Datasheet TLV5620IN, TLV5620IDR, TLV5620ID, TLV5620CN, TLV5620CDR Datasheet (Texas Instruments)
...
TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
D
Four 8-Bit Voltage Output DACs
D
3-V Single-Supply Operation
D
Serial Interface
D
High-Impedance Reference Inputs
D
Programmable for 1 or 2 Times Output
Range
D
Simultaneous Update Facility
D
Internal Power-On Reset
D
Low-Power Consumption
D
Half-Buffered Output
applications
D
Programmable V oltage Sources
D
Digitally Controlled Amplifiers/Attenuators
D
Mobile Communications
D
Automatic Test Equipment
D
Process Monitoring and Control
D
Signal Synthesis
description
The TLV5620C and TLV5620I are quadruple 8-bit voltage output digital-to-analog converters (DACs) with
buffered reference inputs (high impedance). The DACs produce an output voltage that ranges between either
one or two times the reference voltages and GND; and, the DACs are monotonic. The device is simple to use,
because it runs from a single supply of 3 V to 3.6 V. A power-on reset function is incorporated to ensure
repeatable start-up conditions.
Digital control of the TL V5620C and TLV5620I is over a simple three-wire serial bus that is CMOS compatible
and easily interfaced to all popular microprocessor and microcontroller devices. The 11-bit command word
comprises eight bits of data, two DAC select bits, and a range bit, the latter allowing selection between the times
1 or times 2 output range. The DAC registers are double buffered, allowing a complete set of new values to be
written to the device, then all DAC outputs update simultaneously through control of LDAC. The digital inputs
feature Schmitt triggers for high noise immunity.
The 14-terminal small-outline (SO) package allows digital control of analog functions in space-critical
applications. The TLV5620C is characterized for operation from 0°C to 70°C. The TLV5620I is characterized
for operation from –40°C to 85°C. The TLV5620C and TLV5620I do not require external trimming.
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PACKAGE
T
A
SMALL OUTLINE
(D)
PLASTIC DIP
(N)
0°C to 70°C TLV5620CD TLV5620CN
–40°C to 85°C TLV5620ID TLV5620IN
Copyright 1997, Texas Instruments Incorporated
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
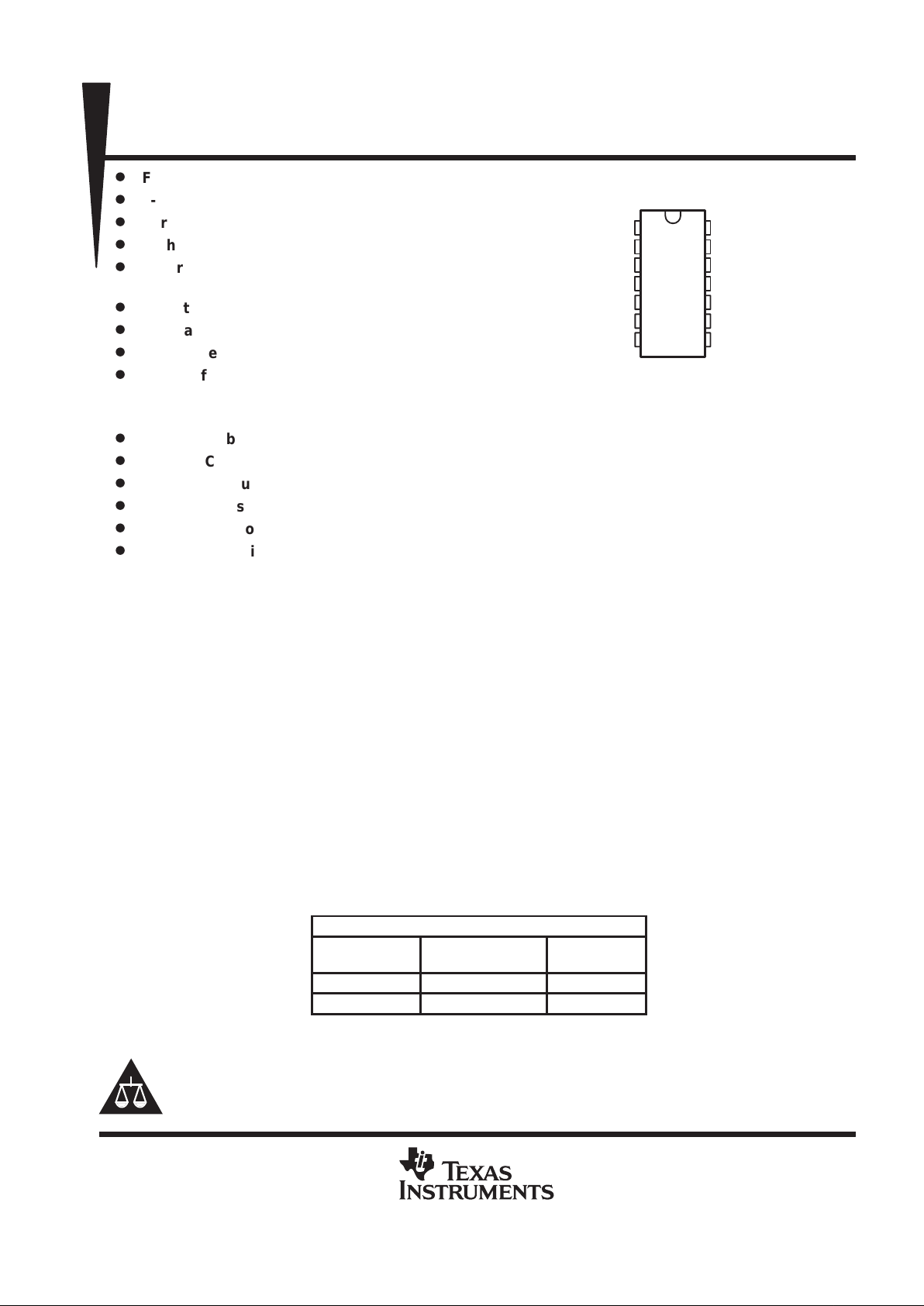
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
GND
REFA
REFB
REFC
REFD
DATA
CLK
V
DD
LDAC
DACA
DACB
DACC
DACD
LOAD
D OR N PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
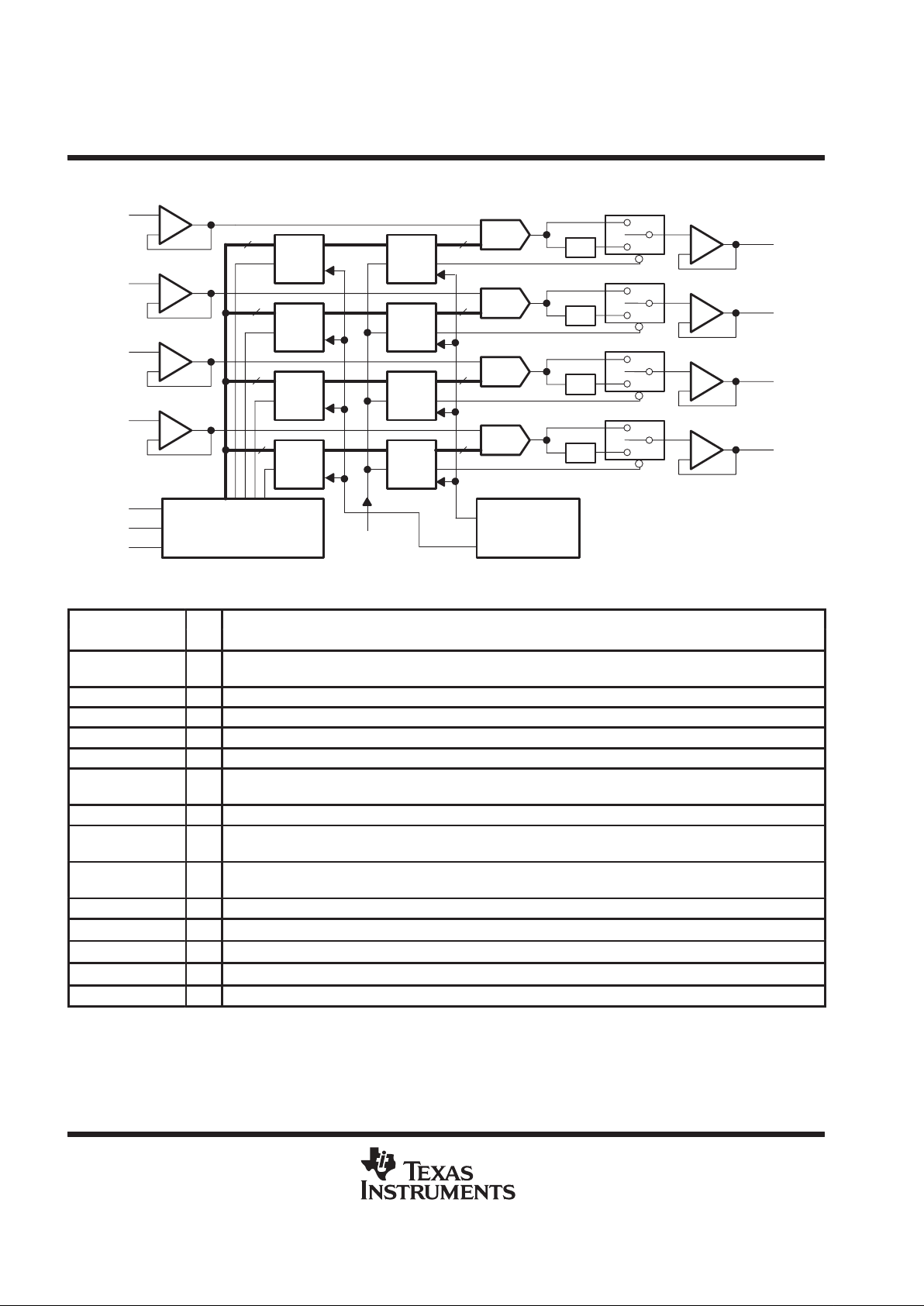
functional block diagram
Power-On
Reset
Serial
Interface
× 2
DAC
DAC
× 2
× 2
DAC
DAC
× 2
LDAC
REFA
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
REFB
REFC
CLK
REFD
DATA
LOAD
DACA
DACB
DACC
DACD
8 8
8
8
8
8
8
8
LatchLatch
Latch Latch
Latch
Latch
Latch Latch
2
3
4
5
7
6
8
13
12
11
10
9
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
I/O
DESCRIPTION
CLK 7 I Serial interface clock. The input digital data is shifted into the serial interface register on the falling edge of the clock
applied to the CLK terminal.
DACA 12 O DAC A analog output
DACB 11 O DAC B analog output
DACC 10 O DAC C analog output
DACD 9 O DAC D analog output
DATA 6 I Serial interface digital data input. The digital code for the DAC is clocked into the serial interface register serially.
Each data bit is clocked into the register on the falling edge of the clock signal.
GND 1 I Ground return and reference terminal
LDAC 13 I Load DAC. When this signal is high, no DAC output updates occur when the input digital data is read into the serial
interface. The DAC outputs are only updated when LDAC is taken from high to low.
LOAD 8 I Serial interface load control. When the LDAC terminal is low, the falling edge of the LOAD signal latches the digital
data into the output latch and immediately produces the analog voltage at the DAC output terminal.
REFA 2 I Reference voltage input to DAC A. This voltage defines the output analog range.
REFB 3 I Reference voltage input to DAC B. This voltage defines the analog output range.
REFC 4 I Reference voltage input to DAC C. This voltage defines the analog output range.
REFD 5 I Reference voltage input to DAC D. This voltage defines the analog output range.
V
DD
14 I Positive supply voltage
TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
detailed description
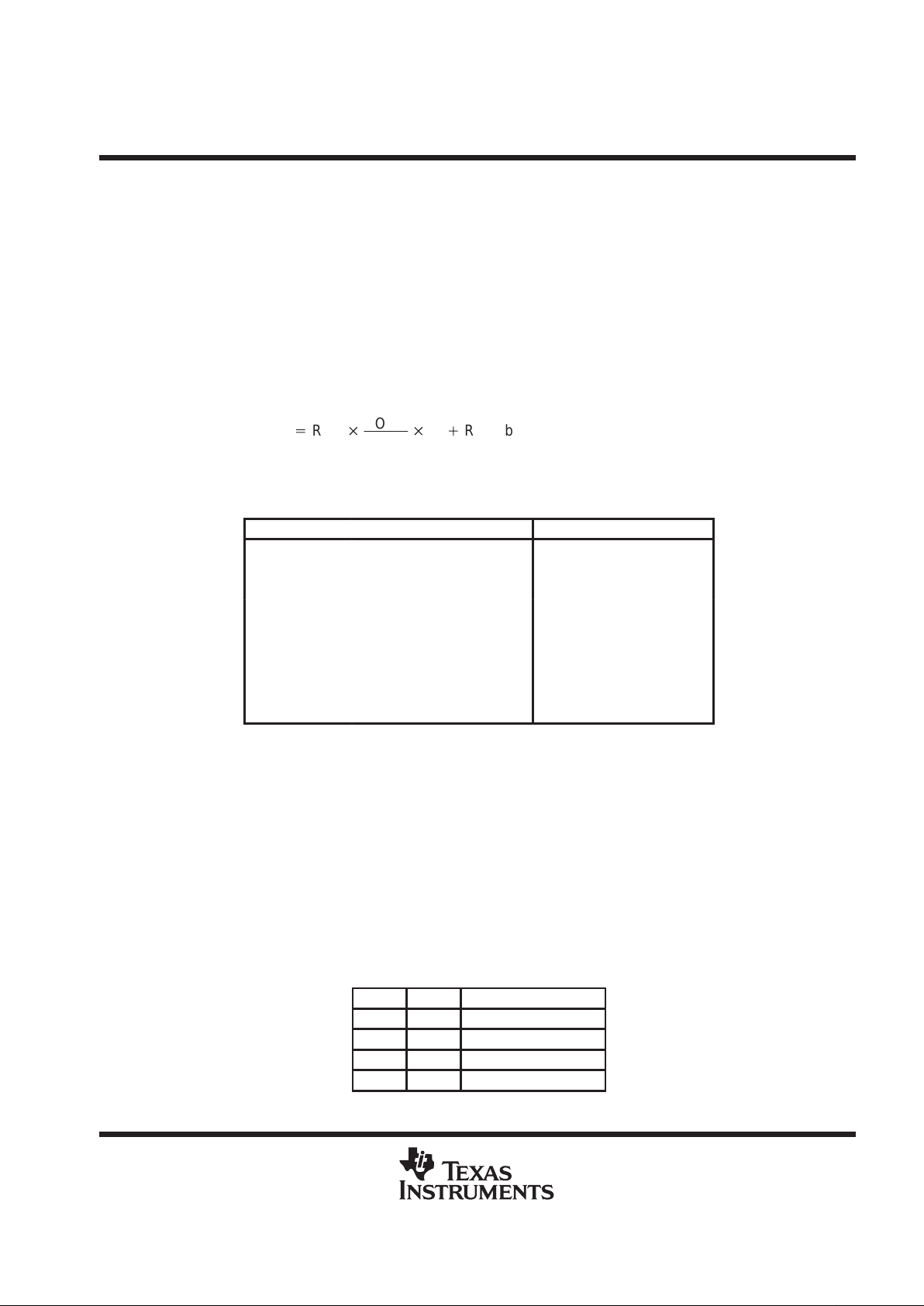
The TLV5620 is implemented using four resistor-string DACs. The core of each DAC is a single resistor with
256 taps, corresponding to the 256 possible codes listed in T able 1. One end of each resistor string is connected
to GND and the other end is fed from the output of the reference input buffer . Monotonicity is maintained by use
of the resistor strings. Linearity depends upon the matching of the resistor segments and upon the performance
of the output buffer. Since the inputs are buffered, the DACs always presents a high-impedance load to the
reference source.
Each DAC output is buffered by a configurable-gain output amplifier, which can be programmed to times 1 or
times 2 gain.
On power up, the DACs are reset to CODE 0.
Each output voltage is given by:
VO(DACA|B|C|D)+REF
CODE
256
(1)
RNG bit value)
where CODE is in the range 0 to 255 and the range (RNG) bit is a 0 or 1 within the serial control word.
Table 1. Ideal Output Transfer
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 OUTPUT VOLTAGE
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 GND
0 0000001 (1/256) × REF (1+RNG)
• ••••••• •
• ••••••• •
0 1111111 (127/256) × REF (1+RNG)
1 0000000 (128/256) × REF (1+RNG)
• ••••••• •
• ••••••• •
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (255/256) × REF (1+RNG)
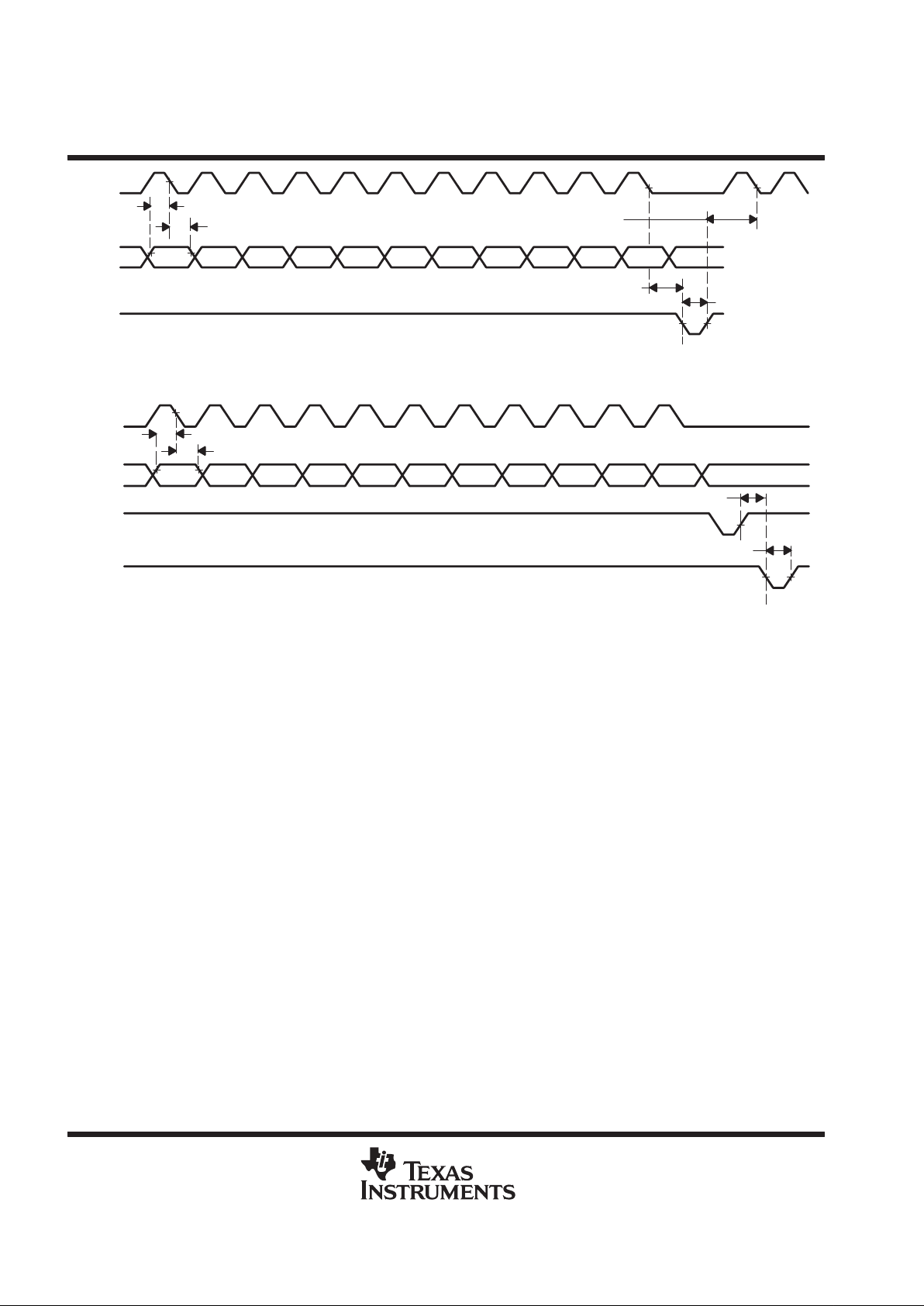
data interface
With LOAD high, data is clocked into the DATA terminal on each falling edge of CLK. Once all data bits have
been clocked in, LOAD is pulsed low to transfer the data from the serial input register to the selected DAC as
shown in Figure 1. When LDAC is low, the selected DAC output voltage is updated when LOAD goes low . When
LDAC is high during serial programming, the new value is stored within the device and can be transferred to
the DAC output at a later time by pulsing LDAC low as shown in Figure 2. Data is entered MSB first. Data
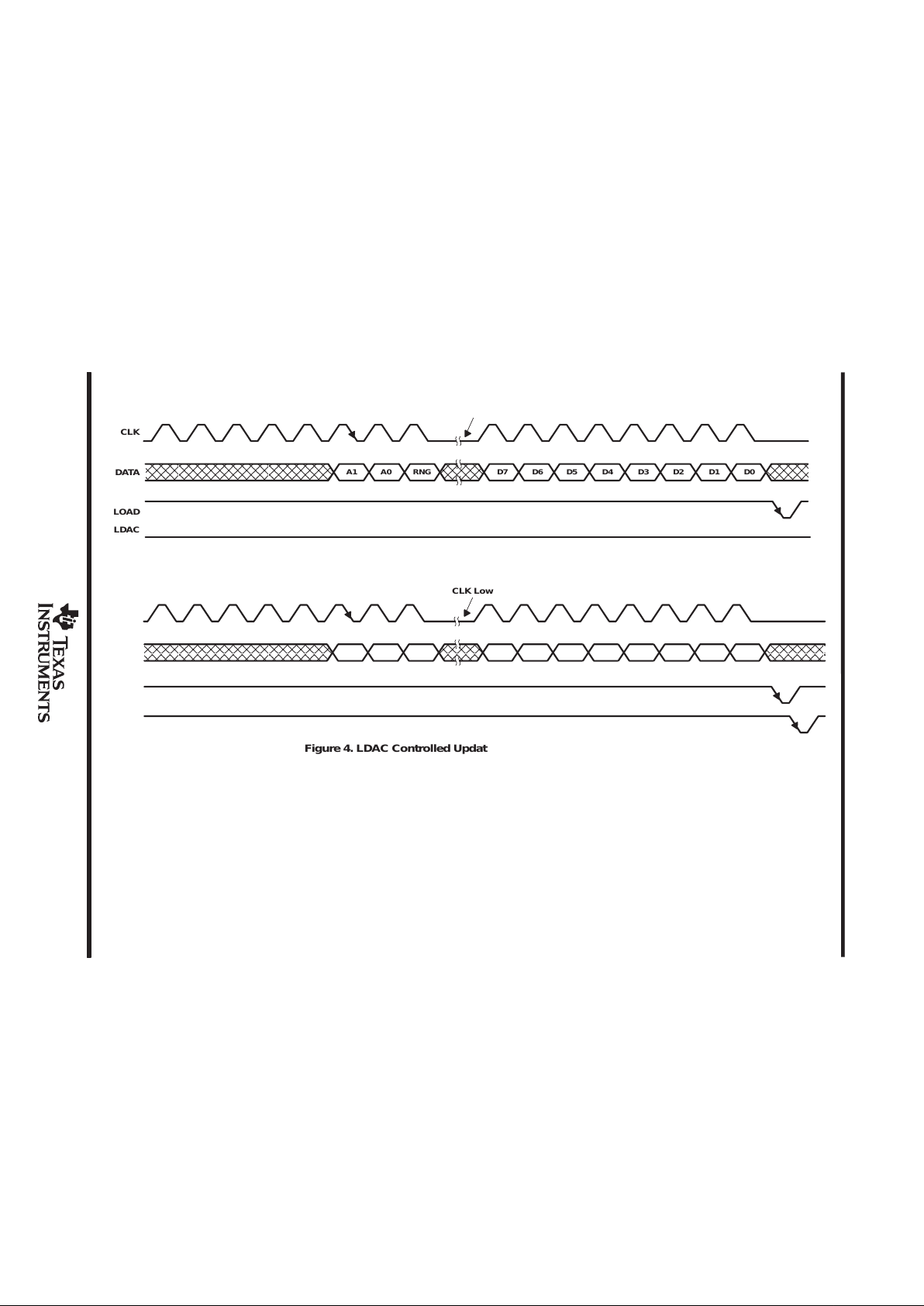
transfers using two 8-clock-cycle periods are shown in Figures 3 and 4.
Table 2 lists the A1 and A0 bits and the selection of the updated DACs. The RNG bit controls the DAC output
range. When RNG = low, the output range is between the applied reference voltage and GND, and when
RNG = high, the range is between twice the applied reference voltage and GND.
Table 2. Serial Input Decode
A1 A0 DAC UPDATED
0 0 DACA
0 1 DACB
1 0 DACC
1 1 DACD
TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
A1 A0 RNG D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DAC Update
CLK
DATA
LOAD
t
su(DATA-CLK)
t
v(DATA-CLK)
t
su(CLK-LOAD)
t
w(LOAD)
t
su(LOAD-CLK)
Figure 1. LOAD-Controlled Update (LDAC = Low)
CLK
DATA
LOAD
LDAC
DAC Update
A1 A0 RNG D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
t
su(DATA-CLK)
t
v(DATA-CLK)
t
w(LDAC)
t
su(LOAD-LDAC)
Figure 2. LDAC-Controlled Update
TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
• 5
A1 A0 RNG D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
CLK
DATA
LOAD
LDAC
CLK Low
Figure 3. Load Controlled Update Using 8-Bit Serial Word (LDAC = Low)
A1 A0 RNG D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
CLK
DATA
LOAD
LDAC
CLK Low
Figure 4. LDAC Controlled Update Using 8-Bit Serial Word

TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
linearity, offset, and gain error using single-end supplies
When an amplifier is operated from a single supply , the voltage offset can still be either positive or negative. With
a positive offset voltage, the output voltage changes on the first code change. With a negative offset the output
voltage may not change with the first code depending on the magnitude of the offset voltage.
The output amplifier, therefore, attempts to drive the output to a negative voltage. However, because the most
negative supply rail is ground, the output cannot drive below ground and clamps the output at 0 V.
The output voltage remains at zero until the input code value produces a sufficient positive output voltage to
overcome the negative offset voltage, resulting in the transfer function shown in Figure 5.
DAC Code
Output
Voltage
0 V
Negative
Offset
Figure 5. Effect of Negative Offset (Single Supply)
This offset error, not the linearity error , produces this breakpoint. The transfer function would have followed the
dotted line if the output buffer could drive below ground.
For a DAC, linearity is measured between zero-input code (all inputs 0) and full-scale code (all inputs 1) after
offset and full scale are adjusted out or accounted for in some way . However , single-supply operation does not
allow for adjustment when the offset is negative due to the breakpoint in the transfer function. So the linearity
is measured between full-scale code and the lowest code that produces a positive output voltage. The code is
calculated from the maximum specification for the negative offset.

TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
7
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
equivalent inputs and outputs
GND
V
ref
Input
V
DD
To DAC
Resistor
String
_
+
V
DD
DAC
Voltage Output
I
SINK
60 µA
Typical
84 kΩ
84 kΩ
× 1
× 2
Output
Range
Select
Input from
Decoded DAC
Register String
INPUT CIRCUIT OUTPUT CIRCUIT
GND
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
†
Supply voltage (VDD – GND) 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Digital input voltage range GND – 0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reference input voltage range, VID GND – 0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range, TA: TLV5620C 0°C to 70°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TLV5620I –40°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
stg
–50°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, V
DD
2.7 3.3 5.25 V
High-level input voltage, V
IH
0.8 V
DD
V
Low-level input voltage, V
IL
0.8 V
Reference voltage, V
ref
[A|B|C|D], x1 gain VDD–1.5 V
Load resistance, R
L
10 kΩ
Setup time, data input, t
su(DATA-CLK)
(see Figures 1 and 2) 50 ns
Valid time, data input valid after CLK↓, t
v(DATA-CLK)
(see Figures 1 and 2) 50 ns
Setup time, CLK eleventh falling edge to LOAD, t
su(CLK-LOAD)
(see Figure 1) 50 ns
Setup time, LOAD↑ to CLK↓, t
su(LOAD-CLK)
(see Figure 1) 50 ns
Pulse duration, LOAD, t
w(LOAD)
(see Figure 1) 250 ns
Pulse duration, LDAC, t
w(LDAC)
(see Figure 2) 250 ns
Setup time, LOAD↑ to LDAC↓,t
su(LOAD-LDAC)
(see Figure 2) 0 ns
CLK frequency 1 MHz
p
p
TLV5620C 0 70
°
Operating free-air temperature, T
A
TLV5620I –40 85
°C

TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range,
V
DD
= 3 V to 3.6 V, V
ref
= 2 V, × 1 gain output range (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
I
IH
High-level input current VI = V
DD
±10 µA
I
IL
Low-level input current VI = 0 V ±10 µA
I
O(sink)
Output sink current
p
20 µA
I
O(source)
Output source current
Each DAC output
1 mA
Input capacitance 15
p
C
i
Reference input capacitance 15
pF
I
DD
Supply current VDD = 3.3 V 2 mA
I
ref
Reference input current VDD = 3.3 V, V
ref
= 1.5 V ±10 µA
E
L
Linearity error (end point corrected) V
ref
= 1.25 V , × 2 gain, See Note 1 ±1 LSB
E
D
Differential linearity error V
ref
= 1.25 V , × 2 gain, See Note 2 ±0.9 LSB
E
ZS
Zero-scale error V
ref
= 1.25 V , × 2 gain, See Note 3 0 30 mV
Zero-scale error temperature coefficient V
ref
= 1.25 V , × 2 gain, See Note 4 10 µV/°C
E
FS
Full-scale error V
ref
= 1.25 V , × 2 gain, See Note 5 ±60 mV
Full-scale error temperature coefficient V
ref
= 1.25 V , × 2 gain, See Note 6 ±25 µV/°C
PSRR Power-supply sensitivity See Notes 7 and 8 0.5 mV/V
NOTES: 1. Integral nonlinearity (INL) is the maximum deviation of the output from the line between zero and full scale (excluding the effects
of zero code and full-scale errors).
2. Differential nonlinearity (DNL) is the difference between the measured and ideal 1 LSB amplitude change of any two adjacent codes.
Monotonic means the output voltage changes in the same direction (or remains constant) as a change in the digital input code.
3. Zero-scale error is the deviation from zero voltage output when the digital input code is zero.
4. Zero-scale error temperature coefficient is given by: ZSETC = [ZSE(T
max
) – ZSE(T
min
)]/V
ref
× 106/(T
max
– T
min
).
5. Full-scale error is the deviation from the ideal full-scale output (V
ref
– 1 LSB) with an output load of 10 kΩ.
6. Full-scale error temperature coefficient is given by: FSETC = [FSE(T
max
) – FSE (T
min
)]/V
ref
× 106/(T
max
– T
min
).
7. Zero-scale error rejection ratio (ZSE-RR) is measured by varying the VDD voltage from 4.5 V to 5.5 V dc and measuring the effect
of this signal on the zero-code output voltage.
8. Full-scale error rejection ratio (FSE-RR) is measured by varing the VDD voltage from 3 V to 3.6 V dc and measuring the effect of
this signal on the full-scale output voltage.
operating characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range,
V
DD
= 3 V to 3.6 V, V
ref
= 2 V, × 1 gain output range (unless otherwise noted)
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Output slew rate CL = 100 pF RL = 10 kΩ 1 V/µs
Output settling time To ±0.5 LSB, CL = 100 pF, RL = 10 kΩ, See Note 9 10 µs
Large-signal bandwidth Measured at –3 dB point 100 kHz
Digital crosstalk CLK = 1-MHz square wave measured at DACA-DACD –50 dB
Reference feedthrough See Note 10 –60 dB
Channel-to-channel isolation See Note 11 –60 dB
Reference input bandwidth See Note 12 100 kHz
NOTES: 9. Settling time is the time between a LOAD falling edge and the DAC output reaching full-scale voltage within ± 0.5 LSB starting from
an initial output voltage equal to zero.
10. Reference feedthrough is measured at any DAC output with an input code = 00 hex with a V
ref
input = 1 V dc + 1 VPP at 10 kHz.
11. Channel-to-channel isolation is measured by setting the input code of one DAC to FF hex and the code of all other DACs to 00 hex
with V
ref
input = 1 V dc + 1 VPP at 10 kHz.
12. Reference bandwidth is the –3 dB bandwidth with an input at V
ref
= 1.25 V dc + 2 VPP and with a digital input code of full-scale.

TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
9
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
10 kΩ
CL = 100 pF
TLV5620
DACA
DACB
DACC
DACD
Figure 6. Slew, Settling Time, and Linearity Measurements
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 7
POSITIVE RISE TIME AND SETTLING TIME
VDD = 3 V
TA = 25°C
Code 00 to
FF Hex
Range = ×2
V
ref
= 1.25 V
(see Note A)
Time – µs
024681012
– Output Voltage – V
14 16 18 20
–1
–0.5
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
0
3
V
O
NOTE A: Rise time = 2.05 µs, positive slew rate = 0.96 V/µs, settling
time = 4.5 µs.
Figure 8
NEGATIVE FALL TIME AND SETTLING TIME
VDD = 3 V
TA = 25°C
Code FF to
00 Hex
Range = ×2
V
ref
= 1.25 V
(see Note A)
Time – µs
024681012
– Output Voltage – V
14 16 18 20
–1
–0.5
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
0
3
V
O
NOTE A: Fall time = 4.25 µs, negative slew rate = 0.46 V/µs, settling
time = 8.5 µs.

TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 9
2
1.8
1.4
1.2
1
2.8
1.6
0 102030405060
– DAC Output Voltage – V
2.4
2.2
2.6
DAC OUTPUT VOLTAGE
vs
OUTPUT LOAD
3
70 80 90 100
V
O
RL – Output Load – kΩ
VDD = 3 V,
V
ref
= 1.5 V,
Range = 2x
Figure 10
0.8
0.6
0.2
0
0102030405060
1
1.4
1.6
70 80 90 100
0.4
1.2
DAC OUTPUT VOLTAGE
vs
OUTPUT LOAD
VDD = 3 V,
V
ref
= 1.5 V,
Range = 1x
– DAC Output Voltage – V
V
O
RL – Output Load – kΩ
1
0.9
0.85
0.8
– Supply Current – mA
1.1
1.15
SUPPLY CURRENT
vs
TEMPERATURE
1.2
1.05
0.95
–50 0 50 100
Range = ×2
Input Code = 255
VDD = 3 V
V
ref
= 1.25 V
I
DD
t – Temperature – °C
Figure 11

TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
11
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
NOTE A: Resistor R w 10 kΩ
R
TLV5620
DACA
DACB
DACC
DACD
_
+
V
O
Figure 12. Output Buffering Scheme

TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
MECHANICAL DATA
D (R-PDSO-G**) PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
14 PIN SHOWN
4040047/B 10/94
0.228 (5,80)
0.244 (6,20)
0.069 (1,75) MAX
0.010 (0,25)
0.004 (0,10)
1
14
0.014 (0,35)
0.020 (0,51)
A
0.157 (4,00)
0.150 (3,81)
7
8
0.044 (1,12)
0.016 (0,40)
Seating Plane
0.010 (0,25)
PINS **
0.008 (0,20) NOM
A MIN
A MAX
DIM
Gage Plane
0.189
(4,80)
(5,00)
0.197
8
(8,55)
(8,75)
0.337
14
0.344
(9,80)
16
0.394
(10,00)
0.386
0.004 (0,10)
M
0.010 (0,25)
0.050 (1,27)
0°–8°
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion not to exceed 0.006 (0,15).
D. Four center pins are connected to die mount pad
E. Falls within JEDEC MS-012

TLV5620C, TLV5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS110B – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED APRIL 1997
13
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
MECHANICAL DATA
N (R-PDIP-T**) PLASTIC DUAL-IN-LINE PACKAGE
4040049/C 7/95
16 PIN SHOWN
0.310 (7,87)
0.290 (7,37)
Seating Plane
0.010 (0,25) NOM
14 Pin Only
9
8
0.070 (1,78) MAX
A
0.035 (0,89) MAX
0.020 (0,51) MIN
16
1
0.015 (0,38)
0.021 (0,53)
0.200 (5,08) MAX
0.125 (3,18) MIN
0.240 (6,10)
0.260 (6,60)
0.100 (2,54)
M
0.010 (0,25)
0°–15°
20
0.975
(24,77)
(23,88)
0.940
18
0.920
0.850
14
0.775
(19,69)
0.745
(18,92)
16
0.775
(19,69)
(18,92)
0.745
PINS **
A MIN
DIM
A MAX
(23.37)
(21.59)
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Falls within JEDEC MS-001 (20-pin package is shorter than MS-001)

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICA TIONS IS UNDERSTOOD T O
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...