Page 1

TMS320DM641/TMS320DM640
Video/Imaging Fixed-Point Digital
Signal Processors
Data Manual
Literature Number: SPRS222F
June 2003 − Revised October 2010
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Page 2

This page intentionally left blank
Page 3

Revision History
Revision History
This data sheet revision history highlights the technical changes made to the SPRS222E device-specific data
sheet to make it an SPRS222F revision.
PAGE(s)
NO.
82 Added note for VOH and VOL.
ADDS/CHANGES/DELETES
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
3
Page 4

Contents
Contents
Section Page
1 Device Overview 15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.1 Features 15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2 Description 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3 Device Characteristics 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4 Device Compatibility 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.5 Functional Block Diagram 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.6 CPU (DSP Core) Description 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.6.1 CPU Core Registers 25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.7 Memory Map Summary 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.7.1 L2 Architecture Expanded 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.8 Bootmode 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.9 Pin Assignments 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.9.1 Pin Map 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.9.2 Signal Groups Description 36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.9.3 Terminal Functions 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.10 Development 64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.10.1 Development Support 64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.10.2 Device Support 65. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.10.2.1 Device and Development-Support Tool Nomenclature 65. . . . . . . . .
1.10.2.2 Documentation Support 66. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.10.2.3 Device Silicon Revision 67. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Device Configurations 68. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1 Configurations at Reset 68. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1.1 Peripheral Selection at Device Reset 68. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1.2 Device Configuration at Device Reset 69. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2 Configurations After Reset 69. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2.1 Peripheral Selection After Device Reset 69. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.3 Peripheral Configuration Lock 72. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.4 Device Status Register Description 74. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.5 Multiplexed Pin Configurations 76. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6 Debugging Considerations 77. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.7 Configuration Examples 77. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Device Operating Conditions 82. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Case Temperature Range 82. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2 Recommended Operating Conditions 82. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Ranges of Supply Voltage and
4 DM641/DM640 Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications 84. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1 Parameter Information 84. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating Case Temperature 83. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.1 Parameter Information Device-Specific Information 84. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.1.1 Signal Transition Levels 84. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.1.2 Signal Transition Rates 84. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 5

Contents
Section Page
4.1.1.3 AC Transient Rise/Fall Time Specifications 85. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.1.4 Timing Parameters and Board Routing Analysis 85. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior 86. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3 Power Supplies 86. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3.1 Power-Supply Sequencing 86. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3.2 Power-Supply Design Considerations 87. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3.3 Power-Supply Decoupling 87. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3.4 Peripheral Power-Down Operation 88. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3.5 Power-Down Modes Logic 88. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3.6 Triggering, Wake-up, and Effects 89. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3.7 C64x Power-Down Mode with an Emulator 90. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.4 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller 90. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.4.1 EDMA Device-Specific Information 90. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.4.1.1 EDMA Channel Synchronization Events 90. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.4.2 EDMA Peripheral Register Description(s) 92. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.5 Interrupts 95. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.5.1 Interrupt Sources and Interrupt Selector 95. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.5.2 Interrupts Peripheral Register Description(s) 96. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.5.3 External Interrupts Electrical Data/Timing 96. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.6 Reset 96. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.6.1 Reset Electrical Data/Timing 97. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.7 Clock PLL 99. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.7.1 Clock PLL Device-Specific Information 99. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.7.2 Clock PLL Electrical Data/Timing (Input and Output Clocks) 101. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.8 External Memory Interface (EMIIF) 105. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.8.1 EMIF Device-Specific Information 105. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.8.2 EMIF Peripheral Register Description(s) 105. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.8.3 EMIF Electrical Data/Timing 106. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.8.3.1 Asynchronous Memory Timing 106. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.8.3.2 Programmable Synchronous Interface Timing 109. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.8.3.3 Synchronous DRAM Timing 113. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.8.3.4 HOLD
/HOLDA Timing 119. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.8.3.5 BUSREQ Timing 120. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.9 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP0) Peripheral 121. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.9.1 McASP0 Device-Specific Information 121. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.9.1.1 McASP Block Diagram 121. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.9.2 McASP0 Peripheral Register Description(s) 123. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.9.3 McASP0 Electrical Data/Timing 125. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.9.3.1 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP) Timing 125. . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.10 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) 129. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.10.1 I2C Device-Specific Information 129. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.10.2 I2C Peripheral Register Description(s) 130. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.10.3 I2C Electrical Data/Timing 131. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.10.3.1 Inter-Integrated Circuits (I2C) Timing 131. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.11 Host-Port Interface (HPI) [DM641 Only] 133. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.11.1 HPI Peripheral Register Description(s) [DM641 Only] 133. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.11.2 Host-Port Interface (HPI) Electrical Data/Timing [DM641 Only] 133. . . . . . . . . . . .
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
5
Page 6

Contents
Section Page
4.12 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP) 137. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.12.1 McBSP Peripheral Register Description(s) 137. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.12.2 McBSP Electrical Data/Timing 139. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.12.2.1 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP) Timing 139. . . . . . . . . . .
4.13 Video Port 146. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.13.1 Video Port Device-Specific Information 146. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.13.2 Video Port Peripheral Register Description(s) 146. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.13.3 Video Port (VP0 [DM641/DM640], VP1 [DM641 Only]) Electrical
Data/Timing 149. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.13.3.1 VCLKIN Timing (Video Capture Mode) 149. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.13.3.2 Video Data and Control Timing (Video Capture Mode) 150. . . . . . . .
4.13.3.3 VCLKIN Timing (Video Display Mode) 151. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.13.3.4 Video Control Input/Output and Video Display Data Output
Timing With Respect to VPxCLKINx and VPxCLKOUTx
(Video Display Mode) 151. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.13.3.5 Video Dual-Display Sync Mode Timing (With Respect to
VPxCLKINx) 153. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.14 VCXO Interpolated Control (VIC) 154. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.14.1 VIC Device-Specific Information 154. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.14.2 VIC Peripheral Register Description(s) 154. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.14.3 VIC Electrical Data/Timing 155. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.14.3.1 STCLK Timing 155. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.15 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) 156. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.15.1 EMAC Device-Specific Information 156. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.15.2 EMAC Peripheral Register Description(s) 156. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.15.3 EMAC Electrical Data/Timing 160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.16 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) 162. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.16.1 Device-Specific Information 162. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.16.2 Peripheral Register Description(s) 162. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.16.3 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) Electrical Data/Timing 163. . . . . . . . . . . .
4.17 Timer 164. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.17.1 Timer Device-Specific Information 164. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.17.2 Timer Peripheral Register Description(s) 164. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.17.3 Timer Electrical Data/Timing 165. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.18 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) 166. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.18.1 GPIO Device-Specific Information 166. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.18.2 GPIO Peripheral Register Description(s) 167. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.18.3 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Electrical Data/Timing 167. . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.19 JTAG 168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.19.1 JTAG Device-Specific Information 168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.19.1.1 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Compatibility Statement 168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.19.1.2 JTAG ID Register Description 168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.19.2 JTAG Peripheral Register Description(s) 169. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.19.3 JTAG Test-Port Electrical Data/Timing 169. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 Mechanical Data 170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1 Thermal Data 170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 7

Figures
List of Figures
Figure Page
1−1 Functional Block Diagram 21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1−2 TMS320C64x CPU (DSP Core) Data Paths 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1−3 TMS320DM641/DM640 L2 Architecture Memory Configuration 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1−4 DM641/DM640 Pin Map [Quadrant A] 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1−5 CPU and Peripheral Signals 36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1−6 Peripheral Signals 37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1−7 TMS320DM64x DSP Device Nomenclature (Including the DM641 and DM640 Devices) 66. . . . . . . . . .
2−1 Peripheral Configuration Register (PERCFG) [Address Location: 0x01B3F000 − 0x01B3F003] 70. . . .
2−2 VP1, VP0, McBSP1, and McBSP0 Pin Muxing 71. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−3 Peripheral Enable/Disable Flow Diagram 72. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−4 PCFGLOCK Register Diagram [Address Location: 0x01B3 F018] − Read/Write Accesses 73. . . . . . . .
2−5 Device Status Register (DEVSTAT) Description − 0x01B3 F004 74. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−6 Configuration Example A for DM641 (2 8-Bit Video Ports + 1 McASP0 + VIC + I2C0 + EMIF) 78. . . . .
2−7 Configuration Example B for DM641 (1 McASP0 + 2 McBSPs + VIC + I2C0 + EMIF) 79. . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−8 Configuration Example A for DM640 (1 8-Bit Video Port + 1 McASP0 + VIC + I2C0 + EMIF) 80. . . . . .
2−9 Configuration Example B for DM640 (1 McASP0 + 2 McBSPs + VIC + I2C0 + EMIF) 81. . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−1 Test Load Circuit for AC Timing Measurements 84. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−2 Input and Output Voltage Reference Levels for AC Timing Measurements 84. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−3 Rise and Fall Transition Time Voltage Reference Levels 84. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−4 AC Transient Specification Rise Time 85. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−5 AC Transient Specification Fall Time 85. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−6 Board-Level Input/Output Timings 86. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−7 Schottky Diode Diagram 87. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−8 Power-Down Mode Logic 88. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−9 PWRD Field of the CSR Register 89. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−10 External/NMI Interrupt Timing 96. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−11 Reset Timing 98. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−12 External PLL Circuitry for Either PLL Multiply Modes or x1 (Bypass) Mode 100. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−13 CLKIN Timing 102. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−14 CLKOUT4 Timing 102. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−15 CLKOUT6 Timing 103. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−16 AECLKIN Timing for EMIFA 103. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−17 AECLKOUT1 Timing for the EMIFA Module 104. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−18 AECLKOUT2 Timing for the EMIFA Module 104. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−19 Asynchronous Memory Read Timing for EMIFA 107. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−20 Asynchronous Memory Write Timing for EMIFA 108. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−21 Programmable Synchronous Interface Read Timing for EMIFA (With Read Latency = 2) 110. . . . . . . . .
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
7
Page 8

Figures
Figure Page
4−22 Programmable Synchronous Interface Write Timing for EMIFA (With Write Latency = 0) 111. . . . . . . . .
4−23 Programmable Synchronous Interface Write Timing for EMIFA (With Write Latency = 1) 112. . . . . . . . .
4−24 SDRAM Read Command (CAS Latency 3) for EMIFA 114. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−25 SDRAM Write Command for EMIFA 115. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−26 SDRAM ACTV Command for EMIFA 116. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−27 SDRAM DCAB Command for EMIFA 116. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−28 SDRAM DEAC Command for EMIFA 117. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−29 SDRAM REFR Command for EMIFA 117. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−30 SDRAM MRS Command for EMIFA 118. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−31 SDRAM Self-Refresh Timing for EMIFA 118. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−32 HOLD
/HOLDA Timing for EMIFA 119. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−33 BUSREQ Timing for EMIFA 120. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−34 McASP0 Configuration 122. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−35 McASP Input Timings 127. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−36 McASP Output Timings 128. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−37 I2C0 Module Block Diagram 129. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−38 I2C Receive Timings 131. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−39 I2C Transmit Timings 132. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−40 HPI16 Read Timing (HAS Not Used, Tied High) [DM641 Only] 134. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−41 HPI16 Read Timing (HAS Used) [DM641 Only] 135. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−42 HPI16 Write Timing (HAS Not Used, Tied High) [DM641 Only] 135. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−43 HPI16 Write Timing (HAS Used) [DM641 Only] 136. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−44 McBSP Timing 141. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−45 FSR Timing When GSYNC = 1 141. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−46 McBSP Timing as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0 142. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−47 McBSP Timing as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0 143. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−48 McBSP Timing as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1 144. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−49 McBSP Timing as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1 145. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−50 Video Port Capture VPxCLKINx TIming 149. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−51 Video Port Capture Data and Control Input Timing 150. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−52 Video Port Display VPxCLKINx Timing 151. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−53 Video Port Display Data Output Timing and Control Input/Output Timing With Respect to
VPxCLKINx and VPxCLKOUTx 152. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−54 Video Port Dual-Display Sync Timing 153. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−55 STCLK Timing 155. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−56 MRCLK Timing (EMAC − Receive) 160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−57 MTCLK Timing (EMAC − Transmit) 160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−58 EMAC Receive Interface Timing 161. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−59 EMAC Transmit Interface Timing 161. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−60 MDIO Input Timing 163. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−61 MDIO Output Timing 163. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−62 Timer Timing 165. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 9

Figures
Figure Page
4−63 GPIO Enable Register (GPEN) [Hex Address: 01B0 0000] 166. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−64 GPIO Direction Register (GPDIR) [Hex Address: 01B0 0004] 166. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−65 GPIO Port Timing 167. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−66 JTAG ID Register Description − TMS320DM641/DM640 Register Value − 0x0007 902F 168. . . . . . . . .
4−67 JTAG Test-Port Timing 169. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
9
Page 10

Tables
List of Tables
Table Page
1−1 Characteristics of the DM641 Processor 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1−2 Characteristics of the DM640 Processor 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1−3 Peripherals Available on the DM641 and DM640 Devices 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1−4 L2 Cache Registers (C64x) 25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1−5 TMS320DM641/DM640 Memory Map Summary 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1−6 Terminal Functions 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−1 MAC_EN Peripheral Selection (EMAC and MDIO) 68. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−2 DM641/DM640 Device Configuration Pins (TOUT1/LENDIAN, AEA[22:19], and
TOUT0/MAC_EN) 69. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−3 Peripheral Configuration (PERCFG) Register Selection Bit Descriptions 70. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−4 PCFGLOCK Register Selection Bit Descriptions − Read Accesses 73. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−5 PCFGLOCK Register Selection Bit Descriptions − Write Accesses 73. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−6 Device Status (DEVSTAT) Register Selection Bit Descriptions 74. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−7 DM641/DM640 Device Multiplexed Pin Configurations 76. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−1 Board-Level Timing Example 86. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−2 Characteristics of the Power-Down Modes 90. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−3 TMS320DM641/DM640 EDMA Channel Synchronization Events 91. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−4 EDMA Registers (C64x) 92. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−5 Quick DMA (QDMA) and Pseudo Registers 93. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−6 EDMA Parameter RAM (C64x) 94. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−7 DM641/DM640 DSP Interrupts 95. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−8 Interrupt Selector Registers (C64x) 96. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−9 Timing Requirements for External Interrupts 96. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−10 Timing Requirements for Reset 97. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−11 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions During Reset 97. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−12 TMS320DM641/DM640 PLL Multiply Factor Options, Clock Frequency Ranges, and Typical
Lock Time 101. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−13 Timing Requirements for CLKIN for −400 Devices 101. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−14 Timing Requirements for CLKIN for −500 Devices 101. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−15 Timing Requirements for CLKIN for −600 Devices 102. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−16 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for CLKOUT4 102. . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−17 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for CLKOUT6 103. . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−18 Timing Requirements for AECLKIN for EMIFA 103. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−19 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for AECLKOUT1 for the
EMIFA Module 104. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−20 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for AECLKOUT2 for the
EMIFA Module 104. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−21 EMIFA Registers 105. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−22 Timing Requirements for Asynchronous Memory Cycles for EMIFA Module 106. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−23 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for Asynchronous Memory
Cycles for EMIFA Module 106. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−24 Timing Requirements for Programmable Synchronous Interface Cycles for EMIFA Module 109. . . . . . .
4−25 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for Programmable
Synchronous Interface Cycles for EMIFA Module 109. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 11

Tables
Table Page
4−26 Timing Requirements for Synchronous DRAM Cycles for EMIFA Module 113. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−27 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for Synchronous DRAM
Cycles for EMIFA Module 113. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−28 Timing Requirements for the HOLD
/HOLDA Cycles for EMIFA Module 119. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−29 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for the HOLD/HOLDA
Cycles for EMIFA Module 119. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−30 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for the BUSREQ Cycles
for EMIFA Module 120. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−31 McASP0 Control Registers 123. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−32 McASP0 Data Registers 125. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−33 Timing Requirements for McASP 125. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−34 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McASP 126. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−35 I2C0 Registers 130. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−36 Timing Requirements for I2C Timings 131. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−37 Switching Characteristics for I2C Timings 132. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−38 HPI Registers [DM641 Only] 133. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−39 Timing Requirements for Host-Port Interface Cycles [DM641 Only] 133. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−40 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions During Host-Port Interface
Cycles [DM641 Only] 134. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−41 McBSP 0 Registers 137. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−42 McBSP 1 Registers 138. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−43 Timing Requirements for McBSP 139. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−44 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McBSP 140. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−45 Timing Requirements for FSR When GSYNC = 1 141. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−46 Timing Requirements for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0 142. . . . . . . . . .
4−47 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McBSP as SPI
Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0 142. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−48 Timing Requirements for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0 143. . . . . . . . . .
4−49 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McBSP as SPI
Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0 143. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−50 Timing Requirements for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1 144. . . . . . . . . .
4−51 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McBSP as SPI
Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1 144. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−52 Timing Requirements for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1 145. . . . . . . . . .
4−53 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McBSP as SPI
Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1 145. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−54 Video Port 0 and 1 (VP0 and VP1) Control Registers 146. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−55 Timing Requirements for Video Capture Mode for VPxCLKINx 149. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−56 Timing Requirements in Video Capture Mode for Video Data and Control Inputs 150. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−57 Timing Requirements for Video Display Mode for VPxCLKINx 151. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−58 Timing Requirements in Video Display Mode for Video Control Input Shown With Respect to
VPxCLKINx and VPxCLKOUTx 151. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−59 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions in Video Display Mode
for Video Data and Control Output Shown With Respect to VPxCLKINx and VPxCLKOUTx 152. . . . . .
4−60 Timing Requirements for Dual-Display Sync Mode for VPxCLKINx 153. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−61 VCXO Interpolated Control (VIC) Port Registers 154. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−62 Timing Requirments for STCLK 155. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−63 Ethernet MAC (EMAC) Control Registers 156. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−64 EMAC Statistics Registers 159. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−65 EMAC Wrapper 159. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
11
Page 12

Tables
Table Page
4−66 EWRAP Registers 160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−67 Timing Requirements for MRCLK 160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−68 Timing Requirements for MTCLK 160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−69 Timing Requirements for EMAC MII Receive 10/100 Mbit/s 161. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−70 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for EMAC MII Transmit
10/100 Mbit/s 161. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−71 MDIO Registers 162. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−72 Timing Requirements for MDIO Input 163. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−73 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for MDIO Output 163. . . . . . . . . .
4−74 Timer 0 Registers 164. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−75 Timer 1 Registers 164. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−76 Timer 2 Registers 164. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−77 Timing Requirements for Timer Inputs 165. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−78 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for Timer Outputs 165. . . . . . . . .
4−79 GP0 Registers 167. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−80 Timing Requirements for GPIO Inputs 167. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−81 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for GPIO Outputs 167. . . . . . . . .
4−82 JTAG ID Register Selection Bit Descriptions 169. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−83 JTAG ID Register 169. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−84 Timing Requirements for JTAG Test Port 169. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−85 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for JTAG Test Port 169. . . . . . . .
5−1 Thermal Resistance Characteristics (S-PBGA Package) [GDK] 170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5−2 Thermal Resistance Characteristics (S-PBGA Package) [GNZ] 170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 13

This page intentionally left blank
Tables
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
13
Page 14

Device Overview
1 Device Overview
1.1 Features
D High-Performance Digital Media Processor
(TMS320DM641/TMS320DM640)
− 2.5-, 2-, 1.67-ns Instruction Cycle Time
− 400-, 500-, 600-MHz Clock Rate
− Eight 32-Bit Instructions/Cycle
− 3200, 4000, 4800 MIPS
− Fully Software-Compatible With C64x™
D VelociTI.2™ Extensions to VelociTI™
Advanced Very-Long-Instruction-Word
(VLIW) TMS320C64x™ DSP Core
− Eight Highly Independent Functional
Units With VelociTI.2™ Extensions:
− Six ALUs (32-/40-Bit), Each Supports
Single 32-Bit, Dual 16-Bit, or Quad
8-Bit Arithmetic per Clock Cycle
− Two Multipliers Support
Four 16 x 16-Bit Multiplies
(32-Bit Results) per Clock Cycle or
Eight 8 x 8-Bit Multiplies
(16-Bit Results) per Clock Cycle
− Load-Store Architecture With
Non-Aligned Support
− 64 32-Bit General-Purpose Registers
− Instruction Packing Reduces Code Size
− All Instructions Conditional
D Instruction Set Features
− Byte-Addressable (8-/16-/32-/64-Bit Data)
− 8-Bit Overflow Protection
− Bit-Field Extract, Set, Clear
− Normalization, Saturation, Bit-Counting
− VelociTI.2™ Increased Orthogonality
D L1/L2 Memory Architecture
− 128K-Bit (16K-Byte) L1P Program Cache
(Direct Mapped)
− 128K-Bit (16K-Byte) L1D Data Cache
(2-Way Set-Associative)
− 1M-Bit (128K-Byte) L2 Unified Mapped
RAM/Cache
(Flexible RAM/Cache Allocation)
D Endianess: Little Endian, Big Endian
D 32-Bit External Memory Interface (EMIF)
− Glueless Interface to Asynchronous
Memories (SRAM and EPROM) and
Synchronous Memories (SDRAM,
SBSRAM, ZBT SRAM, and FIFO)
− 1024M-Byte Total Addressable External
Memory Space
D Enhanced Direct-Memory-Access (EDMA)
Controller (64 Independent Channels)
D 10/100 Mb/s Ethernet MAC (EMAC)
− IEEE 802.3 Compliant
− Media Independent Interface (MII)
− 8 Independent Transmit (TX) Channels
and 1 Receive (RX) Channel
D Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
D Two Configurable Video Ports (DM641)
D One Configurable Video Port (DM640)
− Providing a Glueless I/F to Common
Video Decoder and Encoder Devices
− Supports Multiple Resolutions and Video
Standards
D VCXO Interpolated Control Port (VIC)
− Supports Audio/Video Synchronization
D Host-Port Interface (HPI) [16-Bit] (DM641)
D Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
− Four Serial Data Pins
− Wide Variety of I2S and Similar Bit
Stream Format
− Integrated Digital Audio I/F Transmitter
Supports S/PDIF, IEC60958-1, AES-3,
CP-430 Formats
D Inter-Integrated Circuit (I
2
C) Bus
D Two Multichannel Buffered Serial Ports
D Three 32-Bit General-Purpose Timers
D Eight General-Purpose I/O (GPIO) Pins
D Flexible PLL Clock Generator
D IEEE-1149.1 (JTAG
Boundary-Scan-Compatible
†
)
D 548-Pin Ball Grid Array (BGA) Package
(GDK and ZDK Suffixes), 0.8-mm Ball Pitch
D 548-Pin Ball Grid Array (BGA) Package
(GNZ and ZNZ Suffixes), 1.0-mm Ball Pitch
D 0.13-μm/6-Level Cu Metal Process (CMOS)
D 3.3-V I/O, 1.2-V Internal (-400, -500)
D 3.3-V I/O, 1.4-V Internal (-600)
C64x, VelociTI.2, VelociTI, and TMS320C64x are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
†
IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990 Standard-Test-Access Port and Boundary Scan Architecture.
14
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 15

1.2 Description
The TMS320C64x™ DSPs (including the TMS320DM641 and TMS320DM640 devices) are the
highest-performance fixed-point DSP generation in the TMS320C6000™ DSP platform. The TMS320DM641
(DM641) and TMS320DM640 (DM640) devices are based on the second-generation high-performance,
advanced VelociTI™ very-long-instruction-word (VLIW) architecture (VelociTI.2™) developed by Texas
Instruments (TI), making these DSPs an excellent choice for digital media applications. The C64x™ is a
code-compatible member of the C6000™ DSP platform.
With performance of up to 4800 million instructions per second (MIPS) at a clock rate of 600 MHz, the DM641
device offers cost-effective solutions to high-performance DSP programming challenges.
With performance of up to 3200 million instructions per second (MIPS) at a clock rate of 400 MHz, the DM640
device offers cost-effective solutions to high-performance DSP programming challenges.
The DM641/DM640 DSP possesses the operational flexibility of high-speed controllers and the numerical
capability of array processors. The C64x™ DSP core processor has 64 general-purpose registers of 32-bit
word length and eight highly independent functional units—two multipliers for a 32-bit result and six arithmetic
logic units (ALUs)— with VelociTI.2™ extensions. The VelociTI.2™ extensions in the eight functional units
include new instructions to accelerate the performance in video and imaging applications and extend the
parallelism of the VelociTI™ architecture. The DM641 can produce four 16-bit multiply-accumulates (MACs)
per cycle for a total of 2400 million MACs per second (MMACS), or eight 8-bit MACs per cycle for a total of
4800 MMACS. The DM640 can produce four 16-bit multiply-accumulates (MACs) per cycle for a total of
1600 million MACs per second (MMACS), or eight 8-bit MACs per cycle for a total of 3200 MMACS. The
DM641/DM640 DSP also has application-specific hardware logic, on-chip memory, and additional on-chip
peripherals similar to the other C6000™ DSP platform devices.
Description
The DM641/DM640 uses a two-level cache-based architecture and has a powerful and diverse set of
peripherals. The Level 1 program cache (L1P) is a 128-Kbit direct mapped cache and the Level 1 data cache
(L1D) is a 128-Kbit 2-way set-associative cache. The Level 2 memory/cache (L2) consists of a 1-Mbit memory
space that is shared between program and data space. L2 memory can be configured as mapped memory,
cache, or combinations of the two. The peripheral set includes: two configurable video ports (DM641); one
configurable video port (DM640); a 10/100 Mb/s Ethernet MAC (EMAC); a management data input/output
(MDIO) module; a VCXO interpolated control port (VIC); one 4-bit multichannel buffered audio serial port
(McASP0); an inter-integrated circuit (I2C) Bus module; two multichannel buffered serial ports (McBSPs);
three 32-bit general-purpose timers; a 16-bit host-port interface (HPI16) [DM641]; an 8-pin general-purpose
input/output port (GP0) with programmable interrupt/event generation modes; and a 32-bit glueless external
memory interface (EMIF A), which is capable of interfacing to synchronous and asynchronous memories and
peripherals.
The DM641 device has two single-channel 8-bit configurable video port peripherals (VP0 and VP1). The
DM640 device has one single-channel 8-bit configurable video port peripheral (VP0). These video port
peripherals provide a glueless interface to common video decoder and encoder devices. The DM641/DM640
video port peripherals support multiple resolutions and video standards (e. g., CCIR601 and ITU−BT.656).
These video port peripherals are configurable and can support either video capture and/or video display
modes.
For more details on the Video Port peripherals, see the TMS320C64x DSP Video Port/VCXO Interpolated
Control (VIC) Port Reference Guide (literature number SPRU629).
The McASP0 port supports one transmit and one receive clock zone, with four serial data pins which can be
individually allocated to any of the two zones. The serial port supports time-division multiplexing on each pin
from 2 to 32 time slots. The DM641/DM640 has sufficient bandwidth to support all 4 serial data pins
transmitting a 192-kHz stereo signal. Serial data in each zone may be transmitted and received on multiple
serial data pins simultaneously and formatted in a multitude of variations on the Philips Inter-IC Sound (I2S)
format.
TMS320C6000, and C6000 are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
15
Page 16

Description
In addition, the McASP0 transmitter may be programmed to output multiple S/PDIF, IEC60958, AES-3,
CP-430 encoded data channels simultaneously, with a single RAM containing the full implementation of user
data and channel status fields.
McASP0 also provides extensive error-checking and recovery features, such as the bad clock detection circuit
for each high-frequency master clock which verifies that the master clock is within a programmed frequency
range.
The VCXO interpolated control (VIC) port provides digital-to-analog conversion with resolution from 9-bits to
up to 16-bits. The output of the VIC is a single bit interpolated D/A output. For more details on the VIC port,
see the TMS320C64x DSP Video Port/VCXO Interpolated Control (VIC) Port Reference Guide (literature
number SPRU629).
The ethernet media access controller (EMAC) provides an efficient interface between the DM641/DM640 DSP
core processor and the network. The DM641/DM640 EMAC support both 10Base-T and 100Base-TX, or 10
Mbits/second (Mbps) and 100 Mbps in either half- or full-duplex, with hardware flow control and quality of
service (QOS) support. The DM641/DM640 EMAC makes use of a custom interface to the DSP core that
allows ef ficient data transmission and reception. For more details on the EMAC, see the TMS320C6000 DSP
Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) / Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) Module Reference
Guide (literature number SPRU628).
The management data input/output (MDIO) module continuously polls all 32 MDIO addresses in order to
enumerate all PHY devices in the system. Once a PHY candidate has been selected by the DSP, the MDIO
module transparently monitors its link state by reading the PHY status register. Link change events are stored
in the MDIO module and can optionally interrupt the DSP, allowing the DSP to poll the link status of the device
without continuously performing costly MDIO accesses. For more details on the MDIO, see the
TMS320C6000 DSP Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) / Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
Module Reference Guide (literature number SPRU628).
The I2C0 port on the TMS320DM641/DM640 allows the DSP to easily control peripheral devices and
communicate with a host processor. In addition, the standard multichannel buffered serial port (McBSP) may
be used to communicate with serial peripheral interface (SPI) mode peripheral devices.
The DM641/DM640 has a complete set of development tools which includes: a new C compiler, an assembly
optimizer to simplify programming and scheduling, and a Windows™ debugger interface for visibility into
source code execution.
Windows is a registered trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.
16
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 17
Device Characteristics
available at the same time
available at the same time
(For more detail, see the
section).
Voltage
Voltage
BGA Package
1.3 Device Characteristics
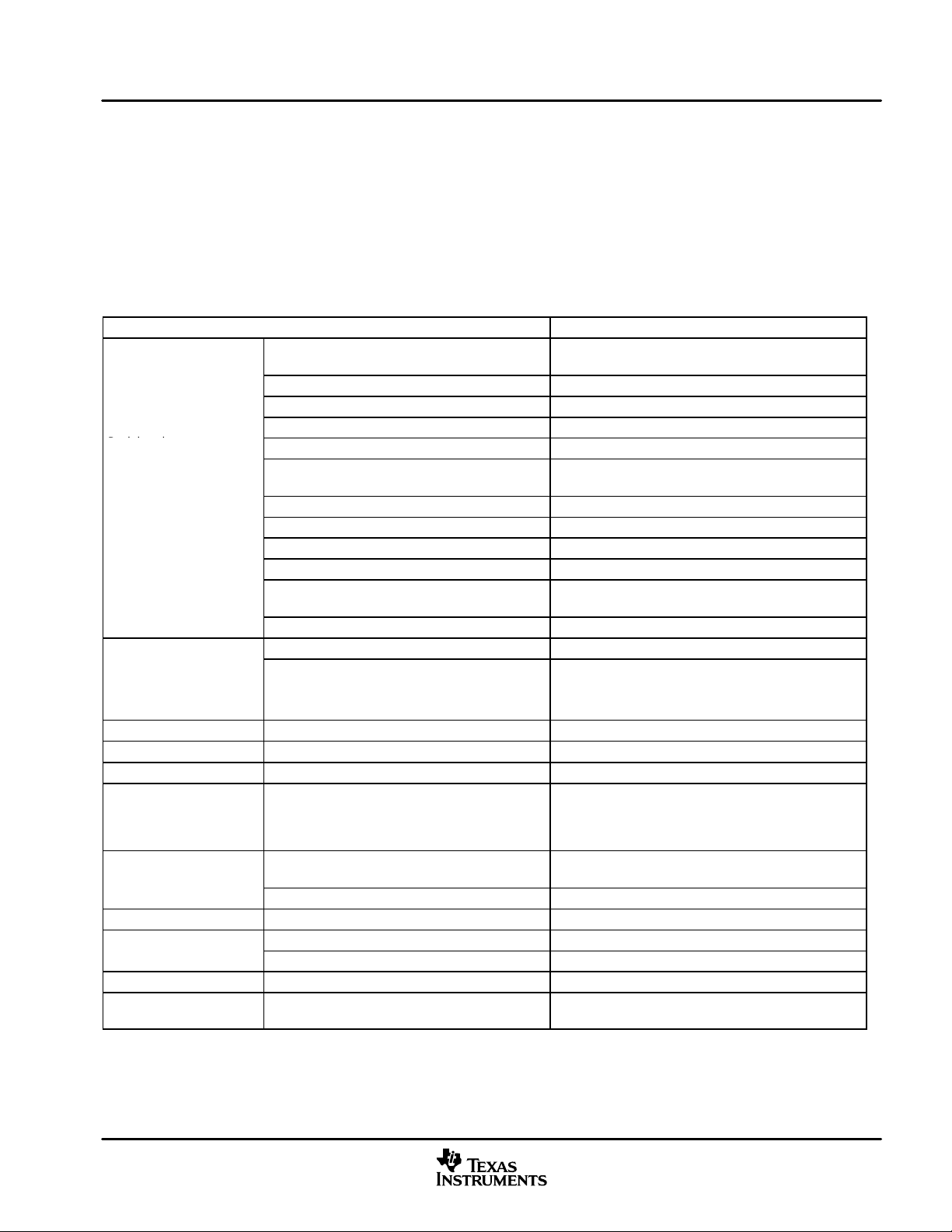
Table 1−1 provides an overview of the DM641 DSP. The table shows significant features of the DM641 device,
including the capacity of on-chip RAM, the peripherals, the CPU frequency, and the package type with pin
count.
Table 1−1. Characteristics of the DM641 Processor
HARDWARE FEATURES DM641
EMIFA (32-bit bus width)
(clock source = AECLKIN)
EDMA (64 independent channels) 1
McASP0 (uses Peripheral Clock [AUXCLK]) 1
Peripherals
Not all peripherals pins are
(For more detail, see the
Device Configuration
On-Chip Memory
CPU ID + CPU Rev ID Control Status Register (CSR.[31:16]) 0x0C01
JTAG BSDL_ID JTAGID register (address location: 0x01B3F008) 0x0007902F
Frequency MHz 500, 600
Cycle Time ns
PLL Options CLKIN frequency multiplier Bypass (x1), x6, x12
Process Technology μm 0.13 μm
Product Status
†
On this DM64x™ device, the rated EMIF speed affects only the SDRAM interface on the EMIF. For more detailed information, see the EMIF device
speed portion of this data sheet.
‡
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments standard
warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all parameters.
‡
I2C0 (uses Peripheral Clock) 1
HPI (16-bit) 1 (HPI16)
McBSPs
(internal clock source = CPU/4 clock frequency)
Configurable Video Ports (VP0 and VP1) 2
10/100 Ethernet MAC (EMAC) 1
Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) 1
VCXO Interpolated Control Port (VIC) 1
32-Bit Timers
(internal clock source = CPU/8 clock frequency)
General-Purpose Input/Output Port (GP0) 8
Size (Bytes) 160K
16K-Byte (16KB) L1 Program (L1P) Cache
Organization
Core (V)
I/O (V) 3.3 V
23 x 23 mm 548-Pin BGA (GDK and ZDK)
27 x 27 mm 548-Pin BGA (GNZ and ZNZ)
Product Preview (PP), Advance Information (AI),
or Production Data (PD)
16KB L1 Data (L1D) Cache
128KB Unified Mapped RAM/Cache (L2)
2 ns (DM641-500)
[500-MHz CPU, 100 MHz EMIF†]
1.67 ns (DM641-600)
[600-MHz CPU, 133 MHz EMIF†]
1
2
3
1.2 V (-500)
1.4 V (-600)
PD
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
17
Page 18
Device Characteristics
Peripherals
Peripherals
Not all peripherals pins are
(For more detail, see the
Device Configuration
Voltage
BGA Package
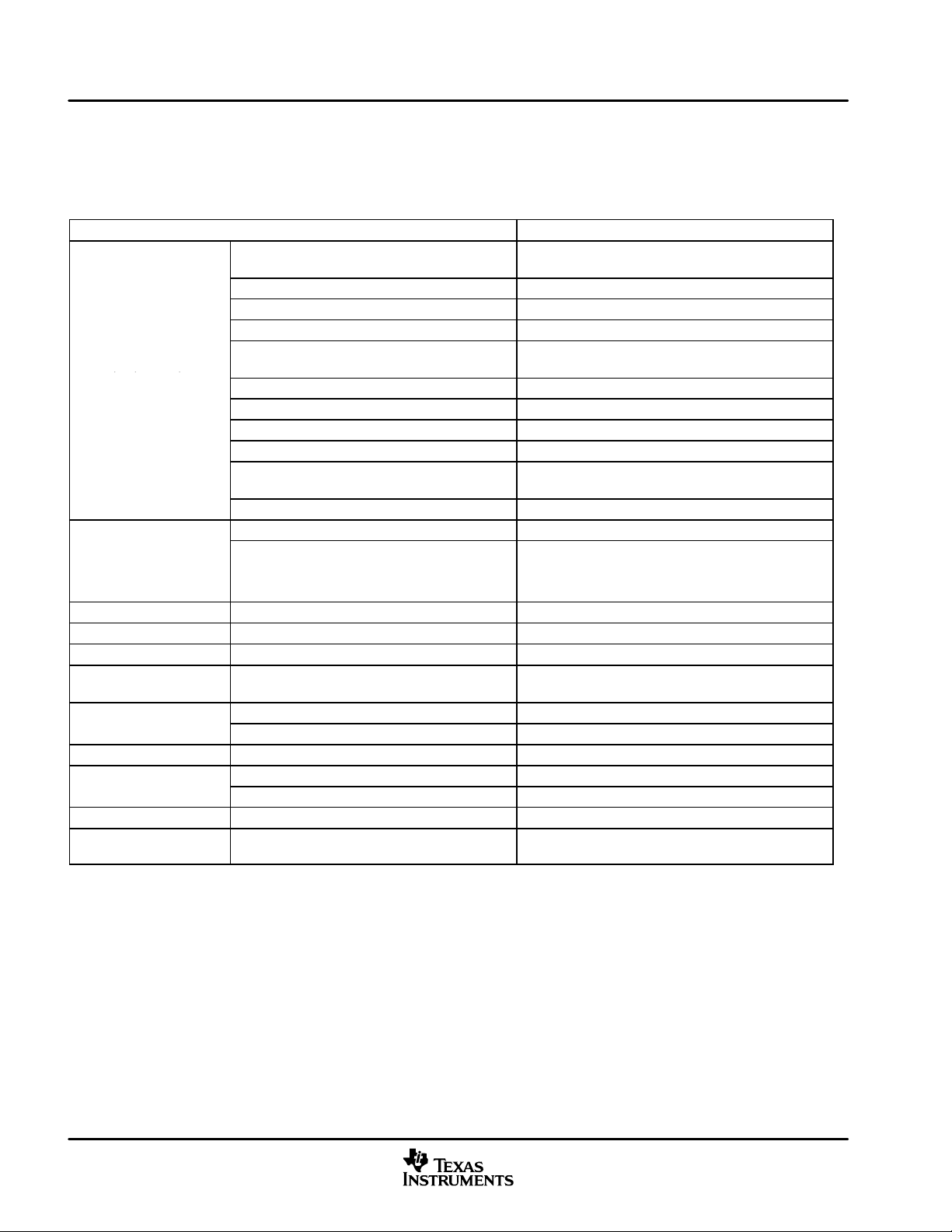
Table 1−2 provides an overview of the DM640 DSP. The table shows significant features of the DM640 device,
including the capacity of on-chip RAM, the peripherals, the CPU frequency, and the package type with pin
count.
Table 1−2. Characteristics of the DM640 Processor
HARDWARE FEATURES DM640
EMIFA (32-bit bus width)
(clock source = AECLKIN)
EDMA (64 independent channels) 1
McASP0 (uses Peripheral Clock [AUXCLK]) 1
I2C0 (uses Peripheral Clock) 1
Not all peripherals pins are
available at the same time
Device Configuration
section).
On-Chip Memory
CPU ID + CPU Rev ID Control Status Register (CSR.[31:16]) 0x0C01
JTAG BSDL_ID JTAGID register (address location: 0x01B3F008) 0x0007902F
Frequency MHz 400
Cycle Time ns
PLL Options CLKIN frequency multiplier Bypass (x1), x6, x12
Process Technology μm 0.13 μm
Product Status
†
On this DM64x™ device, the rated EMIF speed affects only the SDRAM interface on the EMIF. For more detailed information, see the EMIF device
speed portion of this data sheet.
‡
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments standard
warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all parameters.
‡
McBSPs
(internal clock source = CPU/4 clock frequency)
Configurable Video Port (VP0) 1
10/100 Ethernet MAC (EMAC) 1
Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) 1
VCXO Interpolated Control Port (VIC) 1
32-Bit Timers
(internal clock source = CPU/8 clock frequency)
General-Purpose Input/Output Port (GP0) 8
Size (Bytes) 160K
16K-Byte (16KB) L1 Program (L1P) Cache
Organization
Core (V) 1.2 V (-400)
I/O (V) 3.3 V
23 x 23 mm 548-Pin BGA (GDK and ZDK)
27 x 27 mm 548-Pin BGA (GNZ and ZNZ)
Product Preview (PP), Advance Information (AI),
or Production Data (PD)
16KB L1 Data (L1D) Cache
128KB Unified Mapped RAM/Cache (L2)
2.5 ns (DM640-400)
[400-MHz CPU, 100 MHz EMIF†]
1
2
3
PD
18
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 19

1.4 Device Compatibility
The DM641/DM640 device is a code-compatible member of the C6000™ DSP platform.
The C64x™ DSP generation of devices has a diverse and powerful set of peripherals. The common peripheral
set and pin-compatibility that the DM641 and DM640 devices offer lead to easier system designs and faster
time to market.
The DM640 device is a sub-set of the DM641 device and does not support an HPI peripheral or a second Video
Port (VP1) peripheral. Table 1−3 identifies the peripherals that are available on the DM641 and DM640
devices.
Table 1−3. Peripherals Available on the DM641 and DM640 Devices
EMIFA (32-bit bus width) √ √
EDMA (64 independent channels) √ √
10/100 EMAC √ √
MDIO √ √
HPI (16-bit) √ —
McBSPs (McBSP0, McBSP1) √ √
McASP (4-bit) √ √
8-bit Video Port (VP0) √ √
8-bit Video Port (VP1) √ —
VIC √ √
I2C √ √
Timers (32-bit) [TIMER0, TIMER1, TIMER2] √ √
GPIOs (GP[7:0]) √ √
†
— denotes peripheral/coprocessor is not available on this device.
‡
Not all peripherals pins are available at the same time. (For more details, see the Device
Configuration section.)
Device Compatibility
†‡
PERIPHERALS/COPROCESSORS DM641 DM640
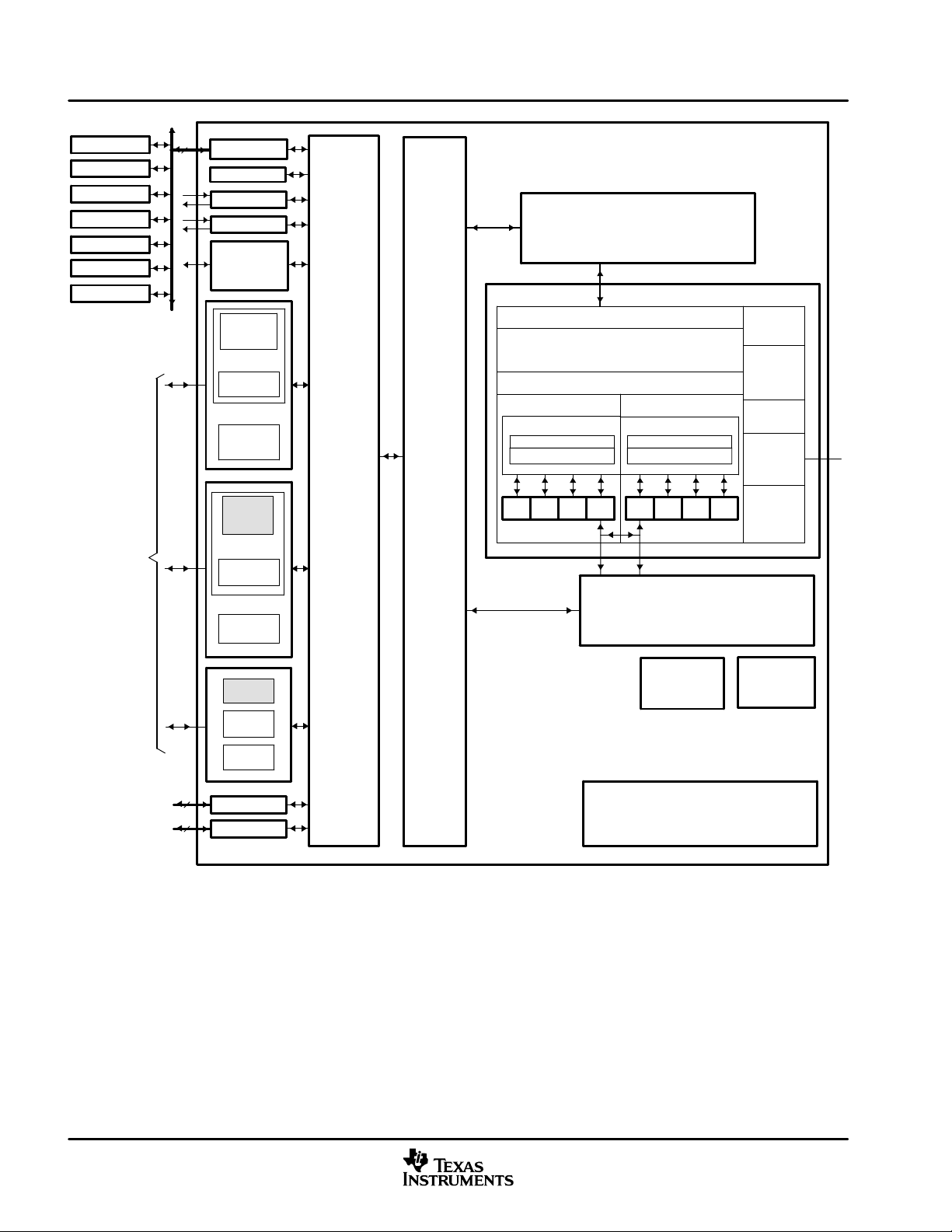
1.5 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1−1 shows the functional block diagram of the DM641/DM640 devices.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
19
Page 20
Functional Block Diagram
SDRAM
SBSRAM
ZBT SRAM
FIFO
SRAM
ROM/FLASH
I/O Devices
See Note A
32
EMIF A
Timer 2
Timer 1
Timer 0
VCXO
Interpolated
Control Port
(VIC)
8-Bit
VP0
OR
McBSP0
AND
McASP0
Control
8-Bit
†
VP1
OR
McBSP1
‡
A Register File
Enhanced
DMA
Controller
(EDMA)
‡
L2
Cache
Memory
128KBytes
.L1 .S1 .M1 .D1 .D2 .M2 .S2 .L2
TMS320DM641/TMS320DM640
L1P Cache
Direct-Mapped
16K Bytes Total
C64x DSP Core
Instruction Fetch
Instruction Dispatch
Advanced Instruction Packet
Instruction Decode
Data Path A
A31−A16
A15−A0
Data Path B
B Register File
B31−B16
B15−B0
Control
Registers
Control
Logic
Test
Advanced
In-Circuit
Emulation
Interrupt
Control
AND
McASP0
Data
†
HPI
L1D Cache 2-Way Set-Associative
16K Bytes Total
PLL
(x1, x6, x12)
Power-Down
Logic
EMAC
MDIO
8
16
†
HPI and VP1 are not supported on the DM640 device.
‡
McBSPs: Framing Chips − H.100, MVIP, SCSA, T1, E1; AC97 Devices; SPI Devices; Codecs
GP0
I2C0
Boot Configuration
NOTE A: The Video Port 0 (VP0) peripheral is muxed with the McBSP0 peripheral and the McASP0 control pins (DM641/DM640). The Video
Port 1 (VP1) peripheral is muxed with the McBSP1 peripheral and the McASP0 data pins (DM641 only). For more details on the
multiplexed pins of these peripherals, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
Figure 1−1. Functional Block Diagram
20
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 21

1.6 CPU (DSP Core) Description
The CPU fetches VelociTI™ advanced very-long instruction words (VLIWs) (256 bits wide) to supply up to
eight 32-bit instructions to the eight functional units during every clock cycle. The VelociTI™ VLIW architecture
features controls by which all eight units do not have to be supplied with instructions if they are not ready to
execute. The first bit of every 32-bit instruction determines if the next instruction belongs to the same execute
packet as the previous instruction, or whether it should be executed in the following clock as a part of the next
execute packet. Fetch packets are always 256 bits wide; however , the execute packets can vary in size. The
variable-length execute packets are a key memory-saving feature, distinguishing the C64x CPUs from other
VLIW architectures. The C64x™ VelociTI.2™ extensions add enhancements to the TMS320C62x™ DSP
VelociTI™ architecture. These enhancements include:
• Register file enhancements
• Data path extensions
• Quad 8-bit and dual 16-bit extensions with data flow enhancements
• Additional functional unit hardware
• Increased orthogonality of the instruction set
• Additional instructions that reduce code size and increase register flexibility
The CPU features two sets of functional units. Each set contains four units and a register file. One set contains
functional units .L1, .S1, .M1, and .D1; the other set contains units .D2, .M2, .S2, and .L2. The two register
files each contain 32 32-bit registers for a total of 64 general-purpose registers. In addition to supporting the
packed 16-bit and 32-/40-bit fixed-point data types found in the C62x™ VelociTI™ VLIW architecture, the
C64x™ register files also support packed 8-bit data and 64-bit fixed-point data types. The two sets of functional
units, along with two register files, compose sides A and B of the CPU [see the functional block and CPU (DSP
core) diagram, and Figure 1−2]. The four functional units on each side of the CPU can freely share the 32
registers belonging to that side. Additionally, each side features a “data cross path”—a single data bus
connected to all the registers on the other side, by which the two sets of functional units can access data from
the register files on the opposite side. The C64x CPU pipelines data-cross-path accesses over multiple clock
cycles. This allows the same register to be used as a data-cross-path operand by multiple functional units in
the same execute packet. All functional units in the C64x CPU can access operands via the data cross path.
Register access by functional units on the same side of the CPU as the register file can service all the units
in a single clock cycle. On the C64x CPU, a delay clock is introduced whenever an instruction attempts to read
a register via a data cross path if that register was updated in the previous clock cycle.
CPU (DSP Core) Description
In addition to the C62x™ DSP fixed-point instructions, the C64x™ DSP includes a comprehensive collection
of quad 8-bit and dual 16-bit instruction set extensions. These VelociTI.2™ extensions allow the C64x CPU
to operate directly on packed data to streamline data flow and increase instruction set efficiency. This is a key
factor for video and imaging applications.
Another key feature of the C64x CPU is the load/store architecture, where all instructions operate on registers
(as opposed to data in memory). Two sets of data-addressing units (.D1 and .D2) are responsible for all data
transfers between the register files and the memory. The data address driven by the .D units allows data
addresses generated from one register file to be used to load or store data to or from the other register file.
The C64x .D units can load and store bytes (8 bits), half-words (16 bits), and words (32 bits) with a single
instruction. And with the new data path extensions, the C64x .D unit can load and store doublewords (64 bits)
with a single instruction. Furthermore, the non-aligned load and store instructions allow the .D units to access
words and doublewords on any byte boundary. The C64x CPU supports a variety of indirect addressing modes
using either linear- or circular-addressing with 5- or 15-bit offsets. All instructions are conditional, and most
can access any one of the 64 registers. Some registers, however, are singled out to support specific
addressing modes or to hold the condition for conditional instructions (if the condition is not automatically
“true”).
TMS320C62x and C62x are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
21
Page 22

CPU (DSP Core) Description
The two .M functional units perform all multiplication operations. Each of the C64x .M units can perform two
16 × 16-bit multiplies or four 8 ×8-bit multiplies per clock cycle. The .M unit can also perform 16 ×32-bit multiply
operations, dual 16 × 16-bit multiplies with add/subtract operations, and quad 8 × 8-bit multiplies with add
operations. In a ddition to standard multiplies, the C64x .M units include bit-count, rotate, Galois field multiplies,
and bidirectional variable shift hardware.
The two .S and .L functional units perform a general set of arithmetic, logical, and branch functions with results
available every clock cycle. The arithmetic and logical functions on the C64x CPU include single 32-bit, dual
16-bit, and quad 8-bit operations.
The processing flow begins when a 256-bit-wide instruction fetch packet is fetched from a program memory.
The 32-bit instructions destined for the individual functional units are “linked” together by “1” bits in the least
significant bit (LSB) position of the instructions. The instructions that are “chained” together for simultaneous
execution (up to eight in total) compose an execute packet. A “0” in the LSB of an instruction breaks the chain,
effectively placing the instructions that follow it in the next execute packet. A C64x™ DSP device enhancement
now allows execute packets to cross fetch-packet boundaries. In the TMS320C62x™/TMS320C67x™ DSP
devices, if an execute packet crosses the fetch-packet boundary (256 bits wide), the assembler places it in
the next fetch packet, while the remainder of the current fetch packet is padded with NOP instructions. In the
C64x™ DSP device, the execute boundary restrictions have been removed, thereby, eliminating all of the
NOPs added to pad the fetch packet, and thus, decreasing the overall code size. The number of execute
packets within a fetch packet can vary from one to eight. Execute packets are dispatched to their respective
functional units at the rate of one per clock cycle and the next 256-bit fetch packet is not fetched until all the
execute packets from the current fetch packet have been dispatched. After decoding, the instructions
simultaneously drive all active functional units for a maximum execution rate of eight instructions every clock
cycle. While most results are stored in 32-bit registers, they can be subsequently moved to memory as bytes,
half-words, or doublewords. All load and store instructions are byte-, half-word-, word-, or
doubleword-addressable.
For more details on the C64x CPU functional units enhancements, see the following documents:
• TMS320C6000 CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide (literature number SPRU189)
• TMS320C64x Technical Overview (literature number SPRU395)
TMS320C67x is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
22
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 23
Data Path A
ST1b (Store Data)
ST1a (Store Data)
LD1b (Load Data)
LD1a (Load Data)
DA1 (Address)
32 MSBs
32 LSBs
32 MSBs
32 LSBs
src1
.L1
src2
long dst
long src
long src
long dst
src1
.S1
src2
long dst
long dst
src1
.M1
src2
src2
src1
.D1
src2
dst
dst
dst
dst
dst
CPU (DSP Core) Description
8
8
8
8
Register
File A
(A0−A31)
See Note A
See Note A
2X
Data Path B
DA2 (Address)
LD2a (Load Data)
LD2b (Load Data)
ST2a (Store Data)
ST2b (Store Data)
32 LSBs
32 MSBs
32 MSBs
32 LSBs
src2
.D2
src1
src2
src1
.M2
long dst
src2
.S2
src1
long dst
long src
long src
long dst
src2
.L2
src1
dst
dst
dst
dst
1X
See Note A
See Note A
Register
File B
(B0− B31)
8
8
8
8
Control Register
File
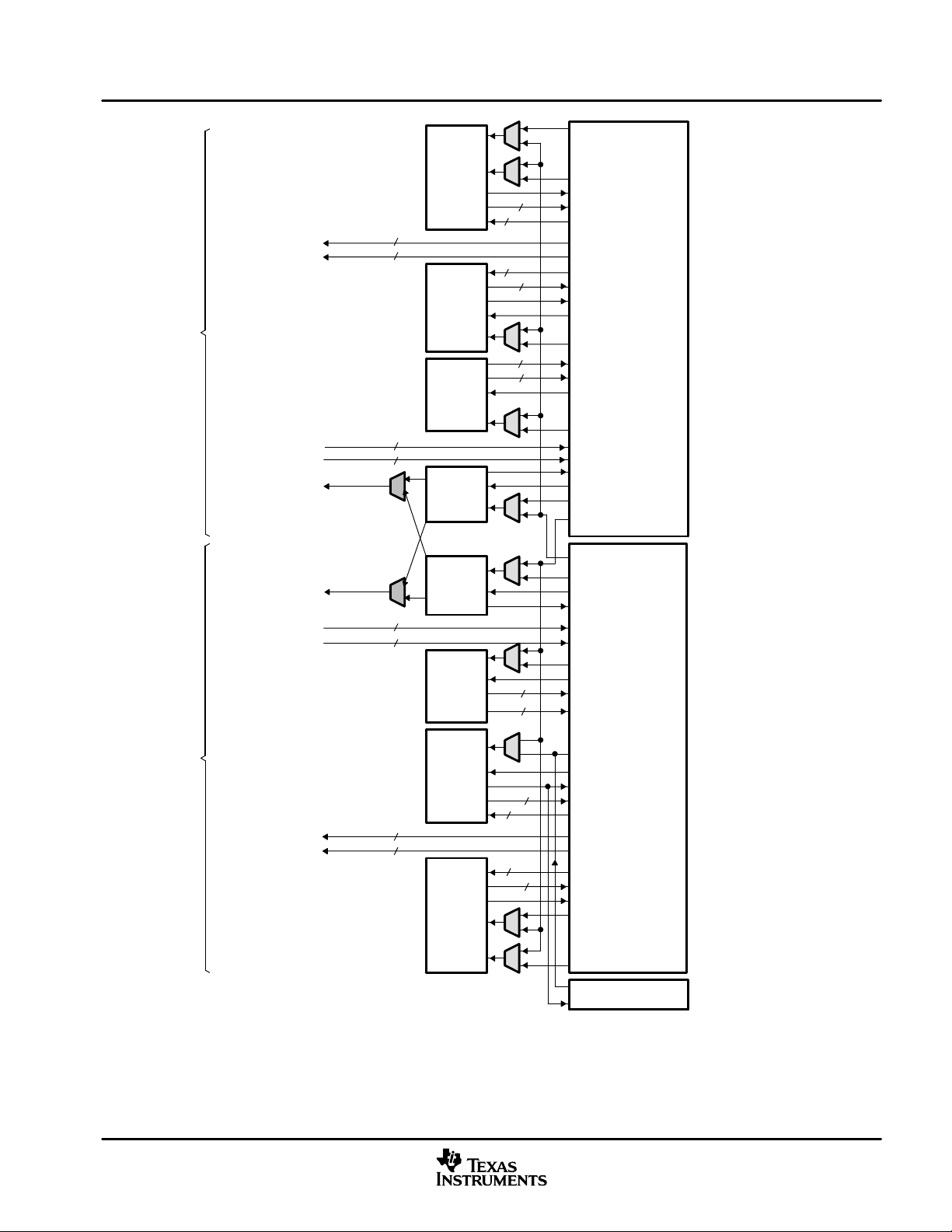
NOTE A: For the .M functional units, the long dst is 32 MSBs and the dst is 32 LSBs.
Figure 1−2. TMS320C64x™ CPU (DSP Core) Data Paths
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
23
Page 24
CPU (DSP Core) Description
1.6.1 CPU Core Registers
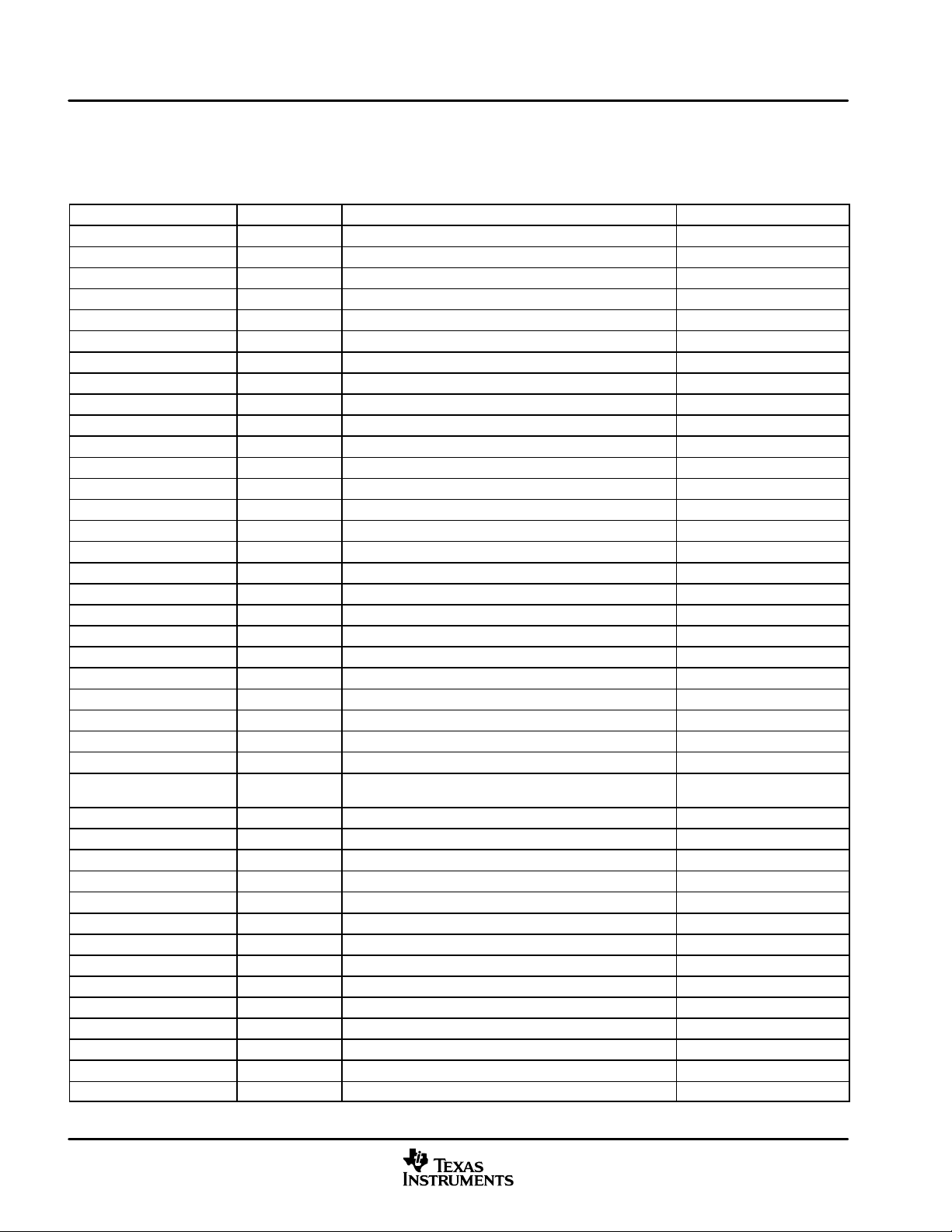
T able 1−4. L2 Cache Registers (C64x)
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME COMMENTS
0184 0000 CCFG Cache configuration register
0184 0004 − 0184 0FFC − Reserved
0184 1000 EDMAWEIGHT L2 EDMA access control register
0184 1004 − 0184 1FFC − Reserved
0184 2000 L2ALLOC0 L2 allocation register 0
0184 2004 L2ALLOC1 L2 allocation register 1
0184 2008 L2ALLOC2 L2 allocation register 2
0184 200C L2ALLOC3 L2 allocation register 3
0184 2010 − 0184 3FFC − Reserved
0184 4000 L2WBAR L2 writeback base address register
0184 4004 L2WWC L2 writeback word count register
0184 4010 L2WIBAR L2 writeback invalidate base address register
0184 4014 L2WIWC L2 writeback invalidate word count register
0184 4018 L2IBAR L2 invalidate base address register
0184 401C L2IWC L2 invalidate word count register
0184 4020 L1PIBAR L1P invalidate base address register
0184 4024 L1PIWC L1P invalidate word count register
0184 4030 L1DWIBAR L1D writeback invalidate base address register
0184 4034 L1DWIWC L1D writeback invalidate word count register
0184 4038 − 0184 4044 − Reserved
0184 4048 L1DIBAR L1D invalidate base address register
0184 404C L1DIWC L1D invalidate word count register
0184 4050 − 0184 4FFC − Reserved
0184 5000 L2WB L2 writeback all register
0184 5004 L2WBINV L2 writeback invalidate all register
0184 5008 − 0184 7FFC − Reserved
0184 8000 −0184 81FC
0184 8200 MAR128 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8000 0000 − 80FF FFFF
0184 8204 MAR129 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8100 0000 − 81FF FFFF
0184 8208 MAR130 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8200 0000 − 82FF FFFF
0184 820C MAR131 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8300 0000 − 83FF FFFF
0184 8210 MAR132 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8400 0000 − 84FF FFFF
0184 8214 MAR133 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8500 0000 − 85FF FFFF
0184 8218 MAR134 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8600 0000 − 86FF FFFF
0184 821C MAR135 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8700 0000 − 87FF FFFF
0184 8220 MAR136 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8800 0000 − 88FF FFFF
0184 8224 MAR137 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8900 0000 − 89FF FFFF
0184 8228 MAR138 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8A00 0000 − 8AFF FFFF
0184 822C MAR139 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8B00 0000 − 8BFF FFFF
0184 8230 MAR140 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8C00 0000 − 8CFF FFFF
0184 8234 MAR141 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8D00 0000 − 8DFF FFFF
MAR0 to
MAR127
Reserved
24
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 25
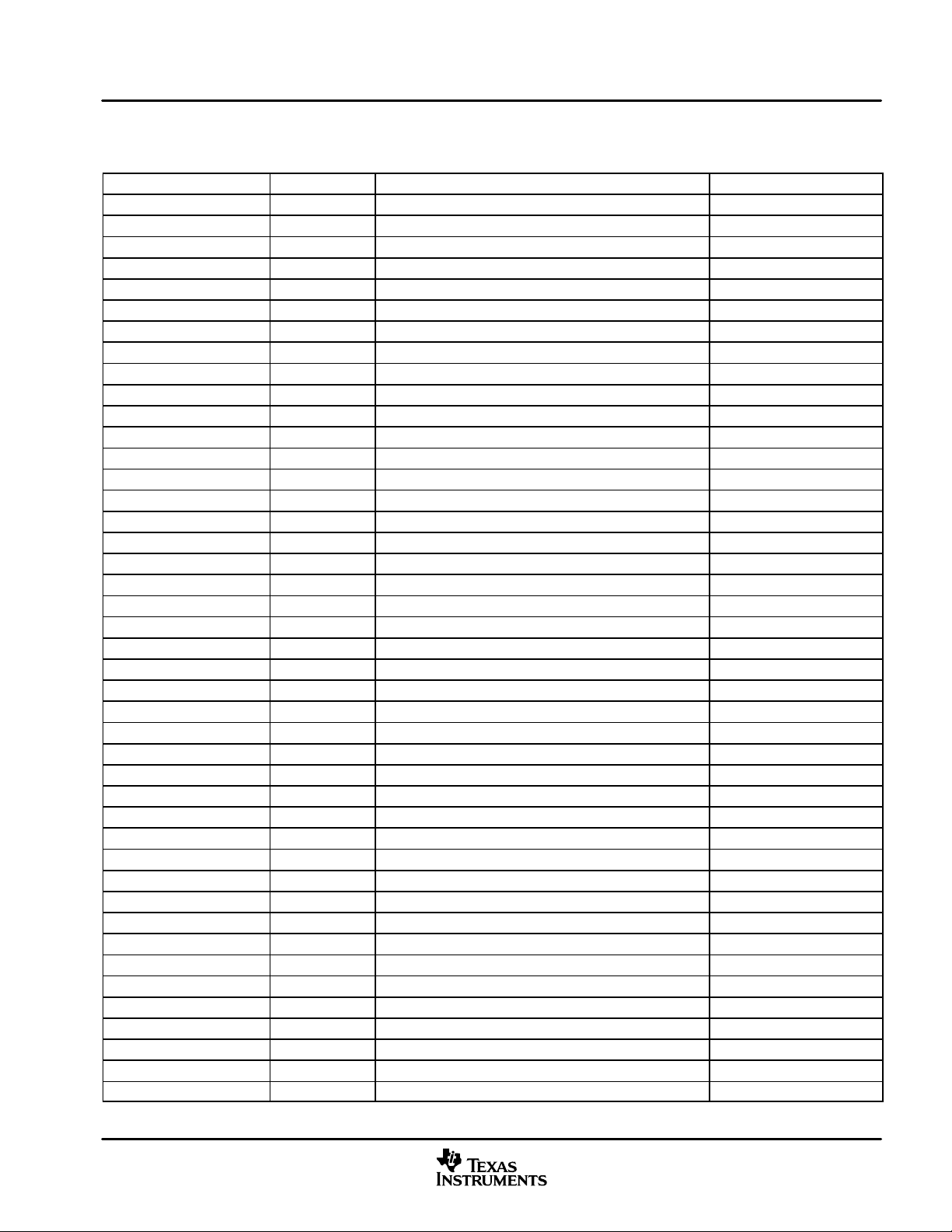
Table 1−4. L2 Cache Registers (C64x) (Continued)
HEX ADDRESS RANGE COMMENTSREGISTER NAMEACRONYM
0184 8238 MAR142 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8E00 0000 − 8EFF FFFF
0184 823C MAR143 Controls EMIFA CE0 range 8F00 0000 − 8FFF FFFF
0184 8240 MAR144 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9000 0000 − 90FF FFFF
0184 8244 MAR145 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9100 0000 − 91FF FFFF
0184 8248 MAR146 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9200 0000 − 92FF FFFF
0184 824C MAR147 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9300 0000 − 93FF FFFF
0184 8250 MAR148 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9400 0000 − 94FF FFFF
0184 8254 MAR149 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9500 0000 − 95FF FFFF
0184 8258 MAR150 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9600 0000 − 96FF FFFF
0184 825C MAR151 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9700 0000 − 97FF FFFF
0184 8260 MAR152 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9800 0000 − 98FF FFFF
0184 8264 MAR153 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9900 0000 − 99FF FFFF
0184 8268 MAR154 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9A00 0000 − 9AFF FFFF
0184 826C MAR155 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9B00 0000 − 9BFF FFFF
0184 8270 MAR156 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9C00 0000 − 9CFF FFFF
0184 8274 MAR157 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9D00 0000 − 9DFF FFFF
0184 8278 MAR158 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9E00 0000 − 9EFF FFFF
0184 827C MAR159 Controls EMIFA CE1 range 9F00 0000 − 9FFF FFFF
0184 8280 MAR160 Controls EMIFA CE2 range A000 0000 − A0FF FFFF
0184 8284 MAR161 Controls EMIFA CE2 range A100 0000 − A1FF FFFF
0184 8288 MAR162 Controls EMIFA CE2 range A200 0000 − A2FF FFFF
0184 828C MAR163 Controls EMIFA CE2 range A300 0000 − A3FF FFFF
0184 8290 MAR164 Controls EMIFA CE2 range A400 0000 − A4FF FFFF
0184 8294 MAR165 Controls EMIFA CE2 range A500 0000 − A5FF FFFF
0184 8298 MAR166 Controls EMIFA CE2 range A600 0000 − A6FF FFFF
0184 829C MAR167 Controls EMIFA CE2 range A700 0000 − A7FF FFFF
0184 82A0 MAR168 Controls EMIFA CE2 range A800 0000 − A8FF FFFF
0184 82A4 MAR169 Controls EMIFA CE2 range A900 0000 − A9FF FFFF
0184 82A8 MAR170 Controls EMIFA CE2 range AA00 0000 − AAFF FFFF
0184 82AC MAR171 Controls EMIFA CE2 range AB00 0000 − ABFF FFFF
0184 82B0 MAR172 Controls EMIFA CE2 range AC00 0000 − ACFF FFFF
0184 82B4 MAR173 Controls EMIFA CE2 range AD00 0000 − ADFF FFFF
0184 82B8 MAR174 Controls EMIFA CE2 range AE00 0000 − AEFF FFFF
0184 82BC MAR175 Controls EMIFA CE2 range AF00 0000 − AFFF FFFF
0184 82C0 MAR176 Controls EMIFA CE3 range B000 0000 − B0FF FFFF
0184 82C4 MAR177 Controls EMIFA CE3 range B100 0000 − B1FF FFFF
0184 82C8 MAR178 Controls EMIFA CE3 range B200 0000 − B2FF FFFF
0184 82CC MAR179 Controls EMIFA CE3 range B300 0000 − B3FF FFFF
0184 82D0 MAR180 Controls EMIFA CE3 range B400 0000 − B4FF FFFF
0184 82D4 MAR181 Controls EMIFA CE3 range B500 0000 − B5FF FFFF
0184 82D8 MAR182 Controls EMIFA CE3 range B600 0000 − B6FF FFFF
0184 82DC MAR183 Controls EMIFA CE3 range B700 0000 − B7FF FFFF
0184 82E0 MAR184 Controls EMIFA CE3 range B800 0000 − B8FF FFFF
CPU (DSP Core) Description
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
25
Page 26
CPU (DSP Core) Description
Table 1−4. L2 Cache Registers (C64x) (Continued)
HEX ADDRESS RANGE COMMENTSREGISTER NAMEACRONYM
0184 82E4 MAR185 Controls EMIFA CE3 range B900 0000 − B9FF FFFF
0184 82E8 MAR186 Controls EMIFA CE3 range BA00 0000 − BAFF FFFF
0184 82EC MAR187 Controls EMIFA CE3 range BB00 0000 − BBFF FFFF
0184 82F0 MAR188 Controls EMIFA CE3 range BC00 0000 − BCFF FFFF
0184 82F4 MAR189 Controls EMIFA CE3 range BD00 0000 − BDFF FFFF
0184 82F8 MAR190 Controls EMIFA CE3 range BE00 0000 − BEFF FFFF
0184 82FC MAR191 Controls EMIFA CE3 range BF00 0000 − BFFF FFFF
0184 8300 −0184 83FC
0184 8400 −0187 FFFF − Reserved
MAR192 to
MAR255
Reserved
26
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 27
1.7 Memory Map Summary
Table 1−5 shows the memory map address ranges of the DM641/DM640 device. Internal memory is always
located at address 0 and can be used as both program and data memory. The external memory address
ranges in the DM641/DM640 device begin at the hex address location 0x8000 0000 for EMIF A.
T able 1−5. TMS320DM641/DM640 Memory Map Summary
Memory Map Summary
MEMORY BLOCK DESCRIPTION
Internal RAM (L2) 128K
Reserved 768K
Reserved 23M
External Memory Interface A (EMIFA) Registers 256K
L2 Registers 256K
HPI Registers (DM641 only)
McBSP 0 Registers 256K
McBSP 1 Registers 256K
Timer 0 Registers 256K
Timer 1 Registers 256K
Interrupt Selector Registers 256K
EDMA RAM and EDMA Registers 256K
Reserved 512K
Timer 2 Registers 256K
GP0 Registers 256K − 4K
Device Configuration Registers 4K
I2C0 Data and Control Registers 16K
Reserved 32K
McASP0 Control Registers 16K
Reserved 192K
Reserved 256K
Emulation 256K
Reserved 256K
VP0 Control 16K
VP1 Control (DM641 only)
Reserved 32K
Reserved 192K
EMAC Control 4K
EMAC Wrapper 8K
EWRAP Registers 2K
MDIO Control Registers 2K
Reserved 3.5M
QDMA Registers 52
Reserved 928M – 52
McBSP 0 Data 64M
†
For the DM640 device, these memory address locations are reserved.The DM640 device does not support the HPI and VP1 peripherals.
†
†
BLOCK SIZE
(BYTES)
256K
16K
HEX ADDRESS RANGE
0000 0000 – 0001 FFFF
0004 0000 – 000F FFFF
0010 0000 – 017F FFFF
0180 0000 – 0183 FFFF
0184 0000 – 0187 FFFF
0188 0000 – 018B FFFF
018C 0000 – 018F FFFF
0190 0000 – 0193 FFFF
0194 0000 – 0197 FFFF
0198 0000 – 019B FFFF
019C 0000 – 019F FFFF
01A0 0000 – 01A3 FFFF
01A4 0000 – 01AB FFFF
01AC 0000 – 01AF FFFF
01B0 0000 – 01B3 EFFF
01B3 F000 – 01B3 FFFF
01B4 0000 – 01B4 3FFF
01B4 4000 – 01B4 BFFF
01B4 C000 – 01B4 FFFF
01B5 0000 – 01B7 FFFF
01B8 0000 – 01BB FFFF
01BC 0000 – 01BF FFFF
01C0 0000 – 01C3 FFFF
01C4 0000 – 01C4 3FFF
01C4 4000 – 01C4 7FFF
01C4 8000 – 01C4 FFFF
01C5 0000 – 01C7 FFFF
01C8 0000 – 01C8 0FFF
01C8 1000 – 01C8 2FFF
01C8 3000 – 01C8 37FF
01C8 3800 – 01C8 3FFF
01C8 4000 – 01FF FFFF
0200 0000 – 0200 0033
0200 0034 – 2FFF FFFF
3000 0000 – 33FF FFFF
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
27
Page 28
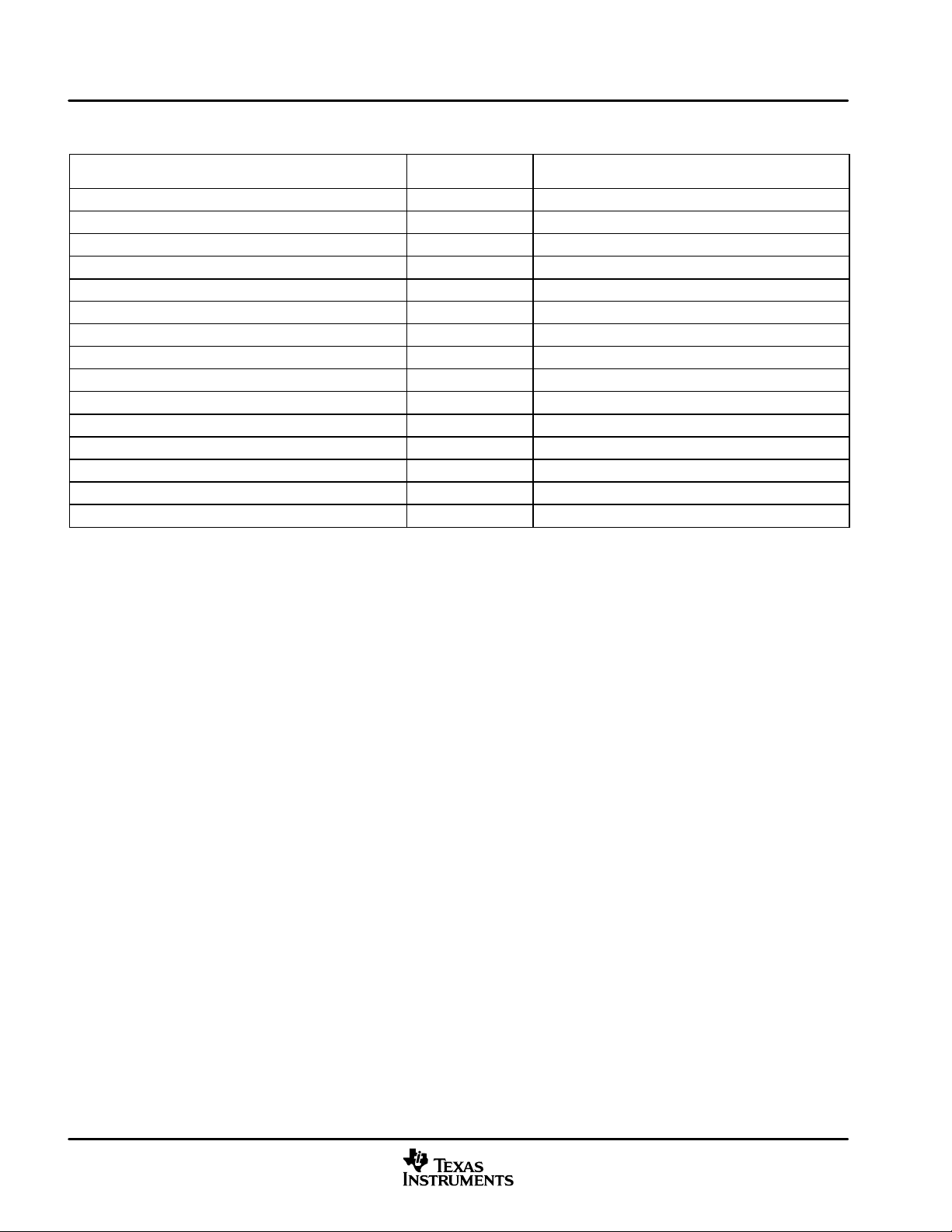
Memory Map Summary
Table 1−5. TMS320DM641/DM640 Memory Map Summary (Continued)
MEMORY BLOCK DESCRIPTION HEX ADDRESS RANGE
McBSP 1 Data 64M
Reserved 64M
McASP0 Data 1M
Reserved 64M − 1M
Reserved 832M
VP0 Channel A Data 32M
Reserved 32M
VP1 Channel A Data (DM641 only)
Reserved 32M
Reserved 64M
EMIFA CE0 256M
EMIFA CE1 256M
EMIFA CE2 256M
EMIFA CE3 256M
Reserved 1G
†
For the DM640 device, these memory address locations are reserved.The DM640 device does not support the HPI and VP1 peripherals.
†
BLOCK SIZE
(BYTES)
32M
3400 0000 – 37FF FFFF
3800 0000 – 3BFF FFFF
3C00 0000 – 3C0F FFFF
3C10 0000 – 3FFF FFFF
4000 0000 – 73FF FFFF
7400 0000 – 75FF FFFF
7600 0000 – 77FF FFFF
7800 0000 – 79FF FFFF
7A00 0000 – 7BFF FFFF
7C00 0000 – 7FFF FFFF
8000 0000 – 8FFF FFFF
9000 0000 – 9FFF FFFF
A000 0000 – AFFF FFFF
B000 0000 – BFFF FFFF
C000 0000 – FFFF FFFF
28
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 29

1.7.1 L2 Architecture Expanded
Figure 1−3 shows the detail of the L2 architecture on the TMS320DM641/DM640 devices. For more
information on the L2MODE bits, see the cache configuration (CCFG) register bit field descriptions in the
TMS320C64x Two-Level Internal Memory Reference Guide (literature number SPRU610).
Memory Map Summary
L2MODE
000
†
L2 Memory Block Base Address
011010001
64K-Byte RAM
64K SRAM
96K SRAM
128K SRAM (All)
(4 Way)
32K Cache
†
The L2MODE = 111b is not supported on the DM641/DM640 devices.
64K Cache (4 Way)
128K Cache (4 Way)
32K-Byte RAM
32K-Byte RAM
Figure 1−3. TMS320DM641/DM640 L2 Architecture Memory Configuration
0x0000 0000
0x0001 0000
0x0001 8000
0x0001 FFFF
0x0002 0000
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
29
Page 30

Bootmode
1.8 Bootmode
The DM641/DM640 device resets using the active-low signal RESET. While RESET is low, the device is held
in reset and is initialized to the prescribed reset state. Refer to reset timing for reset timing characteristics and
states of device pins during reset. The release of RESET starts the processor running with the prescribed
device configuration and boot mode.
The DM641 has three types of boot modes while the DM640 has only two types of boot modes:
• Host boot [DM641 only]
If host boot is selected, upon release of RESET, the CPU is internally “stalled” while the remainder of the
device is released. During this period, an external host can initialize the CPU’s memory space as
necessary through the host interface, including internal configuration registers, such as those that control
the EMIF or other peripherals. For the DM641 device, the HPI peripheral is used for host boot. Once the
host is finished with all necessary initialization, it must set the DSPINT bit in the HPIC register to complete
the boot process. This transition causes the boot configuration logic to bring the CPU out of the “stalled”
state. The CPU then begins execution from address 0. The DSPINT condition is not latched by the CPU,
because it o c c u r s w h i l e t h e C P U i s still internally “stalled”. Also, DSPINT brings the CPU out of the “stalled”
state only if the host boot process is selected. All memory may be written to and read by the host. This
allows for the host to verify what it sends to the DSP if required. After the CPU is out of the “stalled” state,
the CPU needs to clear the DSPINT, otherwise, no more DSPINTs can be received.
• EMIF boot (using default ROM timings)
Upon the release of RESET, the 1K-Byte ROM code located in the beginning of CE1 is copied to address 0
by the EDMA using the default ROM timings, while the CPU is internally “stalled”. The data should be
stored in the endian format that the system is using. In this case, the EMIF automatically assembles
consecutive 8-bit bytes to form the 32-bit instruction words to be copied. The transfer is automatically done
by the EDMA as a single-frame block transfer from the ROM to address 0. After completion of the block
transfer, the CPU is released from the “stalled” state and starts running from address 0.
• No boot
With no boot, the CPU begins direct execution from the memory located at address 0. Note: operation is
undefined if invalid code is located at address 0.
30
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 31

1.9 Pin Assignments
On Quadrants A, B, C, and D, shading denotes pin assignments that have different functionality between the
DM641 and DM640 devices [DM640 denoted within ( )]. See the Terminal Functions table for details.
1.9.1 Pin Map
Pin Assignments
13121110987654321
AF
AE
AD
AC
AB
AA
V
SS
DV
VDAC
STCLK
V
SS
HD1
(RSV111)
HD5
Y
(RSV115)
W
V
SS
DV
DV
DD
V
CLKIN V
V
CLKMODE0
HD3
(RSV113)
HD7
(RSV117)
RSV04
DD
DD
SS
V
RSV03
V
RSV01
SS
RSV00
HD0
(RSV110)
HD4
(RSV114)
VP1CTL0
(RSV15)
CLKMODE1
SS
V
RSV02
SS
V
V
HD2
(RSV112)
HD6
(RSV116)
RSV13
(RSV18)
VP1CTL1
(RSV16)
VP1CTL2
SS
(RSV17)
SS
SS
DV
V
DV
DV
RSV14
(RSV19)
VP1D[0]/
CLKX1
VP1D[1]/
VP1D[3]/
CLKS1
VP1D[4]/
FSX1
VP1D[2]/
SS
DD
SS
DD
DD
DX1
V
CV
CV
V
VP1D[5]/
FSR1
SS
SS
DV
CV
DD
CV
DD
RSV06
V
DR1
VP1CLK0
SS
(RSV13)
V
VP1D[6]/
CLKR1
VP1D[7]
(RSV20)
DV
DD
DD
DD
V
CV
RSV15
SS
(RSV21)
RSV16
(RSV22)
AXR0[0]
DD
SS
DV
DD
VP1CLK1
VSSV
SS
(RSV14)
V
AXR0[1]
AXR0[3]
SS
RSV17
VP0CLK1
V
SS
V
SS
AFSX0
V
SS
DV
DD
AMUTEIN0
(RSV23)
AXR0[2]
V
SS
V
SS
DV
DD
V
CV
RSV18
(RSV24)
RSV19
DD
(RSV25)
SS
CV
DD
AHCLKX0
RSV20
(RSV26)
V
SS
DV
DD
V
AMUTE0
ACLKX0
DD
SS
V
SS
CV
DD
V
U
R
P
T
HD10
(RSV120)
HD14
(RSV124)
V
SS
HCS
(RSV109)
HCNTL1
(RSV107)
HD8
(RSV118)
HD12
(RSV122)
HDS2
(RSV101)
HDS1
(RSV100)
V
SS
HD9
(RSV119)
HD13
(RSV123)
HD15
(RSV125)
HCNTL0
(RSV106)
HAS
(RSV108)
RSV54
(RSV60)
HD11
(RSV121)
RSV55
(RSV61)
RSV56
(RSV62)
RESET
V
SS
DV
DD
V
SS
MDCLK
MDIO
PLLV
V
SS
V
SS
RSV08
V
SS
V
SS
CV
DD
CV
DD
V
SS
CV
DD
Figure 1−4. DM641/DM640 Pin Map [Quadrant A]
V
SS
CV
CV
DD
DD
V
SS
13121110987654321
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
31
Page 32
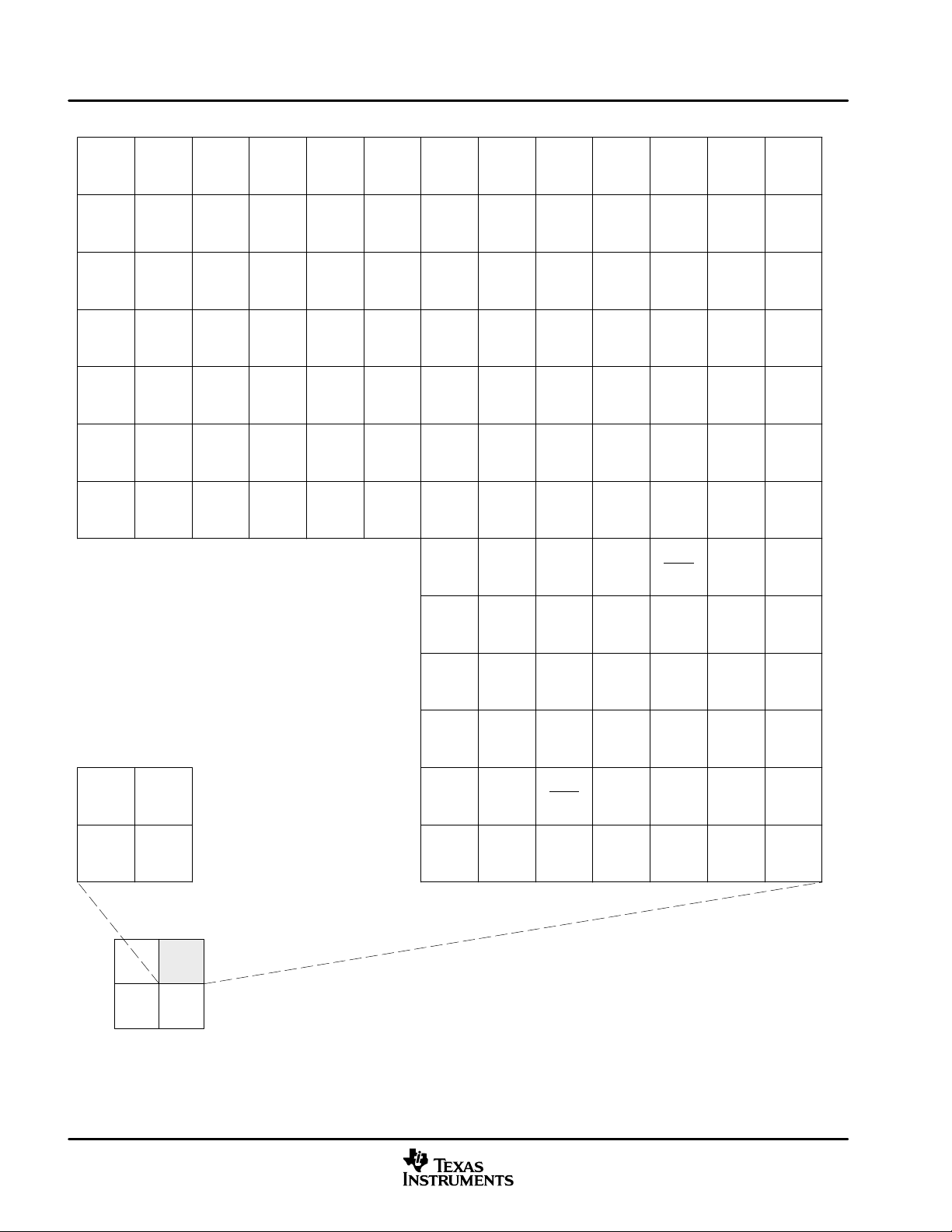
Pin Assignments
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
V
SS
ACLKR0
AFSR0
AHCLKR0
V
SS
CV
DD
V
SS
VP0D[6]/
CLKR0
VP0D[7]
RSV11
RSV12
DV
DD
V
SS
VP0D[1]/
FSX0
VP0D[2]/
DX0
VP0D[3]/
CLKS0
VP0D[4]/
DR0
VP0D[5]/
FSR0
V
SS
CV
DD
VP0D[0]/
CLKX0
VP0CTL0
VP0CTL2
VP0CTL1
DV
DD
V
SS
CV
DD
RSV09VP0CLK0
RSV10
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
DV
DD
VSSV
SS
V
SS
V
SS
RSV74
(RSV80)
RSV75
(RSV81)
DV
DD
V
SS
CV
DD
RSV76
(RSV82)
RSV78
(RSV84)
RSV79
(RSV85)
RSV77
(RSV83)
DVDDDV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
RSV80
(RSV86)
RSV82
(RSV88)
RSV83
(RSV89)
RSV81
(RSV87)
V
SS
CV
DD
CV
DD
V
SS
V
SS
RSV84
(RSV90)
RSV85
(RSV91)
V
SS
DV
DD
V
SS
DV
DD
DD
RSV88
(RSV94)
RSV87
(RSV93)
RSV86
(RSV92)
DV
DD
RSV64
(RSV70)
RSV67
(RSV73)
RSV71
(RSV77)
RSV73
(RSV79)
RSV89
(RSV95)
V
SS
DV
DD
V
SS
RSV62
(RSV68)
RSV65
(RSV71)
RSV69
(RSV75)
AHOLDDV
DV
DD
DV
DD
RSV59
(RSV65)
RSV60
(RSV66)
RSV63
(RSV69)
RSV66
(RSV72)
RSV70
(RSV76)
DV
DD
V
SS
DV
DD
RSV58
(RSV64)
RSV61
(RSV67)
V
SS
RSV68
(RSV74)
RSV72
(RSV78)
V
SS
AF
AE
AD
AC
AB
AA
Y
W
V
SS
CV
CV
V
SS
CV
CV
DD
DD
V
SS
V
SS
CV
DVDDDV
DD
DD
DD
DD
V
SS
V
SS
DV
DD
V
SS
V
SS
DV
DD
RSV93
(RSV99)
ASOE3
ABUSREQ
AEA22
RSV92
(RSV98)
AEA12 AEA11
AEA10 AEA9 AEA8
AEA21 AEA20 AEA19AEA18
AEA17 AEA16 AEA15
AEA14 AEA13
RSV91
(RSV97)
DV
(RSV96)
DD
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
V
SS
RSV90
V
U
T
R
P
32
Figure 1−4. DM641/DM640 Pin Map (Continued) [Quadrant B]
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 33

Pin Assignments
13121110987654321
HRDY
N
(RSV105)
HR/W
M
(RSV102)
L
V
SS
RSV57
K
(RSV63)
J
H
V
SS
G
MRCLK
RSV48
F
(RSV54)
DV
MCOL
RSV47
(RSV53)
MRXD3
MRXER
GP0[6]/
EXT_INT6
HHWIL
DD
(RSV104)
MTXENMTXD3
RSV46
(RSV52)
MRXD2MRXD1
MCRS
RSV52
(RSV58)
GP0[5]/
EXT_INT5
HINT
(RSV103)
MTXD2MTXD1 MTXD0
MTCLK
HD24/
AD24/
MRXD0
MRXDV
RSV49
(RSV55)
RSV50
(RSV56)
GP0[4]/
EXT_INT4
V
SS
GP0[0]
GP0[3]
DV
DD
V
SS
DV
DD
DVDDDV
DD
V
SS
V
SS
DV
V
SS
V
SS
DV
V
SS
CV
CV
CV
DD
DD
DD
V
SS
CV
DD
CV
DD
V
SS
V
SS
CV
RSV07
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
DD
DD
V
SS
V
SS
DV
CV
DD
V
SS
CV
DD
DD
V
SS
V
SS
DV
CV
DD
DD
DD
V
SS
CV
DD
VSSV
SS
GP0[7]/
E
EXT_INT7
D
V
RSV51
C
(RSV57)
B
DV
A
V
RSV53
(RSV59)
SS
DD
SS
V
SS
V
SS
DV
DD
DV
DD
V
SS
SDA0 DV
DV
V
SS
V
SS
SCL0
DD
V
SS
NMI
TINP0
DV
DD
V
DD
SS
TOUT0/
MAC_EN
TOUT1/
LENDIAN
TINP1
V
SS
CLKOUT4/
GP0[1]
CLKOUT6/
GP0[2]
V
SS
V
SS
DV
DD
RSV24
(RSV30)
RSV25
(RSV31)
V
SS
RSV21
(RSV27)
DV
DD
RSV27
(RSV33)
RSV26
(RSV32)
RSV23
(RSV29)
V
SS
V
SS
RSV31
(RSV37)
RSV30
(RSV36)
RSV29
(RSV35)
RSV28
(RSV34)
DV
RSV35
(RSV41)
RSV34
(RSV40)
RSV33
(RSV39)
RSV32
(RSV38)
RSV40
DD
(RSV46)
RSV39
(RSV45)
RSV38
(RSV44)
RSV37
(RSV43)
RSV36
(RSV42)
RSV44
(RSV50)
RSV43
(RSV49)
RSV42
(RSV48)
RSV41
(RSV47)
V
SS
Figure 1−4. DM641/DM640 Pin Map (Continued) [Quadrant C]
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
RSV45
(RSV51)
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
RSV22
(RSV28)
13121110987654321
33
Page 34
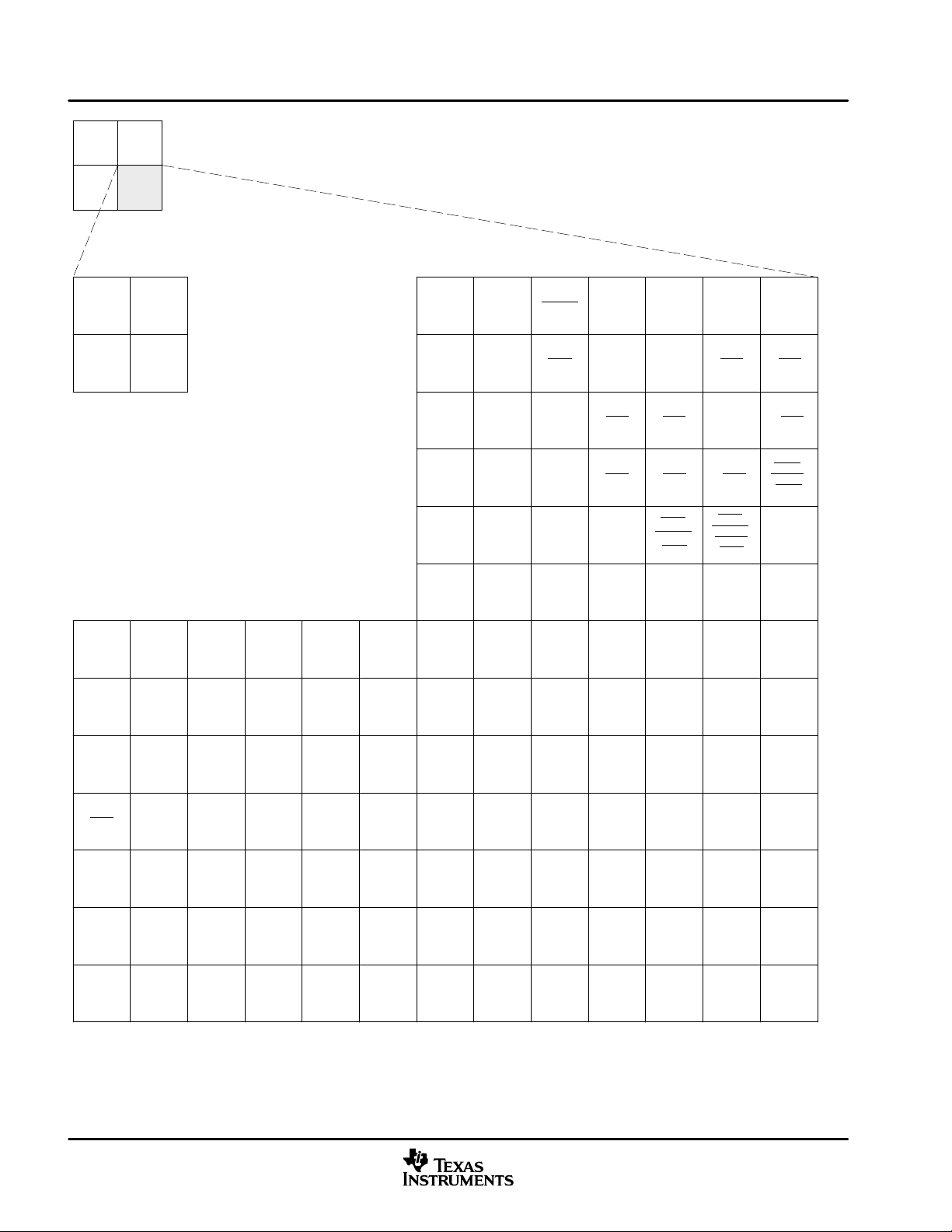
Pin Assignments
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
ACE3
V
SS
N
M
L
K
/
J
H
G
F
V
SS
CV
CV
V
SS
CV
DD
DD
DD
V
SS
V
SS
DV
CV
DD
V
SS
CV
DD
DD
V
SS
V
SS
DV
CV
DD
V
CV
DD
V
SS
CV
CV
V
SS
CV
CV
DD
CV
SS
DV
DD
DD
DV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
AHOLDA
V
SS
APDT
DD
V
V
V
AARDY
SS
DVDDDV
SS
DD
SS
DD
DD
V
SS
DV
DV
V
SS
AEA7 AEA6 AEA5
AEA4AEA4 AEA3
ABE1 ABE0
ACE2 ACE1 ACE0
DD
AECLKOUT2
AAOE
ASDRAS
ASOE
AED17 AED16
DD
DD
AED21 AED20AED19 AED18
AED25 AED24AED23 AED22
ASDCKE
AARE
/
ASDCAS
/
ASADS/
ASRE
AECLKIN
V
SS
ABE3 ABE2
AAWE/
ASDWE
ASWE
/
/
AECLKOUT1
RSV05
TRST
EMU1
DV
V
SS
TMS
EMU4
EMU3
EMU2
DD
V
SS
EMU8
EMU6
EMU5
EMU0
DV
DD
EMU11
EMU10
EMU9
EMU7
V
V
V
TDO
TDITCK
SS
SS
SS
DV
AED14
AED15
V
V
DV
DD
DD
AED12
AED10
AED11
SS
AED13
SS
V
AED8
AED6 AED4
AED7
AED9
DV
SS
DD
V
SS
AED3
V
SS
V
SS
DV
V
SS
AED2
AED5
DD
AED27 AED26
V
SS
DV
DD
AED0
AED1
DV
DV
DD
DD
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
Figure 1−4. DM641/DM640 Pin Map (Continued) [Quadrant D]
34
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
E
V
SS
AED29AED28
AED31AED30
DV
D
C
B
DD
A
V
SS
Page 35

1.9.2 Signal Groups Description
Pin Assignments
CLKIN
CLKOUT4/GP0[1]
CLKOUT6/GP0[2]
CLKMODE1
CLKMODE0
PLLV
TMS
TDO
TDI
TCK
TRST
EMU0
EMU1
EMU2
EMU3
EMU4
EMU5
EMU6
EMU7
EMU8
EMU9
EMU10
EMU11
RESET
NMI
†
†
Clock/PLL
Reset and
Interrupts
GP0[7]/EXT_INT7
GP0[6]/EXT_INT6
GP0[5]/EXT_INT5
GP0[4]/EXT_INT4
‡
‡
‡
‡
RSV00
RSV01
RSV02
Reserved
IEEE Standard
1149.1
(JTAG)
RSV91(123)
RSV92(124)
RSV93(125)
Emulation
Peripheral
Control/Status
TOUT0/MAC_EN
Control/Status
GP0[7]/EXT_INT7
GP0[6]/EXT_INT6
GP0[5]/EXT_INT5
GP0[4]/EXT_INT4
‡
‡
‡
‡
GP0
(8-Bit)
GP0[3]
CLKOUT6/GP0[2]
CLKOUT4/GP0[1]
GP0[0]
General-Purpose Input/Output 0 (GP0) Port
†
These pins are muxed with the GP0 pins and by default these signals function as clocks (CLKOUT4 or CLKOUT6). To use these
muxed pins as GPIO signals, the appropriate GPIO register bits (GPxEN and GPxDIR) must be properly enabled and configured.
For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
‡
These pins are GP0 pins that can also function as external interrupt sources (EXT_INT[7:4]). Default after reset is EXT_INTx or
GPIO as input-only.
Figure 1−5. CPU and Peripheral Signals
†
†
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
35
Page 36

Pin Assignments
E
AED[31:0]
ACE3
ACE2
ACE1
ACE0
AEA[22:3]
ABE3
ABE2
ABE1
ABE0
32
20
VCXO Interpolated
Control Port (VIC)
Data
Memory Map
Space Select
Address
Byte Enables
External
Memory I/F
Control
Bus
Arbitration
EMIFA (32-bit)
Data
AECLKIN
AECLKOUT1
AECLKOUT2
ASDCKE
AARE/ASDCAS/ASADS/ASR
AAOE/ASDRAS/ASOE
AAWE/ASDWE/ASWE
AARDY
ASOE3
APDT
AHOLD
AHOLDA
ABUSREQ
VDAC
HD[15:0]
HCNTL0
HCNTL1
HHWIL
16
Data
Register Select
Half-Word
Select
Figure 1−6. Peripheral Signals
(Host-Port Interface)
HPI
[DM641 only]
Control
HAS
HR/W
HCS
HDS1
HDS2
HRDY
HINT
36
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 37

VP1D[0]/CLKX1
VP1D[1]/FSX1
VP1D[2]/DX1
Pin Assignments
DM641/DM640
McBSP1
†§
†§
†§
Transmit
McBSP0
Transmit
VP0D[0]/CLKX0
VP0D[1]/FSX0
VP0D[2]/DX0
†‡
†‡
†‡
VP1D[6]/CLKR1
VP1D[5]/FSR1
VP1D[4]/DR1
VP1D[3]/CLKS1
†§
†§
†§
†§
Receive
Clock
Receive
Clock
VP0D[6]/CLKR0
VP0D[5]/FSR0
VP0D[4]/DR0
VP0D[3]/CLKS0
McBSPs
(Multichannel Buffered Serial Ports)
TOUT1/LENDIAN
TINP1
Timer 1
Timer 0
TOUT0/MAC_EN
TINP0
Timer 2
Timers
I2C0
SCL0
SDA0
I2C0
†
For DM641, these McBSP1 and McBSP0 pins are muxed with the Video Port 1 (VP1) and Video Port 0 (VP0) peripherals, respectively. By
default, these signals function as VP1 and VP0, respectively. For more details on these muxed pins, see the Device Configurations section
of this data sheet.
‡
For DM640, these McBSP0 pins are muxed with the Video Port 0 (VP0) peripheral. By default, these signals function as VP0. For more details
on these muxed pins, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
§
The DM640 device does not support the VP1 peripheral; therefore, the McBSP1 peripheral pins are standalone perpheral functions, not
muxed.
†‡
†‡
†‡
†‡
Figure 1−6. Peripheral Signals (Continued)
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
37
Page 38

Pin Assignments
MTXD0
MTXD1
MTXD2
MTXD3
MRXD0
MRXD1
MRXD2
MRXD3
EMAC
Transmit
Receive
MDIO
Input/Output
MDIO
MTXEN
MRXER
MRXDV
MCOL
MCRS
MTCLK
MRCLK
Error Detect
and Control
Clocks
Clock
Ethernet MAC (EMAC)
and MDIO
Figure 1−6. Peripheral Signals (Continued)
MDCLK
38
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 39

STCLK
VP0CLK0
VP0CLK1
VP0CTL0
VP0CTL1
VP0CTL2
Pin Assignments
Timing and
Control Logic
VP0D[0]/CLKX0
VP0D[1]/FSX0
VP0D[2]/DX0
VP0D[3]/CLKS0
†
Channel A supports: BT.656 (8-bit) display pipeline mode and BT.656 (8-bit) capture pipeline mode [TSI (8-bit) capture
pipeline mode].
Capture/Display
Buffer
(2560 Bytes)
Channel A
Video Port 0 (VP0)
†
VP0D[4]/DR0
VP0D[5]/FSR0
VP0D[6]/CLKR0
VP0D[7]
Figure 1−6. Peripheral Signals (Continued)
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
39
Page 40

Pin Assignments
STCLK
VP1CLK0
VP1CLK1
VP1CTL0
VP1CTL1
VP1CTL2
‡
Timing and
Control Logic
VP1D[0]/CLKX1
VP1D[1]/FSX1
VP1D[2]/DX1
VP1D[3]/CLKS1
Capture/Display
Buffer
(2560 Bytes)
Channel A
†
VP1D[4]/DR1
VP1D[5]/FSR1
VP1D[6]/CLKR1
VP1D[7]
Video Port 1 (VP1) [DM641 only]
†
Channel A supports: BT.656 (8-bit) display pipeline mode and BT.656 (8-bit) capture pipeline mode [TSI (8-bit) capture
pipeline mode].
‡
For DM641, the same STCLK signal is used for both video ports (VP0 and VP1).
Figure 1−6. Peripheral Signals (Continued)
40
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 41

AXR0[0]
AXR0[1]
8-Serial Ports
Flexible
Partitioning
Tx, Rx, OFF
Pin Assignments
(Transmit/Receive Data Pins)(Transmit/Receive Data Pins)
AXR0[2]
AXR0[3]
(Receive Bit Clock)
ACLKR0
AHCLKR0
(Receive Master Clock) (Transmit Master Clock)
AFSR0
(Receive Frame Sync or
Left/Right Clock)
NOTES: A. The McASPs’ Error Detect function detects underruns, overruns, early/late frame syncs, DMA errors, and external mute input.
B. Bolded and italicized text within parentheses denotes the function of the pins in an audio system.
Receive Clock
Generator
Receive Clock
Check Circuit
Receive
Frame Sync
Error Detect
(see Note A )
McASP0
(Multichannel Audio Serial Port 0)
Transmit
Clock
Generator
Transmit
Clock Check
Circuit
Transmit
Frame Sync
Auto Mute
Logic
(Transmit Bit Clock)
ACLKX0
AHCLKX0
AFSX0
(Transmit Frame Sync or
Left/Right Clock)
AMUTE0
AMUTEIN0
Figure 1−6. Peripheral Signals (Continued)
1.9.3 Terminal Functions
The terminal functions table (Table 1−6) identifies the external signal names, the associated pin (ball) numbers
along with the mechanical package designator, the pin type (I, O/Z, or I/O/Z), whether the pin has any internal
pullup/pulldown resistors and a functional pin description. For more detailed information on device
configuration, peripheral selection, multiplexed/shared pins, and debugging considerations, see the Device
Configurations section of this data sheet.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
41
Page 42
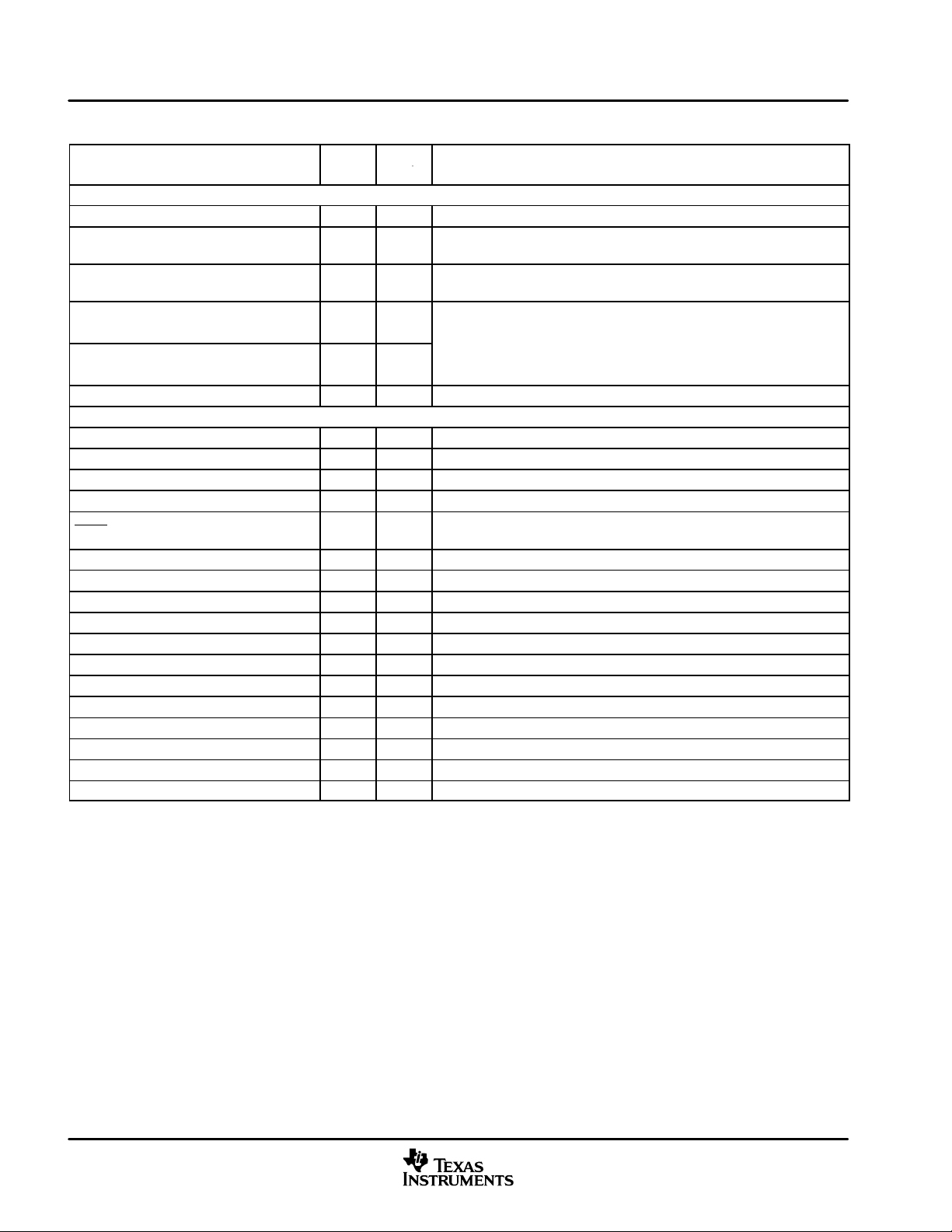
Pin Assignments
TYPE
†
IPD/
DESCRIPTION
(Bypass), x6, or x12.
T able 1−6. T erminal Functions
SIGNAL
NAME DM641 DM640
IPD/
IPU
‡
CLOCK/PLL CONFIGURATION
CLKIN AC2 AC2 I Clock Input. This clock is the input to the on-chip PLL.
CLKOUT4/GP0[1]
CLKOUT6/GP0[2]
§
§
D6 D6 I/O/Z IPU
C6 C6 I/O/Z IPU
CLKMODE1 AE4 AE4 I IPD
CLKMODE0 AA2 AA2 I IPD
PLLV
¶
V6 V6 A
#
Clock output at 1/4 of the device speed (O/Z) [default] or this pin can be
programmed as a GP0 1 pin (I/O/Z).
Clock output at 1/6 of the device speed (O/Z) [default] or this pin can be
programmed as a GP0 2 pin (I/O/Z).
Clock mode select
• Selects whether the CPU clock frequency = input clock frequency x1
For more d e tails on the CLKMODE pins and the PLL multiply factors, see
the Clock PLL section of this data sheet.
PLL voltage supply
JTAG EMULATION
TMS E15 E15 I IPU JTAG test-port mode select
TDO B18 B18 O/Z IPU JTAG test-port data out
TDI A18 A18 I IPU JTAG test-port data in
TCK A16 A16 I IPU JTAG test-port clock
TRST D14 D14 I IPD
JTAG test-port reset. For IEEE 1149.1 JTAG compatibility, see the IEEE
1149.1 JTAG compatibility statement portion of this data sheet.
EMU11 D17 D17 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 11. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU10 C17 C17 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 10. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU9 B17 B17 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 9. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU8 D16 D16 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 8. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU7 A17 A17 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 7. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU6 C16 C16 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 6. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU5 B16 B16 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 5. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU4 D15 D15 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 4. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU3 C15 C15 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 3. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU2 B15 B15 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 2. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU1 C14 C14 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 1
EMU0 A15 A15 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 0
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
§
These pins are multiplexed pins. For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
¶
PLLV is not part of external voltage supply. See the Clock PLL section for information on how to connect this pin.
#
A = Analog signal (PLL Filter)
||
The EMU0 and EMU1 pins are internally pulled up with 30-kΩ resistors; therefore, for emulation and normal operation, no external
||
||
pullup/pulldown resistors are necessary. However, for boundary scan operation, pull down the EMU1 and EMU0 pins with a dedicated 1-kΩ
resistor.
42
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 43

Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
TYPE
†
IPD/
DESCRIPTION
s
General-purpose input/output (GPIO) pins (I/O/Z) or external interrupts
.
When these pins function as External Interrupts [by selecting the
• When these pins function as External Interrupts [by selecting the
edge-driven and the polarity can be independently selected via the
Pin Assignments
SIGNAL
NAME DM641 DM640
IPD/
IPU
‡
RESETS, INTERRUPTS, AND GENERAL-PURPOSE INPUT/OUTPUTS
RESET P4 P4 I Device reset
Nonmaskable interrupt, edge-driven (rising edge)
NMI B4 B4 I IPD
Note: Any noise on the NMI pin may trigger an NMI interrupt; therefore, if the
NMI pin is not used, it is recommended that the NMI pin be grounded versus
relying on the IPD.
GP0[7]/EXT_INT7 E1 E1 I/O/Z IPU
GP0[6]/EXT_INT6 F2 F2 I/O/Z IPU
GP0[5]/EXT_INT5 F3 F3 I/O/Z IPU
GP0[4]/EXT_INT4 F4 F4 I/O/Z IPU
General-purpose input/output (GPIO) pins (I/O/Z) or external interrupt
(input only). The default after reset setting is GPIO enabled as input-only
•
corresponding interrupt enable register bit (IER.[7:4])], they are
External Interrupt Polarity Register bits (EXTPOL.[3:0]).
GP0[3] L5 L5 I/O/Z IPD The general-purpose 0 pin (GP0[3]) (I/O/Z).
GP0 0 pin (I/O/Z) [default]
This pin can be programmed as GPIO 0 (input only) [default] or as GP0[0]
GP0[0] M5 M5 I/O/Z IPD
(output only) pin or output as a general-purpose interrupt (GP0INT) signal
(output only).
Note: This pin must remain low during device reset.
CLKOUT6/
§
GP0[2]
CLKOUT4/
§
GP0[1]
C6 C6 I/O/Z IPU
D6 D6 I/O/Z IPU
Clock output at 1/6 of the device speed (O/Z) [default] or this pin can be
programmed as a GP0 2 pin (I/O/Z).
Clock output at 1/4 of the device speed (O/Z) [default] or this pin can be
programmed as a GP0 1 pin (I/O/Z).
HOST-PORT INTERFACE (HPI) [DM641 ONLY]
HINT N4 — I/O/Z Host interrupt from DSP to host (O) [default]
HCNTL1 P1 — I/O/Z Host control − selects between control, address, or data registers (I) [default]
HCNTL0 R3 — I/O/Z Host control − selects between control, address, or data registers (I) [default]
HHWIL N3 — I/O/Z
Host half-word select − first or second half-word (not necessarily high or low
order) [For HPI16 bus width selection only] (I) [default]
HR/W M1 — I/O/Z Host read or write select (I) [default]
HAS P3 — I/O/Z Host address strobe (I) [default]
HCS R1 — I/O/Z Host chip select (I) [default]
HDS1 R2 — I/O/Z Host data strobe 1 (I) [default]
HDS2 T2 — I/O/Z Host data strobe 2 (I) [default]
HRDY N1 — I/O/Z Host ready from DSP to host (O) [default]
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
§
These pins are multiplexed pins. For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
43
Page 44

Pin Assignments
Host-port data (I/O/Z) [DM641 Only]
I/O/Z
Used for transfer of data, address, and control
For proper DM641 device operation, the HD5 pin at device reset must be
Enabled by bits 28 through 31 of the word address
Only one pin is asserted during any external data access
• Only one pin is asserted during any external data access
EMIFA byte-enable control
or byte enables used depends on the width of external memory.
or byte enables used depends on the width of external memory.
Can be directly connected to SDRAM read and write mask
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
HOST-PORT INTERFACE (HPI) [DM641 ONLY] (CONTINUED)
HD15 T3 —
HD14 U1 —
HD13 U3 —
HD12 U2 —
HD11 U4 —
HD10 V1 —
HD9 V3 —
HD8 V2 —
HD7 W2 —
HD6 W4 —
HD5 Y1 —
As HPI data bus
•
For proper DM641 device operation, the HD5 pin at device reset must be
pulldown via a 10-kΩ resistor.
HD4 W3 —
HD3 Y2 —
HD2 Y4 —
HD1 AA1 —
HD0 Y3 —
EMIFA (32-BIT) − CONTROL SIGNALS COMMON TO ALL TYPES OF MEMORY
ACE3 L26 L26 O/Z IPU
ACE2 K23 K23 O/Z IPU
ACE1 K24 K24 O/Z IPU
EMIFA memory space enables
•
•
ACE0 K25 K25 O/Z IPU
ABE3 M25 M25 O/Z IPU
ABE2 M26 M26 O/Z IPU
ABE1 L23 L23 O/Z IPU
ABE0 L24 L24 O/Z IPU
APDT M22 M22 O/Z IPU
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
§
These pins are multiplexed pins. For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
EMIFA byte-enable control
• Decoded from the low-order address bits. The number of address bits
• Byte-write enables for most types of memory
•
signal (SDQM)
EMIFA peripheral data transfer, allows direct transfer between external
peripherals
44
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 45

Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
Pin Assignments
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
EMIFA (32-BIT) − BUS ARBITRATION
AHOLDA N22 N22 O IPU EMIFA hold-request-acknowledge to the host
AHOLD W24 W24 I IPU EMIFA hold request from the host
ABUSREQ P22 P22 O IPU EMIFA bus request output
EMIFA (32-BIT) − ASYNCHRONOUS/SYNCHRONOUS MEMORY CONTROL
EMIFA external input clock. The EMIFA input clock (AECLKIN, CPU/4 clock,
AECLKIN H25 H25 I IPD
or CPU/6 clock) is selected at reset via the pullup/pulldown resistors on the
AEA[20:19] pins.
AECLKIN is the default for the EMIFA input clock.
AECLKOUT2 J23 J23 O/Z IPD
AECLKOUT1 J26 J26 O/Z IPD
EMIFA output clock 2. Programmable to be EMIFA input clock (AECLKIN,
CPU/4 clock, or CPU/6 clock) frequency divided-by-1, -2, or -4.
EMIFA output clock 1 [at EMIFA input clock (AECLKIN, CPU/4 clock, or
CPU/6 clock) frequency].
EMIFA asynchronous memory read-enable/SDRAM column-address
strobe/programmable synchronous interface-address strobe or read-enable
• For programmable synchronous interface, the RENEN field in the CE
AARE/
ASDCAS/
ASADS/ASRE
J25 J25 O/Z IPU
Space Secondary Control Register (CExSEC) selects between ASADS
and ASRE:
If RENEN = 0, then the ASADS/ASRE signal functions as the ASADS
signal.
If RENEN = 1, then the ASADS/ASRE signal functions as the ASRE
signal.
AAOE/
ASDRAS/
ASOE
AAWE/
ASDWE/
ASWE
J24 J24 O/Z IPU
K26 K26 O/Z IPU
EMIFA asynchronous memory output-enable/SDRAM row-address
strobe/programmable synchronous interface output-enable
EMIFA asynchronous memory write-enable/SDRAM
write-enable/programmable synchronous interface write-enable
EMIFA SDRAM clock-enable (used for self-refresh mode).
ASDCKE L25 L25 O/Z IPU
• If SDRAM is not in system, ASDCKE can be used as a general-purpose
output.
ASOE3 R22 R22 O/Z IPU
EMIFA synchronous memory output-enable for ACE3 (for glueless FIFO
interface)
AARDY L22 L22 I IPU Asynchronous memory ready input
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
§
These pins are multiplexed pins. For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
45
Page 46

Pin Assignments
EMIFA address numbering for the DM641/DM640 devices start with AEA3 to
,
maintain signal name compatibility with other C64x devices (e.g., C6414,
e
(literature number SPRU266)].
Controls initialization of DSP modes at reset (I) via pullup/pulldown
resistors
− Boot mode (AEA[22:21]):
O/Z
IPD
01 − HPI [DM641 only]; Reserved [For DM640 device]
10 − Reserved
11 − EMIFA 8−bit ROM boot
− EMIF clock select
− AEA[20:19]: Clock mode select for EMIFA (AECLKIN_SEL[1:0])
01 − CPU/4 Clock Rate
10 − CPU/6 Clock Rate
10 − CPU/6 Clock Rate
11 − Reserved
For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
I/O/Z
IPU
EMIFA external data
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
EMIFA (32-BIT) − ADDRESS
AEA22 U23 U23
AEA21 V24 V24
AEA20 V25 V25
AEA19 V26 V26
AEA18 V23 V23
EMIFA external address (doubleword address)
maintain signal name compatibility with other C64x™ devices (e.g., C6414
C6415, and C6416) [see the 32-bit EMIF addressing scheme in the
TMS320C6000 DSP External Memory Interface (EMIF) Reference Guid
AEA17 U24 U24
AEA16 U25 U25
AEA15 U26 U26
AEA14 T24 T24
AEA13 T25 T25
Boot Configuration:
•
− Boot mode (AEA[22:21]):
00 – No boot (default mode)
AEA12 R23 R23
AEA11 R24 R24
11 − EMIFA 8−bit ROM boot
AEA10 P23 P23
AEA9 P24 P24
AEA8 P26 P26
AEA7 N23 N23
− AEA[20:19]: Clock mode select for EMIFA (AECLKIN_SEL[1:0])
00 – AECLKIN (default mode)
AEA6 N24 N24
AEA5 N26 N26
11 − Reserved
AEA4 M23 M23
AEA3 M24 M24
EMIFA (32-BIT) − DATA
AED31 C26 C26
AED30 C25 C25
AED29 D26 D26
AED28 D25 D25
AED27 E24 E24
AED26 E25 E25
AED25 F24 F24
AED24 F25 F25
AED23 F23 F23
AED22 F26 F26
AED21 G24 G24
AED20 G25 G25
AED19 G23 G23
AED18 G26 G26
AED17 H23 H23
AED16 H24 H24
AED15 C19 C19
AED14 D19 D19
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
§
These pins are multiplexed pins. For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
46
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 47
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
I/O/Z
IPU
EMIFA external data
Video port 1 (VP1) data input/output (I/O/Z) or McBSP1 data input/output
(I/O/Z) [default] [DM641 only]
I/O/Z
IPD
McBSP1 peripheral pins are standalone peripheral functions, not muxed.
For more details on the McBSP1 pin functions [for both the DM641 and
Configurations section of this data sheet.
I/O/Z
IPD
Pin Assignments
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
EMIFA (32-BIT) − DATA (CONTINUED)
AED13 A20 A20
AED12 D20 D20
AED11 B20 B20
AED10 C20 C20
AED9 A21 A21
AED8 D21 D21
AED7 B21 B21
AED6 C21 C21
AED5 A23 A23
AED4 C22 C22
AED3 B22 B22
AED2 B23 B23
AED1 A24 A24
AED0 B24 B24
MANAGEMENT DATA INPUT/OUTPUT (MDIO)
MDCLK R5 R5 I/O/Z IPD MDIO serial clock input/output (I/O/Z).
MDIO P5 P5 I/O/Z IPU MDIO serial data input/output (I/O/Z).
VCX0 INTERPOLATED CONTROL PORT (VIC)
VDAC AD1 AD1 O/Z IPD
VCXO Interpolated Control Port (VIC) single-bit digital-to-analog converter
(VDAC) output [output only].
VIDEO PORTS (VP0 [DM641/DM640] AND VP1 [DM641 ONLY])
STCLK AC1 AC1 I IPD The STCLK signal drives the hardware counter on the video ports.
8-BIT VIDEO PORT 1 (VP1) [DM641 ONLY]
VP1D[7] AC8 —
VP1D[6]/CLKR1
VP1D[5]/FSR1
VP1D[4]/DR1
VP1D[3]/CLKS1
VP1D[2]/DX1
VP1D[1]/FSX1
VP1D[0]/CLKX1
§
§
§
§
§
§
§
AD8 ***
AC7 ***
AD7 ***
AE7 ***
AC6 ***
AD6 ***
AE6 ***
*** − The DM640 device does not support the VP1 peripheral; therefore, the
For more details on the McBSP1 pin functions [for both the DM641 and
DM640 devices], see McBSP1 section of this table and the Device
VP1CLK1 AF10 — I/O/Z IPD VP1 clock 1 (I/O/Z)
VP1CLK0 AF8 — I IPD VP1 clock 0 (I)
VP1CTL2 AD5 — VP1 control 2 (I/O/Z)
VP1CTL1 AE5 —
I/O/Z IPD
VP1CTL0 AF4 —
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
§
These pins are multiplexed pins. For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
VP1 control 1 (I/O/Z)
VP1 control 0 (I/O/Z)
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
47
Page 48

Pin Assignments
Video port 0 (VP0) data input/output (I/O/Z) or McBSP0 data input/output
I/O/Z
IPD
For more details on the McBSP0 pin functions, see McBSP0 section of this
table and the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
I/O/Z
IPD
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
8-BIT VIDEO PORT 0 (VP0) [DM641 AND DM640]
VP0D[7] AD15 AD15
VP0D[6]/CLKR0
VP0D[5]/FSR0
VP0D[4]/DR0
VP0D[3]/CLKS0
VP0D[2]/DX0
VP0D[1]/FSX0
VP0D[0]/CLKX0
§
§
§
§
§
§
§
AE15 AE15
AB16 AB16
AC16 AC16
AD16 AD16
AE16 AE16
AF16 AF16
AF17 AF17
Video port 0 (VP0) data input/output (I/O/Z) or McBSP0 data input/output
(I/O/Z) [default]
table and the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
VP0CLK1 AF12 AF12 I/O/Z IPD VP0 clock 1 (I/O/Z)
VP0CLK0 AF14 AF14 I IPD VP0 clock 0 (I)
VP0CTL2 AD17 AD17 VP0 control 2 (I/O/Z)
VP0CTL1 AC17 AC17
VP0CTL0 AE17 AE17
I/O/Z IPD
VP0 control 1 (I/O/Z)
VP0control 0 (I/O/Z)
TIMER 2
— —
No external pins. The timer 2 peripheral pins are not pinned out as external
pins.
TIMER 1
Timer 1 output (O/Z)
Boot Configuration: Device endian mode [LENDIAN] (I).
Controls initialization of DSP modes at reset via pullup/pulldown resistors
TOUT1/LENDIAN B5 B5 O/Z IPU
− Device Endian mode
0 – Big Endian
1 − Little Endian (default)
For more details on LENDIAN, see the Device Configurations section of this
data sheet.
TINP1 A5 A5 I IPD Timer 1 or general-purpose input
TIMER 0
Timer 0 output (O/Z)
Boot Configuration: MAC enable pin [MAC_EN] (I)
TOUT0/MAC_EN C5 C5 O/Z IPD
The MAC_EN pin controls the selection (enable/disable) of the EMAC and
MDIO peripherals.
TINP0 A4 A4 I IPD Timer 0 or general-purpose input
INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 0 (I2C0)
SCL0 E4 E4 I/O/Z — I2C0 clock.
SDA0 D3 D3 I/O/Z — I2C0 data.
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
§
These pins are multiplexed pins. For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
48
For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 49

Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
Pin Assignments
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
MULTICHANNEL BUFFERED SERIAL PORT 1 (McBSP1) [DM641 ONLY]
VP1D[6]/CLKR1
VP1D[5]/FSR1
VP1D[4]/DR1
§
VP1D[3]/CLKS1
VP1D[2]/DX1
§
VP1D[1]/FSX1
VP1D[0]/CLKX1
§
§
AD8 — I/O/Z IPD
AC7 — I/O/Z IPD
AD7 — I IPD VP1 input/output data 4 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP1 receive data (I) [default]
§
AE7 — I IPD
AC6 — I/O/Z IPD VP1 input/output data 2 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP1 transmit data (O/Z) [default]
§
§
AD6 — I/O/Z IPD
AE6 — I/O/Z IPD VP1 input/output data 0 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP1 transmit clock (I/O/Z) [default]
Video Port 1 (VP1) input/output data 6 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP1 receive clock
(I/O/Z) [default]
VP1 input/output data 5 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP1 receive frame sync (I/O/Z)
[default]
VP1 input/output data 3 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP1 external clock source (I)
(as opposed to internal) [default]
VP1 input/output data 1 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP1 transmit frame sync (I/O/Z)
[default]
MULTICHANNEL BUFFERED SERIAL PORT 1 (McBSP1) [DM640 ONLY]
CLKR1 — AD8 I/O/Z IPD McBSP1 receive clock (I/O/Z)
FSR1 — AC7 I/O/Z IPD McBSP1 receive frame sync (I/O/Z)
DR1 — AD7 I IPD McBSP1 receive data (I)
CLKS1 — AE7 I IPD McBSP1 external clock source (I) (as opposed to internal)
DX1 — AC6 I/O/Z IPD McBSP1 transmit data (O/Z)
FSX1 — AD6 I/O/Z IPD McBSP1 transmit frame sync (I/O/Z)
CLKX1 — AE6 I/O/Z IPD McBSP1 transmit clock (I/O/Z)
MULTICHANNEL BUFFERED SERIAL PORT 0 (McBSP0)
VP0D[6]/CLKR0
VP0D[5]/FSR0
VP0D[4]/DR0
VP0D[3]/CLKS0
VP0D[2]/DX0
VP0D[1]/FSX0
VP0D[0]/CLKX0
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
§
These pins are multiplexed pins. For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
§
§
§
§
§
§
§
AE15 AE15 I/O/Z IPD
AB16 AB16 I/O/Z IPD
AC16 AC16 I IPD VP0 input/output data 4 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP0 receive data (I) [default]
AD16 AD16 I IPD
AE16 AE16 O/Z IPD VP0 input/output data 2 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP0 transmit data (O/Z) [default]
AF16 AF16 I/O/Z IPD
AF17 AF17 I/O/Z IPD VP0 input/output data 0 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP0 transmit clock (I/O/Z) [default]
Video Port 0 (VP0) input/output data 6 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP0 receive clock
(I/O/Z) [default]
VP0 input/output data 5 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP0 receive frame sync (I/O/Z)
[default]
VP0 input/output data 3 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP0 external clock source (I)
(as opposed to internal) [default]
VP0 input/output data 1 pin (I/O/Z) or McBSP0 transmit frame sync (I/O/Z)
[default]
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
49
Page 50

Pin Assignments
EMAC Media Independent I/F (MII) data, clocks, and control pins for
MII transmit clock (MTCLK),
MII transmit clock (MTCLK),
MII transmit data (MTXD[3:0]),
This signal indicates a valid transmit data on the transmit data pins
MII collision sense (MCOL)
MII collision sense (MCOL)
collision.
During full-duplex operation, transmission of new frames will not begin if
MII carrier sense (MCRS)
MII receive data (MRXD[3:0]),
MII receive clock (MRCLK),
Receive clock source from the attached PHY.
This signal indicates a valid data nibble on the receive data pins
MII receive error (MRXER),
I/O/Z
IPD
McASP0 TX/RX data pins [3:0] (I/O/Z).
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
ETHERNET MAC (EMAC)
MRCLK G1 G1 I
MCRS H3 H3 I
MRXER G2 G2 I
MRXDV J4 J4 I
MRXD3 H2 H2 I
MRXD2 J3 J3 I
MRXD1 J1 J1 I
MRXD0 K4 K4 I
MTCLK L4 L4 I
MCOL K2 K2 I
MTXEN L3 L3 O/Z
MTXD3 L2 L2 O/Z
MTXD2 M4 M4 O/Z
MTXD1 M2 M2 O/Z
MTXD0 M3 M3 O/Z
EMAC Media Independent I/F (MII) data, clocks, and control pins for
Transmit/Receive.
Transmit clock source from the attached PHY.
Transmit data nibble synchronous with transmit clock (MTCLK).
MII transmit enable (MTXEN),
This signal indicates a valid transmit data on the transmit data pins
(MTDX[3:0]).
Assertion of this signal during half-duplex operation indicates network
During full-duplex operation, transmission of new frames will not begin if
this pin is asserted.
MII carrier sense (MCRS)
Indicates a frame carrier signal is being received.
Receive data nibble synchronous with receive clock (MRCLK).
Receive clock source from the attached PHY.
MII receive data valid (MRXDV),
This signal indicates a valid data nibble on the receive data pins
(MRDX[3:0]).
Indicates reception of a coding error on the receive data.
MULTICHANNEL AUDIO SERIAL PORT 0 (McASP0) CONTROL
AHCLKX0 AC12 AC12 I/O/Z IPD McASP0 transmit high-frequency master clock (I/O/Z).
AFSX0 AD12 AD12 I/O/Z IPD McASP0 transmit frame sync or left/right clock (LRCLK) (I/O/Z).
ACLKX0 AB13 AB13 I/O/Z IPD McASP0 transmit bit clock (I/O/Z).
AMUTE0 AC13 AC13 O/Z IPD McASP0 mute output (O/Z).
AMUTEIN0 AD13 AD13 I/O/Z IPD McASP0 mute input (I/O/Z).
AHCLKR0 AB14 AB14 I/O/Z IPD McASP0 receive high-frequency master clock (I/O/Z).
AFSR0 AC14 AC14 I/O/Z IPD McASP0 receive frame sync or left/right clock (LRCLK) (I/O/Z).
ACLKR0 AD14 AD14 I/O/Z IPD McASP0 receive bit clock (I/O/Z).
MULTICHANNEL AUDIO SERIAL PORT 0 (McASP0) DATA
AXR0[3] AE11 AE11
AXR0[2] AC10 AC10
AXR0[1] AD10 AD10
AXR0[0] AC9 AC9
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
§
These pins are multiplexed pins. For more details, see the Device Configurations section of this data sheet.
50
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 51

Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
TYPE
†
IPD/
DESCRIPTION
Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
RSV
Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
Pull down via a 10-kΩ resistor
Pin Assignments
SIGNAL
NAME DM641 DM640
IPD/
IPU
‡
RESERVED FOR TEST
RSV E2 E2 I IPD
RSV — Y1 I/O/Z —
RSV H7 H7 A —
RSV R6 R6 A —
Reserved. For proper DM641/DM640 device operation, this pin at device
reset must be pulled down via a 10-kΩ resistor.
Reserved [for DM640 Only]. For proper DM640 device operation, this pin at
device reset must be pulled down via a 10-kΩ resistor.
Reserved. This pin must be connected directly to CVDD for proper device
operation.
Reserved. This pin must be connected directly to DVDD for proper device
operation.
ADDITIONAL RESERVED FOR TEST
A7 A7 I IPD
A9 A9 I/O/Z IPD
A10 A10 I/O/Z IPD
A11 A11 I/O/Z IPD
A13 A13 I/O/Z IPD
B8 B8 I/O/Z IPD
B9 B9 I/O/Z IPD
B10 B10 I/O/Z IPD
B11 B11 I/O/Z IPD
B12 B12 I/O/Z IPD
C1 C1 I/O/Z — Pull down via a 10-kΩ resistor
C7 C7 I/O/Z IPD
C8 C8 I/O/Z IPD
C9 C9 I/O/Z IPD
C10 C10 I/O/Z IPD
RSV
C11 C11 I/O/Z IPD
C12 C12 I/O/Z IPD
D7 D7 I/O/Z IPD
D8 D8 I/O/Z IPD
D9 D9 I/O/Z IPD
D10 D10 I/O/Z IPD
D11 D11 I/O/Z IPD
D12 D12 I/O/Z IPD
E11 E11 I/O/Z IPD
E12 E12 I/O/Z IPD
E13 E13 I/O/Z IPD
E14 E14 I IPD
F1 F1 I/O/Z —
G3 G3 I/O/Z —
G4 G4 I/O/Z —
H4 H4 I/O/Z —
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
51
Page 52

Pin Assignments
Pull down via a 10-kΩ resistor
Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
RSV
Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
RSV
NAME
SIGNAL
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
TYPE
J2 J2 I/O/Z —
K1 K1 I/O/Z —
Pull down via a 10-kΩ resistor
K3 K3 I/O/Z —
R4 R4 I IPU
R25 R25 O/Z IPU
R26 R26 O/Z IPU
T4 T4 O IPD
T22 T22 O/Z IPU
T23 T23 O/Z IPU
V4 V4 I/O/Z — Pull down via a 10-kΩ resistor
W7 W7 A —
W23 W23 I/O/Z IPU
Y23 Y23 I/O/Z IPU
Y24 Y24 I/O/Z IPU
Y25 Y25 I/O/Z IPU
Y26 Y26 I/O/Z IPU
AA3 AA3 A —
AA23 AA23 I/O/Z IPU
AA24 AA24 I/O/Z IPU
AA25 AA25 I/O/Z IPU
AA26 AA26 I/O/Z IPU
AB3 AB3 I —
AB11 AB11 I/O/Z IPD
AB12 AB12 I/O/Z IPD
AB15 AB15 I/O/Z IPD
AB23 AB23 I/O/Z IPU
AB24 AB24 I/O/Z IPU
AB25 AB25 I/O/Z IPU
AC4 AC4 O/Z —
AC11 AC11 I/O/Z IPD
AC15 AC15 I/O/Z IPD
AC19 AC19 I/O/Z IPU
AC20 AC20 I/O/Z IPU
AC21 AC21 I/O/Z IPU
AC25 AC25 I/O/Z IPU
AC26 AC26 I/O/Z IPU
AD3 AD3 O/Z —
AD9 AD9 I/O/Z IPD
AD11 AD11 I/O/Z IPD
AD19 AD19 I/O/Z IPU
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
52
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 53

Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
RSV
Pull up via a 10-kΩ resistor
Pull down via a 10-kΩ resistor
Pin Assignments
RSV
NAME
SIGNAL
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
TYPE
AD20 AD20 I/O/Z IPU
AD21 AD21 I/O/Z IPU
AD22 AD22 I/O/Z IPU
AD23 AD23 I/O/Z IPU
AD25 AD25 I/O/Z IPU
AD26 AD26 I/O/Z IPU
AE9 AE9 I/O/Z IPD
AE18 AE18 I/O/Z IPD
AE20 AE20 I/O/Z IPU
AE21 AE21 I/O/Z IPU
AE22 AE22 I/O/Z IPU
AE23 AE23 I/O/Z IPU
AF3 AF3 O IPU
AF5 AF5 I/O/Z IPD
AF6 AF6 I/O/Z IPD
AF18 AF18 I/O/Z IPD
AF20 AF20 I/O/Z IPU
AF21 AF21 I/O/Z IPU
AF23 AF23 I/O/Z IPU
AF24 AF24 I/O/Z IPU
— M1 I/O/Z — Pull up via a 10-kΩ resistor
— N1 I/O/Z — Pull down via a 10-kΩ resistor
— N3 I/O/Z —
— N4 I/O/Z —
— P1 I/O/Z —
— P3 I/O/Z —
— R1 I/O/Z —
— R2 I/O/Z —
— R3 I/O/Z —
— T2 I/O/Z —
— T3 I/O/Z —
— U1 I/O/Z —
— U2 I/O/Z —
— U3 I/O/Z —
— U4 I/O/Z —
— V1 I/O/Z —
— V2 I/O/Z —
— V3 I/O/Z —
— W2 I/O/Z —
— W3 I/O/Z —
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
53
Page 54

Pin Assignments
Pull down via a 10-kΩ resistor
RSV
Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
DV
S
3.3-V supply voltage
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
— W4 I/O/Z —
— Y2 I/O/Z —
— Y3 I/O/Z —
Pull down via a 10-kΩ resistor
— Y4 I/O/Z —
— AA1 I/O/Z —
RSV
— AC8 I/O/Z IPD
— AD5 I/O/Z IPD
— AE5 I/O/Z IPD
— AF4 I/O/Z IPD
— AF8 I IPD
— AF10 I/O/Z IPD
SUPPLY VOLTAGE PINS
A2 A2
A25 A25
B1 B1
B2 B2
B14 B14
B25 B25
B26 B26
C3 C3
C24 C24
D4 D4
D23 D23
DD
E5 E5
E7 E7
E8 E8
E10 E10
E17 E17
E19 E19
E20 E20
E22 E22
F9 F9
F12 F12
F15 F15
F18 F18
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
54
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 55

Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
Pin Assignments
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
SUPPLY VOLTAGE PINS (CONTINUED)
G5 G5
G22 G22
H5 H5
H22 H22
J6 J6
J21 J21
K5 K5
K22 K22
M6 M6
M21 M21
N2 N2
P25 P25
R21 R21
U5 U5
U22 U22
V21 V21
DV
DD
W5 W5
S 3.3-V supply voltage
W22 W22
W25 W25
Y5 Y5
Y22 Y22
AA9 AA9
AA12 AA12
AA15 AA15
AA18 AA18
AB5 AB5
AB7 AB7
AB8 AB8
AB10 AB10
AB17 AB17
AB19 AB19
AB20 AB20
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
55
Page 56

Pin Assignments
DV
S
3.3-V supply voltage
1.2-V supply voltage (-400, -500 devices)
CV
S
1.2-V supply voltage (-400, -500 devices)
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
SUPPLY VOLTAGE PINS (CONTINUED)
AB22 AB22
AC23 AC23
AD24 AD24
AE1 AE1
AE2 AE2
DD
AE13 AE13
AE25 AE25
AE26 AE26
AF2 AF2
AF25 AF25
F6 F6
F7 F7
F20 F20
F21 F21
G6 G6
G7 G7
G8 G8
G10 G10
G11 G11
G13 G13
G14 G14
G16 G16
DD
G17 G17
1.4-V supply voltage (-600 device)
G19 G19
G20 G20
G21 G21
H20 H20
K7 K7
K20 K20
L7 L7
L20 L20
M12 M12
M14 M14
N7 N7
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
56
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 57

Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
1.2-V supply voltage (-400, -500 devices)
CV
S
1.2-V supply voltage (-400, -500 devices)
Pin Assignments
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
SUPPLY VOLTAGE PINS (CONTINUED)
N13 N13
N15 N15
N20 N20
P7 P7
P12 P12
P14 P14
P20 P20
R13 R13
R15 R15
T7 T7
T20 T20
U7 U7
U20 U20
W20 W20
Y6 Y6
DD
Y7 Y7
1.4-V supply voltage (-600 device)
Y8 Y8
Y10 Y10
Y11 Y11
Y13 Y13
Y14 Y14
Y16 Y16
Y17 Y17
Y19 Y19
Y20 Y20
Y21 Y21
AA6 AA6
AA7 AA7
AA20 AA20
AA21 AA21
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
57
Page 58

Pin Assignments
V
GND
Ground pins
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
GROUND PINS
A1 A1
A3 A3
A6 A6
A8 A8
A12 A12
A14 A14
A19 A19
A22 A22
A26 A26
B3 B3
B6 B6
B7 B7
B13 B13
B19 B19
C2 C2
C4 C4
C13 C13
SS
C18 C18
C23 C23
D1 D1
D2 D2
D5 D5
D13 D13
D18 D18
D22 D22
D24 D24
E3 E3
E6 E6
E9 E9
E16 E16
E18 E18
E21 E21
E23 E23
E26 E26
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
58
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 59

Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
V
GND
Ground pins
Pin Assignments
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
GROUND PINS (CONTINUED)
F5 F5
F8 F8
F10 F10
F11 F11
F13 F13
F14 F14
F16 F16
F17 F17
F19 F19
F22 F22
G9 G9
G12 G12
G15 G15
G18 G18
H1 H1
H6 H6
H21 H21
SS
H26 H26
J5 J5
J7 J7
J20 J20
J22 J22
K6 K6
K21 K21
L1 L1
L6 L6
L21 L21
M7 M7
M13 M13
M15 M15
M20 M20
N5 N5
N6 N6
N12 N12
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
59
Page 60

Pin Assignments
V
GND
Ground pins
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
GROUND PINS (CONTINUED)
N14 N14
N21 N21
N25 N25
P2 P2
P6 P6
P13 P13
P15 P15
P21 P21
R7 R7
R12 R12
R14 R14
R20 R20
T1 T1
T5 T5
T6 T6
T21 T21
T26 T26
SS
U6 U6
U21 U21
V5 V5
V7 V7
V20 V20
V22 V22
W1 W1
W6 W6
W21 W21
W26 W26
Y9 Y9
Y12 Y12
Y15 Y15
Y18 Y18
AA4 AA4
AA5 AA5
AA8 AA8
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
60
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 61
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
Pin Assignments
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
GROUND PINS (CONTINUED)
AA10 AA10
AA11 AA11
AA13 AA13
AA14 AA14
AA16 AA16
AA17 AA17
AA19 AA19
AA22 AA22
AB1 AB1
AB2 AB2
AB4 AB4
AB6 AB6
AB9 AB9
AB18 AB18
AB21 AB21
AB26 AB26
V
SS
AC3 AC3
GND Ground pins
AC5 AC5
AC18 AC18
AC22 AC22
AC24 AC24
AD2 AD2
AD4 AD4
AD18 AD18
AE3 AE3
AE8 AE8
AE10 AE10
AE12 AE12
AE14 AE14
AE19 AE19
AE24 AE24
AF1 AF1
AF7 AF7
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
61
Page 62
Pin Assignments
V
SS
GND
Ground pins
Table 1−6. Terminal Functions (Continued)
NAME
SIGNAL
TYPE
DM640DM641
TYPE
IPD/
IPD/
†
†
IPU
IPU
‡
‡
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
GROUND PINS (CONTINUED)
AF9 AF9
AF11 AF11
AF13 AF13
V
SS
AF15 AF15
GND Ground pins
AF19 AF19
AF22 AF22
AF26 AF26
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
62
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 63

1.10 Development
1.10.1 Development Support
TI offers an extensive line of development tools for the TMS320C6000™ DSP platform, including tools to
evaluate the performance of the processors, generate code, develop algorithm implementations, and fully
integrate and debug software and hardware modules.
The following products support development of C6000™ DSP-based applications:
Software Development Tools:
Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE): including Editor
C/C++/Assembly Code Generation, and Debug plus additional development tools
Scalable, Real-Time Foundation Software (DSP/BIOS™), which provides the basic run-time target software
needed to support any DSP application.
Hardware Development Tools:
Extended Development System (XDS™) Emulator (supports C6000™ DSP multiprocessor system debug)
EVM (Evaluation Module)
For a complete listing of development-support tools for the TMS320C6000™ DSP platform, visit the Texas
Instruments web site on the Worldwide Web at http://www.ti.com uniform resource locator (URL). For
information on pricing and availability, contact the nearest TI field sales office or authorized distributor.
Development
Code Composer Studio, DSP/BIOS, and XDS are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
63
Page 64

Development
1.10.2 Device Support
1.10.2.1 Device and Development-Support Tool Nomenclature
To designate the stages in the product development cycle, TI assigns prefixes to the part numbers of all DSP
devices and support tools. Each DSP commercial family member has one of three prefixes: TMX, TMP, or TMS
(e.g., TMS320DM641GDK600). Texas Instruments recommends two of three possible prefix designators for
its support tools: TMDX and TMDS. These prefixes represent evolutionary stages of product development
from engineering prototypes (TMX/TMDX) through fully qualified production devices/tools (TMS/TMDS).
Device development evolutionary flow:
TMX Experimental device that is not necessarily representative of the final device’s electrical specifications
TMP Final silicon die that conforms to the device’s electrical specifications but has not completed quality
and reliability verification
TMS Fully qualified production device
Support tool development evolutionary flow:
TMDX Development-support product that has not yet completed Texas Instruments internal qualification
testing.
TMDS Fully qualified development-support product
TMX and TMP devices and TMDX development-support tools are shipped against the following disclaimer:
“Developmental product is intended for internal evaluation purposes.”
TMS devices and TMDS development-support tools have been characterized fully, and the quality and
reliability of the device have been demonstrated fully. TI’s standard warranty applies.
Predictions show that prototype devices (TMX or TMP) have a greater failure rate than the standard
production devices. Texas Instruments recommends that these devices not be used in any production system
because their expected end-use failure rate still is undefined. Only qualified production devices are to be used.
TI device nomenclature also includes a suffix with the device family name. This suffix indicates the package
type (for example, GDK), the temperature range (for example, blank is the default commercial temperature
range), and the device speed range in megahertz (for example, -600 is 600 MHz). Figure 1−7 provides a
legend for reading the complete device name for any DSP platform member.
The ZDK package, like the GDK package, is a 548-ball plastic BGA only with Pb-free balls. The ZNZ package
is the Pb−free version of the GNZ package.
For device part numbers and further ordering information for TMS320DM641/DM640 in the GDK, GNZ, ZDK
and ZNZ package types, see the TI website (http://www.ti.com) or contact your TI sales representative.
64
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 65

Development
TMS 320 DM641 GDK 600
( )
PREFIX DEVICE SPEED RANGE
TMX = Experimental device
TMP = Prototype device
TMS = Qualified device
SMX= Experimental device, MIL
SMJ = MIL-PRF-38535, QML
SM = High Rel (non-38535)
DEVICE FAMILY
320 = TMS320t DSP family
†
The extended temperature “A version” devices may have different operating conditions than the commercial temperature devices.
For more details, see the recommended operating conditions portion of this data sheet.
‡
BGA = Ball Grid Array
§
The ZDK and ZNZ mechanical package designators represent the version of the GDK and GNZ packages with Pb-free balls. For
more detailed information, see the Mechanical Data section of this document.
¶
For actual device part numbers (P/Ns) and ordering information, see the TI website (www.ti.com).
TEMPERATURE RANGE (DEFAULT: 0°C TO 90°C)
PACKAGE TYPE
DEVICE
DM64x DSP:
400 (400-MHz CPU, 100-MHz EMIF)
500 (500-MHz CPU, 100-MHz EMIF)
600 (600-MHz CPU, 133-MHz EMIF)
†
Blank = 0°C to 90°C, commercial temperature
A = −40°C to 105°C, extended temperature
§
‡
GDK = 548-pin plastic BGA
GNZ = 548-pin plastic BGA
ZDK = 548-pin plastic BGA, with Pb-free soldered balls
ZNZ = 548-pin plastic BGA, with Pb-free soldered balls
¶
643
642
641
640
Figure 1−7. TMS320DM64x™ DSP Device Nomenclature (Including the DM641 and DM640 Devices)
1.10.2.2 Documentation Support
Extensive documentation supports all TMS320™ DSP family generations of devices from product
announcement through applications development. The types of documentation available include: data
sheets, such as this document, with design specifications; complete user’s reference guides for all devices
and tools; technical briefs; development-support tools; on-line help; and hardware and software applications.
The following is a brief, descriptive list of support documentation specific to the C6000™ DSP devices:
The TMS320C6000 CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide (literature number SPRU189) describes the
C6000™ DSP CPU (core) architecture, instruction set, pipeline, and associated interrupts.
The TMS320C6000 DSP Peripherals Overview Reference Guide (literature number SPRU190) provides an
overview and briefly describes the functionality of the peripherals available on the C6000™ DSP platform of
devices. This document also includes a table listing the peripherals available on the C6000 devices along with
literature numbers and hyperlinks to the associated peripheral documents.
The TMS320C64x Technical Overview (literature number SPRU395) gives an introduction to the C64x™
digital signal processor, and discusses the application areas that are enhanced by the C64x™ DSP
VelociTI.2™ VLIW architecture.
The TMS320C64x DSP Video Port/VCXO Interpolated Control (VIC) Port Reference Guide (literature number
SPRU629) describes the functionality of the Video Port and VIC Port peripherals.
The TMS320C6000 DSP Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP) Reference Guide (literature number
SPRU041) describes the functionality of the McASP peripheral.
TMS320C6000 DSP Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Module Reference Guide (literature number SPRU175)
describes the functionality of the I2C peripheral.
TMS320C6000 DSP Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)/ Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
Module Reference Guide (literature number SPRU628) describes the functionality of the EMAC and MDIO
peripherals.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
65
Page 66

Development
The TMS320DM641/TMS320DM640 Digital Signal Processors Silicon Errata (literature number SPRZ201)
describes the known exceptions to the functional specifications for particular silicon revisions of the
TMS320DM641 and TMS320DM640 devices.
The TMS320DM64x Power Consumption Summary application report (literature number SPRA962)
discusses the power consumption for user applications with the TMS320DM641/DM640 DSP devices.
The TMS320DM640/1 Hardware Designer’s Resource Guide (literature number SPRAA50) is organized by
development flow and functional areas to make design efforts as seamless as possible. This document
includes getting started, board design, system testing, and checklists to aid in initial designs and debug efforts.
Each section of this document includes pointers to valuable information including: technical documentation,
models, symbols, and reference designs for use in each phase of design. Particular attention is given to
peripheral interfacing and system-level design concerns.
The Using IBIS Models for Timing Analysis application report (literature number SPRA839) describes how to
properly use IBIS models to attain accurate timing analysis for a given system.
The tools support documentation is electronically available within the Code Composer Studio™ Integrated
Development Environment (IDE). For a complete listing of C6000™ DSP latest documentation, visit the Texas
Instruments web site on the Worldwide Web at http://www.ti.com uniform resource locator (URL).
1.10.2.3 Device Silicon Revision
The device silicon revision can be determined by the “Die PG code” marked on the top of the package. For
more detailed information on the DM641/DM640 silicon revision, package markings, and the known
exceptions to the functional specifications as well as any usage notes, refer to the device-specific silicon
errata: TMS320DM641, TMS320DM640 Digital Signal Processors Silicon Errata (literature number
SPRZ201).
66
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 67

2 Device Configurations
On the DM641/DM640 device, bootmode and certain device configurations/peripheral selections are
determined at device reset, while other device configurations/peripheral selections are software-configurable
via the peripheral configurations register (PERCFG) [address location 0x01B3F000] after device reset.
2.1 Configurations at Reset
For proper device operation; the following external pins must be configured correctly:
• For proper DM641 device operation, the HD5 [pin Y1] at device reset must be pulled down via a 10-kΩ
resistor.
• For proper DM641/DM640 device operation, the reserved (RSV) [E2] pin at device reset must be pulled
down via a 10-kΩ resistor.
• For proper DM641/DM640 device operation, the GP0[0] [pin M5] (IPD) must remain low at device reset.
2.1.1 Peripheral Selection at Device Reset
On the DM641/DM640 devices there are NO peripherals sharing the same pins (internally muxed, yet mutually
exclusive) that are controlled via external pins.
• EMAC and MDIO peripherals
The MAC_EN pin is latched at reset. This pin determines specific peripheral selection, summarized in
Table 2−1.
Device Configurations
T able 2−1. MAC_EN Peripheral Selection (EMAC and MDIO)
PERIPHERAL SELECTION PERIPHERALS SELECTED
MAC_EN
Pin [C5]
0 √ Disabled
1 √ √
HPI Data
(16-Bit) [DM641 Only]
EMAC and MDIO
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
67
Page 68

Device Configurations
2.1.2 Device Configuration at Device Reset
Table 2−2 describes the DM641/DM640 device configuration pins, which are set up via external
pullup/pulldown resistors through the specified EMIFA address bus pins (AEA[22:19]) and the
TOUT1/LENDIAN pin (all of which are latched during device reset).
T able 2−2. DM641/DM640 Device Configuration Pins
(TOUT1/LENDIAN, AEA[22:19], and TOUT0/MAC_EN)
CONFIGURATION
PIN
TOUT1/LENDIAN B5
AEA[22:21]
AEA[20:19]
TOUT0/MAC_EN C5
NO. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Device Endian mode (LEND)
0 – System operates in Big Endian mode
1 − System operates in Little Endian mode (default)
Bootmode [1:0]
[U23,
V24]
[V25,
V26]
− Boot mode (AEA[22:21]):
00 – No boot (default mode)
01 − HPI [DM641 only]; Reserved [For DM640 device]
10 − Reserved
11 − EMIFA 8−bit ROM boot
EMIFA input clock select
Clock mode select for EMIFA (AECLKIN_SEL[1:0])
00 – AECLKIN (default mode)
01 − CPU/4 Clock Rate
10 − CPU/6 Clock Rate
11 − Reserved
Peripheral Selection
1 − EMAC and MDIO enabled
0 − EMAC and MDIO disabled
2.2 Configurations After Reset
2.2.1 Peripheral Selection After Device Reset
68
Video Ports, McBSP1, McBSP0, McASP0, and I2C0
The DM641/DM640 device has designated registers for peripheral configuration (PERCFG), device status
(DEVSTAT), and JTAG identification (JTAGID). These registers are part of the Device Configuration module
and are mapped to a 4K block memory starting at 0x01B3F000. The CPU accesses these registers via the
CFGBUS.
The peripheral configuration register (PERCFG), allows the user to control the peripheral selection of the
Video Ports (VP0 and VP1 [DM641 only]) McBSP0, McBSP1, McASP0, and I2C0 peripherals. For more
detailed information on the PERCFG register control bits, see Figure 2−1 and Table 2−3.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 69
Device Configurations
31 24
Reserved
R-0
23 16
Reserved
R-0
15 8
Reserved
R-0
76543210
Reserved Reserved VP1EN
R-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-0
Legend: R = Read only; R/W = Read/Write; -n = value after reset
†
The DM640 device does not support the VP1 peripheral; therefore, this bit is Reserved.
†
VP0EN I2C0EN MCBSP1EN MCBSP0EN MCASP0EN
Figure 2−1. Peripheral Configuration Register (PERCFG) [Address Location: 0x01B3F000 − 0x01B3F003]
Table 2−3. Peripheral Configuration (PERCFG) Register Selection Bit Descriptions
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
31:6 Reserved Reserved. Read-only, writes have no effect.
VP1 Enable bit [DM641 only].
Determines whether the VP1 peripheral is enabled or disabled.
0 = VP1 is disabled, and the module is powered down (default).
5 VP1EN
4 VP0EN
3 I2C0EN
2 MCBSP1EN
(This feature allows power savings by disabling the peripheral when not in use.)
1 = VP1 is enabled.
The DM640 device does not support the VP1 peripheral; therefore, this bit is Reserved.
VP0 Enable bit.
Determines whether the VP0 peripheral is enabled or disabled.
0 = VP0 is disabled, and the module is powered down (default).
(This feature allows power savings by disabling the peripheral when not in use.)
1 = VP0 is enabled.
Inter-integrated circuit 0 (I2C0) enable bit.
Selects whether I2C0 peripheral is enabled or disabled (default).
0 = I2C0 is disabled, and the module is powered down (default).
1 = I2C0 is enabled.
Video Port 1 (VP1) lower data pins vs. McBSP1 enable bit.
Selects whether VP1 peripheral lower-data pins or the McBSP1 peripheral is enabled.
0 = VP1 lower-data pins are enabled and function (if VP1EN=1), McBSP1 is disabled; the
remaining VP1 upper-data pins are dependent on the MCASP0EN bit and the VP1EN bit
settings.
1 = McBSP1 is enabled, VP1 lower-data pin functions are disabled (default).
For a graphic (logic) representation of this Peripheral Configuration (PERCFG) Register selection bit and
the signal pins controlled/selected, see Figure 2−2.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
69
Page 70

Device Configurations
Table 2−3. Peripheral Configuration (PERCFG) Register Selection Bit Descriptions (Continued)
DESCRIPTIONNAMEBIT
Video Port 0 (VP0) lower data pins vs. McBSP0 enable bit.
Selects whether VP0 peripheral lower-data pins or the McBSP1 peripheral is enabled.
0 = VP0 lower-data pins are enabled and function (if VP0EN=1), McBSP0 is disabled; the
1 MCBSP0EN
For a graphic (logic) representation of this Peripheral Configuration (PERCFG) Register selection bit and
the signal pins controlled/selected, see Figure 2−2.
McASP0 select bit.
Selects whether the McASP0 peripheral or the VP0 and VP1 upper-data pins are enabled.
0 MCASP0EN
For proper DM641/DM640 device operation, the pin must be set to a “1”.
remaining VP0 upper-data pins are dependent on the MCASP0EN bit and the VP1EN bit
settings.
1 = McBSP0 is enabled, VP0 lower-data pin functions are disabled (default).
0 = Reserved [default].
1 = McASP0 is enabled.
McBSP0EN [PERCFG.1]
VP0 Data (8 pins)
VP0D[6:0] Muxed
VP0D[7] Standalone
VP1 Data (8 pins)
VP1D[6:0] Muxed
VP1D[7] Standalone
†
Consists of: VP0D[6]/CLKR0, VP0D[5]/FSR0, VP0D[4]/DR0, VP0D[3]/CLKS0, VP0D[2]/DX0, VP0D[1]/FSX0, VP0D[0]/CLKX0.
‡
Consists of: VP1D[6]/CLKR1, VP1D[5]/FSR1, VP1D[4]/DR1, VP1D[3]/CLKS1, VP1D[2]/DX1, VP1D[1]/FSX1, VP1D[0]/CLKX1.
†
‡
1
0
McBSP1EN [PERCFG.2]
1
0
McBSP0
VP0 (Channel A)
McBSP1
VP1 (Channel A) [DM641 Only]
Figure 2−2. VP1, VP0, McBSP1, and McBSP0 Pin Muxing
70
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 71

2.3 Peripheral Configuration Lock
By default, the McASP0, VP0, VP1 [DM641 only], and I2C peripherals are disabled on power up. In order to
use these peripherals on the DM641/DM640 device, the peripheral must first be enabled in the Peripheral
Configuration register (PERCFG). Software muxed pins should not be programmed to switch
functionalities during run-time. Care should also be taken to ensure that no accesses are being
performed before disabling the peripherals. To help minimize power consumption in the DM641/DM640
device, unused peripherals may be disabled.
Figure 2−3 shows the flow needed to enable (or disable) a given peripheral on the DM641/DM640 devices.
Device Configurations
Unlock the PERCFG Register
Using the PCFGLOCK Register
Write to
PERCFG Register
to Enable/Disable Peripherals
Read from
PERCFG Register
Wait 128 CPU Cycles Before
Accessing Enabled Peripherals
Figure 2−3. Peripheral Enable/Disable Flow Diagram
A 32-bit key (value = 0x10C0010C) must be written to the Peripheral Configuration Lock register
(PCFGLOCK) in order to unlock access to the PERCFG register. Reading the PCFGLOCK register
determines whether the PERCFG register is currently locked (LOCKSTAT bit = 1) or unlocked (LOCKSTAT
bit = 0), see Figure 2−4. A peripheral can only be enabled when the PERCFG register is “unlocked”
(LOCKSTAT bit = 0).
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
71
Page 72

Device Configurations
Read Accesses
31 10
Reserved LOCKSTAT
R-0 R-1
Write Accesses
31 0
LOCK
W-0
Legend: R = Read only; R/W = Read/Write; -n = value after reset
Figure 2−4. PCFGLOCK Register Diagram [Address Location: 0x01B3 F018] − Read/Write Accesses
T able 2−4. PCFGLOCK Register Selection Bit Descriptions − Read Accesses
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
31:1 Reserved Reserved. Read-only, writes have no effect.
Lock status bit.
Determines whether the PERCFG register is locked or unlocked.
0 LOCKSTAT
0 = Unlocked, read accesses to the PERCFG register allowed.
1 = Locked, write accesses to the PERCFG register do not modify the register state [default].
Reads are unaffected by Lock Status.
Table 2−5. PCFGLOCK Register Selection Bit Descriptions − Write Accesses
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
31:0 LOCK
Lock bits.
0x10C0010C = Unlocks PERCFG register accesses.
Any write to the PERCFG register will automatically relock the register. In order to avoid the unnecessary
overhead of multiple unlock/enable sequences, all peripherals should be enabled with a single write to the
PERCFG register with the necessary enable bits set.
Prior to waiting 128 CPU cycles, the PERCFG register should be read. There is no direct correlation between
the CPU issuing a write to the PERCFG register and the write actually occurring. Reading the PERCFG
register after the write is issued forces the CPU to wait for the write to the PERCFG register to occur .
Once a peripheral is enabled, the DSP (or other peripherals such as the HPI) must wait a minimum of 128 CPU
cycles before accessing the enabled peripheral. The user must ensure that no accesses are performed to a
peripheral while it is disabled.
72
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 73

Device Configurations
00 – Bypass (x1) (default mode)
00 – Bypass (x1) (default mode)
00 – No boot (default mode)
2.4 Device Status Register Description
The device status register depicts the status of the device peripheral selection. For the actual register bit
names and their associated bit field descriptions, see Figure 2−5 and Table 2−6.
31 24
Reserved
R-0
23 16
Reserved
R-0
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Reserved MAC_EN Reserved Reserved Reserved
R-0 R-x R-0 R-x R-0
76543210
Reserved CLKMODE1 CLKMODE0 LENDIAN BOOTMODE1 BOOTMODE0 AECLKINSEL1 AECLKINSEL0
R-x R-x R-x R-x R-x R-x R-x R-x
Legend: R = Read only; R/W = Read/Write; -n = value after reset
Figure 2−5. Device Status Register (DEVSTAT) Description − 0x01B3 F004
T able 2−6. Device Status (DEVSTAT) Register Selection Bit Descriptions
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
31:12 Reserved Reserved. Read-only, writes have no effect.
EMAC enable bit.
11 MAC_EN
10:7 Reserved Reserved. Read-only, writes have no effect.
6 CLKMODE1
5 CLKMODE0
4 LENDIAN
3 BOOTMODE1
Shows the status of whether EMAC peripheral is enabled or disabled (default).
0 = EMAC is disabled, and the module is powered down (default).
1 = EMAC is enabled.
Clock mode select bits
Shows the status of whether the CPU clock frequency equals the input clock frequency X1 (Bypass), x6,
or x12.
Clock mode select for CPU clock frequency (CLKMODE[1:0])
01 − x6
10 − x12
11 − Reserved
For more details on the CLKMODE pins and the PLL multiply factors, see the Clock PLL section of this
data sheet.
Device Endian mode (LEND)
Shows the status of whether the system is operating in Big Endian mode or Little Endian mode (default).
0 – System is operating in Big Endian mode
1 − System is operating in Little Endian mode (default)
Bootmode configuration bits
Shows the status of what device bootmode configuration is operational.
Bootmode [1:0]
2 BOOTMODE0
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
01 − HPI [DM641 only]; Reserved [For DM640 device]
10 − Reserved
11 − EMIFA 8−bit ROM boot
73
Page 74

Device Configurations
00 – AECLKIN (default mode)
T able 2−6. Device Status (DEVSTAT) Register Selection Bit Descriptions (Continued)
1 AECLKINSEL1
DESCRIPTIONNAMEBIT
EMIFA input clock select
Shows the status of what clock mode is enabled or disabled for the EMIF.
Clock mode select for EMIFA (AECLKIN_SEL[1:0])
0 AECLKINSEL0
01 − CPU/4 Clock Rate
10 − CPU/6 Clock Rate
11 − Reserved
74
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 75

2.5 Multiplexed Pin Configurations
DEFAULT
DEFAULT
DEFAULT
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
s
properly configured.
Muxed on the DM641 device only
l;
therefore, the McBSP1 peripheral pins are standalone
VP1EN bit = 0
peripheral functions, not muxed.]
functions
MCBSP1EN bit = 1
(enabled)
(enabled)
reset (MCBSP1EN bit = 1).
To enable the Video Port 1 data pins, the VP1EN bit in the
To enable the Video Port 1 data pins, the VP1EN bit in the
VP0EN bit = 0
By default, the McBSP0 peripheral function is enabled upon
functions
MCBSP0EN bit = 1
(enabled)
To enable the Video Port 0 data pins, the VP0EN bit in the
PERCFG register must be set to a 1.
(enabled)
PERCFG register must be set to a 1.
Multiplexed pins are pins that are shared by more than one peripheral and are internally multiplexed. Some
of these pins are configured by software, and the others are configured by external pullup/pulldown resistors
only at reset. Those muxed pins that are configured by software should not be programmed to switch
functionalities during run-time. Those muxed pins that are configured by external pullup/pulldown resistors
are mutually exclusive; only one peripheral has primary control of the function of these pins after reset.
Table 2−7 identifies the multiplexed pins on the DM641/DM640 device; shows the default (primary) function
and the default settings after reset; and describes the pins, registers, etc. necessary to configure specific
multiplexed functions.
T able 2−7. DM641/DM640 Device Multiplexed Pin Configurations
MULTIPLEXED PINS
NAME NO.
CLKOUT4/GP0[1] D6 CLKOUT4 GP1EN = 0 (disabled)
FUNCTION
SETTING
Device Configurations
These pins are software-configurable. To use these pins a
GPIO pins, the GPxEN bits in the GPIO Enable Register and
the GPxDIR bits in the GPIO Direction Register must be
CLKOUT6/GP0[2] C6 CLKOUT6 GP2EN = 0 (disabled)
VP1D[6]/CLKR1 AD8
VP1D[5]/FSR1 AC7
VP1D[4]/DR1 AD7
VP1D[3]/CLKS1 AE7
VP1D[2]/DX1 AC6
VP1D[1]/FSX1 AD6
VP1D[0]/CLKX1 AE6
VP0D[6]/CLKR0 AE15
VP0D[5]/FSR0 AB16
VP0D[4]/DR0 AC16
VP0D[3]/CLKS0 AD16
VP0D[2]/DX0 AE16
VP0D[1]/FSX0 AF16
VP0D[0]/CLKX0 AF17
McBSP1
McBSP0
VP1EN bit = 0
(disabled)
VP0EN bit = 0
(disabled)
GPxEN = 1: GPx pin enabled
GPxDIR = 0: GPx pin is an input
GPxDIR = 1: GPx pin is an output
Muxed on the DM641 device only
[The DM640 device does not support the VP1 periphera
By default, the McBSP1 peripheral, function is enabled upon
PERCFG register must be set to a 1.
By default, the McBSP0 peripheral function is enabled upon
reset (MCBSP0EN bit = 1).
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
75
Page 76

Device Configurations
2.6 Debugging Considerations
It is recommended that external connections be provided to device configuration pins, including
TOUT1/LENDIAN, AEA[22:19] and TOUT0/MAC_EN. Although internal pullup/pulldown resistors exist on
these pins, providing external connectivity adds convenience to the user in debugging and flexibility in
switching operating modes.
Internal pullup/pulldown resistors also exist on the non-configuration pins on the AEA bus (AEA[18:0]). Do not
oppose the internal pullup/pulldown resistors on these non-configuration pins with external pullup/pulldown
resistors. If an external controller provides signals to these non-configuration pins, these signals must be
driven to the default state of the pins at reset, or not be driven at all.
For the internal pullup/pulldown resistors for all device pins, see the terminal functions table.
2.7 Configuration Examples
Figure 2−6 through Figure 2−9 illustrate examples of peripheral selections that are configurable on the DM641
and DM640 devices.
76
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 77

HD[15:0]
,
,
V
HRDY, HINT
HCNTL0, HCNTL1,
HHWIL, HAS, HR/W,
HCS, HDS1, HDS2
MTXD[3:0], MTXEN
MRXD[3:0], MRXER,
MRXDV, MCOL, MCRS,
MTCLK, MRCLK
MDIO, MDCLK
16
HPI
(16-Bit)
EMAC
MDIO
EMIFA
Clock
and
System
TIMER2
TIMER1
32
Device Configurations
AED[31:0]
AECLKIN, AARDY, AHOLD
AEA[22:3], ACE[3:0], ABE[3:0]
AECLKOUT1, AECLKOUT2,
ASDCKE, ASOE3, APDT,
AHOLDA, ABUSREQ,
AARE/ASDCAS/ASADS/ASRE
AAOE/ASDRAS/ASOE,
AAWE/ASDWE/ASWE
CLKIN,
CLKMODE0, CLKMODE1
CLKOUT4, CLKOUT6, PLL
TINP1
TOUT1/LENDIAN
STCLK
VP0CLK0
VP0CLK1,
VP0CTL[2:0],
VP0D[7:0]
AHCLKX0, AFSX0,
ACLKX0, AMUTE0,
AMUTEIN0,
AHCLKR0, AFSR0,
ACLKR0
AXR0[3:0]
STCLK
VP1CLK0
VP1CLK1,
VP1CTL[2:0],
VP1D[7:0]
†
VP0
(8-Bit)
McBSP0
McASP0 Control
McASP0 Data
McBSP1
†
VP1
(8-Bit)
Shading denotes a peripheral module not available for this configuration.
†
STCLK supports both video ports (VP1 and VP0).
TIMER0
GP0
and
EXT_INT
I2C0
VIC
TINP0
TOUT0/MAC_EN
GP0[3:0]
GP0[7:4]
SCL0
SDA0
VDAC
PERCFG Register Value: 0x0000 0039
Extenal Pins: TOUT0/MAC_EN = 1
Figure 2−6. Configuration Example A for DM641
(2 8-Bit Video Ports + 1 McASP0 + VIC + I2C0 + EMIF)
[TBD Application]
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
77
Page 78

Device Configurations
,
,
V
HD[15:0]
HRDY, HINT
HCNTL0, HCNTL1,
HHWIL, HAS, HR/W,
HCS, HDS1, HDS2
MTXD[3:0], MTXEN
MRXD[3:0], MRXER,
MRXDV, MCOL, MCRS,
MTCLK, MRCLK
MDIO, MDCLK
16
HPI
(16-Bit)
EMAC
MDIO
EMIFA
Clock
and
System
TIMER2
TIMER1
32
AED[31:0]
AECLKIN, AARDY, AHOLD
AEA[22:3], ACE[3:0], ABE[3:0]
AECLKOUT1, AECLKOUT2,
ASDCKE, ASOE3, APDT,
AHOLDA, ABUSREQ,
AARE/ASDCAS/ASADS/ASRE
AAOE/ASDRAS/ASOE,
AAWE/ASDWE/ASWE
CLKIN,
CLKMODE0, CLKMODE1
CLKOUT4, CLKOUT6, PLL
TINP1
TOUT1/LENDIAN
CLKR0, FSR0, DR0,
CLKS0, DX0, FSX0,
CLKX0
AHCLKX0, AFSX0,
ACLKX0, AMUTE0,
AMUTEIN0, AHCLKR0,
AFSR0, ACLKR0
AXR0[3:0]
CLKR1, FSR1, DR1,
CLKS1, DX1, FSX1,
CLKX1
VP0
(8-Bit)
McBSP0
McASP0 Control
McASP0 Data
McBSP1
VP1
(8-Bit)
Shading denotes a peripheral module not available for this configuration.
TIMER0
GP0
and
EXT_INT
I2C0
VIC
TINP0
TOUT0/MAC_EN
GP0[3:0]
GP0[7:4]
SCL0
SDA0
VDAC
PERCFG Register Value: 0x0000 000F
Extenal Pins: TOUT0/MAC_EN = 1
Figure 2−7. Configuration Example B for DM641
(1 McASP0 + 2 McBSPs + VIC + I2C0 + EMIF)
78
[TBD Application]
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 79
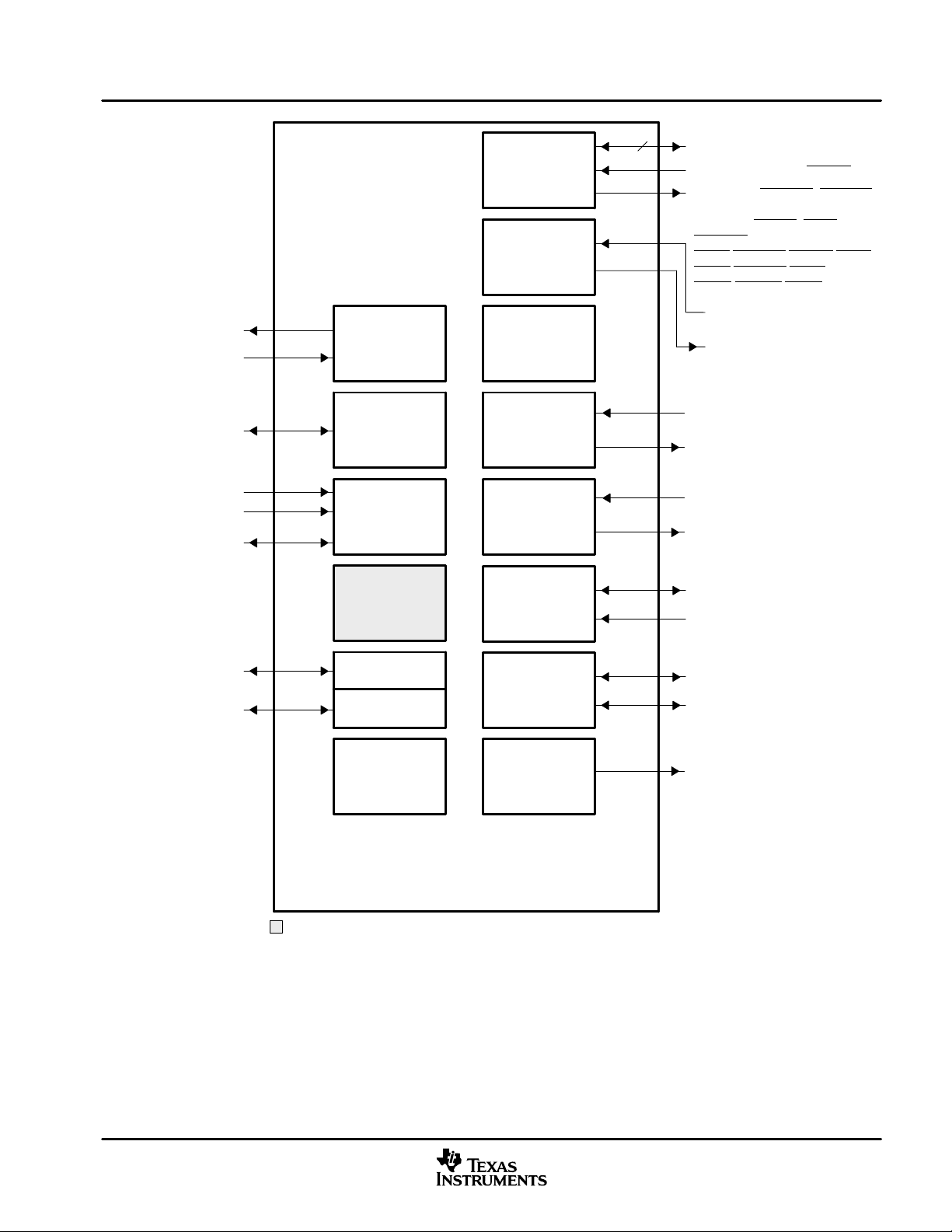
MTXD[3:0], MTXEN
,
,
V
MRXD[3:0], MRXER,
MRXDV, MCOL, MCRS,
MTCLK, MRCLK
MDIO, MDCLK
EMAC
MDIO
EMIFA
Clock
and
System
TIMER2
TIMER1
32
Device Configurations
AED[31:0]
AECLKIN, AARDY, AHOLD
AEA[22:3], ACE[3:0], ABE[3:0]
AECLKOUT1, AECLKOUT2,
ASDCKE, ASOE3, APDT,
AHOLDA, ABUSREQ,
AARE/ASDCAS/ASADS/ASRE
AAOE/ASDRAS/ASOE,
AAWE/ASDWE/ASWE
CLKIN,
CLKMODE0, CLKMODE1
CLKOUT4, CLKOUT6, PLL
TINP1
TOUT1/LENDIAN
STCLK
VP0CLK0
VP0CLK1,
VP0CTL[2:0],
VP0D[7:0]
AHCLKX0, AFSX0,
ACLKX0, AMUTE0,
AMUTEIN0,
AHCLKR0, AFSR0,
ACLKR0
AXR0[3:0]
VP0
(8-Bit)
McBSP0
McASP0 Control
McASP0 Data
McBSP1
Shading denotes a peripheral module not available for this configuration.
TIMER0
GP0
and
EXT_INT
I2C0
VIC
TINP0
TOUT0/MAC_EN
GP0[3:0]
GP0[7:4]
SCL0
SDA0
VDAC
PERCFG Register Value: 0x0000 0019
Extenal Pins: TOUT0/MAC_EN = 1
Figure 2−8. Configuration Example A for DM640
(1 8-Bit Video Port + 1 McASP0 + VIC + I2C0 + EMIF)
[TBD Application]
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
79
Page 80

Device Configurations
,
,
V
MTXD[3:0], MTXEN
MRXD[3:0], MRXER,
MRXDV, MCOL, MCRS,
MTCLK, MRCLK
MDIO, MDCLK
EMAC
MDIO
EMIFA
Clock
and
System
TIMER2
TIMER1
32
AED[31:0]
AECLKIN, AARDY, AHOLD
AEA[22:3], ACE[3:0], ABE[3:0]
AECLKOUT1, AECLKOUT2,
ASDCKE, ASOE3, APDT,
AHOLDA, ABUSREQ,
AARE/ASDCAS/ASADS/ASRE
AAOE/ASDRAS/ASOE,
AAWE/ASDWE/ASWE
CLKIN,
CLKMODE0, CLKMODE1
CLKOUT4, CLKOUT6, PLL
TINP1
TOUT1/LENDIAN
CLKR0, FSR0, DR0,
CLKS0, DX0, FSX0,
CLKX0
AHCLKX0, AFSX0,
ACLKX0, AMUTE0,
AMUTEIN0, AHCLKR0,
AFSR0, ACLKR0
AXR0[3:0]
CLKR1, FSR1, DR1,
CLKS1, DX1, FSX1,
CLKX1
VP0
(8-Bit)
McBSP0
McASP0 Control
McASP0 Data
McBSP1
Shading denotes a peripheral module not available for this configuration.
TIMER0
GP0
and
EXT_INT
I2C0
VIC
TINP0
TOUT0/MAC_EN
GP0[3:0]
GP0[7:4]
SCL0
SDA0
VDAC
PERCFG Register Value: 0x0000 000F
Extenal Pins: TOUT0/MAC_EN = 1
Figure 2−9. Configuration Example B for DM640
(1 McASP0 + 2 McBSPs + VIC + I2C0 + EMIF)
80
[TBD Application]
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 81

3 Device Operating Conditions
CV
Device Operating Conditions
3.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Case Temperature Range (Unless Otherwise
Noted)
†
Supply voltage ranges: CVDD (see Note 1) − 0.3 V to 1.8 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DVDD (see Note 1) −0.3 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input voltage ranges: V
Output voltage ranges: V
I
O
−0.3 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
−0.3 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating case temperature ranges, TC: (default) 0_C to 90_C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTE 1: All voltage values are with respect to V
stg
SS
.
−65_C to 150_C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, Core (-400 and -500 devices)
DD
Supply voltage, Core (-600 device)
DV
V
SS
V
IH
V
IL
V
OS
V
US
T
C
‡
Future variants of the C64x DSPs may operate at voltages ranging from 0.9 V to 1.4 V to provide a range of system power/performance options.
TI highly recommends that users design-in a supply that can handle multiple voltages within this range (i.e., 1.2 V, 1.25 V, 1.3 V, 1.35 V, 1.4 V
with ± 3% tolerances) by implementing simple board changes such as reference resistor values or input pin configuration modifications. Examples
of such supplies include the PT4660, PT5500, PT5520, PT6440, and PT6930 series from Power Trends, a subsidiary of Texas Instruments. Not
incorporating a flexible supply may limit the system’s ability to easily adapt to future versions of C64x devices.
§
The absolute maximum ratings should not be exceeded for more than 30% of the cycle period.
Supply voltage, I/O 3.14 3.3 3.46 V
DD
Supply ground 0 0 0 V
High-level input voltage 2 V
Low-level input voltage 0.8 V
Maximum voltage during overshoot (see Figure 4−4) 4.3
Maximum voltage during undershoot (see Figure 4−5) −1.0
Operating case temperature 0 90 _C
‡
‡
1.14 1.2 1.26 V
1.36 1.4 1.44 V
§
§
V
V
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
81
Page 82

Device Operating Conditions
IIInput current
OL
IOLLow-level output current
CDD
I
CDD
Core supply current
DDD
I
DDD
I/O supply current
3.3 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Ranges of Supply Voltage and Operating
Case Temperature (Unless Otherwise Noted)
OH
OL
†
= MAX
= MAX
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
¶
¶
2.4 V
0.4 V
±10 uA
50 100 150 uA
−150 −100 −50 uA
−8 mA
8 mA
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
V
V
I
High-level output voltage DVDD = MIN, I
OH
Low-level output voltage DVDD = MIN, I
OL
I
Input current
VI = VSS to DVDD no opposing internal
resistor
VI = VSS to DVDD opposing internal
pullup resistor
VI = VSS to DVDD opposing internal
pulldown resistor
‡
‡
EMIF, CLKOUT4, CLKOUT6, EMUx −16 mA
I
High-level output current
OH
Video Ports, Timer, TDO, GPIO
(Excluding GP0[2,1]), McBSP
HPI [DM641] −0.5 mA
EMIF, CLKOUT4, CLKOUT6, EMUx 16 mA
Video Ports, Timer, TDO, GPIO
I
Low-level output current
(Excluding GP0[2,1]), McBSP
SCL0 and SDA0 3 mA
HPI [DM641] 1.5 mA
I
Off-state output current VO = DV
OZ
or 0 V ±10 uA
DD
CVDD = 1.4 V, CPU clock = 600 MHz 890 mA
I
Core supply current
§
CVDD = 1.2 V, CPU clock = 500 MHz 620 mA
CVDD = 1.2 V, CPU clock = 400 MHz 510 mA
DVDD = 3.3 V, CPU clock = 600 MHz 210 mA
I
I/O supply current
§
DVDD = 3.3 V, CPU clock = 500 MHz 165 mA
DVDD = 3.3 V, CPU clock = 400 MHz 160 mA
C
C
†
‡
§
Input capacitance 10 pF
i
Output capacitance 10 pF
o
For test conditions shown as MIN, MAX, or NOM, use the appropriate value specified in the recommended operating conditions table.
Applies only to pins with an internal pullup (IPU) or pulldown (IPD) resistor.
Measured with average activity (50% high/50% low power) at 25°C case temperature and 133-MHz EMIF for -600 speed (100-MHz EMIF for
-500 and -400 speeds). This model represents a device performing high-DSP-activity operations 50% of the time, and the remainder performing
low-DSP-activity operations. The high/low-DSP-activity models are defined as follows:
High-DSP-Activity Model:
CPU: 8 instructions/cycle with 2 LDDW instructions [L1 Data Memory: 128 bits/cycle via LDDW instructions;
L1 Program Memory: 256 bits/cycle; L2/EMIF EDMA: 50% writes, 50% reads to/from SDRAM (50% bit-switching)]
McBSP: 2 channels at E1 rate
Timers: 2 timers at maximum rate
Low-DSP-Activity Model:
CPU: 2 instructions/cycle with 1 LDH instruction [L1 Data Memory: 16 bits/cycle; L1 Program Memory: 256 bits per 4 cycles;
L2/EMIF EDMA: None]
McBSP: 2 channels at E1 rate
Timers: 2 timers at maximum rate
The actual current draw is highly application-dependent. For more details on core and I/O activity, refer to the TMS320DMx Power Consumption
Summary application report (literature number SPRA962).
¶
Single pin driving IOH/IOL = MAX.
82
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 83

DM641/DM640 Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
4 DM641/DM640 Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
4.1 Parameter Information
4.1.1 Parameter Information Device-Specific Information
Tester Pin Electronics
42 Ω 3.5 nH
4.0 pF 1.85 pF
NOTE: The data sheet provides timing at the device pin. For output timing analysis, the tester pin electronics and its transmission line effects
must be taken into account. A transmission line with a delay of 2 ns or longer can be used to produce the desired transmission line effect.
The transmission line is intended as a load only. It is not necessary to add or subtract the transmission line delay (2 ns or longer) from
the data sheet timings.
Input requirements in this data sheet are tested with an input slew rate of < 4 Volts per nanosecond (4 V/ns) at the device pin.
Transmission Line
Z0 = 50 Ω
(see note)
Data Sheet Timing Reference Point
Output
Under
Test
Device Pin
(see note)
Figure 4−1. Test Load Circuit for AC Timing Measurements
The load capacitance value stated is only for characterization and measurement of AC timing signals. This
load capacitance value does not indicate the maximum load the device is capable of driving.
4.1.1.1 Signal Transition Levels
All input and output timing parameters are referenced to 1.5 V for both “0” and “1” logic levels.
Figure 4−2. Input and Output Voltage Reference Levels for AC Timing Measurements
All rise and fall transition timing parameters are referenced to VIL MAX and VIH MIN for input clocks, V
and VOH MIN for output clocks.
Figure 4−3. Rise and Fall Transition Time Voltage Reference Levels
4.1.1.2 Signal Transition Rates
All timings are tested with an input edge rate of 4 Volts per nanosecond (4 V/ns).
V
= 1.5 V
ref
V
= VIH MIN (or VOH MIN)
ref
V
= VIL MAX (or VOL MAX)
ref
OL
MAX
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
83
Page 84

Parameter Information
4.1.1.3 AC Transient Rise/Fall Time Specifications
Figure 4−4 and Figure 4−5 show the AC transient specifications for Rise and Fall Time. For device-specific
information on these values, refer to the Recommended Operating Conditions section of this Data Sheet.
†
t = 0.3 t
(max)
c
Ground
Figure 4−4. AC Transient Specification Rise Time
†
tc = the peripheral cycle time in nanoseconds (ns).
VUS (max)
Minimum
Risetime
Waveform
Valid Region
t = 0.3 tc(max)
VOS (max)
VIH (min)
†
VIL (max)
Ground
Figure 4−5. AC Transient Specification Fall Time
†
tc = the peripheral cycle time in nanoseconds (ns).
4.1.1.4 Timing Parameters and Board Routing Analysis
The timing parameter values specified in this data sheet do not include delays by board routings. As a good
board design practice, such delays must always be taken into account. Timing values may be adjusted by
increasing/decreasing such delays. TI recommends utilizing the available I/O buffer information specification
(IBIS) models to analyze the timing characteristics correctly. To properly use IBIS models to attain accurate
timing analysis for a given system, see the Using IBIS Models for Timing Analysis application report (literature
number SPRA839). If needed, external logic hardware such as buffers may be used to compensate any timing
differences.
For inputs, timing is most impacted by the round-trip propagation delay from the DSP to the external device
and from the external device to the DSP. This round-trip delay tends to negatively impact the input setup time
margin, but also tends to improve the input hold time margins (see Table 4−1 and Figure 4−6).
Figure 4−6 represents a general transfer between the DSP and an external device. The figure also represents
board route delays and how they are perceived by the DSP and the external device.
84
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 85

Table 4−1. Board-Level Timing Example (see Figure 4−6)
NO. DESCRIPTION
1 Clock route delay
2 Minimum DSP hold time
3 Minimum DSP setup time
4 External device hold time requirement
5 External device setup time requirement
6 Control signal route delay
7 External device hold time
8 External device access time
9 DSP hold time requirement
10 DSP setup time requirement
11 Data route delay
ECLKOUTx
(Output from DSP)
(Input to External Device)
(Input to External Device)
(Output from External Device)
† Control signals include data for Writes.
‡Data signals are generated during Reads from an external device.
ECLKOUTx
Control Signals†
(Output from DSP)
Control Signals
Data Signals‡
Data Signals‡
(Input to DSP)
3
6
8
Power Supplies
1
2
4
5
7
9
11
10
Figure 4−6. Board-Level Input/Output Timings
4.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
All clocks and control signals must transition between VIH and VIL (or between VIL and VIH) in a monotonic
manner.
4.3 Power Supplies
For more information regarding TI’s power management products and suggested devices to power TI DSPs,
visit www.ti.com/dsppower.
4.3.1 Power-Supply Sequencing
TI DSPs do not require specific power sequencing between the core supply and the I/O supply. However,
systems should be designed to ensure that neither supply is powered up for extended periods of time
(>1 second) if the other supply is below the proper operating voltage.
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
85
Page 86

Power Supplies
4.3.2 Power-Supply Design Considerations
A dual-power supply with simultaneous sequencing can be used to eliminate the delay between core and I/O
power up. A Schottky diode can also be used to tie the core rail to the I/O rail (see Figure 4−7).
I/O Supply
Core Supply
GND
Figure 4−7. Schottky Diode Diagram
Schottky
Diode
DV
CV
V
DD
C6000
DSP
DD
SS
Core and I/O supply voltage regulators should be located close to the DSP (or DSP array) to minimize
inductance and resistance in the power delivery path. Additionally, when designing for high-performance
applications utilizing the C6000™ platform of DSPs, the PC board should include separate power planes for
core, I/O, and ground, all bypassed with high-quality low-ESL/ESR capacitors.
4.3.3 Power-Supply Decoupling
In order to properly decouple the supply planes from system noise, place as many capacitors (caps) as
possible close to the DSP. Assuming 0603 caps, the user should be able to fit a total of 60 caps, 30 for the
core supply and 30 for the I/O supply. These caps need to be close to the DSP power pins, no more than
1.25 cm maximum distance to be effective. Physically smaller caps, such as 0402, are better because of their
lower parasitic inductance. Proper capacitance values are also important. Small bypass caps (near 560 pF)
should be closest to the power pins. Medium bypass caps (220 nF or as large as can be obtained in a small
package) should be next closest. TI recommends no less than 8 small and 8 medium caps per supply (32 total)
be placed immediately next to the BGA vias, using the “interior” BGA space and at least the corners of the
“exterior”.
Eight larger caps (4 for each supply) can be placed further away for bulk decoupling. Large bulk caps (on the
order of 100 μF) should be furthest away (but still as close as possible). No less than 4 large caps per supply
(8 total) should be placed outside of the BGA.
Any cap selection needs to be evaluated from a yield/manufacturing point-of-view. As with the selection of any
component, verification of capacitor availability over the product’s production lifetime should be considered.
86
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 87

4.3.4 Peripheral Power-Down Operation
The DM641/DM640 device can be powered down in three ways:
• Power-down due to pin configuration
• Power-down due to software configuration − relates to the default state of the peripheral configuration bits
in the PERCFG register .
• Power-down during run-time via software configuration
On the DM641/DM640 device, the EMAC and MDIO peripherals are controlled (selected) at the pin level
during chip reset (e.g., using the MAC_EN pin).
The McASP0, McBSP0, McBSP1, VP0, VP1 [DM641 only], and I2C0 peripheral functions are selected via the
peripheral configuration (PERCFG) register bits.
For more detailed information on the peripheral configuration pins and the PERCFG register bits, see the
Device Configurations section of this document.
4.3.5 Power-Down Modes Logic
Figure 4−8 shows the power-down mode logic on the DM641/DM640.
CLKOUT4
Power Supplies
CLKOUT6
Internal Clock Tree
Clock
Distribution
and Dividers
PD1
PD2
CPU
IFR
IER
CSR
Internal
Peripherals
TMS320DM641/DM640
†
PD3
Power-
Down
Logic
PWRD
Clock
PLL
CLKIN RESET
†
External input clocks, with the exception of CLKIN, are not gated by the power-down mode logic.
Figure 4−8. Power-Down Mode Logic
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
87
Page 88

Power Supplies
4.3.6 Triggering, Wake-up, and Effects
The power-down modes and their wake-up methods are programmed by setting the PWRD field (bits 15−10)
of the control status register (CSR). The PWRD field of the CSR is shown in Figure 4−9 and described in
Table 4−2. When writing to the CSR, all bits of the PWRD field should be set at the same time. Logic 0 should
be used when writing to the reserved bit (bit 15) of the PWRD field. The CSR is discussed in detail in the
TMS320C6000 CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide (literature number SPRU189).
31 16
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Enable or
Reserved
R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
7 0
Legend: R/W−x = Read/write reset value
NOTE: The shadowed bits are not part of the power-down logic discussion and therefore are not covered here. For information on these other
bit fields in the CSR register, see the TMS320C6000 CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide (literature number SPRU189).
Non-Enabled
Interrupt Wake
Enabled
Interrupt Wake
PD3 PD2 PD1
Figure 4−9. PWRD Field of the CSR Register
A delay of up t o n ine cl ock cycles may occur a fter the i nstruction that s ets t he P WRD b its i n the C SR b efore t he
PD mode takes effect. As bes t practic e, NOPs should be padded after the PWRD bits are set in the CSR to
account for this delay.
If PD1 mode is terminated by a non-enabled interrupt, the program execution returns to the instruction where
PD1 took ef fect. I f P D1 m ode i s t erminated b y a n e nabled i nterrupt, the i nterrupt service routine w ill b e e xecuted
first, then the program execution returns to the instruction where PD1 took effect. In the case with an enabled
interrupt, the GIE bit in the CSR and t he NMIE b it i n the i nterrupt enable register (IER) m ust also b e s et in o rder
for the interrupt service routine to e xecute; o therwise, execution returns t o t he i nstruction where P D1 t ook ef fect
upon PD1 mode termination by an enabled interrupt.
PD2 and PD3 modes can only be aborted by device reset. Table 4−2 summarizes all the power-down modes.
88
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 89
Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller
Power-down mode blocks the internal clock inputs at the
Table 4−2. Characteristics of the Power-Down Modes
PRWD FIELD
(BITS 15−10)
000000 No power-down — —
001001 PD1 Wake by an enabled interrupt
010001 PD1
011010 PD2
011100 PD3
All others Reserved — —
†
When entering PD2 and PD3, all functional I/O remains in the previous state. However, for peripherals which are asynchronous in nature or
peripherals with an external clock source, output signals may transition in response to stimulus on the inputs. Under these conditions,
peripherals will not operate according to specifications.
POWER-DOWN
MODE
†
†
WAKE-UP METHOD EFFECT ON CHIP’S OPERATION
CPU halted (except for the interrupt logic)
Power-down mode blocks the internal clock inputs at the
Wake by an enabled or
non-enabled interrupt
Wake by a device reset
Wake by a device reset
boundary of the CPU, preventing most of the CPU’s logic from
switching. During P D 1 , EDMA transactions can proceed between
peripherals and internal memory.
Output clock from PLL is halted, stopping the internal clock
structure from switching and resulting in the entire chip being
halted. All register and internal RAM contents are preserved. All
functional I/O “freeze” in the last state when the PLL clock is
turned off.
Input clock to the PLL stops generating clocks. All register and
internal RAM contents are preserved. All functional I/O “freeze” in
the last state when the PLL clock is t urned o f f. F ollowing r eset, the
PLL needs time to re-lock, just as it does following power-up.
Wake-up from PD3 takes longer than wake-up from PD2 because
the PLL needs to be re-locked, just as it does following power-up.
4.3.7 C64x Power-Down Mode with an Emulator
If user power-down modes are programmed, and an emulator is attached, the modes will be masked to allow
the emulator access to the system. This condition prevails until the emulator is reset or the cable is removed
from the header. If power measurements are to be performed when in a power-down mode, the emulator cable
should be removed.
When the DSP is in power-down mode PD2 or PD3, emulation logic will force any emulation execution
command (such as Step or Run) to spin in IDLE. For this reason, PC writes (such as loading code) will fail.
A DSP reset will be required to get the DSP out of PD2/PD3.
4.4 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller
The EDMA controller handles all data transfers between the level-two (L2) cache/memory controller and the
device peripherals on the DM641/DM640 DSP. These data transfers include cache servicing, non-cacheable
memory accesses, user-programmed data transfers, and host accesses.
4.4.1 EDMA Device-Specific Information
4.4.1.1 EDMA Channel Synchronization Events
The C64x EDMA supports up to 64 EDMA channels which service peripheral devices and external memory.
Table 4−3 lists the source of C64x EDMA synchronization events associated with each of the programmable
EDMA channels. For the DM641/DM640 device, the association of an event to a channel is fixed; each of the
EDMA channels has one specific event associated with it. These specific events are captured in the EDMA
event registers (ERL, ERH) even if the events are disabled by the EDMA event enable registers (EERL,
EERH). The priority of each event can be specified independently in the transfer parameters stored in the
EDMA parameter RAM. For more detailed information on the EDMA module and how EDMA events are
enabled, captured, processed, linked, chained, and cleared, etc., see the TMS320C6000 DSP Enhanced
Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller Reference Guide (literature number SPRU234).
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
89
Page 90
Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller
Table 4−3. TMS320DM641/DM640 EDMA Channel Synchronization Events†
EDMA
CHANNEL
0 DSP_INT HPI-to-DSP interrupt [For DM641 Only; “None” for DM640]
1 TINT0 Timer 0 interrupt
2 TINT1 Timer 1 interrupt
3 SD_INTA EMIFA SDRAM timer interrupt
4 GPINT4/EXT_INT4 GP0 event 4/External interrupt pin 4
5 GPINT5/EXT_INT5 GP0 event 5/External interrupt pin 5
6 GPINT6/EXT_INT6 GP0 event 6/External interrupt pin 6
7 GPINT7/EXT_INT7 GP0 event 7/External interrupt pin 7
8 GPINT0 GP0 event 0
9 GPINT1 GP0 event 1
10 GPINT2 GP0 event 2
11 GPINT3 GP0 event 3
12 XEVT0 McBSP0 transmit event
13 REVT0 McBSP0 receive event
14 XEVT1 McBSP1 transmit event
15 REVT1 McBSP1 receive event
16 VP0EVTYA VP0 Channel A Y event DMA request
17 VP0EVTUA VP0 Channel A Cb event DMA request
18 VP0EVTVA VP0 Channel A Cr event DMA request
19 TINT2 Timer 2 interrupt
20−31 – None
32 AXEVTE0 McASP0 transmit even event
33 AXEVTO0 McASP0 transmit odd event
34 AXEVT0 McASP0 transmit event
35 AREVTE0 McASP0 receive even event
36 AREVTO0 McASP0 receive odd event
37 AREVT0 McASP0 receive event
38−43 – None
44 ICREVT0 I2C0 receive event
45 ICXEVT0 I2C0 transmit event
46−47 – None
48 GPINT8 GP0 event 8
49 GPINT9 GP0 event 9
50 GPINT10 GP0 event 10
51 GPINT11 GP0 event 11
52 GPINT12 GP0 event 12
53 GPINT13 GP0 event 13
54 GPINT14 GP0 event 14
55 GPINT15 GP0 event 15
56 VP1EVTYA VP1 Channel A Y event DMA request [For DM641 Only; “None” for DM640]
†
In addition to the events shown in this table, each of the 64 channels can also be synchronized with the transfer completion or alternate transfer
completion events. For more detailed information on EDMA event-transfer chaining, see the TMS320C6000 DSP Enhanced Direct Memory
Access (EDMA) Controller Reference Guide (literature number SPRU234).
EVENT NAME EVENT DESCRIPTION
90
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 91

Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller
Table 4−3. TMS320DM641/DM640 EDMA Channel Synchronization Events† (Continued)
EDMA
CHANNEL
57 VP1EVTUA VP1 Channel A Cb event DMA request [For DM641 Only; “None” for DM640]
58 VP1EVTVA VP1 Channel A Cr event DMA request [For DM641 Only; “None” for DM640]
59−63 – None
†
In addition to the events shown in this table, each of the 64 channels can also be synchronized with the transfer completion or alternate transfer
completion events. For more detailed information on EDMA event-transfer chaining, see the TMS320C6000 DSP Enhanced Direct Memory
Access (EDMA) Controller Reference Guide (literature number SPRU234).
EVENT DESCRIPTIONEVENT NAME
4.4.2 EDMA Peripheral Register Description(s)
T able 4−4. EDMA Registers (C64x)
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME
01A0 0800 − 01A0 FF98 − Reserved
01A0 FF9C EPRH Event polarity high register
01A0 FFA4 CIPRH Channel interrupt pending high register
01A0 FFA8 CIERH Channel interrupt enable high register
01A0 FFAC CCERH Channel chain enable high register
01A0 FFB0 ERH Event high register
01A0 FFB4 EERH Event enable high register
01A0 FFB8 ECRH Event clear high register
01A0 FFBC ESRH Event set high register
01A0 FFC0 PQAR0 Priority queue allocation register 0
01A0 FFC4 PQAR1 Priority queue allocation register 1
01A0 FFC8 PQAR2 Priority queue allocation register 2
01A0 FFCC PQAR3 Priority queue allocation register 3
01A0 FFDC EPRL Event polarity low register
01A0 FFE0 PQSR Priority queue status register
01A0 FFE4 CIPRL Channel interrupt pending low register
01A0 FFE8 CIERL Channel interrupt enable low register
01A0 FFEC CCERL Channel chain enable low register
01A0 FFF0 ERL Event low register
01A0 FFF4 EERL Event enable low register
01A0 FFF8 ECRL Event clear low register
01A0 FFFC ESRL Event set low register
01A1 0000 − 01A3 FFFF – Reserved
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
91
Page 92

Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller
T able 4−5. Quick DMA (QDMA) and Pseudo Registers
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME
0200 0000 QOPT QDMA options parameter register
0200 0004 QSRC QDMA source address register
0200 0008 QCNT QDMA frame count register
0200 000C QDST QDMA destination address register
0200 0010 QIDX QDMA index register
0200 0014 − 0200 001C Reserved
0200 0020 QSOPT QDMA pseudo options register
0200 0024 QSSRC QDMA psuedo source address register
0200 0028 QSCNT QDMA psuedo frame count register
0200 002C QSDST QDMA destination address register
0200 0030 QSIDX QDMA psuedo index register
92
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 93
Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller
T able 4−6. EDMA Parameter RAM (C64x)
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME COMMENTS
01A0 0000 − 01A0 0017 − Parameters for Event 0 (6 words)
01A0 0018 − 01A0 002F − Parameters for Event 1 (6 words)
01A0 0030 − 01A0 0047 − Parameters for Event 2 (6 words)
01A0 0048 − 01A0 005F − Parameters for Event 3 (6 words)
01A0 0060 − 01A0 0077 − Parameters for Event 4 (6 words)
01A0 0078 − 01A0 008F − Parameters for Event 5 (6 words)
01A0 0090 − 01A0 00A7 − Parameters for Event 6 (6 words)
01A0 00A8 − 01A0 00BF − Parameters for Event 7 (6 words)
01A0 00C0 − 01A0 00D7 − Parameters for Event 8 (6 words)
01A0 00D8 − 01A0 00EF − Parameters for Event 9 (6 words)
01A0 00F0 − 01A0 00107 − Parameters for Event 10 (6 words)
01A0 0108 − 01A0 011F − Parameters for Event 11 (6 words)
01A0 0120 − 01A0 0137 − Parameters for Event 12 (6 words)
01A0 0138 − 01A0 014F − Parameters for Event 13 (6 words)
01A0 0150 − 01A0 0167 − Parameters for Event 14 (6 words)
01A0 0168 − 01A0 017F − Parameters for Event 15 (6 words)
01A0 0150 − 01A0 0167 − Parameters for Event 16 (6 words)
01A0 0168 − 01A0 017F − Parameters for Event 17 (6 words)
... ...
01A0 05D0 − 01A0 05E7 − Parameters for Event 62 (6 words)
01A0 05E8 − 01A0 05FF − Parameters for Event 63 (6 words)
01A0 0600 − 01A0 0617 − Reload/link parameters for Event 0 (6 words)
01A0 0618 − 01A0 062F − Reload/link parameters for Event 1 (6 words)
... ...
01A0 07E0 − 01A0 07F7 − Reload/link parameters for Event 20 (6 words)
01A0 07F8 − 01A0 080F − Reload/link parameters for Event 21 (6 words)
01A0 0810 − 01A0 0827 − Reload/link parameters for Event 22 (6 words)
... ...
01A0 13C8 − 01A0 13DF − Reload/link parameters for Event 147 (6 words)
01A0 13E0 − 01A0 13F7 − Reload/link parameters for Event 148 (6 words)
01A0 13F8 − 01A0 13FF − Scratch pad area (2 words)
01A0 1400 − 01A3 FFFF − Reserved
†
The DM641/DM640 device has 213 EDMA parameters total: 64-Event/Reload channels and 149-Reload only parameter sets [six (6) words each]
that can be used to reload/link EDMA transfers.
†
Parameters for Event 0
(6 words) or Reload/Link
Parameters for other Event
Reload/Link Parameters for
other Event 0−15
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
93
Page 94

Interrupts
4.5 Interrupts
4.5.1 Interrupt Sources and Interrupt Selector
The C64x DSP core supports 16 prioritized interrupts, which are listed in Table 4−7. The highest-priority
interrupt is INT_00 (dedicated to RESET) while the lowest-priority interrupt is INT_15. The first four interrupts
(INT_00−INT_03) are non-maskable and fixed. The remaining interrupts (INT_04−INT_15) are maskable and
default to the interrupt source specified in Table 4−7. The interrupt source for interrupts 4−15 can be
programmed by modifying the selector value (binary value) in the corresponding fields of the Interrupt Selector
Control registers: MUXH (address 0x019C0000) and MUXL (address 0x019C0004).
T able 4−7. DM641/DM640 DSP Interrupts
CPU
INTERRUPT
NUMBER
†
INT_00
†
INT_01
†
INT_02
†
INT_03
‡
INT_04
‡
INT_05
‡
INT_06
‡
INT_07
‡
INT_08
‡
INT_09
‡
INT_10
‡
INT_11
‡
INT_12
‡
INT_13
‡
INT_14
‡
INT_15
INTERRUPT
SELECTOR
CONTROL
REGISTER
SELECTOR
VALUE
(BINARY)
INTERRUPT
EVENT
INTERRUPT SOURCE
− − RESET
− − NMI
− − Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
− − Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
MUXL[4:0] 00100 GPINT4/EXT_INT4 GP0 interrupt 4/External interrupt pin 4
MUXL[9:5] 00101 GPINT5/EXT_INT5 GP0 interrupt 5/External interrupt pin 5
MUXL[14:10] 00110 GPINT6/EXT_INT6 GP0 interrupt 6/External interrupt pin 6
MUXL[20:16] 00111 GPINT7/EXT_INT7 GP0 interrupt 7/External interrupt pin 7
MUXL[25:21] 01000 EDMA_INT EDMA channel (0 through 63) interrupt
MUXL[30:26] 01001 EMU_DTDMA EMU DTDMA
MUXH[4:0] 00011 SD_INTA EMIFA SDRAM timer interrupt
MUXH[9:5] 01010 EMU_RTDXRX EMU real-time data exchange (RTDX) receive
MUXH[14:10] 01011 EMU_RTDXTX EMU RTDX transmit
MUXH[20:16] 00000 DSP_INT HPI-to-DSP interrupt [DM641 Only]
MUXH[25:21] 00001 TINT0 Timer 0 interrupt
MUXH[30:26] 00010 TINT1 Timer 1 interrupt
− − 01100 XINT0 McBSP0 transmit interrupt
− − 01101 RINT0 McBSP0 receive interrupt
− − 01110 XINT1 McBSP1 transmit interrupt
− − 01111 RINT1 McBSP1 receive interrupt
− − 10000 GPINT0 GP0 interrupt 0
− − 10001 Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
− − 10010 Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
− − 10011 TINT2 Timer 2 interrupt
− − 10100 Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
− − 10101 Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
− − 10110 ICINT0 I2C0 interrupt
− − 10111 Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
− − 11000 EMAC_MDIO_INT EMAC/MDIO interrupt
− − 11001 VPINT0 VP0 interrupt
†
Interrupts INT_00 through INT_03 are non-maskable and fixed.
‡
Interrupts INT_04 through INT_15 are programmable by modifying the binary selector values in the Interrupt Selector Control registers fields.
Table 4−7 shows the default interrupt sources for Interrupts INT_04 through INT_15. For more detailed information on interrupt sources and
selection, see the TMS320C6000 DSP Interrupt Selector Reference Guide (literature number SPRU646).
94
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 95

Table 4−7. DM641/DM640 DSP Interrupts (Continued)
1
t
2
t
Reset
CPU
INTERRUPT
NUMBER
− − 11010 VPINT1 VP1 interrupt [DM641 Only]
− − 11011 Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
− − 11100 AXINT0 McASP0 transmit interrupt
− − 11101 ARINT0 McASP0 receive interrupt
− − 11110 − 11111 Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
†
Interrupts INT_00 through INT_03 are non-maskable and fixed.
‡
Interrupts INT_04 through INT_15 are programmable by modifying the binary selector values in the Interrupt Selector Control registers fields.
Table 4−7 shows the default interrupt sources for Interrupts INT_04 through INT_15. For more detailed information on interrupt sources and
selection, see the TMS320C6000 DSP Interrupt Selector Reference Guide (literature number SPRU646).
INTERRUPT
SELECTOR
CONTROL
REGISTER
SELECTOR
VALUE
(BINARY)
INTERRUPT
EVENT
INTERRUPT SOURCE
4.5.2 Interrupts Peripheral Register Description(s)
T able 4−8. Interrupt Selector Registers (C64x)
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME COMMENTS
019C 0000 MUXH Interrupt multiplexer high
019C 0004 MUXL Interrupt multiplexer low
019C 0008 EXTPOL External interrupt polarity
019C 000C − 019F FFFF − Reserved
Selects which interrupts drive CPU
interrupts 10−15 (INT10−INT15)
Selects which interrupts drive CPU
interrupts 4−9 (INT04−INT09)
Sets the polarity of the external
interrupts (EXT_INT4−EXT_INT7)
4.5.3 External Interrupts Electrical Data/Timing
T able 4−9. Timing Requirements for External Interrupts† (see Figure 4−10)
NO.
w(ILOW)
w(IHIGH)
†
P = 1/CPU clock frequency in ns. For example, when running parts at 600 MHz, use P = 1.67 ns.
EXT_INTx, NMI
Width of the NMI interrupt pulse low 4P ns
Width of the EXT_INT interrupt pulse low 8P ns
Width of the NMI interrupt pulse high 4P ns
Width of the EXT_INT interrupt pulse high 8P ns
1
2
Figure 4−10. External/NMI Interrupt Timing
4.6 Reset
A hardware reset (RESET) is required to place the DSP into a known good state out of power-up. The RESET
signal can be asserted (pulled low) prior to ramping the core and I/O voltages or after the core and I/O voltages
have reached their proper operating conditions. As a best practice, reset should be held low during power-up.
Prior to deasserting RESET (low-to-high transition), the core and I/O voltages should be at their proper
operating conditions and CLKIN should also be running at the correct frequency.
−400
−500
−600
MIN MAX
UNIT
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
95
Page 96

Reset
For information on peripheral selection at the rising edge of RESET, see the Device Configuration section of
this data manual.
4.6.1 Reset Electrical Data/Timing
T able 4−10. Timing Requirements for Reset (see Figure 4−11)
−400
NO.
−500
−600
UNIT
MIN MAX
1 t
w(RST)
16 t
su(boot)
17 t
†
‡
§
h(boot)
AEA[22:19], LENDIAN, and HD5 are the boot configuration pins during device reset.
E = 1/AECLKIN clock frequency in ns. C = 1/CLKIN clock frequency in ns.
Select the MIN parameter value, whichever value is larger.
P = 1/CPU clock frequency in ns. For example, when running parts at 600 MHz, use P = 1.67 ns.
Table 4−11. Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions During Reset
Width of the RESET pulse 250 μs
Setup time, boot configuration bits valid before RESET high
Hold time, boot configuration bits valid after RESET high
†
†
4E or 4C
4P
‡
§
§¶#
(see Figure 4−11)
−400
NO. PARAMETER
2 t
d(RSTL-ECKI)
3 t
d(RSTH-ECKI)
4 t
d(RSTL-ECKO1HZ)
5 t
d(RSTH-ECKO1V)
6 t
d(RSTL-EMIFZHZ)
7 t
d(RSTH-EMIFZV)
8 t
d(RSTL-EMIFHIV)
9 t
d(RSTH-EMIFHV)
10 t
d(RSTL-EMIFLIV)
11 t
d(RSTH-EMIFLV)
12 t
d(RSTL-LOWIV)
13 t
d(RSTH-LOWV)
14 t
d(RSTL-ZHZ)
15 t
d(RSTH-ZV)
§
P = 1/CPU clock frequency in ns. For example, when running parts at 600 MHz, use P = 1.67 ns.
¶
E = the EMIF input clock (AECLKIN, CPU/4 clock, or CPU/6 clock) period in ns for EMIFA.
#
EMIF Z group consists of: AEA[22:3], AED[31:0], ACE[3:0], ABE[3:0], AARE/ASDCAS/ASADS/ASRE,AAWE/ASDWE/ASWE,
Delay time, RESET low to AECLKIN synchronized internally 2E 3P + 20E ns
Delay time, RESET high to AECLKIN synchronized internally 2E 8P + 20E ns
Delay time, RESET low to AECLKOUT1 high impedance 2E ns
Delay time, RESET high to AECLKOUT1 valid 8P + 20E ns
Delay time, RESET low to EMIF Z high impedance 2E 3P + 4E ns
Delay time, RESET high to EMIF Z valid 16E 8P + 20E ns
Delay time, RESET low to EMIF high group invalid 2E ns
Delay time, RESET high to EMIF high group valid 8P + 20E ns
Delay time, RESET low to EMIF low group invalid 2E ns
Delay time, RESET high to EMIF low group valid 8P + 20E ns
Delay time, RESET low to low group invalid 0 ns
Delay time, RESET high to low group valid 11P ns
Delay time, RESET low to Z group high impedance 0 ns
Delay time, RESET high to Z group valid 2P 8P ns
AAOE/ASDRAS/ASOE, ASOE3, ASDCKE, and APDT.
EMIF high group consists of: AHOLDA (when the corresponding AHOLD input is high)
EMIF low group consists of: ABUSREQ; AHOLDA (when the corresponding AHOLD input is low)
Low group consists of:
Z group consists of: HD[15:0], VP0D[0]/CLKX0, VP0D[1]/FSX0, VP0D[2]/DX0, CLKR0, VP0D[5]/FSR0, TOUT0, TOUT1, VDAC,
GP0[7:0], HR/W, HDS2, HDS1, HCS, HCNTL1, HAS, HCNTL0, HHWIL (16-bit HPI mode only), HRDY, HINT, and
VP0D[4,3].
VP1 signals apply to DM641 only:
VP1D[0]/CLKX1, VP1D[1]/FSX1, VP1D[2]/DX1, VP1D[6]/CLKR1, VP1D[5]/FSR1, and VP1D[4,3].
−500
−600
MIN MAX
UNIT
ns
ns
96
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 97

CLKOUT4
CLKOUT6
RESET
AECLKIN
AECLKOUT1
AECLKOUT2
Reset
1
32
54
EMIF Z Group
EMIF High Group
EMIF Low Group
Low Group
Z Group
Boot and Device
Configuration Inputs
†
EMIF Z group consists of: AEA[22:3], AED[31:0], ACE[3:0], ABE[3:0], AARE/ASDCAS/ASADS/ASRE,AAWE/ASDWE/ASWE,
†‡
†
8
10
†
12
†
14
†‡
16
§
9
11
13
15
17
AAOE/ASDRAS/ASOE, ASOE3, ASDCKE, and APDT.
EMIF high group consists of: AHOLDA (when the corresponding AHOLD input is high)
EMIF low group consists of: ABUSREQ; AHOLDA (when the corresponding AHOLD input is low)
Low group consists of:
Z group consists of: HD[15:0], VP0D[0]/CLKX0, VP0D[1]/FSX0, VP0D[2]/DX0, CLKR0, VP0D[5]/FSR0, TOUT0, TOUT1, VDAC,
GP0[7:0], HR/W, HDS2, HDS1, HCS, HCNTL1, HAS, HCNTL0, HHWIL (16-bit HPI mode only), HRDY, HINT, and
VP0D[4,3].
VP1 signals apply to DM641 only:
76
‡
If AEA[22:19], LENDIAN, and HD5 pins are actively driven, care must be taken to ensure
no timing contention between parameters 6, 7, 14, 15, 16, and 17.
§
Boot and Device Configurations Inputs (during reset) include: AEA[22:19], LENDIAN, and HD5.
VP1D[0]/CLKX1, VP1D[1]/FSX1, VP1D[2]/DX1, VP1D[6]/CLKR1, VP1D[5]/FSR1, and VP1D[4,3].
Figure 4−11. Reset Timing
†
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
97
Page 98

Clock PLL
4.7 Clock PLL
The PLL controller features hardware-configurable PLL multiplier controller, dividers (/2, /4, /6, and /8), and
reset controller. The PLL controller accepts an input clock, as determined by the logic state on the
CLKMODE[1:0] pins, from the CLKIN pin. The resulting clock outputs are passed to the DSP core, peripherals,
and other modules inside the C6000™ DSP.
4.7.1 Clock PLL Device-Specific Information
Most of the internal C64x™ DSP clocks are generated from a single source through the CLKIN pin. This source
clock either drives the PLL, which multiplies the source clock frequency to generate the internal CPU clock,
or bypasses the PLL to become the internal CPU clock.
To use the PLL to generate the CPU clock, the external PLL filter circuit must be properly designed.
Figure 4−12 shows the external PLL circuitry for either x1 (PLL bypass) or other PLL multiply modes.
To minimize the clock jitter, a single clean power supply should power both the C64x™ DSP device and the
external clock oscillator circuit. The minimum CLKIN rise and fall times should also be observed. For the input
clock timing requirements, see the input and output clocks electricals section.
Rise/fall times, duty cycles (high/low pulse durations), and the load capacitance of the external clock source
must meet the DSP requirements in this data sheet (see the electrical characteristics over recommended
ranges of supply voltage and operating case temperature table and the input and output clocks electricals
section).
98
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
Page 99

Clock PLL
3.3 V
CLKMODE0
CLKMODE1
CLKIN
ECLKIN
AEA[20:19]
EMI
filter
Internal to DM641/DM640
10 μF 0.1 μF
PLLMULT
C2C1
PLLV
PLL
x6, x12
PLLCLK
CPU Clock
/2
/8
/4
/6
1
0
00 01 10
/4
/2
EMIF 00 01 10
Peripheral Bus, EDMA
Clock
Timer Internal Clock
CLKOUT4, Peripheral Clock
(AUXCLK for McASP),
McBSP Internal Clock
CLKOUT6
EK2RATE
(GBLCTL.[19,18])
(For the PLL Options, CLKMODE Pins Setup, and
PLL Clock Frequency Ranges, see Table 9.)
NOTES: A. Place all PLL external components (C1, C2, and the EMI Filter) as close to the C6000™ DSP device as possible. For the best
performance, TI recommends that all the PLL external components be on a single side of the board without jumpers, switches, or
components other than the ones shown.
B. For reduced PLL jitter, maximize the spacing between switching signals and the PLL external components (C1, C2, and the EMI
Filter).
C. The 3.3-V supply for the EMI filter must be from the same 3.3-V power plane supplying the I/O voltage, DVDD.
D. EMI filter manufacturer TDK part number ACF451832-333, -223, -153, -103. Panasonic part number EXCCET103U.
ECLKOUT2ECLKOUT1
Figure 4−12. External PLL Circuitry for Either PLL Multiply Modes or x1 (Bypass) Mode
June 2003 − Revised October 2010 SPRS222F
99
Page 100

Clock PLL
75
.
NO.
UNIT
.
NO.
UNIT
Table 4−12. TMS320DM641/DM640 PLL Multiply Factor Options, Clock Frequency Ranges,
and Typical Lock Time
GDK and ZDK PACKAGES − 23 x 23 mm BGA,
GNZ and ZNZ PACKAGES − 27 x 27 mm BGA
CLKMODE
CLKMODE1 CLKMODE0
(PLL MULTIPLY
FACTORS)
0 0 Bypass (x1) 30−75 30−75 7.5−18.8 5−12.5 N/A
0 1 x6 30−75 180−450 45−112.5 30−75
1 0 x12 30−50 360−600 90−150 60−100
1 1 Reserved − − − − −
†
These clock frequency range values are applicable to a DM641−600 speed device. For −400, −500 device speed values, see the CLKIN timing
requirements table for the specific device speed.
‡
Use external pullup resistors on the CLKMODE pins (CLKMODE1 and CLKMODE0) to set the DM641/DM640 device to one of the valid PLL
multiply clock modes (x6 or x12). With internal pulldown resistors on the CLKMODE pins (CLKMODE1, CLKMODE0), the default clock mode
is x1 (bypass).
§
Under some operating conditions, the maximum PLL lock time may vary by as much as 150% from the specified typical value. For example, if
the typical lock time is specified as 100 μs, the maximum value may be as long as 250 μs.
CLKIN
RANGE
(MHz)
CPU CLOCK
FREQUENCY
RANGE (MHz)
†‡
CLKOUT4
RANGE (MHz)
CLKOUT6
RANGE (MHz)
TYPICAL
LOCK TIME
§
(μs)
4.7.2 Clock PLL Electrical Data/Timing (Input and Output Clocks)
T able 4−13. Timing Requirements for CLKIN for −400 Devices
NO
1 t
c(CLKIN)
2 t
w(CLKINH)
3 t
w(CLKINL)
4 t
t(CLKIN)
5 t
J(CLKIN)
†
The reference points for the rise and fall transitions are measured at VIL MAX and VIH MIN.
‡
For more details on the PLL multiplier factors (x6, x12), see the Clock PLL section of this data sheet.
§
C = CLKIN cycle time in ns. For example, when CLKIN frequency is 50 MHz, use C = 20 ns.
Cycle time, CLKIN 30 33.3 13.3 33.3 13.3 33.3 ns
Pulse duration, CLKIN high 0.45C 0.45C 0.45C ns
Pulse duration, CLKIN low 0.45C 0.45C 0.45C ns
Transition time, CLKIN 5 5 1 ns
Period jitter, CLKIN 0.02C 0.02C 0.02C ns
PLL MODE x12 PLL MODE x6 x1 (BYPASS)
MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
T able 4−14. Timing Requirements for CLKIN for −500 Devices
†‡§
(see Figure 4−13)
−400
†‡§
(see Figure 4−13)
UNIT
−500
NO
PLL MODE x12 PLL MODE x6 x1 (BYPASS)
UNIT
MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
1 t
c(CLKIN)
2 t
w(CLKINH)
3 t
w(CLKINL)
4 t
t(CLKIN)
5 t
J(CLKIN)
†
The reference points for the rise and fall transitions are measured at VIL MAX and VIH MIN.
‡
For more details on the PLL multiplier factors (x6, x12), see the Clock PLL section of this data sheet.
§
C = CLKIN cycle time in ns. For example, when CLKIN frequency is 50 MHz, use C = 20 ns.
100
Cycle time, CLKIN 24 33.3 13.3 33.3 13.3 33.3 ns
Pulse duration, CLKIN high 0.45C 0.45C 0.45C ns
Pulse duration, CLKIN low 0.45C 0.45C 0.45C ns
Transition time, CLKIN 5 5 1 ns
Period jitter, CLKIN 0.02C 0.02C 0.02C ns
June 2003 − Revised October 2010SPRS222F
 Loading...
Loading...