Page 1

www.ti.com
V
OUT
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs
FREQUENCY
TYPICAL ARBITARY WAVEFORM
GENERATOR OUTPUT DRIVE CIRCUIT
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−20
1 M 10 M 100 M
f − Frequency − Hz
Total Harmonic Distortion − dBc
G = 5,
RF = 715 Ω,
RL = 100 Ω,
VS = ±15 V
100 k
−30
VO = 20 V
PP
VO = 10 V
PP
VO = 5 V
PP
VO = 2 V
PP
+
−
+
−
THS3092
THS3092
+
−
THS4271
IOUT1
IOUT2
DAC5686
查询THS3092供应商
HIGH-VOLTAGE, LOW-DISTORTION, CURRENT-FEEDBACK
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
FEATURES DESCRIPTION
• Low Distortion
– 66 dBc HD2 at 10 MHz, R
– 76 dBc HD3 at 10 MHz, R
• Low Noise
– 13 pA/√Hz Noninverting Current Noise and VDSL line drivers.
– 13 pA/√Hz Inverting Current Noise
– 2 nV/√Hz Voltage Noise
• High Slew Rate: 5700 V/µs (G = 5, V
• Wide Bandwidth: 160 MHz (G = 5, R
• High Output Current Drive: ±250 mA
• Wide Supply Range: ±5 V to ±15 V
• Power-Down Feature: (THS3096 Only)
APPLICATIONS
• High-Voltage Arbitrary Waveform
• Power FET Driver
• Pin Driver
• VDSL Line Driver
L
L
= 100 Ω
= 100 Ω
= 20 V
O
= 100 Ω)
L
)
PP
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
The THS3092 and THS3096 are dual high-voltage,
low-distortion, high speed, current-feedback
amplifiers designed to operate over a wide supply
range of ±5 V to ±15 V for applications requiring
large, linear output signals such as Pin, Power FET,
The THS3096 features a power-down pin (PD) that
puts the amplifier in low power standby mode, and
lowers the quiescent current from 9.5 mA to 500 µA.
The wide supply range combined with total harmonic
distortion as low as -66 dBc at 10 MHz, in addition, to
the high slew rate of 5700 V/µs makes the
THS3092/6 ideally suited for high-voltage arbitrary
waveform driver applications. Moreover, having the
ability to handle large voltage swings driving into
high-resistance and high-capacitance loads while
maintaining good settling time performance makes
the THS3092/6 ideal for Pin driver and PowerFET
driver applications.
The THS3092 is offered in an 8-pin SOIC (D), and
the 8-pin SOIC (DDA) packages with PowerPAD™.
The THS3096 is offered in the 8-pin SOIC (D) and
the 14-pin TSSOP (PWP) packages with PowerPAD.
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED this document contains PRODUCTION DATA information current as of publication date. Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily
include testing of all parameters.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas
Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
Copyright © 2003–2004, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 2

www.ti.com
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
1V
OUT
1V
IN−
1V
IN+
V
S−
V
S+
2V
OUT
2V
IN−
2V
IN+
D, DDATOP VIEW
THS3092
NC = No Internal Connection
D, PWPTOP VIEW
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
1V
OUT
1V
IN−
1V
IN+
V
S−
V
S+
2V
OUT
2V
IN−
2V
IN+
NC = No Internal Connection
THS3096
See Note A.
NC
REF
NC
NC
PD
NC
Note A: The devices with the power down option defaults to the ON state if no signal is applied to the PD pin. Additionallly, the REF pin
functional range is from VS− to (VS+ − 4 V).
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
These devices have limited built-in ESD protection. The leads should be shorted together or the device placed in conductive foam
during storage or handling to prevent electrostatic damage to the MOS gates.
PART NUMBER PACKAGE TYPE TRANSPORT MEDIA, QUANTITY
THS3092D Rails, 75
THS3092DR Tape and Reel, 2500
THS3092DDA Rails, 75
THS3092DDAR Tape and Reel, 2500
Power-down
THS3096D Rails, 75
THS3096DR Tape and Reel, 2500
THS3096PWP Rails, 90
THS3096PWPR Tape and Reel, 2000
ORDERING INFORMATION
SOIC-8
SOIC-8-PP
SOIC-8
TSSOP-14-PP
(1)
(1)
(1) The PowerPAD is electrically isolated from all other pins.
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
PACKAGE Θ
D-8 38.3 97.5 1.02 W 410 mW
(3)
DDA-8
PWP-14
(1) This data was taken using the JEDEC standard High-K test PCB.
(2) Power rating is determined with a junction temperature of 125°C. This is the point where distortion starts to substantially increase.
Thermal management of the final PCB should strive to keep the junction temperature at or below 125°C for best performance and long
term reliability.
(3) The THS3092 and THS3096 may incorporate a PowerPAD™ on the underside of the chip. This acts as a heatsink and must be
connected to a thermally dissipating plane for proper power dissipation. Failure to do so may result in exceeding the maximum junction
temperature which could permanently damage the device. See TI Technical Brief SLMA002 for more information about utilizing the
PowerPAD™ thermally enhanced package.
(3)
(°C/W) Θ
JC
9.2 45.8 2.18 W 873 mW
2.07 37.5 2.67 W 1.07 W
JA
(1)
(°C/W)
TA≤ 25°C TA= 85°C
2
POWER RATING
(2)
Page 3

www.ti.com
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
MIN MAX UNIT
Supply voltage V
Operating free-air temperature, T
A
Dual supply ±5 ±15
Single supply 10 30
-40 85 °C
THS3092
THS3096
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
over operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage, VS-to V
Input voltage, V
Differential input voltage, V
Output current, I
Continuous power dissipation See Dissipation Ratings Table
Maximum junction temperature, T
Maximum junction temperature, continuous operation, long term reliability, T
Storage temperature, T
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds 300°C
ESD ratings:
(1) The absolute maximum ratings under any condition is limited by the constraints of the silicon process. Stresses above these ratings may
cause permanent damage. Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are
stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is not implied.
(2) The maximum junction temperature for continuous operation is limited by package constraints. Operation above this temperature may
result in reduced reliability and/or lifetime of the device.
S+
I
ID
O
J
stg
HBM 2000
CDM 1500
MM 150
(1)
UNIT
33 V
± V
S
± 4 V
350 mA
150°C
(2)
J
125°C
-65°C to 150°C
3
Page 4

www.ti.com
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
VS= ±15 V, RF= 909 Ω, RL= 100 Ω, and G = 2 (unless otherwise noted)
TYP OVER TEMPERATURE
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
AC PERFORMANCE
G = 1, RF= 1.1 kΩ, VO= 200 mV
Small-signal bandwidth, -3 dB
0.1 dB bandwidth flatness G = 2, RF= 909 Ω, VO= 200 mV
Large-signal bandwidth G = 5, RF= 715 Ω , VO= 5 V
Slew rate (25% to 75% level) V/µs TYP
Rise and fall time G = 2, VO= 5-V
Settling time to 0.1% G = -2, VO= 2 VPPstep 42
Settling time to 0.01% G = -2, VO= 2 VPPstep 72
Harmonic distortion
2nd Harmonic distortion
3rd Harmonic distortion
Input voltage noise f > 10 kHz 2 nV / √Hz TYP
Noninverting input current noise f > 10 kHz 13 pA / √Hz TYP
Inverting input current noise f > 10 kHz 13 pA / √Hz TYP
Differential gain
Differential phase
Crosstalk RL= 100 Ω, dB
DC PERFORMANCE
Transimpedance VO= ±7.5 V, Gain = 1 850 350 300 300 kΩ MIN
Input offset voltage 0.9 3 4 4 mV MAX
Average offset voltage drift ±10 ±10 µV/°C TYP
Noninverting input bias current 4 15 20 20 µA MAX
Average bias current drift ±20 ±20 µA/°C TYP
Inverting input bias current 3.5 15 20 20 µA MAX
Average bias current drift ±20 ±20 µA/°C TYP
Input offset current 1.7 10 15 15 µA MAX
Average offset current drift ±20 ±20 µA/°C TYP
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Common-mode input range ±13.6 ±13.3 ±13 ±13 V MIN
Common-mode rejection ratio VCM= ±10 V 78 68 65 65 dB MIN
Noninverting input resistance 1.3 MΩ TYP
Noninverting input capacitance 0.1 pF TYP
Inverting input resistance 30 Ω TYP
Inverting input capacitance 1.4 pF TYP
G = 2, RF= 909 Ω, VO= 200 mV
G = 5, RF= 715 Ω, VO= 200 mV
G = 10, RF= 604 Ω, VO= 200 mV
G = 2, VO= 10-V step, RF= 909 Ω 4000
G = 5, VO= 20-V step, RF= 715 Ω 5700
, RF= 909 Ω 5 ns TYP
PP
G = 2,
RF= 909 Ω ,
VO= 2 VPP,
f = 10 MHz
G = 2,
RL= 150 Ω, TYP
RF= 909 Ω
G = 2, Ch 1 to 2 60
f = 10 MHz
VCM= 0 V
PP
PP
PP
PP
PP
PP
RL= 100Ω 66
RL= 1 kΩ 66
RL= 100Ω 76
RL= 1 kΩ 78
NTSC 0.013%
PAL 0.011%
NTSC 0.020°
PAL 0.026°
Ch 2 to 1 56
25°C 25°C UNIT
135
145
160
145
50
150
0°C to -40°C to MIN/TYP/
70°C 85°C MAX
MHz TYP
ns TYP
dBc TYP
4
Page 5

www.ti.com
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
VS= ±15 V, RF= 909 Ω, RL= 100 Ω, and G = 2 (unless otherwise noted)
TYP OVER TEMPERATURE
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output voltage swing V MIN
Output current (sourcing) RL= 40 Ω 280 225 200 200 mA MIN
Output current (sinking) RL= 40 Ω 250 200 175 175 mA MIN
Output impedance f = 1 MHz, Closed loop 0.06 Ω TYP
POWER SUPPLY
Specified operating voltage ±15 ±16 ±16 ±16 V MAX
Maximum quiescent current 9.5 10.5 11 11 mA MAX
Minimum quiescent current 9.5 8.5 8 8 mA MIN
Power supply rejection (+PSRR) VS+= 15.5 V to 14.5 V, VS-= 15 V 75 70 65 65 dB MIN
Power supply rejection (-PSRR) VS+= 15 V, VS-= -15.5 V to -14.5 V 73 68 65 65 dB MIN
POWER-DOWN CHARACTERISTICS (THS3096 ONLY)
Power-down voltage level V MAX
Power-down quiescent current PD = 0V 500 700 800 800 µA MAX
VPDquiescent current µA MAX
Turnon time delay 90% of final value 60
Turnoff time delay 10% of final value 150
RL= 1 kΩ ±13.2 ±12.8 ±12.5 ±12.5
RL= 100 Ω ±12.5 ±12.1 ±11.8 ±11.8
Per channel
Enable, REF = 0 V ≤ 0.8
Power-down , REF = 0 V ≥ 2
VPD= 0 V, REF = 0 V, 11 15 20 20
VPD= 3.3 V, REF = 0 V 11 15 20 20
25°C 25°C UNIT
0°C to -40°C to MIN/TYP/
70°C 85°C MAX
µs TYP
THS3092
THS3096
5
Page 6

www.ti.com
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
VS= ±5 V, RF= 909 Ω, RL= 100 Ω, and G = 2 (unless otherwise noted)
TYP OVER TEMPERATURE
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
AC PERFORMANCE
G = 1, RF= 1.1 kΩ, VO= 200 mV
Small-signal bandwidth, -3 dB
0.1 dB bandwidth flatness G = 2, RF= 909 Ω, VO= 200 mV
Large-signal bandwidth G = 2, RF= 909 Ω , VO= 5 V
Slew rate (25% to 75% level) V/µs TYP
Rise and fall time G = 2, VO= 5-V step, RF= 909 Ω 5 ns TYP
Settling time to 0.1% G = -2, VO= 2 VPPstep 35
Settling time to 0.01% G = -2, VO= 2 VPPstep 73
Harmonic distortion
2nd Harmonic distortion
3rd Harmonic distortion
Input voltage noise f > 10 kHz 2 nV / √Hz TYP
Noninverting input current noise f > 10 kHz 13 pA / √Hz TYP
Inverting input current noise f > 10 kHz 13 pA / √Hz TYP
Differential gain
Differential phase
Crosstalk RL= 100 Ω, dB
DC PERFORMANCE
Transimpedance VO= ±2.5 V, Gain = 1 700 250 200 200 kΩ MIN
Input offset voltage 0.3 2 3 3 mV MAX
Average offset voltage drift ±10 ±10 µV/°C TYP
Noninverting input bias current 2 15 20 20 µA MAX
Average bias current drift ±20 ±20 µA/°C TYP
Inverting input bias current 5 15 20 20 µA MAX
Average bias current drift ±20 ±20 µA/°C TYP
Input offset current 1 10 15 15 µA MAX
Average offset current drift ±20 ±20 µA/°C TYP
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Common-mode input range ±3.6 ±3.3 ±3 ±3 V MIN
Common-mode rejection ratio VCM= ±2.0 V, VO= 0 V 66 60 57 57 dB MIN
Noninverting input resistance 1.1 MΩ TYP
Noninverting input capacitance 1.2 pF TYP
Inverting input resistance 32 Ω TYP
Inverting input capacitance 1.5 pF TYP
G = 2, RF= 909 Ω, VO= 200 mV
G = 5, RF= 715 Ω, VO= 200 mV
G = 10, RF= 604 Ω, VO= 200 mV
G = 2, VO= 5-V step, RF= 909 Ω 1050
G = 5, VO= 5-V step, RF= 715 Ω 1350
G = 2,
RF= 909 Ω ,
VO= 2 VPP,
f = 10 MHz
G = 2,
RL= 150 Ω, TYP
RF= 909 Ω
G = 2, Ch 1 to 2 60
f = 10 kHz
VCM= 0 V
PP
PP
PP
PP
PP
PP
RL= 100Ω 64
RL= 1 kΩ 67
RL= 100Ω 75
RL= 1 kΩ 75
NTSC 0.027%
PAL 0.025%
NTSC 0.04°
PAL 0.05°
Ch 2 to 1 56
25°C 25°C UNIT
125
140
145
135
42
125
0°C to -40°C to MIN/TYP/
70°C 85°C MAX
MHz TYP
ns TYP
dBc TYP
6
Page 7

www.ti.com
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
VS= ±5 V, RF= 909 Ω, RL= 100 Ω, and G = 2 (unless otherwise noted)
TYP OVER TEMPERATURE
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output voltage swing V MIN
Output current (sourcing) RL= 10 Ω 200 160 140 140 mA MIN
Output current (sinking) RL= 10 Ω 180 150 125 125 mA MIN
Output impedance f = 1 MHz, Closed loop 0.09 Ω TYP
POWER SUPPLY
Specified operating voltage ±5 ±4.5 ±4.5 ±4.5 V MAX
Maximum quiescent current 8.2 9 9.5 9.5 mA MAX
Minimum quiescent current 8.2 7 6.5 6.5 mA MIN
Power supply rejection (+PSRR) VS+= 5.5 V to 4.5 V, VS-= -5 V 73 68 63 63 dB MIN
Power supply rejection (-PSRR) VS+= 5 V, VS-= -4.5 V to 5.5 V 71 65 60 60 dB MIN
POWER-DOWN CHARACTERISTICS (THS3096 ONLY)
Power-down voltage level V MAX
Power-down quiescent current PD = 0V 300 500 600 600 µA MAX
VPDquiescent current µA MAX
Turnon time delay 90% of final value 60
Turnoff time delay 10% of final value 150
RL= 1 kΩ ±3.4 ±3.1 ±2.8 ±2.8
RL= 100 Ω ±3.1 ±2.7 ±2.5 ±2.5
Per channel
Enable, REF = 0 V ≤ 0.8
Power-down , REF = 0 V ≥ 2
VPD= 0 V, REF = 0 V, 11 15 20 20
VPD= 3.3 V, REF = 0 V 11 15 20 20
25°C 25°C UNIT
0°C to -40°C to MIN/TYP/
70°C 85°C MAX
µs TYP
THS3092
THS3096
7
Page 8

www.ti.com
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
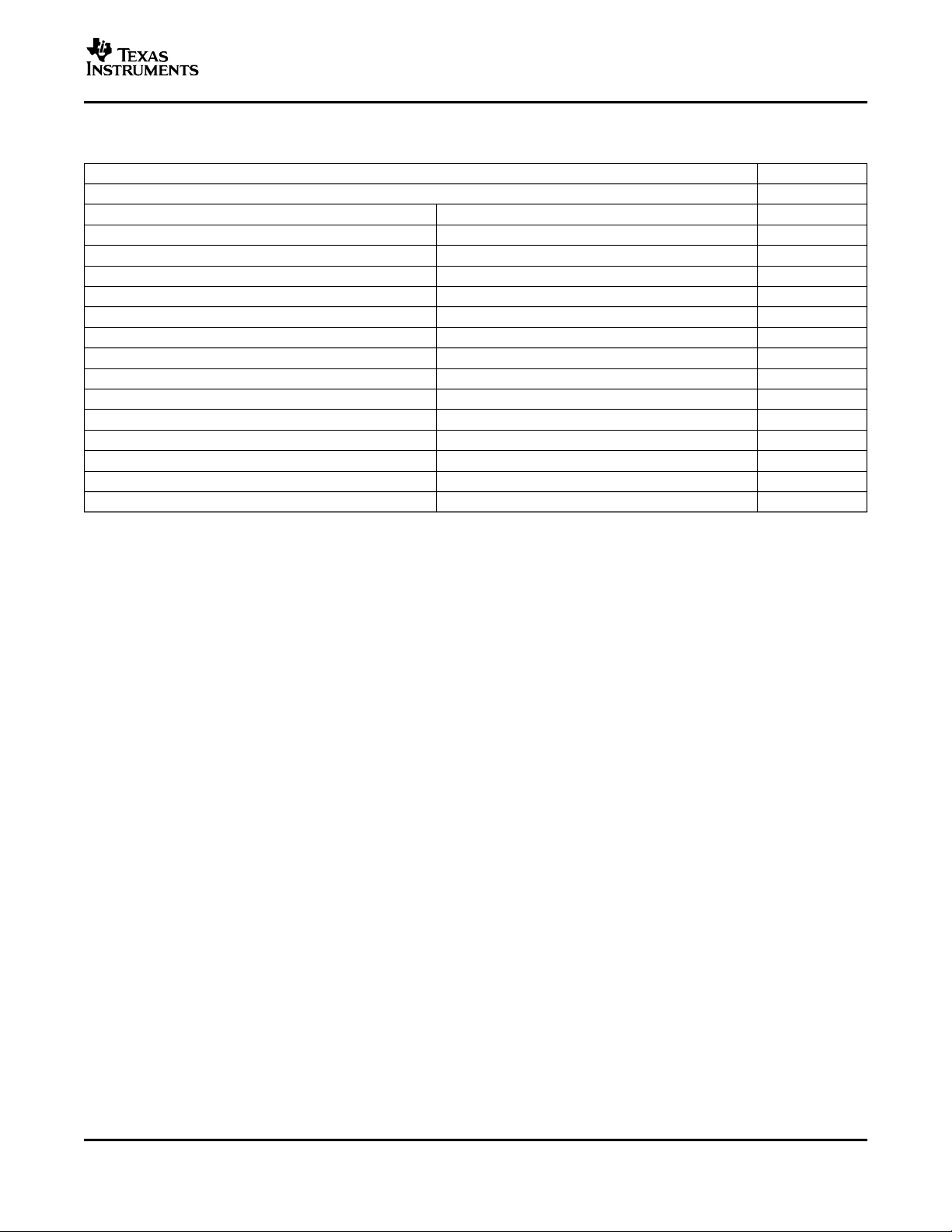
TABLE OF GRAPHS
FIGURE
±15-V graphs
Noninverting frequency response 1, 2
Inverting frequency response 3
0.1 dB flatness 4
Noninverting frequency response 5
Inverting frequency response 6
Frequency response capacitive load 7
Recommended R
2nd Harmonic distortion vs Frequency 9, 11
3rd Harmonic distortion vs Frequency 10, 12
Slew rate vs Output voltage step 13, 14, 15
Noise vs Frequency 16
Settling time 17, 18
Quiescent current vs Supply voltage 19
Output voltage vs Load resistance 20
Input bias and offset current vs Case temperature 21
Input offset voltage vs Case temperature 22
Transimpedance vs Frequency 23
Rejection ratio vs Frequency 24
Noninverting small signal transient response 25
Inverting large signal transient response 26, 27
Overdrive recovery time 28
Differential gain vs Number of loads 29
Differential phase vs Number of loads 30
Closed loop output impedance vs Frequency 31
Crosstalk vs Frequency 32
Power-down quiescent current vs Supply voltage 33
Turnon and turnoff time delay 34
ISO
vs Capacitive load 8
8
Page 9
www.ti.com
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
TABLE OF GRAPHS
FIGURE
±5-V graphs
Noninverting frequency response 35
Inverting frequency response 36
0.1 dB flatness 37
Noninverting frequency response 38
Inverting frequency response 39
Settling time 40
2nd Harmonic distortion vs Frequency 41
3rd Harmonic distortion vs Frequency 42
Slew rate vs Output voltage step 43, 44, 45
Noninverting small signal transient response 46
Output voltage load resistance 47
Input bias and offset current vs Case temperature 48
Overdrive recovery time 49
Rejection ratio vs Frequency 50
Crosstalk vs Frequency 51
9
Page 10

www.ti.com
f − Frequency − Hz
Noninverting Gain − dB
RF = 499 Ω
RF = 1.2 k Ω
Gain = 2,
RL = 100 Ω,
VO = 200 mVPP,
VS = ±15 V
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
RF = 909 Ω
−4
−2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
f − Frequency − Hz
Noninverting Gain − dB
G = 10, RF = 604 Ω
RL = 100 Ω,
VO = 200 mVPP, VS = ±15 V
G = 5, RF = 715 Ω
G =2, RF = 909 Ω
G =1, RF = 1.1 kΩ
−4
−2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
1 M
10 M 100 M 1 G
f − Frequency − Hz
Inverting Gain − dB
G = −1, RF = 909 Ω
G = −10, RF = 604 Ω
G = −5, RF = 715 Ω
G = −2, RF = 806 Ω
RL = 100 Ω,
VO = 200 mVPP, VS = ±15 V
5.7
5.8
5.9
6
6.1
6.2
6.3
100 k
1 M 10 M 100 M
f − Frequency − Hz
Noninverting Gain − dB
Gain = 2,
RF = 909 Ω,
RL = 200 Ω,
VO = 200 mVPP,
VS = ±15 V
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
16
1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
14
f − Frequency − Hz
VO = 5 V
PP
Gain = −5,
RF = 715 Ω,
RL = 100 Ω,
VS = ±15 V
VO = 1 V
PP
VO = 2 V
PP
VO = 10 V
PP
VO = 20 V
PP
Inverting Gain − dB
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
f − Frequency − Hz
VO = 2V
PP
VO = 1V
PP
VO = 20V
PP
VO = 10V
PP
VO = 5V
PP
Gain = 5,
RF = 715 Ω,
RL = 100 Ω,
VS = ±15 V
Noninverting Gain − dB
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
10 100
C
L
− Capacitive Load − pF
Recommended
R
ISO
Ω
Gain = 5,
VS = ±15 V
−
+
−
178 Ω
715 Ω
R
ISO
C
L
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
100 k 1 M 10 M 100 M
f − Frequency − Hz
2nd Harmonic Destortion − dBc
VS = ±15 V,
VO = 2 V
PP
G = 2
RF = 909 Ω,
RL = 1 kΩ
G = 2
RF = 909 Ω,
RL = 100 Ω
G = 1
RF = 1.1 kΩ,
RL = 1 kΩ
G = 1
RF = 1.1 kΩ,
RL = 100 Ω
−2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
10 M 100 M 1 G
f − Frequency − Hz
Signal Gain − dB
R
(ISO)
= 15 Ω
CL = 100 pF
Gain = 5
RL = 100 Ω
VS =±15 V
R
(ISO)
= 39.2 Ω
CL = 10 pF
R
(ISO)
= 30.9 Ω
CL = 22 pF
R
(ISO)
= 20 Ω
CL = 47 pF
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
NONINVERTING NONINVERTING INVERTING
FREQUENCY RESPONSE FREQUENCY RESPONSE FREQUENCY RESPONSE
Figure 1. Figure 2. Figure 3.
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (±15 V)
0.1 dB FLATNESS FREQUENCY RESPONSE FREQUENCY RESPONSE
NONINVERTING INVERTING
Figure 4. Figure 5. Figure 6.
FREQUENCY RESPONSE vs vs
RECOMMENDED R
ISO
2ND HARMONIC DISTORTION
CAPACITIVE LOAD CAPTIVATE LOAD FREQUENCY
10
Figure 7. Figure 8. Figure 9.
Page 11

www.ti.com
−100
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
100 k 1 M 10 M 100 M
f − Frequency − Hz
Harmonic Distortion −dBc
G = 5
RF = 715 Ω,
RL = 100 Ω,
Vs = ±15 V
VO = 20 V
PP
VO = 10 V
PP
VO = 5 V
PP
VO = 2 V
PP
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
100 k 1 M 10 M 100 M
f − Frequency − Hz
3rd Harmonic Distortion − dBc
VS = ±15 V,
VO = 2 V
PP
G = 1
RF = 1.1 kΩ,
RL = 1 kΩ
G = 2
RF = 909 Ω,
R
L
= 1 kΩ
G = 2
RF = 909 Ω,
RL = 100 Ω
G = 1
RF = 1.1 kΩ,
RL = 100 Ω
−100
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
100 k
1 M
10 M 100 M
f − Frequency − Hz
Harmonic Distortion −dBc
G = 5
RF = 715 Ω,
RL = 100 Ω,
Vs = ±15 V
VO = 20 V
PP
VO = 10 V
PP
VO = 5 V
PP
VO = 2 V
PP
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
SR − Slew Rate − V/
V
O
− Output Voltage −V
PP
sµ
Gain = 2
RL = 100 Ω
RF = 909 Ω
VS = ±15 V
Fall
Rise
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
SR − Slew Rate − V/
V
O
− Output Voltage −V
PP
sµ
Gain = 5
RL = 100 Ω
RF = 715 Ω
VS = ±15 V
Fall
Rise
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
SR − Slew Rate − V/
V
O
− Output Voltage − V
PP
sµ
Gain = 1
RL = 100 Ω
RF = 1.1 kΩ
VS = ±15 V
Fall
Rise
1
10
100
1000
10 100 1 k 10 k 100 k
f − Frequency − Hz
− Current Noise −
V
n
I
n
− Voltage Noise −
pA/ Hz
nV/ Hz
I
n−
I
n+
V
n
−1.25
−1
−0.75
−0.5
−0.25
0
0.25
0.5
0.75
1
1.25
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
t − Time − ns
− Output Voltage − VV
O
Gain = −2
RL = 100 Ω
RF =806 Ω
VS = ±15 V
Rising Edge
Falling Edge
−4.5
−4
−3.5
−3
−2.5
−2
−1.5
−1
−0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
t − Time − ns
− Output Voltage − VV
O
Gain = −2
RL = 100 Ω
RF = 806 Ω
VS = ±15 V
Rising Edge
Falling Edge
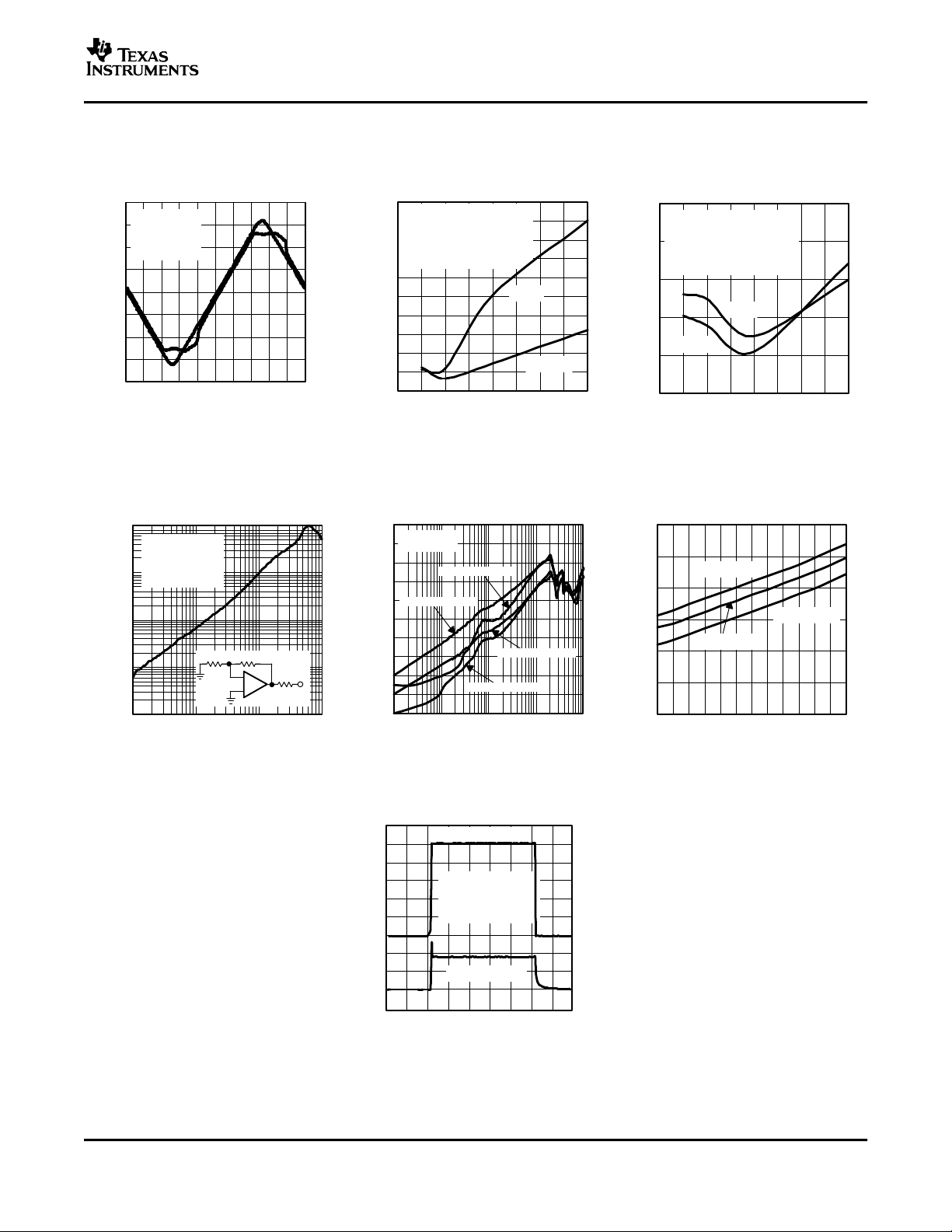
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (±15 V) (continued)
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
3RD HARMONIC DISTORTION 2ND HARMONIC DISTORTION 3RD HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs vs vs
FREQUENCY FREQUENCY FREQUENCY
Figure 10. Figure 11. Figure 12.
SLEW RATE SLEW RATE SLEW RATE
vs vs vs
OUTPUT VOLTAGE STEP OUTPUT VOLTAGE STEP OUTPUT VOLTAGE STEP
Figure 13. Figure 14. Figure 15.
NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY SETTLING TIME SETTLING TIME
Figure 16. Figure 17. Figure 18.
11
Page 12

www.ti.com
-16
-12
-8
-4
0
4
8
12
16
10 100 1000
R
L
- Load Resistance - Ω
- Output Voltage - VV
O
VS = ±15 V
TA = -40 to 85°C
7
7.5
8
8.5
9
9.5
10
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
− Quiescent Current − mAI
Q
VS − Supply Voltage − ±V
TA = −40 °C
TA = 25 °C
10.5
11
TA = 85 °C
Per Channel
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
5
5.5
6
6.5
7
-40-30-20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
T
C
- Case Temperature - °C
- Input Bias Currents -I
IB
I
OS
- Input Offset Currents -
Aµ
Aµ
I
OS
IIB-
IIB+
VS = ±15 V
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
100 k 1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
PSRR+
VS = ±15 V
Rejection Ratios − dB
f − Frequency − Hz
CMRR
PSRR−
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
-40-30-20-10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
T
C
- Case Temperature - °C
- Input Offset Voltage - mV
V
OS
VS = ±5 V
VS = ±15 V
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
100 k 1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
f − Frequency − Hz
Transimpedance Gain − dB Ohms
VS = ±15 V and ±5 V
−6
−5
−4
−3
−2
−1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
−5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
t − Time − ns
− Output Voltage − VV
O
Output
Input
Gain = 2,
RL = 100 Ω,
RF = 715 Ω,
VS = ±15 V
−12
−10
−8
−6
−4
−2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
−10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
t − Time − ns
− Output Voltage − VV
O
Output
Input
Gain = −5,
RL = 100 Ω,
RF = 715 Ω,
VS = ±15 V
−0.3
−0.25
−0.2
−0.15
−0.1
−0.05
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
−10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
t − Time − ns
− Output Voltage − VV
O
Output
Input
Gain = 2,
RL = 100 Ω,
RF = 909 Ω,
VS = ±15 V
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (±15 V) (continued)
QUIESCENT CURRENT OUTPUT VOLTAGE OFFSET CURRENT
INPUT BIAS AND
vs vs vs
SUPPLY VOLTAGE LOAD RESISTANCE CASE TEMPERATURE
Figure 19. Figure 20. Figure 21.
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE TRANSIMPEDANCE REJECTION RATIO
vs vs vs
CASE TEMPERATURE FREQUENCY FREQUENCY
NONINVERTING SMALL SIGNAL INVERTING LARGE SIGNAL INVERTING LARGE SIGNAL
TRANSIENT RESPONSE TRANSIENT RESPONSE TRANSIENT RESPONSE
12
Figure 22. Figure 23. Figure 24.
Figure 25. Figure 26. Figure 27.
Page 13
www.ti.com
−20
−15
−10
−5
0
5
10
15
20
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
−4
−3
−2
−1
0
1
2
3
4
t − Time − µs
− Output Voltage − V
− Input Voltage − VV
I
V
O
G = 5,
RL = 100 Ω,
RF = 715 Ω,
VS = ±15 V
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.08
0.09
0.10
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Number of Loads − 150 Ω
Differential Gain − %
Gain = 2
RF = 909 Ω
VS = ±15 V
40 IRE − NTSC and Pal
Worst Case ±100 IRE Ramp
NTSC
PAL
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Number of Loads − 150 Ω
Differential Phase −
Gain = 2
RF = 909 Ω
VS = ±15 V
40 IRE − NTSC and Pal
Worst Case ±100 IRE Ramp
NTSC
PAL
°
−100
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
−20
−10
0
100 k 1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
f − Frequency − Hz
Crosstalk − dB
G= 5, CH1 to 2
G= 5, CH2 to 1
G= 2, CH2 to 1
G= 2, CH1 to 2
VS = ±15 V,
RL = 100 Ω
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
TA = -40°C
V
S
- Supply Voltage - ±V
Powerdown Quiescent Current -
TA = 85°C
Aµ
TA = 25°C
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
f − Frequency − Hz
Closed-Loop Output Impedance − Ω
Gain = 2,
R
ISO
= 5.11 Ω ,
RF = 909 Ω,
VS = ±15 V
+
−
909 Ω 909 Ω
5.11 Ω
V
O
−0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
t − Time − ms
− Output Voltage Level − VV
O
Output Voltage
PowerDown Pulse − V
Powerdown Pulse
6 7
Gain = 2,
V
I
= 0.1 Vdc
RL = 100 Ω
VS = ±15 V and ±5 V
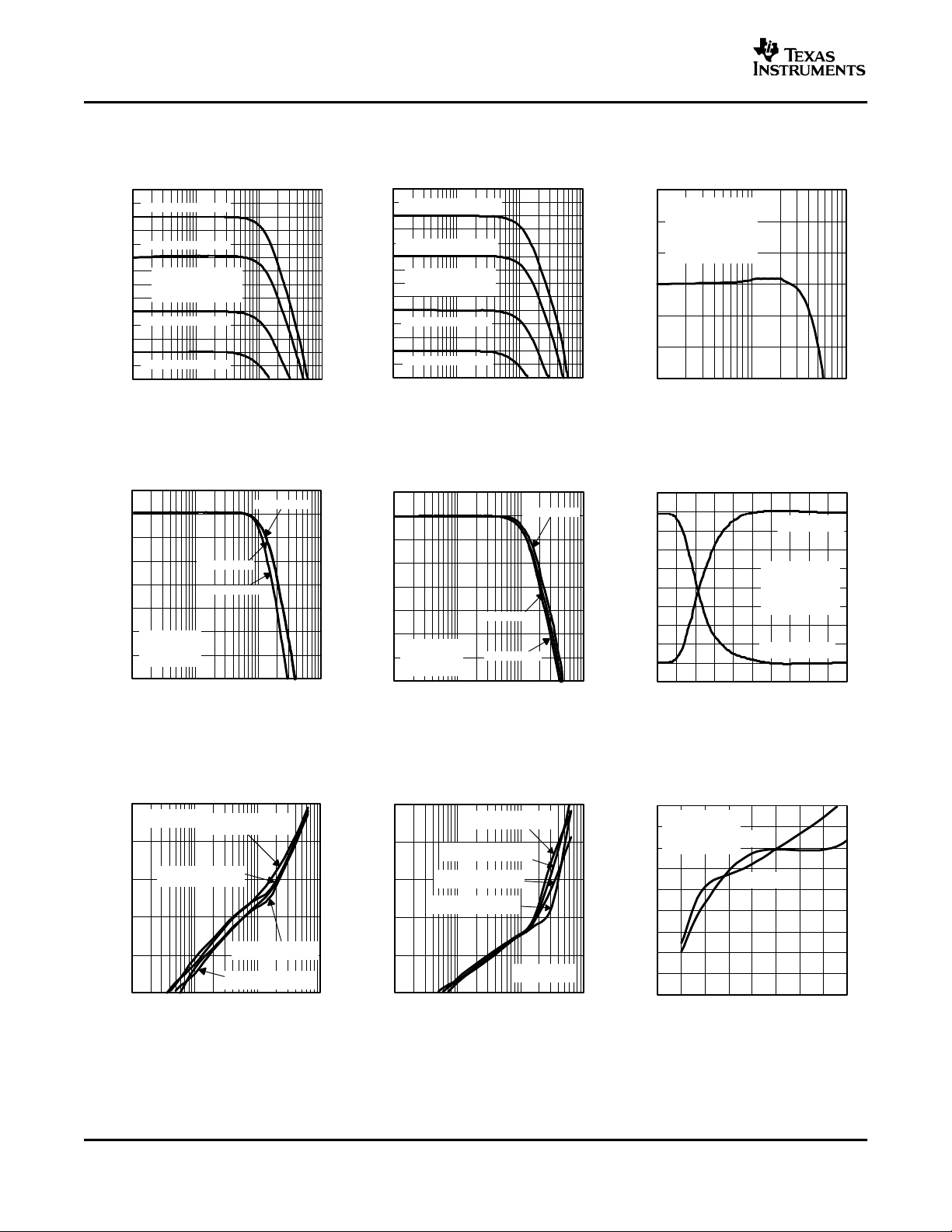
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (±15 V) (continued)
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
DIFFERENTIAL GAIN DIFFERENTIAL PHASE
vs vs
OVERDRIVE RECOVERY TIME NUMBER OF LOADS NUMBER OF LOADS
Figure 28. Figure 29. Figure 30.
CLOSED-LOOP OUTPUT POWER-DOWN QUIESCENT
IMPEDANCE CROSSTALK CURRENT
vs vs vs
FREQUENCY FREQUENCY SUPPLY VOLTAGE
Figure 31. Figure 32. Figure 33.
TURNON AND TURNOFF
TIME DELAY
Figure 34.
13
Page 14
www.ti.com
−4
−2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
f − Frequency − Hz
Inverting Gain − dB
G = −1, RF = 906 Ω
G = −10, RF = 604 Ω
G = −5, RF = 715 Ω
G = −2, RF = 806 Ω
RL = 100 Ω,
VO = 200 mVPP,
VS = ±5 V
5.7
5.8
5.9
6
6.1
6.2
6.3
1 10 100
f − Frequency − MHz
Noniverting Gain −dB
Gain = 2,
RF = 909 Ω,
RL = 100 Ω,
VO = 200 mVPP,
VS = ±5 V
−4
−2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
f − Frequency − Hz
Noninverting Gain − dB
G = 10, RF = 604 Ω
RL = 100 Ω,
VO = 200 mVPP,
VS = ±5 V
G = 5, RF = 715 Ω
G = 2, RF = 909 Ω
G = 1, RF = 1.1 kΩ
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
1 M 10 M
100 M
1 G
VO = 2 V
PP
VO = 1 V
PP
VO = 5 V
PP
G = 5,
RF = 715 Ω,
RL = 100 Ω,
VS = ±5V
f − Frequency − Hz
Noninverting Gain − dB
−1.25
−1
−0.75
−0.5
−0.25
0
0.25
0.5
0.75
1
1.25
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
t − Time − ns
− Output Voltage − VV
O
Gain = −2
RL = 100 Ω
RF = 806 Ω
VS = ±5 V
Rising Edge
Falling Edge
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
1 M
10 M 100 M 1 G
VO = 1 V
PP
VO = 5 V
PP
G = 5,
RF = 715 Ω,
RL = 100 Ω,
VS = ±5V
f − Frequency − Hz
VO = 2 V
PP
Inverting Gain − dB
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
100 k 1 M 10 M
100 M
f − Frequency − Hz
2nd Harmonic Destortion − dBc
G = 2, RF = 909 Ω,
RL = 100 Ω
G =1, RF = 1.1 kΩ,
RL = 100 Ω
G =1, RF = 1.1 kΩ,
RL = 1 kΩ
G = 2, RF = 909 Ω,
RL = 1 kΩ
VS = ±5 V,
VO = 2 V
PP
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
100 k 1 M 10 M 100 M
f − Frequency − Hz
3rd Harmonic Distortion − dBc
VO = 2 VPP,
VS = ±5 V
G = 2, RF = 909Ω,
RL = 100 Ω
G = 1, RF = 1.1 kΩ,
RL = 100 Ω
G = 2, RF = 909Ω,
RL = 1 kΩ
G = 1, RF = 1.1 kΩ,
RL = 1 kΩ
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
SR − Slew Rate − V/
V
O
− Output Voltage −V
PP
sµ
Gain =1
RL = 100 Ω
RF = 1.1 kΩ
VS = ±5 V
Fall
Rise
THS3092
THS3096
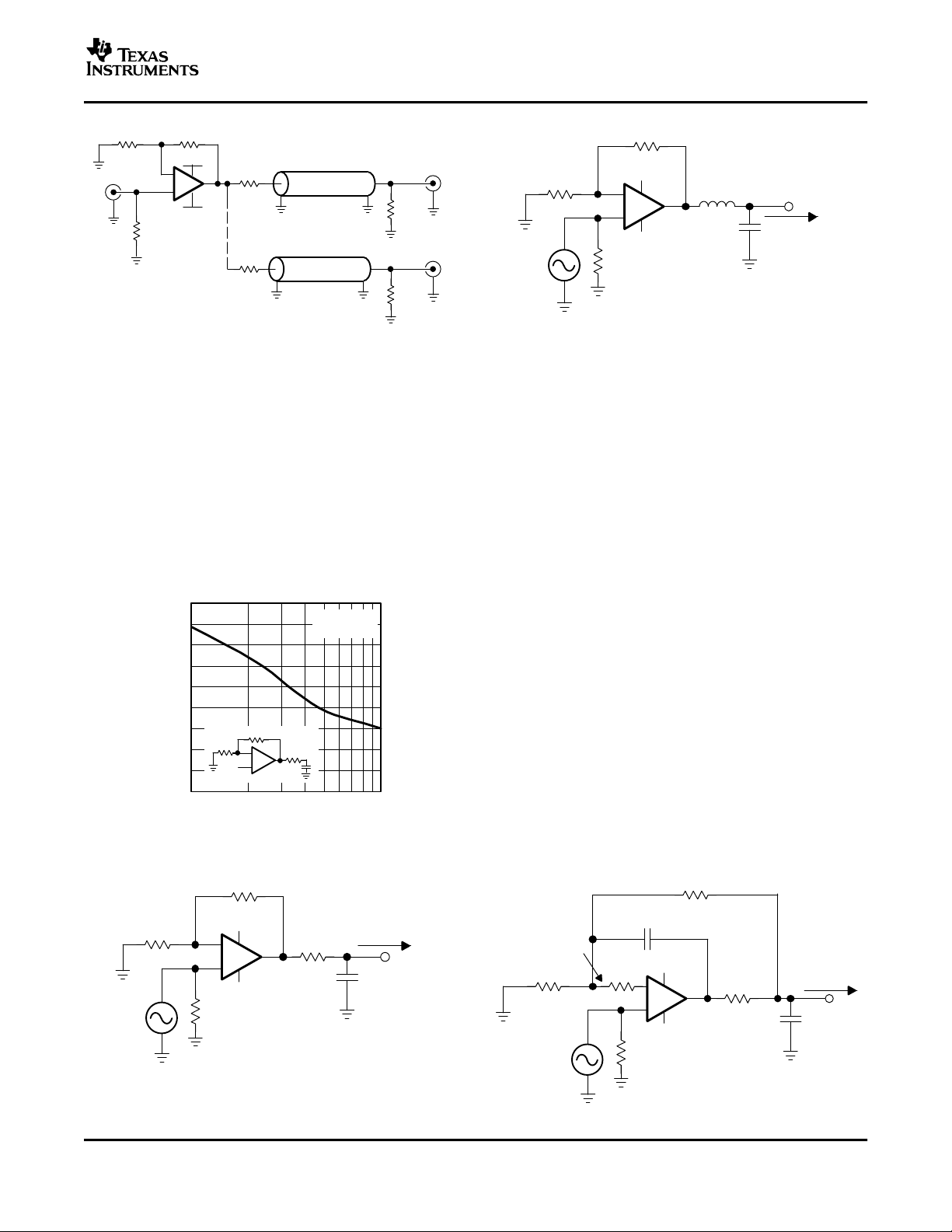
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
NONINVERTING INVERTING
FREQUENCY RESPONSE FREQUENCY RESPONSE 0.1 dB FLATNESS
Figure 35. Figure 36. Figure 37.
NONINVERTING INVERTING
FREQUENCY RESPONSE FREQUENCY RESPONSE SETTLING TIME
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (±5 V)
2ND HARMONIC DISTORTION 3RD HARMONIC DISTORTION SLEW RATE
14
Figure 38. Figure 39. Figure 40.
vs vs vs
FREQUENCY FREQUENCY OUTPUT VOLTAGE STEP
Figure 41. Figure 42. Figure 43.
Page 15

www.ti.com
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
0 1 2 3 4 5
SR − Slew Rate − V/
V
O
− Output Voltage −V
PP
sµ
Gain = 5
RL = 100 Ω
RF = 715 Ω
VS = ±5 V
Fall
Rise
−0.3
−0.25
−0.2
−0.15
−0.1
−0.05
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
−10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
t − Time − ns
− Output Voltage − VV
O
Gain = 2
RL = 100 Ω
R
F
= 909 Ω
VS = ±5 V
Input
Output
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
1100
1200
0 1 2 3 4 5
SR − Slew Rate − V/
V
O
− Output Voltage −V
PP
sµ
Gain = 2
RL = 100 Ω
RF = 909Ω
VS = ±5 V
Fall
Rise
−5
−4
−3
−2
−1
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
−1
−0.8
−0.6
−0.4
−0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
t − Time − µs
− Input Voltage − VV
I
Gain = 5,
RL = 100 Ω,
RF = 715 Ω,
VS = ±5 V
− Output Voltage − AV
O
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
-40 -30 -20-10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
- Input Bias Current -
TC - Case Temperature - °C
VS = ±5 V
- Input Offset Current -
I
IB-
I
IB
Aµ
I
OS
Aµ
I
IB+
I
OS
-3.5
-3
-2.5
-2
-1.5
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
10 100 1000
R
L
- Load Resistance - Ω
- Output Voltage - VV
O
VS = ±5 V
TA = -40 to 85°C
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
100 k 1 M 10 M 100 M
VS = ±5 V
Rejection Ratio - dB
f - Frequency - Hz
PSRR-
PSRR+
CMRR
−100
−90
−80
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
−20
−10
0
100 k 1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
f − Frequency − Hz
Crosstalk − dB
G= 5, CH1 to 2
G= 5, CH2 to 1
G= 2, CH2 to 1
G= 2, CH1 to 2
VS = ±5 V,
RL = 100 Ω
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (±5 V) (continued)
SLEW RATE SLEW RATE
vs vs NONINVERTING SMALL SIGNAL
OUTPUT VOLTAGE STEP OUTPUT VOLTAGE STEP TRANSIENT RESPONSE
Figure 44. Figure 45. Figure 46.
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
OUTPUT VOLTAGE OFFSET CURRENT
INPUT BIAS AND
vs vs
LOAD RESISTANCE CASE TEMPERATURE OVERDRIVE RECOVERY TIME
Figure 47. Figure 48. Figure 49.
REJECTION RATIO CROSSTALK
vs vs
FREQUENCY FREQUENCY
Figure 50. Figure 51.
15
Page 16

www.ti.com
_
+
R
F
909 Ω
49.9 Ω
0.1 µF 6.8 µF
−V
S
−15 V
R
G
50 Ω Source
+
V
I
0.1 µF 6.8 µF
+
+V
S
15 V
909 Ω
49.9 Ω
50 Ω LOAD
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
APPLICATION INFORMATION
WIDEBAND, NONINVERTING OPERATION
The THS3092/6 are unity gain stable 135-MHz
current-feedback operational amplifiers, designed to
operate from a ±5-V to ±15-V power supply.
Figure 52 shows the THS3092 in a noninverting gain
of 2-V/V configuration typically used to generate the
performance curves. Most of the curves were
characterized using signal sources with 50-Ω source
impedance, and with measurement equipment
presenting a 50-Ω load impedance.
Figure 52. Wideband, Noninverting Gain
Configuration
Current-feedback amplifiers are highly dependent on
the feedback resistor R
for maximum performance
F
and stability. Table 1 shows the optimal gain setting
resistors R
and R
F
at different gains to give
G
maximum bandwidth with minimal peaking in the
frequency response. Higher bandwidths can be
achieved, at the expense of added peaking in the
frequency response, by using even lower values for
RF. Conversely, increasing R
decreases the
F
bandwidth, but stability is improved.
Table 1. Recommended Resistor Values for
Optimum Frequency Response
THS3092 and THS3096 RFand RGvalues for minimal peaking
GAIN (V/V) RG(Ω) RF(Ω)
1
2
5
10
-1 ±15 and ±5 909 909
-2 ±15 and ±5 402 806
-5 ±15 and ±5 143 715
-10 ±15 and ±5 60.4 604
with RL= 100 Ω
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(V)
±15 -- 1.1 k
±5 -- 1.1 k
±15 909 909
±5 909 909
±15 178 715
±5 178 715
±15 66.5 604
±5 66.5 604
16
Page 17

www.ti.com
WIDEBAND, INVERTING OPERATION
_
+
R
G
402 Ω
0.1 µF 6.8 µF
−V
S
−15 V
50 Ω Source
+
V
I
0.1 µF 6.8 µF
+
+V
S
15 V
R
F
806 Ω
R
M
57.6 Ω
49.9 Ω
50 Ω LOAD
_
+
49.9 Ω
50 Ω Source
V
I
+V
S
R
F
909 Ω
R
G
909 Ω
+V
S
2
+V
S
2
_
+
402 Ω
50 Ω Source
V
I
V
S
R
F
806 Ω
+V
S
2
+V
S
2
57.6 Ω
R
G
R
T
R
T
49.9 Ω
49.9 Ω
50 Ω LOAD
50 Ω LOAD
Figure 53 shows the THS3092 in a typical inverting
gain configuration where the input and output
impedances and signal gain from Figure 52 are
retained in an inverting circuit configuration.
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
Figure 53. Wideband, Inverting Gain
Configuration
SINGLE SUPPLY OPERATION
The THS3092/6 have the capability to operate from a
single supply voltage ranging from
10 V to 30 V. When operating from a single power
supply, biasing the input and output at mid-supply
allows for the maximum output voltage swing. The
circuits shown in Figure 54 shows inverting and
noninverting amplifiers configured for single supply
operations.
Figure 54. DC-Coupled, Single-Supply Operation
VDSL Driver Circuit
The THS3092 and THS3096 have the ability to drive
over 200 mA of current with very high voltage swings.
Using these amplifiers coupled with the very high
slew rate, low distortion, and low noise required in
VDSL applications, makes for a perfect match. In
VDSL systems where the receive signal is critical, the
use of a low transformer ratio is necessary. With this
low ratio, the output swing required from the line
driver amplifier must increase, especially when driving the VDSL’s full 14.5-dBm power onto the line. The
line driver's low distortion and noise is critical for the
VDSL as the receive bands are intertwined with the
transmit frequency bands up to the 12-MHz VDSL
limit.
17
Page 18

www.ti.com
+
−
THS3092
20 V
−
+
1:1
THS3092
330 pF
330 pF
22 pF
22 pF
10 V
10 V
0.022F
200
100
14.5 dBm
Line Power
200
604
4.99 k
4.99 k
0.01 F
191
604
1.21 k
0.022F
24.9
6.8 F
0.01 F
24.9
*Hybrid Connection Not
Shown For Simplicity
DAC
V
IN+
DAC
V
IN−
1.21 k
+
−
THS3092
26 V
−
+
1:1
THS3092
To RX
Hybrid
330 pF
330 pF
22 pF
13 V
13 V
0.01 F 6.8 F
4.99 k
200
DAC
V
IN+
22 pF
133
604
604
0.015 F
200
4.99 k
49.9
49.9
0.022F
0.022F
14.5 dBm
Line Power
100
DAC
V
IN−
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
Figure 55 shows a traditional hybrid connection One of the concerns about any DSL line driver is the
approach for achieving the 14.5-dBm line power power dissipation. One of the most common ways to
utilizing a 1:1 transformer. Looking at the input to the reduce power is by using active termination, aka
amplifiers shows a low-pass filter consisting of two synthesized impedance. Refer to TI Application Note
separate capacitors to ground. There is an argument SLOA100 for more information on active termination.
that since the signal coming out of the DAC is The drawback to active termination is the received
fully-differential then a single capacitor (10 pF in this signal is reduced by the same synthesis factor
case) is perfectly acceptable. The problem with this utilized in the system. Due to the very high attenuidea is that many DACs have common-mode energy ation of the line at up to 12 MHz, the receive signal
due to images around the sampling frequency which can be severely diminished. Thus, the use of active
must be filtered before reaching the amplifier. An termination should be kept to modest levels at best.
amplifier simply amplifies its input–including the Figure 56 shows an example of utilizing a simple
DAC’s images at high frequencies–and pass it active termination scheme with a synthesis factor of 2
through to the transformer and ultimately to the line, to achieve the same line power, but with a reduced
possibly causing the system to fail EMC compliance. power supply voltage that ultimately saves power in
A single capacitor does not remove these com- the system.
mon-mode images, it only removes the differential
signal images. However, two separate filter capacitors filter both the common-mode signals and the
differential-mode signals. Be sure to place the ground
connection point of the capacitors next to each other,
and then tie a single ground point at the middle of this
trace.
Figure 55.
Additionally, level shifting must be done to center the
common-mode voltage appearing at the amplifier’s
noninverting input to optimally the midpoint of the
power supply. As a side benefit of the
ac-coupling/level shifter, a simple high pass filter is
formed. This is generally a good idea for VDSL
systems where the transmit band is typically above 1
MHz, but can be as low as 25 kHz.
18
Figure 56.
Video Distribution
The wide bandwidth, high slew rate, and high output
drive current of the THS3092/6 matches the demands
for video distribution for delivering video signals down
multiple cables. To ensure high signal quality with
minimal degradation of performance, a 0.1-dB gain
flatness should be at least 7x the passband frequency to minimize group delay variations from the
amplifier. A high slew rate minimizes distortion of the
video signal, and supports component video and
RGB video signals that require fast transition times
and fast settling times for high signal quality.
Page 19
www.ti.com
_
+
V
S
−V
S
49.9 Ω
715 Ω
Ferrite Bead
1 µF
178 Ω
V
S
100 Ω LOAD
+
−
75 Ω
75 Ω
75 Ω
75 Ω
75 Ω
n Lines
V
O(1)
V
O(n)
75-Ω Transmission Line
V
I
909 Ω 909 Ω
−15 V
15 V
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
10 100
C
L
− Capacitive Load − pF
Recommended
R
ISO
Ω
Gain = 5,
VS = ±15 V
−
+
−
178 Ω
715 Ω
R
ISO
C
L
_
+
V
S
−V
S
49.9 Ω
715 Ω
5.11 Ω
1 µF
178 Ω
V
S
100 Ω LOAD
R
ISO
_
+
V
S
−V
S
49.9 Ω
5.11 Ω
1 µF
178 Ω
V
S
27 pF
715 Ω
R
F
R
G
715 Ω
100 Ω LOAD
R
IN
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
Figure 57. Video Distribution Amplifier
Application
Driving Capacitive Loads
Applications such as FET line drivers can be highly
capacitive and cause stability problems for
high-speed amplifiers.
Figure 58 through Figure 63 show recommended
methods for driving capacitive loads. The basic idea
is to use a resistor or ferrite chip to isolate the phase
shift at high frequency caused by the capacitive load
from the amplifier’s feedback path. See Figure 58 for
recommended resistor values versus capacitive load.
Figure 58. Recommended R
vs Capacitive Load
ISO
Figure 60.
Placing a small series resistor, R
, between the
ISO
amplifier’s output and the capacitive load, as shown
in Figure 59 , is an easy way of isolating the load
capacitance.
Using a ferrite chip in place of R
, as shown in
ISO
Figure 60 , is another approach of isolating the output
of the amplifier. The ferrite's impedance characteristic
versus frequency is useful to maintain the low frequency load independence of the amplifier while
isolating the phase shift caused by the capacitance at
high frequency. Use a ferrite with similar impedance
to R
, 20 Ω - 50 Ω, at 100 MHz and low impedance
ISO
at dc.
Figure 61 shows another method used to maintain
the low frequency load independence of the amplifier
while isolating the phase shift caused by the capacitance at high frequency. At low frequency, feedback
is mainly from the load side of R
. At high fre-
ISO
quency, the feedback is mainly via the 27-pF capacitor. The resistor R
in series with the negative input
IN
is used to stabilize the amplifier and should be equal
to the recommended value of R
Replacing R
with a ferrite of similar impedance at
IN
F
at unity gain.
about 100 MHz as shown in Figure 62 gives similar
results with reduced dc offset and low frequency
noise. (See the ADDITIONAL REFERENCE MA-
TERIAL section for Expanding the usability of
current-feedback amplifiers.)
Figure 59.
Figure 61.
19
Page 20

www.ti.com
_
+
V
S
−V
S
49.9 Ω
5.11 Ω
1 µF
178 Ω
V
S
27 pF
715 Ω
R
F
R
G
100 Ω LOAD
F
IN
FB
_
+
V
S
−V
S
_
+
V
S
−V
S
−V
S
V
S
604 Ω
604 Ω
133 Ω
5.11 Ω
5.11 Ω
_
+
V
S
−V
S
715 Ω
5.11 Ω
178 Ω
V
S
_
+
V
S
−V
S
715 Ω
5.11 Ω
178 Ω
24.9 Ω
24.9 Ω
1 nF
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
Figure 62.
Figure 63 is shown using two amplifiers in parallel to
double the output drive current to larger capacitive
loads. This technique is used when more output
current is needed to charge and discharge the load
faster like when driving large FET transistors.
Figure 63.
Figure 64 shows a push-pull FET driver circuit typical
of ultrasound applications with isolation resistors to
isolate the gate capacitance from the amplifier.
20
Figure 64. PowerFET Drive Circuit
SAVING POWER WITH POWER-DOWN
FUNCTIONALITY AND SETTING
THRESHOLD LEVELS WITH THE
REFERENCE PIN
The THS3096 features a power-down pin (PD) which
lowers the quiescent current from 9.5 mA down to
500 µA, ideal for reducing system power.
The power-down pin of the amplifier defaults to the
negative supply voltage in the absence of an applied
voltage, putting the amplifier in the power-on mode of
operation. To turn off the amplifier in an effort to
conserve power, the power-down pin can be driven
towards the positive rail. The threshold voltages for
power-on and power-down are relative to the supply
rails and are given in the specification tables. Below
the Enable Threshold Voltage, the device is on.
Above the Disable Threshold Voltage, the device is
off. Behavior in between these threshold voltages is
not specified.
Note that this power-down functionality is just that;
the amplifier consumes less power in power-down
mode. The power-down mode is not intended to
provide a high-impedance output. In other words, the
power-down functionality is not intended to allow use
as a 3-state bus driver. When in power-down mode,
the impedance looking back into the output of the
amplifier is dominated by the feedback and gain
setting resistors, but the output impedance of the
device itself varies depending on the voltage applied
to the outputs.
Figure 65 shows the total system output impedance
which includes the amplifier output impedance in
parallel with the feedback plus gain resistors, which
cumulate to 2420 Ω. Figure 52 shows this circuit
configuration for reference.
Page 21

www.ti.com
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
100 k 1 M 10 M 100 M 1 G
+
−
1.21 kΩ 1.21 kΩ
50 Ω
V
O
f − Frequency − Hz
− Powerdown Output Impedance −
Z
OPD
Ω
VS = ±15 V and ±5 V
Figure 65. Power-down Output Impedance vs
As with most current feedback amplifiers, the internal
architecture places some limitations on the system
when in power-down mode. Most notably is the fact
that the amplifier actually turns ON if there is a ±0.7 V
or greater difference between the two input nodes
(V+ and V-) of the amplifier. If this difference exceeds
±0.7 V, the output of the amplifier creates an output
voltage equal to approximately
[(V+ - V-) -0.7 V]×Gain. This also implies that if a
voltage is applied to the output while in power-down
mode, the V- node voltage is equal to
V
O(applied)
× R
and a large applied voltage at the output, the amplifier may actually turn ON due to the aforementioned
behavior.
The time delays associated with turning the device on
and off are specified as the time it takes for the
amplifier to reach either 10% or 90% of the final
output voltage. The time delays are in the order of
microseconds because the amplifier moves in and out
of the linear mode of operation in these transitions.
POWER-DOWN REFERENCE PIN
OPERATION
In addition to the power-down pin, the THS3096 and
THS3096 feature a reference pin (REF) which allows
the user to control the enable or disable power-down
voltage levels applied to the PD pin. In most
split-supply applications, the reference pin is connected to ground. In either case, the user needs to be
aware of voltage-level thresholds that apply to the
power-down pin. The usable range at the REF pin is
from V
to (V
S-
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
PRINTED-CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT
TECHNIQUES FOR OPTIMAL
PERFORMANCE
Achieving optimum performance with high frequency
amplifier, like the THS3092/6, requires careful
attention to board layout parasitic and external
component types.
Recommendations that optimize performance include:
• Minimize parasitic capacitance to any ac ground
for all of the signal I/O pins. Parasitic capacitance
on the output and input pins can cause instability.
To reduce unwanted capacitance, a window
around the signal I/O pins should be opened in all
of the ground and power planes around those
Frequency
/(R
+ R
G
F
- 4 V).
S+
). For low gain configurations
G
pins. Otherwise, ground and power planes should
be unbroken elsewhere on the board.
• Minimize the distance (< 0.25”) from the power
supply pins to high frequency 0.1-µF and 100-pF
decoupling capacitors. At the device pins, the
ground and power plane layout should not be in
close proximity to the signal I/O pins. Avoid
narrow power and ground traces to minimize
inductance between the pins and the decoupling
capacitors. The power supply connections should
always be decoupled with these capacitors.
Larger (6.8 µF or more) tantalum decoupling
capacitors, effective at lower frequency, should
also be used on the main supply pins. These may
be placed somewhat farther from the device and
may be shared among several devices in the
same area of the PC board.
• Careful selection and placement of external
components preserve the high frequency performance of the THS3092/6. Resistors should be
a very low reactance type. Surface-mount resistors work best and allow a tighter overall
layout. Again, keep their leads and PC board
trace length as short as possible. Never use
wirebound type resistors in a high frequency
application. Since the output pin and inverting
input pins are the most sensitive to parasitic
capacitance, always position the feedback and
series output resistors, if any, as close as possible to the inverting input pins and output pins.
Other network components, such as input termination resistors, should be placed close to the
gain-setting resistors. Even with a low parasitic
capacitance shunting the external resistors,
excessively high resistor values can create significant time constants that can degrade performance. Good axial metal-film or surface-mount
resistors have approximately 0.2 pF in shunt with
the resistor. For resistor values > 2.0 kΩ, this
parasitic capacitance can add a pole and/or a
zero that can effect circuit operation. Keep
resistor values as low as possible, consistent with
load driving considerations.
21
Page 22

www.ti.com
DIE
Side View (a)
DIE
End View (b)
Thermal
Pad
Bottom View (c)
0.140
0.060
0.060
0.010
vias
Top V iew
0.035
0.080
0.050
0.176
0.030
0.026
0.010
0.035
0.100
0.300
Pin 1
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
• Connections to other wideband devices on the leadframe upon which the die is mounted [see
board may be made with short direct traces or Figure 66 (a) and Figure 66 (b)]. This arrangement
through onboard transmission lines. For short results in the lead frame being exposed as a thermal
connections, consider the trace and the input to pad on the underside of the package [see Figthe next device as a lumped capacitive load. ure 66 (c)]. Because this thermal pad has direct
Relatively wide traces (50 mils to 100 mils) thermal contact with the die, excellent thermal pershould be used, preferably with ground and formance can be achieved by providing a good
power planes opened up around them. Estimate thermal path away from the thermal pad. Note that
the total capacitive load and determine if isolation devices such as the THS3092/6 have no electrical
resistors on the outputs are necessary. Low connection between the PowerPAD and the die.
parasitic capacitive loads (< 4 pF) may not need
an R
since the THS3092/6 are nominally com-
S
pensated to operate with a 2-pF parasitic load.
Higher parasitic capacitive loads without an RS
are allowed as the signal gain increases
(increasing the unloaded phase margin). If a long
trace is required, and the 6-dB signal loss intrinsic to a doubly-terminated transmission line is
acceptable, implement a matched impedance
transmission line using microstrip or stripline
techniques (consult an ECL design handbook for
microstrip and stripline layout techniques). A
50-Ω environment is not necessary onboard, and
in fact, a higher impedance environment improves distortion as shown in the distortion versus load plots. With a characteristic board trace
impedance based on board material and trace
dimensions, a matching series resistor into the
trace from the output of the THS3092/6 is used
as well as a terminating shunt resistor at the input
of the destination device. Remember also that the
terminating impedance is the parallel combination
of the shunt resistor and the input impedance of
the destination device: this total effective impedance should be set to match the trace impedance. If the 6-dB attenuation of a doubly
terminated transmission line is unacceptable, a
long trace can be series-terminated at the source
end only. Treat the trace as a capacitive load in
this case. This does not preserve signal integrity
as well as a doubly-terminated line. If the input
impedance of the destination device is low, there
is some signal attenuation due to the voltage
divider formed by the series output into the
terminating impedance.
• Socketing a high speed part like the THS3092/6
are not recommended. The additional lead length
and pin-to-pin capacitance introduced by the
socket can create an extremely troublesome
parasitic network which can make it almost impossible to achieve a smooth, stable frequency
response. Best results are obtained by soldering
the THS3092/6 parts directly onto the board.
The PowerPAD package allows for both assembly
and thermal management in one manufacturing operation. During the surface-mount solder operation
(when the leads are being soldered), the thermal pad
can also be soldered to a copper area underneath the
package. Through the use of thermal paths within this
copper area, heat can be conducted away from the
package into either a ground plane or other heat
dissipating device.
The PowerPAD package represents a breakthrough
in combining the small area and ease of assembly of
surface mount with the, heretofore, awkward
mechanical methods of heatsinking.
Figure 66. Views of Thermal Enhanced Package
Although there are many ways to properly heatsink
the PowerPAD package, the following steps illustrate
the recommended approach.
PowerPAD™ DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
The THS3092/6 are available in a
thermally-enhanced PowerPAD family of packages.
These packages are constructed using a downset
22
Figure 67. DDA PowerPAD PCB Etch and Via
Pattern
Page 23

www.ti.com
PowerPAD™ LAYOUT CONSIDERATIONS POWER DISSIPATION AND THERMAL
P
Dmax
T
max
T
A
JA
where:
P
Dmax
is the maximum power dissipation in the amplifier (W).
T
max
is the absolute maximum junction temperature (°C).
TA is the ambient temperature (°C).
θJA = θ
JC
+ θ
CA
θJC is the thermal coeffiecient from the silicon junctions to
the case (°C/W).
θCA is the thermal coeffiecient from the case to ambient
air (°C/W).
1. PCB with a top side etch pattern as shown in
Figure 67 . There should be etch for the leads as
well as etch for the thermal pad.
2. Place 13 holes in the area of the thermal pad.
These holes should be 10 mils in diameter. Keep
them small so that solder wicking through the
holes is not a problem during reflow.
3. Additional vias may be placed anywhere along
the thermal plane outside of the thermal pad
area. This helps dissipate the heat generated by
the THS3092/6 IC. These additional vias may be
larger than the 10-mil diameter vias directly under
the thermal pad. They can be larger because
they are not in the thermal pad area to be
soldered so that wicking is not a problem.
4. Connect all holes to the internal ground plane.
Note that the PowerPAD is electrically isolated
from the silicon and all leads. Connecting the
PowerPAD to any potential voltage such as V
is acceptable as there is no electrical connection
to the silicon.
5. When connecting these holes to the ground
plane, do not use the typical web or spoke via
connection methodology. Web connections have
a high thermal resistance connection that is
useful for slowing the heat transfer during
soldering operations. This makes the soldering of
vias that have plane connections easier. In this
application, however, low thermal resistance is
desired for the most efficient heat transfer. Therefore, the holes under the THS3092/6 PowerPAD
package should make their connection to the
internal ground plane with a complete connection
around the entire circumference of the
plated-through hole.
6. The top-side solder mask should leave the terminals of the package and the thermal pad area
with its 13 holes exposed. The bottom-side solder
mask should cover the 13 holes of the thermal
pad area. This prevents solder from being pulled
away from the thermal pad area during the reflow
process.
7. Apply solder paste to the exposed thermal pad
area and all of the IC terminals.
8. With these preparatory steps in place, the IC is
simply placed in position and run through the
solder reflow operation as any standard
surface-mount component. This results in a part
that is properly installed.
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
CONSIDERATIONS
The THS3092/6 incorporates automatic thermal
shutoff protection. This protection circuitry shuts down
the amplifier if the junction temperature exceeds
approximately 160°C. When the junction temperature
reduces to approximately 140°C, the amplifier turns
on again. But, for maximum performance and reliability, the designer must take care to ensure that
the design does not exeed a junction temperature of
125°C. Between 125°C and 150°C, damage does not
occur, but the performance of the amplifier begins to
degrade and long term reliability suffers. The thermal
characteristics of the device are dictated by the
package and the PC board. Maximum power
dissipation for a given package can be calculated
using the following formula.
,
S-
For systems where heat dissipation is more critical,
the THS3092 is offered in an 8-pin SOIC (DDA) with
PowerPAD package, and the THS3096 is offered in a
14-pin TSSOP (PWP) with PowerPAD package for
even better thermal performance. The thermal coefficient for the PowerPAD packages are substantially
improved over the traditional SOIC. Maximum power
dissipation levels are depicted in the graph for the
available packages. The data for the PowerPAD
packages assume a board layout that follows the
PowerPAD layout guidelines referenced above and
detailed in the PowerPAD application note (literature
number SLMA002). The following graph also illustrates the effect of not soldering the PowerPAD to a
PCB. The thermal impedance increases substantially
which may cause serious heat and performance
issues. Be sure to always solder the PowerPAD to
the PCB for optimum performance.
23
Page 24

www.ti.com
4
3.5
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
−40 −20 0 20 40 60 80 100
− Maximum Power Dissipation − W
P
D
TA − Free-Air Temperature − °C
Results are With No Air Flow and PCB Size = 3”x 3”
θJA = 45.8°C/W for 8-Pin SOIC w/PowerPad (DDA)
θJA = 58.4°C/W for 8-Pin MSOP w/PowerPad (DGN)
θJA = 95°C/W for 8-Pin SOIC High−K Test PCB (D)
θJA = 158°C/W for 8-Pin MSOP w/PowerPad w/o Solder
θJA = 58.4°C/W
θJA = 95°C/W
θJA = 158°C/W
ΤJ = 125°C
θJA = 45.8°C/W
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
Figure 68. Maximum Power Distribution vs
Ambient Temperature
When determining whether or not the device satisfies
the maximum power dissipation requirement, it is
important to not only consider quiescent power
dissipation, but also dynamic power dissipation. Often
times, this is difficult to quantify because the signal
pattern is inconsistent, but an estimate of the RMS
power dissipation can provide visibility into a possible
problem.
DESIGN TOOLS
Evaluation Fixtures, Spice Models, and
Application Support
Texas Instruments is committed to providing its
customers with the highest quality of applications
support. To support this goal an evaluation board has
been developed for the THS3092/6 operational amplifier. The board is easy to use, allowing for straightforward evaluation of the device. The evaluation board
can be ordered through the Texas Instruments web
site, www.ti.com, or through your local Texas
Instruments sales representative.
Computer simulation of circuit performance using
SPICE is often useful when analyzing the performance of analog circuits and systems. This is particularly true for video and RF-amplifier circuits where
parasitic capacitance and inductance can have a
major effect on circuit performance. A SPICE model
for the THS3092/6 is available through either the
Texas Instruments web site (www.ti.com) or as one
model on a disk from the Texas Instruments Product
Information Center (1–800–548–6132). The PIC is
also available for design assistance and detailed
product information at this number. These models do
a good job of predicting small-signal ac and transient
performance under a wide variety of operating conditions. They are not intended to model the distortion
characteristics of the amplifier, nor do they attempt to
distinguish between the package types in their
small-signal ac performance. Detailed information
about what is and is not modeled is contained in the
model file itself.
24
Page 25

www.ti.com
THS3092 EVM
+
+
7
5
6
U1:B
3
1
8
2
4
J2
R2
R1
R6
R5
5 V
-5 V
R3
U1:A
J3
R4
J1
R7
R8
R9
J5
R11
R10
R12
J6
J4
-5 V
C3
C1
FB1
J7
- 5 V
J8
GND
FB2
J9
5 V
5 V
C2
C4
TP1 TP2
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
Figure 70. THS3092 EVM Board Layout
(Top Layer)
Figure 69. THS3092 EVM Schematic
Figure 71. THS3092 EVM Board Layout
(Ground Plane)
25
Page 26
www.ti.com
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
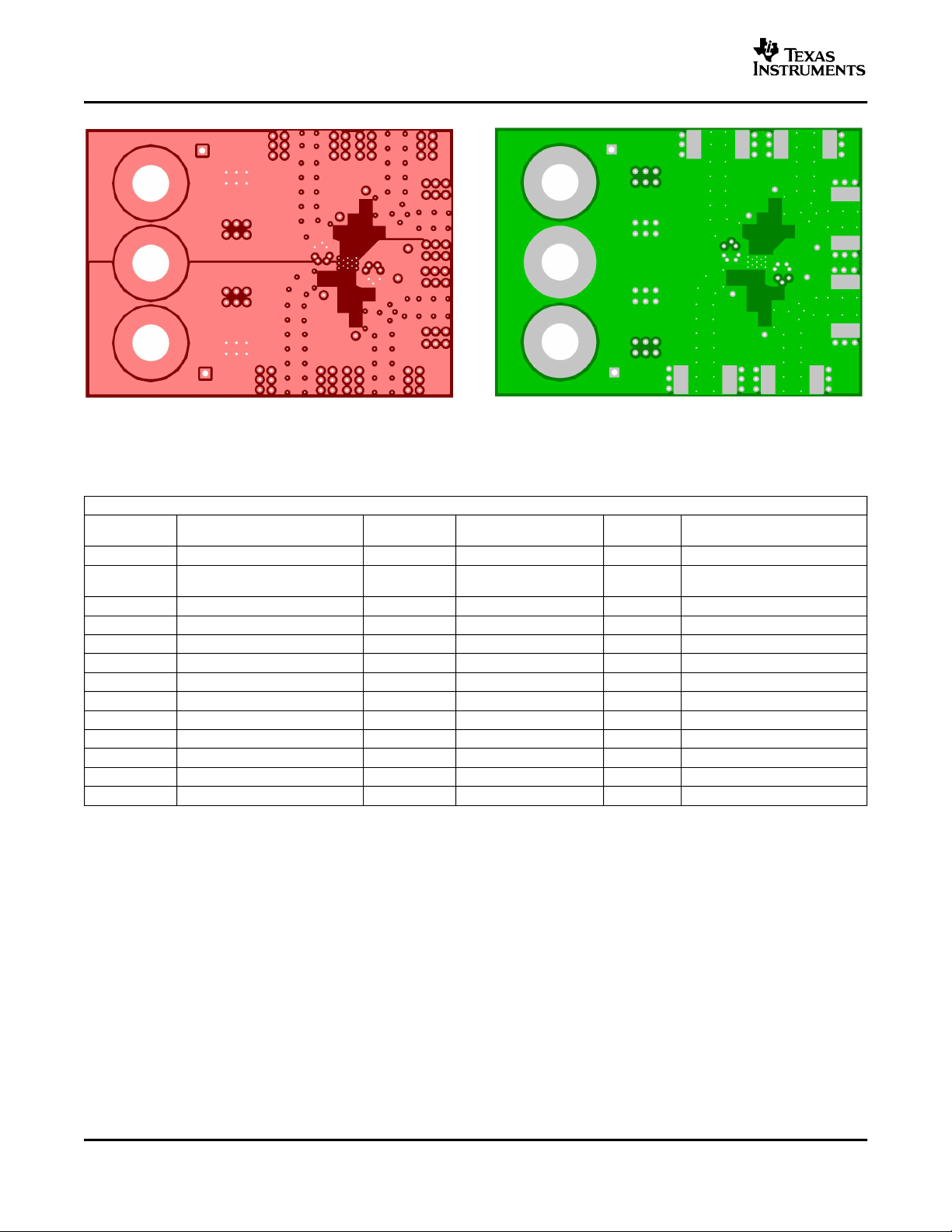
Figure 72. THS3092 EVM Board Layout Figure 73. THS3092 EVM Board Layout
(Power Plane) (Bottom Layer)
Table 2. THS3092 EVM Bill of Materials
THS3092DGN EVM
ITEM DESCRIPTION SMD SIZE
1 Bead, Ferrite, 3 A, 80 Ω 1206 FB1, FB2 2 (Steward) HI1206N800R-00
2 D C1, C2 2 (AVX) TAJD685K035R
3 Cap. 0.1 µF, Ceramic, X7R, 16 V 0805 C3, C4 2 (AVX) 08055C104KAT2A
4 Resistor, 178 Ω, 1/8 W, 1% 0805 R1, R8 2 (KOA) RK73H2ALTD1780F
5 Resistor, 715 Ω, 1/8 W, 1% 0805 R6, R7 2 (KOA) RK73H2ALTD7150F
6 Open 1206 R4, R12 2
7 Resistor, 0 Ω, 1/4 W, 1% 1206 R2, R9 2 (KOA) RK73Z2BLTD
8 Resistor, 49.9 Ω, 1/4 W, 1% 1206 R1, R5, R10, R11 4 (KOA) RK73H2BLTD49R9F
9 Connector, edge, SMA PCB jack J1, J2, J3, J4, J5, J6 6 (Johnson) 142-0701-801
10 Jack, banana, 0.25" dia. hole J7, J8, J9 3 (SPC) 813
11 Test point, black TP1, TP2 2 (Keystone) 5001
12 IC, THS3092 U1 1 (TI) THS3092DDA
13 Board, printed-circuit 1 (TI) EDGE # 6446250 Rev. A
Cap. 22 µF, Tanatalum,
35 V, 10%
(1) The manufacturer's part numbers were used for test purposes only.
REFERENCE PCB MANUFACTURER'S
DESIGNATOR QTY PART NUMBER
(1)
26
Page 27

www.ti.com
THS3096 EVM
11
+
13
6
12
U1:B
3
1
14
2
4
J1
R1
R3
R4
R5
5 V
-5 V
R2
U1:A
J2
R6
J3
R9
R8
R7
J5
R11
R12
R10
J6
J4
5 V
C3
C1
FB1
J7
5 V
J8
GND
FB2
J9
-5 V
-5 V
C2
C4
TP1 TP2
+
15
JP1
R14
R15
J10
5 V
9
R13
C5
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
Figure 75. THS3096 EVM Board Layout
(Top Layer)
Figure 74. THS3096 EVM Schematic
Figure 76. THS3096 EVM Board Layout
(Ground Plane)
27
Page 28

www.ti.com
THS3092
THS3096
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
Figure 77. THS3096 EVM Board Layout Figure 78. THS3096 EVM Board Layout
(Power Plane) (Bottom Layer)
Table 3. THS3096 EVM Bill of Materials
THS3096PWP EVM
ITEM DESCRIPTION SMD SIZE
1 Bead, Ferrite, 3 A, 80 Ω 1206 FB1, FB2 2 (Steward) HI1206N800R-00
2 Cap. 22 µF, Tanatalum, 25 V, 10% D C1, C2 2 (AVX) TAJD226K025R
3 Cap. 0.1 µF, Ceramic, X7R, 50 V 0805 C3, C4 2 (AVX) 08055C104KAT2A
4 Cap. 0.1 µF, Ceramic, X7R, 50 V 1206 C5 1 (AVX) 12065C104KAT2A
5 Resistor, 100 Ω, 1/8W, 1% 0805 R13 1 (KOA) RK73H2ALTD1000F
6 Resistor, 178 Ω, 1/8 W, 1% 0805 R3, R8 2 (KOA) RK73H2ALTD1780F
7 Resistor, 715 Ω, 1/8 W, 1% 0805 R4, R9 2 (KOA) RK73H2ALTD7150F
8 Resistor, 20 kΩ, 1/8 W, 1% 0805 R14, R15 2 (KOA) RK73H2ALTD2002F
9 Open 1206 R6, R10 2
10 Resistor, 0 Ω, 1/4 W, 1% 1206 R1, R7 2 (KOA) RK73Z2BLTD
11 Resistor, 49.9 Ω, 1/4 W, 1% 1206 R2, R5, R11, R12 4 (KOA) RK73H2BLTD49R9F
12 Header, 0.1" ctrs, 0.025" sq. pins 2 pos. JP1 1 (Sullins) PZC36SAAN
13 Shunts JP1 1 (Sullins) SSC02SYAN
14 Connector, SMA PCB jack J1, J2, J3, J4, J5, J6 6 (Amphenol) 901-144-8RFX
15 Jack, banana, 0.25" dia. hole J7, J8, J9 3 (SPC) 813
16 Test point, red J10 1 (Keystone) 5000
17 Test point, black TP1, TP2 2 (Keystone) 5001
18 IC, THS3096 U1 1 (TI) THS3096PWP
19 Board, printed-circuit 1 (TI) EDGE # 6454586 Rev. A
REFERENCE PCB MANUFACTURER'S
DESIGNATOR QTY PART NUMBER
28
Page 29

www.ti.com
SLOS428A – DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2004
ADDITIONAL REFERENCE MATERIAL
• PowerPAD Made Easy, application brief (SLMA004)
• PowerPAD Thermally Enhanced Package, technical brief (SLMA002)
• Voltage Feedback vs Current Feedback Amplifiers, (SLVA051)
• Current Feedback Analysis and Compensation (SLOA021)
• Current Feedback Amplifiers: Review, Stability, and Application (SBOA081)
• Effect of Parasitic Capacitance in Op Amp Circuits (SLOA013)
• Expanding the Usability of Current-Feedback Amplifiers, by Randy Stephens, 3Q 2003 Analog Applications
Journal www.ti.com/sc/analogapps).
• Active Output Impedance for ADSL Line Drivers (SLOA100)
THS3092
THS3096
29
Page 30

Page 31

Page 32

Page 33

Page 34

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications,
enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue
any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing
orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms
and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI
deems necessary to support this warranty . Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all
parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for
their products and applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products
and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right,
copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process
in which TI products or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third-party products or services
does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof.
Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property
of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without
alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction
of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for
such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that
product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and
is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application
solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Interface interface.ti.com Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303 Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2004, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 35

Copyright © Each Manufacturing Company.
All Datasheets cannot be modified without permission.
This datasheet has been download from :
www.AllDataSheet.com
100% Free DataSheet Search Site.
Free Download.
No Register.
Fast Search System.
www.AllDataSheet.com
 Loading...
Loading...