Texas Instruments TIBPAL16R8-12MWB, TIBPAL16R8-12MJB, TIBPAL16R8-12MJ, TIBPAL16R6-12MWB, TIBPAL16R6-12MJB Datasheet
...
TIBPAL16L8-10C, TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
TIBPAL16L8-12M, TIBPAL16R4-12M, TIBPAL16R6-12M, TIBPAL16R8-12M
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
CIRCUITS
• High-Performance Operation:
f
(w/o feedback)
max
TIBPAL16R’-10C Series . . . 62.5 MHz Min
TIBPAL16R’-12M Series . . . 56 MHz Min
f
(with feedback)
max
TIBPAL16R’-10C Series . . . 55.5 MHz Min
TIBPAL16R’-12M Series . . . 48 MHz Min
Propagation Delay
TIBPAL16L’-10C Series . . . 10 ns Max
TIBPAL16L’-12M Series . . . 12 ns Max
• Functionally Equivalent, but Faster than,
Existing 20-Pin PLDs
• Preload Capability on Output Registers
Simplifies Testing
• Power-Up Clear on Registered Devices (All
Register Outputs are Set Low, but Voltage
Levels at the Output Pins Go High)
• Package Options Include Both Plastic and
Ceramic Chip Carriers in Addition to Plastic
and Ceramic DIPs
• Security Fuse Prevents Duplication
• Dependable Texas Instruments Quality and
Reliability
DEVICE
PAL16L8 10 2 0 6
PAL16R4 8 0 4 (3-state buffers) 4
PAL16R6 8 0 6 (3-state buffers) 2
PAL16R8 8 0 8 (3-state buffers) 0
I
INPUTS
description
3-STATE
O OUTPUTS
REGISTERED
Q OUTPUTS
I/O
PORT
S
TIBPAL16L8’
C SUFFIX . . . J OR N PACKAGE
M SUFFIX . . . J PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
I
1
I
2
I
3
I
4
I
5
I
6
I
7
I
8
I
9
GND
C SUFFIX . . . FN PACKAGE
M SUFFIX . . . FK PACKAGE
I
I
I
I
I
10
TIBPAL16L8’
(TOP VIEW)
I
I
3 2 1 20 19
4
5
6
7
8
910111213
I
V
20
CC
O
19
I/O
18
I/O
17
I/O
16
15
I/O
14
I/O
13
I/O
12
O
11
I
CC
I
O
V
I/O
18
I/O
17
I/O
16
I/O
15
I/O
14
I
O
I/O
GND
Pin assignments in operating mode
These programmable array logic devices feature high speed and functional equivalency when compared with
currently available devices. These IMPACT-X circuits combine the latest Advanced Low-Power Schottky
technology with proven titanium-tungsten fuses to provide reliable, high-performance substitutes for
conventional TTL logic. Their easy programmability allows for quick design of custom functions and typically
results in a more compact circuit board. In addition, chip carriers are available for futher reduction in board
space.
All of the register outputs are set to a low level during power up. Extra circuitry has been provided to allow loading
of each register asynchronously to either a high or low state. This feature simplifies testing because the registers
can be set to an initial state prior to executing the test sequence.
The TIBPAL16’ C series is characterized from 0°C to 75°C. The TIBPAL16’ M series is characterized for
operation over the full military temperature range of –55°C to 125°C.
These devices are covered by U.S. Patent 4,410,987.
IMPACT-X is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
PAL is a registered trademark of Advanced Micro Devices Inc.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Copyright 1992, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
TIBPAL16R4-12M, TIBPAL16R6-12M, TIBPAL16R8-12M
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
CIRCUITS
TIBPAL16R4’
C SUFFIX . . . J OR N PACKAGE
M SUFFIX . . . J PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
CLK
1
I
2
I
3
I
4
I
5
I
6
I
7
I
8
I
9
GND
C SUFFIX . . . J OR N PACKAGE
M SUFFIX . . . J PACKAGE
GND
CLK
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
10
TIBPAL16R6’
(TOP VIEW)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
V
I/O
I/O
Q
Q
Q
Q
I/O
I/O
OE
V
I/O
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
I/O
OE
CC
CC
TIBPAL16R4’
C SUFFIX . . . FN PACKAGE
M SUFFIX . . . FK PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
CC
I
CLK
I/O
V
18
17
16
15
14
3 2 1 20 19
I
4
I
5
I
6
I
7
I
8
910111213
I
I
I/O
I/O
OE
GND
TIBPAL16R6’
C SUFFIX . . . FN PACKAGE
M SUFFIX . . . FK PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
I
GND
CLK
OE
CC
V
I/O
I/O
18
17
16
15
14
Q
3 2 1 20 19
I
4
I
5
I
6
I
7
I
8
910111213
I
I
I/O
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
TIBPAL16R8’
C SUFFIX . . . J OR N PACKAGE
M SUFFIX . . . J PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
CLK
1
I
2
I
3
I
4
I
5
I
6
I
7
I
8
I
9
GND
Pin assignments in operating mode
2
10
V
20
CC
Q
19
Q
18
Q
17
Q
16
15
Q
14
Q
13
Q
12
Q
11
OE
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TIBPAL16R8’
C SUFFIX . . . FN PACKAGE
M SUFFIX . . . FK PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
I
GND
CLK
OE
CC
V
Q
Q
18
17
16
15
14
Q
3 2 1 20 19
I
4
I
5
I
6
I
7
I
8
910111213
I
I
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
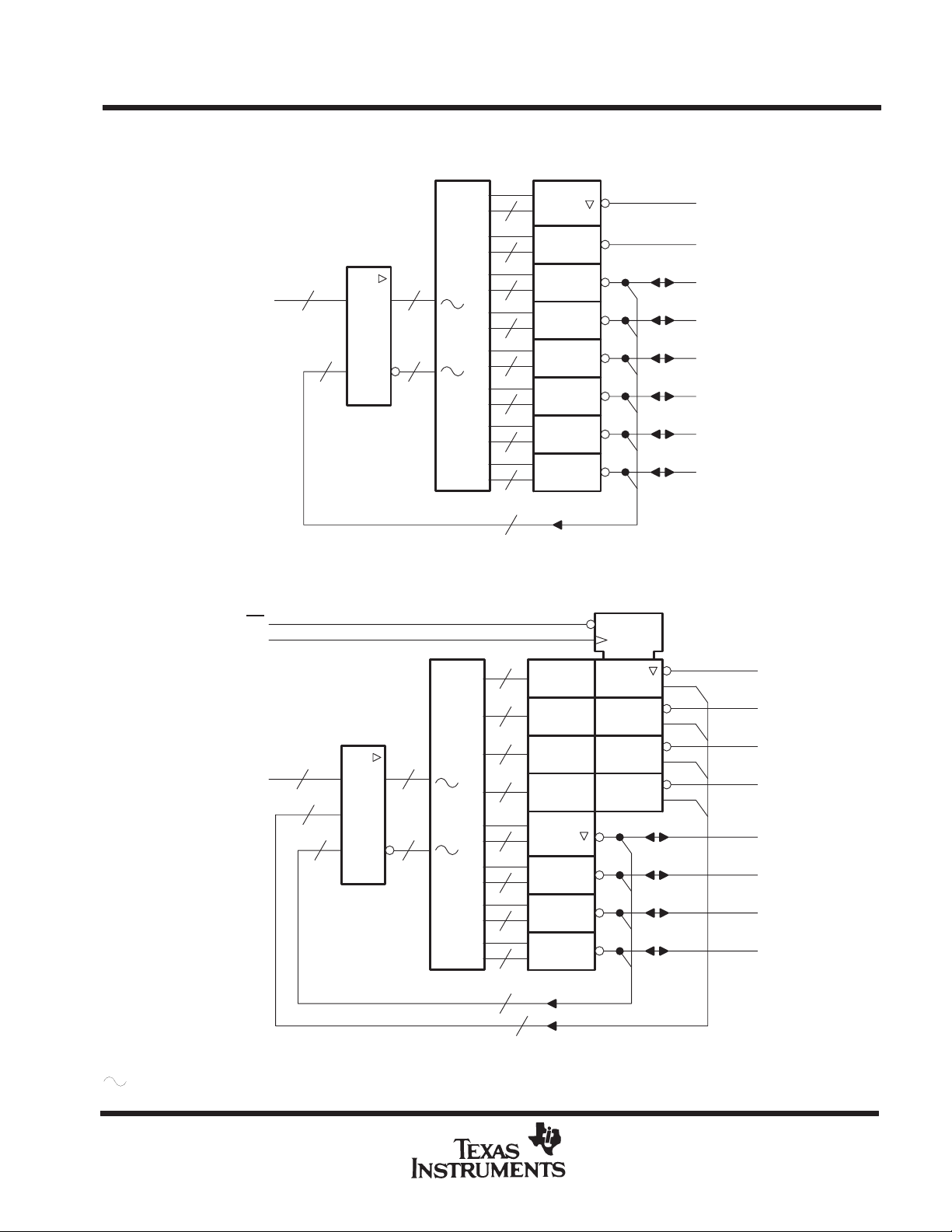
functional block diagrams (positive logic)
TIBPAL16L8-10C, TIBPAL16R4-10C
TIBPAL16L8-12M, TIBPAL16R4-12M
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
TIBPAL16L8 ’
CIRCUITS
OE
CLK
10 16
I
16 x
&
32 X 64
166
TIBPAL16R4’
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
6
EN
≥1
O
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
EN 2
C1
denotes fused inputs
816
I
16 x
4
164
&
32 X 64
1D
I = 0
2
Q
Q
Q
Q
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
7
4
≥1
≥1
EN
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
3
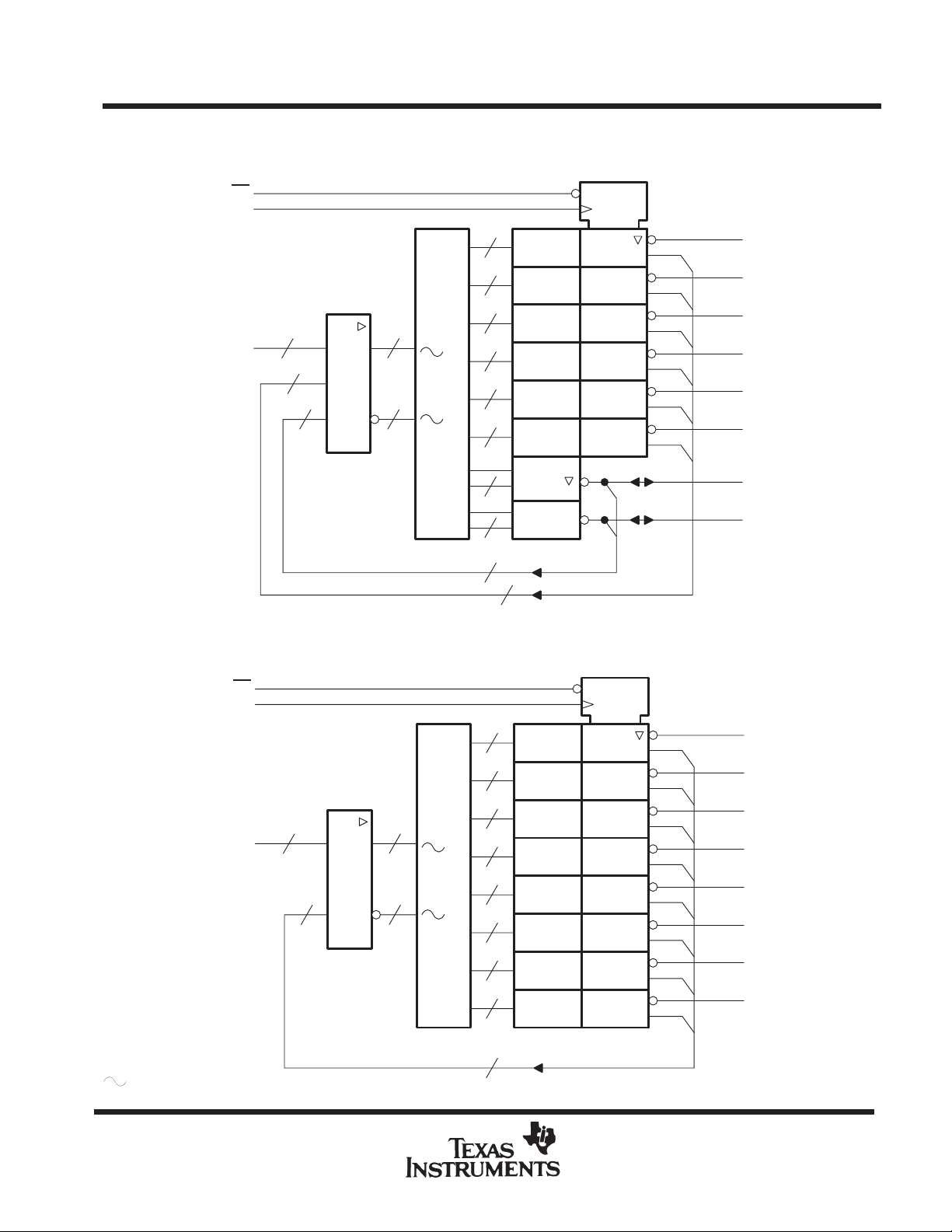
TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
TIBPAL16R6-12M, TIBPAL16R8-12M
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
functional block diagrams (positive logic)
CIRCUITS
TIBPAL16R6 ’
OE
CLK
816
I
16 x
6
162
&
32 X 64
EN 2
C1
1D
I = 0
2
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
I/O
I/O
8
8
8
8
8
8
7
7
2
≥1
≥1
EN
6
OE
CLK
denotes fused inputs
816
I
16 x
168
TIBPAL16R8’
&
32 X 64
EN 2
C1
1D
I = 0
2
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
≥1
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
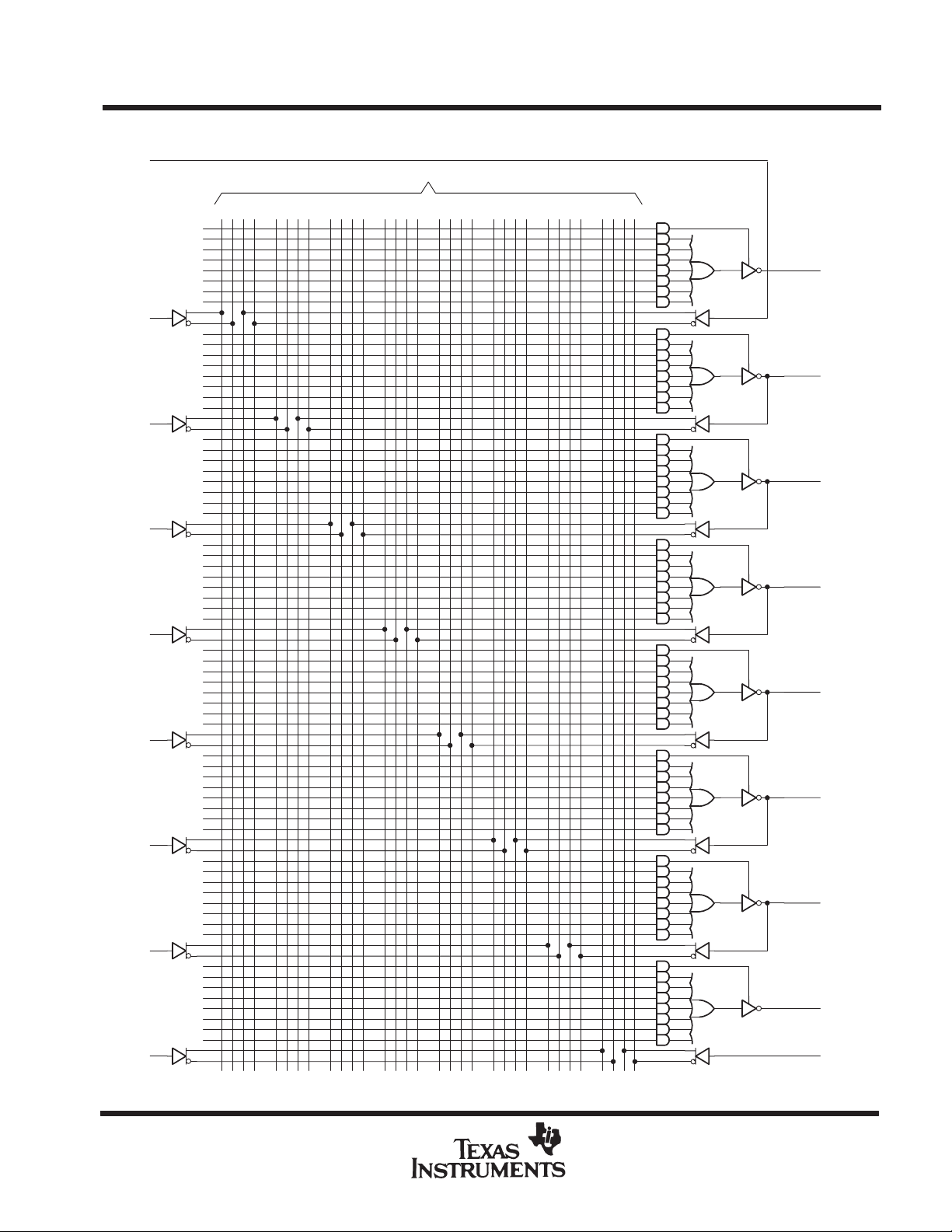
logic diagram (positive logic)
1
I
First
Fuse
Numbers
2
I
3
I
4
I
5
I
6
I
7
I
8
I
9
I
0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 31
0
32
64
96
128
160
192
224
256
288
320
352
384
416
448
480
512
544
576
608
640
672
704
736
768
800
832
864
896
928
960
992
1024
1056
1088
1120
1152
1184
1216
1248
1280
1312
1344
1376
1408
1440
1472
1504
1536
1568
1600
1632
1664
1696
1728
1760
1792
1824
1856
1888
1920
1952
1984
2016
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
Increment
TIBPAL16L8-10C
TIBPAL16L8-12M
CIRCUITS
19
O
18
I/O
17
I/O
16
I/O
15
I/O
14
I/O
13
I/O
12
O
11
I
Fuse number = First fuse number + Increment
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
5
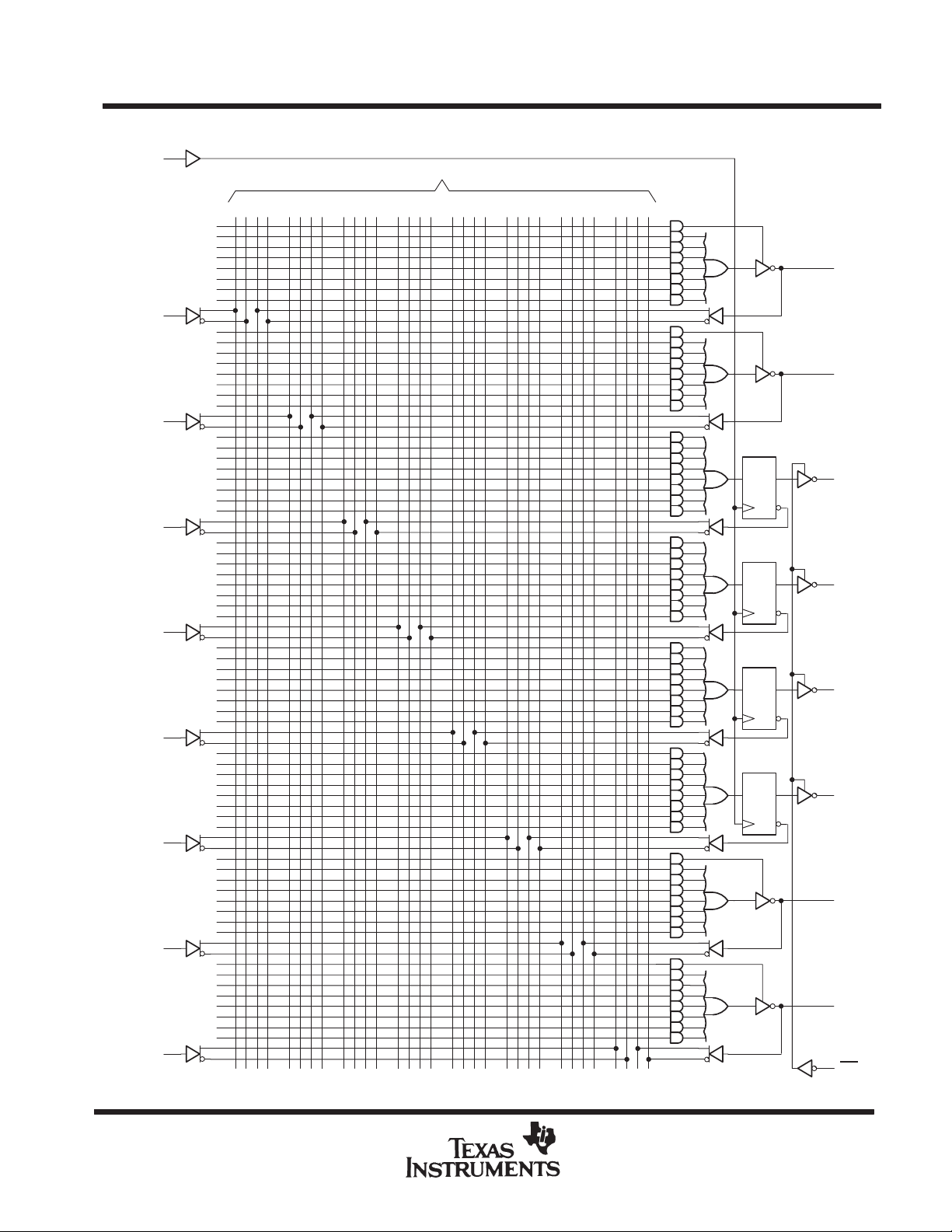
TIBPAL16R4-10C
TIBPAL16R4-12M
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
logic diagram (positive logic)
1
CLK
First
Fuse
Numbers
2
I
3
I
4
I
5
I
6
I
7
I
8
I
9
I
0 4812 16 20 24 28 31
0
32
64
96
128
160
192
224
256
288
320
352
384
416
448
480
512
544
576
608
640
672
704
736
768
800
832
864
896
928
960
992
1024
1056
1088
1120
1152
1184
1216
1248
1280
1312
1344
1376
1408
1440
1472
1504
1536
1568
1600
1632
1664
1696
1728
1760
1792
1824
1856
1888
1920
1952
1984
2016
Fuse number = First fuse number + Increment
Increment
CIRCUITS
I = 0
1D
I = 0
1D
I = 0
1D
I = 0
1D
C1
C1
C1
C1
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
I/O
I/O
Q
Q
Q
Q
I/O
I/O
OE
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
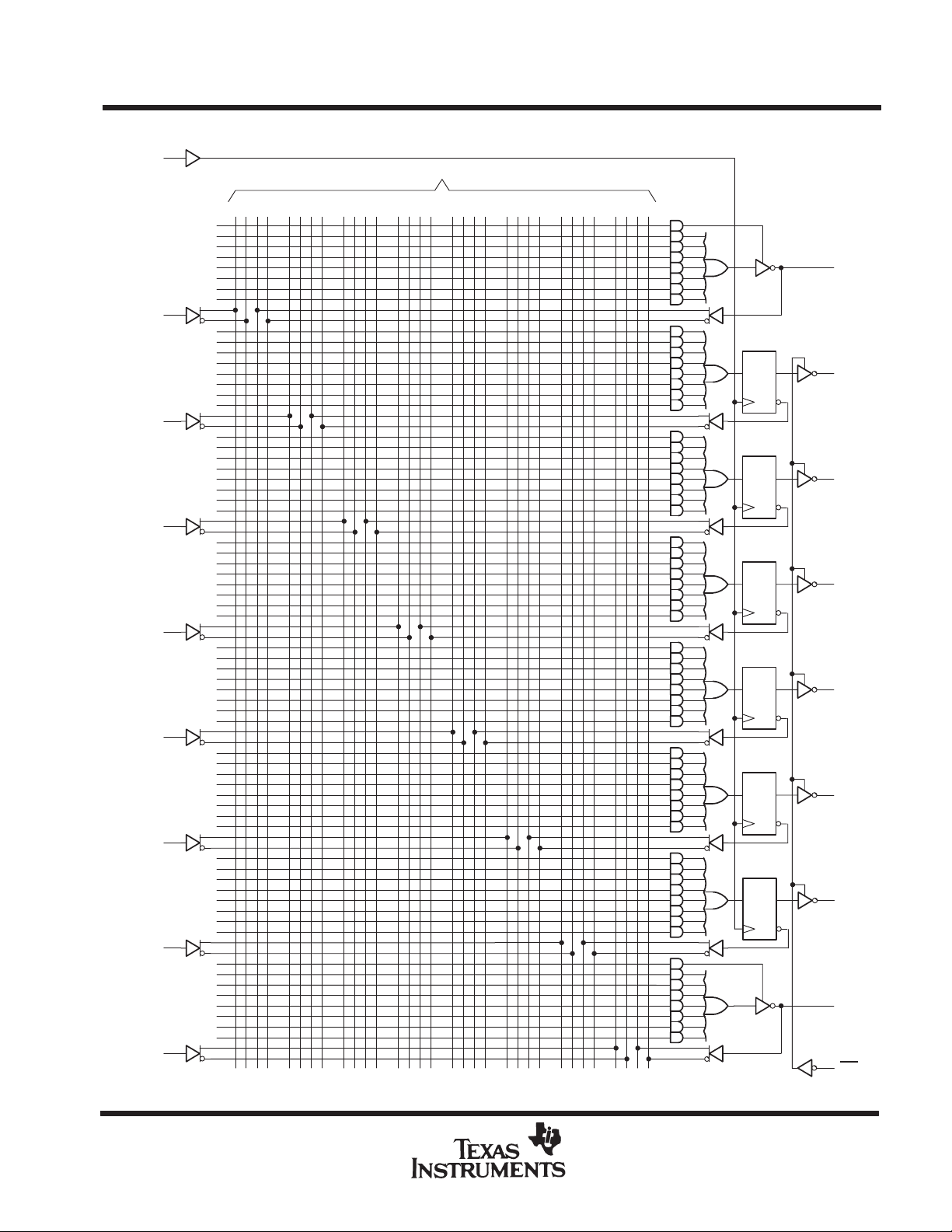
logic diagram (positive logic)
1
CLK
First
Fuse
Numbers
2
I
3
I
4
I
5
I
6
I
7
I
8
I
9
I
Fuse number = First fuse number + Increment
0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 31
0
32
64
96
128
160
192
224
256
288
320
352
384
416
448
480
512
544
576
608
640
672
704
736
768
800
832
864
896
928
960
992
1024
1056
1088
1120
1152
1184
1216
1248
1280
1312
1344
1376
1408
1440
1472
1504
1536
1568
1600
1632
1664
1696
1728
1760
1792
1824
1856
1888
1920
1952
1984
2016
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
Increment
TIBPAL16R6-10C
TIBPAL16R6-12M
CIRCUITS
19
I/O
I = 0
1D
C1
I = 0
1D
C1
I = 0
1D
C1
I = 0
1D
C1
I = 0
1D
C1
I = 0
1D
C1
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
I/O
OE
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
7

TIBPAL16R8-10C
TIBPAL16R8-12M
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
logic diagram (positive logic)
1
CLK
First
Fuse
Numbers
2
I
3
I
4
I
5
I
6
I
7
I
8
I
9
I
0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 31
0
32
64
96
128
160
192
224
256
288
320
352
384
416
448
480
512
544
576
608
640
672
704
736
768
800
832
864
896
928
960
992
1024
1056
1088
1120
1152
1184
1216
1248
1280
1312
1344
1376
1408
1440
1472
1504
1536
1568
1600
1632
1664
1696
1728
1760
1792
1824
1856
1888
1920
1952
1984
2016
Fuse number = First fuse number + Increment
Increment
CIRCUITS
I = 0
1D
I = 0
1D
I = 0
1D
I = 0
1D
I = 0
1D
I = 0
1D
I = 0
1D
I = 0
1D
C1
C1
C1
C1
C1
C1
C1
C1
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
OE
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

TIBPAL16L8-10C, TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage, VCC (see Note 1) 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input voltage (see Note 1) 5.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Voltage applied to disabled output (see Note 1) 5.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range 0°C to 75°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range –65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
NOTE 1: These ratings apply except for programming pins during a programming cycle.
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
V
CC
V
IH
V
IL
I
OH
I
OL
f
clock
t
w
t
su
t
h
T
A
NOTE 2: These are absolute voltage levels with respect to the ground pin of the device and include all overshoots due to system and/or tester
Supply voltage 4.75 5 5.25 V
High-level input voltage (see Note 2) 2 5.5 V
Low-level input voltage (see Note 2) 0.8 V
High-level output current –3.2 mA
Low-level output current 24 mA
Clock frequency 0 62.5 MHz
Pulse duration, clock (see Note 2)
Setup time, input or feedback before clock↑ 10 ns
Hold time, input or feedback after clock↑ 0 ns
Operating free-air temperature 0 25 75 °C
noise. Testing these parameters should not be attempted without suitable equipment.
High 8
Low 8
CIRCUITS
ns
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
V
IK
V
OH
V
OL
‡
I
OZH
‡
I
OZL
I
I
‡
I
IH
‡
I
IL
§
I
OS
I
CC
C
i
C
o
C
i/o
C
clk
†
All typical values are at VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C.
‡
I/O leakage is the worst case of I
§
Not more than one output should be shorted at a time, and the duration of the short circuit should not exceed one second.
VCC = 4.75 V, II = –18 mA –0.8 –1.5 V
VCC = 4.75 V, IOH = –3.2 mA 2.4 3.2 V
VCC = 4.75 V, IOL = 24 mA 0.3 0.5 V
VCC = 5.25 V, VO = 2.4 V 100 µA
VCC = 5.25 V, VO = 0.4 V –100 µA
VCC = 5.25 V, VI = 5.5 V 0.2 mA
VCC = 5.25 V, VI = 2.4 V 25 µA
VCC = 5.25 V, VI = 0.4 V –0.08 –0.25 mA
VCC = 5.25 V, VO = 0 –30 –70 –130 mA
VCC = 5.25 V, VI = 0, Outputs open 140 180 mA
f = 1 MHz, VI = 2 V 5 pF
f = 1 MHz, VO = 2 V 6 pF
f = 1 MHz, V
f = 1 MHz, V
and IIL or I
OZL
OZH
= 2 V 7.5 pF
I/O
= 2 V 6 pF
CLK
and IIH respectively.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
9

TIBPAL16L8-10C, TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
switching characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER
f
max
t
pd
t
pd
t
en
t
dis
t
en
t
†
‡
dis
All typical values are at VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C.
f
(with feedback)
max
FROM
(INPUT)
With feedback 55.5 80
Without feedback 62.5 85
I, I/O O, I/O R1 = 200 Ω, 3 7 10 ns
CLK↑ Q R2 = 390 Ω, 2 5 8 ns
OE↓ Q See Figure 3 1 4 10 ns
OE↑ Q 1 4 10 ns
I, I/O O, I/O 3 8 10 ns
I, I/O O, I/O 3 8 10 ns
+
tsu)
1
tpd(CLK to Q)
,
CIRCUITS
TO
(OUTPUT)
f
(without feedback)
max
TEST CONDITION MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
+
twhigh)twlow
1
MHz
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

TIBPAL16L8-12M, TIBPAL16R4-12M, TIBPAL16R6-12M, TIBPAL16R8-12M
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage, VCC (see Note 1) 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input voltage (see Note 1) 5.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Voltage applied to disabled output (see Note 1) 5.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range –55°C to 125°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range –65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
NOTE 1: These ratings apply except for programming pins during a programming cycle.
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
V
CC
V
IH
V
IL
I
OH
I
OL
f
clock
w
†
t
su
†
t
h
T
A
NOTE 2: These are absolute voltage levels with respect to the ground pin of the device and include all overshoots due to system and/or tester
Supply voltage 4.5 5 5.5 V
High-level input voltage 2 5.5 V
Low-level input voltage 0.8 V
High-level output current –2 mA
Low-level output current 12 mA
†
Clock frequency 0 56 MHz
Pulse duration, clock (see Note 2)t
Setup time, input or feedback before clock↑ 11 ns
Hold time, input or feedback after clock↑ 0 ns
Operating free-air temperature –55 25 125 °C
noise. Testing these parameters should not be attempted without suitable equipment.
High 9
Low 9
CIRCUITS
ns
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
V
IK
V
OH
V
OL
‡
I
OZH
‡
I
OZL
I
I
‡
I
IH
‡
I
IL
§
I
OS
I
CC
C
i
C
o
C
i/o
C
clk
†
All typical values are at VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C.
‡
I/O leakage is the worst case of I
§
Not more than one output should be shorted at a time, and the duration of the short circuit should not exceed one second. VO is set at 0.5 V to
avoid test problems caused by test equipment ground degradation.
VCC = 4.5 V, II = –18 mA –0.8 –1.5 V
VCC = 4.5 V, IOH = –2 mA 2.4 3.2 V
VCC = 4.5 V, IOL = 12 mA 0.3 0.5 V
VCC = 5.5 V, VO = 2.4 V 100 µA
VCC = 5.5 V, VO = 0.4 V –100 µA
VCC = 5.5 V, VI = 5.5 V 0.2 mA
VCC = 5.5 V, VI = 2.4 V 25 µA
VCC = 5.5 V, VI = 0.4 V –0.08 –0.25 mA
VCC = 5.5 V, VO = 0.5 V –30 –70 –250 mA
VCC = 5.5 V, VI = GND, Outputs open 140 220 mA
f = 1 MHz, VI = 2 V 5 pF
f = 1 MHz, VO = 2 V 6 pF
f = 1 MHz, V
f = 1 MHz, V
and IIL or I
OZL
OZH
= 2 V 7.5 pF
I/O
= 2 V 6 pF
CLK
and IIH respectively.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
11

TIBPAL16L8-12M, TIBPAL16R4-12M, TIBPAL16R6-12M, TIBPAL16R8-12M
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
switching characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER
f
max
t
pd
t
pd
t
en
t
dis
t
en
t
†
‡
dis
All typical values are at VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C.
f
(with feedback)
max
FROM
(INPUT)
With feedback 48 80
Without feedback 56 85
I, I/O O, I/O R1 = 390 Ω, 3 7 12 ns
CLK↑ Q R2 = 750 Ω, 2 5 10 ns
OE↓ Q See Figure 3 1 4 10 ns
OE↑ Q 1 4 10 ns
I, I/O O, I/O 3 8 14 ns
I, I/O O, I/O 2 8 12 ns
+
tsu)
1
tpd(CLK to Q)
,
CIRCUITS
TO
(OUTPUT)
f
(without feedback)
max
TEST CONDITION MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
+
twhigh)twlow
1
MHz
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

TIBPAL16L8-10C, TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
TIBPAL16L8-12M, TIBPAL16R4-12M, TIBPAL16R6-12M, TIBPAL16R8-12M
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
programming information
Texas Instruments programmable logic devices can be programmed using widely available software and
inexpensive device programmers.
Complete programming specifications, algorithms, and the latest information on hardware, software, and
firmware are available upon request. Information on programmers capable of programming T exas Instruments
programmable logic is also available, upon request, from the nearest TI field sales office, local authorized TI
distributor, or by calling Texas Instruments at (214) 997-5666.
preload procedure for registered outputs (see Figure 1 and Note 3)
The output registers can be preloaded to any desired state during device testing. This permits any state to be
tested without having to step through the entire state-machine sequence. Each register is preloaded individually
by following the steps given below.
Step 1. With V
at 5 volts and Pin 1 at VIL, raise Pin 11 to V
CC
Step 2. Apply either VIL or VIH to the output corresponding to the register to be preloaded.
Step 3. Pulse Pin 1, clocking in preload data.
Step 4. Remove output voltage, then lower Pin 11 to VIL. Preload can be verified by observing the
voltage level at the output pin.
Pin 11
t
Pin 1
t
d
su
t
w
.
IHH
t
d
CIRCUITS
V
IHH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
Registered I/O Input Output
NOTE 3: td = tsu = th = 100 ns to 1000 ns V
Figure 1. Preload Waveforms
= 10.25 V to 10.75 v
IHH
V
IH
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
13

TIBPAL16L8-10C, TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
TIBPAL16L8-12M, TIBPAL16R4-12M, TIBPAL16R6-12M, TIBPAL16R8-12M
4 V
CIRCUITS
†
t
pd
(600 ns TYP, 1000 ns MAX)
1.5 V
1.5 V
t
w
‡
t
su
1.5 V
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
power-up reset (see Figure 2)
Following power up, all registers are reset to zero. This feature provides extra flexibility to the system designer
and is especially valuable in simplifying state-machine initialization. To ensure a valid power-up reset, it is
important that the rise of VCC be monotonic. Following power-up reset, a low-to-high clock transition must not
occur until all applicable input and feedback setup times are met.
V
CC
Active Low
Registered Output
CLK
5 V
V
V
V
V
OH
OL
IH
IL
†
This is the power-up reset time and applies to registered outputs only. The values shown are from characterization data.
‡
This is the setup time for input or feedback.
Figure 2. Power-Up Reset Waveforms
14
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

TIBPAL16L8-10C, TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
TIBPAL16L8-12M, TIBPAL16R4-12M, TIBPAL16R6-12M, TIBPAL16R8-12M
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
5 V
S1
R1
From Output
Under Test
Test
Point
CIRCUITS
Timing
Input
Data
Input
Input
In-Phase
Output
Out-of-Phase
Output
(see Note D)
1.5 V
t
su
1.5 V
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
SETUP AND HOLD TIMES
1.5 V 1.5 V
t
pd
1.5 V
t
pd
1.5 V 1.5 V
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
PROPAGATION DELAY TIMES
(see Note A)
t
h
1.5 V
t
pd
1.5 V
t
pd
C
L
LOAD CIRCUIT FOR
3-STATE OUTPUTS
(3.5 V) [3 V]
(0.3 V) [0]
(3.5 V) [3 V]
(0.3 V) [0]
(3.5 V) [3 V]
(0.3 V) [0]
V
OH
V
OL
V
OH
V
OL
R2
High-Level
Pulse
Low-Level
Pulse
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
Output
Control
(low-level
enabling)
t
en
Waveform 1
S1 Closed
(see Note B)
t
en
Waveform 2
S1 Open
(see Note B)
ENABLE AND DISABLE TIMES, 3-STATE OUTPUTS
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
1.5 V 1.5 V
t
w
1.5 V 1.5 V
PULSE DURATIONS
1.5 V 1.5 V
t
dis
1.5 V
t
dis
1.5 V
(3.5 V) [3 V]
(0.3 V) [0]
(3.5 V) [3 V]
(0.3 V) [0]
(3.5 V) [3 V]
(0.3 V) [0]
≈ 3.3 V
VOL +0.5 V
V
OL
V
OH
VOH –0.5 V
≈ 0 V
NOTES: A. CL includes probe and jig capacitance and is 50 pF for tpd and ten, 5 pF for t
B. W aveform 1 is for an output with internal conditions such that the output is low except when disabled by the output control. Waveform 2
is for an output with internal conditions such that the output is high except when disabled by the output control.
C. All input pulses have the following characteristics: For C suffix, use the voltage levels indicated in parentheses ( ), PRR ≤ 1 MHz,
tr = tf = 2 ns, duty cycle = 50%; For M suffix, use the voltage levels indicated in brackets [ ], PRR ≤ 10 MHz, tr and tf ≤ 2 ns, duty
cycle = 50%
D. When measuring propagation delay times of 3-state outputs, switch S1 is closed.
E. Equivalent loads may be used for testing.
Figure 3. Load Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
dis
.
15

TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
metastable characteristics of TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, and TIBPAL16R8-10C
At some point a system designer is faced with the problem of synchronizing two digital signals operating at two
different frequencies. This problem is typically overcome by synchronizing one of the signals to the local clock
through use of a flip-flop. However, this solution presents an awkward dilemma since the setup and hold time
specifications associated with the flip-flop are sure to be violated. The metastable characteristics of the flip-flop
can influence overall system reliability.
Whenever the setup and hold times of a flip-flop are violated, its output response becomes uncertain and is said
to be in the metastable state if the output hangs up in the region between V
lasts until the flip-flop falls into one of its two stable states, which takes longer than the specified maximum
propagation delay time (CLK to Q max).
From a system engineering standpoint, a designer cannot use the specified data sheet maximum for
propagation delay time when using the flip-flop as a data synchronizer – how long to wait after the specified data
sheet maximum must be known before using the data in order to guarantee reliable system operation.
The circuit shown in Figure 4 can be used to evaluate MTBF (Mean Time Between Failure) and ∆t for a selected
flip-flop. Whenever the Q output of the DUT is between 0.8 V and 2 V , the comparators are in opposite states.
When the Q output of the DUT is higher than 2 V or lower than 0.8 V , the comparators are at the same logic level.
The outputs of the two comparators are sampled a selected time (∆t) after SCLK. The exclusive OR gate detects
the occurrence of a failure and increments the failure counter.
Noise
Generator
DATA IN
SCLK
DUT
Comparator
1D
Comparator
C1
CIRCUITS
and VIH. This metastable condition
IL
V
IH
1D
C1
V
IL
1D
C1
1D
C1
MTBF
Counter
+
SCLK + ∆t
Figure 4. Metastable Evaluation Test Circuit
In order to maximize the possibility of forcing the DUT into a metastable state, the input data signal is applied
so that it always violates the setup and hold time. This condition is illustrated in the timing diagram in Figure 5.
Any other relationship of SCLK to data will provide less chance for the device to enter into the metastable state.
Data
SCLK
SCLK + ∆t
MTBF
t
rec
Time (sec)
+
# Failures
= ∆t – CLK to Q (max)
∆t
∆t
Figure 5. Timing Diagram
16
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
By using the described test circuit, MTBF can be determined for several different values of ∆t (see Figure 4).
Plotting this information on semilog scale demonstrates the metastable characteristics of the selected flip-flop.
Figure 6 shows the results for the TIBPAL16’-10C operating at 1 MHz.
9
10
10
10
10
10
MTBF (s)
10
10
10
10
10 yr
8
1 yr
7
1 mo
6
1 wk
5
1 day
4
1 hr
3
2
1 min
10 s
1
0 10203040506070
∆t (ns)
f
clk
f
data
= 1 MHz
= 500 kHz
CIRCUITS
Figure 6. Metastable Characteristics
From the data taken in the above experiment, an equation can be derived for the metastable characteristics at
other clock frequencies.
The metastable equation:
1
MTBF
+
f
SCLK
xf
data
xC1e
(*C2 xDt)
The constants C1 and C2 describe the metastable characteristics of the device. From the experimental data,
these constants can be solved for: C1 = 9.15 X 10–7 and C2 = 0.959
Therefore
1
MTBF
+
f
SCLK
xf
x9.15x10
data
*
7e(*0.959 xDt)
definition of variables
DUT (Device Under Test): The DUT is a 10-ns registered PLD programmed with the equation Q : = D.
MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures): The average time (s) between metastable occurrences that cause a
violation of the device specifications.
f
(system clock frequency): Actual clock frequency for the DUT.
SCLK
(data frequency): Actual data frequency for a specified input to the DUT.
f
data
C1: Calculated constant that defines the magnitude of the curve.
C2: Calculated constant that defines the slope of the curve.
t
(metastability recovery time): Minimum time required to guarantee recovery from metastability , at a given
rec
MTBF failure rate. t
∆t: The time difference (ns) from when the synchronizing flip-flop is clocked to when its output is sampled.
rec
= ∆t –
(CLK to Q, max)
tpd
The test described above has shown the metastable characteristics of the TIBP AL16R4/R6/R8-10C series. For
additional information on metastable characteristics of Texas Instruments logic circuits, please refer to TI
Applications publication SDAA004, ”Metastable Characteristics, Design Considerations for ALS, AS, and LS
Circuits.’’
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
17

TIBPAL16L8-10C, TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
TIBPAL16L8-12M, TIBPAL16R4-12M, TIBPAL16R6-12M, TIBPAL16R8-12M
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
CIRCUITS
PROPAGATION DELAY TIME
FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE
VCC = 5 V
CL = 50 pF
R1 = 200 Ω
8
R2 = 390 Ω
1 Output Switching
7
6
t
(CLK to Q)
PHL
5
Propagation Delay Time – ns
4
3
–75 –50 –25 0 25 50
t
(CLK to Q)
PLH
TA – Free-Air Temperature – °C
Figure 7
vs
t
(I, I/O to O, I/O)
PHL
t
PLH
(I, I/O to O, I/O)
75 100 125
PROPAGATION DELAY TIME
vs
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
9
TA = 25 °C
CL = 50 pF
R1 = 200 Ω
8
R2 = 390 Ω
t
(I, I/O to O, I/O)
t
PHL
t
PLH
PHL
t
(I, I/O to O, I/O)
PLH
(CLK to Q)
(CLK to Q)
7
6
5
Propagation Delay Time – ns
4
3
4.5 4.75 5 5.25 5.5
VCC – Supply Voltage – V
Figure 8
PROPAGATION DELAY TIME
NUMBER OF OUTPUTS SWITCHING
11
VCC = 5 V
TA = 25 °C
10
CL = 50 pF
R1 = 200 Ω
R2 = 390 Ω
9
8
7
t
6
5
Propagation Delay Time – ns
4
3
012345
(I, I/O to O, I/O)
PLH
t
(CLK to Q)
PHL
t
(CLK to Q)
PLH
Number of Outputs Switching
Figure 9
vs
t
(I, I/O to O, I/O)
PHL
678
18
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

18
VCC = 5 V
TA = 25 °C
16
R1 = 200 Ω
R2 = 390 Ω
1 Output Switching
14
12
TIBPAL16L8-10C, TIBPAL16R4-10C, TIBPAL16R6-10C, TIBPAL16R8-10C
TIBPAL16L8-12M, TIBPAL16R4-12M, TIBPAL16R6-12M, TIBPAL16R8-12M
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
PROPAGATION DELAY TIME
vs
LOAD CAPACITANCE
HIGH-PERFORMANCE IMPACT-X PAL
SRPS017 – D3023, MA Y 1987 – REVISED MARCH 1992
POWER DISSIPATION
vs
FREQUENCY
8-BIT COUNTER MODE
900
VCC = 5 V
800
CIRCUITS
10
8
6
Propagation Delay Time – ns
4
2
0 600
100 200 300 400
CL – Load Capacitance – pF
t
PLH
t
(I, I/O to O, I/O)
PHL
t
PLH
t
PHL
(I, I/O to O, I/O)
Figure 10
180
Unprogrammed Device
170
160
150
(CLK to Q)
(CLK to Q)
500
FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE
– Power Dissipation – mW
D
P
SUPPLY CURRENT
vs
VCC = 5.5 V
VCC = 5.25 V
TA = 0 °C
700
600
TA = 25 °C
TA = 80 °C
1 4 10 40 100
F – Frequency – MHz
Figure 11
140
130
– Supply Current – mA
CC
120
I
110
100
–75 –50 –25 0 25 50
VCC = 5 V
VCC = 4.75 V
TA – Free-Air Temperature – °C
Figure 12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
VCC = 4.5 V
75 100 125
19

TI North
American Sales
Offices
ALABAMA: Huntsville: (205) 837-7530
ARIZONA: Phoenix: (602) 995-1007
CALIFORNIA: Irvine: (714) 660-1200
San Diego: (619) 278-9600
Santa Clara: (408) 980-9000
Woodland Hills: (818) 704-8100
COLORADO: Aurora: (303) 368-8000
CONNECTICUT: W allingford: (203) 269-0074
FLORIDA: Altamonte Springs: (407) 260-2116
Fort Lauderdale: (305) 973-8502
Tampa: (813) 885-7588
GEORGIA: Norcross: (404) 662-7967
ILLINOIS: Arlington Heights: (708) 640-3000
INDIANA: Carmel: (317) 573-6400
Fort Wayne: (219) 489-4697
KANSAS: Overland Park: (913) 451-4511
MARYLAND: Columbia: (410) 964-2003
MASSACHUSETTS: Waltham: (617) 895-9100
MICHIGAN: Farmington Hills: (313) 553-1581
MINNESOTA: Eden Prairie: (612) 828-9300
MISSOURI: St. Louis: (314) 821-8400
NEW JERSEY: Iselin: (908) 750-1050
NEW MEXICO: Albuquerque: (505) 345-2555
NEW YORK: East Syracuse: (315) 463-9291
Fishkill: (914) 897-2900
Melville: (516) 454-6600
Pittsford: (716) 385-6770
NORTH CAROLINA: Charlotte: (704) 527-0930
Raleigh: (919) 876-2725
OHIO: Beachwood: (216) 765-7258
Beavercreek: (513) 427-6200
OREGON: Beaverton: (503) 643-6758
PENNSYLVANIA: Blue Bell: (215) 825-9500
PUERTO RICO: Hato Rey: (809) 753-8700
TEXAS: Austin: (512) 250-6769
Dallas: (214) 917-1264
Houston: (713) 778-6592
Midland: (915) 561-7137
UTAH: Salt Lake CIty: (801) 466-8972
WISCONSIN: Waukesha: (414) 798-1001
CANADA: Nepean: (613) 726-1970
Richmond Hill: (416) 884-9181
St. Laurent: (514) 335-8392
TI Regional
Technology
Centers
CALIFORNIA: Irvine: (714) 660-8140
Santa Clara: (408) 748-2222
GEORGIA: Norcross: (404) 662-7945
ILLINOIS: Arlington Heights: (708) 640-2909
INDIANA: Indianapolis: (317) 573-6400
MASSACHUSETTS: Waltham: (617) 895-9196
MEXICO: Mexico City: 491-70834
MINNESOTA: Minneapolis: (612) 828-9300
TEXAS: Dallas: (214) 917-3881
CANADA: Nepean: (613) 726-1970
TI Authorized
North American
Distributors
Alliance Electronics, Inc. (military product only)
Almac/Arrow
Anthem Electronics
Arrow/Schweber
Future Electronics (Canada)
GRS Electronics Co., Inc.
Hall-Mark Electronics
Marshall Industries
Newark Electronics
Rochester Electronics, Inc.
(obsolete product only (508) 462-9332)
Wyle Laboratories
Zeus Components
TI Distributors
ALABAMA: Arrow/Schweber (205) 837-6955; Hall-Mark
(205) 837-8700; Marshall (205) 881-9235.
ARIZONA: Anthem (602) 966-6600; Arrow/Schweber (602)
437-0750; Hall-Mark (602) 431-0030; Marshall (602)
496-0290; Wyle (602) 437-2088.
CALIFORNIA: Los Angeles/Orange County: Anthem
(818) 775-1333, (714) 768-4444; Arrow/Schweber (818)
380-9686, (714) 838-5422; Hall-Mark (818) 773-4500, (714)
727-6000; Marshall (818) 878-7000, (714) 458-5301; Wyle
(818) 880-9000, (714) 863-9953; Zeus (714) 921-9000,
(818) 889-3838;
Sacramento: Anthem (916) 624-9744; Hall-Mark (916)
624-9781; Marshall (916) 635-9700; Wyle (916) 638-5282;
San Diego: Anthem (619) 453-9005; Arrow/Schweber
(619) 565-4800; Hall-Mark (619) 268-1201; Marshall (619)
578-9600; Wyle (619) 565-9171; Zeus (619) 277-9681.
San Francisco Bay Area: Anthem (408) 453-1200;
Arrow/Schweber (408) 441-9700, (510) 490-9477;
Hall-Mark (408) 432-4000; Marshall (408) 942-4600;
Wyle (408) 727-2500; Zeus (408) 629-4789.
COLORADO: Anthem (303) 790-4500; Arrow/Schweber
(303) 799-0258; Hall-Mark (303) 790-1662; Marshall (303)
451-8383; Wyle (303) 457-9953.
CONNECTICUT: Anthem (203) 575-1575; Arrow/Schweber
(203) 265-7741; Hall-Mark (203) 271-2844; Marshall (203)
265-3822.
FLORIDA:Fort Lauderdale:Arrow/Schweber (305)
429-8200; Halll-Mark (305) 971-9280; Marshall (305)
977-4880.
Orlando: Arrow/Schweber (407) 333-9300; Hall-Mark (407)
830-5855; Marshall (407) 767-8585; Zeus (407) 788-9100.
Tampa: Hall-Mark (813) 541-7440; Marshall (813)
573-1399.
GEORGIA: Arrow/Schweber (404) 497-1300; Hall-Mark
(404) 623-4400; Marshall (404) 923-5750.
ILLINOIS: Anthem (708) 884-0200; Arrow/Schweber (708)
250-0500; Hall-Mark (312) 860-3800; Marshall (708)
490-0155; Newark (312)784-5100.
INDIANA: Arrow/Schweber (317) 299-2071; Hall-Mark
(317) 872-8875; Marshall (317) 297-0483.
IOWA: Arrow/Schweber (319) 395-7230.
KANSAS: Arrow/Schweber (913) 541-9542; Hall-Mark
(913) 888-4747; Marshall (913) 492-3121.
MARYLAND: Anthem (301) 995-6640; Arrow/Schweber
(301) 596-7800; Hall-Mark (301) 988-9800; Marshall (301)
622-1118; Zeus (301) 997-1118.
MASSACHUSETTS: Anthem (508) 657-5170;
Arrow/Schweber (508) 658-0900; Hall-Mark (508)
667-0902; Marshall (508) 658-0810; Wyle (617) 272-7300;
Zeus (617) 246-8200.
MICHIGAN: Detroit: Arrow/Schweber (313) 462-2290;
Hall-Mark (313) 416-5800; Marshall (313) 525-5850;
Newark (313) 967-0600.
MINNESOTA: Anthem (612) 944-5454; Arrow/Schweber
(612) 941-5280; Hall-Mark (612) 881-2600; Marshall (612)
559-2211.
MISSOURI: Arrow/Schweber (314) 567-6888; Hall-Mark
(314) 291-5350; Marshall (314) 291-4650.
NEW JERSEY: Anthem (201) 227-7960; Arrow/Schweber
(201) 227-7880, (609) 596-8000; Hall-Mark (201) 515-3000,
(609) 235-1900; Marshall (201) 882-0320, (609) 234-9100.
NEW MEXICO: Alliance (505) 292-3360.
NEW YORK: Long Island: Anthem (516) 864-6600;
Arrow/Schweber (516) 231-1000; Hall-Mark (516)
737-0600; Marshall (516) 273-2424; Zeus (914) 937-7400.
Rochester: Arrow/Schweber (716) 427-0300; Hall-Mark
(716) 425-3300; Marshall (716) 235-7620.
Syracuse: Marshall (607) 785-2345.
NORTH CAROLINA: Arrow/Schweber (919) 876-3132;
Hall-Mark (919) 872-0712; Marshall (919) 878-9882.
OHIO: Cleveland: Arrow/Schweber (216) 248-3990;
Hall-Mark (216) 349-4632; Marshall (216) 248-1788.
Columbus: Hall-Mark (614) 888-3313.
Dayton: Arrow/Schweber (513) 435-5563; Marshall (513)
898-4480; Zeus (513) 293-6162.
OKLAHOMA: Arrow/Schweber (918) 252-7537; Hall-Mark
(918) 254-6110.
OREGON: Almac/Arrow (503) 629-8090; Anthem (503)
643-1114; Marshall (503) 644-5050; Wyle (503) 643-7900.
PENNSYLVANIA: Anthem (215) 443-5150;
Arrow/Schweber (215) 928-1800; GRS (215) 922-7037;
(609) 964-8560; Marshall (412) 788-0441.
TEXAS: Austin: Arrow/Schweber (512) 835-4180;
Hall-Mark (512) 258-8848; Marshall (512) 837-1991; Wyle
(512) 345-8853;
Dallas: Anthem (214) 238-7100; Arrow/Schweber (214)
380-6464; Hall-Mark (214) 553-4300; Marshall (214)
233-5200; Wyle (214) 235-9953; Zeus (214) 783-7010;
Houston: Arrow/Schweber (713) 530-4700; Hall-Mark
(713) 781-6100; Marshall (713) 467-1666; Wyle (713)
879-9953.
UTAH: Anthem (801) 973-8555; Arrow/Schweber (801)
973-6913; Marshall (801) 973-2288; Wyle (801) 974-9953.
WASHINGTON: Almac/Arrow (206) 643-9992, Anthem
(206) 483-1700; Marshall (206) 486-5747; Wyle (206)
881-1150.
WISCONSIN: Arrow/Schweber (414) 792-0150; Hall-Mark
(414) 797-7844; Marshall (414) 797-8400.
CANADA: Calgary: Future (403) 235-5325;
Edmonton: Future (403) 438-2858;
Montreal: Arrow/Schweber (514) 421-7411; Future (514)
694-7710; Marshall (514) 694-8142
Ottawa: Arrow/Schweber (613) 226-6903; Future (613)
820-8313.
Quebec: Future (418) 897-6666.
Toronto: Arrow/Schweber (416) 670-7769;
Future (416) 612-9200; Marshall (416) 458-8046.
Vancouver: Arrow/Schweber (604) 421-2333;
Future (604) 294-1166.
TI Die Processors
Chip Supply (407) 298-7100
Elmo Semiconductor (818) 768-7400
Minco T echnology Labs (512) 834-2022
Customer
Response Center
TOLL FREE: (800) 336-5236
OUTSIDE USA: (214) 995-6611
(8:00 a.m. – 5:00 p.m. CST)
1992 T exas Instruments Incorporated
D0892
SRPS017

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty . Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERTAIN APPLICA TIONS USING SEMICONDUCT OR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICA TIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERST OOD TO
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1998, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...