Datasheet TLV2543IN, TLV2543IDWR, TLV2543IDW, TLV2543IDB, TLV2543EVM Datasheet (Texas Instruments)
...
TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
D
12-Bit-Resolution A/D Converter
D
10-µs Conversion Time Over Operating
T emperature Range
D
11 Analog Input Channels
D
3 Built-In Self-Test Modes
D
Inherent Sample and Hold Function
D
Linearity Error...±1 LSB Max
D
On-Chip System Clock
D
End-of-Conversion (EOC) Output
D
Unipolar or Bipolar Output Operation
(Signed Binary With Respect to Half of the
Applied Referenced Voltage)
D
Programmable MSB or LSB First
D
Programmable Power Down
D
Programmable Output Data Length
D
CMOS Technology
description
The TLV2543C and TLV2543I are 12-bit, switched-capacitor, successive-approximation, analog-to-digital
converters (ADCs). Each device has three control inputs [chip select (CS
), the input-output clock (I/O CLOCK),
and the address input (DA TA INPUT)] and is designed for communication with the serial port of a host processor
or peripheral through a serial 3-state output. The device allows high-speed data transfers from the host.
In addition to the high-speed converter and versatile control capability, the device has an on-chip 14-channel
multiplexer that can select any one of 11 inputs or any one of three internal self-test voltages. The
sample-and-hold function is automatic. At the end of conversion, the end-of-conversion (EOC) output goes high
to indicate that conversion is complete. The converter incorporated in the device features differential
high-impedance reference inputs that facilitate ratiometric conversion, scaling, and isolation of analog circuitry
from logic and supply noise. A switched-capacitor design allows low-error conversion over the full operating
temperature range.
The TL V2543 is available in the DW, DB, and N packages. The TL V2543C is characterized for operation from
0°C to 70°C, and the TLV2543I is characterized for operation from –40°C to 85°C.
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PACKAGE
T
A
SMALL OUTLINE PLASTIC DIP
A
DW
†
DB
†
N
0°C to 70°C TLV2543CDW TLV2543CDB TLV2543CN
–40°C to 85°C TLV2543IDW — TLV2543IN
†
Available in tape and reel and ordered as the TL V2543CDWR, TLV2543CDBLE, or TLV2543IDWR.
Copyright 1995, Texas Instruments Incorporated
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
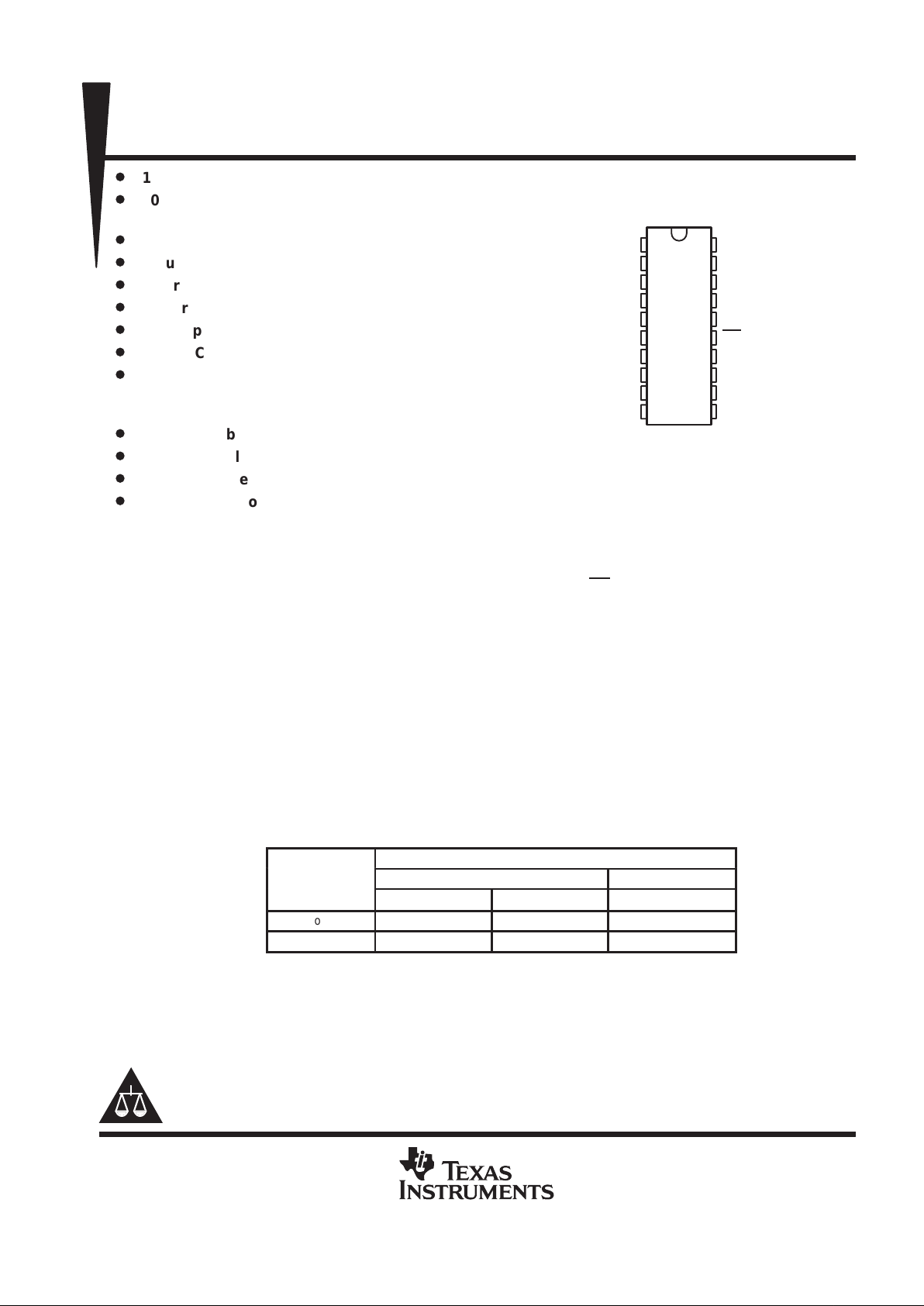
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
AIN0
AIN1
AIN2
AIN3
AIN4
AIN5
AIN6
AIN7
AIN8
GND
V
CC
EOC
I/O CLOCK
DATA INPUT
DATA OUT
CS
REF+
REF–
AIN10
AIN9
(TOP VIEW)
DB, DW, OR N PACKAGE
TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
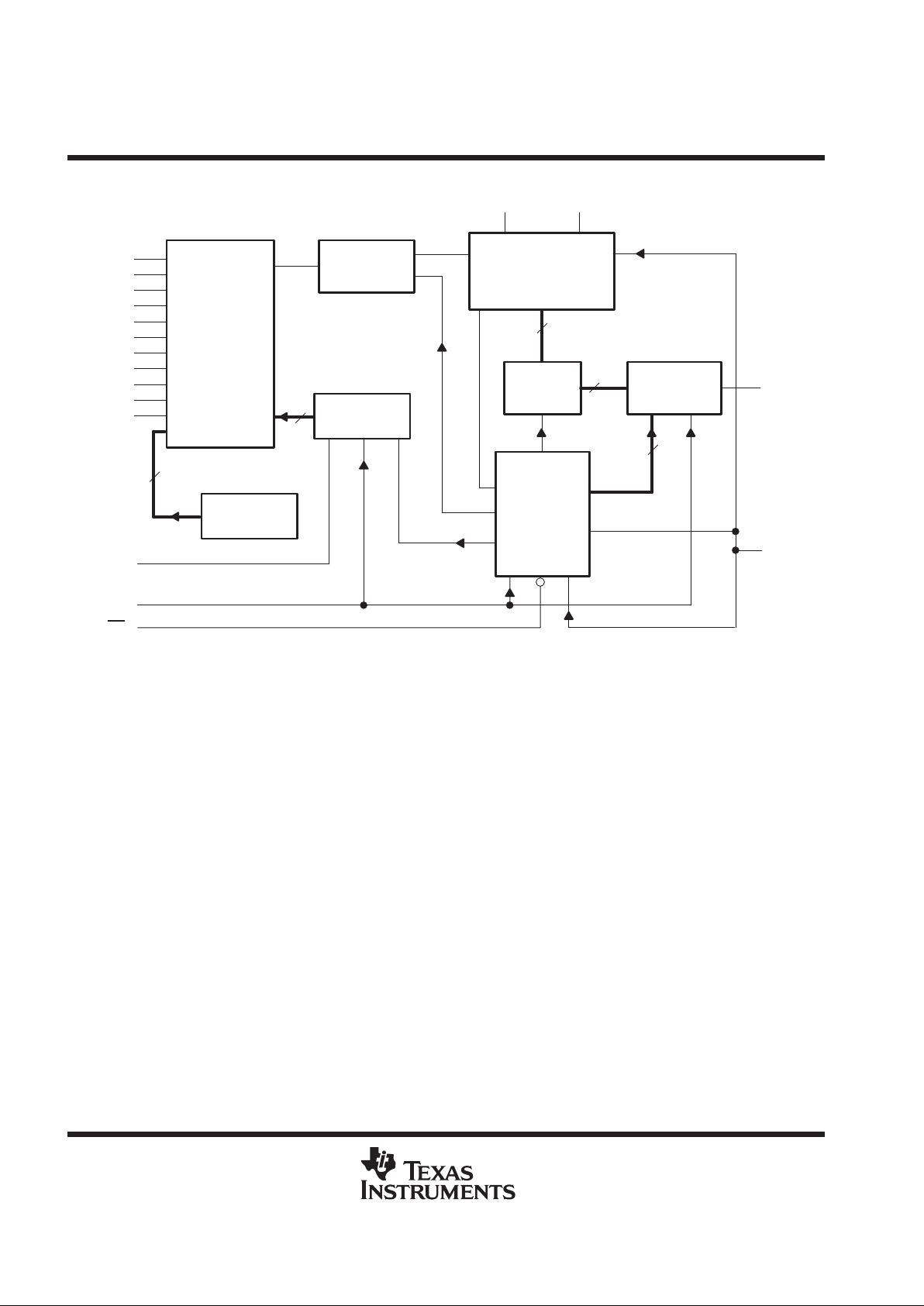
functional block diagram
14-Channel
Analog
Multiplexer
Sample and
Hold
12-Bit
Analog-to-Digital
Converter
(switched capacitors)
Self-Test
Reference
Output
Data
Register
12-to-1 Data
Selector and
Driver
Control Logic
and I/O
Counters
Input Address
Register
4
12
12
4
REF+ REF–
DATA
OUT
DATA
INPUT
I/O CLOCK
CS
3
EOC
17
18
15
AIN0
AIN1
AIN2
AIN3
AIN4
AIN5
AIN6
AIN7
AIN8
AIN9
AIN10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
12
14 13
16
19
TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
I/O
DESCRIPTION
AIN0 – AIN10 1–9,
11, 12
I Analog input. These 1 1 analog-signal inputs are internally multiplexed. The driving source impedance should
be less than or equal to 50 Ω for 4.1-MHz I/O CLOCK operation and capable of slewing the analog input
voltage into a capacitance of 60 pF.
CS 15 I Chip select. A high-to-low transition on CS resets the internal counters and controls and enables DA T A OUT,
DAT A INPUT, and I/O CLOCK. A low-to-high transition disables DAT A INPUT and I/O CLOCK within a setup
time.
DATA INPUT 17 I Serial-data input. A 4-bit serial address selects the desired analog input or test voltage to be converted. The
serial data is presented with the MSB first and is shifted in on the first four rising edges of I/O CLOCK. After
the four address bits are read into the address register, I/O CLOCK clocks the remaining bits in order.
DATA OUT 16 O Serial data output. This is the 3-state serial output for the A/D conversion result. DATA OUT is in the
high-impedance state when CS
is high and active when CS is low. With a valid CS, DAT A OUT is removed
from the high-impedance state and is driven to the logic level corresponding to the MSB/LSB value of the
previous conversion result. The next falling edge of I/O CLOCK drives DATA OUT to the logic level
corresponding to the next MSB/LSB, and the remaining bits are shifted out in order .
EOC 19 O End of conversion. EOC goes from a high to a low logic level after the falling edge of the last I/O CLOCK and
remains low until the conversion is complete and data are ready for transfer.
GND 10 Ground. This is the ground return terminal for the internal circuitry. Unless otherwise noted, all voltage
measurements are with respect to GND.
I/O CLOCK 18 I Input/output clock. I/O CLOCK receives the serial input and performs the following four functions:
1. It clocks the eight input data bits into the input data register on the first eight rising edges of I/O CLOCK
with the multiplexer address available after the fourth rising edge.
2. On the fourth falling edge of I/O CLOCK, the analog input voltage on the selected multiplexer input
begins charging the capacitor array and continues to do so until the last falling edge of I/O
CLOCK.
3. It shifts the 11 remaining bits of the previous conversion data out on DATA OUT. Data changes on
the falling edge of I/O CLOCK.
4. It transfers control of the conversion to the internal state controller on the falling edge of the last
I/O CLOCK.
REF+ 14 I Reference+. The upper reference voltage value (nominally VCC) is applied to REF+. The maximum input
voltage range is determined by the difference between the voltage applied to this terminal and the voltage
applied to the REF– terminal.
REF– 13 I Reference–. The lower reference voltage value (nominally ground) is applied to REF–.
V
CC
20 Positive supply voltage.
detailed description
Initially, with chip select (CS) high, I/O CLOCK and DATA INPUT are disabled and DATA OUT is in the
high-impedance state. CS
, going low, begins the conversion sequence by enabling I/O CLOCK and DATA
INPUT and removes DAT A OUT from the high-impedance state.
The input data is an 8-bit data stream consisting of a 4-bit analog channel address (D7–D4), a 2-bit data length
select (D3–D2), an output MSB or LSB first bit (D1), and a unipolar or bipolar output select bit (D0) that are
applied to DA T A INPUT . The I/O CLOCK sequence applied to the I/O CLOCK terminal transfers this data to the
input data register.
During this transfer, the I/O CLOCK sequence also shifts the previous conversion result from the output data
register to DATA OUT. I/O CLOCK receives the input sequence of 8, 12, or 16 clocks long depending on the
data-length selection in the input data register. Sampling of the analog input begins on the fourth falling edge
of the input I/O CLOCK sequence and is held after the last falling edge of the I/O CLOCK sequence. The last
falling edge of the I/O CLOCK sequence also takes EOC low and begins the conversion.
TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
converter operation
The operation of the converter is organized as a succession of two distinct cycles: 1) the I/O cycle, and 2) the
actual conversion cycle. The I/O cycle is defined by the externally provided I/O CLOCK and lasts 8, 12, or 16
clock periods depending on the selected output data length.
1. I/O cycle
During the I/O cycle, two operations take place simultaneously.
a. An 8-bit data stream consisting of address and control information is provided to DA TA INPUT . This data
is shifted into the device on the rising edge of the first eight I/O CLOCKs. DA T A INPUT is ignored after
the first eight clocks during 12- or 16-clock I/O transfers.
b. The data output with a length of 8, 12, or 16 bits is provided serially on DA TA OUT. When CS
is held low,
the first output data bit occurs on the rising edge of EOC. When CS
is negated between conversions, the
first output data bit occurs on the falling edge of CS
. This data is the result of the previous conversion
period, and after the first output data bit each succeeding bit is clocked out on the falling edge of each
succeeding I/O CLOCK.
2. Conversion cycle
The conversion cycle is transparent to the user, and it is controlled by an internal clock synchronized to the
I/O CLOCK. During the conversion period, the device performs a successive-approximation conversion on
the analog input voltage. The EOC output goes low at the start of the conversion cycle and goes high when
conversion is complete and the output data register is latched. A conversion cycle is started only after the I/O
cycle is completed, which minimizes the influence of external digital noise on the accuracy of the
conversion.
power up and initialization
After power up, CS
must be taken from high to low to begin an I/O cycle. EOC is initially high, and the input data
register is set to all zeros. The contents of the output data register are random, and the first conversion result
should be ignored. To initialize during operation, CS
is taken high and returned low to begin the next I/O cycle.
The first conversion after the device has returned from the power-down state may not read accurately due to
internal device settling.
operational terminology
Previous (N–1) conversion cycle The conversion cycle prior to the current I/O cycle.
Current (N) I/O cycle The entire I/O CLOCK sequence that transfers address and control data into the data register and clocks
the digital result from the previous conversion cycle from DATA OUT. The last falling edge of the clock in
the I/O CLOCK sequence signifies the end of the current I/O cycle.
Current (N) conversion cycle Immediately after the current I/O cycle, the current conversion cycle starts. When the current conversion
cycle is complete, the current conversion result is loaded into the output register.
Current (N) conversion result The result of the current conversion cycle that is serially shifted out during the next I/O cycle.
Next (N+1) I/O cycle The I/O cycle after the current conversion cycle.
Example: In the 12-bit mode, the result of the current conversion cycle is a 12-bit serial-data stream clocked out during
the next I/O cycle. The current I/O cycle must be exactly 12 bits long to maintain synchronization, even
when this corrupts the output data from the previous conversion. The current conversion begins
immediately after the twelfth falling edge of the current I/O cycle.
data input
The data input is internally connected to an 8-bit serial-input address and control register. The register defines
the operation of the converter and the output data length. The host provides the data word with the MSB first.
Each data bit is clocked in on the rising edge of the I/O CLOCK sequence (see Table 1 for the data register
format).
TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
5
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
data input (continued)
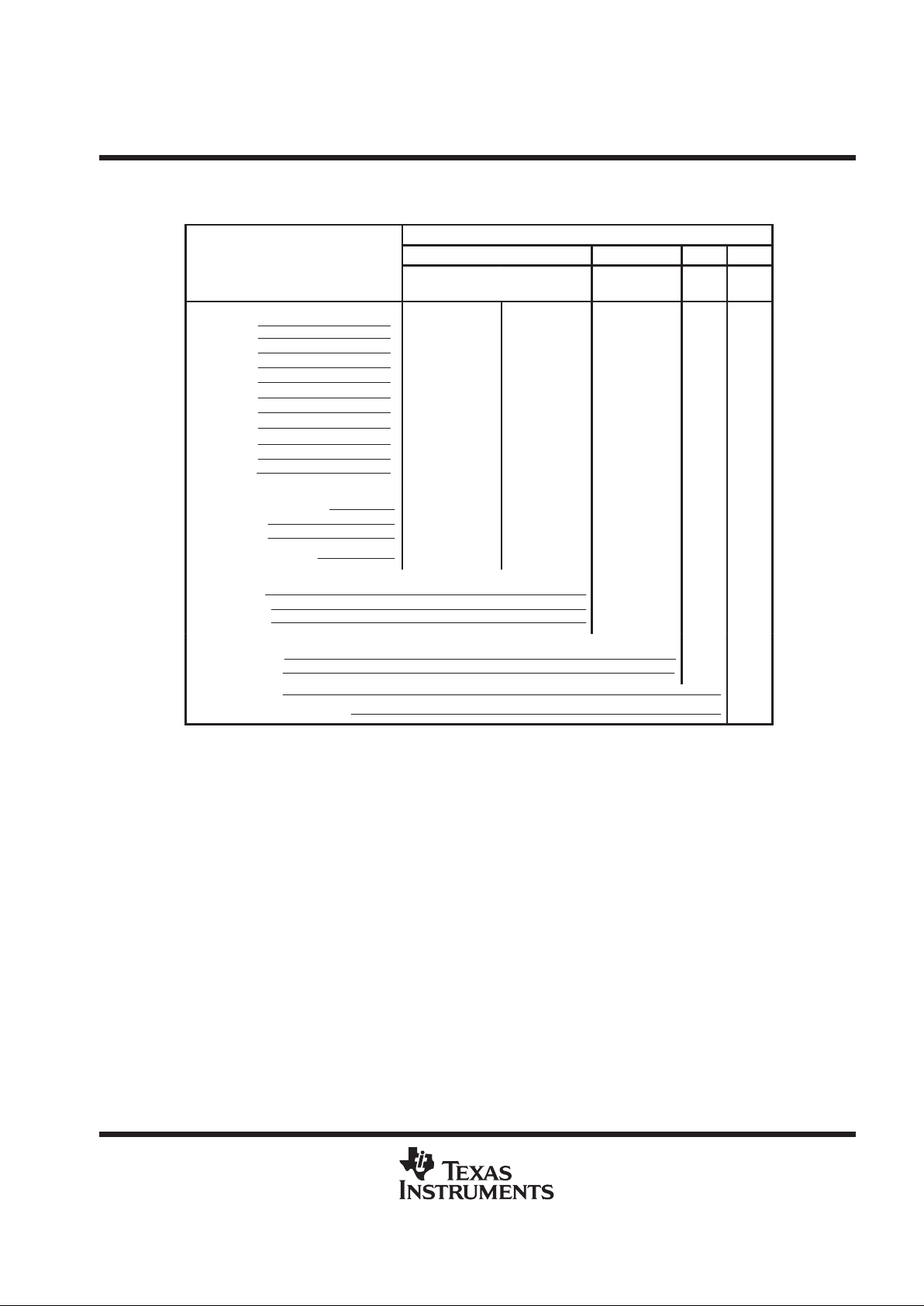
Table 1. Input-Register Format
INPUT DATA BYTE
ADDRESS BITS L1 L0 LSBF BIP
FUNCTION SELECT
D7
(MSB)
D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
(LSB)
Select input channel
AIN0
AIN1
AIN2
AIN3
AIN4
AIN5
AIN6
AIN7
AIN8
AIN9
AIN10
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
Select test voltage
(V
ref+
– V
ref–
)/2
V
ref–
V
ref+
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
Software power down 1 110
Output data length
8 bits
12 bits
16 bits
0
X
1
1
0
1
Output data format
MSB first
LSB first
0
1
Unipolar (binary) 0
Bipolar (BIP, 2s complement) 1
data input address bits
The four MSBs (D7 – D4) of the data register address one of the 11 input channels, a reference-test voltage,
or the power-down mode. The address bits affect the current conversion, which is the conversion that
immediately follows the current I/O cycle. The reference voltage is nominally equal to V
ref+
– V
ref–
.
data output length
The next two bits (D3 and D2) of the data register select the output data length. The data-length selection is
valid for the current I/O cycle (the cycle in which the data is read). The data-length selection, which is valid for
the current I/O cycle, allows device start-up without losing I/O synchronization. A data length of 8, 12, or 16 bits
can be selected. Since the converter has 12-bit resolution, a data length of 12 bits is suggested.
With D3 and D2 set to 00 or 10, the device is in the 12-bit data-length mode and the result of the current
conversion is output as a 12-bit serial-data stream during the next I/O cycle. The current I/O cycle must be
exactly 12 bits long for proper synchronization, even when this means corrupting the output data from a previous
conversion. The current conversion is started immediately after the twelfth falling edge of the current I/O cycle.
With bits D3 and D2 set to 1 1, the 16-bit data-length mode is selected, which allows convenient communication
with 16-bit serial interfaces. In the 16-bit mode, the result of the current conversion is output as a 16-bit
serial-data stream during the next I/O cycle with the four LSBs always set to 0 (pad bits). The current I/O cycle
must be exactly 16 bits long to maintain synchronization even when this means corrupting the output data from
the previous conversion. The current conversion is started immediately after the sixteenth falling edge of the
current I/O cycle.

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
data output length (continued)
With bits D3 and D2 set to 01, the 8-bit data-length mode is selected, which allows fast communication with 8-bit
serial interfaces. In the 8-bit mode, the result of the current conversion is output as an 8-bit serial-data stream
during the next I/O cycle. The current I/O cycle must be exactly 8 bits long to maintain synchronization, even
when this means corrupting the output data from the previous conversion. The four LSBs of the conversion
result are truncated and discarded. The current conversion is immediately started after the eighth falling edge
of the current I/O cycle.
Since D3 and D2 take effect on the current I/O cycle when the data length is programmed, there can be a conflict
with the previous cycle when the data-word length is changed from one cycle to the next. This may occur when
the data format is selected to be least significant bit first, since at the time the data length change becomes
effective (six rising edges of I/O CLOCK), the previous conversion result has already started shifting out.
In actual operation, when different data lengths are required within an application and the data length is changed
between two conversions, no more than one conversion result can be corrupted and only when it is shifted out
in LSB first format.
sampling period
During the sampling period, one of the analog inputs is internally connected to the capacitor array of the
converter to store the analog input signal. The converter starts sampling the selected input immediately after
the four address bits have been clocked into the input data register. Sampling starts on the fourth falling edge
of I/O CLOCK. The converter remains in the sampling mode until the eighth, twelfth, or sixteenth falling edge
of the I/O CLOCK depending on the data-length selection. After the EOC delay time from the last I/O CLOCK
falling edge, the EOC output goes low indicating that the sampling period is over and the conversion period has
begun. After EOC goes low, the analog input can be changed without af fecting the conversion result. Since the
delay from the falling edge of the last I/O CLOCK to EOC low is fixed, time-varying analog input signals can be
digitized at a fixed rate without introducing systematic harmonic distortion or noise due to timing uncertainty.
After the 8-bit data stream has been clocked in, DA TA INPUT should be held at a fixed digital level until EOC
goes high (indicating that the conversion is complete) to maximize the sampling accuracy and minimize the
influence of external digital noise.
data register, LSB first
D1 in the input data register (LSB first) controls the direction of the output binary data transfer. When D1 is set
to 0, the conversion result shifts out MSB first. When set to 1, the data shifts out LSB first. Selection of MSB
first or LSB first always affects the next I/O cycle and not the current I/O cycle. When changing from one data
direction to another, the current I/O cycle is never disrupted.
data register, bipolar format
D0 in the input data register controls the binary data format used to represent the conversion result. When D0
is set to 0, the conversion result is represented as unipolar (unsigned binary) data. Nominally , the conversion
result of an input voltage equal to V
ref–
is a code of all zeros (000...0), the conversion result of an input voltage
equal to V
ref+
is a code of all ones (1 1 1 . . . 1), and the conversion result of (V
ref +
+ V
ref–
)/2 is a code of a one
followed by zeros (100...0).
When D0 is set to 1, the conversion result is represented as bipolar data (signed binary). Nominally , conversion
of an input voltage equal to V
ref–
is a code of a 1 followed by zeros (100...0), conversion of an input voltage
equal to V
ref+
is a code of a 0 followed by all ones (01 1 . . . 1), and the conversion of (V
ref+
+ V
ref–
)/2 is a code
of all zeros (000...0). The MSB is interpreted as the sign bit. The bipolar data format is related to the unipolar
format in that the MSBs are always each other’s complement.
Selection of the unipolar or bipolar format always affects the current conversion cycle, and the result is output
during the next I/O cycle. When changing between unipolar and bipolar formats, the data output during the
current I/O cycle is not affected.
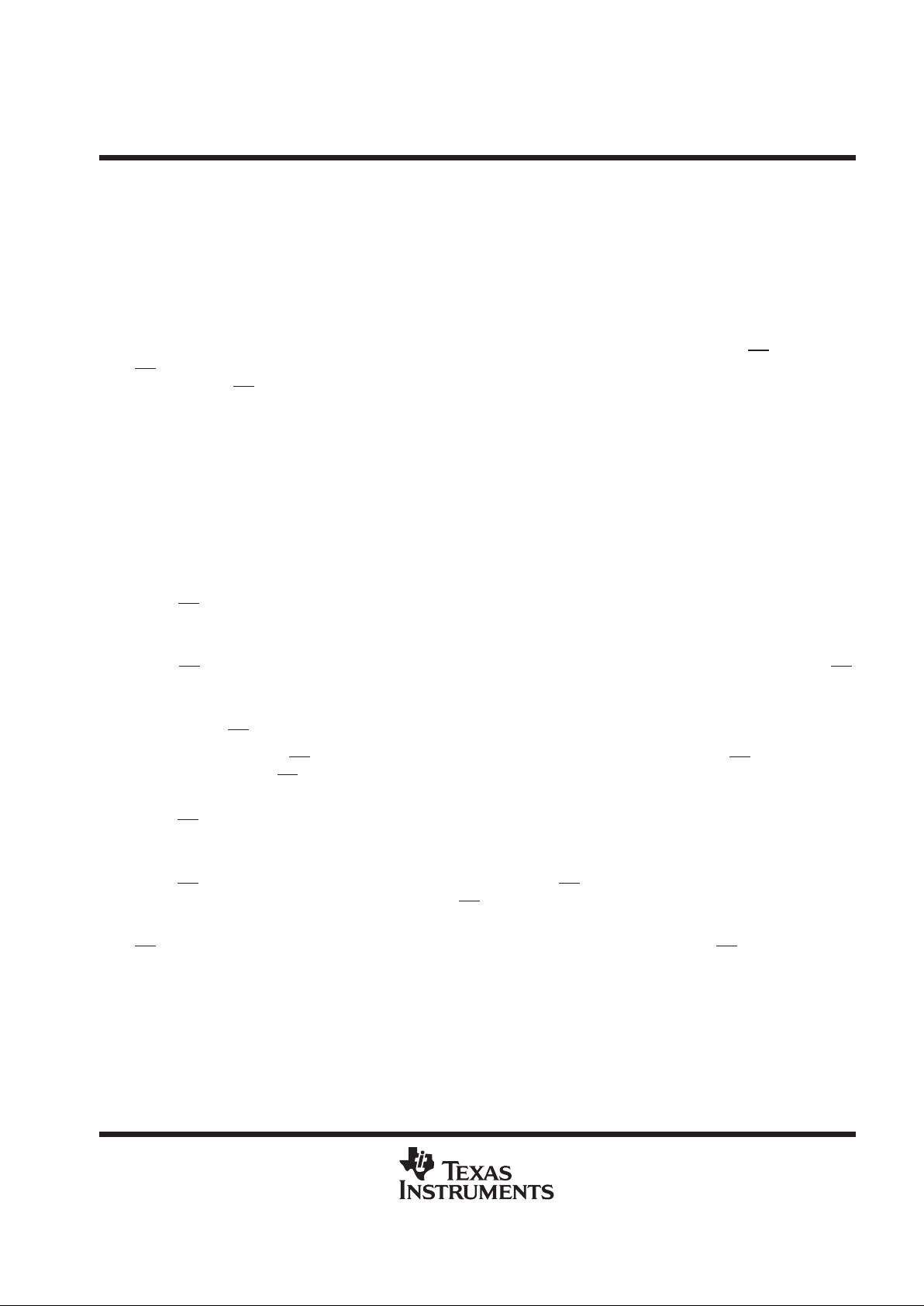
TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
7
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
EOC output
The EOC signal indicates the beginning and the end of conversion. In the reset state, EOC is always high. During
the sampling period (beginning after the fourth falling edge of the I/O CLOCK sequence), EOC remains high
until the internal sampling switch of the converter is safely opened. The opening of the sampling switch occurs
after the eighth, twelfth, or sixteenth I/O CLOCK falling edge, depending on the data-length selection in the input
data register. After the EOC signal goes low, the analog input signal can be changed without affecting the
conversion result.
The EOC signal goes high again after the conversion completes and the conversion result is latched into the
output data register. The rising edge of EOC returns the converter to a reset state and a new I/O cycle begins.
On the rising edge of EOC, the first bit of the current conversion result is on DA T A OUT when CS
is low. When
CS
is negated between conversions, the first bit of the current conversion result occurs at DATA OUT on the
falling edge of CS
.
data format and pad bits
D3 and D2 of the input data register determine the number of significant bits in the digital output that represent
the conversion result. The LSB-first bit determines the direction of the data transfer while the BIP bit determines
the arithmetic conversion. The numerical data is always justified toward the MSB in any output format.
The internal conversion result is always 12 bits long. When an 8-bit data transfer is selected, the four LSBs of
the internal result are discarded to provide a faster one-byte transfer. When a 12-bit transfer is used, all bits are
transferred. When a 16-bit transfer is used, four LSB pad bits are always appended to the internal conversion
result. In the LSB-first mode, four leading zeros are output. In the MSB-first mode, the last four bits output are
zeros.
When CS
is held low continuously , the first data bit of the just completed conversion occurs on DATA OUT on
the rising edge of EOC. When a new conversion is started after the last falling edge of I/O CLOCK, EOC goes
low and the serial output is forced to a logic zero until EOC goes high again.
When CS
is negated between conversions, the first data bit occurs on DATA OUT on the falling edge of CS.
On each subsequent falling edge of I/O CLOCK after the first data bit appears, the data is changed to the next
bit in the serial conversion result until the required number of bits has been output.
chip-select input (CS
)
The chip-select input (CS
) enables and disables the device. During normal operation, CS should be low.
Although the use of CS
is not necessary to synchronize a data transfer, it can be brought high between
conversions to coordinate the data transfer of several devices sharing the same bus.
When CS
is brought high, the serial-data output is immediately brought to the high-impedance state, releasing
its output data line to other devices that may share it. After an internally generated debounce time, the I/O
CLOCK is inhibited, thus preventing any further change in the internal state.
When CS
is subsequently brought low again, the device is reset. CS must be held low for an internal debounce
time before the reset operation takes effect. After CS
is debounced low, I/O CLOCK must remain inactive (low)
for a minimum time before a new I/O cycle can start.
CS
can be used to interrupt any ongoing data transfer or any ongoing conversion. When CS is debounced low
long enough before the end of the current conversion cycle, the previous conversion result is saved in the
internal output buffer and then shifted out during the next I/O cycle.
TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
power-down features
When a binary address of 1110 is clocked into the input data register during the first four I/O CLOCK cycles,
the power-down mode is selected. Power down is activated on the falling edge of the fourth I/O CLOCK pulse.
During power down, all internal circuitry is put in a low-current standby mode. No conversions are performed,
and the internal output buffer keeps the previous conversion cycle data results, provided that all digital inputs
are held above V
CC
– 0.3 V or below 0.3 V. The I/O logic remains active so the current I/O cycle must be
completed even when the power-down mode is selected. Upon power-on reset and before the first I/O cycle,
the converter normally begins in the power-down mode. The device remains in the power-down mode until a
valid (other than 1110) input address clocks in. Upon completion of that I/O cycle, a normal conversion is
performed with the results being shifted out during the next I/O cycle.
analog input, test, and power-down mode
The 11 analog inputs, three internal voltages, and power-down mode are selected by the input multiplexer
according to the input addresses shown in T ables 2, 3, and 4. The input multiplexer is a break-before-make type
to reduce input-to-input noise rejection resulting from channel switching. Sampling of the analog input starts on
the falling edge of the fourth I/O CLOCK and continues for the remaining I/O CLOCK pulses. The sample is held
on the falling edge of the last I/O CLOCK pulse. The three internal test inputs are applied to the multiplexer,
sampled, and converted in the same manner as the external analog inputs. The first conversion after the device
has returned from the power-down state may not read accurately due to internal device settling.
Table 2. Analog-Channel-Select Address
ANALOG INPUT
VALUE SHIFTED INTO
DATA INPUT
SELECTED
BINARY HEX
AIN0 0000 0
AIN1 0001 1
AIN2 0010 2
AIN3 0011 3
AIN4 0100 4
AIN5 0101 5
AIN6 0110 6
AIN7 0111 7
AIN8 1000 8
AIN9 1001 9
AIN10 1010 A
Table 3. Test-Mode-Select Address
INTERNAL
SELF-TEST
VALUE SHIFTED INTO
DATA INPUT
UNIPOLAR OUTPUT
VOLTAGE
SELECTED
†
BINARY HEX
RESULT (HEX)
‡
V
ref+
– V
ref–
2
1011 B 200
V
ref–
1100 C 000
V
ref+
1101 D 3FF
†
V
ref+
is the voltage applied to REF+, and V
ref–
is the voltage applied to REF–.
‡
The output results shown are the ideal values and may vary with the reference stability
and with internal offsets.

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
9
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
analog input, test, and power-down mode (continued)
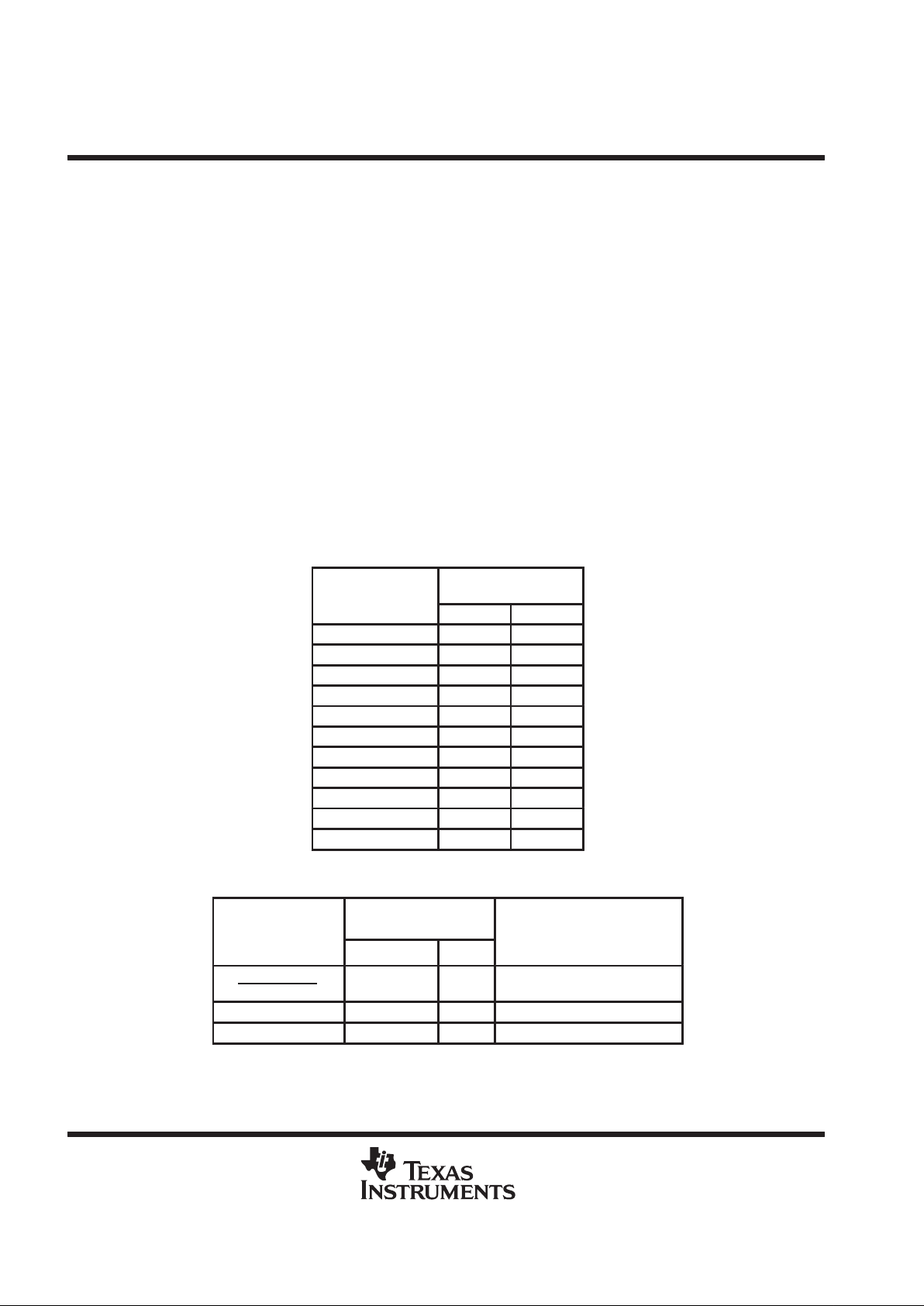
T able 4. Power-Down-Select Address
INPUT COMMAND
VALUE SHIFTED INTO
DATA INPUT
RESULT
BINARY HEX
Power down 1110 E ICC ≤ 25 µA
converter and analog input
The CMOS threshold detector in the successive-approximation conversion system determines each bit by
examining the charge on a series of binary-weighted capacitors (see Figure 1). In the first phase of the
conversion process, the analog input is sampled by closing the S
C
switch and all ST switches simultaneously .
This action charges all the capacitors to the input voltage.
In the next phase of the conversion process, all S
T
and SC switches are opened and the threshold detector
begins identifying bits by identifying the charge (voltage) on each capacitor relative to the reference (REF–)
voltage. In the switching sequence, 12 capacitors are examined separately until all 12 bits are identified and
the charge-convert sequence is repeated. In the first step of the conversion phase, the threshold detector looks
at the first capacitor (weight = 4096). Node 4096 of this capacitor is switched to the REF+ voltage, and the
equivalent nodes of all the other capacitors on the ladder are switched to REF –. When the voltage at the
summing node is greater than the trip point of the threshold detector (approximately one-half V
CC
), a bit 0 is
placed in the output register and the 4096-weight capacitor is switched to REF –. When the voltage at the
summing node is less than the trip point of the threshold detector, a bit 1 is placed in the register and the
4096-weight capacitor remains connected to REF+ through the remainder of the successive-approximation
process. The process is repeated for the 2048-weight capacitor, the 1024-weight capacitor, and so forth down
the line until all bits are determined. With each step of the successive-approximation process, the initial charge
is redistributed among the capacitors. The conversion process relies on charge redistribution to determine the
bits from MSB to LSB.
S
C
Threshold
Detector
Node 4096
REF–
REF+
S
T
4096
V
I
To Output
Latches
REF–
S
T
REF+
REF–
S
T
REF+
REF–
S
T
REF+
REF–
S
T
REF+
REF–
S
T
REF+
REF–
S
T
REF+
REF–
S
T
REF–
S
T
112481610242048
Figure 1. Simplified Model of the Successive-Approximation System

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
reference voltage inputs
There are two reference voltage inputs on the device, REF+ and REF–. The voltage values on these terminals
establish the upper and lower limits of the analog input to produce a full-scale and zero-scale reading
respectively . These voltages and the analog input should not exceed the positive supply or be lower than ground
consistent with the specified absolute maximum ratings. The digital output is at full scale when the input signal
is equal to or higher than REF+ terminal voltage and at zero when the input signal is equal to or lower than REF–
terminal voltage.
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
†
Supply voltage range, V
CC
(see Note 1) –0.5 V to 6.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input voltage range, V
I
(any input) –0.3 V to VCC + 0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output voltage range, V
O
–0.3 V to VCC + 0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Positive reference voltage, V
ref+
V
CC
+ 0.1 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Negative reference voltage, V
ref–
–0.1 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Peak input current, I
I
(any input) ±20 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Peak total input current (all inputs) ±30 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range, T
A
: TLV2543C 0°C to 70°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TLV2543I –40°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
stg
–65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from the case for 10 seconds 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTE 1: All voltage values are with respect to the GND terminal with REF– and GND wired together (unless otherwise noted).

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
11
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, V
CC
3 3.3 3.6 V
Positive reference voltage, V
ref+
(see Note 2) V
CC
V
Negative reference voltage, V
ref–
(see Note 2) 0 V
Differential reference voltage, V
ref+
– V
ref–
(see Note 2) 2.5 VCCVCC+0.1 V
Analog input voltage (see Note 2) 0 V
CC
V
High-level control input voltage, V
IH
VCC = 3 V to 3.6 V 2.1 V
Low-level control input voltage, V
IL
VCC = 3 V to 3.6 V 0.6 V
Clock frequency at I/O CLOCK 0 3 4.1 MHz
Setup time, address bits at DATA INPUT before I/O CLOCK↑, t
su(A)
(see Figure 5) 100 ns
Hold time, address bits at DATA INPUT after I/O CLOCK↑, t
h(A)
(see Figure 5) 0 ns
Hold time, CS low after last I/O CLOCK↓, t
h(CS)
(see Figure 6) 0 ns
Setup time, CS low before clocking in first address bit, t
su(CS)
(see Note 3 and Figure 6) 1.425 µs
Pulse duration, I/O CLOCK high, t
wH(I/O)
190 ns
Pulse duration, I/O CLOCK low, t
wL(I/O)
190 ns
Transition time, I/O CLOCK, t
t(I/O)
(see Note 4 and Figure 7) 1 µs
Transition time, DATA INPUT and CS, t
t(CS)
10 µs
p
p
TLV2543C 0 70
°
Operating free-air temperature, T
A
TLV2543I –40 85
°C
NOTES: 2. Analog input voltages greater than the voltage applied to REF+ convert as all ones (111111111111), while input voltages less than
the voltage applied to REF– convert as all zeros (000000000000).
3. T o minimize errors caused by noise at the CS
input, the internal circuitry waits for a setup time after CS↓ before responding to control
input signals. No attempt should be made to clock in an address until the minimum CS
setup time elapses.
4. This is the time required for the clock input signal to fall from VIHmin to VILmax or to rise from VILmax to VIHmin. In the vicinity of
normal room temperature, the devices function with input clock transition time as slow as 1 µs for remote data acquisition applications
where the sensor and the A/D converter are placed several feet away from the controlling microprocessor.

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range,
V
CC
= V
ref+
= 3 V to 3.6 V (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP
†
MAX UNIT
p
VCC = 3 V, IOH = –0.2 mA 2.4
VOHHigh-level output voltage
VCC = 3 V to 3.6 V, IOH = –20 µA VCC–0.1
V
p
VCC = 3 V, IOL = 0.8 mA 0.4
VOLLow-level output voltage
VCC = 3 V to 3.6 V, IOL = 20 µA 0.1
V
Off-state (high-impedance-state)
VO = VCC, CS at V
CC
1 2.5
I
OZ
(g )
output current
VO = 0,
CS at V
CC
1 –2.5
µ
A
I
IH
High-level input current VI = V
CC
1 2.5 µA
I
IL
Low-level input current VI = 0 1 –2.5 µA
I
CC
Operating supply current CS at 0 V 1 2.5 mA
I
CC(PD)
Power-down current
For all digital inputs,
0 ≤ VI ≤ 0.3 V or VI ≥ VCC – 0.3 V
4 25 µA
Selected channel leakage
Selected channel at VCC, Unselected channel at 0 V 1
I
lkg
g
current
Selected channel at 0 V , Unselected channel at V
CC
–1
µ
A
Maximum static analog
reference current into REF+
V
ref+
= VCC, V
ref–
= GND 1 2.5 µA
Input
Analog inputs 30 60
p
C
i
capacitance
Control inputs 5 15
pF
†
All typical values are at VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C.

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
13
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
operating characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range,
V
CC
= V
ref+
= 3 V to 3.6 V, I/O CLOCK frequency = 4.1 MHz, (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP
†
MAX UNIT
E
L
Linearity error (see Note 6) See Figure 2 ±1 LSB
E
D
Differential linearity error See Figure 2 ±1 LSB
E
O
Offset error (see Note 7)
See Note 2 and
Figure 2
±1.5 LSB
E
G
Gain error (see Note 7)
See Note 2 and
Figure 2
±1 LSB
E
T
Total unadjusted error (see Note 8) ±1.75 LSB
DATA INPUT = 1011 2038 2048 2058
Self-test output code (see Table 3 and Note 9)
DATA INPUT = 1100
0 10
DATA INPUT = 1101 4075 4095
t
conv
Conversion time See Figures 10–15 8 10 µs
t
c
Total cycle time (access, sample, and conversion)
See Figures 10–15
and Note 10
10 + total
I/O CLOCK
periods +
t
d(I/O-EOC)
µs
t
acq
Channel acquisition time (sample)
See Figures 10–15
and Note 10
4 12
I/O
CLOCK
periods
t
v
Valid time, DATA OUT remains valid after I/O CLOCK↓ See Figure 7 10 ns
t
d(I/O-DATA)
Delay time, I/O CLOCK↓ to DATA OUT valid See Figure 7 250 ns
t
d(I/O-EOC)
Delay time, last I/O CLOCK↓ to EOC↓ See Figure 8 1.5 2.2 µs
t
d(EOC-DATA)
Delay time, EOC↑ to DATA OUT (MSB/LSB) See Figure 9 200 ns
t
PZH
, t
PZL
Enable time, CS↓ to DATA OUT (MSB/LSB driven) See Figure 4 0.7 1.3 µs
t
PHZ
, t
PLZ
Disable time, CS↑ to DATA OUT (high impedance) See Figure 4 70 150 ns
t
r(EOC)
Rise time, EOC See Figure 9 15 50 ns
t
f(EOC)
Fall time, EOC See Figure 8 15 50 ns
t
r(bus)
Rise time, data bus See Figure 7 15 50 ns
t
f(bus)
Fall time, data bus See Figure 7 15 50 ns
t
d(I/O-CS)
Delay time, last I/O CLOCK↓ to CS↓ to abort conversion
(see Note 11)
5 µs
†
All typical values are at TA = 25°C.
NOTES: 2. Analog input voltages greater than that applied to REF+ convert as all ones (111111111111), while input voltages less than that
applied to REF– convert as all zeros (000000000000).
6. Linearity error is the maximum deviation from the best straight line through the A/D transfer characteristics.
7. Gain error is the difference between the actual midstep value and the nominal midstep value in the transfer diagram at the specified
gain point after the offset error has been adjusted to zero. Offset error is the difference between the actual midstep value an d the
nominal midstep value at the offset point.
8. Total unadjusted error comprises linearity, zero-scale, and full-scale errors.
9. Both the input address and the output codes are expressed in positive logic.
10. I/O CLOCK period = 1/(I/O CLOCK frequency) (see Figure 7).
11. Any transitions of CS
are recognized as valid only when the level is maintained for a setup time. CS must be taken low at ≤ 5 µs
of the tenth I/O CLOCK falling edge to ensure that a conversion is aborted. Between 5 µs and 10 µs, the result is uncertain as to
whether the conversion is aborted or the conversion results are valid.

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
14
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
_
+
C2
0.1 µF
C1
10 µF
C3
470 pF
50 Ω
15 V
50 Ω
–15 V
V
I
AIN0–AIN10
TLV2543
10 Ω
U1
C1
10 µF
C3
470 pF
C2
0.1 µF
LOCATION
U1
C1
C2
C3
DESCRIPTION
OP27
10-µF 35-V tantalum capacitor
0.1-µF ceramic NPO SMD capacitor
470-pF porcelain high-Q SMD capacitor
PART NUMBER
—
—
AVX 12105C104KA105 or equivalent
Johanson 201S420471JG4L or equivalent
Figure 2. Analog Input Buffer to Analog Inputs AIN0–AIN10
Test Point
Output
Under Test
CL = 100 pF
I
source
0.8 mA
See Note A
Vcp = 2 V
I
sink
–0.2 mA
NOTE A: Equivalent load circuit of the Teradyne A580 tester for timing
parameter measurement.
Figure 3. Timing Load Circuits
CS
DATA
OUT
2.4 V
0.4 V
90%
10%
t
PZH
, t
PZL
t
PHZ
, t
PLZ
2 V
Figure 4. DATA OUT to Hi-Z Voltage Waveforms
0.8 V
DATA INPUT
t
h(A)
0.8 V
2 V
I/O CLOCK
Data
Valid
t
su(A)
0.8 V
Figure 5. DATA INPUT and I/O CLOCK
Voltage Waveforms

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
15
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
Last
Clock
CS
0.8 V
2 V
0.8 V
t
su(CS)
0.8 V
I/O CLOCK
t
h(CS)
Figure 6. CS and I/O CLOCK Voltage Waveforms
†
†
T o ensure full conversion accuracy , it is recommended that no input signal change occurs while
a conversion is ongoing.
0.4 V
2.4 V
0.4 V
2.4 V
2 V
0.8 V
I/O CLOCK
DATA OUT
t
t(I/O)
0.8 V
2 V
t
r(bus)
, t
f(bus)
t
d(I/O-DATA)
t
v
t
t(I/O)
0.8 V
I/O CLOCK Period
Figure 7. I/O CLOCK and DATA OUT Voltage Waveforms
Last
Clock
0.8 V
2.4 V
0.4 V
t
f(EOC)
t
d(I/O-EOC)
I/O CLOCK
EOC
Figure 8. I/O CLOCK and EOC Voltage Waveforms
0.4 V
2.4 V
EOC
t
d(EOC-DATA)
Valid MSB
DATA OUT
0.4 V
2.4 V
t
r(EOC)
Figure 9. EOC and DATA OUT Voltage Waveforms

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
16
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
Access Cycle B
Shift in New Multiplexer Address,
Simultaneously Shift Out Previous
Conversion Value
Sample Cycle B
A/D Conversion
Interval
InitializeInitialize
MSB LSB
Previous Conversion Data
MSB LSB
B7 B6 B5 B4
C7
B11A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A1 A0
Hi-Z State
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 11 12 1
I/O
CLOCK
DATA
OUT
DATA
INPUT
CS
EOC
(see Note A)
B3 B2 B1 B0
t
conv
Figure 10. Timing for 12-Clock Transfer Using CS With MSB First
Access Cycle B
Shift in New Multiplexer Address,
Simultaneously Shift Out Previous
Conversion Value
Sample Cycle B
A/D Conversion
Interval
Initialize
MSB LSB
Previous Conversion Data
MSB LSB
B7 B6 B5 B4 C7
B11A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A1 A0
Low Level
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 11 12 1
I/O
CLOCK
DATA
OUT
DATA
INPUT
CS
EOC
Initialize
(see Note A)
B3 B2 B1 B0
t
conv
Figure 11. Timing for 12-Clock Transfer Not Using CS With MSB First
NOTE A: To minimize errors caused by noise at CS, the internal circuitry waits for a setup time after CS↓ before responding to control input signals.
Therefore, no attempt should be made to clock in an address until the minimum CS
setup time has elapsed.

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
17
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
Access Cycle B
Shift in New Multiplexer Address,
Simultaneously Shift Out Previous
Conversion Value
Sample Cycle B
A/D Conversion
Interval
Initialize
MSB LSB
Previous Conversion Data
MSB LSB
B7 B6 B5 B4 C7
B7A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
12345678 1
I/O CLOCK
DATA OUT
DATA INPUT
CS
EOC
Initialize
Hi-Z
(see Note A)
B3 B2 B1 B0
t
conv
Figure 12. Timing for 8-Clock Transfer Using CS
With MSB First
Access Cycle B Sample Cycle B
A/D Conversion
Interval
Initialize
MSB LSB
Previous Conversion Data
MSB LSB
B7 B6 B5 B4 C7
B7A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Low Level
12345678 1
I/O CLOCK
DATA OUT
DATA INPUT
CS
EOC
Initialize
(see Note A)
B3 B2 B1 B0
t
conv
Shift in New Multiplexer Address,
Simultaneously Shift Out Previous
Conversion Value
Figure 13. Timing for 8-Clock Transfer Not Using CS With MSB First
NOTE A: To minimize errors caused by noise at CS, the internal circuitry waits for a setup time after CS↓ before responding to control
input signals. Therefore, no attempt should be made to clock in an address until the minimum CS
setup time has elapsed.

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
18
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
ÎÎ
A/D Conversion
Interval
Initialize
MSB LSB
MSB LSB
B7 B6 B5 B4 C7
B15A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A1 A0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 15 16 1
I/O
CLOCK
DATA
OUT
DATA
INPUT
CS
EOC
Initialize
Hi-Z State
(see Note A)
B3 B2 B1 B0
Access Cycle B Sample Cycle B
Previous Conversion Data
t
conv
Shift in New Multiplexer Address,
Simultaneously Shift Out Previous
Conversion Value
Figure 14. Timing for 16-Clock Transfer Using CS With MSB First
A/D Conversion
Interval
Initialize
MSB LSB
MSB LSB
B7 B6 B5 B4 C7
B15A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A1 A0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 15 16 1
I/O
CLOCK
DATA
OUT
DATA
INPUT
CS
EOC
Low Level
(see Note A)
B3 B2 B1 B0
Sample Cycle B
Access Cycle B
Previous Conversion Data
t
conv
Shift in New Multiplexer Address,
Simultaneously Shift Out Previous
Conversion Value
Figure 15. Timing for 16-Clock Transfer Not Using CS With MSB First
NOTE A: To minimize errors caused by noise at CS, the internal circuitry waits for a setup time after CS↓ before responding to control input signals.
Therefore, no attempt should be made to clock in an address until the minimum CS
setup time has elapsed.

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
19
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
100000000000
011111111111
000000000010
000000000001
000000000000
111111111110
0 0.0016 1.6376 1.6384 1.6392
Digital Output Code
100000000001
111111111101
111111111111
3.2752 3.2760 3.2768
2048
2047
2
1
0
4094
Step
2049
4093
4095
0.0004
VI – Analog Input Voltage – V
VZT = VZS + 1/2 LSB
V
ZS
See Notes A and B
3.2756
0.0008
VFT = VFS – 1/2 LSB
V
FS
V
FSnom
NOTES: A. This curve is based on the assumption that V
ref+
and V
ref–
have been adjusted so that the voltage at the transition from digital 0
to 1 (VZT) is 0.0004 V and the transition to full scale (VFT) is 3.2756 V . 1 LSB = 0.8 mV.
B. The full-scale value (VFS) is the step whose nominal midstep value has the highest absolute value. The zero-scale value (VZS) is
the step whose nominal midstep value equals zero.
Figure 16. Ideal Conversion Characteristics
Processor
Control
Circuit
Analog
Inputs
AIN0
AIN1
AIN2
AIN3
AIN4
AIN5
AIN6
AIN7
AIN8
AIN9
AIN10
I/O CLOCK
CS
DATA INPUT
DATA OUT
EOC
REF+
REF–
GND
TLV2543
To Source
Ground
3-V DC Regulated
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
12
15
18
17
16
19
14
13
10
Figure 17. Serial Interface

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
20
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
simplified analog input analysis
Using the equivalent circuit in Figure 18, the time required to charge the analog input capacitance from 0 to V
S
within 1/2 LSB can be derived as follows:
The capacitance charging voltage is given by
(1)
where
R
t
= Rs + r
i
VC+
V
S
ǒ
1–e
–tcń
RtC
i
Ǔ
The final voltage to 1/2 LSB is given by
(2)V
C
(1/2 LSB) = VS – (VS/8192)
Equating equation 1 to equation 2 and solving for time t
c
gives
(3)
and
t
c
(1/2 LSB) = Rt × Ci × ln(8192) (4)
VS*
ǒ
VSń
58192Ǔ+
V
S
ǒ
1–e
–tcń
RtC
i
Ǔ
Therefore, with the values given the time for the analog input signal to settle is
(5)
t
c
(1/2 LSB) = (Rs + 1 kΩ) × 60 pF × ln(8192)
This time must be less than the converter sample time shown in the timing diagrams.
R
s
r
i
V
S
V
C
50 pF MAX
1 kΩ MAX
Driving Source
†
TLV2543
C
i
V
I
VI= Input Voltage at AIN
VS= External Driving Source Voltage
Rs= Source Resistance
ri= Input Resistance
Ci= Input Capacitance
†
Driving source requirements:
• Noise and distortion for the source must be equivalent to the
resolution of the converter.
• Rs must be real at the input frequency.
Figure 18. Equivalent Input Circuit Including the Driving Source

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
21
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
MECHANICAL DATA
DB (R-PDSO-G**) PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
4040065 /B 10/94
28 PIN SHOWN
Gage Plane
8,20
7,40
0,15 NOM
0,63
1,03
0,25
38
12,90
12,30
28
10,50
24
8,50
Seating Plane
9,907,90
30
10,50
9,90
0,38
5,60
5,00
15
0,22
14
A
28
1
2016
6,50
6,50
14
0,05 MIN
5,905,90
DIM
A MAX
A MIN
PINS **
2,00 MAX
6,90
7,50
0,65
M
0,15
0°–8°
0,10
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion not to exceed 0,15.
D. Falls within JEDEC MO-150

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
22
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
MECHANICAL DATA
DW (R-PDSO-G**) PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
16 PIN SHOWN
4040000/B 10/94
Seating Plane
0.400 (10,15)
0.419 (10,65)
0.104 (2,65) MAX
1
0.012 (0,30)
0.004 (0,10)
A
8
16
0.020 (0,51)
0.014 (0,35)
0.293 (7,45)
0.299 (7,59)
9
0.010 (0,25)
0.050 (1,27)
0.016 (0,40)
(15,24)
(15,49)
PINS **
0.010 (0,25) NOM
A MAX
DIM
A MIN
Gage Plane
20
0.500
(12,70)
(12,95)
0.510
(10,16)
(10,41)
0.400
0.410
16
0.600
24
0.610
(17,78)
28
0.700
(18,03)
0.710
0.004 (0,10)
M
0.010 (0,25)
0.050 (1,27)
0°–8°
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion not to exceed 0.006 (0,15).
D. Falls within JEDEC MS-013

TLV2543C, TLV2543I
12-BIT ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
WITH SERIAL CONTROL AND 11 ANALOG INPUTS
SLAS096B – MARCH 1995 – REVISED OCTOBER 1995
23
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
MECHANICAL DATA
N (R-PDIP-T**) PLASTIC DUAL-IN-LINE PACKAGE
4040049/C 7/95
16 PIN SHOWN
0.310 (7,87)
0.290 (7,37)
Seating Plane
0.010 (0,25) NOM
14 Pin Only
9
8
0.070 (1,78) MAX
A
0.035 (0,89) MAX
0.020 (0,51) MIN
16
1
0.015 (0,38)
0.021 (0,53)
0.200 (5,08) MAX
0.125 (3,18) MIN
0.240 (6,10)
0.260 (6,60)
0.100 (2,54)
M
0.010 (0,25)
0°–15°
20
0.975
(24,77)
(23,88)
0.940
18
0.920
0.850
14
0.775
(19,69)
0.745
(18,92)
16
0.775
(19,69)
(18,92)
0.745
PINS **
A MIN
DIM
A MAX
(23.37)
(21.59)
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Falls within JEDEC MS-001 (20-pin package is shorter than MS-001)

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICA TIONS IS UNDERST OOD TO
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1998, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...