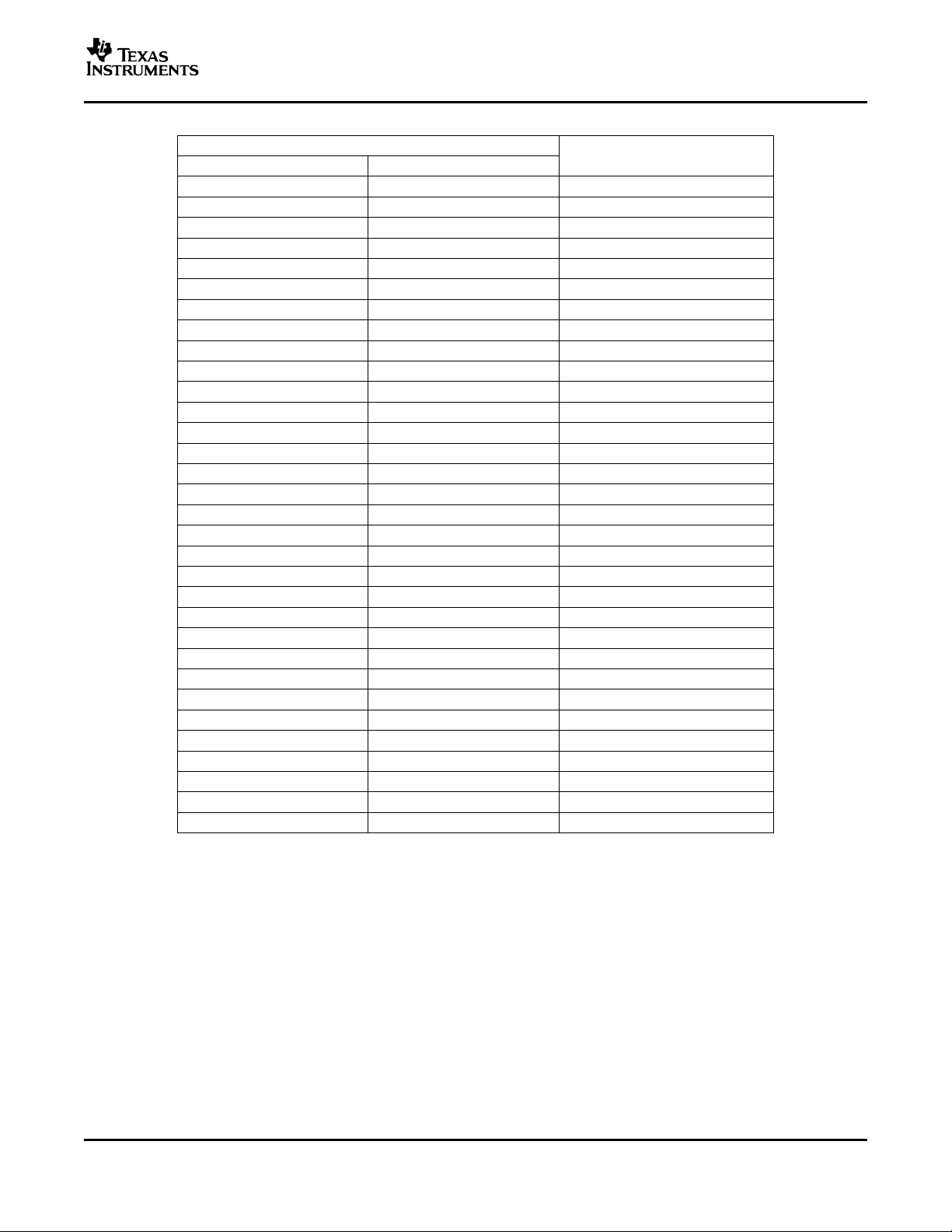
Table 2. DC Volume Control (SE Mode, V
DD
SE_VOLUME = VOLUME - SEDIFF or SEMAX
FROM (V) TO (V)
0.00 0.26 -85
0.33 0.37 -46
0.44 0.48 -44
0.56 0.59 -42
0.67 0.70 -40
0.78 0.82 -38
0.89 0.93 -36
1.01 1.04 -34
1.12 1.16 -32
1.23 1.27 -30
1.35 1.38 -28
1.46 1.49 -26
1.57 1.60 -24
1.68 1.72 -22
1.79 1.83 -20
1.91 1.94 -18
2.02 2.06 -16
2.13 2.17 -14
2.25 2.28 -12
2.36 2.39 -10
2.47 2.50 -8
2.58 2.61 -6
2.70 2.73 -4
2.81 2.83 -2
2.92 2.95 0
3.04 3.06 2
3.15 3.17 4
3.26 3.29 6
3.38 3.40 8
3.49 3.51 10
3.60 3.63 12
3.71 5.00 14
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
(1)
= 5 V)
GAIN OF AMPLIFIER
(Typ)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(1) For other values of VDD, scale the voltage values in the table by a factor of VDD/5.
(2) Tested in production. Remaining gain steps are specified by design.
7
www.ti.com
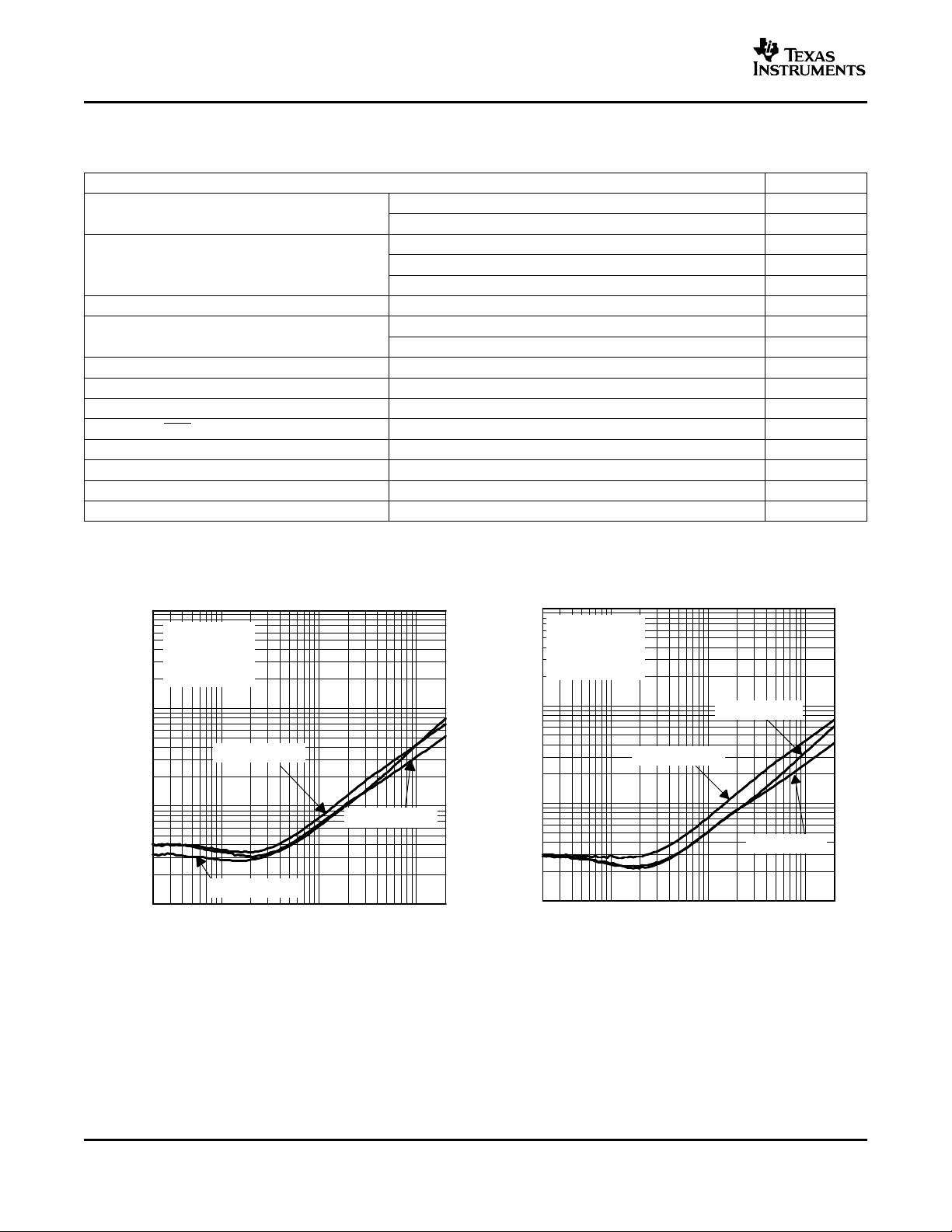
10
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.5
1
2
5
20 20 k100 1 k 10 k
VDD = 5 V
RL = 3 Ω
Gain = 20 dB
BTL
PO = 1.75 W
PO = 0.5 W
PO = 1 W
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (BTL) − %
f − Frequency − Hz
10
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.5
1
2
5
20 20 k50 100 200 500 1 k 2 k 5 k 10 k
PO = 0.25 W
PO = 1.5 W
PO = 1 W
f − Frequency − Hz
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (BTL) − %
VDD = 5 V
RL = 4 Ω
Gain = 20 dB
BTL
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Table of Graphs
THD+N Total harmonic distortion plus noise (BTL)
THD+N Total harmonic distortion plus noise (SE) vs Output power 9
Closed loop response 11, 12
I
CC
P
P
Supply current
Power Dissipation vs Output power 17, 18
D
Output power vs Load resistance 19, 20
O
Crosstalk vs Frequency 21, 22
HP/ LINE attenuation vs Frequency 23
PSRR Power supply ripple rejection (BTL) vs Frequency 24
PSRR Power supply ripple rejection (SE) vs Frequency 25
Z
V
Input impedance vs BTL gain 26
I
Output noise voltage vs Frequency 27
n
vs Frequency 1, 2 3
vs Output power 6, 7, 8
vs Frequency 4, 5
vs Output voltage 10
vs Temperature 13
vs Supply voltage 14, 15, 16
FIGURE
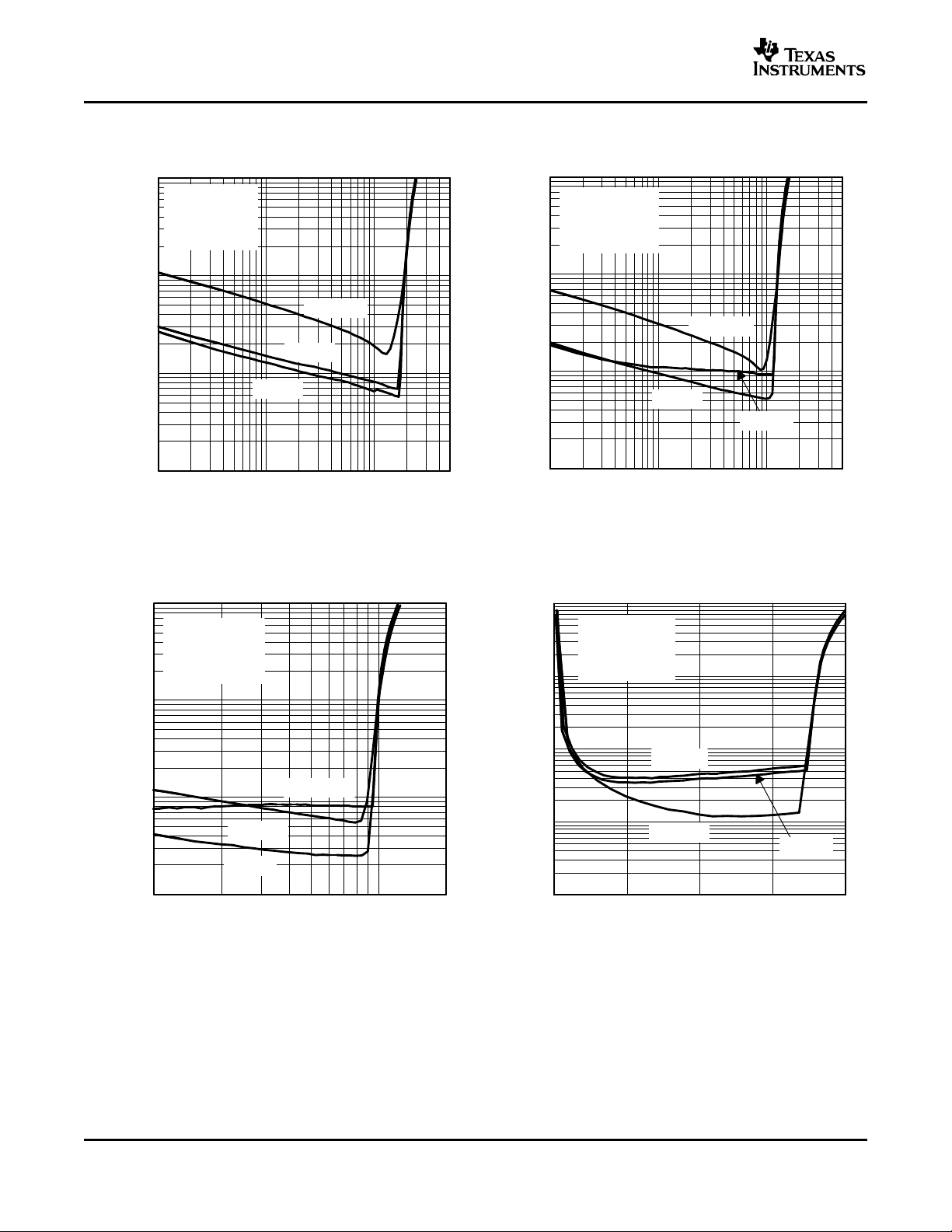
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE (BTL) TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE (BTL)
8
vs vs
FREQUENCY FREQUENCY
Figure 1. Figure 2.
www.ti.com
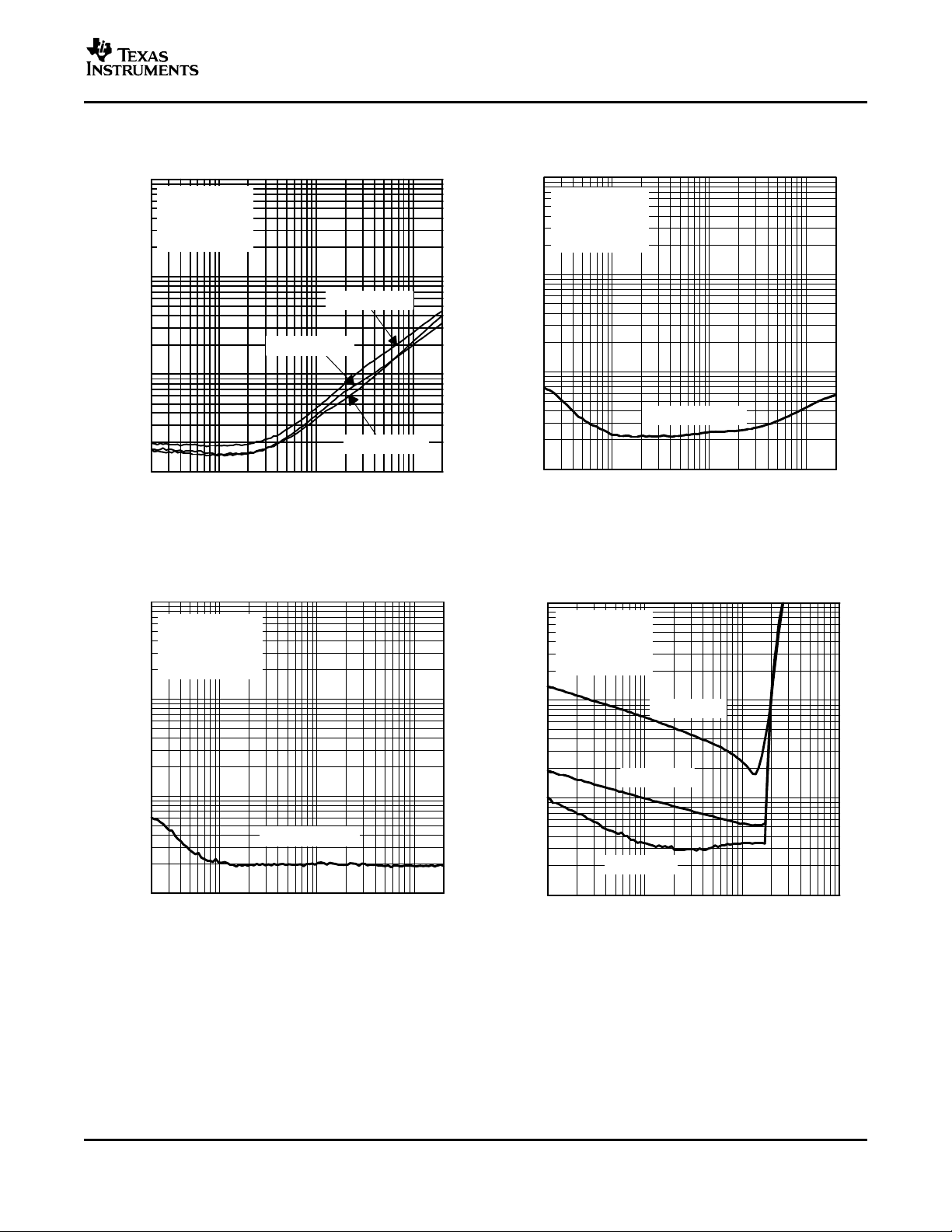
10
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.5
1
2
5
20
20 k50 100 200 500 1 k 2 k 5 k 10 k
f − Frequency − Hz
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (SE) − %
PO = 75 mW
VDD = 5 V
RL = 32 Ω
Gain = 14 dB
SE
0.01
10
0.02
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.5
1
2
5
20 20 k50 100 200 500 1 k 2 k 5 k 10 k
PO = 1 W
VDD = 5 V
RL = 8 Ω
Gain = 20 dB
BTL
f − Frequency − Hz
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (BTL) − %
PO = 0.25 W
PO = 0.5 W
10
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.5
1
2
5
20 20 k50 100 200 500 1 k 2 k 5 k 10 k
f − Frequency − Hz
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (SE) − %
VO = 1 V
RMS
VDD = 5 V
RL = 10 kΩ
Gain = 14 dB
SE
PO − Output Power − W
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (BTL) − %
0.01
10
0.02
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.5
1
2
5
0.01 100.1 1
f = 20 kHz
f = 1 kHz
f = 20 Hz
VDD = 5 V
RL = 3 Ω
Gain = 20 dB
BTL
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE (BTL) TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE (SE)
vs vs
FREQUENCY FREQUENCY
Figure 3. Figure 4.
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE (SE) TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE (BTL)
vs vs
FREQUENCY OUTPUT POWER
Figure 5. Figure 6.
9
www.ti.com
10
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.5
1
2
5
50.02 0.05 0.1 0.2 0.5 1 2
PO − Output Power − W
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (BTL) − %
1 kHz
20 kHz
VDD = 5 V
RL = 8 Ω
Gain = 20 dB
BTL
20 Hz
10
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.5
1
2
5
50.02 0.05 0.1 0.2 0.5 1 2
PO − Output Power − W
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (BTL) − %
1 kHz
20 kHz
20 Hz
VDD = 5 V
RL = 4 Ω
Gain = 20 dB
BTL
10
0.001
0.002
0.005
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.5
1
2
5
0 500 m 1 1.5 2
VO − Output Voltage − rms
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (SE) − %
1 kHz
20 kHz
20 Hz
VDD = 5 V
RL = 10 kΩ
Gain = 14 dB
SE
10
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.5
1
2
5
10 m 200 m50 m 100 m
PO − Output Power − W
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (SE) − %
1 kHz
20 kHz
20 Hz
VDD = 5 V
RL = 32 Ω
Gain = 14 dB
SE
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
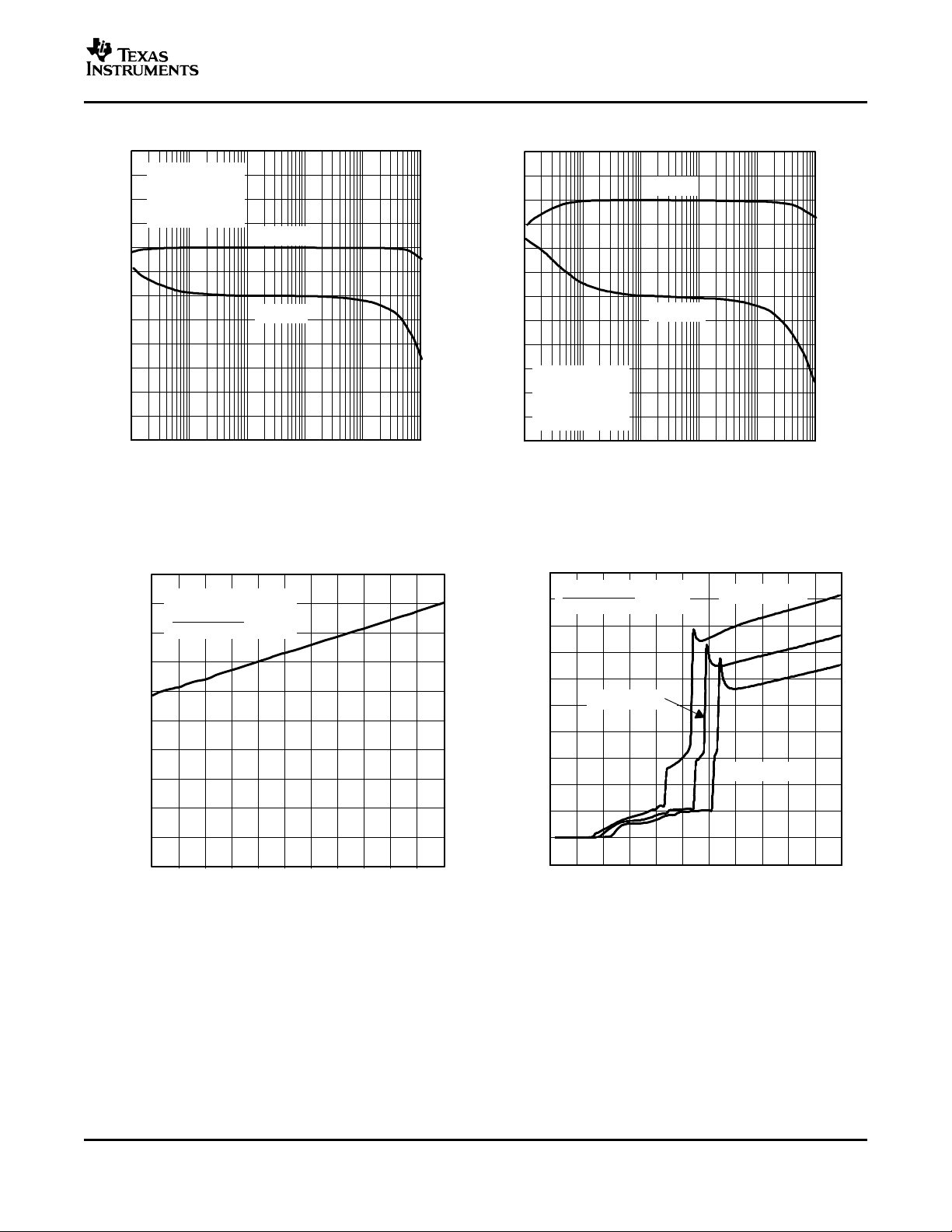
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE (BTL) TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE (BTL)
vs vs
OUTPUT POWER OUTPUT POWER
Figure 7. Figure 8.
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE (SE) TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE (SE)
vs vs
OUTPUT POWER OUTPUT VOLTAGE
10
Figure 9. Figure 10.
www.ti.com
150
120
90
60
30
0
−30
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
−20
−10
0
10
20
30
40
10 100 1 k 10 k 100 k 1 M
−180
−150
−120
−90
−60
180
Gain
Phase
VDD = 5 Vdc
RL = 8 Ω
Mode = BTL
Gain = 0 dB
f − Frequency − Hz
Closed Loop Gain − dB
Phase − Degrees
150
120
90
60
30
0
−30
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
−20
−10
0
10
20
30
40
10 100 1 k 10 k 100 k 1 M
−180
−150
−120
−90
−60
180
Gain
Phase
VDD = 5 Vdc
RL = 8 Ω
Mode = BTL
Gain = 20 dB
f − Frequency − Hz
Closed Loop Gain − dB
Phase − Degrees
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
−40 −25 5 20 35 50 65 95−10 110 125
− Supply Current − mA
TA − Free-Air Temperature − °C
I
DD
VDD = 5 V
Mode = BTL
SHUTDOWN = V
DD
80
−1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
0
0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5
Mode = BTL
SHUTDOWN = V
DD
VDD − Supply Voltage − V
T
A
= 125°C
T
A
= 25°C
T
A
= −40°C
− Supply Current − mA
I
DD
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
CLOSED LOOP RESPONSE CLOSED LOOP RESPONSE
Figure 11. Figure 12.
TPA6011A4
SUPPLY CURRENT SUPPLY CURRENT
FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
Figure 13. Figure 14.
vs vs
11
www.ti.com
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
Mode = SD
SHUTDOWN = 0 V
VDD − Supply Voltage − V
− Supply Current −
I
DD
T
A
= 125°C
T
A
= 25°C
T
A
= −40°C
nA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5
Mode = SE
SHUTDOWN = V
DD
VDD − Supply Voltage − V
− Supply Current − mAI
DD
T
A
= 125°C
T
A
= 25°C
T
A
=−40°C
0
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
PO − Output Power − W
− Power Dissipation (PER CHANNEL) − WP
D
VDD = 5 V
BTL
4 Ω
8 Ω
3 Ω
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
200
0 100 150 200 250 30050
8 Ω
16 Ω
32 Ω
PO − Output Power − mW
VDD = 5 V
SE
− Power Dissipation (PER CHANNEL) − mWP
D
TPA6011A4
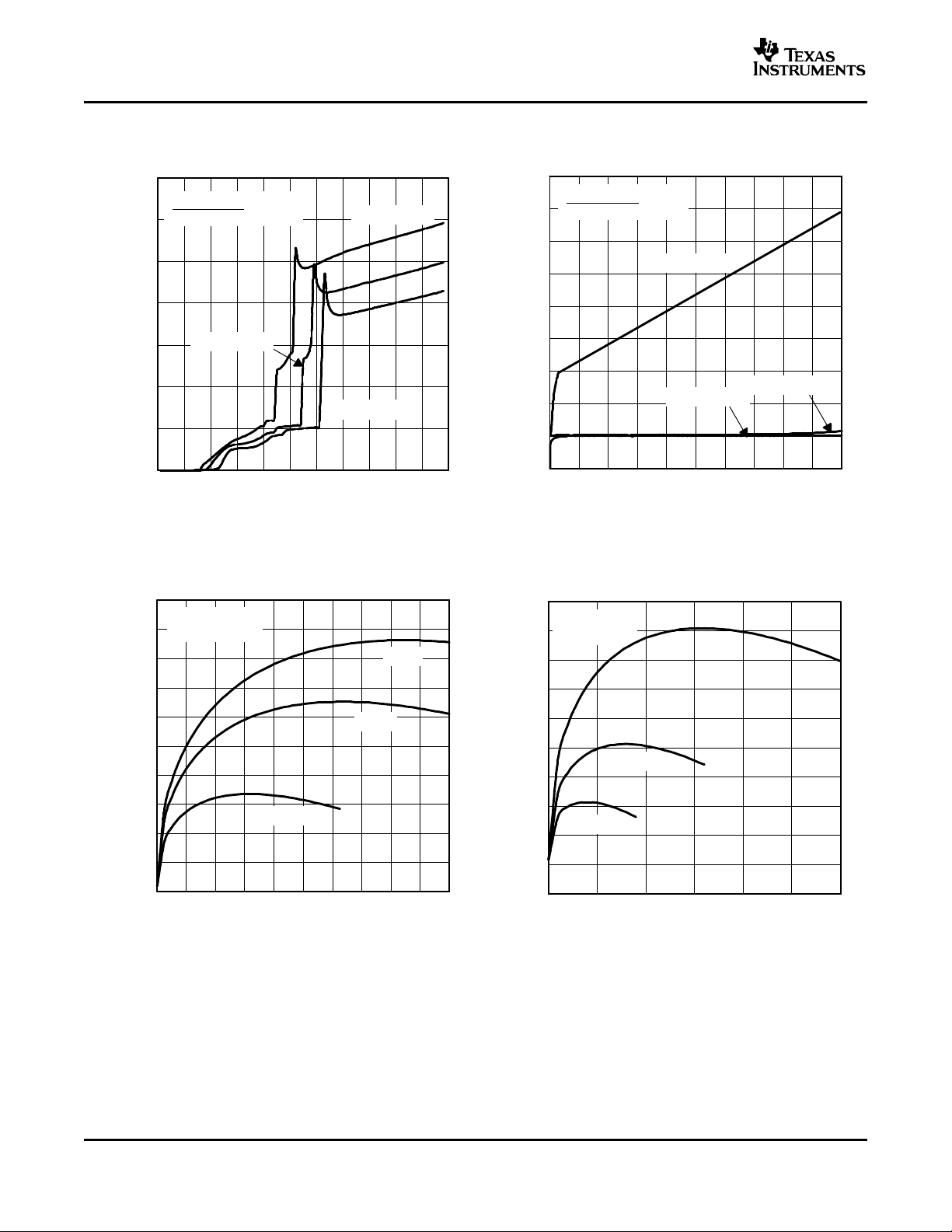
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
SUPPLY CURRENT SUPPLY CURRENT
vs vs
SUPPLY VOLTAGE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
Figure 15. Figure 16.
POWER DISSIPATION (PER CHANNEL) POWER DISSIPATION (PER CHANNEL)
vs vs
OUTPUT POWER OUTPUT POWER
12
Figure 17. Figure 18.

www.ti.com
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2
2.2
0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64
RL − Load Resistance − Ω
− Output Power − WP
O
VDD = 5 V
THD+N = 1%
Gain = 20 dB
BTL
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2
2.2
0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64
RL − Load Resistance − Ω
− Output Power − WP
O
VDD = 5.5 V
Gain = 20 dB
BTL
2.4
2.6
2.8
3
THD+N = 10%
THD+N = 1%
3.2
−120
0
−110
−100
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
−20
−10
20 20 k100 1 k 10 k
f − Frequency − Hz
Crosstalk − dB
Left to Right
Right to Left
VDD = 5 V
PO = 1 W
RL = 8 Ω
Gain = 0dB
BTL
−120
0
−110
−100
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
−20
−10
20 20 k100 1 k 10 k
f − Frequency − Hz
Crosstalk − dB
Left to Right
Right to Left
VDD = 5 V
PO = 1 W
RL = 8 Ω
Gain = 20 dB
BTL
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
OUTPUT POWER OUTPUT POWER
vs vs
LOAD RESISTANCE LOAD RESISTANCE
Figure 19. Figure 20.
TPA6011A4
CROSSTALK CROSSTALK
vs vs
FREQUENCY FREQUENCY
Figure 21. Figure 22.
13

www.ti.com
20 20 k100 1 k 10 k
f − Frequency − Hz
PSRR − Power Supply Rejection Ratio (BTL) − dB
0
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
−20
−10
VDD = 5 V
RL = 8 Ω
C
(BYP)
=0.47 µF
BTL
Gain = 1
Gain = 10
−120
0
−110
−100
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
−20
−10
20 20 k100 1 k 10 k
f − Frequency − Hz
HP/Line Attenuation − dB
Line Active
HP Active
VDD = 5 V
VI = 1 V
RMS
RL = 8 Ω
BTL
20 20 k100 1 k 10 k
f − Frequency − Hz
PSRR − Power Supply Rejection Ratio (SE) − dB
−100
+0
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
−20
−10
Gain = 14 dB
Gain = 0 dB
VDD = 5 V
RL = 32 Ω
C
(BYP)
=0.47 µF
SE
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
−40 −30 −20 −10
0
10 20
BTL Gain − dB
− Input Impedamce − Z
I
kΩ
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
HP/LINE ATTENUATION POWER SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO (BTL)
vs vs
FREQUENCY FREQUENCY
Figure 23. Figure 24.
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO (SE) INPUT IMPEDANCE
vs vs
FREQUENCY BTL GAIN
14
Figure 25. Figure 26.

www.ti.com
100
80
20
10 100 1 k
− Output Noise Voltage −
120
140
10 k 20 k
180
40
0
60
160
V
n
Vµ
RMS
Gain = 0 dB
VDD = 5 V
BW = 22 Hz to 22 kHz
RL = 8 Ω
BTL
Gain = 20 dB
f − Frequency − Hz
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
OUTPUT NOISE VOLTAGE
vs
FREQUENCY
Figure 27.
15

www.ti.com
PGND
ROUT-
PV
DD
RHPIN
RLINEIN
RIN
V
DD
LIN
LLINEIN
LHPIN
PV
DD
LOUT-
1
ROUT+
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
VOLUME
SEDIFF
SEMAX
AGND
BYPASS
FADE
SHUTDOWN
LOUT+
PGND
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
C
S
C
i
V
DD
Right HP
Audio Source
C
i
C
i
C
S
C
i
C
i
C
i
C
S
Power Supply
Right Line
Audio Source
Left Line
Audio Source
Left HP
Audio Source
Power Supply
V
DD
100 kΩ
100 kΩ
C
C
In From DAC
or
Potentiometer
(DC Voltage)
C
(BYP)
System
Control
C
C
Right
Speaker
Left
Speaker
Headphones
1 kΩ
1 kΩ
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
APPLICATION INFORMATION
SELECTION OF COMPONENTS
Figure 28 and Figure 29 are schematic diagrams of typical notebook computer application circuits.
A. A 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor should be placed as close as possible to the IC. For filtering lower-frequency noise
signals, a larger electrolytic capacitor of 10 µF or greater should be placed near the audio power amplifier.
Figure 28. Typical TPA6011A4 Application Circuit Using Single-Ended Inputs and Input MUX
16

www.ti.com
PGND
ROUT-
PV
DD
RHPIN
RLINEIN
RIN
V
DD
LIN
LLINEIN
LHPIN
PV
DD
LOUT-
1
ROUT+
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
VOLUME
SEDIFF
SEMAX
AGND
BYPASS
FADE
SHUTDOWN
LOUT+
PGND
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
C
S
NC
V
DD
C
i
C
i
C
S
C
i
C
i
C
S
Power Supply
Left Negative
Differential Input Signal
Power Supply
V
DD
100 kΩ
100 kΩ
C
C
In From DAC
or
Potentiometer
(DC Voltage)
C
(BYP)
System
Control
C
C
Right
Speaker
Left
Speaker
Headphones
1 kΩ
1 kΩ
NC
Left Positive Differential
Input Signal
Right Negative
Differential Input Signal
Right Positive
Differential Input Signal
APPLICATION INFORMATION (continued)
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
A. A 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor should be placed as close as possible to the IC. For filtering lower-frequency noise
SE/ BTL OPERATION
The ability of the TPA6011A4 to easily switch between BTL and SE modes is one of its most important cost
saving features. This feature eliminates the requirement for an additional headphone amplifier in applications
where internal stereo speakers are driven in BTL mode but external headphone or speakers must be
accommodated. Internal to the TPA6011A4, two separate amplifiers drive OUT+ and OUT-. The SE/ BTL input
controls the operation of the follower amplifier that drives LOUT- and ROUT-. When SE/ BTL is held low, the
amplifier is on and the TPA6011A4 is in the BTL mode. When SE/ BTL is held high, the OUT- amplifiers are in a
high output impedance state, which configures the TPA6011A4 as an SE driver from LOUT+ and ROUT+. IDDis
reduced by approximately one-third in SE mode. Control of the SE/ BTL input can be from a logic-level CMOS
source or, more typically, from a resistor divider network as shown in Figure 30 . The trip level for the SE/ BTL
input can be found in the recommended operating conditions table.
signals, a larger electrolytic capacitor of 10 µF or greater should be placed near the audio power amplifier.
Figure 29. Typical TPA6011A4 Application Circuit Using Differential Inputs
17

www.ti.com
SE/BTL
ROUT+ 24
R
MUX
RHPIN
RLINEIN5
4
6 RIN
ROUT- 2
1 kΩ
C
O
330 µF
100 kΩ
23
100 kΩ
V
DD
Input
MUX
Control
22 HP/LINE
_
+
_
+
Bypass
_
+
Bypass
EN
_
+
Bypass
LOUT+
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
APPLICATION INFORMATION (continued)
Figure 30. TPA6011A4 Resistor Divider Network Circuit
Using a 1/8-in. (3,5 mm) stereo headphone jack, the control switch is closed when no plug is inserted. When
closed the 100-k Ω /1-k Ω divider pulls the SE/ BTL input low. When a plug is inserted, the 1-k Ω resistor is
disconnected and the SE/ BTL input is pulled high. When the input goes high, the OUT- amplifier is shut down
causing the speaker to mute (open-circuits the speaker). The OUT+ amplifier then drives through the output
capacitor (C
) into the headphone jack.
o
HP/ LINE OPERATION
The HP/ LINE input controls the internal input multiplexer (MUX). Refer to the block diagram in Figure 30 . This
allows the device to switch between two separate stereo inputs to the amplifier. For design flexibility, the
HP/ LINE control is independent of the output mode, SE or BTL, which is controlled by the aforementioned
SE/ BTL pin. To allow the amplifier to switch from the LINE inputs to the HP inputs when the output switches from
BTL mode to SE mode, simply connect the SE/ BTL control input to the HP/ LINE input.
When this input is logic high, the RHPIN and LHPIN inputs are selected. When this terminal is logic low, the
RLINEIN and LLINEIN inputs are selected. This operation is also detailed in Table 3 and the trip levels for a logic
low (V
SHUTDOWN MODES
The TPA6011A4 employs a shutdown mode of operation designed to reduce supply current (I
minimum level during periods of nonuse for battery-power conservation. The SHUTDOWN input terminal should
be held high during normal operation when the amplifier is in use. Pulling SHUTDOWN low causes the outputs to
mute and the amplifier to enter a low-current state, IDD= 20 µA. SHUTDOWN should never be left unconnected
because amplifier operation would be unpredictable.
18
) or logic high (V
IL
) can be found in the recommended operating conditions table.
IH
) to the absolute
DD

www.ti.com
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
Table 3. HP/ LINE, SE/ BTL, and Shutdown Functions
INPUTS
HP/ LINE SE/ BTL SHUTDOWN INPUT OUTPUT
X X Low X Mute
Low Low High Line BTL
Low High High Line SE
High Low High HP BTL
High High High HP SE
(1) Inputs should never be left unconnected.
FADE OPERATION
For design flexibility, a fade mode is provided to slowly ramp up the amplifier gain when coming out of shutdown
mode and conversely ramp the gain down when going into shutdown. This mode provides a smooth transition
between the active and shutdown states and virtually eliminates any pops or clicks on the outputs.
When the FADE input is a logic low, the device is placed into fade-on mode. A logic high on this pin places the
amplifier in the fade-off mode. The voltage trip levels for a logic low (V
recommended operating conditions table.
When a logic low is applied to the FADE pin and a logic low is then applied on the SHUTDOWN pin, the channel
gain steps down from gain step to gain step at a rate of two clock cycles per step. With a nominal internal clock
frequency of 58 Hz, this equates to 34 ms (1/24 Hz) per step. The gain steps down until the lowest gain step is
reached. The time it takes to reach this step depends on the gain setting prior to placing the device in shutdown.
For example, if the amplifier is in the highest gain mode of 20 dB, the time it takes to ramp down the channel
gain is 1.05 seconds. This number is calculated by taking the number of steps to reach the lowest gain from the
highest gain, or 31 steps, and multiplying by the time per step, or 34 ms.
After the channel gain is stepped down to the lowest gain, the amplifier begins discharging the bypass capacitor
from the nominal voltage of V
0.47-µF capacitor that is used in the application diagram in Figure 28 , the time is approximately 500 ms. This
time scales linearly with the value of bypass capacitor. For example, if a 1-µF capacitor is used for bypass, the
time period to discharge the capacitor to ground is twice that of the 0.47-µF capacitor, or 1 second. Figure 30
below is a waveform captured at the output during the shutdown sequence when the part is in fade-on mode.
The gain is set to the highest level and the output is at V
When a logic high is placed on the SHUTDOWN pin and the FADE pin is still held low, the device begins the
start-up process. The bypass capacitor will begin charging. Once the bypass voltage reaches the final value of
V
/2, the gain increases in 2-dB steps from the lowest gain level to the gain level set by the dc voltage applied
DD
to the VOLUME, SEDIFF, and SEMAX pins.
In the fade-off mode, the amplifier stores the gain value prior to starting the shutdown sequence. The output of
the amplifier immediately drops to V
shutdown is released, the bypass capacitor charges up to V
value stored in memory. Figure 31 below is a waveform captured at the output during the shutdown sequence
when the part is in the fade-off mode. The gain is set to the highest level, and the output is at V
amplifier is shut down.
The power-up sequence is different from the shutdown sequence and the voltage on the FADE pin does not
change the power-up sequence. Upon a power-up condition, the TPA6011A4 begins in the lowest gain setting
and steps up 2 dB every 2 clock cycles until the final value is reached as determined by the dc voltage applied to
the VOLUME, SEDIFF, and SEMAX pins.
/2 to ground. This time is dependent on the value of the bypass capacitor. For a
DD
(1)
when the amplifier is shut down.
DD
/2 and the bypass capacitor begins a smooth discharge to ground. When
DD
/2 and the channel gain returns immediately to the
DD
AMPLIFIER STATE
) or logic high (V
IL
) can be found in the
IH
when the
DD
19

www.ti.com
ROUT+
Device Shutdown
ROUT+
Device Shutdown
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
Figure 31. Shutdown Sequence in the Figure 32. Shutdown Sequence in the
Fade-on Mode Fade-off Mode
VOLUME, SEDIFF, AND SEMAX OPERATION
Three pins labeled VOLUME, SEDIFF, and SEMAX control the BTL volume when driving speakers and the SE
volume when driving headphones. All of these pins are controlled with a dc voltage, which should not exceed
V
.
DD
When driving speakers in BTL mode, the VOLUME pin is the only pin that controls the gain. Table 1 shows the
gain for the BTL mode. The voltages listed in the table are for V
table scale linearly. If V
= 4 V, multiply all the voltages in the table by 4 V/5 V, or 0.8.
DD
The TPA6011A4 allows the user to specify a difference between BTL gain and SE gain. This is desirable to avoid
any listening discomfort when plugging in headphones. When switching to SE mode, the SEDIFF and SEMAX
pins control the singe-ended gain proportional to the gain set by the voltage on the VOLUME pin. When SEDIFF
= 0 V, the difference between the BTL gain and the SE gain is 6 dB. Refer to the section labeled bridged-tied
load versus single-ended load for an explanation on why the gain in BTL mode is 2x that of single-ended mode,
or 6dB greater. As the voltage on the SEDIFF terminal is increased, the gain in SE mode decreases. The voltage
on the SEDIFF terminal is subtracted from the voltage on the VOLUME terminal and this value is used to
determine the SE gain.
Some audio systems require that the gain be limited in the single-ended mode to a level that is comfortable for
headphone listening. Most volume control devices only have one terminal for setting the gain. For example, if the
speaker gain is 20 dB, the gain in the headphone channel is fixed at 14 dB. This level of gain could cause
discomfort to listeners and the SEMAX pin allows the designer to limit this discomfort when plugging in
headphones. The SEMAX terminal controls the maximum gain for single-ended mode.
The functionality of the SEDIFF and SEMAX pin are combined to set the SE gain. A block diagram of the
combined functionality is shown in Figure 33 . The value obtained from the block diagram for SE_VOLUME is a
dc voltage that can be used in conjunction with Table 2 to determine the SE gain. Again, the voltages listed in
the table are for V
DD
= 5 V. The values must be scaled for other values of V
Table 1 and Table 2 show a range of voltages for each gain step. There is a gap in the voltage between each
gain step. This gap represents the hysteresis about each trip point in the internal comparator. The hysteresis
ensures that the gain control is monotonic and does not oscillate from one gain step to another. If a
potentiometer is used to adjust the voltage on the control terminals, the gain increases as the potentiometer is
turned in one direction and decreases as it is turned back the other direction. The trip point, where the gain
= 5 V. For a different V
DD
.
DD
, the values in the
DD
20

www.ti.com
SEMAX (V)
VOLUME-SEDIFF
SEDIFF (V)
-
+
VOLUME (V)
YES
NO
SE_VOLUME (V) = VOLUME (V) - SEDIFF (V)
SE_VOLUME (V) = SEMAX (V)
Is SEMAX>
(VOLUME-SEDIFF)
?
0
2
4
2.702.61 2.73 2.81
BTL Gain - dB
Voltage on VOLUME Pin - V
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
actually changes, is different depending on whether the voltage is increased or decreased as a result of the
hysteresis about each trip point. The gaps in Table 1 and Table 2 can also be thought of as indeterminate states
where the gain could be in the next higher gain step or the lower gain step depending on the direction the
voltage is changing. If using a DAC to control the volume, set the voltage in the middle of each range to ensure
that the desired gain is achieved.
A pictorial representation of the volume control can be found in Figure 34 . The graph focuses on three gain steps
with the trip points defined in Table 1 for BTL gain. The dotted line represents the hysteresis about each gain
step.
Figure 33. Block Diagram of SE Volume Control
Figure 34. DC Volume Control Operation
21

www.ti.com
C
IN
R
i
R
f
Input Signal
ƒ
3 dB
1
2 CR
i
f
c(highpass)
1
2 RiC
i
−3 dB
f
c
C
i
1
2 Rif
c
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
INPUT RESISTANCE
Each gain setting is achieved by varying the input resistance of the amplifier, which can range from its smallest
value to over six times that value. As a result, if a single capacitor is used in the input high-pass filter, the -3 dB
or cutoff frequency also changes by over six times.
Figure 35. Resistor on Input for Cut-Off Frequency
The input resistance at each gain setting is given in Figure 26 .
The -3-dB frequency can be calculated using Equation 1 .
(1)
INPUT CAPACITOR, C
In the typical application an input capacitor (C
proper dc level for optimum operation. In this case, C
i
) is required to allow the amplifier to bias the input signal to the
i
and the input impedance of the amplifier (R
i
) form a
i
high-pass filter with the corner frequency determined in Equation 2 .
The value of Ciis important to consider as it directly affects the bass (low frequency) performance of the circuit.
Consider the example where Riis 70 k Ω and the specification calls for a flat-bass response down to 40 Hz.
Equation 2 is reconfigured as Equation 3 .
In this example, C
consideration for this capacitor is the leakage path from the input source through the input network (C
is 56.8 nF, so one would likely choose a value in the range of 56 nF to 1 µF. A further
i
) and the
i
feedback network to the load. This leakage current creates a dc offset voltage at the input to the amplifier that
reduces useful headroom, especially in high gain applications. For this reason, a low-leakage tantalum or
ceramic capacitor is the best choice. When polarized capacitors are used, the positive side of the capacitor
should face the amplifier input in most applications as the dc level there is held at V
/2, which is likely higher
DD
than the source dc level. Note that it is important to confirm the capacitor polarity in the application.
(2)
(3)
22

www.ti.com
f
c(high)
1
2 RLC
(C)
−3 dB
f
c
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
POWER SUPPLY DECOUPLING, C
(S)
The TPA6011A4 is a high-performance CMOS audio amplifier that requires adequate power supply decoupling to
ensure the output total harmonic distortion (THD) is as low as possible. Power supply decoupling also prevents
oscillations for long lead lengths between the amplifier and the speaker. The optimum decoupling is achieved by
using two capacitors of different types that target different types of noise on the power supply leads. For higher
frequency transients, spikes, or digital hash on the line, a good low equivalent-series-resistance (ESR) ceramic
capacitor, typically 0.1 µF placed as close as possible to the device V
lead, works best. For filtering
DD
lower-frequency noise signals, a larger aluminum electrolytic capacitor of 10 µF or greater placed near the audio
power amplifier is recommended.
MIDRAIL BYPASS CAPACITOR, C
The midrail bypass capacitor (C
start-up or recovery from shutdown mode, C
(BYP)
(BYP)
) is the most critical capacitor and serves several important functions. During
determines the rate at which the amplifier starts up. The second
(BYP)
function is to reduce noise produced by the power supply caused by coupling into the output drive signal. This
noise is from the midrail generation circuit internal to the amplifier, which appears as degraded PSRR and
THD+N.
Bypass capacitor (C
for the best THD and noise performance. For the best pop performance, choose a value for C
) values of 0.47-µF to 1-µF ceramic or tantalum low-ESR capacitors are recommended
(BYP)
(BYP)
that is equal to
or greater than the value chosen for Ci. This ensures that the input capacitors are charged up to the midrail
voltage before C
OUTPUT COUPLING CAPACITOR, C
In the typical single-supply SE configuration, an output coupling capacitor (C
is fully charged to the midrail voltage.
(BYP)
(C)
) is required to block the dc bias at
(C)
the output of the amplifier, thus preventing dc currents in the load. As with the input coupling capacitor, the
output coupling capacitor and impedance of the load form a high-pass filter governed by Equation 4 .
The main disadvantage, from a performance standpoint, is the load impedances are typically small, which drives
the low-frequency corner higher, degrading the bass response. Large values of C
frequencies into the load. Consider the example where a C
of 330 µF is chosen and loads vary from 3 Ω ,4 Ω ,
(C)
are required to pass low
(C)
8 Ω , 32 Ω , 10 k Ω , and 47 k Ω . Table 4 summarizes the frequency response characteristics of each configuration.
Table 4. Common Load Impedances vs Low Frequency
Output Characteristics in SE Mode
R
L
3 Ω 330 µF 161 Hz
4 Ω 330 µF 120 Hz
8 Ω 330 µF 60 Hz
32 Ω 330 µF 15 Hz
10,000 Ω 330 µF 0.05 Hz
47,000 Ω 330 µF 0.01 Hz
C
(C)
LOWEST
FREQUENCY
(4)
23

www.ti.com
Power
V
(rms)
2
R
L
V
(rms)
V
O(PP)
2 2
R
L
2x V
O(PP)
V
O(PP)
-V
O(PP)
V
DD
V
DD
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
As Table 4 indicates, most of the bass response is attenuated into a 4- Ω load, an 8- Ω load is adequate,
headphone response is good, and drive into line level inputs (a home stereo for example) is exceptional.
USING LOW-ESR CAPACITORS
Low-ESR capacitors are recommended throughout this applications section. A real (as opposed to ideal)
capacitor can be modeled simply as a resistor in series with an ideal capacitor. The voltage drop across this
resistor minimizes the beneficial effects of the capacitor in the circuit. The lower the equivalent value of this
resistance, the more the real capacitor behaves like an ideal capacitor.
BRIDGED-TIED LOAD vs SINGLE-ENDED LOAD
Figure 36 shows a Class-AB audio power amplifier (APA) in a BTL configuration. The TPA6011A4 BTL amplifier
consists of two Class-AB amplifiers driving both ends of the load. There are several potential benefits to this
differential drive configuration, but, initially consider power to the load. The differential drive to the speaker
means that as one side is slewing up, the other side is slewing down, and vice versa. This in effect doubles the
voltage swing on the load as compared to a ground referenced load. Plugging 2 × V
where voltage is squared, yields 4 × the output power from the same supply rail and load impedance (see
Equation 5 ).
into the power equation,
O(PP)
(5)
Figure 36. Bridge-Tied Load Configuration
24

www.ti.com
f
(c)
1
2 R
LCC
R
L
C
(C)
V
O(PP)
V
O(PP)
V
DD
-3 dB
f
c
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
In a typical computer sound channel operating at 5 V, bridging raises the power into an 8- Ω speaker from a
singled-ended (SE, ground reference) limit of 250 mW to 1 W. In sound power that is a 6-dB improvement, which
is loudness that can be heard. In addition to increased power there are frequency response concerns. Consider
the single-supply SE configuration shown in Figure 37 . A coupling capacitor is required to block the dc offset
voltage from reaching the load. These capacitors can be quite large (approximately 33 µF to 1000 µF), so they
tend to be expensive, heavy, occupy valuable PCB area, and have the additional drawback of limiting
low-frequency performance of the system. This frequency limiting effect is due to the high-pass filter network
created with the speaker impedance and the coupling capacitance and is calculated with Equation 6 .
For example, a 68-µF capacitor with an 8- Ω speaker would attenuate low frequencies below 293 Hz. The BTL
configuration cancels the dc offsets, which eliminates the need for the blocking capacitors. Low-frequency
performance is then limited only by the input network and speaker response. Cost and PCB space are also
minimized by eliminating the bulky coupling capacitor.
(6)
Figure 37. Single-Ended Configuration and Frequency Response
Increasing power to the load does carry a penalty of increased internal power dissipation. The increased
dissipation is understandable considering that the BTL configuration produces 4 × the output power of the SE
configuration. Internal dissipation versus output power is discussed further in the crest factor and thermal
considerations section.
SINGLE-ENDED OPERATION
In SE mode (see Figure 37 ), the load is driven from the primary amplifier output for each channel (OUT+).
The amplifier switches single-ended operation when the SE/ BTL terminal is held high. This puts the negative
outputs in a high-impedance state, and effectively reduces the amplifier's gain by 6 dB.
BTL AMPLIFIER EFFICIENCY
Class-AB amplifiers are inefficient. The primary cause of these inefficiencies is voltage drop across the output
stage transistors. There are two components of the internal voltage drop. One is the headroom or dc voltage
drop that varies inversely to output power. The second component is due to the sinewave nature of the output.
The total voltage drop can be calculated by subtracting the RMS value of the output voltage from V
internal voltage drop multiplied by the RMS value of the supply current (I
rms) determines the internal power
DD
dissipation of the amplifier.
An easy-to-use equation to calculate efficiency starts out as being equal to the ratio of power from the power
supply to the power delivered to the load. To accurately calculate the RMS and average values of power in the
load and in the amplifier, the current and voltage waveform shapes must first be understood (see Figure 38 ).
DD
. The
25

www.ti.com
V
(LRMS)
V
O
I
DD
I
DD(avg)
Efficiency of a BTL amplifier
P
L
P
SUP
Where:
P
L
VLrms
2
R
L
, andV
LRMS
V
P
2
, therefore, P
L
V
P
2
2R
L
and
P
SUP
VDDIDDavg
and
IDDavg
1
0
V
P
R
L
sin(t) dt
1
V
P
R
L
[cos(t)]
0
2V
P
R
L
Therefore,
P
SUP
2 VDDV
P
R
L
Efficiency of a BTL amplifier
V
P
2
2 R
L
2 VDDV
P
R
L
V
P
4 V
DD
PL = Power delivered to load
P
SUP
= Power drawn from power supply
V
LRMS
= RMS voltage on BTL load
R
L
= Load resistance
VP 2 PLR
L
BTL
2 PLR
L
4 V
DD
Where:
Therefore,
VP = Peak voltage on BTL load
IDDavg = Average current drawn from the power supply
VDD = Power supply voltage
η
BTL
= Efficiency of a BTL amplifier
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
Figure 38. Voltage and Current Waveforms for BTL Amplifiers
Although the voltages and currents for SE and BTL are sinusoidal in the load, currents from the supply are very
different between SE and BTL configurations. In an SE application the current waveform is a half-wave rectified
shape, whereas in BTL it is a full-wave rectified waveform. This means RMS conversion factors are different.
Keep in mind that for most of the waveform both the push and pull transistors are not on at the same time, which
supports the fact that each amplifier in the BTL device only draws current from the supply for half the waveform.
The following equations are the basis for calculating amplifier efficiency.
substituting PL and PSUP into Equation 7 ,
Table 5 employs Equation 8 to calculate efficiencies for four different output power levels. Note that the efficiency
of the amplifier is quite low for lower power levels and rises sharply as power to the load is increased resulting in
a nearly flat internal power dissipation over the normal operating range. Note that the internal dissipation at full
output power is less than in the half power range. Calculating the efficiency for a specific system is the key to
proper power supply design. For a stereo 1-W audio system with 8- Ω loads and a 5-V supply, the maximum draw
on the power supply is almost 3.25 W.
26
(7)
(8)

www.ti.com
PdB 10Log
P
W
P
ref
10Log
4 W
1 W
6 dB
PW 10
PdB10
P
ref
= 250 mW (12-db crest factor)
= 125 mW (15-db crest factor)
= 63 mW (18-db crest factor)
= 500 mW (9-db crest factor)
= 1000 mW (6-db crest factor)
= 2000 mW (3-db crest factor)
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
Table 5. Efficiency vs Output Power in 5-V, 8- Ω BTL Systems
OUTPUT POWER EFFICIENCY PEAK VOLTAGE INTERNAL DISSIPATION
(W) (%) (V) (W)
0.25 31.4 2.00 0.55
0.50 44.4 2.83 0.62
1.00 62.8 4.00 0.59
1.25 70.2 4.47
(1) High peak voltages cause the THD to increase.
A final point to remember about Class-AB amplifiers (either SE or BTL) is how to manipulate the terms in the
efficiency equation to utmost advantage when possible. Note that in equation 8, V
indicates that as V
goes down, efficiency goes up.
DD
CREST FACTOR AND THERMAL CONSIDERATIONS
Class-AB power amplifiers dissipate a significant amount of heat in the package under normal operating
conditions. A typical music CD requires 12 dB to 15 dB of dynamic range, or headroom above the average power
output, to pass the loudest portions of the signal without distortion. In other words, music typically has a crest
factor between 12 dB and 15 dB. When determining the optimal ambient operating temperature, the internal
dissipated power at the average output power level must be used. From the TPA6011A4 data sheet, one can
see that when the TPA6011A4 is operating from a 5-V supply into a 3- Ω speaker, that 4-W peaks are available.
Use equation 9 to convert watts to dB.
(1)
0.53
is in the denominator. This
DD
Subtracting the headroom restriction to obtain the average listening level without distortion yields:
• 6 dB - 15 dB = -9 dB (15-dB crest factor)
• 6 dB - 12 dB = -6 dB (12-dB crest factor)
• 6 dB - 9 dB = -3 dB (9-dB crest factor)
• 6 dB - 6 dB = 0 dB (6-dB crest factor)
• 6 dB - 3 dB = 3 dB (3-dB crest factor)
To convert dB back into watts use equation 10.
This is valuable information to consider when attempting to estimate the heat dissipation requirements for the
amplifier system. Comparing the worst case, which is 2 W of continuous power output with a 3-dB crest factor,
against 12-dB and 15-dB applications significantly affects maximum ambient temperature ratings for the system.
Using the power dissipation curves for a 5-V, 3- Ω system, the internal dissipation in the TPA6011A4 and
maximum ambient temperatures is shown in Table 6 .
(9)
(10)
27

www.ti.com
P
D(max)
2V
2
DD
2
R
L
Θ
JA
1
Derating Factor
1
0.022
45°CW
TAMax TJMax ΘJAP
D
150 45(0.6 2) 96°C(15-dB crest factor
)
TPA6011A4
SLOS392A – FEBRUARY 2002 – REVISED JULY 2004
Table 6. TPA6011A4 Power Rating, 5-V, 3- Ω Stereo
PEAK OUTPUT POWER POWER DISSIPATION MAXIMUM AMBIENT
(W) (W/Channel) TEMPERATURE
4 2 W (3 dB) 1.7 -3 ° C
4 1 W (6 dB) 1.6 6 ° C
4 500 mW (9 dB) 1.4 24 ° C
4 250 mW (12 dB) 1.1 51 ° C
4 125 mW (15 dB) 0.8 78 ° C
4 63 mW (18 dB) 0.6 96 ° C
PEAK OUTPUT POWER POWER DISSIPATION MAXIMUM AMBIENT
(W) (W/Channel) TEMPERATURE
2.5 1250 mW (3-dB crest factor) 0.55 100 ° C
2.5 1000 mW (4-dB crest factor) 0.62 94 ° C
2.5 500 mW (7-dB crest factor) 0.59 97 ° C
2.5 250 mW (10-dB crest factor) 0.53 102 ° C
AVERAGE OUTPUT POWER
Table 7. TPA6011A4 Power Rating, 5-V, 8- Ω Stereo
AVERAGE OUTPUT POWER
The maximum dissipated power (P
a 3- Ω load. As a result, this simple formula for calculating P
However, in the case of a 3- Ω load, the P
The amplifier may therefore be operated at a higher ambient temperature than required by the P
) is reached at a much lower output power level for an 8- Ω load than for
D(max)
occurs at a point well above the normal operating power level.
D(max)
D(max)
may be used for an 8- Ω application.
formula for
D(max)
a 3- Ω load.
The maximum ambient temperature depends on the heat-sinking ability of the PCB system. The derating factor
for the PWP package is shown in the dissipation rating table. Use equation 12 to convert this to θ
.
JA.
To calculate maximum ambient temperatures, first consider that the numbers from the dissipation graphs are per
channel, so the dissipated power needs to be doubled for two channel operation. Given θ
, the maximum
JA
allowable junction temperature, and the total internal dissipation, the maximum ambient temperature can be
calculated using Equation 13 . The maximum recommended junction temperature for the TPA6011A4 is 150 ° C.
The internal dissipation figures are taken from the Power Dissipation vs Output Power graphs.
NOTE:
Internal dissipation of 0.6 W is estimated for a 2-W system with 15-dB crest factor per
channel.
Table 6 and Table 7 show that some applications require no airflow to keep junction temperatures in the
specified range. The TPA6011A4 is designed with thermal protection that turns the device off when the junction
temperature surpasses 150 ° C to prevent damage to the IC. Table 6 and Table 7 were calculated for maximum
listening volume without distortion. When the output level is reduced the numbers in the table change
significantly. Also, using 8- Ω speakers increases the thermal performance by increasing amplifier efficiency.
(11)
(12)
(13)
28

THERMAL PAD MECHANICAL DATA
www.ti.com
PWP (R-PDSO-G24)
THERMAL INFORMATION
This PowerPAD™ package incorporates an exposed thermal pad that is designed to be attached directly to an
external heatsink. When the thermal pad is soldered directly to the printed circuit board (PCB), the PCB can be
used as a heatsink. In addition, through the use of thermal vias, the thermal pad can be attached directly to a
ground plane or special heatsink structure designed into the PCB. This design optimizes the heat transfer from
the integrated circuit (IC).
For additional information on the PowerPAD package and how to take advantage of its heat dissipating abilities,
refer to Technical Brief, PowerPAD Thermally Enhanced Package, Texas Inst ruments Literature No. SLMA002
and Application Brief, PowerPAD Made Easy, Texas Instrume n ts Literature No. SL MA004. Both documents are
available at www.ti.com.
The exposed thermal pad dimensions for this package are shown in the following illustration.
24
13
Exposed Thermal Pad
2,40
1,65
1
NOTE: All linear dimensions are in millimeters
Exposed Thermal Pad Dimensions
12
5,16
4,10
Top View
PPTD030
PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments


PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
18-Jul-2006
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
TPA6011A4PWP ACTIVE HTSSOP PWP 24 60 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TPA6011A4PWPG4 ACTIVE HTSSOP PWP 24 60 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TPA6011A4PWPR ACTIVE HTSSOP PWP 24 2000 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TPA6011A4PWPRG4 ACTIVE HTSSOP PWP 24 2000 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and
package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS
compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
(3)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
Addendum-Page 1

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION
11-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package
TPA6011A4PWPR HTSSOP PWP 24 2000 330.0 16.4 6.95 8.3 1.6 8.0 16.0 Q1
TPA6011A4PWPR HTSSOP PWP 24 2000 330.0 16.4 6.95 8.3 1.6 8.0 16.0 Q1
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0 (mm) B0 (mm) K0 (mm) P1
(mm)W(mm)
Pin1
Quadrant
Pack Materials-Page 1

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
11-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
TPA6011A4PWPR HTSSOP PWP 24 2000 346.0 346.0 33.0
TPA6011A4PWPR HTSSOP PWP 24 2000 346.0 346.0 33.0
Pack Materials-Page 2



IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
 Loading...
Loading...