
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
Check for Samples: TMS320DM355
1 TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
1.1 Features
123
• Highlights
– High-Performance Digital Media
System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
– Up to 270-MHz ARM926EJ-S™ Clock Rate
– MPEG4/JPEG Coprocessor Supports
• Up to 720p MPEG4 SP
• Up to 50M Pixels per Second JPEG
– Video Processing Subsystem
• Hardware IPIPE for Real-Time Image
Processing • MPEG4/JPEG Coprocessor
• Up to 14-bit CCD/CMOS Digital Interface – Fixed Function Coprocessor Supports:
• Histogram Module • MPEG4 SP Codec at HD (720p), D1, VGA,
• Resize Image 1/16x to 8x
• Hardware On-Screen Display
• Supports digital HDTV (720p/1080i) output
for connection to external encoder – Front End Provides:
– Peripherals include DDR and mDDR SDRAM, • Hardware IPIPE for Real-Time Image
2 MMC/SD/SDIO and SmartMedia Flash Card Processing
Interfaces, USB 2.0, 3 UARTs and 3 SPIs
– Configurable Power-Saving Modes
– On-Chip ARM ROM Bootloader (RBL) to Boot (BT.601)
From NAND Flash, MMC/SD, or UART
– Extended Temperature 135- and 216-MHz
Devices are Available
– 3.3-V and 1.8-V I/O, 1.3-V Core
– Debug Interface Support
– 337-Pin Ball Grid Array at 65 nm Process
Technology
• High-Performance Digital Media
System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
– 135-, 216-, and 270-MHz ARM926EJ-S™
Clock Rate
– Fully Software-Compatible With ARM9™
– Extended temperature support for 135- and
216-MHz devices
• ARM926EJ-S Core
– Support for 32-Bit and 16-Bit (Thumb Mode)
Instruction Sets
– DSP Instruction Extensions and Single Cycle
MAC
1
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas
Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
2Windows is a trademark of Microsoft.
3All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
– ARM® Jazelle® Technology
– EmbeddedICE-RT™ Logic for Real-Time
Debug
• ARM9 Memory Architecture
– 16K-Byte Instruction Cache
– 8K-Byte Data Cache
– 32K-Byte RAM
– 8K-Byte ROM
– Little Endian
SIF
• JPEG Codec up to 50M Pixels per Second
• Video Processing Subsystem
• Up to 14-bit CCD/CMOS Digital Interface
• 16-/8-bit Generic YcBcR-4:2 Interface
• 10-/8-bit CCIR6565/BT655 Interface
• Up to 75-MHz Pixel Clock
• Histogram Module
• Resize Engine
– Resize Images From 1/16x to 8x
– Separate Horizontal/Vertical Control
– Two Simultaneous Output Paths
– Back End Provides:
• Hardware On-Screen Display (OSD)
• Composite NTSC/PAL video encoder
output
• 8-/16-bit YCC and Up to 18-Bit RGB666
Digital Output
• BT.601/BT.656 Digital YCbCr 4:2:2
(8-/16-Bit) Interface
• Supports digital HDTV (720p/1080i) output
for connection to external encoder
• External Memory Interfaces (EMIFs)
– DDR2 and mDDR SDRAM 16-bit wide EMIF
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
www.ti.com
With 256 MByte Address Space (1.8-V I/O) – S/PDIF via Software
– Asynchronous16-/8-bit Wide EMIF (AEMIF) – Standard Voice Codec Interface (AIC12)
• Flash Memory Interfaces – SPI Protocol (Master Mode Only)
– NAND (8-/16-bit Wide Data) • Four Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) Outputs
– OneNAND(16-bit Wide Data) • Four RTO (Real Time Out) Outputs
• Flash Card Interfaces • Up to 104 General-Purpose I/O (GPIO) Pins
– Two Multimedia Card (MMC) / Secure Digital
(Multiplexed with Other Device Functions)
(SD/SDIO) • On-Chip ARM ROM Bootloader (RBL) to Boot
– SmartMedia
• Enhanced Direct-Memory-Access (EDMA)
Controller (64 Independent Channels)
• USB Port with Integrated 2.0 High-Speed PHY
that Supports
– USB 2.0 Full and High-Speed Device
– USB 2.0 Low, Full, and High-Speed Host
• Three 64-Bit General-Purpose Timers (each
configurable as two 32-bit timers)
• One 64-Bit Watch Dog Timer
• Three UARTs (One fast UART with RTS and
CTS Flow Control)
• Three Serial Port Interfaces (SPI) each with two
Chip-Selects
• One Master/Slave Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
From NAND Flash (with SPI EEPROM Boot
option), MMC/SD, or UART
• Configurable Power-Saving Modes
• Crystal or External Clock Input (typically
24 MHz or 36 MHz)
• Flexible PLL Clock Generators
• Debug Interface Support
– IEEE-1149.1 (JTAG)
Boundary-Scan-Compatible
– ETB™ (Embedded Trace Buffer™) with
4K-Bytes Trace Buffer memory
– Device Revision ID Readable by ARM
• 337-Pin Ball Grid Array (BGA) Package
(ZCE Suffix), 0.65-mm Ball Pitch
• 90nm Process Technology
Bus® • 3.3-V and 1.8-V I/O, 1.3-V Internal
• Two Audio Serial Port (ASP) • Community Resources
– I2S and TDM I2S – TI E2E Community
– AC97 Audio Codec Interface – TI Embedded Processors Wiki
2 TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
1.2 Description
The DM355 is a highly integrated, programmable platform for digital still camera, digital photo frames, IP
security cameras, 4-channel digital video recorders, video door bell application, and other low cost
portable digital video applications. Designed to offer portable video designers and manufacturers the
ability to produce affordable portable digital video solutions with high picture quality, the DM355 combines
high performance MPEG4 HD (720p) codecs and JPEG codecs up to 50M pixels per second, high quality,
and low power consumption at a very low price point. The DM355 also enables seamless interface to most
additional external devices required for a complete digital camera implementation. The interface is flexible
enough to support various types of CCD and CMOS sensors, signal conditioning circuits, power
management, DDR/mDDR memory, SRAM, NAND, shutter, Iris and auto-focus motor controls, etc.
The DM355 processor core is an ARM926EJ-S RISC processor. The ARM926EJ-S is a 32-bit processor
core that performs 32-bit and 16-bit instructions and processes 32-bit, 16-bit, and 8-bit data. The core
uses pipelining so that all parts of the processor and memory system can operate continuously. The ARM
core incorporates:
• A coprocessor 15 (CP15) and protection module
• Data and program Memory Management Units (MMUs) with table look-aside buffers.
• Separate 16K-byte instruction and 8K-byte data caches. Both are four-way associative with virtual
index virtual tag (VIVT).
DM355 performance is enhanced by its MPEG4/JPEG coprocessor. The MPEG4/JPEG coprocessor
performs the computational operations required for image processing; JPEG compression and MPEG4
video and imaging standard. The MPEG4/JPEG coprocessor supports MPEG4 SP at HD (720p), D1,
VGA, SIF encode/decode resolutions and JPEG encode/decode up to 50M pixels per second.
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
The DM355 device has a Video Processing Subsystem (VPSS) with two configurable video/imaging
peripherals:
• A Video Processing Front-End (VPFE)
• A Video Processing Back-End (VPBE)
The VPFE port provides an interface for CCD/CMOS imager modules and video decoders. The VPBE
provides hardware On Screen Display (OSD) support and composite NTSC/PAL and digital LCD output.
The DM355 peripheral set includes:
• An inter-integrated circuit (I2C) Bus interface
• Two audio serial ports (ASP)
• Three 64-bit general-purpose timers each configurable as two independent 32-bit timers
• A 64-bit watchdog timer
• Up to 104-pins of general-purpose input/output (GPIO) with programmable interrupt/event generation
modes, multiplexed with other peripherals
• Three UARTs with hardware handshaking support on one UART
• Three serial port Interfaces (SPI)
• Four pulse width modulator (PWM) peripherals
• Four real time out (RTO) outputs
• Two Multi-Media Card / Secure Digital (MMC/SD/SDIO) interfaces
• Wireless interfaces (Bluetooth, WLAN, WUSB) through SDIO
• A USB 2.0 full and high-speed device and host interface
• Two external memory interfaces:
– An asynchronous external memory interface (AEMIF) for slower memories/peripherals such as
NAND and OneNAND,
– A high speed synchronous memory interface for DDR2/mDDR.
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) 3
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
For software development support the DM355 has a complete set of ARM development tools which
include: C compilers, assembly optimizers to simplify programming and scheduling, and a Windows™
debugger interface for visibility into source code execution.
www.ti.com
4 TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
Peripherals
64bitDMA/DataBus
JTAG
24MHz
or36MHz
27MHz
(optional)
CCD/
CMOS
Module
DDR2/mDDR16
CLOCK
PLL
CLOCKctrl
PLLs
JTA
JTAG
I/F
Clocks
ARM
z )
ARM926EJ-S_Z8
I-
cach
e
16 K
B
l-cache
16KB
B
RA
M
32 K
B
RAM
32KB
B
D-
cach
e
8K
D-cache
8KB
RO
M
8 K
ROM
8KB
CCD
C
3A
H3A
DMA / Dataandconfigurationbus
DMA/Dataandconfigurationbus
DDR
MH
z )
DDR
controller
DL
DLL/
PHY
16bit
32bitConfigurationBus
CCDC
IPIPE
VPBE
Vide
o
Encod
er
Video
Encoder
10b
DAC
OS
D
OSD
er
c
ARM
ARMINTC
Enhanced
channels
3PCC / TC
(100 MHz
EnhancedDMA
64channels
Compositevideo
DigitalRGB/YUV
Nand /
Nand/SM/
Async/OneNand
(AEMIF)
USB 2 .0
USB2.0PHY
Speaker
microphone
ASP (2x)
BufferLogic
VPSS
MMC/SD(x2)
SPII/F(x3)
UART (x3)
I2C
Timer/
WDT (x4-64)
GIO
PWM(x4)
RTO
VPFE
Enhanced
channels
3PCC / TC
(100 MHz
MPEG4/JPEG
Coprocessor
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
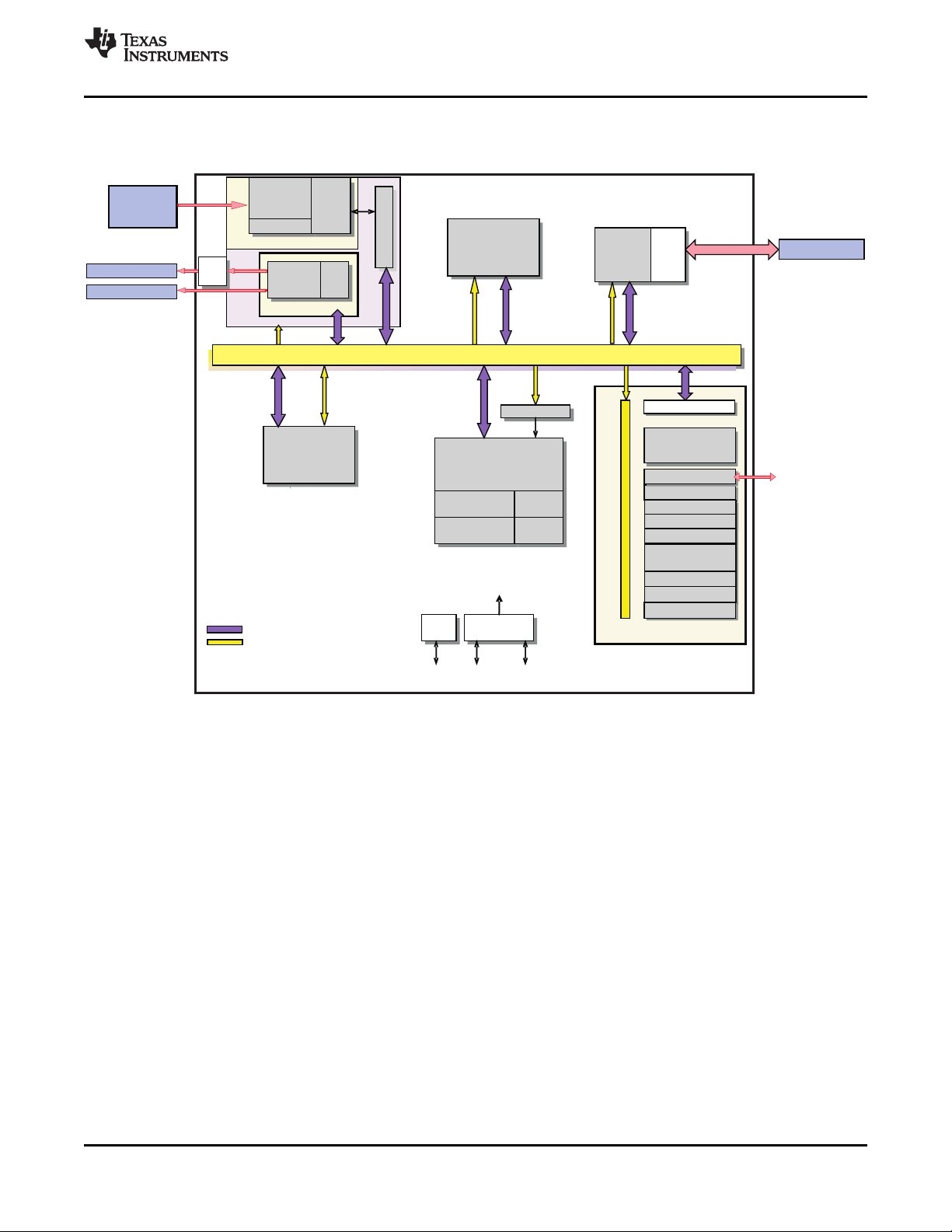
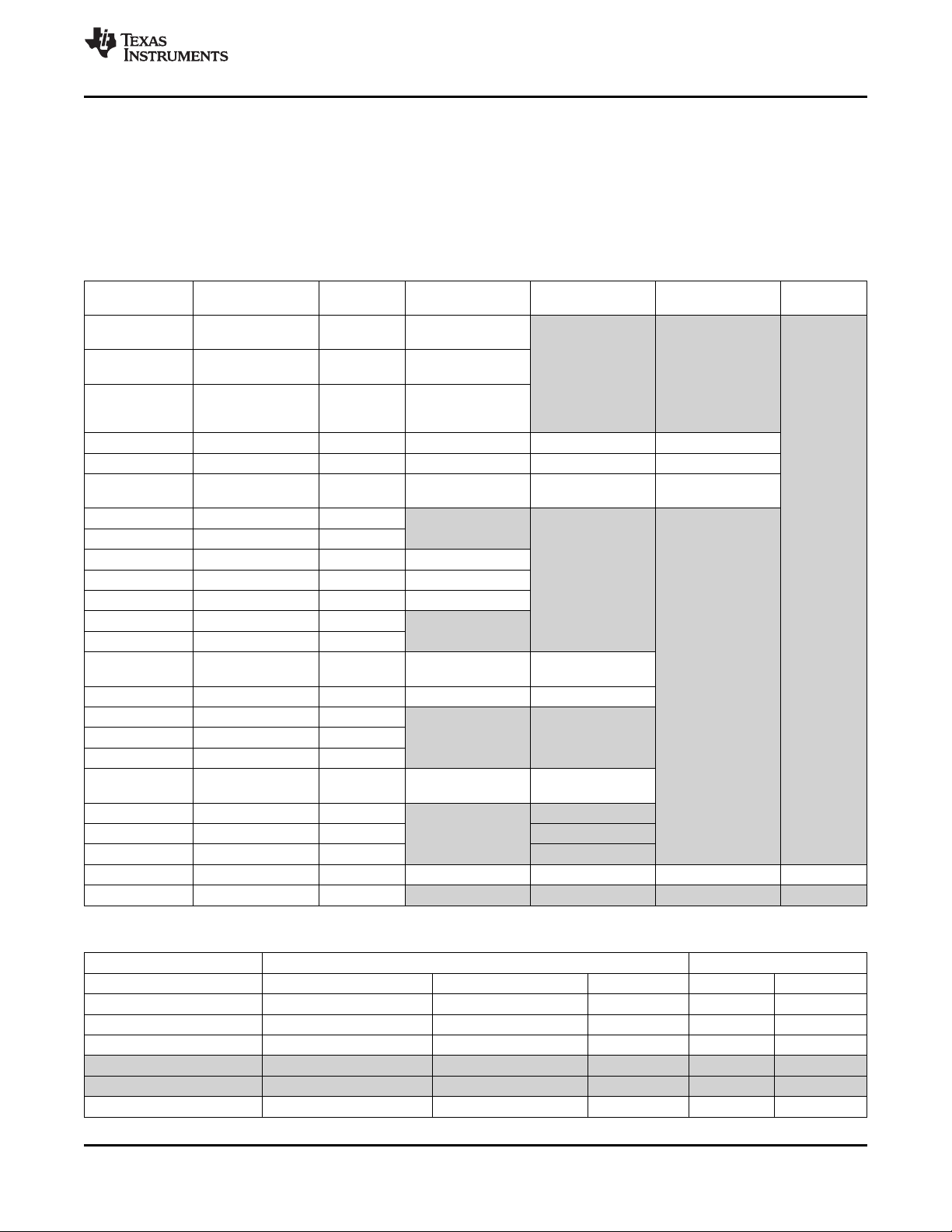
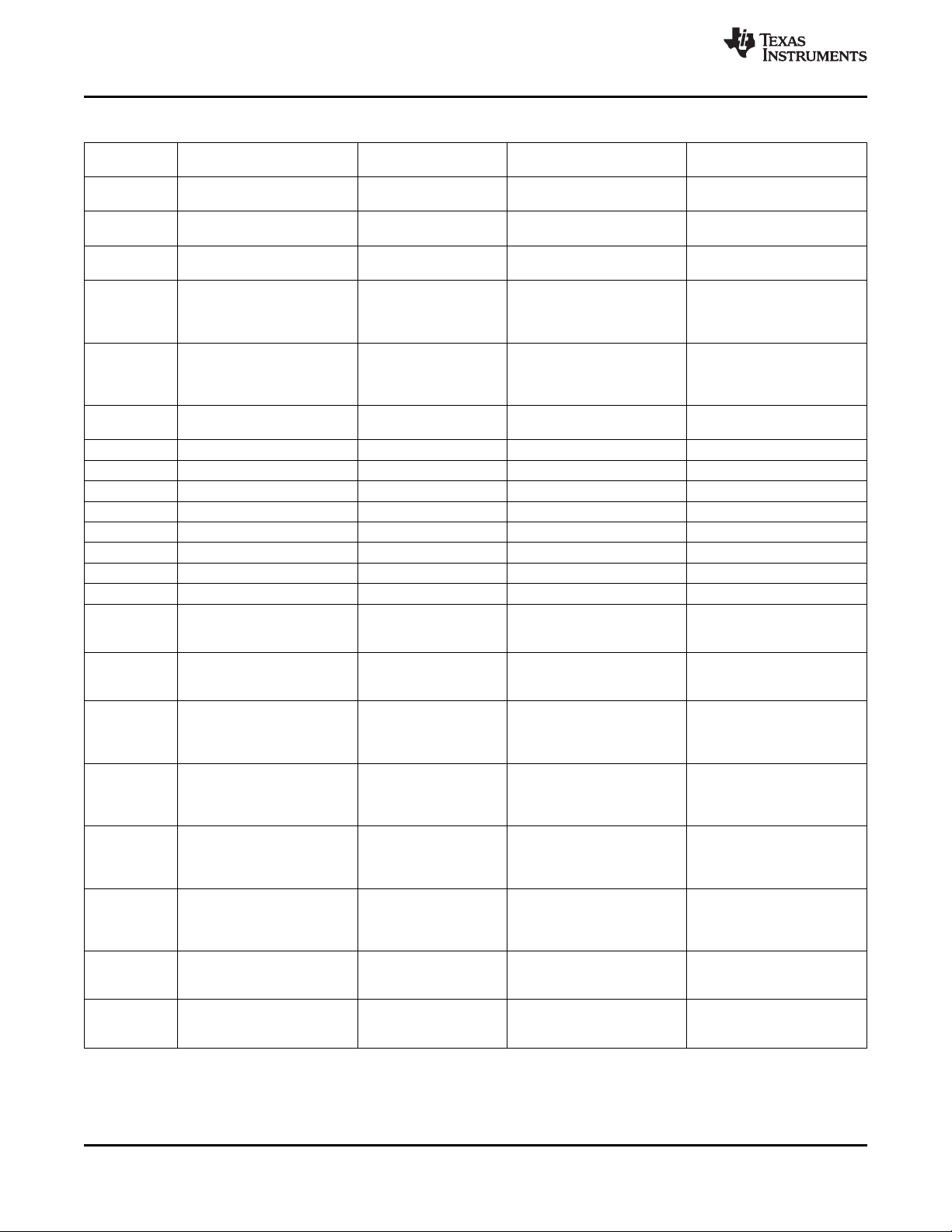
1.3 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 shows the functional block diagram of the DM355 device.
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Figure 1-1. Functional Block Diagram
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) 5
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
1 TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip
(DMSoC) ................................................... 1
1.1 Features .............................................. 1
1.2 Description ........................................... 3
1.3 Functional Block Diagram ............................ 5
Revision History .............................................. 7
2 Device Overview ........................................ 8
2.1 Device Characteristics ............................... 8
2.2 Memory Map Summary .............................. 9
2.3 Pin Assignments .................................... 11
2.4 Pin Functions ....................................... 15
2.5 Image Data Output - Video Processing Back End
(VPBE) .............................................. 17
2.6 Asynchronous External Memory Interface (AEMIF)
...................................................... 20
2.7 DDR Memory Interface ............................. 22
2.8 GPIO ................................................ 24
2.9 Multi-Media Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD)
Interfaces ........................................... 29
2.10 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Interface ............... 30
2.11 Audio Interfaces .................................... 31
2.12 UART Interface ..................................... 32
2
2.13 I
C Interface ........................................ 33
2.14 Serial Interface ..................................... 33
2.15 Clock Interface ...................................... 34
2.16 Real Time Output (RTO) Interface ................. 35
2.17 Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) Interface ........... 35
2.18 System Configuration Interface ..................... 36
2.19 Emulation ........................................... 37
2.20 Pin List .............................................. 38
2.21 Device Support ..................................... 57
3 Detailed Device Description ......................... 61
3.1 ARM Subsystem Overview ......................... 61
3.2 ARM926EJ-S RISC CPU ........................... 62
3.3 Memory Mapping ................................... 64
3.4 ARM Interrupt Controller (AINTC) .................. 65
3.5 Device Clocking .................................... 67
3.6 PLL Controller (PLLC) .............................. 78
3.7 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC) ................. 82
www.ti.com
3.8 System Control Module ............................. 82
3.9 Pin Multiplexing ..................................... 83
3.10 Device Reset ....................................... 84
3.11 Default Device Configurations ...................... 85
3.12 Device Boot Modes ................................. 89
3.13 Power Management ................................ 94
3.14 64-Bit Crossbar Architecture ....................... 95
3.15 MPEG4/JPEG Overview ............................ 98
4 Device Operating Conditions ....................... 99
4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Case
Temperature Range
(Unless Otherwise Noted) ................................. 99
4.2 Recommended Operating Conditions ............. 100
4.3 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended
Ranges of Supply Voltage and Operating Case
Temperature (Unless Otherwise Noted) .......... 101
5 DM355 Peripheral Information and Electrical
Specifications ......................................... 102
5.1 Parameter Information Device-Specific Information
..................................................... 102
5.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition
Behavior ........................................... 103
5.3 Power Supplies .................................... 103
5.4 Reset .............................................. 105
5.5 Oscillators and Clocks ............................ 106
5.6 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) ............ 111
5.7 External Memory Interface (EMIF) ................ 113
5.8 MMC/SD ........................................... 120
5.9 Video Processing Sub-System (VPSS) Overview
..................................................... 122
5.10 USB 2.0 ........................................... 134
5.11 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
(UART) ............................................ 136
5.12 Serial Port Interface (SPI) ......................... 138
5.13 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) ...................... 141
5.14 Audio Serial Port (ASP) ........................... 144
5.15 Timer .............................................. 152
5.16 Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) .................... 153
5.17 Real Time Out (RTO) ............................. 155
5.18 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG ................................ 156
6 Mechanical Data ...................................... 159
6.1 Thermal Data for ZCE ............................. 159
6.2 Packaging Information ............................ 159
6 Contents Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
This data sheet revision history highlights the technical changes made to the SPRS463F device-specific
data sheet to make it an SPRS463G revision.
Scope: Applicable updates to the DM35x DMSoC device family, specifically relating to the
TMS320DM355 device, have been incorporated.
Note: DM355 27J supports 198MHz max DDR.
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Revision History
NOTE: Page numbers for previous revisions may differ from page numbers in the current version.
Revision G Updates
ADDS/CHANGES/DELETES
Section 1.1 Changed Feature bullet from NAND Flash to NAND Flash (with SPI EEPROM Boot option).
Section 2.4 Table 2-9 and Table 2-11
• Added "Used to drive boot status LED signal (active low) in ROM boot modes." to pin number
P16.
• Deleted "Used to drive boot status LED signal (active low) in ROM boot modes." from pin
number V19.
Section 2.21.2 Updated Figure 2-5, Device Nomenclature.
Section 2.20 Updated Table 2-23, changed Reset State values.
Section 3.2.4 Changed NAND to NAND (with SPI EEPROM Boot option).
Section 3.5 Table 3-4, Table 3-10, and Table 3-13:
• Updated/Changed "(/2 or /1 programmable)" to "POSTDIV" and added "(/2 or /1
programmable)" to 2nd row
Section 3.5.4
Table 3-21 Updated BTSEL Function and NAND configuration in table.
Table 3-22 Updated table:
Section 3.12 Added Section 3.12.2, "RBL NAND Boot Process" and associated Standard and Compatibility
Section 3.12.1 Added ARM ROM Boot - SPI boot in NAND Mode bullet and sub-bullets.
Figure 3-6 Added SPI Flash to Diagram.
Section 4.2 Added last row to table including table note.
Section 4.3 Updated/Changed the following values in Section 4.3:
Table 5-5 Changed parameter 4 on table and added table note.
Table 5-6 Changed parameter 4 on table and added table note.
Table 5-45 Changed parameter 4 on table and added table note.
Section 5.7.1.3 Added table note to Table 5-14.
• Added Section 3.5.4.1.3.
• Added Section 3.5.4.2.3.
• Changed BTSEL[1:0] = 00 – Enable (NAND) to BTSEL[1:0] = 00 – Enable (NAND, SPI)
Changed SPI0 Module State from SyncRst to:
• BTSEL[1:0] = 00 – Enable (NAND, SPI)
• BTSEL[1:0] = 01 – SyncRst (OneNAND)
• BTSEL[1:0] = 10 – Enable (MMC/SD)
• BTSEL[1:0] = 11 – Enable (UART)
mode references throughout the document.
• IOHMAX value from "-100 mA" to "-4000 mA"
• IOZTYP (IPU disabled) value from "±10 µA" to "±20 µA"
• IOZTYP (IPU enabled) added value of ±100 µA"
Added "Test Conditions" for IOHand IOLparameters
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Contents 7
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
www.ti.com
2 Device Overview
2.1 Device Characteristics
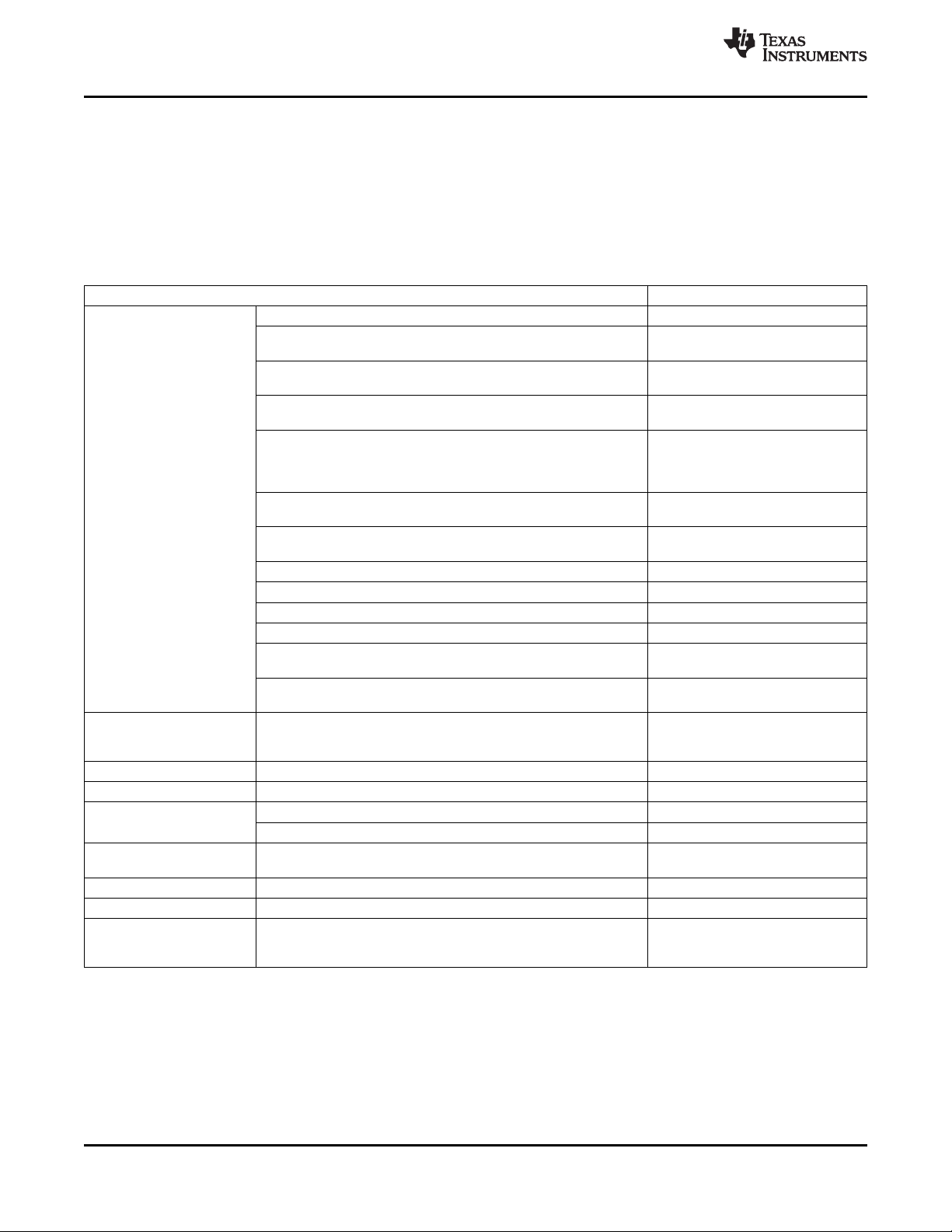
Table 2-1 provides an overview of the DMSoC. The table shows significant features of the device,
including the peripherals, capacity of on-chip RAM, ARM operating frequency, the package type with pin
count, etc.
Table 2-1. Characteristics of the Processor
HARDWARE FEATURES DM355
DDR2 / mDDR Memory Controller DDR2 / mDDR (16-bit bus width)
Asynchronous EMIF (AEMIF)
Flash Card Interfaces
EDMA
Peripherals
Not all peripherals pins are
available at the same time
(For more detail, see the
Device Configuration
section).
On-Chip CPU Memory Organization 16-KB I-cache, 8-KB D-cache,
JTAG BSDL_ID JTAGID register (address location: 0x01C4 0028) 0x0B73B01F
CPU Frequency (Maximum) MHz ARM 135, 216
Voltage
PLL Options
BGA Package 13 x 13 mm 337-Pin BGA (ZCE)
Process Technology 90 nm
Product Status
(1) Extended temperature supported for A216 and A135 devices.
(2) PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all parameters.
(2)
Timers
UART
SPI
I2C One (Master/Slave)
Audio Serial Port [ASP] Two ASP
General-Purpose Input/Output Port Up to 104
Pulse width modulator (PWM) Four outputs
Configurable Video Ports
USB 2.0
Core (V) 1.3 V
I/O (V) 3.3 V, 1.8 V
Reference frequency options 24 MHz (typical), 36 MHz
Configurable PLL controller PLL bypass, programmable PLL
Product Preview (PP),
Advance Information (AI), PD
or Production Data (PD)
Asynchronous (8/16-bit bus width)
RAM, Flash (NAND, OneNAND)
Two MMC/SD
One SmartMedia/xD
64 independent DMA channels
Eight EDMA channels
Three 64-Bit General Purpose (each
configurable as two separate 32-bit
Three (one with RTS and CTS flow
Three (each supports two slave
High, Full Speed Device
High, Full, Low Speed Host
32-KB RAM, 8-KB ROM
timers)
One 64-Bit Watch Dog
control)
devices)
One Input (VPFE)
One Output (VPBE)
ARM
(1)
, and 270 MHz
8 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
2.2 Memory Map Summary
Table 2-3 shows the memory map address ranges of the device. Table 2-3 depicts the expanded map of
the Configuration Space (0x01C0 0000 through 0x01FF FFFF). The device has multiple on-chip memories
associated with its processor and various subsystems. To help simplify software development a unified
memory map is used where possible to maintain a consistent view of device resources across all bus
masters. The bus masters are the ARM, EDMA, USB, and VPSS.
Table 2-2. DM355 Memory Map
Start Address End Address Size (Bytes) ARM EDMA USB VPSS
0x0000 0000 0x0000 3FFF 16K ARM RAM0
0x0000 4000 0x0000 7FFF 16K ARM RAM1
0x0000 8000 0x0000 FFFF 32K ARM ROM
0x0001 0000 0x0001 3FFF 16K ARM RAM0 (Data) ARM RAM0 ARM RAM0
0x0001 4000 0x0001 7FFF 16K ARM RAM1 (Data) ARM RAM1 ARM RAM1
0x0001 8000 0x0001 FFFF 32K ARM ROM (Data) ARM ROM ARM ROM
0x0002 0000 0x000F FFFF 896K Reserved
0x0010 0000 0x01BB FFFF 26M
0x01BC 0000 0x01BC 0FFF 4K ARM ETB Mem
0x01BC 1000 0x01BC 17FF 2K ARM ETB Reg Reserved
0x01BC 1800 0x01BC 18FF 256 ARM IceCrusher Reserved
0x01BC 1900 0x01BC FFFF 59136 Reserved
0x01BD 0000 0x01BF FFFF 192K
0x01C0 0000 0x01FF FFFF 4M CFG Bus CFG Bus
0x0200 0000 0x09FF FFFF 128M ASYNC EMIF (Data) ASYNC EMIF (Data)
0x0A00 0000 0x11EF FFFF 127M - 16K
0x11F0 0000 0x11F1 FFFF 128K Reserved Reserved
0x11F2 0000 0x1FFF FFFF 141M-64K
0x2000 0000 0x2000 7FFF 32K DDR EMIF Control DDR EMIF Control
0x2000 8000 0x41FF FFFF 544M-32K Reserved
0x4200 0000 0x49FF FFFF 128M Reserved Reserved
0x4A00 0000 0x7FFF FFFF 864M Reserved
0x8000 0000 0x8FFF FFFF 256M DDR EMIF DDR EMIF DDR EMIF DDR EMIF
0x9000 0000 0xFFFF FFFF 1792M Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
Mem Map Mem Map Mem Map Mem Map
(Instruction)
(Instruction)
(Instruction)
- only 8K used
- only 8K used
Peripherals Peripherals
Regs Regs
Reserved Reserved
Reserved
Table 2-3. DM355 ARM Configuration Bus Access to Peripherals
Address Accessibility
Region Start End Size ARM EDMA
EDMA CC 0x01C0 0000 0x01C0 FFFF 64K √ √
EDMA TC0 0x01C1 0000 0x01C1 03FF 1K √ √
EDMA TC1 0x01C1 0400 0x01C1 07FF 1K √ √
Reserved 0x01C1 0800 0x01C1 9FFF 38K √ √
Reserved 0x01C1 A000 0x01C1 FFFF 24K √ √
UART0 0x01C2 0000 0x01C2 03FF 1K √ √
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 9
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-3. DM355 ARM Configuration Bus Access to Peripherals (continued)
Address Accessibility
UART1 0x01C2 0400 0x01C2 07FF 1K √ √
Timer4/5 0x01C2 0800 0x01C2 0BFF 1K √ √
Real-time out 0x01C2 0C00 0x01C2 0FFF 1K √ √
I2C 0x01C2 1000 0x01C2 13FF 1K √ √
Timer0/1 0x01C2 1400 0x01C2 17FF 1K √ √
Timer2/3 0x01C2 1800 0x01C2 1BFF 1K √ √
WatchDog Timer 0x01C2 1C00 0x01C2 1FFF 1K √ √
PWM0 0x01C2 2000 0x01C2 23FF 1K √ √
PWM1 0x01C2 2400 0x01C2 27FF 1K √ √
PWM2 0x01C2 2800 0x01C2 2BFF 1K √ √
PWM3 0x01C2 2C00 0x01C2 2FFF 1K √ √
System Module 0x01C4 0000 0x01C4 07FF 2K √ √
PLL Controller 0 0x01C4 0800 0x01C4 0BFF 1K √ √
PLL Controller 1 0x01C4 0C00 0x01C4 0FFF 1K √ √
Power/Sleep Controller 0x01C4 1000 0x01C4 1FFF 4K √ √
Reserved 0x01C4 2000 0x01C4 7FFF 24K √ √
ARM Interrupt Controller 0x01C4 8000 0x01C4 83FF 1K √ √
Reserved 0x01C4 8400 0x01C6 3FFF 111K √ √
USB OTG 2.0 Regs / RAM 0x01C6 4000 0x01C6 5FFF 8K √ √
SPI0 0x01C6 6000 0x01C6 67FF 2K √ √
SPI1 0x01C6 6800 0x01C6 6FFF 2K √ √
GPIO 0x01C6 7000 0x01C6 77FF 2K √ √
SPI2 0x01C6 7800 0x01C6 FFFF 2K √ √
VPSS Subsystem 0x01C7 0000 0x01C7 FFFF 64K √ √
VPSS Clock Control 0x01C7 0000 0x01C7 007F 128 √ √
Hardware 3A 0x01C7 0080 0x01C7 00FF 128 √ √
Image Pipe (IPIPE) Interface 0x01C7 0100 0x01C7 01FF 256 √ √
On Screen Display 0x01C7 0200 0x01C7 02FF 256 √ √
Reserved 0x01C7 0300 0x01C7 03FF 256 √ √
Video Encoder 0x01C7 0400 0x01C7 05FF 512 √ √
CCD Controller 0x01C7 0600 0x01C7 07FF 256 √ √
VPSS Buffer Logic 0x01C7 0800 0x01C7 08FF 256 √ √
Reserved 0x01C7 0900 0x01C7 09FF 256 √ √
Image Pipe (IPIPE) 0x01C7 1000 0x01C7 3FFF 12K √ √
Reserved 0x01C7 4000 0x01CD FFFF 432K √ √
Multimedia / SD 1 0x01E0 0000 0x01E0 1FFF 8K √ √
ASP0 0x01E0 2000 0x01E0 3FFF 8K √ √
ASP1 0x01E0 4000 0x01E0 5FFF 8K √ √
UART2 0x01E0 6000 0x01E0 63FF 1K √ √
Reserved 0x01E0 6400 0x01E0 FFFF 39K √ √
ASYNC EMIF Control 0x01E1 0000 0x01E1 0FFF 4K √ √
Multimedia / SD 0 0x01E1 1000 0x01E1 FFFF 60K √ √
Reserved 0x01E2 0000 0x01FF FFFF 1792K √ √
ASYNC EMIF Data (CE0) 0x0200 0000 0x03FF FFFF 32M √ √
ASYNC EMIF Data (CE1) 0x0400 0000 0x05FF FFFF 32M √ √
Reserved 0x0600 0000 0x09FF FFFF 64M √ √
Reserved 0x0A00 0000 0x0BFF FFFF 32M √ √
www.ti.com
10 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
9
J
8
V
SSA_PLL2
7
V
DDA33_USB
6
5
4
31
H
G
V
DDA13_USB
V
SS
F
E
D
CIN2
C
B
A
VREF
CIN3CIN0
V
DDA_PLL2
V
SS
LCD_OE
FIELDVCLK
V
SS
V
SS
CV
DD
VSYNCEXTCLKVFB
V
DD_VOUT
V
DD_VOUT
V
DD_VOUT
HSYNCCOUT0COUT1TVOUT
TDOEMU0EMU1
V
SS_USB
USB_VBUS
COUT2COUT3IOUT
TDITMS
V
SS_USB
USB_IDCOUT4
V
SS
TRST
V
SS_USB_REF
USB_R1
V
DDD13_USB
USB_DRV
VBUS
CV
DD
YOUT7COUT5
MXO1
V
SS
V
SS_USB
V
DDA33_USB_
PLL
V
SS
YOUT5YOUT4YOUT0
MXI1
V
SS
USB_DPUSB_DM
V
SS
YOUT6YOUT2
CV
DD
2
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
IBIAS
V
SS
COUT6
COUT7
YOUT3
YOUT1
RSV01
V
DD
V
DD
NC
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
Table 2-3. DM355 ARM Configuration Bus Access to Peripherals (continued)
Reserved 0x0C00 0000 0x0FFF FFFF 64M √ √
2.3 Pin Assignments
Extensive use of pin multiplexing is used to accommodate the largest number of peripheral functions in
the smallest possible package. Pin multiplexing is controlled using a combination of hardware
configuration at device reset and software programmable register settings.
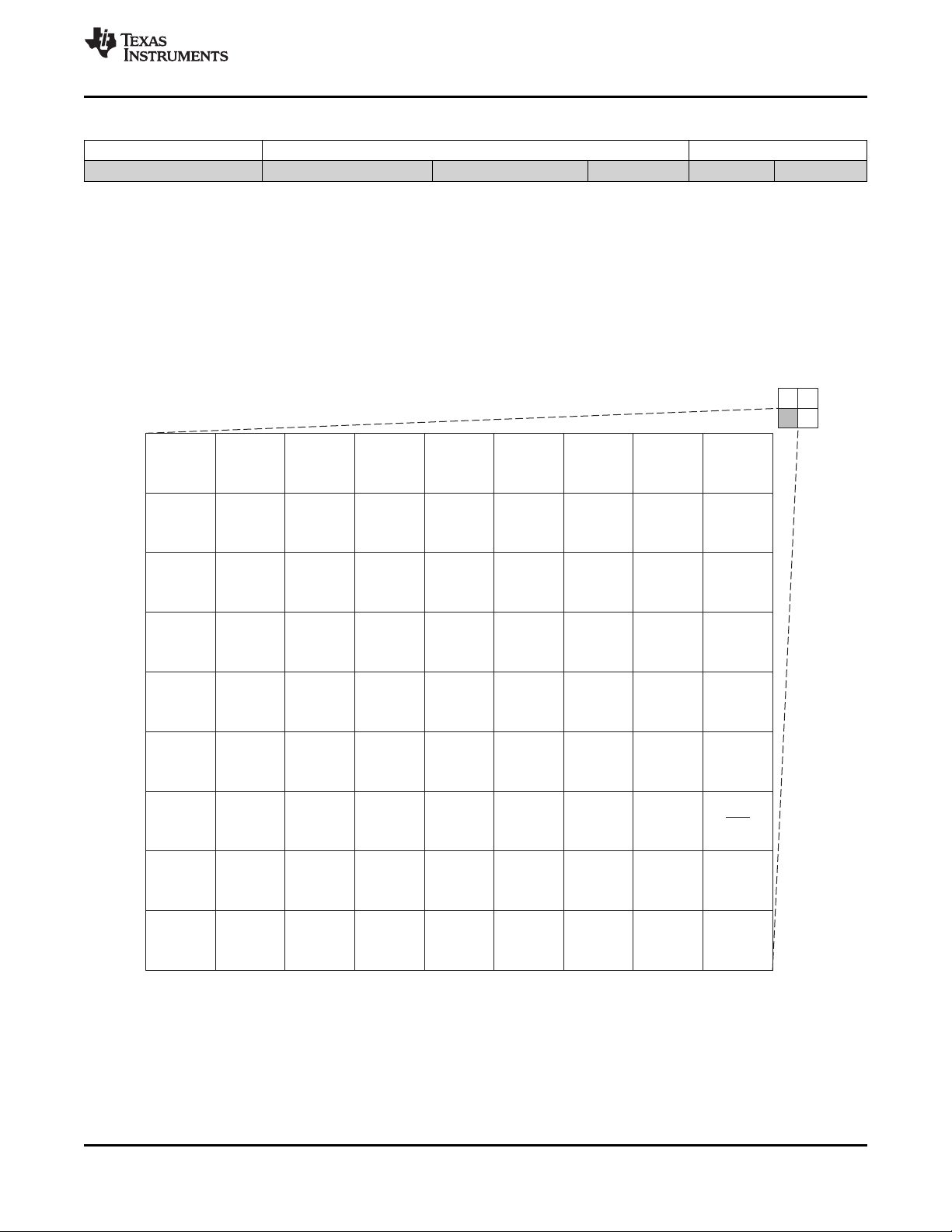
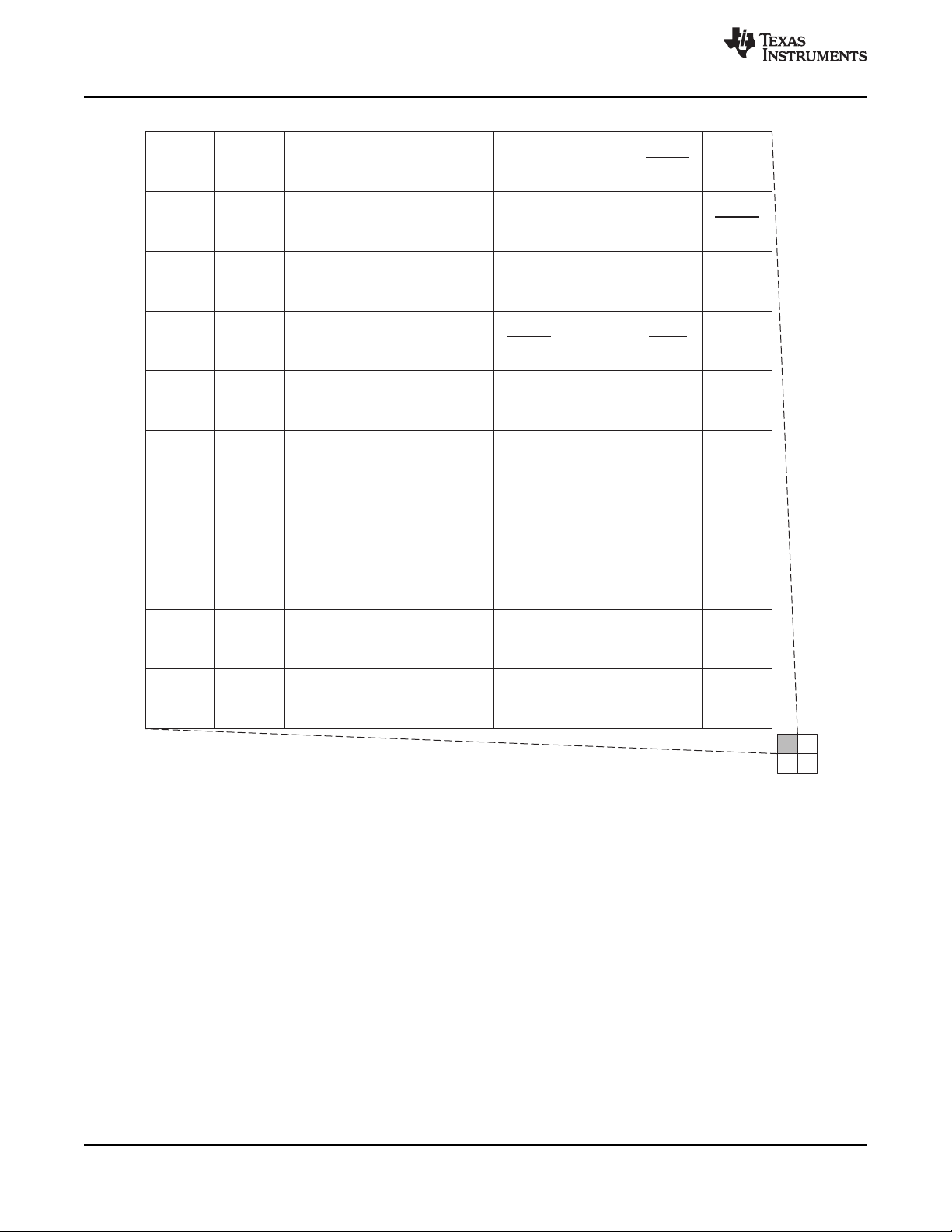
2.3.1 Pin Map (Bottom View)
Figure 2-1 through Figure 2-4 show the pin assignments in four quadrants (A, B, C, and D). Note that
micro-vias are not required. Contact your TI representative for routing recommendations.
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Address Accessibility
Figure 2-1. Pin Map [Quadrant A]
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 11
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
W
9
DDR_CLK
8
DDR_CLK
7654
DDR_A05
32
DDR_A02
1
V
DDR_A07DDR_A04DDR_A00
U
V
SS
T
PCLK
R
P
N
M
L
K
DDR_A11DDR_A09DDR_A08
V
SS
DDR_CAS
DDR_BA[2]
DDR_A12DDR_A10DDR_A01
V
SS
DDR_BA[0]DDR_BA[1]
DDR_A13DDR_A06
DDR_A03
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
DDR_ZNDDR_CSDDR_RAS
V
SS
V
SS
MXO2
V
DD_DDR
CV
DD
CV
DD
V
SS
CAM_WEN_
FIELD
CAM_VDYIN3
V
SS
MXI2
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_VIN
YIN0YIN2YIN4YIN1V
SS_MX2
V
SS
V
SS
CV
DD
CAM_HDCIN7
RSV05
V
SS
V
DD_DDR
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
YIN5
YIN6CIN5
RSV06
RSV04
V
SS
V
SS_DAC
V
DDA18V_DAC
V
DD
YIN7CIN4CIN1
V
SS
RSV03
V
SS
V
DD
CV
DD
CIN6
V
SS
RSV07RSV02
V
DD_VIN
V
DD_VIN
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
www.ti.com
Figure 2-2. Pin Map [Quadrant B]
12 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
CV
DD
19
W
18
DDR_
DQGATE0
17
DDR_DQ15
16
DDR_DQ13
15
DDR_DQ11
14
DDR_DQ10
13
DDR_DQ07
12
DDR_DQ05
11
DDR_DQ01
10
DDR_WE
EM_A13
V
V
SS
DDR_
DQGATE1
DDR_DQ14DDR_DQS[1]
DDR_DQ09DDR_DQ06
DDR_DQS[0]DDR_DQ00
DDR_CKE
EM_A12
U
UART0_RXD
V
SS
DDR_DQ12DDR_DQM[1]
V
SS
DDR_DQ08DDR_DQ04DDR_DQ02
DDR_VREF
EM_A08
T
UART0_TXD
CV
DD
V
SS
V
DD_DDR
DDR_DQM[0]
DDR_DQ03
EM_A05
R
EM_A10
UART1_TXD
EM_A11
UART1_RXD
I2C_SCLI2C_SDA
V
DD_DDR
V
SSA_DLL
V
DDA33_DDRDLL
EM_BA1
P
EM_A06
EM_A09EM_A07EM_A04
V
DD_DDR
EM_BA0
N
EM_A03EM_A01EM_A02
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
EM_D14
M
EM_D15
V
SS
EM_A00EM_D13
V
SS
V
DD
EM_D10
L
EM_D12EM_D11EM_D08EM_D04
CV
DD
V
SS
EM_D07
K
EM_D09EM_D06
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
CV
DD
V
DD
V
SS
CV
DD
CV
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
DD
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Figure 2-3. Pin Map [Quadrant C]
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 13
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
19181716151413121110
EM_D05
J
EM_D02
H
EM_CE1
G
F
E
D
C
V
DD
B
A
EM_D03EM_D01EM_CE0EM_WE
V
SS
EM_D00
EM_ADV
ASP0_DX
V
SSA_PLL1
CV
DD
EM_WAIT
ASP0_FSX
GIO003
V
DDA_PLL1
EM_OE
ASP0_CLKXASP0_CLKRASP0_FSR
GIO002
EM_CLK
ASP0_DRASP1_FSRASP1_FSX
GIO001
SPI1_
SDENA[0]
SPI1_SDORTCKTCK
ASP1_CLKXASP1_CLKRASP1_CLKS
GIO005
MMCSD0_
DATA1
CLKOUT1RESET
ASP1_DRASP1_DX
GIO007GIO000
MMCSD1_CLK
MMCSD0_CMDSPI1_SCLKSPI0_SCLK
CLKOUT3
V
SS_MX1
GIO006
MMCSD1_
DATA0
MMCSD1_
DATA3
MMCSD1_
DATA2
GIO004
MMCSD1_
CMD
MMCSD1_
DATA1
MMCSD0_
CLK
MMCSD0_
DATA0
MMCSD0_
DATA3
MMCSD0_
DATA2
SPI1_SDI
SPI0_
SDENA[0]
SPI0_SDI
SPI0_SDO
CLKOUT2
V
SS
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
V
SS
CV
DD
V
SS
CV
DD
CV
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
CV
DD
V
SS
V
SS
CV
DD
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
www.ti.com
Figure 2-4. Pin Map [Quadrant D]
14 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
2.4 Pin Functions
The pin functions tables (Table 2-4 through Table 2-22) identify the external signal names, the associated
pin (ball) numbers along with the mechanical package designator, the pin type, whether the pin has any
internal pullup or pulldown resistors, and a functional pin description. For more detailed information on
device configuration, peripheral selection, multiplexed/shared pins, and debugging considerations, see
Section 3. For the list of all pin in chronological order see Section 2.20
2.4.1 Image Data Input - Video Processing Front End
The CCD Controller module in the Video Processing Front End has an external signal interface for image
data input. It supports YUV (YC) inputs as well as Bayer RGB and complementary input signals (I.e.,
image data input).
The definition of the CCD controller data input signals depend on the input mode selected.
• In 16-bit YCbCr mode, the Cb and Cr signals are multiplexed on the Cl signals and the order is
configurable (i.e., Cb first or Cr first).
• In 8-bit YCbCr mode, the Y, Cb, and Cr signals are multiplexed and not only is the order selectable,
but also the half of the bus used.
Table 2-4. CCD Controller Signals for Each Input Mode
PIN NAME CCD 16-BIT YCbCr 8-BIT YCbCr
Cl7 Cb7,Cr7 Y7,Cb7,Cr7
Cl6 Cb6,Cr6 Y6,Cb6,Cr6
Cl5 CCD13 Cb5,Cr5 Y5,Cb5,Cr5
Cl4 CCD12 Cb4,Cr4 Y4,Cb4,Cr4
Cl3 CCD11 Cb3,Cr3 Y3,Cb3,Cr3
Cl2 CCD10 Cb2,Cr2 Y2,Cb2,Cr2
Cl1 CCD9 Cb1,Cr1 Y1,Cb1,Cr1
Cl0 CCD8 Cb0,Cr0 Y0,Cb0,Cr0
Yl7 CCD7 Y7 Y7,Cb7,Cr7
Yl6 CCD6 Y6 Y6,Cb6,Cr6
Yl5 CCD5 Y5 Y5,Cb5,Cr5
Yl4 CCD4 Y4 Y4,Cb4,Cr4
Yl3 CCD3 Y3 Y3,Cb3,Cr3
Yl2 CCD2 Y2 Y2,Cb2,Cr2
Yl1 CCD1 Y1 Y1,Cb1,Cr1
Yl0 CCD0 Y0 Y0,Cb0,Cr0
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 15
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-5. CCD Controller/Video Input Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
CIN7/
GIO101/ N3 I/O/Z
SPI2_SCLK
CIN6/
GIO100/ K5 I/O/Z
SPI2_SDO
CIN5/ • YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[05]
GIO099/ PD
SPI2_SDEN V
M3 I/O/Z
A[0]
CIN4/ • YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[04]
GIO098/ PD
SPI2_SDEN V
L4 I/O/Z
A[1]
CIN3/ PD
GIO097/ V
CIN2/ PD
GIO096/ V
CIN1/ PD
GIO095/ V
CIN0/ PD
GIO094/ V
YIN7/ PD
GIO093 V
YIN6/ PD
GIO092 V
J4 I/O/Z
J5 I/O/Z
L3 I/O/Z
J3 I/O/Z
L5 I/O/Z
M4 I/O/Z
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
Standard CCD/CMOS input: NOT USED
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[07]
PD
V
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[07]
SPI: SPI2 Clock
GIO: GIO[101]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: NOT USED
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[06]
PD
V
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[06]
SPI: SPI2 Data Out
GIO: GIO[100]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[13]
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[05]
SPI: SPI2 Chip Select
GIO: GIO[099]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[12]
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[04]
SPI: SPI2 Data In
GIO: GIO[098]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[11]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[03]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[03]
GIO: GIO[097]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[10]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[02]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[02]
GIO: GIO[097]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[09]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[01]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[01]
GIO: GIO[095]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[08]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[00]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[00]
GIO: GIO[094]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[07]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[07]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[07]
GIO: GIO[093]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[06]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[06]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[06]
GIO: GIO[092]
www.ti.com
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) PD = internal pull-down, PU = internal pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
(3) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
16 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-5. CCD Controller/Video Input Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
YIN5/ PD
GIO091 V
YIN4/ PD
GIO090 V
YIN3/ PD
GIO089 V
YIN2/ PD
GIO088 V
YIN1/ PD
GIO087 V
YIN0/ PD
GIO086 V
CAM_HD/ PD
GIO085 V
CAM_VD PD
GIO084 V
M5 I/O/Z
P3 I/O/Z
R3 I/O/Z
P4 I/O/Z
P2 I/O/Z
P5 I/O/Z
N5 I/O/Z output (master mode). Tells the CCDC when a new line starts.
R4 I/O/Z (master mode). Tells the CCDC when a new frame starts.
CAM_WEN
_FIELD\ R5 I/O/Z
GIO083
PCLK/ PD Pixel clock input (strobe for lines C17 through Y10)
GIO082 V
T3 I/O/Z
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[05]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[05]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[05]
GIO: GIO[091]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[04]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[04]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[04]
GIO: GIO[090]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[03]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[03]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[03]
GIO: GIO[089]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[02]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[02]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[02]
GIO: GIO[088]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[01]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[01]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[01]
GIO: GIO[087]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[00]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[00]
DD_VIN
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[00]
GIO: GIO[086]
Horizontal synchronization signal that can be either an input (slave mode) or an
DD_VIN
GIO: GIO[085]
Vertical synchronization signal that can be either an input (slave mode) or an output
DD_VIN
GIO: GIO[084]
Write enable input signal is used by external device (AFE/TG) to gate the DDR
output of the CCDC module. Alternately, the field identification input signal is used
PD by external device (AFE/TG) to indicate which of two frames is input to the CCDC
V
DD_VIN
module for sensors with interlaced output. CCDC handles 1- or 2-field sensors in
hardware.
GIO: GIO[083]
DD_VIN
GIO: GIO[0082]
2.5 Image Data Output - Video Processing Back End (VPBE)
The Video Encoder/Digital LCD interface module in the video processing back end has an external signal
interface for digital image data output as described in Table 2-7 and Table 2-8.
The digital image data output signals support multiple functions / interfaces, depending on the display
mode selected. The following table describes these modes. Parallel RGB mode with more than RGB565
signals requires enabling pin multiplexing to support (i.e., for RGB666 mode).
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 17
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-6. Signals for VPBE Display Modes
PIN NAME YCC16 YCC8/ PRGB SRGB
REC656
HSYNC HSYNC HSYNC HSYNC HSYNC
GIO073
VSYNC VSYNC VSYNC VSYNC VSYNC
GIO072
LCD_OE As needed As needed As needed As needed
GIO071
FIELD As needed As needed As needed As needed
GIO070
R2
PWM3C
EXTCLK As needed As needed As needed As needed
GIO069
B2
PWM3D
VCLK VCLK VCLK VCLK VCLK
GIO068
YOUT7 Y7 Y7,Cb7,Cr7 R7 Data7
YOUT6 Y6 Y6,Cb6,Cr6 R6 Data6
YOUT5 Y5 Y5,Cb5,Cr5 R5 Data5
YOUT4 Y4 Y4,Cb4,Cr4 R4 Data4
YOUT3 Y3 Y3,Cb3,Cr3 R3 Data3
YOUT2 Y2 Y2,Cb2,Cr2 G7 Data2
YOUT1 Y1 Y1,Cb1,Cr1 G6 Data1
YOUT0 Y0 Y0,Cb0,Cr0 G5 Data0
COUT7 C7 LCD_AC G4 LCD_AC
GIO081
PWM0
COUT6 C6 LCD_OE G3 LCD_OE
GIO080
PWM1
COUT5 C5 BRIGHT G2 BRIGHT
GIO079
PWM2A
RTO0
COUT4 C4 PWM B7 PWM
GIO078
PWM2B
RTO1
COUT3 C3 CSYNC B6 CSYNC
GIO077
PWM2C
RTO2
COUT2 C2 - B5 GIO076
PWM2D
RTO3
COUT1 C1 - B4 GIO075
PWM3A
COUT0 C0 - B3 GIO074
PWM3B
www.ti.com
18 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-7. Digital Video Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
YOUT7-R7 C3 I/O/Z V
YOUT6-R6 A4 I/O/Z V
YOUT5-R5 B4 I/O/Z V
YOUT4-R4 B3 I/O/Z V
YOUT3-R3 B2 I/O/Z V
YOUT2-G7 A3 I/O/Z V
YOUT1-G6 A2 I/O/Z V
YOUT0-G5 B1 I/O/Z V
COUT7-
G4/GIO081 C2 I/O/Z V
/PWM0
COUT6-G3
/GIO080 D2 I/O/Z V
/PWM1
COUT5-G2
/ GIO079 /
PWM2A /
C1 I/O/Z V
RTO0
COUT4-B7 /
GIO078 /
PWM2B /
D3 I/O/Z V
RTO1
COUT3-B6 /
GIO077 /
PWM2C /
E3 I/O/Z V
RTO2
COUT2-B5 /
GIO076 /
PWM2D /
E4 I/O/Z V
RTO3
COUT1-B4 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
GIO075 / F3 I/O/Z V
PWM3A PWM3A
COUT0-B3 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
GIO074 / F4 I/O/Z V
PWM3B PWM3B
HSYNC / PD Video Encoder: Horizontal Sync
GIO073 V
VSYNC / PD Video Encoder: Vertical Sync
GIO072 V
F5 I/O/Z
G5 I/O/Z
FIELD / Video Encoder: Field identifier for interlaced display formats
GIO070 / GIO: GIO[070]
R2 / Digital Video Out: R2
H4 I/O/Z V
PWM3C PWM3C
EXTCLK /
GIO069 / PD
B2 / V
G3 I/O/Z GIO: GIO[069]
PWM3D
VCLK / Video Encoder: Video Output Clock
GIO068 GIO: GIO[068]
H3 I/O/Z V
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
(4) To reduce EMI and reflections, depending on the trace length, approximately 22 Ω to 50 Ω damping resistors are recommend on the
following outputs placed near the DM355: YOUT(0-7),COUT(0-7), HSYNC,VSYNC,LCD_OE,FIELD,EXTCLK,VCLK. The trace lengths
should be minimized.
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
(4)
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[081] PWM0
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[080] PWM1
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[079] PWM2A RTO0
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[078] PWM2B RTO1
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[077] PWM2C RTO2
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[076] PWM2D RTO3
GIO: GIO[075]
GIO: GIO[074]
GIO: GIO[073]
GIO: GIO[072]
Video Encoder: External clock input, used if clock rates > 27 MHz are needed, e.g.
74.25 MHz for HDTV digital output
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: B2
PWM3D
DD_VOUT
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 19
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
www.ti.com
Table 2-8. Analog Video Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
VREF J7 A I/O/Z
IOUT E1 A I/O/Z
IBIAS F2 A I/O/Z configuration. When the DAC is not used, the IBIAS signal should be connected to
VFB G1 A I/O/Z
TVOUT F1 A I/O/Z V circuit connection). When the DAC is not used, the TVOUT signal should be left as a
V
DDA18_DAC
V
SSA_DAC
L7 PWR
L8 GND
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal. Specifies the operating I/O supply
voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(2) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2)
DESCRIPTION
Video DAC: Reference voltage output (0.45V, 0.1uF to GND). When the DAC is not
used, the VREF signal should be connected to VSS.
Video DAC: Pre video buffer DAC output (1000 ohm to VFB). When the DAC is not
used, the IOUT signal should be connected to VSS.
Video DAC: External resistor (2550 Ohms to GND) connection for current bias
VSS.
Video DAC: Pre video buffer DAC output (1000 Ohms to IOUT, 1070 Ohms to
TVOUT). When the DAC is not used, the VFB signal should be connected to VSS.
Video DAC: Analog Composite NTSC/PAL output (SeeFigure 5-31 andFigure 5-32 for
No Connect or connected to VSS.
Video DAC: Analog 1.8V power. When the DAC is not used, the V
should be connected to VSS.
Video DAC: Analog 1.8V ground. When the DAC is not used, the V
should be connected to VSS.
DDA18_DAC
SSA_DAC
signal
signal
2.6 Asynchronous External Memory Interface (AEMIF)
The Asynchronous External Memory Interface (AEMIF) signals support AEMIF, NAND, and OneNAND.
Table 2-9. Asynchronous EMIF/NAND/OneNAND Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
EM_A13/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[13]
GIO067/ V19 I/O/Z GIO: GIO[67]
BTSEL[1] System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at power-on-reset to determine boot method.
EM_A12/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[12]
GIO066/ U19 I/O/Z GIO: GIO[66]
BTSEL[0] System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at power-on-reset to determine boot method.
EM_A11/
GIO065/ R16 I/O/Z
AECFG[3]
EM_A10/ GIO: GIO[64]
GIO064/ R18 I/O/Z AECFG[3:0] sampled at power-on-reset to AECFG configuration. AECFG[2:1]
AECFG[2] sets default for PinMux2_EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0 definition (EM_BA0,
EM_A09/ GIO: GIO[63]
GIO063/ P17 I/O/Z AECFG[3:0] sampled at power-on-reset to AECFG configuration. AECFG[2:1]
AECFG[1] sets default for PinMux2_EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0 definition (EM_BA0,
EM_A08/
GIO062/ T19 I/O/Z
AECFG[0] • PinMux2_EM_A0_BA1: AEMIF address width (OneNAND or NAND)
EM_A07/
GIO061
P16 I/O/Z V
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
PD
V
DD
PD
V
DD
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[11]
PU GIO: GIO[65]
V
DD
AECFG[3:0] sampled at power-on-reset to AECFG configuration. AECFG[3] sets
default for PinMux2_EM_D15_8: AEMIF default bus width (16 or 8 bits)
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[10]
PU
V
DD
EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[09]
PD
V
DD
EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[08]
GIO: GIO[62]
AECFG[0] sets default for:
V
PU
DD
• PinMux2_EM_A13_3: AEMIF address width (OneNAND or NAND)
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[07]
DD
GIO: GIO[61]
Used to drive boot status LED signal (active low) in ROM boot modes.
20 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-9. Asynchronous EMIF/NAND/OneNAND Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
EM_A06/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[06]
GIO060 GIO: GIO[60]
EM_A05/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[05]
GIO059 GIO: GIO[59]
EM_A04/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[04]
GIO058 GIO: GIO[58]
EM_A03/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[03]
GIO057 GIO: GIO[57]
P18 I/O/Z V
R19 I/O/Z V
P15 I/O/Z V
N18 I/O/Z V
EM_A02/ N15 I/O/Z V
EM_A01/ N17 I/O/Z V
EM_A00/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[00]
GIO056 GIO: GIO[56]
EM_BA1/ • In 16-bit mode, lowest address bit.
GIO055
M16 I/O/Z V
P19 I/O/Z V
EM_BA0/
GIO054 N19 I/O/Z V
EM_A14
EM_D15/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 15
GIO053 GIO: GIO[053]
EM_D14/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 14
GIO052 GIO: GIO[052]
EM_D13/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 13
GIO051 GIO: GIO[051]
EM_D12/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 12
GIO050 GIO: GIO[050]
EM_D11/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 11
GIO049 GIO: GIO[049]
EM_D10/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 10
GIO048 GIO: GIO[048]
EM_D09/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 09
GIO047 GIO: GIO[047]
EM_D08/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 08
GIO046 GIO: GIO[046]
EM_D07/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 07
GIO045 GIO: GIO[045]
EM_D06/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 06
GIO044 GIO: GIO[044]
EM_D05/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 05
GIO043 GIO: GIO[043]
EM_D04/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 04
GIO042 GIO: GIO[042]
EM_D03/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 03
GIO041 GIO: GIO[041]
EM_D02/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 02
GIO040 GIO: GIO[040]
EM_D01/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 01
GIO039 GIO: GIO[039]
EM_D00/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 00
GIO038 GIO: GIO[038]
M18 I/O/Z V
M19 I/O/Z V
M15 I/O/Z V
L18 I/O/Z V
L17 I/O/Z V
L19 I/O/Z V
K18 I/O/Z V
L16 I/O/Z V
K19 I/O/Z V
K17 I/O/Z V
J19 I/O/Z V
L15 I/O/Z V
J18 I/O/Z V
H19 I/O/Z V
J17 I/O/Z V
H18 I/O/Z V
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[02]
NAND/SM/xD: CLE - Command latch enable output
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[01]
NAND/SM/xD: ALE - Address latch enable output
Async EMIF: Bank address 1 signal - 16-bit address:
DD
• In 8-bit mode, second lowest address bit.
GIO: GIO[055]
Async EMIF: Bank address 0 signal - 8-bit address:
DD
• In 8-bit mode, lowest address bit. or can be used as an extra address line
(bit14) when using 16-bit memories.
GIO: GIO[054]
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 21
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-9. Asynchronous EMIF/NAND/OneNAND Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
EM_CE0/ standard asynchronous memories (example: flash), OneNAND, or NAND
GIO037 memory. Used for the default boot and ROM boot modes.
EM_CE1/
GIO036
EM_WE/
GIO035
EM_OE/
GIO034
EM_WAIT/
GIO033
EM_ADV/ OneNAND: Address valid detect for OneNAND interface
GIO032 GIO: GIO[032]
EM_CLK/ OneNAND: Clock for OneNAND flash interface
GIO031 GIO: GIO[031]
J16 I/O/Z V
G19 I/O/Z V
J15 I/O/Z V
F19 I/O/Z V
G18 I/O/Z V
H16 I/O/Z V
E19 I/O/Z V
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
Async EMIF: Lowest numbered chip select. Can be programmed to be used for
DD
GIO: GIO[037]
Async EMIF: Second chip select. Can be programmed to be used for standard
DD
asynchronous memories(example: flash), OneNAND, or NAND memory.
GIO: GIO[036]
Async EMIF: Write Enable
DD
NAND/SM/xD: WE (Write Enable) output
GIO: GIO[035]
Async EMIF: Output Enable
DD
NAND/SM/xD: RE (Read Enable) output
GIO: GIO[034]
Async EMIF: Async WAIT
DD
DD
DD
NAND/SM/xD: RDY/ BSY input
GIO: GIO[033]
2.7 DDR Memory Interface
www.ti.com
The DDR EMIF supports DDR2 and mobile DDR.
Table 2-10. DDR Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
DDR_CLK W9 I/O/Z V
DDR_CLK W8 I/O/Z V
DDR_RAS T6 I/O/Z V
DDR_CAS V9 I/O/Z V
DDR_WE W10 I/O/Z V
DDR_CS T8 I/O/Z V
DDR_CKE V10 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQM[1] U15 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQM[0] T12 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQS[1] V15 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQS[0] V12 I/O/Z V
DDR_BA[2] V8 I/O/Z V
DDR_BA[1] U7 I/O/Z V
DDR_BA[0] U8 I/O/Z V
DDR_A13 U6 I/O/Z V
DDR_A12 V7 I/O/Z V
DDR_A11 W7 I/O/Z V
DDR_A10 V6 I/O/Z V
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
DDR Data Clock
DDR Complementary Data Clock
DDR Row Address Strobe
DDR Column Address Strobe
DDR Write Enable
DDR Chip Select
DDR Clock Enable
Data mask outputs:
• DDR_DQM[1] - For DDR_DQ[15:8]
• DDR_DQM[0] - For DDR_DQ[7:0]
Data strobe input/outputs for each byte of the 16-bit data bus used to
synchronize the data transfers. Output to DDR when writing and inputs when
reading.
• DDR_DQS[1] - For DDR_DQ[15:8]
• DDR_DQS[0] - For DDR_DQ[7:0]
Bank select outputs. Two are required for 1Gb DDR2 memories.
Bank select outputs. Two are required for 1Gb DDR2 memories.
Bank select outputs. Two are required for 1Gb DDR2 memories.
DDR Address Bus bit 13
DDR Address Bus bit 12
DDR Address Bus bit 11
DDR Address Bus bit 10
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
22 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-10. DDR Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
DDR_A09 W6 I/O/Z V
DDR_A08 W5 I/O/Z V
DDR_A07 V5 I/O/Z V
DDR_A06 U5 I/O/Z V
DDR_A05 W4 I/O/Z V
DDR_A04 V4 I/O/Z V
DDR_A03 W3 I/O/Z V
DDR_A02 W2 I/O/Z V
DDR_A01 V3 I/O/Z V
DDR_A00 V2 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ15 W17 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ14 V16 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ13 W16 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ12 U16 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ11 W15 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ10 W14 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ09 V14 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ08 U13 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ07 W13 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ06 V13 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ05 W12 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ04 U12 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ03 T11 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ02 U11 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ01 W11 I/O/Z V
DDR_DQ00 V11 I/O/Z V
DDR_ DDR: Loopback signal for external DQS gating. Route to DDR and back to
DQGATE0 DDR_DQGATE1 with same constraints as used for DDR clock and data.
DDR_ DDR: Loopback signal for external DQS gating. Route to DDR and back to
DQGATE1 DDR_DQGATE0 with same constraints as used for DDR clock and data.
W18 I/O/Z V
V17 I/O/Z V
DDR_VREF U10 I/O/Z V
V
SSA_DLL
V
DDA33_DDRDL
L
R11 I/O/Z V
R10 I/O/Z V
DDR_ZN T9 I/O/Z V
TYPE
(1)
(2) (3)
OTHER
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
SSA_DLL
DDA33_DDRDLL
DD_DDR
DESCRIPTION
DDR Address Bus bit 09
DDR Address Bus bit 08
DDR Address Bus bit 07
DDR Address Bus bit 06
DDR Address Bus bit 05
DDR Address Bus bit 04
DDR Address Bus bit 03
DDR Address Bus bit 02
DDR Address Bus bit 01
DDR Address Bus bit 00
DDR Data Bus bit 15
DDR Data Bus bit 14
DDR Data Bus bit 13
DDR Data Bus bit 12
DDR Data Bus bit 11
DDR Data Bus bit 10
DDR Data Bus bit 09
DDR Data Bus bit 08
DDR Data Bus bit 07
DDR Data Bus bit 06
DDR Data Bus bit 05
DDR Data Bus bit 04
DDR Data Bus bit 03
DDR Data Bus bit 02
DDR Data Bus bit 01
DDR Data Bus bit 00
DDR: Voltage input for the SSTL_18 I/O buffers. Note even in the case of
mDDR an external resistor divider connected to this pin is necessary.
DDR: Ground for the DDR DLL
DDR: Power (3.3 V) for the DDR DLL
DDR: Reference output for drive strength calibration of N and P channel
outputs. Tie to ground via 50 ohm resistor @ 0.5% tolerance.
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 23
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
2.8 GPIO
The General Purpose I/O signals provide generic I/O to external devices. Most of the GIO signals are
multiplexed with other functions.
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
GIO000 C16 I/O/Z V
GIO001 E14 I/O/Z V
GIO002 F15 I/O/Z V
GIO003 G15 I/O/Z V
GIO004 B17 I/O/Z V
GIO005 D15 I/O/Z V
GIO006 B18 I/O/Z V
GIO007 /
SPI0_SDE C17 I/O/Z V
NA[1]
SPI1_SD
O / E12 I/O/Z V
GIO008
SPI1_SDI
/ GIO009 /
SPI1_SDE
A13 I/O/Z V
NA[1]
SPI1_SCL
K / C13 I/O/Z V
GIO010
SPI1_SDE
NA[0] / E13 I/O/Z V
GIO011
UART1_T
XD / R17 I/O/Z V
GIO012
UART1_R
XD / R15 I/O/Z V
GIO013
I2C_SCL / I2C: Serial Clock GIO:
GIO014 GIO[014]
I2C_SDA / I2C: Serial Data
GIO015 GIO: GIO[015]
CLKOUT3 CLKOUT: Output Clock 3
/ GIO016 GIO: GIO[016]
CLKOUT2 CLKOUT: Output Clock 2
/ GIO017 GIO: GIO[017]
CLKOUT1 CLKOUT: Output Clock 1
/ GIO018 GIO: GIO[018]
R14 I/O/Z V
R13 I/O/Z V
C11 I/O/Z V
A11 I/O/Z V
D12 I/O/Z V
MMCSD1
_DATA0 / MMCSD1: DATA0
GIO019 / A18 I/O/Z V
UART2_T UART2: Transmit Data
XD
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
GIO:GIO[000] is sampled at reset and stored in the GIO0_RESET bit of the
BOOTCFG register.
DD
Active low during MMC/SD boot (can be used as MMC/SD power control).
Can be used as external clock input for Timer 3.
Note: The GIO000 pin must be held high during NAND boot for the boot
process to fuction properly.
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
GIO: GIO[001] Can be used as external clock input for Timer 3.
GIO: GIO[002] Can be used as external clock input for Timer 3.
GIO: GIO[003] Can be used as external clock input for Timer 3.
GIO: GIO[004]
GIO: GIO[005]
GIO: GIO[006]
GIO: GIO[007]
SPI0: Chip Select 1
SPI1: Data Out
GIO: GIO[008]
SPI1: Data In -OR- SPI1: Chip Select 1 GIO: GIO[009]
SPI1: Clock GIO:
GIO[010]
SPI1: Chip Select 0
GIO: GIO[011]
UART1: Transmit Data
GIO: GIO[012]
UART1: Receive Data
GIO: GIO[013]
GIO: GIO[019]
www.ti.com
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
24 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
MMCSD1
_DATA1 / MMCSD1: DATA1
GIO020 / B15 I/O/Z V
UART2_R UART2: Receive Data
XD
MMCSD1
_DATA2 / MMCSD1: DATA2
GIO021 / A16 I/O/Z V
UART2_C UART2: CTS
TS
MMCSD1
_DATA3 / MMCSD1: DATA3
GIO022 / B16 I/O/Z V
UART2_R UART2: RTS
TS
MMCSD1
_CMD / A17 I/O/Z V
GIO023
MMCSD1
_CLK / C15 I/O/Z V
GIO024
ASP0_FS
R / F16 I/O/Z V
GIO025
ASP0_CL
KR / F17 I/O/Z V
GIO026
ASP0_DR ASP0: Receive Data
/ GIO027 GIO: GIO[027]
E18 I/O/Z V
ASP0_FS
X / G17 I/O/Z V
GIO028
ASP0_CL
KX / F18 I/O/Z V
GIO029
ASP0_DX ASP0: Transmit Data
/ GIO030 GIO: GIO[030]
EM_CLK /
GIO031
EM_ADV / PD OneNAND: Address Valid Detect for OneNAND interface
GIO032 V
EM_WAIT PU Async EMIF: Async WAIT NAND/SM/xD: RDY/_BSY input
/ GIO033 V
EM_OE /
GIO034
EM_WE /
GIO035
EM_CE1 /
GIO036
EM_CE0 / standard asynchronous memories (example: flash), OneNand or NAND memory.
GIO037 Used for the default boot and ROM boot modes.
EM_D00 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[00]
GIO038 GIO: GIO[038]
H15 I/O/Z V
E19 I/O/Z V
H16 I/O/Z
G18 I/O/Z
F19 I/O/Z V
J15 I/O/Z V
G19 I/O/Z V
J16 I/O/Z V
H18 I/O/Z V
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
GIO: GIO[020]
GIO: GIO[021]
GIO: GIO[022]
MMCSD1: Command
GIO: GIO[023]
MMCSD1: Clock
GIO: GIO[024]
ASP0: Receive Frame Synch
GIO: GIO[025]
ASP0: Receive Clock
GIO: GIO[026]
ASP0: Transmit Frame Synch
GIO: GIO[028]
ASP0: Transmit Clock
GIO: GIO[029]
OneNAND: Clock signal for OneNAND flash interface GIO: GIO[031]
GIO: GIO[032]
GIO: GIO[033]
Async EMIF: Output Enable
DD
NAND/SM/xD: RE (Read Enable) output
GIO: GIO[034]
Async EMIF: Write Enable
DD
NAND/SM/xD: WE (Write Enable) output
GIO: GIO[035]
Async EMIF: Second Chip Select., Can be programmed to be used for standard
DD
asynchronous memories (example: flash), OneNand or NAND memory.
GIO: GIO[036]
Async EMIF: Lowest numbered Chip Select. Can be programmed to be used for
DD
GIO: GIO[037]
DD
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 25
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
EM_D01 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[01]
GIO039 GIO: GIO[039]
EM_D02 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[02]
GIO040 GIO: GIO[040]
EM_D03 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[03]
GIO041 GIO: GIO[041]
EM_D04 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[04]
GIO042 GIO: GIO[042]
EM_D05 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[05]
GIO043 GIO: GIO[043]
EM_D06 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[06]
GIO044 GIO: GIO[044]
EM_D07 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[07]
GIO045 GIO: GIO[045]
EM_D08 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[08]
GIO046 GIO: GIO[046]
EM_D09 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[09]
GIO047 GIO: GIO[047]
EM_D10 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[10]
GIO048 GIO: GIO[048]
EM_D11 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[11]
GIO049 GIO: GIO[049]
EM_D12 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[12]
GIO050 GIO: GIO[050]
EM_D13 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[13]
GIO051 GIO: GIO[051]
EM_D14 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[14]
GIO052 GIO: GIO[052]
EM_D15 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[15]
GIO053 GIO: GIO[053]
J17 I/O/Z V
H19 I/O/Z V
J18 I/O/Z V
L15 I/O/Z V
J19 I/O/Z V
K17 I/O/Z V
K19 I/O/Z V
L16 I/O/Z V
K18 I/O/Z V
L19 I/O/Z V
L17 I/O/Z V
L18 I/O/Z V
M15 I/O/Z V
M19 I/O/Z V
M18 I/O/Z V
EM_BA0 /
GIO054 / N19 I/O/Z V
EM_A14
EM_BA1 /
GIO055
EM_A00 /
GIO056
EM_A03 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[03]
GIO057 GIO: GIO[057]
EM_A04 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[04]
GIO058 GIO: GIO[058]
EM_A05 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[05]
GIO059 GIO: GIO[059]
EM_A06 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[06]
GIO060 GIO: GIO[060]
EM_A07 /
GIO061
P19 I/O/Z V
M16 I/O/Z V
N18 I/O/Z V
P15 I/O/Z V
R19 I/O/Z V
P18 I/O/Z V
P16 I/O/Z V
EM_A08 /
GIO062 / T19 I/O/Z
AECFG[0]
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
Async EMIF: Bank Address 0 signal = 8-bit address. In 8-bit mode, lowest
DD
address bit. Or, can be used as an extra Address line (bit[14] when using 16-bit
memories.
GIO: GIO[054]
Async EMIF: Bank Address 1 signal = 16-bit address. In 16-bit mode, lowest
DD
address bit. In 8-bit mode, second lowest address bit
GIO: GIO[055]
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[00] Note that the EM_A0 is always a 32-bit
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
address
GIO: GIO[056]
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[07]
DD
GIO: GIO[061] - Used to drive boot status LED signal (active low) in ROM boot
modes.
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[08]
PU GIO: GIO[062] AECFG[0] sets default for - PinMux2.EM_A0_BA1: AEMIF
V
DD
Address Width (OneNAND or NAND) - PinMux2.EM_A13_3: AEMIF Address
Width (OneNAND or NAND)
www.ti.com
26 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
EM_A09 /
GIO063 / P17 I/O/Z
AECFG[1]
EM_A10 /
GIO064 / R18 I/O/Z
AECFG[2]
EM_A11 /
GIO065 / R16 I/O/Z
AECFG[3]
EM_A12 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[12]
GIO066 / U19 I/O/Z GIO: GIO[066] System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to determine
BTSEL[0] Boot method
EM_A13 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[13]
GIO067 / V19 I/O/Z GIO: GIO[067] System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to determine
BTSEL[1] Boot method.
VCLK / Video Encoder: Video Output Clock
GIO068 GIO: GIO[068]
H3 I/O/Z V
EXTCLK /
GIO069 / PD
B2 / V
G3 I/O/Z e.g. 74.25 MHz for HDTV digital output
PWM3D
FIELD /
GIO070 / Video Encoder: Field identifier for interlaced display formats
R2 / GIO: GIO[070] Digital Video Out: R2 PWM3C
H4 I/O/Z V
PWM3C
VSYNC / PD Video Encoder: Vertical Sync
GIO072 V
HSYNC / PD Video Encoder: Horizontal Sync
GIO073 V
G5 I/O/Z
F5 I/O/Z
COUT0-
B3 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[074]
GIO074 / PWM3B
F4 I/O/Z V
PWM3B
COUT1-
B4 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[075]
GIO075 / PWM3A
F3 I/O/Z V
PWM3A
COUT2-
B5 /
GIO076 / E4 I/O/Z V
PWM2D /
RTO3
COUT3B6 /
GIO077 / E3 I/O/Z V
PWM2C /
RTO2
COUT4B7 /
GIO078 / D3 I/O/Z V
PWM2B /
RTO1
COUT5G2 /
GIO079 / C1 I/O/Z V
PWM2A /
RTO0
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[09]
PD GIO: GIO[063] System: AECFG[3:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to set AEMIF
V
DD
Configuration AECFG[2:1] sets default for PinMux2.EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0
Definition (EM_BA0, EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[10]
PU GIO: GIO[064] System: AECFG[3:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to set AEMIF
V
DD
Configuration AECFG[2:1] sets default for PinMux2.EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0
Definition (EM_BA0, EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[11]
PU GIO: GIO[065] System: AECFG[3:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to set AEMIF
V
DD
Configuration AECFG[3] sets default for PinMux2.EM_D15_8: AEMIF Default
Bus Width (16 or 8 bits)
PD
V
DD
PD
V
DD
DD_VOUT
Video Encoder: External clock input, used if clock rates > 27 MHz are needed,
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
GIO: GIO[069] Digital Video Out: B2 PWM3D
GIO: GIO[072]
GIO: GIO[073]
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[076] PWM2D
RTO3
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[077] PWM2C
RTO2
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[078] PWM2B
RTO1
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[079] PWM2A
RTO0
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 27
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
www.ti.com
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
COUT6G3 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[080]
GIO080 / PWM1
D2 I/O/Z V
PWM1
COUT7-
G4 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[081]
GIO081 / PWM0
C2 I/O/Z V
PWM0
PCLK / PD
GIO082 V
T3 I/O/Z Pixel clock input (strobe for lines CI7 through YI0) GIO: GIO[082]
CAM_WE output of the CCDC module. Alternately, the field identification input signal is
N_FIELD / R5 I/O/Z used by external device (AFE/TG) to indicate the which of two frames is input to
GIO083 the CCDC module for sensors with interlaced output. CCDC handles 1- or 2-field
CAM_VD / PD
GIO084 V
CAM_HD / PD
GIO085 V
YIN0 / PD Y[00] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO086 V
YIN1 / PD Y[01] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO087 V
YIN2 / PD Y[02] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO088 V
YIN3 / PD Y[03] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO089 V
YIN4 / PD Y[04] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO090 V
YIN5 / PD Y[05] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO091 V
YIN6 / PD Y[06] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO092 V
YIN7 / PD Y[07] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO093 V
CIN0 / PD
GIO094 V
R4 I/O/Z output (master mode). Tells the CCDC when a new frame starts.
N5 I/O/Z output (master mode). Tells the CCDC when a new line starts.
P5 I/O/Z
P2 I/O/Z
P4 I/O/Z
R3 I/O/Z
P3 I/O/Z
M5 I/O/Z
M4 I/O/Z
L5 I/O/Z
J3 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VIN
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
Write enable input signal is used by external device (AFE/TG) to gate the DDR
PD
V
DD_VIN
sensors in hardware. GIO: GIO[083]
Vertical synchronization signal that can be either an input (slave mode) or an
DD_VIN
GIO: GIO[084]
Horizontal synchronization signal that can be either an input (slave mode) or an
DD_VIN
GIO: GIO[085]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[00] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[00]
GIO: GIO[086]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[01] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[01]
GIO: GIO[087]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[02] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[02]
GIO: GIO[088]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[03] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[03]
GIO: GIO[089]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[04] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[04]
GIO: GIO[090]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[05] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[05]
GIO: GIO[091]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[06] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[06]
GIO: GIO[092]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[07] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[07]
GIO: GIO[093]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[08] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[00] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[00]
GIO: GIO[094]
28 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
CIN1 / PD
GIO095 V
CIN2 / PD
GIO096 V
CIN3 / PD
GIO097 V
L3 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
J5 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
J4 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
CIN4 /
GIO098 /
SPI2_SDI PD
/ V
L4 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
SPI2_SDE
NA[1]
CIN5 /
GIO099 / PD
SPI2_SDE V
M3 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
NA[0]
CIN6 /
GIO100 / PD
SPI2_SD V
K5 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
O
CIN7 /
GIO101 / PD
SPI2_SCL V
N3 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
K
SPI0_SDI SPI0: Data In
/ GIO102 GIO: GIO[102]
A12 I/O/Z V
SPI0_SDE
NA[0] / B12 I/O/Z V
GIO103
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[09] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[01] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[01]
GIO: GIO[095]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[10] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[02] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[02]
GIO: GIO[096]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[11] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[03] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[03]
GIO: GIO[097]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[12] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[04] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[04] SPI: SPI2 Data In -OR- SPI2 Chip select 1.
GIO: GIO[098]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[13] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[05] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[05] SPI: SPI2 Chip Select 0.
GIO: GIO[99]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: NOT USED YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[06] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[06] SPI: SPI2 Data Out
GIO: GIO[100]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: NOT USED YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[07] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[07] SPI: SPI2 Clock
GIO: GIO[101]
DD
DD
SPI0: Chip Select 0
GIO: GIO[103]
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
2.9 Multi-Media Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD) Interfaces
The DM355 includes two Multi-Media Card/Secure Digital card interfaces that are compatible with the
MMC/SD and SDIO protocol.
Table 2-12. MMC/SD Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
MMCSD0_
CLK
MMCSD0_
CMD
MMCSD0_
DATA0
A15 I/O/Z V
C14 I/O/Z V
B14 I/O/Z V
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 29
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD
DD
DD
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
MMCSD0: Clock
MMCSD0: Command
MMCSD0: DATA0
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
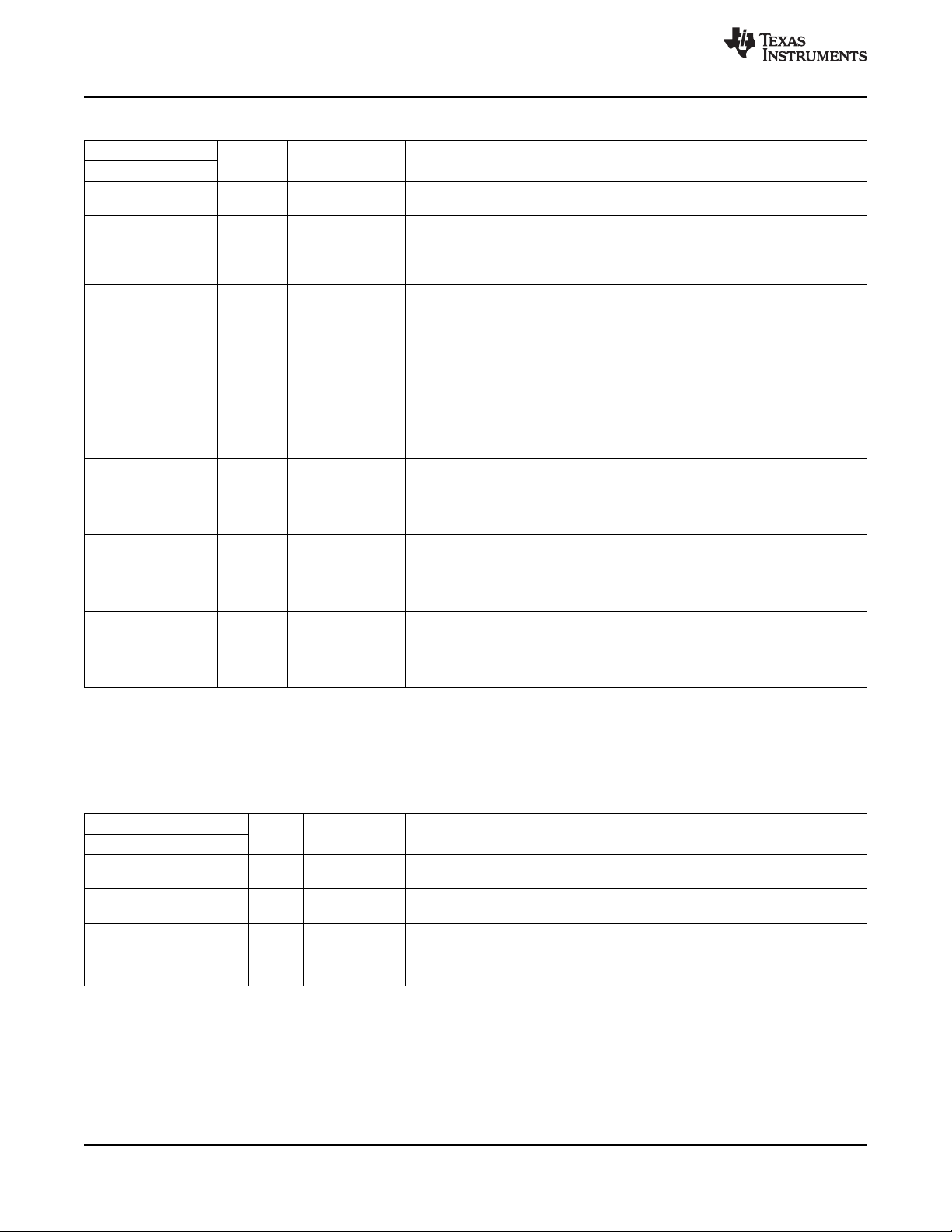
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-12. MMC/SD Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
MMCSD0_
DATA1
MMCSD0_
DATA2
MMCSD0_
DATA3
D14 I/O/Z V
B13 I/O/Z V
A14 I/O/Z V
MMCSD1_
CLK/ C15 I/O/Z V
GIO024
MMCSD1_
CMD/ A17 I/O/Z V
GIO023
MMCSD1_
DATA0/ MMCSD1: DATA0
GIO019/ A18 I/O/Z V
UART2_T UART2: Transmit data
XD
MMCSD1_
DATA1/ MMCSD1: DATA1
GIO020/ B15 I/O/Z V
UART2_R UART2: Receive data
XD
MMCSD1_
DATA2/ MMCSD1: DATA2
GIO021/ A16 I/O/Z V
UART2_C UART2: CTS
TS
MMCSD1_
DATA3/ MMCSD1: DATA3
GIO022/ B16 I/O/Z V
UART2_R UART2: RTS
TS
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
MMCSD0: DATA1
MMCSD0: DATA2
MMCSD0: DATA3
MMCSD1: Clock
GIO: GIO[024]
MMCSD1: Command
GIO: GIO[023]
GIO: GIO[019]
GIO: GIO[020]
GIO: GIO[021]
GIO: GIO[022]
www.ti.com
2.10 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Interface
The Universal Serial Bus (USB) interface supports the USB2.0 High-Speed protocol and includes dual-role
Host/Slave support. However, no charge pump is included.
Table 2-13. USB Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
USB_DP A7 A I/O/Z V
USB_DM A6 A I/O/Z V
USB_R1 C7 A I/O/Z
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
30 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DDA33_USB
DDA33_USB
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
USB D+ (differential signal pair).
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
USB D- (differential signal pair).
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
USB reference current output
Connect to V
as possible.
SS_USB_REF
via 10K ohm , 1% resistor placed as close to the device
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
SS_USB
SS_USB
SS_USB
.
.
.

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
Table 2-13. USB Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
USB_ID D5 A I/O/Z V
USB_VBUS E5 A I/O/Z V
USB_DRVVBUS C5 O/Z V
V
SS_USB_REF
V
DDA33_USB
V
DDA33_USB_PLL
V
DDA13_USB
V
DDD13_USB
C8 GND V
J8 PWR V
B6 PWR V
H7 PWR V
C6 PWR V
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DDA33_USB
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
DESCRIPTION
USB operating mode identification pin
For Device mode operation only, pull up this pin to VDDwith a 1.5K ohm resistor.
For Host mode operation only, pull down this pin to ground (VSS) with a 1.5K ohm
resistor.
If using an OTG or mini-USB connector, this pin will be set properly via the
cable/connector configuration.
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
For host or device mode operation, tie the VBUS/USB power signal to the USB
connector.
When used in OTG mode operation, tie VBUS to the external charge pump and
to the VBUS signal on the USB connector.
When the USB is not used, tie VBUS to V
SS_USB
.
Digital output to control external 5 V supply
When USB is not used, this signal should be left as a No Connect.
USB Ground Reference
Connect directly to ground and to USB_R1 via 10K ohm, 1% resistor placed as
close to the device as possible.
Analog 3.3 V power USBPHY
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
Common mode 3.3 V power for USB PHY (PLL)
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
Analog 1.3 V power for USB PHY
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
Digital 1.3 V power for USB PHY
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
2.11 Audio Interfaces
The DM355 includes two Audio Serial Ports (ASP ports), which are backward compatible with other TI
ASP serial ports and provide I2S audio interface. One interface is multiplexed with GIO signals.
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
ASP0_CL
KR/ F17 I/O/Z V
GIO026
ASP0_CL
KX / F18 I/O/Z V
GIO029
ASP0_DR
/ E18 I/O/Z V
GIO027
ASP0_DX
/ H15 I/O/Z V
GIO030
ASP0_FS
R / F16 I/O/Z V
GIO025
ASP0_FS
X / G17 I/O/Z V
GIO028
ASP1_CL
KR
D18 I/O/Z V
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
Table 2-14. ASP Terminal Functions
(2) (3)
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DESCRIPTION
ASP0: Receive Clock
GIO: GIO[026]
ASP0: Transmit Clock
GIO: GIO[029]
ASP0: Receive Data
GIO: GIO[027]
ASP0: Transmit Data
GIO: GIO[030]
ASP0: Receive Frame Synch
GIO: GIO[025]
ASP0: Transmit Frame SynchGIO: GIO[028]
ASP1: Receive Clock
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 31
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-14. ASP Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
ASP1_CL
KS
ASP1_CL
KX
D17 I/Z V
D19 I/O/Z V
ASP1_DR C19 I/O/Z V
ASP1_DX C18 I/O/Z V
ASP1_FS
R
ASP1_FS
X
E17 I/O/Z V
E16 I/O/Z V
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
ASP1: Master Clock
ASP1: Transmit Clock
ASP1: Receive Data
ASP1: Transmit Data
ASP1: Receive Frame Synch
ASP1: Transmit Frame Sync
2.12 UART Interface
The DM355 includes three UART ports. These ports are multiplexed with GIO and other signals.
Table 2-15. UART Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
UART0_RXD U18 I V
UART0_TXD T18 O V
UART1_RXD/ UART1: Receive data.
GIO013 GIO: GIO013
UART1_TXD/ UART1: Transmit data.
GIO012 GIO: GIO012
R15 I/O/Z V
R17 I/O/Z V
MMCSD1_DA
TA2/
GIO021/
A16 I/O/Z V
UART2_CTS
MMCSD1_DA
TA3/
GIO022/
B16 I/O/Z V
UART2_RTS
MMCSD1_DA
TA1/
GIO020/
B15 I/O/Z V
UART2_RXD
MMCSD1_DA
TA0/
GIO019/
A18 I/O/Z V
UART2_TXD
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD
DD
DD
DD
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
UART0: Receive data. Used for UART boot mode
UART0: Transmit data. Used for UART boot mode
MMCSD1: DATA2
DD
GIO: GIO021
UART2: CTS
MMCSD1: DATA3
DD
GIO: GIO022
UART2: RTS
MMCSD1: DATA1
DD
GIO: GIO020
UART2: RXD
MMCSD1: DATA0
DD
GIO: GIO019
UART2: TXD
www.ti.com
32 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
2.13 I2C Interface
The DM355 includes an I2C two-wire serial interface for control of external peripherals. This interface is
multiplexed with GIO signals.
Table 2-16. I2C Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
I2C_SDA/ I2C: Serial data
GIO015 GIO: GIO015
I2C_SCL/ I2C: Serial clock
GIO014 GIO: GIO014
R13 I/O/Z V
R14 I/O/Z V
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD
DD
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
2.14 Serial Interface
The DM355 includes three independent serial ports. These interfaces are multiplexed with GIO and other
signals.
Table 2-17. SPI Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
TYPE
(1)
SPI0_SCLK C12 I/O/Z V
SPI0_SDENA[0]/ SPI0: Chip select 0
GIO103 GIO: GIO[103]
GIO007 GIO: GIO[007]
SPI0_SDENA[1] SPI0: Chip select 1
SPI0_SDI/ SPI0: Data in
GIO102 GIO: GIO[102]
B12 I/O/Z V
C17 I/O/Z V
A12 I/O/Z V
SPI0_SDO B11 I/O/Z V
SPI1_SCLK/ SPI1: Clock
GIO010 GIO: GIO[010]
SPI1_SDENA[0]/
GIO011
C13 I/O/Z V
E13 I/O/Z V
SPI1_SDI/ SPI1: Data in or
GIO009/ A13 I/O/Z V
SPI1_SDENA[1] GIO: GIO[09]
SPI1_SDO/ SPI1: Data out
GIO008 GIO: GIO[008]
E12 I/O/Z V
CIN7/
GIO101/ N3 I/O/Z
SPI2_SCLK
CIN5/
GIO099/ M3 I/O/Z
SPI2_SDENA[0]
OTHER
(3)
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
PD
V
DD_VIN
PD
V
DD_VIN
(2)
DESCRIPTION
SPI0: Clock
SPI0: Data out
SPI1: Chip select 0
GIO: GIO[011] - Active low during MMC/SD boot (can be used as
MMC/SD power control)
SPI1: Chip select 1
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Not used
• YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma. CB/CR[07]
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is
time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
Y/CB/CR[07]
SPI: SPI2 clock
GIO: GIO[101]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[13]
• YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma. CB/CR[05]
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is
time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
Y/CB/CR[07]
SPI: SPI2 chip select 0
GIO: GIO[099]
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 33
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-17. SPI Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
TYPE
(1)
CIN4/
GIO098/ PD
SPI2_SDI/ V
L4 I/O/Z
SPI2_SDENA[1]
CIN6/
GIO100/ K5 I/O/Z
SPI2_SDO/
OTHER
(3)
DD_VIN
PD
V
DD_VIN
(2)
DESCRIPTION
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Raw[12]
• YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma. CB/CR[04]
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is
time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
Y/CB/CR[04]
SPI: SPI2 Data in -OR- SPI2 Chip select 1
GIO: GIO[0998]
Standard CCD/CMOS input: Not used
• YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma. CB/CR[06]
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is
time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel.
Y/CB/CR[06]
SPI: SPI2 Data out
GIO: GIO[100]
2.15 Clock Interface
The DM355 provides interface with the system clocks.
Table 2-18. Clocks Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
CLKOUT1 CLKOUT: Output Clock 1
/ GIO018 GIO: GIO[018]
CLKOUT2 CLKOUT: Output Clock 2
/ GIO017 GIO: GIO[017]
CLKOUT3 CLKOUT: Output Clock 3
/ GIO016 GIO: GIO[016]
D12 I/O/Z V
A11 I/O/Z V
C11 I/O/Z V
MXI1 A9 I V
MXO1 B9 O V
MXI2 R1 I V
MXO2 T1 O V
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
Crystal input for system oscillator (24 MHz or 36 MHz)
Output for system oscillator (24 MHz or 36 MHz). When the MX02 is not used,
the MX02 signal can be left open.
Crystal input for video oscillator (27 MHz) Optional, use only if 27MHz derived
DD
from MXI1 and PLL does not provide sufficient performance for Video DAC.
When the MXI2 is not used and powered down, the MXI2 signal should be left
as a No Connect
Output for video oscillator (27 MHz) Optional, use only if 27MHz derived from
DD
MXI1 and PLL does not provide sufficient performance for Video DAC When the
MXO2 is not used and powered down, the MXO2 signal should be left as a No
Connect.
www.ti.com
34 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
2.16 Real Time Output (RTO) Interface
The DM355 provides Real Time Output (RTO) interface.
Table 2-19. RTO Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
COUT5G2 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[079]
GIO079 / C1 I/O/Z V
PWM2A / RTO0
RTO0
COUT4B7 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[078]
GIO078 / D3 I/O/Z V
PWM2B / RTO1
RTO1
COUT3B6 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[077]
GIO077 / E3 I/O/Z V
PWM2C / RTO2
RTO2
COUT2B5 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[076]
GIO076 / E4 I/O/Z V
PWM2D / RTO3
RTO3
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
PWM2A
PWM2B
PWM2C
PWM2D
2.17 Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) Interface
The DM355 provides Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) interface.
Table 2-20. PWM Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
COUT7G4 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[081]
GIO081 / PWM0
C2 I/O/Z V
PWM0
COUT6-
G3 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[080]
GIO080 / PWM1
D2 I/O/Z V
PWM1
COUT5-
G2 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[079]
GIO079 / C1 I/O/Z V
PWM2A / RTO0
RTO0
COUT4B7 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[078]
GIO078 / D3 I/O/Z V
PWM2B / RTO1
RTO1
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
PWM2A
PWM2B
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 35
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-20. PWM Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
COUT3B6 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[077]
GIO077 / E3 I/O/Z V
PWM2C / RTO2
RTO2
COUT2B5 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[076]
GIO076 / E4 I/O/Z V
PWM2D / RTO3
RTO3
COUT1B4 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[075]
GIO075 / PWM3A
F3 I/O/Z V
PWM3A
COUT0-
B3 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[074]
GIO074 / PWM3B
F4 I/O/Z V
PWM3B
FIELD /
GIO070 /
R2 /
H4 I/O/Z V
PWM3C
EXTCLK /
GIO069 / PD
B2 / V
G3 I/O/Z e.g. 74.25 MHz for HDTV digital output GIO: GIO[069] Digital Video Out: B2
PWM3D
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
PWM2C
PWM2D
Video Encoder: Field identifier for interlaced display formats GIO: GIO[070]
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: R2
PWM3C
Video Encoder: External clock input, used if clock rates > 27 MHz are needed,
DD_VOUT
PWM3D
www.ti.com
2.18 System Configuration Interface
The DM355 provides interfaces for system configuration and boot load.
Table 2-21. System/Boot Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
EM_A13/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit 13
GIO067/ V19 I/O/Z GIO: GIO[067]
BTSEL[1] System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at power-on-reset to determine boot method.
EM_A12/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit 12
GIO066/ U19 I/O/Z GIO: GIO[066]
BTSEL[0] System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at power-on-reset to determine boot method.
EM_A11/ GIO: GIO[065]
GIO065/ R16 I/O/Z System: AECFG[3:0] sampled a power-on-reset to set AEMIF configuration.
AECFG[3] AECFG[3] sets default fo PinMux2.EM_D15_8. AEMIF default bus width (16 or 8
EM_A10/ GIO: GIO[064]
GIO064/ R18 I/O/Z System: AECFG[3:0] sampled a power-on-reset to set AEMIF configuration.
AECFG[2] AECFG[2:1] sets default fo PinMux2.EM_BA0. AEMIF EM_BA0 definition:
EM_A09/ GIO: GIO[063]
GIO063/ P17 I/O/Z System: AECFG[3:0] sampled a power-on-reset to set AEMIF configuration.
AECFG[1] AECFG[2:1] sets default fo PinMux2.EM_BA0. AEMIF EM_BA0 definition:
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
PD
V
DD
PD
V
DD
Async EMIF: Address bus bit 11
PU
V
DD
bits).
Async EMIF: Address bus bit 10
PU
V
DD
(EM_BA0, EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
Async EMIF: Address bus bit 09
PD
V
DD
(EM_BA0, EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
36 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-21. System/Boot Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
EM_A08/
GIO062/ T19 I/O/Z
AECFG[0] • PinMux2.EM_A0_BA1 - AEMIF address width (OneNAND, or NAND)
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
Async EMIF: Address bus bit 08
GIO: GIO[062]
System: AECFG[0] sets default for:
V
PU
DD
• PinMux2.EM_A13_3 - AEMIF address width (OneNAND, or NAND)
2.19 Emulation
The emulation interface allow software and hardware debugging.
Table 2-22. Emulation Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
TCK E10 I V
TDI D9 I JTAG test data input
TDO E9 O V
TMS D8 I JTAG test mode select
TRST C9 I JTAG test logic reset (active low)
RTCK E11 O V
EMU0 E8 I/O/Z EMU[1:0] = 00 - Force Debug Scan chain (ARM and ARM ETB TAPs connected)
EMU1 E7 I/O/Z EMU[1:0] = 00 - Force Debug Scan chain (ARM and ARM ETB TAPs connected)
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
DD
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
JTAG test clock input
PU
V
DD
DD
JTAG test data output
PU
V
DD
PD
V
DD
JTAG test clock output
JTAG emulation 0 I/O
EMU[1:0] = 11 - Normal Scan chain (ICEpick only)
JTAG emulation 1 I/O
EMU[1:0] = 11 - Normal Scan chain (ICEpick only)
V
V
DD
PU
DD
PU
DD
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 37
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
2.20 Pin List
Table 2-23 provides a complete pin description list in pin number order.
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
CIN7 / GIO101 / N3 I/O CCDC V
SPI2_SCLK / GIO / 7
(1)
ID
SPI2
Supply
DD_VIN
(2)
PD
(3)
State
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: NOT USED PINMUX0[1:0].CIN_
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[07]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between
luma and chroma of the upper channel.
Y/CB/CR[07]
SPI: SPI2 Clock
GIO: GIO[101]
CIN6 / GIO100 / K5 I/O CCDC V
SPI2_SDO / GIO / 6
DD_VIN
SPI2
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: NOT USED PINMUX0[3:2].CIN_
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[06]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the upper
channel. Y/CB/CR[06]
SPI: SPI2 Data Out
GIO: GIO[100]
CIN5 / GIO099 / M3 I/O CCDC V
SPI2_SDENA[0] / GIO / 5
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[13] PINMUX0[5:4].CIN_
SPI2
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[05]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the upper
channel. Y/CB/CR[05]
SPI: SPI2 Chip Select 0
GIO: GIO[99]
CIN4 / GIO098 / L4 I/O CCDC V
SPI2_SDI / / GIO / 4
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[12] PINMUX0[7:6].CIN_
SPI2_SDENA[1] SPI2 /
SPI2
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[04]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the upper
channel. Y/CB/CR[04]
SPI: SPI2 Data In -OR- SPI2 Chip select 1
GIO: GIO[098]
(4)
www.ti.com
Mux Control
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 kΩ resistor should be used.)
(4) To reduce EMI and reflections, depending on the trace length, approximately 22 Ω to 50 Ω damping resistors are recommend on the
following outputs placed near the DM355: YOUT(0-7),COUT(0-7), HSYNC,VSYNC,LCD_OE,FIELD,EXTCLK,VCLK. The trace lengths
should be minimized.
38 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
CIN3 / GIO097 J4 I/O CCDC V
CIN2 / GIO096 J5 I/O CCDC V
CIN1 / GIO095 L3 I/O CCDC V
CIN0 / GIO094 J3 I/O CCDC V
YIN7 / GIO093 L5 I/O CCDC V
YIN6 / GIO092 M4 I/O CCDC V
(1)
ID
/ GIO
Supply
DD_VIN
(2)
PD
(3)
State
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[11] PINMUX0[8].CIN_32
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[03]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the upper
channel. Y/CB/CR[03]
GIO: GIO[097]
/ GIO
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[10] PINMUX0[8].CIN_32
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[02]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the upper
channel. Y/CB/CR[02]
GIO: GIO[096]
/ GIO
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[09] PINMUX0[9].CIN_10
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[01]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the upper
channel. Y/CB/CR[01]
GIO: GIO[095]
/ GIO
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[08] PINMUX0[9].CIN_10
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between
chroma: CB/CR[00]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the upper
channel. Y/CB/CR[00]
GIO: GIO[094]
/ GIO 0
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[07] PINMUX0[10].YIN_7
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
Y[07]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the lower
channel. Y/CB/CR[07]
GIO: GIO[093]
/ GIO 0
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[06] PINMUX0[10].YIN_7
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
Y[06]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the lower
channel. Y/CB/CR[06]
GIO: GIO[092]
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
(4)
Mux Control
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 39
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
YIN5 / GIO091 M5 I/O CCDC V
YIN4 / GIO090 P3 I/O CCDC V
YIN3 / GIO089 R3 I/O CCDC V
YIN2 / GIO088 P4 I/O CCDC V
YIN1 / GIO087 P2 I/O CCDC V
YIN0 / GIO086 P5 I/O CCDC V
(1)
ID
/ GIO 0
Supply
DD_VIN
(2)
PD
(3)
State
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[05] PINMUX0[10].YIN_7
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
Y[05]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the lower
channel. Y/CB/CR[05]
GIO: GIO[091]
/ GIO 0
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[04] PINMUX0[10].YIN_7
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
Y[04]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the lower
channel. Y/CB/CR[04]
GIO: GIO[090]
/ GIO 0
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[03] PINMUX0[10].YIN_7
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
Y[03]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the lower
channel. Y/CB/CR[03]
GIO: GIO[089]
/ GIO 0
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[02] PINMUX0[10].YIN_7
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
Y[02]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the lower
channel. Y/CB/CR[02]
GIO: GIO[088]
/ GIO 0
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[01] PINMUX0[10].YIN_7
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
Y[01]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the lower
channel. Y/CB/CR[01]
GIO: GIO[087]
/ GIO 0
DD_VIN
PD in Standard CCD/CMOS input: raw[00] PINMUX0[10].YIN_7
YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma:
Y[00]
YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed
between luma and chroma of the lower
channel. Y/CB/CR[00]
GIO: GIO[086]
www.ti.com
(4)
Mux Control
40 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
CAM_HD / N5 I/O CCDC V
GIO085 / GIO either an input (slave mode) or an output HD
(1)
ID
Supply
DD_VIN
(2)
PD
(3)
State
PD in Horizontal synchronization signal that can be PINMUX0[11].CAM_
(master mode). Tells the CCDC when a new
line starts.
GIO: GIO[085]
CAM_VD / R4 I/O CCDC V
GIO084 / GIO either an input (slave mode) or an output VD
DD_VIN
PD in Vertical synchronization signal that can be PINMUX0[12].CAM_
(master mode). Tells the CCDC when a new
frame starts.
GIO: GIO[084]
CAM_WEN_FIE R5 I/O CCDC V
LD / GIO083 / GIO device (AFE/TG) to gate the DDR output of WEN
DD_VIN
PD in Write enable input signal is used by external PINMUX0[13].CAM_
the CCDC module.
Alternately, the field identification input plus
signal is used by external device (AFE/TG)
to indicate the which of two frames is input
to the CCDC module for sensors with
interlaced output. CCDC handles 1- or
2-field sensors in hardware.
GIO: GIO[083] CCDC.MODE[7].CC
PCLK / GIO082 T3 I/O CCDC V
/ GIO YI0)
DD_VIN
PD in Pixel clock input (strobe for lines CI7 through PINMUX0[14].PCLK
GIO: GIO[082]
YOUT7-R7 C3 I/O VENC V
YOUT6-R6 A4 I/O VENC V
YOUT5-R5 B4 I/O VENC V
YOUT4-R4 B3 I/O VENC V
YOUT3-R3 B2 I/O VENC V
YOUT2-G7 A3 I/O VENC V
YOUT1-G6 A2 I/O VENC V
YOUT0-G5 B1 I/O VENC V
COUT7-G4 / C2 I/O VENC V
GIO081 / PWM0 / GIO / function T_7
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine
function
function
function
function
function
function
function
function
(5)
(5)
(5)
(5)
(5)
(5)
(5)
(5)
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine PINMUX1[1:0].COU
PWM0
GIO: GIO[081]
PWM0
COUT6-G3 / D2 I/O VENC V
GIO080 / PWM1 / GIO / function T_6
DD_VOUT
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine PINMUX1[3:2].COU
PWM1
GIO: GIO[080]
(5)
PWM1
(4)
DMD &
CCDC.MODE[5].SW
EN
Mux Control
(5) To reduce EMI and reflections, depending on the trace length, approximately 22 Ω to 50 Ω damping resistors are recommend on the
following outputs placed near the DM355: YOUT(0-7),COUT(0-7), HSYNC,VSYNC,LCD_OE,FIELD,EXTCLK,VCLK. The trace lengths
should be minimized.
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 41
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
COUT5-G2 / C1 I/O VENC V
GIO079 / / GIO / function T_5
(1)
ID
Supply
DD_VOUT
(2)
PD
(3)
State
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine PINMUX1[5:4].COU
PWM2A / RTO0 PWM2
/ RTO
GIO: GIO[079]
PWM2A
(5)
RTO0
COUT4-B7 / D3 I/O VENC V
GIO078 / / GIO / function T_4
DD_VOUT
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine PINMUX1[7:6].COU
PWM2B / RTO1 PWM2
/ RTO
GIO: GIO[078]
PWM2B
(5)
RTO1
COUT3-B6 / E3 I/O VENC V
GIO077 / / GIO / function T_3
DD_VOUT
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine PINMUX1[9:8].COU
PWM2C / RTO2 PWM2
/ RTO
GIO: GIO[077]
PWM2C
(5)
RTO2
COUT2-B5 / E4 I/O VENC V
GIO076 / / GIO / function UT_2
DD_VOUT
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine PINMUX1[11:10].CO
PWM2D / RTO3 PWM2
/ RTO
GIO: GIO[076]
PWM2D
(6)
RTO3
COUT1-B4 / F3 I/O VENC V
GIO075 / / GIO / function UT_1
DD_VOUT
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine PINMUX1[13:12].CO
PWM3A PWM3
GIO: GIO[075]
(6)
PWM3A
COUT0-B3 / F4 I/O VENC V
GIO074 / / GIO / function UT_0
DD_VOUT
in Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine PINMUX1[15:14].CO
PWM3B PWM3
GIO: GIO[074]
(6)
PWM3B
HSYNC / F5 I/O VENC V
GIO073 / GIO NC
VSYNC / G5 I/O VENC V
GIO072 / GIO NC
LCD_OE / H5 I/O VENC V
GIO071 / GIO BRIGHT signal
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
DD_VOUT
PD in Video Encoder: Horizontal Sync PINMUX1[16].HVSY
GIO: GIO[073]
(6)
PD in Video Encoder: Vertical Sync PINMUX1[16].HVSY
GIO: GIO[072]
(6)
out Video Encoder: LCD Output Enable or PINMUX1[17].DLCD
GIO: GIO[071]
(6)
(4)
www.ti.com
Mux Control
(6) To reduce EMI and reflections, depending on the trace length, approximately 22 Ω to 50 Ω damping resistors are recommend on the
following outputs placed near the DM355: YOUT(0-7),COUT(0-7), HSYNC,VSYNC,LCD_OE,FIELD,EXTCLK,VCLK. The trace lengths
should be minimized.
42 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
FIELD / GIO070 H4 I/O VENC V
/ R2 / PWM3C / GIO / display formats ELD
(1)
ID
Supply
DD_VOUT
(2)
PD
(3)
State
in Video Encoder: Field identifier for interlaced PINMUX1[19:18].FI
VENC
/
PWM3
GIO: GIO[070]
Digital Video Out: R2
PWM3C
EXTCLK / G3 I/O VENC V
GIO069 / B2 / / GIO / clock rates > 27 MHz are needed, e.g. 74.25 TCLK
DD_VOUT
PD in Video Encoder: External clock input, used if PINMUX1[21:20].EX
(6)
PWM3D VENC MHz for HDTV digital output
/
PWM3
GIO: GIO[069]
Digital Video Out: B2
(6)
(6)
VCLK / GIO068 H3 I/O VENC V
/ GIO
DD_VOUT
PWM3D
in Video Encoder: Video Output Clock PINMUX1[22].VCLK
GIO: GIO[068]
VREF J7 A I/O Video Video DAC: Reference voltage output
DAC (0.45V, 0.1uF to GND)
IOUT E1 A I/O Video Video DAC: Pre video buffer DAC output
DAC (1000 ohm to VFB)
IBIAS F2 A I/O Video Video DAC: External resistor (2550 Ohms to
DAC GND) connection for current bias
configuration
VFB G1 A I/O Video Video DAC: Pre video buffer DAC output
DAC (1000 ohm to IOUT, 1070 ohm to TVOUT)
TVOUT F1 A I/O Video V
DAC output (SeeFigure 5-31 andFigure 5-32 for
DDA18_DAC
Video DAC: Analog Composite NTSC/PAL
circuit connection)
V
DDA18V_DAC
V
SSA_DAC
DDR_CLK W9 I/O DDR V
DDR_CLK W8 I/O DDR V
DDR_RAS T6 I/O DDR V
DDR_CAS V9 I/O DDR V
DDR_WE W10 I/O DDR V
DDR_CS T8 I/O DDR V
DDR_CKE V10 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQM[1] U15 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQM[0] T12 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQS[1] V15 I/O DDR V
L7 PWR Video Video DAC: Analog 1.8V power
DAC
L8 GND Video Video DAC: Analog 1.8V ground
DAC
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
out L DDR Data Clock
out H DDR Complementary Data Clock
out H DDR Row Address Strobe
out H DDR Column Address Strobe
out H DDR Write Enable (active low)
out H DDR Chip Select (active low)
out L DDR Clock Enable
in Data mask outputs: DDR_DQM1: For
DDR_DQ[15:8]
in Data mask outputs: DDR_DQM0: For
DDR_DQ[7:0]
in Data strobe input/outputs for each byte of
the 16 bit data bus used to synchronize the
data transfers. Output to DDR when writing
and inputs when reading.
DDR_DQS1: For DDR_DQ[15:8]
(4)
Mux Control
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 43
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
DDR_DQS[0] V12 I/O DDR V
(1)
ID
Supply
DD_DDR
(2)
PD
(3)
State
in Data strobe input/outputs for each byte of
the 16 bit data bus used to synchronize the
data transfers. Output to DDR when writing
and inputs when reading.
DDR_DQS0: For DDR_DQ[7:0]
DDR_BA[2] V8 I/O DDR V
DDR_BA[1] U7 I/O DDR V
DDR_BA[0] U8 I/O DDR V
DDR_A13 U6 I/O DDR V
DDR_A12 V7 I/O DDR V
DDR_A11 W7 I/O DDR V
DDR_A10 V6 I/O DDR V
DDR_A09 W6 I/O DDR V
DDR_A08 W5 I/O DDR V
DDR_A07 V5 I/O DDR V
DDR_A06 U5 I/O DDR V
DDR_A05 W4 I/O DDR V
DDR_A04 V4 I/O DDR V
DDR_A03 W3 I/O DDR V
DDR_A02 W2 I/O DDR V
DDR_A01 V3 I/O DDR V
DDR_A00 V2 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ15 W17 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ14 V16 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ13 W16 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ12 U16 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ11 W15 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ10 W14 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ09 V14 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ08 U13 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ07 W13 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ06 V13 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ05 W12 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ04 U12 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ03 T11 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ02 U11 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ01 W11 I/O DDR V
DDR_DQ00 V11 I/O DDR V
DDR_ W18 I/O DDR V
DQGATE0 gating. Route to DDR and back to
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
DD_DDR
out L Bank select outputs. Two are required for
1Gb DDR2 memories.
out L Bank select outputs. Two are required for
1Gb DDR2 memories.
out L Bank select outputs. Two are required for
1Gb DDR2 memories.
out L DDR Address Bus bit 13
out L DDR Address Bus bit 12
out L DDR Address Bus bit 11
out L DDR Address Bus bit 10
out L DDR Address Bus bit 09
out L DDR Address Bus bit 08
out L DDR Address Bus bit 07
out L DDR Address Bus bit 06
out L DDR Address Bus bit 05
out L DDR Address Bus bit 04
out L DDR Address Bus bit 03
out L DDR Address Bus bit 02
out L DDR Address Bus bit 01
out L DDR Address Bus bit 00
in DDR Data Bus bit 15
in DDR Data Bus bit 14
in DDR Data Bus bit 13
in DDR Data Bus bit 12
in DDR Data Bus bit 11
in DDR Data Bus bit 10
in DDR Data Bus bit 09
in DDR Data Bus bit 08
in DDR Data Bus bit 07
in DDR Data Bus bit 06
in DDR Data Bus bit 05
in DDR Data Bus bit 04
in DDR Data Bus bit 03
in DDR Data Bus bit 02
in DDR Data Bus bit 01
in DDR Data Bus bit 00
out DDR: Loopback signal for external DQS
DDR_DQGATE1 with same constraints as
used for DDR clock and data.
DDR_ V17 I/O DDR V
DQGATE1 gating. Route to DDR and back to
DD_DDR
in DDR: Loopback signal for external DQS
DDR_DQGATE0 with same constraints as
used for DDR clock and data.
(4)
www.ti.com
Mux Control
44 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
DDR_VREF U10 PWR DDRI V
V
SSA_DLL
V
DDA33_DDRDLL
R11 GND DDRD V
R10 PWR DDRD V
DDR_ZN T9 I/O DDRI V
(1)
ID
O buffers
LL
LL
O calibration of N and P channel outputs. Tie
Supply
DD_DDR
SSA_DLL
DDA33_DDR
DLL
DD_DDR
(2)
PD
(3)
State
DDR: Voltage input for the SSTL_18 IO
DDR: Ground for the DDR DLL
DDR: Power (3.3 Volts) for the DDR DLL
DDR: Reference output for drive strength
to ground via 50 ohm resistor @ 0.5%
tolerance.
EM_A13 / V19 I/O AEMI V
GIO067 / F / 3_3,
DD
PD in L Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[13] PINMUX2[0].EM_A1
BTSEL[1] GIO /
syste
m
GIO: GIO[067] default set by
System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at
Power-on-Reset to determine Boot method
(00:NAND, 01:Flash, 10:MMC/SD, 11:UART
)
EM_A12 / U19 I/O AEMI V
GIO066 / F / 3_3,
DD
PD in L Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[12] PINMUX2[0].EM_A1
BTSEL[0] GIO /
syste
m
GIO: GIO[066] default set by
System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at
Power-on-Reset to determine Boot method
(00:NAND, 01:Flash, 10:MMC/SD, 11:UART)
EM_A11 / R16 I/O AEMI V
GIO065 / F / 3_3,
DD
PU in H Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[11] PINMUX2[0].EM_A1
AECFG[3] GIO /
syste
m
GIO: GIO[065] default set by
System: AECFG[3:0] sampled at
Power-on-Reset to set AEMIF Configuration
AECFG[3] sets default for
PinMux2.EM_D15_8: AEMIF Default Bus
Width (0:16 or 1:8 bits)
EM_A10 / R18 I/O AEMI V
GIO064 / F / 3_3,
DD
PU in H Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[10] PINMUX2[0].EM_A1
AECFG[2] GIO /
syste
m
GIO: GIO[064] default set by
System: AECFG[3:0] sampled at
Power-on-Reset to set AEMIF Configuration
AECFG[2:1] sets default for
PinMux2.EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0
Definition (00: EM_BA0, 01: EM_A14,
10:GIO[054], 11:rsvd)
(4)
AECFG[0]
AECFG[0]
AECFG[0]
AECFG[0]
Mux Control
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 45
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
EM_A09 / P17 I/O AEMI V
GIO063 / F / 3_3,
(1)
ID
Supply
DD
(2)
PD
(3)
State
PD in L Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[09] PINMUX2[0].EM_A1
AECFG[1] GIO /
syste
m
GIO: GIO[063] default set by
System: AECFG[3:0] sampled at
Power-on-Reset to set AEMIF Configuration
AECFG[2:1] sets default for
PinMux2.EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0
Definition (00: EM_BA0, 01: EM_A14,
10:GIO[054], 11:rsvd)
EM_A08 / T19 I/O AEMI V
GIO062 / F / 3_3,
DD
PU in H Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[08] PINMUX2[0].EM_A1
AECFG[0] GIO /
syste
m
GIO: GIO[062] default set by
AECFG[0] sets default for
- PinMux2.EM_A0_BA1: AEMIF Address
Width (OneNAND or NAND)
- PinMux2.EM_A13_3: AEMIF Address
Width (OneNAND or NAND)
(0:AEMIF address bits, 1:GIO[67:57])
EM_A07 / P16 I/O AEMI V
GIO061 F / 3_3,
DD
out L Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[07] PINMUX2[0].EM_A1
GIO
GIO: GIO[061] - Used to drive boot status default set by
LED signal (active low) in ROM boot modes. AECFG[0]
EM_A06 / P18 I/O AEMI V
GIO060 F / 3_3,
DD
out L Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[06] PINMUX2[0].EM_A1
GIO
GIO: GIO[060] default set by
EM_A05 / R19 I/O AEMI V
GIO059 F / 3_3,
DD
out L Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[05] PINMUX2[0].EM_A1
GIO
GIO: GIO[059] default set by
EM_A04 / P15 I/O AEMI V
GIO058 F / 3_3,
DD
out L Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[04] PINMUX2[0].EM_A1
GIO
GIO: GIO[058] default set by
EM_A03 / N18 I/O AEMI V
GIO057 F / 3_3,
DD
out L Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[03] PINMUX2[0].EM_A1
GIO
GIO: GIO[057] default set by
EM_A02 N15 I/O AEMI V
F
DD
out L Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[02]
NAND/SM/xD: CLE - Command Latch
Enable output
(4)
AECFG[0]
AECFG[0]
AECFG[0]
AECFG[0]
AECFG[0]
AECFG[0]
www.ti.com
Mux Control
46 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
EM_A01 N17 I/O AEMI V
(1)
ID
F
Supply
DD
(2)
PD
(3)
State
out L Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[01]
NAND/SM/xD: ALE - Address Latch Enable
output
EM_A00 / M16 I/O AEMI V
GIO056 F / the EM_A0 is always a 32-bit address _BA1,
DD
out L Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[00] Note that PINMUX2[1].EM_A0
GIO
GIO: GIO[056] default set by
EM_BA1 / P19 I/O AEMI V
GIO055 F / address. _BA1,
DD
out H Async EMIF: Bank Address 1 signal = 16-bit PINMUX2[1].EM_A0
GIO
In 16-bit mode, lowest address bit. default set by
In 8-bit mode, second lowest address bit
GIO: GIO[055]
EM_BA0 / N19 I/O AEMI V
GIO054 / F / address. BA0,
DD
out H Async EMIF: Bank Address 0 signal = 8-bit PINMUX2[3:2].EM_
EM_A14 GIO
In 8-bit mode, lowest address bit. default set by
Or, can be used as an extra Address line
(bit[14] when using 16-bit memories.
GIO: GIO[054]
EM_D15 / M18 I/O AEMI V
GIO053 F / 5_8,
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[15] PINMUX2[4].EM_D1
GIO
GIO: GIO[053] default set by
EM_D14 / M19 I/O AEMI V
GIO052 F / 5_8,
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[14] PINMUX2[4].EM_D1
GIO
GIO: GIO[052] default set by
EM_D13 / M15 I/O AEMI V
GIO051 F / 5_8,
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[13] PINMUX2[4].EM_D1
GIO
GIO: GIO[051] default set by
EM_D12 / L18 I/O AEMI V
GIO050 F / 5_8,
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[12] PINMUX2[4].EM_D1
GIO
GIO: GIO[050] default set by
EM_D11 / L17 I/O AEMI V
GIO049 F / 5_8,
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[11] PINMUX2[4].EM_D1
GIO
GIO: GIO[049] default set by
EM_D10 / L19 I/O AEMI V
GIO048 F / 5_8,
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[10] PINMUX2[4].EM_D1
GIO
GIO: GIO[048] default set by
(4)
AECFG[0]
AECFG[0]
AECFG[2:1]
AECFG[3]
AECFG[3]
AECFG[3]
AECFG[3]
AECFG[3]
AECFG[3]
Mux Control
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 47
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
EM_D09 / K18 I/O AEMI V
GIO047 F / 5_8,
(1)
ID
Supply
DD
(2)
PD
(3)
State
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[09] PINMUX2[4].EM_D1
GIO
GIO: GIO[047] default set by
EM_D08 / L16 I/O AEMI V
GIO046 F / 5_8,
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[08] PINMUX2[4].EM_D1
GIO
GIO: GIO[046] default set by
EM_D07 / K19 I/O AEMI V
GIO045 F / _0
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[07] PINMUX2[5].EM_D7
GIO
GIO: GIO[045]
EM_D06 / K17 I/O AEMI V
GIO044 F / _0
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[06] PINMUX2[5].EM_D7
GIO
GIO: GIO[044]
EM_D05 / J19 I/O AEMI V
GIO043 F / _0
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[05] PINMUX2[5].EM_D7
GIO
GIO: GIO[043]
EM_D04 / L15 I/O AEMI V
GIO042 F / _0
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[04] PINMUX2[5].EM_D7
GIO
GIO: GIO[042]
EM_D03 / J18 I/O AEMI V
GIO041 F / _0
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[03] PINMUX2[5].EM_D7
GIO
GIO: GIO[041]
EM_D02 / H19 I/O AEMI V
GIO040 F / _0
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[02] PINMUX2[5].EM_D7
GIO
GIO: GIO[040]
EM_D01 / J17 I/O AEMI V
GIO039 F / _0
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[01] PINMUX2[5].EM_D7
GIO
GIO: GIO[039]
EM_D00 / H18 I/O AEMI V
GIO038 F / _0
DD
in Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[00] PINMUX2[5].EM_D7
GIO
GIO: GIO[038]
EM_CE0 / J16 I/O AEMI V
GIO037 F / Can be programmed to be used for standard 0
DD
out H Async EMIF: Lowest numbered Chip Select. PINMUX2[6].EM_CE
GIO asynchronous memories (example:flash),
OneNand or NAND memory. Used for the
default boot and ROM boot modes.
GIO: GIO[037]
EM_CE1 / G19 I/O AEMI V
GIO036 F / programmed to be used for standard 1
DD
out H Async EMIF: Second Chip Select., Can be PINMUX2[7].EM_CE
GIO asynchronous memories (example: flash),
OneNand or NAND memory.
GIO: GIO[036]
(4)
AECFG[3]
AECFG[3]
www.ti.com
Mux Control
48 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
EM_WE / J15 I/O AEMI V
GIO035 F / E_OE
(1)
ID
Supply
DD
(2)
PD
(3)
State
out H Async EMIF: Write Enable PINMUX2[8].EM_W
GIO
NAND/SM/xD: WE (Write Enable) output
GIO: GIO[035]
EM_OE / F19 I/O AEMI V
GIO034 F / E_OE
DD
out H Async EMIF: Output Enable PINMUX2[8].EM_W
GIO
NAND/SM/xD: RE (Read Enable) output
GIO: GIO[034]
EM_WAIT / G18 I/O AEMI V
GIO033 F / AIT
DD
PU in H Async EMIF: Async WAIT PINMUX2[9].EM_W
GIO
NAND/SM/xD: RDY/_BSY input
GIO: GIO[033]
EM_ADV / H16 I/O AEMI V
GIO032 F / OneNAND interface DV
DD
PD in L OneNAND: Address Valid Detect for PINMUX2[10].EM_A
GIO
GIO: GIO[032]
EM_CLK / E19 I/O AEMI V
GIO031 F / interface LK
DD
out L OneNAND: Clock signal for OneNAND flash PINMUX2[11].EM_C
GIO
GIO: GIO[031]
ASP0_DX / H15 I/O ASP0 V
GIO030 / GIO
DD
in ASP0: Transmit Data PINMUX3[0].GIO30
GIO: GIO[030]
ASP0_CLKX / F18 I/O ASP0 V
GIO029 / GIO
DD
in ASP0: Transmit Clock PINMUX3[1].GIO29
GIO: GIO[029]
ASP0_FSX / G17 I/O ASP0 V
GIO028 / GIO
DD
in ASP0: Transmit Frame Synch PINMUX3[2].GIO28
GIO: GIO[028]
ASP0_DR / E18 I/O ASP0 V
GIO027 / GIO
DD
in ASP0: Receive Data PINMUX3[3].GIO27
GIO: GIO[027]
ASP0_CLKR / F17 I/O ASP0 V
GIO026 / GIO
DD
in ASP0: Receive Clock PINMUX3[4].GIO26
GIO: GIO[026]
ASP0_FSR / F16 I/O ASP0 V
GIO025 / GIO
DD
in ASP0: Receive Frame Synch PINMUX3[5].GIO25
GIO: GIO[025]
MMCSD1_CLK / C15 I/O MMC V
GIO024 SD /
DD
in MMCSD1: Clock PINMUX3[6].GIO24
GIO
GIO: GIO[024]
MMCSD1_CMD A17 I/O MMC V
/ GIO023 SD /
DD
in MMCSD1: Command PINMUX3[7].GIO23
GIO
GIO: GIO[023]
(4)
Mux Control
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 49
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
MMCSD1_DAT B16 I/O MMC V
A3 / GIO022 / SD / 2
(1)
ID
Supply
DD
(2)
PD
(3)
State
in MMCSD1: DATA3 PINMUX3[9:8].GIO2
UART2_RTS GIO /
UART
2
GIO: GIO[022]
UART2: RTS
MMCSD1_DAT A16 I/O MMC V
A2 / GIO021 / SD / O21
DD
in MMCSD1: DATA2 PINMUX3[11:10].GI
UART2_CTS GIO /
UART
2
GIO: GIO[021]
UART2: CTS
MMCSD1_DAT B15 I/O MMC V
A1 / GIO020 / SD / O20
DD
in MMCSD1: DATA1 PINMUX3[13:12].GI
UART2_RXD GIO /
UART
2
GIO: GIO[020]
UART2: Receive Data
MMCSD1_DAT A18 I/O MMC V
A0 / GIO019 / SD / O19
DD
in MMCSD1: DATA0 PINMUX3[15:14].GI
UART2_TXD GIO /
UART
2
GIO: GIO[019]
UART2: Transmit Data
CLKOUT1 / D12 I/O Clocks V
GIO018 / GIO 8
DD
in CLKOUT: Output Clock 1 PINMUX3[16].GIO1
GIO: GIO[018]
CLKOUT2 / A11 I/O Clocks V
GIO017 / GIO 7
DD
in CLKOUT: Output Clock 2 PINMUX3[17].GIO1
GIO: GIO[017]
CLKOUT3 / C11 I/O Clocks V
GIO016 / GIO 6
DD
in CLKOUT: Output Clock 3 PINMUX3[18].GIO1
GIO: GIO[016]
I2C_SDA / R13 I/O I2C / V
GIO015 GIO 5
DD
in I2C: Serial Data PINMUX3[19].GIO1
GIO: GIO[015]
I2C_SCL / R14 I/O I2C / V
GIO014 GIO 4
DD
in I2C: Serial Clock PINMUX3[20].GIO1
GIO: GIO[014]
UART1_RXD / R15 I/O UART V
GIO013 1 / 3
DD
in UART1: Receive Data PINMUX3[21].GIO1
GIO
GIO: GIO[013]
UART1_TXD / R17 I/O UART V
GIO012 1 / 2
DD
in UART1: Transmit Data PINMUX3[22].GIO1
GIO
GIO: GIO[012]
SPI1_SDENA[0] E13 I/O SPI1 / V
/ GIO011 GIO 1
DD
in SPI1: Chip Select 0 PINMUX3[23].GIO1
GIO: GIO[011]
(4)
www.ti.com
Mux Control
50 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
SPI1_SCLK / C13 I/O SPI1 / V
GIO010 GIO 0
(1)
ID
Supply
DD
(2)
PD
(3)
State
in SPI1: Clock PINMUX3[24].GIO1
GIO: GIO[010]
SPI1_SDI / A13 I/O SPI1 / V
GIO009 / GIO / O9
DD
in SPI1: Data In -OR- SPI1: Chip Select 1 PINMUX3[26:25].GI
SPI1_SDENA[1] SPI1
GIO: GIO[009]
SPI1_SDO / E12 I/O SPI1 / V
GIO008 GIO
DD
in SPI1: Data Out PINMUX3[27].GIO8
GIO: GIO[008]
GIO007 / C17 I/O GIO V
SPI0_SDENA[1] debou
DD
in GIO: GIO[007] PINMUX3[28].GIO7
nce /
SPI0
SPI0: Chip Select 1
GIO006 B18 I/O GIO V
debou
DD
in GIO: GIO[006]
nce
GIO005 D15 I/O GIO V
debou
DD
in GIO: GIO[005]
nce
GIO004 B17 I/O GIO V
debou
DD
in GIO: GIO[004]
nce
GIO003 G15 I/O GIO V
debou
DD
in GIO: GIO[003]
nce
GIO002 F15 I/O GIO V
debou
DD
in GIO: GIO[002]
nce
GIO001 E14 I/O GIO V
debou
DD
in GIO: GIO[001]
nce
GIO000 C16 I/O GIO V
debou Note: The GIO000 pin must be held high
DD
in GIO: GIO[000]
nce during NAND boot for the boot process to
fuction properly.
USB_DP A7 A I/O USBP V
HY
USB_DM A6 A I/O USBP V
HY
DDA33_USB
DDA33_USB
USB D+ (differential signal pair)
USB D- (differential signal pair)
USB_R1 C7 A I/O USBP USB Reference current output
HY
Connect to V
resistor placed as close to the device as
SS_USB_REF
possible.
USB_ID D5 A I/O USBP V
HY
DDA33_USB
USB operating mode identification pin
For Device mode operation only, pull up this
pin to VDDwith a 1.5K ohm resistor.
For Host mode operation only, pull down this
pin to ground (VSS) with a 1.5K ohm resistor.
If using an OTG or mini-USB connector, this
pin will be set properly via the
cable/connector configuration.
(4)
via 10K Ω ±1%
Mux Control
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 51
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
(1)
ID
Supply
(2)
PD
(3)
State
USB_VBUS E5 A I/O USBP For host or device mode operation, tie the
HY VBUS/USB power signal to the USB
connector.
When used in OTG mode operation, tie
VBUS to the external charge pump and to
the VBUS signal on the USB connector.
When the USB is not used, tie VBUS to
V
.
SS_USB
USB_DRVVBU C5 O USBP V
S HY
V
SS_USB_REF
C8 GND USBP V
HY
DD
DD
Digital output to control external 5 V supply
USB Ground Reference
Connect directly to ground and to USB_R1
via 10K Ω ±1% resistor placed as close to
the device as possible.
V
DDA33_USB
V
SS_USB
V
DDA33_USB_PLL
V
SS_USB
V
DDA13_USB
V
SS_USB
V
DDD13_USB
MMCSD0_CLK A15 I/O MMC V
MMCSD0_CMD C14 I/O MMC V
MMCSD0_DAT A14 I/O MMC V
A3 SD0 D0_MS
MMCSD0_DAT B13 I/O MMC V
A2 SD0 D0_MS
MMCSD0_DAT D14 I/O MMC V
A1 SD0 D0_MS
MMCSD0_DAT B14 I/O MMC V
A0 SD0 D0_MS
UART0_RXD U18 I UART V
J8 PWR USBP V
HY
B7 GND USBP V
HY (Transceiver)
B6 PWR USBP V
HY (PLL)
D6 GND USBP V
HY (PLL)
H7 PWR USBP V
HY
E6 GND USBP V
HY
C6 PWR USBP V
HY
SD0 D0_MS
SD0 D0_MS
0
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
Analog 3.3 V power USB PHY (Transceiver)
Analog 3.3 V ground for USB PHY
Common mode 3.3 V power for USB PHY
Common mode 3.3 V ground for USB PHY
Analog 1.3 V power for USB PHY
Analog 1.3 V ground for USB PHY
Digital 1.3 V power for USB PHY
out L MMCSD0: Clock PINMUX4[2].MMCS
in MMCSD0: Command PINMUX4[2].MMCS
in MMCSD0: DATA3 PINMUX4[2].MMCS
in MMCSD0: DATA2 PINMUX4[2].MMCS
in MMCSD0: DATA1 PINMUX4[2].MMCS
in MMCSD0: DATA0 PINMUX4[2].MMCS
in UART0: Receive Data
Used for UART boot mode
UART0_TXD T18 O UART V
0
DD
out H UART0: Transmit Data
Used for UART boot mode
SPI0_SDENA[0] B12 I/O SPI0 / V
/ GIO103 GIO DENA
DD
in SPI0: Enable / Chip Select 0 PINMUX4[0].SPI0_S
GIO: GIO[103]
SPI0_SCLK C12 I/O SPI0 V
SPI0_SDI / A12 I/O SPI0 / V
GIO102 GIO DI
DD
DD
in SPI0: Clock
in SPI0: Data In PINMUX4[1].SPI0_S
GIO: GIO[102]
SPI0_SDO B11 I/O SPI0 V
DD
in SPI0: Data Out
(4)
www.ti.com
Mux Control
52 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
ASP1_DX C18 I/O ASP1 V
ASP1_CLKX D19 I/O ASP1 V
ASP1_FSX E16 I/O ASP1 V
ASP1_DR C19 I/O ASP1 V
ASP1_CLKR D18 I/O ASP1 V
ASP1_FSR E17 I/O ASP1 V
ASP1_CLKS D17 I ASP1 V
RESET D11 I V
MXI1 A9 I Clocks V
MXO1 B9 O Clocks V
MXI2 R1 I Clocks V
MXO2 T1 O Clocks V
TCK E10 I EMUL V
(1)
ID
ATIO
Supply
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
(2)
PD
(3)
State
in ASP1: Transmit Data
in ASP1: Transmit Clock
in ASP1: Transmit Frame Sync
in ASP1: Receive Data
in ASP1: Receive Clock
in ASP1: Receive Frame Synch
in ASP1: Master Clock
PU in Global Chip Reset (active low)
in Crystal input for system oscillator (24 MHz)
out Output for system oscillator (24 MHz)
in Crystal input for video oscillator (27 MHz).
This crystal is not required
V
DD
out Output for video oscillator (27 MHz). This
crystal is not required.
V
DD
PU in JTAG test clock input
N
TDI D9 I EMUL V
ATIO
DD
PU in JTAG test data input
N
TDO E9 O EMUL V
ATIO
DD
out L JTAG test data output
N
TMS D8 I EMUL V
ATIO
DD
PU in JTAG test mode select
N
TRST C9 I EMUL V
ATIO
DD
PD in JTAG test logic reset (active low)
N
RTCK E11 O EMUL V
ATIO
DD
out L JTAG test clock output
N
EMU0 E8 I/O EMUL V
ATIO
N
EMU1 E7 I/O EMUL V
ATIO
N
DD
DD
PU in JTAG emulation 0 I/O
V
DD
V
DD
PU in JTAG emulation 1 I/O
EMU[1:0] = 00 - Force Debug Scan chain
(ARM and ARM ETB TAPs connected)
EMU[1:0] = 11 - Normal Scan chain (ICEpick
only)
RSV01 J1 A Reserved. This signal should be left as a No
I/O/Z Connect or connected to VSS.
RSV02 K1 A Reserved. This signal should be left as a No
I/O/Z Connect or connected to VSS.
RSV03 L1 A Reserved. This signal should be left as a No
I/O/Z Connect or connected to VSS.
RSV04 M1 A Reserved. This signal should be left as a No
I/O/Z Connect or connected to VSS.
RSV05 N2 A Reserved. This signal should be connected
I/O/Z to VSS.
(4)
Mux Control
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 53
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
(1)
ID
Supply
(2)
PD
(3)
State
RSV06 M2 PWR Reserved. This signal should be connected
to VSS.
RSV07 K2 GND Reserved. This signal should be connected
to VSS.
NC H8 No connect
V
DD_VIN
V
DD_VIN
V
DD_VIN
V
DD_VOUT
V
DD_VOUT
V
DD_VOUT
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DD_DDR
V
DDA_PLL1
V
DDA_PLL2
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
CV
DD
V
DD
V
DD
P6 PWR Power for Digital Video Input IO (3.3 V)
P7 PWR Power for Digital Video Input IO (3.3 V)
P8 PWR Power for Digital Video Input IO (3.3 V)
F6 PWR Power for Digital Video Output IO (3.3 V)
F7 PWR Power for Digital Video Output IO (3.3 V)
F8 PWR Power for Digital Video Output IO (3.3 V)
M9 PWR Power for DDR I/O (1.8 V)
P9 PWR Power for DDR I/O (1.8 V)
P10 PWR Power for DDR I/O (1.8 V)
P11 PWR Power for DDR I/O (1.8 V)
P12 PWR Power for DDR I/O (1.8 V)
P13 PWR Power for DDR I/O (1.8 V)
P14 PWR Power for DDR I/O (1.8 V)
R9 PWR Power for DDR I/O (1.8 V)
R12 PWR Power for DDR I/O (1.8 V)
T14 PWR Power for DDR I/O (1.8 V)
G12 PWR Analog Power for PLL1 (1.3 V)
H9 PWR Analog Power for PLL2 (1.3 V)
A1 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
A10 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
B19 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
C4 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
G6 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
G11 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
H10 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
H13 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
H17 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
J11 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
J12 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
J13 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
K6 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
K11 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
K12 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
L11 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
L12 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
N6 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
R7 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
R8 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
T17 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
W19 PWR Core power (1.3 V)
F9 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
F10 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
(4)
www.ti.com
Mux Control
54 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS_MX1
V
SS_MX2
V
SSA_PLL1
V
SSA_PLL2
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
F11 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
F12 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
F13 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
F14 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
G14 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
K15 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
L13 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
M10 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
M11 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
M12 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
M13 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
N11 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
N12 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
C10 GND System oscillator (24 MHz) - ground
H12 GND Analog Ground for PLL1
A19 GND Digital ground
B10 GND Digital ground
E15 GND Digital ground
H11 GND Digital ground
H14 GND Digital ground
J10 GND Digital ground
J14 GND Digital ground
K10 GND Digital ground
K14 GND Digital ground
(1)
ID
Supply
(2)
PD
(3)
State
G8 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
K8 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
L6 PWR Power for Digital IO (3.3 V)
P1 GND Video oscillator (27 MHz) - ground
J9 GND Analog Ground for PLL2
A5 GND Digital ground
A8 GND Digital ground
B5 GND Digital ground
B8 GND Digital ground
D1 GND Digital ground
E2 GND Digital ground
G2 GND Digital ground
G9 GND Digital ground
H1 GND Digital ground
H2 GND Digital ground
H6 GND Digital ground
J2 GND Digital ground
J6 GND Digital ground
K3 GND Digital ground
K9 GND Digital ground
L2 GND Digital ground
L9 GND Digital ground
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
(4)
Mux Control
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 55
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 2-23. DM355 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Name BGA Type Group Power PU Reset Description
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
L10 GND Digital ground
L14 GND Digital ground
M14 GND Digital ground
M17 GND Digital ground
N14 GND Digital ground
T15 GND Digital ground
U14 GND Digital ground
U17 GND Digital ground
V18 GND Digital ground
W1 GND Digital ground
(1)
ID
Supply
(2)
PD
(3)
State
M6 GND Digital ground
M7 GND Digital ground
M8 GND Digital ground
N1 GND Digital ground
N8 GND Digital ground
N9 GND Digital ground
R2 GND Digital ground
R6 GND Digital ground
T2 GND Digital ground
T5 GND Digital ground
U1 GND Digital ground
U2 GND Digital ground
U3 GND Digital ground
U4 GND Digital ground
U9 GND Digital ground
V1 GND Digital ground
www.ti.com
(4)
Mux Control
56 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
2.21 Device Support
2.21.1 Development Tools
TI offers an extensive line of development tools for DM355 systems, including tools to evaluate the
performance of the processors, generate code, develop algorithm implementations, and fully integrate and
debug software and hardware modules. The tools support documentation is electronically available within
the Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE).
The following products support development of DM355 based applications:
Software Development Tools:
Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE): including Editor
C/C++/Assembly Code Generation, and Debug plus additional development tools
Hardware Development Tools:
Extended Development System (XDS™) Emulator (supports TMS320DM355 DMSoC multiprocessor
system debug) EVM (Evaluation Module)
For a complete listing of development-support tools for the TMS320DM355 DMSoC platform, visit the
Texas Instruments web site on the Worldwide Web at http://www.ti.com. For information on pricing and
availability, contact the nearest TI field sales office or authorized distributor.
2.21.2 Device Nomenclature
To designate the stages in the product development cycle, TI assigns prefixes to the part numbers of all
DSP devices and support tools. Each DSP commercial family member has one of three prefixes: TMX,
TMP, or TMS (e.g., ). Texas Instruments recommends two of three possible prefix designators for its
support tools: TMDX and TMDS. These prefixes represent evolutionary stages of product development
from engineering prototypes (TMX/TMDX) through fully qualified production devices/tools (TMS/TMDS).
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Device development evolutionary flow:
TMX Experimental device that is not necessarily representative of the final device's electrical
specifications.
TMP Final silicon die that conforms to the device's electrical specifications but has not completed
quality and reliability verification.
TMS Fully-qualified production device.
Support tool development evolutionary flow:
TMDX Development-support product that has not yet completed Texas Instruments internal
qualification testing.
TMDS Fully qualified development-support product.
TMX and TMP devices and TMDX development-support tools are shipped against the following
disclaimer:
"Developmental product is intended for internal evaluation purposes."
TMS devices and TMDS development-support tools have been characterized fully, and the quality and
reliability of the device have been demonstrated fully. TI's standard warranty applies.
Predictions show that prototype devices (TMX or TMP) have a greater failure rate than the standard
production devices. Texas Instruments recommends that these devices not be used in any production
system because their expected end-use failure rate is undefined. Only qualified production devices are to
be used in production.
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 57
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

DM355
PREFIX
TMS
320 DM355
ZCE
TMX = Experimental device
TMS = Qualified device
DEVICE FAMILY
320 = TMS320 DSPfamily
PACKAGE TYPE
(A)
ZCE = 337-pin plastic BGA, with Pb-free soldered balls
DEVICE
(B)
( )
SILICON REVISION
( ) ( )
TEMPERATURE RANGE (DEFAULT: 0°C TO 85°C)
0°C to 85°C, commercial temperature
A =
40°C to 10 °C– 0 , extended temperature
Blank =
SPEED GRADE
216 or 21 = 216 MHz
270 = 270 MHz (with 216 MHz Max DDR)
135 or 13 = 135 MHz
27J = 270 MHz (with 198 MHz Max DDR)
(
C)
A. BGA = Ball Grid Array
B. For actual device part numbers (P/Ns) and ordering information, contact your nearest TI Sales representative.
C. For more information on silicon revision, see (literature number SPRZ264).TMS320DM355 DMSoC Silicon Errata
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
TI device nomenclature also includes a suffix with the device family name. This suffix indicates the
package type (for example, ZCE), the temperature range (for example, "Blank" is the commercial
temperature range), and the device speed range in megahertz (for example, 202 is 202.5 MHz). The
following figure provides a legend for reading the complete device name for any TMS320DM355 DMSoC
platform member.
www.ti.com
Figure 2-5. Device Nomenclature
2.21.3 Device Documentation
2.21.3.1 Related Documentation From Texas Instruments
The following documents describe the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). Copies of
these documents are available on the internet at www.ti.com.
SPRS463 TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Data Manual This document
describes the overall TMS320DM355 system, including device architecture and features,
memory map, pin descriptions, timing characteristics and requirements, device mechanicals,
etc.
SPRZ264 TMS320DM355 DMSoC Silicon Errata Describes the known exceptions to the functional
specifications for the TMS320DM355 DMSoC.
SPRUFB3 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem Reference
Guide This document describes the ARM Subsystem in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media
System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The ARM subsystem is designed to give the ARM926EJ-S
(ARM9) master control of the device. In general, the ARM is responsible for configuration
and control of the device; including the components of the ARM Subsystem, the peripherals,
and the external memories.
SPRUED1 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Asynchronous External
Memory Interface (EMIF) Reference Guide This document describes the asynchronous
SPRUED2 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Universal Serial Bus (USB)
external memory interface (EMIF) in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip
(DMSoC). The EMIF supports a glueless interface to a variety of external devices.
Controller Reference Guide This document describes the universal serial bus (USB)
controller in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The USB controller
supports data throughput rates up to 480 Mbps. It provides a mechanism for data transfer
between USB devices and also supports host negotiation.
SPRUED3 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Audio Serial Port (ASP)
58 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRUED4 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
SPRUED9 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Universal Asynchronous
SPRUEE0 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Reference Guide This document describes the operation of the audio serial port (ASP)
audio interface in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The primary
audio modes that are supported by the ASP are the AC97 and IIS modes. In addition to the
primary audio modes, the ASP supports general serial port receive and transmit operation,
but is not intended to be used as a high-speed interface.
Reference Guide This document describes the serial peripheral interface (SPI) in the
TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The SPI is a high-speed
synchronous serial input/output port that allows a serial bit stream of programmed length (1
to 16 bits) to be shifted into and out of the device at a programmed bit-transfer rate. The SPI
is normally used for communication between the DMSoC and external peripherals. Typical
applications include an interface to external I/O or peripheral expansion via devices such as
shift registers, display drivers, SPI EPROMs and analog-to-digital converters.
Receiver/Transmitter (UART) Reference Guide This document describes the universal
asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART) peripheral in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media
System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The UART peripheral performs serial-to-parallel conversion on
data received from a peripheral device, and parallel-to-serial conversion on data received
from the CPU.
Peripheral Reference Guide This document describes the inter-integrated circuit (I2C)
peripheral in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The I2C peripheral
provides an interface between the DMSoC and other devices compliant with the I2C-bus
specification and connected by way of an I2C-bus. External components attached to this
2-wire serial bus can transmit and receive up to 8-bit wide data to and from the DMSoC
through the I2C peripheral. This document assumes the reader is familiar with the I2C-bus
specification.
SPRUEE2 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Multimedia Card (MMC)/Secure
Digital (SD) Card Controller Reference Guide This document describes the multimedia
card (MMC)/secure digital (SD) card controller in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media
System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The MMC/SD card is used in a number of applications to provide
removable data storage. The MMC/SD controller provides an interface to external MMC and
SD cards. The communication between the MMC/SD controller and MMC/SD card(s) is
performed by the MMC/SD protocol.
SPRUEE4 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Enhanced Direct Memory
Access (EDMA) Controller Reference Guide This document describes the operation of the
enhanced direct memory access (EDMA3) controller in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media
System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The EDMA controller's primary purpose is to service
user-programmed data transfers between two memory-mapped slave endpoints on the
DMSoC.
SPRUEE5 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) 64-bit Timer Reference Guide
This document describes the operation of the software-programmable 64-bit timers in the
TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). Timer 0, Timer 1, and Timer 3 are
used as general-purpose (GP) timers and can be programmed in 64-bit mode, dual 32-bit
unchained mode, or dual 32-bit chained mode; Timer 2 is used only as a watchdog timer.
The GP timer modes can be used to generate periodic interrupts or enhanced direct memory
access (EDMA) synchronization events and Real Time Output (RTO) events (Timer 3 only).
The watchdog timer mode is used to provide a recovery mechanism for the device in the
event of a fault condition, such as a non-exiting code loop.
SPRUEE6 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) General-Purpose Input/Output
(GPIO) Reference Guide This document describes the general-purpose input/output (GPIO)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Overview 59
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
peripheral in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The GPIO
peripheral provides dedicated general-purpose pins that can be configured as either inputs
or outputs. When configured as an input, you can detect the state of the input by reading the
state of an internal register. When configured as an output, you can write to an internal
register to control the state driven on the output pin.
SPRUEE7 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Pulse-Width Modulator (PWM)
Reference Guide This document describes the pulse-width modulator (PWM) peripheral in
the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
SPRUEH7 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) DDR2/Mobile DDR
(DDR2/mDDR) Memory Controller Reference Guide This document describes the
DDR2/mDDR memory controller in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip
(DMSoC). The DDR2/mDDR memory controller is used to interface with JESD79D-2A
standard compliant DDR2 SDRAM and mobile DDR devices.
SPRUF71 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Video Processing Front End
(VPFE) Reference Guide This document describes the Video Processing Front End (VPFE)
in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
SPRUF72 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Video Processing Back End
(VPBE) Reference Guide This document describes the Video Processing Back End (VPBE)
in the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
SPRUF74 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Real-Time Out (RTO) Controller
Reference Guide This document describes the Real Time Out (RTO) controller in the
TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
www.ti.com
SPRUFC8 TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Peripherals Overview
Reference Guide This document provides an overview of the peripherals in the
TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
SPRAAR3 Implementing DDR2/mDDR PCB Layout on the TMS320DM35x DMSoC This provides
board design recommendations and guidelines for DDR2 and mobile DDR.
SPRAAR7 USB 2.0 Board Design and Layout Guidelines This provides board design
recommendations and guidelines for high speed USB.
60 Device Overview Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
3 Detailed Device Description
This section provides a detailed overview of the DM355 device.
3.1 ARM Subsystem Overview
The ARM Subsystem contains components required to provide the ARM926EJ-S (ARM) master control of
the overall DM355 system, including the components of the ARM Subsystem, the peripherals, and the
external memories.
The ARM is responsible for handling system functions such as system-level initialization, configuration,
user interface, user command execution, connectivity functions, interface and control of the subsystem,
etc. The ARM is master and performs these functions because it has a large program memory space and
fast context switching capability, and is thus suitable for complex, multi-tasking, and general-purpose
control tasks.
3.1.1 Components of the ARM Subsystem
The ARM Subsystem in DM355 consists of the following components:
• ARM926EJ-S RISC processor, including:
– coprocessor 15 (CP15)
– MMU
– 16KB Instruction cache
– 8KB Data cache
– Write Buffer
– Java accelerator
• ARM Internal Memories
– 32KB Internal RAM (32-bit wide access)
– 8KB Internal ROM (ARM bootloader for non-AEMIF boot options)
• Embedded Trace Module and Embedded Trace Buffer (ETM/ETB)
• System Control Peripherals
– ARM Interrupt Controller
– PLL Controller
– Power and Sleep Controller
– System Control Module
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
The ARM also manages/controls all the device peripherals:
• DDR2 / mDDR EMIF Controller
• AEMIF Controller, including the OneNAND and NAND flash interface
• Enhanced DMA (EDMA)
• UART
• Timers
• Real Time Out (RTO)
• Pulse Width Modulator (PWM)
• Inter-IC Communication (I2C)
• Multi-Media Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD)
• Audio Serial Port (ASP)
• Universal Serial Bus Controller (USB)
• Serial Port Interface (SPI)
• Video Processing Front End (VPFE)
– CCD Controller (CCDC)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 61
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

ARM926EJ-S
16KI$
8KD$ MMU
CP15
Arbiter Arbiter
I-AHB
D-AHB
Master
IF
DMA Bus
I-TCM
D-TCM
16K
RAM0
RAM1
16K
ROM
8K
Arbiter
Slave
IF
MasterIF
CFGBus
ARM
Interrupt
Controller
(AINTC)
Control
System
PLLC2
PLLC1
(PSC)
Controller
Sleep
Power
Peripherals
...
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
– Image Pipe (IPIPE)
– H3A Engine (Hardware engine for computing Auto-focus, Auto white balance, and Auto exposure)
• Video Processing Back End (VPBE)
– On Screen Display (OSD)
– Video Encoder Engine (VENC)
Figure 3-1 shows the functional block diagram of the DM355 ARM Subsystem.
www.ti.com
3.2 ARM926EJ-S RISC CPU
The ARM Subsystem integrates the ARM926EJ-S processor. The ARM926EJ-S processor is a member of
ARM9 family of general-purpose microprocessors. This processor is targeted at multi-tasking applications
where full memory management, high performance, low die size, and low power are all important. The
ARM926EJ-S processor supports the 32-bit ARM and 16 bit THUMB instruction sets, enabling the user to
trade off between high performance and high code density. Specifically, the ARM926EJ-S processor
supports the ARMv5TEJ instruction set, which includes features for efficient execution of Java byte codes,
providing Java performance similar to Just in Time (JIT) Java interpreter, but without associated code
overhead.
The ARM926EJ-S processor supports the ARM debug architecture and includes logic to assist in both
hardware and software debug. The ARM926EJ-S processor has a Harvard architecture and provides a
complete high performance subsystem, including:
• ARM926EJ -S integer core
• CP15 system control coprocessor
• Memory Management Unit (MMU)
• Separate instruction and data Caches
• Write buffer
• Separate instruction and data Tightly-Coupled Memories (TCMs) [internal RAM] interfaces
• Separate instruction and data AHB bus interfaces
Figure 3-1. DM355 ARM Subsystem Block Diagram
62 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
• Embedded Trace Module and Embedded Trace Buffer (ETM/ETB)
For more complete details on the ARM9, refer to the ARM926EJ-S Technical Reference Manual, available
at http://www.arm.com
3.2.1 CP15
The ARM926EJ-S system control coprocessor (CP15) is used to configure and control instruction and
data caches, Tightly-Coupled Memories (TCMs), Memory Management Unit (MMU), and other ARM
subsystem functions. The CP15 registers are programmed using the MRC and MCR ARM instructions,
when the ARM in a privileged mode such as supervisor or system mode.
3.2.2 MMU
The ARM926EJ-S MMU provides virtual memory features required by operating systems such as Linux,
WindowCE, ultron, ThreadX, etc. A single set of two level page tables stored in main memory is used to
control the address translation, permission checks and memory region attributes for both data and
instruction accesses. The MMU uses a single unified Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) to cache the
information held in the page tables. The MMU features are:
• Standard ARM architecture v4 and v5 MMU mapping sizes, domains and access protection scheme.
• Mapping sizes are:
– 1MB (sections)
– 64KB (large pages)
– 4KB (small pages)
– 1KB (tiny pages)
• Access permissions for large pages and small pages can be specified separately for each quarter of
the page (subpage permissions)
• Hardware page table walks
• Invalidate entire TLB, using CP15 register 8
• Invalidate TLB entry, selected by MVA, using CP15 register 8
• Lockdown of TLB entries, using CP15 register 10
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
3.2.3 Caches and Write Buffer
The size of the Instruction Cache is 16KB, Data cache is 8KB. Additionally, the Caches have the following
features:
• Virtual index, virtual tag, and addressed using the Modified Virtual Address (MVA)
• Four-way set associative, with a cache line length of eight words per line (32-bytes per line) and with
two dirty bits in the Dcache
• Dcache supports write-through and write-back (or copy back) cache operation, selected by memory
region using the C and B bits in the MMU translation tables.
• Critical-word first cache refilling
• Cache lockdown registers enable control over which cache ways are used for allocation on a line fill,
providing a mechanism for both lockdown, and controlling cache corruption
• Dcache stores the Physical Address TAG (PA TAG) corresponding to each Dcache entry in the TAG
RAM for use during the cache line write-backs, in addition to the Virtual Address TAG stored in the
TAG RAM. This means that the MMU is not involved in Dcache write-back operations, removing the
possibility of TLB misses related to the write-back address.
• Cache maintenance operations provide efficient invalidation of, the entire Dcache or Icache, regions of
the Dcache or Icache, and regions of virtual memory.
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 63
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
The write buffer is used for all writes to a noncachable bufferable region, write-through region and write
misses to a write-back region. A separate buffer is incorporated in the Dcache for holding write-back for
cache line evictions or cleaning of dirty cache lines. The main write buffer has 16-word data buffer and a
four-address buffer. The Dcache write-back has eight data word entries and a single address entry.
3.2.4 Tightly Coupled Memory (TCM)
ARM internal RAM is provided for storing real-time and performance-critical code/data and the Interrupt
Vector table. ARM internal ROM boot options include—NAND (with SPI EEPROM Boot option), SPI,
UART and MMC/SD. The RAM and ROM memories interfaced to the ARM926EJ-S via the tightly coupled
memory interface that provides for separate instruction and data bus connections. Since the ARM TCM
does not allow instructions on the D-TCM bus or data on the I-TCM bus, an arbiter is included so that both
data and instructions can be stored in the internal RAM/ROM. The arbiter also allows accesses to the
RAM/ROM from extra-ARM sources (e.g., EDMA or other masters). The ARM926EJ-S has built-in DMA
support for direct accesses to the ARM internal memory from a non-ARM master. Because of the
time-critical nature of the TCM link to the ARM internal memory, all accesses from non-ARM devices are
treated as DMA transfers.
Instruction and Data accesses are differentiated via accessing different memory map regions, with the
instruction region from 0x0000 through 0x7FFF and data from 0x10000 through 0x17FFF. Placing the
instruction region at 0x0000 is necessary to allow the ARM Interrupt Vector table to be placed at 0x0000,
as required by the ARM architecture. The internal 32-KB RAM is split into two physical banks of 16KB
each, which allows simultaneous instruction and data accesses to be accomplished if the code and data
are in separate banks.
www.ti.com
3.2.5 Advanced High-performance Bus (AHB)
The ARM Subsystem uses the AHB port of the ARM926EJ-S to connect the ARM to the configuration bus
and the external memories. Arbiters are employed to arbitrate access to the separate D-AHB and I-AHB
by the configuration bus and the external memories bus.
3.2.6 Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM) and Embedded Trace Buffer (ETB)
To support real-time trace, the ARM926EJ-S processor provides an interface to enable connection of an
Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM). The ARM926ES-J Subsystem in DM355 also includes the Embedded
Trace Buffer (ETB). The ETM consists of two parts:
• Trace Port provides real-time trace capability for the ARM9.
• Triggering facilities provide trigger resources, which include address and data comparators, counter,
and sequencers.
The DM355 trace port is not pinned out and is instead only connected to the Embedded Trace Buffer. The
ETB has a 4KB buffer memory. ETB enabled debug tools are required to read/interpret the captured trace
data.
3.3 Memory Mapping
The ARM memory map is shown in Table 2-2 and Table 2-3. This section describes the memories and
interfaces within the ARM's memory map.
3.3.1 ARM Internal Memories
The ARM has access to the following ARM internal memories:
• 32KB ARM Internal RAM on TCM interface, logically separated into two 16KB pages to allow
simultaneous access on any given cycle if there are separate accesses for code (I-TCM bus) and data
(D-TCM) to the different memory regions.
• 8KB ARM Internal ROM
64 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
3.3.2 External Memories
The ARM has access to the following External memories:
• DDR2 / mDDR Synchronous DRAM
• Asynchronous EMIF / OneNAND
• NAND Flash
• Flash card devices:
– MMC/SD
– xD
– SmartMedia
3.3.3 Peripherals
The ARM has access to all of the peripherals on the DM355 device.
3.4 ARM Interrupt Controller (AINTC)
The DM355 ARM Interrupt Controller (AINTC) has the following features:
• Supports up to 64 interrupt channels (16 external channels)
• Interrupt mask for each channel
• Each interrupt channel can be mapped to a Fast Interrupt Request (FIQ) or to an Interrupt Request
(IRQ) type of interrupt.
• Hardware prioritization of simultaneous interrupts
• Configurable interrupt priority (2 levels of FIQ and 6 levels of IRQ)
• Configurable interrupt entry table (FIQ and IRQ priority table entry) to reduce interrupt processing time
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
The ARM core supports two interrupt types: FIQ and IRQ. See the ARM926EJ-S Technical Reference
Manual for detailed information about the ARM’s FIQ and IRQ interrupts. Each interrupt channel is
mappable to an FIQ or to an IRQ type of interrupt, and each channel can be enabled or disabled. The
INTC supports user-configurable interrupt-priority and interrupt entry addresses. Entry addresses minimize
the time spent jumping to interrupt service routines (ISRs). When an interrupt occurs, the corresponding
highest priority ISR’s address is stored in the INTC’s ENTRY register. The IRQ or FIQ interrupt routine can
read the ENTRY register and jump to the corresponding ISR directly. Thus, the ARM does not require a
software dispatcher to determine the asserted interrupt.
3.4.1 Interrupt Mapping
The AINTC takes up to 64 ARM device interrupts and maps them to either the IRQ or to the FIQ of the
ARM. Each interrupt is also assigned one of 8 priority levels (2 for FIQ, 6 for IRQ). For interrupts with the
same priority level, the priority is determined by the hardware interrupt number (the lowest number has the
highest priority). Table 3-1 shows the connection of device interrupts to the ARM.
Table 3-1. AINTC Interrupt Connections
Interrupt Acronym Source Interrupt Acronym Source
Number Number
0 VPSSINT0 VPSS - INT0, 32 TINT0 Timer 0 - TINT12
Configurable via
VPSSBL register:
INTSEL
1 VPSSINT1 VPSS - INT1 33 TINT1 Timer 0 - TINT34
2 VPSSINT2 VPSS - INT2 34 TINT2 Timer 1 - TINT12
(1)
(1) The total number of interrupts in DM355 exceeds 64, which is the maximum value of the AINTC module. Therefore, several interrupts
are multiplexed and you must use the register ARM_INTMUX in the System Control Module to select the interrupt source for multiplexed
interrupts. Refer to TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem Reference Guide (literature number
SPRUFB3) for more information on the System Control Module register ARM_INTMUX.
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 65
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 3-1. AINTC Interrupt Connections
Interrupt Acronym Source Interrupt Acronym Source
Number Number
3 VPSSINT3 VPSS - INT3 35 TINT3 Timer 1 - TINT34
4 VPSSINT4 VPSS - INT4 36 PWMINT0 PWM0
5 VPSSINT5 VPSS - INT5 37 PWMINT1 PWM 1
6 VPSSINT6 VPSS - INT6 38 PWMINT2 PWM2
7 VPSSINT7 VPSS - INT7 39 I2CINT I2C
8 VPSSINT8 VPSS - INT8 40 UARTINT0 UART0
9 Reserved 41 UARTINT1 UART1
10 Reserved 42 SPINT0-0 SPI0
11 Reserved 43 SPINT0-1 SPI0
12 USBINT USB OTG Collector 44 GPIO0 GPIO
13 RTOINT or RTO or 45 GPIO1 GPIO
TINT4 Timer 2 - TINT12
SYS.ARM_INTMUX
14 UARTINT2 or UART2 or 46 GPIO2 GPIO
TINT5 Timer 2 - TINT34
15 TINT6 Timer 3 TINT12 47 GPIO3 GPIO
16 CCINT0 EDMA CC Region 0 48 GPIO4 GPIO
17 SPINT1-0 or SPI1 or 49 GPIO5 GPIO
CCERRINT EDMA CC Error
18 SPINT1-1 or SPI1 or 50 GPIO6 GPIO
TCERRINT0 EDMA TC0 Error
19 SPINT2-0 or SPI2 or 51 GPIO7 GPIO
TCERRINT1 EDMA TC1 Error
20 PSCINT PSC - ALLINT 52 GPIO8 GPIO
21 SPINT2-1 SPI2 53 GPIO9 GPIO
22 TINT7 Timer3 - TINT34 54 GPIOBNK0 GPIO
23 SDIOINT0 MMC/SD0 55 GPIOBNK1 GPIO
24 MBXINT0 or ASP0 or 56 GPIOBNK2 GPIO
MBXINT1 ASP1
25 MBRINT0 or ASP0 or 57 GPIOBNK3 GPIO
MBRINT1 ASP1
26 MMCINT0 MMC/SD0 58 GPIOBNK4 GPIO
27 MMCINT1 MMC/SC1 59 GPIOBNK5 GPIO
28 PWMINT3 PWM3 60 GPIOBNK6 GPIO
29 DDRINT DDR EMIF 61 COMMTX ARMSS
30 AEMIFINT Async EMIF 62 COMMRX ARMSS
31 SDIOINT1 SDIO1 63 EMUINT E2ICE
(1)
(continued)
www.ti.com
66 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
3.5 Device Clocking
3.5.1 Overview
The DM355 requires one primary reference clock . The reference clock frequency may be generated
either by crystal input or by external oscillator. The reference clock is the clock at the pins named
MXI1/MXO1. The reference clock drives two separate PLL controllers (PLLC1 and PLLC2). PLLC1
generates the clocks required by the ARM, MPEG4 and JPEG coprocessor, VPBE, VPSS, and
peripherals. PLL2 generates the clock required by the DDR PHY. A block diagram of DM355's clocking
architecture is shown in Figure 3-2. The PLLs are described further in Section 3.6.
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 67
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

ARMSubsystem
MPEG/JPEG
Coprocessor
SYSCLK1
SYSCLK2
VPFE
VPBE
DAC
DDRPHY
DDR
PLLDIV1(/1)
BPDIV(/8)
PLL Controller2
PLL Controller1
PLLDIV3(/n)
PLLDIV2(/4)
PLLDIV1(/2)
SYSCLK3
I2C
Timers(x4)
PWMs(x4)
SPI(x3)
MMC/SD(x2)
EMIF/NAND
ASP (x2)
GPIO
UART2
ARMINTC
USB
60MHz
Reference
Clock
(MXI/MXO)
(24MHzor
36MHz)
ReferenceClock
(MXI/MXO)
24MHzor36MHz
PCLK
AUXCLK(/1)
BPDIV(/3)
SYSCLK1
CLKOUT3
SYSCLKBP
CLKOUT2
EDMA
BusLogic
SysLogic
PSC
IcePick
EXTCLK
RTO
USBPhy
SYSCLKBP
AUXCLK
PLLDIV4(/4or/2)
VPSS
UART0,1
CLKOUT1
Sequencer
SYSCLK4
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
www.ti.com
Figure 3-2. Device Clocking Block Diagram
68 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
3.5.2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-135
This section describes the only supported device clocking configurations for DM355-135. The DM355
supports either 24 MHz (typical) or 36 MHz reference clock (crystal or external oscillator input).
Configurations are shown for both cases.
3.5.2.1 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-135 (24 MHz reference)
3.5.2.1.1 DM355-135 PLL1 (24 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-135 PLL1 with 24 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-2.
Table 3-2. PLL1 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-135 (24 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL1 ARM / Peripherals VENC VPSS
(/8 fixed) (m programmable) (/2 or /1 (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 PLLDIV2 SYSCLK2 PLLDIV3 SYSCLK3 PLLDIV4 SYSCLK4
bypass bypass bypass bypass 2 12 4 6 10 2.4 4 6
8 180 2 270 2 135 4 67.5 10 27 2 135
8 162 2 243 2 121.5 4 60.75 9 27 2 121.5
8 144 2 216 2 108 4 54 8 27 2 108
8 126 2 189 2 94.5 4 47.25 7 27 2 94.5
8 108 2 162 2 81 4 40.5 6 27 2 81
programmable) (/2 fixed) (MHz) (/4 fixed) (MHz) (/n (MHz) (/4 or /2 (MHz)
VCO MPEG4 and JPEG
Coprocessor
programmable) programmable)
3.5.2.1.2 DM355-135 PLL2 (24 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-135 PLL2 with 24 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-3.
Table 3-3. PLL2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-135 (24 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL2 VCO DDR PHY DDR Clock
(/n programmable) (m programmable) (/1 fixed) (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 DDR_CLK
bypass bypass bypass bypass 1 24 12
12 133 1 266 1 266 133
12 100 1 200 1 200 100
15 100 1 160 1 160 80
(/1 fixed) (MHz) (MHz)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 69
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
www.ti.com
3.5.2.2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-135 (36 MHz reference)
3.5.2.2.1 DM355-135PLL1 (36 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-135 PLL1 with 36 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-4.
Table 3-4. PLL1 Supported Clocking Configurations DM355-135 (36 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL1 ARM / Peripherals VENC VPSS
(/8 fixed) (m (/2 or /1 (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 PLLDIV2 SYSCLK2 PLLDIV3 SYSCLK3 PLLDIV4 SYSCLK4
bypass bypass bypass bypass 2 18 4 9 10 3.6 4 18
programmable) programmable) (/2 fixed) (MHz) (/4 fixed) (MHz) (/n (MHz) (/4 or /2 (MHz)
8 120 2 270 2 135 4 67.5 10 27 2 135
8 108 2 243 2 121.5 4 60.75 9 27 2 121.5
8 96 2 216 2 108 4 54 8 27 2 108
VCO MPEG4 and JPEG
Coprocessor
programmable) programmable)
3.5.2.2.2 DM355-135 PLL2 (36 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-135 PLL2 with 36 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-5.
Table 3-5. PLL2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-135 (36 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL2 VCO DDR PHY DDR Clock
(/n programmable) (m programmable) (/1 fixed) (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 DDR_CLK
bypass bypass bypass bypass 1 36 18
18 133 1 266 1 266 133
27 150 1 200 1 200 100
27 120 1 160 1 160 80
(/1 fixed) (MHz) (MHz)
70 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
3.5.3 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-216
This section describes the only supported device clocking configurations for DM355-216. The DM355
supports either 24 MHz (typical) or 36 MHz reference clock (crystal or external oscillator input).
Configurations are shown for both cases.
3.5.3.1 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-216 (24 MHz reference)
3.5.3.1.1 DM355-216 PLL1 (24 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-216 PLL1 with 24 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-6.
Table 3-6. PLL1 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-216 (24 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL1 ARM / Peripherals VENC VPSS
(/8 fixed) (m programmable) (/2 or /1 (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 PLLDIV2 SYSCLK2 PLLDIV3 SYSCLK3 PLLDIV4 SYSCLK4
bypass bypass bypass bypass 2 12 4 6 10 2.4 4 6
8 144 1 432 2 216 4 108 16 27 4 108
8 135 1 405 2 202.5 4 101.25 15 27 4 101.25
8 126 1 378 2 189 4 94.5 14 27 4 94.5
8 117 1 351 2 175.5 4 87.75 13 27 4 87.75
8 108 1 324 2 162 4 81 12 27 4 81
8 99 1 297 2 148.5 4 74.25 11 27 4 74.25
8 180 2 270 2 135 4 67.5 10 27 2 135
8 162 2 243 2 121.5 4 60.75 9 27 2 121.5
8 144 2 216 2 108 4 54 8 27 2 108
8 126 2 189 2 94.5 4 47.25 7 27 2 94.5
8 108 2 162 2 81 4 40.5 6 27 2 81
programmable) (/2 fixed) (MHz) (/4 fixed) (MHz) (/n (MHz) (/4 or /2 (MHz)
VCO MPEG4 and JPEG
Coprocessor
programmable) programmable)
3.5.3.1.2 DM355-216 PLL2 (24 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-216 PLL2 with 24 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-7.
Table 3-7. PLL2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-216 (24 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL2 VCO DDR PHY DDR Clock
(/n programmable) (m programmable) (/1 fixed) (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 DDR_CLK
bypass bypass bypass bypass 1 24 12
8 114 1 342 1 342 171
8 108 1 324 1 324 162
8 102 1 306 1 306 153
8 96 1 288 1 288 144
12 133 1 266 1 266 133
12 100 1 200 1 200 100
15 100 1 160 1 160 80
(/1 fixed) (MHz) (MHz)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 71
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
www.ti.com
3.5.3.2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-216 (36 MHz reference)
3.5.3.2.1 DM355-216 PLL1 (36 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-216 PLL1 with 36 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-8.
Table 3-8. PLL1 Supported Clocking Configurations DM355-216 (36 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL1 ARM / Peripherals VENC VPSS
(/8 fixed) (m programmable) (/2 or /1 (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 PLLDIV2 SYSCLK2 PLLDIV3 SYSCLK3 PLLDIV4 SYSCLK4
bypass bypass bypass bypass 2 18 4 9 10 3.6 4 9
8 96 1 432 2 216 4 108 16 27 4 108
8 180 2 405 2 202.5 4 101.25 15 27 4 101.25
8 168 2 378 2 189 4 94.5 14 27 4 94.5
8 156 2 351 2 175.5 4 87.75 13 27 4 87.75
8 144 2 324 2 162 4 81 12 27 4 81
8 132 2 297 2 148.5 4 74.25 11 27 4 74.25
8 120 2 270 2 135 4 67.5 10 27 2 135
8 108 2 243 2 121.5 4 60.75 9 27 2 121.5
8 96 2 216 2 108 4 54 8 27 2 108
programmable) (/2 fixed) (MHz) (/4 fixed) (MHz) (/n (MHz) (/4 or /2 (MHz)
VCO MPEG4 and JPEG
Coprocessor
programmable) programmable)
3.5.3.2.2 DM355-216 PLL2 (36 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-216 PLL2 with 36 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-9.
Table 3-9. PLL2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-216 (36 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL2 VCO DDR PHY DDR Clock
(/n programmable) (m programmable) (/1 fixed) (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 DDR_CLK
bypass bypass bypass bypass 1 36 18
12 114 1 342 1 342 171
12 108 1 324 1 324 162
12 102 1 306 1 306 153
12 96 1 288 1 288 144
18 133 1 266 1 266 133
27 150 1 200 1 200 100
27 120 1 160 1 160 80
(/1 fixed) (MHz) (MHz)
72 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
3.5.4 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-270
This section describes the only supported device clocking configurations for DM355-270. The DM355
supports either 24 MHz (typical) or 36 MHz reference clock (crystal or external oscillator input).
Configurations are shown for both cases.
Note : DM355-270 devices support only commercial temperature ranges.
3.5.4.1 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-270 (24 MHz reference)
3.5.4.1.1 DM355-270 PLL1 (24 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-270 PLL1 with 24 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-10.
Table 3-10. PLL1 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-270 (24 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL1 ARM / Peripherals VENC VPSS
(/8 fixed) (m programmable) (/2 or /1 (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 PLLDIV2 SYSCLK2 PLLDIV3 SYSCLK3 PLLDIV4 SYSCLK4
bypass bypass bypass bypass 2 12 4 6 10 2.4 4 6
8 180 1 540 2 270 4 135 20 27 4 135
8 171 1 513 2 256.5 4 128.25 19 27 4 128.25
8 162 1 486 2 243 4 121.5 18 27 4 121.5
8 153 1 459 2 229.5 4 114.75 17 27 4 114.75
8 144 1 432 2 216 4 108 16 27 4 108
8 135 1 405 2 202.5 4 101.25 15 27 4 101.25
8 126 1 378 2 189 4 94.5 14 27 4 94.5
8 117 1 351 2 175.5 4 87.75 13 27 4 87.75
8 108 1 324 2 162 4 81 12 27 4 81
8 99 1 297 2 148.5 4 74.25 11 27 4 74.25
8 180 2 270 2 135 4 67.5 10 27 2 135
8 162 2 243 2 121.5 4 60.75 9 27 2 121.5
8 144 2 216 2 108 4 54 8 27 2 108
8 126 2 189 2 94.5 4 47.25 7 27 2 94.5
8 108 2 162 2 81 4 40.5 6 27 2 81
programmable) (/2 fixed) (MHz) (/4 fixed) (MHz) (/n programmable) (MHz) (/4 or /2 (MHz)
VCO MPEG4 and JPEG
Coprocessor
programmable)
3.5.4.1.2 DM355-270 PLL2 (24 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-270 PLL2 with 24 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-11.
Table 3-11. PLL2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-270 (24 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL2 VCO DDR PHY DDR Clock
(/n programmable) (m programmable) (/1 fixed) (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 DDR_CLK
bypass bypass bypass bypass 1 24 12
8 144 1 432 1 432 216
8 138 1 414 1 414 207
8 132 1 396 1 396 198
8 126 1 378 1 378 189
8 120 1 360 1 360 180
8 114 1 342 1 342 171
8 108 1 324 1 324 162
8 102 1 306 1 306 153
8 96 1 288 1 288 144
12 133 1 266 1 266 133
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 73
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
(/1 fixed) (MHz) (MHz)

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 3-11. PLL2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-270 (24 MHz reference) (continued)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL2 VCO DDR PHY DDR Clock
12 100 1 200 1 200 100
15 100 1 160 1 160 80
3.5.4.1.3 DM355-27J PLL2 (24 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-27J PLL2 with 24 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-12.
Table 3-12. PLL2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-27J (24 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL2 VCO DDR PHY DDR Clock
(/n programmable) (m programmable) (/1 fixed) (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 DDR_CLK
bypass bypass bypass bypass 1 24 12
8 132 1 396 1 396 198
8 126 1 378 1 378 189
8 120 1 360 1 360 180
8 114 1 342 1 342 171
8 108 1 324 1 324 162
8 102 1 306 1 306 153
8 96 1 288 1 288 144
12 133 1 266 1 266 133
12 100 1 200 1 200 100
15 100 1 160 1 160 80
(/1 fixed) (MHz) (MHz)
www.ti.com
3.5.4.2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-270 (36 MHz reference)
3.5.4.2.1 DM355-270 PLL1 (36 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-270 PLL1 with 36 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-13.
Table 3-13. PLL1 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-270 (36 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL1 ARM / Peripherals VENC VPSS
(/8 fixed) (m programmable) (/2 or /1 (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 PLLDIV2 SYSCLK2 PLLDIV3 SYSCLK3 PLLDIV4 SYSCLK4
bypass bypass bypass bypass 2 18 4 9 10 3.6 4 18
8 120 1 540 2 270 4 135 20 27 4 135
8 114 1 513 2 256.5 4 128.25 19 27 4 128.25
8 108 1 486 2 243 4 121.5 18 27 4 121.5
8 102 1 459 2 229.5 4 114.75 17 27 4 114.75
8 96 2 432 2 216 4 108 16 27 4 108
8 180 2 405 2 202.5 4 101.25 15 27 2 202.5
8 168 2 378 2 189 4 94.5 14 27 2 189
8 156 2 351 2 175.5 4 87.75 13 27 2 175.5
8 144 2 324 2 162 4 81 12 27 2 162
8 132 2 297 2 148.5 4 74.25 11 27 2 148.5
8 120 2 270 2 135 4 67.5 10 27 2 135
8 108 2 243 2 121.5 4 60.75 9 27 2 121.5
8 96 2 216 2 108 4 54 8 27 2 108
programmab (/2 fixed) (MHz) (/4 fixed) (MHz) (/n programmable) (MHz) (/4 or /2 (MHz)
VCO MPEG4 and JPEG
Coprocessor
programmable)
74 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
3.5.4.2.2 DM355-270 PLL2 (36 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-270 PLL2 with 36 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-14.
Table 3-14. PLL2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-270 (36 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL2 VCO DDR PHY DDR Clock
(/n programmable) (m programmable) (/1 fixed) (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 DDR_CLK
bypass bypass bypass bypass 1 36 18
12 144 1 432 1 432 216
12 138 1 414 1 414 207
12 132 1 396 1 396 198
12 126 1 378 1 378 189
12 120 1 360 1 360 180
12 114 1 342 1 342 171
12 108 1 324 1 324 162
12 102 1 306 1 306 153
12 96 1 288 1 288 144
18 133 1 266 1 266 133
27 150 1 200 1 200 100
27 120 1 160 1 160 80
(/1 fixed) (MHz) (MHz)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 75
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
3.5.4.2.3 DM355-27J PLL2 (36 MHz reference)
All supported clocking configurations for DM355-27J PLL2 with 36 MHz reference clock are shown in
Table 3-15.
Table 3-15. PLL2 Supported Clocking Configurations for DM355-27J (36 MHz reference)
PREDIV PLLM POSTDIV PLL2 VCO DDR PHY DDR Clock
(/n programmable) (m programmable) (/1 fixed) (MHz) PLLDIV1 SYSCLK1 DDR_CLK
bypass bypass bypass bypass 1 36 18
12 132 1 396 1 396 198
12 126 1 378 1 378 189
12 120 1 360 1 360 180
12 114 1 342 1 342 171
12 108 1 324 1 324 162
12 102 1 306 1 306 153
12 96 1 288 1 288 144
18 133 1 266 1 266 133
27 150 1 200 1 200 100
27 120 1 160 1 160 80
(/1 fixed) (MHz) (MHz)
www.ti.com
76 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
3.5.5 Peripheral Clocking Considerations
3.5.5.1 Video Processing Back End Clocking
The Video Processing Back End (VPBE) is a sub-module of the Video Processing Subsystem (VPSS).
The VPBE is designed to interface with a variety of LCDs and an internal DAC module. There are two
asynchronous clock domains in the VPBE: an internal clock domain and an external clock domain. The
internal clock domain is driven by the VPSS clock (PLL1 SYSCLK4). The external clock domain is
configurable; you can select one of five source:
• 24 MHz crystal input at MXI1
• 27 MHz crystal input at MXI2 (optional feature, not typically used)
• PLL1 SYSCLK3
• EXTCLK pin (external VPBE clock input pin)
• PCLK pin (VPFE pixel clock input pin)
See the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip Video Processing Back End (VPBE) Reference
Guide (literature number SPRUF72) for complete information on VPBE clocking.
3.5.5.2 USB Clocking
The USB Controller is driven by two clocks: an output clock of PLL1 (SYSCLK2) and an output clock of
the USB PHY.
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
NOTE
For proper USB 2.0 function, SYSCLK2 must be greater than 60 MHz.
The USB PHY takes an input clock that is configurable by the USB PHY clock source bits (PHYCLKSRC)
in the USB PHY control register (USB_PHY_CTL) in the System Control Module. When a 24 MHz crystal
is used at MXI1/MXO1, set PHYCLKSRC to 0. This will present a 24 MHz clock to the USB PHY. When a
36 MHz crystal is used at MXI1/MXO1, set PHYCLKSRC to 1. This will present a 12 MHz clock (36 MHz
divided internally by three) to the USB PHY. The USB PHY is capable of accepting only 24 MHz and 12
MHz; thus you must use either a 24 MHz or 36 MHz crystal at MXI1/MXO1. See the TMS320DM355
DMSoC Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controller User's Guide (literature number SPRUED2) for more
information. See the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem Reference
Guide (literature number SPRUFB3) for more information on the System Control Module.
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 77
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
3.6 PLL Controller (PLLC)
This section describes the PLL Controllers for PLL1 and PLL2. See the TMS320DM35x Digital Media
System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem Reference Guide (literature number SPRUFB3) for more
information on the PLL controllers.
3.6.1 PLL Controller Module
The DM355 has two PLL controllers that provide clocks to different components of the chip. PLL controller
1 (PLLC1) provides clocks to most of the components of the chip. PLL controller 2 (PLLC2) provides
clocks to the DDR PHY.
As a module, the PLL controller provides the following:
• Glitch-free transitions (on changing PLL settings)
• Domain clocks alignment
• Clock gating
• PLL bypass
• PLL power down
The various clock outputs given by the PLL controller are as follows:
• Domain clocks: SYSCLKn
• Bypass domain clock: SYSCLKBP
• Auxiliary clock from reference clock: AUXCLK
www.ti.com
Various dividers that can be used are as follows:
• Pre-PLL divider: PREDIV
• Post-PLL divider: POSTDIV
• SYSCLK divider: PLLDIV1, …, PLLDIVn
• SYSCLKBP divider: BPDIV
Multipliers supported are as follows:
• PLL multiplier control: PLLM
78 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
3.6.2 PLLC1
PLLC1 provides most of the DM355 clocks. Software controls PLLC1 operation through the PLLC1
registers. The following list, Table 3-16, and Figure 3-3 describe the customizations of PLLC1 in the
DM355.
• Provides primary DM355 system clock
• Software configurable
• Accepts clock input or internal oscillator input
• PLL pre-divider value is fixed to (/8)
• PLL multiplier value is programmable
• PLL post-divider
• Only SYSCLK[4:1] are used
• SYSCLK1 divider value is fixed to (/2)
• SYSCLK2 divider value is fixed to (/4)
• SYSCLK3 divider value is programmable
• SYSCLK4 divider value is programmable to (/4) or (/2)
• SYSCLKBP divider value is fixed to (/3)
• SYSCLK1 is routed to the ARM Subsystem
• SYSCLK2 is routed to peripherals
• SYSCLK3 is routed to the VPBE module
• SYSCLK4 is routed to the VPSS module
• AUXCLK is routed to peripherals with fixed clock domain and also to the output pin CLKOUT1
• SYSCLKBP is routed to the output pin CLKOUT2
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 3-16. PLLC1 Output Clocks
Output Clock Used By PLLDIV Notes
SYSCLK1 ARM Subsystem / MPEG4 and JPEG Coprocessor /2 Fixed divider
SYSCLK2 Peripherals /4 Fixed divider
SYSCLK3 VPBE (VENC module) /n Programmable divider (used to get 27
SYSCLK4 VPSS /4 or /2 Programmable divider
AUXCLK Peripherals, CLKOUT1 none No divider
SYSCLKBP CLKOUT2 /3 Fixed divider
Divider
MHz for VENC)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 79
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

PLLDIV1(/2)
PLLDIV2(/4)
PLLDIV3(/3)
SYSCLK1
(ARMandMPEG4/
JPEGCoprocessor)
SYSCLK2
(Peripherals)
SYSCLK3
(VPBE)
1
0
PLL
0
1
CLKMODE
CLKIN
OSCIN
PLLEN
AUXCLK
(Peripherals,
CLKOUT1)
SYSCLKBP
(CLKOUT2)
Pre-DIV
(/8)
Post-DIV
(/2or/1)
PLLM
(Programmable)
BPDIV(/3)
PLLDIV4
(/4or/2)
SYSCLK4
(VPSS)
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Figure 3-3. PLLC1 Configuration in DM355
www.ti.com
80 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

PLLDIV1(/1)
1
0
PLL
0
1
CLKMODE
CLKIN
OSCIN
PLLEN
SYSCLK1
(DDRPHY)
SYSCLKBP
(CLKOUT3)
BPDIV(/8)
PLLM
(Programmable)
Pre-DIV
(Programmable)
Post-DIV
(/1)
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
3.6.3 PLLC2
PLLC2 provides the DDR PHY clock and CLKOUT3. Software controls PLLC2 operation through the
PLLC2 registers. The following list, Table 3-17, and Figure 3-4 describe the customizations of PLLC2 in
the DM355.
• Provides DDR PHY clock and CLKOUT3
• Software configurable
• Accepts clock input or internal oscillator input (same input as PLLC1)
• PLL pre-divider value is programmable
• PLL multiplier value is programmable
• PLL post-divider value is fixed to (/1)
• Only SYSCLK[1] is used
• SYSCLK1 divider value is fixed to (/1)
• SYSCLKBP divider value is fixed to (/8)
• SYSCLK1 is routed to the DDR PHY
• SYSCLKBP is routed to the output pin CLKOUT3
• AUXCLK is not used.
Table 3-17. PLLC2 Output Clocks
Output Clock Used by PLLDIV Divider Notes
SYSCLK1 DDR PHY /1 Fixed divider
SYSCLKBP CLKOUT3 /8 Fixed divider
Figure 3-4. PLLC2 Configuration in DM355
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 81
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

arm_clock
arm_mreset
arm_power
AINTC
ARM
module_power
module_mreset
MODx
module_clock
Alwayson
domain
Interrupt
PSC
clks
PLLC
Emulation
RESET
V
DD
DMSoC
TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
3.7 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC)
In the DM355 system, the Power and Sleep Controller (PSC) is responsible for managing transitions of
system power on/off, clock on/off, and reset. A block diagram of the PSC is shown in Figure 3-5. Many of
the operations of the PSC are transparent to software, such as power-on-reset operations. However, the
PSC provides you with an interface to control several important clock and reset operations.
The PSC includes the following features:
• Manages chip power-on/off, clock on/off, and resets
• Provides a software interface to:
– Control module clock ON/OFF
– Control module resets
• Supports IcePick emulation features: power, clock, and reset
For more information on the PSC, see the TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM
Subsystem Reference Guide (literature number SPRUFB3) .
www.ti.com
Figure 3-5. DM355 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC)
3.8 System Control Module
The DM355’s system control module is a system-level module containing status and top-level control logic
required by the device. The system control module consists of a miscellaneous set of status and control
registers, accessible by the ARM and supporting all of the following system features and operations:
• Device identification
• Device configuration
– Pin multiplexing control
– Device boot configuration status
• ARM interrupt and EDMA event multiplexing control
• Special peripheral status and control
– Timer64+
– USB PHY control
– VPSS clock and video DAC control and status
– DDR VTP control
– Clockout circuitry
– GIO de-bounce control
82 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
• Power management
– Deep sleep mode
• Bandwidth Management
– Bus master DMA priority control
For more information on the System Control Module refer to TMS320DM35x Digital Media
System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem Reference Guide (literature number SPRUFB3) .
3.9 Pin Multiplexing
The DM355 makes extensive use of pin multiplexing to accommodate the large number of peripheral
functions in the smallest possible package. In order to accomplish this, pin multiplexing is controlled using
a combination of hardware configuration (at device reset) and software control. No attempt is made by the
DM355 hardware to ensure that the proper pin muxing has been selected for the peripherals or interface
mode being used, thus proper pin muxing configuration is the responsibility of the board and software
designers. An overview of the pin multiplexing is shown in Table 3-18.
Table 3-18. Peripheral Pin Mux Overview
Peripheral Muxed With Primary Function Secondary Function Tertiary Function
VPFE (video in) GPIO and SPI2 VPFE (video in) SPI2 GPIO
VPBE (video out) GPIO, PWM, and RTO VPBE (video out) PWM and RTO GPIO
AEMIF GPIO AEMIF GPIO none
ASP0 GPIO ASP0 GPIO none
MMC/SD1 GPIO and UART2 MMC/SD1 GPIO UART2
CLKOUT GPIO CLKOUT GPIO none
I2C GPIO I2C GPIO none
UART1 GPIO UART1 GPIO none
SPI1 GPIO SPI1 GPIO none
SPI0 GPIO SPI0 GPIO none
3.9.1 Hardware Controlled Pin Multiplexing
Use the Asynchronous EMIF configuration pins (AECFG[3:0]) for hardware pin mux control. AECFG[3:0]
control the partitioning of the AEMIF addresses and GPIOs at reset, which allows you to properly
configure the number of AEMIF address pins required by the boot device while unused addresses pins are
available as GPIOs. These settings may be changed by software after reset by programming the PinMux2
register The PinMux2 register is in the System Control Module. As shown in Table 3-19, the number of
address bits enabled on the AEMIF is selectable from 0 to 16. Pins that are not assigned to another
peripheral and not enabled as address signals become GPIOs (except EM_A[2:1]). The enabled address
signals are always contiguous from EM_BA[1] upwards; bits cannot be skipped. The exception to this are
EM_A[2:1]. These signals (can be used to) represent the ALE and CLE signals for the NAND Flash mode
of the AEMIF and are always enabled. Note that EM_A[0] does not represent the lowest AEMIF address
bit. DM355 supports only 16-bit and 8-bit data widths for the AEMIF. In 16-bit mode, EM_BA[1] represents
the LS address bit (the half-word address) and EM_BA[0] represents the MS address bit (A[14]). In 8-bit
mode, EM_BA[1:0] represent the 2 LS address bits. Note that additional selections are available by
programming the PinMux2 register in software after boot. Note that AECFG selection of ‘0010’ selects
OneNAND interface. The AEMIF needs to operate in the half-rate mode (full_rate = 0) to meet frequency
requirements. Software should not change the PINMUX2 register setting to affect the AEMIF rate
operation. A soft reset of the AEMIF should be performed any time a rate change is made.
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 83
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 3-19. AECFG (Async EMIF Configuration) Pin Mux Coding
1101(NAND) 1100 1010 1000 (8-bit SRAM) 0010 (16-bit SRAM, 0000
OneNAND)
GPIO[54] GPIO[54] EM_A[14] EM_BA[0] EM_A[14] EM_BA[0]
GPIO[55] EM_BA[1] EM_BA[1] EM_BA[1] EM_BA[1] EM_BA[1]
GPIO[56] EM_A[0] EM_A[0] EM_A[0] EM_A[0] EM_A[0]
EM_A[1] EM_A[1] EM_A[1] EM_A[1] EM_A[1] EM_A[1]
EM_A[2] EM_A[2] EM_A[2] EM_A[2] EM_A[2] EM_A[2]
GPIO[57] EM_A[3] EM_A[3] EM_A[3] EM_A[3] EM_A[3]
GPIO[58] EM_A[4] EM_A[4] EM_A[4] EM_A[4] EM_A[4]
GPIO[59] EM_A[5] EM_A[5] EM_A[5] EM_A[5] EM_A[5]
GPIO[60] EM_A[6] EM_A[6] EM_A[6] EM_A[6] EM_A[6]
GPIO[61] EM_A[7] EM_A[7] EM_A[7] EM_A[7] EM_A[7]
GPIO[62] EM_A[8] EM_A[8] EM_A[8] EM_A[8] EM_A[8]
GPIO[63] EM_A[9] EM_A[9] EM_A[9] EM_A[9] EM_A[9]
GPIO[64] EM_A[10] EM_A[10] EM_A[10] EM_A[10] EM_A[10]
GPIO[65] EM_A[11] EM_A[11] EM_A[11] EM_A[11] EM_A[11]
GPIO[66] EM_A[12] EM_A[12] EM_A[12] EM_A[12] EM_A[12]
GPIO[67] EM_A[13] EM_A[13] EM_A[13] EM_A[13] EM_A[13]
GPIO[46] GPIO[46] GPIO[46] GPIO[46] EM_D[8] EM_D[8]
GPIO[47] GPIO[47] GPIO[47] GPIO[47] EM_D[9] EM_D[9]
GPIO[48] GPIO[48] GPIO[48] GPIO[48] EM_D[10] EM_D[10]
GPIO[49] GPIO[49] GPIO[49] GPIO[49] EM_D[11] EM_D[11]
GPIO[50] GPIO[50] GPIO[50] GPIO[50] EM_D[12] EM_D[12]
GPIO[51] GPIO[51] GPIO[51] GPIO[51] EM_D[13] EM_D[13]
GPIO[52] GPIO[52] GPIO[52] GPIO[52] EM_D[14] EM_D[14]
GPIO[53] GPIO[53] GPIO[53] GPIO[53] EM_D[15] EM_D[15]
www.ti.com
3.9.2 Software Controlled Pin Multiplexing
All pin multiplexing options are configurable by software via pin mux registers that reside in the System
Control Module. The PinMux0 Register controls the Video In muxing, PinMux1 register controls Video Out
signals, PinMux2 register controls AEMIF signals, PinMux3 registers control the multiplexing of the GIO
signals, the PinMux4 register controls the SPI and MMC/SD0 signals. Refer to TMS320DM35x Digital
Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem Reference Guide (literature numberSPRUFB3) for
complete descriptions of the pin mux registers.
3.10 Device Reset
There are five types of reset in DM355. The types of reset differ by how they are initiated and/or by their
effect on the chip. Each type is briefly described in Table 3-20 and further described in TMS320DM35x
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem Reference Guide (literature number SPRUFB3).
Table 3-20. Reset Types
Type Initiator Effect
POR (Power-On-Reset) RESET pin low and TRST low Total reset of the chip (cold reset). Resets all modules
Warm Reset RESET pin low and TRST high (initiated by ARM Resets all modules including memory, except ARM
emulator). emulation.
Max Reset ARM emulator or Watchdog Timer (WDT). Same effect as warm reset.
including memory and emulation.
84 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 3-20. Reset Types (continued)
Type Initiator Effect
System Reset ARM emulator Resets all modules except memory and ARM
Module Reset ARM software Resets a specific module. Allows the ARM to
emulation. It is a soft reset that maintains memory
contents and does not affect or reset clocks or power
states.
independently reset any module. Module reset is
intended as a debug tool not as a tool to use in
production.
3.11 Default Device Configurations
After POR, warm reset, and max reset, the chip is in its default configuration. This section highlights the
default configurations associated with PLLs, clocks, ARM boot mode, and AEMIF.
NOTE
Default configuration is the configuration immediately after POR, warm reset, and max reset
and just before the boot process begins. The boot ROM updates the configuration. See
Section 3.12 for more information on the boot process.
3.11.1 Device Configuration Pins
The device configuration pins are described in Table 3-21. The device configuration pins are latched at
reset and allow you to configure all of the following options at reset:
• ARM Boot Mode
• Asynchronous EMIF pin configuration
These pins are described further in the following sections.
NOTE
The device configuration pins are multiplexed with AEMIF pins. After the device configuration
pins are sampled at reset, they automatically change to function as AEMIF pins. Pin
multiplexing is described in Section 3.8.
Table 3-21. Device Configuration
Default Setting (by
Device Sampled pull-up/
Configuration Input Function Pin pull-down) Device Configuration Affected
BTSEL[1:0] Selects ARM boot mode EM_A[13:12] 00 If any ROM boot mode is selected, GIO61
00 = Boot from ROM (NAND (NAND) is used to indicated boot status.
with SPI EEPROM boot If NAND boot is selected, CE0 is used for
option) NAND and SPI0 is used for SPI boot
01 = Boot from AEMIF option. Use AECFG[3:0] to configure
10 = Boot from ROM AEMIF pins for NAND.
(MMC/SD) If AEMIF boot is selected, CE0 is used for
11 = Boot from ROM (UART) AEMIF device (OneNAND, ROM). Use
AECFG[3:0] Selects AEMIF pin EM_A[11:8] 1101 Selects the AEMIF pin configuration. Refer
configuration (NAND) to pin-muxing information in Section 3.9.1.
internal
AECFG[3:0] to configure AEMIF pins for
NAND.
If MMC/SD boot is selected, MMC/SD0 is
used.
Note that AECFG[3:0] affects both AEMIF
(BTSEL[1:0]=01) and NAND
(BTSEL[1:0]=00) boot modes.
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 85
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
3.11.2 PLL Configuration
After POR, warm reset, and max reset, the PLLs and clocks are set to their default configurations. The
PLLs are in bypass mode and disabled by default. This means that the input reference clock at MXI1
(typically 24 MHz) drives the chip after reset. For more information on device clocking, see Section 3.5
and Section 3.6. The default state of the PLLs is reflected in the default state of the register bits in the
PLLC registers. Refer to TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem
Reference Guide (literature number SPRUFB3) for PLLC register descriptions.
3.11.3 Power Domain and Module State Configuration
Only a subset of modules are enabled after reset by default. Table 3-22 shows which modules are
enabled after reset. Table 3-22 as shows that the following modules are enabled depending on the
sampled state of the device configuration pins: EDMA (CC, TC0 and TC1), AEMIF, MMC/SD0, UART0,
and Timer0. For example, UART0 is enabled after reset when the device configuration pins (BTSEL[1:0] =
11 - Enable UART) select UART boot mode. For more information on module configuration refer to
TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem Reference Guide (literature
number SPRUFB3).
www.ti.com
86 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 3-22. Module Configuration
Default States
Module Module Name Power Domain Power Domain State Module State
Number
0 VPSS Master AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
1 VPSS Slave AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
2 EDMA (CC) AlwaysOn ON BTSEL[1:0] = 00 – Enable (NAND, SPI)
BTSEL[1:0] = 01 – Enable (OneNAND)
3 EDMA (TC0) AlwaysOn ON BTSEL[1:0] = 10 – SyncRst (MMC/SD)
4 EDMA (TC1) AlwaysOn ON
5 Timer3 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
6 SPI1 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
7 MMC/SD1 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
8 ASP1 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
9 USB AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
10 PWM3 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
11 SPI2 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
12 RTO AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
13 DDR EMIF AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
14 AEMIF AlwaysOn ON BTSEL[1:0] = 00 – Enable (NAND, SPI)
15 MMC/SD0 AlwaysOn ON BTSEL[1:0] = 00 – SyncRst (NAND, SPI)
16 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
17 ASP AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
18 I2C AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
19 UART0 AlwaysOn ON BTSEL[1:0] = 00 – SyncRst (NAND, SPI)
20 UART1 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
21 UART2 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
22 SPI0 AlwaysOn ON BTSEL[1:0] = 00 – Enable (NAND, SPI)
23 PWM0 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
24 PWM1 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
25 PWM2 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
26 GPIO AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
27 TIMER0 AlwaysOn ON BTSEL[1:0] = 00 – Enable (NAND, SPI)
28 TIMER1 AlwaysOn ON SyncRst
BTSEL[1:0] = 11 – Enable (UART)
BTSEL[1:0] = 01 – Enable (OneNAND)
BTSEL[1:0] = 10 – SyncRst (MMC/SD)
BTSEL[1:0] = 11 – Enable (UART)
BTSEL[1:0] = 01 – SyncRst (OneNAND)
BTSEL[1:0] = 10 – Enable (MMC/SD)
BTSEL[1:0] = 11 – SyncRst (UART)
BTSEL[1:0] = 01 – SyncRst (OneNAND)
BTSEL[1:0] = 10 – SyncRst (MMC/SD)
BTSEL[1:0] = 11 – Enable (UART)
BTSEL[1:0] = 01 – SyncRst (OneNAND)
BTSEL[1:0] = 10 – Enable (MMC/SD)
BTSEL[1:0] = 11 – Enable (UART)
BTSEL[1:0] = 01 – Enable (OneNAND)
BTSEL[1:0] = 10 – Enable (MMC/SD)
BTSEL[1:0] = 11 – Enable (UART)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 87
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 3-22. Module Configuration (continued)
Default States
29 TIMER2 AlwaysOn ON Enable
30 System Module AlwaysOn ON Enable
31 ARM AlwaysOn ON Enable
32 BUS AlwaysOn ON Enable
33 BUS AlwaysOn ON Enable
34 BUS AlwaysOn ON Enable
35 BUS AlwaysOn ON Enable
36 BUS AlwaysOn ON Enable
37 BUS AlwaysOn ON Enable
38 BUS AlwaysOn ON Enable
39 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
40 VPSS DAC Always On ON SyncRst
3.11.4 ARM Boot Mode Configuration
The input pins BTSEL[1:0] determine whether the ARM will boot from its ROM or from the Asynchronous
EMIF (AEMIF). When ROM boot is selected (BTSEL[1:0] = 00, 10, or 11), a jump to the start of internal
ROM (address 0x0000: 8000) is forced into the first fetched instruction word. The embedded ROM boot
loader code (RBL) then performs certain configuration steps, reads the BOOTCFG register to determine
the desired boot method, and branches to the appropriate boot routine (i.e., a NAND/SPI, MMC/SD, or
UART loader routine).
www.ti.com
If AEMIF boot is selected (BTSEL[1:0] = 01), a jump to the start of AEMIF (address 0x0200: 0000) is
forced into the first fetched instruction word. The ARM then continues executing from external
asynchronous memory using the default AEMIF timings until modified by software.
For AEMIF boot, the OneNAND must be connected to the first AEMIF chip select space
(EM_CE0). Also, the AEMIF does not support direct execution from NAND Flash.
Boot modes are further described in Section 3.12.
3.11.5 AEMIF Configuration
3.11.5.1 AEMIF Pin Configuration
The input pins AECFG[3:0] determine the AEMIF configuration immediately after reset. Use AECFG[3:0]
to properly configure the pins of the AEMIF. Refer to the section on pin multiplexing in Section 3.9.
Also, see the Asynchronous External Memory Interface (AEMIF) Peripheral Reference Guide (literature
number SPRUED1) for more information on the AEMIF.
3.11.5.2 AEMIF Timing Configuration
When AEMIF is enabled, the wait state registers are reset to the slowest possible configuration, which is
88 cycles per access (16 cycles of setup, 64 cycles of strobe, and 8 cycles of hold). Thus, with a 24 MHz
clock at MXI1, the AEMIF is configured to run at 6 MHz/88 which equals approximately 68 kHz by default.
See the Asynchronous External Memory Interface (AEMIF) Peripheral Reference Guide (literature number
SPRUED1) for more information on the AEMIF.
NOTE
88 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
3.12 Device Boot Modes
The DM355 ARM can boot from either Async EMIF (AEMIF/OneNand) or from ARM ROM, as determined
by the setting of the device configuration pins BTSEL[1:0]. The BTSEL[1:0] pins can define the ROM boot
mode further as well.
The boot selection pins (BTSEL[1:0]) determine the ARM boot process. After reset (POR, warm reset, or
max reset), ARM program execution begins in ARM ROM at 0x0000: 8000, except when BTSEL[1:0] = 01,
indicating AEMIF (AEMIF/OneNand) boot. See Section 3.11.1 for information on the boot selection pins.
3.12.1 Boot Modes Overview
DM355’s ARM ROM boot loader (RBL) executes when the BTSEL[1:0] pins indicate a condition other than
the normal ARM EMIF boot.
• If BTSEL[1:0] = 01 - Asynchronous EMIF (AEMIF) boot. This mode is handled by hardware control and
does not involve the ROM. In the case of OneNAND, the user is responsible for putting any necessary
boot code in the OneNAND's boot page. This code shall configure the AEMIF module for the
OneNAND device. After the AEMIF module is configured, booting will continue immediately after the
OneNAND’s boot page with the AEMIF module managing pages thereafter.
• The RBL supports 3 distinct boot modes:
– BTSEL[1:0] = 00 - ARM NAND/SPI Boot
– BTSEL[1:0] = 10 - ARM MMC/SD Boot
– BTSEL[1:0] = 11 - ARM UART Boot
• In NAND mode if SPI boot fails, then NAND mode is tried. If NAND boot fails, then MMC/SD mode is
tried.
• If MMC/SD boot fails, then MMC/SD boot is tried again.
• If UART boot fails, then UART boot is tried again.
• RBL uses GIO61 to indicate boot status (can use to blink LED):
– After reset, GIO61 is initially driven low (e.g LED off)
– If NAND boot fails, then GIO61 shall toggle at 4Hz while MMC/SD boot is tried.
– If MMC/SD boot fails, then GIO61 shall toggle at 4Hz while MMC/SD boot is retried.
– If UART boot fails, then GIO61 shall toggle at 2Hz while UART boot is retried.
– When boot is successful, just before program control is given to UBL, GIO61 is driven high (e.g.
LED on)
– DM355 Timer0 shall be used to accurately toggle GIO61 at 4Hz and 2Hz
• ARM ROM Boot - SPI boot in NAND Mode
– No support for a full firmware boot. Instead, copies a second stage User Boot Loader (UBL) from
SPI to ARM Internal RAM (AIM) and transfers control to the user software.
– Support for 16 and 24 bit SPI EEPROMs
– Support for up to 30KB UBL (32KB - ~2KB for RBL stack)
– RBL will copy UBL to ARM Internal RAM (AIM) via SPI interface from a SPI peripheral like SPI
EEPROM. RBL will then transfer control to the UBL.
• ARM ROM Boot - NAND Mode (See Section 3.12.2 for a full explanation of the differences between
Standard Mode and Compatibility Mode.):
– No support for a full firmware boot. Instead, copies a second stage User Boot Loader (UBL) from
NAND flash to ARM internal RAM (AIM) and transfers control to the user-defined UBL.
– Support for NAND with page sizes up to 8192 bytes in Standard Mode and 2048 bytes in
Compatibility Mode
Note: At the time of documentation for this device, 8192-byte devices were not available for testing.
The code does contain support for these devices; however, it has not yet been tested.
– Support for magic number error detection and retry (up to 24 times) when loading UBL
– Support for up to 30KB UBL (32KB IRAM - ~2KB for RBL stack)
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 89
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
– Optional, user-selectable, support for use of DMA and I-cache during RBL execution (i.e.,while
loading UBL)
– Supports booting from 8-bit NAND devices (16-bit NAND devices are not supported)
– Uses/Requires 4-bit HW ECC (NAND devices with ECC requirements ≤ 4 bits per 512 bytes are
supported)
– Supports NAND flash that requires chip select to stay low during the tR read time
Notes:
– See Section 3.12.2 for a full explanation of the differences between Standard Mode and
Compatibility Mode.
– The GIO000 pin must be held high during NAND boot for the boot process to fuction properly.
• ARM ROM Boot - MMC/SD Mode
– No support for a full firmware boot. Instead, copies a second stage User Boot Loader (UBL) from
MMC/SD to ARM Internal RAM (AIM) and transfers control to the user software.
– Support for MMC/SD Native protocol (MMC/SD SPI protocol is not supported)
– Support for descriptor error detection and retry (up to 24 times) when loading UBL
– Support for up to 30KB UBL (32KB - ~2KB for RBL stack)
• ARM ROM Boot - UART mode
– No support for a full firmware boot. Instead, loads a second stage User Boot Loader (UBL) via
UART to ARM internal RAM (AIM) and transfers control to the user software.
– Support for up to 30KB UBL (32KB - ~2KB for RBL stack)
www.ti.com
The general boot sequence is shown in Figure 3-6. For more information, refer to TMS320DM35x Digital
Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem Reference Guide (literature number SPRUFB3).
90 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

Boot
mode
?
Boot
mode
?
Internal ROM
Invoke loaded
Program
Invoke
OneNAND
Yes
Boot from
UART
Boot OK ?
No
Boot from
NAND flash
Boot OK ?
No
Yes
Boot from
MMC/SD
Boot OK ?
Yes
No
Reset
Boot from
SPI flash
Boot OK ?
No
Yes
TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Figure 3-6. Boot Mode Functional Block Diagram
3.12.2 RBL NAND Boot Process
The RBL NAND boot process is described as follows:
• Upon NAND boot, if a SPI EEPROM is present, RBL reads first 32 bytes and look for magic pattern at
• If SPI boot, then NAND boot is bypassed.
• Otherwise NAND boot is continued. If NAND parameters are found in the SPI EEPROM (as indicated
• Else the following steps are used to determine NAND parameters:
offset 0x8. This magic number indicates if this is a SPI boot or beginning of NAND parameters.
by magic number), these parameters are used.
– If the device is ONFI, read the parameters page. Else command is sent to the NAND device
requesting four bytes (called the NAND READ_ID) which contain the manufacturer, device and 4th
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 91
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
ID.
– The RBL contains an internal table with a list of known NAND devices. Table 3-23 shows the
devices contained in the tables.
– If the device ID is not found in the table, then the RBL use the fourth byte of the NAND to decode
this to obtain the necessary parameters.
• Once a device ID is identified, the first 24 blocks of the NAND are read sequentially starting with page
0 with an offset of 512 bytes. The purpose of the read is to locate a magic number which will identify
the revision of the silicon. Table 3-24 contains magic numbers and their functions.
• If a Compatibility mode magic number is read, then the device enters compatibility mode. In
compatibility mode, NAND layout is identical to that used in previous revisions of the silicon as shown
in Table 3-25. Only 512-byte small blocks and 2048-byte big blocks are supported.
• If a Standard mode magic number is read, the NAND layout is as shown in Table 3-26: 512-bytes
small block and 2048- and 4096- big block devices are supported. 8192-block devices are also
supported. Note: At the time of production of this document revision, only 4096-block devices were
available for testing.
• Once a magic number is identified, the User Boot Loader (UBL) is loaded from the NAND, stored to
internal RAM, and executed.
Table 3-23. NAND Devices in NAND Device ID Table
DEVICE ID PAGES PER BLOCK BYTES PER PAGE BLOCK SHIFT VALUE NUMBER OF ADDRESS
0xE3 16 512+16 12 3
0xE5 16 512+16 12 3
0xE6 16 512+16 12 3
(1)
0x39
0x6B 16 512+16 13 3
0x73 32 512+16 13 3
0x33 32 512+16 13 3
0x75 32 512+16 13 3
0x35 32 512+16 13 3
0x43 32 512+16 13 4
0x45 32 512+16 13 4
0x53 32 512+16 13 4
0x55 32 512+16 13 4
0x76 32 512+16 13 4
0x36 32 512+16 13 4
0x79 32 512+16 13 4
0x71 32 512+16 13 4
0x46 32 512+16 13 4
0x56 32 512+16 13 4
0x74 32 512+16 13 4
0xF1 64 2048+64 22 4
0xA1 64 2048+64 22 4
0xAA 64 2048+64 22 5
0xDA 64 2048+64 22 5
0xAC 64 2048+64 22 5
0xDC 64 2048+64 22 5
0xB1 64 2048+64 22 5
0xC1 64 2048+64 22 5
(1) Present only on silicon revision 1.1.
16 512+16 13 3
www.ti.com
FOR ADDRESS CYCLES
92 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 3-24. UBL Signature and Special Modes for NAND Boot Mode
MODE VALUE
UBL_MAGIC_SAFE 0xA1AC ED00 Safe boot mode
UBL_MAGIC_DMA 0xA1AC ED11 DMA boot mode
UBL_MAGIC_IC 0xA1AC ED22 I Cache boot mode
UBL_MAGIC_FAST 0xA1AC ED33 Fast EMIF boot mode
UBL_MAGIC_DMA_IC 0xA1AC ED44 DMA + I Cache boot mode
UBL_MAGIC_DMA_IC_FAST 0xA1AC ED55 DMA + I Cache + Fast EMIF boot mode
UBL_MAGIC_SPI_PARAMS 0xA1AC EDAA NAND parameters from SPI EEPROM
(1) The values listed only apply when operating in compatibility mode. These values follow the form 0xA1BCEDxx when operating in
standard mode.
Example: UBL_MAGIC_SAFE VALUE = 0xA1ACED00; Safe boot mode will configure the device to run in safe boot mode and in
compatibility mode. However, when using standard mode, the value should be 0xA1BCD00.
(1)
DESCRIPTION
Table 3-25. NAND Layout (Compatibility Mode)
512 Byte Page Size 2048 Byte Page Size
512 bytes Data 512 bytes Data
16 bytes ECC Data 16 bytes ECC Data
512 bytes Data
16 bytes ECC Data
512 bytes Data
16 bytes ECC Data
512 bytes Data
16 bytes ECC Data
Table 3-26. NAND Layout (Standard Mode)
512 Byte Page Size 2048 Byte Page Size 4096 Byte Page Size
512 bytes Data 2048 bytes Data 4096 bytes Data
16 bytes ECC Data 64 bytes ECC Data 128 bytes ECC Data
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 93
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
www.ti.com
3.13 Power Management
The DM355 is designed for minimal power consumption. There are two components to power
consumption: active power and leakage power. Active power is the power consumed to perform work and
scales with clock frequency and the amount of computations being performed. Active power can be
reduced by controlling the clocks in such a way as to either operate at a clock setting just high enough to
complete the required operation in the required timeline or to run at a clock setting until the work is
complete and then drastically cut the clocks (e.g. to PLL Bypass mode) until additional work must be
performed. Leakage power is due to static current leakage and occurs regardless of the clock rate.
Leakage, or standby power, is unavoidable while power is applied and scales roughly with the operating
junction temperatures. Leakage power can only be avoided by removing power completely from a device
or subsystem. The DM355 includes several power management features which are briefly described in
Table 3-17. Refer to TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem Reference
Guide (literature number SPRUFB3) for more information on power management.
Table 3-27. Power Management Features
Power Management Features Description
Clock Management
Module clock disable Module clocks can be disabled to reduce switching power
Module clock frequency scaling Module clock frequency can be scaled to reduce switching power
PLL power-down The PLLs can be powered-down when not in use to reduce
ARM Sleep Mode
ARM Wait-for-Interrupt sleep mode Disable ARM clock to reduce active power
System Sleep Modes
Deep Sleep mode Stop all device clocks and power down internal oscillators to reduce
I/O Management
USB Phy power-down The USB Phy can be powered-down to reduce USB I/O power
DAC power-down The DAC's can be powered-down to reduce DAC power
DDR self-refresh and power down The DDR / mDDR device can be put into self-refresh and power
switching power
active power to a minimum. Registers and memory are preserved.
down states
94 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
3.14 64-Bit Crossbar Architecture
The DM355 uses a 64-bit crossbar architecture to control access between device processors, subsystems
and peripherals. It includes an EDMA Controller consisting of a DMA Transfer Controller (TC) and a DMA
Channel Controller (CC). The TC provides two DMA channels for transfer between slave peripherals. The
CC provides a user and event interface to the EDMA system. It includes up to 64 event channels to which
all system synchronization events can be mapped and 8 auto submit “quick” channels (QDMA). In most
ways, these channels are identical. A channel refers to a specific ‘event’ that can cause a transfer to be
submitted to the TC as a Transfer Request.
3.14.1 Crossbar Connections
There are five transfer masters (TCs have separate read and write connections) connected to the
crossbar; ARM, the Video Processing Sub-system (VPSS), the master peripherals (USB), and two EDMA
transfer controllers. These can be connected to four separate slave ports; ARM, the DDR EMIF, and CFG
bus peripherals. Not all masters may connect to all slaves. Connection paths are indicated by √ at
intersection points shown in Table 3-28
Table 3-28. Crossbar Connection Matrix
Slave Module
DMA Master ARM Internal MPEG4/JPEG Config Bus Registers and DDR EMIF Memory
ARM √ √ √ √
VPSS √
DMA Master Peripherals (USB) √ √ √
EDMA3TC0 √ √ √ √
EDMA3TC1 √ √ √ √
Memory Coprocessor Memory
Memory
3.14.2 EDMA Controller
The EDMA controller handles all data transfers between memories and the device slave peripherals on
the DM355 device. These are summarized as follows:
• Transfer to/from on-chip memories
– ARM program/data RAM
– MPEG4/JPEG Coprocessor memory
• Transfer to/from external storage
– DDR2 / mDDR SDRAM
– Asynchronous EMIF
– OneNAND flash
– NAND flash
– Smart Media, SD, MMC, xD media storage
• Transfer to/from peripherals
– ASP
– SPI
– I2C
– PWM
– RTO
– GPIO
– Timer/WDT
– UART
– MMC/SD
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 95
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
The EDMA Controller consists of two major blocks: the Transfer Controller (TC) and the Channel
Controller (CC). The CC is a highly flexible Channel Controller that serves as the user interface and event
interface for the EDMA system. The CC supports 64-event channels and 8 QDMA channels. The CC
consists of a scalable Parameter RAM (PaRAM) that supports flexible ping-pong, circular buffering,
channel-chaining, auto-reloading, and memory protection.
The EDMA Channel Controller has the following features:
• Fully orthogonal transfer description
– Three transfer dimensions
– A-synchronized transfers: one dimension serviced per event
– AB- synchronized transfers: two dimensions serviced per event
– Independent indexes on source and destination
– Chaining feature allows 3-D transfer based on single event
• Flexible transfer definition
– Increment and constant addressing modes
– Linking mechanism allows automatic PaRAM set update
– Chaining allows multiple transfers to execute with one event
• Interrupt generation for:
– DMA completion
– Error conditions
• Debug visibility
– Queue watermarking/threshold
– Error and status recording to facilitate debug
• 64 DMA channels
– Event synchronization
– Manual synchronization (CPU(s) write to event set register)
– Chain synchronization (completion of one transfer chains to next)
• 8 QDMA channels
– QDMA channels are triggered automatically upon writing to a PaRAM set entry
– Support for programmable QDMA channel to PaRAM mapping
• 128 PaRAM sets
– Each PaRAM set can be used for a DMA channel, QDMA channel, or link set (remaining)
• Two transfer controllers/event queues. The system-level priority of these queues is user programmable
• 16 event entries per event queue
• External events (for example, ASP TX Evt and RX Evt)
The EDMA Transfer Controller has the following features:
www.ti.com
• Two transfer controllers
• 64-bit wide read and write ports per channel
• Up to four in-flight transfer requests (TR)
• Programmable priority level
• Supports two dimensional transfers with independent indexes on source and destination (EDMA3CC
manages the 3rd dimension)
• Support for increment and constant addressing modes
• Interrupt and error support
Parameter RAM: Each EDMA is specified by an eight word (32-byte) parameter table contained in
Parameter RAM (PaRAM) within the CC. DM355 provides 128 PaRAM entries, one for each of the 64
DMA channels and for 64 QDMA / Linked DMA entries.
96 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
DMA Channels: Can be triggered by: " External events (for example, ASP TX Evt and RX Evt), " Software
writing a '1' to the given bit location, or channel, of the Event Set register, or, " Chaining to other DMAs.
QDMA: The Quick DMA (QDMA) function is contained within the CC. DM355 implements 8 QDMA
channels. Each QDMA channel has a selectable PaRAM entry used to specify the transfer. A QDMA
transfer is submitted immediately upon writing of the "trigger" parameter (as opposed to the occurrence of
an event as with EDMA). The QDMA parameter RAM may be written by any Config bus master through
the Config Bus and by DMAs through the Config Bus bridge.
QDMA Channels: Triggered by a configuration bus write to a designated 'QDMA trigger word'. QDMAs
allow a minimum number of linear writes (optimized for GEM IDMA feature) to be issued to the CC to
force a series of transfers to take place.
3.14.2.1 EDMA Channel Synchronization Events
The EDMA supports up to 64 EDMA channels which service peripheral devices and external memory.
Table 3-29 lists the source of EDMA synchronization events associated with each of the programmable
EDMA channels. For the DM355 device, the association of an event to a channel is fixed; each of the
EDMA channels has one specific event associated with it. These specific events are captured in the
EDMA event registers (ER, ERH) even if the events are disabled by the EDMA event enable registers
(EER, EERH). For more detailed information on the EDMA module and how EDMA events are enabled,
captured, processed, linked, chained, and cleared, etc., see the TMS320DM35x Digital Media
System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller Reference Guide
(literature number SPRUEE4).
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 3-29. DM355 EDMA Channel Synchronization Events
EDMA
CHANNEL
0 TIMER3: TINT6 Timer 3 Interrupt (TINT6) Event
1 TIMER3 TINT7 Timer 3 Interrupt (TINT7) Event
2 ASP0: XEVT ASP0 Transmit Event
3 ASP0: REVT ASP0 Receive Event
4 VPSS: EVT1 VPSS Event 1
5 VPSS: EVT2 VPSS Event 2
6 VPSS: EVT3 VPSS Event 3
7 VPSS: EVT4 VPSS Event 4
8 ASP1 Transmit Event or Timer 2 interrupt (TINT4) Event
9 ASP1 Receive Event or Timer 2 interrupt (TINT5) Event
10 SPI2: SPI2XEVT SPI2 Transmit Event
11 SPI2: SPI2REVT SPI2 Receive Event
12 Reserved
13 Reserved
14 SPI1: SPI1XEVT SPI1 Transmit Event
15 SPI1: SPI1REVT SPI1 Receive Event
16 SPI0: SPI0XEVT SP0I Transmit Event
17 SPI0: SPI0REVT SPI0 Receive Event
18 UART0: URXEVT0 UART 0 Receive Event
(1) In addition to the events shown in this table, each of the 64 channels can also be synchronized with the transfer completion or
intermediate transfer completion events. For more detailed information on EDMA event-transfer chaining, see the TMS320DM35x Digital
Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller Reference Guide (literature number SPRUEE4).
(2) The total number of EDMA events in DM355 exceeds 64, which is the maximum value of the EDMA module. Therefore, several events
are multiplexed and you must use the register EDMA_EVTMUX in the System Control Module to select the event source for multiplexed
events. Refer to TMS320DM35x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem Reference Guide (literature number
SPRUFB3) for more information on the System Control Module register EDMA_EVTMUX.
EVENT NAME EVENT DESCRIPTION
ASP1: XEVT or TIMER2:
TINT4
ASP1: REVT or TIMER2:
TINT5
(1) (2)
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Detailed Device Description 97
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
Table 3-29. DM355 EDMA Channel Synchronization Events
EDMA
CHANNEL
19 UART0: UTXEVT0 UART 0 Transmit Event
20 UART1: URXEVT1 UART 1 Receive Event
21 UART1: UTXEVT1 UART 1 Transmit Event
22 UART2: URXEVT2 UART 2 Receive Event
23 UART2: UTXEVT2 UART 2 Transmit Event
24 Reserved
25 GPIO: GPINT9 GPIO 9 Interrupt Event
26 MMC0RXEVT MMC/SD0 Receive Event
27 MMC0TXEVT MMC/SD0 Transmit Event
28 I2CREVT I2C Receive Event
29 I2CXEVT I2C Transmit Event
30 MMC1RXEVT MMC/SD1 Receive Event
31 MMC1TXEVT MMC/SD1 Transmit Event
32 GPINT0 GPIO 0 Interrupt Event
33 GPINT1 GPIO 1 Interrupt Event
34 GPINT2 GPIO 2 Interrupt Event
35 GPINT3 GPIO 3 Interrupt Event
36 GPINT4 GPIO 4 Interrupt Event
37 GPINT5 GPIO 5 Interrupt Event
38 GPINT6 GPIO 6 Interrupt Event
39 GPINT7 GPIO 7 Interrupt Event
40 GPBNKINT0 GPIO Bank 0 Interrupt Event
41 GPBNKINT1 GPIO Bank 1 Interrupt Event
42 GPBNKINT2 GPIO Bank 2 Interrupt Event
43 GPBNKINT3 GPIO Bank 3 Interrupt Event
44 GPBNKINT4 GPIO Bank 4 Interrupt Event
45 GPBNKINT5 GPIO Bank 5 Interrupt Event
46 GPBNKINT6 GPIO Bank 6 Interrupt Event
47 GPINT8 GPIO 8 Interrupt Event
48 TIMER0: TINT0 Timer 0 Interrupt Event
49 TIMER0: TINT1 Timer 1 Interrupt Event
50 TIMER1: TINT2 Timer 2 Interrupt Event
51 TIMER1: TINT3 Timer 3 Interrupt Event
52 PWM0 PWM 0 Event
53 PWM1 PWM 1 Event
54 PWM2 PWM 2 Event
55 PWM3 PWM 3 Event
56 - 63 Reserved
EVENT NAME EVENT DESCRIPTION
(1) (2)
www.ti.com
(continued)
3.15 MPEG4/JPEG Overview
The DM355 supports the computational operations used for image processing, JPEG compression and
MPEG4 video and imaging standard.
98 Detailed Device Description Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
www.ti.com
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
4 Device Operating Conditions
4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Case Temperature Range (Unless Otherwise Noted)
Supply voltage ranges
Input voltage ranges All 3.3 V I/Os -0.5 V to 3.8 V
Clamp current for input or output
Operating case temperature ranges
Storage temperature ranges T
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under "absolute maximum ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings
only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under "recommended operating
conditions" is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltage values are with respect to V
(3) Clamp current flows from an input or output pad to a supply rail through a clamp circuit or an intrinsic diode. Positive current results from
an applied input or output voltage that is more than 0.5 V higher (more positive) than the supply voltage,
VDD/V
DDA_PLL1/2/VDD_USB/VDD_DDR
(more negative) than the VSSvoltage..
(1) (2)
All 1.3 V supplies -0.5 V to 1.7 V
All digital 1.8 V supplies -0.5 V to 2.5 V
All analog 1.8 V supplies -0.5 V to 1.89 V
All 3.3 V supplies -0.5 V to 4.4 V
All 1.8 V I/Os -0.5 V to 2.3 V
VBUS 0.0 V to 5.5 V
(3)
SS.
I
clamp
Commercial T
c
Extended Temperature [A216 and A135 devices] T
stg
-20 mA to 20 mA
c
-40°C to 100 °C
-65°C to 150 °C
for dual-supply macros. Negative current results from an applied voltage that is more than 0.5 V less
0°C to 85 °C
Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated Device Operating Conditions 99
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355

TMS320DM355
SPRS463G–SEPTEMBER 2007–REVISED JUNE 2010
www.ti.com
4.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
NAME DESCRIPTION MIN NOM MAX UNIT
CV
DD
V
DDA_PLL1
V
DDA_PLL2
V
DDD13_USB
V
DDA13_USB
V
DDA33_USB
Supply Voltage V
Supply Ground
Voltage Input High V
Voltage Input Low V
(3)
DAC
Video Buffer
(3)
USB
Temperature T
Transition Time t
DDA33_USB_PLL
V
DD_DDR
V
DDA33_DDRDLL
V
DD_VIN
V
DD_VOUT
V
DDA18_DAC
V
DD
V
SS
V
SSA_PLL1
V
SSA_PLL2
V
SS_USB
V
SSA_DLL
V
SSA_DAC
V
SS_MX1
V
SS_MX2
IH
IL
V
REF
R
BIAS
R
LOAD
C
BG
R
OUT
R
FB
R
BIAS
C
BG
USB_VBUS USB external charge pump input 4.85 5 5.25 V
R1 USB reference resistor
c
t
(1) Oscillator ground must be kept separate from other grounds and connected directly to the crystal load capacitor ground (see
Section 5.5.1 ).
(2) These I/O specifications apply to regular 3.3 V I/Os and do not apply to DDR2/mDDR, USB I/Os. DDR2/mDDR I/Os are 1.8 V I/Os and
adhere to JESD79-2A standard, USB I/Os adhere to USB2.0 spec.
(3) See Section 5.9.2.4 . Also, resistors should be E-96 spec line (3 digits with 1% accuracy).
(4) Connect USB_R1 to V
(5) Whichever is smaller. P = the period of the applied signal. Maintaining transition times as fast as possible is recommended to improve
SS_USB_REF
noise immunity on input signals.
Supply voltage, Core 1.235 1.3 1.365 V
Supply voltage, PLL1 1.235 1.3 1.365 V
Supply voltage, PLL2 1.235 1.3 1.365 V
Supply voltage, USB Digital 1.235 1.3 1.365 V
Supply voltage, USB Analog 1.235 1.3 1.365 V
Supply voltage, USB Analog 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
Supply voltage, USB Common PLL 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
Supply voltage, DDR2 / MDDR 1.71 1.8 1.89 V
Supply voltage, DDR DLL Analog 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
Supply voltage, Digital video In 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
Supply voltage, Digital Video Out 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
Supply voltage, DAC Analog 1.71 1.8 1.89 V
Supply voltage, I/Os 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
Supply ground, Core, USB Digital 0 0 0 V
Supply ground, PLL1 0 0 0 V
Supply ground, PLL2 0 0 0 V
Supply ground, USB 0 0 0 V
Supply ground, DLL 0 0 0 V
Supply ground, DAC Analog 0 0 0 V
MXI1 osc ground
MXI2 osc ground
High-level input voltage
Low-level input voltage
(1)
(1)
(2)
(2)
0 0 0 V
0 0 0 V
2 V
0.8 V
DAC reference voltage 450 mV
DAC full-scale current adjust resistor 2550 Ω
Output resistor 499 Ω
Bypass capacitor 0.1 mF
Output resistor (ROUT), between TVOUT and VFB pins 1070
Feedback resistor, between VFB and IOUT pins. 1000
DAC full-scale current adjust resistor 2550 Ω
Bypass capacitor 0.1 mA
(4)
9.9 10 10.1 kΩ
Commercial 0 85 °C
Operating case temperature range
Extended
(A216 and -40 100 °C
A135 devices)
Transition time, 10% - 90%, All Inputs
(unless otherwise specified in the ns
electrical data sections)
0.25P
or 10
(5)
via 10K ohm, 1% resistor placed as close to the device as possible.
Ω
100 Device Operating Conditions Copyright © 2007–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Link(s): TMS320DM355
 Loading...
Loading...