Datasheet TLV571EVM, TLV571IPW, TLV571IPWR, TLV571IDWR, TLV571IDW Datasheet (Texas Instruments)
TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
features
D
Fast Throughput Rate: 1.25 MSPS at 5 V,
625 KSPS at 3 V
D
Wide Analog Input: 0 V to AV
DD
D
Differential Nonlinearity Error: < ± 0.5 LSB
D
Integral Nonlinearity Error: < ± 0.5 LSB
D
Single 2.7-V to 5.5-V Supply Operation
D
Low Power: 12 mW at 3 V and 35 mW at 5 V
D
Auto Power Down of 1 mA Max
D
Software Power Down: 10 µA Max
D
Internal OSC
D
Hardware Configurable
D
DSP and Microcontroller Compatible
Parallel Interface
D
Binary/Twos Complement Output
D
Hardware Controlled Extended Sampling
D
Hardware or Software Start of Conversion
applications
D
Mass Storage and HDD
D
Automotive
D
Digital Servos
D
Process Control
D
General-Purpose DSP
D
Image Sensor Processing
description
The TLV571 is an 8-bit data acquisition system
that combines a high-speed 8-bit ADC and a
parallel interface. The device contains two on-chip control registers allowing control of software conversion start
and power down via the bidirectional parallel port. The control registers can be set to a default mode using a
dummy RD
while WR is tied low allowing the registers to be hardware configurable.
The TL V571 operates from a single 2.7-V to 5.5-V power supply. It accepts an analog input range from 0 V to
AVDD and digitizes the input at a maximum 1.25 MSPS throughput rate at 5 V . The power dissipations are only
12 mW with a 3-V supply or 35 mW with a 5-V supply. The device features an auto power-down mode that
automatically powers down to 1 mA 50 ns after conversion is performed. In software power-down mode, the
ADC is further powered down to only 10 µA.
Very high throughput rate, simple parallel interface, and low power consumption make the TLV571 an ideal
choice for high-speed digital signal processing.
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PACKAGE
T
A
24 TSSOP
(PW)
24 SOIC
(DW)
–40°C to 85°C TLV571IPW TLV571IDW
Copyright 2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
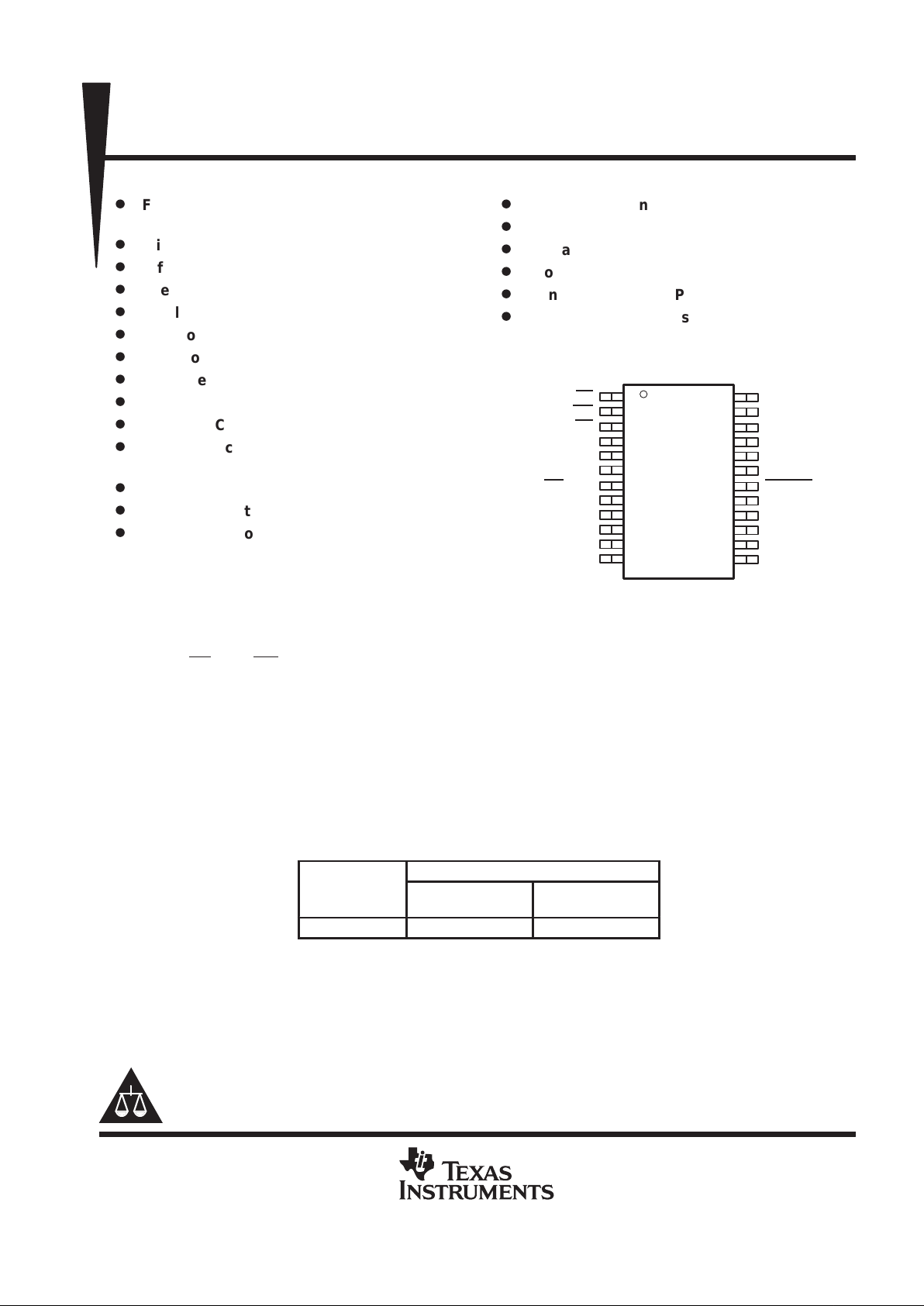
NC – No internal connection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
CS
WR
RD
CLK
DGND
DV
DD
INT/EOC
DGND
DGND
D0
D1
D2
NC
AIN
AV
DD
AGND
REFM
REFP
CSTART
A1/D7
A0/D6
D5
D4
D3
DW OR PW PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
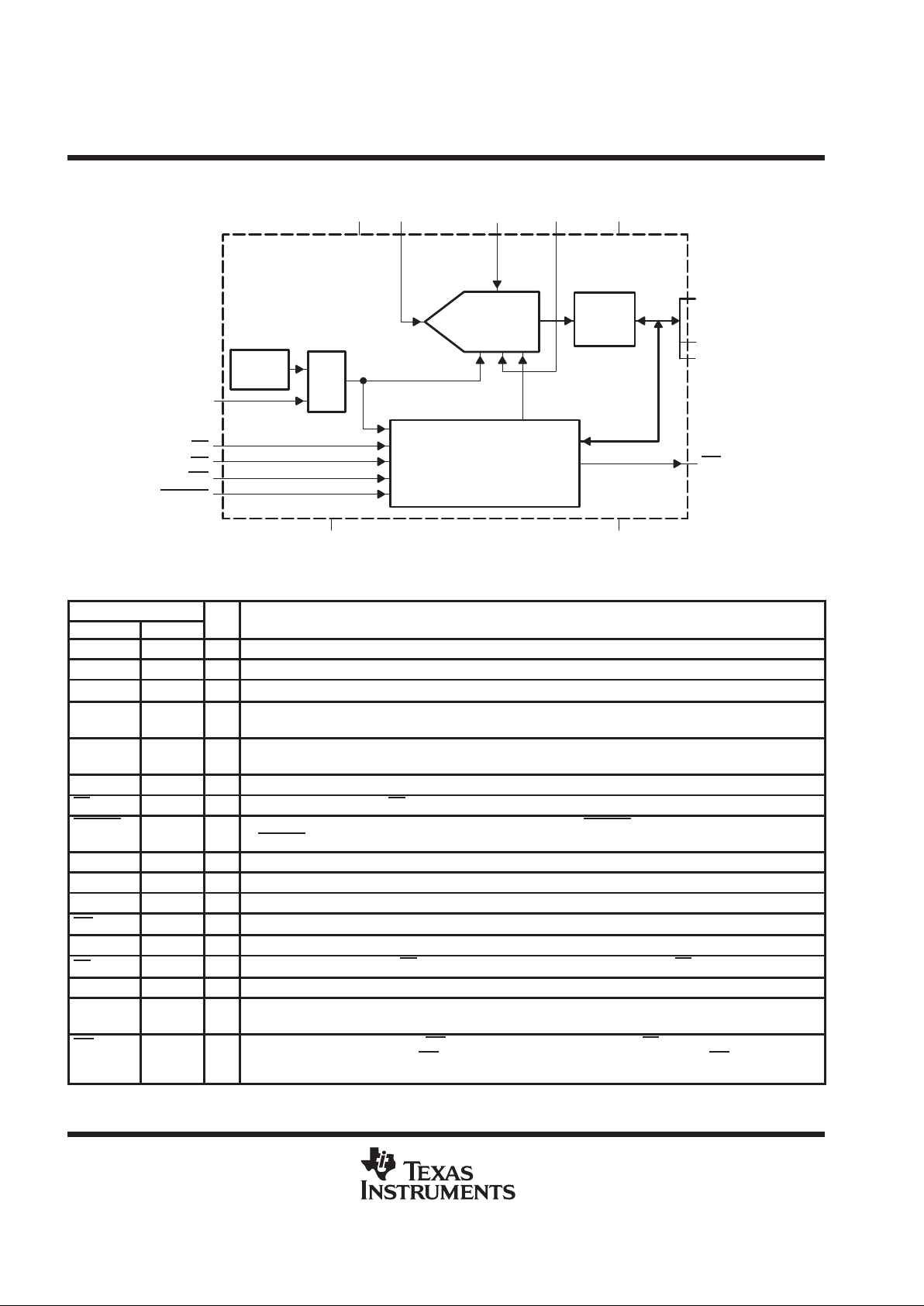
functional block diagram
Internal
Clock
CLK
CS
RD
INT/EOC
MUX
8-BIT
SAR ADC
Input Registers
and Control Logic
WR
CSTART
REFP
Three
State
Latch
AV
DD
D0 – D5
D6/A0
D7/A1
REFM DV
DD
DGNDAGND
AIN
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
I/O
DESCRIPTION
AGND 21 Analog ground
AIN 23 I ADC analog input
AV
DD
22 Analog supply voltage, 2.7 V to 5.5 V
A0/D6 16 I/O Bidirectional 3-state data bus. D6/A0 along with D7/A1 is used as address lines to access CR0 and CR1 for
initialization.
A1/D7 17 I/O Bidirectional 3-state data bus. D7/A1 along with D6/A0 is used as address lines to access CR0 and CR1 for
initialization.
CLK 4 I External clock input
CS 1 I Chip select. A logic low on CS enables the TLV571.
CSTAR T 18 I Hardware sample and conversion start input. The falling edge of CST AR T starts sampling and the rising edge
of CSTART
starts conversion.
DGND 5, 8, 9 Digital ground
DV
DD
6 Digital supply voltage, 2.7 V to 5.5 V
D0 – D5 10–15 I/O Bidirectional 3-state data bus
INT/EOC
7 O End-of-conversion/interrupt
NC 24 Not connected
RD
3 I Read data. A falling edge on RD enables a read operation on the data bus when CS is low.
REFM 20 I Lower reference voltage (nominally ground). REFM must be supplied or REFM pin must be grounded.
REFP 19 I Upper reference voltage (nominally AVDD). The maximum input voltage range is determined by the difference
between the voltage applied to REFP and REFM.
WR
2 I Write data. A rising edge on the WR latches in configuration data when CS is low. When using software
conversion start, a rising edge on WR
also initiates an internal sampling start pulse. When WR is tied to ground,
the ADC in nonprogrammable (hardware configuration mode).
TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
detailed description
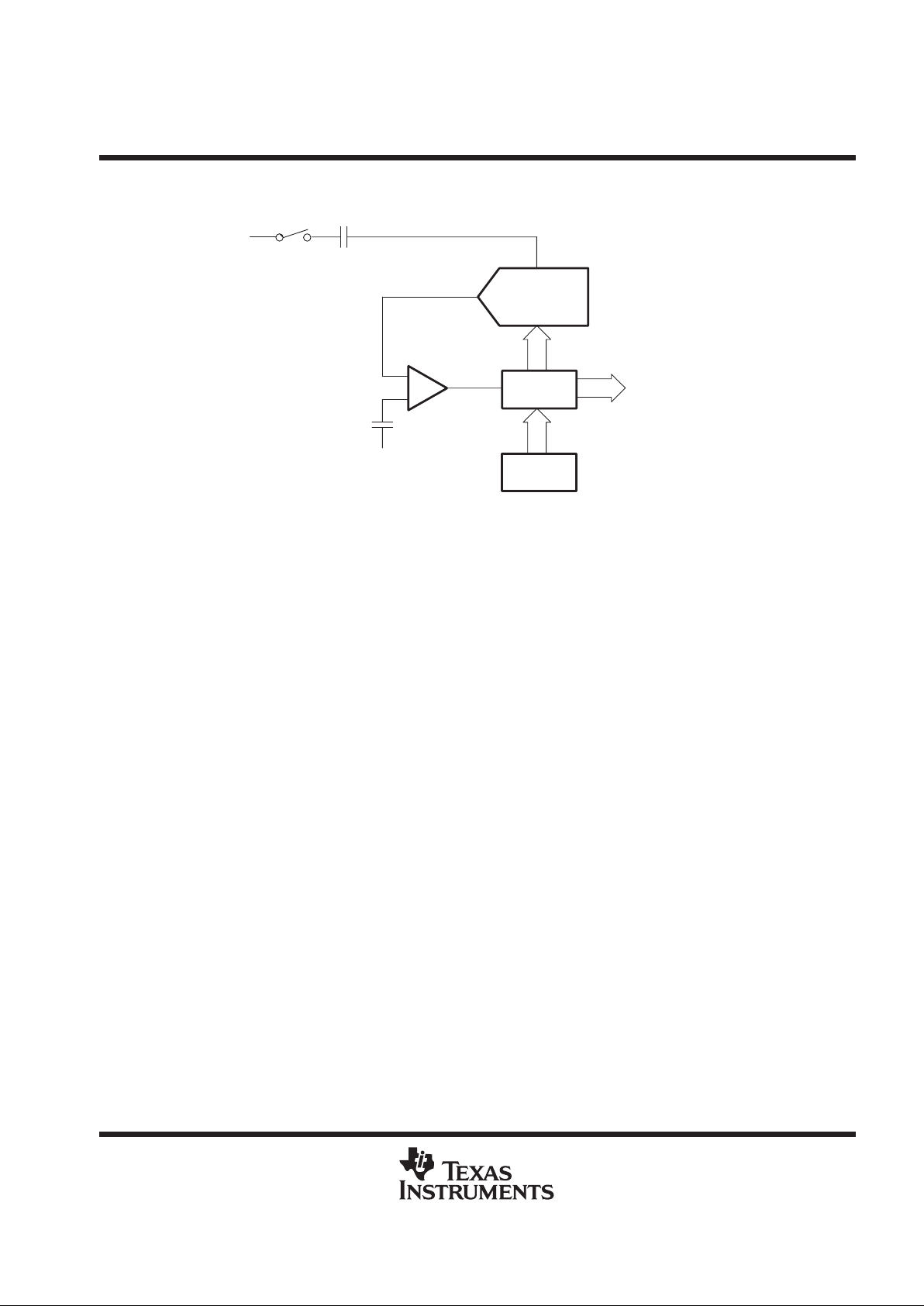
analog-to-digital SAR converter
_
+
Charge
Redistribution
DAC
SAR
Register
REFM
ADC Code
Control
Logic
Ain
Figure 1
The TLV571 is a successive-approximation ADC utilizing a charge redistribution DAC. Figure 1 shows a
simplified version of the ADC.
The sampling capacitor acquires the signal on Ain during the sampling period. When the conversion process
starts, the SAR control logic and charge redistribution DAC are used to add and subtract fixed amounts of charge
from the sampling capacitor to bring the comparator into a balanced condition. When the comparator is
balanced, the conversion is complete and the ADC output code is generated.
sampling frequency, f
s
The TLV571 requires 16 CLKs for each conversion, therefore the equivalent maximum sampling frequency
achievable with a given CLK frequency is:
f
s(max)
= (1/16) f
CLK
The TL V571 is software configurable. The first two MSB bits, D(7,6) are used to address which register to set.
The remaining six bits are used as control data bits. There are two control registers, CR0 and CR1, that are user
configurable. All of the register bits are written to the control register during write cycles. A description of the
control registers is shown in Figure 2.
TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
detailed description (continued)
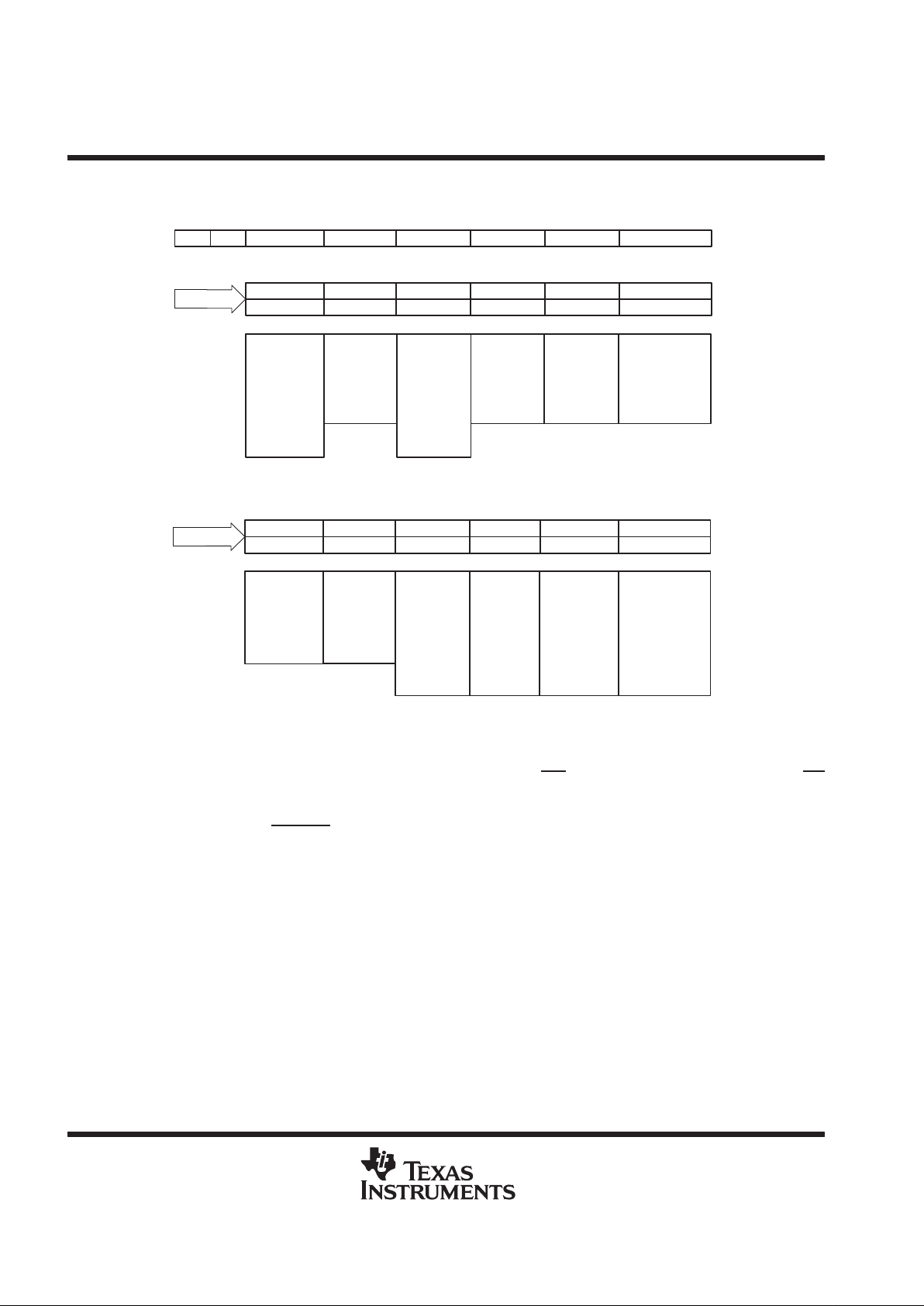
control registers
0:
Binary
1:
2’s
Complement
0:
Reserved
Bit,
Always
Write 0
0:
INT. OSC.
SLOW
1:
INT. OSC.
FAST
STARTSEL
A1 A0 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0D5
Control Register Zero (CR0)
D4D5 D3 D2 D1 D0
PROGEOC
CLKSEL SWPWDN Don’t Care
0:
HARDWARE
START
(CSTART)
A(1:0)=00
1:
SOFTWARE
START
0:
INT
1:
EOC
0:
Internal
Clock
1:
External
Clock
0:
NORMAL
1:
Powerdown
Reserved
Control Register One (CR1)
D4D5 D1 D0
OSCSPD 0 Reserved 0 Reserved OUTCODE Reserved
0:
Reserved
Bit
Always
Write 0
A(1:0)=01
0:
Reserved
Bit
Always
Write 0
D3 D2
Don’t Care
Don’t Care
Don’t Care
0:
Reserved
Bit,
Always
Write 0
Figure 2. Input Data Format
hardware configuration option
The TLV571 can configure itself. This option is enabled when the WR
pin is tied to ground and a dummy RD
signal is applied. The ADC is now fully configured. Zeros or default values are applied to both control registers.
The ADC is configured ideally for 3-V operation, which means the internal OSC is set at 10 MHz and hardware
start of conversion using CSTART.
ADC conversion modes
The TLV571 provides two start of conversion modes. Table 1 explains these modes in more detail.
TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
5
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
detailed description (continued)
Table 1. Conversion Modes
START OF
CONVERSION
OPERATION COMMENTS – FOR INPUT
Hardware start
(CSTAR T)
CR0.D5 = 0
• Repeated conversions from AIN
• CSTART
falling edge to start sampling
• CSTART
rising edge to start conversion
• If in INT mode, one INT
pulse generated after each conversion
• If in EOC mode, EOC will go high to low at start of conversion, and return high
at end of conversion.
CSTAR T rising edge must be applied
a minimum of 5 ns before or after CLK
rising edge.
Software start
CR0.D5 = 1
• Repeated conversions from AIN
• WR
rising edge to start sampling initially. Thereafter, sampling occurs at the
rising edge of RD
.
• Conversion begins after 6 clocks after sampling has begun. Thereafter, if in INT
mode, one INT
pulse generated after each conversion
• If in EOC mode, EOC will go high to low at start of conversion and return high at
end of conversion.
With external clock, WR and RD rising
edge must be a minimum 5 ns before
or after CLK rising edge.
configure the device
The device can be configured by writing to control registers CR0 and CR1.
Table 2. TLV571 Programming Examples
INDEX
REGISTER
D7 D6
D5D4D3D2D1
D0
COMMENT
EXAMPLE1
CR0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Normal, INT OSC
CR1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 Binary
EXAMPLE2
CR0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 Power down, EXT OSC
CR1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 2’s complement output
power down
The TLV571 offers two power down modes, auto power down and software power down. This device will
automatically proceed to auto power down mode if RD is not present one clock after conversion. Software power
down is controlled directly by the user by pulling CS to DVDD.
Table 3. Power Down Modes
PARAMETERS/MODES AUTO POWER DOWN
SOFTWARE POWER DOWN
(CS
= DVDD)
Maximum power down dissipation current 1 mA 10 µA
Comparator Power down Power down
Clock buffer Power down Power down
Control registers Saved Saved
Minimum power down time 1 CLK 2 CLK
Minimum resume time 1 CLK 2 CLK
TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
detailed description (continued)
reference voltage input
The TL V571 has two reference input pins: REFP and REFM. The voltage levels applied to these pins establish
the upper and lower limits of the analog inputs to produce a full-scale and zero-scale reading respectively . The
values of REFP, REFM, and the analog input should not exceed the positive supply or be less than GND
consistent with the specified absolute maximum ratings. The digital output is at full scale when the input signal
is equal to or higher than REFP and is at zero when the input signal is equal to or lower than REFM.
sampling/conversion
All sampling, conversion, and data output in the device are started by a trigger. This could be the RD, WR, or
CST ART signal depending on the mode of conversion and configuration. The rising edge of RD, WR, and
CSTART signal are extremely important, since they are used to start the conversion. These edges need to stay
close to the rising edge of the external clock (if it is used as CLK). The minimum setup and hold time with respect
to the rising edge of the external clock should be 5 ns minimum. When the internal clock is used, this is not an
issue since these two edges will start the internal clock automatically . Therefore, the setup time is always met.
Software controlled sampling lasts 6 clock cycles. This is done via the CLK input or the internal oscillator if
enabled. The input clock frequency can be 1 MHz to 20 MHz, translating into a sampling time from 0.6 µs to
0.3 µs. The internal oscillator frequency is 9 MHz minimum (ocillator frequency is between 9 MHz to 22 MHz),
translating into a sampling time from 0.6 µs to 0.3 µs. Conversion begins immediately after sampling and lasts
10 clock cycles. This is again done using the external clock input (1 MHz–20 MHz) or the internal oscillator
(9 MHz minimum) if enabled. Hardware controlled sampling, via CST AR T
, begins on falling CST AR T lasts the
length of the active CSTART
signal. This allows more control over the sampling time, which is useful when
sampling sources with large output impedances. On rising CSTART, conversion begins. Conversion in
hardware controlled mode also lasts 10 clock cycles. This is done using the external clock input (1 MHz–20 MHz)
or the internal oscillator (9 MHz minimum) as is the case in software controlled mode.
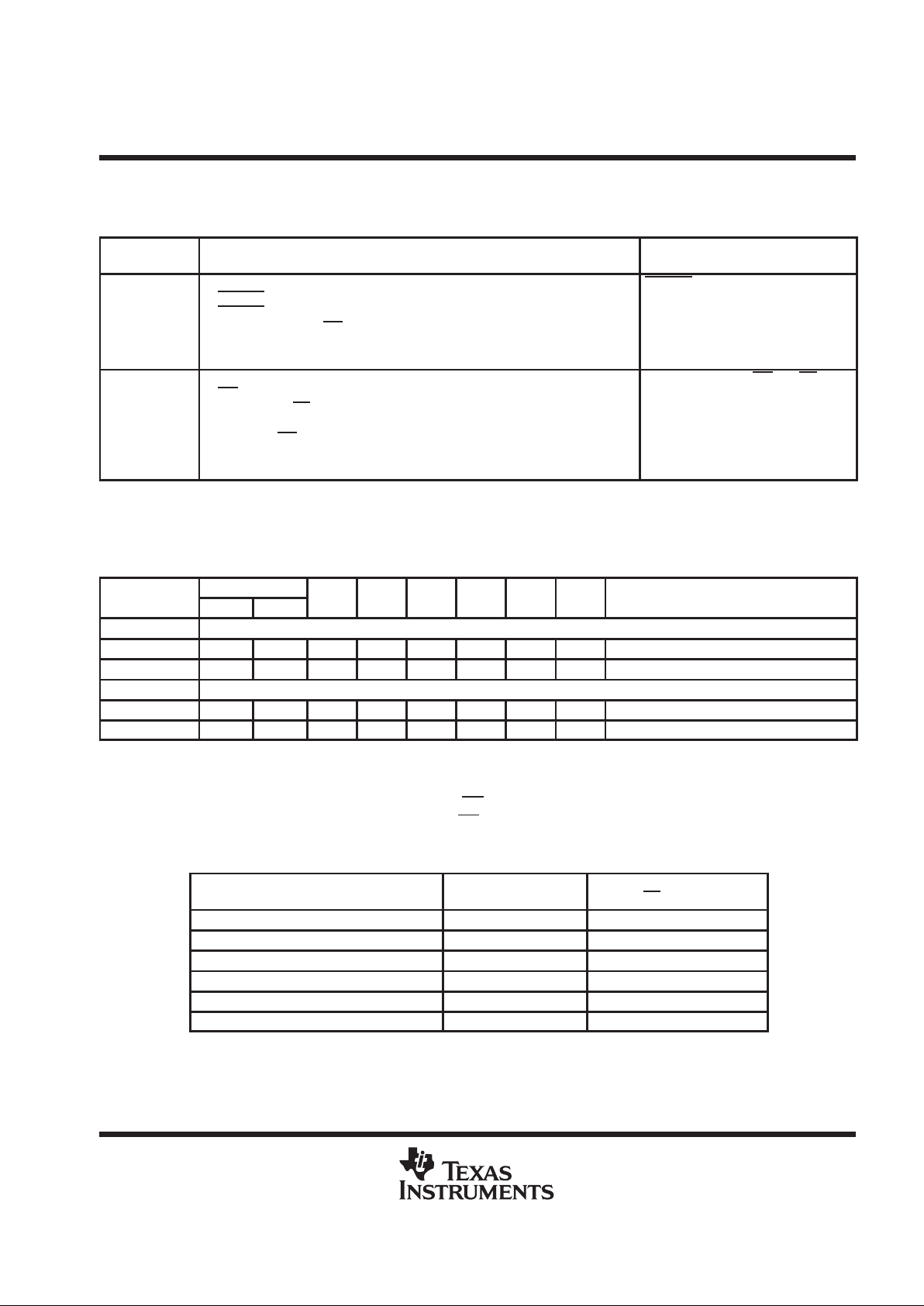
NOTE: tsu = setup time, th = hold time
ExtClk
WR
RD
CSTART
t
su(WRH_EXTCLKH)
≥5 ns
t
h(WRL_EXTCLKH)
≥5 ns
t
h(RDL_EXTCLKH)
≥5 ns
t
d(EXTCLK_CSTARTL)
≥5 ns
t
h(CSTARTL_EXTCLKH)
≥5 ns
t
su(CSTARTH_EXTCLKH)
≥5 ns
OR
OR
t
su(RDH_EXTCLKH)
≥5 ns
Figure 3. Trigger Timing – Software Start Mode Using External Clock

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
7
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
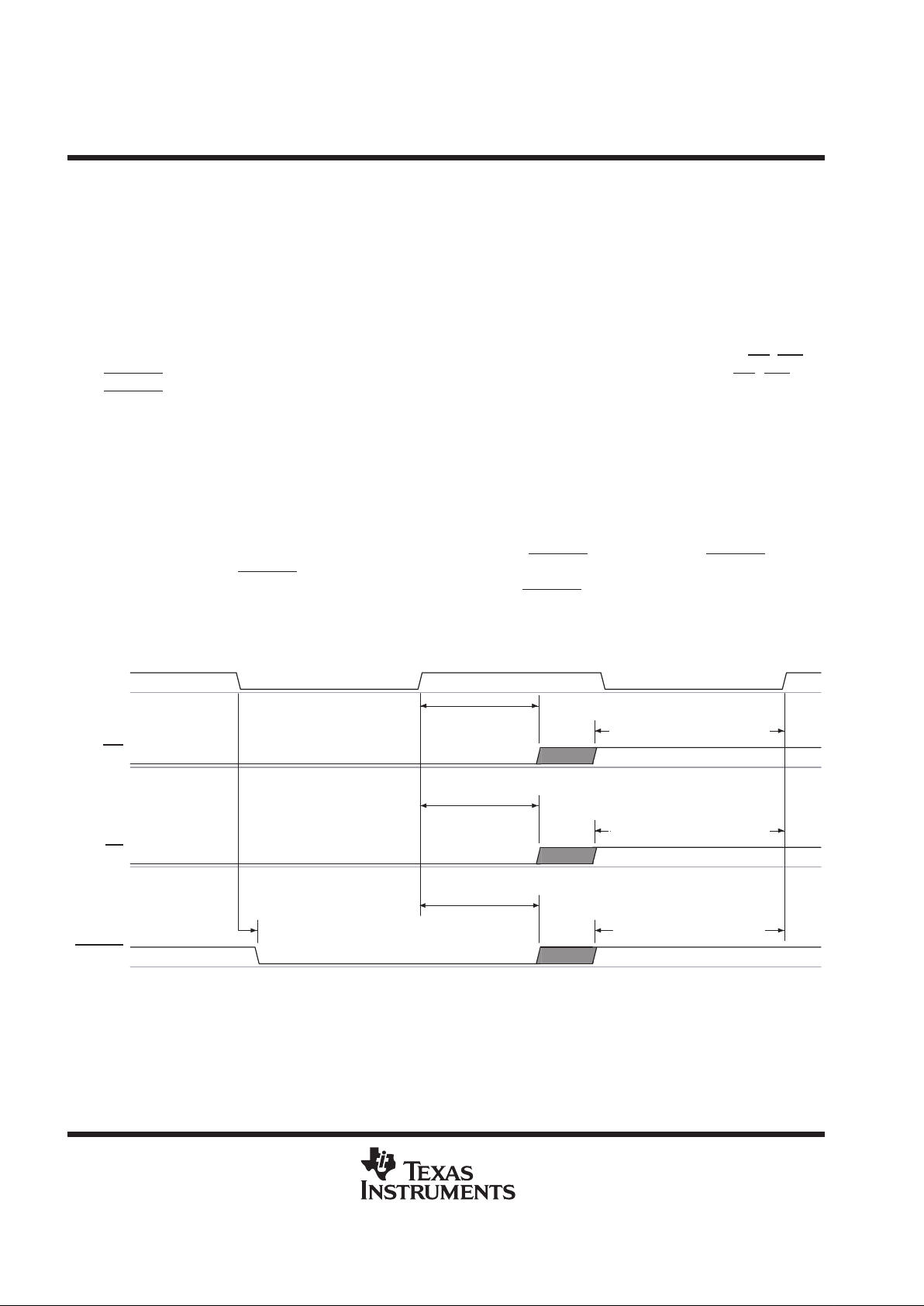
start of conversion mechanism
There are two ways to convert data: hardware and software. In the hardware conversion mode the ADC begins
sampling at the falling edge of CSTART and begins conversion at the rising edge of CSTART. Software start
mode ADC samples for 6 clocks, then conversion occurs for ten clocks. The total sampling and conversion
process lasts only 16 clocks in this case. If RD
is not detected during the next clock cycle, the ADC automatically
proceeds to a power-down state. Data is valid on the rising edge of INT in both conversion modes.
hardware CST ART conversion
external clock
With CS low and WR low, data is written into the ADC. The sampling begins at the falling edge of CSTART and
conversion begins at the rising edge of CST AR T. At the end of conversion, EOC goes from low to high, telling
the host that conversion is ready to be read out. The external clock is active and is used as the reference at all
times. With this mode, it is required that CST ART is not applied at the rising edge of the clock (see Figure 4).
TLV571
2.7 V to 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT
RARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGIT AL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
•
start of conversion mechanism (continued)
CLK
D[0:7]
EOC
t
su(CSL_WRL)
t
h(WRH_CSH)
t
d(CSH_CSTARTL)
t
(sample)
t
su(DAV_WRH)
t
h(WRH_DAV)
t
c
(10 CLKs)
t
en(RDL_DAV)
t
dis(RDH_DAV)
t
c
t
su(CSL_RDL)
t
en(RDL_DAV)
OR
Auto Powerdown
ADC ADC
Config
Data
t
(sample)
su(CSL_RDL)
t
h(RDH_CSH)
t
CS
WR
CSTART
RD
INT
Figure 4. Input Conversion – Hardware CSTART, External Clock
TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
• 9
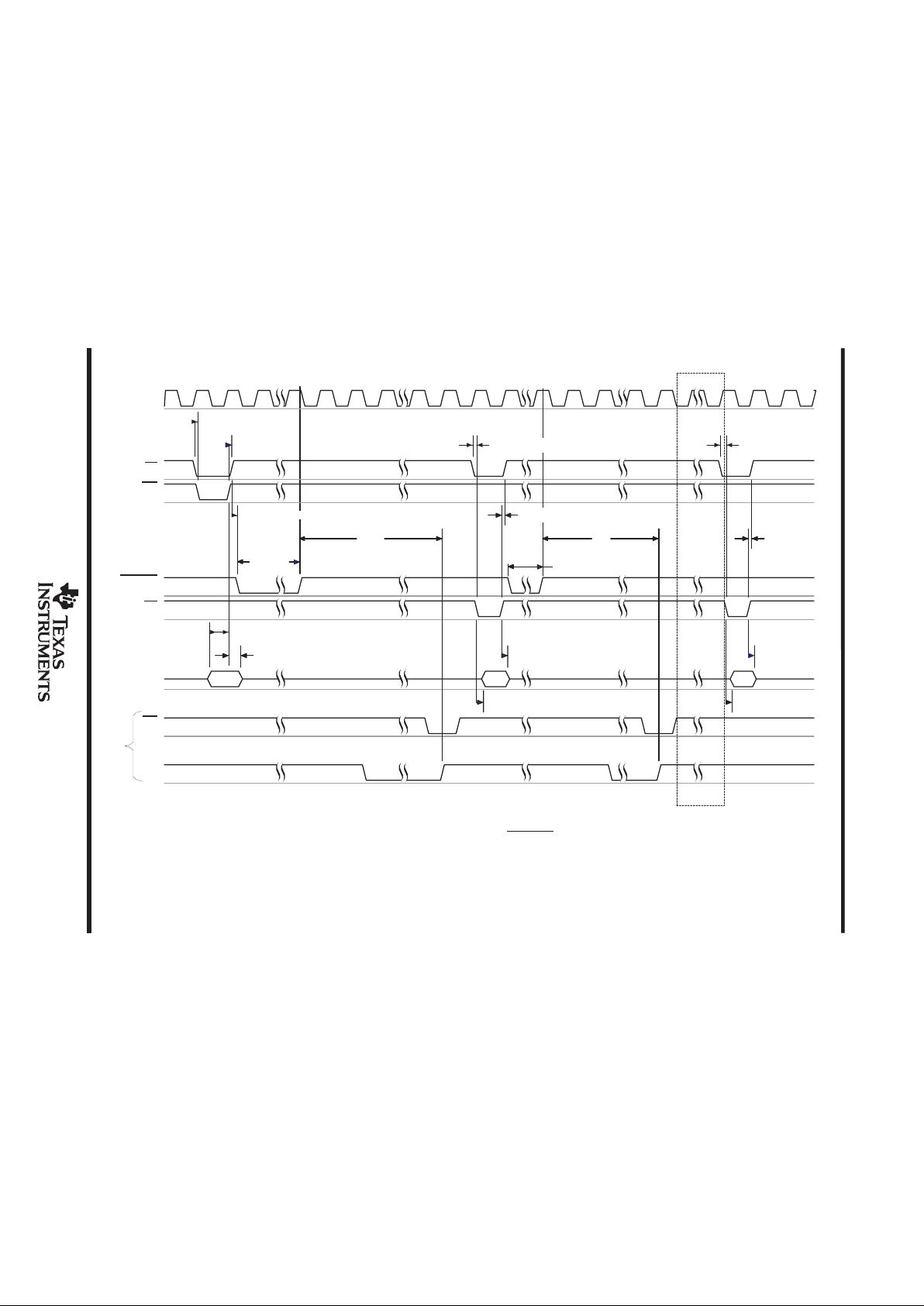
internal clock
With CS low and WR low, data is written into the ADC. The sampling begins at the falling edge of CST ART, and conversion begins at the rising
edge of CSTART. The internal clock turns on at the rising edge of CSTART. The internal clock is disabled after each conversion.
OR
Auto Powerdown
CS
WR
CSTART
INTCLK
RD
D[0:7]
INT
EOC
Config
Data
ADC
Data
ADC
Data
t
su(CSL_WRL)
t
h(WRH_CSH)
t
d(CSH_CSTARTL)
t
(sample)
t
su(DAV_WRH)
t
h(WRH_DAV)
t
c
t
su(CSL_RDL)
t
h(RDH_CSH)
t
en(RDL_DAV)
t
dis(RDH_DAV)
t
c
t
su(CSL_RDL)
t
en(RDL_DAV)
t
(STARTOSC)
t
(STARTOSC)
9
10
10
Auto Powerdown
Figure 5. Input Conversion – Hardware CSTART, Internal Clock

TLV571
2.7 V to 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT
RARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGIT AL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
•
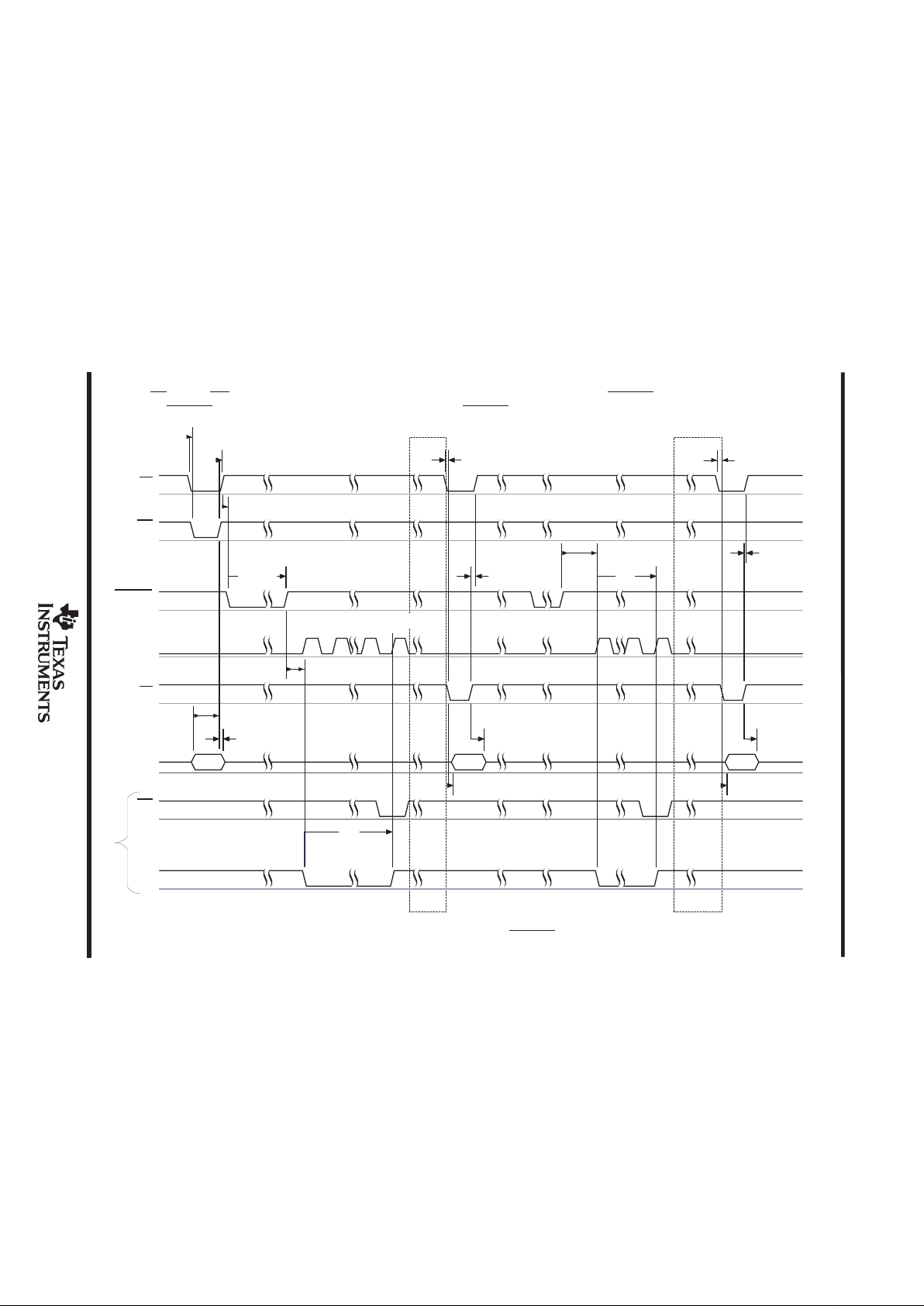
software START conversion
external clock
With CS low and WR low, data is written into the ADC. Sampling begins at the rising edge of WR. The conversion process begins 6 clocks
after sampling begins. At the end of conversion, the INT goes low telling the host that conversion is ready to be read out. EOC B low during
the conversion. The external clock is active and used as the reference at all times. With this mode, WR and RD should not be applied at the
rising edge of the clock (see Figure 3).
Auto Powerdown
CLK
CS
WR
RD
D[0:7]
INT
EOC
Config
Data
ADC Data ADC Data
t
su(CSL_WRL)
t
h(WRH_CSH)
t
su(DAV_WRH)
t
h(WRH_DAV)
t
c
t
su(CSL_RDL)
t
h(RDH_CSH)
t
en(RDL_DAV)
t
dis(RDH_DAV)
t
c
t
t
en(RDL_DAV)
015671516
OR
su(CSL_RDL)
t
(sample)
t
(sample)
04515
Figure 6. Input Conversion – Software Start, External Clock

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
• 11
software START conversion (continued)
internal clock
With CS low and WR low, data is written into the ADC. Sampling begins at the rising edge of WR. Conversion begins 6 clocks after sampling
begins. The internal clock begins at the rising edge of WR. The internal clock is disabled after each conversion. Subsequent sampling begins
at the rising edge of RD.
OR
Auto Powerdown
ADC
CS
WR
RD
INTCLK
D[0:7]
INT
EOC
Config
Data
ADC
Data
t
su(CSL_WRL)
t
h(WRH_CSH)
t
(sample)
t
su(DAV_WRH)
t
h(WRH_DAV)
t
c
t
su(CSL_RDL)
t
h(RDH_CSH)
t
en(RDL_DAV)
t
dis(RDH_DAV)
t
c
t
(STARTOSC)
t
(STARTOSC)
t
(sample)
456 045015 15
Auto Powerdown
Figure 7. Input Conversion – Software Start, Internal Clock

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
software START conversion (continued)
system clock source
The TLV571 internally derives multiple clocks from the SYSCLK for different tasks. SYSCLK is used for most
conversion subtasks. The source of SYSCLK is programmable via control register zero, bit 3. The source of
SYSCLK is changed at the rising edge of WR
of the cycle when CR0.D3 is programmed.
internal clock (CR0.D3 = 0, SYSCLK = internal OSC)
The TLV571 has a built-in 10 MHz OSC. When the internal OSC is selected as the source of SYSCLK, the
internal clock starts with a delay (one half of the OSC period max) after the falling edge of the conversion trigger
(either WR, RD, or CST ART). The OSC speed can be set to 10 ± 1 MHz or 20 ± 2 MHz by setting register bit
CR1.D4.
external clock (CR0.D3 = 1, SYSCLK = external clock)
The TLV571 is designed to accept an external clock input (CMOS/TTL logic) with frequencies from 1 MHz to
20 MHz.
host processor interface
The TLV571 provides a generic high-speed parallel interface that is compatible with high-performance DSPs
and general-purpose microprocessors. The interface includes D(0–7), INT/EOC, RD, and WR.
output format
The data output format is unipolar (code 0 to 255). The output code format can be either binary or twos
complement by setting register bit CR1.D1.
power up and initialization
After power up, CS
must be low to begin an I/O cycle. INT/EOC is initially high. The TL V571 requires two write
cycles to configure the two control registers. The first conversion after the device has returned from the power
down state may be invalid and should be disregarded.
definitions of specifications and terminology
integral nonlinearity
Integral nonlinearity refers to the deviation of each individual code from a line drawn from zero through full scale.
The point used as zero occurs 1/2 LSB before the first code transition. The full-scale point is defined as level
1/2 LSB beyond the last code transition. The deviation is measured from the center of each particular code to
the true straight line between these two points.
differential nonlinearity
An ideal ADC exhibits code transitions that are exactly 1 LSB apart. DNL is the deviation from this ideal value.
A differential nonlinearity error of less than ±1 LSB ensures no missing codes.
zero offset
The major carry transition should occur when the analog input is at zero volts. Zero error is defined as the
deviation of the actual transition from that point.
gain error
The first code transition should occur at an analog value 1/2 LSB above negative full scale. The last transition
should occur at an analog value 1 1/2 LSB below the nominal full scale. Gain error is the deviation of the actual
difference between first and last code transitions and the ideal difference between first and last code transitions.

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
13
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
software START conversion (continued)
signal-to-noise ratio + distortion (SINAD)
Signal-to-noise ratio + disortion is the ratio of the rms value of the measured input signal to the rms sum of all
other spectral components below the Nyquist frequency, including harmonics but excluding dc. The value for
SINAD is expressed in decibels.
effective number of bits (ENOB)
For a sine wave, SINAD can be expressed in terms of the number of bits. Using the following formula,
N = (SINAD – 1.76)/6.02
it is possible to get a measure of performance expressed as N, the effective number of bits. Thus, the effective
number of bits for a device for sine wave inputs at a given input frequency can be calculated directly from its
measured SINAD.
total harmonic distortion (THD)
T otal harmonic distortion is the ratio of the rms sum of the first six harmonic components to the rms value of the
measured input signal and is expressed as a percentage or in decibels.
spurious free dynamic range (SFDR)
Spurious free dynamic range is the difference in dB between the rms amplitude of the input signal and the peak
spurious signal.
DSP interface
The TL V571 is a 8-bit single input channel analog-to-digital converter with throughput up to 1.25 MSPS at 5 V
and up to 625 KSPS at 3 V . To achieve 1.25 MSPS throughput, the ADC must be clocked at 20 MHz. Likewise
to achieve 625 KSPS throughout, the ADC must be clocked at 10 MHz. The TL V571 can be easily interfaced
to microcontrollers, ASICs, and DSPs. Figure 8 shows the pin connections to interface the TLV571 to the
TMS320C6x DSP.
Address
Decoder
EN
A0–A15
TMS320C6X
HW
HR
INTx
D0–D15
D0–D7
CS
WR
RD
EOC
TLV571
REF
AIN
REFP
REFM
Figure 8. TMS320C6x DSP Interface

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
14
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
grounding and decoupling considerations
General practices should apply to the PCB design to limit high frequency transients and noise that are fed back
into the supply and reference lines. This requires that the supply and reference pins be sufficiently bypassed.
In most cases 0.1-µF ceramic chip capacitors are adequate to keep the impedance low over a wide frequency
range. Since their effectiveness depends largely on the proximity to the individual supply pin, they should be
placed as close to the supply pins as possible.
To reduce high frequency and noise coupling, it is highly recommended that digital and analog grounds be
shorted immediately outside the package. This can be accomplished by running a low impedance line between
DGND and AGND under the package.
TLV571
100 nF
DGND
DV
DD
AV
DD
AGND
REFP
REFM
100 nF
100 nF
V
REFP
V
REFM
AV
DD
DV
DD
Figure 9. Placement for Decoupling Capacitors
power supply ground layout
Printed-circuit boards that use separate analog and digital ground planes offer the best system performance.
Wire-wrap boards do not perform well and should not be used. The two ground planes should be connected
together at the low-impedance power-supply source. The best ground connection may be achieved by
connecting the ADC AGND terminal to the system analog ground plane making sure that analog ground
currents are well managed.
R
s
V
S
V
C
15 pF
Driving Source
†
TLV571
C
i
V
I
VI= Input Voltage at AIN
VS= External Driving Source Voltage
Rs= Source Resistance
R
i(ADC)
= Input Resistance of ADC
Ci= Input Capacitance
VC= Capacitance Charging Voltage
†
Driving source requirements:
• Noise and distortion for the source must be equivalent to the resolution of the converter.
• Rs must be real at the input frequency.
R
i(ADC)
AIN
Figure 10. Equivalent Input Circuit Including the Driving Source

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
15
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
simplified analog input analysis
Using the equivalent circuit in Figure 10, the time required to charge the analog input capacitance from 0 to V
S
within 1/2 LSB, tch(1/2 LSB), can be derived as follows.
The capacitance charging voltage is given by:
Where
R
t
= Rs + R
i
Ri = R
i(ADC)
tch = Charge time
V
C(t)
+
V
S
ǒ
1–e
–tchń
RtC
i
Ǔ
The input impedance Ri is 718 Ω at 5 V , and is higher (~ 1.25 kΩ) at 2.7 V. The final voltage to 1/2 LSB is given
by:
VC (1/2 LSB) = VS – (VS/512)
Equating equation 1 to equation 2 and solving for cycle time tc gives:
and time to change to 1/2 LSB (minimum sampling time) is:
t
ch
(1/2 LSB) = Rt × Ci × ln(512)
VS*
ǒ
VSń
512Ǔ+
V
S
ǒ
1–e
–tchń
RtC
i
Ǔ
Where
ln(512) = 6.238
Therefore, with the values given, the time for the analog input signal to settle is:
tch (1/2 LSB) = (Rs + 718 Ω) × 15 pF × ln(512)
This time must be less than the converter sample time shown in the timing diagrams. Which is 6x SCLK.
tch (1/2 LSB) ≤ 6x 1/f
(SCLK)
Therefore the maximum SCLK frequency is:
Max(f
(SCLK)
) = 6/tch (1/2 LSB) = 6/(ln(512) × Rt × Ci)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
16
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
†
Supply voltage, GND to VCC –0.3 V to 6.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Analog input voltage range –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reference input voltage range AVDD + 0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Digital input voltage range –0.3 V to DV
DD
+ 0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating virtual junction temperature range, TJ –40°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range, TA, –40°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
stg
–65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
recommended operating conditions
power supplies
MIN MAX UNIT
Analog supply voltage, A V
DD
2.7 5.5 V
Digital supply voltage, DV
DD
2.7 5.5 V
NOTE 1: Abs (AVDD – DVDD) < 0.5 V
analog inputs
MIN MAX UNIT
Analog input voltage, AIN AGND VREFP V
digital inputs
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
High-level input voltage, V
IH
DVDD = 2.7 V to 5.5 V 2.1 2.4 V
Low level input voltage, V
IL
DVDD = 2.7 V to 5.5 V 0.8 V
p
DVDD = 4.5 V to 5.5 V 20 MHz
Input CLK frequenc
y
DVDD = 2.7 V to 3.3 V 10 MHz
DVDD = 4.5 V to 5.5 V, f
CLK
= 20 MHz 23 ns
Pulse duration, CLK high, t
w(CLKH)
DVDD = 2.7 V to 3.3 V, f
CLK
= 10 MHz 46 ns
DVDD = 4.5 V to 5.5 V, f
CLK
= 20 MHz 23 ns
Pulse duration, CLK low, t
w
(CLKL)
DVDD = 2.7 V to 3.3 V, f
CLK
= 10 MHz 46 ns
Rise time, I/O and control, CLK, CS 50 pF output load 4
Fall time, I/O and control, CLK, CS 50 pF output load 4
ns
reference specifications
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
AVDD = 3 V 2 AV
DD
V
VREFP
AVDD = 5 V 2.5 AV
DD
V
External reference voltage
AVDD = 3 V AGND 1 V
VREFM
AVDD = 5 V AGND 2 V
VREFP – VREFM 2 AVDD–AGND V

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
17
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range, supply
voltages, and reference voltages (unless otherwise noted)
digital specifications
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Logic inputs
I
IH
High-level input current DVDD = 5 V, DVDD = 3 V, Input = DV
DD
–1 1 µA
I
IL
Low-level input current DVDD = 5 V, DVDD = 3 V, Input = 0 V –1 1 µA
C
i
Input capacitance 10 15 pF
Logic outputs
V
OH
High-level output voltage IOH = 50 µA to 0.5 mA DVDD–0.4 V
V
OL
Low-level output voltage IOL = 50 µA to 0.5 mA 0.4 V
I
OZ
High-impedance-state output current DVDD = 5 V, DVDD = 3 V, Input = DV
DD
1 µA
I
OL
Low-impedance-state output current DVDD = 5 V, DVDD = 3 V, Input = 0 V –1 µA
C
o
Output capacitance 5 pF
3 V, AVDD = DV
DD
9 10 11
Internal clock
5 V, AVDD = DV
DD
18 20 22
MHz
dc specifications
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Resolution 8 Bits
Accuracy
Integral nonlinearity, INL Best fit ±0.3 ±0.5 LSB
Differential nonlinearity , DNL ±0.3 ±0.5 LSB
Missing codes 0
E
O
Offset error ±0.15% ±0.3% FSR
E
G
Gain error ±0.2% ±0.4% FSR
Analog input
p
p
AIN, AVDD = 3 V, AVDD = 5 V 15 pF
CiInput capacitance
MUX input, AVDD = 3 V, AVDD = 5 V 25 pF
I
lkg
Input leakage current V
AIN
= 0 to AV
DD
±1 µA
Voltage reference input
r
i
Input resistance 2 kΩ
C
i
Input capacitance 300 pF
Power supply
p
pp
AVDD = DVDD = 3 V, f
CLK
= 10 MHz 4 5.5 mA
Operating supply current, I
DD
+
I
REF
AVDD = DVDD = 5 V, f
CLK
= 20 MHz
7 8.5 mA
p
AVDD+DVDD = 3 V 12 17 mW
PD
Power dissipation
AVDD+DVDD = 5 V 35 43 mW
AVDD = 3 V 1 8 µA
pp
p
Software
I
DD
+
I
REF
AVDD = 5 V 2 10 µA
IPDSupply current in power-down mode
AVDD = 3 V 0.5 1 mA
Auto
I
DD
+
I
REF
AVDD = 5 V 0.5 1 mA

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
18
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range, supply
voltages, and reference voltages (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
ac specifications, AVDD = DVDD = 5 V (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
f
= 100 kHz,
fs = 1.25 MSPS, AVDD = 5 V 47 49 dB
Signal-to-noise ratio, SNR
I
,
80% of FS
fs = 625 KSPS, AVDD = 3 V 47 49 dB
f
= 100 kHz,
fs = 1.25 MSPS, AVDD = 5 V 47 49 dB
Signal-to-noise ratio
+
distortion, SINAD
I
,
80% of FS
fs = 625 KSPS, AVDD = 3 V 47 49 dB
f
= 100 kHz,
fs = 1.25 MSPS, AVDD = 5 V –64 –52 dB
Total harmonic distortion, THD
I
,
80% of FS
fs = 625 KSPS, AVDD = 3 V –62 –52 dB
f
= 100 kHz,
fs = 1.25 MSPS, AVDD = 5 V 7.5 7.9 Bits
Effective number of bits, ENOB
I
,
80% of FS
fs = 625 KSPS, AVDD = 3 V 7.5 7.9 Bits
p
f
= 100 kHz,
fs = 1.25 MSPS, AVDD = 5 V –65 –51 dB
Spurious free dynamic range, SFDR
I
,
80% of FS
fs = 625 KSPS, AVDD = 3 V –64 –51 dB
Analog input
p
–1 dB Full-scale 0 dB input sine wave 12 18 MHz
Full-power bandwidth
–3 dB Full-scale 0 dB input sine wave 30 MHz
–1 dB –20 dB input sine wave 15 20 MHz
Small-signal bandwidth
–3 dB –20 dB input sine wave 35 MHz
p
AVDD = 4.5 V to 5.5 V 0.0625 1.25 MSPS
Sam ling rate, f
s
AVDD = 2.7 V to 3.3 V 0.0625 0.625 MSPS

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
19
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
timing requirements, AVDD = DVDD = 5 V (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
p
DVDD = 4.5 V to 5.5 V 50 ns
t
c
(CLK)
In ut clock Cycle time
DVDD = 2.7 V to 3.3 V 100 ns
t
(sample)
Reset and sampling time 6
SYSCLK
Cycles
t
c
Total conversion time 10
SYSCLK
Cycles
t
wL(EOC)
Pulse width, end of conversion, EOC 10
SYSCLK
Cycles
t
wL(INT)
Pulse width, interrupt 1
SYSCLK
Cycles
t
(STARTOSC)
Start-up time, internal oscillator 100 ns
t
d(CSH_CSTARTL)
Delay time, CS high to CSTAR T low 10 ns
DVDD = 5 V at 50 pF 20 ns
t
en
(RDL_DAV)
Enable time, data out
DVDD = 3 V at 50 pF 40 ns
DVDD = 5 V at 50 pF 5 ns
t
dis(RDH_DAV)
Disable time, data out
DVDD = 3 V at 50 pF 10 ns
t
su(CSL_WRL)
Setup time, CS to WR 5 ns
t
h(WRH_CSH)
Hold time, CS to WR 5 ns
t
w(WR)
Pulse width, write 1
Clock
Period
t
w(RD)
Pulse width, read 1
Clock
Period
t
su(DAV_WRH)
Setup time, data valid to WR 10 ns
t
h(WRH_DAV)
Hold time, data valid to WR 5 ns
t
su(CSL_RDL)
Setup time, CS to RD 5 ns
t
h(RDH_CSH)
Hold time, CS to RD 5 ns
t
h(WRL_EXTXLKH)
Hold time WR to clock high 5 ns
t
h(RDL_EXTCLKH)
Hold time RD to clock high 5 ns
t
h(CSTARTL_EXTCLKH)
Hold time CSTAR T to clock high 5 ns
t
su(WRH_EXTCLKH)
Setup time WR high to clock high 5 ns
t
su(RDH_EXTCLKH)
Setup time RD high to clock high 5 ns
t
su(CSTARTH_EXTCLKH)
Setup time CSTAR T high to clock high 5 ns
t
d(EXTCLK_CSTARTL)
Delay time clock low to CSTART low 5 ns
NOTE: Specifications subject to change without notice.
Data valid is denoted as DAV.

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
20
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 11
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
5.5
6.0
6.5
7.0
7.5
8.0
–40 –30 –20 –10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
SUPPLY CURRENT
vs
FREE AIR TEMPERATURE
AVDD = DVDD = 5 V, 20 MHz
TA – Free Air Temperature – °C
AVDD = DVDD = 3 V, 10 MHz
I
CC
– Supply Current – mA
Figure 12
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0 2 4 6 8 101214161820
SUPPLY CURRENT
vs
CLOCK FREQUENCY
f
clock
– Clock Frequency – MHz
AVDD = DVDD = 5 V
AVDD = DVDD = 3 V
I
CC
– Supply Current – mA
Figure 13
ANALOG INPUT BANDWIDTH
vs
FREQUENCY
AVDD = DVDD = 5 V,
AIN = 90% of FS,
REF = 5 V,
TA = 25°C
f – Frequency – MHz
Analog Input Bandwidth – dB
–2
–3
–4
–6
0.1 1
–1
0
1
10 100
–5

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
21
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 14
–0.15
–0.10
–0.05
–0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0 64 128 192 256
DNL – Differential Nonlinearity – LSB
Digital Output Code
DIFFERENTIAL NONLINEARITY
vs
DIGITAL OUTPUT CODE
AVDD = DVDD = 3 V,
External Ref = 3 V,
CLK = 10 MHz,
TA = 25°C
Figure 15
–0.06
–0.04
–0.02
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.10
0.12
0.14
0 64 128 192 256
INL – Integral Nonlinearity – LSB
Digital Output Code
INTEGRAL NONLINEARITY
vs
DIGITAL OUTPUT CODE
AVDD = DVDD = 3 V,
External Ref = 3 V,
CLK = 10 MHz,
TA = 25°C

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
22
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 16
–0.08
–0.06
–0.04
–0.02
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.10
0.12
0 64 128 192 256
DNL – Differential Nonlinearity – LSB
Digital Output Code
DIFFERENTIAL NONLINEARITY
vs
DIGITAL OUTPUT CODE
AVDD = DVDD = 5 V,
External Ref = 5 V,
CLK = 20 MHz,
TA = 25
°C
Figure 17
–0.08
–0.06
–0.04
–0.02
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.10
0.12
0.14
0 64 128 192 256
INL – Integral Nonlinearity – LSB
Digital Output Code
INTEGRAL NONLINEARITY
vs
DIGITAL OUTPUT CODE
AVDD = DVDD = 5 V,
External Ref = 5 V,
CLK = 20 MHz,
TA = 25°C

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
23
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 18
5
6
7
8
9
10
0 100 200 300
ENOB – Effective Number of Bits – BITS
f – Frequency – kHz
EFFECTIVE NUMBER OF BITS
vs
FREQUENCY
AVDD = DVDD = 3 V,
External Ref = 3 V
Figure 19
5
6
7
8
9
10
0 200 400 600
ENOB – Effective Number of Bits – BITS
f – Frequency – kHz
EFFECTIVE NUMBER OF BITS
vs
FREQUENCY
AVDD = DVDD = 5 V,
External Ref = 5 V

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
24
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 20
–140
–120
–100
–80
–60
–40
–20
0
20
0 100000 200000 300000
Magnitude – dB
f – Frequency – Hz
FAST FOURIER TRANSFORM
vs
FREQUENCY
AIN = 200 KHz
CLK = 10 MHz
AVDD = DVDD = 3 V
External Ref = 3 V
Figure 21
–140
–120
–100
–80
–60
–40
–20
0
20
0 200000 400000 600000
Magnitude – dB
f – Frequency – Hz
FAST FOURIER TRANSFORM
vs
FREQUENCY
AIN = 200 KHz
CLK = 20 MHz
AVDD = DVDD = 5 V
External Ref = 5 V

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
25
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
MECHANICAL DATA
DW (R-PDSO-G**) PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
16 PINS SHOWN
4040000/C 07/96
Seating Plane
0.400 (10,15)
0.419 (10,65)
0.104 (2,65) MAX
1
0.012 (0,30)
0.004 (0,10)
A
8
16
0.020 (0,51)
0.014 (0,35)
0.293 (7,45)
0.299 (7,59)
9
0.010 (0,25)
0.050 (1,27)
0.016 (0,40)
(15,24)
(15,49)
PINS **
0.010 (0,25) NOM
A MAX
DIM
A MIN
Gage Plane
20
0.500
(12,70)
(12,95)
0.510
(10,16)
(10,41)
0.400
0.410
16
0.600
24
0.610
(17,78)
28
0.700
(18,03)
0.710
0.004 (0,10)
M
0.010 (0,25)
0.050 (1,27)
0°–8°
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion not to exceed 0.006 (0,15).
D. Falls within JEDEC MS-013

TLV571
2.7 V TO 5.5 V, 1-CHANNEL, 8-BIT,
PARALLEL ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
SLAS239A – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2000
26
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
MECHANICAL DATA
PW (R-PDSO-G**) PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
14 PINS SHOWN
0,65
M
0,10
0,10
0,25
0,50
0,75
0,15 NOM
Gage Plane
28
9,80
9,60
24
7,90
7,70
2016
6,60
6,40
4040064/F 01/97
0,30
6,60
6,20
8
0,19
4,30
4,50
7
0,15
14
A
1
1,20 MAX
14
5,10
4,90
8
3,10
2,90
A MAX
A MIN
DIM
PINS **
0,05
4,90
5,10
Seating Plane
0°–8°
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion not to exceed 0,15.
D. Falls within JEDEC MO-153

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICA TIONS IS UNDERSTOOD T O
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...