Page 1
查询TAS5100供应商
TAS5100A
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
TRUE DIGITAL AUDIO AMPLIFIER
TAS5100A PWM POWER OUTPUT STAGE
FEATURES
TAS5000 + TAS5100A TDAA System-High
D
Quality Digital Audio Amplification
D 93-dB Dynamic Range (TDAA System)
D THD+N < 0.08% (1 kHz, 1 W to 30 W RMS
Into 6 Ω)
D Power Efficiency > 90% Into 8-Ω Load
D Low Profile, SMD 32-Pin PowerPAD Package
Requires No Heat-Sink When Using
Recommended Layout
D 30-W RMS Continuous Power Into 4 Ω to 8 Ω
D Self-Protecting Design
D 3.3-V Digital Interface
D EMI Compliant When Used With
Recommended System Design
APPLICATIONS
DVD Receiver
D
D Home Theater
D Car Audio Amplifiers and Head Units
D Internet Music Appliance
D Mini/Micro Component Systems
DESCRIPTION
True digital audio amplifier (TDAA) is a new paradigm
in digital audio. The TDAA system currently consists of
the TAS5000 PCM-PWM modulator device +
TAS5100A PWM power output device. This system
accepts a serial PCM digital audio stream and converts
it to a 3.3-V PWM audio stream (TAS5000). The
TAS5100A device then provides a large-signal PWM
output. This digital PWM signal is then demodulated
providing power output for driving loudspeakers. This
patented technology provides low-cost, high-quality,
high-efficient digital audio applicable to many audio
systems developed for the digital age. The TAS5100A
is a single-channel PWM power audio device. It
contains integrated gate drivers, four matched and
electrically isolated enhancement- mode N-channel
power DMOS transistors. Also, included are protection
and fault-reporting circuitry . This device is optimized for
use with the TAS5000 digital modulator.
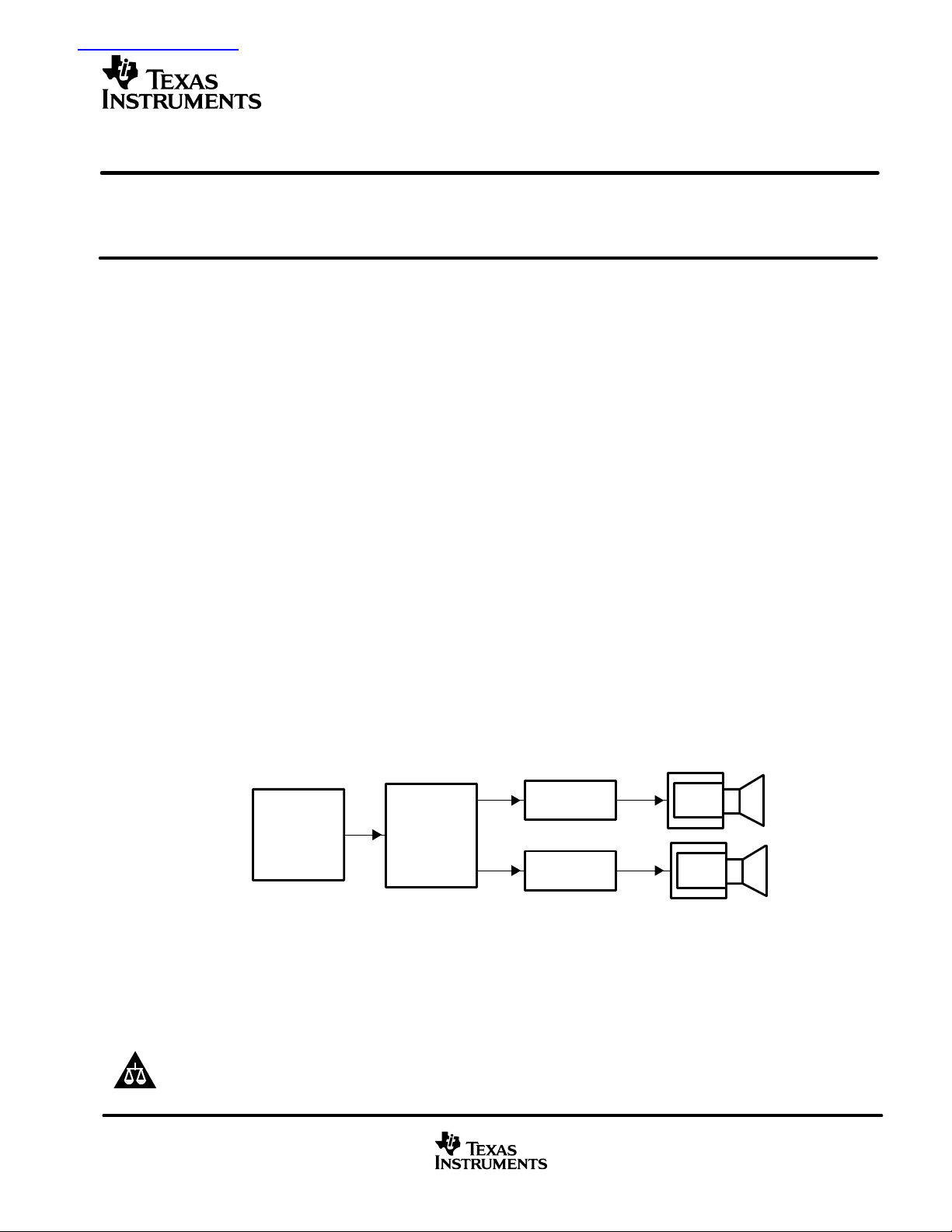
TYPICAL TDAA STEREO AUDIO SYSTEM
Digital Audio
• TAS3001
• DSP
• SPDIF
• 1394
• Volume
• EQ
• DRC
• Bass
• Treble
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
PowerPAD and Equibit are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
• Serial Audio Input Port
• Internal PLL
• PCM–PWM Modulator
TAS5000
Left
Right
www.ti.com
TAS5100
A
TAS5100
A
• 2 H-Bridge Power Devices
Copyright 2002, Texas Instruments Incorporated
L-C
Filter
L-C
Filter
1
Page 2
TAS5100A
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
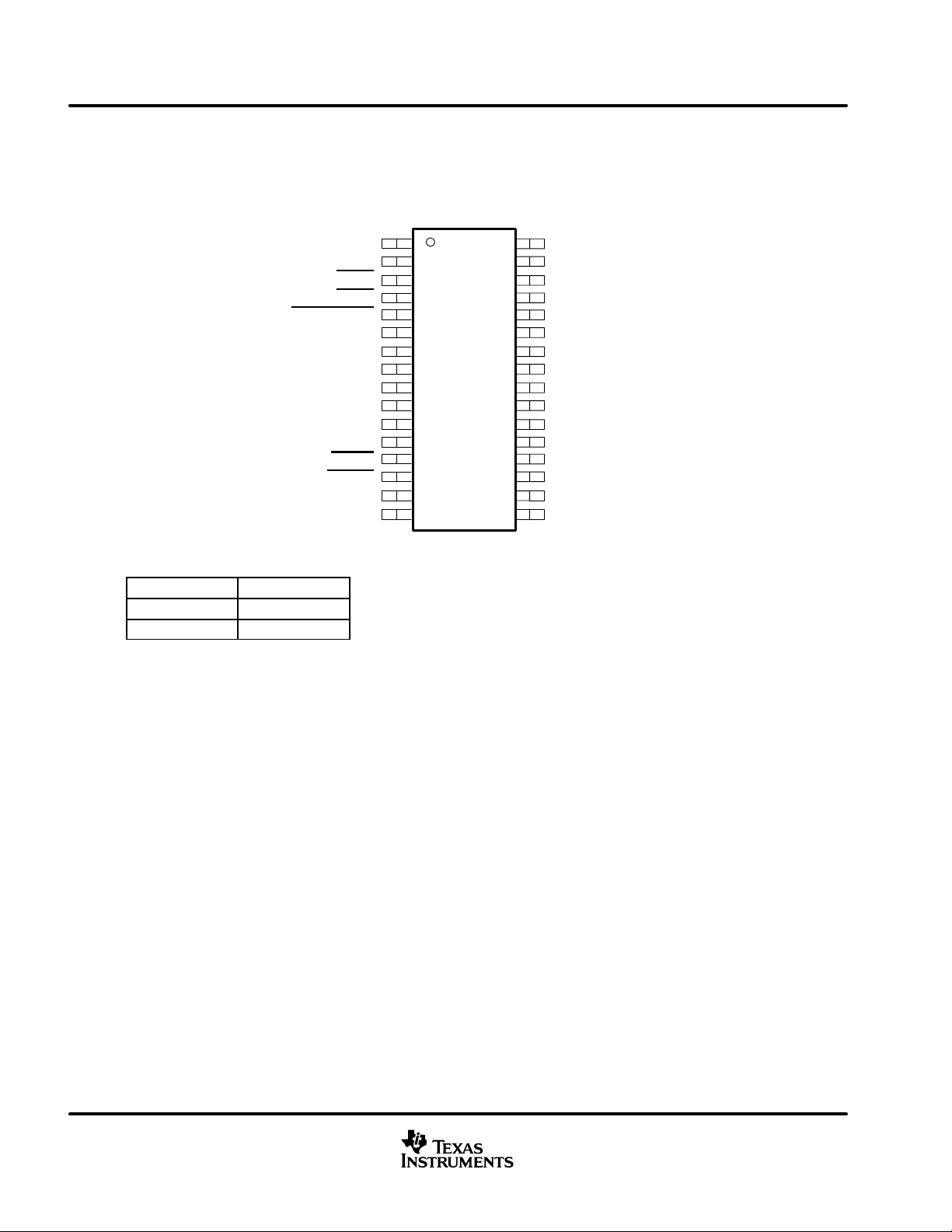
terminal assignments
The TAS5100A is offered in a thermally enhanced 32-pin HTSSOP surface-mount package (DAP).
DAP PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
ordering information
T
A
0°C to 70°C TAS5100ADAP
–40°C to 85°C TAS5100AIDAP
references
SHUTDOWN
PACKAGE
PWM_AP
PWM_AM
ERR1
ERR0
DVDD
DVSS
DVSS
DVSS
VRFILT
BIAS_A
BIAS_B
PWDN
RESET
PWM_BM
PWM_BP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
PVDDA2
LDROUTA
BOOTSTRAPA
PVDDA1
PVDDA1
OUTPUTA
OUTPUTA
PVSS
PVSS
OUTPUTB
OUTPUTB
PVDDB1
PVDDB1
BOOTSTRAPB
LDROUTB
PVDDB2
TAS5000 Digital Audio PWM Process Data Manual – TI Literature Number SLAS270
System Design Considerations for True Digital Audio Power Amplifiers – TI Literature Number SLAA117
Digital Audio Measurements – TI Literature Number SLAA114
PowerPAD Thermally Enhanced Package – TI Literature Number SLMA002
2
www.ti.com
Page 3
A
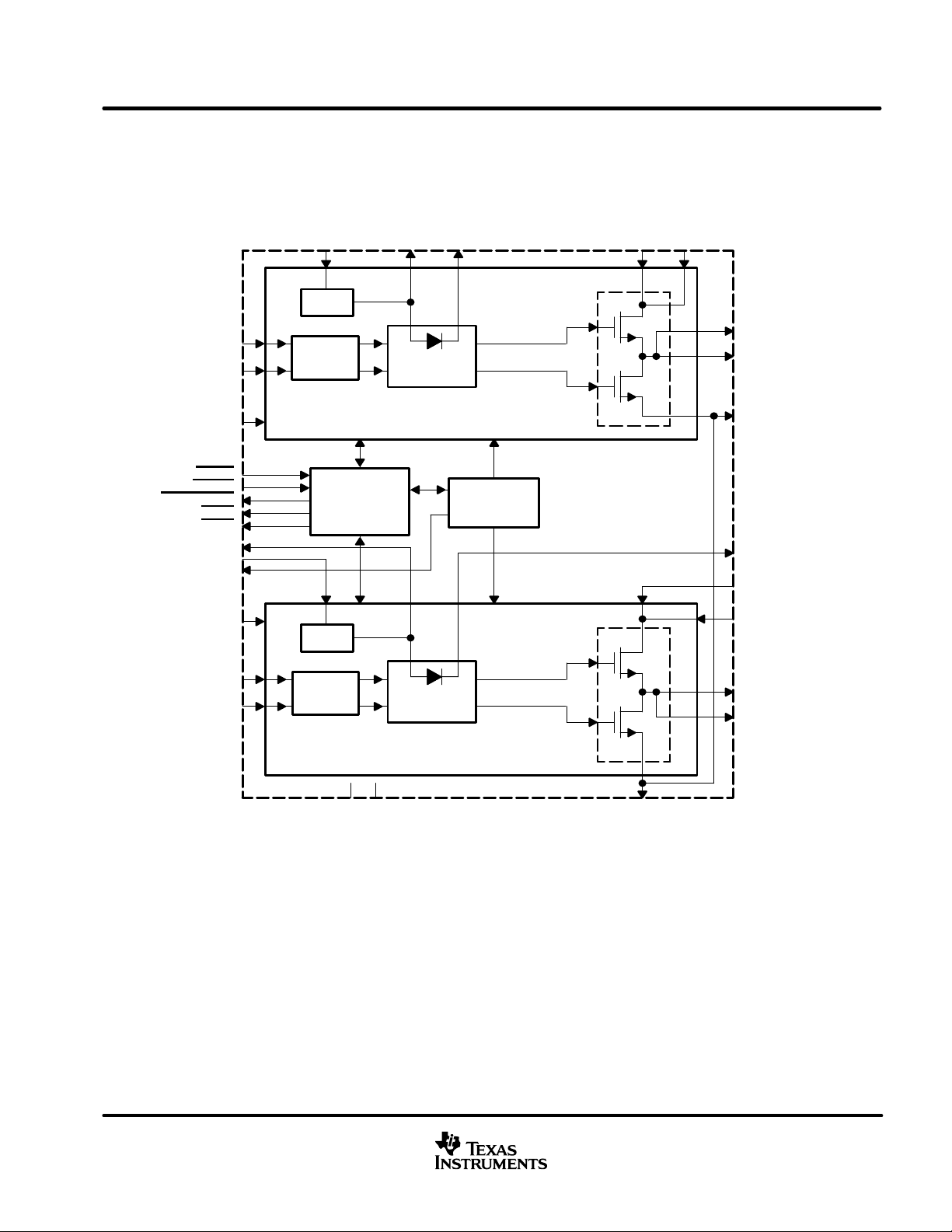
functional block diagram
TAS5100A
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
PWM_AP
PWM_AM
BIAS_A
PWDN
RESET
SHUTDOWN
ERR1
ERR0
LDROUTB
PVDDB2
VRFILT
BIAS_B
PWM_BM
PWM_BP
PVDDA2
LDR
DIFF
RCVR
Control/Sense
Circuit
LDR
DIFF
RCVR
LDROUTA
Boot Strap
Gate Drive
Boot Strap
Gate Drive
BOOTSTRAP
1/2 H-Bridge
Bandgap
Reference
1/2 H-Bridge
PVDDA1
PVDDA1
OUTPUTA
OUTPUTA
PVSS
BOOTSTRAPB
PVDDB1
PVDDB1
OUTPUTB
OUTPUTB
DVDD
DVSS
www.ti.com
PVSS
3
Page 4
TAS5100A
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
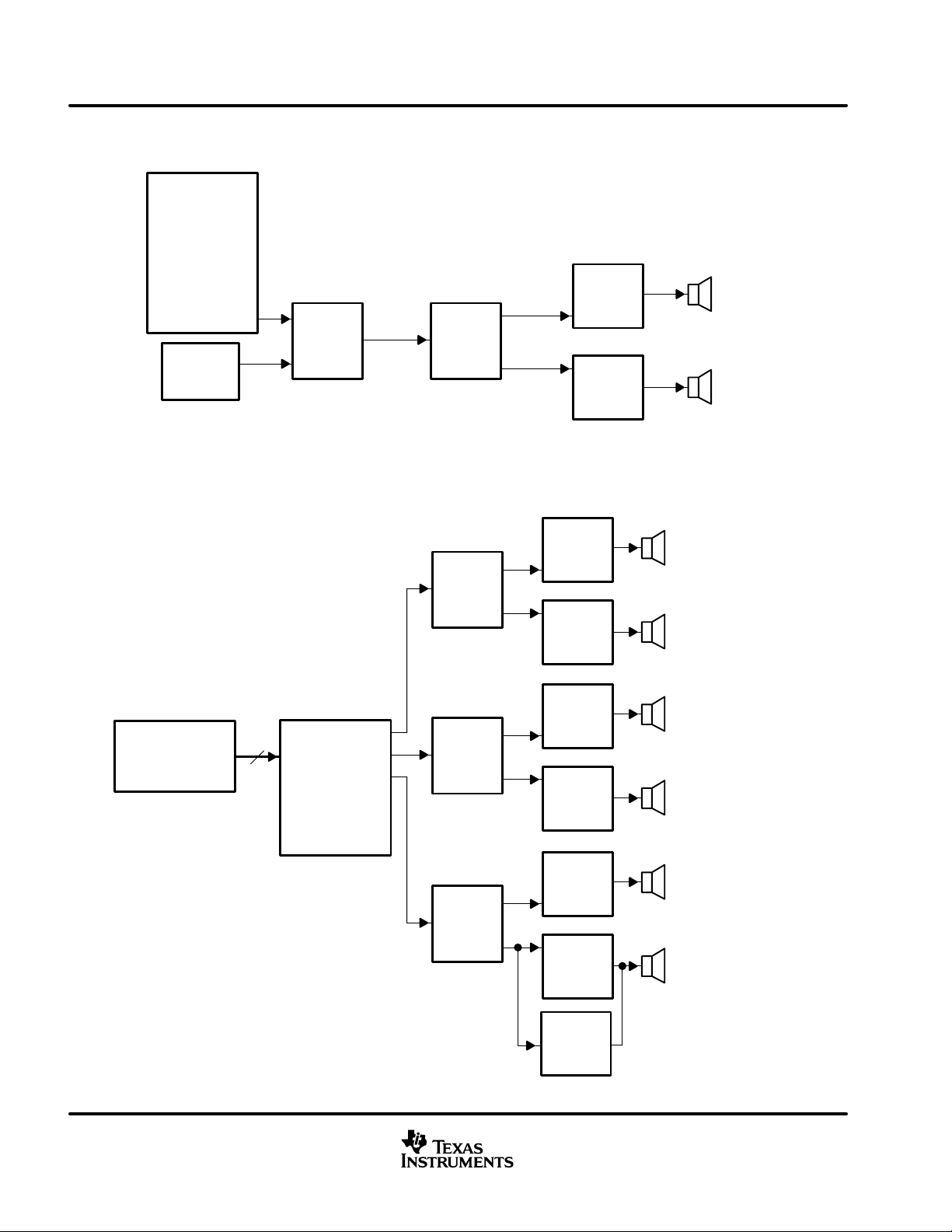
suggested system block diagrams
See application note SLAA117 for more details.
Digital Audio
• USB
• IEEE 1394
• SPDIF
• ADC
• Automotive
MOST
Network
IIC
Audio
Control
Figure 1. System #1: Stereo Configuration With TAS3001 Digital Audio Processor
TAS3001
• Digital Parametric EQ
• Volume
• DRC
• Bass
• Treble
Left
TAS5000
Right
• Serial Audio Input Port
• Internal PLL
TAS5100A
TAS5100A
• Two H-Bridges
Home Theater
DVD 6-Channel
Encoded Digital
Audio Source
6
TI DSP
• Dolby AC-3
• DTS
• Volume
• EQ
• DRC
• Bass
• Treble
TAS5000
TAS5000
TAS5000
CH1
CH2
CH3
CH4
CH5
CH6
TAS5100A
TAS5100A
TAS5100A
TAS5100A
TAS5100A
TAS5100A
Left
Right
Surround Left
Surround Right
Center
Subwoofer
TAS5100A
Figure 2. System #3: 6-Channel Audio Playback
4
www.ti.com
Page 5
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
TAS5100A
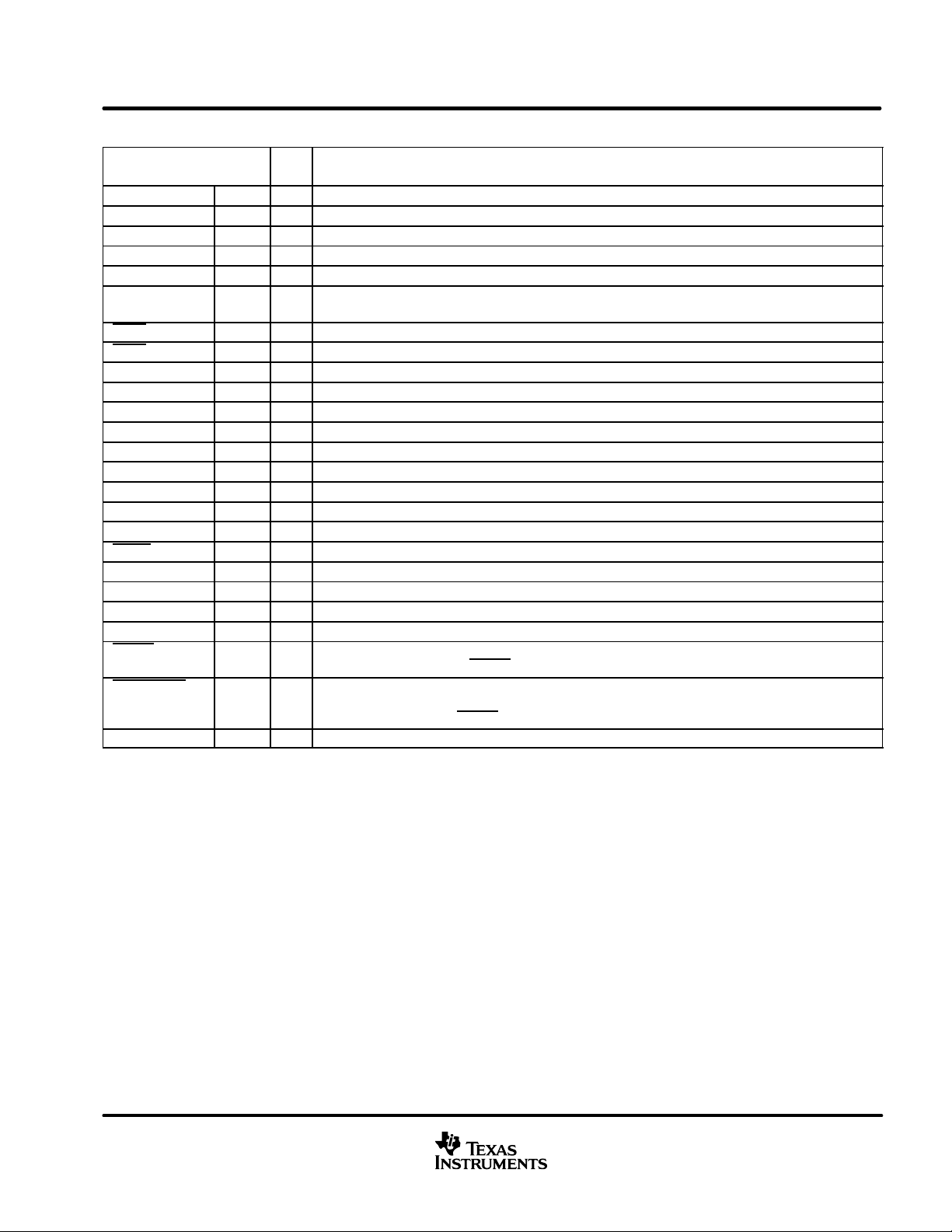
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
BIAS_A 11 I Connect external resistor to DVSS. See application note SLAA117
BIAS_B 12 I Connect external resistor to DVSS. See application note SLAA1 17
BOOTSTRAPA 30 O Bootstrap capacitor pin for H-bridge A
BOOTSTRAPB 19 O Bootstrap capacitor pin for H-bridge B
DVDD 6 I 3.3-V digital voltage supply for logic
DVSS 7, 8, 9 I Digital ground for logic is internally connected to PVSS. All three pins must be tied together but not
ERR1 3 O Error/warning report indicator. This output is open drain with internal pullup resistor.
ERR0 4 O Error/warning report indicator. This output is open drain with internal pullup resistor.
LDROUTA 31 O Low voltage drop-out regulator output A (not to be used to supply current to external circuitry)
LDROUTB 18 O Low voltage drop-out regulator output B (not to be used to supply current to external circuitry)
OUTPUTA 26, 27 O H-bridge output A
OUTPUTB 22, 23 O H-bridge output B
PVDDA1 28, 29 I High voltage power supply, H-bridge A
PVDDA2 32 I High voltage power supply for low-dropout voltage regulator A-side
PVDDB1 20, 21 I High voltage power supply, H-bridge B
PVDDB2 17 I High voltage power supply for low-dropout voltage regulator B-side
PVSS 24, 25 I High voltage power supply ground
PWDN 13 I Power down = 0, normal mode = 1
PWM_AP 1 I PWM input A(+)
PWM_AM 2 I PWM input A(–)
PWM_BP 16 I PWM input B(+)
PWM_BM 15 I PWM input B(–)
RESET 14 I Reset and mute mode = 0, normal mode = 1, when in reset mode, H-bridge MOSFET s are in low-low
SHUTDOWN 5 O Device is in shutdown due to fault condition, normal mode = 1, shutdown = 0, when device is in
VRFILT 10 O A filter capacitor must be added between VRFILT and DVSS pins.
NOTE: The four PWM inputs: PWM_AP , PWM_AM, PWM_BP, and PWM_BM must always be connected to the TAS5000 output pins, and never
left floating. Floating PWM input pins causes an illegal PWM input state signal to be asserted.
I/O
connected externally to PVSS. See Figure 5.
output state. Asserting the RESET
shutdown mode the H-bridge MOSFETs are in low-low output state. The latched output can be
cleared by asserting the RESET signal. This output is open drain with internal pullup resistor.
DESCRIPTION
signal low causes all fault conditions to be cleared.
Dual pins: OUTPUTA, OUTPUTB, PVDDA1 and PVDDB1 must have both pins connected externally to the same point on the circuit board,
respectively. Both PVSS pins must also be connected together externally. These multiple pins are for the high current DMOS output
devices. Failure to connect all the multiple pins to the same respective node results in excessive current flow in the internal bond wires
and can cause the device to fail. All electrical characteristics are specified and measured with all of the multiple pins conne cted to the same
node, respectively .
www.ti.com
5
Page 6

TAS5100A
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
functional description
PWM H-bridge state control
The digital interface control signals consists of PWM_AP, PWM_AM, PWM_BP, and PWM_BM. These signals
are a complementary differential signal format for the A-side H-bridge and the B-side H-bridge.
bootstrapped gate drive
The TAS5100A includes two dedicated bootstrapped power supplies. A bootstrap capacitor is connected
between the individual bootstrap pin and the associated output as described in the application note SLAA1 17.
For example, a capacitor is connected between the BOOTSTRAPA pin and OUTPUTA pin, and another
capacitor is connected between the BOOTSTRAPB pin and the OUTPUTB pin. The bootstrap power supply
minimizes the number of high voltage power supply levels externally supplied to the system while providing a
low noise supply level for driving the high-side N-channel DMOS transistors. See application note SLAA1 17 for
details.
low-dropout voltage regulator
Two on-chip low-dropout voltage regulators (LDO) are provided to minimize the number of external power
supplies needed for the system. These voltage regulators are for internal circuits only and cannot be used for
external circuitry. Each LDO is dedicated to an H-bridge and its gate driver. An LDO output capacitor is
connected between the individual LDO output pin and the associated output return as described in the
application note SLAA1 17. For example, a capacitor is connected between the LDROUTA pin and PVSS pin,
and another capacitor is connected between the LDROUTB pin and PVSS pin.
high-current H-bridge output stage
The positive outputs of the H-bridge are the two OUTPUT A pins. The negative outputs of the H-bridge are the
two OUTPUTB pins. The logic for the input command to H-bridge outputs is described in the H-bridge output
mapping section below. When the TAS5100A is in the normal mode, as seen in the H-bridge output mapping
tables, the outputs are decoded from the inputs. However, the TAS5100A is immediately shut down if any of
the following error conditions occur: over-current, over-temperature, low regulator output voltage, or an illegal
PWM input state is applied. For these conditions, the outputs are set to the appropriate disabled state as
specified in the H-bridge output mapping section, and the SHUTDOWN
pin is set low.
H-bridge output mapping
The A-side H-bridge output is designed to the following truth table:
INPUTS OUTPUTS
RESET PWDN PWM_AP PWM_AM SHUTDOWN OUTPUTA
X X X X 0 0 or Hi-Z
X 0 X X 1 Hi-Z Powerdown
0 1 X X 1 0 Reset
1 1 0 0 0 0 Shutdown
1 1 0 1 1 0 Normal
1 1 1 0 1 1 Normal
1 1 1 1 0 0 Shutdown
†
Output is 0 for low voltage, over temperature, and illegal input. Hi-Z is for over current.
†
DESCRIPTION
Shutdown
6
www.ti.com
Page 7

H-bridge output mapping (continued)
The B-side H-bridge output is designed to the following truth table:
TAS5100A
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
INPUTS OUTPUTS
RESET PWDN PWM_BP PWM_BM SHUTDOWN OUTPUTB
X X X X 0 0 or Hi-Z
X 0 X X 1 Hi-Z Powerdown
0 1 X X 1 0 Reset
1 1 0 0 0 0 Shutdown
1 1 0 1 1 0 Normal
1 1 1 0 1 1 Normal
1 1 1 1 0 0 Shutdown
†
Output is 0 for low voltage, over temperature, or illegal input. Hi-Z is for over current.
†
DESCRIPTION
Shutdown
control/sense circuitry
The control/sense circuitry consists of the following 3.3-V logic level pins: PWDN
SHUTDOWN
to the Hi-Z state. When the PWDN
disabled so that their outputs can be pulled high. The active-low RESET
. The active-low PWDN input pin powers down all internal circuitry and forces the H-bridge outputs
pin is low, the open drain ERR0, ERR1, and SHUTDOWN pins are also
input pin forces the H-bridge outputs
to the low-low state and resets the over-current shutdown latch. The PWDN
ERR0
, ERR1, and SHUTDOWN outputs indicate the following conditions in the T AS5100A as shown in the table
, RESET, ERR0, ERR1, and
pin overrides the RESET pin. The
below. These three outputs are open-drain connections with internal pullup resistors so that wire-ORed
connections can be made by the user with other external control devices. The short circuit protect error condition
latches the TAS5100A in this shutdown state and force the H-bridge outputs to the Hi-Z state until the device
is reset by means of the RESET
pin. The illegal PWM input state, over-temperature, and low regulator voltage
error conditions do not latch the device in the shutdown condition. Instead the H-bridge outputs are forced to
the low-low state and the T AS5100A returns to normal operation as soon as the error condition ends. Loss of
clocking PWM signal is also considered an illegal PWM input state.
SHUTDOWN ERR1 ERR0 FUNCTION OUTPUTA OUTPUTB
0 0 0 Illegal PWM input state Low Low
0 0 1 Short circuit protect (latch) Hi-Z Hi-Z
0 1 0 Over temperature protect Low Low
0 1 1 Low regulator voltage protect Low Low
1 0 0 Reserved — —
1 0 1 Reserved — —
1 1 0 High temperature – warning Normal Normal
1 1 1 Normal operation Normal Normal
www.ti.com
7
Page 8

TAS5100A
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
device operation
power sequences
system power-up/power-down sequencing
The recommended power-up/power-down sequence is shown in Figure 3. For proper operation the RESET
signal should be kept LOW when both DVDD and output power (PVDDA1, PVDDA2, PVDDB1, and PVDDB2)
are being applied. The RESET
†
DVDD
PWDN
PVDDA1
PVDDA2
PVDDB1
PVDDB2
> 100 µs
RESET
signal should remain LOW for at least 1 ms after output power is applied.
> 1 ms
> 1 ms
†
For most applications, it is recommended that pin 13 (PWDN) be connected directly to pin 6 (DVDD).
Figure 3. Power-Up/Power-Down Sequence
RESET
function
The device is put into a reset condition when the (active low) RESET
signal is asserted. While in the reset state,
the input H-bridge control signals consisting of PWM_AP , PWM_AM, PWM_BP , and PWM_BM are ignored, and
the H-bridge MOSFETs are placed in a state where OUTPUTA and OUTPUTB are both low. Asserting the
RESET
signal low also causes the short circuit protection latch to be reset. The RESET signal is normally
connected to the VALID signal from the TAS5000.
reinitialization sequence
Proper initial conditions for this device include asserting the RESET
signal until the reset operation has
completed (1 ms). Additionally, when using this device with the TAS5000 controller, this function can be
accomplished by asserting the reset pin on the TAS5000 during the reset sequence (see Figure 3).
audio application considerations
power supply decoupling
Power supply decoupling and layout optimization information should be obtained by following the detailed
information in the application note SLAA117.
optimal power transfer for H-bridge
The T AS5100A is a power H-bridge that is designed to deliver 30 W/rms into loads of 4 Ω to 8 Ω. Rather than
requiring the usual heatsink, the package is designed to deliver this wattage by careful layout as described in
the application note SLAA117. Careful attention must be given to the value of the high-voltage power supply
level for a given load resistance. See recommended operating conditions.
8
www.ti.com
Page 9

SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
TAS5100A
audio application considerations (continued)
reconstruction output filter
An output reconstruction filter is required between the H-bridge outputs and the loudspeaker load. This second
order low-pass filter passes the audio information to the loudspeaker, while filtering out the high frequency
out-of-band information contained in the H-bridge output PWM pulses. The values of the L and C components
selected are dependent on the loudspeaker load impedance. See application note SLAA117.
fault indicator usage
The TAS5100A is a self-protecting device that provides device fault reporting, including over-temperature
protect, under-voltage lockout (low-regulator voltage), and short circuit protection. The short circuit protection
protects against short circuits that may occur at the loudspeaker load when configured according to the
application note SLAA1 17. The TAS5100A is not recommended for driving loads less than 4 Ω, since the internal
current limit protection might be activated.
An under-voltage lockout signal occurs when an insufficient voltage level is present on the LDROUTA or
LDROUTB pins. During this condition gate drive levels are not sufficient for driving the power MOSFET s. Normal
operation is resumed when the minimum proper LDROUT A or LDROUTB level is obtained, and the low regulator
voltage protect signal is de-asserted. See the control/sense circuitry section for error and warning conditions.
A high temperature warning signal is asserted on pin ERR0
when the device temperature exceeds 130°C
typical.
If the internal device temperature exceeds 150°C typical, the over temperature protect signal is asserted and
the TAS5100A is shut down. The device re-enables once the temperature drops to 130°C typical. See the
control/sense circuitry section for error and warning conditions.
Detection of an illegal PWM input state or the loss of a clocking PWM input signal causes an illegal PWM input
state signal to be asserted on the ERR1
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
and ERR0 pins and sets the SHUTDOWN pin to the low state.
†
DC supply voltage range: DVDD to DVSS –0.3 V to 4.2 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PWM_AP, PWM_AM, PWM_BP, PWM_BM –0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RESET
, PWDN –0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PVDDA1 to PVSS, PVDDB1 to PVSS –0.3 V to 28 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PVDDA2 to PVSS, PVDDB2 to PVSS –0.3 V to 27 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output DMOS drain-to-source breakdown voltage 28 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous DMOS RMS drain current, each output 3 A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous source-to-drain RMS body diode current 3 A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating junction temperature range, T
Storage temperature range, T
stg
–40°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J
–65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds) 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
DISSIPATION DERATING TABLE
PACKAGE
DAP 5.3 W 42.5 mW/°C 3.4 W
†
See the Texas Instruments document, PowerPAD Thermally Enhanced Package Application
Report (literature number SLMA002), for more information on the PowerPAD package. The
thermal data was measured on a PCB layout based on the information in the section entitled Texas
Instruments Recommended Board for PowerPAD of the before mentioned document. Data in
table is for specified layout. Under other conditions the thermal performance may vary. See T exas
Instruments document SLAA117 for more detailed application information.
TA ≤ 25°C
POWER RATING
†
www.ti.com
DERATING FACTOR
ABOVE TA = 25°C
TA = 70°C
POWER RATING
9
Page 10

TAS5100A
yg
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
recommended operating conditions (nominal output power = 30 W (RMS), TA = 25°C)
thermal data
Shutdown junction temperature, T
Warning junction temperature, T
Operating ambient temperature, T
Thermal resistance junction-to-case, θ
Thermal resistance junction-to-ambient, θ
Thermal resistance junction-to-case, θ
Thermal resistance junction-to-ambient, θ
†
One of the most influential components on the thermal performance of a package is board design. In order to take full advantage of the heat
dissipating abilities of the PowerP AD packages, a board must be used that acts similar to a heat sink and allows for the use of the exposed (and
solderable), deep downset pad. See Appendix A of the PowerP AD Thermally Enhanced Package application note, TI literature number SLMA002
and the Thermal Design of the PowerPad PCB Layout section of the System Design Considerations for True Digital Audio Power Amplifiers
application note, TI literature number SLAA117.
†
PARAMETER MIN NOM MAX UNIT
J(SD)
J(W)
A
jc
jc
2 oz. trace and copper pad with solder 0.32 °C/W
2 oz. trace and copper pad with solder 23.5 °C/W
ja
2 oz. trace and copper pad without solder 0.32 °C/W
2 oz. trace and copper pad without solder 44.3 °C/W
ja
150 °C
130 °C
0 25 70 °C
RL = 4 Ω to 8 Ω
PARAMETER MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Digital DVDD to DVSS 3 3.3 3.6 V
PVDDA2 to PVSS 16.5 22 24
Supply voltage
‡
Connect LDROUTA to PVDDA2 and connect LDROUTB to PVDDB2. Under this condition H-Bridge forward on-state resistance is increased.
This increases internal power dissipation. Maximum output power may need to be reduced to meet thermal conditions.
Regulator
PVDDB2 to PVSS 16.5 22 24
PVDDA2 to PVSS
PVDDB2 to PVSS
}
}
10.5 16.5
10.5 16.5
V
RL = 8 Ω
pp
Supply voltage Power
RL = 6 Ω
pp
Supply voltage Power
RL = 4 Ω
pp
Supply voltage Power
PARAMETER MIN NOM MAX UNIT
PVDDA1 to DVSS 0 26 27
PVDDB1 to PVSS 0 26 27
PARAMETER MIN NOM MAX UNIT
PVDDA1 to DVSS 0 23 24
PVDDB1 to PVSS 0 23 24
PARAMETER MIN NOM MAX UNIT
PVDDA1 to DVSS 0 20 21
PVDDB1 to PVSS 0 20 21
V
V
V
10
www.ti.com
Page 11

PVDDA1
PVDDA2
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
TAS5100A
static digital specifications
RESET, PWDN, PWM_AP, PWM_AM, PWM_BP, PWM_BM, TA = 25°C, DVDD = 3.3 V
PARAMETERS MIN MAX UNIT
High-level input voltage, V
Low-level input voltage, V
Input leakage current –10 10 µA
IH
IL
2 V
0.8 V
ERR0, ERR1, SHUTDOWN, (open drain with internal pullup resistor) TA = 25°C, DVDD = 3.3 V)
PARAMETERS MIN MAX UNIT
Internal pullup resistors from SHUTDOWN, ERR0, ERR1 to DVDD 15 kΩ
Low-level output voltage (IO = 4 mA), V
OL
0.4 V
TAS5000/TAS5100A system performance measured at the speaker terminals
See the TI Literature Number SLAA117 for TAS5000/TAS5100A system performance.
electrical characteristics
supply, TA = 25°C (F
switching
= 384 kHz, OUTPUTA and OUTPUTB not connected, DVDD = 3.3 V,
PVDDA1 = 25 V, PVDDB1 = 25 V, PVDDA2 = 22 V, PVDDB2 = 22 V, 50% input duty cycle)
PARAMETER TYP MAX UNIT
DVDD
Supply current
†
13-kΩ resistor from BIAS_A (pin 11) to DVSS and 13-kΩ resistor from BIAS_B (pin 12) to DVSS.
PVDDA1
PVDDB1
PVDDA2
PVDDB2
Operating 2 mA
PWDN = 0 500 µA
Operating
PWDN = 0 25 µA
Operating 6.5 mA
PWDN = 0 250 µA
†
6.3 mA
H-Bridge transistors, PVDDA2 = PVDDB2 = 22 V, DVDD = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Drain-to-source breakdown voltage ID = 1 mA, PWDN = 0, Hi-Z state 28 V
Forward on-state resistance, low side drivers
OUTPUTA and OUTPUTB to PVSS
Forward on-state resistance, high side drivers
PVDDA1 to OUTPUTA, PVDDB1 to OUTPUTB
On-state resistance matching low-side drivers 98%
On-state resistance matching high-side drivers 98%
NOTES: 1. Test time should be < 1 ms to avoid temperature change.
2. These parameters are measured with voltage-sensing contacts separate from the current-carrying contacts.
3. Connect PVDDA2 and PVDDB2 to 22-V power supply with respect to PVSS. LDROUTA, LDROUTB, BOOTSTRAPA, and
BOOTSTRAPB pins open.
4. Connect PVDDA2 to 22-V power supply with respect to PVSS. LDROUTA, LDROUTB, BOOTSTRAPA and BOOTSTRAPB
capacitors are connected respectively. Clock PWM inputs to allow bootstrap capacitors to charge. 93–99% modulation must be used
on PWM_AP , PWM_AM, PWM_BP, and PWM_BM inputs to prevent the activity detector from shutting down the device during this
measurement. Note that F
switching
I
= 2.5 A,
SINK
See Notes 2, 3, and 4,
I
SOURCE
See Notes 2, 3, and 5,
= 384 kHz.
= 2.5 A,
PWM_AP = PWM_BP = 0,
PWM_AM = PWM_BM = 1
PWM_AP = PWM_BP = 1,
PWM_AM = PWM_BM = 0
0.2
0.2 Ω
Ω
www.ti.com
11
Page 12

TAS5100A
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
electrical characteristics, voltage regulator, TA = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Output voltage (LDROUTA, LDROUTB)
NOTE 5: These voltage regulators are for internal gate drive circuits only and are not to be used under any circumstances to supply current to
external circuity .
The thermally enhanced DAP package is based on the 32-pin HTSSOP, but includes a thermal pad (see
Figure 4) to provide an effective thermal contact between the IC and the PWB.
Traditionally, surface mount and power have been mutually exclusive terms. A variety of scaled-down TO-220
type packages have leads formed as gull wings to make them applicable for surface-mount applications. These
packages, however, have two shortcomings: they do not address the low profile requirements (<2 mm) of many
of today’s advanced systems, and they do not offer a terminal-count high enough to accommodate increasing
integration. On the other hand, traditional low-power surface-mount packages require power-dissipation
derating that severely limits the usable range of many high-performance analog circuits.
The PowerPAD package (thermally enhanced HTSSOP) combines fine-pitch surface-mount technology with
thermal performance comparable to much larger power packages.
IO = 5 mA, PVDDA2=PVDDB2 = 18 V to 27 V,
See Note 6, DVDD = 3.3 V
THERMAL INFORMATION
14.5 15.3 16 V
The PowerP AD package is designed to optimize the heat transfer to the PWB. Because of the very small size
and limited mass of a HTSSOP package, thermal enhancement is achieved by improving the thermal
conduction paths that remove heat from the component. The thermal pad is formed using a patented lead-frame
design and manufacturing technique to provide a direct connection to the heat-generating IC. When this pad
is soldered or otherwise thermally coupled to an external heat dissipater, high power dissipation in the ultrathin,
fine-pitch, surface-mount package can be reliably achieved. See dissipation derating table.
DIE
Side View (a)
DIE
End View (b)
Thermal
Pad
Bottom View (c)
12
Figure 4. Views of Thermally Enhanced DAP Package
www.ti.com
Page 13

TAS5000
PWM_M_L
PWM_P_L
RESET
VALID
3.3 V
Error
Reporting
APPLICATION INFORMATION
TAS5100A
1
C2
C7
R2
R1
PWM_AP
2
PWM_AM
3
ERR1
4
ERR0
5
SHUTDOWN
6
DVDD
7
DVSS
8
DVSS
9
DVSS
10
VRFILT
11
BIAS_A
12
BIAS_B
13
PWDN
14
RESET
15
PWM_BM
16
PWM_BP
PVDDA2
LDROUTA
BOOTSTRAPA
PVDDA1
PVDDA1
OUTPUTA
OUTPUTA
OUTPUTB
OUTPUTB
PVDDB1
PVDDB1
BOOTSTRAPB
LDROUTB
PVDDB2
PVSS
PVSS
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
C5
22 V
C3 C4
C6
22 V
TAS5100A
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
Snubber
Circuit
L1
dc
C1
L2
Snubber
Circuit
+
_
Figure 5. Typical TAS5100A Application (One Channel Shown)
See the application note, TI literature number SLAA117 for detailed application information.
www.ti.com
13
Page 14

TAS5100A
SLES030 – FEBRUARY 2002
MECHANICAL DATA
DAP (R-PDSO-G**) PowerPAD PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
38 PINS SHOWN
0,65
38
1
1,20 MAX
0,30
0,19
20
19
A
0,15
0,05
0,13
6,20
NOM
M
Thermal Pad
(see Note D)
8,40
7,80
0,15 NOM
Gage Plane
0,25
0°–ā8°
0,75
0,50
Seating Plane
0,10
PINS **
DIM
A MAX
A MIN
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion.
D. The package thermal performance may be enhanced by bonding the thermal pad to an external thermal plane. This pad is electrically
and thermally connected to the backside of the die and possibly selected leads. Thermal pad size is 3,86 mm X 3,91 mm for the
32-pin T AS5100A device.
E. Falls within JEDEC MO-153
PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
14
28
9,80
9,60
30
11,10
10,90
www.ti.com
32
11,10
38
12,60
12,4010,90
4073257/A 07/97
Page 15

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
27-Sep-2005
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
TAS5100ADAP NRND HTSSOP DAP 32 46 TBD CU NIPDAU Level-3-220C-168 HR
TAS5100ADAPR NRND HTSSOP DAP 32 2000 TBD CU NIPDAU Level-3-220C-168 HR
TAS5100ADAPRG4 NRND HTSSOP DAP 32 2000 TBD CU NIPDAU Level-3-220C-168 HR
TAS5100AIDAP NRND HTSSOP DAP 32 46 TBD CU NIPDAU Level-3-220C-168 HR
TAS5100AIDAPR NRND HTSSOP DAP 32 2000 TBD CU NIPDAU Level-3-220C-168 HR
TAS5100AIDAPRG4 NRND HTSSOP DAP 32 2000 TBD CU NIPDAU Level-3-220C-168 HR
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS) or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
(3)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
Addendum-Page 1
Page 16

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications,
enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue
any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing
orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms
and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI
deems necessary to support this warranty . Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all
parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for
their products and applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products
and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right,
copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process
in which TI products or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third-party products or services
does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof.
Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property
of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without
alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction
of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for
such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that
product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and
is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application
solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Interface interface.ti.com Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303 Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2005, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...