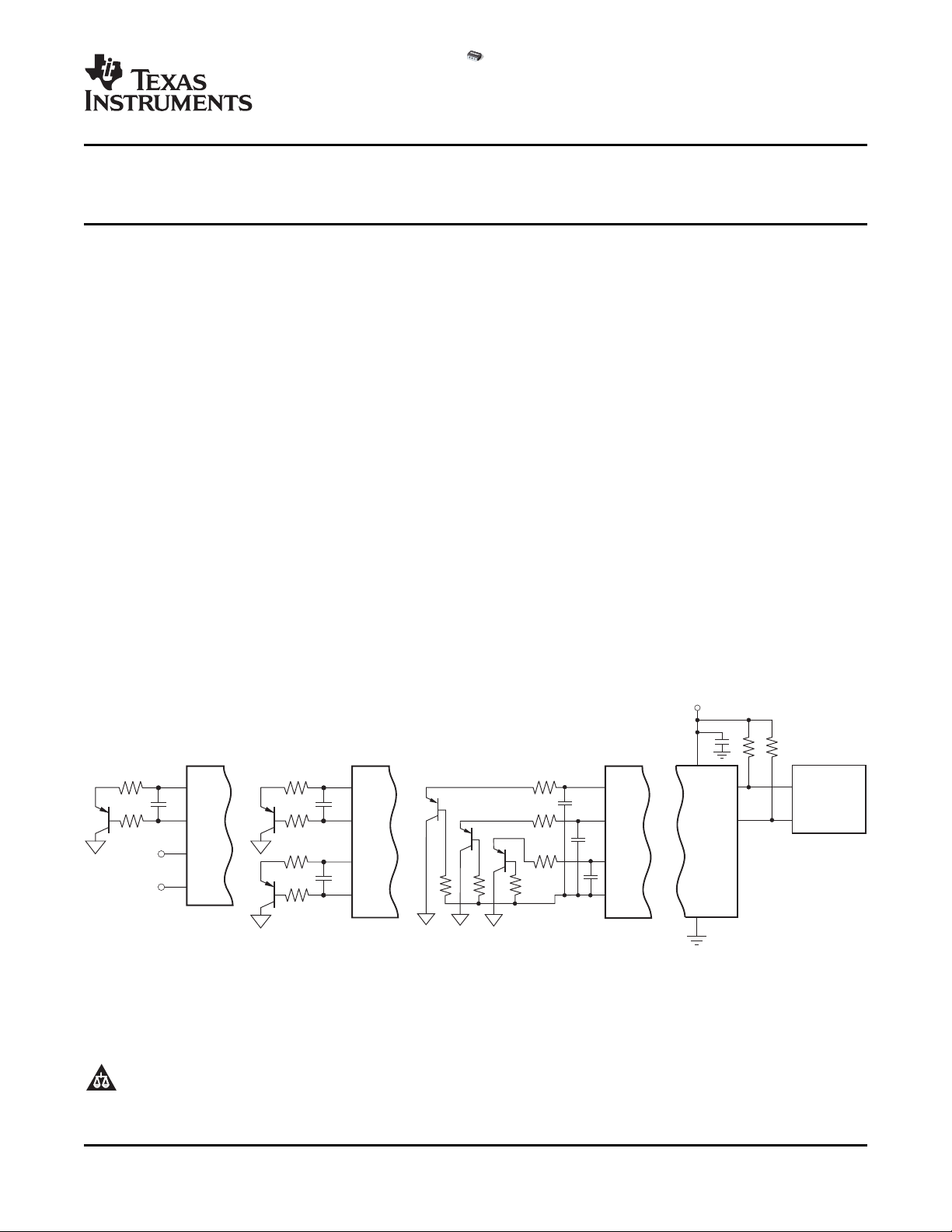
+5V
SCL
GND
SDA
V+
SMBus
Controller
8
5
7
6
TMP421
DXP
DXN
A1
A0
1
2
3
4
1ChannelLocal
1ChannelRemote
TMP422
DX1
DX2
DX3
DX4
1
2
3
4
1ChannelLocal
2ChannelsRemote
TMP423
DXP1
DXP2
DXP3
DXN
1
2
3
4
1ChannelLocal
3ChannelsRemote
TMP421
TMP422
www.ti.com
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
TMP423
± 1 ° C Remote and Local TEMPERATURE SENSOR
in SOT23-8
1
FEATURES DESCRIPTION
234
• SOT23-8 PACKAGE
• ± 1 ° C REMOTE DIODE SENSOR (MAX)
• ± 1.5 ° C LOCAL TEMPERATURE SENSOR (MAX)
• SERIES RESISTANCE CANCELLATION
• n-FACTOR CORRECTION integral part of microcontrollers, microprocessors, or
• TWO-WIRE/ SMBus™ SERIAL INTERFACE
• MULTIPLE INTERFACE ADDRESSES
• DIODE FAULT DETECTION
• RoHS COMPLIANT AND NO Sb/Br
APPLICATIONS
• PROCESSOR/FPGA TEMPERATURE
MONITORING
• LCD/ DLP
• SERVERS
• CENTRAL OFFICE TELECOM EQUIPMENT
• STORAGE AREA NETWORKS (SAN)
®
/LCOS PROJECTORS
The TMP421, TMP422, and TMP423 are remote
temperature sensor monitors with a built-in local
temperature sensor. The remote temperature sensor
diode-connected transistors are typically low-cost,
NPN- or PNP-type transistors or diodes that are an
FPGAs.
Remote accuracy is ± 1 ° C for multiple IC
manufacturers, with no calibration needed. The
two-wire serial interface accepts SMBus write byte,
read byte, send byte, and receive byte commands to
configure the device.
The TMP421, TMP422, and TMP423 include series
resistance cancellation, programmable non-ideality
factor, wide remote temperature measurement range
(up to +150 ° C), and diode fault detection.
The TMP421, TMP422, and TMP423 are all available
in a SOT23-8 package.
1
2 DLP is a registered trademark of Texas Instruments.
3 SMBus is a trademark of Intel Corporation.
4 All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
www.ti.com
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with
appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may be more
susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published specifications.
PACKAGE INFORMATION
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION ADDRESS PACKAGE-LEAD DESIGNATOR MARKING
TMP421 Remote Junction 100 11xx SOT23-8 DCN DACI
TMP422 Remote Junction 100 11xx SOT23-8 DCN DADI
TMP423A Triple Channel 100 1100 SOT23-8 DCN DAEI
TMP423B 100 1101 SOT23-8 DCN DAFI
(1) For the most current package and ordering information see the Package Option Addendum at the end of this document, or see the TI
web site at www.ti.com .
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Single Channel
Temperature Sensor
Dual Channel
Temperature Sensor
Remote Junction
Temperature Sensor
(1)
TWO-WIRE PACKAGE PACKAGE
(1)
Over operating free-air temperature range, unless otherwise noted.
TMP421, TMP422, TMP423 UNIT
Power Supply, V
Input Voltage
Input Current 10 mA
Operating Temperature Range – 55 to +127 ° C
Storage Temperature Range – 60 to +130 ° C
Junction Temperature (T
ESD Rating Charged Device Model (CDM) 1000 V
(1) Stresses above these ratings may cause permanent damage. Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may
degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond
those specified is not implied.
S
Pins 1, 2, 3, and 4 only – 0.5 to VS+ 0.5 V
Pins 6 and 7 only – 0.5 to 7 V
max) +150 ° C
J
Human Body Model (HBM) 3000 V
Machine Model (MM) 200 V
+7 V
2 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423
www.ti.com
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
At TA= – 40 ° C to +125 ° C and VS= 2.7V to 5.5V, unless otherwise noted.
TMP421, TMP422, TMP423
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
TEMPERATURE ERROR
Local Temperature Sensor TE
Remote Temperature Sensor
vs Supply (Local/Remote) VS= 2.7V to 5.5V ± 0.2 ± 0.5 ° C/V
TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT
Conversion Time (per channel) 100 115 130 ms
Resolution
Local Temperature Sensor (programmable) 12 Bits
Remote Temperature Sensor 12 Bits
Remote Sensor Source Currents
High Series Resistance 3k Ω Max 120 µ A
Medium High 60 µ A
Medium Low 12 µ A
Low 6 µ A
Remote Transistor Ideality Factor η TMP421/22/23 Optimized Ideality Factor 1.008
SMBus INTERFACE
Logic Input High Voltage (SCL, SDA) V
Logic Input Low Voltage (SCL, SDA) V
Hysteresis 500 mV
SMBus Output Low Sink Current 6 mA
SDA Output Low Voltage V
Logic Input Current 0 ≤ VIN≤ 6V – 1 +1 µ A
SMBus Input Capacitance (SCL, SDA) 3 pF
SMBus Clock Frequency 3.4 MHz
SMBus Timeout 25 30 35 ms
SCL Falling Edge to SDA Valid Time 1 µ s
DIGITAL INPUTS
Input Capacitance 3 pF
Input Logic Levels
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Leakage Input Current I
POWER SUPPLY
Specified Voltage Range V
Quiescent Current I
Undervoltage Lockout UVLO 2.3 2.4 2.6 V
Power-On Reset Threshold POR 1.6 2.3 V
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Specified Range – 40 +125 ° C
Storage Range – 60 +130 ° C
Thermal Resistance, SOT23 θ
(1)
LOCAL
TE
REMOTE
TA= +15 ° C to +85 ° C, TD= – 40 ° C to +150 ° C, VS= 3.3V ± 0.25 ± 1 ° C
TA= – 40 ° C to +100 ° C, TD= – 40 ° C to +150 ° C, VS= 3.3V ± 1 ± 3 ° C
TA= – 40 ° C to +125 ° C, TD= – 40 ° C to +150 ° C ± 3 ± 5 ° C
IH
IL
OL
IH
IL
IN
S
Q
Serial Bus Active, fS= 400kHz, Shutdown Mode 90 µ A
Serial Bus Active, fS= 3.4MHz, Shutdown Mode 350 µ A
JA
(1) Tested with less than 5 Ω effective series resistance and 100pF differential input capacitance.
TA= – 40 ° C to +125 ° C ± 1.25 ± 2.5 ° C
TA= +15 ° C to +85 ° C, VS= 3.3V ± 0.25 ± 1.5 ° C
2.1 V
0.8 V
I
= 6mA 0.15 0.4 V
OUT
0.7(V+) (V+)+0.5 V
– 0.5 0.3(V+) V
0V ≤ VIN≤ V
0.0625 Conversions per Second 32 38 µ A
Eight Conversions per Second 400 525 µ A
Serial Bus Inactive, Shutdown Mode 3 10 µ A
S
2.7 5.5 V
100 ° C/W
1 µ A
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 3
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
V+
SCL
GND
DXP
DXN
A1
A0
SDA
TMP421
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
V+
SCL
GND
DX1
DX2
DX3
DX4
SDA
TMP422
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
TMP421 PIN CONFIGURATION
DCN PACKAGE
SOT23-8
(TOP VIEW)
TMP421 PIN ASSIGNMENTS
TMP421
NO. NAME DESCRIPTION
1 DXP Positive connection to remote temperature sensor.
2 DXN Negative connection to remote temperature sensor.
3 A1 Address pin
4 A0 Address pin
5 GND Ground
6 SDA Serial data line for SMBus, open-drain; requires pull-up resistor to V+.
7 SCL Serial clock line for SMBus, open-drain; requires pull-up resistor to V+.
8 V+ Positive supply voltage (2.7V to 5.5V)
TMP422 PIN CONFIGURATION
DCN PACKAGE
SOT23-8
(TOP VIEW)
TMP422 PIN ASSIGNMENTS
TMP422
NO. NAME DESCRIPTION
1 DX1 Channel 1 remote temperature sensor connection pin. Also sets the TMP422 address; see Table 10 .
2 DX2 Channel 1 remote temperature sensor connection pin. Also sets the TMP422 address; see Table 10 .
3 DX3 Channel 2 remote temperature sensor connection pin. Also sets the TMP422 address; see Table 10 .
4 DX4 Channel 2 remote temperature sensor connection pin. Also sets the TMP422 address; see Table 10 .
5 GND Ground
6 SDA Serial data line for SMBus, open-drain; requires pull-up resistor to V+.
7 SCL Serial clock line for SMBus, open-drain; requires pull-up resistor to V+.
8 V+ Positive supply voltage (2.7V to 5.5V)
4 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423
www.ti.com
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
V+
SCL
GND
DXP1
DXP2
DXP3
DXN
SDA
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
TMP423 PIN CONFIGURATION
DCN PACKAGE
SOT23-8
(TOP VIEW)
TMP423 PIN ASSIGNMENTS
TMP423
NO. NAME DESCRIPTION
1 DXP1 Channel 1 positive connection to remote temperature sensor.
2 DXP2 Channel 2 positive connection to remote temperature sensor.
3 DXP3 Channel 3 positive connection to remote temperature sensor.
4 DXN Common negative connection to remote temperature sensors, Channel 1, Channel 2, Channel 3.
5 GND Ground
6 SDA Serial data line for SMBus, open-drain; requires pull-up resistor to V+.
7 SCL Serial clock line for SMBus, open-drain; requires pull-up resistor to V+.
8 V+ Positive supply voltage (2.7V to 5.5V)
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 5
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423
www.ti.com
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
AmbientTemperature,T ( C)°
A
-50 -25 1251007550250
RemoteTemperatureError( C)°
V =3.3V
S
T =+25 C
REMOTE
°
30TypicalUnitsShown
h =1.008
LocalTemperatureError( )
°C
AmbientTemperature,T (A°C)
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
-50 125-25 0 25 50 75 100
50UnitsShown
V =3.3V
S
60
40
20
0
-20
-40
-60
LeakageResistance(M )W
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
RemoteT
emperatureError( C)°
R GND-
R V-
S
RemoteTemperatureError( )
°C
R W( )
S
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
-0.5
-1.0
-1.5
-2.0
0 3500500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
V =2.7V
S
V =5.5V
S
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
Capacitance(nF)
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
RemoteTemperatureError( C)°
RemoteTemperatureError( )
°C
R (W)
S
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
-0.5
-1.0
-1.5
-2.0
0 3500500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
V =2.7V
S
V =5.5V
S
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
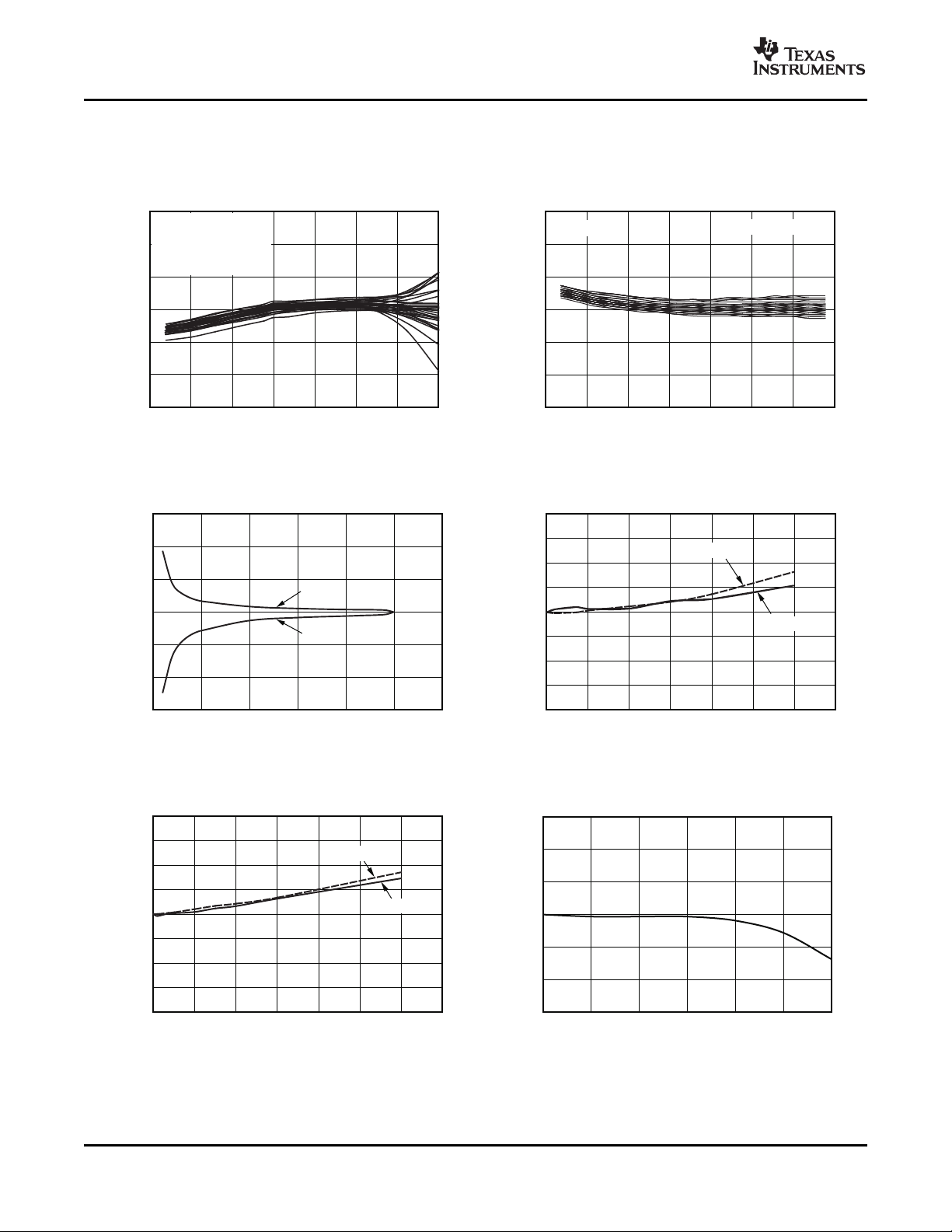
REMOTE TEMPERATURE ERROR LOCAL TEMPERATURE ERROR
vs TEMPERATURE vs TEMPERATURE
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
At TA= +25 ° C and VS= +5.0V, unless otherwise noted.
Figure 1. Figure 2.
REMOTE TEMPERATURE ERROR REMOTE TEMPERATURE ERROR vs SERIES RESISTANCE
vs LEAKAGE RESISTANCE (Diode-Connected Transistor, 2N3906 PNP)
Figure 3. Figure 4.
REMOTE TEMPERATURE ERROR vs SERIES RESISTANCE REMOTE TEMPERATURE ERROR
(GND Collector-Connected Transistor, 2N3906 PNP) vs DIFFERENTIAL CAPACITANCE
6 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 5. Figure 6.
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423
www.ti.com
500
450
400
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
ConversionRate(conversions/sec)
0.0625 0.125 0.25 0.5 1 2 4 8
I (mA)
Q
V =2.7V
S
V =5.5V
S
25
20
15
10
5
0
-5
-10
-15
-20
-25
Frequency(MHz)
0 5 10 15
TemperatureError( C)°
Local100mV Noise
PP
Remote100mV Noise
PP
Local250mV Noise
PP
Remote250mV Noise
PP
500
450
400
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
SCLCLockFrequency(Hz)
1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
I
( A)m
Q
V =3.3V
S
V =5.5V
S
I ( )
Q
mA
V (SV)
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
4.53.0 3.5 4.0 5.55.02.5
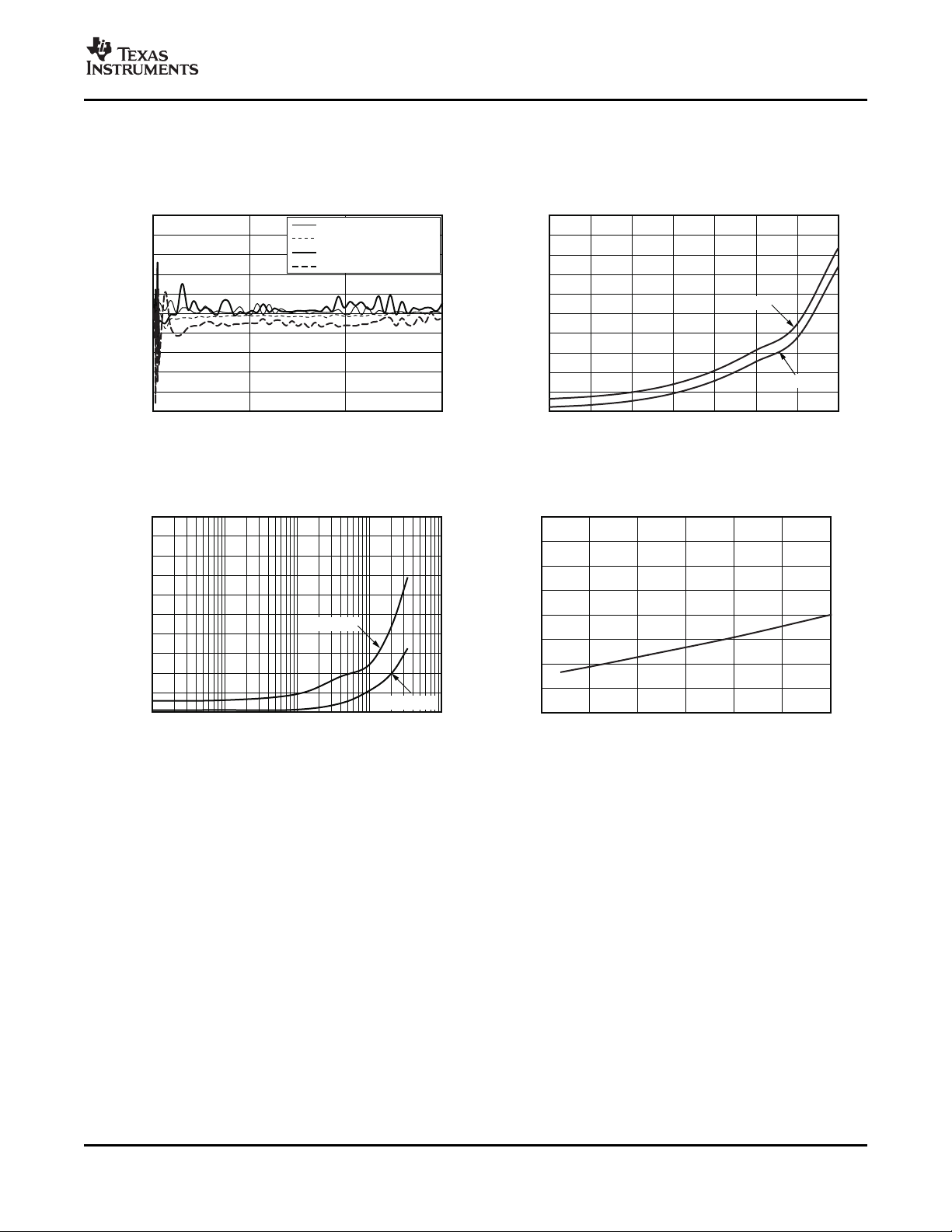
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
At TA= +25 ° C and VS= +5.0V, unless otherwise noted.
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
vs POWER-SUPPLY NOISE FREQUENCY vs CONVERSION RATE
TEMPERATURE ERROR QUIESCENT CURRENT
Figure 7. Figure 8.
SHUTDOWN QUIESCENT CURRENT SHUTDOWN QUIESCENT CURRENT
vs SCL CLOCK FREQUENCY vs SUPPLY VOLTAGE
Figure 9. Figure 10.
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 7
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423
www.ti.com
0.1 Fm
10kW
(typ)
10kW
(typ)
TMP421
DXP
DXN
V+
8
7
6
5
2
1
R
S
(2)
R
S
(2)
C
DIFF
(3)
C
DIFF
(3)
R
S
(2)
R
S
(2)
GND
SCL
SDA
+5V
SMBus
Controller
Diode-connectedconfiguration :
(1)
SeriesResistance
Transistor-connectedconfiguration :
(1)
A1
A0
4
3
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
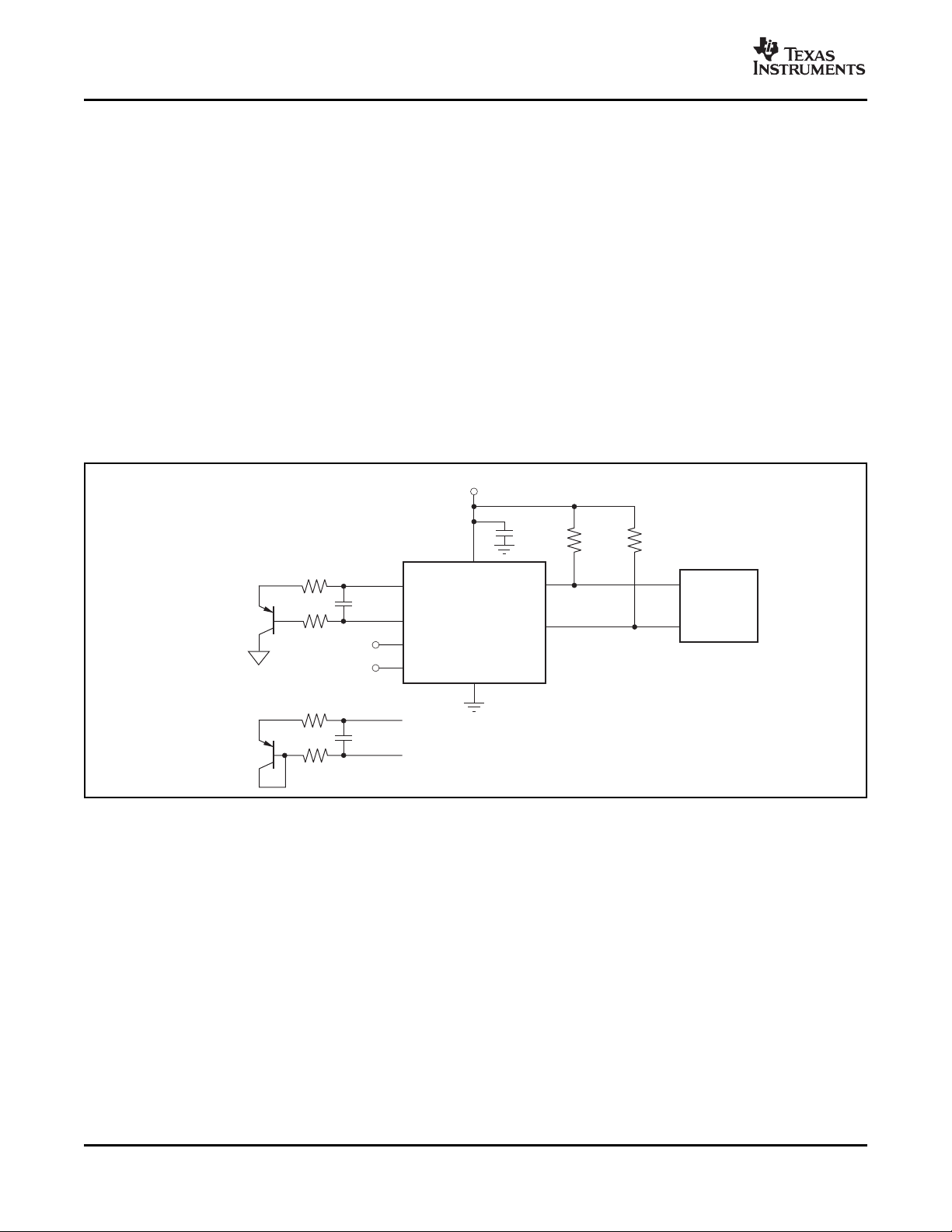
APPLICATION INFORMATION
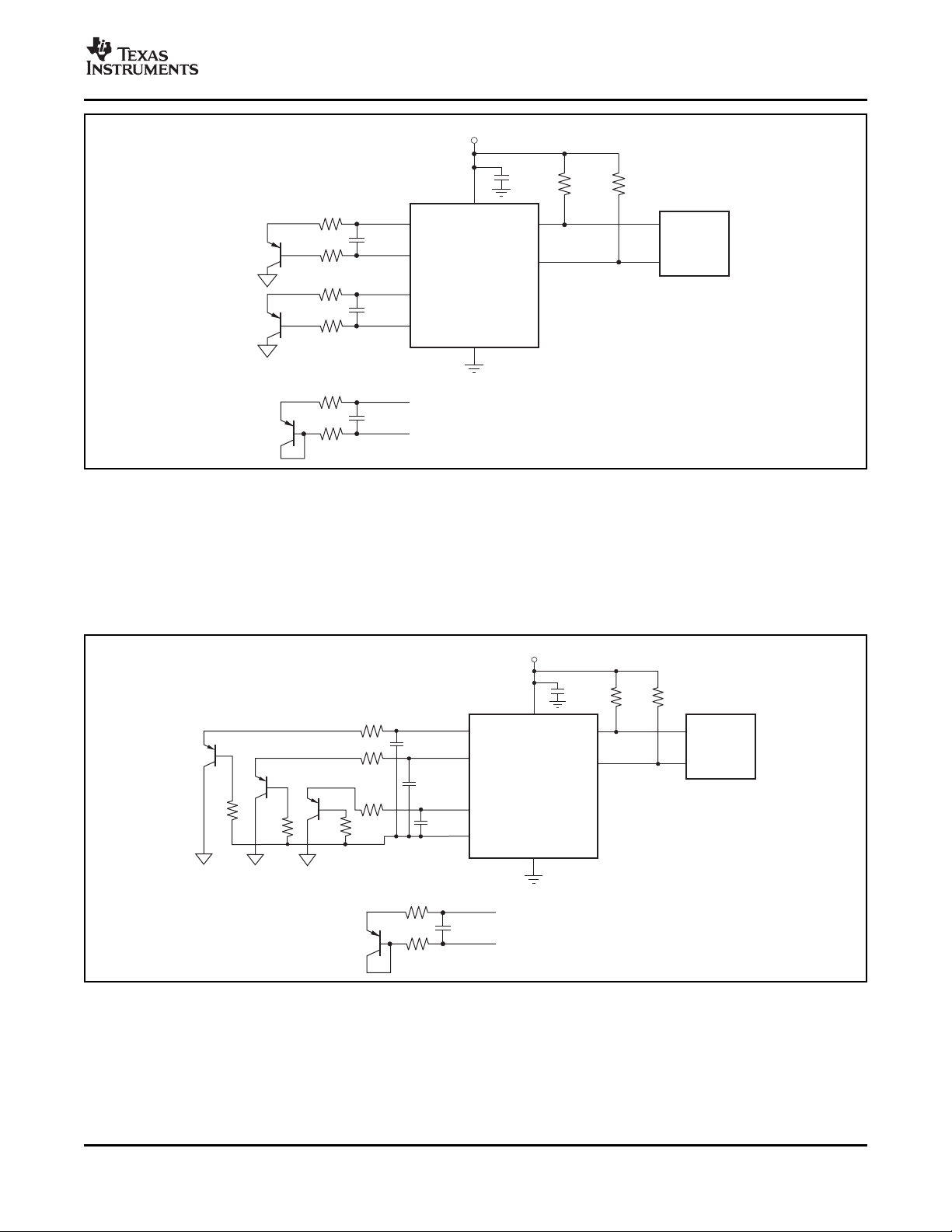
The TMP421 (two-channel), TMP422 (three-channel), The TMP422 requires transistors connected between
and TMP423 (four-channel) are digital temperature DX1 and DX2 and between DX3 and DX4. Unused
sensors that combine a local die temperature channels on the TMP422 must be connected to GND.
measurement channel and one, two, or three remote The TMP423 requires a transistor connected to each
junction temperature measurement channels in a positive channel (DXP1, DXP2, and DXP3), with the
single SOT23-8 package. These devices are base of each channel tied to the common negative,
two-wire- and SMBus interface-compatible and are DXN. For an unused channel, the TMP423 DXP pin
specified over a temperature range of – 40 ° C to can be left open or tied to GND.
+125 ° C. The TMP421/22/23 each contain multiple
registers for holding configuration information and
temperature measurement results.
For proper remote temperature sensing operation, the recommended for local bypassing. Figure 11 shows a
TMP421 requires only a transistor connected typical configuration for the TMP421; Figure 12
between DXP and DXN pins. If the remote channel is illustrates a typical application for the TMP422.
not utilized, DXP can be left open or tied to GND. Figure 13 illustrates a typical application for the
The TMP421/22/23 SCL and SDA interface pins each
require pull-up resistors as part of the communication
bus. A 0.1 µ F power-supply bypass capacitor is
TMP423.
(1) Diode-connected configuration provides better settling time. Transistor-connected configuration provides better series resistance
cancellation.
(2) RS(optional) should be < 1.5k Ω in most applications. Selection of RSdepends on application; see the Filtering section.
(3) C
(optional) should be < 1000pF in most applications. Selection of C
DIFF
Figure 6 , Remote Temperature Error vs Differential Capacitance.
8 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
depends on application; see the Filtering section and
DIFF
Figure 11. TMP421 Basic Connections
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423
www.ti.com
TMP422
DX1
(4)
DX2
(4)
5
2
1
R
S
(2)
R
S
(2)
C
DIFF
(3)
C
DIFF
(3)
R
S
(2)
R
S
(2)
GND
Diode-connectedconfiguration :
(1)
SeriesResistance
Transistor-connectedconfiguration :
(1)
DX3
(4)
DX4
(4)
4
3
R
S
(2)
R
S
(2)
C
DIFF
(3)
0.1 Fm
10kW
(typ)
10kW
(typ)
V+
8
7
6
SCL
SDA
+5V
SMBus
Controller
DXP1
DXN1
DXP2
DXN2
+5V
TMP423
DXP1
DXP2
DXP3
DXP
DXN
DXN
SCL
GND
SDA
V+
2
3
4
7
1
6
8
R
S
(2)
R
S
(2)
R
S
(2)
R
S
(2)
R
S
(2)
R
S
(2)
C
DIFF
(3)
C
DIFF
(3)
C
DIFF
(3)
Transistor-connectedconfiguration :
(1)
C
DIFF
(3)
R
S
(2)
R
S
(2)
Diode-connectedconfiguration :
(1)
5
0.1 Fm
10kW
(typ)
10kW
(typ)
SMBus
Controller
SeriesResistance
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
(1) Diode-connected configuration provides better settling time. Transistor-connected configuration provides better series resistance
cancellation.
(2) RS(optional) should be < 1.5k Ω in most applications. Selection of RSdepends on application; see the Filtering section.
(3) C
(optional) should be < 1000pF in most applications. Selection of C
DIFF
Figure 6 , Remote Temperature Error vs Differential Capacitance.
(4) TMP422 SMBus slave address is 1001 100 when connected as shown.
(1) Diode-connected configuration provides better settling time. Transistor-connected configuration provides better series resistance
cancellation.
(2) RS(optional) should be < 1.5k Ω in most applications. Selection of RSdepends on application; see the Filtering section.
(3) C
Figure 6 , Remote Temperature Error vs Differential Capacitance.
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 9
(optional) should be < 1000pF in most applications. Selection of C
DIFF
Figure 12. TMP422 Basic Connections
Figure 13. TMP423 Basic Connections
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423
DIFF
DIFF
depends on application; see the Filtering section and
depends on application; see the Filtering section and
www.ti.com
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
SERIES RESISTANCE CANCELLATION
Series resistance in an application circuit that typically
results from printed circuit board (PCB) trace
resistance and remote line length is automatically
cancelled by the TMP421/22/23, preventing what
would otherwise result in a temperature offset. A total
of up to 3k Ω of series line resistance is cancelled by
the TMP421/22/23, eliminating the need for additional
characterization and temperature offset correction.
See the two Remote Temperature Error vs Series
Resistance typical characteristic curves (Figure 4 and
Figure 5 ) for details on the effects of series resistance
and power-supply voltage on sensed remote
temperature error.
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT CAPACITANCE
The TMP421/22/23 tolerate differential input
capacitance of up to 1000pF with minimal change in
temperature error. The effect of capacitance on
sensed remote temperature error is illustrated in
from low to high. The change in measurement range
and data format from standard binary to extended
binary occurs at the next temperature conversion. For
data captured in the extended temperature range
configuration, an offset of 64 (40h) is added to the
standard binary value, as shown in the Extended
Binary column of Table 1 . This configuration allows
measurement of temperatures as low as – 64 ° C, and
as high as +191 ° C; however, most
temperature-sensing diodes only measure with the
range of – 55 ° C to +150 ° C. Additionally, the
TMP421/22/23 are rated only for ambient
temperatures ranging from – 40 ° C to +125 ° C.
Parameters in the Absolute Maximum Ratings table
must be observed.
Table 1. Temperature Data Format (Local and
Remote Temperature High Bytes)
LOCAL/REMOTE TEMPERATURE REGISTER
HIGH BYTE VALUE (1 ° C RESOLUTION)
TEMP
STANDARD BINARY
(1)
EXTENDED BINARY
Figure 6 , Remote Temperature Error vs Differential ( ° C) BINARY HEX BINARY HEX
Capacitance.
TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT DATA
Temperature measurement data may be taken over
an operating range of – 40 ° C to +127 ° C for both local
and remote locations.
However, measurements from – 55 ° C to +150 ° C can
be made both locally and remotely by reconfiguring
the TMP421/22/23 for the extended temperature
range, as described below.
Temperature data that result from conversions within
the default measurement range are represented in
binary form, as shown in Table 1 , Standard Binary
column. Note that although the device is rated to only
measure temperatures down to – 55 ° C, it may read
temperatures below this level. However, any
– 64 1100 0000 C0 0000 0000 00
– 50 1100 1110 CE 0000 1110 0E
– 25 1110 0111 E7 0010 0111 27
0 0000 0000 00 0100 0000 40
1 0000 0001 01 0100 0001 41
5 0000 0101 05 0100 0101 45
10 0000 1010 0A 0100 1010 4A
25 0001 1001 19 0101 1001 59
50 0011 0010 32 0111 0010 72
75 0100 1011 4B 1000 1011 8B
100 0110 0100 64 1010 0100 A4
125 0111 1101 7D 1011 1101 BD
127 0111 1111 7F 1011 1111 BF
150 0111 1111 7F 1101 0110 D6
175 0111 1111 7F 1110 1111 EF
191 0111 1111 7F 1111 1111 FF
temperature below – 64 ° C results in a data value of
– 64 (C0h). Likewise, temperatures above +127 ° C
result in a value of 127 (7Fh). The device can be set
to measure over an extended temperature range by
(1) Resolution is 1 ° C/count. Negative numbers are represented in
two's complement format.
(2) Resolution is 1 ° C/count. All values are unsigned with a – 64 ° C
changing bit 2 (RANGE) of Configuration Register 1 offset.
(2)
10 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
One-ShotStartRegister
ConfigurationRegisters
StatusRegister
IdentificationRegisters
N-FactorCorrectionRegisters
ConversionRateRegister
LocalandRemoteTemperatureRegisters
SDA
SCL
PointerRegister
I/O
Control
Interface
SoftwareReset
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Both local and remote temperature data use two
bytes for data storage. The high byte stores the
temperature with 1 ° C resolution. The second or low
byte stores the decimal fraction value of the
temperature and allows a higher measurement
resolution, as shown in Table 2 . The measurement
resolution for the both the local and remote channels
is 0.0625 ° C, and is not adjustable.
Table 2. Decimal Fraction Temperature Data
Format (Local and Remote Temperature Low
TEMPERATURE REGISTER LOW BYTE VALUE
TEMP
( ° C) STANDARD AND EXTENDED BINARY HEX
0 0000 0000 00
0.0625 0001 0000 10
0.1250 0010 0000 20
0.1875 0011 0000 30
0.2500 0100 0000 40
0.3125 0101 0000 50
0.3750 0110 0000 60
0.4375 0111 0000 70
0.5000 1000 0000 80
0.5625 1001 0000 90
0.6250 1010 0000 A0
0.6875 1011 0000 B0
0.7500 1100 0000 C0
0.8125 1101 0000 D0
0.8750 1110 0000 E0
0.9385 1111 0000 F0
(1) Resolution is 0.0625 ° C/count. All possible values are shown.
Standard Binary to Decimal Temperature Data Calculation Example
High byte conversion (for example, 0111 0011):
Convert the right-justified binary high byte to
hexadecimal.
From hexadecimal, multiply the first number by
0
16
= 1 and the second number by 16
The sum equals the decimal equivalent.
0111 0011b → 73h → (3 × 16
Low byte conversion (for example, 0111 0000):
To convert the left-justified binary low-byte to
decimal, use bits 7 through 4 and ignore bits 3
through 0 because they do not affect the value of
the number.
0111b → (0 × 1/2)
Note that the final numerical result is the sum of the
high byte and low byte. In negative temperatures, the
unsigned low byte adds to the negative high byte to
result in a value less than the high byte (for instance,
– 15 + 0.75 = – 14.25, not – 15.75).
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 11
4
1/2)
= 0.4375
Bytes)
1
+ (1 × 1/2)
(0.0625 ° C RESOLUTION)
1
= 16.
0
) + (7 × 16
2
+ (1 × 1/2)
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423
1
) = 115
3
+ (1 ×
Standard Decimal to Binary Temperature Data Calculation Example
For positive temperatures (for example, +20 ° C):
(+20 ° C)/(+1 ° C/count) = 20 → 14h → 0001 0100
Convert the number to binary code with 8-bit,
right-justified format, and MSB = '0' to denote a
positive sign.
+20 ° C is stored as 0001 0100 → 14h.
For negative temperatures (for example, – 20 ° C):
(| – 20|)/(+1 ° C/count) = 20 → 14h → 0001 0100
Generate the two's complement of a negative
number by complementing the absolute value
binary number and adding 1.
– 20 ° C is stored as 1110 1100 → ECh.
REGISTER INFORMATION
The TMP421/22/23 contain multiple registers for
holding configuration information, temperature
measurement results, and status information. These
registers are described in Figure 14 and Table 3 .
POINTER REGISTER
Figure 14 shows the internal register structure of the
TMP421/22/23. The 8-bit Pointer Register is used to
address a given data register. The Pointer Register
identifies which of the data registers should respond
to a read or write command on the two-wire bus. This
register is set with every write command. A write
command must be issued to set the proper value in
the Pointer Register before executing a read
command. Table 3 describes the pointer address of
the TMP421/22/23 registers. The power-on reset
(POR) value of the Pointer Register is 00h (0000
0000b).
Figure 14. Internal Register Structure

www.ti.com
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
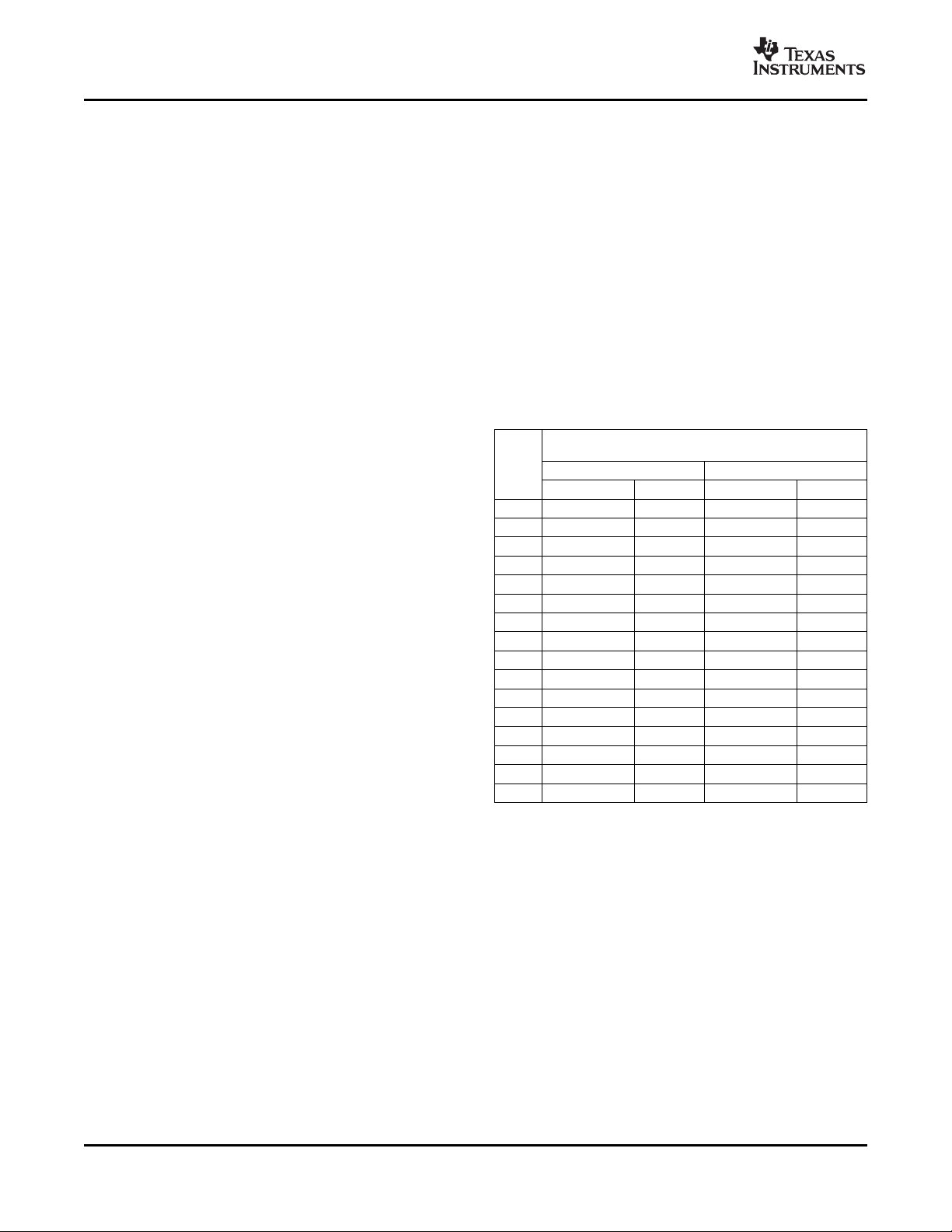
Table 3. Register Map
POINTER
(HEX) POR (HEX) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 REGISTER DESCRIPTION
00 00 LT11 LT10 LT9 LT8 LT7 LT6 LT5 LT4 Local Temperature (High Byte)
01 00 RT11 RT10 RT9 RT8 RT7 RT6 RT5 RT4
02 00 RT11 RT10 RT9 RT8 RT7 RT6 RT5 RT4
03 00 RT11 RT10 RT9 RT8 RT7 RT6 RT5 RT4
08 BUSY 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Status Register
09 00 0 SD 0 0 0 RANGE 0 0 Configuration Register 1
0A 0 REN3
0B 07 0 0 0 0 0 R2 R1 R0 Conversion Rate Register
0F X X X X X X X X One-Shot Start
10 00 LT3 LT2 LT1 LT0 0 0 PVLD 0 Local Temperature (Low Byte)
11 00 RT3 RT2 RT1 RT0 0 0 PVLD OPEN Remote Temperature 1 (Low Byte)
12 00 RT3 RT2 RT1 RT0 0 0 PVLD OPEN
13 00 RT3 RT2 RT1 RT0 0 0 PLVD OPEN Remote Temperature 3 (Low Byte)
21 00 NC7 NC6 NC5 NC4 NC3 NC2 NC1 NC0 N Correction 1
22 00 NC7 NC6 NC5 NC4 NC3 NC2 NC1 NC0 N Correction 2
23 00 NC7 NC6 NC5 NC4 NC3 NC2 NC1 NC0 N Correction 3
FC X X X X X X X X Software Reset
FE 55 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 Manufacturer ID
FF 21 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 TMP422 Device ID
(1) Compatible with Two-Byte Read; see Figure 19 .
(2) TMP422.
(3) TMP423.
(4) X = undefined. Writing any value to this register initiates a one-shot start; see the One-Shot Conversion section.
(5) X = undefined. Writing any value to this register initiates a software reset; see the Software Reset section.
(2)
1C/3C
/
(3)
7C
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 TMP421 Device ID
0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 TMP423 Device ID
(3)
REN2
TEMPERATURE REGISTERS
The TMP421/22/23 have multiple 8-bit registers that
hold temperature measurement results. The local
channel and each of the remote channels have a high
byte register that contains the most significant bits
(MSBs) of the temperature analog-to-digital converter
(ADC) result and a low byte register that contains the
least significant bits (LSBs) of the temperature ADC
result. The local channel high byte address is 00h;
the local channel low byte address is 10h. The
remote channel high byte is at address 01h; the
remote channel low byte address is 11h. For the
TMP422, the second remote channel high byte
address is 02h; the second remote channel low byte
is 12h. The TMP 423 uses the same local and remote
address as the TMP421 and TMP422, with the third
remote channel high byte of 03h; the third remote
channel low byte is 13h. These registers are
read-only and are updated by the ADC each time a
temperature measurement is completed.
BIT DESCRIPTION
Remote Temperature 1
(High Byte)
Remote Temperature 2
(High Byte)
Remote Temperature 3
(High Byte)
(2) (3)
REN LEN RC 0 0 Configuration Register 2
Remote Temperature 2
(Low Byte)
(2) (3)
The TMP421/22/23 contain circuitry to assure that a
low byte register read command returns data from the
same ADC conversion as the immediately preceding
high byte read command. This assurance remains
valid only until another register is read. For proper
operation, the high byte of a temperature register
should be read first. The low byte register should be
read in the next read command. The low byte register
may be left unread if the LSBs are not needed.
Alternatively, the temperature registers may be read
as a 16-bit register by using a single two-byte read
command from address 00h for the local channel
result, or from address 01h for the remote channel
result (02h for the second remote channel result, and
03h for the third remote channel). The high byte is
output first, followed by the low byte. Both bytes of
this read operation are from the same ADC
conversion. The power-on reset value of all
temperature registers is 00h.
(1)
(1)
(1) (2) (3)
(1) (3)
(4)
(3)
(2) (3)
(3)
(5)
12 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
STATUS REGISTER
The Status Register reports the state of the
temperature ADCs. Table 4 summarizes the Status
Register bits. The Status Register is read-only, and is
read by accessing pointer address 08h.
The BUSY bit = '1' if the ADC is making a conversion;
it is set to '0' if the ADC is not converting.
CONFIGURATION REGISTER 1
Configuration Register 1 (pointer address 09h) sets
the temperature range and controls the shutdown
mode. The Configuration Register is set by writing to
pointer address 09h and read by reading from pointer
address 09h. Table 5 summarizes the bits of
Configuration Register 1.
The shutdown (SD) bit (bit 6) enables or disables the
temperature measurement circuitry. If SD = '0', the
TMP421/22/23 convert continuously at the rate set in
the conversion rate register. When SD is set to '1',
the TMP421/22/23 stop converting when the current
conversion sequence is complete and enter a
shutdown mode. When SD is set to '0' again, the
TMP421/22/23 resume continuous conversions.
When SD = '1', a single conversion can be started by
writing to the One-Shot Register. See the One-Shot
Conversion section for more information.
The temperature range is set by configuring the
RANGE bit (bit 2) of the Configuration Register.
Setting this bit low configures the TMP421/22/23 for
the standard measurement range ( – 40 ° C to +127 ° C);
temperature conversions will be stored in the
standard binary format. Setting bit 2 high configures
the TMP421/22/23 for the extended measurement
range ( – 55 ° C to +150 ° C); temperature conversions
will be stored in the extended binary format (see
Table 1 ).
The remaining bits of the Configuration Register are
reserved and must always be set to '0'. The power-on
reset value for this register is 00h.
CONFIGURATION REGISTER 2
Configuration Register 2 (pointer address 0Ah)
controls which temperature measurement channels
are enabled and whether the external channels have
the resistance correction feature enabled or not.
Table 6 summarizes the bits of Configuration
Register 2.
Table 4. Status Register Format
STATUS REGISTER (Read = 08h, Write = NA)
BIT # D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
BIT NAME BUSY 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
POR VALUE 0
(1) FOR TMP421/TMP423: The BUSY changes to '1' almost immediately (< 100 µ s) following power-up, as the TMP421/TMP423 begin the
first temperature conversion. It is high whenever the TMP421/TMP423 convert a temperature reading.
FOR TMP422: The BUSY bit changes to '1' approximately 1ms following power-up. It is high whenever the TMP422 converts a
temperature reading.
(1)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 5. Configuration Register 1 Bit Descriptions
CONFIGURATION REGISTER 1 (Read/Write = 09h, POR = 00h)
BIT NAME FUNCTION VALUE
7 Reserved — 0
6 SD 0
5, 4, 3 Reserved — 0
2 Temperature Range 0
1, 0 Reserved — 0
0 = Run
1 = Shut Down
0 = – 55 ° C to +127 ° C
1 = – 55 ° C to +150 ° C
POWER-ON RESET
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 13
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
The RC bit (bit 2) enables the resistance correction For the TMP423 only, the REN3 bit (bit 6) enables
feature for the external temperature channels. If RC = the third external measurement channel. If REN3 =
'1', series resistance correction is enabled; if RC = '0', '1', the third external channel is enabled; if REN3 =
resistance correction is disabled. Resistance '0', the third external channel is disabled.
correction should be enabled for most applications.
However, disabling the resistance correction may
yield slightly improved temperature measurement
noise performance, and reduce conversion time by
about 50%, which could lower power consumption
when conversion rates of two per second or less are
selected.
The LEN bit (bit 3) enables the local temperature
measurement channel. If LEN = '1', the local channel
is enabled; if LEN = '0', the local channel is disabled.
The REN bit (bit 4) enables external temperature
measurement for channel 1. If REN = '1', the first
external channel is enabled; if REN = '0', the external
channel is disabled.
For the TMP422 and TMP423 only, the REN2 bit (bit
5) enables the second external measurement
channel. If REN2 = '1', the second external channel is
enabled; if REN2 = '0', the second external channel is
disabled.
The temperature measurement sequence is: local
channel, external channel 1, external channel 2,
external channel 3, shutdown, and delay (to set
conversion rate, if necessary). The sequence starts
over with the local channel. If any of the channels are
disabled, they are bypassed in the sequence.
CONVERSION RATE REGISTER
The Conversion Rate Register (pointer address 0Bh)
controls the rate at which temperature conversions
are performed. This register adjusts the idle time
between conversions but not the conversion timing
itself, thereby allowing the TMP421/22/23 power
dissipation to be balanced with the temperature
register update rate. Table 7 describes the
conversion rate options and corresponding current
consumption. A one-shot command can be used
during the idle time between conversions to
immediately start temperature conversions on all
enabled channels.
Table 6. Configuration Register 2 Bit Descriptions
CONFIGURATION REGISTER 2 (Read/Write = 0Ah, POR = 1Ch for TMP421; 3Ch for TMP422; 7Ch for TMP423)
BIT NAME FUNCTION VALUE
7 Reserved — 0
6 REN3
5 REN2
4 REN 1
3 LEN 1
2 RC 1
1, 0 Reserved — 0
0 = External Channel 3 Disabled 1 (TMP423)
1 = External Channel 3 Enabled 0 (TMP421, TMP422)
0 = External Channel 2 Disabled 1 (TMP422, TMP423)
1 = External Channel 2 Enabled 0 (TMP421)
0 = External Channel 1 Disabled
1 = External Channel 1 Enabled
0 = Local Channel Disabled
1 = Local Channel Enabled
0 = Resistance Correction Disabled
1 = Resistance Correction Enabled
POWER-ON RESET
14 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
V
BE2*VBE1
+
nkT
q
ln
ǒ
I
2
I
1
Ǔ
n
eff
+
1.008 300
ǒ
300* N
ADJUST
Ǔ
N
ADJUST
+ 300 *
ǒ
300 1.008
n
eff
Ǔ
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 7. Conversion Rate Register
CONVERSION RATE REGISTER (Read/Write = 0Bh, POR = 07h)
AVERAGE IQ(TYP) ( µ A)
R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0 CONVERSIONS/SEC VS= 2.7V VS= 5.5V
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.0625 11 32
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0.125 17 38
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0.25 28 49
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0.5 47 69
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 80 103
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 2 128 155
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 4
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 8
(1) Conversion rate shown is for only one or two enabled measurement channels. When three channels are enabled, the conversion rate is
2 and 2/3 conversions-per-second. When four channels are enabled, the conversion rate is 2 per second.
(2) Conversion rate shown is for only one enabled measurement channel. When two channels are enabled, the conversion rate is 4
conversions-per-second. When three channels are enabled, the conversion rate is 2 and 2/3 conversions-per-second. When four
channels are enabled, the conversion rate is 2 conversions-per-second.
(1)
(2)
190 220
373 413
ONE-SHOT CONVERSION
When the TMP421/22/23 are in shutdown mode
(SD = 1 in the Configuration Register 1), a single
conversion is started on all enabled channels by
writing any value to the One-Shot Start Register,
pointer address 0Fh. This write operation starts one
conversion; the TMP421/22/23 return to shutdown
mode when that conversion completes. The value of
the data sent in the write command is irrelevant and
is not stored by the TMP421/22/23. When the
TMP421/22/23 are in shutdown mode, the conversion
sequence currently in process must be completed
before a one-shot command can be issued. One-shot
commands issued during a conversion are ignored.
n-FACTOR CORRECTION REGISTER
The TMP421/22/23 allow for a different n-factor value
to be used for converting remote channel
measurements to temperature. The remote channel
uses sequential current excitation to extract a
differential V
the temperature of the remote transistor. Equation 1
describes this voltage and temperature.
voltage measurement to determine
BE
(1)
The value n in Equation 1 is a characteristic of the
particular transistor used for the remote channel. The
power-on reset value for the TMP421/22/23 is n =
1.008. The value in the n-Factor Correction Register
may be used to adjust the effective n-factor according
to Equation 2 and Equation 3 .
(2)
(3)
The n-correction value must be stored in
two's-complement format, yielding an effective data
range from – 128 to +127. The n-correction value may
be written to and read from pointer address 21h. The
n-correction value for the second remote channel
(TMP422 and TMP423) may be written and read from
pointer address 22h. The n-correction value for the
third remote channel (TMP423 only) may be written
to and read from pointer address 23h. The register
power-on reset value is 00h, thus having no effect
unless the register is written to.
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 15
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
SOFTWARE RESET
The TMP421/22/23 may be reset by writing any value
to the Software Reset Register (pointer address
FCh). This action restores the power-on reset state to
all of the TMP421/22/23 registers as well as aborts
any conversion in process. The TMP421/22/23 also
support reset via the two-wire general call address
(0000 0000). The General Call Reset section contains
more information.
Table 8. n-Factor Range
N
ADJUST
BINARY HEX DECIMAL n
0111 1111 7F 127 1.747977
0000 1010 0A 10 1.042759
0000 1000 08 8 1.035616
0000 0110 06 6 1.028571
0000 0100 04 4 1.021622
0000 0010 02 2 1.014765
0000 0001 01 1 1.011371
0000 0000 00 0 1.008
1111 1111 FF – 1 1.004651
1111 1110 FE – 2 1.001325
1111 1100 FC – 4 0.994737
1111 1010 FA – 6 0.988235
1111 1000 F8 – 8 0.981818
1111 0110 F6 – 10 0.975484
1000 0000 80 – 128 0.706542
GENERAL CALL RESET
The TMP421/22/23 support reset via the two-wire
General Call address 00h (0000 0000b). The
TMP421/22/23 acknowledge the General Call
address and respond to the second byte. If the
second byte is 06h (0000 0110b), the TMP421/22/23
execute a software reset. This software reset restores
the power-on reset state to all TMP421/22/23
registers, and aborts any conversion in progress. The
TMP421/22/23 take no action in response to other
values in the second byte.
IDENTIFICATION REGISTERS
The TMP421/22/23 allow for the two-wire bus
controller to query the device for manufacturer and
device IDs to enable software identification of the
device at the particular two-wire bus address. The
manufacturer ID is obtained by reading from pointer
address FEh. The device ID is obtained by reading
from pointer address FFh. The TMP421/22/23 each
return 55h for the manufacturer code. The TMP421
returns 21h for the device ID; the TMP422 returns
22h for the device ID; and the TMP423 returns 23h
for the device ID. These registers are read-only.
BUS OVERVIEW
The TMP421/22/23 are SMBus interface-compatible.
In SMBus protocol, the device that initiates the
transfer is called a master, and the devices controlled
by the master are slaves. The bus must be controlled
by a master device that generates the serial clock
(SCL), controls the bus access, and generates the
START and STOP conditions.
To address a specific device, a START condition is
initiated. START is indicated by pulling the data line
(SDA) from a high-to-low logic level while SCL is
high. All slaves on the bus shift in the slave address
byte, with the last bit indicating whether a read or
write operation is intended. During the ninth clock
pulse, the slave being addressed responds to the
master by generating an Acknowledge and pulling
SDA low.
Data transfer is then initiated and sent over eight
clock pulses followed by an Acknowledge bit. During
data transfer SDA must remain stable while SCL is
high, because any change in SDA while SCL is high
is interpreted as a control signal.
Once all data have been transferred, the master
generates a STOP condition. STOP is indicated by
pulling SDA from low to high, while SCL is high.
SERIAL INTERFACE
The TMP421/22/23 operate only as a slave device on
either the two-wire bus or the SMBus. Connections to
either bus are made via the open-drain I/O lines, SDA
and SCL. The SDA and SCL pins feature integrated
spike suppression filters and Schmitt triggers to
minimize the effects of input spikes and bus noise.
The TMP421/22/23 support the transmission protocol
for fast (1kHz to 400kHz) and high-speed (1kHz to
3.4MHz) modes. All data bytes are transmitted MSB
first.
16 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
DX1
DX2
DX3
DX4
SCL
SDA
V+
Q0
Address=1001100 Address=1001101 Address=1001110 Address=1001111
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
V+
SCL
SDA
GND
Q7
DX1
DX2
DX3
DX4
V+
SCL
SDA
GND
DX1
DX2
DX3
DX4
V+
SCL
SDA
GND
DX1
DX2
DX3
DX4
V+
SCL
SDA
GND
Q6
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
SERIAL BUS ADDRESS
To communicate with the TMP421/22/23, the master
must first address slave devices via a slave address
byte. The slave address byte consists of seven
address bits, and a direction bit indicating the intent
of executing a read or write operation.
Two-Wire Interface Slave Device Addresses
The TMP421 supports nine slave device addresses
and the TMP422 supports four slave device
addresses. The TMP423 has one of two
factory-preset slave addresses.
The slave device address for the TMP421 is set by
the A1 and A0 pins according to Table 9 .
The slave device address for the TMP422 is set by
the connections between the external transistors and
the TMP422 according to Figure 15 and Table 10 . If
one of the channels is unused, the respective DXP
connection should be connected to GND, and the
DXN connection should be left unconnected. The
polarity of the transistor for external channel 2 (pins 3
and 4) sets the least significant bit of the slave
address. The polarity of the transistor for external
channel 1 (pins 1 and 2) sets the next least
significant bit of the slave address.
Table 9. TMP421 Slave Address Options
TWO-WIRE SLAVE
ADDRESS A1 A0
0011 100 Float 0
0011 101 Float 1
0011 110 0 Float
0011 111 1 Float
0101 010 Float Float
1001 100 0 0
1001 101 0 1
1001 110 1 0
1001 111 1 1
Table 10. TMP422 Slave Address Options
TWO-WIRE SLAVE ADDRESS DX1 DX2 DX3 DX4
1001 100 DXP1 DXN1 DXP2 DXN2
1001 101 DXP1 DXN1 DXN2 DXP2
1001 110 DXN1 DXP1 DXP2 DXN2
1001 111 DXN1 DXP1 DXN2 DXP2
Figure 15. TMP422 Connections for Device Address Setup
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 17
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
The TMP422 checks the polarity of the external
transistor at power-on, or after software reset, by
forcing current to pin 1 while connecting pin 2 to
approximately 0.6V. If the voltage on pin 1 does not
pull up to near the V+ of the TMP422, pin 1 functions
as DXP for channel 1, and the second LSB of the
slave address is '0'. If the voltage on pin 1 does pull
up to near V+, the TMP422 forces current to pin 2
while connecting pin 1 to 0.6V. If the voltage on pin 2
does not pull up to near V+, the TMP422 uses pin 2
for DXP of channel 1, and sets the second LSB of the
slave address to '1'. If both pins are shorted to GND
or if both pins are open, the TMP422 uses pin 1 as
DXP and sets the address bit to '0'. This process is
then repeated for channel 2 (pins 3 and 4).
If the TMP422 is to be used with transistors that are
located on another IC (such as a CPU, DSP, or
graphics processor), it is recommended to use pin 1
or pin 3 as DXP to ensure correct address detection.
If the other IC has a lower supply voltage or is not
powered when the TMP422 tries to detect the slave
address, a protection diode may turn on during the
detection process and the TMP422 may incorrectly
choose the DXP pin and corresponding slave
address. Using pin 1 and/or pin 3 for transistors that
are on other ICs ensures correct operation
independent of supply sequencing or levels.
The TMP423 has a factory-preset slave address. The
TMP423A slave address is 1001100b, and the
TMP423B slave address is 1001101b. The
configuration of the DXP and DXN channels are
independent of the address. Unused DXP channels
can be left open or tied to GND.
READ/WRITE OPERATIONS
Accessing a particular register on the TMP421/22/23
is accomplished by writing the appropriate value to
the Pointer Register. The value for the Pointer
Register is the first byte transferred after the slave
address byte with the R/ W bit low. Every write
operation to the TMP421/22/23 requires a value for
the Pointer Register (see Figure 17 ).
When reading from the TMP421/22/23, the last value
stored in the Pointer Register by a write operation is
used to determine which register is read by a read
operation. To change which register is read for a read
operation, a new value must be written to the Pointer
Register. This transaction is accomplished by issuing
a slave address byte with the R/ W bit low, followed
by the Pointer Register byte; no additional data are
required. The master can then generate a START
condition and send the slave address byte with the
R/ W bit high to initiate the read command. See
Figure 19 for details of this sequence. If repeated
reads from the same register are desired, it is not
necessary to continually send the Pointer Register
bytes, because the TMP421/22/23 retain the Pointer
Register value until it is changed by the next write
operation. Note that register bytes are sent MSB first,
followed by the LSB.
Read operations should be terminated by issuing a
Not-Acknowledge command at the end of the last
byte to be read. For a single-byte operation, the
master should leave the SDA line high during the
Acknowledge time of the first byte that is read from
the slave. For a two-byte read operation, the master
must pull SDA low during the Acknowledge time of
the first byte read, and should leave SDA high during
the Acknowledge time of the second byte read from
the slave.
18 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
SCL
SDA
t
(LOW)
t
R
t
F
t
(HDSTA)
t
(HDSTA)
t
(HDDAT)
t
(BUF)
t
(SUDAT)
t
(HIGH)
t
(SUSTA)
t
(SUSTO)
P S S P
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
TIMING DIAGRAMS
The TMP421/22/23 are two-wire and
SMBus-compatible. Figure 16 to Figure 19 describe
the timing for various operations on the
Data Transfer: The number of data bytes transferred
between a START and a STOP condition is not
limited and is determined by the master device. The
receiver acknowledges data transfer.
TMP421/22/23. Parameters for Figure 16 are defined Acknowledge: Each receiving device, when
in Table 11 . Bus definitions are: addressed, is obliged to generate an Acknowledge
Bus Idle: Both SDA and SCL lines remain high.
Start Data Transfer: A change in the state of the
SDA line, from high to low, while the SCL line is high,
defines a START condition. Each data transfer
initiates with a START condition. Denoted as S in
Figure 16 .
Stop Data Transfer: A change in the state of the
bit. A device that acknowledges must pull down the
SDA line during the Acknowledge clock pulse in such
a way that the SDA line is stable low during the high
period of the Acknowledge clock pulse. Setup and
hold times must be taken into account. On a master
receive, data transfer termination can be signaled by
the master generating a Not-Acknowledge on the last
byte that has been transmitted by the slave.
SDA line from low to high while the SCL line is high
defines a STOP condition. Each data transfer
terminates with a repeated START or STOP
condition. Denoted as P in Figure 16 .
Figure 16. Two-Wire Timing Diagram
Table 11. Timing Characteristics for Figure 16
FAST MODE HIGH-SPEED MODE
PARAMETER MIN MAX MIN MAX UNIT
SCL Operating Frequency f
Bus Free Time Between STOP and START Condition t
Hold time after repeated START condition. After this period, the first clock
is generated.
Repeated START Condition Setup Time t
STOP Condition Setup Time t
Data Hold Time t
Data Setup Time t
SCL Clock LOW Period t
SCL Clock HIGH Period t
Clock/Data Fall Time t
Clock/Data Rise Time t
for SCL ≤ 100kHz t
t
(HDSTA)
(SUSTA)
(SUSTO)
(HDDAT)
(SUDAT)
(LOW)
(HIGH)
(1) For cases with fall time of SCL less than 20ns and/or the rise or fall time of SDA less than 20ns, the hold time should be greater than
20ns.
(2) For cases with a fall time of SCL less than 10ns and/or the rise or fall time of SDA less than 10ns, the hold time should be greater than
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 19
10ns.
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423
0.001 0.4 0.001 3.4 MHz
(SCL)
(BUF)
600 160 ns
100 100 ns
100 100 ns
100 100 ns
(1)
0
100 10 ns
1300 160 ns
600 60 ns
F
R
R
(2)
0
300 160 ns
300 160
1000
ns
ns

www.ti.com
Frame1Two-WireSlaveAddressByte
Frame2PointerRegisterByte
1
StartBy
Master
ACKBy
TMP421/22/23
ACKBy
TMP421/22/23
1 9 1
Frame3DataByte1
ACKBy
TMP421/22/23
1
D7
SDA
(Continued)
SCL
(Continued)
D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
9
9
SDA
SCL
0 0 1 1 0 0
(1)
R/W P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 P0
¼
¼
StopBy
Master
Frame1Two-WireSlaveAddressByte Frame2PointerRegisterByte
1
StartBy
Master
ACKBy
TMP421/22/23
ACKBy
TMP421/22/23
Frame3Two-WireSlaveAddressByte Frame4DataByte1ReadRegister
StartBy
Master
ACKBy
TMP421/22/23
NACKBy
Master
(2)
From
TMP421/22/23
1 9 1
9
1 9 1
9
SDA
SCL
0 0 1 R/
W P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 P0
¼
¼
¼
¼
SDA
(Continued)
SCL
(Continued)
1 0 0 1
1 0 0
(1)
1 0 0
(1)
R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
(1) Slave address 1001100 shown.
Figure 17. Two-Wire Timing Diagram for Write Word Format
(1) Slave address 1001100 shown.
(2) Master should leave SDA high to terminate a single-byte read operation.
Figure 18. Two-Wire Timing Diagram for Single-Byte Read Format
20 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
Frame1Two-WireSlaveAddressByte Frame2PointerRegisterByte
1
StartBy
Master
ACKBy
TMP421/22/23
ACKBy
TMP421/22/23
Frame3Two-WireSlaveAddressByte Frame4DataByte1ReadRegister
StartBy
Master
ACKBy
TMP421/22/23
ACKBy
Master
From
TMP421/22/23
1 9 1
9
1 9 1
9
SDA
SCL
0 0 1 R/
W P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 P0
¼
¼
¼
¼
SDA
(Continued)
SCL
(Continued)
SDA
(Continued)
SCL
(Continued)
1 0 0 1
1 0 0
(1)
1 0 0
(1)
R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Frame5DataByte2ReadRegister
StopBy
Master
NACKBy
Master
(2)
From
TMP421/22/23
1
9
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
(1) Slave address 1001100 shown.
(2) Master should leave SDA high to terminate a two-byte read operation.
Figure 19. Two-Wire Timing Diagram for Two-Byte Read Format
HIGH-SPEED MODE TIMEOUT FUNCTION
In order for the two-wire bus to operate at frequencies The TMP421/22/23 reset the serial interface if either
above 400kHz, the master device must issue a SCL or SDA are held low for 30ms (typical) between
High-Speed mode (Hs-mode) master code (0000 a START and STOP condition. If the TMP421/22/23
1xxx) as the first byte after a START condition to are holding the bus low, the device releases the bus
switch the bus to high-speed operation. The and waits for a START condition. To avoid activating
TMP421/22/23 do not acknowledge this byte, but the timeout function, it is necessary to maintain a
switch the input filters on SDA and SCL and the communication speed of at least 1kHz for the SCL
output filter on SDA to operate in Hs-mode, allowing operating frequency.
transfers at up to 3.4MHz. After the Hs-mode master
code has been issued, the master transmits a
two-wire slave address to initiate a data transfer
operation. The bus continues to operate in Hs-mode
until a STOP condition occurs on the bus. Upon
receiving the STOP condition, the TMP421/22/23
switch the input and output filters back to fast mode
operation.
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 21
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
T
ERR
+
ǒ
n * 1.008
1.008
Ǔ
ǒ
273.15) Tǒ°C
Ǔ
Ǔ
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
SHUTDOWN MODE (SD)
The TMP421/22/23 Shutdown Mode allows the user
to save maximum power by shutting down all device
circuitry other than the serial interface, reducing
current consumption to typically less than 3 µ A; see
Figure 10 , Shutdown Quiescent Current vs Supply
Voltage. Shutdown Mode is enabled when the SD bit
(bit 6) of Configuration Register 1 is high; the device
shuts down once the current conversion is completed.
When SD is low, the device maintains a continuous
conversion state.
SENSOR FAULT
The TMP421 can sense a fault at the DXP input
resulting from incorrect diode connection. The
TMP421/22/23 can all sense an open circuit.
Short-circuit conditions return a value of – 64 ° C. The
detection circuitry consists of a voltage comparator
that trips when the voltage at DXP exceeds
(V+) – 0.6V (typical). The comparator output is
continuously checked during a conversion. If a fault is
detected, the OPEN bit (bit 0) in the temperature
result register is set to '1' and the rest of the register
bits should be ignored.
When not using the remote sensor with the TMP421,
the DXP and DXN inputs must be connected together
to prevent meaningless fault warnings. When not
using a remote sensor with the TMP422, the DX pins
should be connected (refer to Table 10 ) such that
DXP connections are grounded and DXN connections
are left open (unconnected). Unused TMP423 DXP
pins can be left open or connected to GND.
UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT
The TMP421/22/23 sense when the power-supply
voltage has reached a minimum voltage level for the
ADC to function. The detection circuitry consists of a
voltage comparator that enables the ADC after the
power supply (V+) exceeds 2.45V (typical). The
comparator output is continuously checked during a
conversion. The TMP421/22/23 do not perform a
temperature conversion if the power supply is not
valid. The PVLD bit (bit 1, see Table 3 ) of the
individual Local/Remote Temperature Register is set
to '1' and the temperature result may be incorrect.
FILTERING
Remote junction temperature sensors are usually
implemented in a noisy environment. Noise is most
often created by fast digital signals, and it can corrupt
measurements. The TMP421/22/23 have a built-in
65kHz filter on the inputs of DXP and DXN
(TMP421/TMP423), or on the inputs of DX1 through
DX4 (TMP422), to minimize the effects of noise.
However, a bypass capacitor placed differentially
across the inputs of the remote temperature sensor is
recommended to make the application more robust
against unwanted coupled signals. The value of this
capacitor should be between 100pF and 1nF. Some
applications attain better overall accuracy with
additional series resistance; however, this increased
accuracy is application-specific. When series
resistance is added, the total value should not be
greater than 3k Ω . If filtering is needed, suggested
component values are 100pF and 50 Ω on each input;
exact values are application-specific.
REMOTE SENSING
The TMP421/22/23 are designed to be used with
either discrete transistors or substrate transistors built
into processor chips and ASICs. Either NPN or PNP
transistors can be used, as long as the base-emitter
junction is used as the remote temperature sense.
NPN transistors must be diode-connected. PNP
transistors can either be transistor- or
diode-connected (see Figure 11 , Figure 12 , and
Figure 13 ).
Errors in remote temperature sensor readings are
typically the consequence of the ideality factor and
current excitation used by the TMP421/22/23 versus
the manufacturer-specified operating current for a
given transistor. Some manufacturers specify a
high-level and low-level current for the
temperature-sensing substrate transistors. The
TMP421/22/23 use 6 µ A for I
The ideality factor ( n) is a measured characteristic of
a remote temperature sensor diode as compared to
an ideal diode. The TMP421/22/23 allow for different
n-factor values; see the N-Factor Correction Register
section.
The ideality factor for the TMP421/22/23 is trimmed
to be 1.008. For transistors that have an ideality
factor that does not match the TMP421/22/23,
Equation 4 can be used to calculate the temperature
error. Note that for the equation to be used correctly,
actual temperature ( ° C) must be converted to kelvins
(K).
Where:
n = ideality factor of remote temperature sensor
T( ° C) = actual temperature
T
= error in TMP421/22/23 because n ≠ 1.008
ERR
Degree delta is the same for ° C and K
and 120 µ A for I
LOW
HIGH
.
(4)
22 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
T
ERR
+
ǒ
1.004* 1.008
1.008
Ǔ
ǒ
273.15) 100°C
Ǔ
T
ERR
+ 1.48°C
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
For n = 1.004 and T( ° C) = 100 ° C: power dissipated as a result of exciting the remote
temperature sensor is negligible because of the small
currents used. For a 5.5V supply and maximum
conversion rate of eight conversions per second, the
TMP421/22/23 dissipate 2.3mW (PD
If a discrete transistor is used as the remote
temperature sensor with the TMP421/22/23, the best
accuracy can be achieved by selecting the transistor
according to the following criteria:
1. Base-emitter voltage > 0.25V at 6 µ A, at the
highest sensed temperature.
2. Base-emitter voltage < 0.95V at 120 µ A, at the
lowest sensed temperature.
3. Base resistance < 100 Ω .
4. Tight control of V
small variations in h
Based on these criteria, two recommended
small-signal transistors are the 2N3904 (NPN) or
2N3906 (PNP).
characteristics indicated by
BE
(that is, 50 to 150).
FE
MEASUREMENT ACCURACY AND THERMAL
(5)
415 µ A). A θ
temperature to rise approximately +0.23 ° C above the
ambient.
of 100 ° C/W causes the junction
JA
LAYOUT CONSIDERATIONS
Remote temperature sensing on the TMP421/22/23
measures very small voltages using very low
currents; therefore, noise at the IC inputs must be
minimized. Most applications using the
TMP421/22/23 will have high digital content, with
several clocks and logic level transitions creating a
noisy environment. Layout should adhere to the
following guidelines:
1. Place the TMP421/22/23 as close to the remote
junction sensor as possible.
2. Route the DXP and DXN traces next to each
other and shield them from adjacent signals
through the use of ground guard traces; see
CONSIDERATIONS Figure 20 . If a multilayer PCB is used, bury these
The temperature measurement accuracy of the
TMP421/22/23 depends on the remote and/or local
temperature sensor being at the same temperature
as the system point being monitored. Clearly, if the
temperature sensor is not in good thermal contact
with the part of the system being monitored, then
there will be a delay in the response of the sensor to
a temperature change in the system. For remote
temperature-sensing applications using a substrate
transistor (or a small, SOT23 transistor) placed close 4. Use a 0.1 µ F local bypass capacitor directly
to the device being monitored, this delay is usually between the V+ and GND of the TMP421/22/23;
not a concern. see Figure 21 . Minimize filter capacitance
The local temperature sensor inside the
TMP421/22/23 monitors the ambient air around the
device. The thermal time constant for the
TMP421/22/23 is approximately two seconds. This
constant implies that if the ambient air changes
quickly by 100 ° C, it would take the TMP421/22/23
about 10 seconds (that is, five thermal time
constants) to settle to within 1 ° C of the final value. In
most applications, the TMP421/22/23 package is in
electrical, and therefore thermal, contact with the
printed circuit board (PCB), as well as subjected to
forced airflow. The accuracy of the measured
temperature directly depends on how accurately the
PCB and forced airflow temperatures represent the 6. Thoroughly clean and remove all flux residue in
temperature that the TMP421/22/23 is measuring. and around the pins of the TMP421/22/23 to
Additionally, the internal power dissipation of the avoid temperature offset readings as a result of
TMP421/22/23 can cause the temperature to rise leakage paths between DXP or DXN and GND,
above the ambient or PCB temperature. The internal or between DXP or DXN and V+.
traces between ground or V
them from extrinsic noise sources. 5 mil
(0.127mm) PCB traces are recommended.
3. Minimize additional thermocouple junctions
caused by copper-to-solder connections. If these
junctions are used, make the same number and
approximate locations of copper-to-solder
connections in both the DXP and DXN
connections to cancel any thermocouple effects.
between DXP and DXN to 1000pF or less for
optimum measurement performance. This
capacitance includes any cable capacitance
between the remote temperature sensor and the
TMP421/22/23.
5. If the connection between the remote
temperature sensor and the TMP421/22/23 is
less than 8 in (20.32 cm) long, use a twisted-wire
pair connection. Beyond 8 in, use a twisted,
shielded pair with the shield grounded as close to
the TMP421/22/23 as possible. Leave the remote
sensor connection end of the shield wire open to
avoid ground loops and 60Hz pickup.
DD
IQ
planes to shield
= 5.5V ×
Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 23
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

www.ti.com
V+
DXP
DXN
GND
GroundorV+layer
onbottomand/or
top,ifpossible.
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
TMP421
0.1mFCapacitor
V+
GND
PCBVia
DXP
DXN
A1
A0
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
TMP422
0.1mFCapacitor
V+
GND
PCBVia
DX1
DX2
DX3
DX4
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
TMP423
0.1mFCapacitor
V+
GND
PCBVia
DXP1
DXP2
DXP3
DXN
TMP421
TMP422
TMP423
SBOS398B – JULY 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
NOTE: Use minimum 5 mil (0.127mm) traces with 5 mil spacing.
Figure 20. Suggested PCB Layer Cross-Section
Figure 21. Suggested Bypass Capacitor Placement and Trace Shielding
24 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TMP421 TMP422 TMP423

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
27-Mar-2008
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
TMP421AIDCNR ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TMP421AIDCNRG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TMP421AIDCNT ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 250 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TMP421AIDCNTG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 250 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TMP422AIDCNR ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TMP422AIDCNRG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TMP422AIDCNT ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 250 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TMP422AIDCNTG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 250 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TMP423AIDCNR ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TMP423AIDCNT ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 250 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TMP423BIDCNR ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TMP423BIDCNT ACTIVE SOT-23 DCN 8 250 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
(3)
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and
package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS
compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
Addendum-Page 1

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
27-Mar-2008
Addendum-Page 2

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION
13-May-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package
Type
TMP421AIDCNR SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q1
TMP421AIDCNT SOT-23 DCN 8 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q1
TMP422AIDCNR SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q1
TMP422AIDCNT SOT-23 DCN 8 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q1
TMP423AIDCNR SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q1
TMP423AIDCNT SOT-23 DCN 8 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q1
TMP423BIDCNR SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q1
TMP423BIDCNT SOT-23 DCN 8 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q1
Package
Drawing
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0 (mm) B0 (mm) K0 (mm) P1
(mm)W(mm)
Pin1
Quadrant
Pack Materials-Page 1

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
13-May-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
TMP421AIDCNR SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TMP421AIDCNT SOT-23 DCN 8 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
TMP422AIDCNR SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TMP422AIDCNT SOT-23 DCN 8 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
TMP423AIDCNR SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TMP423AIDCNT SOT-23 DCN 8 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
TMP423BIDCNR SOT-23 DCN 8 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TMP423BIDCNT SOT-23 DCN 8 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
Pack Materials-Page 2


IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless

 Loading...
Loading...