TC254P
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
• Medium-Resolution, Solid-State Image
Sensor for Low-Cost Color TV Applications
• 324(H) x 243(V) Active Elements in Image
Sensing Area
• 10-µm Square Pixels
• Small Size
• Low Cost
• Fast Clear Capability
• Electronic Shutter Function From
1/60–1/50000 s
• Low Dark Current
• Electron-Hole Recombination Antiblooming
• Dynamic Range...66 dB Typical
• High Sensitivity
• High Blue Response
• 8-Pin Dual-In-Line Plastic Package
• 4-mm Image-Area Diagonal
• Solid-State Reliability With No Image
Burn-In, Residual Imaging, Image
Distortion, Image Lag, or Microphonics
description
IAG2
ADB
SUB
OUT
DUAL-IN-LINE PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
1
2
3
4
ABG
8
IAG1
7
6
SAG
SRG
5
The TC254P is a frame-transfer charge-coupled device (CCD) designed for use in color NTSC TV and specialpurpose applications requiring low cost and small size.
The image-sensing area of the TC254P is configured in 243 lines with 336 elements in each line. Twelve
elements are provided in each line for dark reference. The blooming-protection feature of the sensor is based
on recombining excess charge with charge of opposite polarity in the substrate. This antiblooming is activated
by supplying clocking pulses to the antiblooming gate, which is an integral part of each image-sensing element.
The sensor can be operated in a non-interlace mode as a 324(H) by 243(V) square color pixel mode by
alternately averaging two red pixels for red pixels and two blue pixels for blue pixels. Because the human eye
is most sensitive to the green light wavelength, the 324×243 resolution is preserved due to the orientation of
the green pixels in the Bayer mosaic color filter pattern.
The device can also be operated in a 162(H) by 121(V) square color pixel mode by utilizing a separate red, two
averaged greens, and a blue pixel for each color pixel. In this mode, true interlaced video is possible, effectively
increasing the vertical resolution, by performing a one pixel shift during the off-chip video processing.
One important aspect of this image sensor is its high-speed image-transfer capability . This capability allows for
an electronic shutter function comparable to interline-transfer and frame-interline-transfer sensors without the
loss of sensitivity and resolution inherent in those technologies.
This MOS device contains limited built-in gate protection. During storage or handling, the device leads should be shorted together
or the device should be placed in conductive foam. In a circuit, unused inputs should always be connected to SUB. Under no
circumstances should pin voltages exceed absolute maximum ratings. Avoid shorting OUTn to ADB during operation to prevent
allowed to flow. Specific guidelines for handling devices of this type are contained in the publication
Electrostatic-Discharge-Sensitive (ESDS) Devices and Assemblies
damage to the amplifier. The device can also be damaged if the output terminals are reverse-biased and an excessive current is
Guidelines for Handling
available from Texas Instruments.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Copyright 1998, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
TC254P
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
description (continued)
Charge is converted to signal voltage with a 12-µV per electron conversion factor by a high-performance
charge-detection structure with built-in automatic reset and a voltage reference generator. The signal is buf fered
by a low-noise two-stage source-follower amplifier to provide high output-drive capability.
The TC254P is built using TI-proprietary virtual-phase technology, which provides devices with high blue
response, low dark current, high photoresponse uniformity, and single-phase clocking. The TC254P is
characterized for operation from –10°C to 45°C.
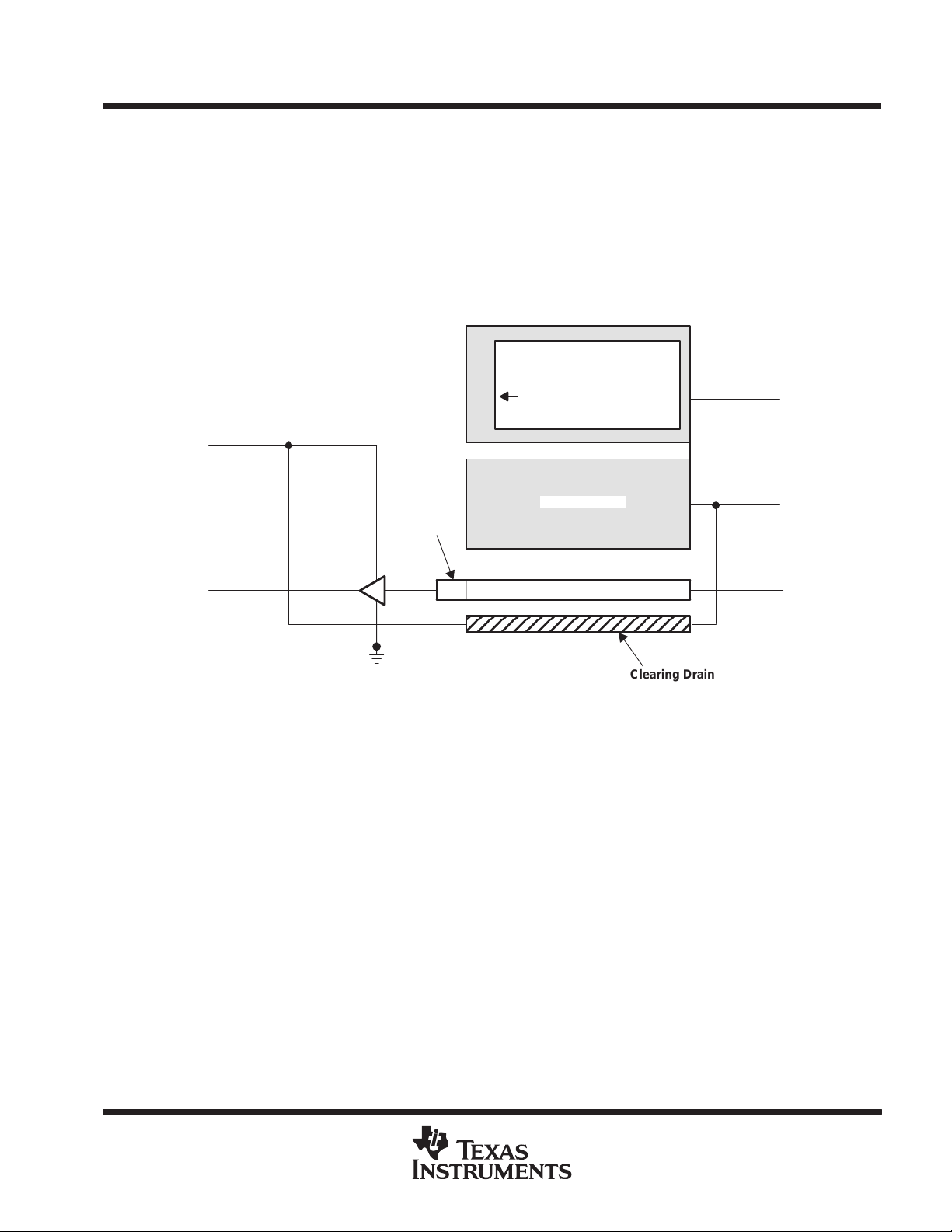
functional block diagram
IAG2
ADB
OUT
SUB
Image Area With
Blooming Protection
1
2
2 Dummy
Elements
Amplifier
4
3
Dark Reference Elements
Clear Line
Storage Area
Serial Register
Clearing Drain
8
7
6
5
ABG
IAG1
SAG
SRG
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
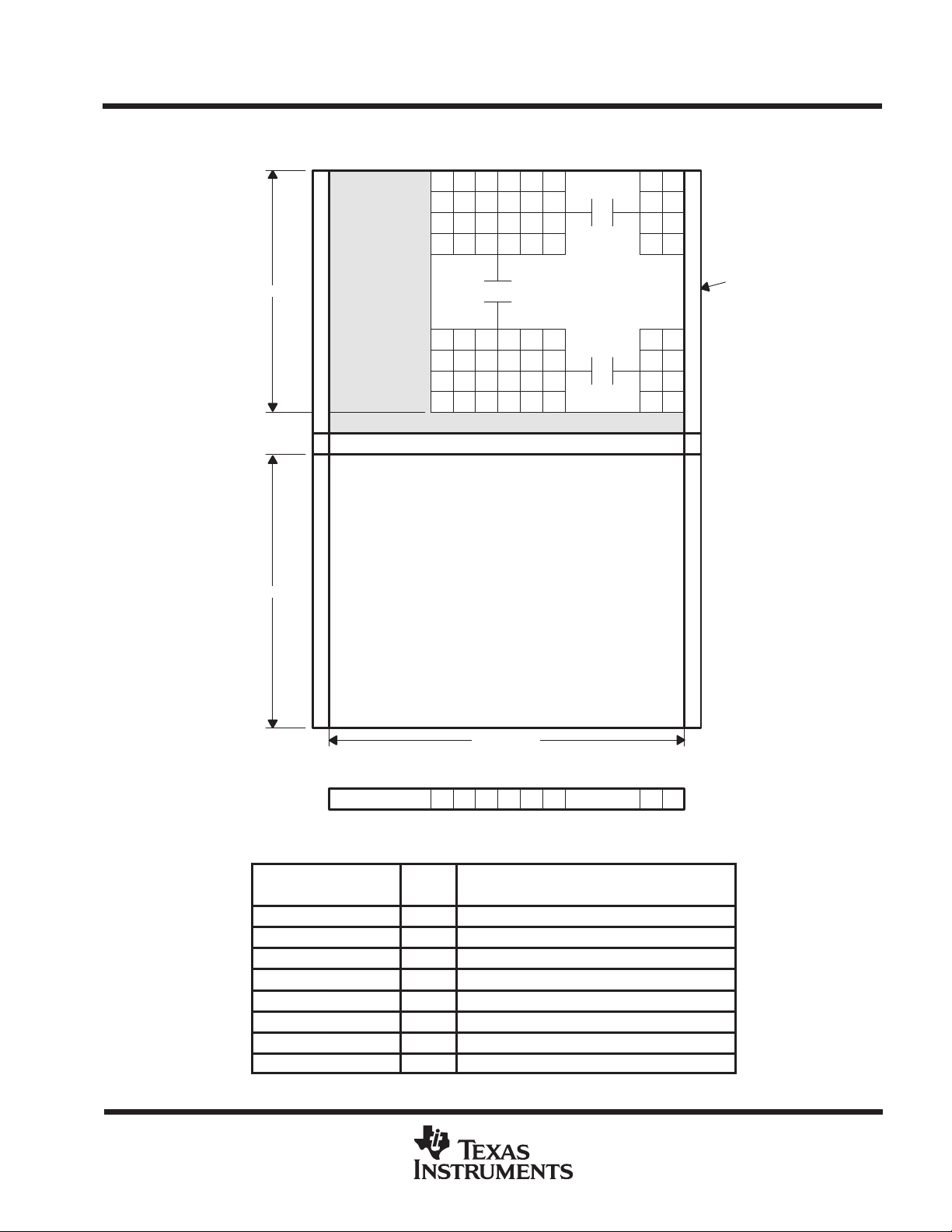
sensor topology diagram
I/O
DESCRIPTION
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
123456 323324
Pixel
R G R G R G R G
G B G B G B G B
R G R G R G R G
G B G B G B G B
TC254P
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
Line 243
Line 242
Line 241
Line 240
243 Lines
244 Lines
12 OB
R G R G R G R G
G B G B G B G B
R G R G R G R G
G B G B G B G B
1 Dark Line
1Clear Line
Storage Area
Buffer Column
Line 4
Line 3
Line 2
Line 1
OB = Optical Black
R = Red
B = Blue
G = Green
336 Pixels
123456
12 OB R G
323 324
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
ABG 8 I Antiblooming gate
ADB 2 I Supply voltage for amplifier-drain bias
SUB 3 Substrate
IAG1 7 I Image-area gate 1
IAG2 1 I Image-area gate 2
OUT 4 O Output
SAG 6 I Storage-area gate
SRG 5 I Serial-register gate
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SRG
3
TC254P
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
detailed description
The TC254P consists of five basic functional blocks: (1) the image-sensing area, (2) the image-clear line,
(3) the storage area, (4) the serial register, and (5) the charge-detection node and output amplifier.
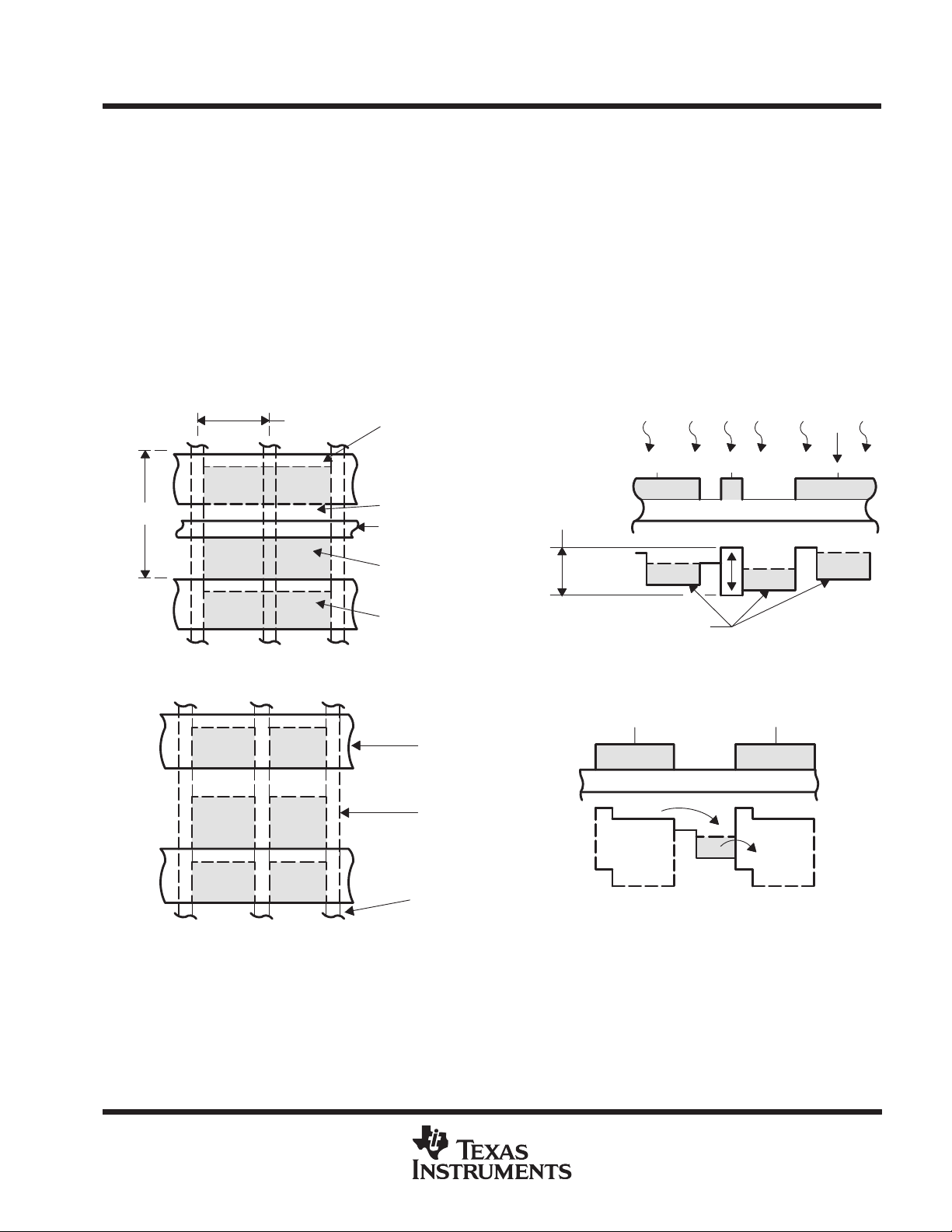
image-sensing area
Cross sections with potential well diagrams and top views of image-sensing and storage-area elements are
shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2. As light enters the silicon in the image-sensing area, free electrons are
generated and collected in the potential wells of the sensing elements. During this time, the antiblooming gate
is activated by the application of a burst of pulses every horizontal blanking interval. This prevents blooming
caused by the spilling of charge from overexposed elements into neighboring elements. Twelve columns of
shielded-from-light elements on the left edge of the image-sensing area generate the dark reference necessary
in subsequent video processing circuits for restoration of the video-black level. There is also one column of
elements on the right side of the image-sensing area and one line between the image-sensing area and the
image-clearing line.
10 µm
10 µm
Clocked Barrier
Virtual Barrier
Antiblooming Gate
Virtual Well
Clocked Well
Antiblooming
Clocking Levels
Accumulated Charge
Figure 1. Charge-Accumulation Process
SAG
Clocked Phase
Virtual Phase
IAG
Light
ABG
Channel Stops
Figure 2. Charge-Transfer Process
image-clear line
During start-up or electronic-shutter operations, it is necessary to clear the image area of charge without
transferring it to the storage area. In such situations, the two-image area gates are clocked 244 times without
clocking the storage-area gate. The charge in the image area is then cleared through the image-clear line.
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
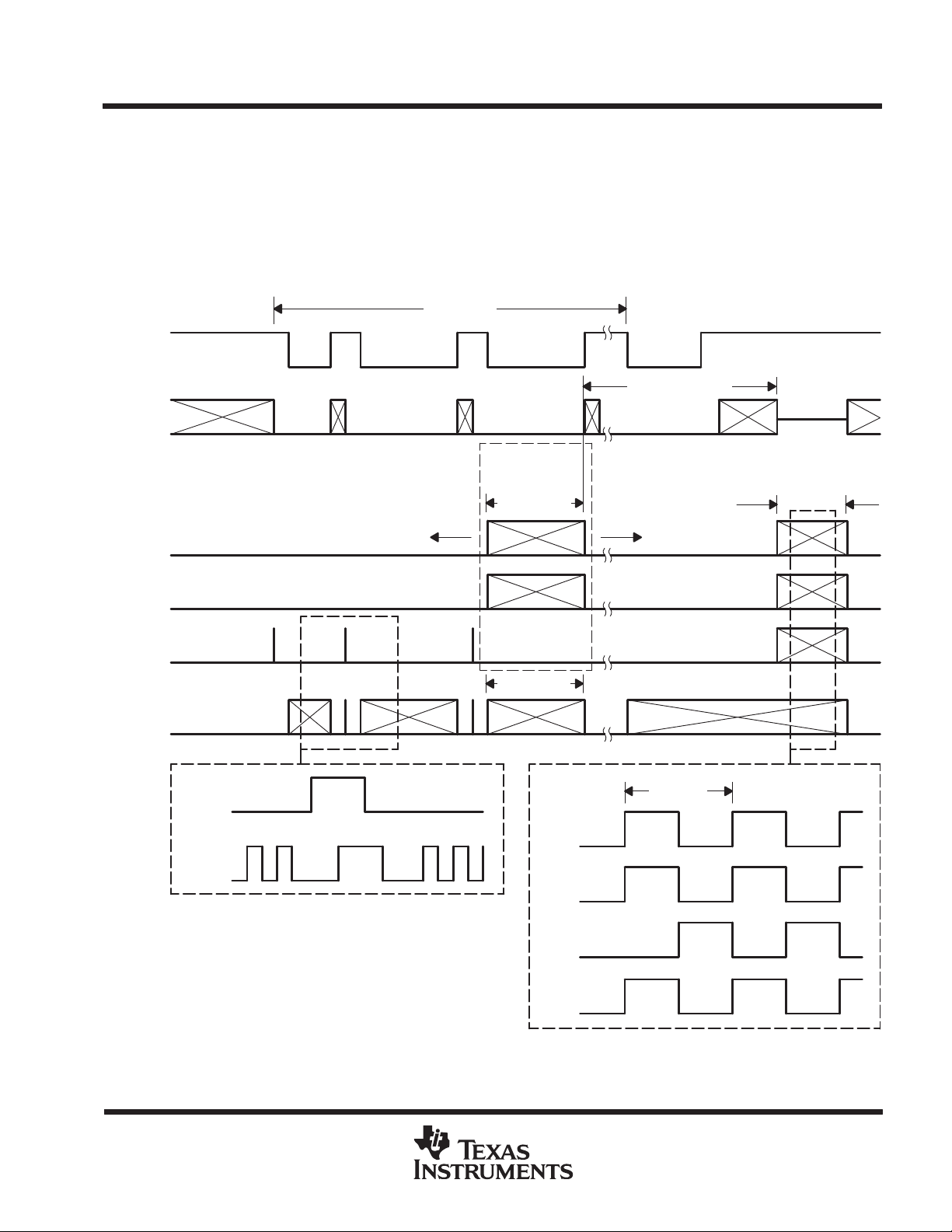
storage area
After exposure, the charge captured in each image-area is transferred through the image clear line to the
storage area. The stored charge is then transferred line by line into the serial register for readout. Figure 3
illustrates the timing to (1) transfer the image to the storage area, and (2) to transfer each line from the storage
area to the serial register.
serial register
Each line, after it is clocked into the serial register, is read out pixel by pixel. Figure 3 illustrates the serial-register
clock sequence.
244 Cycles
Composite
Blank
Integration Time
ABG
Electronic
Shutter
Operation
244 Clocks
244 Clocks
TC254P
IAG1
IAG2
SAG
SRG
SAG
1) 2) 3)
SRG
1) End of serial readout of line
2) Transfer of new line to serial register
3) Beginning of readout of new line
339 Cycles
t = 80 ns
IAG1
IAG2
SAG
SRG
Figure 3. Timing Diagram
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Expanded Section of Parallel Transfer
5

TC254P
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
charge-detection node and output amplifier
The buffer amplifier converts the charge into a video signal. Figure 4 shows the circuit diagram of the
charge-detection node and output amplifier. As charge is transferred into the detection node, the potential of
this node changes in proportion to the amount of signal received. This change is sensed by a MOS transistor
and, after proper buffering, the signal is supplied to the output terminal of the image sensor . After the potential
change is sensed, the node is reset to a reference voltage supplied by an on-chip reference generator. The reset
is accomplished by a reset gate that is connected internally to the serial register. The detection node and buf fer
amplifier are located a short distance away from the edge of the storage area; therefore, two dummy cells are
used to span this distance.
SRG
Reference
Generator
QR
Detection
Node
Q0
Q2
Q1
Q3
Q4
Figure 4. Buffer Amplifier and Charge-Detection Node
Q5
Q6
ADB
V
O
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
spurious-nonuniformity specification
The spurious-nonuniformity specification of the TC254P is based on several sensor characteristics:
• Amplitude of the nonuniform pixel
• Polarity of the nonuniform pixel
– Black
– White
• Column amplitude
The CCD sensor is characterized in both an illuminated condition and a dark condition. In the dark condition,
the nonuniformity is specified in terms of absolute amplitude, as shown in Figure 5. In the illuminated condition,
the nonuniformity is specified as a percentage of the total illumination, as shown in Figure 6.
The specification for the TC254P is as follows:
TC254P
WHITE SPOT
(DARK)
x < 15 mV x < 15% x < 0.5 mV x < 1 mV x < 15% x < 9mV
†
A white/black pair nonuniformity will be no more than 2 pixels even for integration times of 1/60 second.
WHITE SPOT
(ILLUMINATED)
COLUMN
(DARK)
COLUMN
(ILLUMINATED)
BLACK SPOT
(ILLUMINATED)
WHITE/BLACK
The conditions under which this specification is defined are as follows:
• The integration time is 1/60 second except for illuminated white spots, illuminated black spots, and
white/black pair nonuniformities; in these three cases, the integration time is 1/120 second.
• The temperature is 45°C.
• The CCD video-output signal is 60 mV ± 10 mV.
mV
Amplitude
Illumination
t
%
% of Total
†
PAIR
t
Figure 5. Pixel Nonuniformity, Figure 6. Pixel Nonuniformity,
Dark Condition Illuminated Condition
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
7

TC254P
IAG1, IAG2
SAG
SRG
Clock frequenc
f
MH
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage range, V
Input voltage range, V
Operating free-air temperature range, T
Storage temperature range, T
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTE 1: All voltages are with respect to the substrate terminal.
: ADB (see Note 1) 0 V to 15 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CC
: ABG, IAG1, IAG2, SAG, SRG –15 V to 15 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
I
–30°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
STG
–10°C to 45°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
†
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, V
Substrate bias voltage 0 V
Input voltage, V
Load capacitance OUT 6 pF
Plastic package thermal conductivity 0.008 J/cm•s•°C
Operating free-air temperature, T
‡
Adjustment is required for optimum performance.
y,
CC
I
clock
A
ADB 11 12 13 V
High level 1.5 2 2.5
Low level –10.5 –10 –9.5
High level 1.5 2 2.5
Low level –10.5 –10 –9.5
High level 1.5 2 2.5
Low level –10.5 –10 –9.5
High level 3.5 4 4.5
ABG
ABG 6.25 12.5
IAG1, IAG2
SAG
SRG
Intermediate level
Low level –8 –7 –6
‡
–2.5
6.25 12.5
–10 45 °C
25
12.5
V
z
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

TC254P
Input capacitance, C
pF
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
electrical characteristics over recommended operating ranges of supply voltage and free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Dynamic range (see Note 2) Antiblooming disabled (see Note 3) 66 dB
Charge-conversion factor 11 12 13 µV/e
Charge-transfer efficiency (see Note 4) 0.9999 1
Signal-response delay time, τ (see Note 5) 20 ns
Gamma (see Note 6) 0.97 0.98 0.99
Output resistance 350 Ω
Noise-equivalent signal without correlated double sampling 62 electrons
Noise-equivalent signal with correlated double sampling (see Note 7) 31 electrons
ADB (see Note 8) 13 15 18
Rejection ratio
Supply current 5 10 mA
p
p
NOTES: 2. Dynamic range is –20 times the logarithm of the mean-noise signal divided by saturation-output signal.
3. For this test, the antiblooming gate must be biased at the intermediate level.
4. Charge-transfer efficiency is one minus the charge loss per transfer in the output register. The test is performed in the dark using
5. Signal-response delay time is the time between the falling edge of the SRG pulse and the output-signal valid state.
6. Gamma (γ) is the value of the exponent in the equation below for two points on the linear portion of the transfer-function curve (this
i
an electrical-input signal.
value represents points near saturation).
Exposure (2)
ǒ
Exposure (1)
SRG (see Note 9) 50
ABG (see Note 10) 40
IAG1, IAG2 1000
SRG 22
ABG 850
SAG 2000
g
Ǔ
Output signal (2)
ǒ
+
Output signal (1)
Ǔ
dB
p
7. A three-level serial-gate clock is necessary to implement correlated double sampling.
8. ADB rejection ratio is –20 times the logarithm of the ac amplitude at the output divided by the ac amplitude at ADB. See Figure 7
for measured ADB rejection ratio as a function of frequency.
9. SRG rejection ratio is –20 times the logarithm of the ac amplitude at the output divided by the ac amplitude at SRG.
10. ABG rejection ratio is –20 times the logarithm of the ac amplitude at the output divided by the ac amplitude at ABG.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
9

TC254P
†
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
optical characteristics, TA = 40°C (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Red with CM500 IR filter 9.5
Sensitivity
Saturation signal, V
Maximum usable signal, V
Blooming-overload ratio (see Note 12) 100 200
Image-area well capacity 43000 62500 electrons
Smear (see Notes 13 and 14) 0.00012
Dark current Interlace disabled, TA = 21°C 0.20 nA/cm
Dark signal 200 µV
Pixel uniformity Output signal = 60 mV ± 10 mV 15 mV
Column uniformity Output signal = 60 mV ± 10 mV 0.5 mV
Shading 15 %
Electronic-shutter capability 1/15000 1/60 s
†
Standard illuminates 2856K
NOTES: 11. Saturation is the condition in which further increase in exposure does not lead to further increase in output signal.
12. Blooming is the condition in which charge is induced in an element by light incident on another element. Blooming-overload ratio
is the ratio of blooming exposure to saturation exposure.
13. Smear is a measure of the error introduced by transferring charge through an illuminated pixel in shutterless operation. It is equivalent
to the ratio of the single-pixel transfer time to the exposure time using an illuminated section that is 1/10 of the image area vertical
height with recommended clock frequencies.
14. The exposure time is 16.67 ms, the fast-dump clocking rate during vertical transfer is 12.5 MHz, and the illuminated section is 1/10
of the height of the image section.
(see Note 11) Antiblooming disabled, Interlace off 600 750 mV
sat
use
Green with CM500 IR filter 10
Blue with CM500 IR filter 7
Antiblooming enabled 200 250 mV
mV/lux
2
timing requirements
t
t
Rise time
r
Fall time
f
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
ABG 10 40
IAG1, IAG2 (fast clear) 10 10
IAG1, IAG2 (image transfer) 10 20
SAG 10 20
SRG 10 40
ABG 10 40
IAG1, IAG2 (fast clear) 10 10
IAG1, IAG2 (image transfer)
SAG 10 20
SRG 10 40
10 20
ns
ns
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
TC254P
V
O
V
sat (min)
V
use (max)
V
use (typ)
V
n
DR (dynamic range)+20 log
SNR
ǒ
V
sat
V
Blooming Point
With Antiblooming
Blooming Point
With Antiblooming
Disabled
Level Dependent
Upon Antiblooming
Gate High Level
Ǔ
ē
B
n
Enabled
Dependent on
Well Capacity
DR
Lux
(light input)
SNR (signal-to-noise-rate)+20 log
Vn = noise-floor voltage
V
sat (min)
V
use (max)
V
use (typ)
NOTES: A. V
= minimum saturation voltage
= maximum usable voltage
= typical user voltage (camera white clip)
use (typ)
(max)
B. A system trade-off is necessary to determine the system light sensitivity versus the signal/noise ratio. By lowering
the V
the light sensitivity of the camera is increased; however, this sacrifices the signal/noise ratio of the camera.
is defined as the voltage determined to equal the camera white clip. This voltage must be less than V
.
,
use(typ)
Figure 7. Typical V
ǒ
Ǔ
V
use
ē
B
V
n
use
V
Relationship
sat,
use
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
11

TC254P
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
SRG
OUT
90%
100%
– 8.5 V
1.5 V to 2.5 V
– 8.5 V to –10 V
0%
Sample
and
Hold
CCD Delay
t
15 ns10 ns
Figure 8. SRG and CCD Output Waveforms
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
TC254 SPECTRAL RESPONSE WITH CM500
TOPPAN DYE COLOR FILTER
12
11
10
2
9
∧
8
7
6
5
4
Responsivity – V/W/m
3
2
1
0
300 340 380 420 460 500 540
Green
Blue
Wavelength – nm
TC254P
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
Red
580 620 700 740
660
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
13

TC254P
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
APPLICATION INFORMATION
V
CC
WIN
16
CC
ED
EU
CBLK
CSYNC
CPOB1
V
CC
S/H
CDS
V
WSEL2
17
ED
18
EU
19
TEST4
20
CBLK
21
CSYNC
22
GND
23
CPOB1
24
CPOB2
25
SSEL1
26
V
CC
27
SSEL2
28
SSEL3
29
VR
30
HR
31
SHTCOM
32
V
ACT
V
CC
5 V
GND
25 MHz
WINDOW
S/H
SHTMON
33
OUT
WSEL1
CDS
GND
MINSEL
EFSEL3
MCLK/4
MCLK/2
MON4
EFSEL2
EFSEL1
TMC57750
XSEL
XOUT
XIN
V
CC
MON3
MON2
CLKIN
SCAN
56789101112131415
4321
GND
MON1
TEST3
TEST2
CC
PUCHDVD
V
4443424140393837363534
45 46 47 48
V
CC
TEST1
DSSEL
FSSEL
ABGSEL
ABG
ABM
V
CC
IAG1
IAG2
SAG
GND
SRG
SRM
DLSEL
PHSEL2
PHSEL1
SRGSEL
FI
TMC57253
V
AB
V
CC
64
63
62
61
60
V
59
CC
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
1
V
AB
2
V
ABOUT
CC
3
GND
4
EN
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
(see Note B)
To V ideo Processing
ABIN
ABMIN
IA1IN
IA2IN
SAIN
SRIN
SRMIN
GND
IA1OUT
IA2OUT
SAOUT
SROUT
V
ABM
V
ABL
GND
V
GND
V
V
SM
24
V
ABM
23
22
V
ABL
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
ABG
IAG1
SAG
SRG
V
IA
V
S
V
SM
TC254P
IAG2
ADB
SUB
OUT
1
2
ADB
3
SUB
4
Buffer
and
Preamp
IA
S
8
7
6
5
Figure 9. Typical Application Circuit Diagram
NOTES: A. Decoupling capacitors are not shown.
B. TI recommends designing AC coupled systems.
14
DC VOLTAGES
VIA, VSM, V
V
CC
S
12 V
5 V
ADB 22 V
SUB 10 V
V
ABM
V
AB
V
ABL
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
7.5 V
14 V
3 V

TC254P
Î
Î
Î
Î
336- × 244-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS060B – JUNE 1997 – REVISED JULY 1998
MECHANICAL DATA
The package for the TC254P consists of a plastic base, a glass window, and an 8-lead frame. The glass window is
sealed to the package by an epoxy adhesive. The package leads are configured in a dual in-line organization and
fit into mounting holes with 2,54 mm (0.1 in) center-to-center spacings.
Package Center
10,05
9,95
9,00
8,90
Optical
Center
0,80
0,70
2,67
2,53
5,19
4,93
10,05
9,95
9,00
8,90
1,273,50
2,54
4,20
3,93
Package Center
0,64
0,50
0,46
0,30
ALL LINEAR DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS
10,16
0,27
0,23
Chip Surface
1,10
1,20
1,50
1,40
6/96
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
15

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty . Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICA TIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERST OOD TO
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1998, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...