Page 1
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas Instruments
查询TAS5112DFD供应商
www.ti.com
FEATURES
D 50 W per Channel (BTL) Into 6 Ω (Stereo)
D 95-dB Dynamic Range With TAS5026
D Less Than 0.1% THD+N (1 W RMS Into 6 Ω)
D Less Than 0.2% THD+N (50 W RMS into 6 Ω)
D Power Efficiency Typically 90% Into 6-Ω Load
D Self-Protecting Design (Undervoltage,
Overtemperature and Short Conditions) With
Error Reporting
D Internal Gate Drive Supply Voltage Regulator
D EMI Compliant When Used With
Recommended System Design
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
APPLICATIONS
D DVD Receiver
D Home Theatre
D Mini/Micro Component Systems
D Internet Music Appliance
DESCRIPTION
The TAS5112 is a high-performance, integrated stereo
digital amplifier power stage designed to drive 6-Ω
speakers at up to 50 W per channel. The device
incorporates TI’s PurePath Digitalt technology and is
used with a digital audio PWM processor (TAS50XX) and
a simple passive demodulation filter to deliver high-quality,
high-efficiency, true-digital audio amplification.
The efficiency of this digital amplifier is typically 90%,
reducing the size of both the power supplies and heatsinks
needed. Overcurrent protection, overtemperature
protection, and undervoltage protection are built into the
TAS5112, safeguarding the device and speakers against
fault conditions that could damage the system.
TM
1
0.1
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
0.01
100m
PurePath Digital and PowerPAD are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
Other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
! "#$ %!& %
"! "! '! ! !( ! %% )*&
% "!+ %! !!$* $%! !+ $$ "!!&
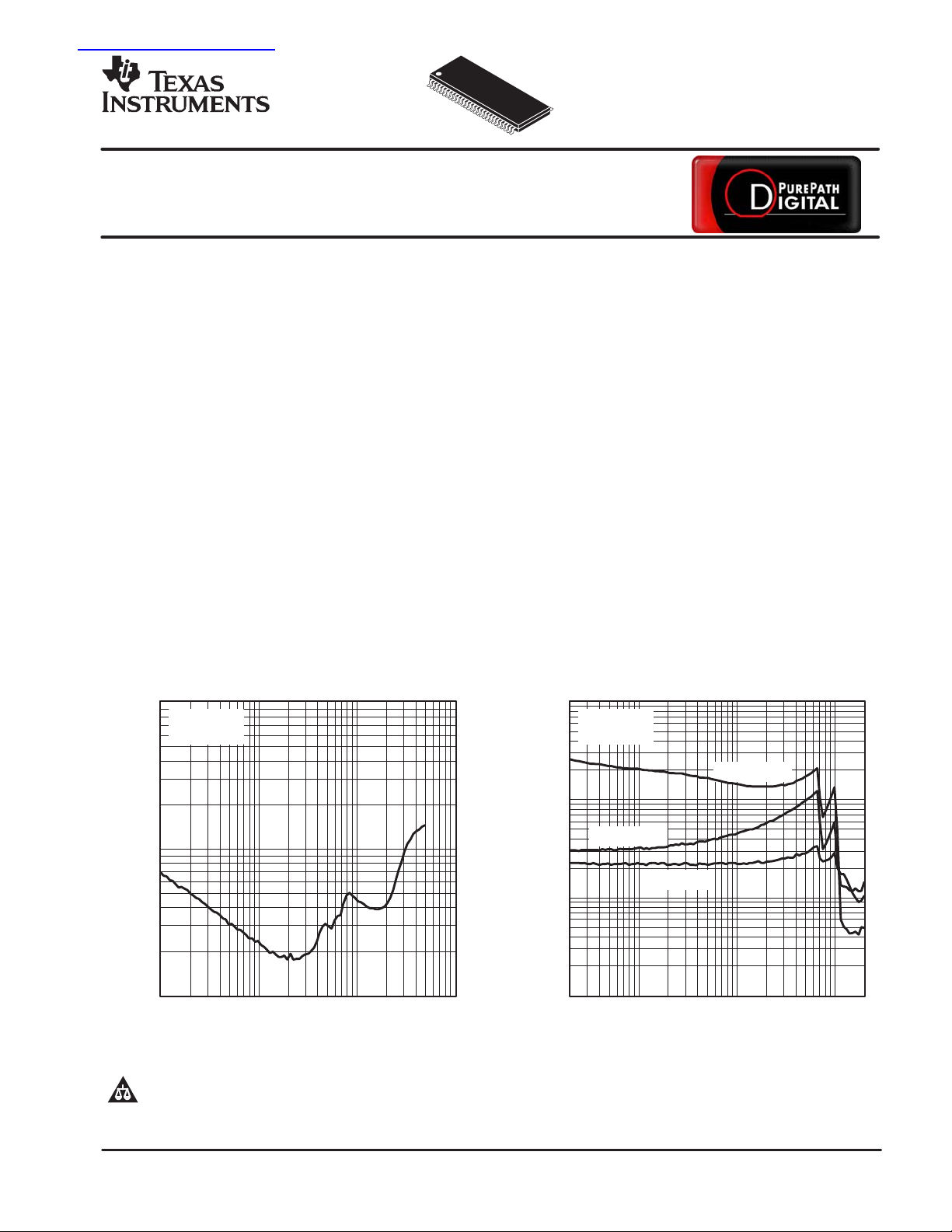
THD + NOISE vs OUTPUT POWER
RL = 6 Ω
TC = 75°C
1 10 100
PO − Output Power − W
semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
1
0.1
0.01
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
0.001
20 100 1k 10k
THD + NOISE vs FREQUENCY
RL = 6 Ω
TC = 75°C
PO = 50 W
PO = 10 W
PO = 1 W
f − Frequency − Hz
Copyright 2004, Texas Instruments Incorporated
20k
Page 2
R
D
D
D
C
C
B
B
A
A
DFD PACKAGE
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
These devices have limited built-in ESD protection. The leads should be shorted together or the device placed in conductive foam during
storage or handling to prevent electrostatic damage to the MOS gates.
www.ti.com
GENERAL INFORMATION
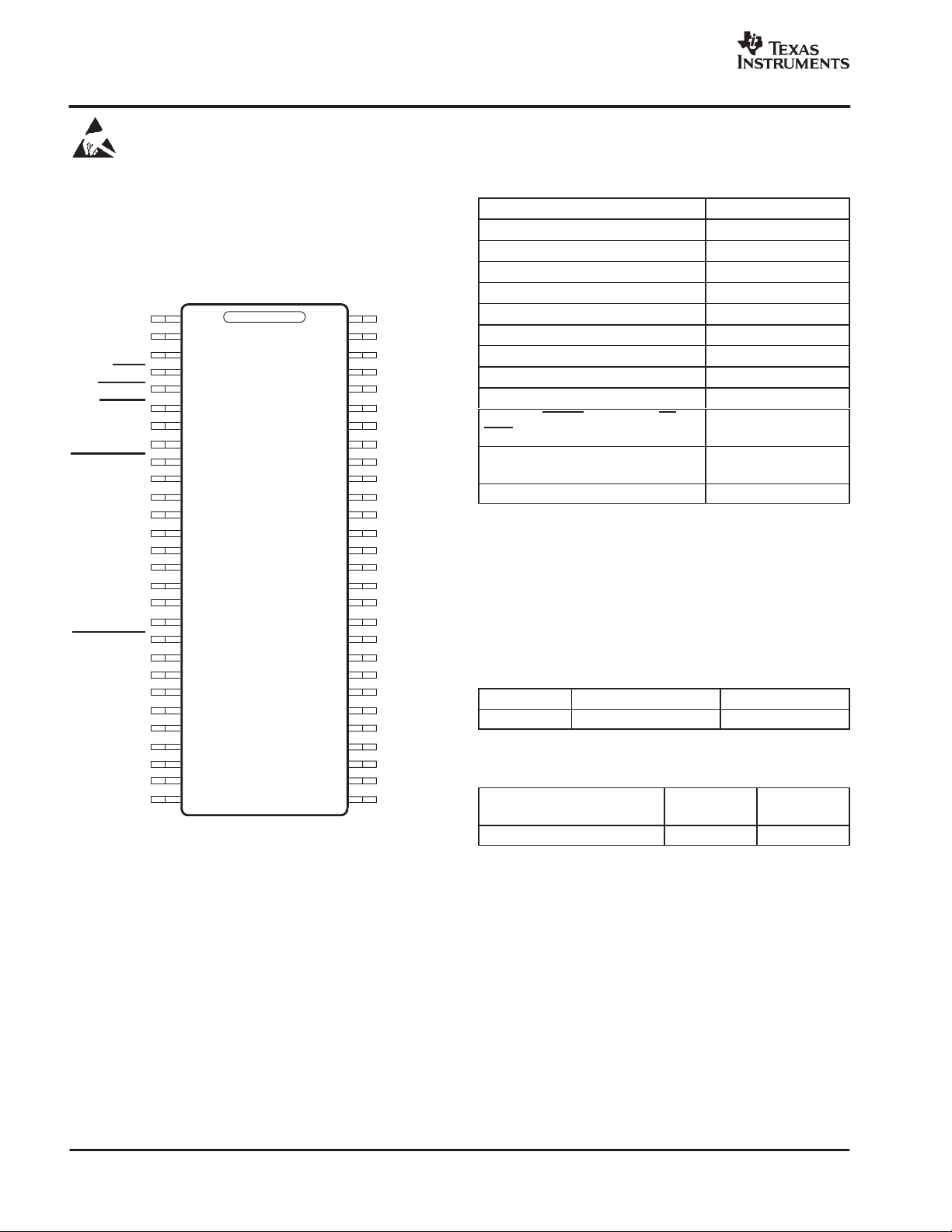
Terminal Assignment
The TAS5112 is offered in a thermally enhanced 56-pin
TSSOP DFD (thermal pad is on the top), shown as follows.
(TOP VIEW)
GND
GVDD
BST_D
PVDD_
PVDD_
OUT_D
OUT_D
GND
GND
OUT_C
OUT_C
PVDD_
PVDD_
BST_C
BST_B
PVDD_
PVDD_
OUT_B
OUT_B
GND
GND
OUT_A
OUT_A
PVDD_
PVDD_
BST_A
GVDD
GND
GND
GND
GREG
OTW
SD_CD
SD_AB
PWM_DP
PWM_DM
ESET_CD
PWM_CM
PWM_CP
REG_RTN
M3
M2
M1
DREG
PWM_BP
PWM_BM
RESET_AB
PWM_AM
PWM_AP
GND
DGND
GND
DVDD
GREG
GND
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
over operating free-air temperature range unless otherwise noted
TAS5112
DVDD TO DGND –0.3 V to 4.2 V
GVDD TO GND 33.5 V
PVDD_X TO GND (dc voltage) 33.5 V
PVDD_X TO GND (spike voltage
OUT_X TO GND (dc voltage) 33.5 V
OUT_X TO GND (spike voltage
BST_X TO GND (dc voltage) 48 V
BST_X TO GND (spike voltage
GREG TO GND
PWM_XP, RESET, M1, M2, M3, SD,
OTW
Maximum operating junction
temperature, T
Storage temperature –40°C to 125°C
(1)
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings”
may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress
ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended
operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to absolutemaximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device
reliability.
(2)
The duration of voltage spike should be less than 100 ns.
(3)
GREG is treated as an input when the GREG pin is overdriven by
GVDD of 12 V .
(3)
J
(2)
) 48 V
(2)
) 48 V
(2)
) 53 V
UNITS
14.2 V
–0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
–40°C to 150°C
ORDERING INFORMATION
T
A
0°C to 70°C TAS5112DFD 56-pin small TSSOP
(1)
For the most current specification and package information, refer to
our Web site at www.ti.com.
PACKAGE DESCRIPTION
PACKAGE DISSIPATION RATINGS
R
PACKAGE
56-pin DAD TSSOP 1.14 See Note 1
(1)
The TAS5112 package is thermally enhanced for conductive
cooling using an exposed metal pad area. It is impractical to use the
device with the pad exposed to ambient air as the only heat sinking
of the device.
For this reason, R
thermal treatment, is provided in the Application Information section
of the data sheet. An example and discussion of typical system
R
values are provided in the Thermal Information section. This
θJA
example provides additional information regarding the power
dissipation ratings. This example should be used as a reference to
calculate the heat dissipation ratings for a specific application. TI
application engineering provides technical support to design
heatsinks if needed.
a system parameter that characterizes the
θJA,
θJC
(°C/W)
R
θJA
(°C/W)
(1)
2
Page 3
www.ti.com
FUNCTION
(1)
DESCRIPTION
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
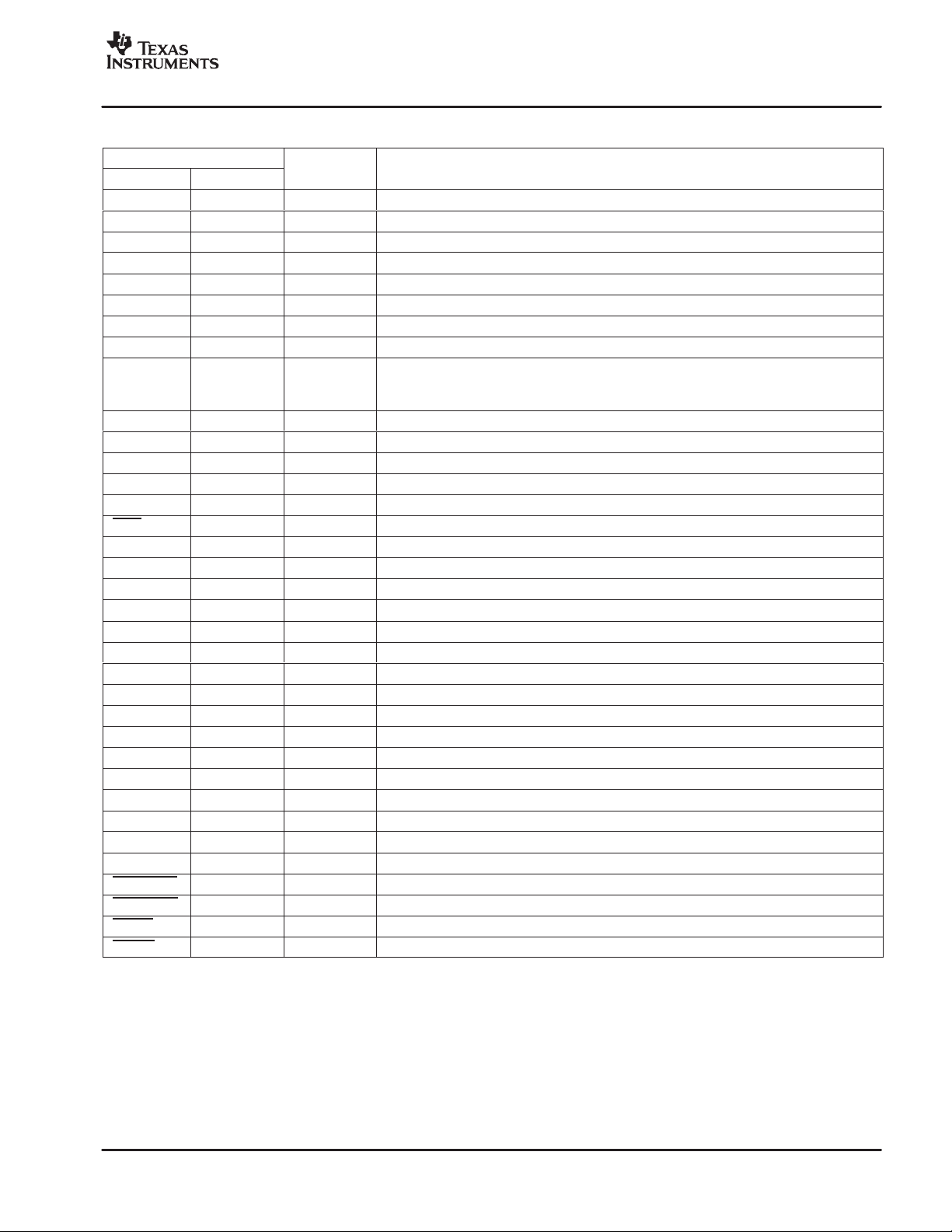
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
BST_A 31 P High-side bootstrap supply (BST), external capacitor to OUT_A required
BST_B 42 P High-side bootstrap supply (BST), external capacitor to OUT_B required
BST_C 43 P HS bootstrap supply (BST), external capacitor to OUT_C required
BST_D 54 P HS bootstrap supply (BST), external capacitor to OUT_D required
DGND 23 P Digital I/O reference ground
DREG 16 P Digital supply voltage regulator decoupling pin, capacitor connected to GND
DREG_RTN 12 P Digital supply voltage regulator decoupling return pin
DVDD 25 P I/O reference supply input (3.3 V)
GND 1, 2, 22, 24,
27, 28, 29, 36,
37, 48, 49, 56
GREG 3, 26 P Gate drive voltage regulator decoupling pin, capacitor to REG_GND
GVDD 30, 55 P Voltage supply to on-chip gate drive and digital supply voltage regulators
M1 (TST0) 15 I Mode selection pin
M2 14 I Mode selection pin
M3 13 I Mode selection pin
OTW 4 O Overtemperature warning output, open drain with internal pullup resistor
OUT_A 34, 35 O Output, half-bridge A
OUT_B 38, 39 O Output, half-bridge B
OUT_C 46, 47 O Output, half-bridge C
OUT_D 50, 51 O Output, half-bridge D
PVDD_A 32, 33 P Power supply input for half-bridge A
PVDD_B 40, 41 P Power supply input for half-bridge B
PVDD_C 44, 45 P Power supply input for half-bridge C
PVDD_D 52, 53 P Power supply input for half-bridge D
PWM_AM 20 I Input signal (negative), half-bridge A
PWM_AP 21 I Input signal (positive), half-bridge A
PWM_BM 18 I Input signal (negative), half-bridge B
PWM_BP 17 I Input signal (positive), half-bridge B
PWM_CM 10 I Input signal (negative), half-bridge C
PWM_CP 11 I Input signal (positive), half-bridge C
PWM_DM 8 I Input signal (negative), half-bridge D
PWM_DP 7 I Input signal (positive), half-bridge D
RESET_AB 19 I Reset signal, active low
RESET_CD 9 I Reset signal, active low
SD_AB 6 O Shutdown signal for half-bridges A and B, active-low
SD_CD 5 O Shutdown signal for half-bridges C and D, active-low
(1)
I = input, O = Output, P = Power
P Power ground
3
Page 4
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
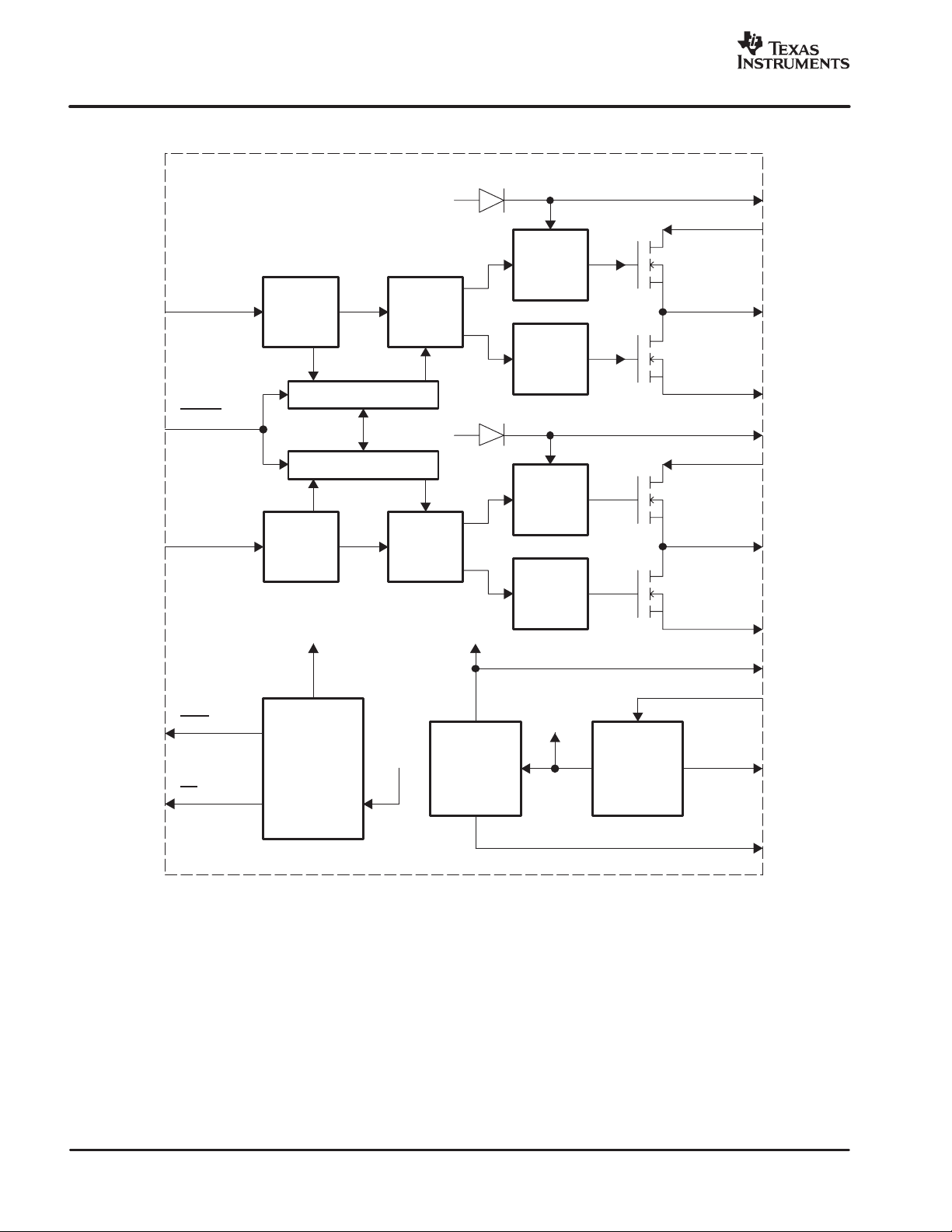
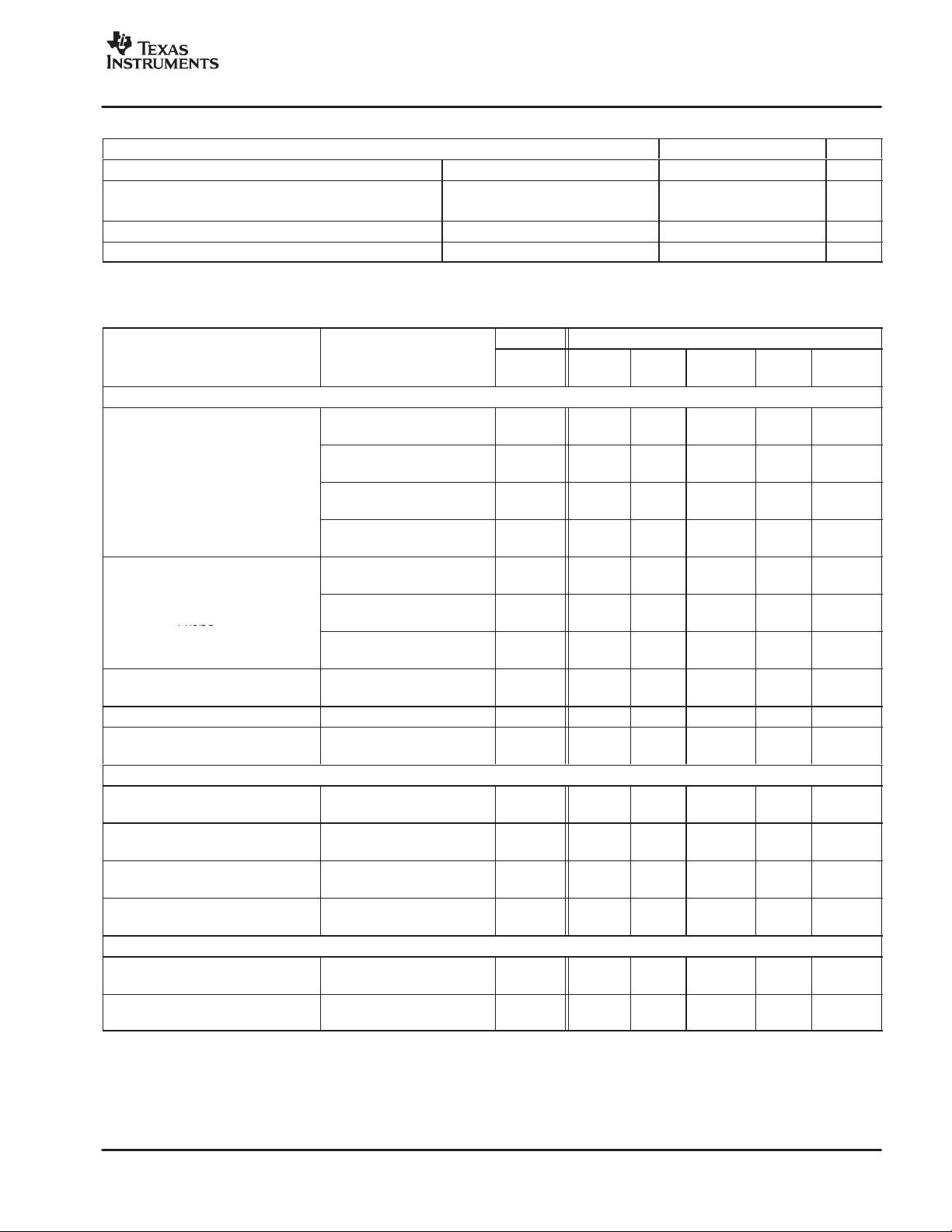
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
PWM_AP
RESET
PWM
Receiver
Protection A
Protection B
GREG
Timing
Control
GREG
Gate
Drive
Gate
Drive
Gate
Drive
www.ti.com
BST_A
PVDD_A
OUT_A
GND
BST_B
PVDD_B
PWM_BP
OTW
SD
PWM
Receiver
To Protection
Blocks
OT
Protection
UVP
This diagram shows one channel.
Control
GREG
Timing
DREG
DREG
Gate
Drive
GREG
DREG_RTN
OUT_B
GND
DREG
GVDD
GREG
GREG
DREG_RTN
4
Page 5
www.ti.com
Po
Output power
+ noise
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
DVDD Digital supply
GVDD
PVDD_x Half-bridge supply Relative to GND, RL= 6 Ω to 8 Ω 0 29.5 30.5 V
T
J
(1)
It is recommended for DVDD to be connected to DREG via a 100-Ω resistor.
Supply for internal gate drive and logic
regulators
Junction temperature 0 125 _C
(1)
Relative to DGND 3 3.3 3.6 V
Relative to GND 16 29.5 30.5 V
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
PVDD_X = 29.5 V, GVDD = 29.5 V, DVDD connected to DREG via a 100-Ω resistor, RL = 6 Ω, 8X fs = 384 kHz, unless otherwise noted
TYPICAL OVER TEMPERATURE
SYMBOL PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
AC PERFORMANCE, BTL Mode, 1 kHz
RL = 8 Ω, THD = 0.2%,
AES17 filter, 1 kHz
RL = 8 Ω, THD = 10%, AES17
filter, 1 kHz
RL = 6 Ω, THD = 0.2%,
AES17 filter, 1 kHz
RL = 6 Ω, THD = 10%, AES17
filter, 1 kHz
Po = 1 W/ channel, RL = 6 Ω,
AES17 filter
THD+N
V
n
SNR Signal-to-noise ratio A-weighted, AES17 filter 96 dB Typ
DR Dynamic range
INTERNAL VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DREG Voltage regulator
GREG Voltage regulator
IVGDD
IDVDD
OUTPUT STAGE MOSFETs
R
on,LS
R
on,HS
Total harmonic distortion
+ noise
Output integrated voltage
noise
GVDD supply current,
operating
DVDD supply current,
operating
Forward on-resistance,
low side
Forward on-resistance,
high side
Po = 10 W/channel, RL = 6 Ω,
AES17 filter
Po = 50 W/channel, RL = 6 Ω,
AES17 filter
A-weighted, mute, RL = 6 Ω,,
20 Hz to 20 kHz, AES17 filter
f = 1 kHz, A-weighted,
AES17 filter
Io = 1 mA,
PVDD = 18 V−30.5 V
Io = 1.2 mA,
PVDD = 18 V−30.5 V
fS = 384 kHz, no load, 50%
duty cycle
fS = 384 kHz, no load 1 5 mA Max
TJ = 25°C 155 mΩ Typ
TJ = 25°C 155 mΩ Typ
TA=25°C TA=25°C
3.1 V Typ
13.4 V Typ
24 mA Max
T
=
Case
75°C
0.03% Typ
0.04% Typ
0.2% Typ
260 µV Max
TA=40°C
TO 85°C
40 W Typ
50 W Typ
50 W Typ
62 W Typ
96 dB Typ
UNITS
MIN/TYP/
MAX
5
Page 6
Undervoltage protection
V
Undervoltage protection
GVDD up and down. Monitor
7.4
VIHHigh-level input voltage
Leakage
Input leakage current
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
www.ti.com
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
PVDD_x = 29.5 V, GVDD = 29.5 V, DVDD connected to DREG via a 100-Ω resistor, RL = 6 Ω, 8X fs = 384 kHz, unless otherwise noted
TYPICAL OVER TEMPERATURE
SYMBOL PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
INPUT/OUTPUT PROTECTION
Set the DUT in normal
operation mode with all the
protections enabled. Sweep
uvp,G
OTW
OTE
OC Overcurrent protection See Note 1. 5.8 A Typ
STATIC DIGITAL SPECIFICATION
V
IL
OTW/SHUTDOWN (SD)
V
OL
(1)
To optimize device performance and prevent overcurrent (OC) protection tripping, the demodulation filter must be designed with special care. See
Demodulation Filter Design in the Application Information section of the data sheet and consider the recommended inductors and capacitors for
optimal performance. It is also important to consider PCB design and layout for optimum performance of the TAS5112. It is recommended to follow
the TAS5112F2EVM (S/N 1 12) design and layout guidelines for best performance.
limit, GVDD
Overtemperature warning,
junction temperature
Overtemperature error,
junction temperature
PWM_AP, PWM_BP, M1,
M2, M3, SD, OTW
Low-level input voltage 0.8 V Max
Internally pull up R from
OTW/SD to DVDD
Low-level output voltage IO = 4 mA 0.4 V Max
SD output. Record the
GREG reading when SD is
triggered.
TA=25°C TA=25°C
6.9 V Min
7.9 V Max
125 °C Typ
150 °C Typ
DVDD V Max
−10 µA Min
10 µA Max
30 22.5 kΩ Min
T
=
Case
75°C
2 V Min
TA=40°C
TO 85°C
UNITS
MIN/TYP/
MAX
6
Page 7
www.ti.com
Gate-Drive
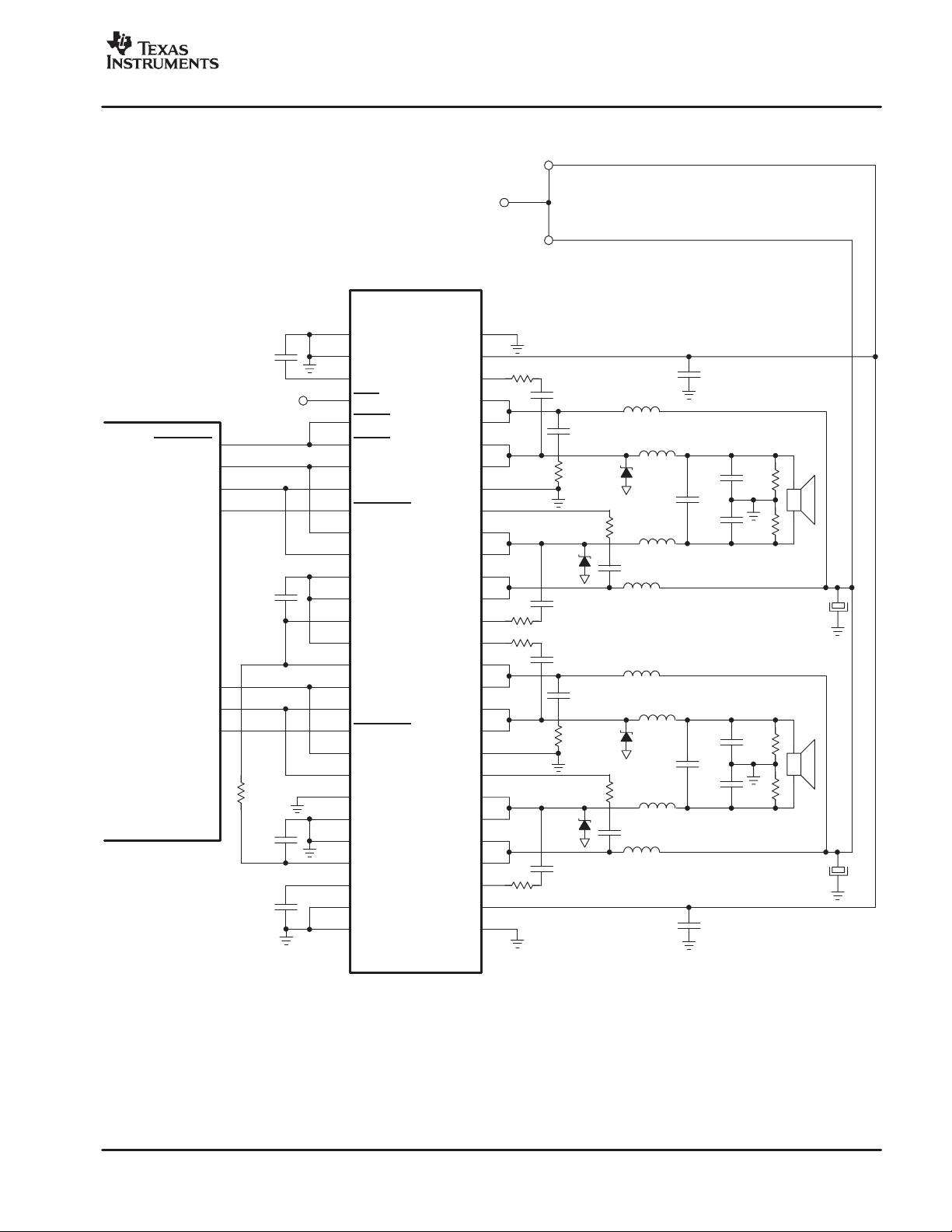
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION USED FOR CHARACTERIZATION
Power Supply
External Power Supply
H-Bridge
Power Supply
TAS5112DFD
ERR_RCVY
PWM_AP_1
PWM_AM_1
VALID_1
PWM PROCESSOR
TAS5026
PWM_AP_2
PWM_AM_2
VALID_2
1 µF
100 nF
100 Ω
100 nF
1 µF
1
GND
2
GND
3
GREG
4
OTW
5
SD_CD
6
SD_AB
7
PWM_DP
8
PWM_DM
9
RESET_CD
10
PWM_CM
11
PWM_CP
12
DREG_RTN
13
M3
14
M2
15
M1
16
DREG
17
PWM_BP
18
PWM_BM
19
RESET_AB
20
PWM_AM
21
PWM_AP
22
GND
23
DGND
24
GND
25
DVDD
26
GREG
27
GND
28
GND
BST_D
PVDD_D
PVDD_D
OUT_D
OUT_D
OUT_C
OUT_C
PVDD_C
PVDD_C
BST_C
BST_B
PVDD_B
PVDD_B
OUT_B
OUT_B
OUT_A
OUT_A
PVDD_A
PVDD_A
BST_A
GND
GVDD
GND
GND
GND
GND
GVDD
GND
56
55
1.5 Ω
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
1.5 Ω
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
1.5 Ω
30
29
33 nF
100 nF
1.5 Ω
1.5 Ω
33 nF
33 nF
100 nF
1.5 Ω
1.5 Ω
33 nF
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
100 nF
L
PCB
10 µH
{
470 nF
10 µH
{
100 nF
L
PCB
L
PCB
10 µH
{
470 nF
10 µH
{
100 nF
L
PCB
100 nF
100 nF
100 nF
100 nF
100 nF
4.7 kΩ
4.7 kΩ
4.7 kΩ
4.7 kΩ
1000 µF
1000 µF
L
: TRACK IN THE PCB (1,0 mm wide and 50 mm long)
PCB
{
Voltage Suppressor Diode: 1SMA33CAT
7
Page 8

THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
THD+N − Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND SYSTEM PERFORMANCE
OF TAS5112 EVM WITH TAS5026 PWM PROCESSOR
www.ti.com
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
1
RL = 6 Ω
TC = 75°C
PO = 50 W
0.1
PO = 10 W
PO = 1 W
0.01
0.001
20 100 1k 10k
f − Frequency − Hz
Figure 1
20k
NOISE AMPLITUDE
vs
FREQUENCY
0
RL = 6 Ω
FFT = −60 dB
−20
TC = 75°C
TAS5026 Front End Device
−40
−60
−80
−100
Noise Amplitude − dBr
−120
−140
−160
0 2 4 6 8 10121416182022
f − Frequency − kHz
Figure 2
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE
10
RL = 6 Ω
TC = 75°C
1
0.1
0.01
100m
PO − Output Power − W
8
vs
OUTPUT POWER
1 10 100
Figure 3
OUTPUT POWER
vs
H-BRIDGE VOLTAGE
60
TA = 75°C
50
40
RL = 6 Ω
30
− Output Power − W
20
O
P
10
0
0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32
VDD − Supply Voltage − V
Figure 4
RL = 8 Ω
Page 9

www.ti.com
− System Output Stage Efficiency − %
P
− Output Power − W
k
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
SYSTEM OUTPUT STAGE EFFICIENCY
vs
OUTPUT POWER
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
η
10
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65
PO − Output Power − W
Figure 5
f = 1 kHz
RL = 6 Ω
TC = 75°C
POWER LOSS
vs
OUTPUT POWER
11
f = 1 kHz
10
RL = 6 Ω
9
TC = 75°C
8
7
6
5
− Power Loss − W
4
tot
P
3
2
1
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65
PO − Output Power − W
Figure 6
O
OUTPUT POWER
vs
CASE TEMPERATURE
60
PVDD = 29.5 V
58
RL = 6 Ω
56
54
52
50
48
46
44
42
40
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
TC − Case Temperature − °C
Channel 2
Channel 1
Figure 7
AMPLITUDE
vs
FREQUENCY
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
−0.5
Amplitude − dBr
−1.0
−1.5
−2.0
−2.5
−3.0
10 100 1k 50
f − Frequency − Hz
RL = 6 Ω
Figure 8
RL = 8 Ω
10k
9
Page 10

SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
200
190
180
170
160
150
− On-State Resistance − mΩ
140
on
r
130
120
www.ti.com
ON-STATE RESISTANCE
vs
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE
0 102030405060708090100
TJ − Junction Temperature − °C
Figure 9
10
Page 11

www.ti.com
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
THEORY OF OPERATION
POWER SUPPLIES
The power device only requires two supply voltages,
GVDD and PVDD_X.
GVDD is the gate drive supply for the device, regulated
internally down to approximately 12 V, and decoupled with
regards to board GND on the GREG pins through an
external capacitor. GREG powers both the low side and
high side via a bootstrap step-up conversion. The
bootstrap supply is charged after the first low-side turn-on
pulse. Internal digital core voltage DREG is also derived
from GVDD and regulated down by internal circuitry to
3.3 V.
The gate-driver regulator can be bypassed for reducing
idle loss in the device by shorting GREG to GVDD and
directly feeding in 12.0 V. This can be useful in an
application where thermal conduction of heat from the
device is difficult.
PVDD_X is the H-bridge power supply pin. T wo power pins
exists for each half-bridge to handle the current density . It
is important that the circuitry recommendations around
the PVDD_X pins are followed carefully both topologyand layout-wise. For topology recommendations, see the
Typical System Configuration section. Following these
recommendations is important for parameters like EMI,
reliability, and performance.
POWERING UP
This precharges the bootstrap supply capacitors and
discharges the output filter capacitor (see the Typical
TAS5112 Application Configuration section).
After GVDD has been applied, it takes approximately 800
µs to fully charge the BST capacitor. Within this time,
RESET must be kept low. After approximately 1 ms, the
back-end bootstrap capacitor is charged.
RESET can now be released if the modulator is powered
up and streaming valid PWM signals to the back-end
PWM_xP. Valid means a switching PWM signal which
complies with the frequency and duty cycle ranges stated
in the Recommended Operating Conditions.
A constant HIGH dc level on the PWM_xP is not permitted,
because it would force the high-side MOSFET ON until it
eventually ran out of BST capacitor energy and might
damage the device.
An unknown state of the PWM output signals from the
modulator is illegal and should be avoided, which in
practice means that the PWM processor must be powered
up and initialized before RESET is de-asserted HIGH to
the back end.
POWERING DOWN
For power down of the back end, an opposite approach is
necessary. The RESET must be asserted LOW before the
valid PWM signal is removed.
When PWM processors are used with TI PurePath Digital
amplifiers, the correct timing control of RESET and
PWM_xP is performed by the modulator.
> 1 ms
> 1 ms
RESET
GVDD
PVDD_x
PWM_xP
NOTE: PVDD should not be powered up before GVDD.
During power up when RESET is asserted LOW, all
MOSFETs are turned off and the two internal half-bridges
are in the high-impedance state (Hi-Z). The bootstrap
capacitors supplying high-side gate drive are not charged
at this point. T o comply with the click and pop scheme and
use of non-TI modulators it is recommended to use a 4-kΩ
pulldown resistor on each PWM output node to ground.
PRECAUTION
The TAS5112 must always start up in the high-impedance
(Hi-Z) state. In this state, the bootstrap (BST) capacitor is
precharged by a resistor on each PWM output node to
ground. See the system configuration. This ensures that
the back end is ready for receiving PWM pulses, indicating
either HIGH- or LOW-side turnon after RESET is
de-asserted to the back end.
With the following pulldown resistor and BST capacitor
size, the charge time is:
C = 33 nF, R = 4.7 kΩ
R × C × 5 = 775.5 µs
After GVDD has been applied, it takes approximately 800
µs to fully charge the BST capacitor. During this time,
RESET must be kept low. After approximately 1 ms the
back end BST is charged and ready. RESET can now be
released if the PWM modulator is ready and is streaming
valid PWM signals to the back end. Valid PWM signals are
switching PWM signals with a frequency between
350−400 kHz. A constant HIGH level on the PWM+ would
force the high-side MOSFET ON until it eventually ran out
of BST capacitor energy. Putting the device in this
condition should be avoided.
11
Page 12

SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
www.ti.com
In practice this means that the DVDD-to-PWM processor
(front-end) should be stable and initialization should be
completed before RESET is de-asserted to the back end.
CONTROL I/O
Shutdown Pin: SD
The SD pin functions as an output pin and is intended for
protection-mode signaling to, for example, a controller or
other front-end device. The pin is open-drain with an
internal pullup resistor to DVDD.
The logic output is, as shown in the following table, a
combination of the device state and RESET input:
SD RESET DESCRIPTION
0 0 Not used
0 1 Device in protection mode, i.e., UVP and/or OC
and/or OT error
(1)
1
1 1 Normal operation
(1)
SD is pulled high when RESET is asserted low independent of chip
state (i.e., protection mode). This is desirable to maintain
compatibility with some TI PWM front ends.
Temperature Warning Pin: OTW
The OTW pin gives a temperature warning signal when
temperature exceeds the set limit. The pin is of the
open-drain type with an internal pullup resistor to DVDD.
Overall Reporting
The SD pin, together with the OTW pin, gives chip state
information as described in Table 1.
0 Device set high-impedance (Hi-Z), SD forced high
OTW DESCRIPTION
0 Junction temperature higher than 125°C
1 Junction temperature lower than 125°C
The device can be recovered by toggling RESET low and
then high, after all errors are cleared.
Overcurrent (OC) Protection
The device has individual forward current protection on
both high-side and low-side power stage FETs. The OC
protection works only with the demodulation filter present
at the output. See Demodulation Filter Design in the
Application Information section of the data sheet for design
constraints.
Overtemperature (OT) Protection
A dual temperature protection system asserts a warning
signal when the device junction temperature exceeds
125°C. The OT protection circuit is shared by all
half-bridges.
Undervoltage (UV) Protection
Undervoltage lockout occurs when GVDD is insufficient
for proper device operation. The UV protection system
protects the device under power-up and power-down
situations. The UV protection circuits are shared by all
half-bridges.
Reset Function
The function of the reset input is twofold:
D Reset is used for re-enabling operation after a
latching error event.
D Reset is used for disabling output stage
switching (mute function).
The error latch is cleared on the falling edge of reset and
normal operation is resumed when reset goes high.
Table 1. Error Signal Decoding
OTW SD DESCRIPTION
0 0 Overtemperature error (OTE)
0 1 Overtemperature warning (OTW)
1 0 Overcurrent (OC) or undervoltage (UVP) error
1 1 Normal operation, no errors/warnings
Chip Protection
The TAS5112 protection function is implemented in a
closed loop with, for example, a system controller and TI
PWM processor. The TAS5112 contains three individual
systems protecting the device against error conditions. All
of the error events covered result in the output stage being
set in a high-impedance state (Hi-Z) for maximum
protection of the device and connected equipment.
12
PROTECTION MODE
Autorecovery (AR) After Errors (PMODE0)
In autorecovery mode (PMODE0) the TAS5112 is
self-supported i n handling of error situations. All protection
systems are active, setting the output stage in the
high-impedance state to protect the output stage and
connected equipment. However, after a short time the
device autorecovers, i.e., operation is automatically
resumed provided that the system is fully operational.
The autorecovery timing is set by counting PWM input
cycles, i.e., the timing is relative to the switching frequency.
The AR system is common to both half-bridges.
Page 13

www.ti.com
A
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
Timing and Function
The function of the autorecovery circuit is as follows:
1. An error event occurs and sets the
protection latch (output stage goes Hi-Z).
2. The counter is started.
3. After n/2 cycles, the protection latch is
cleared but the output stage remains Hi-Z
(identical to pulling RESET
low).
4. After n cycles, operation is resumed
(identical to pulling RESET high) (n = 512).
Error
Protection
Latch
Shutdown
SD
Autorecovery
PWM
Counter
Table 3. Output Mode Selection
M3 OUTPUT MODE
0 Bridge-tied load output stage (BTL)
1 Reserved
APPLICATION INFORMATION
DEMODULATION FILTER DESIGN
The PurePath Digital amplifier outputs are driven by
heavy-duty DMOS transistors in an H-bridge
configuration. These transistors are either off or fully on,
which reduces the DMOS transistor on-state resistance,
R(DMOSon), and the power dissipated in the device,
thereby increasing efficiency.
The result is a square-wave output signal with a duty cycle
that is proportional to the amplitude of the audio signal. It
is recommended that a second-order LC filter be used to
recover the audio signal. For this application, EMI is
considered important; therefore, the selected filter is the
full-output type shown in Figure 11.
TAS51xx
Output A
L
R-RESET
Figure 10. Autorecovery Function
Latching Shutdown on All Errors (PMODE1)
In latching shutdown mode, all error situations result in a
power down (output stage Hi-Z). Re-enabling can be done
by toggling the RESET pin.
All Protection Systems Disabled (PMODE2)
In PMODE2, all protection systems are disabled. This
mode is purely intended for testing and characterization
purposes and thus not recommended for normal device
operation.
MODE Pins Selection
The protection mode is selected by shorting M1/M2 to
DREG or DGND according to Table 2.
Table 2. Protection Mode Selection
M1 M2 PROTECTION MODE
0 0 Autorecovery after errors (PMODE 0)
0 1 Latching shutdown on all errors (PMODE 1)
1 0 All protection systems disabled (PMODE 2)
1 1 Reserved
The output configuration mode is selected by shorting the
M3 pin to DREG or DGND according to Table 3.
R
(Load)
Output B
C1A
C2
C1B
L
Figure 11. Demodulation Filter
The main purpose of the output filter is to attenuate the
high-frequency switching component of the PurePath
Digital amplifier while preserving the signals in the audio
band.
Design of the demodulation filter affects the performance
of the power amplifier significantly. As a result, to ensure
proper operation of the overcurrent (OC) protection circuit
and meet the device THD+N specifications, the selection
of the inductors used in the output filter must be considered
according to the following. The rule is that the inductance
should remain stable within the range of peak current seen
at maximum output power and deliver at least 5 µH of
inductance at 15 A.
If this rule is observed, the TAS5112 does not have
distortion issues due to the output inductors and
overcurrent conditions do not occur due to inductor
saturation in the output filter.
13
Page 14
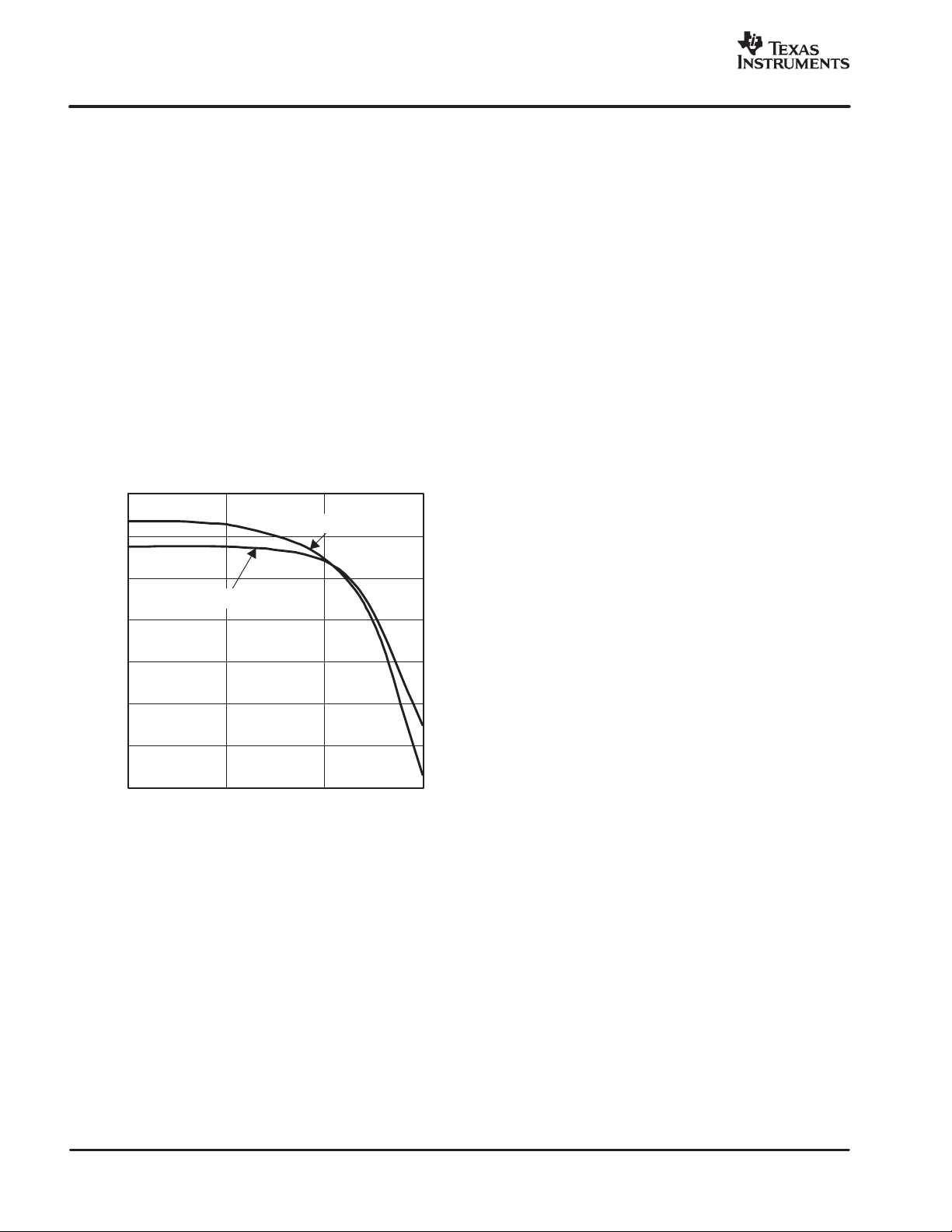
L − Inductance −
H
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
www.ti.com
Another par a meter to be considered is the idle current loss
in the inductor. This can be measured or specified as
inductor dissipation (D). The target specification for
dissipation is less than 0.05.
In general, 10-µH inductors suffice for most applications.
The frequency response of the amplifier is slightly altered
by the change in output load resistance; however, unless
tight control of frequency response is necessary (better
than 0.5 dB), it is not necessary to deviate from 10 µH.
The graphs in Figure 12 display the inductance vs current
characteristics of two inductors that are recommended for
use with the TAS5112.
INDUCTANCE
vs
CURRENT
11
10
9
µ
8
7
6
5
DASL983XX−1023
DFB1310A
THERMAL INFORMATION
The thermally augmented package provided with the
TAS5112 is designed to be interfaced directly to heatsinks
using a thermal interface compound (for example,
Wakefield Engineering type 126 thermal grease.) The
heatsink then absorbs heat from the ICs and couples it to
the local air. If the heatsink is carefully designed, this
process can reach equilibrium and heat can be continually
removed from the ICs. Because of the efficiency of the
TAS5112, heatsinks can be smaller than those required for
linear amplifiers of equivalent performance.
is a system thermal resistance from junction to
R
θ
JA
ambient ai r. As such, it is a system parameter with roughly
the following components:
D R
(the thermal resistance from junction to
θ
JC
case, or in this case the metal pad)
D Thermal grease thermal resistance
D Heatsink thermal resistance
R
has been provided in the General Information
θ
JC
section.
The thermal grease thermal resistance can be calculated
from the exposed pad area and the thermal grease
manufacturer’s area thermal resistance (expressed in
°C-in2/W). The area thermal resistance of the example
thermal grease with a 0.002-inch thick layer is about 0.1
°C-in2/W. The approximate exposed pad area is as
follows:
56-pin HTSSOP 0.045 in
Dividing the example thermal grease area resistance by
the surface area gives the actual resistance through the
thermal grease for both ICs inside the package:
2
The selection of the capacitor that is placed across the
output of each inductor (C2 in Figure 11) is simple. To
complete the output filter, use a 0.47-µF capacitor with a
voltage rating at least twice the voltage applied to the
output stage (PVDD).
This capacitor should be a good quality polyester dielectric
such as a Wima MKS2-047ufd/100/10 or equivalent.
In order to minimize the EMI effect of unbalanced ripple
loss in the inductors, 0.1-µF 50-V SMD capacitors (X7R or
better) (C1A and C1B in Figure 11) should be added from
the output of each inductor to ground.
14
4
0 5 10 15
I − Current − A
Figure 12. Inductance Saturation
56-pin HTSSOP 2.27 °C/W
The thermal resistance of thermal pads is generally
considerably higher than a thin thermal grease layer.
Thermal tape has an even higher thermal resistance.
Neither pads nor tape should be used with either of these
two packages. A thin layer of thermal grease with careful
clamping of the heatsink is recommended. It may be
difficult to achieve a layer 0.001-inch thick or less, so the
modeling below is done with a 0.002-inch thick layer,
which may be more representative of production thermal
grease thickness.
Heatsink thermal resistance is generally predicted by the
heatsink vendor, modeled using a continuous flow
dynamics (CFD) model, or measured.
Thus, for a single monaural IC, the system R
= R
θ
JA
+
θ
JC
thermal-grease resistance + heatsink resistance.
Table 4, Table 5, and Table 6 indicate modeled
parameters for one or two TAS5112 ICs on a single
heatsink. The final junction temperature is set at 110°C in
Page 15
www.ti.com
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
all cases. It is assumed that the thermal grease is 0.002
inch thick and that it is similar in performance to Wakefield
Type 126 thermal grease. It is important that the thermal
grease layer is ≤0.002 inches thick and that thermal pads
or tape are not used in the pad-to-heatsink interface due
to the high power density that results in these extreme
power cases.
Table 4. Case 1 (2 × 50 W Unclipped Into 6 Ω,
Both Channels in Same IC)
Ambient temperature 25°C
Power to load (per channel) 50 W (unclipped)
Power dissipation 4.5 W
Delta T inside package
Delta T through thermal grease
Required heatsink thermal resistance 4.2°C/W
Junction temperature 110°C
System R
R
Junction temperature 85°C + 25°C = 110°C
(1)
θJA
* power dissipation 85°C
θJA
This case represents a stereo system with only one package. See
Case 2 and Case 2A if doing a full-power, 2-channel test in a
multichannel system.
(1)
56-Pin HTSSOP
10.2°C, note 2 ×
channel dissipation
37.1°C, note 2 ×
channel dissipation
19°C/W
Table 6. Case 2A (2 × 60 W Unclipped Into 6 Ω,
Channels in Separate IC Packages)
56-Pin HTSSOP
Ambient temperature 25°C
Power to load (per channel) 60 W (10% THD)
Power dissipation per channel 5.4 W
Delta T inside package
Delta T through thermal grease
Required heatsink thermal resistance 5.3°C/W
Junction temperature 110°C
System R
R
Junction temperature 85°C + 25°C = 110°C
(1)
θJA
* power dissipation 85°C
θJA
In this case, the power is also separated into two packages, but
overdriving causes clipping to 10% THD. In this case, the high
power requires extreme care in attachment of the heatsink to
ensure that the thermal grease layer is ≤ 0.002 inches thick. Note
that this power level should not be attempted with both channels in
a single IC because of the high power density through the thermal
grease layer.
6.1°C, note 2 ×
channel dissipation
22.3°C, note 2 ×
channel dissipation
15.9°C/W
(1)
Table 5. Case 2 (2 × 50 W Unclipped Into 6 Ω,
Channels in Separate Packages)
Ambient temperature 25°C
Power to load (per channel) 50 W (unclipped)
Power dissipation 4.5 W
Delta T inside package 5.1°C
Delta T through thermal grease 18.6°C
Required heatsink thermal resistance 6.9°C/W
Junction temperature 110°C
System R
R
Junction temperature 85°C + 25°C = 110°C
(1)
θJA
* power dissipation 85°C
θJA
In this case, the power is separated into two packages. Note that
this allows a considerably smaller heatsink because twice as much
area is available for heat transfer through the thermal grease. For
this reason, separating the stereo channels into two ICs is
recommended in full-power stereo tests made on multichannel
systems.
19°C/W
(1)
56-Pin HTSSOP
Thermal
Pad
3,90 mm
2,98 mm
8,20 mm
7,20 mm
15
Page 16

SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
www.ti.com
CLICK AND POP REDUCTION
TI modulators feature a pop and click reduction system
that controls the timing when switching starts and stops.
Going from nonswitching to switching operation causes a
spectral energy burst to occur within the audio bandwidth,
which is heard in the speaker as an audible click, for
instance, after having asserted RESET LH during a
system start-up.
To make this system work properly, the following design
rules must be followed when using the TAS5112 back end:
D The relative timing between the PWM_AP/M_x
signals and their corresponding VALID_x signal
should not be skewed by inserting delays,
because this increases the audible amplitude
level of the click.
D The output stage must start switching from a
fully discharged output filter capacitor. Because
the output stage prior to operation is in the
high-impedance state, this is done by having a
passive pulldown resistor on each speaker
output to GND (see Typical System
Configuration).
Other things that can affect the audible click level:
D The spectrum of the click seems to follow the
speaker impedance vs. frequency curve—the
higher the impedance, the higher the click
energy.
D Crossover filters used between woofer and
tweeter in a speaker can have high impedance
in the audio band, which should be avoided if
possible.
Another way to look at it is that the speaker impulse
response is a major contributor to how the click energy is
shaped in the audio band and how audible the click will be.
The following mode transitions feature click and pop
reduction.
REFERENCES
1. TAS5000 Digital Audio PWM Processor data
manual—TI (SLAS270)
2. True Digital Audio Amplifier TAS5001 Digital Audio
PWM Processor data sheet—TI (SLES009)
3. True Digital Audio Amplifier TAS5010 Digital Audio
PWM Processor data sheet—TI (SLAS328)
4. True Digital Audio Amplifier TAS5012 Digital Audio
PWM Processor data sheet—TI (SLES006)
5. TAS5026 Six-Channel Digital Audio PWM
Processor data manual—TI (SLES041)
6. TAS5036A Six-Channel Digital Audio PWM
Processor data manual—TI (SLES061)
7. TAS3103 Digital Audio Processor With 3D Effects
data manual—TI (SLES038)
8. Digital Audio Measurements application report—TI
(SLAA114)
9. PowerPAD Thermally Enhanced Package
technical brief—TI (SLMA002)
10. System Design Considerations for True Digital
Audio Power Amplifiers application report—TI
(SLAA117)
(1)
Normal
Mute → Normal
(1)
Normal
Error recovery → Normal
(1)
Normal
Hard Reset → Normal
(1)
Normal = switching
16
STATE
→ Mute Yes
(1)
Error recovery
→
(ERRCVY)
(1)
→ Hard Reset No
(1)
CLICK AND
POP REDUCED
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Page 17

www.ti.com
SLES048C − JULY 2003 − REVISED MARCH 2004
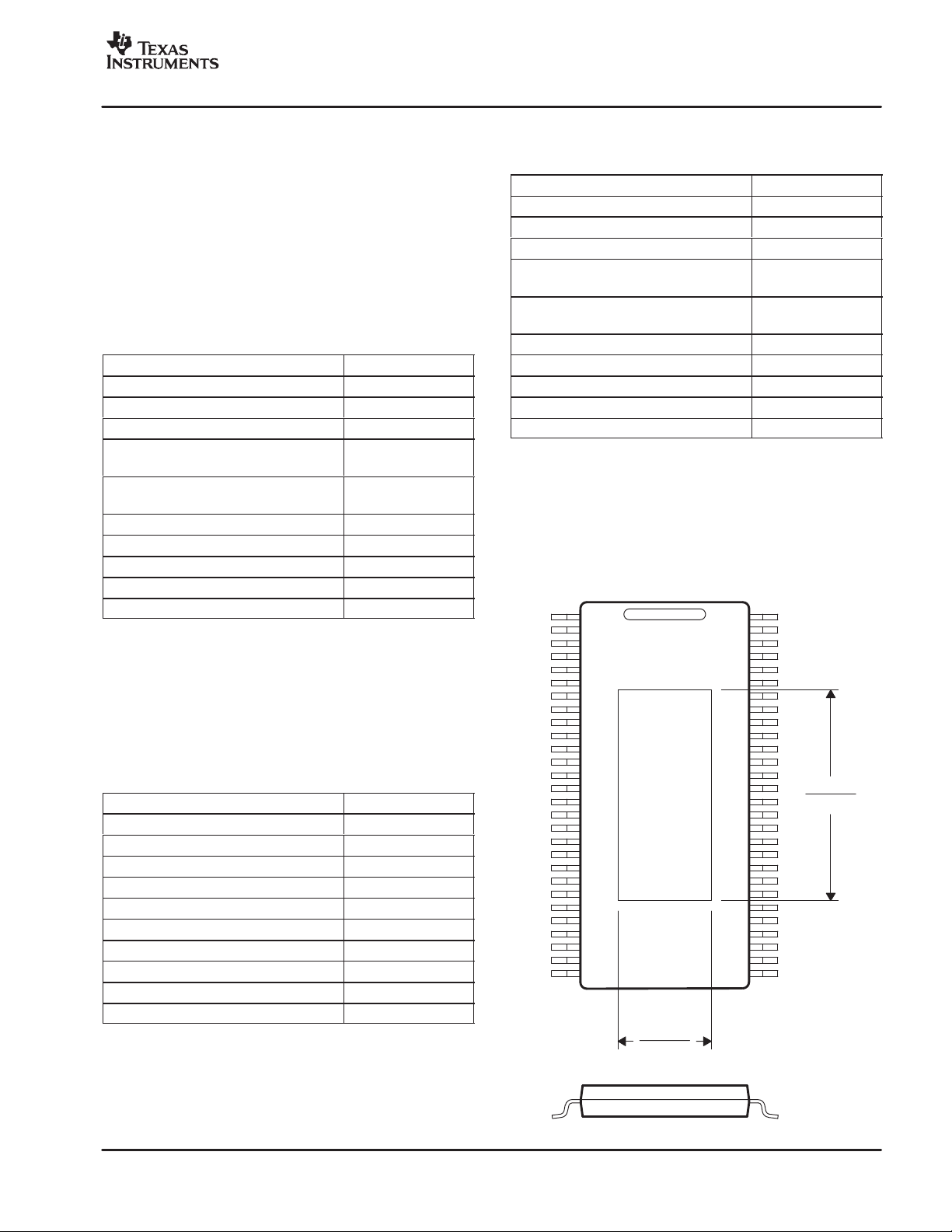
MECHANICAL DATA
17
Page 18

Page 19

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications,
enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue
any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing
orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms
and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI
deems necessary to support this warranty . Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all
parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for
their products and applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products
and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right,
copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process
in which TI products or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third-party products or services
does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof.
Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property
of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without
alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction
of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for
such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that
product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and
is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application
solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Interface interface.ti.com Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303 Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2004, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...